|
|
You are not currently logged in. Are you accessing the unsecure (http) portal? Click here to switch to the secure portal. |
Gérard Thibault d'Anvers
| Gérard Thibault d'Anvers | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Born | 1574 |
| Died | 1629 |
| Occupation | Fencing master |
| Nationality | Dutch |
| Movement | La Verdadera Destreza |
| Influences | |
| Genres | Fencing manual |
| Language | French |
| Notable work(s) | Academie de l'Espée (1630) |
Gérard Thibault d'Anvers (ca. 1574–1629)[1] was a 17th century Dutch fencing master and author of the 1628 rapier manual Academie de l'Espée, one of the most detailed and elaborate sources ever written on fencing. Details about Thibault's life are sparse and what we know is based on his book and his album amicorum.[2] The latter contains handwritten notes and celebratory poems from Thibault's friends, relatives, pupils, and colleagues, included among whom are several contemporary fencing masters.[3]
Thibault was born in or around 1574 in Antwerp, son of Hendrick Thibaut and Margaretha van Nispen.[4] Although his father used the surname "Thibaut," Gérard used the French form "Thibault."[4] Hendrick Thibaut came from a well-known family in Ypres, living in Ghent and Antwerp before going into exile in the northern Netherlands.[4] Henrick's eldest son, Christiaen, founded the noble family Thibaut van Aegtekerke.[5]
Thibault first studied swordsmanship in Antwerp under Lambert van Someron, who taught between the years of 1564 and 1584.[6] In 1605, Thibault was a wool merchant in Sanlúcar de Barrameda, south of Seville on the Guadalquivir river, and the hometown of Jerónimo Sánchez de Carranza.[2] There, he took an interest in swordsmanship, studying the Spanish rapier system of Destreza.[2]
Thibault left Spain to return to the Netherlands, and was in Amsterdam as early as 1610.[2] In or around 1611, he presented his system to an assembly of Dutch masters at a competition in Rotterdam.[7] Thibault won first prize, earning an invitation to the court of Prince Maurice of Nassau, where the Prince observed Thibault's system in a multi-day demonstration.[6]
Although initially met with skepticism, Thibault convinced his fellow Dutch fencing masters, including Johannes Damius of Haarlem, Dirck van Stervergen of Leiden, Cornelis Cornelisz van Heusden of Amsterdam, and Thibault's former teacher Lambert von Someron.[6] In 1615, Thibault was invited to the court at Cleves and left Amsterdam, where he once again demonstrated his system successfully.[8] Over the next several years, Thibault traveled from Cleves, Amsterdam, to Spain, back to Amsterdam, and finally to Leiden in 1622.[9] There, Thibault studied mathematics at Leiden University.[10] It is unclear whether Thibault taught his system at the university.[10] It is during his time in Leiden that Thibault likely began working on Academie de l'Espée and employed a team of sixteen master engravers.[11]
Thibault died in 1629, a year before his masterpiece was finally published (despite the date on the title page of 1628, it was not published until 1630).[12]
Contents
- 1 Treatise
- 1.1 Book 1 - Introduction. Arms of Patrons and supporters of Thibault
- 1.2 Book 1 - Tableau / Plate I - Philosophical Discussion; Construction and Mathematics of the Circle; Concerning the Sword: Proper Length and Introduction.
- 1.3 Book 1 - Tableau / Plate II - Comparing the ideal figure to a real figure; Sword scabbards
- 1.4 Book 1 - Tableau / Plate III - Drawing the sword; approaching an opponent (part 1)
- 1.5 Book 1 - Tableau / Plate IIII - Approaching an opponent (part 2); Direct Line Posture
- 1.6 Book 1 - Tableau / Plate V - Counters to Feints and thrusts
- 1.7 Book 1 - Tableau / Plate VI - Basic Attack; initial parries and counters.
- 1.8 Book 1 - Tableau / Plate VII - Counters to circular disengagements.
- 1.9 Book 1 - Tableau / Plate VIII - Counters to Imbroccata attacks.
- 1.10 Book 1 - Tableau / Plate IX - Introduction to Degrees of Force
- 1.11 Book 1 - Tableau / Plate X - More on parries by force.
- 1.12 Book 1 - Tableau / Plate XI - Refining the Sense of Feeling.
- 1.13 Book 1 - Tableau / Plate XII - Stepping inside the Angle betweeen the Swords.
- 1.14 Book 1 - Tableau / Plate XIII - Defeating or Defending With The Guard Raised High to Protect the Face
- 1.15 Copyright and License Summary
- 2 Additional Resources
- 3 References
Treatise
The Academie de l'Espée (1630) is presented in two books. Book 1 consists of a short introduction, populated with plates showing the coats of arms of several nobles who were prominent in and around the court of the low countries at the time he wrote this book, and then introduces training in the use of his system of swordplay.
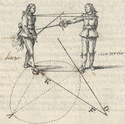
Thibault, although he does not explain until Plate 8, uses the term estocade to describe a thrust to the near, right side, and the term imbrocade to describe a thrust to the far, left side, from the Italian terms stoccata and imbroccata. English has a single term thrust to mean either, but did borrow the Italian term imbroccata to specifically refer to the latter type of thrust.
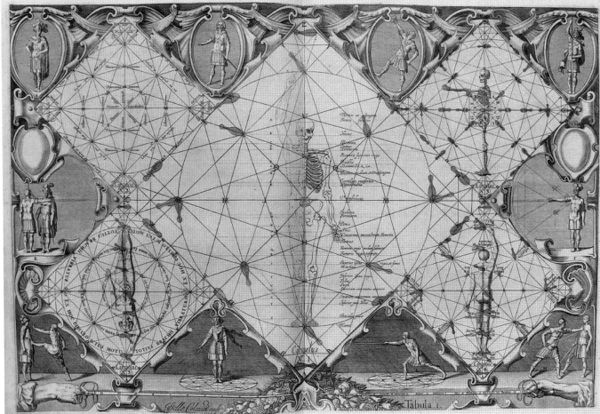
Plate I begins with a long philosophical discussion of his worldview. It is a good insight into the late Renaissance worldview relating mathematics and Christian religious beliefs to an idealized human figure. It then explains how to construct his Mysterious Circle. This includes a lengthy discussion of how the circle relates geometrically to the ideal body size, based on Vitruvius, and notes about how the lines and crossing points of the circle will be used. This is the basic reference diagram for the entire system. It also includes explanations of how to measure for the correct sword size for any given person, and some explanation of why this is so, and some introductory explanation of appropriate ranges for swordplay.
Plate II compares his ideal body measurements against a figure by Albrecht Durer. Part 2 discusses his ideal sword scabbard and how to construct and wear it.
Plates III & IV deal with how to properly draw a sword and how to approach an adversary.
Plate V introduces his fighting system. First, how to deal with feints (typical of the schools of the time) and defend against typical thrusts.
Plate VI introduces several basic concepts. The importance of maintaining contact between swords, not typical of schools of the time, and the basic steps to close with and thrust into an opponent. The first steps show the attack as if he were to make no defense. Then he assumes the opponent will try to disrupt the attack, and discusses how to deal with interruptions if they occur at various points during the movement.
Plate VII introduces an opponent using circular disengagements and counterthrusts to disrupt an attack, and how to counter them.
Plate VIII introduces the imbroccata attack against the left side and exercises to counter them when they occur at various stages of the attack.
Plates IX & X introduces the idea of blade control and various degrees of force which can be applied against the blade to parry an attack. He defines several increasing degrees of pressure and introduces exercises to learn to distinguish them, and how to counter parries by force.
Plate XI continues the exploration of how to deal with different degrees of force against the blade.
Plate XII shows how to create an angle between blades to move in against the opponent
Book 2 lacks an explanation of the complex frontspiece, and was incomplete at the time of his death, but what he does have shows how to use his style against other systems and weapons then in use, including shields, longsword, and firearms.
The plates uploaded to WikTenauer are sufficient to follow the text, but if anyone wishes to see very high definition images, they can be found on [www.geheugenvannederland.nl]. Search on Girard Thibault.
| Images | Translation by Bruce G. Hearns |
Transcription by Bruce G. Hearns |
|---|---|---|

|
Academy of the Sword by Girard Thibeault of Antwerp, wherein is demonstrated by means of mathematical rules, upon the foundation of the mysterious Circle, the Theory and Practise of the true and, until present, unknown secrets of the handling of arms both on foot and on horseback.
M.DC.XXXVIII (1628) |
Academie de L'ESPÉE de Girard Thibault d'Anvers ou ſe demonſtrent par Reigles mathematiques ſur le fondemont d'un Cercle mysterieux la theorie et pratique des vrais et iuſq'a preſent incognus ſecrets du maniement DES ARMES a Pied et a Cheval.
M.DC.XXVIII |

|
In tranquil reason, not impatient in his work, leads us courageously along his meandering path.
Gerard Thibault of Antwerp Rejoice. Patience endures. |
TRANQVILLA RATIO, NEC SVI IMPATIENS LABOR, MODUM EVAGANTI PRÆSTRVIT FEROCIÆ.
Gerard Tibault d'Anvers Gaudet Patientia duris |

|
To the valliant heart, nothing is impossible.
Arms and sundry titles of [William] (1595 – 1640), Elector of Brandenburg (1619 – 1640). |
Au coeur vaillant rien n'est impossible
Serenissimo Principi ac Domino Domino Georgio Guilermo Marchioni Brandenburgensi S. Romani imperii Archicamerario et Electori; Borussiæ, Iuliæ, Cliviæ, Montium Stetini, Pomeraniæ, Cassubiorum, Vandalorum et in Silesia Crosnæ, Carnovi, æ’que Duci Burggravio Norimbergensi Principi Rugiæ. Comiti Marchiæ, ac Ravensbergi. Dynatæ Ravenstein y, &c. |

|
Work well without pause, and the hours pass quickly.
Arms and sundry titles of [Sigismund] (1572 – 1619), Elector of Brandenburg (1608 – 1619) |
Fais biens sans demeure, et peu de temps se passe l’heure
Serenissimo Principi ac Domino Do. Io. Achimo Sigismundo. Marchioni Brandenburgensi, Borussiæ, Iuliæ, Cliviæ, Montium Stetini, Pomeraniæ, Cassubiorum, Vandalorum, et in Silesia Crosnæ, Carnoviæ ‘que Ducter |

|
Everything with God, Nothing without Reason.
Arms and title of [(the Elder)] (1566 - 1633), Duke of Brunswick and Lunenbourg. |
Tout Avec Dieu, Rien Sans Raison
Serenissimo Principi ac Domino Domino Christiano Duci Brunswicensi et Lunenburgensi |

|
(Order of the Garter about the arms – Shame to him who evil thinks)
I maintain Arms and titles of [[1]] (1567 - 1625), Prince of Orange (1618 – 1625) |
(Order of the Garter about the arms – Honi soit qui mal y pense)
Ie Maintiendray Ilustrissimo Heroi Muritio Principia Auraico, Comiti Nassoviæ, Cattimeliboci, Viandæ, Diestii, Lingæ, Mursiæ, Bueræ, Leerdami, &c. Marchioni Veriæ, ac Frissinge Baroni Bredæ. Civitatis Graviæ, ac ditionis Cuyckiæ, Herrstas, Cranendonc, Warneston, Arlaii, Svti Viti. Daesburgi &c. Vicecomiti Hæreditario Antwerpiæ, et Bizantii &c. Gubernatoi Geldriæ, Hollandie,, Lelandiæ, Westfrisiæ Zutphaniæ, Ultraiecti, Transisalaniæ, Groninge et Omlandiæ; Summo earundem Provinciarum terra mario, misitiæ Duci |

|
Of the homeland. With the homeland.
Arms and titles of [Henry] (1584 - 1647), Prince of Orange (1625-1647) |
Patriæ. Patrique
Illustrissimo Principi ac Domino D. Frederico Henrico Principi Auraico. Comiti Nassoviæ, Dominio Geertrudis-bergæ, utriusque Swaluæ, Naeldwici. Marischalco Hæreditario Hollandiæ, Unitarum Provinciarum Equitum Præfecto Generali &c. |

|
Constant
Arms & titles of [Casimir] (1573-1632), Count of Nassau-Dietz (1606-1632) |
Constant
Illust[rissi]mo Principi Ernesto Casimiro Comiti Nassoviæ, Catimeliboci, Viandæ, Dies Rii; Domino Bilsteiniæ, Castrorum Unitarum Provenciarum Praefecto; Gubernatori Frisiæ &c. |

|
God and all
Dedication and Arms of [VII] (1587-1627), Count of Lippe (1613-1627), and his brother [[2]] (1589 – 1657), Count of Lippe-Brake (1621-1657) |
Deo et Cunctis
Generosis vere’q Germanis Fratribus, Simoni et Otthoni, Comitibus et Nobisibus Dominis de Lippia |

|
Nothing without God
Arms of Stephan Gans, [Putlitz] |
Rien sans Dieu
Nobilissimo, Generosissimoq; Heroi Domino Stephano Gans, Libero Baroni PotlitzI, Nec non Wolffshagiæ, turmæ equestris sub ductu et moderamine Illustrissimi Principis Auraici præfecto |

|
Arms of Louis XIII
[[3]] de Bourbon, called the Just, by grace of God, most-Christian King of France and Navarre, thirteenth of this name. 1628 |
LOVIS DE BOVRBON DICT LE IUSTE PAR LA GRACE DE DIEV TRES-CHESTIEN ROY DE FRANCE ET DE NAVARRE. TREIZIESME DE CE NOM
1628 |

|
To the most august, most high, most powerful, high, magnficent Emperors, Kings, Princes, Dukes, Counts, and all other Lords and noble Teachers and Amateurs, of the most noble science of handling Arms | Aux tresauguste, treshaults, trespuissants, tresillustres, hautes, magnfiques, Empereur
Roys Princes Ducs Comtes et touts autres seigneurs et nobles Fauteurs & Amateurs de La tresnoble science de manier les armes |

|
In nob. Et eximii viri D. GERARDI THIBAULTII | |

|
GRANT OF PRIVILEGE BY THE KING OF FRANCE
By grace and privilege of the King, it has been permitted and granted to Gerard Thibault native of Antwerp, to print, sell, and distribute the present book and figures, in such character and volume as to him seems fit, in all the Kingdoms, lands, and holdings of his Majesty during a period of nine years counting from the day he shall have it printed, with all protections from all persons of whatever quality and condition they may be, to sell and distribute the said book, in part or portion thereof, whether a lithograph, woodcut, etched plate, stolen or counterfeit, or to sell the said figures alone or with summary of what they represent, either separately or jointly, on pain of contravention of loss of goods and five thousand pounds fine, half applicable to his Majesty, and the other to the said Thibault; who, moreover carries full letters to this effect, given in Paris, the XXI Day of December, in the year of grace one thousand six hundred and twenty and in fourth of the reign of the said King. Signed by the King in his Council and sealed with the great seal of his Majesty in yellow wax on a ribbon. |
EXTRAICT DU PRIVILEGE DU ROY DE FRANCE
Par grace & privilege du Roy, il a eſté permis & oćtroyé à Gerard Thibault natif d'Anvers, d'imprimer vendre & debiter le preſent livre & figures, en tel charaćter & volume que bon luy ſemblera, par tous les Royaumes pays terres & Seigneuries de ſa Majeſté, pandant le temps de neuf ans à compter du jour qu'il ſera achevé d'imprimer: avec deffences à toutes perſonnes de quelque qualité & condition qu'ils ſoyent, de vendre & debiter ledićt livre part ou portion d'iceluy, avec leſdites figures ſeuls ou ſans icelles, ſoit taille douce, de bois, d’eau forte, de le pocher ou contrefaire, ou vendres leſdites figures ſeules ou avec ſomaire de ce qu'elles repreſentent, ſoit ſeparemant ou conjoinćtment, ſur pene au contrevenant de perte des exemplaires, & de cincq mille livres d'amande; moitie applicable à ſa Majeſté, & l'autre audićt Thibault; comme plus a plein eſt porté aux lettres ſur ce obtenues, données à Paris le XXI. Jour de Decembre, l'an de grace mil ſix cent vengt, & du regne du dićt Seigneur le quatieſme. Seignées par le Roy en ſon Conſeil Perrochet, & ſcellees du grand ſeau de ſa Maieſté en cire jaune à queue pendant. |
| PRIVILEGE
The Estates General of the United Provinces of the Netherlands, have consented and granted, and do consent and grant to the named Gerald Thibault, that be during the time of next thirty years to come, alone in these united Lands, affiliated lands and towns, full rights and privileges that he may print, sell, and distribute this treatise, engravings, instructions, knowlege, & exercises entitled “Academie de GIRARD THIBAULT d'Anvers, ou ſe demonſtrent d'un cercle mysſterieus la theorie & praćticque des vrais, & juſtes à preſent ingcognus ſecrets du maniement de Armes à pied & à cheval.” Forbidding one and all within the jursdiction of these lands, to offer for sale copies of the aforesaid book for the aforsaid time of thirty years, directly or indirectly, in whole, or in part either greater or lesser, neither the imprint, nor the engravings, nor the explanations of the engravings. Upon pain of forfeture of all copies and payment of a fine of the sum of nine hundred guilders. One third part thereof to be given to the officer who performed the arrest, the second third to the watchmen, and the remaining third to the aforesaid Girardo Thibault. Given in Graven-Hague this fifth of June Sixteen-Twenty-Seven. Gaspar van Vosgbergen. By order of the President of the Estates-General. I. van GOCH. |
PRIVILEGIE
De Staten Generael der Vereenighde Nederlanden, hebben gheconſenteert ende gheoćtroyeert, conſenteren ende oćtoyeren by deſen d'erfghanamen van Giraldo Thibault, dat ſy gheduerende den tijdt van dertich eerſt-ckomende Iaren, alleene in deſe vereenighde Landen, gheaſſocieerde Landtſchappen ende Steden, ſullen moghen Drucken, doen Drucken, ende uytgheven ſeeckere Wapen-kunſt, beſtaende in Figuren, met regulen, aenwijſinghen ende leer-ſstucken, gheinſituleert Academie de GIRARD THIBAULT d'Anvers, ou ſe demonſtrent d'un cercle mysſterieus la theorie & praćticque des vrais, & juſtes à preſent ingcognus ſecrets du maniement de Armes à pied & à cheval. Verbiedende allen ende een yeghelijck Ingheſetenen van deſe Landen, de voorſchreven Wapen-konſte binnen den voorſchreven tijdt van dertich Iaren, direćtelijck ofte indirećtelijck, in't geheel, ofte ten deele, in't groot oſte in't kleyne, na te Drucken, ende uyt te gheven, oſte elders na ghedruct, hier te Lande te brenghen om verkoſt te werden, by verbeurte van alle de na-ghedruckte exemplaren, ende daer-en-boven van de ſomme van neghen hondert guldens; 'tappliceren een derdendeel daer van ten behoeve van Officier die de calangie doen ſal, het tweede derdendeel ten behoeve van de armen, ende het reſterend derdendeel ten behove van de voorſchreven erfghenamen van Girardo Thibault. Ghedaen in s'Graven-Haghe op den vijfden Iunij ſeſthein-hondert ſeven en twintich. Gaſpar van Vosberghen Vt. Ter ordonnantie van de Hooch-ghemelte Heeren Staten Generael. I. van GOCH | |

|
NOTICE CONCERNING
the figures of this book. |
AVERTISSEMENT SVR LA CONSI-
deration des figures de ce livre. |
| Because the reader shall find it strange that many of the images are not placed upon the ground, but are above or below the horizon, we think it best they be conceived of as paintings upon the walls; this being because of the unequal circles above the horizon compared to the ground, and for more convenient representation of the doctrine, & for easier intelligbility in a manner which does not extend perspectives. Thus in Plate 3, high on both sides, we see 4 men painted on the walls, & in Plate 5 there are four pieces in the form of paintings in the middle of the masonry wall each with its own appropriately-sized circle. In Plates 6, 16, 21, 22, 25, & 28 we find painted canvasses & murals on the sides, and on the lower parts of the walls. In Plates 7 & 27 we understand they are made in the form of charts. In Plate 19, a tapestry hangs in the middle, in which the doctrines are embroidered. The Plates 5, 8, 14, 17, 18, 20, 22, 25, 26, 27, 28, & 29 likewise have painted walls, but the most important parts are shown alive on the ground or as painting on the wall base, because we have put there the means to see how the position of the swords relates to the lines of the Circle in the form of shadows on the lower line or base. We can see the positions of the blades, on the ground of the circle, by which means the capability to work out the movements of the swords the figures have in their hands becomes quite easy. | Pource que le ſpećtateur trouveroit eſtrange, que pluſieurs Images ne ſont fixement poſées ſur le fondement, taut au deſſus qu'au deſſoubs de l'Horiſon: nous avons touvé bon de l'advertir, qu'il les faut concevoir comme eſtant deſpeintes aux murailles; cela eſtant fait à cauſe des Cercles inegaux tant au deſſus de l'Horiſon que ſur le plan, pour la repreſentation plus commode de la doćtrine, & pour l'intelligence plus facile du commun qui n'entend les perſpećtives: ainſi au Tableau 3. au deſſus d'un & d'autre coſté ſont deſpeints 4. hommes aux parois, & en la Table 5. il y à quatre pieces en forme de peinture au millieu de la muraille ou maſſonerie, deſquels Cercles chaſcun ſuſſit pour ſoy, & es Tables 6. 16. 21. 22. 25. & 28. au millieu des toilles peinturées, & au coſtez ſont deſpeintes à la paroy, es Tables 7. & 27. faut entendre que cela eſt fait en forme de chartes, & en la Table 19. un tapi tendu ou pendu au millieu, dans leſquel les doćtrines ſont tiſſues, & es Tables 5. 8. 14. 17. 18. 20. 22. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. de meſme deſpeint aux murailles, mais les premieres pieces ſe demonſtrent plus vivement ſur le fond ou baſe que les autres, car la ſe voit la façon des accords des eſpées & leur operation par les lignes du Cercle; pour ce que en forme d'Eſquierre de la ligne Inferieure ou baſe, on trouve un accord des lames, fait au fond ou Cercle, par lequel le jugement des operations mouvantes des eſpées que les figures tiennent en main, eſt rendu tres-facile. |
| Translation by Bruce G. Hearns |
Transcription by Bruce G. Hearns |
|---|---|
| |
| EXPLANATION OF THE FIRST PLATE | DECLARATION DV TABLEAV PREMIER |
| Contents The proportions of the body, their relationship to the dimensions of our Circle, and the proper length of the sword. |
Contenant Les proportions du corps de l'homme, rapportées à la figure de noſtre Cercle; & à la iuſte longeur de l'Eſpée. |
| A discourse on the superiority & perfection of man, declaring that his body is comprised of an exact relationship of Divisions, Weights, & Measurements, having movements that relate to the Circle. | Diſcours de l'excellence & perfećtion de l'homme, dećlarant que ſon corps eſt exaćtement compaſſé par Nombres, Poids, & Meſures, ayant des mouvements qui ſe rapportent à la figure Circulaire |
| Man is the most perfect and most superior of all the creatures in the world, in which is found, amongst the other marks of divine wisdom, such an exquisite representation of the entire universe, in his whole and in his principal parts, that he has been rightly called by the ancient philosophers “microcosm” which is to say, the small world. For beyond the dignity of the soul, which has so many advantanges above all thats is perishable, his body contains a an abridgement, not only of all that we see down here on Earth, but also that which is in Heaven itself. Representing the whole with a harmony so delicate, so beautiful, and complete, and with such concurrence of Divisions, Measures, and Weights, which relates so marvellously to the virtues of the Four Elements, and to the influences of the Planets, that there is no other like it to be found. That most-perfect number Ten continually appears before his eyes, and in its entirety on his digits; and again in two equal halves on his two hands, on each by the number of 5 digits; which are also unequally partitioned by the thumb and by the rest into One and Four, of which the One is composed of two phalanxes, and each the Four of Three: in such fashion this structure has always in view the first and most beautiful Numbers: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, & 10, which so many illustrious philosophers, like Pythagoras, and Plato, & all those of their schools, held in such esteem, that they sought hide away and so deduce from them the greatest mysteries of their doctrines. As well, we see in the height, width, and thickness of the human body, which has been so precisely measured, that the greatest Architects, both Ancient and Modern, could concieve of no other thing in the world that would make a better basis for the architectural orders than this model, based on man. In this they saw a divine proportion that God Himself put into the human body, from which they took their inspiration to build, from that time on, into the architecture of Temples, Theaters, Amphitheaters, Palaces, Towers, Vessels, and all other constructions, some of peace, some of war, not just in the whole, but also reflected in the parts: the columns, the peristyles, capitals, pedistals, and other such parts. Thus we read that the Temple of Salomon, this great adornment and miracle of the flourishing Republic of the Jews, was sized according to this same proportion: and what is more, God Himself commanded the Patriarch Noah, upon building of the Ark, to follow the same rule. So that in each one the length is six times the width, and ten times the depth. This is a proportion for which the numbers are always right in front of our eyes, and can be demonstrated clearly on our fingers, where we are accustomed to learning the earliest lessons in natural arithmetic. For this whole sum, which is 10, when multiplied by 3, makes 30 for the depth; and by 5, makes 50 for the width; and multiplied by 10, and by 3 again, makes 300 for the length. These measurements agree with what several noted Authors wrote concerning the same matter. Vitruvius, amongst others, reported the stature of man to be 6 feet measured geometrically. Divide each foot into 10 degrees, and each degree into 5 minutes, gives 60 degrees and 300 minutes, echoing exactly the three hundred cubits of the Ark. As much as I do not wish to rest so precisely on Vitruvius' authority and accept his geometrical figure of six feet length; it is enough that we can divide the body into six equal measures. Pliny also notes in book 7, chapter 17, that this natural stature of a well-proportioned man accords exactly with the measure of his own arms from the tips of the fingers on one to the end of the other. In summary, all philosophers have made so much of these measurements, and of the proportions of the human body, and have researched so much in one fashion or another that Pythagoras dared declare man as the Measure of All Things. As to the proportion of weight, we cannot doubt that this was also observed with as much art as the numbers or the measurements. All of which is easy to recognize, because man alone, of all the animals, walks upright; in such fashion he holds himself always in counterweight and in balance in all actions, otherwise he would be constantly inconvenienced. For his structure is such, that as each part (except the arms) is higher from the ground, it also increases more and more in weight; so that the lighter and more fragile parts support the other heavier and more robust parts: which would be against Nature and would make it utterly impossible to continue long, in doing so many kinds of movements as we can see performed by the human body, were this not moderated with regard to weight in all the parts from the top of the head to the soles of the feet, in a singular and perfectly artful way. A more complete discussion of this material belongs to anatomists, whose profession is to discuss the particuliarities of this noble structure. We who seek only to explore that which concerns the use of weapons, shall be content to discuss some generalities, notably about the external proportions, so that it shall be much easier to judge the nature and reach of each movement, as we proceed. Since the movements are sometimes made with the whole body, sometimes and more usually with just the arms and hands, and other times with the legs and feet, we shall demonstrate presently that men are capable of performing these necessary and useful movements more easily and promptly than other animals do. What one must know that it is ordinarily, and properly, the job of the arms and hands to carry out the actions of our Will, as use or need requires. The legs and feet serve only to move and turn the body, so as to place the arms and hands so they can properly perform the task we wish to perform where we wish to perform it. Furthermore there is this difference, that the arms and legs are especially suited to perform large movements, whereas the feet and hands perform smaller ones; and as the arms are best used in moves that require strength, the hands are best used in work that requires dexterity. The feet, as pillars that support the body, are, almost immobile when the weight is on the heels, but when on the toes, move quite promptly. Because of this difference, the body can stand firmly by means of the one and yet move and turn swiftly and conveniently by means of the other. From heel to toe, the size of the foot gives him a solid and stable base when he stops, and when he moves, helps to push him forward and give him speed. All parts of the hands are quite agile, and contain, in their width, exactly half the width of the face, which is a quarter of the trunk; the length of the hand is two times the width, and if the hand is closed, the contour of the fist is one third the contour of the trunk: and the hand can naturally act as a small shield, held out in front, either open and extended, or firmly closed. This is why the Jewish author Philo is very right to say that, instead of the natural weapons and defenses of other animals, man was blessed with Reason as his Guide, and Hands as Tools to do as Reason wills; and in that Reason is the Hand of Understanding, the Hand of Reason is the Word, and our hands perform as the Word commands.
Instruments which have within them all the abilities of the other creatures, and are, consequently, at least equal in greatness, if not superior. This is why man comes into the world deprived of all natural weapons either offensive or defensive, and has but this sole instrument of the hand, by which he may prevail over all. The other animals defend and attack their opponent, one with teeth, another with claws, with hooves, with horns; thus it is wth Elefants, Lions, Bears, Horses, Bulls, Tigers, & other beasts, to whom nature gave each one a single type of natural weapon for their own defence, but to Man, who appears deprived, was blessed with Understanding to know things, Wit to forge things, and Hands to use each and every thing that he can create. In the same way so that he could have even greater advantage, nature gave him, as a special privilege, the power to flex his arms behind and his feet in front at the same time, something impossible for other creatures: and also for the same, or possibly similar reason, the arms were placed in such a way as to be always in view and so help and assist more easily the other parts as they need. So just as the above-mentioned Artists, Architects, Perspectivists, & others have tried to prove the foundations of their rules via the proportions of the human body, so have we navigated the same course, but more adeptly, and have found, with the aid of this same compass, the actual and proportional measure of all Movements, of all the Tempos and Distances necessary to observe in our Training: as it shall be demonstrated in a moment in the description of our Circle; where the measurements and proportions of Man are applied to man himself, and to the movements he makes with his own limbs, from where we derive the aforesaid proportion, and without which it is impossible for him to perform the slightest action in the world. In the practice of swordplay, which I have done for several years, in different countries, and with great experts; of which some come from French schools, others from Italian, and, in sum, each in his own way, I have seen people all over accustom themselves to strange postures, body twisted, feet and hands disjointed out of all natural positions, and in postures inconsistent with the ordinary way in which we walk or stand: such that, instead of evoking through these contortions some sort of power, it impairs and minimizes one's own strength, rather than producing the intended effect. Thus, considering closely, and knowing that in other cases all Arts follow Nature, without ever contravening her, I have chosen to conduct our Training within the same school as this Sovereign Mistress of all good inventions. About which I said at first, that all the Distances and Instances (i.e. steps in the process of fighting) to be observed in training (which are the basic foundations and support for all the following parts) proceed from the proportions of Man, therefore without this same awareness, they cannot be duly comprehended, nor practiced with confidence. And the same goes for the Steps and Approaches, short and long, required by the variety of positions in the performance of these Exercises. From which it is apparent that one must begin with a good knowledge of the proportion of limbs and body parts, that one may at least be able to make some reasonable judgement on the reach of each movement, proportionally to the limb, or limbs, on which the movement depends, and from which it must be continued, ended, turned, returned, released, bound, or changed in a thousand different ways. |
L'homme eſt la plus parfaite & la plus excellente de toutes les Creatures du Monde; auquel ſe trouve, parmy les autres marques de la ſageſſe divine, une ſi exquiſe repreſentation de tout l'Vnivers, en ſon entier & en ſes principales parties, qu'il en a eſté appellé à bon droit par les anciens Philoſophes Microcoſme, c'eſt à dire, le Petit Monde. Car outre la dignité de l'ame, qui a tant d'avantages par deſſus tout ce qui eſt periſſable, ſon corps contient un abbregé, non ſeulement de tout ce qu'on voit icy bas en terre, mais encores de ce qui eſt au Ciel meſme; repreſentent le tout avec une harmonie, ſi douce, belle, & entiere, & avec une ſi juſte convenance de Nombre, Meſures, & Poids, qui ſe rapportent ſi merveilleuſement aux vertus des Quatre Elements, & aux influences des Planetes, qu'il ne ſ'en trouve nulle autre ſemblable. Le tres-parfait nombre de Dix luy eſt continuellement repreſenté devant les yeux, en ſon entier ſur ſes propres doigts; & derechef en deux moitiez egales ſur ſes deux mains, à chaſcune par le nombre de Cinq doigts; qui ſont derechef partis inegalement par la poulce, & par le reſte en Vn & Quatre, dont l'Vn eſt compoſé de Deux articles, & les Quatre de Trois: de façon que ceſte ſtructure luy met touſiours en veuë les premiers & plus excellents Nombres 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 10. dont tant d'Illuſtres Philoſophes, comme Pythagoras, & Platon, & tout ceux de leurs Eſcholes, on fait tant d'eſtime, qu'ils y ont voulu cacher, & en deduire les plus grands myſteres de leur doćtrine. En outre on voit auſi en la longeur, largeur, & eſpeſſeur de ce meſme corps, que les meſures y ſont ſi jusſtement obſervées, que les plus grands Architećts Anciens & Modernes n'ont ſcue choiſir aucune choſe au Monde plus propre pour leur ſervir de regle, ſelon laquelle ils deuſſent former les ordonnances de leurs ouvrages, que ce ſeul patron de l'homme; auquel ils ont remarqué une perpetuelle proportion gardée de Dieu meſme en la fabrique du corps; laquelle ils ont prinſe en exemple, pour façonner à l'advenant les Architećtures des Temples, Theatres, Amphitheatres, Palais, Tours, Vaiſſeaux, & autres Instruments, ſoit de paix, ſoit de guerre, non ſeulement en leur entier, mais auſi en chaſcune des principales parties, Colomnes, Poſteaux, Chapiteaux, Piedeſteaux, & autres membres ſemblables.
Ainſi lit on, que le Temple de Salomon, ce grand ornement & miracle de la Republique floriſſante de Iuifs, a eſté compaſſé ſelon ceſt meſme proportion: Et qui plus eſt, que Dieu meſme auroit commandé au Patriarche Noë, en baſtiſſant l'Arche, d'enſuivre la meſme regle. Car tout ainſi que le corps de l'homme contient 300 minutes en longeur; 50 en largeur; & 30 en eſpeſſeur par le milieu de la poitrine: auſſi pareillement l'ordonnance de l'Arche a eſté faite à 300 coudées de longeur; 50 de largeur; & 30 de hauteur: de ſorte qu'en l'un & en l'autre la longeur eſt ſix fois autant que la largeur, & dix fois, que la profondeur. Qui eſt une proportion, donc nous avons touſjours devant nos yeux les nombres, & les pouvons nous demonſtrer clairement ſur nos doigts, où nous avons couſtume d'apprendre les premieres leçons de l'Arithmetique naturelle. Car la ſomme entiere, qui en eſt 10, eſtant multipliée par 3, fait 30 pour l'eſpeſſeur; & par 5, fait 50 pour la largeur; & multipliée par 10, avec le redouble de 3, fait 300 pour la longeur. Et à ces meſures s'accorde auſſi ce que pluſieurs graves Auteurs eſcrivent en touchant la meſme matiere: comme entre autres, que Vitruve a rapporté la ſtature de l'homme à 6 pieds de meſure Geometrique; le pied à 10 degrez; & chaſque degré en 5 minutes; qui font 60 degrez, & 300 minutes, retirants juſtement aux trois cents coudees de l'Arche. Combien que je ne veuille pas m'arreſter ſi preciſement ſur l'authorité de Vitruve, à luy donner ſix pieds Geometriques de longeur; ce m'eſt aſſez qu'on la puiſſe partir en ſix meſures égales. Pline remarque auſſi livre 7. chapitre 17. que ceſte ſtature naturelle de l'homme bien proportionné s'accorde exaćtement à measure de ſa propre braſſee, depuis le bout des doigts de l'une des mains juſques au bout de l'autre. En ſomme touts Philoſophes ont fait tant d'eſtime de ceſte meſure, & de la proportion de ce corps humain, & l'ont tant recerchée, les uns d'une façon, les autres de l'autre, que Pythagoras a oſé nomme l'homme La Meſure de tout. Quant à la proportion des Poids, il ne faut pas douter, qu'elle n'y ſoit auſſi obſervée avec tout autant d'artifice, que les Nombres, ou les meſures. Ce qui eſt aiſé à cognoiſtre, par ce qu c'eſt l'homme ſeul de touts les animaux qui marche droit; de façon qu'il ſe tient touſiours en contrepoids & en balance en toutes aćtions, autrement il en ſeroit à touts moments incommodé. Car ſa ſtrućture eſt telle, que touts ſes membres (exceptez le bras) à meſure qu'ils ſont plus relevez de la terre, auſſi ſont ils plus peſants de plus en plus; ſi que les parties plus legeres & plus foibles ſoutiennent les autres plus peſantes & plus robuſtes: qui ſeroit choſe contre Nature & du tout inſupportable pour continuer longuement, en tant & en ſi diverſes ſortes de mouvements, comme on voit que ce corps humain pratique, s'il n'eſtoit moderé au regard du Poids en toutes ſes parties depuis le ſommet de la teſte juſqu'aux plantes des pieds, d'un ſingulier & parfait artifice. La declaration plus ample de ceſte matiere appartient aux Anatomiſtes, qui font profeſſion de declarer les partiularitez de ceſte noble ſtrućture: nous qui ne pretendons que d'en expoſer ſeulement ce qui touche l'exercise des Armes, ſerons contents d'en declarer quelques choſes en gros, notamment touchant les proportions exterieures; afin q'il ſoit par cy apres d'autant plus facile à juger de la nature & portee de chaſcun des mouvemēts, qui en procedent. Puis donc que les mouvements ſe font quelques fois avec le tronc entier du corps, quelquesfois & plus ſouvent avec les bras & les mains, & autres fois avec les jambes & les pieds, nous demonſtrerons preſentement, que les hommes ſont capables d'exploiter leurs movemēts neceſſaires & utils en plus grand nombre & plus aiſeement & plus promptement, que ne font les autres animaux. Dont il faut ſçavoir, que c'eſt ordinaire & proprement l'office des bras & des mains d'executer le commandement de la volonté, en faiſant les aćtions que l'utilité ou la neceſſité demande; & que les jambes & les pieds ne ſervent communement à autre choſe, au'à tranſporter et à tourner le corps, & à mettre le bras & mains en places, où la Volonté pretend quel execution ſoit fait: & d'avantage qu'il y a ceſte difference, que les bras & les jambes ſont ſpecialement propres à faire les grands mouvements, ainſi que les pieds & les mains ſont propres aux moindres: & comme les bras ſont particulierement capables à executer ce où il faut de la force, ainſi les main le ſont d'autrepart pour travailler avec dexterité. Les Pieds, comme pilliers qui ſouſiennent le corps, ſont devers les talons quaſi immobiles, mais devers les orteils ils ſe mouvent aſſez promptement: de ſorte quepar l'inegalité de ceſte ſtrućture le corps ſe peut affermir deſſus, au moyen de l'un, comme il ſe peut d'autrepart remuer & tourner viſtement & commodement de touts coſtez, au moyen de l'autre. En l'un & en l'autre derechef il reçoit un grand ſoulas par la juſte longueur, qui luy fournit un fondement ſtable & ſolide quand il s'arreſte; & quand it marche, elle aide à le pouſſer & luy donner ſa courſe. Les Mains ſe meuvent fort agilement en toutes leurs parties, & contiennent en leur plus large la juſte moitié de la largeur du viſage, qui eſt le quart au regard de la poitrine: la longueur en eſt deuz fois autant: & eſtant la main fermée, le contour du poing ſera le tiers du contour de la poitrine: en ſorte qu'elle luy peut naturellement ſervir d'eſcuſſon pour la defendre, en la tenant devant, ſoit ouverte et eſtendue, ou bien ſoit fermée. Ceſt pour quoy Philo, autheur Iuif, a tres-bien rencontré à dire, qu'au lieu de touts les ornements & defenſes naturelles des autres animaux, l'homme a eſté doué de la Raiſon, comme Direćtrice, & de Mains, comme Inſtruments pour executer ce qu'elle veut: & que la Raiſon eſt la Main de l'Entendement; la main de la Raiſon c'eſt la Parole; & les Mains corporelles celles qui font l'execution de ce que la Parole commande. Inſtruments, qui contiennent en eux toute la ſuffiſance des autres, & qui par conſequent les egalent en dignité, voire les ſurmontent. Pour laquelle cauſe il vient au Monde deſpourveu de toutes armes, tant offenſives que defenſives, & n'a que ce ſeul inſtrument de la main, au moyen duque il ſe puiſſe prevaloir de toutes. Les autres animaux ſe defendent & offenſent leurs contraires, l'un avec les dents, l'autre avec les ongles, les pieds, les cornes; ainſi quil ſe voit és Elefans, Lions, Ours, Chevaux, Taureaux, Tigres, & autres beſtes, à qui la Nature a departiaſſez chichement une ſeule eſpece d'Armes a chaſcune, pour la neceſſité de leur defenſe; mais à l'homme, qui en ſemble eſtre du tout privé, en recompenſe elle l'a doüé d'Entendement pour les cognoiſtre, d'Eſprit pour les forger, & de Mains pour s'en aider de toutes & telles qu'il en puiſſe eſtre. meſme afin qu'il s'en peuſt aider avec plus d'avantage, elle luy a donné par ſpecial privilege de pouvoir à meſme inſtant fleſhir les bras en arriere & les pieds en avant, choſe impoſible aux autres creatures: comme auſsi pour la meſme, ou pour ſemblable cauſe, la ſituation naturelle des bras a eſté placée en tel endroit, que les operations des mains fuſſent touſiours ſous le gouvernement de la veuë, pour en ſecourir & aſsiſter tand plus aiſement le reſte des membres en leurs neceſsitez. Tout ainſi donc que le ſuſdits Artiſtes, Architećtes, Perſpećtiviſtes, & autres on taſché de prouver les fondements de leurs regles par les proportions du corps de l'homme, ainſi avons nous pareillement tenu la meſme courſe, mais avec meilleure adreſſe, & avons trouvé à l'aide de ceſte meſme buxole la vraye & proportionelle meſure de touts les Mouvements, de touts les Temps, & Diſtances, neceſſaires à obſerver en noſtre Pratique: comme il vous ſera demonſtré tout à l'inſtant en la declaration de noſtre Cercle; où les meſures & proportions de l'homme ſont appliquées à l'homme meſme, & aux movements qu'il fait avec ſes propres membres, où ladite proportion ſe trouve, & ſans laquelle il luy eſt impoſſible de faire la moindre aćtion du Monde. En pratiquant donc ceſt Exercice, comme i'ay fait par pluſieurs annees, en divers pays, & avec de grands amateurs; dont les uns tiroyent à la Françoiſe, les autres à l'Italienne, & en ſomme chaſcun à ſa mode; j'ay veu qu'on s'accouſtume par tout à des poſtures eſtranges, le corps plié en pluſiurs courbures à pieds & jambes diſioinćtes hors de proportion naturelle, & en ſituations du tout repugnantes à la mode ordinaire qu'on tient en cheminant ou en demeurant ferme: de ſorte qu'au lieu de faire paroiſtre par ces mines quelque grand courage, on s'incommode & amoindrit on ſes propres forces, pluſtoſt que d'en obtenir l'effećt de l'intention pretendue. Ce que conſiderant de pres, & ſachant d'autrepart, que touts les Arts enſuivent la Nature, sans jamais y contrevenir, j'en ay prins occaſion de vouloir conduire auſsi noſtre Exercise à la meſme Eſchole de ceſte Souveraine Maiſtreſſe des bonnes inventions. En quoy j'ay remarqué premierement, que toutes les Meſures & Inſtances à obſerver en ceſt Pratique (qui ſont les premiers fondements & l'appuy de toutes le parties ſuivantes) procedent de la proportion du corps de l'homme, comme auſsi ſans la meſme cognoiſſance elles ne ſçauroyent eſtre deuemēt comprinſes, non plus que d'eſtre pratiquées avec aſſeurance. & qu'auſsi le ſemblabe en eſt il de Pas & Demarches ordinaires ou extraordinaires, que l'uſage de l'Exercise & la varieté des occaſions requierent. Par où il appert, qu'il faut entrer ſi avant en ceſte cognoiſſance de la proportion des membres & parties du corps humain, qu'on puiſſe à tout le moins faire quelque raiſonnable jugement de la portée de chaſcun mouvement, à proportion du membre ou des membres, d'où il depend, & desquels il doit eſtre continué, fini, tourné, retourné, laſché, bandé, ou changé en mille & mille manieres. |
| The first thing to know is that the philosophers attibuted to the microcosm of the human body various figures, of which we will later discuss the triangle, the quadrangle, and the pentagon. For the moment, we shall say the figures made by the body are also round or circular, in accordance with Hippocrates, Prince of Doctors, who said that the body is a circle. Which can be understood as much in regard to the actions and operations of its interal parts, and their attendent functions, so reciprocal and each following one on the other, so we can find no beginning and no end, as if following the circumference, as it can be also to movements of his limbs which always go around, from the strength of the centre to the weakness of the extreme circumference. Thus, as it is now time to turn to the question of, and to discuss, Range, which is appropriately proportional to stature, position, approaches, and generally all external movements of this same body, I now introduce our Circle, which, as I say, contains all the above-mentioned qualities, and is taken from the correct measurements and proportions of a man. All mathematicians know that the circle or round figure is the simplest, primary, and moreover most perfect, superior, and most useful of all for defense; a figure which has only one point of contact on its surface at only one point at a time: thus such a noble thing as our body cannot help but make use of such a useful figure: to which also can be demonstrated in many ways and principally on the long extension; which is, when standing straight upright, feet joined, and the arms extended directly above, so that the elbows are by the top of the head. For when he holds himself thusly, either upright beside a wall, or extended in the same way on the ground, and we place one branch of a compass on his navel, and the other on his fingernails or at the soles of his feet, and we draw about him a circumference, we create a circle of which the centre will be on the person's navel, the Diameter will be the person's extended height, and the circomference will touch, on one side, the soles of the feet, on the opposite, the tips of the fingers. If one finds it does not fit, the body has not been exactly positioned following the rules of composition. Thus the Circle, which we intend to use throughout this book to perform our exercises, which is proportional to all the movements we shall make, with arms, and legs, and the body as a whole. One could draw still other Circles from man's proportions in many ways (such as putting the Centre on the shameful parts and draw the Circumference at the top of the head and the soles of the feet) but these cannot suffice, nor have the convenient measure we are looking for, because they have no relation to the proportions of the extended arms, which is the principal aspect required for this Training, which is why, together with certain other considerations with respect to the question of using the Circle, we must use the extended length as an exact measure for the Diameter, and not any other. | Il faut donc ſçavoir pour le premier, que les Philoſophes attribuent à ce Microcoſme du corps humain diverſes figures, dont it ſera parlé autrement de la triangulaire, quadrangulaire, & pentagone. Preſentement nous diſons, qu'il eſt auſſi rond ou circulaire en la figure de ſes mouvements, à quoy s'accorde le dire d'Hippocras Prince de Medecins, que le corps eſt un Cercle. Ce qui ſe peut entendre tant au regard des aćtions & operations naturelles de ſes parties interieures, & de leurs alterations ſubalternes, tellement reciproques & ſuccedantes les unes aux autres, qu'il ne s'y trouve non plus de commencement ne de fin, qu'en la rondeur d'une circonference, auſſi ſe peut il rapporter à la figure de touts ſes mouvements locaux, qui va touſiours en rond, s'eſtendant depuis le centre de ſa force juſqu'à l'extreme circonference de ſa foibleſſe.
Or puis qu'il eſt donc preſentement queſtion, de vous faire voir la Meſure, qui ſoit convenable & proportionée à la ſtature, ſituations, demarches, & generalement à touts les mouvements exterieurs de ce meſme corps, voicy la figure de noſtre Cercle, que nous diſons contenire toutes les ſuſdites qualitez, & eſtre tiré de la propre meſure & proportions du corps de l'homme. Touts les Mathematiciens ſçavent, que la figure circulaire ou ronde eſt la plus ſimple, la permiere, voire auſſi la plus parfaite, la plus excellente, & la plus capable de toutes pour la defenſe; comme celle qui ne ſe laiſſe toucher en la ſurface, qu'en un ſeul point à la fois: dont une figure ſi accomplie ne devoit pas manquer à un corps ſi noble: auquel auſsi elle peut eſtre demonſtrée in diverſes manieres; & principalement ſur la longeur eſtenue; ceſt à dir quant il ſe tient droit ſur ſes jambes, à pieds joinćts, & les bras éſtendus droitement en haut, tellement que les coudes luy egalent le ſommet de la teſte. Car lors qu'il ſe tient en telle ſituation, ſoit debout contre un mur, ſoit eſtendu en la meſme ſorte par terre, & qu'on luy mette l'une des branches d'un grand compas ſur le nombril, & l'autre ſur les orteils ou contre la plante des pieds, & qu'on en tire en rond une circonference, il en ſourdra un Cercle; dont le Centre ſera ſur le nombril de la perſonne, le Diametre en ſera comme la hauteru eſtendue, & la Circonference en touchera d'un coſté la plante des pieds, & à l'oppoſite les bouts des ſes doights. Si on y trouve de la faute, le corps n'a pas eſté exaćtement proportionné ſuivant les regles de ſa compoſition. Or voilà maintenant le Cercle, duquel nous pretendons uſer en tout ce Livre pour l'adreſſe de noſtre Exercice: lequel, d'autant qu'il eſt proportionné à touts le mouuements qu'il ſçauroit faire, avec bras & jambes, & avec tout le corps entier, ou avec chaſcune de ſes parties. On pourroit tirer encor d'autres Cercles de ceſte proportion de l'homme en diverſes manieres (comme en mettant le Centre ſur les parties honteuſes, & la Circonference au ſommet de la teſte & à la plante des pieds.) mais iceux ne peuvent avoir la meſme ſuffiſance, ne la convenance des meſures que nous cherchons preſentment; à raiſon qu'ils n'ont pas de proportions avec les bras eſtendus, auxquels il appartient en ceſt Exercice d'executer la principale partie de la beſoigne: pour laquelle cauſe, enſemble auſsi pour quelques autres conſiderations, s'il eſt question de ſe ſervir icy de Cercle, il n'y faut advouer autre meſure de Diametre, que celle qui s'accorde exaćtement avec ceſte longeur eſtendue. |
| HERE FOLLOWS THE METHOD
of drawing upon the floor, the Circle and all its components |
S’ENSVIT LA MANIERE DE
covcher le cercle svr le plan, avec tovtes ses appartenances |
| Having shown the dimensions of the Diameter, Centre, and Circumference, it now follows that we describe the rest; to find the proportions on which the circle depends: and to this end, must, of necessity, enscribe the entire Circle on a smooth floor, in its appropriate size, using as the measure of the diameter, the extended length of the person who shall do the moves. This is how to proceed. | Ayant monſtré la dimenſion du Diametre, le Centre, & la Circonference, il s'enſuit maintenant que nous declarions auſſi le reſte; pour venir apres aux proportions qui en dependent: & à ceſte fin, faut neceſſairement deſcrire le Cercle entier ſur un plan bien uni en ſa juſte & convenable grandeur, en prenant la meſure du diametre ſur la longeur eſtendue d'une perſonne, au corps de laquelle on voudra faire les preuves. Or voicy comme il y faudra proceder. |
| Choose an appropriate place, with a flat, solid floor, on which you shall first mark the Centre point with chalk, in the location most suitable for training. | Choiſiſſiz un lieu propre, ou il y ait un plancher bien uni, ſur lequel vous marquerez pour le premier avec de la croye le poinćt du Centre, en tel endroit qui vous ſemblera plus commode. |
| This done, take a sword of one half-diameter length, so that when the tip is placed upon the ground between the person's two feet, the crosspiece of the hilt will come just to the height of the navel, and place one of the ends of the crosspiece on the centre point; and use the tip to draw the circle by holding a piece of chalk in your fingers, thus describing the Circumference. | Cela fait, prenez une eſpee de la longeur du demi-diametre, telle que la poinćt eſtant miſe en terre entre les deux pieds de la perſonne, les branches de la garde luy viennent juſtement à la hauteur du nombril: & en mettez l'une des branches ſur le poinćt du centre; & laiſſez mener la poinćte à un ſecond avec un morceau de croye entre les doigts en rond, deſrivant ainſi la Circonference. |
| This being drawn, take a chalked carpenter's cord, and snap the Diameter according to the most suitable use of the space, extending both ends two feet (60 cm) beyond the circumference: and label these two crossing-points of the Circumference; the one below the centre with a C, and the other, opposite, with an X. | Laquelle eſtant tracée, prenez une cordelle à la mode des charpentiers, que vous frotterez avec de la croye, & en couchez le Diametre ſelon la commodité de la place, le prologneant à toutes ſes deux extremitez de la longeur de deux pieds outre la circonference: & marquerez les deux coupures de la Circonference; celle qui eſt par decà le Centre, d'un C, & L'autre, à l'oppoſite, d'un X. |
| Next, through the Centre, draw a perpendicular line across, which shall be the Perpendicular Diameter, each of the two ends likewise passing two feet beyond the circumference: and also label both of these crossing-points of the Circumference with an N. | Menez apres en la meſme ſorte par le Centre une ligne coiſiere & perpenduculaire, qui ſera le Diametre perpendiculaire, outrepaſſant pareillement de ſes deux bouts la Circonference à deux pieds de longeur: & marquez encor ſemblablement les deux coupures de la Circonference, chaſcune d'un N. |
| To find this Perpendicular Diameter, first put the tip of the sword on the letter C and one of the arms of the crosspiece along the circumference. | Pour trouver ce Diametre perpendiculaire, mettez premierement la poinćte de l'eſpee ſur la lettre C. & l'une des branches de la croiſee ſur la Circonference, |
| Using the crosspiece as a pivot, move the tip 180 degrees away from C and, again using the tip, draw an arc outside the circle. | menant derechef la poinćte circulairement en avant, & en deſcrivant ſur le ſeuil au dehors de la circonference un arc, reſpondant en droite ligne à la lettre C par le poinćte de l'attouchement de la branche. |
| Do the same, starting from the letter X, so the two arcs cross each other. | Ce qu'il faudra faire auſſi pareillement en commenent par la lettre X, dont le ſuſdit arc ſera coupé en croiſade d'un autre ſemblable. |
| This cross will act as a guide for drawing the perpendicular diameter, by taking the cord from there and through the centre beyond the circumference to the opposite side. | Ceſte croix vous ſervira de guide à tirer le Diametre perpendiculaire, en menant la cordelled par icelle & par le centre outre la circonference do coſté oppoſite. |
| Once again, place one end of the crosspiece on each of the four letters C, N, X, & N in turn, and, with the tip, draw arcs just outside the circumference between the four letters, thus marking four crossing-points, which will be the guide-points for the two Oblique Diameters. | Mettez apres derechef la croix de l'eſpee avec l'une des branches ſur chaſcune de ces quatre lettres C.N.X.N. & en faites tirer avec la poinćte dehors le Cercle à chaſcune deux arcs, reſpondants l'un à l'autre en droite ligne par leſdits lettres: dont il fourdra quatre croiſades, qui donneront l'adreſſe pour couche les deux Diametres obliques. |
| Again, in the same way, place the crosspieces on the ends of the Oblique Diameters, mark outside the circle where the tip crosses the extensions both the Principal and Perpendicular Diameters. These marks define the terminals of the lines beyond the circle, the ends of which are labelled with letters; the one below C with A; the one opposite with Z; the two others with O. | Tirez lors derechef en la meſme ſorte des arc dehors le Cercle ſur les quatre bouts de ces deux Diametres obliques, deux & deux pour chaſcun poinćt, allants par les Diametres prolongez principal & perpendiculaire. Ces arcs ſeront les bornes des parties adjoinćtes, dont les extremitez ſeront marquées de lettres; celle qui eſt deſſous le C, d'un A; & à l'oppoſite d'un Z; les deux aures chaſcune d'un O. |
| From these four points, we draw the Outside Square, drawing lines from A to O on the right & left sides and likewise from Z to O. | Sur ces quatre poinćts ſera tiré le Quarré circonſrit, en menant une ligne de l'A juſques à l'O à droite, & une autre pareillement à gauche; puis ſemblablement deux autres, l'une à droite, & l'autre à gauche depuis le Z juſqu'au deux O. |
| Using the points C, N, X, & N, you will draw the Inside Square, as well as the four Quadrangles; draw the line on the right hand side through C and N from one edge of the Outside Square to the other and another to the left side. Label the mid-points, where these lines cross the Oblique Diameters with a G. Next draw two more similar lines through the points X & N on the left & right sides and label the mid-point of each of these lines with an S. | Ce fait par les quatre poinćts C. N. X. N. vous deſcrirez le Quarre Inſcrit, enſemble avec les quatre Quadrangles; en menant une ligne à main droite par le C & par l'N, ſur les coſtez oppoſites du Quarré circonſcrit; puis encor une autre pareille à main gauche; & puis deux autres par les lettres X & N, l'une à droite, & l'autre à gauche, leſquelles lignes faudra marquer ſur les poinćts du mitan, qui ſont coupez par les Diametres obliques, entre les deux lettres C. & N. à chaſcun des coſtez deſſous le Centre d'un G; & deſſus au mitan des lettres N. & X. à chaſcun des coſtez d'un S. |
| Then draw two Interior Collaterals through C & S to the left and right. | Apres tirez par les lettres C. & S. deux Collaterales Interieures, l'une à droite, & l'autre à gauche. |
| Likewise draw two more through the letters X & G. | Semblablement tirez en deux autres par les lettres X & G. |
| Then draw two Interior Transverses on the right hand side above the Centre from the letter N across the Diameter line through S and below the centre across the Diameter through G. | Apres deux Traverſantes Interieures par la lettre N. à main droite; l'une par deſſus le Centre par l'S; & l'autre au deſſous par le G oppoſite. |
| Likewise draw two more in the same way through the same letters from the opposite side. | Semblablement encor deux autres, à tirer en la meſme ſorte & par les meſmes lettres du coſté oppoſite. |
| This done, label the four sides of the Outside Square in the following manner. First the side A-O on the right hand side. From A, label the first angle of the quadrangle with B; label the end of the Interior Collateral that passes through G below the oblique diameter, with D; label the end of Interior Traverse that passes through the same point G, with F; label the angle of the quadrangle at O-N, with K. | Ce qu'eſtant fait, il faudra marquer de lettres les quatre coſtez du quarré circonſcrit, en la maniere suivante. Premierement le coſté A O à main droite de la figure. Sur l'angle du Quadrangle ſoit eſcrit un B: ſur la fin de la collaterale interieure qui vient par le G en deçà le Diametre oblique, un D: ſur le bout de la traversante interieure, qui passe à travers le mesme poinćte, un F: & sur l'angle du prochain quadrangle, un K. |
| After that, on the two other sides O-Z, begin again on the right side; label the angle of the quadrangle O-N with P; label the end of the Interior Transverse through S that ends before the Oblique Diameter, with T; label the end of the Interior Collateral through S that ends just beyond that, with W; label the angle of the Quadrangle Z-X, with a Y. Then do likewise on the left hand side. | Les meſmes lettres ſeront auſſi marquées A O, à main gauche.
Label the same letters along the line A-O on the left hand side. En apres ſur les deux autres coſtez O Z, commencez derechef à droite; & mettez ſur l'angle du Quadrangle O N, un P: sur le bout de la traverſante, qui ſe finit en deçà le Diametre oblique, un T: sur la collaterale, qui finit au delà, W: sur l'angle du dernier Quadrangle, un Y. Et en ſoit fait paraillement le meſme à l'autre coſté, qui est à main gauche. |
| After this, trace two Exterior Transverse lines, one on the right hand side, the other on the left, from D, across the Principal Diameter, through G opposite. | Apres il faudra tracer deux Traverſantes exterieures, l'une à main droite, & l'autre à gauche, allants depuis les D, par le Diametre principal, & par les G opposites. |
| Likewise draw two more in the upper half of the circle from W, across the centre, through S opposite. | En ſemblable encor deux autres en la partie ſuperieure du Cercle, depuis les W. par le Diametre, & par les S oppoſites. |
| Similarly on the right side of the Circle, draw two Exterior Collaterals one from the side A-O, through G, to T; & the other from F through S, out to the side O-Z. | Pareillement auſſi en la partie droite du Cercle deux Collaterales exterieures, à mener, l'une du coſté droit A O, par le G, juſques au T: & l'autre à tirer de l'F, & à continuer par l'S, juſques au coſté droit de la partie ſuperieure du Quarré circonſcrit. |
| Likewise also, draw two others on the left side of the figure in the same way. | Semblablement encor deux autres en la partie gauche de la figure, à tracer en la meſme ſorte. |
| Thus we have drawn all the lines within the Circumferance. Label each double-cut (except the Centre), with the following letters. Along the Principal Diameter label the first cross-cut line above C with E; label the second with H; label the third, beyond the centre, with R; label the fourth with V. There are, likewise, four sections along the Perpendicular Diameter; the two closest to the centre labelled L, & the two others each labelled M. Where the Interior Collateral lines cross the oblique diagonals and the Interior Transverse line, label the lower ones (near H) with I and the upper ones (near R) with Q. | Et par ainſi voilà achevées toutes les lignes, qui entrent dans le pourpris de la Circonference, ſur leſquelles il faudra mettre à chaſque double entrecoupure de lignes (excepté le Centre) les lettres ſuivantes. Premierement ſur le Diametre principal, à la permiere entrecoupure apres le C, il faut un E: à la seconde, un H: à la troisieme, qui est par delà le Centre, un R: & finalement à la quatrieme, un V. Sur le Diametre perpendiculaire y a pareillement quatre sećtions; dont les deux plus proches du Centre porteront, chaſcune un L: & les deux autres, chaſcune un M. Aux doubles entrecoupures de chaſcune des collaterales interieures par deça le Centre, mettez à chaſune un I. & aux autres qui sont par delà, un Q. à chaſcune. |
| As to the lines outside the Circumference, first draw in each of the Quadrangles its Diagonal, across the Extended Diameters, from B to B, from Y to Y, and from K to P. | Quant aux lignes qui demeurent hors de la Circonference, tirez premierement à chaſcun des Quadrangles ſa Diagonale, à travers les Diametres prolongez, de B à B: de Y à Y: & de K à P, dans les deux Quadrangles opposites de main droite & gauche. |
| Second, draw a Foot-Line or Pedal Line across these same Quadrangles between the end-points of the Collateral lines and between the end-points of the Transverse lines. | Secondement tirez dans ces meſmes Quadrangles, du bout de l'une des lignes collaterales au bout de l'autre, à chaſcun une ligne de pied, ou ligne Pedale. |
| And finally, add the lines we shall call the length & width of the Square Extension. | Et finalement adjouſtez y celles que nous apellerons les longeur & largeur des Eſquierres. |
| First, to fit the lengths, pass the cord through the centres of two nearest Quadrangles; trace a line from the end of the Foot-Line to where the cord crosses the circumference; likewise trace a line opposite from the circumference to the end of the other Pedal Line. Do this all around the Circumference. | Pour adjuster permierement les longeurs; compassez voſtre cordelle par les centres de deux prochains Quadrangles; & tracez en ceſte ſorte une ligne de longueur depuis le bout de la ligne de Pied juſques à la circonference du Cercle; & en ſemblable tracez en encore une autre à depuis la circonference juſques au bout de l'autre ligne Pedale. & voilà comme il en faudra faire tout alentour de la Circonference. |
| To fit the widths of the Square Extensions (these lines stay outside the edges of the Quadrangles) pass your cord on the ends of one Exterior Collateral Line and one Exterior Transverse Line on the ends which are not labelled with letters, & trace two lines of width, one below the other beyond the Circle, again going all around the Circumference.
|
Pour adjuſter les Largeurs des Eſquierres, (ce ſont les lignes qui demeurent au dehors aux coſtez des Quadrangles) compaſſez voſtre cordelle ſur les bouts d'une Collaterale & d'une Traverſante exterieure, aſſavoir ſur les bouts qui ne ſont point marquez de lettres, & tracez en ceſte ſorte deux lignes de largeur, l'une deçà & l'autre delà, en la meſme façon que vous venez de faire le Longueurs, en allant derechef tout à l'entour de la Circonference. |
| This, in sum, is the way to lay out this plan for our Training, simple & easy, but in any case most useful if it is drawn very carefully. Meanwhile I would advise, if you do not have a sword of the correct length of a radius with which to draw the circumference, and subsequently the arcs for the cross-points to position the Diameters and the Outside Square, that in that case you can use the cord, pinning it to the Centre, to draw the Circonference & the rest. However, nothing is as sure as the sword itself, with its solid blade that will not stretch and will remain the same length. Otherwise faults could be introduced. | Voilà en ſomme la mode d'accommoder le Plan de ceſtuy noſtre Exercice, ſimple & facile, mais par adventure plus utile que ſi elle ſuſt dreſſée fort curieuſement. Cependent je vous aviſe, ſi c'eſt que vous n'ayaez point d'eſpee de ceſte juſte longeur du demi-Diametre pour en tirer la Circonference, & conſequemment les croiſades des arcs pour l’adreſſe des Diametres, & du Quarré circonſcrit; qu'en ce cas vous vous ſerviez de la cordelle, l'attachant en poinçon fiché sur le poinćt du Centre, pour en tirer en rond ladite Circonference, & le reſte à l'advenenant: toutesfois il n'eſt rien plus ſeur que l'eſpee meſme, qui demeure jouſiours immobile en une meſme longueur, par la ſolidité de la lame: de ſorte que malaiſement y peut il avenir de la faute. |
| Now, to clarify this material, here follows a catalogue of the names of the lines, so that the reader may have a reference to the Plate of all the lines and figures of this Circle which are needed for practical use. | Maintenant afin que ceſte Matiere ſoit un peu eſclaircie, & que le Lećteur puiſſe avoir devant ſes yeux une Table de toutes les lignes & figures de ce Cercle, qui sont neceſſaires à observer en l’uſage de la Pratique, nos en metrons icy le Catalogue. |
| LIST AND NAMES
of all the lines and figures of the circle, needed for practical use |
DENOMBREMENT ET APPELATIONS
de tovtes les lignes et figvres dv cercle, necessaires a observer en la pratique |
| The whole figure is called the Circle : because the circle forms the base on which all the other parts depend and remains the principal subject, the foundation of all the rest with regard to the Training, as they appear hereafter, as to the proportions and measures of Man. | La figure entiere ſera appellée Cercle: pource que c'eſt du Cercle qu'elle depend en ſon entier & en toutes ſes parties; iceluy Cercle en demeurant le ſujet principal, voire le fondement de tout le reſte, tant au regard de l'Exercice, comme il paroiſtra cy apres, qu'au regard des proportions & des meſures du corps de l'homme. |
| Centre is the point in the middle of the Circle. | Centre c'eſt le point du milieu du Cercle. |
| Circumference is the round line that forms the Circle. | Circonference c'eſt la ligne rond qui fait le Cercle. |
| C-X is the Diameter. In truth, there are four Diameters found in this figure; However to avoid confusion, it is necessary to distinguish between them. This is why I have left the general term Diameter to this which is the principal one in the Training: such that I even refer to the parts beyond the circumference as the Diameter, from the letter A to Z. | C X. Eſt le Diametre. Il eſt vray, qu'il ſe trouve quatre Diametres en ceſt figure; toutes fois pour eviter confuſion, il eſt neceſſaire qu'ils ſoyent diſtinguez. C'eſt pourquoy nous avons laiſſé le nom general de Diametre, à ceſtuy-cy qui eſt le principal en l'Exerciſe: de ſorte que nous l'appellons meſme Diametre en ſes parties adjouſtées au dehors de la circonference, depuis la lettre A, juſques au Z. |
| O-O or N-N is the Perpendicular Diameter. | OO ou NN. Eſt le Diametre perpendiculaire. |
| G-S. Oblique Diameter, which goes obliquely across the circle. | GS. Diametre oblique, comme allant par le Cercle obliquement. |
| C-W or X-D. Interior Collateral. | CW ou XD. Collaterale interieure. |
| G-T or S-F. Exterior Collateral. These last two lines go two by two from one side to the other, without actually being parallel, but which I found best to call Collaterals. | GT ou SF. Collaterale exterieure. Ces deux dernieres lignes vont deux & deux l'une à coſté l'autre, ſans toutefous qu'elles ſoyent paralleles, dont nous avons trouvé bon de les nommer Collaterales. |
| N-T or N-F. Interior Transverses. | NT ou NF. Traverſante interieure. |
| W-S or D-G. Exterior Transverses. These last line also go two by two from one side to the other, in the same way as the preceeding ones, called Collaterals. However because they are different and cross the Principal Diameter (the others remain on each side) I wished to distinguish from the Collateral lines by calling them Transverses. | WS ou DG. Traverſante exterieure. Ces derniers lignes vont auſſi deux & deux l'une à coſté l'autre, en la meſme ſorte que les precedentes, appellées collaterales: toutesfois pource qu'elles en different, en ce qu'elles vont à travers le Diametre principal (les autres demeurants à coſté) nous les avons voulu diſcerner d'avec leſdites Collaterales, par le Nom de Traverſantes. |
| A-O-Z-O is the Outside Square. | AOZO. Eſt le Quarré circonſcrit. |
| A-O. Side of the Outside Square. | AO. Coſté du Quarré circonſcrit. |
| C-D-F-N, with the Centre, is one Quadrant du Cercle. | CDFN avec le Centre, font un Quadrant du Cercle. |
| C-N-X-N. The Inside Square. | CNXN. Le Quarré inſcrit. |
| C-N. Side of the Inside Square. | CN. Coſté du Quarré inſcrit. |
| A-B-C-B. Quadrangle. So that the name ‘Square’ is not overused and would consequently lead to confusion by the reader, we have found it best to refer to these small Squares as Quadrangles. | ABCB. Quadrangle. Afin que ce nom de Quarré ne ſuiſt trop frequent, & conſequemment, ſujet à troubler la conſideration du Lećteur, nous avons trouvé bon, de nommer ces petits Quarrez, Quadrangles. |
| C-A. Extended Diameter. | CA. Diametre prolongé. |
| B-B. the Diagonal of the Quadrangle. | BB. La Diagonale du Quadrangle. |
| The little line that goes between the aforesaid Diagonal & the exterior angle across the Extended Diameter, shall be called the Foot-Line or Pedal Line, because it is exactly the length of the foot. | Ceſt petite ligne qui va entre ladite Diagonale & l'angle exterieur, croiſant le Diametre prolongé, ſera nommée ligne du Pied, ou ligne Pedale, pour ce qu'elle egale juſtement la longueur de la plante. |
| The figures which take up three-quarters of the Quadrangles and which extend in a parallelgram along the each of the edges of outside square to the meet the circumference are called the Square Extension, and consequently the line, drawn from the end of the Foot-Line through the centre of the Quadrangle to the edge of the Circumference is called the Length of the Square Extension: the other running from the circumference to the edge of the Outside Square is called the Width of the Square Extension. | La figure qui comprend au dedans de chaſcun des Quadrangles les trois quarts, avec deux egaux parallelogrammes au dehors, l'un à l'un des coſtez, & l'autre à l'autre, allants juſques à la circonference, ſera nommée l'Eſquierre, & conſequemment la ligne, tirée depuis le bout de la ligne Pedale par le centre & le coſté du Quadrangle juſques à la circonference du Cercle, ſera dite la longeur de l'Eſquierre: l'autre allant depuis le coſté du Quarré circonſcrit juſques à la meſme circonference la largeur de l'Eſquierre. |
| These are the names of all the lines which we will use in practice: of course those lines not expressly specified in this list by their letters will have the same names as the opposite and similar lines or figures. Also note that the names are for the entire line, from one end to the other, we have referred to letters not for measurement, but only to show where they go. | Voilà les noms de toutes les lignes, qui ont de l'uſage en la Pratique: bien entendu que celles qui ſe ſont pas expreſſement ſpecifiées en ce denombrement par leurs lettres, auront les meſmes appellations que les lignes ou figures oppoſites, & ſemblables. Et faut ſçavoir, que leſdites appellations leur ſont attribuées en leur entier, depuis l'un bout juſqu'à l'autre; car nous ne mettons pas les lettres pour meſurer, mais ſeulement pour montrer les lignes. |
| Circle No 1. | Cercle N.1. |
| Representation and relation of the proportions of the body & limbs of Man to the figure of our circle. | Repreſentant & rapportant les proportions du Corps & des Membres exterieurs de l’Homme à la figure de noſtre cercle. |
| We begin now to measure the proportions of Man, and relate them to this circle where they will be perchance be perceived with far more appreciation than we had above, when the proportions were found by chance. The reason for such admiration is that lines drawn between angles opposite to each other, themselves derived from no other reference than just the length of the Radius, accord so exactly with so many proportions of the body, as presented in this Circle No 1. It is not merely observation and practice that demonstrates this truth is as amazing as it is useful. It shall be made manifest to all those, who would take pains to examine the demonstrations which shall be proposed following this same explanation. Into which we shall enter through the description of Circle No 1, which represents all the proportions of Man, from the front, and therein is the significance which follows. | Nous commencerons maintenant à meſurer les proportions de l’Homme, en les rapportant à la figure de ce Cercle, où elles ſeront recogneuës paradventure avec plus d’admiration qu’elles ont eſté trouvées deſſus avec hazard. Car quelle raiſon, que les lignes d’une figure tirées des angles oppoſites les uns aux autres (ſans nulle adreſſe, que de la ſeule longeur de demi-Diametre) ſe puiſſent accorder ſi juſtement avec tant de proportions, comme il eſt repreſenté ſur ce Cercle N.1. ſinon la ſeule obſervation & l’experience, qui en demonſtre la verité auſſi admirable, que l’utilité en eſt grande; comme il ſera manifeſte à touts ceux, qui voudront prendre la peine d’en examiner les demonſtrations, qui ſeront propoſées à la ſuite de ceſte meſme explication. A laquelle nous ferons l’entrée par la declaration du Cercle N.1. repreſentent les proportions de l’homme, à le regarder de front; & en eſt la ſignification telle qu’il s’enſuit |
| C-X: The entire Diameter is equal the the extended height of the hand raised directly overhead. | CX. Le Diametre entier eſt egal à ſa hauteur eſtendue, en eſlevant les bras droitement en haut. |
| V: From C to V, is exactly the length of a person, from the soles of the feet to the top of the head. | V. Depuis le C. juſques à l’V, c’eſt juſtement la longeur de la personne, depuis les plantes des pieds juſqu’au plus haut de la teſte. |
| A: This first dotted line, labelled with a small-A, shows the height of the forehead. | A. Ceſte permiere ligne poinćtée, qui eſt marqée à coſté d’un petit A, demonſtre la hauteur du front. |
| B: The line B, taken across the Principal Diameter from one S to the other, is exactly at the tip of the nose. | B. La ligne B, menée à travers le Diametre principal, de l’un S, à l’autre, reſpond juſtement ſur le bout du nez. |
| C: This line shows the chin | C. Ceſte-cy demonſtre le menton. |
| D: The larynx. | D. Le noeud de la gorge. |
| E: The height of the shoulders. | E. Le haut des eſpaules. |
| R: This is the top of the chest. | R. Ceſt le plus haut de la poitrine. |
| F: The exact height of the armpits. | F. Reſpond ſur la juſte hauteur des aixelles. |
| G: On the breast (pectorals). | G. Sur les mammelles. |
| H: On the middle of the chest. | H. Sur le mitan de la poitrine. |
| I: On the tip of the breastbone. | I. Sur le brechet. |
| K: On the floating ribs & the diaphragm. | K. Sure les fauſſe coſtes, & ſur le Diaphragme. |
| The centre is on the navel. | Le Centre vient ſur le nombril. |
| L: On the head of the thigh-bone. | L. Sur la teſte de l’os de la cuiſſe. |
| M: On the peritoneum. | M. Sur le perinee. |
| N: On the virile member. | N. Sur le membre viril. |
| O: On the thumb. | O. Sur le podex. |
| P: On the top of the thigh. | P. Sur le haut de la cuiſſe. |
| H: The thickest part of the thigh. | H: Reſpond au plus gros de la cuiſſe. |
| Q: shows the concavity of the same. | Q. Demonſre le concave de la meſme. |
| R: The bottom of the thigh | R. Le bas de la cuiſſe. |
| S: The top of the kneecap. | S. Le ſur-genouil. |
| T. The bottom of the kneecap. | T. Le ſous-genoil. |
| E: This is the highest point on the shin. | E. C’eſt le plus haut de la greve. |
| V: The inside top of the calf. | V. Le haut de gras de la jambe en dedans. |
W: The same on the outside.
|
W. Le meſme en dehors. |
| X: The lowest part of the calf on the inside. | X. Le plus bas du meſme en dedans. |
| Y: The bottom of the shin. | Y. Le bas de la greve. |
| Z: The ankle. | Z. La cheville du pied. |
| C: the soles. | C. Les Plantes. |
| Anyone interested in reducing these same proportions to some particular measure, to better understand the rationale, could divide the Diameter into 24 Spans, & subdivide each of these into 10 parts, & each part into 10 minutes. Thus it will be the same with stick or with cord, with which one would measure a person. And thus he will find, by the comparison with this figure, the lengths and widths of each of his limbs, which any could easily check. What is more, these measures always match, each one to its own line, parts of lines, which we see in this same Circle. | Qui ſera cuirieux de reduire ces meſmes proportions à quelque certaine meſure, pour en ſçavoir rendre la raiſon plus exaćtemēt, il pourra pour ceſt effect partir le Diametre entier en 24. Nombres, & à chaſcun d’iceux il y pourra imaginer 10. parcelles; & à chaſcune parcelle 10. minutes: dont il fera pareillement le ſemblable du baſton ou de la cordelle, dequoy il prendra les meſures au corps de la perſonne. Et par ainſi il trouvera par la confrontation de ceſte figure, raportée à l’experience meſme, à combien montront les longeurs & largeurs de chaſcun des membres, deſquels il voudra faire preuve. Et qui plus eſt, il les trouvera touſiours accordantes en leurdite meſure, à l’une ou à l’autre ligne, ou à certaines parties de lignes, qu’on voit en ce meſme Cercle. |
| As the size of the head from the from the top to the chin matches the length of the Foot-Line, or to the half-diagonal of the Quadrangle, therefore it equals the length of the sole of the foot. | Car la longeur de la teſte depuis le ſommet jusſques au menton, s’accord juſtement à la meſure de la ligne Pedale, ou à la demie Diagonale de Quadrangle, eſtant par conſequent egale à la meſure de la plante des Pieds. |
| Its width is equal to the half-side of the Quadrangle, which is also equal to the length of the hand, from the wrist to the fingertips. | Sa largeur eſt egal au demi-coſté du meſme, qui eſt auſſi egale à la longeur de la main, depuis le poignet jusſques aux bouts des doights. |
| The length of the arm, with the hand, is equal to one third the Diameter, that is, from the letter R to the letter H, or from H to C, as the lengths are equal, and contain precisely the extension of 8 Spans, since there are 12 on the radius, or on the blade of our sword, as shall be discussed later. | La longeur du bras enſemble avec la main, eſt egale à la troiſieme partie du Diametre entier, aſſavoire depuis la lettre R, juſques à l’H. ou depuis ledit H, juſques au C. car ces longeurs ſont egales; & contiennet juſtement l’eſtendue de 8. Nombres, tels qu’il y en 12 ſur le demi-Diametre, ou ſur la lame de noſtre eſpee, commeil ſera diſcouru cy apres. |
| All these proportions that are found so amazingly well on these lines, which cut across this figure from one angle to the other, are here shown, in this No 1 Circle on the front of the figure, on the fleshed side as on the skeletal side, because these are the principle basis of the lengths, widths, and all dimensions of Man which is necessary to show on both sides, on the right hand side and the left hand side. The same proportions are shown as well on the profile of the skeleton in Circle No 3. And in No 4, on the backside, showing the person from behind. Again, it is shown in Circle No 5 by the inverted figure, that these same proportions remain invariable whether one begins at one end of the Diameter or the other. | Toutes ces proportions ſe rencontrants ſi merveilleuſement ſur ces lignes, qui procedent des entrecoupures de ceſte figure, de l’un des angles oppoſites à l’autre, ſont icy repreſentées en ce Cercle N. 1. ſur le devant de la perſonne, tand ſur la chair, que ſur les oſſements nuds, à raiſon qu’iceux ſont le principal fondement des longeurs, des largeurs, de toutes les dimenſions de l’homme: dont it nous a ſemblé neceſſaire de le repreſenter en toutes les deux manieres, l’une à main droite, & l’autre à gauche. Les meſmes proportions ſont demonſrées areillement ſur le poufil des oſſements au Cercle N.3. Et au N.4. ſur le derriere, en regardant la perſonne de dos. Comme il eſt derechef repreſenté au Cercel N.5. par la figure renverſée, que ces meſmes proportions demeurent invariables tant à commencer de l’un bout du Diametre, que de l’autre. |
| Circle No 2. | Cercle N. 2. |
| This circle contains only the names of the lines of this figure, as detailed above. | Ce Cercle ne contient autre choſe, que les noms des lignes de ceſte figure, en la meſme ſorte qu’ils on eſté declarez cy deſſus. |
| Circle No 3. | Cercle N.3. |
| In which one sees how the natural pace which men ordinarily use as they walk, reliably matches with the measurements of this same Circle. | Auquel on voit, comment les pas naturels, dont les Hommes uſent en leur demarche ordinaire, s’accordent fort raiſuement avec de meſures de ce meſme Cercle. |
| Thus as we have shown how this Circle comes from the proportions of Man, we also do the same with regard to the steps and paces he shall use in our Training. Insofar as the proportions are again represented in Circle No 3 on the skeleton profile, there is no point to say anything other than to refer the reader to what has already been explained about Circle No 1.
Note: The text of the square in the centre reads: "Gerardus Thibault Inventor" |
Ainſi que nous venons de representer la convenance de ceſt figure du Cercle avec les proportions de l’Homme faiſons en auſſi le ſemblable au regard de la demarche & des pas, deſquels il qu’il uſe en ceſtuy noſtre Exercice. Car touchant ce que les proportions de l’homme font derechef repreſentées en ce Cercle N.3. ſur le pourfil des oſſements, il n’en eſchet point de propoſer icy autre choſe, que d’en renvoiyer ſimplement le Lećteur à ce qui a eſté ſpecifié au Cercle N.1. |
| The footprints, which go in and about Circle No 3, marked with different numbers, demonstrate the concordance between the ordinary walking pace of a man and the Circle. Their significance is as follows. | Les traces donc les pieds, qui vont dedans & alentour de ce Cercle N.3. cottés en chifre de differents nombres, demonſtrent la convenance de la demarche ordinaire de l’homme avec ceſte meſme figure du Cercle, & en eſt la ſignification telle, que s’enſuit. |
| Those which go along the Perpendicular Diameter, marked number 1, demonstrate that the length of this Extended Diameter equals four ordinary paces, in doing three or four paces before coming into the circle, for balance, begin stepping with the right foot on the Foot-Line and end likewise on the opposite Foot-Line with the left foot. Which one can also observe similarly in the other paces which follow. | Celles qui vont le long du Diametre perpendiculaire, cottées en chifre 1, demonſtrent que la longeur de cedit Diametre perpendiculaire prolongé, revient à quatre pas ordinaire, en faiſant deux ou trois pas avant que de venir au Cercle, afin que le corps ſoit en train, pour commencer la demarche à main droite ſur la ligne Pedale, & a finir pareillement ſur la ligne Pedale à main gauche. Ce qui doit auſſi eſtre obſervé ſemblablement és autres demarches ſuivantes. |
| Those which go along the same Diameter within the circumference, marked number 2, demonstrate that three normal paces is the length of this Diameter from circumference to circumference. | Celles qui vont le long du meſme Diametre au dedans de la circonference, marquées en chifre 2, demonſtrent qu la longeur de ce Diametre eſt de trois pas de la demarche ordinaire, en allant de circonference à circonference. |
| The same proportion is shown on the two Oblique Diameters by the footprints numbered 3 & 4 as well as those which are marked number 5 on the four sides of the Outside Square, which are equal to those along the Oblique Diameters, which go from one edge to the other. | La meſme proportion eſt repreſenté ſur les deux Diametres obliques par les ſemelles, qui portent le Nombre 3. & 4. & pareillment par celles qui portent le Nombre 5. ſur les quatre coſtez du Quarré circonſcrit, comme eſtants egaux à iceux Diametres obliques, en allant touſiours de l’un bout juſqu’a l’autre. |
| Those marked with number 6 demonstrate how the circumference, along with the Inside Square, matches eight steps at an ordinary pace, which can be done by putting the left foot along the circumference line at C, then moving the other forward and place it at G, in the middle of the line. Then drawing the left circularly along circumference from C to N. Then again advancing the right along the same side of the Inside Square close to the left & then continuing to follow along the next side of the Inside Square to S, and so on, so the right foot always follows the four lines of the Inside Square, and the left is carried around always following the circumference. The right foot reaches two half-sides of the Inside Square with each step, and the left moves a Quadrant of the circumference each time. | Celles qui ſont marquées du Nombre 6. demonſtrent la convenance de la Circonference, enſemble avec le Quarré Inscrit, à la demarche de huićt pas ordinaires: leſquels on y pourra pratiquer en mettant premierement le pied gauche ſur la lettre C. & cheminant de l’autre en avant juſques à le planter à plein, ſur le G. au milieu de la ligne; menant apres le gauche circulairement le long de la circonference depuis C juſques à N: puis avançant derechef le droit le long du meſme coſté du Quarré inscrit jusſques à bien pres de l’autre, & continuant à le porter par la trace d l’autre prochain coſté du Quarré inſcrit juſques à l’S. & ainſi conſequemment du reſte, en ſorte que le pied droit aille touſiours ſuivant les quatres lignes du Quarré Inſcrit, & le gauche ſoit porté en rond coſtoyant touſiours la circonference; le pied droit achevant à chaſque demarche deux moitiez de deux coſtez du Quarré inſcrit, & la gauche achevant à chaſque fois un Quadrant du circonference. |
| One should always be very aware of this concordance, in as much as this, the length of a man’s ordinary walking pace, is our exemplar. So our imitation of which always informs the style of our School. This shall be shown throughout the rest of this book and by which means we avoid awkward and inconvenient poses, which we shall see when and where an example requires a more precise explanation. | L’obſervation de ceſte convenance doit eſtre tenue en grande eſtime, d’autant que ce ſont là les pas ordinaires de la demarche de l’homme, à l’exemple & imitation de laquelle nous devons touſiours former le ſtile de noſtre Pratique, ainſi qu’il paroiſtra par la ſuite de tout le livre, & que ſans iceux il ne ſeroit poſſible d’eviter des grandes incommoditez, qui ſeront données à cognoiſtre, où il ſera queſtion d’en rendre la raiſon plus exaćte. |
| Circle No 4. | Cercle N.4. |
| Which Contains the explanation of the Range of the three Approaches, or Instances, & how they are represented on our Circle, both along the Diameter, and on the sides of the Inside Square, to close with the Enemy from the side. | Contenant la declaration de la Meſure des trois Approches, ou Inſtances, & comment elles ſont repreſentées ſur noſtre Cercle, tant ſur le Diametre, que ſur les coſtez du Quarrée Inſcrit, pour aborder l’Ennemi de travers. |
| First, is shown here the proportions of Man as seen from the back. | Pour le premier on vous repreſente icy les proportions de l’Homme, à le regarder de dos. |
| Second, from the footprints, to the right and left of the figure, demonstrate the concordance of paces which was observed in the previous Circle. | Secondement par les traces des ſemelles, à droite & à gauche de lafigure, on y pourroit demonſtrer la meſme convenance des pas, qui a eſté remarquée au Cercle precedent. |
| To understand this, one must know that the two adversaries will first close with each other at the First Instance, that is, when one, in the Z-X Quadrangle, places his right foot on the extended side and the left foot on the Foot-line, the other does the same in the A-C Quadrangle, opposite, as is clearly shown by the footprints marked on them. While they are at this range, we say they are at the First Instance, for if they were further away, they would be out of range, because they would be unable to hit each other even in the slowest time because they would be almost completely beyond their reach. | Pour l’intelligence deſquelles il faut ſçavoir, que les deux Contraires ſe viennent premierement aborder à la Premiere Inſtance. c’eſt à dire, quand l’un ſe vient placer ſur le Quadrangle ZX, le pied droit ſur le coſté exterieur, & pied gauche ſur la ligne Pedale; que l’autre ſe vient pareillement placer alencontre ſur le Quadrangle oppoſite AC; comme il eſt clairement repreſenté par les traces des pieds, qui ſont marquez deſſus. Tandis qu’ils ſont en ceſte meſure nous diſons qu’ils ſont à la Premiere Inſtance; car s’ils ſe tiennent plus loing, ils ſont comme hors de meſure, à cauſe qu’ils ne ſe peuvent toucher l’un l’autre en temps mediocre, par ce qu’ils ſont quaſi hors de leur portée. |
| The Second Instance is that which comes so close to the adversary, either directly by the path of the Diameter, or in approaching from the side by the Quadrants, that one can put the point of the sword on the elbow, and, consequently, hit him in half-time with a simple bow of the body with the feet firmly planted. Which one can do by moving along the diameter to the letter E, and on the G by the sides of the Inside Square. This range is called the Second Instance, because one cannot approach that close as the point of first contact without first having previously secured one’s line of approach. And once there, one works from a superior postion, because it merely requires a simple extension of the arm, assisted by a simple bow of the body, which has no effect on one’s balance, to hit the enemy. | La Seconde Inſtance eſt celle qui vient ſi pres de la partie adverſe, ſoit en allant droićtement ſur luy par la voye du Diametre, ou en l’approchant de travers par les Quadrants, qu’on luy puiſſe mettre la pointe de l’eſpee ſur le coude, & par conſequent on le peut toucher en un demi-temps avec un ſimple panchement du corps & à pied ferme. Ce qu’on pourra faire en arrivant par le Diametre à la lettre E. & ſur le G, par les coſtez du Quarré Inſcrit. Ceſte meſure ſe nomme Seconde Inſtance, pource qu’on n’y peut venir de permier abordee, ſans avoir aſſeuré preallablement ſes approches: & y eſtant, on travaille avec plus d’avantage, car il ne faut qu’une ſimple extenſion du bras, aſſiſté d’un panchement de corps, qui n’empeſche pas de le retenir en balance, pour toucher l’Ennemy. |
| From the Second Instance, we come to the Third, which is at the letter H on the Diameter, or along the sides of the Inside Square at the letter N. It is a range at which one can hit the foe while keeping the body straight and upright, without moving the feet, by doing nothing more than extending the arm. | De la Seconde Inſtance on vient à la Troiſieme, qui eſt à la lettre H, ſur le Diametre, ou ſur les coſtez du Quarré Inscrit, à la lettre N. ceſt une meſure en laquelle on peut donner l’atteinte au Contraire, en tenant le corps droit & eſtēdu ſans aucun avancement pieds, ne faiſant rien autre que d’allonger le bras. |
| Those are our Three Instances, along the Diameter, as along the sides of the Inside Square, to the right and the left, where they are clearly marked by the footprints, which show the situation as stationary paces, one foot distinguished from the other by a single foot (distance) between the arches of each footprint, as we are used to when standing upright. | Et voilà nos Trois Inſtances, tant ſur le Diametre, que ſur les coſtez du Quarré Inſcrit, à droite & à gauche, où elles ſont repreſentées aſſez clairement par les semelles, qui en demonſtrent la ſituation en forme de pas arreſté, l’un pied eſtant diſioinćt de l’autre de l’intervalle d’un pied tant ſeulement, entre le creux de l’un & de l’autre, ainſi qu’on eſt accouſtumé de ſe tenir debout à pieds arreſtez. |
| Also, as much as it is a very important point in the practice of arms, to know these three Approches distinctly, as they are represented on the Circle. It is also an important point in Theory to consider how these ranges are taken solely from the proportions of Man. As such it is more and more apparent, that we always take Nature as our guide, and from these proportions, we align our steps, our approaches, and our distances, either when we stay or when we move. Because if you look only at the figure of the man, here shown from the back, you will see that,in the First Instance, the interval from circumference to circumference is equal to the extended height of a person, so that when the two Parties are in this First Instance, there is always this same gap equal to the extended height of a person between them. And if they are at the Second, either straight across the Diameter or to one side along the edges of the Square, the distance between them is equal to the natural height of that same person, from the soles of the feet to the top of the head. And finally, the interval of the Third is equal to the height of the stomach. | Or comme c’eſt un poinćt de treſgrande importance en la Pratique des armes, de cognoiſtre ces trois Approches diſtinćtement, comme elles ſont repreſentées par le Cercle: auſſi eſt ce choſe tres digne de conſideration en la Theorie de contempler, comment les meſures en ſont tirées de la ſeule Proportion de l’Homme; afin qu’il apparoiſſe de plus en plus, que nous prenons touſiours la Nature pour guide; & que ſelon les proportions d’icelle, nous dreſſons touts nos pas, nos approches, & nos diſtances, ſoit à demeurer, ſoit à bouger de la place. Car ſi vous regardez tant ſeulement la figure de l’Homme, qui eſt icy representé de dos, vous verrez, que l’intervalle de la Premiere Inſtance de Cironference à Circonference, eſt egale à la hauteur eſtendue de la perſonne, de ſorte que quand les deux Parties ſont en ceſte Premiere Inſtance, il y a touſiours entre deux la meſure de ceſte hauteur eſtendue d’une perſonne. Et s’ils ſont à la Seconde, ſoit de droit ſur le Diametre, ou de travers ſur les coſtez du Quarré ; la diſtance qui eſt entre deux eſt egale à la hauteur & ſtature naturelle du corps de la meſme perſonne, depuis la plante des pieds juſqu’au ſommet de la teſte. Et finalement, l’intervalle de la Troiſieme, eſt egale à la hauteur de la poitrine. |
| If I am asked what is the meaning of these fourth pair of footprints at the centre, and if they represent a Fourth Instance on the Diameter, I answer, no, and add that they were added to show how four static paces accord with half the distance of the extended diameter, which is equal to four ordinary steps, which was explained in Circle No 3 & marked number 1. As such, there are but the three pairs of footprints which show the Diametrical Instances, as well as the three others, which go off to the the sides and show the lateral ones. | Si on me demande, qu’eſt ce que ſignifie ceſte quatrieme paire de ſemelles, qui attouche le Centre, & ſi elle ne repreſente pas la Quatrieme Inſtance Diametrale, je reſpons, que non; & qu’elle y eſt adjouſtée, pour repreſenter ſimplement la convenance du demi-Diametre prolongé avec quatre pas à pieds arreſtez, comme l’entier eſt egal à quatre pas ordinaires de demarche: ainſi qu’il eſt expliqué au Cercle N. 3. & marqué en ciffre 1. De ſorte qu’il n’y a que les trois premieres paires de semelles, qui demonſtrent les Inſtances Diametrales; ainſi que les trois autres, qui vont aux coſtez, demonſtrent les Laterales. |
| Now, everything I have said about these Instances, starting from Quadrangle A-C when the adversary is on Quadrangle Z-X must also be understood to apply conversely, when beginning the approach from the Quadrangle opposite, which is easy to understand from the footprints along the Diameter as well as along the edges of the Inside Square. | Or tout ce que nos avons dit de ces Instances, en commenceant par le Quadrangle AC. quand l’Adverſaire ſe tient deſſus le Quadrangle ZX. celà meſme ſe doit auſſi entendre à l’oppoſite, en occaſion, qu’il nous touche de commencer les Approches par le Quadrangle oppoſite ainſi qu’il eſt aiſé à comprendre par les traces des pieds, qui en font la declaration tant ſur le Diametre, que ſur l‘un & l’autre coſté du Quarré Inſcrit. |
| To know the exact ranges of each of these three Instances, as well as the basis of several observations, which we shall explore later, one must know that the blades of our swords are differentiated by twelve numbers into equal parts, as shown along the bottom left of the table. The reason for this will be explained following this section. Eight of these parts are the exact length of the arm, which is evident from the figure in Circle No 1, where it clearly shows that length of the arm is equal to one third the Diameter, from R to H: and since the Diameter is two times longer than the blade, that is, twenty-four Spans, it clearly follows that one third equals eight. Also this proof can demonstrate the truth, if one places the tip of the blade at the armpit and extends the arm along the blade, the finger tips only reach as far as the number eight. And therefore, when gripping the sword in hand, the sword has a length of 12, and that of the arm of 8, from which one must subtract about 1 for the shortening of the fingers when one grips, it appears then that holding the sword in hand, one can reach straight ahead a length of 19 Spans. Disregarding other considerations, let us suppose, for a moment, that the two swords are both equal to the radius; there will be more about this later. In this way we can calculate the measurements of these Instances from part 47, book 1 of Euclid in this way. | Pour coignoiſtre exaćtement les meſures de chaſcune de ces trois Inſtances, enſemble auſſi le fondement de pluſieurs obſervations, dont il ſera parlé cy apres, il faut ſçavoir, que les lames de nos eſpees ſont diſtinguées par chifres en douze parties egales, comme il eſt repreſenté au bas du Tableau à main gauche, & en ſera la raiſon declarée à la ſuite de ce meſme diſcours. Huićt de ces parties font la juſte longeur du bras, ainſi qu’il eſt evident par la figure du Cercle N.1. où il ſe voit clairement que la longeur du bras eſt egale à un tiers du Diametre, depuis l’R juſques à l’H: & d’autant que le Diametre entier a deux fois autant de longeur que la lame, ce qui monte à vingt & quatre Nombres, s’enſuit neceſſairement que le tiers en ſera comme huićt. Auſſi la preuve en peut demonſtrer la verité; par ce qu’en mettant la poinćt de la lame contre l’aixelle, & eſtendent le bras deſſus, on ne peut atteindre du bout des doigts plus avant que juſqu’au Nombre huićt. Et comme ainſi ſoit, qu’en tenant l’eſpee au poing, on aye la longeur de la lame, comme 12, & celle du bras comme 8: deſquels il en faut ſoubſtraire quaſi 1 pour le raccourciſſement des doigts, qui font le poing, il paroiſt donc qu’en tenant l’eſpee au poing, on peut atteindre en droite ligne ſi avant que la longeur de 19 de ces meſmes Nombres. Faut d’avantage preſuppoſer pour le ſecōd, que les eſpees ſont egales au demi-Diametre; comme vous entendrez plus particulierement cy apres. Et voilà par où lon pourra calculer les meſures de ceſdites Inſtances par la 47. Liv.1. Eucl. en ceſte maniere. |
| The radius from X to the Centre is 12 | Le demi-Diametre depuis X juſqu’au Centre, eſt 12 |
| Likewise the perpedicular radius, 12 | Pareillement le demi-Diametre perpendiculaire, 12 |
| The Centre is a right-angle. | L’angle de Centre eſt droit. |
| Therefore the line subtended from X to N is approx. 16.97 | Doncques la ligne X N, qui le ſouſtient, 16,97@ |
| That is the line which measures the Third Instance, going by the quadrants of the Circle. | Voilà la ligne qui meſure la Troiſieme Inſtance, en allant par les quadrants de Cercle. |
| The range of the Second is found in the same way. To do this, first imagine a line perpendicular to the Diametre from G to G. This will cut the radius at a right angle, in the exact middle between C and the Centre. Let’s say, then: | La meſure de la Seconde ſe trouve en la meſme ſorte. Et pour ce faire imaginez permierement une ligne allant perpendiculairement par le Diametre, de G à G. Icelle coupera le demi-Diametre en angle droit, au juſte mitan entre le C et le Centre. Dites donc |
| The radius is 12, and half of the other radius 6, added together, so the line that goes from X to the right angle is 18 | Le demi-Diametre 12 & la moitié de l’autre demi-Diametre 6, ſont enſemble, pour la ligne qui va depuis l’X juſques à l’angle droit 18 |
| The imaginary line being equal to the radius, half of that from the right angle to G must necessarily be 6 | La ligne imaginée eſtant egale au demi-Diametre, faut neceſſairement, que la moitié, depuis l’angle droit juſques au G, en ſoit 6 |
| The angle at the Diameter is a right angle. | L’angle qui touche le Diametre eſt droit. |
| Therefore the line subtended from X to G, is about 18.97 | Doncques la ligne X G, qui le ſoutient, 18,97@ |
| The range of the First Instance appears by itself, being two times the radius, which makes 24 | La meſure de la Permier Inſtance paroiſt d’elle meſme, eſtant deux fois le demi-Diametre: qui font par enſemble 24 |
| Next, then, the arm, extended straight with the sword, makes a length of 19 Spans. The distance of the First Instance is only 24 so one might conclude that from there, one can hit the adversary from the First Instance, by moving only 5 Spans forward, but this is false, which we can physically demonstrate. When two adversaries stand in the opposite Quadrangles, with swords and arms extended in a straight line the tips of the blades will only reach to just before the other’s hilts, as is shown in Circle No 1 of Plate IV: as such that they cannot reach the other’s body without advancing at least as far as the length of their adversary’s arm, that is 7 or 8 Spans. | Puis donc que le bras avec l’eſpee font enſemble en droite ligne la longeur de 19 Nombres; & que l’eſpace de la Premiere Inſtance n’en contient que 24, paradventure quelqu’un voudra conclurre de là, qu’on puiſſe toucher ſa partie adverſe depuis la Permiere Inſtance, in avançant ſeluement la meſure de 5 Nombres; ce qui eſt faux, comme on le peut demonſtrer par experience. car quand les deux parties adverſes ſe tiennent ſur les Quadrangles oppoſites en la forme requiſe, avec les bras & eſpees eſtendus en droite ligne les poinćtes des lames n’arriveront chaſqu une, que juſques au devant de la garde contraire: ainſi qu’il eſt repreſenté ſur le Cercle N.1. du Tableau IV: de ſorte qu’ils ne peuvent arriver au corps contraire ſi ce n’eſt qu’ils s’avancent pour le moins, autant que tout le bras entier de leur partie adverſe, qui eſt de 7. à 8. Nombres. |
| The reason for this is when the body is held erect on both feet, with one foot on the edge of the Quadrangle and the other on the Foot-Line, one does not balance over the ball of the right foot at the Circumference, but rather between the two feet over the centre of the Quadrangle. Having considered and looked at the placement of the feet, which are separated by about a foot, on can conclude with assurance that each of the adversaries is half-foot back. And from this comes the increase in distance of the First Instance. | La cauſe en eſt, que le corps, ſe tenant ainſi debout ſur ſes pieds, placez l’un ſur l’un des coſtez du Quadrangle, & l’autre ſur la ligne Pedale, ne repoſe pas ſur la poinćte du pied droićt qui aboutit à la Circonference; mais il revient entre les deux pieds par deſſus le Centre du Quadrangle. Ce qu’eſtant bien conſideré, & confronté à la ſituation deſdits pieds, qui ſont ſeparez entre eux d’un pied entier d’intervalle; on pourra conclurre aſſurement, que chaſcun des Contraires ſe recule d’un demi-pied en arriere. Et voilà d’où procede l’aggrandiſſement de la Permiere Inſtance. |
| As to the range of the Second, it must be expanded likewise, adding the slight withdrawal of the two bodies, following the placement of the feet, which together comes to one extra foot length between the two. Therefore it follows that, as much as the Collateral X-G only goes to about 18.97 Spans, we must always count the distance as about 21, 45, which is just about 21 ½. As such one cannot hit the adversary without advancing by one foot distance, which can be reached by simply leaning forwards with the torso. | Quant à la meſure de la Seconde, il la faut aggrandir pareillement, en y adjouſtant le reculement des deux corps, procedant de la ſituation de leurs pieds, qui revient auſſi à un pied de longeur pour touts les deux ensemble. Suivant quoy, combien que la ligne Collaterale X G ne monte qu’à 18,97@ Nombres; toutesfois il en faut conter pour la diſtance 21,45@ qui eſt à bien peu pres 21½. En ſorte qu’on n’y peut toucher la partie adverſe, ſinon qu’on s’avance environ la meſure d’un pied, laquelle on peut atteindre en panchent ſeulement du corps ſur le devant. |
| The line of the Third Instance X-N was calculated at about 16.97 Spans, to which we again add the distance of one foot to adjust for the stance, which comes to a about 19.45 Spans, just a little less than 19 ½. So, as the extension of the arm with the sword comes to 19 Spans, that leaves about ½ Span to hit. Thus it is easy to understand how, in this Third Instance, one can hit an adversary while standing erect, with only the slightest bow. | La ligne de la Troiſieme Inſtance X N a eſté calculée 16,97@. à laquelle adjouſtant derechef la meſure d’un pied en recompenſe de la ſituation; il en vient Nombres 19,45@ qui font un peu moins que 19½ . De ſorte que, l’extenſion du bras avec l’eſpee faiſant enſemble 19, il en reſte environ ½ Nombre de meſure pour atteindre. Dont il eſt aiſé à comprendre, qu’à ceſte Troiſieme Inſtance on peut toucher ſa partie adverſe, en ſe tenant droit, avec le moindre panchement du monde. |
| Then, because we have explained the ranges of the Lateral Instances, it makes sense to to the same with the others. And this, furthermore, because of the differences which are found between the two, could perhaps give reason to someone to suspect some fault, as if the Instances on the Diameter were not properly aligned. | Or puis que nous avons declaré les meſures des Inſtances Laterales, il eſt raiſon de faire auſſi le ſemblable des autres. Et ce d’autant plus, parce que la difference, qui ſe trouve entre deux, pourra donner paraventure occaſion à quelqu’un d’y ſoupçonner quelque faute, comme ſi les Inſtances Diametrales n’eſtoyent pas bien aſſignées. |
| In fact the line X-H, which represents the Third Instance interval, is shorter than the line X-N. Because that one was calculated to be about 16.97 Spans & this one is no more than 16. This is easy to show by the rule of Proportion: imagine again the triangle, which was described above for the calculation of the line X-G. Let’s say the length from X to the middle of the cross radius is 18, for the base, which gives 6 for the height to G. Therefore the base from X to the centre being 12, the height from this Centre to the letter L will be 4. So it is that the lines from the Centre to L & to H are equal by proposition 4 of Euclid’s 1st book. These 4, added to the radius 12, for the line X-H comes to 16. Thus this line of the Third Instance on the Diameter comes to only 16 Spans, and the other about 16.97. In any case the difference is made up in another way as we shall soon see. Similarly there is a difference between the lines X-G & X-E for the Second Instance: as the first is about 18.97 Spans, and the other about 19.69, calculation of which we shall leave for the present as this would involve too many sums, you may, meanwhile find this by means of the two triangles G-C w. | Et de fait la ligne X H, qui y repreſente l’intervalle de la Troiſieme Inſtance, eſt plus courte que n’a eſté la ligne X N. Car ceſte-là a eſté calculée à Nombres 16,97@: & celle-cy n’en contient que 16. ſans plus. Ce qui eſt aiſé à demonſtrer par le regle de Proportion: imaginant derechef le triangle, qui a eſté declaré cy deſſus pour la calculation de la ligne X G. Diſons, la longeur depuis X juſques au milieu de l’autre demi-Diametre 18, pour la baſe; donnent 6, pour la hauteur juſques à G. Doncques la baſe depuis X juſques au Centre eſtant 12; la hauterur depuis ledit Centre juſques à la lettre L, fera 4. Or eſt il que les lignes depuis le Centre juſqu’à L, & juſqu’à H, ſont egales par la prop.4. liv.1. d’Euclid. Iceux 4. adjouſtez au demi-Diametre 12; il en vient pour la ligne X H, 16. Ainſi donc ceſte ligne de la Troiſieme Inſtance Diametrale ne fait que 16 Nombres; & l’autre, 16,97@. Toutesfois la difference en eſt recompenſée par une autre voye, comme il ſera declaré tantoſt. Semblablement il y a de la difference entre les lignes X G & X E. pour la Seconde Inſtance: car la permiere eſt de 18,97@ Nombres, & l’autre de 19,69@ ce que nous laiſſerons pour le preſent de calculer, à cauſe que le choſe requerroit trop de ſommes; vous advertiſſant cependent, qu’on en trouvera l’iſſue par les deux triangles G C w. |
| In order to reconcile the reason for this difference, you must understand that the usual means of approaching an adversary in our Training is to always move a bit to the side, that will be described elsewhere, to avoid motion directly along the Diameter, which is very hazardous. Thus it is more necessary to understand the distances of these Instances, which approach from the side, than those which go directly towards the Enemy along the Diameter. In any case, the fact of these differences, which appear in the relative distances between the Second and Third Instances, are, practically, of little import, because the inequality between the two lines in the Second Instance is compensated for in the different positions of the body. For one who approaches, coming to the Lateral Second Instance, turns on the heels, in such a way as to move the body backwards about a half-foot; and in the Diametrical Second Instance, will have his heels further forward and his body in profile, so that the slight interval between these two Instances is equalized by the position of the body. As to the difference between the two Third Instance lines X-N & X-H, this is equalized because when one strikes from the Lateral Third Instance, one leans forward. Thus the range is shortened by as much as the line appears to be longer. | Pour accorder le different, ſachez que c’eſt l’ordinaire de noſtre Exerice d’aborder le Contraire, en allant touſiours un peu à coſté, pour eviter la trace du Diametre, qui eſt plen de hazard, pour les conſiderations, qui ſeront delcarées autrepart. Dont nous eſtimons, qu’il eſt plus neceſſaire de cognoiſtre les meſures des Inſtances, qui vont en traverſe, que celles qui vont tout droitement ſur l’Ennemi par la voye du Diametre. Toutesfois qu’à la verité la difference, qui ſemble eſtre entre ces meſures des Inſtances Secondes & Troiſiemes, ne donne point de difference en la Pratique, puis que l’inegalité, qui eſt entre les deux lignes des Inſtances Secondes, ſe recompenſe par la diverſe ſituation du corps. Car celuy qui fait les approches, venant à la Seconde Inſtance Laterale, ſe deſtourne avec les talons, en ſorte qu’il ſe recule le corps d’un demi pied de longeur en arriere: & eſtant à la Seconde Inſtance Diametrale, il tient les talons plus avancez, & le corps tout en pourfil: de ſorte que l’intervalle de ces deux Inſtances en eſt egalée par la diverſe ſituation de ſon corps. Et quant à la difference, qui eſt entre les deux lignes des Inſtances Troiſiemes, aſſafoir X N, & X H: elles ſont egalées par ce que quand on donne l’atteinte à la Troiſieme Inſtance Laterale, cela ſe fait avec le corps panché en avant. Dont la meſure eſt racourcie, autant, que la ligne ſemble eſtre plus longue. |
| In sum, these considerations do not diminish the worth of this Circle, as much as they improve it. Because these same difficulties, which are proposed against it, clarify the concurrence with Nature itself, to which our ideas must always refer. | En fin, ces conſiderations ne diminuent pas l’eſtime de noſtre Cercle, ains elles l’augmentent; puis que les difficultez meſmes, qui ſont propoſées alencontre, en eſclarciſſent davantage la convenance avec la Nature meſme, à laquelle il faut que toutes nos inventions ſe raportent. |
| So, to make it easier to remember, here is a Table of measurements of all these Instances and their differences. To begin, for the Lateral Instances, there are | Or pour vous en confirmer d’autant plus la memoire, voicy un Tableau de la meſure de toutes ces Inſtances avec leurs aggrandiſſements. Et premierement pour les Inſtances Laterales, il y a |
| First Instance........About 26.48 Spans | Pour la Premiere......Nombres 26,48@ |
| Second Instance.......About 22.45 Spans | Pour la Seconde.......Nombres 22,45@ |
| Third Instance........About 19.45 Spans | Pour la Troiſieme.....Nombres 19,45@ |
| For the Instances on the Diameter: | Touchant les Inſtance Diametrales: |
| First Instance........About 26.48 Spans | Pour la Premiere......Nombres 26,48@ |
| Second Instance.......About 22.17 Spans | Pour la Seconde.......Nombres 22,17@ |
| Third Instance........About 18.48 Spans | Pour la Troiſieme.....Nombres 18,48@ |
| As for the tip of the sword, how far it must travel to hit the adversary’s body: | Et touchant la pointe de l’eſpee, combien qu’il faut qu’elle chemine, pour toucher le corps contraire: |
| From the First Instance......One Arms Length | A la Premiere.............La longeur de bras. |
| From the Second Instance.........One Forearm | A la Seconde......................Vne coudee. |
| From the Third Instance..........A half-palm | A la Troiſieme...............Vne demi paulme. |
| Those who are curious and wish to check these calculations, will find them mathematically accurate, and for those who are only interested simply for practical use can measure the ground. Use a stick as long as the Diameter divided into 24 Spans, each Span divided into 10 Parts, and each Part divided into 10 Minutes. Checking the aforesaid lines against this stick, they will find the correct measurements for our Instances, and by this can be assured of the accuracy of several observations that shall be set out, below. | Ceux qui ſeront curieux d’examiner ces calculations de plus pres, les trouveront aſſez accordantes aux regles de la Mathematique, & pour ceux qui n’en quierent que la ſimple Pratique, ils en pourront prendre la meſure ſur le terroir avec un baſton de la longeur du Diametre parti en 24.Nombres, & chaſqun d’icieux nombres en 10.parties, & les parties on 10.minutes. En appliquant lequel ſur leſdites lignes, ils recognoiſtront les juſtes meſures de nos Inſtances, & par icelles ſe pourront aſſeurer de la certitude de pluſieurs obſervations, qui ſeront propoſées cy apres. |
| As for the rest, be advised that, for all practical use, the lines will be enough to provide proper alignments and ranges, even without calculations. | Au reſte on vous advertit, qu’on ſe peut contenter en la Pratique de la ſeule meſure des lignes, qui donneront aſſez d’adreſſe d’elles meſmes, encores qu’elles ne ſoyent pas calculées. |
| Circle No 5. | Cercle N.5. |
| Showing the concordance of the Circle, & of the Instances, with Man’s Movements, and so understand accurately timing & reach. | Repreſentent la convenance de Cercle, & des Inſtances, avec les Mouvements de l’Homme, pour en cognoiſtre la juſteſſe du Temps, & de leur portee. |
| In the plane of Circle No 5 we first show the proportions of Man, the same as in Circle No 1, even though the figure is inverted, head downwards & feet upwards, to demonstrate that the aforesaid proportions remain the same, whether starting from one end of the Diameter or the other. | Au plan de ce Cercle N.5, ſont repreſentées en premier lieu les proportions de l’Homme, toutes les meſmes qu’au Cercle N.1, y eſtant toutesfois la figure de la perſonne renverſée, la teſte embas, & les pieds en haut, pour demonſtrer, que leſdites proportions demeurent jouſiours immobiles, tant à commencer de l’un bout du Diametre, que de l’autre. |
| The same figure demonstrates that the distance for the First Instance is equal to the extended height of the person. As well, the distance of the Second Instance is equal the natural stature from sole of the feet to the top of the head. And the distance of the Third to the height of the chest, which is also shown in the preceeding Circle. | Il eſt auſſi demonſtré par la meſme figure, que l’intervalle de la Premiere Inſtance, eſt egale à la hauteur eſtendue de la perſonne: Pareillement, que l’intervale de la Seconde Inſtance eſt egale à la ſtature naturelle du corps depuis la plante des pieds juſqu’au ſommet de la teſte: Et l’intervalle de la Troiſieſme à la hauteur de la poitrine, comme auſſi il a eſté demonſtré au Cercle precedent. |
| Furthermore, there are three inscriptions running around the circle. The first, running along the entire Circumference, says that one must move the entire arm when striking from the First Instance. The second, which is the middle one, says one need only move from the elbow to do the same from the Second. And the third, which likewise corresponds to the Third Instance, that from here one need only use the wrist. For as much as it requires effort to raise the sword and arm up high, when the body stays withdrawn, as it is in the First Instance. When the sword descends it moves forward and gets closer but this is with the advantage of natural motion, which is dropping to break and counter all the adversary’s initiatives. But in the Second and Third Instances, the body is so close that if he were to move his entire arm, he would be entrely uncovered and completely give the initiative to his adversary, which would be wholly inevitable danger, were he to try it. And so, in the one only the movment of the elbow can be allowed and in the other no more than the wrist. | Il y a davantage en ceſty cy trois eſcriteaux, qui vont en rond. Le premier, coſtoyant toute la Circonference, & ſignifiant qu’il eſt loiſible de mouvoir le bras entier, pour mener ſur l’Ennemi un coup de taille depuis la Premiere Inſtance. Le ſeconde, qui eſt celuy du milieu, contient en ſubſtance, qu’on ne doit mouvoir que le coude tant ſeulement, pour faire le meſme à la Seconde. Et le troiſieſme, qui reſpond pareillement ſur la Troiſieſme Inſtance, qu’en icelle on ne le peut faire, ſinon ſeulement du poignet de la main. Car encore que l’eſpee & le bras montent en haut avec un movemēt violent, ſi eſt ce que le corps demeure eſloigné tandis qu’il eſt en ſa Premiere Inſtance, & quand l’eſpee vient à deſcendre, il s’avance & approche, mais c’eſt avec l’avantage du mouvement naturel, qui eſt baſtant à rompre & dompter toutes les entreprinſes contraires. Mais à la Seconde & Troiſieſme Inſtance le corps eſt ſi pres, que tout autant qu’il ſe deſcouvre, & autant de temps qu’il accorde à ſon Contraire de faire quelque entrepinſe, ce ſont tout autant de dangers inevitables, où il ſe hazarde. Et partant, en l’une il n’eſt permis de mouvoir que le coude, & en l’autre non plus que le poignet. |
| The variety of situations comes from the inequality of the spaces between the two Opponents, which means one has more or fewer options to change or modify one’s movements. Which is a general warning to students never to attempt to do anything that he can only succeed in doing by chance. And at all the Distances, where he finds himself, that he holds himself always on guard against beginning something which cannot do confidently. This is worth exploring in more detail. | La diverſité procede de l’inegalité de l’eſpace qui demeure entre les deux Contraires, ſuivant laquelle on a plus ou moins de loiſir pour changer où moderer ſes mouvements. Qui eſt un advertiſſement general au diſciple, afin qu’il n’entreprenne jamais de faire, ce qui ne peut reuſſir à bien, que par hazard; & en toutes les Diſtances, où il ſe trouve, qu’il ſe tienne touſiours ſur ſes gardes, pour ne commencer choſe qui ne ſoit conjoinćte avec aſſurance. Or il vaut la peine de declarer ceſte matiere un peu diſtinćtement. |
| As I have said, that anyone who would strike from the First Instance must move his tip an entire arm’s length: which is a distance so long that one has ample time to turn the entire arm aside, and even to bring the hand above the head, and to change position in time to interrupt any of the Opponent’s actions before he can move his tip such a long distance. | Nous avons dit, que celuy qui nous veut atteindre depuis la Permiere Inſtance, qu’il luy convient avancer ſa poinćte de la longeur entiere de noſtre bras: qui eſt une eſpace ſi grande qu’on y a loiſir de tourner & virer le bras entier, & mener meſme la main par deſſus la teſte, & de changer touſiours à temps pour empeſcher l’effet de l’entreprinſe du Contraire, avant que ſa pointe puiſſe achever une ſi longue courſe. |
| In the Second Instance, to hit the opponents body, requires no more than a foot distance and it is inadvisable in such dangerous circumstances to move the hand off the centre-line, as happens when using the entire arm to carry the movement. Which is why, to guard against surprises one must not make any movements larger than those that come from the elbow, which shall be explored more exactly in the Practical discussion. | A la Seconde Inſtance pour toucher le corps contraire, il ne faut qu’environ un pied de longeur, de façon qu’il n’eſt pas loiſible en un danger ſi evident d’eſcarter la main hors de preſence, comme il en advient quant on le transporte avec le movement du bras entier. Parquoy pour s’aſſurer contre les ſurprinſes, il n’y faut point faire de plus grands mouvements, que ne ſont ceux qui procedent du coude, en y apportant meſmes la circonſpećtion requiſe, de quoy ſera parlé plus exaćtement en la Practique. |
| In the Third Instance, one can be hit with the smallest move. It is clear that at so close a distance no movement of the sword other than with the wrist can be permitted; for if one opens oneself up, for no matter how small a time, one cannot avoid being hit, if the Opponent takes full advantage of the opening he is given. | A la Troiſieme Inſtance on eſt atteint avec le moindre avancement du monde. Dont il appert clairement, qu’en une ſi petite diſtance il n’eſt aucunement permis de faire autre mouvement avec l’eſpee, que du poignet tant ſeulement: car ſi on ſe forligne, pour peu que ce ſoit, on ne pourra eviter de recevoir l’atteinte, ſi le Contraire prend bonne garde à l’occaſion, qui luy en eſt donnée. |
| All that has been said about close hits applies to long, hard strikes. This observation gives us the skill to adjust our timing according to the distance as we approach. | Ce que nout diſons de coups de taille, ſoit auſsi entendu à l’advenant des eſtocades. Car c’eſt l’obſervation, qui nous donne l’adreſſe de modere touts les movements à l’advenant du temps. |
| ON THE SUPERIORITY AND ELEGANCE
of this present circle in this training |
DE L'EXCELLENCE ET DIGNITE
de ce present cercle en cest exercice |
| In conclusion, the Circle is the foundation of the science of Arms; it is this that allows us to perceive all the dangers which might present themselves during a fight, guides our movements, focuses our intentions, gives assurance to our steps, and from which proceeds all the rest of the demonstrations that follow, and that we shall use to serve us, during the perilous voyage of our Training, as sailors use a compass and map to avoid the shoals and sandbanks of the sea, and so, in the end, arrive safely in the intended port. All good and secure offence and defence derives from this point of origin and for this good reason it can be called the Key to Training. For just as a key has three jobs: to open, close, and guard, so does this figure, which opens for us the means to attack, and to defend by closing the door to attacks by the Adversary, & furnishes us with protection, like a solid rampart, against all disruptive moves, a job which it accomplishes and effectively guards us, as Practical Training shall prove. | Pour concluſion, le Cercle c’eſt le fondement de la Science des Armes; c’eſt celuy qui nous deſcouvre touts les dangers, qui ſe peuvent preſenter par tout le diſcours d’une bataille; guide de nos mouvements, adreſſe des intentions, aſſeurance des pas, duquel auſſi tout le reſte des demonſtrations ſuivantes procede, & duquel on ſe ſervira parmy les perilleuſes vagues de ceſt Exercise, comme les Matelots de la buſſole, & d’une bonne carte Marine, pour eviter les eſceuils & bancs de mer, & en fin parvenir au repos au port qu’ils ſe propoſent. Toute bonne & ſeure offenſion & defenſe prend d’icy ſon origine, en ſorte qu’à bon droit peut il eſtre appellé la Clef de l’Exercice. Car ainſi qu’une clef a trois offices, ſçavoir Ouvrir, Fermer, & Garder, auſſi eſt ce ceſte figure, dont l’uſage nous ouvre la maniere d’aſſaillir & de defendre, ferme la porte aux intentions & entrepinſes du Contraire, & nous munit, comme d’un ſolide rempart, contre touts ſes mouvements deſordonnez, en quoy elle accompit l’office & l’effećt de nous contregarder; ainſi que la Pratique en fera l’eſpreuve. |
| ON THE CORRECT LENGTH OF THE SWORD,
which everyone should carry for defence, based on one’s own limbs. |
DE LA IVSTE LONGVEVR DE
l’espee, qve chascvn doit porter pour sa defense, accordant avec les membres de son corps. |
| Enough has been said describing the Circle. Now let us turn our attention to the Sword and it’s correct length, which is proportional and fits with all movements of the human body, and is consequently the best size of all. | A tant ſoit aſſez dit de la declaration du Cercle. Parlons maintenant de l’Eſpee, & de ſa juste longeur, qui ſoit proportionée & convenable à touts les mouvements du corps humain, & par conſequent auſsi la meilleure de toutes. |
| It is amazing how, among those who make a living in the profession of Martial Arts, and who have published writings to the world, so few concern themselves with this matter, principally because this comes up in the constant discussions on the advantages of longer or shorter swords against each other, and because all confidence concerning timing and range, the two most important aspects of Training, depends absolutely on this knowledge, and because we use the sword to execute almost every move, in attack as in defence, it must follow that if the range and size are not well known, all moves become uncertain and hazardous. | C’eſt merveille, qu’entre ceux, qui ont fait tout le temps de leur vie profeſsion des Armes, & en ont publié des eſcrits parmy le Monde, il s’en trouve ſi peu qui touchent à ceſte matiere: & principalement puis qu’il ſe preſente journellemēt à diſcourir touchant l’avantage des eſpees longues ou courtes les unes contre les autres; & que de ceſte ſeule cognoiſſance depend toute laſſeurance des temps & des meſures, deux parties principales de l’Exercice: & puis que c’eſt l’eſpee, qui fait quaſi ſeule toutes les executions, tant en aſſaut qu’en defenſe, il s’enſuit neceſſairemēt, que la meſure & la portee en eſtant incognue, toutes les operations en deviennent incertaines & hazardeuſes. |
| Nontheless, there are a few who discuss this and who determine proper sword-length, but for the the most part, as cowards, who use very long blades to stay at a distance, than to show any real science of arms. And such is the opinion of those who swear that the length of the blade should be two arms length, so that if the point were put into the ground beside a man, the crosspiece would come to the armpit; which is, in effect, more like the length of the Espadon [great-sword], than a sword: other than this would necessarily be as annoying and inconvenient to wear at the side, as it would be to draw from the scabbard, as it would be dangerous and clumsy to use. | Toutesfois il s’en eſt trouvé quelques uns, qui en ont voulu parler, & ont meſmes determiné la meſure de l’eſpee; mais pluſtoſt à l’appetit de quelques couards, qui ſe plaiſent à des armes fort longues, pour demeurer touſiours en diſtance, que par aucune vraye demōſtration de Science. Et telle eſt l’opinion de ceux qui veulent, que les lames doivent eſtre egales à deux bras entiers, de ſorte que la pointe eſtant miſe à coſté de l’homme en terre, le pommeau de la guarde luy vienne à toucher l’aixelle; qui eſt en effet pluſtoſt la longeur d’un Eſpadon, que d’une Eſpee : outre ce qu’elle ſera neceſſairement auſsi malfeant et incommode, tant à porter au coſté, que pour tirer hors du fourreau, comme dangereuſe & peu manniable en l’uſage. |
| Leaving aside for the moment all other considerations which we could bring up on the subject of the correct size of the Sword, besides those of the most convenient and advantageous use and handling, I will say that there are times when a longer or shorter sword is better. And yet, to answer the question as to determine a length, it should be between these two extremes, in the middle; not too short against long swords, nor likewise too long against short swords, and such that it is always easy to handle however one wishes. And because of this, as it means that the length should be proportional to the person, we have taken the size from his own body. Everyone should have his weapons sized proportionally to their own person. Thus the size of the Sword should be such that the length of the blade from the tip to the crosspiece is equal to half the Diameter, that is to say, if the tip is placed on the ground between the feet, the crosspiece of the handguard will come up to the navel, just as explained in Circle No 1, and the more exactly one can achieve this, the better, for many reasons. So there are ten small figures, labelled with letters A to K along the edges of the Plate, which will serve, for now, as a practice guide; the meaning of these follows. | Laiſſant donc preſentement à coſté toutes autres conſiderations, qu’on pourroit mettre en avant touchant la vraye Meſure de l’Eſpee, horsmis celle de l’uſage & du maniement le plus commode & le plus avantageux, je di, qu’il y a des occaſions plus favorables pour les eſpees longues, & des autres qui le ſont plus pour les courtes. Et par tant s’il eſt queſtion de luy aſsigner une meſure, qu’il la faut mettre entre les deux extremes, ſi bien qu’elle ſoit mediocre; non trop courte contre les eſpees longues, ne pareillemēt trop longue contre les eſpees courtes, & qu’elle ſoit en toutes occaſions maniable à ſouhait. Et puis qu’il faut neceſſairement qu’une telle longueur ſoit proportionnée à la perſonne meſme, nous l’avons tirée & demonſtrée hors de la meſure de ſon corps; & voulons que chaſcun ait ſes armes proportionnée à l’advenant de ſa propre perſonne. Dont la meſure de l’Eſpee ſera telle, que la longueur de ſa lame depuis la pointe juſques à la croiſee, ſoit egale au demi Diametre; c’eſt aſſavoir, que la pointe eſtant miſe en terre entre le creux de ſes deux pieds, les branches de la garde luy viennent à reſpondre juſtement ſur la haueur de nombril; cōme il ſe voit exprimé au Cercle N. 1. Et le plus exaćtement qu’on le pourra pratiquer, ce ſera le meilleur, pour diverſes raiſons; dont nous avons mis icy par proviſion des dix petites figures, marquées de lettres ſuivant l’ordre alphabetique depuis l’A juſques au K au long des bords du Tableau, qui en ſerviront pour le preſent de preuve: & en eſt la ſignification telle que s’enſuit. |
| In any case, before the explanation, you should know that the proportions of the images of these people represented by the said figures, are drawn from and adjusted to the measure of the two small Circles I & K set on the plane of the pavement at the bottom of the Table. About this, if there arise any doubts, and to be entirely certain, one may measure the figures with a compass, and find the natural body height of each of these persons will be the same as the line C-V; the size of their swords, like the half Diametre; and the length of their arms, like C-H. | Toutesfois avāt l’explication je vous adverti, que le proportions des images de ces perſōnes repreſentées par leſdites figures, ſont tirées & adjuſtées ſur la meſure de ces deux petits Cercles I & K, couchez ſur le plan du pavé au bas de la Table. Touchant quoy, pour en avoir pleine intelligence, & pour l’explictation des doutes, qui en pourrouyent ſourdre, il ſera expedient de les meſurer au compas. Car la hauteur naturelle des corps de caſcune de ce dites perſonnes ſera comme la ligne CV; la meſure de leurs Eſpees, comme le demi Dimametre; & la longeur du bras, comme CH. |
| FIGURE A | FIGVRE A |
| To begin with Figure A, here we see that the length that we have determined for the sword does not bother anyone, whether in casual conversations, or in a crowd, or moving through narrow passages, or similar situations where one would ordinarily be encumbered by a sidearm. On the contrary, with a blade of this length, and in a belt and hanger, of a design which we shall show in the following Plate, drawing the handle towards oneself with the right hand, the point by itself falls perpendicularly to the ground beside the person, the hilt a little forward, together with the handle falls in its proper place, on the hip, at the height of the navel, when one moves the left foot a half-pace forward, one can comfortably rest the elbow and in fact the left side on it; as such it serves as a rest, rather than an encumbrance like all other swords not proportionally sized. | Pour le premier il eſt repreſenté par ceſt figure A, que la longueur, que nous mettons pour l’Eſpee, ne donne point de faſcherie à la perſonne, quād on eſt en converſation avec des gens, ou qu’on ſe trouve en la foule, ou cheminant par des eſtroits paſſages, ou en ſemblable occaſions, eſquelles on eſt ordinairement embaraſſé par les armes qu’on porte. Au contraire eſtant la lame de ceſte longueur, que nous luy avons aſsignée, & la portant à coſté avec un tel ceinturon & pēdant d’eſpee, qu’il ſera domonſtré en la Table ſuivante, moyennant qu’on tire la garde devers ſoy avec la main droite, la pointe viendra à tomber d’elle meſme perpendiculairement en terre à coſté de la perſonne, un peu devant, enſemble auſſi la garde en viendra à ſe mettre en ſa juſte place, ſi bien à point, & à l’egal de la hauteur du nombril, qu’en avançant le pied gauche environ d’un demi pas, on aura la commodité de repoſer le coude, & enſemble tout le coſté gauche du corps deſſus; en ſorte qu’elle ſervira d’un appuy, pluſtoſt que de nous empeſcher, comme font neceſſairement toutes les eſpees, qui n’ont pas la longueur proportionée. |
| FIGURE B | FIGVRE B |
| The same length of sword is also very convenient for drawing the blade. For, as shall be explained in the next Table, and as the Circle itself shows, when carrying the sword on a belt & hanging as described, the guard comes slightly forward beside the hip, the scabbard angles towards the rear; each at its correct height, and so one may easily use both hands at the same time, with the left hand grips the scabbard just below the guard and the right hand reaches circularly across in front to grip the handle, in a way that requires no other preparation, no twisting the body, as we ordinarily see done by others, as if they had to search for their sword, or as if it were not properly attached to their side, a very clumsy, if common, arrangement. | La meſme longueur d’eſpee eſt auſſi tres commode pour le deſgainement. Car en la portant avec le ceinturon & le pendent de noſtre deſcription, qui ſera propoſé au prochain Tableau ſuivant, & que le Cercle meſme demonſtre; la garde en vient un peu en avant à coſté du corps, le fourreau tirant vers le derriere; chaſcun en ſa juſte hauteur, & en telle ſorte qu’on peut travailler à ſon aiſe en un meſme temps de la main droite & de la gauche, en portant la main gauche embas, pour empoigner le fourreau pres de la garde, & la droite circulairement en avant, pour prendre l’eſpee, ſans aucune autre preparation, ne ſans courber le corps, comme on voit faire ordinairement aux autres, quaſi comme s’il la falloit cercher, ou qu’elle ne fuſt aſſez à commandement attachée au flanc de celuy qui la porte. choſe qui eſt de tres mauvaiſe grace, encor qu’elle ſoit assez commune. |
| FIGURE C | FIGVRE C |
| Next we see the operation of drawing the sword, which, we shall describe more fully in Plate III with all the various circumstances and reasons for which, in drawing the sword, one is constrained to raise one’s hand and arm as high as possible, even to raise the right leg, or any other bodily action, which may even include opening the fingers, to raise the hand sufficiently to clear the scabbard. All of which are necessary to assist in drawing because of the length of the blade. Thus it is apparent that our size of blade is so large that it could not be made longer without causing considerable inconvenience. | S’enſuit l’operation meſme du deſgainement, que nous deſcrirons plus particulierement au Tableau III. avec toutes ſes circonſtances, & les raiſons, pour leſquelles en faiſant le deſgainement on eſt contraint de hauſſer le bras, enſemble avec la main, tant qu’il eſt poſſible, meſmes de lever auſſi la jambe droite, & d’accomoder toutes les aćtions du corps, à celle fin que la main puiſſe monter à ſuffiſance, pour laquelle meſme conſideration il convient auſſi ouvrir les doigts. Leſquelles choſes ſont toutes neceſſaires à cauſe de ceſte longueur de la lame, qui a beſoin d’eſtre aſſiſtée de toutes ces aides. Dont it appert que noſtre meſure de lame eſt ſi grande, qu’elle ne pourroit eſtre de plus ſans des notables incommoditez. |
| FIGURE D | FIGVRE D |
| So, as this blade length is equal to the lower half of the extended body, from the soles of the feet to the navel, it is also equal to the upper half, from the navel to the highest that the hand can be raised above the head and as we see from the figure these two halves are equal. This is easy to show, as it is here. If we put the tip on the ground with one end of the crosspiece on the navel, and rotate the the tip upwards around the crosspiece, one will find the tip is as high as one’s fingers can reach. | Or tout ainſi que ceſte meſure eſt egale à la partie inferieure du corps eſtendu, depuis la plante des pieds juſqu’à la hauteur du nombril, auſſi l’eſt elle pareillement à la partie ſuperieur, depuis le nombril en ſus juſques au plus haut que la main peut atteindre, comme on voit en la figure que ces deux parties ſont egales en longeur; auſſi la preuve en eſt facile, comme elle eſt icy repreſentée. Car en mettant la pointe de l’eſpee en terre avec l’une des branches de la croix ſur le nombril, & tournant en apres la pointe droitement en haut, l’on trouvera, qu’elle viendra au plus haut qu’on pourra toucher du bout des doights. |
| And thus it can be seen once again, that the size of the blade is equal to half of the extended length of a person, and equal to the radius of our Circle, taking the navel for the Centre and the extended length as the the Diameter. | Et voilà comme il appert derechef, que la meſure de la lame eſt egale à la juſte moitié de la longueur eſtendu de la perſonne, & pareillement au demi-Diametre de noſtre Cercle, prenant le nombril pour le Centre, & la longueure eſtendue pour le Diametre. |
| FIGURE E | FIGVRE E |
| As for the natural height of a person from the soles of the feet to the top of the head, this can also be measured and is here shown to be measured with the sword. For if we grip the handle in the style of our training, about which we shall discuss more later, and one extends the sword and arm in a straight line, as we can see with one of these two persons, keeping the tip, the guard, and the shoulder at the same height, the line of the sword and arm, from the tip to the shoulder or the armpit, will be found to be equal to the height of the person. If one wishes proof, take a long stick or half-lance, and measure the distance from the tip of the blade to the armpit, then place the end of the stick on the ground between the feet and and stand it upright. It will be found that the measurement is exactly the size of the person. | Quant à la hauteur naturelle de la perſonne depuis la plante des pieds juſques au ſommet de la teſte, icelle ſe peut auſſi meſurer, & eſt icy repreſentée à meſurer avec l’eſpee. Car ſi on la prend au poing ſuivant le ſtile de ceſtuy noſtre Exercice, dont il ſera parlé cy apres, & qu’on l’eſtende enſembe avec le bras en droite ligne, ainſi qu’il ſe voit en l’une de ces deux perſonnes, tenant la point, & la garde, & l’eſpaule en egale hauteur; la ligne de l’eſpee avec le bras, depuis la pointe de la lame juſques à l’eſpaule ou à l’aixelle, ſera trouvée egale à la ſtature de la perſonne. Si vous en demandez la preuve, prenez un long baſton ou un demie lance, et en meſurez de longeur depuis la pointe de la lame juſques a l’aixelle: puis appliquez ceſte meſme ligne à la hauteur de la perſonne, mettant le ſuſdite baſton entre le creux de ſes deux pieds, & le dreſſant tout drout contre le corps pour le meſurer. Et ce faiſant ſera trouvé, que la meſure en accordera juſtement à la hauteur de la perſonne. |
| FIGURE F | FIGVRE F |
| SHOWING HOW
the when the body is erect and in profile, the arm and sword extended in a straight line, the reach is further than any other. |
DEMONSTRE QV'ESTANT LE
corps perpendicvlaire et en povrfil, le bras et l’espee estendvs en droite ligne, atteignent plvs loing qv’avtrement |
| Now we shall prove that this same length of sword can be increased or shortened, according to the reach of various distances, depending on where one is. This is shown by the three following figures, F, G, & H, the first of which, marked F, shows how the arm and sword extended out in a straight line is the longest reach of all positions, as long as the body position does not change, of course. If one stands erect on both legs, neither leaning forwards, nor backwards, and one extends the sword and straightens the arm in a line, that is, with the tip and the guard at shoulder height, one will reach further forward than if one raises or lowers the tip. For one cannot do either without the tip following a curve along a circumference, which is also shown in the figure. By which it is evident that the more the tip rises or lowers, the further it moves from the nearest point of contact. | Maintenant nous proverons, que ceſte meſme longueur d’eſpee eſt capable de s’allonger, & de ſe raccoucir, ſelon la meſure des diſtances, où on ſe trouve. Ce que nous ferons paroiſtre par les trois figures ſuivantes, F.G.H. dont la premiere, qui porte la marque d’un F. repreſente, que la droite ligne, qu’on fait avec l’eſpee & le bras eſtendu, eſt la plus longue de toutes celles qui peuvent eſtre faites avec ladite eſpee, à condition toutesfois, que le corps demeure en une meſme poſture. Car ſi on ſe tient droit ſur ſes jambes, ſans que le corps s’avance, ne ſe recule, & qu’on eſtende le bras avec l’eſpee en droite ligne, c’eſt à dire, mettant la garde & la pointe juſtement en la hauteur de l’eſpaule; on attendra plus avant, que ſi la pointe monte, ou qu’elle s’abaiſſe. Car elle ne peut faire ne l’un ne l’autre, ſinon en allent courbe, à la maniere d’une circonference, comme il eſt auſſi repreſenté en la figure. Par la quelle il eſt evident, que d’autant plus que la pointe continue à monter ou à deſcendre, d’autant plus elle s’eſcarte du plus prochain endroit de l’attouchement |
| To be more precise, we divide the blade into 12 Spans, with the length of the arm at about 8 Spans, and the elbow, which is almost in the middle of the arm, at about 4 Spans long. So, the blade can rise or descend in a circular arc three ways; through the movement of the entire arm, by the movement of the elbow, or by the movement of just the wrist. It follows in the first case when one moves the entire arm, that the centre of this circle is at the shoulder, and consequently, the radius, which determines this arc of circumference, rising or descending, is the line of the sword together with the entire arm, which together equals about 20 Spans. In the second case, moving from the elbow, the centre is at the elbow, the length of the radius is 12 Spans plus 4 Spans, which together makes 16 Spans. In the third case, when one moves only from the wrist, the centre is the person’s fist, only the blade moves, which makes a radius of 12 Spans. Now everyone, with any knowledge of mathematics, knows that the circumference of a circle is proportional to its radius: and these become shorter; also, therefore a radius of 20 is greater than 16, and that of 16 greater than the third which is 12. It follows that, raising or lowering the tip with just the wrist, shortens our distance to the tip, more than if one uses the elbow, and with the elbow likewise more than using the entire arm. | Pour en parler plus exaćtement, ſachez que nous partiſſons la lame in 12. Nombres, dont la meſure du bras en contient auſſi environ 8. en ſorte que le coude, qui en eſt quaſi la juſte moitié, en revient comme à 4. Nombres. Or eſt il que la pointe de l’eſpee peut monter ou deſcendre circulairement en trois ſortes; aſſavoir par le mouvement du bras entier, par le mouvemēt du coude, ou par le mouvement du ſeul poignet de la main. Dont il s’enſuit au premier ſens quand on fait le mouvement du bras entier, que le centre d’iceluy giſt en l’eſpaule, & par conſequent, le demi-Diametre, qui doit faire la ſuſdite circonference, montante ou deſcendante, c’eſt la ligne de l’eſpee enſemble avec le bras entier, qui font enſemble bien pres de 20. Nombres. Et au ſecond, en faiſant le mouvement du coude, le centre eſtant au coude, la longueur de la ligne totale contient 12. & 4. qui font enſemble 16. Et pour le troiſieme, quand on fait le mouvement du ſeul poignet, le centre eſtant le poing de la perſonne, il n’y a que la lame ſeule, qui fait 12. Nombres pour la ligne du demi-Diametre. Maintenant chaſcun, qui a quelque intelligence des Mathematiques, ſçait que les circonferences ſont proportionelles à leurs demi-Diametres: & que les circonferences ſe raccourciſſent à l’advenant: & partant puis que le demi-Diametre 20. eſt plus grand que celuy de 16. & celuy de 16. plus grand que le troiſieme de 12. il s’enſuit qu’en hauſſāt ou abaiſſant la pointe, du poignet de la main tant ſeulement, on raccourcit le chemin de la pointe, qui eſt la circonference plus, qu’on le faiſant du coude: & avec le coude pareillement plus, qu’en faiſant le mouvement avec le bras entier. |
| It would be very easy to mathematically calculate the differences of distance, but it is enough to show only one small example, from which it will be very simple to understand the rest that follows. | Il ſeroit bien aiſé de calculer par raiſon Mathematique, combien ces differences portent: mais il nous ſuffira d’en propoſer ſeulement un petit exemple, par le quel is ſera facile d’entendre auſſi à l’advenant le reste. |
| Take the case where the tip of the sword is raised using just the wrist, so that the centre of motion is the hand, and consequently the radius is only the length of the sword, making 12 Spans and suppose the tip rises likewise a distance of 12 Spans along the circumference; drop a line perpendicularly from the tip to the ground and one will find the line 12 Spans long shortened by 6 Spans, that is, by half. | Poſons donc le cas, qu’on hauſſe la pointe de l’eſpee du ſeul poignet; en ſorte que le centre de l’aſcenſion ſoit en la main, & par conſequent le demi-Diametre ſoit la ſeule longueur de la lame, faiſant 12. & que la pointe monte pareillement en circonference à 12. Nombres en haut; alors en laiſſant deſcendre une ligne perpendiculare du lieu de la pointe vers la terre, on trouvera, que la ligne 12 ſera raccourcie de 6. Nombres; c’eſt à dire, de la juſte moitié. |
| If the tip rises by only 6 Spans, which is half of the previous rise, one finds the line shortened by only 1½ Spans, or one quarter the previous distance. | Si la pointe ne monte, que 6. Nombres, qui eſt la moitié de l’aſcenſion precedente, on trouvera par la ligne perpendiculaire, qu’ell ſera racourcie de 1½, qui n’eſt, que le quart du precedent raccouciſſement. |
| If it rises only 3 Spans, the line will again be shortened by one quarter of the previous distance or ¾ Spans. | Si elle ne monte qu’à 3. Nombres de hauteur, la ligne du raccouriſſement ſera derechef le jusſte quart du precedent, aſſavoir ¾. |
| Likewise the same happens when we raise the tip from the elbow. Because if the tip rises 16 spans, the distance shall be shortened by 8. If raised up to 8 Spans, it will be shorter by 2. And if it is raised by only 4, it will be shorter by ½, which is only a quarter of the preceeding step. | Ainſi en eſt il pareillement des autres aſcenſions, mettent le centre ſur le coude. car ſi la pointe en monte à 16. Nombres, elle ſe raccoucira de 8. Si juſques à 8. Nombres, elle s’en racourcira de 2. Et ſi elle ne monte qu’à 4. elle en ſera raccourcie ½, qui n’eſt que le quart du precedent. |
| Of course the same happens when the motion is done with the entire arm. | Il faut entendre auſſi le ſemblable des mouvements qui ſe font avec le bras entier. |
| Thus this is the difference between the straight line versus the other lines at different heights, and we have not even considered shortening the reach either by bending the arm, or changing the posture, or even simply moving the feet. For there is no doubt that one can reach further than the straight line, if one leans the body forward, or one steps forward: this is not apropos, and beyond doubt, because in such a case, there are two lines, not one, because the extension of the arm with the sword is one line, the movement of the body is yet another. That these two lines together reach further than just the straight arm line alone is not the point. Because to comprehend the reach of each line, we must compare and consider each one independently. To do this, we must leave the body in its natural posture, so as not to skew one way or the other. | Voilà doncques la difference de la droite ligne contre les autres, qui ne demeurent pas en egale hauteur; ſans toutesfois conſiderer pour le preſent le raccourciſſemēt, ne la courbure du bras, ne la changement de la poſture du corps, moins encore l’avancemēt qu’il peut faire moyennant la demarche des pieds. Car is ne faut pas douter, qu’on puiſſe atteindre plus loing que la droite ligne, ſi on panche le corps ſur le devant, ou qu’on l’avance avec le demarche: ce qui eſt hors de ce propos & hors de doute, à cauſe qu’en tel cas, il ſe trouve deux lignes contre une, car l’extenſion du bras avec l’eſpee font une ligne, l’avancement du corps en fait encor une autre. Que ces deux lignes, eſtans jointes par enſemble, ſoyent plus longues que la droite ligne ſeule, celà ne touche pa à ceſte queſtion. Car pour ſçavoir la portee de chacune ligne à part, il les faut conſiderer & comparer les unes aux autres diſtinćtement. Et pour ce faire il convient, qu’on laiſſe le corps en ſon eſtat naturel, qui ne favoriſe non plus l’une, que l’autre. |
| Which is why, should one with to confirm the above, stand straight on both feet, hold the sword with the arm outstretched in a straight line, as shown in the figure, just touching the tip to a wall, or some other object at shoulder height, and then raise or lower the tip, with the entire arm, with the elbow, or with just the wrist; without any doubt in the world, you will find your line shortened, more or less, to the degree the centre of motion is more or less distant from the tip as it moves along the circumference. | Parquoy ſi vous avez envie de faire preuve de ce que deſſus, mettez vous droit ſur vos pieds, & tenez premierement l’eſpee avec le bras eſtendus en droite ligne, en la maniere qu’il eſt icy repreſenté par la figure, en touchant de la pointe un certain endroit d’un mur, ou de quelque autre corps que ce ſoit ſur la hauteur de l’eſpaule; & puis eſſayez de monter ou d’abaiſſer voſtre pointe, avec le bras entier, ou avec le coude, ou avec la main tant ſeulement; il n’y a point de faute, le moins du monde que vous la montiez ou deſcendez, vous troverez voſtre ligne raccoucie, plus ou moins, au rebours que le centre du movement ſera plus ou moins eſloigné de la pointe, qui fait la circonference. |
| Part of the reason for this difference is when moving the entire arm from the shoulder, the line stays straight, notwithstanding it may move off the most direct path: but when moving from the elbow, one makes an angle, which is, of necessity, a break in the line: and it must also follow that this makes it ever shorter as it moves from the straight line. But as this break angle increases as it moves to the middle, as well as when one performs the moves with the hand, there is yet more shortening: for when the angle is close to the extremity of the line, there is but a small part which draws from the straightness.
Dont il s’entend auſſi, qu’elle s’accourcira encor d’avantage, en cas qu’on y face deux courbures, l’une ſure le coude, & l’autre ſur le poignet de la main. Of course this shortens even further when faced with two bends, one at the elbow, the other on the wrist. |
La cauſe de ceſte difference giſt auſſi en partie, en ce que quand le mouvement ſe fait avec le bras entier, eſtant le centre en l’eſpaule; la ligne droit demeure en ſon entier ſans aucune courbure, nonobſtant qu’elle forligne quelque peu de la droite voye: mais quand on le fait avec le coude, on fait un angle, qui eſt necessairement une encogneure ſur la ligne: dont s’enfuit auſſi neceſſairement, qu’elle s’accourcit d’avantage, entant qu’elle s’eloigne plus de la droiture. Que ſi ceſte encoigneure de l’angle approche encor plus du milieu de la ligne, ainſi qu’il en advient quand on fait le mouvement avec la main, il y a touſiours encor plus d’accourciſſement; car quand l’angel eſt environ les extremitez de la ligne, il n’y en a qu’une petite partie qui s’esloigne de la droiture. |
| This straight line is of very great use in Training, and shall be the basis for several observations; as such it is worth being carefully described, and well understood. It is the longest and surest of all positions, the most capable in defense of holding off the Enemy at a distance, and the most powerful way to hit offensively. And above all, the straight line can reach the closest target most securely, and without fear of also being struck at the same time. This is why one must always take care to keep this position foremost in training. | Ceſte droite ligne aura un fort grand uſage en noſtre Pratique, & ſera le fondement de pluſieurs obſervations, de ſorte qu’elle merite d’eſtre curieuſement declarée, & bien entendu. C’eſt la plus longue & la plus ſeure de toutes, la plus capable en defenſe à tenire l’Ennemi eſloigné, & la plus puiſſante en offenſion pour l’atteindre. Et ce pour autant, que celuy qui en donne l’atteinte au plus proche endroit d’attouchement, il le fait à ſeur, ſans aucun danger de recevoir au meſme temps la pareille. Et pour ceſte cauſe, il faudra touſiours taſcher de s’en prevaloir en la Pratique. |
| FIGURE G | FIGVRE G |
| Nevertheless there are times when one finds oneself in close, where the long lines are useless and even damaging, because the distances are entirely too short for a blade held out at arms length in a straight line (where one must shorten the arm, or even draw it back, to be able to use the tip.) At these close distances the length of our blade is not always comfortable and sufficiently easy to use: so we must shorten the line to close distances as it is to reach at longer ones. This is what is shown by the following two figures; the one marked G demonstrates how one may shorten the line, if the ennemy runs up to get past the tip, by stopping him with your foot and firmly placing the guard against the right hip, the tip will just reach his chest, which would otherwise pass beyond the shoulder if the sword were longer. | Neantmoins quand c’eſt qu’on entre en meſure etroite, où toutes les lignes longues ſont inutiles, & dommageables, à cauſe que les diſtances y ſont aucunefois plus courtes, que les lames eſtendues avec le bras en droite ligne (dont on eſt contraint de raccourcir le bras, ou meſmes de le retirer arriere, afin de ſe pouvoir ſervir de la pointe.) En ces meſures eſtroites noſtre longueur d’eſpee ne laiſſe pas d’y eſtre touſiours commode & maniable à ſuffiſance: car elle eſt autant propre pour raccourcir ſa ligne en ladite meſure eſtroite, qu’elle eſt capable de l’allonger en la grande. C’eſt ce qui eſt repreſenté par les deux figures ſuivantes; dont celle qui eſt marquée de la lettre G. demonſtre comment on la peut raccourcir, en cas que l’Ennemi nous veuille courrir ſus, pour venir au dedans de la pointe. car en luy mettant le pied contre le corps, & affermiſſant la garde ſur la hanche droite, la pointe luy en viendra juſtement devant la poitrine, qui luy paſſeroit autrement par deſſus l’eſpaule, en cas que l’eſpee fuſt plus longue. |
| FIGURE H | FIGVRE H |
| This same shortening can be accomplished another way, by placing the left hand firmly against the chest instead of using your foot, again firmly placing the guard against your right hip, because between the hip and the extended left hand is just enough space to comfortably use the sword as needed. | Ce meſme accourciſſement de ligne ſe pourra pratiquer encor en une autre ſorte, en luy mettant la main contre la poitrine, au lieu de ſe ſervir du pied, en affermiſſant derechef la garde de l’eſpee ſur la hanche droite, car entre ladite hanche, & la main gauche eſtendue, il reſtera juſtement l’eſpace de la longueur de l’eſpee, pour la commodité de la manier & appliquer ſelon l’exigence. |
| FIGURE I | FIGVRE I |
| This length of sword is also equal to the double-length step, which is the longest one a person can make without losing power, as shown in Figure I. Since we declared the length of the blade equal to one half-diameter, we can estimate that the step, which is shown along the half-diameter, is also understood to be the length of the blade. Place the toes of the left foot on the letter X, it is impossible for a man to pass beyond the centre in one single step, unless he raises the heel and puts his weight over his right toes, as shown here. Doing this is not a single step with one foot, but two: since both feet move forward, one more, the other less. | Ceſte longueur d’eſpee eſt auſſi egale à la longueur du pas double, qui eſt leplus grand que la perſonne puiſſe faire de toute ſa force, ainſi que la Figure I le demonſtre. Car puis que nous ordonnons la longueur de la lame à l’egal du demi-Diametre: il faut eſtimer que le pas, qui eſt representé ſur la ligne du demi-Diametre, s’entend auſſi eſtre fait ſur la longueur de la lame. Mettant donc les orteils du pied gauche ſur la lettre X, je di, qu’il eſt impoſſible à l’homme de paſſer en un ſeul pas outre le centre, ſi ce n’eſt qu’il y accommode auſſi l’autre pied, en eſleveant le talon, & y ſouſlevant le corps ſur les orteils; comme on le voit icy exprimé. Quoy faiſant, ce n’eſt point le pas d’un pied ſeul, mais de deux: à cauſe que tous les deux s’avancent, l’un plus & l’autre moins. |
| FIGURE K | FIGVRE K |
| Finally taking the sword in hand, and standing erect at the Centre, with the arm and the same sword stretched out to the side in a single line, the point going down to touch the ground in an acute angle, as shown in figure K, we can see that the tip of the sword is just on the Circumference: in such a way that one could mark it on the pavement with just the single sword held in hand, without leaning. In any case, it is more expedient in something so important, to follow the order which we listed, above; more so as it is nearly impossible, just in turning around, to keep it steady and round as needed, to mark the circumference. Moreover, there is nothing more accurate than to put one of the ends of the cross-guard at the Centre point, and use the point to draw the Circumference, so the all rest can be drawn with confidence. | Finalement ſi on prend ceſt eſpee au poing, & qu’on ſe mette perpendiculairement debout ſur le Centre, avec le bras & la meſme eſpee eſtendus à coſté en droite ligne, la pointe tirāt vers la terre en angle aigu, comme il eſt repreſenté en ceſte figure K, on verra que la pointe de l’eſpee viendra juſtement ſur la Circonference: en ſorte qu’on pourroit deſcrir ſur le pavé avec la ſeule eſpee à tenir en la main, ſans aucun abaiſſement du corps. Toutesfois il ſera plus expedient en choſe de ſi grande conſequence de ſuivre l’ordre que nous avons baillé cy deſſus; d’autant qu’il eſt quaſi impoſſible, en tournant le corps pour deſcrire la dite circonference, de le gouverner & moderer ſi juſtement ſans varier, comme il ſeroit à ſouhaiter. Partant n’y a rien plus ſeur, que de le faire avec l’eſpee meſme, en mettant l’une des branches de la croix ſur le point du Centre, & tirer la Circonference avec la pointe, pour venir tant plus ſeurement à l’accompliſſement du reſte. |
| One could propose other considerations concerning the correct length of the sword: but is seems to me that enough has been said for those who like the elegance of wearing a sword by their side, the ease of drawing, the advantage of using it under all circumstances, and, principally, the necessity even, for those who would practice our training, using our Circle. Use will give them a good understanding of the need for this length and without this it would be impossible to understand the demonstrations of our precepts. | On pourroit propoſer encor d’autres conſiderations touchant ceſte juſte longueur de l’eſpee: mais il me ſemble que c’en eſt aſſez dit à ceux qui aiment la bien-ſeance de porter l’eſpee à coſté, la commodité de la tirer, l’avantage de la manier en toutes occurrences, & principalement la neceſſité meſme, pour le regard de ceux qui voudront prendre la peine de faire exercice à noſtre mode, & ſur le plan, de noſtre Cercle: car l’uſage leur en fera bien entendre la neceſſité, & que ſans icelle il leur ſeroit impoſſible de comprendre les demonſtrations de nos preceptes. |
| Because we have discussed the correct length of the sword, it would be reasonable if we finish by speaking, for the moment, as we did on the blade, about the entire hilt, or each of its parts. It is only reasonable that the observations which we have concerning arms, should be discussed before we come to the exercises. In any case we have found it best to put everything concerning the hilt in the next Plate, as this material cannot be deduced from this First Plate other than by bits as it appears in one image or another. It shall suffice for the present, to advise you to take a good look at the images of the hilt, which are at the bottom of the Plate and as seen from above in Circle No 1, until it can be discussed more fully with distinct description of all the parts in Plate II. | Puis que nous avons donc traitté de la vraye longueur de l’eſpee, il ſeroit raiſonnable que nous vinſſions à parler doreſenavant de la façon, tant au regard de la lame qu’au regard de la garde en ſon entier, ou en chaſcune de ſes parties; eſtāt raiſonnable, que les obſervations, que nous avons touchant les armes, ſoyent declarées avant que devenir à l’exercice meſme. Toutesfois nous avons trouvé bon de remettre ce qui touche la garde, au Tableau ſuivant, pour ce que la matiere n’en pourroit eſtre deduite en ce Tableau pemier, ſinon par loppins, comme il paroiſtra par les figures de l’autre. Il nous ſuffira donc pour le preſent, de vous advertir de prendre bon eſgard à la figure de ces gardes, qui ſont icy representées au bas du Tableau, & au plan du Cercle N.1. juſqu’à ce qu’il en ſoit diſcouru plus amplement avec diſtinćtion de caſcune des parties; ce qui ſera fait au Tableau II. |
| CONCERNING the 12 SPANS
of the blade and of Sliding the point of contact up and down the blade |
TOVCHANT LES 12 NOMBRES
de la lame, et de la gradvation et desgradvation |
| Speaking again of the blade and explaining the significance and use of the 12 Spans, by which the length is divided into 12 equal parts, as shown on the bottom of the Plate on both sides; the left side numbered, the right side of the same length, also numbered with twelve points, with each of the twelve Spans inscribed in Latin, corresponding the the twelve parts of the ancient Roman Pound weight. | Parlons derechef de la lame, & expliquons la ſignification, & l’uſage de ces 12. Nombres, par leſquels elle eſt diviſée en 12. parties egales de longueur, comme il ſe voit au bas du Tableau à la main gauche; le ſemblable eſtant auſſi repreſenté au coſté oppoſite, ſur une autre lame de la meſme longueur, diſtinguée pareillement par nombres en douze points, & par des noms, empruntez du Latin, en douze parties, reſpondantes au douze parties de la livre Romaine à l’ancienne. |
| All that is needed to follow all sorts of demonstrations are these 12 spans that divide the blade by degree of strength, from the tip to the crosspiece. These are of such importance that there will always be more to discuss no matter how much is already written. Because the principle advantages for practical work, for certainty in demonstrations, for understanding the relative weights, for governing sensitivity of the hands, for attending to timing, and to approaches, are all found in whole or for the most part in the use of these Spans. | Il n’y a rien plus neceſſaire, pour examiner tout ſorte de demōſtrations, que ces 12. Nombres, par leſquels la lame eſt diſtinguée en autāt de degrez de force, en allant depuis la pointe juſqu’à la croiſee: & ſont de ſi grande importance, que jamais on n’en pourra tant eſcrire, qu’il n’en reſte encor à dire d’avantage. Pource que les principaux avantages de la Pratique, la certitude des demonſtrations, les proportions des poids, la moderation du ſentiment, les addreſſes des temps, & des approches, ſe trouvent toutes, ou en leur total, ou en leurs principales parties en l’uſage de ces Nombres. |
| The first point one mus know is that the twelve degrees of strength begin at the tip, the weakest part, and run up the blade, each section increasing strength by degrees up to the strongest part, the crosspiece of the hilt. | Touchant quoy il faut premierement ſçavoir, que ces douze degrez de force commencent depuis la pointe de la lame juſqu’à la croix de la garde: & que la pointe c’eſt le foible de l’eſpee; la garde c’en eſt le fort; ce qui eſt entre deux, tirant de la pointe vers la garde, ſe renforce tout de ſuite de degré en degré. |
| People wrongly attribute actions to the sword, but the sword itself is nothing more than a lifeless, immobile, material object, which only comes alive only through the hand that guides it. Yet because the liveliness of the sword depends only on the hand, it follows that the partition that is closest and most affected by the power of the hand should also be the strongest, those further away must consequently be weaker. The one that is first and most immediately affected by force from the hand, is called the strong part of the sword, point number 12. The partitions which receive power from the previous one and transmit it to the next and weaker one are said to be more or less strong or weak, according the the number of degrees along the blade. The last partition, preceeded by all the others, is called the weak part. | Car l’eſpee n’eſtant qu’une choſe materielle, eſt d’elle meſme ſans acune vigueur, & immobile, recevent toute ſa force de la main, qui la gouverne; de la quelle auſſi dependent toutes les aćtions, qui ſont attribuées improprement à l’eſpee. Et partant, puis que toute ſa vigueur depend de ceſt main ſeule, il faut neceſſairemēt, que la partie, qui en eſt plus proche & plus propre à recevoir ſon influence, ſoit auſſi la plus forte; celle qui s’en eſloinge, ſoit auſſi conſequément plus foible. Celle qui reçoit l’influence de force immediatement & la premiere de toutes, ſoit dite le fort de l’eſpee, cōme le point 12. Celles qui la recoivent mediatement par des autres precedentes, & la communiquent derechef à d’autres parties ſuivantes & inferieures, ſoyent dites plus ou moins fortes ou foibes, ſelon le nōbre des degrez qu’ils portent. Celle qui la reçoit la derniere de toutes, & par le moyen de toutes les autres precedentes, ſoit dite le foible. |
| Finally, the reason why I chose the number 12 and not another, was to keep the sword in proportion to the length of the arm, which is two cubits, while the sword is three, and as we showed above, that the blade being equal to the half-diameter and he arm equal to only one third, as the Diametre is divided into 24 partitions, the arm into 8, and so consequently the blade into 12. | Au reſte la cauſe pourquoy nous avons plustoſt choiſi ce nombre de 12. que nul autre, c’a eſté pour garder la proportion de ceſte longueur de la lame au bras de la perſonne: qui eſt de deux coudees, & l’eſpee de trois, auſſi a il eſté dit & demonſtré cy deſſus, que la lame eſt egale à la moitié du Diametre, & le bras n’en eſt egal, qu’à un tiers, de ſorte que le Diametre eſtant 24. le bras ſera 8. & la lame par conſequent 12. |
| Those who divide the blade into two equal parts, known as strong and weak, with the weak starting from the tip to the middle and the strong from the middle to the hilt, have made note of some difference between the partitions, but not enough. | Ceux qui l’ont partie en deux moitiez egales, aſſavoir au fort & au foible: commençant le foible depuis la pointe juſques au milieu, & le fort de là en avant juſques à la garde, y ont bien remarqué quelque difference de parties; mais inſuffiſament. |
| There are others who have divided the blade into three equal parts, with a middle section between the strong and the weak parts, because they have noticed that the middle section is sometimes used as a strong part, sometimes as a weak part. | Il y en a eu d’autres qui l’ont diſtinguée en trois parties egales, mettant entre le fort & le foible le mediocre: par ce qu’ils remarquoyent que le milieu de l’eſpee participe de l’un & de l’autre, & qu’on s’en ſert tantoſt comme dufort, & autresfois comme du foible. |
| Others, following the same logic, distinguish four parts: the strong, the semi-strong, the semi-weak, and the weak. But all without showing in their Style any evidence of use, or of noteworthy advantages or disadvantages of these differences. | D’autres ſuivants la meſme trace, ſont venus un peu plus avant, & l’ont diſtinguée en quatre parties, leſquelles ils ont nommées le fort, le demi-fort, demi-foible, & foible. Mais le tout ſans en monſtrer en toute leur Pratique aucun evident uſage, ou difference remarquable d’avantage, ou de deſavantage. |
| All these divisions of the blade into 2, 3, or 4 parts are insufficient, principally because when we consider two swords working at the same time, one against the other, it is impossible to distinguish with certainty which is the strong or the weak when divided into only 2, 3 or 4 parts. So suppose we distinguish the blades into 3 parts, and that we wish to press the medium against the weak part. It is impossible to do this with assurance: the measure of the weak goes from the tip to number 4, and the medium goes from 4 to 8, so that pitting the medium against the weak can mean the 7th Span against the first or the 4th against the 3rd. These two cases are so completely different in nature, that it is absolutely impossible to produce the same effects or demonstrate the same techniques. Thus it follows that if one does not divide the blade into enough parts, one cannot guarantee with certainty the same techniques, and therefore, we need to use a larger number. The most convenient is 12, which is proportional to the arm, as well as similar to the 12 parts of the Roman Pound, the Latin names of which are inscribed on the blade on the right hand bottom. | Toutes ces diviſions de 2. 3. ou 4. parties ſur la lame, ſont inſuffiſantes: & principalement à cauſe qu’il faut icy conſiderer deux eſpees, qui travaillent à meſme temps enſemble, l’une contre l’autre: dont is ſeroit impoſſible d’en aſſigner aucune certaine diſtinćtion, du fort ne du foible, pour la grande meſure de chaſcune de ces 2. 3. ou 4. parties, en quoy la lame ſeroit diviſée. Car poſé que qu’elles fuſſent diſtinguées en trois parties, & qu’il fuſt queſtion de les accoupler, le mediocre avec le foible, je dis, qu’il ſeroit impoſſible de le pratiquer avec aſſurance: eſtant la meſure du foible, depuis la pointe juſques à 4. & du mediocre depuis le 4. juſques au N.8. en ſorte qu’on ne ſe pourroit reſoudre d’accouppler le Nombre 1. au N.7. de la lame contraire; ou le Nombre 3. avec le 4. car en l’un & en l’autre il ſe trouve le foible avec le mediocre. Etants toutesfois lesdits accouplements & aſſemblages des eſpees di ſi differente nature & condition, qu’il eſt abſolument impoſſible d’en tirer les meſmes effets, ne d’y faire paroiſtre les meſmes demonſtrations. Dont s’enſuit que quand on ne met aſſez de parties ſur la lame, qu’on en oſte auſſi par meſme voye toute la certitude des demonſtrations: & par tant, qu’il eſt neceſſaire d’en venir à un plus grand Nombre. Dont le plus convenable c’eſt celuy de 12. qui retient la proportion du bras avec l’eſpee, outre la ſimilitude des 12. parties de la livre Romaine, dont les noms Latins en ſont eſcrits au bas de ce Tableau ſur la lame, qui eſt à main droite. |
| The names are as follows: 1. Vecia, one ounce. 2. Sextans, the 6th part of a pound, or two ounces. 3. Quadrans, the quarter-pound. 4. Triens, the third, or four ounces. 5. Quincunx, five ounces. 6. Semis, the half-pound. 7. Spetunx, seven ounces. 8. Bes, two thirds, or eight ounces. 9. Dodrans, three-quarters, or nine ounces. 10. Dextans, ten ounces. 11. Deunx, eleven ounces. 12. As, the whole, either the pound or the sum. It was not only their custom to divide up pounds this way, but also from then to now entire inheritances, which is still done today amongst Jurists, to express through these names, the value of each of the parts. | Les noms en ſont tels qu’il s’enſuit. 1. Vecia, une once. 2. Sextans, la ſixieme partie de la livre, ce ſont deux onces. 3. Quadrans, le quart. 4. Triens, le tiers, qui ſont quatre onces. 5. Quincunx, cinq onces. 6. Semis, la demie livre. 7. Septunx, Sept onces. 8. Bes, deux tiers, ce ſont huit onces. 9. Dodrans, trois quarts, ce ſont neuf onces. 10. Dextans, dix onces. 11. Deunx, onze onces. 12. As, l’entier ſoit livre ou ſomme. Car ils n’avoyent pas ſeulement couſtume de diviſer ainſi les livres, mais auſſi à l’advenant d’icelles les ſommes entieres des heritages, ce qui ſe pratique encor aujourdhuy entre les Iuriſtes, pour exprimer par l’appropritation de ces dits noms, la valeur ce chaſcune des parties. |
| We could do the same, using these same or similar names for the 12 degrees of strength. But the best and most sensible way would be to simply use the use the numbers, by which the length of the blade is divided into 12 equal parts; which also reflects the relative strength of each, for, as explained above, as the parts by degree get closer to the hand, which controls the entire sword, they become stronger, and conversely, as they move away, become weaker. But be that as it may, it is of little import to us: for use does not require exact knowledge of the relative force, but we only to know which is greater and which is lesser, in order to act against the incoming blade, whether it is necessary to increase, to hold, or lessen the force, to overcome, or to cede to the counter-force. | Nous en pourrions auſſi faire le ſemblable, en nous ſervant de ces meſmes ou de ſemblables appellations, pour exprimer les 12. degrez de force. Mais le meilleur & le plus intelligible ſera de nous tenir ſimplement aux chifres, par leſquels ceſte lame eſt diſtinguée en 12. parties egales de longueur; n’empeſchant toutesfois rien, qu’elles ne ſoyent aucunement diſſemblables en puiſſance: car ainſi qu’il a eſté declaré cy deſſus, autant que les degrez s’approchent de la main, qui gouverne toute l’eſpee, d’autant ſeront elles trouvée plus fortes; & au contraire plus debiles. Mais quoy qu’il en ſoit, celà ne nous importe guere: d’autant que l’uſage ne requiert pas d’en ſçavoir ſi exaćtement la proportion, ains ſeulement de cognoiſtre le plus & le moins, pour ſe conduire à l’advenant, ſoit qu’il ſoit neceſſaire d’accroiſtre, ou de moderer, ou d’amoindrir ſa force, ou de ſurmonter, ou de ceder à la force contraire. |
| These are, in effect, the two goals, to which we aspire, and which can be found by means of these same numbers. The most important thing to know is precisely the amount of one’s own force, or of the opponent, as is necessary in practice, and next how to moderate, to increase, to diminish, this force as needed under different conditions, and as the occasion demands. | Et ce ſont en effećt lex deux intentions, qu’on devra pretendre, & les pourra on obtenir par le moyen de ces dits nombres. C’eſt aſſavoir premierement de congoiſtre preciſement la quantité de ſa propre force, ou de la contraire, tant qu’il eſt neceſſaire en la Pratique: & pour le ſecond de moderer, augmenter, & diminuer ſa dite force ſelon l’exigence de la diverſité, que les occaſions demandent. |
| The first point is very easy: because numbers that are equal in quantity are also equal in force. The difference in force is shown by inequality of the numbers. As 5 is 1 degree stronger than 4, & 6 is stronger by 2 degrees, and so on for the rest. | Le permier uſage en eſt fort facile: car les nombres egaux en quantité ſont auſſi egaux en force: la difference de force ſe demonſtrant par l’inegalité des nombres. Car 5 eſt 1 degré plus fort que 4, & 6 en eſt plus fort de 2. & ainſi du reſte à l’advenant. |
| The second point is easy to understand from the first one. Say my intent is to increase my force, I must assess and increase my own numbers. For example: if the blades are crossed 6 against 6, and I wish to increase my force, I change the point of contact so that the 7, 8, or 9 of my blade crosses with the 6 of the other sword; and by this means, I shall have increased my force 1, 2, or 3, or as many degress as I wish. If the intent is to diminish my force, the sword must be withdrawn towards the tip, so the point of contact moves to smaller numbers. This is what we call decreasing. Sometimes, one increases one’s own blade with the decrease of the opponent’s. For example, say two blades are in contact in the exact middle, which is in Span 6, and say that I move the point of contact so that mine becomes number 8, and my adversary to number 4; then that would mean an increase in my blade with a decrease on the opposing blade. Or, say, initial contact begins with unequal numbers, for example number 5 against number 8 and I change the point of contact by sliding the blades so that I bring my 8 or 9 against his 4 or 5: so that from three numbers weaker, I have moved to four numbers stronger. Contrarywise, one may decreases one’s own blade with an increase of the opposing blade, diminishing one’s own strength, and increasing that of the other party. Likewise, the increase of both swords happens at the same time, and likewise again, a double decrease. | Le ſecond point ſera facile à comprendre par le premier. Car s’il eſt queſtion d’augmenter ſa force, il faut graduer & augmenter ſes nombres. par example: si les lames ſont aſſemblées 6. contre 6. & que je veuille augmenter ma force, je les reculeray en telle ſorte, que le 7. 8. ou 9. de la mienne, ſe viennet accoupler avec le 6. de l’eſpee contraire; & par ce moyen j’auray augmenté ma force, de 1, 2, ou 3, ou autant de degrez, que je voudray. S’il eſt question de la diminuer, il la faudra reculer devers la pointe, qui en eſt le foible, en ſorte que l’aſſemblement en vienne à moins de nombres. C’eſt que nous appellons deſgraduer. Aucunefois on fera la graduation de ſa propre lame avec degraduation de la lame contraire: par example. Soyent accouplées les deux lames chaſcune au juſte milieu, qui eſt au Nombre 6. & que je tranſmue tellement le point de l’attouchement, que la mienne vienne au nombre 8. & celle de ma partie adverſe au nombre 4; alors ſera faite la graduation avec la degraduation de la partie contraire. Ou que l’accouplement ſoit premierement de nombres inegaux, par example, du nombre 5. contre le nombre 8. & qu’on change tellement le point d’attouchement par la raclure des eſpees, qu’on en mene le 8. ou 9. contre le 4. ou 5. de la partie adverſe: en ſorte que de trois nombres plus foible, on vienne à ſe rendre de quatre nombres plus fort. Il adviendra auſſi au contraire, qu’on fera la deſgraduation de ſa propre lame, avec graduation de la lame contraire, diminuant ſes propres forces, & augmentant celles de ſa partie. Aucunefois on en fera la graduation de toutes les deux eſpees enſemble: & aucunesfois derechef double degraduation. |
| The same things may be done with blades when they are not divided into 12 parts, but this will be ragged, and without any certainty of results; likewise when showing a proof, or wishing closer examination of some interesting aspect that comes about from a particular crossing of swords, it would be impossible to make any display of the contact, or to recreate a situation, which is, of course, absolutely necessary each and every time one wishes to examine any operation, without exception, whatever it may be. | Les meſmes effećts ſe pourroyent auſſi pratiquer avec des lames qui ne fuſſent pas diſtinguée en ces 12. nombres: mais ce ſeroit comme à taſtons, ſans aucune certitude: auſſi quand il ſeroit queſtion d’en faire les preuves, ou d’examiner quelque beau trait, qui ſe ſeroit preſenté à l’occaſion de l’accouplement des eſpees, il ſeroit impoſſible, de faire aucune demonſtration de l’attouchement, ou de la ſituation; ce qui eſt toutesfois neceſſaire toutes & quantesfois qu’il ſe preſente à examiner aucune operation, ſans nulle exception, qui puiſſe eſtre. |
| If one can imagine, that it is absolutely necessary to know exactly the proportions of all unequal forces, to make use of all their advantages, but that adroitness, which it gives us, is not enough to fully comprehend all the differences. If two blades are crossed, for example 2 against 4 or 10 against 8, the difference between the stronger and weaker numbers in each case is the equal to 2. But the relative values are not the same when we come to compare these two different cases to each other, they will be proportionally significantly different, because 4 is the double of 2, but 8 is only one third more than 6. In this way the relative proportions of force are unequal, even when the numeric differences are equal. Because the proportional difference between these numbers, when we compare two numbers to two other numbers, will always lessen as they approach the hilt, as the lesser of the two numbers becomes greater; so the proportion of the difference between 2 & 3 is found to be greater than the proportional difference between 3 & 4 or between 4 & 5 and so on, the differences becoming ever smaller, as the numbers become larger. It might seem to some that we should simply make a list of the relative differences, by point of contact along the sword, and so one could quickly see and work with the proportional increase or decrease of forces, for each point of graduation along the blades. | Si quelqu’un s’imagine, qu’il ſoit abſoluement neceſſaire de cognoiſtre exaćtement les proportions de toutes les forces inegales, pour ſe ſervir à touts propos de leurs avantages; & que l’adreſſe, que nous en baillons, n’eſt pas ſuffiſante pour en comprendre à plein toutes les differences. Car ſi les deux lames ſont accouplées, par example 2. contre 4. ou 10. contre 8. la difference in ſera egalement de deux nombres plus fort ou plus foible, auſſi bien en l’un qu’en l’autre de ces deux accomplements: mais quand ce viendroit à comparer ces deux differences l’une à l’autre au regard des nombres, qui ſont diſſemblables, la proportion en ſeroit grandement differente: à cauſe que 4. eſt le double de 2. & 8. n’eſt qu’une troiſieme partie plus que 6. de maniere que les proportions de force ſont ſouventesfois inegales, nonobſtant que les nombres de leur difference ſoyent egaux. Car les proportions des differences des nombres, qui ſont mis en compariſon deux & deux contre deux & deux autres, vont touſiours en amoindriſſant à l’advenant, que le moindre de cesdites deux Nombres à comparer enſemble s’augmente; ſi que la proportion de la difference, qui eſt entre 2. & 3. eſt trouvée plus grande, que celle qui eſt entre 3. & 4. ou entre 4. & 5. & ainſi conſequemment; eſtant touſiours les differences plus petites, à meſure que les nombres s’aggrandiſſent. Dont il ſemblera par adventure à un tel, que nous devions expliquer l’inegalité de toutes ces differences par le menu, & aſſigner à chaſcun accouplement d’eſpees ſa proportion, afin qu’on peuſt ſçavoir par ce moyen, combien c’eſt qu’on augmente ou diminue la proportion de ſes forces, avec chaſcune ſorte de graduations, petites ou grandes, telles, qu’elles pourront eſtre, & ſur tels endroits des lames, où on les voudra mettre en oeuvre. |
| To the above, I would respond, that it is true, the proportional differences change, increasing or decreasing inversely with numerical values of the point of contact. Consequently, as the numbers, against which we measure the graduation, become larger, one must make larger increases towards the hilt to make any gains. And yet, as these numbers become larger, we have less ability to increase them. Nevertheless, it is enough to have a general awareness, without needing a close examination of the details. Technically, the force between the two swords can always be considered equal, since both swords have12 partitions. If two blades come together unequally, for example, one blade contacts at number 7 and the other at number 4, they will behave differently against each other, one with more, the other with less force; but alternatively, the sword at number 4 can reinforce itself with a graduation of 8 degrees up to 12, whereas the sword at number 7 can increase to 12 by only 5 degrees, because the number of partitions of the swords are equal. Because such a large change can happen in a moment, & this is even expected, it is enough to know the difference in forces from the number of degrees, which can easily determine if the difference is large, medium, or small. Because 1 degree is a little stronger, 2 degrees is evidently more, and 3 degrees is much more. Those are all the distinctions we need, since seeking to know exactly all the relative proprotions of each and every possible crossing of swords that can be imagined is not only impossible to observe at speed in our training, but it would also be useless. | Là deſſus je luy reſpondray, que c’eſt la verité, que les proportions des differences ſe changent, en augmentant & en diminuant au rebours de l’accroiſſement de leurs nombres: & par conſequent, d’autant que les nombres, contre leſquels on fera la graduation, ſeront plus grands, auſſi faudra il faire à l’advenant la dite graduation plus grande pour gaigner quelque choſe: & au rebours, d’autant que les nombres, avec leſquels la graduation ſera faite, ſeront plus grands, d’autant en pourra eſtre la graduation plus petite. Et cependant il ſuffit d’avoir de cecy une cognoiſſance generale, ſans qu’il ſoit beſoin d’en examiner les particularitiez. Car s’il faut parler proprement, la force des deux eſpees eſt touſiours egale. Car elles ſont toutes deux comme 12. S’il advient qu’elles ſoyent accouplées inegalement; par exemple, le nombre 7. de l’une au nombre 4. de l’autre, il eſt bien vray qu’elles ſont alors diverſement gouvernées, l’une avec plus, & l’autre avec moins de puiſſance; mais en eſchange il faut conſiderer, que l’eſpee de 4. ſe peut renforcer en un inſtant juſqu’à 12, augmentant ſa force par la graduation de 8. degrez entiers; là ou l’eſpee de 7 ne ſe peut renforcer, que juſqu’à 12. pareillement, qui ne font que 5 degrez, à cauſe que les nōbres des eſpees ſont egaux. Puis qu’il peut donc advenir un ſi grand changement en un moment de temps, & meſmes qu’on le doit comme pour certain attendre, qu’il nous ſuffiſe de ſçavoir la difference des forces par le nombre des degrez: leſquels nous peuvent aſſez declarer ſi la difference en eſt grande, petite, ou moyenne. Car 1. degré, c’eſt un peu plus fort: 2. degrez, c’eſt evidement plus: 3. degrez, c’eſt beaucoup plus. Voilà les diſtinćtions, qui nous doivent ſuffire. Car de vouloir ſçavoir exaćtement toutes les proportions de tant & tant aſſemblages d’eſpees, qu’on pourroit imaginer, ne ſeroit pas ſeulement impoſſibe à obſerver en des occaſions ſi viſtes, comme ſont celles de ceſtuy noſtre Exercie, mais il ſeroit auſſi inutile. |
| Finally, all we have said up to now about the gradation of the sword, must be understood simply with regard to these twelve numbers, by which one adjusts one’s own force and likewise counters the opposing force, notwithstanding that there are still other aspects to consider, each of which shall be discussed, in its proper place. | Au reſte tout ce qui eſt dit juſqu’à preſent touchant la graduation & deſgraduation des eſpees, pour moderer par icelles ſa propre force, & pareillement la force contraire; ſe doit entendre ſimplement au regard de ces douze nombres, ce qui n’empeſche toutesfois qu’il n’y ait encor pluſieurs autres manieres de renforcements: deſquels il ſera traité, de chaſcune en ſon propre lieu. |
| HOW TO HOLD
the sword in the hand to practice the drills |
LA MANIERE DE TENIR
l’espee av poing, povr pratiqver nos receptes. |
| The last point illustrated on this Plate concerning the sword is the manner of holding it, which is quite different from other methods. As is shown, on the two numbered swords at the bottom, place the index finger over the exterior branch of the crosspiece, and wrap it around the end of the blade, and the thumb either over, or around, the crossguard likewise inside the guard, with the rest of the fingers wrapped around the handle, so it lies in the hollow of the palm, with the crosspiece held horizontally. | Le dernier point qui eſt repreſenté en ceſt Table touchant l’eſpee, c’eſt la maniere de la tenir au poing, grandement differente de l’ordinaire des autres. Car ainſi qu’il eſt exprimé icy bas en ces deux eſpees nombrées, nous mettons le doigt indice dans la garde par deſſus la branche exterieure, & alentour du talon de la lame, & le pouce à l’autre coſté, ſur la branche interieure, ou alencontre, par dedans la garde pareillement, avec le reſte des doigts bien eſtoitement ſerrez alentour de la poignee, en ſorte que le pommeau ſoit affermi dedans le creux du poignet, & les branches horizontales, l’une à coſté de l’autre. |
| It is absolutely necessary for all those who would learn anything of our Style, to hold the sword in this way, and not in any other; this grip is the only sure way to perform most of the operations, and is the foundation of the best sword-work for the thrust, either to aim, or to defend. This confidence is principally founded on the proper angle of the crosspiece, and on the force of the blade, held in this said manner. This shall be discussed further elsewhere, where the comparison of this grip to others, shall evince the superiority, through the coming together of the effects and advantages of this grip compared to all others. | Il eſt abſoluement neceſſaire à touts ceux qui voudront faire aucune recerche de noſtre Pratique, de faire l’empoignement de l’eſpee en ceſte ſeule maniere, & non pas en quelque autre ſorte, que ce ſoit: d’autant que de ceſte ſeule depend la certitude d’une bonne partie de toutes les operations, & y ſont fondez les plus nobles exploits des eſtocades, à tirer, ou à defendre; dequoy l’aſſeurance eſt principalement fondeée ſur la ſituation de la croix, & ſur la force de la lame, tenue en ceſte maniere dernierement dite. dont il ſera diſcouru autrepart; où nous mettrons en comparaiſon, & en ferons paroiſtre l’excellence, par la conference des effećts & des avantages de ceſte cy au regard de toutes les autres. |
| The practical point of this discussion on the concurrence of the Circle, the Sword, and the Human Body has been to show how easy it is for everyone to have a sword of the proper size.
But there is a concern about the permanently-inscribed Circle, wherein one must oftentimes test between people of unequal stature, for which each should have his own properly-sized Circle, or between people of equal size, but who are both either larger or smaller than the Diameter, such that the Circle is not drawn proportionally to their bodies. To minimize this inconvenience, the permanent Circle should be drawn to the proportions of an average person, to accomodate everyone. Those who are larger can make the ranges of their Instances a bit larger. Such as the first, outside the Circumference, a bit inside the Quadrangle. The second, near the middle of the Inside Square, a bit outside, on the oblique Diameter. And the third, likewise, a bit outside the Circumference, on the extended Perpendicular Diameter. Those smaller can shorten all the distances of their Instances against the opponent; and take the first, in contrast to those larger, a bit inside the Circumference along the Diameter. The second on the Oblique Diameter, a bit inside. And the third, again on the Perpendicular Diameter inside the Circumference. That is how the Circle can be of use to all sorts of people, without ever changing it. Thus I am quite certain this explanation is sufficient proof of the usefulness of both these two lengths, of the Sword, which, as I say, is the instrument used for every action, and of the Circle, which is the terrain, containing the correct and proportional distances for the actions, so they may be exploited confidently. It is true, that we have been somewhat particular in the research of some parts of this treatise, such as the deduction of the range of the Instances, the graduations, of the proportions of the body, and several other similar things, which we have calculated exactly; nevertheless, those who have no knowledge of mathematics should not be discouraged. Because what we have done was more for the contentment of those who would make a close study of our Theory, than it is something necessary for our Training. Other than that, we have tried to put everything in good order, so that each can easily distinguish between those things necessary for Practice, from those which are only for Theorists, as long as they read our writings attentively. |
Pour venir à la Pratique de tout ce qui a eſté diſcouru, touchant la convenance du Cercle, & de l’Eſpee, avec le Corps de l’Homme; il eſt aiſé à un chaſcun d’avoir une Eſpee de ſa juſte meſure.
Mais pour le Cercle, qu’on deſcrit une fois pour toutes, où il faut ſouventesfois faire des preuves avec perſonnes inegales de ſtature, aux quels il faudroit à chaſcun ſon propre Cercle; ou bien avec perſonnes egales, mais plus grandes, ou plus petites, que la ligne du Diametre, en ſorte que le Cercle ne ſeroit pas compaſſé à la proportion de leurs corps. Pour obvier à ces inconvenients, il le faut tirer ſur la meſure d’une perſonne moyenne, afin qu’il ſoit capable d’eſtre accommodé à toutes. Car les plus grands y pourront prendre les meſures de leurs Inſtances un peu largement. Comme, la permiere, dehors la Circonference un peu au dedans du Quadrangle. La ſeconde, pres le milieu du coſté du Quarré inſcrit, un peu au dehors, ſurle Diametre oblic. Et la troiſieme ſemblablement un peu au dehors de la Circonference, ſur le Diametre perpendiculaire prolongé. Les plus petits y raccourciront auſſi les meſures de leurs Inſtances à l’advenant; & en prendront la premiere au contraire des grands, un peu dedans la Circonference ſur le Diametre. La ſeconde ſur le Diametre oblic, un peu en dedans. Et la troiſieme derechef ſur le Diametre perpendiculaire au dedans de la Circonference. Voilà comment ce Cercle pourra ſervir à toutes ſortes de perſonnes, ſans qu’il le faille jamais changer. Or je m’aſſeure que ceſte explication ſera pour le commencement une preuve ſuffiſante de a grande utilité de l’une & de l’autre de ces deux meſures, de l’Eſpee di-je, qui eſt ‘inſtrumēt de toutes les operations, & du Cercle, qui eſt la deſcription du Terrain, contenant les vrayes & proportionnelles diſtances, correſpondantes aux operations, pour les exploiter avec aſſeurance. Il eſt vray, que nous avons eſté quelque peu curieux en la recerche de quelques parties de ce traitté, comme en la dedućtion de la meſure des Inſtances, des graduations, & de a proportion du corps, & en quelques autres choſes ſemblables, que nous avons calculées aſſex exaćtement: toutesfois il ne faut pas que ceux, qui n’ont point de cognoiſſance des Mathematiques, en perdent pourtant courage. Car ce que nous en avons fait, c’a eſté plustoſt pour le contentement de ceux qui voudront examiner de pres noſtre Theorie, que pour ce que la choſe fuſt d’elle meſme neceſſaire en l’Exercice. Outre ce que nous avons taſché de mettre le tout ſi bien par ordre, que chaſcun y pourra aiſement diſtinguer les choſes neceſſaires à la Pratique, d’avec celles qui ne ſont que pour les Theoriſtes, moyennant qu’il liſe noſtre eſcrit avec attention. |
| Translation by Bruce G. Hearns |
Transcription by Bruce G. Hearns |
|---|---|
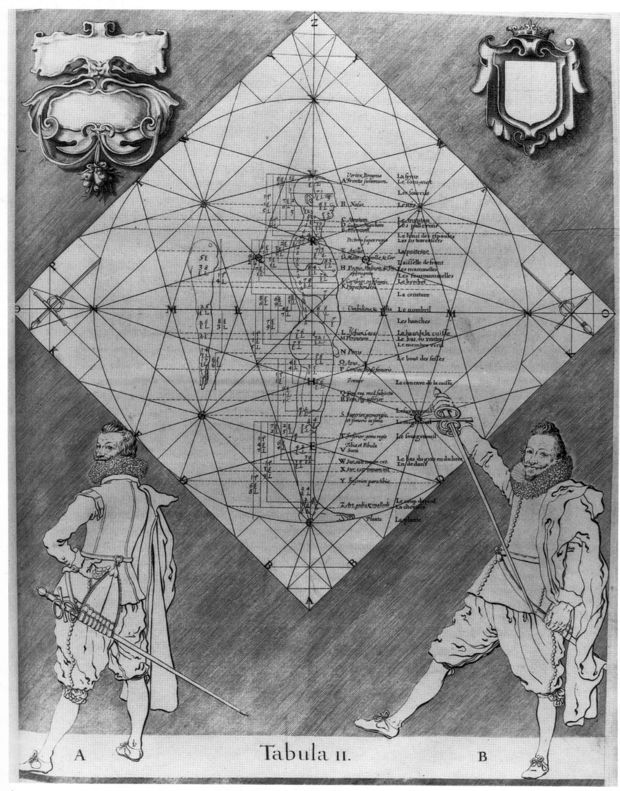
| |
| EXPLANATION OF THE SECOND PLATE | DECLARATION DV TABLEAV DEUXIEME |
| A COMPARISON OF THE PROPORTIONS OF THE HUMAN BODY drawn by m. Albrecht dürer, in his second book of proportions, folio 60, with the proportions from the Circle, and an explanation of the proper size of the sword-strap and sword-hanger. | CONFRONTANT LES PROPORTIONS DV CORPS DE
l’homme tirees de nostre cercle a celles de m. albert dvrer en son livre devxieme de proportions, fveille 60, et déclarant les ivstes mesvres dv centvron et dv pendant de l’espee. |
| All knowlegeable people admit that it would be highly desireable, for the skillful practice of arms, if there were a defined and fixed Range, according to which one can adjust distances exactly against all opponents, and, as it happens, all movements, large and small, swift and slow. And, as this involves movements of the human body using the sword, it is obvious that the proportions of the human body should be the most appropriate measure to use and that these measurements should apply to the sword as well as to the training area. This would be the only means by which one could produce a reliable and accurate method to assess distances, which has up until now been unknown, or at the very least, has never been evident in any demonstration. | Toutes perſonnes de iugement confeſſent, qu’il ſeroit fort à deſiderer pour l’adreſſe de l’Exercise des Armes, qu’il y euſt une certaine & inviolable Meſure, ſelon laquelle on peuſt regler exaćtement toutes les Diſtances, & à l’advenant auſſi touts les mouvements, grands & petits, tardiſs & viſtes. Et puis qu’il eſt icy queſtion des mouvements qui ſe ſont à l’aide de l’Eſpee, & avec les membres du corps; que le plus apparent ſeroit de la trouver par les proportions de l’Homme meſme; & eſtant trouvée, le plus expedient de l’appliquer ſur l’Eſpee, & ſur le plan du Terrain, où l’on pretend de faire l’Exercice. Ce ſeroit le ſeul moyen, par lequel on pourroit parvenir à former un jugement ſolide touchant les vrayes proportions des diſtances, qui ont eſté juſqu’à maintenant du tout incognues, ou à tout le moins, il n’en a eſté jamais faite aucune demonſtration evidente. |
| And therein one can see the great use of our Circle, which shows so clearly and perfectly, with confident skill, how to take advantage of the above usage and style of swordplay. Just like the advantage that a well-disciplined army on campaign, encamped in good order with organization has over the confused multitude of a barbarian horde. For just as it is important for a commander in the field, about to lay siege, to reconnoiter the ground for routes, heights, marshes, and, in sum, the entire situation about him, it is important in our Traning for us to know the delineations of the Circle, which is like a map of all the steps we can take or positions we can adopt, according to how the situation varies. | Et par là ſe voit la grande utilité de noſtre Cercle, qui la repreſente ſi claire & ſi parfaite, avec une adreſſe de l’aſſeurance à prendre ſi avantageuſement par le deſſus le precedent uſage & ſtile des Armes, comme la bonne ordonnance d’une armee logée en campagne diſtinćtement à loiſir & à ſouhait, par deſſus la confuſion d’une multitude de Barbares. Car autant qu’il importe à un Condućteur d’armee, pour mettre le ſiege devant quelque place, d’en cognoiſtre les plus ſeures approches, les paſſages, les prochaines hauteurs, les eaux, & en ſomme toute la ſituation d’alentour: autant nous importe en noſtre Exercice la delineation de ce Cercle, qui eſt comme une carte de toutes les demarches, à faire & à changer ſelon la varieté des occaſions. |
| This gives me hope and a belief that this invention will be praised by all those have a heart free from this ignominious desire to simply criticize the works of others without themselves offering anything better. For they can recognize that this Circle is proportional to human limbs, consequently as well to all movements which might be by one of the two adversaries, and that the proof of ranges and distances, which no one has adequately explained until now, depends on this same concurrance. | Ce qui me fait eſperer & croire, que l’invention en ſera louée de touts ceux qui ont le coeur libre de ceſt infame deſir de calomnier les ouvrages d’autruy, ſans taſcher de mettre eux meſmes en avant choſes meilleures. Car ils pourront recognoiſtre, qu’elle eſt proportionnée à touts les membres, & conſequemment auſſi à touts les mouvements, qui peuvent eſtre faits tant de l’un que de l’autre des parties adverſes; & que de ceſt meſme convenance depend la demonſration des Meſures & des Diſtances, que perſonne n’a ſceu declarer juſques à preſent. |
| But as great as the concurrance is between the body and the lines of the Circle, as one could see from the portrait of the person in Circle No 1, someone may happen to suspect that this figure was somehow altered to fit the lines to support my desires rather than to expose a truth about nature, which would greatly diminish the value of the Circle and leave it partly useless for our Training. Thererfore, to show that I went about my work honestly, here is the proof in the Second Plate, where I show the same Circle with the portrait taken from The Proportions of Man, written over a hundred years ago, by the great painter and geometrician Albrecht Dürer. I shall apply the Circle to this portrait with all the pertinant lines, so that with the belly-button at the centre, the soles of the feet on the circumference, & the top of the head reaches just to the letter V, exactly as with my own figure. | Mais d’autant que ceſt convenance eſt ſi extremement grande, comme il ſe voit notamment au pourtrait de la perſonne, au Tableau precedent Cercle N.1: par adventure quelquun en prendra occaſion de ſoupçonner, que nous avons accommodé ladite figure pluſtoſt ſelon noſtre fantaſie, pour en tirer les proportions deſirées, que d’enſuivre ſimplement la verité naturelle: ce qui amoindriroit de beaucoup la dignité du Cercle, & le rendroit en partie inutile pour l’Exercice. Pour donc faire paroiſtre, que nous y ſommes allez rondement, en voicy la preuve en ce Tableau Deuxieme, où nous appliquons le meſme Cercle au pourtrait d’un perſonnage tiré du livre de Proportions de l’Homme, eſcrit il y a plus de cent ans par ce grand Peintre & Geometricien Albert Durer: appliquant ſur ledit perſonnage noſtre Cercle avec toutes les lignes y appartenantes; en ſorte que le nombril ſoit prins pour le Centre, la plante des pieds ſe repoſe ſur la Circonference, & le ſommet de la teſte atteigne juſtement à la derniere entrecoupure du Diametre à la lettre V. tout de meſme qu’il en a eſté fait en noſtre figure. |
| So I have chosen to show this using the portrait of an overall well-proportioned man which is presented in the aforesaid book of Proportions, Book 2, Folio 60. This figure displays all the measurements that this great Master made through his mathematical calculations and through his long observations as a painter. These measurments accord almost perfectly and effortlessly with the lines drawn between opposite angles across the diameter of the Circle. | Or avons nous choiſi pour ceſt effećt le pourtrait d’un homme parcreu & bien proportionné en touts ſes membres, tel que l’ordonnance en eſt faite audit livre des Proportions, Liv. 2. feuillet 60. En laquelle figure il paroiſtra, que toutes les meſures que ce grand Maiſtre a ſceu remarquer par ſes calculations Mathematiques, & par ſes longues obſervations en l’art de Peinture, ſe diſcouvrent icy quaſi toutes ſans artifice & plus parfaitement, par les aſſignations de nos lignes tirées perpendiculairement à travers le Diametre aux angles oppoſez, des uns aux autres. |
| To perform the comparison, because a large number of lines must be compared, and so that they do not create confusion, and to check the various assignations between the two parts, they are shown differently: dotted lines from the Diameter to the angles, solid lines to show Dürer’s proportions drawn from behind the person to the front of the body. Thus those which are in common will be partially dotted solid and partially dotted extending beyond Dürer’s parallelograms. | Pour venir doncques à la confrontation, puis qu’il faudra compater icy un grand nombre de lignes, afin qu’elles n’engedrent confuſion, pour examiner la verité de aſſignations de part & d’autre, nous les repreſentons en differentes manieres. Les noſtres ſont poinćtées, allant par le Diametre juſqu’aux angles oppoſez: le ſiennes ſolides, tirées par le derriere de la perſonne juſqu’au devant du corps. Dont celles qu’il a communes & accordantes avec les noſtres, ſont en partie ſolides, & en partie poinćtées, aſſavoir au dehors de ſes parallelogrammes. |
| The figure has, therefore, been arranged like this, and when one considers the degree of overlap between the lines from the Circle and that of such a Great Master of proportions, we can see the proof on a well-proportioned body. I believe that everyone can be satisfied with such a proof, rather than a face a great mass of arguments, which would serve to obscure the matter and give rise to more doubts rather than settle any existing ones. | La figure eſtant ainſi dreſſée, & conſideré le grand accord, qui ſe trouve entre noſtre invention & celle d’un ſi grand Maiſtre des proportions, de quoy on voit la preuve ſur un corps qui eſt des mieux proportionnez; j’eſtime que chaſcun ſe contentera plus d’une telle demonſtration, que d’un grand amas d’arguments controuvez, qui ſerviroyent pluſtoſt d’offuſquer la matiere, & tendroyent à engendrer des nouvelles doutes, au lieu de reſoudre les anciennes. |
| To the degree that I may say, we all agree, if I dare be so bold, that where there are differences, the Circle will serve to settle the question and to correct any errors which could not be avoided even by such a great mind, and such an exacting judge of proportions. This should make the Circle more impressive than if all the lines matched exactly. Now here is the proof, reminding you once again, that my lines are drawn from intersection to intersection, as if by chance, and his are artificially ordered, and arranged in five parallelograms. Thus here is the explanation. | Et combien que je ne puiſſe dire, que nous ſommes partout d’accord, ſi oſerayje bien affermer pourtant, où il y a de la difference, que c’eſt noſtre Cercle qui en vuidera la queſtion, & corrigera les fautes, qui n’ont ſceu eſtre evitées par un eſprit ſi noble, & par un jugement des proportions ſi exaćte. Et c’eſt ce qui en doit augmenter l’eſtime, plus que ſi les aſſignations fuſſent trouvées s’accorder toutes enſemble. Maintenant venons a la preuve, vous advertiſſant derechef, que nos lignes ſont tirées ſimplement de l’un angle à l’autre, quaſi à l’adventure, & les ſiennes ſont artificiellement ordonnées, & rangées en cinq figures parallelogrammes. Dont voicy l’explication qui s’enſuit. |
| The first of all his lines corresponds on the last cross-cut line on the Diameter, marked with a capital V, & shows the top of the head. | La premiere de toutes ſes lignes reſpond juſtement ſur noſtre derniere entrecoupure du Diametre, marquée de la lettre V capitale; & demonſtre la ſyme, ou le Vertex de la Perſonne. |
| The second, which matches the second cross-cut line marked B, shows the tip of the nose. | La ſeconde, s’accordant pareillment à la ſeconde des noſtres marquée B, demonſtrant le bout du nez. |
| The third is not found amongst the lines of the Circle, and shows the eyebrows. | La troſieme des ſiennes ne ſe trouve point parymy les noſtres, & demonſre le ſourcils. |
| The fourth matches my line B, which shows the tip of the nose. | La quatrieme s’accorde à la noſtre marquée B, demonſtrant le bout du nez. |
| The fifth, matching my line C, shows the chin. | La cinquieme, revenant juſtement ſur la noſtre de C, demonſtre le menton. |
| The sixth, matching my line D, shows the top of the trapezoid muscles. | La ſixieme demonſtre le pallerons; auſſi fait ſemblablement la noſtre marqée de la lettre D; & reviennent en une. |
| The next line is only on the circle, marked E, which marks the shoulders. | Il s’en enſuit apres une des noſtres particuleres, marquée de la lettre E, qui vient juſtement ſur le haut des eſpaules. |
| Again, by contrast, a bit further down, are one of his lines, which shows the same. This difference shall be discussed shortly. | Derechef, en eſchange un peu plus bas, il s’en enſuit une des ſiennes, pour demonſtrer le meſme; de laquelle difference il ſera parlé tantoſt. |
| Next comes the second parallelogram, of which the first line, which matches exactly with our third cross-cut of the Diameter, marked R, shows the the collar bones, or, as we described it, the top of the chest. | S’enſuit apres le ſecond parallelogramme: dont la premiere ligne, s’accordant juſtement avec noſtre troiſieme entrecoupure du Diametre, marquée d’R, demonſtre les os traverſiers; ou bien ſelon noſtre deſcription, le plus haut de la poitrine. |
| The second, matching my line F, shows the chest, and, particularly, according to the preceeding Plate, the armpits. | La ſeconde, accordant avec noſtre F, demonſtre la poitrine, & ſpecialement, ſelon la repreſentation du Tableau precedent, le aiſſelles. |
| The next line is only on the circle, marked G, which shows the breasts. | Il s’en enſuit apres une, qui nous eſt particuliere, marquée de G, qui demonſtre le mamelles. |
| And in contrast, another line particular to him, shows the armpit, much lower than seen from the front, as I showed in my figure. This follows from the mistake that the Author made placing the shoulders too low, and, consequently, the armpits to far forward. | Et en eſchange une autre particuliere à luy, qui demonſtre l’aixelle, à regarder la perſonne de front, beaucoup plus bas, qu’il n’eſt repreſenté en noſtre figure: procedant l’erreur de ce que l’Autheur a placé le haut des eſpaules plus bas, qui’il ne devoit; & par conſequent auſſi les aixelles à l’advenant. |
| The fourth line on his second parallelogram matches my line H, & shows, following the previous error, the tips of the nipples but is, in fact, in right in the middle and centre of the chest. | La quatrieme ligne on ſon deuxieme parallelogramme revient ſur la noſtre marquée de H, & demonſtre, ſelon l’erreur precedente, les tetins des mammelles, mais en effet c’eſt le beau milieu & comme le centre de la poitrine. |
| Next, again, is one of his, which continues the same mistake, & consequently shows the bottom of the pectorals. | S’enſuit derechef une autre des ſiennes, qui continue la meſme erreur, & demonſtre conſequemment les ſous-mamelles. |
| The sixth matches my line I, and shows the tip of the breastbone. | La ſixieme s’accorde à la noſtre marquée de la lettre I, & demonſtre le brechet. |
| The next line is only on the circle, marked K, which shows the floating ribs. | Apres laquelle y a la noſtre marquée de K, qui demonſtre le hypochondres, ou les fauſſes coſtes. |
| The seventh, & last of this parallelogram, which is also only one of his, shows the waist. | La ſeptieme & derniere de ce meſme parallel, qui luy eſt auſſi propre demonſtre la ceinture de la perſonne. |
| The first line of the third parallelogram, which matches exactly the Centre, shows the navel. | La premiere du Troiſieme ordre, qui vient juſtement ſur le Centre, demonſtre le nombril. |
| The second line of his shows the loins. | la ſeconde, à luy particuliere, demonſtre les hanches. |
| The third matches my line L, which purports to show the top of the thigh, but actually matches exactly the hip, as it is higher than the muscle. | La troiſieme revient à la noſtre, marquée de la lettre L, voulant demonſtrer le haut de la cuiſſe; mais en effet elle reſpond juſtement ſur l’endroit de la jointure, combien que le muſcle en vienne plus haut. |
| The fourth matches my line M, and shows the bottom of the stomach. | La quatrieme s’accorde à la noſtre marquée de M, demonſtrant le bas du ventre. |
| The fifth line of his, shows the virile member. | La cinquieme qui luy eſt propre, demonſtre le membre viril. |
| The next line is only on the circle, marked N, which also shows the virile member. His line is at the top, mine at the bottom. | Comme auſſi fait pareillement la noſtre marquée d’N. Toutesfois, la ſienne le demonſtre par haut, & la noſtre par bas. |
| The sixth line of his mistakenly shows the bottom of the butt-cheeks. I shall say more on this shortly. | Sa ſixieme demonſtre fauſſement le bout des feſſes: dequoy il ſera parlé tout à l’inſtant. |
| After this one, the next line is only on the circle, marked O, which shows the height of the anus. | Apres icelle s’en enſuit une des noſtres particulieres, marquée d’un O, qui demonſtre la hauteur du fondement. |
| And again another, only on the circle, marked P, which shows the concavity, or the top of the thigh muscle. | Puis encore une, ſemblablement à nous particuliere, marquée de P. Qui demonſtre le concave ou le commencement du muſcle de la cuiſſe. |
| And a third one, only on the circle, the next cross-cut along the Diameter, marked H, shows the middle of the thigh. | Et pour le troiſieme s’enſuit la ſeconde Sećtion du Diametre, qui eſt marquée ſur ledit Diametre d’un grand H, demonſtrant le milieu de la cuiſſe. |
| After which follows, a bit lower down, the first line of his forth parallelogram, which is one of his, and shows, in his opinion, the concavity of the thigh. | Apres laquelle s’enſuit un peu plus bas la premiere ligne du quatrieme parallelogramme, qui luy eſt particuliere, & demonſtre ſelon ſon opinion, le concave de la cuiſſe. |
| The next is again one of mine, marked Q, showing the same muscle, which is below the middle. | En vient apres derechef une parmy les noſtres, marquée de Q, demonſtrant l’endroit du meſme muſcle, qui eſt deſſous le milieu. |
| A bit lower still another of mine, marked R, which shows the lower part of the thigh. | Vn peu plus bas encore une autre, marquée R. qui en demonſtre la partie inferieure. |
| A bit below that is the second and last line of his parallelogram showing the muscle just above the kneecap, slightly above where it ought to be. This can be seen from the following line, one of mine, marked S, which shows the true top of the kneecap. This is obvious to the eye, as much on Msr Albert’s drawing as on the one in the Circle No 1 in the First Plate. | Puis apres la ſeconde & derniere de ce meſme parallelogramme, demōſrtant le ſurgenouil, un peu plus haut, qu’il ne devoit eſtre; comme il ſe voit par la ligne ſuivante, c’eſt aſſavoir la noſtre, marquée de la lettre S, qui demonſtre le vray endroit de la partie ſuperieure du genouil; comme il paroiſt à veuë d’œil, tant en ceſte figure de Mre Albert meſme, qu’en la noſtre au premier Cercle du Tableau premier. |
| This is the top of the kneecap is along the line marked S. | Soit donc le ſurgenoil placé à l’endroit de la ligne S. |
| The first line of his last parallelogram does not match one of mine and marks the mid-point of the kneecap. | La premiere ligne de ſon dernier parallelogramme ne ſe trouve pas parmy les noſtres, & demonſtre le my-genouil. |
| His second line, which matches the one on the circle marked T, shows the lower-kneecap. | La ſeconde, qui revient à la noſtre marquée de T, demonſtre conſequemment le ſous-genouil. |
| Next is the cross-cut that marks the first section of the Diameter, marked with a capital Roman letter E, which shows the top of the shin. | S’enſuit apres la premiere ſećtion du Diametre, marquée en grande lettre Romaine d’un E, qui demonſtre le plus haut de la greve. |
| And again one only on the circle, marked V, which shows the thickest outside part of the calf. | Et derechef encor une autre des noſtres, marquée V, qui demonſtre le gras de la jambe en dehors. |
| Right after is the bottom of the calf, shown by the third line of this parallelogramme, which is not found in mine. | Tantoſt apres s’en enſuit le bas, repreſenté par la troiſieme ligne de ce dernier parallelogramme, qui ne ſe trouve pas entre les noſtres. |
| The same is likewise shown on the inside of the leg, a bit lower by his fourth line, which corresponds to the one on the circle marked W. Note that there is a slight difference between the two assignations, but of little importance, since he put his lines on the bottom of the thick part of the leg, on the inside and outside, a bit higher than we did, which we put on lines W & X. | Le meſme eſt pareillement demonſtré au dedans de la jambe un peu plus bas, par la quatrieme, qui s’accorde à la noſtre marquée d’W. Touchant quoy il y a quelque difference entre nos aſſignations, mais de petite importance, en ce que luy il a placé le bas du gras de la jambe, tant en dehors comme en dedans, un peu plus haut que nous, qui l’avons ordonné ſur les lignes W & X. |
| Next is the line marked Y, which is only on the circle, and shows the lower part of the shin. | Apres s’enſuit la ligne Y, qui nous eſt propre, & demonſtre la partie inferieure de la greve. |
| The fifth of his lines shows the top of the foot. | La cinquieme de ſes paralleles demonſtre le coup du pied. |
| And finally the sixth line, which matches the line on the circle marked Z, the bottom of the outside of the ankle. | Et conſequemment la ſixieme, qui revient ſur la noſtre marquée de Z, le bas de la cheville en dehors. |
| Finally, the end of the Diameter , and the last of these parallels, shows the soles of the feet. | Finalement le bout du Diametre, & la derniere de ſes paralleles, demonſtrent les plantes des pieds. |
| That then is the comparison between the two sets of lines and their interpretations, to demonstrate the true proportions of the human body. About this there is only to debate the differences, and to demonstrate through careful reasoning the errors made by Dürer, and to show that the attribution of our Circle are more exact and closer to Reality. | Voilà donc la confrontation de toutes nos lignes, & de leurs interpretations, pour demonſtrer les vrayes proportions du corps de l’homme: touchant leſquelles il ne reſte deſormais qu’à en debatre les differences, & à demonſtrer par bonnes raiſons les fautes commiſes en l’ouvrage du Durer, & que les aſſignations de noſtre Cercle ſont plus juſtes & plus appprochantes de la Verité. |
| I very much did not intend to boast about overturning, or to take away from this leading light of painters in the science of proportions, when he has made such an effort in his studies, and truly merits praise. Because we hold one thing certain, that is, in his aforsaid Book of Proportions, his intention was to show many different types of persons: some beautifully or badly, or more or less proportioned than others. As such it would be very wrong to try and find in each of his figures the most exact and correct proportions, such as the ones presently needed and which can be found by way of our Circle, according to the before described attributions. Which is even more evident when we look at the mistakes he made, this being one of the best-proportioned figures of all the ones in his book, we shall be discussing it as one of the most perfect examples he could show. | Combien que nous ne voulions pas nous vanter de conteroller, ne de reprendre ce grād flambeau des Peintres en la ſcience des proportions, où il a mis tant d’eſtude, & en a merité ſi grande louange. Car nous tenons pour choſe ſeure, qu’en ſondit livre de Proportions, ſon intention a eſté de repreſenter pluſieurs & differentes ſortes de perſonnes; les unes bien ou mal, ou moins ou mieux proportionnées, que les autres: en ſorte que ce ſeroit luy faire un grād tort de recercher en chaſque figure la plus exaćte & correćte proportion, que nous requerons preſentement, & nous perſuadons de l’avoir trouvée par ceſtuy noſtre Cercle, ſelon les aſſignations au paravant declarées. Ce qui ſera encor plus manifeſte par la confrontation des fautes de la ſienne, laquelle eſtant l’une des mieux proportionnées d’entre toutes celles qui ſoyent dedans ſon livre, nous en parlerons comme de l’un des plus parfaits exemplaires, qu’il a ſceu propoſer. |
| Firstly, then, there is a fault in that the neck is far too long, and consequently the height of the shoulders, the underarms, and nipples are all too low. The error in the length of the neck is immediately evident on closer inspection. The distance between the top of the shoulders and the earlobes is the same as or more than the length of the face, which should not be so. | Premierement donc il y a de la faute en ce qu’il en a fait le col de beaucoup trop long, & par conſequent le haut des eſpaules, les aixelles, & les mammelles trop baſſes. Dont la faute touchant la meſure du col eſt toute evidente, en y prenant garde de pres. Car l’eſpace, qui eſt depuis le haut des eſpaules juſqu’au mollet de l’oreille, eſt autant ou plus, que l’entiere longueur de la face: ce qui ne peut nullement conſiſter. |
| Next there is another error, that he has drawn the bottom of the butt-cheeks too high, so that they are hardly proportioned compared to the rest of the body. To correct this fault, it is necessary to have the bottom of the pelvis slightly lower, as shown by line O. From this same fault, several more follow in locating the thigh muscles. | Apres il y en a encore une, en ce qu’il a placé le bout des feſſes trop haut, en ſorte qu’elles ne ſont guere proportionnées en grande à tout le reſte de la perſonne. Pour corriger la faute, il eſt neceſſaire, que l’endroit du fondement ſoit ordonné plus bas, comme il eſt monſtré par la ligne O. Or de ceſte meſme faute il en procede encores quelques autres à l’endroit du muſcle de la cuiſſe. |
| The third error consists of his putting the top of the knee too high. Thus he made the thigh too short, and the leg too long, attibuting to both almost the same length, which is not according to nature. The thigh is longer, so that the top of the knee should be at the level of the line S. Consequently the knee should be lower and the shin shorter. | La troiſieme erreur conſiſte en ce qu’il met la partie ſuperieure du genou trop haute. Dont s’enſuit qu’il fait la cuiſſe trop courte, & la jambe trop longue, attribuant quaſi une meſme longueur à l’une & à l’autre; ce qu eſt contre nature. Car la cuiſſe eſt plus longue; de ſorte que le ſurgenou doit eſtre placé à l’endroit de la ligne S; & par conſequent auſſi le genou plus bas, afin que la greve en ſoit accourcie. |
| As to the rest, if there are any differences or unjustified manipulation concerning the leg, that hardly matters at all. | Au reſte s’il y a quelque difference, ou abus, en ce qui touche le mollet de la jambe, celà n’importe point grand choſe. |
| But much more serious is the fault made in the length of the foot. He made it almost as large as the entire shin-bone. I percieve it should not be longer than the size of the head, as is shown in the preceeding Plate. | Mais bien plus grand eſt la faute commiſe en l’ordonnance de la longueur du pied; le quel il a fait quaſi auſſi grand qu l’os de la greve tout entier; jaçoit qu’il ne deuſt eſtre que la longueur de la teſte. comme il eſt monſtré en la Table precedente. |
| As to the arm, which is shown behind the back of the figure, there is a big mistake in the sizing of the hand. As demonstrated on the Circle in the previous Plate, the length of the hand should be the same as the width of the face, which is equal to half of one side of the Quadrangles. This proportion he should have followed, and would not have tripped into the big mistake of making the hand almost as long as the lower half of the arm. | Touchant le bras, qui eſt repreſenté derriere le dos de la figure, il y a une grande faute en l’ordonnance de la main. Car ſuivant les demonſtrations du Cercle cy deſſus expliquées, la longueur d’icelle ne devoit eſtre, que de la largeur de viſage, qui eſt egale à la moitié des coſtes des Quadrangles. Laquelle proportion il devoit avoir ſuivie, & ne fuſt point treſbuché en ceſte lourde faute de mettre, comme il a fait, la longueur de la main quaſi tout auſſi grande, que l’enferieure moitié du bras. |
| It is my estimation that this comparison will demonstrate one superior use for this Circle, and could be the only, that these proportions, from which we draw our skill in this activity, would be seized upon by all those who wish to honestly study this subject. I have also been in communication with several knowledgeable people, anatomists and painters whose opinions, for the most part, favoured my side. The correctness of my attributes can be quickly judged by eye, and experimentally by taking measurments. This way, as done with this figure, anyone can discover and correct faults which have been made by artists in their works. | I’eſtime que ceſte confrontation demonſtrera une excellence en l’uſage de ce Cercle, & ne pourra eſtre, que les proportions, que nous en tirons pour l’adreſſe de noſtre exercice, ne ſoyent grandement priſées de tous ceux qui voudront examiner la choſe ſans aucun prejudice. Auſſi en avons nous communiqué avec pluſieurs perſonnes curieuſes & d’entendement, Anatomiſtes & Peintres, qui ſont tombez pour la plus part de noſtre coſté: par ce que la verité de nos aſſignations ſe peut comme juger à l’œil, & par l’experience d’en prendre la meſure; juſques là meſmes que par ceſte figure ſe peuvent deſcouvrir & corriger les fautes, qui auront eſté commiſes par les Peintres és ordonnances de leurs ouvrages. |
| So this is what I thought it best to add to the above explanation of the preceeding Plate, concerning the concordance between the Circle and all the principle dimensions of the human body, so as to make even clearer how this figure can be used to understand the ground, or the Traning Plan, and to describe all the proportions of the Distances, and consequently the confidence to perform the appropriate movements. As well, so that those who will make the effort to spend time on their exercises on it, will soon come to admire its effeciveness. | Et voilà ce que nous avons trouvé bon d’adjouſter par deſſus l’explication du Tableau precedent, touchant la convenance de ceſt figure avec le corps humain en toutes ſes principales parties: afin qu’il paroiſſe d’autant plus clairement, comment elle nous doit ſervir d’une delineation du Terrain, ou du Plan d’Armes, pour declarer toutes les proportions des Diſtances, & conſequemment auſſi l’aſſeurance d’y appliquer les mouvements convenables; ainſi que ceux, qui prendront la peine de faire quelque eſpace de temps leurs exercices deſſus, le trouveront en effećt & avec admiration. |
| THE PROPER DIMENSIONS OF | LES IVSTES MESVRES DE LA |
| the hilt, the handle, and the pommel, the sword-hanger and sword-strap, as shown within the Circle, and in relation to the body of the person, wherein one can see their perfection through the elegance of each part, and by the ease of use. | Garde, de la Poignee, & du Pommeau, du Pendant de l’eſpee, & du Ceinturon, demonſtrées par noſtre Cercle, & rappportées au corps de la perſonne, où elles font voire leur perfećtion par la bienfeance du part, & par la comodité de l’uſage. |
| Now it is necessary that the sword itself have its own proportion with regard to the human body, and to the Circle (which we have already shown in the preceeding Plate) , I shall demonstrate the rest, so one may see how I have not introduced a single change, subtle or obvious, not to the hilt, nor to the sword-strap, nor the sword-hanger, that does not have a good reason for it. | Maintenant puis qu’il eſt neceſſaire, que l’Eſpee meſme ait auſſi ſa proportion, qui correſponde au corps de la perſonne, & au Cercle (comme nous l’avons deſia fait paroiſtre au Tableau precedent pour le regard de la lame) nous pourſuivrons à ceſte heure à en demonſtrer auſſi le reſte; afin qu’on voye, tant en la Garde, comme au Ceinturon, & au Pendant d’Eſpee, que nous n’avons introduit aucun changement du monde ſans raiſon non moins evidente, que grande. |
| In each of the two Quadrangles at the end of the Perpendicular Diameter line, along the edge of the Square Extension, is an image of the entire hilt, including the handle and pommel, which you can see is divided into three parts. Firstly, the image is divided into equal halves by the line across the centre of the Quadrangle. Then one of these parts is divided again in half by the Collateral Line. As I say, the length of the hilt should be the same as the distance from the point where the Collateral Line crosses the centre-line of the Quadrangle to the edge. The handle together with the pommel should be as long as the distance from the centre of the Quadrangle to the edge, which is twice as long as the Guard in front of the crosspiece. The pommel should be of a form more extended than oval. | Or donc voicy que nous vous repreſentons la forme entiere de la Garde, & de la Poignee, enſemble avec le Pommeau, au dedans de ces deux Quadrangles oppoſites ſur la longueur de l’Eſquirre: laquelle piece on voit eſtre diviſée en trois parties. car premierement elle y eſt my-partie en deux moitiez egales à travers le centre du Quadrangle; & puis l’une deſdites moitiez derechef en deux egales moindres parties par la ligne Collaterale. Suivant laquelle preſuppoſition je dis, que la Garde doit avoir en longueur autant qu’il y a depuis l’entrecoupure de la Collateralle juſqu’au Centre: & la Poignee enſemble avec le Pommeau, autant qu’il y a depuis le Centre juſqu’au coſté du Quadrangle, qui eſt deux fois autant, vous avertiſſant par meſme voye, que le pommeau doit eſtre de forme un peu plus longue, que ovale. |
| The length of the crossguard should be equal the the Pedal line, that is, the length of the foot. The rest will be covered later on. | La longueur des Branches de la croix dit eſtre comme la ligne Pedale, & par conſequent egale à la longueur de la plante d’un pied. Le reſte ſoit fait à l’advenant. |
| From these measurements it is easily understood that this shall be the form of the hilt, not the new designs that appear almost daily with so little basis, that it appears to no more than a simple ornament for decoration rather than something that one will use in a time of dire need. Some have crosspieces twisted, or bent; others have large handles, round, or flattened; others will have bows sweeping around the hand. All this for the sake of, I don’t know what display of courage, or more likely cowardice, according to the Spanish proverb: “Cargado de hierro, cargado miedo.” (Loaded with steel, loaded with fear) The form we have given it is simple and honest, just as in polite, civil conversation, and yet leaves out nothing that would be needed for defense. | Par leſquelles meſures il s’entend, qu’elle ſera la forme de la Garde, alentour de laquelle on apporte journellement tant de nouvelles inventions & avec ſi peu de fondement, comme ſi la façon n’eſtoit que pour ſervir d’un ſimple ornement de la perſonne, pluſtoſt que pour quelque à faire, qu’on en pourroit avoir en tēps de neceſſité. Les uns font les banches crochues, ou courbées; le pommeaux grands, rond, plats par deſſus; d’autres y font comme des corbeilles alentour de la poignee; le tout pour faire, je ne ſçay quelle parade de courage, ou pluſtoſt de couradiſe, ſelon le proverbe E-pagnol, qui dit, Cargado de hierro, cargado miedo. La forme que nous luy donnons eſt ſimple & honeſte, meſme en la converſation civile; & ne laiſſe portant d’eſtre du tout ſuffiſante à la defenſe. |
| After this description of the form of the hilt, it is only reasonable to explain the reasons for these measurements, to show how perfectly they work. | Apres la deſcription de ceſte forme, il eſt raiſonnable d’en expliquer auſſi les raiſons des meſures, pour demonſtrer ſa perfećtion. |
| The length of the pommel and handle were made equal to half the width of the Quadrangle: the distance from the edge to the line of the Extended Square which passes through the centre, which is the length of a hand. Of this, the Pommel takes up about half the length, so the rest of the handle is slightly longer than the width of a palm. This is a proper size to take the hilt in hand, however one chooses, and principally in my method. This length, almost the width of a palm, fits exactly into the hand of a person, which is what makes this size so very convenient. | La longueur du Pommeau avec la Poignee, nous l’avons faite egale à la ligne de l’Eſquierre depuis le coſté du Quadrangle juſques au centre, qui eſt la juſte longueur d’un main, dont it faut un peu moins que la moitié pour le Pommeau, en ſorte que le reſte en demeure un pau davantage qu’une paulme; qui eſt une juſte meſure de la garde pour eſtre empoignée, en toutes ſortes qu’on voudra, & principalement à noſtre mode. Et en procede la commodité de ce que une telle longueur eſt juſtement capable de loger le poing de la perſonne, qui eſt à peu pres egal à une paulme. |
| The Guard in front of the crosspiece must also have its proper length, which is half the size of the handle and pommel. It shall become apparent in our exercise, at times when one must close the direct line with a simultaneous parry and thrust, without taking the hand off the line, even for a moment, that it will be possible when the guard is this proper length, but otherwise not. | La Garde doit auſſi avoir ſa juſte longueur depuis les branches en avant, aſſavoir la juſte moitié de la longueur precedente. Ce qui approiſtra par experience en noſtre exercice, quād il ſera queſtion de fermer la droite ligne, en parant & bleſſant tout à meſme temps, ſans forligner de la main, prou ne peu, car en cas que la garde ait ceſte cōpetente meſure de longueur, elle y ſera capable, & autrement point. |
| The same applies to the crosspiece, which, if they are not of the proper length, will be inconvenient and will fail in their principal function. That is, they catch, sieze, and constrain the opponent’s blade from making any large movements around the hilt. Just as city’s ramparts are there not just to stop the enemy’s attack with their thickness, they are also there to provide an offensive defense, to throw them back, and knock them over. Likewise the hilt is the person’s rampart, who uses the crosspieces to undermine his Adversary, as well as it provides a simple defense, and works as a form of small-shield behind as much as one can use for cover or to hide behind. | Le meſme en ſera touchant les Branches de la croix, leſquelles, ſi elles defaillent de la juſte proportion de leur meſure, en ſeront incommodées & defaillantes en leur principal uſage; qui eſt de ſurprendre, ſerrer, & contraindre la lame contraire à faire des grands mouvements & des grand circuits à l’entour de la garde. Car ainſi que les remparts d’une ville ne doivent pas ſimplement empeſcher les aſſauts de Ennemis par l’entremiſe de leur corpulence, mail beaucoup plus par les defenſes offenſives, qui les puiſſent rembarer & renverſer par terre; ainſi la garde, qui eſt le rempart de la perſonne, ſe doit prevaloir principalement de ſes branches pour contreminer l’Adverſaire, auſſi bien qu’elle fait une ſimple defenſe, & parade en forme d’eſcuſſon, entant que le corps s’en peut aucunement couvrir, ou ſe cacher derriere. |
| So, having now dealt with the correct and most advantageous dimensions of the sword, we subsequently, with equal brevity and clarity, turn to the most suitable Sword-strap and Hanger, both for carrying the sword at the side and for drawing from its scabbard. | Voilà donc juſqu’à maintenant les vrayes & les plus avantageuſes meſures de l’Eſpee, leſquelles eſtant achevées, nous traitterons conſequement avec pareille brieſveté & perſpicuité du Ceinturon & du Pendant d’eſpee, qui ſoyent les mieux feants, & les plus-commodes, tant pour la porter à coſté, que pour la deſgainer. |
| Let us first speak of the dimensions of the hanger and each part of it. The length from the belt to the blade should be equal to the distance along the Diameter from the Circumference to the Pedal Line. This is the most convenient size as much for wearing the sword, as for ease in drawing it from its scabbard. | Parlons premierent des meſures du Pendant de l’eſpee, & de chaſcune à part. Nous diſons, que ſa longueur doit eſtre egale à la partie adjouſtée du Diametre depuis la Circonference juſqu’à la ligne Pedale; & que c’eſt là la plus convenable meſure de toutes en longueur, tant pour tenir l’eſpee attachée au corps, que pour en faire le deſgainement avec plus de facilité. |
| As to the width, it should be equal the the Pedal Line of the Circle. This shows that the bottom of the circle can be used as a pattern for the hanger. | Et au regard de ſa largeur, en voilà la meſure, qui eſt repreſentée ſur noſtre Cercle par la ligne Pedale; demonſtrant le plus bas & comme la baſe de la figure entiere de noſtre Pendent de l’eſpee. |
| The entire sword hanger should be made in the form of a triangle, such as the one that appears again in each of the four Quadrangles of the Circle, with the Pedal Line as the base and the two Collaterals for the two sides, which can be used as the pattern. The illustrator did not follow this rule when he drew the hanger, visible on the first figure at the bottom of the Plate, showing the current vulgar fashion of having curved edges, which are not the best form. It would be better and more useful to have straight edges, like the form of the triangles in the Circle. The reason is the outwardly curved edges can rub and catch on various pieces of clothing and accoutrements one may be wearing. This makes carrying a sword far more annoying than if the edges were straight. | Car il faut que la figure entiere en ſoit faite en forme triangulaire, comme il eſt repreſenté derechef en ce meſme Cercle au dedās de chaſcun des Quadrangles, prenant la ligne Pedale pour la baſe, & les deux Collaterales pour les deux coſtez, à l’imitation duquel triangle il faut auſſi façonner le pendant de l’eſpee. Encores que le Peintre n’a pas bien enſuivi ceſte regle, quand il a repreſenté les deux coſtez du pendent de l’eſpee courbez, en la Premiere figure de ces deux perſonnages, qui ſont au bas de la Table, il a enſuivi la mode vulgaire, qui n’eſt pas la meilleure, il vaudroit mieux, & ſeroit plus commode que les bords fuſſent droits, ſelon la figure du triangle, qui en demonſtre la forme; à raiſon qu’eſtants courbez en dehors, il peut advenir qu’ils aboutiſſent & s’attachent quelque part au corps, ou aux accouſtrements, & qu’ils donnent alors plus de faſcherie à porter l’eſpee, ce qu’ils ne feroyent pas, s’ils eſtoyent droits. |
| As to the length of the sword-strap, we take the length on our Circle, that is the part of the Diameter from the Circumference to the very end of the Circumscribed Square. This line is equal to the diagonal of the Quadrangle, which is twice the Pedal line. From C to A is 4, the perpendicular length of the Hanger is 3, from C to the Pedal Line. Finally across the base at its largest is 2, from C to the centre of the Quadrangle. | Quant eſt de la longueur du Ceinturon, nous en prenons auſſi la meſure ſur noſtre Cercle, aſſavoir en la partie adjouſtée au Diametre depuis la Circōference juſqu’au dernier bout du Quarré circonſcrit. Et puis que ceſte ligne eſt egale à la Diagonale du Quadrangle, qui eſt le double de la ligne Pedale; comme 4. de C juſques à A, que le Pendent en ſa longueur perpendiculaire en ſera comme 3. de C juſqu’à la Pedale; & finalement ſur la baſe en ſon plus large comme 2. de C juſqu’au centre du Quadrangle. |
| A MORE PARTICULAR DISCUSSION AND EXPLANATION
of the use and sizing of the sword-belt and hanger taken from the measurements of our circle and in response to the abuse from several others who have a different style. |
DISCOVRS ET DECLARATION PLVS PARTICULIERE DE
|
| The topic of the correct sizes for the sword-strap and hanger will, I believe, produce many more counterarguments than the sword itself, since the changes we are introducing are greater than for the sword. We have the hanger longer and the strap shorter than usual. The means of wearing the sword by the side, with the strap and hanger (as shown by the two figures at the bottom of the Plate), is quite different from the usual way. We attach the belt-strap to the belt-buckle in front, and the hanger well forward in back, instead of the typical means of attaching the hanger to the left side at the hip and the belt-strap across the back to the right side, almost under the arm. I could cut all arguments short by simply referring to the two figures A & B which are sized proportionally to the same Circle: their heights equal CV, their swords half the diameter, their arms a third of the Diameter, and so on. Their sword-straps are equal to the Extended Diameter, their hangers equal to one third that length, the hanger widths the same as the Pedal Line, they are wearing these as I described and one can easily see from these images how easily and gracefully the sword can be worn and drawn, more than if it were carried in the usual style. These figures alone could be sufficient proof of what I am saying, being perfectly proportioned. Nontheless, to answer clearly to all counters and objections, I shall put forth further clarifications enough to convince them to change the way they carry their swords. | Ie croy bien que nous aurons plus de contrediſants en ceſte matiere, qui eſt de recercher les juſtes meſures du Ceinturon & du Pendant de l’Eſpee, qu’en la precedente, qui a eſté de l’eſpee meſme. Auſſi le changement, que nous y introduiſons, eſt plus grand, que l’autre. Car nous prenons le ceinturon plus court, & le pendant plus long, qu’à l’ordinaire. Et touchant la maniere de porter l’eſpee à coſté, avec leſdites ceinturons & pendants (qui eſt repreſentée par les deux perſonnages d’embas;) la difference en eſt auſsi fort remarquable d’avec la mode vulgaire: parce qu nous attachons le ceinturon ſur le milieu du ventre, & conſequemment auſsi le pendant de l’eſpee bien avant en derriere; au lieu de les attacher & pendre, à la mode ordinaire, l’un au coſté droit, quaſi deſſous le bras, & l’autre ſur la hanche due coſté gauche. Il eſt vray que pour couper broche à toutes diſputes, qui en pourroyent fourdre, nous nous pourrions rapporter ſimplement à ces deux perſonnages A. B. qui ſont meſurez ſelon la proportion du meſme Cercle: eſtant leurs hauteurs compaſſées ſur la longueur de CV; les eſpees ſur la moitié du Diametre; les bras ſur un tiers du meſme; & le reſte à l’advenant: auſsi les ceinturons ſur l’une des parties prolongées du Diametre, les pendants de leurs eſpees ſur trois quarts de la meſme partie en longueur, & en largeur ſur la ligne Pedale: portants leſdits ceinturons & pendants ſelon noſtre deſcription; & que leurs figures eſtants repreſentées, on y voit une merveilleuſe grace à porter & à deſgainer l’eſpee, plus grande qu’elle n’eſt en la façon ordinaire. de ſorte que le ſeul regard de ces figures nous pourroit ſervir de ſuffiſante preuve pour ce que nous en pretendons, puis qu’il y appparoiſt la plus parfaite proportion, qu’on pourroit ſouhaiter en telle choſe. Toutesfois pour reſpondre clairement à tout ce que pluſierurs voudront objećter alencontre, nous mettrons icy les conſiderations en avant, qui nous ont perſuadez à quitter leur coſtume, pour en ordonner une autre meillure. |
| The principal motivation for change was the graceless, inconvenient manner in which most hang their swords at their sides, loosely, without any support from the sword-strap, which is too long, and which cannot do anything but keep the sword from swinging too far around, and does not support it at all. There are many who wrap the strap around their belt to shorten it, so that it can provide some support, which is an indisputable argument that this is not the proper length. Even without mentioning as well, that the tip of their sword is usually so high, and notably while running or when on horseback, that apart from the inelegance, man and horse are both inconvenienced, the tip of the sword falling down, like a spur, across the back, instead of hanging conveniently by the side, as a weapon intended to be aid. In fact one can see, in several Gentlemen and Knights, who are of a certain age, will carry their swords in the way I have described which is an older, easier, and better style of carrying a sword. Many were recklessly mislead from this path, by those who, in the past few years, have also introduced a clumsy style, used principally by the French, that seems to be adapted to fit the equipment, but not the wearer, and with no regard for the mechanics of using the sword, which should be the sole consideration in the design of the hanger. The mistake originated from the lack of any definite measurement for the sword-strap or the hanger, which means that at various times, fashion changed how they were made, long, sometimes longer, sometimes shorter again, than it should be according to my measurements, so one should not be astonished that people are making mistakes. | Le Principal motif du changement a eſté, de voir la male grace, & l’incommodité de leur maniere; qui eſt telle que les eſpees leur pendent ordinairement au corps, ſans aucune fermeté, ſans eſtre ſouſtenues par le ceinturon, à cauſe de ſa longueur, qui ne peut faire autre choſe, que retenir ſeulement l’eſpee qu’elle ne ſe recule pas trop en arriere, non pas la ſouſtenir. dont il y en a pluſieurs qui s’entortillent le ceinturon alentour de la ceinture, pour le raccourcir, afin qu’il aide à ſouſtenir; qui eſt un argument infallible, de n’avoir pas ſa juſte meſure: ſans ce qu’on voit pareillement, que la pointe de l’eſpee leur vient ordinairement ſi haut, & notamment en courrant, ou allant à cheval, que outre la malſeance, ils en ſont incommodez homme & cheval touts enſemble, la pointe de l’eſpee luy tombant, quaſi comme un eſperon, ſur le dos, au lieu de s’accommoder honneſtement au corps de la perſonne, car les armes ſont inventées pour aides. Et de fait on voit, que pluſieurs Gentils hommes & Chevaliers, qui ſont un peu en aage, portent leurs eſpees à la mode de noſtre deſcription, qui eſt la plus ancienne, plus facile, & mieux fondée de toutes les autres: de laquelle ſe ſont temerairement fourvoyez, ceux qui en ont introduit depuis quelques annees une autre de fort mauvaiſe grace, uſitée principalement des François, & accommodée, ſelon qu’il me ſemble, pluſtoſt à la proportion de leurs accouſtrements, que de leurs corps, ſans nul eſgard de l’uſage, qui devoit eſtre la ſeule & unique intention de l’ordonnance. Or l’erreur a prins ſon origine de ce qu’il n’y a pas eu de certaine meſure ſur les Ceinturons & Pendants d’eſpees, de ſorte qu’on les a changez de temps en temps, & les a on portez aucunesfois longs, & plus longs, & plus courts derechef, que noſtre aſsignation ne monſtre, dont il ne ſe faut pas esbahir, s’il en procede des fautes. |
| These inconveniences and others are avoided by my method of using a shorter sword-strap, which is able to lift and support the weight of the hanger and sword, along with a longer hanger than usual, attached behind the left shoulder, as is portrayed at the bottom of the Plate by the first person. It is quite true that this hanger would be too long if it were not pulled towards the front, and thus shortened by the sword-strap. The shortness of the sword-strap lifts it so that the hilt, the scabbard, and the tip are all pulled into their proper height, and snugly held against the body, in a way that is both convenient and elegant. I think most should find this arrangement convenient, both for carrying, as the first figure in the Plate shows, and for drawing, as the second one shows. One draws the sword with easy, natural movements, without any need for extra force or awkward moves. | Ces inconvenients, & pluſieurs autres ſemblables on les previendra, en uſant à noſtre mode d’un centuron plus court, qui ſoit capable de ſouslever la charge du pendent de l’eſpee; & d’un pendant plus long qu’à l’ordinaire, attaché derriere l’eſpaule gauche, ainſi qu’il eſt pourtrait, au bas de ce Tableau en la premiere perſonne. Or il eſt vray que ce pendant d’eſpee ſeroit ſans faute trop long, s’il n’eſtoit retiré en avant, & comme raccourci par l’aſſiſtence du ceinturon: duquel la briefveté le ſouſlage tellement, que la garde & le fourreau, & la pointe en viennent chaſcun en leur juſte & convenable hauteur; ayant le ceinturon, le fourreau, & le pendant d’eſpee tellement affermis & ſerrez contre le corps, qu’il en reuſſit la parfaite proportion de la commodité & de la bienſeance, qu’on y pourroit ſouhaiter pour entier contentement, tant en matiere de porter l’eſpee au coſté, que pour la tirer hors du fourreau, dont l’un ſe voit en la premiere, & l’autre en la ſeconde figure au bas de la Table. Car au fait du deſgainement, ceſte maniere s’y accommode ſi parfaitment, qu’on le peut parfaire ſans y appliquer aucune force, ny aucun mouvement, que naturel & ordinaire. |
| Because we propose to cover the drawing of the sword more completely in the next Plate, all that is to say here is to note that this means of carrying is elegant, and no more than that. I shall only add here the reasons for this change and why one should attach the sword-strap to the belt-buckle in front and the hanger on the back below the left shoulder, as shown in the figures. To begin with, do not attach either in a way that does not carry some of the weight; just as one would not attach two horses to a carriage in a way that only one does the work. Just as both work together to carry the load, and are support each other, likewise the strap and hanger work together to support the sword and hold it firmly by the side, whether on horseback, or on foot. From this hypothesis I draw the following conclusions. | Mais puis que nous avons propoſé de traiter ceſte matiere du deſgainement tout à plein en la Table ſuivante, & que ce n’eſt icy proprement le lieu de parler, que de la bienſeance du port; nous ne paſſerons point plus outre, nous contentants d’adjouſter icy ſimplement les raiſons du changement; & les cauſes pour leſquelles on doit attacher les ſuſdits ceinturon, & pendant d’eſpee, ſur le milieu du ventre, & derriere l’eſpaule gauche, comme les figures demonſtrent. A l’entree de ces conſiderations nous mettons pour fondement general, que ny le Centuron, ny le Pendant, ne doivent pas eſtre attaches au corps de la perſonne ſans aucun uſage: car comme on ne met pas une couple de chevaux à la charue, afin qu’un ſeul en ſouſtienne toute la charge, mais qu’ils s’entraident, & ſoulagent mutuellement: auſsi voulons nous pareillement, que le ceinturon & le pendant s’entreaident à porter l’eſpee, & à la tenir deuement affermie contre le corps, tant à cheval, qu’à pied. De ceſte hypotheſe ſont tirées les concluſions ſuivantes. |
| First, do not attach the strap to the right and the hanger on the left side, as is the usual custom. Because if the strap is not supporting the sword, it will drop down in a loop across the knees. That is why it should attach to the middle of the torso, and from that, it follows that I attach the hanger more in back, so the sword is at the side, a little behind, supported by the hanger with help from the strap. The sword is firmly held against the side by the proper proportion of tension between the two. Secondly, it is apparent that the belt-strap should be shorter than is typical, because otherwise it cannot support the hanger, and will be too slack. Thirdly, it follows, that, in contrast, the hanger should be longer, because, by degrees that it becomes shorter, the belt-strap becomes looser, and would need to be shortened proportionally, which it cannot. It is also apparent that the Pendent should be a little shorter than the belt-strap, so that the sword hangs a little behind the hip, rather than at the side. If it were equal in length to the belt-strap, then the sword would hang equally between the two. As it is shorter, the sword is pulled comfortably around towards the back. Fifthly, it is also apparent why the belt-strap and hanger should have the exact lengths that I have given, neither longer, nor shorter, because there is no other length that puts the hilt at such a convenient height that the right hand can easily and quickly reach across and grab ahold of the handle while the left hand holds the scabbard so as to quickly draw the sword, which is the first move in self-defense. It is also the perfect height to rest one’s elbow on, as shown and explained by figure A in Plate I. Finally, for these reasons, one can easily see how my way of carrying the sword is not only the more convenient than the typical method, but it takes the prize for elegance and appearance. Which is why one comes to the same conclusion in almost everything, as the Father of Roman Eloquence said, ‘beauty consists of, and is found in, Utility.’ If something is not practical, it may be appear beautiful to an untutored onlooker, but the discerning gentleman will recognize the inferiority and imperfection that patinas the lustre of appearance. | Premierement qu’on ne doit attacher le Ceinturon ſur le coſté droit, & le pendant ſur le coſté gauche, comme quelques uns on le couſtume. Car en ce faiſant, ſi le ceinturon ſouſtient aucunement l’eſpee, il aviendra qu’elle pendra par devant la perſonne de travers, en loy croiſant les genoux. Pour ceſte cauſe nous avons ordonné de l’attacher ſur le milieu du ventre, & le pendant de l’eſpee à l’advenant, autant plus en arriere; afin que l’eſpee revienne ſur le coſté de la perſonneun peu vers le derriere, & qu’elle ſoit ſouſtenue par le pendant à l’aide du Centuron; & affermie contre le corps par la juſte proportion de la diſtance de l’un à l’autre. Secondement il appert, que le Ceinturon doit eſtre plus court, qu’on ne le fait ordinairement; car ſans cela il ne peut ſoulager le pendant; d’autant qu’il demeure trop laſche. Pour le troiſieme s’enſuit, que le Pendant doit eſtre au contraire, plus long: car à meſure qu’on le prent plus court, le ceinturon s’en relaſche à l’advenant; de ſorte que’il faudroit auſsi raccoucir à meſme proportion le ceinturon: ce qui ne peut eſtre. Il en paroiſt auſſi ſemblablement, que le Pendant doit eſtre un peu plus court que’ n’eſt le ceinturon: pour ce qu’on ne porte pas l’eſpee juſtement au coſté, mais un peu en arriere devers le pendant de l’eſpee, qui doit eſtre le plus court, afin qu’il la tire d’avantage, car s’il eſtoit egal au ceinturon, l’eſpee pendroit au juſte entredeux. Maintenant qu’il eſt plus court, auſſi l’eſpee s’en accommode un peu d’avantage en arriere. Il en appert auſſi pour le cinquieme, pourquoy le Ceinturon & le Pendāt doivent avoir la juſte longueur, que nous leur avons aſſigné, non plus grande, & auſſi non plus petite: pour ce qu’il n’y a point d’autre meſure, que ceſte-cy ſeule, qui ſoit proportionnée à tenir la garde en ſa convenable hauteur, & à luy donner la ſituation la plus parfaite de toutes, pour mettre à meſme temps & à ſon aiſe la main droite à l’eſpee, & la gauche au fourreau, pour accomplir conſecutivement l’operation du deſgainement, qui eſt la premiere preparation pour ſe mettre en defenſe: voire auſſi pour repoſer le coude du bras gauche deſſus, en la maniere, & pour les cauſes, qui ſont expliquées au Tableau precedent ſur la figure A. En fin par ces raiſons il ſe voit, que noſtre façon de porter l’eſpee, n’eſt pas ſeulement plus commode, que la vulgaire; mais qu’elle en gaigne auſſi le prix au regard de la bienſeance, & de l’ornement de proportion; duquoy on voit quaſi arriver le ſemblable en toutes choſes, car ſelon ce qu’en a teſmoigné le grand Orateur & Pere de l’Eloquence Romaine, la beauté conſiſte, & ſe deſcouvre en l’Vſage meſme. Si quelque choſe eſloignée de l’utilité, ne laiſſe pas de ſembler aucunefois belle aux ignorants, toutesfois les gens de jugement y recognoiſſent touſiours une imperfećtion, qui obſeurcit le luſtre de leur apparence. |
| Translation by Bruce G. Hearns |
Transcription by Bruce G. Hearns |
|---|---|

| |
| EXPLANATION OF THE ACTIONS IN THE THIRD PLATE | DECLARATION DES OPERATIONS DV TABLEAV TROISIEME |
| Having described in Plate I the proper size of the sword for each person, and in the description of Plate II the length and size of the hanger, which is likewise proportional to the the individual, it follows that next topic of discussion is the Draw, which is the first action that anyone does with a sword. About which we shall now discuss at some length, as this is of greater importance than many realize. I have seen in different ways how unpleasant it can be for those who do not know the proper way to draw, so that when they were surprised by their Adversaries, their swords were useless. To remedy this, one must learn to draw skillfully, so well that one does not get in one’s own way, nor can anyone else. There are two principal ways of drawing: moving forwards and moving backwards. | Ayant demonſtré par la declaration du Tableau I. la iuſte meſure de l’Eſpee de chaſquune perſonne; & en la deſcription du II. la vraye longueur & largeur du pendant, qui luy ſoit pareillement proportionné: il s’enſuit par ordre à parler du Deſgainement, qui eſt la premiere aćtion de toutes celles de l’eſpee: de laquelle nous traitterons icy un peu au large, comme de choſe, qui eſt de plus grande importance, que pluſieurs ne penſent; & de laquelle on a veu à diverſes fois advenir de grands inconvenients à ceu qui n’en ſavoyent pas la vraye maniere, de ſorte qu’ils y ont eſté ſurprins par leurs Adverſaires, tellement que l’eſpee leur a eſté rendue inutile. Pour y remedier, il faut qu’on la ſache tirer dextrement, ſi bien qu’on ne s’y empeſche pas ſoy meſme, ou qu’on ne le puiſſe eſtre par autruy. Or il y a deux manieres principales de le faire; l’une en avançant, & l’autre en reculant. |
| HOW TO DRAW THE SWORD
while advancing |
LA MANIERE DE TIRER L'E-
spee en avanceant |
| The time to draw sword when moving forwards is when the enemy is in front at a reasonable distance, and there is a pressing need for self-defence. Moving backwards at such a moment would encourage the adversary by an apparent retreat, he would take it to mean he has the advantage, as if one is too frightened to approach. This is why one should move forward boldly and directly, to face the attack with firm resolve. It is far better to do what one must with courage than by constraint. So, march forward, draw the sword as illustrated by the four smaller figures on the left side of the Plate, labelled A, B, C, & D. | L’occaſion de tirer l’eſpee en avançant ſe preſente, quand l’Ennemi eſt au devant de nous en raiſonnable diſtance, & que la neceſſité nous preſſe à noſtre defenſe. Car de reculer en arriere en une occurrence ſi neceſſaire & ſi evidente que ſeroit ce, ſinon allumer d’autant plus le courage de la partie adverſe par une eſpece de retirade, qu’il pourroit prendre à ſon advantage, comme ſi on ne l’oſaiſt point approcher. C’eſt pourquoy il luy faut aller hardiment au devant & alencontre, pour le recevoir avec une reſolution animeuſe; car mieux vaut faire ſon devoir par courage, que par contrainte. Allez donc, marchez, & tirez l’eſpee ſelon la maniere, que nous pretendons de monſtrer, par la repreſentation de ces quatre figures de moindre taille à gauche de la Table, marquées A.B.C.D. |
| Figure A | Figvre A |
| First, after having taken two, three, or four paces, as you find convenient, as the left foot steps forward, grab the hanger and scabbard in the left hand, and as the foot lands on the ground, take the sword in your other hand, putting your index finger around the outside branch of the crosspiece, and inside the guard. | Premierement, apres avoir marché deux, trois, ou quatre pas en avant ſelon voſtre commodité, vous empoignerez de la main gauche le pendent avec le fourreau de l’eſpee, joignant la garde, durant la demarche du pied gauche, & quand il tombe à terre, de l’autre main vous prendez voſtre eſpee, entourant avec le doight indice la brāche exterieure par dedans la garde. |
| Figure B | Figvre B |
| As you take another step forward, at the same time as you raise your right leg, increase your grip on the scabbard and draw it slightly downwards and to the rear. Raise the right foot slightly more than usual (to help the right side of the body, and especially the right arm to reach higher) and at the same time draw the sword from the scabbard using the index finger that is wrapped around the outside of the crosspiece and open the hand to raise the blade more easily, until the sword is clear of the scabbard. This way the foot, the right and left hands, the shoulder, the arm, and every part of the body works together. This is in contrast to those who have learned to draw the sword while keeping the right foot planted on the ground because this way one is never inconvenienced. After having drawn the sword in this way, pause with the right foot in the air to make the following actions easier and smoother. This is what the figure shows, as you can see, his sword is barely drawn from the scabbard, yet his foot is still in the air. | Pourſuivant à marcher plus outre, à meſme temps que vous leverez le pied droit, vous fermerez bien for la main gauche, à ce que l’eſpee & le fourreau ne s’entreſuivent; & en en continuant à la reſtraindre en arriere & vers le bas, comme auſſi à porter le pied en l’air à coſté, un peu plus haut qu’en la demarche ordinaire, (afin qu’à l’aide & à l’advenant d’iceluy tout le coſté droit du corps, & notamment le bras puiſſe monter plus haut) au meſme temps vous tirerez l’eſpee avec le doigt, qui enſerre la branche exterieure; en ouvrant la main, afin qu’elle monte plus aiſemēnt, juſqu’à tant que la lame ſoit dehors le fourreau. De ſorte qu’en ceſte aćtion, le pied, la main, gauche, & droite, l’eſpaule, le bras, & en ſomme touts les membres ſe donnent mutuelle aſſtence, l’un à l’autre. Ce qui advient au contraire à ceux qui s’accouſtument à deſainer l’eſpee en laiſſant le pied droit en terre, car il eſt impoſſible qu’ils ne s’en trouvent incommodez. Apres donc que vous aurez tiré l’eſpee en ceſte maniere, vous arreſterez un bien peu le pied droit en l’air à coſté de vous, pour en continuer plus aiſement les aćtions ſuivantes. Et c’eſt proprement ce qu la figure repreſente: car vous voyez, qu ſon pied droit eſt encor eſlevé en haut, & l’eſpee à peine eſt elle hors du fourreau. |
| Figure C | Figvre C |
| To continue, during the brief pause while the foot is in the air, close your hand again on the grip and turning the wrist over, bring the blade circularly upwards, so it follows a half-circle in the air, until it is above your right shoulder, about even with and to one side of the head, tip pointing backwards, pommel towards the front, the arm bent, as shown in the figure. | Pour continuer ce qui s’enſuit, durant la pauſe du pied droit vous fermerez derechef la main droite, & tournant le poignet du bras porterez la pointe de voſtre la lame circulairement en haut, de ſorte qu’elle face une demie circonference en l’air, juſqu’à ce qu’elle vienne au deſſus de voſtre eſpaule droite, ſur la hauteur & à coſté de la teſte, ayant la pointe en arriere, & le pommeau en avant, avec le bras un peu courbé; comme il ſe voit en la figure. |
| Figure C | Figvre C |
| Continuing from the preceeding action, bring the sword down from above the shoulder as the right foot touches the ground. As the left foot moves deliberately forward, bring your arm with the sword down across your front so the arm reaches full extension downwards at the same time as the left foot touches the ground. The left foot is now forward and the right arm is extended, with the sword pointing forward at the height of the thigh. At the same time, turn the inside branch of the crosspiece towards you and wrap your thumb over it and around the blade. In this way you will be holding the sword according the manner used in this System, and this will make all your actions prompt, vigourous, elegant, and easy to keep walking without interruption. | Continuant l’operation precedente, vous ramenerez l’eſpee de haut en bas, comme d’un arriere main, par devant voſtre teſte, en mettant quand & quād le pied droit en terre; & durant que le gauche ſera en aćtion de cheminer, continuerez à porter le bras & l’eſpee par devant voſtre poitrine, tellement que la demarche du pied, & la deſcente de l’eſpee finiſſent au meſme inſtant; mettant le pied en terre, & laiſſant deſcendre le bras eſtendu enſemble avec l’eſpee à coſté de la cuiſſe droite, en tournant au meſme temps la branche interieure en dedans, & mettant le poulce alencontre. Par ainſi vous aurez l’eſpee dans la main ſelon la maniere de noſtre Pratique, & ſeront toutes vos aćtions promptes, gaillardes, bien-ſeants, & convenables à marcher touſiours avant ſans nulle interruption. |
| This action done, you will again advance the right foot, and keep the arm straight, slightly higher than the belt, and the blade held level and flat in front of the body across the lower chest, the tip slightly raised. This is how to walk towards your opponent, until you reach the distance where you can just touch each other, carefully, depending on the opportunities as they present themselves. There are plenty of examples in this book, with plenty of advice and instructions, as much for attack as defence. | L’operation eſtant achevée, vous avancerez derechef le pied droit, & porterez au meſme temps le bras aucunement courbé, un peu plus haut que la ceinture, & la lame de travers par devant le corps, en croiſant de biaiz la poitrine, avec la pointe un peu montante. Voilà comment il faudra marcher tout droit à voſtre homme, juſqu’à ce qu’eſtants venus à meſure des vous pouvoir toucher l’un l’autre, vous vous alliez, gouverner ſelon que les occaſions ſe preſenteront. Dequoy, vous trouverez aſſez d’exemples en ce livre, avec ſuffiſantes regles & inſtrućtions, tant pour l’aſſaut, que pour la defenſe. |
| HOW TO DRAW THE SWORD
while stepping backwards |
LA MANIERE DE TIRER L'E-
spee en recvleant |
| Now we shall describe how to draw the sword while moving backwards. Because it happens often, when in the company of several persons, instead of engaging in pleasant conversation, the mood sours and you are forced to draw your sword. This is dangerous and difficult enough to do, but more so when it is usual to be standing close to others that one could easily jump on you, grab your arm, or the hilt of your sword, so that one is forced to use any means for self-defence. To this situation, the only solution is to draw your sword while moving backwards. This is illustrated by the four smaller figures on the right side of the Plate, labelled E, F, G, & H. | Il s’enſuit que nous deſcrivions maintenant la maniere de tirer l’eſpee en reculant. Car il advient ſouvant, quād on ſe trouve en companie avec pluſieurs perſonnes, qu’au lieu de converſer honneſtemēt enſemble, il s’y eſmeut des queſtions, par leſquelles on eſt contraint de mettre la main aux armes, ce qui eſt aſſez difficile & dangereux à faire, d’autant que c’eſt l’ordinaire de ſe tenir en compagnie les uns ſi pres des autres, qu’on nous pourroit aiſement ſauter au corps, ou prendre le bras, ou la garde de l’eſpee, en ſorte que’on nous oſteroit tout moyen de nous defendre. A cela il n’y a autre remede qu’une bonne façon de deſgainer l’eſpee en reculant: laquelle iſt icy repreſentée par les quatre figures ſuivantes E.F.G.H.qui ſont à l’oppoſite des quatre precedentes. |
| Figure E | Figvre E |
| Taking two or three steps backwards, beginning with either foot, as the left foot takes a backwards step, grab the hanger and scabbard with the left hand. As the foot falls on the ground, reach across with the right hand and grab the hilt, as shown in the picture, putting the right index finger around the crossbar and into the guard. | Faiſant deux ou trois pas en arriere, ſoit qu’on ait commencé avec le pied droit ou le gauche, faut aviſer d’empoigner de la main gauche le pendent de l’eſpee, enſemble avec le fourreau, tout joignant la garde, durant la demarche du pied gauche; & en le mettant à terre, de l’autre main on prendra l’eſpee, en embraſſant avec le doigt indice la branche exterieure par dedans la garde; comme la figure demonſtre. |
| Figure F | Figvre F |
| With the sword firmly in hand and the left foot firmly on the ground, grab the hanger and scabbard with the left hand, pulling down and back, while stepping backwards with the right foot, step a bit slower and raise the foot a little higher than normal to make it easier to draw the sword, as similarly described for Figure B. These are the same movements, the only difference being that one is done moving forward, the other moving backwards. | L’eſpee donc prinſe, & le pied gauche planté en terre, tout à l’inſtant on eſlevera l’autre, pour continuer la meſme retirade, en ſerrant cependant bien fort la main gauche, qui tient le pendant avec le fourreau de l’eſpee, la pouſſant meſmes un peu vers le bas, pour tirer l’eſpee tant plus aiſement, durant la continuation de monter le pied droit en l’air à coſté, un peu plus qu’en la demarche ordinaire; ſuivant au reſte en tout & par tout les obſervations qui en ſont dechifrées en a deſcription de la figure B. Car ce ſont toutes les meſmes aćtions, & n’y que ceſte difference, que l’une des figures travaille en avançant, & l’autre en reculant. |
| Figure G | Figvre G |
| When you draw the sword from the scabbard, again, pause slightly with the right foot, holding it raised and off to the side, while doing this, move the tip of the blade circularly outside the arm, so it rises diagnoally in front of the chest, with a turn of the wrist, helped a bit by the arm, until the hilt is at the height of the head, a little to one side, the blade above the shoulder, with the point above and behind you. At this instant begin to lean slightly forward, pull the right foot back, as shown in the picture. | Quand l’eſpee ſera hors du fourreau, on fera derechef une petite pauſe du pied droit, le tenant eſlevé à coſté, & durant icelle on menera la pointe de ſa lame circulairement en haut dehors le bras, en ſorte qu’on la face monter diagonalement par devant la poitrine, avec un tour de la main, aſſiſté de quelque petite accommodation du bras, juſqu’à tant que la garde arrive à l’endroit du ſommet de la teſte un peu à cartier, la lame reſpondant par deſſus l’eſpaule, avec la pointe un peu hauſſée derriere le dos; auquel inſtant on commencera enſemblement à pancher du corps ſur le devant, & à retirer en arriere le pied droit, qui eſt pour le preſent encore eſlevé; ſuivant ce qu’on voit en la figure. |
| Figure H | Figvre H |
| Finally, after bringing the blade over the head from the left side and continuing to lean slightly forward bring the hand downwards, as if you were striking, diagonally across the chest, and as it passes the chest and the upper body, step back onto the right foot with as large a step as possible. As the foot touches the ground, straighten the arm down by your side, and draw the left foot back towards you as you straighten up. At the same time, turn the crossguard from vertical to horizontal, and move the thumb over the crosspiece, so as to hold the sword in hand as it should be according to the manner used in this System. | Finalement on pourſuivra à mener la lame circulairement par deſſus ſa teſte devers le coſté gauche, & en continuant à pancher du corps, on fera comme un coup de revers en l’air, deſcendant diagonalement par devant la poitrine; & à l’inſtant qu’il paſſe ladite poitrine: & la partie ſuperieure du corps, on ſe retirera avec le pied droit, qui eſt encores eſlevé, en arriere, autant qu’un grand pas ſe peut eſtendre; & à l’inſtant qu’il ſe mettra en terre, on retirera pareillement le bras droit eſtendu à coſté; & laiſſera on ſuivre le pied gauche en trainant, laſchant au meſme temps la main, & tournant la branche interieure de la garde horizontale, de verticale qu’elle eſtoit, & enſemblement retirant le poulce de deſſous icelle en deſſus. Ce qu’eſtant fait, on aura l’eſpee à la main, ainſi qu’on la doit tenir, ſelon la mode de noſtre Pratique. |
| You may find these actions difficult or even impossible at first, as there are so many points to pay attention to in such a short time, but after a bit of practice, it will seem, on the contrary, to natural and easy. | Il eſt bien certain que ces operations vous ſembleront du commencement fort difficiles ou meſme impoſſibles à faire, à cauſe de tant de petits points à obſerver en ſi peu de temps, mais l’accouſtumance vous en fera paroiſtre le contraire, de ſorte que vous recognoiſtrez à la fin, que ce ſont toutes choſes naturelles & faciles. |
| As for the backwards blow, which was mentioned in the discription of this figure, it is not a useless gesture. On the contrary, it is very useful to keep men from following too closely and to keep them back, to gain space to adopt a defensive posture. After this last step, you must decide if you still need to step back further, or if you need to step in. This is done in the same way as described above, that is, putting the right foot forward again, and placing the sword across your front, the arm strait, with the right hand and guard about level with the belt, the tip slightly raised. | Touchant le coup de revers, dont nous faiſons mention en la declaration de ceſte figure, il faut ſavoir, qu’il n’eſt pas inutile: car au contraire il ſert grandement à tenir les gens tant plus eſloignez, & pour ſe faire largue, au moyen dequoy on a plus e commodité de ſe mettre en defenſe. Ayant donc achevé ceſte derniere aćtion, il faudra juger, s’il eſt deſormais beſoing de reculer encores davantage, ou s’il eſt temps de faire ſes approches. Leſquelles il faudra faire en la meſme ſorte qu’il eſt dit cy deſſus, aſſavoir en avançant derechef le pied droit, & ſe mettant au meſme temps l’eſpee de travers par devant le corps, le bras aucunement courbé, la main droite, avec la garde, environ la hauteur de la ceinture; en ſe croiſant la poitrine avec la pointe un peu aſcendante. |
| HOW TO PRESENT THE SWORD
to your opponent in the direct line posture |
LA MANIERE DE PRESENTER A SON
contraire l’espee en droite ligne |
| That, in essence, is what seems to me to be important about drawing the sword. Now to the practical exercises and we start with the Direct Line posture. What must be learned before anything else is how to present yourself deftly to your adversary, through precise and suitable motions. At the same time, you must know the proper way to approch the adversary. I shall leave aside an infinity of other postures, and choose this one, which is the most suitable for demonstrating the precepts of my system, as well as being superior to all others. I admit that there are more delicate and more ferocious postures, But if these appear more polished, or present a hostile expression, this one has the advantage of both caution and strength. So, I leave these other postures to those who wish to adopt them, and content myself for the moment with the Direct Line. In this Plate, I shall describe the manner and steps to adopt the posture, and shall discuss its worthiness and its advantages in the next section. | Voilà en ſomme ce qui m’a ſemblé neceſſaire de vous propoſer touchant le deſgainement de l’eſpee. Venons à la Pratique de l’Exercice, & commençons par la Droite Ligne, laquelle il faut apprendre avant toute autre choſe à preſenter dextrement à voſtre partie adverſe, avec geſtes propres & convenables pour l’attendre; & la meſme eſtant pareillement preſentée, que vous ſachiez auſſi la maniere de faire vos approches alencontre. Nous laiſſons à part une infinité d’autres postures, & en choiſiſſons ceſte ſeule, qui eſt la plus convenable pour la demonſtration de nos precepts, voire auſſi la meilleure de toutes. I’advoue bien qu’il y en a de plus mignardes, & de plus furieuses en apparence: mais ſi celles-là ſont accompagnées de plus de luſtre, ou de mauvaiſes mines, ceſte-cy l’eſt davantage de prudence & de force. Parquoy laiſſant les autres à ceux qui s’y plaiſent, nous nous contenterons pour le preſent de ceſte droite ligne, de laquelle nous deſcrirons en ce Tableau la maniere & l’ordre, comme il y faut proceder, nous remettants à diſcourir de ſa noblesse & de ſes avantages au prochain enſuivant. |
| A final note, which holds for all the examples throughout the book, that the swordsman who is on the Circle on the side of the letter A will always be called Alexander and his opponent Zachary. Alexander will normally be the one who follows my principles, but never Zachary, except as he is in this Plate III, where he is shown by four figures moving through consecutive actions, that show the means and steps by which you move into the Circle and adopt the direct line posture, which is explained, below. | Il faut que je die en paſſant, & une fois pour toutes, que celuy des deux Contraires qui commence à travailler ſur le Cercle du coſté de la lettre A, ſera touſiours appellé Alexandre, & l’autre Zacharie: dont Alexandre ſera ordinairement l’observateur de no precepts, & aucunefois pareillement Zacharie: comme il l’eſt auſſi preſentement en ce Tableau III. où il repreſente en quatre figures & aćtions conſecutives, en quelle maniere & avec quels geſtes on ſe mettra ſur le Cercle en la poſture de la droite ligne; dont voicy l’explication qui s’eſuit. |
| FIRST ACTION | PREMIERE ACTION |
| Zachary is right in front of Circle No 1, facing the Z-X Quadrangle, carrying his sword in the crook of his left arm, and his left hand resting on the hilt. | Zacharie ſe met droit devant le Cercle N.1. viz à viz du Quadrangle ZX, tenant l’eſpee ſur le coude du bras gauche, & en empoignant la garde par deſſous avec la main gauche. |
| To show this action as simply as possible, Zachary is standing straight, facing front along the Diameter, about one blade-length away from the Circle. He can check this by putting his blade on the ground. If he were to put his tip at the letter X, the crossguard would be exactly between his two feet. However, there is another method of checking and adjusting the distance, by extending the arm and the sword in a straight line and bringing the tip down to just touch the ground. If you stand up straight, and do not bend over or twist, or change your posture, the tip will just touch the ground at X on the Circumference. Zachary thus waits, in this relaxed posture, sword in the left arm, left hand over the hilt, hands resting on his stomach, so the tip of the sword is behind his shoulder, until he sees his adversary in order to present the direct line. | Pour repreſenter ceſte aćtion le plus ſimplement qu’il ſoit poſſible, Zacharie ſe met icy tout droit ſur ſes jambes viz à viz du Diametre, les pieds egalement avancez, s’en tenant eſloigné de la juſte meſure de ſa lame. Dequoy il peut prendre la meſure avec l’eſpee meſme, en la mettant à terre. Car s’il en met la point ſur la Circonference à la lette X, les branches de la garde luy en reviendront juſtement entre le creux des ſes deux pieds. Toutesfois il y a encore une autre maniere, plus facile pour examiner & adjuster ceſte meſme distance, aſſavoir en eſtendant le bras avec l’eſpee droitement en une ligne, & la menant de haut en bas juſqu’à toucher la terre. Car le point d’attouchement viendra touſiours au meſme endroit de la Circonference à la lettre X, moyennant que la ſituation du corps ne ſoit point changée, & qu’on ne le plie, ny en avant, ny en arriere, mais qu’il demeure droitement debout & perpendiculaire. Zacharie donc ſe tenant eſloigné en ceſte bras gauche, empoignant auſſi de la main gauche la garde par deſſous, ſe laiſſant prendre & repoſer les bras ſur le ventre, en ſorte que la pointe de l’eſpee luy va derriere l’eſpaule. Et voilà comme il s’eſt mis en eſtat d’attendre, juſqu’à tant qu’il voye ſa partie adverſe en ordre, pour luy donner la droite ligne. |
| SECOND ACTION | SECONDE ACTION |
| In front of Circle No 2, he moves his left foot forward with a small step, bringing the sword circularly down in front until he holds it to the side, arm out straight, in an acute angle, point down. | Devant le Cercle N.2. il s’avance avec le pied gauche d’un pas moderé, en menant l’eſpee circulairement par devant ſoy avec le bras raide, & la mettant à ſon coſté droit en angle aigu, la pointe baiſsée. |
| As he approaches the Circle, he first moves his left side and foot a medium step directly forward and at the same time straightens his sword arm, swinging it through a semi-circle diagnoally downwards across his chest and down into an acute angle off to his right side, the tip about one hand width off the ground. All of the movements, of the arm, of the hand, of the sword must begin and finish at the same time as the step, to keep everything together. Be aware of a common mistake by novices, which is to cross-step and put the left foot in front of the right foot, instead of moving the left foot straight ahead, and so find themselves instantly entangled when performing the next actions. | En approchant donc du Cercle, il avance premierement le coſté, & le pied gauche d’un pas mediocre en ligne droite, & cependent roidit le bras de l’eſpee, la menant par une demie-circonference diagonale par devant ſa poitrine, de haut en bas, en angle aigu à ſon coſté droit, & en mettant la pointe environ à la meſure d’une paume de la terre. Au reſte toutes ces aćtions, tant du bras, que de la main, & de l’eſpee, ſe doivent commencer & terminer enſemble avec le pas du pied, afin qu’il n’y ait rien de mal proportionné. Faut auſſi ſe donner garde, en apprenant ceſte demarche, d’une faute aſſez ordinaire & commune à la plus part des Eſcholiers; qui eſt de croiſer le pas, & porter le pied gauche en avant à la main droite, au lieu de marcher en droite ligne tout droit devant eux, dont ils ſe trouvent tout à l’inſtant embrouillez à faire les operations ſuivantes. |
| THIRD ACTION | TROISIEME ACTION |
| In front of Circle No 3, he raises his right foot as he steps and raises the sword up with his straight arm, so it points up at an obtuse angle. | Devant le Cercle N.3.il eſleve & hauſſe le pied droit à coſté, enſemble auſsi l’eſpee de meſme avec le bras roide, en ſorte qu’ils viennent à y faire une ligne montante en angle obtus. |
| Here he raises the right foot to take the second step, and at the same time he raises his extended arm to the side, upwards at an obtuse angle. Since he intends to put the tip of his foot at the letter X, having already moved forward, together with his arm and sword, he looks down at the Circle to check his foot will land where he intends to place it, so the rest of the steps can flow uninterrupted, as shall be worked out in the next Circle. | Voicy qu’il leve le pied droit pour faire le ſecond pas, & au meſme temps il porte auſſi le bras eſtendu avec l’eſpee en haut en angle obtus, juſtement à coſté. Et puis que c’eſt ſon intention de mettre le bout du pied droit à lettre X; l’ayant preallablement un peu avancé, enſemble auſſi le bras & l’eſpee meſme; il tourne les yeux en bas ſur la figure du Cercle, pour y prendre l’adreſſe du pas, qui luy reſte à faire, au point qu’il pretend de toucher: pourſuivant au reſte à marcher & à continuer ſans interruption, comme il ſera deduit au Cercle ſuivant. |
| Note that I said to lift the right foot at the same time as your arm and sword, so they are raised to the side, in profile. If they were raised to the front, it would cause difficulties in the following actions, and something badly started cannot end well. | Notez bien ce que nous diſons de porter le pied droit avec le bras & l’eſpee, cependant qu’ils montent, juſtement à coſté reſpondants ſur le pourfil du corps. Car ſi on les avance du commencement, on en ſera fort incommodé à la continuation des aćtions ſuivantes, ce qui eſt mal commencé ne pouvant avoir bonne fin. |
| FOURTH ACTION | QUATRIEME ACTION |
| In Circle No 4, he has stepped forward with right foot, and planted it at the point X, thrusting his sword out in a straight line over the Diameter, with the left foot following at the same time to arrive on the Pedal Line. | Au Cercle N.4. il a marché du pied droit, & l’a planté à la Circonference au point X, jettant enſemblement l’eſpee en droite ligne au deſſus du Diametre, avec le pied gauche trainant à meſme temps derriere juſqu’à venir deſſus la ligne Pedale. |
| While on the left foot, his other moving forward, along with his arm and his sword, & looking at the ground to adjust his step, he proceeds as follows: he carries the sword forward, with his arm extended, in a slightly downward circular motion. At the same time as his right foot comes down, his toes on the point X, and his heel along the Collateral inside the Quadrangle on the right hand side. Continuing the circular motion with the sword, keeping his arm and sword extended and straight, he brings it up not quite overhead, forward, and down until his arm and sword are horizontal over the Diameter and perpendicular to his torso. As he places his foot on the ground, and as he carries the sword circularly overhead, it is done with an impetus from the arm, with tension from all the nerves and muscles of the body, so that the right side is pulled forward, the heel of his right foot is turned to follow the line X-Y, and finally his left foot is drawn forward into balance until it rests on the Pedal Line at Z. Once planted, the he stands erect and in profile, sword and arm extended in a straight line parallel to the Diameter, shoulder, arm, the hilt, and the point held horizontally. | Eſtant ſur le pied gauche, & ayant avancé l’autre, enſemble avec le bras & l’eſpee, & regardé en terre, pour adjuster le pas, il pourſuit en ceſte ſorte: c’eſt qu’il porte l’eſpee avec le bras eſtendu, circulairement en avant, un peu vers le bas; mettant au meſme temps le pied en terre, les orteils ſur le point X, & le talon ſur la collaterale dedans le Quadrangle à main droite. Et en continuant touſiours le ſuſdit mouvement circulaire de l’eſpee, il la ramene en haut avec quelque petite accommodation du poignet, en finiſſant le mouvement du bras (qui demeure touſiours eſtendu avec l’eſpee en droite ligne) juſtement au deſſus du Diametre, en angle droit & ligne perpendiculaire au regard du corps, & au regard du Diametre en ligne parallele. Or quand il plante le pied à terre, & qu’il porte l’eſpee circulairement en haut, celà ſe fait avec une impetuoſité du bras; dont touts les nerfs & muſcles du corps ſe tendent, le coſté droit en eſt tiré en avant, le talon du pied droit s’en tourne en dehors ſur la ligne XY, & finalement le pied gauche en eſt contraint & comme forcé à ſuivre & ſe laiſſer entrainer apres l’autre juſqu’à tant qu’il vienne ſur la ligne Pedale Z, où il doit demeurer, & redreſſer au meſme temps, qu’il y arrive, le corps droit & en pourfil, l’eſpee enſemble avec le bras eſtendus en ligne droite parallele au Diametre, en ſorte que l’eſpaule, & le bras, la garde, & la pointe de l’eſpee ſe retrouvent toutes en egale hauteur. |
| After all these actions are done, if there is any doubt about the posture, to check that it is correct, he need only extend the left arm in the same way towards the rear, at the same height. If his posture is correct, then the two arms and the sword will be on a straight line, while all the rest of his body is relaxed, so there is no tension and no deformation, since this is the most natural posture in the world. If there is any fault, either in the position of the body or the sword, it is easily determined because the line of the arms is not straight, or because the body is not upright, or because of the discomfort caused by contortions, as can be seen in all other postures, when they are forced to present the sword in the direct line. | Apres toutes les aćtions faites, s’il eſt queſtion d’examiner la poſture, pour voir s’il y a de la faute; il ne faut qu’eſtentre pareillement le bras gauche en droite ligne, en arriere à la meſme hauteur. Car ſi la poſture eſt juſte, les deux bras enſemble avec l’eſpee, ne feront qu’une droite ligne, & en ſeront touts les membres du corps tellemēt à leur aiſe, qu’il n’y en aura de contraint ny de contrefait, d’autant qu c’eſt la poſture du Monde la plus naturelle. En ſomme, s’il y a faute, ſoit en la ſituation du corps, ou en la tenue de l’eſpee, elle ſe deſcouvrira d’elle meſme par l’inegalité de la ligne, qui devoit eſtre droite, ou par la meſſeance du corps qui ſe devoit tenir perpendiculaire, ou par le malaiſe procedant de la contorſion des membres, comme il en prend à toutes le autres poſtures, quand elles s’efforcent de preſenter l’eſpee en droite ligne. |
| HOW TO APPROACH AGAINST THE DIRECT LINE POSTURE
and against the Obtuse Angle posture |
COMMENT IL FAVT FAIRE SES AP-
proches contre la droite ligne, et contre l’angle obtvs |
| Having explained the actions of Zachary, I shall now likewise describe those of Alexander, as shown by the four figures, showing the different means of approaching against an opponent who has adopted the posture of a sword held in the direct line and the obtuse angle. But these postures are not shown by Zachary in this Plate, but rather in the fourth Plate, which follows this one. In each Circle of Plate IV, Zachary has adopted his posture, with the sword either in the direct line or at an obtuse angle. Alexander’s approaches to each posture begins on the numbered Circle in this Plate, and finishes in the same numbered Circle in the next Plate. | Ayant ores declaré les operations de Zacharie, il ſera bien que nous commencions pareillement à deſcrire celles d’Alexandre; qui nous monſtre par ſes quatre figures, autant de differentes manieres de faire ſes approches contre la droite ligne & contre l’angle obtus. Mais puis que ces dites poſtures ne luy ſont pas preſentées en ce preſent Tableau par Zacharie, il faut ſavoir qu’elles ſeront repreſentées au quatrieme, qui eſt le prochain enſuivant, chaſcune à tour, ſur les Cercles, marquez de meſme nombre. Auſſi que les approches d’Alexandre ne ſont icy repreſentées à plein; mais que le ſurplus en eſt reſervé pour le meſme Tableau quatrieme, chaſcun à repreſenter ſur ſon propre Cercle. Cependant ſachez que les poſtures de Zacharie ſont telles. |
| On Circle No 1, Zachary presents his sword in the direct line, as in Circle No 4 in this Plate. | Sur le Cercle N.1. il preſente la droite ligne, tout ainſi qu’au Cercle N.4. de ce Tableau preſent. |
| On Circle No 2, he presents his sword at an obtuse angle. | Sur le N.2. il preſente l’eſpee en angle obtus. |
| On No 3, he is doing the same. | Sur le N.3. il fait le meſme |
| It is against these postures the Alexander must approach, the first half of which are shown here, and the finish will be shown against those postures. | C’eſt alencontre de ces poſtures qu’Alexandre ſe met icy en devoir de faire ſes approches, qui n’y ſont toutesfois repreſentées qu’à demi, dont l’accompliſſement ſera veu, là où les poſtures ſe voyent alencontre. |
| FIRST ACTION | PREMIERE ACTION |
| Alexander has advanced two or three paces towards Circle No 1, at the moment he placed his left foot on the ground, he set his sword at an acute angle to his right side, and is now raising his right foot to land outside of the circle, and has raised his arm and sword up to an obtuse angle. The ending to this move will be shown in Circle No 1 in the following Plate. | Alexandre s’eſtant preallablement avancé deux ou trois pas devers le Cercle N.1. en plantant le pied gauche en terre, il a mis l’eſpee en angle aigu à ſon coſté droit, ce qu’eſtant fait, il hauſſe le pied droit en dehors, comme auſsi le bras avec l’eſpee, les mettant en ange obtus; le ſurplus de ceſte approche ſera repreſenté au Cercle N.1. du Tableau ſuivant. |
| Supposing Zacharie has adopted the fighting posture of the direct line to receive Alexander’s attack. Here we see Alexander making his approach against him. While he was out of range, he walked as far forwards as the distance required, carrying his sword freely, however he wishes, neither concerned about starting on the right or left foot, nor with the exact distance to his adversary. But when he puts his left foot down within one pace of the Circumference, he moves his sword off to his right side in a circular motion until it forms an acute angle, using the same motions at the same distance as Zachary before Circle N0 2. This done, as he raises his right foot, he raises his sword and straight arm up to an obtuse angle, just as Zachary before Circle No 3. There is only one difference, that is, when Zachary approached, he looked to the ground to check the distance so as to place his right foot along the Collateral line on the right side of the Quadrangle, with his toes exactly on the circumference at X, which he must do to be first in position on the Circle, and which can do as he has no opponent to face. But Alexander cannot do this, as he must focus during all his actions, in his approach, in his comportment, and in assessing his distance, the long and short of it, on his adversary who is waiting for him, without ever looking away. If he did otherwise, he would never be able to put his sword into the direct line, parallel to and below the other, as is shown in the following Plate. This is why Alexander keeps his eyes fixed on his enemy. | Preſuppoſant donc que Zacharie ſe ſoit mis le premier en campagne in la poſture de la droite ligne, pour attendre. Voicy Alexandre qui commence à faire ſes approches alencontre, en ceſte ſorte. Durant qu’il a eſté hors de meſure, il a marché autant de pas en avant, que la diſtane requeroit, menant l’eſpee librement à ſa fantaſie, ſans eſtre en peine de commencer la demarche avec le pied droit ou avec le gauche, ny de ſçavoir exaćtemēt la diſtance de l’Adverſaire. Mais quand il a mis le pied gauche en terre ſi pres du Cercle, qu’il pouvoit arriver en un ſeul pas à la Circonference; c’eſt alors qu’il a porté ſon eſpee circulairement avec une demie-circonference diagonale à ſon coſté droit en angle aigu, uſant des meſmes aćtions, & ſe mettant à la meſme diſtance, qu’il a eſté dit cy devant en la perſonne de Zacharie N.2. Ce fait, il leve le pied droit, & hauſſe enſemblement le bras avec l’eſpee en angle obtus; tout ainſi qu’en a fait Zacharie devant le Cercle N.3. Il n’y a que ceſte difference, que Zacharie regarde la terre pour compaſſer la demarche, & mettre le pied droit juſtement ſur la collaterale droite de ſon Quadrangle, avec les orteils touchants la Circonference; ce qu’il peut & doit faire pour ſe mettre le premier en poſture ſur le Cercle, d’autant qu’il n’a null autre adreſſe. Mais à Alexandre il n’eſt permis de ce faire; d’autant qu’il doit prendre l’adreſſe de toutes ſes aćtions, & de ſon approche, au comportement & à la diſtance de ſon Contraire qui l’attend, & la dite diſtance à l’aulne de la veuë, ſans jamais en deſtourner ſes yeux; car autrement il ne pourroit porter l’eſpee au ſuivant mouvement en ligne droite & parallele deſſous l’autre, comme il ſe voit en la Table ſuivante. C’eſt la cauſe, pourquoy Alexandre tient icy les yeux fichez ſur l’Ennemy. |
| SECOND ACTION | SECONDE ACTION |
| Alexander has advanced two or three paces towards Circle No 2 at the moment he placed his left foot on the ground, he swung his sword out and down at an acute angle, then, as he lifted his right foot to step forward, he raised his hand up and rested his sword on his right shoulder, with the point behind him. | Alexandre s’eſtant preallablement avancé deux ou trois pas, devers le Cercle N.2. en plantant le pied gauche, il a jetté l’eſpee deſcendante en angle aigu, puis en eſlevant le pied droit en avant, il porte le bras avec leſpee en haut, le mettant par deſſus ſes eſpaule droite à coſté de la teſte avec la pointe en arriere. |
| In Circle No 2, let us suppose Zachary is waiting with his sword raised to an obtuse angle, as shown in the next Plate. To approach, Alexander has placed himself in front and taken two, three or more steps forward, as needed, to close the distance, carrying his sword freely, however he wants. But, when he puts his left foot down no more than a pace from the edge of the Circle, about to come into range, at the same time he moves his right hand forward and points the sword down at an acute angle in front. Then, as he raises his right foot to take a careful step, he brings the sword up and beside his head onto his right shoulder with the tip a little behind. As he takes his next step, he brings his sword forward and into contact with his opponent’s sword to the inside, as shall be more fully explained in Plate IV. | En ce Cercle N.2. nous preſuppoſons, que Zacharie luy preſente l’eſpee en angle obtus, comme il ſera repreſenté au Tableau ſuivant. Pour travailler alencontre, Alexandre s’eſt mis tout droit devant; puis a marché deux, trois, ou quatre pas en avant, plus, ou moins, ſelon la diſtance, menant librement l’eſpee ſelon qu’il luy eſt venu à gré. Mais en venant ſi pres du Cercle avec le pied gauche, qu’il ne reſte plus qu’un pas, pour venir en meſure; en meſme temps il avance l’eſpee un peu à main droite, la portant de haut en bas en angle aigu; puis en eſlevant tout à l’inſtant le pied doit, & commençant à cheminer, il la ramene en haut à coſté de ſa teſte à la hauteur de l’eſpaule, la pointe d’icelle un peu montante en arriere. Leſquelles aćtions il a faites, en intention d’avancer l’eſpee avec le pas enſuivant, & la mettre au meſme inſtant qu’il viendra en meſure, contre la lame contraire en dedans, comme il ſera dit plus amplement en la declaration du Tableau IV. |
| THIRD ACTION | TROISIEME ACTION |
| Alexander has advanced two or three paces before Circle No 3, and, at the same moment he has placed his right foot close enough that his left foot is one pace from the Circumference, he points his sword down towards his right side at an acute angle. As he moves his left foot forward to place it at the Circumference, he again raises his sword to an obtuse angle under the opponent’s blade and above the Diameter, with his body leaning backwards. | Alexandre s’eſtant avancé deux, ou trois pas devant le Cercle N.3. au meſme inſtant qu’il plante le pied droit ſi pres, qu’il peut atteindre la Circonference avec l’autre, il avance l’eſpee devers ſon coſté droit en angle aigu; laquelle il porte derechef en haut en angle obtus en avancant le pied gauche; & en le mettant à terre à la Circonference, derechef il la ramene de haut en bas en angle aigu deſſous l’eſpee contraire & au deſsus du Diametre, avec le corps panché à l’envers. |
| Coming to Circle No 3, suppose Zachary is again waiting in the same posture, presenting his sword at an obtuse angle, as shown in the following Plate. To approach, Alexander has again walked forward the same way as in the previous Circle, until his right foot is one pace from the Circumference, at the same time he moved his sword and arm down at an acute angle, off to the right side. Again, as he raises his left foot and steps forward, he again brings his sword upwards to an obtuse angle. At the instant his foot touches the ground with the toes on the Circumference at C, he brings the sword diagonally beneath his opponent’s sword at an acute angle, his body leaning slightly backwards. That much is shown here; the next step will be described later. | Touchant le Cercle N.3. il faut preſuppoſer, que Zacharie l’attend derechef en la meſme poſture, luy preſentant l’eſpee en angle obtus, comme on le voit depeint au Tableau ſuivant. Pour l’aborder, Alexandre a marché encores tout de meſme, qu’au Cercle precedēt, juſqu’à ce qu’en approchant le pied droit ſi pres, qu’il ne reſte plus qu’un pas pour atteindre la Circonference, il a avancé au meſme temps le bras avec l’eſpee vers le bas en angle aigu, tirant un peu à main droite; & derechef, il l’a ramenée circulairement en haut en angle obtus, durant l’eſlevation & l’avancement du pied gauche, lequel en venant à planter en terre ſur la Circonference au point C, au meſme inſtant il porte ſon eſpee diagonalement deſſous la contraire in angle aigu le corps un peu renverſé. Voilà tout ce qu’il fait juſqu’icy: la ſuite ſera declarée en ſon lieu. |
| FOURTH ACTION | QUATRIEME ACTION |
| In Circle No 4, he has stepped forward with right foot, and planted it at the point X, thrusting his sword out in a straight line over the Diameter, with the left foot following at the same time to arrive on the Pedal Line.Alexander has advanced two or three paces and as he placed his left foot in front of Circle No 4, he moved his sword forward at an acute angle, which he then raised back up while stepping with the right foot, and brought it up beside his head over his right shoulder, with the point behind. | Alexandre apres s’eſtre avancé deux ou trois pas, en venant à planter le pied gauche devant le Cercle N.4. avance l’eſpee en angle aigu, laquelle il ramene derechef en haut durant la demarche du pied droit, & la porte à coſté de ſa teſte au deſſus de l’eſpaule droite, avec la pointe tournée en arriere. |
| Here, in Circle No 4, suppose Zachary has adopted the direct line posture. Alexander again approaches in the same way, having taken two or three paces, as he puts his left foot down by the point of the Circumscribed Square, he moves the sword downwards at an acute angle. As he continues to step with his right foot into range, as he raises it and moves it forward, he brings the sword back up beside his head, over his right shoulder, with the tip pointing behind, and the guard about the height of the shoulder, and a little forward, as shown in the figure. | Icy en ce Cercle N.4.preſuppoſant que Zacharie ſe ſoit mis en la poſture de la droite ligne. Alexandre vient derechef alencontre, ayant preallablement fait deux, trois, ou quatre pas en la meſme ſorte que deſſus, à la fin deſquels en mettant le pied gauche en terre devant l’angle du Quarré circonſcrit, il avance l’eſpee vers le bas an angle aigu; puis en continuant à marcher du pied droit pour entrer en meſure, durant l’eſlevation & l’avancement d’iceluy, il la raporte en haut à coſté de ſa teſte au deſſus de l’eſpaule droite, la pointe hauſſée en derriere, & la garde environ la hauteur de l’eſpaule, un peu en avant; comme il eſt repreſenté en la figure. |
| These are the actions he has done as shown in this Plate. The next will contain how he moves into range, advancing the right foot to the Circumference of the Circle, meanwhile swinging the tip of sword inversely from high to low, which he does with a twist of the wrist and a little motion of the arm and continuing on until he has put his blade underneath his opponent’s in parallel and in a direct line. But as these things are shown in the following Plate, I shall finish my explanation of the Third Plate and move on. | Telles ſont les aćtions qu’il a faites en ce Tableau preſent; la ſuite contiendra cōment c’eſt qu’il entre en meſure, en avançant le pied droit juſqu’à la Circonference du Cercle, & tournant ce temps pendant la pointe de ſa lame circulairement à l’envers du haut en bas à ſon coſté; ce qu’il fait du poignet de la main avec quelque petite accommodation du bras, en continuant le meſme tour juſqu’à tant qu’il ait mis ſa lame deſſous l’eſpee contraire en ligne droite & parallele. Mais puis que ces choſes ſeront repreſentées au Tableau ſuivant, faiſons icy la fin du Troiſieme, & paſſons outre. |
| Translation by Bruce G. Hearns |
Transcription by Bruce G. Hearns |
|---|---|

| |
| EXPLANATION OF THE ACTIONS IN THE FOURTH PLATE | DECLARATION DES OPERATIONS DV TABLEAV QUATRIEME |
| I believe there will be some who, barely having glanced at Plate IV and its text, who will instantly decide that the topic should have been far too simple for such a long discussion, that we should not have tried earlier to expand the material, that it should be made simple to understand. But I ask them to consider that these are the basic foundations of this science, which will draw after them a long train of incomplete problems, which are impossible to solve if they are not closely examined at the beginning of training. Because, just as effects flow from causes, so there must be neither doubt, nor failure to understand, that all of the teachings which follow are devoid of mistakes and falsehoods. That is why I intend to use very precise descriptions of these initial moves, because the consequences are so important. Having shown, through the four images of Zachary in Plate III, how to adopt the direct line, on the Circle, or on some other ground wherever it is, we shall now begin to describe Alexander’s actions, which were started and partially explained in Plate III, to show how to approach against the direct line posture and against the obtuse angle posture. Then we shall enter into a discussion of the value of the direct line posture, and the range of the First Instance (i.e. the first step in the fight sequence), to which we shall finally add the means of changing and adapting to different lengths of swords. | Ie croy, qu’il y en aura pluſieurs, qui n’auront pas ſi toſt jetté les yeux ſur ce Tableau IV. & ſur ſes eſcrits, qu’ils ne jugent tout à l’inſtant, que le ſujet en euſt eſté trop maigre pour un ſi long diſcours, ſi nous n’euſſions taſché plus toſt d’amplifier la matiere, que de la rendre ſimplement intelligible. Mais je les prie de conſiderer, que ce ſont icy les premiers fondements de la ſcience, qui tireroyent apres eux une trainee de difficultez infinies, & impoſsibles à reſoudre, en cas qu’ils ne fuſſent examinez curieuſement à l’entree de la diſcipline. Car comme les effećts ſe conforment touſiours à leurs cauſes, auſsi il ne faut pas douter, erreur eſtant le premier maiſtre, que toute la doćtrine enſuivante ne fuſt pleine d’abus & de tromperie. C’eſt pourqouy j’entends d’uſer d’une exaćt declaration de ces premiers commencements, puis qu’il en depend de ſi grandes conſequences. Ayant donc enſeigné par les quatre figures de Zacharie au Tabl. III. la maniere de donner la droite ligne, ſur le Cercle, ou ſur quelque autre plan, que ce ſoit; nous commencerons à deſcrire preſentement la pourſuite des operations d’Alexandre, à demi parachevées audit Tabl. III. pour faire ſes approches contre la droite ligne, & contre l’angle obtus; puis entrerons en diſcours touchant l’excellence du ceſte poſture de la droite ligne, & de la meſure de la premiere Inſtance; à quoy nous adjouſterons finalement la maniere de la changer & accommoder ſelon les diverſes meſures des Eſpees.
|
| Circle No 1. | Cercle N.1. |
| Alexander began his approach against the direct line, as shown by Circle No 1 in Plate III. Here he proceeds with the rest of it, as he arrives at the First Instance with the sword extended in direct line below his adversary’s sword. | Alexandre ayant commencé à faire ſes approches contre la droite ligne, en la forme qu’il eſt repreſentée au Tabl. III. Cercle N.1: il en pouſuit icy le reſte, en venant ſur la Permiere Inſtance avec l’eſpee eſtendue en droite ligne au deſſous de l’eſpee contraire. |
| In Circle No 1, as was explained in the preceding Plate, Zacharie has put himself on guard first, in the direct line posture, his right foot on the line X–Y, his toes touching the end at the circumference, his left foot on the Pedal Line Z, holding his body erect, and showing his profile to the enemy, in such a way that his head and the centre of his body are over the middle of the Quadrangle on which he stands. | Touchant le Cercle N.1. il a eſté dit au precedent Tableau, que Zacharie s’eſt mis le premier en campagne, en la posture de la droite ligne, le pied droit ſur la ligne XY, en touchant du bout d’iceluy la Circonference; & le pied gauche ſur la ligne Pedale Z, tenant le corps eſtendu en ligne perpendiculaire, & flanqué en pourfil ſur l’Ennemi; en telle ſorte que la teſte & le centre du corps reſpondent juſtement deſſus le milieu du Quadrangle, où il eſt placé. |
| To reach him, Alexander has taken two, three, or four paces forward, more or less, according to the distance, while freely carrying his sword however he wished. Then as he put his left foot down near the Circle, about one pace distant, so one more step with his right foot to C would put him into range in the First Instance, he straightened his arm and extended his sword out and down to the right. Following that, as he raises his right foot, he lifts the sword high up into an obtuse angle on the same side, as he prepares to make the final step, taking everything into account to precisely guage the distance to his adversary’s body, arm, and sword so he can put the tip of his sword near to the opponent’s guard and just underneath it along the same line, as he comes into range, and which will put him exactly at the First Instance, which will be described shortly. | Pour l’aborder, Alexandre fait deux, trois, ou quatre pas en avant, plus ou moins, ſelon la diſtance, & a porté ce temps pendant l’eſpee librement à ſa fantasie: puis en faiſant la demarche du pied gauche, & le venant à planter ſi pres du Cercle, qu’il pouvoit arriver du prochain pas, à faire du pied droit, ſur la Premiere Inſtance au point C, durant icelle demarche il a porté le bras eſtendu enſemble avec l’eſpee, en ligne droite, en bas, à ſon coſté droit; & en pourſuivant à eſlever le pied droit, & porter enſemblement le bras avec l’eſpee en haut, en angle obtus au meſme coſté, il s’eſt preparé pour faire le pas enſuivant tant plus juſte, en prenant la meſure à l’aulne de la veuë, au regard de la diſtance du corps, du bras, & de l’eſpee contraire; afin de porter ſa pointe tout pres de la garde contraire, & juſtement deſſous la meſme ligne, au meſme temps, qu’il entrera en meſure, & qu’il ſe mettra exaćtement ſur la Premiere Inſtance, en la maniere qui ſera tantoſt deſcrite. |
| All of these steps were previously shown and described in Circle No 1, in Plate III. In any case, it seemed necessary to show at this point, so as to explain certain points more fully, and likewise, to illustrate for you the full approach, rather than one or two disparate images in two Plates, neither of which would sufficiently clarify the other to the satisfaction of the reader. So let us see how he accomplishes this first approach, as shown here. | Iuſques icy toutes ſes aćtions ont eſté representées & declarées au Cercle N.1. du Tableau III. dont toutesfous il me ſemble, que la repreſentation a eſté neceſſaire en ceſt endroit, afin d’en expliquer quelques particularitez de plus pres, & pareillement pour vous mettre devant les yeux tout d’une approche, qui autrement reſembleront à un corps deſmembré, comme eſtant diviſé en deux Tableaux, ſans que l’un fuſt ſuffiſamment eſclarcy par l’autre au contentemēt du Lećteur. Voyons donc le parachevement de ceſte premiere approche, qui eſt tel. |
| Alexander begins by advancing the entire right side of his body, foot, arm, and sword together, dropping the blade downwards as it makes a circular sweep towards the front. At the same time as he puts his foot down on the circumference of the Circle, his toes at the point C, with his heel along the right hand side of the collateral line of the Quadrangle, he stiffens his arm and wrist, and circles the blade back upwards under the adversary’s sword until it is parallel, with the tip as close as possible to his opponent’s hilt without touching it, as shown by the figure. | Alexandre commençant à advancer egalement le coſté droit du corps, pied, bras, & eſpee enſemble; abaiſſe tout à l’inſtant ſa lame un peu circulairement vers le devant; & en metant le pied à terre ſur la Circonference du Cercle au point C, le talon d’iceluy ſur la ligne collaterale du Quadrangle à main droite, au meſme temps en roidiſſant le bras & le poignet de la main, il avance ſa lame circulairement en haut deſſous l’eſpee contraire en ligne parallele, en aſſituant la pointe droit à la garde contraire, le plus pres qu’il a peu faire, ſans toucher, ainſi qu’on voit en ſa figure. |
| This last motion of carrying the sword up under the opponent’s sword is made with impetus, so that the right side is pulled forward and so that the right foot easily spins on the ball of the foot onto the line C–B, and drawing the left foot along the ground to its natural place along the Pedal Line. At this instant, he straightens and draws upright, standing in profile, and finishes the movement of the sword in a direct line underneath his opponent’s sword. | Ce dernier mouvement de porter l’eſpee en haut deſſous l’eſpee contraire, il le fait avec une certaine impetuoſité, dequoy le coſté droit du corps eſt tiré en avant, & conſequemment le talon du meſme pied ſe gliſſe en dehors ſur la ligne CB, entrainant quand & quand le pied gauche par terre, juſqu’à ſa place ordinaire, qui eſt a ligne Pedale; auquel inſtant il ſe redreſſe le corps perpendiculairement, le mettant en pourfil, & finiſſant le mouvement de l’eſpee en ligne droite au deſſous de l’eſpee contraire. |
| In this way, they both stand in the same posture, with feet planted on the same lines, head and body centred over the same point, each on their own end, standing upright and tall and sideways, their nerves and muscles tensed, their knees and sword-arms straight, the handle held firmly in the fist, both blades parallel, side-by-side, above and below. The tip, the hilt, and the shoulder extending out in as straight a line as possible, parallel to the ground. A natural posture, which is very advantageous and convenient for both remaining in place and for moving, right, left, forwards, or backwards, without any hindrance. This is not true of other postures, such as they are. Because whatever advantages they have, they are outweighed by disadvantages. Only the direct line is a posture equiped equally well for attacking in all directions and also for defending against all attacks. | Par ainſi les voilà touts deux en pareille poſture, ayants les pieds plātez ſur meſmes lignes, la teſte & le centre du corps reſpondants au deſſus du meſme centre, chaſcun au ſien, les corps eſtendus perpendiculairemēt, & en flanc, touts les nerfs & muſcles tendus, les genoux, & le bras de l’eſpee roides, la poignee bien fort ſerrée dedans le poing, les deux lames colloquées en lignes paralleles deſſous & deſſus; la pointe, la garde, & l’eſpaule droite, tant qu’il eſt poſſible, en egale hauteur. Poſture du tout naturelle, qui a l’aſſituation des pieds, du corps, & de l’eſpee grandement favorable & avantageuſe, tant pour demeurer, que pour ſe bouger, à droite, à gauche, en avant, & en arriere, ſans nulle incommodité. Ce qui ne ſe rencontrera pas en des autres poſtures, quelles quelles ſoyent. Car pour les avantages qu’elles donnent, touſiours elles donnent pareillement autant ou plus de deſavantage en contreſchange. La ſeule droite ligne eſt une poſture à tout faire, munie de touts coſtez egalement, & egalement preparée de touts coſtez à ſa defenſe. |
| Circle No 2. | Cercle N.2. |
| Alexander follows the initial approach against the obtuse angle posture, which he started and half-completed in Circle N0 2 in the preceeding Plate, where he had just put the sword up beside his head, with his right foot raised and slightly ahead. As he is about to step to the First Instance, he will likewise adopt the obtuse posture against the opponent’s sword to the inside of the arm. | Alexandre pourſuit la premiere approche contre l’angle obtus, par luy commencé & à demi faite au Tableau precedent Cercle N.2. où il eſtoit venu juſqu’à ſe mettre l’eſpee à coſté de la teſte, avec le pied droit un peu avancé en l’air: maintenant en venant ſur la Premiere Inſtance, il la met pareillement en angle obtus contre l’autre en dedans du bras. |
| On Circle No 2, Zachary presents his sword in the obtuse angle posture, the rest of his body held the same as the previous Circle, so that these two postures are almost the same. Observe now how Alexander works against him. Having turned his toso to face him, he has approached with two, three, or four paces, more or less, according to the distance between them. He held his sword in the meantime in the crux of his left arm while stepping with the right foot. Again advancing,and putting his left foot on the ground about one pace away from the Circle, he turned the sword diagonally down at an acute angle towards his right side. As he lifted his right foot to step forward, he then raised the sword again, up beside his head, over his right shoulder, with the hilt in front of and about even with the shoulder and the tip up behind his head. | Sur le Cercle N.2. Zacharie preſente l’eſpee en angle obtus, tenant au reſte le corps tout de meſme, qu’au Cercle precedent; de façon que ces deux poſtures reviennent quaſi en une. Voyons comment c’eſt que Alexandre travaille alencontre. Ayant tourné la poitrine contre ſa partie, il s’eſt acheminé tout droit a luy, en faiſant deux, trois, ou quatre pas, plus ou moins, à meſure de la diſtance, qui eſt entre deux; ſe mettant cependant l’eſpee ſur le coude du bras gauche in avançant le pied droit; & derechef avançant, & mettant le gauche en terre, ſi pres du Cercle, qu’il peut atteindre la Circonference au premier pas enſuivant; il l’a portée diagonalement en avant vers ſa main droite en angle aigu: & puis l’a remontée encor pour la ſeconde fois, durant l’elevation & l’avancemēt du pied droit, à coſté de ſa teſte par deſſus l’eſpaule droite; tenant la garde un peu avancée ſur la hauteur d’icelle eſpaule, & la pointe un peu contremont par derriere la teſte. |
| All his actions to this point were described in the preceeding Plate. The rest follows here. | Iuſques à icy ſes aćtions on eſté deſcrites au Tableau precedent: s’en enſuit maintenant le reſte. |
| He advances the right side of his body, bringing the foot, his arm, and the sword forward at the same time. He places his foot on the side of the Quadrangle line C–B (Not on the collateral line as in the previous demonstration) drawing the left foot after, up to the Pedal Line. At the same time, he carries the sword forward, towards the enemy, raising it to an obtuse angle, and crossing both swords to the inside, with his 5th Span against Zachary’s 5th Span, but without doing anything against the sword. By this means, he readys himself to move in this way along the Diameter, by dominating the opponent’s sword at the Second Instance, which shall be explained elsewhere. | Il avance le coſté droit du corps, menant egalement au meſme tēps le pied, le bras, & l’eſpee; dont il plante le pied ſur le coſté du Quadrangle CB. (non pas ſur la collaterale, comme il a fait en la demonſtration precedente) laiſſant trainer le pied gauche apres, ſur la ligne Pedale; & au meſme temps, il porte l’eſpee en avant droit à l’Ennemi, la mettant contre icelle en angle obtus, en dedans du bras, Nombre 5. contre Nombre 5, ſans faire aucun effort alencontre; s’appreſtant par ce moyen à marcher par deçà le Diametre, en aſſujettiſſant l’eſpee contraire à la Seconde Inſtance, comme il ſera declaré autrepart. |
| Of all the postures which one might adopt, the Obtuse Angle is the strongest. No one wishes to give their adversary any advantage when he uses this one, so one must bring his sword to the same obtuse angle against it, and particularly if he intends to attack. If he were to try anything else, say, an attack along the direct line, the adversary would drop his blade down and interrupt the thrust along the direct line by taking a similar direct line, but over top of the other, and in a more natural and more powerful position. This is because movments which descend from above are assisted by forces of Nature. We call them natural moves. The other movements are unnatural and consequently weaker, some more, and some less. This can be manfestly seen when one person drops a rock from high up, and another person throws a rock upwards from below. One loses energy at every instant until it starts to fall back to the ground, as if exhausted from work. The other, falling from above, continuously gains energy. If the one should happen to hit the other, everyone knows that the one falling from above will affect the other more than the one thrown from below can affect the one falling, because the unnatural cannot resist natural forces any more than the weak can resist the strong, any more than one who is missing limbs can against someone fit, vigorous, and able. | Entre toutes ces poſtures, qui puiſſent eſtre, celle de l’angle obtus eſt la plus forte. Partant quiconque ne veut donner à ſa partie adverſe de l’avantage, lors qu’il en uſe; il faut qu’il porte ſon eſpee de meſme en angle obtus alencontre, & principalemēt s’il pretend de luy donner l’aſſaut. Car s’il y veut aller autrement, comme poſé qu’il le veuille attaquer avec la droite ligne, l’Adverſaire pourra laiſſer deſcendre au meſme temps l’eſpee de haut à bas, d’angle obtus en angle droit, & par ainſi rencontrer l’eſtocade de la ligne droite inferieure d’une ſemblable ligne droite, mais ſuperieur, & par conſequent plus naturelle, & plus puiſſante. Car les mouvements qui viennent de haut, ont la nature en aide; nous les appellons naturels. Les auſtres ſont violents, & par conſequent auſſi plus foibles, qui plus, & qui moins. Cela ſe voit manifeſtement par exemple, quand une pierre eſt jettée de haut en bas, & une autre jettée de la main d’une perſonne contremont. L’une perd à touts moments de ſa vigeur, de plus en plus juſqu’à tant qu’elle retombe d’elle meſme à terre, comme laſſée du travail, & opprimée de ſa propre charge. L’autre qui vient de haut, augmente continuellement ſa force. S’il advient, que ces deux pierres ſe rencontrent & choquent en l’air l’une contre l’autre, tout le monde ſait, que celle d’enhaut enforcera l’autre, & que le Violent ne pourra reſiſter au Naturel, non plus, que le foible au fort, ne celuy qui ſeroit perclus de ſes membres à un qui fuſt diſpoſt, gaillard, & habile. |
| It is the same with the practice of arms. The strong overcomes the weak, the natural defeats the unnatural. The superior and descending dominates the lower and ascending. To conclude, when the enemy has his sword at an obtuse angle, it is always necessary for us to adopt the same angle against him, so his moves are not more powerful than ours. | De meſme en eſt il en la Pratique des armes. Le fort a l’avantage par deſſus le foible, le naturel vainc le violent: le ſuperieur & deſcendant, domine l’inferieur, & aſcendant. Concluons donc, quand c’eſt qu l’Ennemi tient ſon eſpee en angle obtus, ſoit qu’il eſt touſiours neceſſaire de nous ſervir du meſme angle obtus alencontre, afin que ſes mouvements ne ſoyent ſuperieurs aux noſtres. |
| Circle No 3. | Cercle N.3. |
| Alexander has placed his left foot on the circumference at point C, and has moved his sword under the opponent’s sword, as shown in Circle No 3, in Plate III. He follows on by coming into the First Instance, crossing swords in an obtuse angle, on the outside of the arm. | Alexandre eſtant venu à planter le pied gauche à la Circonference au C, & enſemblement à mettre l’eſpee en angle aigu deſſous de l’eſpee contraire, ſuivant la Representation du Tabl. III. Cercle N.3. il pouſuit icy le reſte de ceſte ſeconde approche, en venant ſur la Premiere Inſtance, & accouplant derechef les eſpees en angle obtus en dehors du bras. |
| In Circle No 3, Zachary’s posture has not changed from the one before. But Alexander’s approach has, as described, below. | En ce Cercle N.3. la poſture de Zacharie ne differe en rien de la precedente: mais bien l’approche d’Alexandre, comme il apparoiſtra par la deſcription ſuivante. |
| As I say, Alexander has taken three or four steps according to the distance, holding the sword across the stomach, as described before after drawing the sword, or having rested it in the crook of his left arm. Finally, as he as come close enough to the circle with his right foot that one more pace will bring him to the First Instance, he raised his arm with the sword up at an obtuse angle a bit to the right. Again, as he raised, moved, and placed his left foot on the ground at the Circumference point C, he dropped the sword down to an acute angle, swinging it diagonally under his opponent’s sword, with his body leaning slightly back on the right knee, which is bent. | Ie di donc, qu’Alexandre a marché trois ou quatre pas en avant, à meſure de la diſtance; tenant du commencement l’eſpee de travers par devant ſa poitrine, en la maniere, qu’il a eſté dit cy deſſus apres le deſgainement, ou l’ayant couchée ſur le coude du bras gauche, & que finalement en approchant le pied droit ſi pres du Cercle, qu’il ne reſtoit qu’un pas à faire, pour venir à la Premiere Inſtance, il a hauſſé egalement le bras avec l’eſpee, en angle obtus un peu à coſté: & derechef en levant, avançant, & abaiſſant le pied gauche à terre, à la Circonference lettre C. il les a deſcendus egalemēt de haut en bas, portant l’eſpee diagonalement deſſous l’eſpee contraire en angle aigu, avec le corps panché un peu à l’envers ſur le genouil droit, iceluy eſtant plié. |
| Because this action will be used frequently at various occasions, I must caution you, when stepping into the First Instance with the left foot, and bringing the sword underneath the opposing blade at an acute angle, as much for attacking the enemy as for awaiting his attack, to always lean back on the right leg, with the right knee bent, to stay out of range this way, so he must take a larger step and take a longer time if he wishes to take advantage of his present superior position and attack, which is, at this point on his side. You, on the contrary, will find it easier to defend. | Puis que l’uſage de ceſte operation viendra ſouvant à point en pluſieurs occaſions, je vous averti, en mettant le pied gauche en terre, à la Premiere Inſtance, & portant l’eſpee deſſous l’eſpee contraire en angle aigu, tant pour travailler ſur l’Ennemi, que pour attendre ſa charge, de ce faire en toutes occaſions avec le ſuſdit panchement du corps ſur la jambe droite, le genouil d’icelle plié, pour demeurer tant plus hors de preſence, afin que s’il vouluſt travailler ſur vous avec l’avantage de la ſuperiorité, qui eſt pour le preſent de ſon coſté, il euſt beſoin d’un plus grand temps pour vous atteindre; & vous, au contraire plus de commodité pour faire la defence. |
| Everything Alexander has done up to this point was explained fully in the description of Plate III. Here is the rest. | Tout ce qu’Alexandre a fait juſques icy, a eſté declaré aſſez particulierement en la deſcription du Tableau III. En voicy donc à ceſte heure la pourſuite. |
| After having put his left foot on the Circumference at point C, he begins to shift his weight onto it, while lifting and moving his right foot forward, he raises his arm and sword at the same time into an obtuse angle. He contacts the opponent’s blade on the outside of the arm, his 6th Span against Zachary’s 5th Span, as shown in the picture. Thus having prepared to step with the right foot, which is at this moment in the air, with the right hand he subjugates the opponent’s sword at the Second Instance, as shall be shown hereafter in several places. | Ayant mis le pied gauche à la Circonference au point C, il commence à ſouſlever ſur iceluy ſon corps, en eſlevant & avancant le pied droit, & hauſſant au meſme temps le bras avec l’eſpee en angle obtus; l’accouplant avec l’eſpee contraire en dehors du bras Nombre 6. au Nombre 5: ainſi qu’il eſt demonſtré à ſa pourtraiture. S’eſtant par ainſi appreſté à marcher du pied droit, qui eſt à preſent en l’air, à main doite, en aſſujettiſſant l’eſpee contraire à la Seconde Inſtance; comme il ſera monſtré cy apres en pluſieurs endroits. |
| A note to the reader concerning this portrait of Alexander, that is does not match the description exactly. The left foot, which should be on the Circumference, is only about the middle of the Quadrangle. This was deliberate, so that it would not obscure the view of the figure behind, on the fourth Circle. | Cependent Lećteur ſoyez adverti touchant la pourtrait de ceſt figure d’Alexandre, qu’elle n’accorde pas du tout à noſtre deſcription: car le pied gauche, qui devoit eſtre toucher la Circonference, ne vient qu’environ le milieu du Quadrangle; ce qui a eſté fait out expres, afin qu’il n’empeſchaſt la veüe de la figure, qui ſe tient derriere, ſur le plan quatrieme. |
| Circle No 4. | Cercle N.4. |
| Alexandre has, once again, started to make his second approach against the direct line posture, and proceeded to the point where he has raised his sword up next to his head, with the right foot raised to step (as shown in the previous Plate, Circle No 4). He is about to enter into range in the First Instance, turning, and advancing his sword in a line parallel to and above his opponent’s. | Alexandre ayant recommencé à faire une ſeconde approche contre la droite ligne, & icelle pourſuivie juſqu’à porter l’eſpee à coſté de ſa teſte, avec le pied droit eſlevé (comme il eſt repreſenté au Tableau precedent Cercle N.4.) il entre icy en meſure à Premiere Inſtance, en tournant & avancant l’eſpee en ligne parallele au deſſus de l’autre. |
| Zacharie is again waiting in the direct line posture. Alexandre came up to him in the following way, that is, he took three or four steps and held the sword at an acute angle, down and forward until he took a step with his left foot, which brought him within one pace of the Circle, so that the next step would put him into the First Instance. As he raised his right foot and stepped forward, he brought the sword up high, beside his head, holding the hilt in front of his shoulder, and the tip up behind. This is according to the explanation in Plate III. I shall now explain how he proceeds. | Zacharie ſe tenant derechef en la posture de la droite ligne, Alexandre le vient aborder en la maniere ſuivante; c’eſt aſſavoir, qu’en ayant preallablement fait trois, ou quatre pas, & porté l’eſpee en avant en angle aigu, durant la demarche du pied gauche, par laquelle il s’eſt approché ſi pres du Cercle, qu’il pouvoit arriver deſormais en un pas à la Permiere Inſtance; conſequemment en eſlevant & avançant le pied droit, il a ramené l’eſpee en haut, à coſté de ſa teſte, tenant le pommeau d’icelle au devant, à la hauteur de l’eſpaule, & la pointe en derriere un peu hauſſée. Le tout ſuivant la declaration plus particuliere du Tableau III. Diſons maintenant comment il pourſuit à parachever le ſurplus. |
| He puts his right foot down at the letter C, turning the tip of his blade behind. He turns his wrist with a slight drop of the arm, until he brings it parallel to and above his opponent’s sword. | Le pied droit il met en terre à la lettre C, voltant la pointe de ſa lame en arriere: en touranant le poignet avec quelque petite deſcente du bras, juſques à la porter finalement par deſſus l’eſpee contraire en ce ligne parallele. |
| So, we have two ways to approach against a direct line position: one is shown in the first circle, the other in the fourth; of the two, the first is safest. Because, to move the sword-tip behind or to the side while moving into range with the right foot, against an enemy already on guard in the First Instance, what does that do, if not to give him a clear advantage to risk a good thrust, to naturally try, and close up, on one who has put himself into a position to have to make an unnatural, rising defence with slower, bigger movements, from further away? This is why I say, that this last method of approach by Alexander is quite a graceful way to move into position, but too dangerous when coming into range, and that the first method is the best in all sorts of circumstances. | Voilà donc deux manieres de faire ses approches contre la droite ligne: l’une qui est demonſtrée ſur le cercle premier, & l’autre ſur le quatrieme; dont la premiere eſt la plus ſeure. Car de porter ſa pointe derriere le dos, ou à coſté, cependant qu’on entre avec le pied droit en meſure, eſtant l’Ennemi ſur ſes gardes à la Premiere Inſtance, qu’eſt ce, ſinon luy donner un franc avantage de hazarder au meſme temps une bonne eſtocade, à tirer naturellement & de pres, ſur celuy qui ſe met en eſtat de faire ſa defenſe violentement contremont, avec des mouvements plus grands, & de plus loing? C’eſt ce qui me fait dire, que ceſte derniere operation d’Alexandre eſt aſſez gratieuſe pour ſe mettre le premier en poſture; mais trop dangereuſe pour entrer en meſure: & que la premiere c’eſt la meilleure en toute ſorte d’occurrences. |
| A DISCUSSION ON THE SUPERIORITY OF THE DIRECT LINE | DISCOVRS SUR L'EXCELLENCE DE LA DROITE LIGNE |
| This Direct Line posture that we have described is flawless and superior to all other postures. For this reason, throughout the book, Zachary will usually adopt it for his defence. We give Alexander, who is his adversary, an infinity of opportunities to start from this, because it is the most adaptable, and consequently most useful for instruction, and for exercises for Scholars, than any other. I assure you, that anyone who knows how to handle himself against this posture will, as well, fully understand how to face various other styles, whether against a single sword, or with weapons in the left-hand. By the end of the first book, we shall have seen so many of these postures and their counters, that all the rest can be easily worked out from the same lessons. | C’eſt poſture de la Droite ligne, que nous venons de deſcrir, eſt la plus noble; & la plus parfaite, de toutes: à raiſon dequoy Zacharie s’en ſervira ordinairement en ce livre pour defenſe, en donnant à Alexandre, qui eſt ſa partie adverſe, une infinité de differentes occaſions, dont elle eſt plus capable, & conſequemment auſsi plus utile aux inſtrućtions, & aux exercises des Eſcholiers, que nulle autre. Vous aſſeurant, que celuy qui ſe ſçaura bien gouverner alencontre d’icelle, comprenra auſsi bien tant de diverſes manieres, ſoit qu’ils ſe ſervent de l’eſpee ſeule, ou qu’ils l’aſsiſtent auſsi de la main gauche. Deſquelles poſtures, & de leurs contraires, nous avons inſeré ſur la fin du premier livre telle quantité, que tout le reſte s’en pourra facilement rapporter aux meſmes leçons. |
| Concerning the use of postures, it is my estimation that, when it comes to the question of skillful sword use, that someone who knows how to properly present a Direct Line posture, needs no other, for his defence, as far as defense depends on posture. One can see how much this burdens an attacker, when used skillfully, to wait, to beat back, and to dominate even the most forceful attacks, even from the greatest swordsman, if he practises only the old styles. But when it comes to serious swordplay, and above all when life is in danger, there is no guard, neither high nor low, neither distant or close, no body position, no special way of gripping the sword, that could make this better. It is true that this book is filled with examples of Direct Line postures, but this is for instruction. When it comes to practice, I wish that our scholar should abandon all that, and that he take upon himself the same expessions and attitudes as those who have elegant fighting styles, whether his enemy is standing in a posture, advancing, or using his sword. He shall continue to move, using a frank, natural pace, to one or the other of the two sides, always avoiding the Diameter Line, where the Enemy stands erect, and always keeps, to the extent possible, the bodies, the Diameters, the positions, and movements in an unequal state. Because to work against an adversary, one must have an advantage, and to have an advantage, one must have inequality. Between things that are equal, being equal, there is no prerogative. As soon as he comes into range, he must make sure of his adversary’s sword, attacking it to subjugate it, or force it aside, or to cover it, or using it to conveniently guide his critical thrusts. He must continually step without interruption. Of course he must adapt to different circumstances, but never plant his feet on the ground as if in a posture, except when safely and securely inside his opponent’s line while at the same time executing an opportunistic strike. Then, and only then, he may break the continuous flow of motion, but absolutely not before this. Because a body in motion is also quicker to change and adapt its movements to all occasions, than one frozen in a posture, and because, as much as to take command of the situation, one must first begin to take action, which makes you ready to turn, return, step aside, avoid, and, in sum, make all the required moves promptly, with swiftness and ease. | Touchant l’uſage des poſtures, j’eſtime, s’il eſt queſtion de tirer des armes par courtoiſie, celuy qui ſçaura bien preſenter la droite ligne, n’en avoir beſoin de nulle autre, pour ſa defenſe, ſi la defenſe depend deſ poſtures; voire qu’elle ſera baſtante à celuy, qui en ſçaura dextrement uſer, pour attendre, rabatre, & domter touts les plus rudes aſſauts, meſme du plus grād tireur d’armes, moyennant qu’il ne pratique que le vieil ſtile. Mais quand il ſeroit queſtion de tirer à bon, & ſur tout, quand il y iroit de la vie, il n’y a nulle garde, haute ne baſſe, longue ne courte, nulle poſture de corps, nulle tenue d’eſpee, & fuſt elle qualifiée de touts les avantages poſsibles, en laquelle on ſe doive arreſter pour attendre. Il eſt vray, que ce livre eſt grandement rempli des poſtures de la droite ligne; mais ce n’eſt que pour donner inſtrućtion. Quand ce viendra à l’a Pratique, je veux que noſtre Eſcholier abandonne tout celà; & qu’il tienne, quant à luy, la meſme contenance & les mines de ceux qui ſe donnent l’aſſaut à bon eſcient, ſoit que l’Ennemi ſe tienne arreſté en poſture, ſoit qu’il s’avance, ou qu’il travaille. Il continuera touſiours à cheminer, en uſant d’une demarche franche & naturelle, vers l’un ou l’autre des deux coſtez, fuyant ſur tout la ligne du Diametre, où le corps de l’Ennemi eſt dreſſé, & tenant perpetuellement, tant qu’il ſera poſsible, les corps, les diametres, inſtances, & mouvements en deſgalité. Car pour bien travailler ſur l’Adverſaire, il faut de l’avantage; & pour avoir de l’avantage il faut de la deſgalité; eſtant impoſſible qu’entre choſes egales, entant qu’egales, il y ait aucune prerogative. Si toſt qu’il viendra à meſure, il s’aſſeurera de l’eſpee contraire, en l’attaquant pour l’aſſujettir, ou obliger, ou en la couvrant, ou en tirant au long d’icelle des eſtocades de premiere intention, s’il en a la commodité; continuant touſiours ſa demarche ſans nulle interruption: vray eſt qu’il ſe comportera diverſement ſelon la diverſité des occaſions; mais jamais ne plantera les deux pieds enſemble en terre en forme de poſture, ſi ce n’eſt quand il ſe mettra dedans la ligne de l’eſpee contraire en lieu ſeur & libre, en executant au meſme temps le coup qui ſera donné ſelon l’exigence. Là luy eſt permis de rompre aucunement la courſe de ſes aćtions, mais point devant; à raiſon que le corps qui eſt en aćte de ſe mouvoir, eſt auſsi plus prompt à changer & accommoder ſes mouvements à toutes occaſions, que non pas quand il ſe tient arreſté en poſture. Car auſsi bien pour l’avoir à commandement, on eſt contraint de le met~re premierement en branſle, qui luy ſert d’une preparation pour ſe diſpoſer à ſe tourner, retourner, virer, & en ſomme à faire toutes ſes affaires avec viſteſſe, promptitude, & facilité requiſe. |
| Enough concerning postures in general. Let us return now to the subject of the Direct Line. As I have said, it is the best posture of all, and I shall now prove how True this statement is. All the postures that try to avoid contact with the blade before striking (these are the ones which get away from presenting the sword in a straight line) can be made useless, by taking aim at them when you make the first strike. Thus the enemy is hit, or he is forced to parry, and in parrying, he uncovers some new part of himself. This way, if one threatens with the tip it will force him out of his posture, and enter into a labyrinth of strikes and counters. This is also the reason why those who use these postures, recognizing through experience their defects, only half-trust them, relying on the dagger in their left hand to fight. Which shows how little confidence they have, and how little knowledge, of the power of the sword. They do not know it is sufficient by itself, it is all that is needed to attack and defend. But what am I saying? One should not be surprised, if those who have no interest in the science of fighting with weapons try to become very fast only through long and continual practice, and so they may succeed by overcoming and beating their opponents, rather than constraining them, not understanding the secrets of such an impressive shield. Nothing they do is founded on true reason and solid theory, but in simple and badly-founded practice, so that comparing their Fencing to the True Art of Wielding Arms, is like elevating a manual of mechanics to be equal to mathematical ingeniousness. The first are content merely to produce an effect, even if it is by chance, and the others champion nothing that is not built upon infallable rules. | Voilà touchant les poſtures en general; retournons à la Droite ligne; & puis que nous venons de dire, que c’eſt la plus parfaite de toutes, faiſons paroiſtre ceſte verité par bonnes preuves. Toutes les poſtures qui ne contraignent pas de toucher la lame, avant que de tirer, (ce ſont celles qui s’eſloignent de preſenter l’eſpee en ligne droite) on les peut rendre inutiles, en tirant deſſus pour fraper tout du premier abord; dont l’Ennemi en demeure atteint, ou il eſt contraint de parer, & en parant il ſe deſcouvre touſiours en quelque nouvel endroit du corps; de façon que ſi on dreſſe là ſa pointe, on le fera ſortir de ſa poſture, & entrer en un labirinthe de parades. C’eſt auſsi la cauſe, pourquoy ceux qui uſent de ces poſtures, en recognoiſſants par experience l’imperfećtion, ne s’y fient qu’à demi prennants recours à l’aſsiſtance de la main gauche. En quoy ils demonſtrent bien le peu d’eſtime, & le peu de cognoiſſance, qu’ils ont, du grand pouvoir de l’eſpee; ne ſachants pas qu’elle eſt ſuffiſament qualifiée d’elle meſme, de tout ce qui eſt requis & à donner l’aſſaut, & à faire la defence. Mais que di-je? Il ne ſe faut pas eſtonner, ſi ceux qui n’aſpirent à aucune ſcience des armes, ains ſeulement taſchent de parvenir par longs & continuels exercices à une viſteſſe du corps, & du bras, dont ils ſe puiſſent prevaloir, en prevenant & abuſant leurs Contraires, plus toſt que de les contraintre, ne comprennent pas les ſecrets d’une Armure ſi noble; & que tout ce qu’ils font n’eſt fondé en aucune raiſon de vraye & ſolide Theorie, mais en ſimple & mal aſſeurée Pratique, de façon que de vouloir comparer leur Eſcrime au vray Art de manier les armes, c’eſt tout autant que de mettre en parangon le manuel des œuvres Mechaniques avec les inventions des Mathematiques; dont les unes ſe contentent d’obtenir ſeulement l’effećt, encor que ce fuſt par hazard; & les autres n’advouent rien pour bon qui ne ſoit fondé ſur des regles infallibles. |
| Thus, to understand the superiority of the Direct Line, the foremost of all the postures, let us consider that the body is in an entirely natural position, convenient and ready to work, to move in all directions equally: forward, backwards, left, and right, extending, or shortening the paces as needed, with no other preparation, having the arm and sword out in front in a straight line, and ready to parry all sorts of thrusts, cuts, and back-cuts, without using any excessive motions against them. Observe how the head, shoulders, and trunk down to the pectorals are covered by the guard. So well, that the enemy cannot attack them, not without passing his tip, which is the weak part of the sword, over your guard, which is the strongest part of the sword. It can be compared to a town’s boulevard, or a fortress, built to withstand a large army with a small garrison. Because if your enemy should chance to take aim at these above-listed body parts, as soon as your eye catches the beginning of his movement, you prepare to defend against him, to receive the weak part of his blade with the crosspiece of your guard, at about the 3rd or 4th Span, before the point can pass or reach your elbow. As you continue to slide the point of contact along the blade, you move forward and flank him from a little bit beside the Diameter. In this way he will be forced to withdraw from the direct line which you will now control, and all you will need to do is put the point between his eyes, stopping exactly in front or driving forcefully in, as you desire. | Pour donc comprendre l’excellence de ceſte Droite ligne, la premiere de toutes les poſtures; conſiderons qu’elle retient le corps en une ſituation du tout naturelle, & commode, & diſpoſée à travailler, & à ſe tranſporter de toutes parts egalement; en avant, en arriere, à droite, & à gauche, en allongeant, ou en raccouciſſant la demarche, ainſi que bon luy ſemble, ſans nulle autre preparation: ayant le bras & l’eſpee avancez en ligne droite, & appreſtez à parer toute ſorte d’eſtocades, eſtramaçons, & revers, ſans uſer alencontre d’aucuns mouvements extremes. Voire que la teſte, & les eſpaules, & la poitrine juſqu’à l’endroit des tetins, y ſont couverts de la garde; ſi bien que l’Ennemi ne les peut offenſer, ſi non en paſſant de ſa pointe, qui eſt le foible de l’eſpee, du long de la garde, qui en eſt le fort: & à bon droit ſe compare à un boulevart de ville, ou à une fortereſſe, baſtante à ſouſtenir l’effort d’une grande armee avec bien peu de gens. Que s’il advient donc, que l’Ennemi ſe hazarde de tirer vers les parties ſuſdites, tout à l’inſtant que vous appercevrez à veue d’œil le commencement de ſon mouvement, vous ferez voſtre preparation alencontre, pour accueillir de la branche voſtre garde le foible ſa lame à Nombre 3. ou 4. avant que ſa pointe puiſſe arriver, ou paſſer l’endroit de voſtre coude; en continuant à la graduer, & vous avancer & flancquer ſur luy un peu à coſté le Diametre; en ſorte qu’il ſera contraint de vous quitter la droite ligne, laquelle vous demeurera franche, & ne tiendra qu’à vous, de luy mettre la pointe devant les yeux, en l’arreſtant par courtoiſie, ou de l’executer par rigueur, ſelon voſtre appetit. |
| For one who percieves the lack of advantage he would have by coming so close to your guard, either to the inside or the outside of the arm, he might try to hit you in the stomach, by dropping the point. He would not be considering the fact that the more he moves off the straight line and the closest place he could reach, which is your shoulder, the more he loses from the length of his sword, which is why by doing this, he is giving you more time to see, observe, and judge all his moves. You will have little other to do than fold the stomach while leaning the torso forward, and placing the tip of your sword on his shoulder. Because by doing this, if you are equals, if you have likewise equal swords, your Direct line will be able to hit him, while his tip will still be at least a foot away from you. Thus all these actions along with several others, which demonstrate so clearly the advantages of this posture, are shown in Plate V, which shall serve in this regard as proof of the Direct Line, as it shall be, in the majority of the Plates that follow, the principal subject of the exercises. | Que ſi en recognoiſſant le peu d’avantage, qu’il auroit à venir ſi pres de voſtre garde, tant en dehors, comme en dedans du bras, il taſche à vous fraper au ventre, en abaiſſant la pointe; ſans conſiderer qu’autant qu’il s’eſloigne de la droite ligne, & du plus prochain endroit de l’attouchement, qui eſt voſtre eſpaule droite, autant il perd ſur la longueur de ſon eſpee, à raiſon dequoy il vous donne auſsi plus de loiſir de voir, diſcerner, & juger touts ſes mouvements: vous n’aurez autre choſe à faire, ſinon de creuſer au meſme temps un peu le ventre, en panchant de la poitrine ſur le devant, & aſſituant la pointe de voſtre eſpee à ſon eſpaule. Car en ce faiſant, ſi vous eſtes egauz, & que vous ayez pareillement les eſpees egales, voſtre droite ligne le pourra toucher, lors que ſa pointe ſera encor eſloignée de vous de plus d’un pied de diſtance. Or toutes ces operations avec quelques autres, qui demonſtrent ſi clairement les avantages de ceſte poſture, ſeront repreſentées au Tabl.V. qui nous ſervira pour ceſt eſgard d’une preuve de la droite ligne, comme de celle qui ſera en la pluspart des Tables ſuivantes le principal ſujet de l’exercice. |
| Some wish to approach this posture with feints from a distance and out of range, following the ordinary practice of the old mode, and trying, by these means, to confuse the Adversary, to be able to hit him while he is uncovered. All of this is for nothing, as the Direct line is sufficient to defend oneself, inasmuch as one does not need to move oneself against these feints, any more than a horse stops at the yapping of a small beast. But if he dares come into range with his feints, and his blade passes your guard as far as Span 2, 3, or 4, either inside or outside, thinking to make you parry and move your sword to the side, he, himself, runs the risk of receiving rather than giving, if you, yourself, approach him in a Direct Line, at the same instant that he approaches, keeping your sword moving forward in a straight line. He can hardly keep from being wounded himself. | De voulouir aborder ceſte poſture avec des feintes tirées de loing & hors de meſure, ſuivant l’ordinaire de la vieille mode, en taſchant par icelles de mettre l’Averſaire en confuſion, pour le fraper au deſcouvert de ſes arme: tout cela n’en eſt rien, d’autant que la droite ligne eſt ſuffiſante à s’en defendre d’elle meſme, de ſorte qu’elle ne ſe doit mouvoir à l’occaſion de telles feintes, non plus qu’un cheval ne s’arreſte à l’abbayement temeraire de quelque petite beſtiole. Mais s’il oſe entrer avec ſes feintes en meſure, & paſſer de ſa lame voſtre garde juſqu’aux Nombres 2. 3. ou 4. ſoit en dehors, ſoit en dedans, penſant de vous faire parer & eſcarter voſtre eſpee; il courra luy meſme grand fortune de recevoir au lieu de donner, ſi vous vous approchez devers luy à meſme grand inſtant qu’il s’approche, en continuant à advancer ſeulement voſtre eſpee en droite ligne: car à peine ſe pourra il garder de ne ſe bleſſer luy meſme. |
| Say he intends to clear your sword from the line, he attacks in the ancient style, either to the inside or outside to engage your sword, while at the same time he advances one foot or the other along the Diameter, so as to come within range to hit you. It will be necessary, for him to achieve this effect, to create a large opening by moving his tip so far away from you, that he will deprive himself of all defense, and will make himself a target for various thrusts and cuts, as shall be satisfactorily shown, below. | Si pour faire ſortir voſtre eſpee de la ſituation, il la vient attaquer à la mode ancienne, en dehors ou en dedans, pour l’engager, en avançant quand & quand l’un ou l’autre des pieds ſur le Diametre, afin de gagner la meſure de vous pouvoir toucher; il luy ſera beſoing pour trouver ceſt effećt de faire avec ſon eſpee une grande ouverture, en eſcartant la pointe ſi loing de vous, qu’il ſe prive luy meſme de toute defenſe, & ſe mette en bute à pluſieurs coups de pointe & de taille, comme il ſera monſtré en la dedućtion de ces eſcrits, à voſtre entier contentement. |
| He might use another means, to attack you. He will try to bring his blade under yours, by bending his body and moving the right arm forward, together with the left hand, hoping to get close enough to your tip to beat it, and then hit you with a thrust in second time. If he makes his approach in this manner, here is the solution. At the same instant that he moves into place, where he hopes to beat aside your tip, you must likewise close on him, stepping a bit outside on the right hand side, turning your right side towards him, raising your sword-tip up and the guard down, to protect your lower areas. When this preparation is skillfully done, whether he follows up with an attack or whether he stays on guard, you will have the means to hit your target. These and other such proofs will be explored in Plate XXVII, where you will likewise find the reasons, drawn from fine, clear, beautiful, and self-evident demonstrations. | Il pourra uſer d’encor une autre pratique, pour vous aſſaillir. c’eſt qu’il viendra porter ſa lame deſſous la voſtre, en courbant le corps, & avançant le bras droit, enſemble avec la main gauche, en eſpoir de l’approcher aſſez pres de voſtre pointe, pour le battre, & puis vous tirer une eſtocade au ſecond temps. S’il fait ſon approche en ceſte maniere, en voycy le remede. Au meſme inſtant qu’il entre ſur le lieu, où il s’attend de vous battre la pointe, il faut que vous entriez pareillement deſſus luy, en marchant un peu en dehors à main droite, vous mettant ſur le coſté droit, la pointe montante, & la garde baſſe, pour vous en couvrir les parties inferieures. ceſte preparation eſtant dextrement faite, ſoit qu’il pourſuive à travailler ſur vous, ſoit qu’il demeure ſur la parade, vous aurez moyen de le toucher à voſtre poſte. Telles & ſemblables preuves ſeront propoſées au Tabl. XXVII. où vous en trouverez pareillement les raiſons, tirées de demonſtrations autant evidentes, & certaines, que belles, & admirables. |
| One could suggest even more tests of the Direct Line if these here were not sufficient to carry the knowledge that this is the finest, and most secure of all the positions with regard to defense. It is true that those who are not adept at this Exercise, may not be able to use this to defend themselves against the aforesaid tests, but the imperfection of their ignorance should not become a prejudice against the perfection of this posture. The fault is in those who do not know how to apply this at the proper timing and distance, which is easy for others. However much we praise and applaud this, that is not to say that there aren’t a number of ways to work against it, even gaining some advantage. But I conclude it would be very difficult, even impossible, for all those who have not seriously trained in the practical application of our principles. The principal reason comes from the fact that when the tip of the sword is in the Direct line, is such a threat to the adversary, that he does not know how to work against it, except by moving it away. For this reason he is constrained to cross swords, and thereby give you the means to know his intent by the feel of the weight and force he uses. This is an warning of his plans, and a guide for counter actions. By this way, this posture is like a closed room, where one cannot enter without the goodwill of the master of the house. So one is constrainted to strike against him, to come in. All the other positions, as many as they are, even that of the obtuse angle, are like open rooms, where one can rummage around however one likes. For one can hit their body, without running into their sword. It follows then, that the difficulty of working against the Direct line is entirely evident. Thus one must also conclude that one’s adversaries will need to be very talented and able, which is why, as much because one is able to use it in a wide variety of occasions, we chose it to train our scholar. So that, having first learned to overcome this difficult point, he will be even easily able to work through the rest, which will be for him but the least amount of effort. | L’on pourroit propoſer encore d’autres preuves de la Droite ligne, ſi celles cy ne fuſſent baſtantes pour donner à cognoiſtre, qu’elle eſt la premiere, & la plus ſeure de toutes au regard de la defenſe. Il eſt vray que ceux qui ne ſont pas adroits en l’Exercice, ne ſe pourront pas defendre avec icelle contre les ſuſdites preuves; mais l’imperfećtion de leur ignorance ne doit tourner en prejudice à la perfećtion de la poſture. la faute en ſera en ce qu’ils ne la ſçauront appliquer aux temps & aux diſtances, qu’elle demande; ce qui ſera facile aux autres. Or quoy que nous la priſons & exaltions tant, ce n’eſt pas pourtant à dire, qu’il ne ſe trouve aſſez de moyens de travailler alencontre, meſmes avec avantage: mais nous jugeons que cela ſera tres difficile, voire impoſſible à touts ceux qui ne ſe ſeront exercez ſerieuſement en la meſme pratique de nos preceptes. Dont la cauſe principale giſt en ce, que la pointe de l’eſpee ſituée en ligne droite, eſt ſi fort en preſence à l’Adverſaire, qu’il ne ſçauroit travailler, ſinon en la divertiſſant de ſa ſituation. à raiſon dequoy il eſt contraint de venir à l’attouchement, & de vous preſenter le moyen de cognoiſtre par le ſentiment le poids & la force, dequoy il uſe. qui eſt un advertiſſement de touts les deſſeins, & une reigle de toutes les aćtions contraires. De maniere que ceſte poſture reſſemble à une chambre fermée, où lon ne peut entrer ſans congé du maiſtre de la maiſon; ains eſt on contraint de fraper à l’huis, pour entrer avec permiſſion. Toutes les autres, tant qu’il y en a, meſmes celle de l’angle obtus, reſemblent à une chambre ouverte, où on ſe peut fourrer dedans maugré qu’ils en ayent: car on leur peut toucher le corps, ſans venir à l’eſpee. S’enſuit donc que la difficulté de travailler ſur la droite ligne eſt toute evidente. dont il faut auſſi conclure, que ſes contraires ont beſoing de plus grand artifice: pour laquelle cauſe, comme auſſi pour ce qu’elle eſt capable d’une grande varieté de diverſifier ſes occaſions, nous l’avons choiſie, pour y exercer noſtre Eſcholier; afin que ayant premierement rompu ceſte pointe de difficultez, il ſe rende en apres tant plus aiſement capable de foncer tout le ſurplus, qui ne ſera que la moindre partie de la beſogne. |
| All that we have discussed up until this point has been concerned with the superiority of the Direct line with respect to the sword. We now shall speak more particularly with regard to the feet. Because the feet govern all movement, extending or shortening steps, speeding them up or slowing them down, they support, raise, lower, and straighten the body, there is nothing more necessary than to understand how to use them in the most convenient and natural way, so as to always be at the closest possible distance at all times. This is the situation: Zachary is standing firm, right foot on the outside edge of the Quadrangle that runs X-Y with his toes on the circumference of the Circle at X and the left foot along the Pedal Line. Alexander is also standing with his feet at the opposite end of the diagram, his right foot on the side of the Quadrangle that runs C-B, likewise with his toes at C and his left foot on the Pedal Line at A. All this is clearly is clearly shown in the diagram of Circle No 1 in Plate I where we have shown through the footprints how the two adversaries should stand in the First Instance. This is what we call the true foundation of all the ranges, and the single beginning of all attacks and defenses. This arrangement of the feet is not only correct as a way to present your sword in the Direct Line posture, but also to hold it together, so the body is naturally ready for any changes, and to move easily (which is the function of the feet) from one place to another. | Par ce qui a eſté diſcouru juſqu’à preſent, a eſté demonſtrée l’excellence de la Droite ligne au regard de la tenue de l’eſpee: maintenant nous en parlerons auſsi plus particulierement au regard de la ſituation des pieds. Car puis que les pieds moderent touts les mouvements, allongent les pas, les raccourciſſent, les haſtent, ou les retardent, ils ſouſlevent, hauſſent, baiſſent, redreſſent le corps, il n’eſt rien plus neceſſaire, que de bien entendre, quelle en eſt la ſituation la plus commode & naturelle, afin de s’en eſloigner le moins, qu’il eſt poſsible, en toutes ſes aćtions. Or voicy la ſituation dont nous parlons: Zacharie ſe tient planté, le pied droit ſur le coſté exterieure du Quadrangle XY. en touchant de ſes orteils la Circonference du Cercle à la lettre X. & le pied gauche ſur la ligne Pedale. Alexandre tenant auſſi les pieds de meſme à l’autre bout du plan: le pied droit ſur le coſté du Quadrangle CB. en touchant pareillement la lettre C. & le pied gauche ſur la Pedale A. le tout ſe voit plus clairement tracé en figure plane au premier Cercle du Tabl. I. où nous avons exprimé par la repreſentation des pieds, comment parties ſe doivent mettre ſur la Premiere Inſtance: laquelle nous tenons pour le vray fondement de toutes les meſures, & pour l’unique entree de touts aſſauts & defenſes. Ceſte ſituation de pieds n’eſt pas ſeulement propre pour l’effećt de preſenter l’eſpee en ligne droite, mais auſsi pour tenir les forces touſiours unies & le corps naturellement preſt à touts changemens, & à ſe tranſporter aiſement (qui eſt le propre office des pieds) de l’une place en l’autre. |
| If you wish to see the proof, leave the left foot where it is, on the Pedal Line, and turn the heel of your right foot inside, along the extended Diameter, leaving your toes at C without changing anything, the sword and arm extended in a straight line above the Diameter. I assure you that you will find the limbs of the upper body straining against the limbs of the lower body. You will find it very difficult to keep the sword in the same line. Furthermore, when trying to move the right foot to the Second Instance, either to the left or to the right, it cannot be done without being forced to turn the foot in mid-step, into its true aspect, as it was at first. Otherwise the pace would be cramped and slow. It is true that if you change the foot as just described you will increase the force of the sword to the outside. If the enemy tries to cross your sword from that side, either to move it away or subjugate it, you can resist him with less force, if you are holding your sword as we described. But as much as it is useful against the outside line, it is that much less useful to the inside, because as much as the force is increased to one side, it is weakened on the other. | Si vous en demandez la preuve. Laiſſez le pied gauche, ainſi qu’il eſt, ſur la ligne ordinaire; & tournez ſeulement le talon du pied droit en dedans ſur le Diametre prolongé, laiſſant les orteils à la lettre C. ſans varier, le bras eſtendu avec l’eſpee en ligne droite au deſſus du Diametre. je di qu’en ce faiſant vous ſentirez que les membres de la partie ſuperieure du corps conteſteront contre les membres de la partie inferieure; & qu’à grand peine pourrez vous continuer à tenir l’eſpee en la meſme ligne. D’avantage en cheminant avec le pied droit vers la Deuxieme Inſtance, ſoit à main droite, ſoit à gauche, il ne ſe pourra faire, que vous ne ſoyez contraint de tourner le pied environ la mi voye en ſa vraye ſituation, où il avoit premierement eſté. autrement la demarche en ſera plus moleſte, & plus tardive. Il eſt vray que le changement du pied, eſtant fait en la forme dernierement dite, vous augmentera la force de l’eſpee par dehors; & que ſi l’Ennemi la vient toucher de ce coſté là, pour l’emmener, ou pour l’aſſujetir, vous luy pourrez faire reſiſtence avec moins de force, qu’en le tenant ſelon la forme de noſtre deſcription: mais autant que cela vous ſera profitable en dehors, autant il ſera nuiſible en dedans: car à meſure que la vigueur ſe reforce de l’un des coſtez, autant elles s’affoiblit de l’autre. |
| For the second proof, do like this. Leave the left foot where itis, turning the heel of the right foot outwards, until it is on the Circumference of the Circle. By doing this, I assure you, that if the Enemy tries to contact your sword to the inside to subjugate it, or move it aside, it will be very easy for you to resist, because of the increased force to the inside. But in exchange, you will be equally weakened to the outside. In summary, the situation is exactly the opposite of the previous one, and the effects are exactly opposite. | Pour la ſeconde preuve, faites ainſi. Laiſſez le pied gauche, & tournez ſeulement le talon du pied droit en dehors juſqu’à la Circonference du Cercle. En ce faiſant, je di, que ſi l’Ennemi vient toucher voſtre eſpee en dedans pour l’aſſujetir, ou pour la tranſporter, il vous ſera tres-facile de luy reſiſter, à cauſe de l’accroiſſement de la force en dedans: mais en eſchange vous ſerez d’autant plus affoibli en dehors. Somme ceſte ſituation du pied eſtant direćtement contraire à la precedente, auſſi les effećts en ſont du tout contraires. |
| Another proof. Leave the right foot where it is, and turn the toes of the left foot inwards onto the Extended Diameter, without moving the sword off the Direct Line. I tell you now that, by doing this, apart from the discomfort to the body that comes from the twisting of the limbs, if the Enemy tries to attack you from inside, he will have the advantage. For, just as the position of the feet weakens the sword, it also turns the whole body rightwards, to the outside. | Autre preuve. Laiſſez le pied droit immobile, & tournez ſeulement les orteils du pied gauche en dedans ſur le Diametre prolongé, ſans ſortir l’eſpee de la droite ligne; je di qu’en ce faiſant, outre le mal-aiſe du corps, procedant du retorſement des membres; ſi l’Ennemi vous vient attaquer par dedans, il ye trouvera de l’avantage: d’autant que le dedans de l’eſpee eſt affoibli par la ſituation des pieds, eſtant le corps incliné de luy meſme à ſe tourner en dehors à la main droite. |
| The contrary will happen if you turn the left foot outwards, with the toes back along the Extended Diameter, while leaving the sword in the direct line, as before. For apart from the discomfort of the posture, the sword will be weakened to the outside, which means you cannot resist on that side, except with difficulty. Because the arm of the sword will be forced by the location of the foot and the tension on the muscles of the left leg, to turn to the left. | Le contraire en aviendra, ſi vous tournez le pied gauche en dehors, avec les orteils en arriere ſur le Diametre prolongé, laſſant l’eſpee en ligne droite, comme au paravant. Car outre le malaiſe de la poſture, l’eſpee ſera tellement affoiblie par dehors, que vous n’en pourrez faire aucune reſiſtence de ce coſté là ſi ce n’eſt avec grand travail: à cauſe que le bras de l’eſpee ſera comme forcé, par la collocation du pied & des muſcles de la jambe gauche, à ſe tourner devers le coſté gauche. |
| We have described situations that are, admittedly, extreme. It would be unusual if someone placed their feet down in such a disorderly way that we have described. But that is not really the problem. Anyone who fully understands the greater possible faults will be able to understand as well the subtler ones, providing they can be shown through the same means. What we have done is to make obvious the difference in strengthening and weakening according to the position of the feet. As to the use of these proofs and even the precepts, it is completely obvious: the knowledge of how to attack the adversary’s sword on the side which will be weakest. As much as the weak part of the blade can not resist, and will be overcome by its opponent, so the strong part can govern all its actions with a little work. The weak part of the blade is restricted, in sum, to exploiting opportunities to wound in various ways, by those with sufficient sensitivity. This shall be explained further in our Plates. | Nous avons deſcrit ces examples aſſez extremes. car de vray il aviendra peu ſouvent, que quelquun plante ſes pieds ſi deſordonnement, comme nous venons de prepreſenter. mais il n’y a point de difficulté en cela; car qui entendra bien les fautes plus lourdes, il comprendra auſſi bien toſt les plus ſubtiles, moyennant qu’elles puiſſent eſtre deſcouvertes par les meſmes preuves: ce que nous en avons fait, c’à eſté afin que la difference du renforcement & de l’affoibliſſement en fuſt d’autant plus evidente. Quant à l’uſage de ces preuves & des preceptes meſmes, il eſt tout manifeſte: c’eſt aſſavoir, de monſtrer la maniere d’attaquer l’eſpee contraire par le coſté qui ſera plus foible. d’autant que le foible eſt incapable de reſiſter, & preſt à eſtre ſurmonté de ſon contraire. le fort peut moderer toutes ſes aćtions avec un peu de travail: le foible eſt contraint ſomme à donner occaſions de bleſſer en pluſieurs manieres, pour celuy qui cognoiſt la valeur du ſentiment: comme il ſera declaré en la ſuite de nos Tableaux. |
| One must also observe the correct space between the two feet. This is shown clearly enough by the lines in the Quadrangle. If one stands otherwise, for example, with feet together and one tries to raise the right foot to take a step forward, the centre of mass must stay on the left foot, and will be forced to perform some other preparation (for example leaning the body forward) to give his pace impetus before he moves. Which is a superfluous move and noticeable warning to the enemy who can see what you are about to try. | Il faut auſſi obſerver en ceſte ſituation des pieds la juſte eſpace qui eſt entre deux; qui eſt repreſentée aſſez clairement par les lignes du Quadrangle. Car ſi on met autrement, par exemple à pieds joints, & qu’on commence à lever le pied droit pour marcher, le centre du corps demeurera ſur le gauche, & ſera on contraint d’y adjouſter encor quelque autre preparation (comme depancher le corps un peu en avant) pour luy donner ſa courſe, devant qu’il chemine. Qui eſt un mouvement ſuperflu, & un remarquable advertiſſement à l’Ennemi pour deſcouvrir & prevenir toutes vos entrepriſes. |
| All this is without considering how firmly the body stands when the feet are the proper distance apart. When they are, one need only lift the forward foot when one wishes to take a step forward. The body will move of its own accord, so that, rather than needing to be moved, it needs instead to be stopped from moving. | Sans compter que le corps ſe tient encores beaucoup plus ferme, quand on a les pieds en juſte diſtance; laquelle eſtant prinſe, il ne faut que lever tant ſeulement le pied de devant, quand on veut marcher. car le corps ſe preparera de luy meſme à partir du lieu, de ſorte qu’il ſera pluſtoſt beſoing de le retenir, que de l’inciter d’avantage. |
| The basis of all this discussion consists of that the position of the feet is entirely natural. I admit that, one might, nonetheless, object that at the beginning of the exercise, one needs to carefully place the feet on their lines, in the required form. But this is at the beginning of the exercise, and for those who are not accustomed to it. The difficulty is not from the fact that this is not entirely in accordance with a natural posture, as much as the fact that these actions are not customarily practised in this way, and accompanied by such movements. Thus it is easy to prove, following the way I practised myself several times with those who steadfastly held to a contrary opinion. In the middle of the dispute, I stepped away, five or six paces. Then, I immediately called them over, as if I wanted to show them something new, then asked them to stop, suddenly, in place, without moving their feet. They always found that the majority of those who held their bodies erect and with knees straight, had their feet placed exactly as I have described. Often, this was enough to end our disputes. | Le fondement de tout ce diſcours conſiſte en ce, que ceſte ſituation des pieds eſt toute naturelle. On me pourra cependant objećter, qu’au commencement de l’exercice, on y trouve bien de la beſoigne, tant pour bien porter & tenir l’eſpee en ligne droite, comme auſſi à planter chaſcun des pieds ſur ſa ligne, & en ſa forme requiſe. Ie le confeſſe; mais c’eſt au commencement de l’exercice, & à ceux qui n’y ſont pas accouſtumez. La difficulté ne depend point de ce que la choſe ne ſoit du tout accordante à la nature, ains de ce que ces aćtions ne ſont point accouſtumées d’eſtre pratiquées en telles occurrences, & accompagnées de tels mouvements. Dont il eſt aiſé de faire la preuve, ſuivant ce que j’en ay pratiqué moy meſme à pluſieurs fois entre ceux qui ſouſtenoyent fort & ferme le contraire de ceſte ſituation. Au milieu de la diſpute je me retiray cinq ou ſix pas à l’eſcart; puis à l’improviſte je les appellay à moy, en faiſant ſembland de vouloir dire ou monſtrer quelque choſe nouvelle, les priant de s’arreſter tout court en leurs places, ſans bouger des pieds. Fut touſiours touvé que la plus part de ceux qui tenoyent le corps perpendiculaire, & les genoux roides, avoyent les pieds ſituez ſelon la forme de noſtre deſcription: de ſorte que ceſte preuve a ſouvent terminé nos diſputes. |
| This, then, is how we intend to use Nature as our guide everywhere, rejecting all unnatural movements and all extreme postures, which have been used in the past among those who practised the profession of arms. All our precepts are drawn from observations of Nature herself, to benefit from the help she offers, and so follow the path to the highest degree of perfection. | Et voilà comment nous pretendons de ſuivre partout la Nature pour guide, rejettants touts movements violents, & toutes les poſtures extremes, qui ont eſté pratiquées par le paſsé entre ceux qui faiſoyent profeſſion des armes. Touts nos preceptes ſeront tirez des obſervations de la Nature meſme, pour l’aſſiſter du ſecours qu’elle meſme nous offre, & l’acheminer au plus haut degré de ſa perfećtion. |
| A DISCUSSION ON THE USE AND SUPERIORITY OF THE FIRST POSITION,
along with the means of changing it to accommodate various sizes of swords. |
DISCOVRS DE L'VSAGE ET EXCELLENCE DE LA
premiere instance, avec la maniere de la changer et accommoder selon les diverses mesvres des espees. |
| This is enough about the posture. Now let us speak briefly of the range, at which the two parties stand on the four Circles of this Plate. The distance is such that when they each present their swords in the Direct Line, they are both the same distance. This is the First Instance, the true start of the play, at which the two parties are at a proper distance, and totally propotioned to their bodies and weapons. Not too far, because they can hit the enemy in slow time, not too close because they have enough time to defend against an attack from their adversary. Those who ignore this range, keep themselves further away than they should, where, if they wish to move in closer, inevitably put themselves into danger before they can reach their intended distance. This is why in all the discussion about this exercise, knowledge of this range will be our guide, to reach the distances proportional to our intended actions. As such it will be like a turret from which we may discover the intended actions of our adversary. Of course it is understood that any actions of the sword must pass through this First Instance before they can reach the body. All of the thousands of sequences of moves, the ways in which the play can go, start, properly speaking, from this position. In the end, this is the compass which shows us, amid the tempestuous waves of this sea, the course we must take, to arrive at the port of Victory. But that is enough for the present, without engaging in further discussion. The properties of the First Instance, just like the Second and Third, cannot be listed in a menu, without listing at the same time the situations that bring us there, which are so many. And yet they must be found in the Plates which follow. | Or c’eſt aſſez dit de la poſture: parlons à cette heure & briefvement de la meſure, en quoy les parties ſe tiennent ſur les quatre Cercles de ce Tableau: qui eſt telle, que quand ils s’entrepreſentent leurs eſpees en lignes droites, elles viennent à ſe meſurer les unes les autres. C’eſt la Premiere Inſtance, vray commencement du jeu, tenant les parties en une diſtance juſte & totalement proportionnée aux corps & aux armes: non trop large; car on y peut toucher l’Ennemi en un temps mediocre; & not trop eſtroite; car en icelle on ſe peut aſſez defendre à temps de touts les aſſauts du Contraire. Ceux qui ignorent ceſte meſure, ſe tiennent plus eſloignez de ce qu’ils ne devroyent: ou, s’ils ſe veulent approcher d’avantage, ils ſe mettent en un danger inevitable, avant que d’arriver à la meſure pretendue. C’eſt pourquoy en tout le diſcours de ceſt exercice, la cognoiſſance de ceſte meſure nous ſervira de guide, pour arriver aux diſtances proportionnées à nos deſſeins: en ſorte qu’elle nous ſera comme une eſchaugette, de laquelle on deſcouvre toutes les entriprinſes contraires; attendu que toutes les operations de l’eſpee ſont contraintes de paſſer le paſſage de ceſte Premiere Inſtance, avant qu’elles puiſſent attenter ſur le corps. Toutes les aćtions, par leſquelles le jeu ſe peut diverſifier en mille & mille manieres, prennent icy, à proprement parler, leur origine. En fin c’eſt le compas, qui nous monſtre parmy les vagues impetueuſes de ceſte mer, la courſe, qu’on doit prendre, pour arriver au port de Vićtoire. Mais c’eſt aſſez pour le preſent, ſans entrer en ce diſcours plus avant; car les proprietez de la Premiere Inſtance, comme auſſi de la Seconde, & Troiſieme, ne ſe peuvent declarer par le menu, ſans declarer quand & quand les occaſions, qui nous y ameinent, leſquelles ſont en grand nombre: & partant les faudra chercher és Tables ſuivantes. |
| Note that we are supposing that these two people are equal, and their weapons are likewise equal, and proportional to their bodies. In this way it is the bodies and swords which give the true distance of this First Instance. For if the weapons were unequal, it would change the Instance. If the Enemy has a longer sword than yours, watch out that the tip of his sword does not go past the crosspiece of your guard, so that there is always an arms-length between you and the tip, which is a reasonable distance, and large enough for you to defend yourself. If you were to move closer, to put your tip at his guard, he would have the advantage, because the length of the weapons favours him, such that at a wide distance he can hit, without risk of being hit back. This is why we must offset this advantage, as soon as he makes contact with his blade, to try to subjugate it, or to control him, to get inside angle of the blades or to move in to a distance so close that he cannot overcome you, or manipulate his weapons as he needs to. If his sword is shorter than yours, or is not proportional to his body, you adopt the First Instance a bit closer, so that your tip is past his guard, making sure his tip does not pass yours, the reasons for this are self-evident. In sum, there is nothing more sure than to have properly proportioned weapons, because the ones too long or too short, if they are of some advantage in certain situations, they are also disadvantageous in others. Proportional weapons are, by contrast, equally useful at large or close range. | Notez, que nous preſuppoſons, que les perſonnages ſoyent egaux, & qu’ils ayent pareillement les armes egales, proportionnées à leurs corps; de maniere que ce ſont les corps & les eſpees, qui donnent la vraye meſure de ceſte Premiere Inſtance. Car les armes eſtants inegales, il faut changer l’Inſtance à l’advenant. Si l’Ennemi a l’eſpee plus longue, que la voſtre, gardez vous bien, que ſa poinćte ne paſſe outre les branches de voſtre garde, afin qu’i y demeure touſiours entre deux la meſure du bras entier, qui eſt une raiſonnable diſtance, & aſſez grande pour vous preparer à temps à la defenſe. Car ſi vous taſchez de vous avancer plus pres, pour mettre la voſtre tout joignant la ſienne garde, il aura de l’avantage, à raiſon de la longueur de ſes armes qui le favoriſe, tellement qu’en meſure large il peut donner des atteints, ſans qu’il ſe mette en hazard d’en recevoir. C’eſt pourquoy on luy doit oſter c’eſt avantage, dés auſſi toſt qu’il preſente ſa lame à toucher, en taſchant de l’aſſujettir, ou de l’obliger, pour entrer dedans ſes angles, ou pour venir en meſure eſtroite, en laquelle il ne s’en puiſſe prevaloir, ny manier ſi promtemēt ſes armes, comme il ſeroit de beſoin. Si ſon eſpee eſt plus courte, que la voſtre, ou que la proportion de ſon corps ne requiert, la voſtre ayant ſa juſte meſure, vous predrez la Premiere Inſtance un peu plus pres, en ſorte que voſtre poinćte pourra paſſer outre ſa garde, moyennant que la ſienne ne paſſe pas la voſtre; dont les raiſons ſont toutes evidentes. En ſomme il n’eſt rien plus certain que d’avoir les armes proportionnées. car les trop longues, & les trop courtes, ſi elles portent quelque avantage en d’aucuns endroits, elles ſont auſſi accompagnées de pareilles imperfećtions en contreſchange: les proportionnées ſont au contraire egalement utiles en la meſure large & en l’eſtroite. |
| In sum, this is the superiority of the Direct Line posture, presented at the distance of the First Instance. We could list even more reasons, if these were not self-evident enough, to persuade those who are open to the Truth. I truly believe that we have not unnecessarily repeated anything, but the usefulness of this subject shall serve as an excuse. Considering that such an important matter merits being treated with thoroughness. At this point, I shall leave the reader who can expect to shortly receive even more, just like a landlord who, allowing the rent to be uncollected one month, expects double the next. | Voilà en ſomme, qu’elle eſt la perfećtion de la Droite ligne, à preſenter ſur la Premiere Inſtance. On en pourroit alleguer encore d’autres raiſons, ſi celles-cy n’eſtoyent aſſez evidentes pour perſuader la Verité à ceux, qui la veulent recevoir. Ie croy bien, que nous avons uſé aucunefois de quelques redites: mais l’utilité du ſujet en fera noſtre excuſe; conſiderant qu’une matiere de ſi grande importance ne meritoit, que d’eſtre traitée bien exaćtement; eſtant expedient d’y arreſter la contemplation du Lećteur, pour imiter en ceſt endroit les avaricieux, qui laiſſent longuement courrir leurs rentes, afin qu’ils les reçoivent par apres avec double uſure. |
| Translation by Bruce G. Hearns |
Transcription by Bruce G. Hearns |
|---|---|
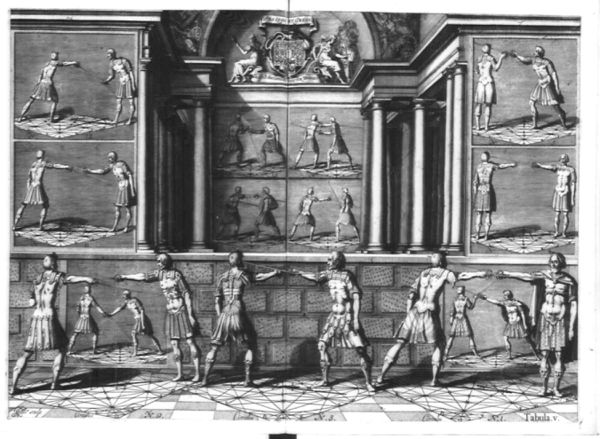
N.B., The coat of arms at the top belongs to John Sigismund (1572 – 1619) of the House of Hohenzollern, Elector of Brandenburg from 1608 and Duke of Prussia, through his wife Anna, from 1618. | |
| EXPLANATION OF THE ACTIONS IN THE FIFTH PLATE | DECLARATION DES OPERATIONS DV TABLEAV CINQUIEME |
| Our intention is to examine the advantages of the Direct Line, adopted carefully at the First Instance, and in the form shown in the foreground of the preceeding Plate, and on which all subsequent actions depend. But seeing how fighters most frequently begin to work with feints as soon as they come into range, to try and draw the opponent’s sword a little out of the way before striking with their thrusts, it seems necessary for your satisfaction, and to clarify the Plate, to have here a short discourse on feints, first, before entering into the particular explanations of the examples, that will be presented. Therefore we posit that Alexander, arrived into position first, right foot along the outside edge of the A-C Quadrangle, and the other on the Pedal Line. Zachary has approached, and is at the First Instance on the other side of the Circle, likewise in the Direct Line posture, on the right side of the Quadrangle and left foot on the usual line, putting his sword above the other, and working with feints inside and outside, sometimes with the foot firmly on the ground, somtimes, and more often, with the foot slightly raised off the ground. Never staying exactly at the First Instance, at other times starting from further back or closer, according to his whim. In sum, he is making such a large number and variety of feints that it is impossible for Alexander to work against him if he cannot distinguish exactly how close each of these will reach. Because the forward movement of the foot and the body, that happens with each move, can be defined in four degrees, from which we derive four types of feints, which are necessary to recognize, to be able to defend against them. The instructions for how to do this are below, and without which, there is no other remedy against these subtle feints, other than a lucky strike, and to open yourself to the enemy, in the hope of hitting him as well, or to break away as a coward, to get away from his strikes. | Noſtre intention eſt d’examiner les avantages de la droite ligne, preſentée à la Permiere Inſtance avec jugement, & en la forme, qui eſt monſtée au premier plan du Tableau precedent: du quel auſsi toutes ces operations ſuivantes dependent. Mais voyant que les tireurs d’Armes commencent le plus ſouvent à travailler avec les feintes, ſi toſt qu’ils viennent à meſure, pour faire ſortir l’eſpee contraire un peu de preſence, avant que tirer leurs eſtocades; il nous ſemble neceſſaire pour voſtre plus grand ſatisfaćtion, & pour l’eſclairciſſement du Tableau, de mettre icy un petit diſcours touchant les feintes, premier que d’entrer en la declaration particuliere des exemples, qui ſont icy propoſez. Dont nous preſuppoſerons, qu’Alexandre s’eſtant mis le premier en poſture, le pied droit ſur le coſté exterieure du Quadrangle AC, & l’autre ſur la ligne Pedale; Zacharie l’eſt venu aborder, en ſe mettant à la Premier Inſtance à l’autre bout du Cercle, en pareille poſture de la ligne droite, ſur le coſté droit du Quadrangle & ſur la ligne ordinaire du pied gauche, portant l’eſpee deſſous l’autre, & pourſuivant à travailler avec feintes par dehors, & par dedans, tantoſt à pied ferme, tantoſt, & le plus ſouvent, avec le pied droit un peu levé; aucunesfois demeurant exaćtement ſur la Premiere Inſtance, autresfois commençant de plus loing ou de plus pres, ſelon qu’il luy vient à gré. Somme il fait un ſi grande varieté de feintes, qu’il eſt impoſsible à Alexandre de bien travailler alencontre, s’il ne diſtingue exaćtement la meſure de l’approchement de chaſquune d’icelles. Car l’advancement du pied & du corps, qui les accompagne, peut eſtre distingué en quatre degréz; dont procedent quatre eſpeces de feintes, qui ſont neceſſaires à cognoiſtre, pour ſe fortifier deuement alencontre, ſelon les inſtrućtions qui s’enſuivent, & ſans leſquelles, il n’y à autre remede contre les feintes ſubtiles, que le ſeul hazard de tirer, & de donner ſur l’ennemi à corps perdu, en eſpoir de luy rendre ſon change, ou de rompre touſiours en covard la meſure, pour eſchapper tant ſeulement les coups. |
| The first type of feint, is that which is made by Zachary from the First Instance, by raising his right foot and setting his weight back on his left, without any noticeable forward movement. In such a way that the tip never passes the guard of his adversary’s sword. The remedy against this feint is to scorn it and to make no move against it, not with the arm, nor with the sword, until the enemy approaches closer. | La premiere eſpece de feintes, c’eſt celle qui eſt fait par Zacharie à la Premiere Inſtance, en levant le pied droit, & faiſant la charge du corps ſur le pied gauche, ſans nul advancement notable; en ſorte que ſa poinćte ne paſſe pas la garde de l’eſpee contraire. La remede de ceſte feinte, c’eſt de la meſpriſer, & de ne faire aucun mouvement alencontre, ny du bras, ny de l’eſpee, juſqu’à tant que l’ennemi s’approche d’avantage. |
| The second type is when he begins to lean his body forward, enough so that, doing his feint to the outside, or inside, the tip can just reach his enemy’s hand. The counter is to tense both the arm and sword-hand at the same time, straightening the body, and lightly lift the heel of the right foot, so that it is ready to work according to circumstances,and raising the tip of the sword upwards towards the side of the feint, above the adversary’s sword, to be able to cover it from a superior position. | La ſeconde eſpece, c’eſt quand il commence à pancher du corps en avant, ſi bien qu’en faiſant la feinte en dehors, ou en dedans, la pointe puiſſe arriver juſqu’à l’endroit du poignet de la main de l’ennemy. Le contraire, c’est d’aviver au meſme temps le bras & la main de l’eſpee, roidiſſant le corps, & eſlevant le talon du pied droit, afin qu’il ſoit preſt à travailler ſelon les occurrances, & eſlevant enſemblement la poinćte de l’eſpee en haut du coſté de la feinte, par deſſus l’eſpee contraire, pour la couvrir avec un peu de ſuperiorité. |
| The third type is when he continues to approach with his body so far forward that the tip can reach half-way to the adversary’s elbow. This cannot be done except with a larger and more obvious movement than the one before. The counter to this type of feint is done in almost the same way as above, however by increasing and adjusting ones actions to the actions of one’s adversary. Because at the same time as you must extend your body, raise the right foot, and lift your arm and the sword forwards, while turning the outside branch of the crosspiece a little higher than the other, and raising the tip to an obtuse angle beside the adversary’s sword, to gain a superior position. That is the closest approach you can permit the adversary to make with his body, while remaining on the defensive. If he comes any closer, one must hit him at the same time, or else he will either continue to follow the path of his feint to the inside or the outside, intending to wound on that same side, or he will disengage with a circular move to hit low or sweep over to the opposite side. This preparation against this, done as described, will be used as a universal means to counter his moves and render them useless. | La troisieme eſpece, c’eſt quand il continue ſon approchement du corps ſi en avant, que ſa pointe puiſſe arriver juſqu’à l’endroit due mitandu coude contraire; ce qu’il ne peut faire ſinon avec un mouvement plus grand & plus apparent, que n’a eſté le precedent. Le contraire de ceſte eſpece de feinte, ſe pratique quaſi en la meſme ſorte que deſſus, toutesfois en augmentant & accomodant les aćtions à l’exigence des aćtions conraitres. Car au meſme temps il faut s’eſtendre le corps, lever le pied droit, hauſſer le bras & l’eſpee en avant, en tournant la branche exterieure, du poignet de la main, un peu plus en haut que l’autre, & eſlevant la pointe en angle obtus du coſté de l’eſpee contraire, pour le couvrir avec un petit avantage de ſuperiorité. Voila tout le dernier approchmēt de corps, qu’on peut ou doit permettre au Contraire, tandis qu’on demeure ſur la defenſe: car s’il entre plus avant, il luy faut donner l’atteinte au meſme temps, ſoit qu’il pourſuive le trait de la feinte encommencée dedans, ou en dehors du bras, pour bleſſer de meſme coſté, ou qu’il uſede cavation pour toucher en bas, ou au coſté oppoſité. Auſsi ceſte preparation, que nous venons de deſcrire, eſtant deuement faite, ſervira d’une addreſſe univerſelle, pour rendre touts ſes desseins inutiles. |
| The fourth type is when he moves so far forward with the feint, that the tip of his sword can reach the elbow of his adversary. Which is the last and largest movement that he could do without putting his foot down on the ground. Alexander recognizes this extreme approach by his adversary, by the large and noticeably forward movement which he uses and way the body leans forward. He must be careful if he allows his opponent to follow through with this feint, because there is no remedy against a second motion. Yet he must move from the defense to the attack, moving in at the same time as the enemy moves to try his feint, with a short step along the Diameter, with the body erect, the arm and sword extended, so that he can just hit the opponent’s face with his tip, before the feint can be completed. But all this will be more amply demonstrated in Plate XXVII, which is the proper place to work on feints, and against the left-hand dagger. | La quatrieme eſpece, c’eſt quand il s’avance tellement avec ſa feinte, que la pointe de ſon eſpee pourroit arriver au coude du bras contraire; qui eſt le dernier & le plus grand mouvement qu’il ſçauvit faire, ſans planter le pied à terre. Alexandre recognoiſſant ceſt extreme approchement de ſon Contraire, par le grand & notable avancement & panchement du corps, dequoy il uſe; ſe doibt bien donner garde de luy laiſſer parfaire ceſte feinte encommencée; car au ſecond mouvement il n’y auroit plus de remede. Et pourtant faut, qu’il devienne aſſaillant de defendant qu’il eſtoit, (en entrant, au meſme temps que l’ennemi eſt en aćtion pour faire ſa feinte) d’un petit pas par delà le Diametre, le corps droit, le bras & l’eſpee eſtendues, en ſorte que il touche de ſa poinćte au viſage, avant que la feinte ſoit parachevée. Or toute cecy vous ſera demonſtré plus amplement en la Tableau XXVII. qui eſt le propre lieu ou on travaillera ſur les feintes, & ſur les aſsiſtences de la main gauche. |
| These are the cautions that we felt necessary to give you concerning feints and their counters. These will be very useful to Scholars who have achieved some skill, but can be safely ignored by Novices, who will have enough to do learning to control their swords, arms, hands, & legs, without concerning themselves with such subtle observations. They can be content, for the present, to know they exist as part of the Theory, yet still practise the examples from this Plate simply, without going into too many variations, in order to learn basic thrusts & counters, which shall be explained with their descriptions, rather than trying to acquire and refine skills for every possible response against each type of feint. Because one cannot fly without wings. | Voilà les advertiſſements, que nous avons jugez neceſſaires de vous propoſer touchant les feintes, & leurs contraires: qui ſeront de tres-grande utilité pour les Eſcholiers qui auront fait quelque advancement notable; mais on s’en pourra paſſer pour le regard des Novices, qui auront aſſes à faire à bien gouverner leurs eſpees, mains, bras, & jambes, ſans qu’ils s’embarques en des obſervations ſi ſubtiles. Qu’ils ſe contentent pour le preſent de les recevoir ſeulement,par maniere the Theorie, en pratiquant les exemples de ce Tableau plus groſsierement, ſans beaucoup de circonſtances, pour y apprendre ſimplement les eſtocades, & les rencontres, qui ſeront expliquées en leurs deſcriptions; pluſtoſt que d’approprier artiſtement chaſque remede à chaſque eſpece de feintes. Car auſsi bien ne peut on voler ſans aiſles. |
| Circle No 1. | Cercle N.1. |
| Alexander assumes the Direct Line posture and waits, then, attacked by Zachary with a thrust inside his arm towards the face, at the instant the tip passes his elbow, he parries against the 3rd or 4th Span with the strong part of his own sword, and moving a little to the side with the right foot, he closes the straight line, in a way that he wounds Zachary's face. | Alexandre ſe tenant en la poſture de la droite ligne, & aſſailli par Zacharie d’un coup de pointe en dedans du bras devers le viſage, à l’inſtant que la pointe luy vient paſſer le coude, il la ſur prend au Nombres 3. ou 4. avec le fort de ſa propre eſpee, & allant un peu à coſté avec le pied droit, il luy ferme la droite ligne, de façon qu’il le bleſſe au viſage. |
| Alexander holds himself in the Direct Line posture. Zachary threatens him with a feint of the third type to the outside of his arm by lifting his foot, and moving his body and arm forward, until the tip of his sword is about mid-way to Alexander’s elbow as if Zachary were going to thrust at him in the face. He hopes to make him parry the attack, and consequently have Alexander move his sword out to the side. Then, all at once, he passes his sword back beneath his adversary’s guard, continuing to move his body forward putting the right foot on the ground at R. As he leans his body further forward, he brings the sword back up, drawing his left foot, which is lagging behind, up to the same distance behind his right foot, while at the same time aiming his thrust to the inside of the right arm, straight at his opponent’s face, carrying his arm and sword along the direct line. Alexander’s defence consists of working against the feint, and then against the thrust. Against the feint, using only his wrist, he turns the outside branch of the crosspiece diagonally upwards, moving his sword-tip to the side of the feint to cross over and cover a good bit of his opponent’s blade with his own, without touching it, and without moving off the line, not to the right, nor to the left, not with the arm, nor with the sword. That is the counter to the feint. If Zachary had continued to move his tip from the feint to hit on the same side, this preparation would have been the correct way to break the strike outside the arm, as it is also, at present, the correct way to begin to counter the thrust to the inside. Then, as Zachary passes his sword under his opponent’s guard, to hit on the opposite side from where he made his feint, Alexander, as soon as he percieves the first hint of a change, becomes alert, and comes on guard, straightening the arm and the knees, so well that at the instant the tip of his opponent’s sword is near he elbow, he meets the 3rd or 4th Span of his opponent’s blade with the centre of his own guard, and catches it, and locks it between the blade and the inside branch of his crosspiece as he turns it horizontally, while at the same time stepping with his right foot and moving his body forward, with his arm and sword, the point of contact progressing up his opponent’s sword, so in this way he closes off the straight line letting the tip of his opponent’s sword pass across his chest, as he wounds the enemy in the face. He finally puts his right foot down just along the Diameter between the letters C and E, and draws his left foot behind until he is again erect on his feet in profile and in a perpendicular line. In this way, he increases the force of his thrust so much that he pierces through his opponent’s head. | Alexandre ſe tenant en la poſture de la droite ligne, Zacharie le vient menacer d’une feinte de la troiſieme eſpece en dehors du bras en eſlevant le pied droit, & avançant le corps & le bras de l’eſpee, juſqu’à porter ſa pointe environ le milieu du coude contraire quaſi comme s’il luy vouloit tirer une eſtocade an viſage; ſous eſpoir de l’obliger à parer le coup, & conſequēment à eſcarter l’eſpee. Puis tout à l’inſtant il la repaſſe par deſſous la garde contraire, en continuant l’advancement du corps, avec le pied droit: lequel poſant à terre ſur le diametre à la lettre R. avec quelque augmentation du panchement du corps, il remonte l’eſpee en haut, laiſſant ſuivre & trainer le pied gauche proportionellemēt derriere l’autre, en tirant & dreſſant au meſme temps ſon eſtocade en dedans du bras droite au viſage de ſa partie, portant le bras & eſpee eſtendues en ligne droite. La defenſe d’Alexandre conſiſte à travailler contre le feinte, & contre l’eſtocade. Contre le feinte, en tournant du ſeul poignet de la main la branche exterieure de ſa garde diagonalement en haut, en montant la pointe du coſté de la feinte pour croiſer & convrir un bien peu la lame de ſon contraire de la ſienne ſans la toucher, & ſans forligner ny à droite, ny à gauche, ny du bras, ny de l’eſpee. Voilà le contraire de la feinte. Si Zacharie euſt continué d’avancer ſa pointe avec la feinte pour le toucher du meſme coſté, ceſte preparation euſt eſté le vray moyen de luy rompre le coup en dehors du bras, comme elle eſt à preſent le vray commencement de rencontrer l’eſtocade tiree en dedans. Puis donc que Zacharie repaſſe l’eſpee par deſſoubs la garde de ſon contraire, pour frapper à l’oppoſite du lieu, ou il avoit dreſſé ſa feinte, Alexandre, dés auſſi toſt qu’il apperçoit le premier trait du changement, ſe reſveille, & ſe met ſur ſes gardes, en roidiſſant le bras & les genoux, ſi bien qu’à l’inſtant que la pointe de l’eſpee de ſa partie luy vient à l’endroit du coude, il la reçoit au Nombre 3, ou 4, avec le centre, qui eſt la garde de la ſienne, & la prend & enſerre, entre ſa lame & ſa branche interieure tournée horizontalement, en avançant au meſme temps le pied droit & le corps enſemble, avec le bras & l’eſpee, en graduant l’eſpee contraire & par ce moyen il ferme la droite ligne en laiſſant eſcouler la pointe de ſon contraire à vuide par devant ſa poitrine, bleſſant l’Ennemy au viſage, & abaiſſant finalement le pied droit à terre par delà le Diametre entre les lettres CE, & laiſſant trainer le pied gauche derriere, juſqu’à ce qu’il revienne droit ſur ſes pieds en pourfil, & en ligne perpendiculaire: il accroiſt par ce moyen tellement la vigueur de ſon eſtocade, qu’il le perce au travers la teſte. |
| Circle No 2. | Cercle N.2. |
| Alexander follows the initial approach against the obtuse angle posture, which he started and half-completed in Circle N0 2 in the preceeding Plate, where he had just put the sword up beside his head, with his right foot raised and slightly ahead. As he is about to step to the First Instance, he will likewise adopt the obtuse posture against the opponent’s sword to the inside of the arm. | Alexandre pourſuit la premiere approche contre l’angle obtus, par luy commencé & à demi faite au Tableau precedent Cercle N.2. où il eſtoit venu juſqu’à ſe mettre l’eſpee à coſté de la teſte, avec le pied droit un peu avancé en l’air: maintenant en venant ſur la Premiere Inſtance, il la met pareillement en angle obtus contre l’autre en dedans du bras. |
| Following the thrust, he closes with the enemy, stepping forward with the right foot, up to the letter H, putting his weight on this right foot, bending the knee, and drawing his left foot up behind him as far as the circumference. He continues to push his sword forward with all his strength, striking the enemie’s guard so hard that the enemy is forced to bend his arm, and let his tip fly upwards at an obtuse angle, and so he is safely beneath it, and prevents any attempt at revenge. | Pourſuivant l’execution de l’eſtocade, il entre ſur l’ennemy, en cheminant avec le pied droit juſqu’au lettre H, ou il fait la charge du corps ſur la jambe droite, en pliant le genouil, & trainant le pied gauche derriere juſqu’à la circonference; en continuant a pouſſer l’eſpee en avant de toute ſa force, avec le bras roide, il en choque ſi rudement la garde contraire, qu’il force l’ennemi à ſe courber le bras, & laiſſer aller ſa pointe en haut en angle obtus, venant par ainſi deſſous, & luy oſtant toute apparence de revenge. |
| This precept is very far from common practice, which instructs that after striking one should immediately retire out of range. I shall show you here, that you should follow the tip forward until you are absolute Lord and Master of your enemy. Do not run, nor jump backwards, which would be nothing other than inviting a riposte. It is far better to move in so far as to make his weapons useless. I know well, that those who are used to the old mode will not take up this method, and will hold it as being too dangerous. But this is because they themselves do not understand that one must secure the opponent’s sword before hitting them. And they think that we shall try everything we can to adopt their mode, extending our strikes, leaving swords free, or trying to move them off line by way of feints. Things we we are careful not to do. Because such thrusts are unplanned and chancy, and it would appear they fail as often as they succeed. Even when everything goes as hoped for, if they can, they would yet deny that whatever advantage they had was accompanied by some manifestly obvious danger, and is nearly as dangerous for the person who came out on top as it is for his opponent. Their own practice speaks for itself, where one can see they are ordinarily more at pains to withdraw with haste out of range, than they are of making sure of their hits. See how they withdraw most often, before even finding out if they are well or poorly placed. Which is, in effect, nothing more than taking lucky shots, with no superiority, nor any advantage. It follows then, that they wave their swords freely about, and the one who hits always needs to take two moments, one to move in, the other to get back out of range. We also see how frequently they wound each other which is an infallable argument that luck dominates, and they themselves know the imperfections of their system, because they do not know how to attack artfully with their sword. | Ce precept eſt grandement eſloigné de la Pratique vulgaire, qui commande, qu’on ſe retire tout à l’inſtant hors de meſure, apres qu’on à donné l’atteinte. Icy vous monſtre, qu’il faut pourſuivre la pointe, juſqu’à ſe rendre tout à fait Maiſtre & Seigneur abſolu de l’Ennemy, non pas fuir ny ſauter en arriere, qui ne ſeroit autre choſe, que de le provoquer à la riposte, il vaut pluſtoſt mieux entrer ſi en avant qu’on luy rende les armes inutiles. Ie ſçay bien, que ceux qui ſont accouſtumez à la veille mode ne laiſſeront pas de reprendre ceſte maniere & de la tenir pour trop dangereuſe: mais c’eſt pource qu’ils n’entendent pas eux meſmes, comme on ſe doit aſſeurer de l’eſpee contraire, avant que de porter l’atteinte: & qu’ils penſent que nous nous efforçions à leur mode allongeant nos bottes, en laiſſant les eſpees libres, ou en taſchāt de les faire ſortir de preſence par le moyen de quelques feintes. Ce que nous n’avons guarde de faire. Car telles eſtocades ſont tirées à l’adventure, & y à tout autant d’apparence quelle reuſſiront mal que bien; au fort quand tout eſt allé à ſouhait, ſi ne peuvent, ils nier encores, que l’avantage qu’ils ont eu, n’ait eſté accompangé de quelque danger manifeſte, & à peu pres autant hazardeux pour celuy qui a eu le deſſus, que pour ſon cōtraire. I’en pren à teſmoin la pratique meſme de leurs exercises, ou on le voit, qu’ils ſont ordinairement plus en peine, pour ſe retirer à la haſte hors de Meſure, qu’ils ne ſont aſſeurez à porter les atteintes, voire qu’ils ſe retirent le plus ſouvent, premier que de ſçavoir, s’ils ont bien ou mal addreſſé. Ce qui n’eſt en effet autre choſe, que de tirer ſes coups à l’adventure, ſans nulle ſuperiorite, ny advantage; procedant de ce qu’ils ont les eſpees de part & d’autre egallement libres; & que celuy qui porte la botte à touſiours beſoing de deux temps aſſez remarquables, le premier pour tirer, & le ſecond pour ſortir de preſence. Auſſi voit on, qu’ils s’entrebleſſent ordinairement les uns les autres, qui eſt un argument infallible, que la fortune y domine; & qu’ils recognoiſſe biē eux meſmes l’imperfećtion, & le danger de leur Pratique, par ce quils ne ſçavent que c’eſt d’attaquer artiſtement une eſpee. |
| Circle No 3. | Cercle N.3. |
| Alexander has placed his left foot on the circumference at point C, and has moved his sword under the opponent’s sword, as shown in Circle No 3, in Plate III. He follows on by coming into the First Instance, crossing swords in an obtuse angle, on the outside of the arm. | Alexandre eſtant venu à planter le pied gauche à la Circonference au C, & enſemblement à mettre l’eſpee en angle aigu deſſous de l’eſpee contraire, ſuivant la Representation du Tabl. III. Cercle N.3. il pouſuit icy le reſte de ceſte ſeconde approche, en venant ſur la Premiere Inſtance, & accouplant derechef les eſpees en angle obtus en dehors du bras. |
| Alexander waits in the same position as in Circle No 1. Zachary comes at him in the old style with a feint, either high or low, made with a straight arm to the outside, at the instant he arrives at the circumference of the Circle. Then, moving his left foot closer, he raises his other foot, he begins a circular disengage, which he continues to do while moving his body forward, so that at the same instant he puts his right foot on the ground at the letter R, he thrusts with all his strength at his adversary’s face. Alexander seeing that the feint does not go past the crosspiece of his guard, does not move at all, until Zachary moves forward a little, and begins to bend at the waist with his right foot raised. Then he gets ready, tensing his body, his feet, his hand, and the sword, in the way described, above, against the third type of feint. So that when the enemy enters in, and aims the tip of his sword towards his face on the inside line, as the point reaches the level of his elbow, he catches the sword with the inside branch of his crosspiece at about the 4th or 5th Span, and moves the point of contact up the blade by moving his body forward. He hits Zachary in the face with a straight thrust, putting his foot down further along the Diameter between the letters E and H, continuing to move towards him, and bending his knee to increase the power of his strike, as described above. | Alexandre ſe tenant tout de meſme, qu’au Cercle N.1; Zacharie le vient aborder à la mode ancienne avec une feinte, haute, ou baſſe, tiree d’un bras roide par dehors l’eſpee, à l’inſtant qu’il arrive à la Circonference du Cercle: puis en approchant le pied gauche, & eſlevant l’autre, il commence à faire la cavation; laquelle il continue durant l’avancement du corps, ſi bien qu’au meſme inſtant qu’il met le pied en terre ſur le Diametre à la lettre R, il tire de toute ſa force une eſtocade vers le viſage de ſon Contraire. Alexandre s’appercevant, que la feinte ne paſſe point la branche de ſa garde, ne ſe bouge nullement, juſqu’à tant que Zacharie s’avance un peu d’avantage, & commence à faire la cavation avec le pied droit eſlevé. Car lors il ſe prepare, s’avivant le corps, le pied, le bras, & l’eſpee, en la façon, qui eſt deſcrite en la troiſieme eſpece des feintes; de ſorte que l’ennemi entrant, & dreſſant la pointe de l’eſpee vers ſon viſage en dedans le bras, à l’inſtant qu’elle vient à l’endroit de ſon coude, il la reçoit de la branche interieure de ſa garde au Nombre 4. ou 5. & en la graduant avec un avancement du corps, il luy donne le coup en droite ligne au viſage, abaiſſant le pied un peu au delà le Diametre entre les lettres EH. continuant à charger le corps ſur iceluy, en pliant le genouil, pour augmenter la vigueur de l’eſtocade, en la maniere & pour les conſiderations declarées cy deſſus. |
| To perform this action successfully, one needs to know how to distinguish two distances at which Zachary’s thrusts can commence. | Pour bien pratiquer ceſte operation, il eſt beſoing de ſçavoir diſtinguer deux diſtances, ou les eſtocades de Zacharie ſe peuvent encommencer. |
| If it happens that he lunges to strike from the First Instance, or from even further away, he will necessarily have his body and arm lowered and weak, before his tip can reach the bend in his adversary’s arm. That being so, Alexander can meet him at the same time, likewise leaning forward against him, and crossing the strong part of his sword against the weak of his opponent’s at the 4th or 5th Span. | Car il s’advient, qu’il allonge ſa botte depuis la Premiere Inſtance, ou encor de plus loing, il aura le corps & le bras de l’eſpee necessairemēt abaiſſez & foibles, devant que ſa pointe arrive à l’endroit de la plieure du bras contraire. Cela eſtant, Alexandre le peut rencontrer au meſme temps, en uſant pareillement d’un panchement de corps alencontre, & accouplant le fort de ſon eſpee au foible de l’eſpee contraire au Nombre 4. ou 5. |
| But if he has previously moved his body closer during the feint, as soon as he makes his thrust from closer in, and the tip of his sword could pass beyond his adversary’s elbow without any lowering or weakening of his body, arm, or sword, Alexander will first straighten right up, with the right foot lifted, without leaning his body forward, until just as the adversary’s blade (which he has caught with the strong of his own) is a little off to the side, caused by Zachary’s body moving forward. Then he suddenly closes in, leaning his body forward, and, with his arm out straight, wounds him as he slides along the sword, as shown by the figure. | Mais s’il a fait preallablement quelque approachment du corps, durant la feinte; ſi bien qu’il tire ſon eſtocade de plus pres, & qu’il puiſſe paſſer de ſa pointe plus avant que le coude du bras de ſon contraire, ſans aucun abaiſſemēt ou affoibliſſement du corps, bras, ou eſpee, Alexandre ſe dreſſera premierement tout droit, avec le pied droit eſlevé, ſans pancher du corps en avant, juſques à tant que la lame contraire (eſtant accueillie du fort de la ſienne) ſe ſoit un peu eſcoulée, moyennant l’avancement du corps: & lors il entrera tout ſubitement en panchant ſur le devant, & le bleſſera en luy graduāt l’eſpee avec le bras eſtendu, ſuivant la demonſtration du figure. |
| This manner of receiving a thrust is somewhat different from that of Circle No 1, because this one counters with a single move, whereas the other takes two. This one executes the strike by a bend of the knee, the other requires one to prepare the body by becoming erect in the direct line posture with knees straightened. So it may seem to some that this way of striking and following through all at once, with the legs wide and the knees bent, is quite daring, more active, and more noble than the other because it appears to be much more like the impetuous actions in common use. Whereas the other is so far removed it could not be used this way. However, you may be sure, that the method shown in Circle No 1 is the more sure, being more ready to respond to any changes, and stronger, since all the parts of the body are extended and tensed, and all forces work in conjunction. This gives their movements a vigour and internal liveliness that is not apparent, for the reason that the movements become smaller as they become more powerful. Moreover, as they come from a body that is extended perpendicularly, they are superior to the other. Notably when we employ skills in proportion to the requirements of the situation. Even so, his body is thus ready as much to move and fight on all sides, as it is to engage, stop, and moderate its actions appropriately, for he holds all he needs in reserve. This is why it is very useful to practice the action of these and similar thrusts in two motions, rather than one. It is also never entirely necessary, as shall be shown in the following Circle. Alexander shall be constrained to stand up on his legs, with his body erect and straight, according to our style, to protect himself against the thrust, and so force his opponent to attack from the outside of his arm. If he wished to meet this attack by leaning his body forward over his forward knee, by this lowering of his body, arm, and sword, he would, of necessity, find himself lower than his adversary, who would not be long in taking full advantage of the superior position of his body, which he has kept by staying upright. | Ceſte maniere de rencontrer une eſtocage, eſt aſſez differente de celle du Cercle N.1. Car celle cy fait l’execution de ſon coup en un ſeul temps, & l’autre en deux: celle cy l’execute en pliant le genouil, & l’autre veut que le corps ſoit preallablement dreſſé en ligne perpendiculaire avec les genoux roides. Or il ſemblera bien à pluſieurs, que ceſte façon de donner & achever tout enſemble avec les jambes larges & le genou plié, ſoit plus gaillarde, plus aćtive, & plus noble, que l’autre, par ce qu’elle a en apparance quelque choſe de commun avec les plus furieuſes Aćtions de la Pratique vulgaire; dont l’autre eſt ſi fort eſloignée, qu’elle ne le pourroit eſtre davantage. Cependant ſoyez ſeur, que celle du Cercle N.1. eſt la plus ſeure, plus preſte à prevenir touts les changements, & meſme auſſi plus robuſte, par ce que touts les membres du corps y ſont tendus & reſveillez, & tiennent leurs forces plus unies; ce qui donne à leurs mouvements une vigueur & vie interieur, qui ne paroiſt pas en l’exterieur; à raiſon qu’ils ſont d’autant plus petits, que la force en eſt plus grande. En outre, pour ce qu’ils procedent d’un corps eſtendu perpendiculairement, ils ſe font avec plus de ſuperiorité, que les autre; notamment quand on y employe l’artifice & la proportion, que les occaſions requierent; meſme que le corps eſt alors preparé tant pour ſe trāſporter & travailler à touts coſtez, qu’à pourſuivre, arreſter, & moderer ſes aćtions tout ainſi que bon luy ſemble; pour ce qu’il a tout en reſerve. C’eſt pourquoy il eſt tres utile de pratiquer les executions de telles & ſemblables eſtocades en deux temps, plustoſt qu’en un: & aucunesfois il eſt du tout neceſſaire, comme il ſera monſtré par la deſcription du Cercle ſuivant: ou Alexandre ſera contraint de ſe mettre droit ſur ſes jambes, pour s’aſſeurer contre l’eſtocade, que ſa partie luy tire en dehors du bras, avec le corps haut & droit, enſuivant le ſtile de noſtre Pratique. Car s’il vouloit rencontrer en panchant du corps en avant ſur le genouil de la jambe anterieure, par l’abaiſſemēt du corps, du bras, & de l’eſpee, il deviendroit neceſſairement inferieur à ſa partie, qui ne s’eſloigne guerre de prendre l’avantage de ſuperiorité, par la hauteur du corps qu’il ſe reſerve. |
| Circle No 4. | Cercle N.4. |
| Zachary again attacks with resolve using a straight thrust to the outside of the arm, towards the face, with the body so upright that he does not pass beyond the letter V. Against this Alexander, having made ready, meets the 4th Span of his opponent’s sword with the strong of his own, raising himself slightly on his toes, by which means he retains his superiority, and sliding the point of contact along his opponent’s sword, keeping his arm straight, with a small step to turn his head and his back towards the thrust, he wounds Zachary in the face instead, recovering into the same posture that he had before. | Zacharie luy tire encore ſur la meſme poſture une autre eſtocade reſolue en droite ligne, dehors du bras, & devers le viſage, avec le corps touſiours ſi haut qu’il ne passe point la lettre V, ſur quoy Alexandre ayant fait ſa preparation, accueile l’eſpee contraire du ſort de la ſienne au Nombre 4, avec un petit ſouſlevement du corps ſur les orteils de ſes pieds, de quoy il retient la ſuperiorité, & en graduant l’eſpee contraire d’un bras roide avec une petite demarche, pour tourner la teſte & le dos devers l’eſtocade, il le bleſſe luy meſme au viſage, en revenant tout droit debout en la meſme poſture qu’il s’eſtoit au paravant. |
| Both parties stand facing each other in the First Instance. Zachary has his sword below the other, parallel, in a direct line. He begins to move his straightened arm to feint to the inside of his opponent’s arm, raising his right foot and moving it slightly forward. Then, continuing the same forward motion, he passes his sword back beneath his opponent’s guard and makes a resolute thrust to his opponent’s face from the outside of the arm, putting his right foot down at the letter V, with the arm extended and the body erect, following with his left foot, as much as he needs to remain upright. Alexander again percieves that the feint does not come any closer than the crosspiece of his sword, and so remains still, waiting until his adversary makes his circular disengage with an obvious forward movement of his body. Then he gets ready to receive the attack, tenses himself, raises his right foot, and moves his sword as previously described. At the instant his opponent’s blade reaches his elbow, he catches the sword at the 4th Span with his strong part of his, but it is enough for him to remain erect, if he raises himself a little, by lifting his left heel and going up onto his left toes, at the same time looking backwards over his shoulder towards the tip of his enemy’s blade. He slides up this blade by stiffening his arm so that, with a small step forward and to the right, putting his food down near the letter E, he forces his opponent off the straight line and wounds him in the face. He allows his left foot to follow, drawing it behind in a circular path, until he returns to face his opponent in profile, in the natural way he was when in the First Instance inside the perpendicular lines. | S’eſtants plantez les deux parties à la Premiere Inſtance; l’eſpee de Zacharie deſſous l’autre en ligne droite & parallele, il commence incontinent à faire avec le bras roide une feinte à ſon Contraire par dedans le bras, en eſlevant & advançant quelque peu le pied droit; puis en continuant le meſme advancement du pied enſemble avec le corps, il repaſſe ſon eſpee par deſſous la garde de ſa partie, & en tire une eſtocade reſolue tout droit vers le viſage d’iceluy en dehors le bras, abaiſſant le pied droit à terre à la lettre V, avec le bras eſtendu & le corps haut, laiſſant trainer le pied gauche derriere, autant qu’il eſt beſoing pour ſe tenir touſiours perpendiculaire. Alexandre s’appercevant derechef, que la feinte ne paſſe pas les branches de ſa garde, attend ſans bouger juſqu’à tant que l’Adversaire face la cavation avec quelque approachement notable du corps; & lors il ſe preſente à le recevoir, en avivant le corps, eſlevant le pied droit, & conduiſant l’eſpee ſelon les inſtrućtions precedentes; & à l’inſtant que la lame contraire luy vient à l’endroit du coude, il la reçoit du centre de la ſienne au Nombre 4. ne luy ſuffiſant pas de ſe tenir droit, ſi ce n’eſt qu’il y adjouſte encor un petit ſouſlevement du corps, pour ſe hauſſer un peu davantage ſur les orteils du pied gauche, en tournant au meſme temps la teſte vers le dos devers la pointe ennemie; laquelle il va graduer en roidiſſant le bras, de telle ſorte, qu’avec un petit pas, poſant le pied droit un peu à coſté environ la lettre E, il le contraint de quitter la droite ligne, & le bleſſe au viſage, laiſſant ſuivre le pied gauche derriere en trainant un peu circulairement, juſqu’à venir en pourfil en la ſituation naturelle de la Premiere Inſtance au dedans de perpendiculaires.
|
| Those who hold to ordinary fencing are greatly astonished at such a precept. Because moving your head and back towards the tip of your adversary’s sword while he is thrusting seems to be rash action that defies Nature herself, given it is natural to try and preserve oneself before attacking one’s Adversary. This is the reason they are accustomed to avoiding the attacking sword, leaning their head and body away from the menacing tip. In response, I must confess, that our exercises are exactly opposite to theirs, and I say they are making a great mistake trying to evade the tip in this way. Because the more they believe they are avoiding the tip by moving their head out of the way, the more they remain in danger of being hit. And on the contrary, the closer one gets, following the instructions in this and similar manoeuvres, the more secure one will be, and one will enter even more forward between the perpendicular lines. Because if Alexander had evaded his opponent’s tip by pulling his head back, I ask you, what would have prevented his opponent’s sword, which is free, from changing direction to pursue his advantage by another means? It is therefore better to counter the attack decisively, than to wait for him to come in to make his move, with the risk of being hit. And it is better to break his thrust than to leave him free. We conclude, then, that the skill and confidence goes to the one who knows how to dominate his adversary’s intentions, and chance and surprise to the one who fears the approach of a tip, as if it was invincible. | Ceux qui tiennent l’Eſcrime vulgaire s’eſtonneront grandement d’un tel precepte. Car porter la teſte & le dos vers la pointe de l’Adverſaire, durant le temps qu’il eſt en aćte de tirer ſon eſtocade, il leur ſemblera que ce ſoit une temerité qui deffie la Nature meſme, laquelle taſche touſiours de ſe conſerver ſoy meſme, avant que d’offenſer le Contraire. Et c’eſt la raiſon pouquoy ils s’acouſtument quant à eux de fuir l’eſpee qui vient contre eux, en panchant de la teſte & du corps à l’oppoſite du poinćt qu’elle menace. Pour reſponce, je confeſſe, que nos exercises ſont direćtement contraires aux leurs, & dis qu’ils font une bien grande faute d’eſquiver la poinćte en ceſte ſorte. Car d’autant plus qu’ils la penſent eviter, en portant la teſte hors de preſence, dautant plus demeurent ils en danger d’en eſtre touchez. Et au contraire d’autant plus qu’on s’en approchera, ſuivant l’inſtrućtion de ceſte & de ſemblables operations, d’autant plus en ſera on aſſeuré, & entrera on plus avant dedans les perpendiculaires. Car ſi Alexandre euſt voulu eviter la poinćte contraire en ſe retirant la teſte, je vous prie, qu’eſt ce qui auroit empeſché l’eſpee contraire, qui eſt libre, de changer le trait, & de pourſuivre ſon advantage en quelque autre ſorte? Il vaut mieux doncq de rencontrer le coup avec ſuperiorité, que d’attendre, qu’il vienne & qu’il aille à ſa poſte, avec hazard d’en recevoir l’atteinte; & mieux vaut le rompre que le laiſſer libre. Concluons donc, que l’Art & l’aſſeurance eſt à celuy qui ſçait domter les pretentions de ſon contraire; le hazard & l’eſpouvante à celuy, qui redoute la venue d’une pointe, comme ſi elle eſtoit invincible. |
| Circle No 5. | Cercle N.5. |
| Alexander follows through and executes his thrust, powering and increasing it by stepping forward with his right foot, putting his whole body weight behind his right hand and his sword. He finally puts his foot down on the Diameter beyond the letter H, shifting the weight of his body to the bent forward knee, while sliding up his opponent’s sword keeping his arm straight until he runs into his opponent’s guard, with such force that that his enemy must bend his arm, let the tip of his sword go up at an obtuse angle as Alexander’s sword goes through his head. | Alexandre pourſuit & execute ſon eſtocade, l’augmentant & parachevant avec eſlevation & avancemēt du pied droit, enſemble du corps, du bras, & de l’eſpee; en abaiſſant finallement le pied ſur le diametre outre la lettre H, menant la charge du corps ſur le genouil anterieur plié, & graduant cependant la lame contraire avec le bras roide, juſqu’à en rencontrer la garde, avec telle violence, que l’ennemy eſt forcé, de ſe courber le bras, laiſſer aller ſa poinćte en angle obtus, & recevoir l’eſpee de l’Adverſaire à travers la teſte. |
| Circle No 6. | Cercle N.6. |
| Zachary advances and again aims a thrust from outside the arm to the face with a bent arm, moving his right foot up to the letter R. Which means Alexander avoids the hit by moving his left side forward, and puts his right foot along the diameter inside the circumference, and, at the same time, crosses the 7th Span of his blade against the 5th or 6th Span of his adversary’s, slides up the blade, lowers the hand, and keeping his elbow close to the side to protect the lower part of his body, he steps forward with his left foot up to the letter I. | Zacharie s’avance, & luy tire derechef une eſtocade par de hors le bras devers le viſage en ligne courbe, portant le pied droit juſqu’à la lettre R; qui faićt qu’Alexandre eſquive le coup en avançant le coſté gauche, & poſant le pied droit ſur le Diametre au dedans de la circonference, & acceuillant au meſme temps du Nombre 7, le 5 ou 6 de l’eſpee contraire, avec quelque deſgraduation, abiſſement de la main, & le coude affermi contre le flanc, en ſorte que la partie inferieure du corps eſtant affranchie, il fait là deſſus ſon intrade, en allant du pied gauche juſqu’à la lettre I. |
| After the two adversaries have adopted their direct line postures at the First Instance, holding their swords parallel to each other, that of Alexander above the other, Zachary once again tries to thrust from the outside, but this time not with a direct line, as in Circle No 4, because Alexander can block him with a similar direct line, overpowering and wounding him at the same time. Therefore, he prefers to strike with his arm bent, as follows. He first moves forward with a feint of the second type inside the arm, moving both his foot and body, with the sword-arm extended, until the tip reaches about even with his opponent’s wrist. Then, still moving forward, he turns his wrist up, bends his arm, passes the tip below his opponent’s sword, and strikes from outside his opponent’s arm with a powerful thrust to his enemy’s face. His right foot comes down on the Diameter, at the letter R, he leans his body forward over his right knee, and allows the left foot to come up in balance to the letter X. Alexander first prepares against the feint, tensing and straightening up his body, while raising his right foot, and extending his right arm, his sword-tip moving against the side of the feint as shown before (Circle No4). He waits in this superior position, a universally applicable response, for any machination his adversary may try following this feint, either continuing the same movement, or making some change through a circular disengagement, or yet something of another sort, as may be. He determines his adversary’s intent, from the first motion of the change by the turning of his shoulder and his arm, and before the tip can even pass the level of his elbow, he clearly sees that it is aimed towards his face in a bent line. In one motion, he avoids this blow by moving his head away out of range by turning and moving his left side forward which he does by setting his right foot, which is raised, on the Diameter just inside the circumference, making contact at the 5th or 6th Span of his opponent’s blade with the 7th Span of his own, and against this sliding the point of contact slightly down with a lowering of his hand and pressing his elbow against his right side to protect against any cuts. He continues the left-forward motion with a circular step with his left foot up to the letter I (at the crossing of the Interior Collaterals and the Oblique Diameter), bending his knee and shifting his weight onto it, while subjugating his opponent’s sword, exactly as shown by the figures in the image. | Apres que les deux Contraires ont eſté plantez à la Premiere Inſtance en poſtures de la droite ligne, tenants les eſpees paralleles l’une à l’autre, celle d’Alexandre deſſus & l’autre deſſous; Zacharie entreprend de luy tirer derechef une eſtocade en dehors du bras, non toutesfois en ligne droite, comme au Cercle N.4. à cauſe qu’Alexandre la luy avoit rencontrée avec pareille ligne droite; domté, & bleſſé au meſme temps; dont il aime mieux de luy porter le coup avec le bras courbé, en la maniere ſuivante. Il s’advance premierement avec une feinte de la ſeconde eſpece en dedans du bras, portant egalement le pied & le corps avec le bras eſtendu, juſques à tant que ſa poinćte arrive alendroit du poignet de la main contraire; & puis en continuant encor le meſme advancement, il la repaſſe par deſſous, & en tir en dehors du bras avec pleine force une eſtocade, au viſage de l’Ennemi en ligne courbe; poſant le pied droit ſure le Diametre à la lettre R, en accommodant le corps en avant ſur le genouil de la jambe droite, & laiſſant trainer le pied gauche proportionnellement derriere juſqu’à la lettre X. Alexandre ſe prepare premierement cōtre la feinte, s’avivant & eſtendant au meſme temps le corps avec eſlevation du pied droit, en eſtendāt le bras avec l’eſpee, la poinćte dreſſée contrement du coſté de la feinte, comme il à eſté monſtré cy deſſus; en attendant avec ceſte ſuperiorité, comme avec un remede univerſel, tout ce que l’Adverſaire luy peut machiner en ſuite de la feinte, ſoit en continuant le trait encommencé, ou en uſant de quelque changement par maniere de cavation, ou de quelque autre ſorte, que ce puiſſe eſtre. S’appercevant donc au premiere trait du changemēt, de l’intention de ſon Adverſaire, par le torſement de l’eſpaule & du bras d’iceluy; avant que la pointe luy paſſe l’endroit du coude, il voit clairemēt, qu’elle eſt dreſſé devers ſon viſage en ligne courbe: à l’occaſion dequoy il eſquive le coup en oſtant ſa teſte hors de preſence, par le moien d’un tournoyement & avancement du coſté gauche qu’il veut faire en poſant le pied droit, à preſent eſlevé, ſur le Diametre au dedans de la Circonference, en acceuillant au meſme temps avec le Nombre 7. de ſa lame dreſſée contremont le 5. ou 6. de l’eſpee contraire, ſur laquelle il fait quelqeu petite deſgraduation avec quelque abaiſſement de la main, s’affermiſſant le coude contre le flanc, pour la defenſe de la partie inferieure du corps; & continuant à ſe tourner & avancer ſur le meſme pied circulairemēt le coſté gauche, juſqu’à en poſer le pied à la lettre I. par deçà le Diametre, pliant le genouil & accommodant le corps deſſus, en aſſujettant l’eſpee contraire; le tout en conformité de ce qui eſt repreſenté par les figures. |
| Circle No 7. | Cercle N.7. |
| Alexander raises his left foot, and driving his adversary’s blade down and away from his own, leans slightly backwards to his starting point, then advancing with the same foot, he inserts the tip of his sword into his opponent’s right armpit. | Alexandre eſlevant le pied gauche, & amortiſſant la lame contraire en oſte la ſienne, ſe panchant un peu du dos a l’envers & derechef en revenant d’ou il eſtoit parti & avançant le meſme pied, il luy aſſene la pointe au coſté droit deſſous le bras. |
| This Circle continues from the preceeding one. Zachary has barely finished the motion of his failed thrust, but Alexander takes advantage of the situation. Raising his left foot while, at the same time, giving his opponent’s blade a push, both to desensitize him to the motion and pull his own sword from on top, he moves the tip in a circular motion up, around his opponent’s arm, and down, and while keeping his elbow against his side, moving the guard close in to his stomach, his back turned slightly away. Then, straightening again, he hits at the same instant that he puts his foot down at the letter L on the Perpendicular Diameter, allowing his right foot to come up as far as needed to be comfortably balanced and to reach the right side of his enemy, underneath the arm, as shown in the figure. | Ce cercle contient la pourſuite du precedent. Car à peine Zacharie a il achevé le mouvement de ſon eſtocade perdue, qu’Alexandre pourſuit ſon advantage; en eſlevent le pied gauche avec un petit pouſſement ſur la lame contraire, pour luy troubler le ſentiment, & pour en oſter par meſme voye la ſienne de deſſus, en menant la pointe circulairement alentour du bras contraire de haut en bas, & s’aſſermiſſant le coude du bras droit contre le coſté, avec la garde au devant pres de la poitrine, le dos un peu à l’envers; puis en revenant droit, il donne l’atteinte, & au meſme inſtant poſe le pied ſur le Diametre perpendiculaire à la lettre L. trainant conſequemment le pied droit derriere, autant qu’il eſt requis pour remettre le corps à ſon aiſe, & pour toucher au coſté droit de l’Ennemi deſſoubs le bras, comme il eſt pourtrait en la figure. |
| Circle No 8. | Cercle N.8. |
| Execution of the final part of the preceeding thrust, with all the force possible from the arm and body, with certain particularities that must be observed. | Finale execution de l’eſtocade precedente, aſſiſtée de toutes les forces du bras & du corps, avec les particularitez qu’il y faut obſerver. |
| To exploit the execution of the final part of this wounding, he moves his body forward, extending his arm with his sword, stepping wih his left foot up to the letter Q, drawing the other along up to the letter H intending to pass right through the body. This is clearly shown in the figure. | Pour exploiter la finale execution de ceſte bleſſure, il s’avāce le corps, avec le bras & l’eſpee eſtendue, portant le pied gauche juſqu’à la lettre Q. en traināt l’autre apres juſques à la lettre H. pourſuivant à luy paſſer le corps tout outre. Le tout ſe voit clairement en la figure. |
| We have divided the operation shown in Circles 7 & 8 into two beats, to help students. Those who are more advanced, can accomplish this in one beat, since they only need to put their left foot down once. What is more, there is a means of shortening the time even more, with an extra step: that is, when one subjugates the opponent’s sword, as described in Circle No 6, one steps forward with the right foot up to the letter E, a bit beside the Diameter line, or even more, and, as following through, while turning the left side of his body forward, he drops the contact with his opponents blade the same way as in Circle No 7, only putting his left foot down at the instant his tip makes contact with his opponent’s armpit, then following through in the same way as before. | Nous avons diviſé ceſte operation des Cercles N.7. & 8. en deux temps, en faveur des diciples. Car ceux qui ſeront plus avancez, la pourront accomplir en un, n’ayans beſoing de mettre le pied gauche en terre, ſinon une fois tant ſeulement. Qui plus eſt, il y aura moyen d’en abbreger le temps encores d’avantage, avec l’execution annexee: c’eſt qu’en aſſujettiſſant l’eſpee du Contraire, en la maniere deſcrite au Cercle N. 6. on entre du pied droit juſques à la lettre E. un peu par deça le Diametre, ou meſmes plus outre: & puis en pourſuivant tourner le coſté gauche en devant, deſtachant les eſpees en la meſme façon comme au Cercle 7. ſans toutefois abaiſſer le pied gauche à terre, ſinon au meſme inſtant qu’on le touche deſſoubs le bras, pourſuivant au reſte l’execution en la meſme ſorte, que deſſus. |
| Note that we presume, in Circle 6, that Zachary has made his thrust with full intent to harm, which is the real situation that prompts the first contact, the continuation, and final execution of the thrusts shown in Circles 6, 7 , and 8. But let us suppose he has not made this thrust with resolute determination, that he moves his tip a little slower, or that he does not move his body forward as much as a determined thrust requires, moving his right foot forward only as far as the letter V. What is the solution? Because if one tried to turn the left side forward and try to subjugate his sword as shown in Circle 6 would be very dangerous, because Zachary can still change his actions and make a circular disengage to wound Alexander inside the arm. Which would be impossible if he were fully committed to the outside thrust. The difference between these two attacks is what Alexander must learn to distinguish, through his adversary’s preparations, and initial motions whether he is attacking with intent, or reserved. Having recognized this, he moves his right foot forward beside the Diameter to about the letter E, closing his elbow by his side as he his body moves forward, and, with a slight drop of the hand and wrist movement, aims his raised tip towards his adversary’s sword, to be able to turn his adversary’s point aside, whether the blades are in contact or not. He is careful not to move his left foot forward, but keeps it slightly raised behind or to the side, and if his enemy continues with his initial movement, he will also continue with his left foot, more slowly than before, in order to maintain the correct amount of contact, to be able to work confidently against any disengagements his enemy might make. These must be met by the strong of his blade going against the weak of his opponent's, and then giving a hit to the face when stepping forward with the left foot. This will be fully explained in the appropriate chapter. So, having prepared, it sometimes happens that the swords touch, and sometimes not, or at least much later than they should. In the first case, you already know what to do, to move in relatively slowly with the left side and foot, maintaining the sensibility of the contact. In the second case, when the opponent does not touch your blade, it is absolutely certain he does not intent to wound you with his bent-arm attack, that he is only pretending to in order to get you to move your sword aside, away from defending the centre line, so he can more easily disengage around your arm. To prevent this, you must take advantage of this feint, by leaning further forward while lowering your hand and guard, catch the weak of his blade, at the 3rd, 4th, or 5th Span, with the strong of your blade as he moves upward from beneath your blade. Continue to move up his blade, aiming the tip of your sword towards his face to wound him following along the line of the blade, stepping forward with the left foot beyond the perpendicular diameter, if he is not fast enough with his disengagement. If he does it at all, considering that he can do this only with a circular motion. | Or notez que on preſuppoſe au Cercle 6. que Zacharie ait tiré ſon eſtocade avec pleine reſolution, qui eſt la vraye occaſion, de laquelle ceſte rencontre, continuation, & execution des ſuſdites Cercles 6. 7. 8. depend. Mais poſé le cas, qu’il ne tiraſt pas avec ceſte reſolution & hardieſſe, ains qu’il portaſt ſa pointe plus lentemēt, ou qu’il n’avançaſt pas le corps, tant que la proportion d’une eſtocade reſolue demande, n’entrant du pied droit que juſqu’à la lettre V. peu plus ou moins. Quel remede? Car de vouloir icy tourner le coſté ſeneſtre devant, & aſſujettir ſa lame à la mode du Cercle 6. c’eſt choſe treſdangereuſe: pource qu’il s’eſt reſervé de pouvoir changer l’operation encommencée, & de faire la cavation pour bleſſer au dedans du bras: ce qui luy ſeroit impoſsible s’il eſtoit en aćte de tirer avec reſolution. La rencontre, c’eſt qu’il faut qu’Alexandre ſache distinguer, par les commencemens & preparations des mouvemens du contraire, s’il tire avec reſolution, ou avec reſerve. Et l’ayant recognu, qu’il entre du pied droit environ la lettre E. par deça le Diametre, en s’affermiſſant le coude du bras droit contre le coſté, avec avancement du corps, & quelque petite deſcente de la main, & accomodation du poignet, par laquelle il dreſſera ſa pointe contremont devers l’eſpee contraire, pour en deſtourner la poinćte au temps convenable, ſoit que les lames s’entretouchent, ou non: ſe gardant cependant d’avancer le pied gauche, mais qu’il le tienne en l’air derriere ou à coſté, & ſi l’Ennemi continue ſon premier mouvement, il continuera auſſi à l’egal d’entrer du pied gauche, pluſtoſt lentement qu’autrement, afin de retenir le ſentiment juſte, pour travailler avec plus d’aſſeurance ſure les cavations qu’on luy pourroit faire; leſquelles il faudra rencōtrer en accueillant le foible de l’eſpee contraire du ſort de la ſienne, & luy donner le coup au viſage avec avancemēt du meſme pied gauche: ainſi qu’il ſera deſcript plus particulierement en ſon lieu. Or en faiſant ceſte preparation, il advient aucunefois que les eſpees s’entretouchent, & aucunefois point, ou pour le moins plus tard, qu’elles ne devroyent. Quand la premiere occurrence ſe preſentera, vous avez deſia voſtre inſtrućtion, d’entrer lentement avec le coſté, & le pied gauche, moyennant l’aſſeurance du ſentiment: Quand la ſeconde ſe preſente; & que l’adverſaire ne touche pas voſtre lame, c’eſt un argument infallible, qu’il n’a pas intention de bleſſer avec ſa courbe; ains ſeulement d’en faire le ſembāt, pour faire ſortir voſtre eſpee hors du centre de ſa defenſe, afin de ſe ſervir en apres de la cavation avec plus d’apparence. Pour y obvier, il faut que vous prenniez ſur ceſte feinte un nouvel amendement de voſtre avantage; en augmentant le panchement du corps en avant, enſemble avec la deſcente de la main & de la garde, en dreſſant la pointe en haut devers ſon viſage pour le bleſſer ſuivant le fil de ſa lame, s’il ne fait aſſez toſt la cavation. Et s’il la fait, conſiderant qu’il ne la peut faire autre, que circulairement; vous accueillirez du fort de voſtre eſpee le foible de la ſienne, Nombre 3, 4, ou 5, cependant qu’elle montera de deſſous voſtre garde en haut: & continuerez à la graduer, & à le bleſſer au viſage, en avançant le coſté gauche, & entrant avec le meſme pied dedans ſes perpendiculaires. |
| Circle No 9. | Cercle N.9. |
| Alexander is waiting in the Direct Line posture, Zacharie tries a thrust to the stomach, with the intention of stepping with his right foot up to the letter R, but Alexander prevents him, turning his right side away with his arm still fully extended and forward to give a hit on Zachary’s own right shoulder, which forces him to shorten his pace and set his foot down on the Diameter at the letter V. | Alexandre eſtant planté en droite ligne, Zacharie luy va tirer un coup d’eſtocade devers le ventre, en avançant le corps avec intention de porter le pied droit juſques à la lettre R. mais comme Alexandre le previent, en deſtournant le coſté droit avec le meſme bras eſtendu & avancé, & luy donne l’atteinte en l’eſpaule droite à luy meſme, il eſt retenu en arriere & contraint de raccourcir le pas à lettre V ſur le Diametre. |
| After having taken a look at the thrusts to Alexander’s face that Zachary might make, to the inside and outside of the sword, it is a good idea to likewise add the thrusts that he could also make towards the stomach, beneath the arm, so that by these proofs one can properly judge the superiority of the direct line posture, which he has, once again, adopted in Circle No 9, on the ordinary lines of the Quadrangle A-C. Zachary has likewise approached, by adopting the direct line posture, setting his blade parallel to and beneath the other, in the usual way of our style. Or, he may have approached up to the First Instance in the old style, with his body bent over. Having arrived there, he strikes outside with a feint of the second type, reaching to the wrist, and moves in closer. Continuing the same advance, he swiftly drops his tip with a circular motion, keeping his arm straight. He advances as he does this, intending to put his foot as far forward as the letter R along the Diameter, and at the same time he aims the tip of his sword at the lower part of his enemy’s body. These are the actions and intentions of the assailant. The instructions for the defender follows. Alexander first responded to the feint. He tensed his body, raised his right heel up, and began working with his sword, as has been described, above. He recognises, as his opponent begins to make the second part of the movement, that his opponent is going to wound him in the stomach or in the right side and as he does this his opponent lowers his arm and sword, so much that he leaves his right shoulder uncovered. At the same time, Alexander turns his right side outwards, withdrawing his right hip, points his feet forward and moves the upper part of his torso forward by leaning his upper body while holding his sword out straight in front, so that he hits his opponent in the right shoulder, which is the closest part of his body, and by this hit, he forces him to shorten his step, putting his foot down at about the letter V, rather than the letter R, as he intended. | Apres avoir propoſé les eſtocades, qui pourroyent eſtre tirées par Zacharie en dehors & en dedans l’eſpee vers le viſage d’Alexandre, il ſera bon d’y adjouſter pareillemēt celles qu’il pourroit tirer vers le ventre au deſſoubs des armes, afin que par ces preuves on puiſſe dignement juger de l’excellence de la droite ligne, en laquelle il s’eſt derechef arreſté en ce Cercle 9. ſur les lignes ordinaires du quadrangle AC. Zacharie l’eſt pareillement venu aborder avec la meſme droite ligne, en aſſeoyant ſa lame parallele au deſſous de l’autre, ſuivant l’ordinaire de noſtre ſtyle: ou bien il eſt venu à la premiere Inſtance avec le corps courbé, ſelon la couſtume ancienne; & y eſtant arrivé, il à tiré par dehors une feinte de la ſeconde eſpece juſqu’au poignet de la main contraire, en levant le pied droit, & commençant à s’avancer: puis continuant le meſme avancement, il à rabaiſſé ſa pointe circulairement avec le bras roide, & avec grande viſteſſe; avançant quand & quand le corps d’avantage, en intention de porter le pied juſques à la lettre R. ſur le Diametre, & d’aſſener au meſme temps le coup de ſa pointe en la partie inferieure du corps de ſon Ennemi. Voilà les aćtions, & l’intention de l’aſſaillant. S’enſuit l’inſtrućtion pour le defendant. Alexandre à fait premierement ſa preparation contre la feinte; s’avivant le corps, avec eſlevation du talon du pied droit, & travaillant de l’eſpee, ſelon ce qui a eſté dit plus particulierement cy deſſus. Puis recognoiſſant au ſecond mouvement le changement, que l’Adverſaire commence, pour le bleſſer au ventre, ou au coſté droit du corps; & que pour ce faire, il s’abaiſſe le bras & l’eſpee, tant qu’il ſe deſcouvre luy meſme l’eſpaule droite; il ſe deſtourne à meſme temps le coſté droit en dehors avec les pointes des deux pieds devant, & avance la partie ſuperieure du corps en la panchant avec le bras eſtendu, de ſorte qu’il luy donne l’atteinte en l’eſpaule droite, qui eſt le plus prochain endroit de lattouchement, le prenant & prevenant par ceſte rencontre, en ſorte qu’il le contraint de raccourcir le pas, & abaiſſer le pied environ la lettre V. au lieu de l’avancer juſques à R. comme il avoit deſſeing. |
| To clarify: Alexander must hit at the same instant that Zachary begins to lower his tip, while his body can still be held back, and before he has taken his large step. As long as Alexander knows how to adjust and use the time he has, he will wound him without moving from his place, doing nothing other than tuning his body, keeping his feet still, as we have described, which he can most certainly do as much as the adversary’s tip will, of its own accord, move away from the closest point of contact, and it will be held even further back because of the impediment of the counter-thrust, which stops the person from continuing the step he intended to make. | Pour en parler plus clairement; il faut que Alexandre luy donne l’atteinte, au meſme inſtant, que Zacharie commence à abaiſſer ſa pointe, durant que ſon corps eſt encor capable d’eſtre retenu en arriere, & avant qu’il ait prins une grande courſe. Car moyennant qu’Alexandre ſache bien prendre & adjuſter ce temps, il le bleſſera ſans bouger de ſa place, ne faiſant autre choſe, que tourner en peu le corps, par le moyen des pieds, ainſi que nous venons de deſcrire. ce qu’il pourra faire aſſeurement pour autant que la pointe contraire s’eſt eſloingnee d’elle meſme du plus prochain point de l’attouchement, & qu’elle eſt retenue encor outre cela en arriere par l’obſtacle de l’eſtocade, arreſtant la perſonne environ le milieu du chemin qu’elle avoit penſé de faire. |
| But let’s suppose, either by his opponent’s speed, or because Alexander is inadvertently slow, that Zachary is now so far forward that there is no longer any means of stopping him, or breaking his step. In this case, it is not advisable for Alexandre to try to reach him with a simple twist of the body. So he must, at the same time, take a small backwards step, out of fear that the adversary’s sword-tip (which is nearby, is free to move, approaching, and cannot be stopped by a straight line counter-thrust) will wound him at the same instant, or just afterwards. In this case, he must draw his feet backwards a little bit, about as much as his adversary’s approach, so that there is no part of his body is left where Zachary intends to strike, or, if Zachary wants to reach even further, he will be forced to make extremely long moves, and to unbalance himself so that he cannot recover quickly, in which case he should meet him at this point, when he is weakest, when he has abandoned himself to the mercy of his adversary, having abandoned his position of superiority in such a way that one can easily use the direct line to hit the nearest open target, as long as one leans a little forward. To accomplish this, being in the Instance is very advantageous for Alexander, because he attacks from the direct line posture, which has the longest range, by leaning his upper body forwards, while withdrawing the lower part, which is where his adversary aimed the tip of his sword, and his enemy has moved himself off of the dirct line by attacking downwards at an acute angle. Finally, which is very important, Alexander works from a position of superiority, and he can surprise the enemy at the very instant that he has expended all his effort, leaving nothing for his defense. | Mais poſons le cas, que par ſa viſteſſe, ou par l’inadvertance d’Alexandre, il ſoit venu ſi avant qu’il n’y ait plus de moyen de l’arreſter, ou de luy rompre le pas. En ceſte occaſion il n’eſt pas loiſible à Alexandre de l’attendre avec un ſimple tournement du corps; ais il eſt contraint de ſe ſervir quand & quand d’une petite retirade; de peur que la pointe contraire, (que eſt en preſence, & libre, & en aćte d’approcher, ni ne peut eſtre arreſtée par l’eſtocade de la droite ligne) ne le bleſſe au meſme inſtant, ou bien peu apres. Il faut donc en ce cas qu’il retire les pieds un peu en arriere, plus ou moins à l’advenant de l’approchement de l’Adverſaire, afin qu’il ny ait point de corps au lieu qu’il pretend de frapper, ou s’il veut pourſuivre ſa poinćte plus avāt, qu’il ſoit contraint à faire des mouvements extremes, & à tresbucher du corps, dequoy il ne ſe peut redreſſer à temps, ſi on adviſe bien de l’accueillir durant le meſme affoibliſſement, au quel il s’eſt comme abandonné à la mercy de l’Adverſaire, luy quittant tout l’advantage de la ſuperiorité. en ſorte qu’on le peut aiſement toucher en droit ligne au plus prochan lieu deſcouvert, moyennāt qu’on ſe panche un peu ſur le devant. Or pour ce faire les Inſtances ſont grandement advantageuſes pour Alexandre, par ce qu’il travaille avec la droite ligne, qui eſt la plus longue meſure, avec panchement de la partie ſuperieure du corps, en ayant en outre retiré la partie inferieure où l’Adverſaire avoit dreſſé ſa poinćte, & que l’ennemi s’eſt eſloigné de luy meſme de la droite ligne, en tirāt le coup vers le bas en angle aigu: & finalement, ce qui importe beaucoup, qu’il travaille avec ſuperiorité, & qu’il ſurprend l’Ennemy à l’inſtant qu’il n’a plus nulle reſerve de force pour ſa defenſe. |
| An observation, at all times, when performing this, take care that you do not withdraw your foot too early, and so allow your adversary come halfway to the next Instance, and so he will continue to press his point even more forcefully, encouraged to expect that it will succeed, which will leave your arms and legs vulnerable to attack. Because otherwise if he has time to observe your change of position, he will likewise change his position in response against it, either by making a circular disengage, or attacking your sword, or moving out of range. Thus, a retreat made too soon will alert him, to his advantage. | Toutesfois pour pratiquer ceſt obſervation prenez bien garde, que vous ne faciez pas la retirade du pied avant qu’il ſoit temps, ains que vous laiſſiez venir l’Adverſaire juſqu’à la moitié de l’Inſtance, afin qu’il continue plus furieuſement à pourſuivre ſa poinćte, en eſperance, & avec apparence de la mettre à execution; ce qui luy ſera faire des extremitez à luy prejudiciables. Car autrement s’il adviſe à temps du changement, que vous faites, il changera pareillement alencontre, ſoit en uſant de cavation, ou en affrontant les eſpees, ou en rompant la meſure; de façon, que la retraite, qui ſera faite avant le temps, luy ſervira d’un advertiſſement pour ſon advantage. |
| There is one more point to make in the explanation of Circle No 9, that is, for one who would make such a thrust, with the tip aimed acutely downwards at his adversary’s chest or shoulder, he take care not to put himself in the inevitable danger of receiving a similar thrust to the stomach, because, it seems, that such a thrust will do nothing in the world to stop his opponent’s body, if he was not moving forward without a pause. I submit the response to this in the description of the following circle, where it shall be self-evident. | Il reſte encor une autre demande pour la declaration de ce Cercle 9. aſſavoir, ſi celuy qui donneroit un tel coup d’eſtocade, avec une poinćte aigue en la poitrine, ou en l’eſpaule de ſa partie adverſe, ne ſe metteroit pas en danger inevitable de recevoir la pareille au ventre, à cauſe qu’il ſemble qu’une poinćte aigue ne pourroit en rien du monde arreſter le corps contraire, qu’il ne s’avançaſt plus outre, ſans null pauſe. I’en remets la reſponce à la deſcription de l’execution qui s’enſuit; où elle ſera evidente d’elle meſme. |
| Circle No 10. | Cercle N.10. |
| Because Alexander leaned the upper part of his body forward to hit, it follows that his arm and hand were lowered by the same degree as a result, and it follows that his guard can contact and block his adversary’s blade, before the tip has time to reach his own body. So that, by the lowering of his arm, that accompanied the forward lean of his torso, he holds the lower blade in subjugation, pushing it further down and away, and what is more, he only gets closer by bending his body further over. Combined with raising his left foot, he enters in against his adversary, stepping forward only with his lower left side, while keeping his right side (which is the target his opponent’s thrust) to the rear. He puts his left foot down at the Letter I, or near there on the Diameter, leaning and moving his right shoulder forward, while keeping his arm straight to force his guard downwards, and moving the contact up his adversary’s blade, until his opponent’s sword tip is almost into the ground, following on by piercing the shoulder and neck of his opponent, in a way that he cannot defend against it. | Puis qu’Alexandre a donné l’atteinte avec panchement du corps, dont la partie ſuperieure, le bras, & la main, deſcendent tout enſemble proportionnellement, il s’enſuit que ſa garde viendra toucher & empeſcher la lame contraire, avant que la poinćte ait le loiſir de parvenir juſqu’à ſon corps: de ſorte que par la deſcente du bras (qui accompagne le panchement de la partie ſuperieure du corps) il tiendra la lame inferieure en ſubjećtion, l’abaiſſant plus loing de ſoy & pluſtoſt, qu’il ne s’en approche par la continuation de ſon panchement encommencé. Ioint auſſi qu’en eſlevant le pied gauche, il entrera ſur ſa partie adverſe, avec la partie inferieure du coſté gauche tant ſeulement, demeurant cependant le coſté droit, (qui eſt le blanc de l’eſtocade contraire) en arriere; & plantera le pied en terre au poinćt I ou environ par deça le Diametre, panchant & avançant davantage la partie ſuperieure du coſté droit, deſcendant touſiours ſa garde avec le bras eſtendu ſur l’eſpee contraire, la graduant juſqu’à la garde, de ſorte que la poinćte viendra quaſi à toucher la terre: pourſuivant au reſte à percer l’eſpaule & le col de ſon Adverſaire, de façon qu’il ne luy reſte plus aucune defenſe. |
| Moreover, it is understood that he will continue and complete this strike by recovering his balance by a step with his right foot, to dominate he enemy still more. This is so very easy that we thought it was enough to mention it, and did not need another figure to illustrate. | Or il s’entend qu’il accomplira la cōtinuation de ceſte execution, avec le pied droit pour ſe redreſſer, & pour dompter l’ennemy encores davantage: laquelle choſe eſtant tresfacile, il nous ſemble, que c’eſt assez d’en avoir donné ce petit advertiſſement, ſans la repreſenter en figure. |
| Circle No 11. | Cercle N.11. |
| Zachary again aims the same thrust to the lower body, but this time with the guard higher up, to protect his shoulder, from which Alexander turns and draws his right hip backwards, while the upper body leans forward and extends his arm with the sword so as to hit him in the face. | Zacharie luy tire encores la meſme eſtocade que deſſus, pour le toucher au bas du corps, mais avec la garde un peu plus haute, en ſorte qu’il ſe couvre l’eſpaule, dont Alexandre ſe deſtourne & retire quelque peu le coſté droit en arriere, avec la partie ſuperieure du corps panchée en avant, & le bras avec l’eſpee eſtendus de façon qu’il le touche au viſage. |
| This action begins the same way as the previous one, that is, the two adversaries face each other at the First Instance. Zachary makes a feint to the inside. This was likewise met, as in Circle No 9, but with the difference that the thrust in Circle No 9 was made so low that his shoulder was exposed, so he guards against that this time. So, as he moves his body forward while making a circular disengagement, in order to attack and move his foot forward to the Letter R, he carries his hand a bit higher, so as to cover his shoulder with his guard. Which is why, as soon as Alexander, having made ready by becoming alert and tensing his body, extended his arm and brought the tip of his sword up at an obtuse angle, as fully described in the previous example, percieves the first indication of a move from the feint, at the instant his adversary’s sword begins to drop down to aim the tip at his lower body, he likewise drops his own, bringing the tip, with his arm extended, to about the height of his adversary’s head, again intending to use the direct line posture to wound him in the shoulder. But seeing that his shoulder is covered by the guard, he immediately turns his right side to the outside, so the toes of his feet point forward, he draws his right hip and foot back slightly, leaning further forward with his upper body. This motion brings his arm down at the same time, dropping the guard onto his opponent’s sword. As he continues to lower it further, he is presented with the opportunity to wound him in the face, as is shown in the figure. | Le commencement de ceſte operation eſt de meſme, que la precedente: aſſavoir, que les deux contraires eſtās venus à meſure de la Premiere Inſtance, Zacharie a tiré ſur Alexandre une feinte en dedans du bras: laquelle à pareillement eſté recontrée, comme au Cercle 9. mais la difference conſiſte en l’eſtocade & en la rencontre a propriée: car l’eſtocade a eſté tirée au dit Cercle 9. en abaiſſant ſi avant le bras & l’eſpee qu’il s’eſt deſcouvert luy meſme l’eſpaule, dont il ſe garde en ceſte operation preſente. Car en avançant le corps avec la cavation, pour tirer & marcher du pied droit juſqu’à la lettre R. il porte le bras un peu plus haut, de ſorte, qu’il ſe couvre l’eſpaule avec ſa garde. Parquoy ſi toſt qu’Alexandre apperçoit le premier trait du changement de la feinte (ayant preallablement fait ſa preparation; enſavivant le corps, eſlevant le pied droit, & eſtendant le bras avec l’eſpee, la pointe d’icelle en angle obtus, comme il a eſté deſcrit plus amplement en l’operation precedente) à l’inſtant que l’eſpee de ſa partie commence à deſcendre, pour luy aſſener la pointe au bas du corps; il abaiſſe pareillement la ſienne, en conduiſant la pointe avec le bras eſtendu environ la hauteur de la teſte de ſon contraire, pour le bleſſer derechef avec la droite ligne, en l’eſaule. Mais la voyant couverte de la garde, à l’inſtant il deſtourne ſon coſté droit un peu en dehors, avec les pointes des deux pieds en devant, & quelque retirade du pied droit, & de a partie inferieure du meſme coſté, panchant d’autant plus en avant de la partie ſuperieure. ce qui luy fait deſcendre au meſme inſtant le bras, & la garde ſur la lame cōtraire; & en continuant à l’abaiſſe d’avantage, luy preſte la commodité de bleſſer ſon Contraire au viſage: ainſi qu’on voit en la figure. |
| What we just described, that is, Zachary’s feints that are made in two moves in Circles 9 & 11 and likewise in 12 which follows, are more often made to the inside rather than the outside. This is because they are more advantageous and easier to do this way, and more common amongst those who take shots at the lower part of the body. In any case, if they wish to aim elsewhere, because anyone is free to aim wherever they imagine, there would be no difference in the result, but in Alexander’s preparation, which will always be to seize the upper hand over his opponent’s blade by moving over to the side of the feint. This way he will meet the thrust in the same way, whether it comes from the outside or the inside line. | Ce que nous avons deſcrit, que les feintes de Zacharie ſont tirées en ces deux operations des Cercles N.9. & 11. & pareillement encor du 12. enſuivant, pluſtoſt en dedans du bras, qu’en dehors; c’eſt pour autant quelles ſont plus avantageuſes & plus aiſées à faire en ceſte ſorte, & plus communes entre ceux qui portent les bottes en la partie inferieure du corps. Toutesfois s’il les veut tirer autrement, puis qu’il eſt libre à chaſcun de faire à ſa fantaſie, il n’en reſourdra autre difference, que de la preparation d’Alexandre, qui prendra touſiours la ſuperiorité des lames du coſté de la feinte: car pour rencontrer l’eſtocade il travaillera touſiours de la meſme ſorte, ſoit qu’elle vienne par dehors, ou par dedans. |
| One must also be careful in this action and all similar ones, withdraw one’s body and feet away a precise distance from the approaching adversary and the tip of his sword, in accordance with the warnings in Circle 9. | Faut auſſi obſerver en ceſte operation, & en toute autre ſemblable, de meſurer & moderer le retirement du corps & des pieds, à l’advenant de l’approchement du corps & de la pointe Contraire, ſuivant l’advertiſſement du Cercle 9.
|
| But as the final action of this hit requires that one add at least one more step beyond what we see demonstrated by the figures, note that when Zachary’s blade ends up below the outside branch of Alexander’s while his guard is above it, then he must step in with his left foot while sliding the contact up the blade as seen in Circle 10. And when it is below [above] the outside branch he must enter in and slide up the blade by stepping forward with his right foot. | Mais d’autant que la finale execution de ceſte atteinte, requiert quon y adjouſte encor un pas par deſſus ce qu’on voit en la demonſtration des figures, notez, que quand la lame de Zacharie ſe retrouve deſſoubs la branche exterieure d’Alexandre, cependant qu’il tient ſa garde deſſus, qu’alors il entrera ſur luy avec le pied gauche, en luy graduant l’eſpee, à l’imitation de ce qui eſt repreſenté au Cercle 10. Et en cas qu’elle ſe retrouve deſſous la branche exterieure, qu’il entrera & fera la graduation en marchant du pied droit devant. |
| Circle No 12. | Cercle N.12. |
| Zachary once again tries to hit his adversary in the lower body, sword-tip pointing down, with his hand held so high that he protects even his head. So, Alexander allows him to approach, moves the tip of his sword up to his adversary’s head, and realizing that it is protected, he attacks the blade to subjugate it, turning to the right side and at the same time lowering the arm and sword onto his adversary’s blade, moving up it. | Zacharie tire encor derechef pour toucher ſon Contraire au bas du corps, avec la main ſi haute qu’il s’en couvre meſme la teſte, & la pointe baſſe; dont Alexandre, le laiſſant approcher, conduit ſa pointe à la hauteur de la teſte contraire, & la recognoiſſant eſtre couverte il travaille ſur ſa lame pour l’aſſujettir, en deſtournant le coſté droit du corps, & par meſe voye s’abaiſſant juſtement le bras & l’eſpee ſur l’eſpee Contraire, en la deſgradant. |
| In this Circle, it is not enough for Zachary, as he makes the same feint to the inside as above, to protect his shoulder as he strikes at his adversary’s right side, he must also raise his guard high enough to cover his head as well. He raised his foot, with a slight forward movement of his body, during his feint. Now he carries on, continuing to move his body forward, aiming to strike with his arm extended, his hand raised high, and his tip low, stepping along the Diameter almost to the centre, drawing his left foot behind him into the circle. | Il ne ſuffit pas à Zacharie en ce preſent Cercle, apres avoit fait encor la meſme feinte que deſſus, en dedans du bras contraire, de ſe couvrir l’eſpaule en tirant le coup d’eſtocade vers le coſté droit de ſa partie, ſi ce n’eſt qu’il porte la garde de ſon eſpee ſi haute, qu’il s’en couvre auſſi toute la teſte. Car ayant levé le pied, avec un petit avancement du corps durant la feinte: il pourſuit preſentement, en continuant ledit avancemēt du corps & du pied, à tirer le coup, avec le bras eſtendu, la main haute, & la pointe baſſe, abaiſſant finalement le pied à terre ſur le Diametre bien pres du centre, trainant l’autre derriere juſqu’au dedans du Cercle.
|
| Alexander has prepared against the feint, raising his right foot, straightening his body, extending his arm, and raising the tip, as previously explained in detail. As soon as he can see that his Enemy has begun to drop his blade with his body noticeably leaning forward to hit the lower part of his body, Alexander keeps his arm extended and he moves the tip of his sword up to about the level of his adversary’s head. But as he cannot see any place to hit, because his opponent has covered his head with his guard, and because the tip of his ennemy’s sword is closing with him below, he turns slightly to the outside, points his toes forward towards the Enemy, withdraws his right side, including his sword and arm, back and to the right, lowering his sword and arm by leaning with his torso, crossing his adversary’s sword and sliding up to subjugate it while controlling it by drawing his guard back towards his side as he turns the crosspiece diagonally so the outer branch is upwards. | Alexandre ayant fait ſa preparation contre la feinte, en eſlevant le pied droit, & dreſſant le corps, eſtendant le bras, & hauſſant la pointe, en la maniere qu’il eſt ſpecifié plus amplement és autres operations: dés qu’il remarque, que l’Ennemi commence à deſcendre ſa lame avec un notable approchement du corps, pour frapper en la partie inferieure, laiſſant le bras eſtendu, il conduit ſa pointe d’en haut juſques environ la hauteur de la teſte contraire: mais comme il ne voit point d’apparence de la toucher, à cauſe qu’elle eſt converte de la garde, & que la pointe ennemie le vient ſerrer par en bas, il s’en deſtourne un peu en dehors dreſſant les orteils de ſes deux pieds en devāt droit devers l’Ennemi, en retirant par ainſi le coſté droit, enſemble le bras & l’eſpee en arriere un peu à coſté, les abaiſſant par le moyen du panchement de la partie ſuperieure, ſur l’eſpee contraire, la croiſant & deſgraduant pour l’aſſujettir & domter parfaitment, en retirant le bras avec la garde à ſon coſté, ſes branches tournées diagonalement. |
| The caution, as was explained above, that one must not be hasty and retire backwards too quickly, applies likewise in this present action. Seeing as how one must lean forward and drop the hand and sword much lower than before to subjugate the adversary’s sword. If one moves too early, this means the hand drops quite far down, leaving one uncovered, and with considerable danger from the outside line. Which is why it is necessary to allow the attack to come as close as possible while still being able to step back, in order to encourage him to fully commit to the thrust onto the target, so as to be more assured of meeting his blade at the end of his movement, when he can no longer defend himself against the counter, and he can no longer change his actions. This precept is repeated here, as much as the danger is even greater now than previously, so this warning becomes even more necessary. | Or comme il a eſté dit cy deſſus, qu’il ne ſe faut pas trop haſter de ſe retirer en arriere, ainſi le faut il pratiquer pareillement en ceſte operation preſente. Voyant qu’il eſt icy beſoing de pancher du corps en avant, avec un plus grand abaiſſement du bras & de l’eſpee qu’auparavāt, pour aſſujettir la lame contraire: choſe qui ne peut eſtre fait ſans deſcendre aſſez notablement, & ſans ſe deſcouvrir avec treſgrand danger en dehors du bras, ſi on ſe precipité à le faire devant le temps. Parquoy ſera beſoin de laiſſer venir le coup ſi pres qu’il eſt poſſible, pourveu ſeulement qu’on ne perde pas le moyen de ſe retirer, afin de luy donner occaſion de pourſuivre ſa pointe, pour l’accueillir aſſeurement ſur la fin du mouvement, quand il n’aura plus de reſerve pour ſa defenſe; tant s’en faut qu’il auroit le moyen de faire & executer de nouveaux deſſeings. Ce precepte vous eſt repeté en ce lieu cy; d’autant que le danger y eſtant plus grand qu’au paravant, auſſi l’advertiſſement en eſtoit plus neceſſaire. |
| As to what we have said, that one must dominate and subjugate the adversary’s sword by leaning the body forward as the arm goes downwards, it should not be taken to mean that the arm makes no move on its own to accomplish this downward motion, but only that it will be drawn further down by bending the body, meanwhile only working with a small movement of the wrist, turning the exterior branch of the crosspiece diagonally upward to the side, while the tip traverses over to the left side, to cross, subjugate, and slide the point of contact up the blade, as is shown by the shadows on the ground. Nothing more is needed, to avoid the danger of a disengage, along with any other actions that he might try to change the position. Because by observing this, as soon as the enemy begins to do anything, the arm is already free, and able to do whatever work it must to defend and attack. Which could not be, if it were already going down. Because it is impossible to raise up and to lower at the same time, nor to accomplish a two-beat move in one instant. This admonishment will be very useful on several occasions, and so it is important to understand this. | Quant à ce que nous avons dit, qu’il faut domter & aſſujettir l’eſpee contraire, en panchant du corps ſur le devant avec deſcente du bras, cela ne ſe doibt pas entendre en telle ſorte, que le bras face aucun mouvement en ſon particulier pour accomplir la dite deſcente, ains ſeulement qu’il ſoit tiré plus bas par l’accommodation du corps, ne travaillant cependant qu’un bien peu du ſeul poignet, en tournant la branche exterieure diagonalement en haut vers le coſté droit, & la pointe traverſée vers le coſté gauche, pour croiſer, aſſujettir, & deſgraduer, comme il eſt repreſenté ſur le plan du Cercle. Pour eviter le danger de cavation, enſemble avec touts les autres changements qui pourroyent ſurvenir; il n’y a rien ſi neceſſaire que ce precepte. Car en l’observant, dés que l’ennemy commence pour peu que ce ſoit, le bras eſt deſia libre, & diſpoſé à travailler en ſon particulier pour defendre & pour offenſer. Ce qui ne ſeroit, en cas qu’il fuſt en aćte de deſcendre: car il eſt impoſſible de le hauſſer & abaiſſer tout enſemble, ny d’accomplir deux temps en un meſme inſtant. Cet advertiſſement aura fort grand uſage en pluſieurs occaſions; & partant il le faut bien comprendre. |
| Circle No 13. | Cercle N.13. |
| This is the completion and final action from the preceding Circle. Alexander has acquired a great advantage, by subjugating his adversary’s sword, sliding the point of contact along the blade, and turning the outside branch of his crossguard diagonally upwards. At this point, he turns the crossguard back to horizontal and moves his tip towards his adversary’s side, underneath the guard and arm. He moves his entire body, arm, and sword forward, and seizes his adversary’s blade by trapping it with the exterior branch of his crossguard, as he slides up to the hilt, and steps with his right foot up to the letter H, putting his weight on it and drawing his other foot behind, up to the circumference. At the same time, he exploits the strike through his enemy’s body, driving forward, hitting with the guard, and forcing him to bend his arm, almost knocking his opponent’s sword from his hand, leaving his opponent at his mercy, as shown by the figures. | Ceſt la pourſuite & l’execution du precedent. Car Alexandre s’eſtant acquis un ſi grand avantage, comme d’avoir aſſujetti l’eſpee contraire, avec deſgraduation, & accomodation de la branche exterieure dreſſée diagonalement en haut: il retourne icy ſes branches horizontales, & ſa poinćte devers le coſté de l’ennemy deſſoubs la garde & le bras, s’avançant tout le corps enſemble avec bras & l’eſpee, & prenant ſubitement avec ſa branche exterieure la lame contraire, en la graduant. & portant le pied droit juſqu’à la lettre H. en menant la charge du corps deſſus, & trainant l’autre par terre juſqu’à la circonference; & au meſme temps il exploite le coup de ſa poinćte à travers le corps de l’ennemy, ſi avant qu’il vient choquer ſa garde, & le contraint de plier le bras, & de laiſſer quaſi tomber l’eſpee hors du poing, à la mercy de ſon Contraire. Comme les figures demonſtrent. |
| To summarize, these are examples which show the great utility of our First Instance, and of the direct line posture when presented from there. One is fortified against all sorts of feints, and assured against all strikes, whether long and determined, or tentative and slow, high or low, made from a direct line or a bent line, on the inside or outside of the arm, to meet probes in one beat, and attacks in two beats, sometimes with the body erect, sometimes bent slightly forward or backwards, always striking with with small movements, which have more force than they seem, with more audacity and assurance than one thinks possible, quite the reverse of what we see in the usual style. If you were to tell me that there does not appear to be an easy way acquire sufficient skill to use this effectively, I would answer that nothing in life worth having comes without effort. In any case, I have made certain of the well-being of those who have not yet any ability, insofar as they put these precepts to the test. Because, just as gold purified in a furnace acquires greater luster, so with our exercises, that, when looked at closely, examined, attentively inspected, and practiced, with each repetition will appear more elegant and beautiful. When one conducts thorough research into these truths and their meaning, one will see they do not depend in any way on chance. The uncertainty of fortune does not appear anywhere. There is only the rules of science that dominate, in such a perfect way that any amateur who applies himself, will gain courage and confidence in his skill at arms, and the certainty and dexterity in their use which, when lacking, leave him weak and vulnerable. | En fin, voilà les exemples, qui demonſtrent le grand uſage de noſtre Premiere Inſtance, & de la droite ligne preſentée en icelle: fortifiée contre toute ſorte de feintes, aſſeurée contre toutes bottes, tant longues & reſolues, que tardives & lentes, hautes, baſſes, tirées en ligne droite ou courbe, en dehors ou en dedans du bras, pour rencontrer otes en un temps & ores en deux, tantoſt avec le corps dreſſé, tantoſt un peu courbe en avant ou en arriere, en donnant touſiours le coup avec des petits mouvements, qui ont plus de force, que d’apparance, & en faiſant l’execution avec les plus hardis & aſſeurez, qu’il eſt poſsible, au rebours de ce que la Pratique vulgaire en monſtre. Si vous me dites, qu’il n’y a pas grande apparence de venir aiſement à ceſte perfećtion d’en monſtrer les effets; ſachez pour reſponſe, que tout ce qui eſt louable ne s’acquiert ordinairement, qu’à grand travail. toutesfois, je m’aſſeure encores pour le regard de ceux qui n’en auront encores nulle habitude, que d’autant plus qu’ils mettront les preceptes à l’eſpreuve, d’autant plus y trouveront ils de perfećtion. Car ainſi que l’or eſtant mis à la fournaiſe, en reçoit un plus grand luſtre, par l’approbation de ſa pureté; tout de meſme nos inſtrućtions, eſtants regardées de pres, examinées, contrerollées, pratiquées, & repetées en paroiſtront touſiours plus belles. Car quand on aura fait une digne recerche de leur Verité, & de leur importance, on verra que l’incertitude de la fortune n’y a nulle part, & que les ſeules regles de la ſcience y dominent en telle perfećtion, quel Amateur, qui s’en ſera rendu capable, empruntera meſme le courage & l’aſſeurance des armes, qui manque à la foibleſſe des ſes forces de la certitude & dexterité de leur uſage. |
| Translation by Bruce G. Hearns |
Transcription by Bruce G. Hearns |
|---|---|
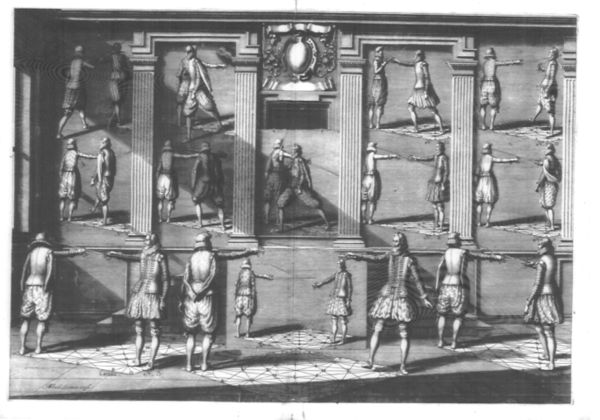
| |
| EXPLANATION OF THE ACTIONS IN THE SIXTH PLATE. | DECLARATION DES OPERATIONS DV TABLEAV SIXIEME. |
| Zachary, having found himself, in the previous table, so thoroughly dominated and contained by the power of the Direct Line posture, now tries to imitate it and use it to his own advantage, expecting to be able to be as successful as Alexander, just as he has seen him do. So he hopefully presents Alexander with the same posture, to force him to come against it the same way. As he has the opportunity of being first in place, he steps onto the Circle, right foot along the line X-Y, toes on the Circumference at X, and the left foot on the Pedal Line, as described previously in Plates III & IV, placing his blade into the Direct Line posture, to await his adversary to come against him. Thus in place, Alexander approaches, also using the Direct Line posture, moving into the First Instance at the other side of the Circle, the toes of his right foot on the letter C, the left foot on the other Pedal line in the Quadrangle, his sword held in the Direct Line posture underneath his opponent’s in the same way as shown in Circle No 1 of Plate IV, on which all the of the present actions of this Plate depend, just as all of those in the Fifth Plate. | Par les preuves de la droite ligne, qui ont eſté faites au Tableau precedent, en prevenant & domtant ſi avantageuſement toutes les intreprinſes de Zacharie, il s’en tient ſi à plein contenté, qu’il ſe diſpoſe preſentement à la vouloir imiter, s’aſſeurant de s’en prevaloir auſsi bien qu’Alexandre, en conforomité de ce qu’il luy a veu faire. Dont il le requiert amiablement de travailler à ſon tour ſur la meſme poſture, qu’il entend luy preſenter à la pareille. Ce que luy eſtant volontiers accordé, il ſe va mettre ſur le Cercle, le pied droit ſur la ligne XY, en touchant la Circonference à la lettre X, & le pied gauche ſur la ligne Pedale, ſuivant les deſcriptions plus particulieres des Tableau III. & IV. aſſituant ſa lame en droite ligne, pour attendre que ſon Contraire vienne travailler alencontre. Eſtant donc ainſi placé en poſture, Alexandre le vient aborder avec pareille ligne droite, ſe mettant à la Premiere Inſtance à l’autre bout du Cercle, le pied droit à la lettre C, le gauche ſur l’autre ligne ordinaire au dedans du Quadrangle, l’eſpee en ligne droite parallele au deſſous de l’eſpee contraire, en la meſme ſorte qu’il eſt repreſenté au Tableau IV. Cercle N.1. dont toutes les operations de ce preſent Tableau dependent, auſſi bien que celles du cinquieme. |
| Circle No 1. | Cercle N.1. |
| Alexander must work against the Direct Line posture, after he has moved to the First Instance, he raises his right foot, together with the tip of his blade, crossing swords with his 8th Span against his opponent’s 3rd Span, with a subtle pause of the body, intending to subjugate his opponent’s blade at the Second Instance. | Alexandre ayant à travailler ſur la poſture de la Droite ligne, apres eſtre venu à la Premiere Inſtance, il level le pied droit, enſemble avec la pointe de ſa lame, en accouplant les eſpees en dedans du bras, Nombre 3, à Nombre 8, avec un arreſt du corps fort ſubtil, en intention d’aſſujettir ſon Contraire à la Seconde Inſtance. |
| Alexander has arrived at the First Instance, and plans to subjugate his adversary’s sword when he moves to the Second Instance, along the Oblique Diameter. To do this, as he begins his move, he raises his right foot, keeping the knee straight, without making any general movement of his body, or of his arm, except a small bend of the wrist to raise his tip up, contacting the inside of his opponents sword at the 3rd Span with the 8th Span of his own, with a slight pause of his body, very subtle and imperceptible because it lasts no longer that the time it takes to raise his tip and make contact with the sword, just in case his Adversary tries to hit him with a thrust, high or low, inside or outside. At that very instant he has his right foot ready and he is able to set it down wherever he needs. | Alexandre eſtant arrivé à la Premiere Inſtance, ſe propoſe d’aſſujettir l’eſpee contraire à la Seconde, par deçà le Diametre, Et pour ce faire, en commençant à travailler, il leve le pied droit, avec le genouil roide, ſans aucun mouvement general du corps, ny du bras in particulier; ſinon que par quelque petite accomodation du poignet, il fait monter ſa poinćte en haut, en touchant l’eſpee contraire en dedans, du Nombre 3. le Nombre 8. avec quelque petite pauſe du corps, tres-ſubtile & fort difficile à recognoiſtre, parce qu’elle ne doit durer non plus, que l’aſcenſion de la poinćte, & l’inſtant de l’attouchement des eſpees, afin que s’il advenoit d’aventure, que l’Adverſaire entreprinſt de luy vouloir tirer au meſme inſtant quelque eſtocade, haute, ou baſſe, en dedans, ou en dehors, qu’il euſt le pied droit tout preſt, & à commandement pour le planter ſelon l’exigence. |
| This is the first entry into all the actions in this Plate and should be very carefully performed, each and every time it is a question of subjugating a blade, whether to the inside or to the outside. Since the interval between C and the Second Instance, whether to one side or the other is a quite large step to take, and to take it, one must have the initiative in both time and movement. I would say it is quite noticeable and obvious, if one tries to do this in one single motion without out the pause, that the Enemy will observe the beginnings of this action and can interrupt it very advantageously, and while performing his own counerattack. All of which can be prevented by means of this raising of the right foot and adding this pause. Of this we shall see several proofs in this book and singularly in the next Plate VII. | Voilà la premiere entree de toutes les operations du Tableau, laquelle il faudra fort curieuſement obſerver, toutes & quantes fois qu’il ſera queſtion d’aſſujettir la lame, ſoit par dedans, ou par dehors. Car l’intervalle, qui eſt depuis la lettre C juſqu’à la Seconde Inſtance, tant de l’un coſté que de l’autre, c’eſt une grande eſpace de chemin, & pour l’achever, il faut que le temps & le mouvement ſoit auſſi à l’advenant. Ie veux dire, qu’il ſera ſi notoire & manifeſte, ſi on entreprend de l’accomplir en un ſeul temps ſans la ſuſdite pauſe, que l’Ennemi en obſervant les commencements de l’operation, la pourra deſtourber fort avantageuſement, & avec apparence de mettre ſon entreprinſe à execution. Ce qu’on pourra prevenir par le moyen de ceſte eſlevation du pied droit, & de la pauſe annexe: dequoy on verra pluſieurs preuves en ce Livre, & ſingulierement au prochain Tableau VII. |
| Circle No 2. | Cercle N.2. |
| Zachary continues to maintain his posture; Alexander continues to subjugate the sword, moving his right foot towards the Second Instance, while sliding the point of contact up the sword, followed by a slight halt of the foot, while he makes sure of his superior position, and, having put his foot down at G, he brings the other along in a slow, circular motion to the Circumscribed Square at the Oblique Diameter. | Puis que Zacharie continue à ſe tenir en la poſture; Alexandre pourſuit à luy aſsujettir l’eſpee, en portant le pied droit devers la Seconde Inſtance, avec deſgraduation, ſuivie d’un petit arreſt du pied, durant lequel il prend l’aſſeurance de la ſuperiorité, & ayant mis ledit pied baſtivement à terre à lettre G, il porte l’autre apres lent & circulairement juſqu’à le mettre ſur le Quarré circonſcrit & ſur le Diametre oblique. |
| Zachary made no movement against the preceeding action, and so waits, alert, waiting to see what follows. Alexander stays on his left foot and advances his right foot towards the Second Instance, sliding his sword up his adversary’s blade so that his 8th Span now contacts the 5th Span of his adversary’s blade, and pauses for a slight moment. When his body, moving along and pushing the blades before him, reaches the point of overbalancing, he hastily puts his right foot down at the Second Instance, his toes on the letter G, and his heel along the line of the Inside Square. He instantly follows this by raising his left foot and advancing it deliberately in a circular path and finally places it parallel to the right foot, with the toes where the Oblique Diameter crosses the Circumference and heels along the Outside Square at the letter D. From this pose, he draws his left side slightly forward, and the heel of his right foot naturally slides inwards onto the Colateral G-M in such a way as to naturally straighten his body, to stand easily, legs straight, to maintain a sense of contact and be able to swiftly respond and defend against an attack. | Puis que Zacharie ne fait aucun mouvemēt contre l’aćtion precedente, ains qu’il demerure ſur la parade, en attendant la pourſuite; Alexandre demeure ſur le pied gauche, & avance un peu le droit devers la Seconde Inſtance, graduant les eſpees de telle ſorte, qu’il met ſon Nombre 8. contre le Nombre 5. de ſa partie adverſe, peu plus ou moins, avec une petite pauſe. Et quand le corps, en cheminant, & tranſportant à l’advenāt les eſpees, vient ſur le point de tresbuſcher, il plante haſtivement le pied à la Seconde Inſtance, les orteils à la lettre G, & le talon ſur le meſme coſté du Quarré inſcrit; pourſuivant à eſlever tout à l’inſtant le pied gauche, & à l’advancer lentement & circulairement, & de le planter finalement parallel avec le pied droit, les orteils ſur le Diametre Oblique, & le talon ſur la lettre D; par laquelle collocation des pieds le coſté gauche du corps eſt tiré un peu en avāt, & le talon du pied droit ſemblablement s’en gliſſe en dedans ſur la collaterale GM. de façon qu’elle met le corps naturellement droit, & à ſon aiſe, avec les jambes roides, pour avoir le ſentiment plus exaćte, & pour eſtre plus prompt à travailler ſelon qu’il ſera de beſoing pour ſa defenſe. |
| Circle No 3. | Cercle N.3. |
| Zachary awaits the follow-up to being subjugated; Alexander will strike with a thrust, sliding the point of contact up the blade and trapping it while his right foot falls to the ground. And, while he moves his left foot quickly and in a circular motion forward to the letter K, he stands erect on his right foot, body slightly forward as he brings his tip up in a circular motion, keeping his arm straight, until the tip is in front of his adversary’s face. | Zacharie attendant la pourſuite de l’aſsujettiſſement; Alexandre luy va tirer une eſtocade, en graduant & enſerrant ſa lame, durant que le pied droit tombe à terre, & durant qu’il continue à porter le pied gauche aſſez viſte & un peu circulairement en avant ſur la lettre K, il ſe dreſſe le corps deſsus, un peu de front, conduiſant cependent ſa pointe circulairement avec le bras roide juſqu’à devant le viſage de ſa partie adverſe. |
| Since Zachary’s sword has been subjugated, (which is to his adversary’s advantage) if Alexander does not allow Zachary to wait for him, Zachary assumes that Alexander will follow on by pushing his sword straight towards him, along the Collateral G-X. His opponent must pass by the strong part of his blade and he would meet it very aptly by taking the direct line, and only needs to prevent his opponent’s move with a counter-thrust. Such is his plan.
|
Encores que l’eſpee de Zacharie ſoit aſſujettie, (qui eſt un grand avantage pour ſon Contraire) ſi ne laiſſe il pas pourtant de l’attendre, eſtimant qu’il en fera la pourſuite par la trace de la ligne Collateralle GX, en pouſſant l’eſpee droitement ſur luy; laquelle eſtant contrainte de paſſer par le fort de la ſienne, il la rencontreroit fort à propos, en prennant la droite ligne, & ne faudroit à prevenir ſon Contraire au meſme temps d’un contrecoup d’eſtocade. Voila donc ſon intention. |
| Alexander, knowing full well the danger, wants to avoid the strong of his opponent’s blade, so he makes his way sideways, raising his right foot and moving it slowly forward, knee straight, towards the Third Instance along the same line of the Inside Square, until, just as he is about to lose his balance, he swiftly slides his sword up his opponent’s blade from the 4th or 5th Span where he pushed it aside. He ensures that, at the same moment as he beings to lean, that he turns the inside arm of the crosspiece horizontally upward, to trap his opponent’s blade from beneath, and moves his own tip circularly towards his enemy, then he puts his foot down on the same line at the letter N. At the same time, he draws his left foot along in a circular motion to put it down at the letter K, half in the Quadrangle, along the line of the Outside Square. At which point he turns his left side slightly forward, so the right foot turns inward, his heel moving to the Circumference line, he stands erect, and, by the same means, hits with a thrust, sliding his opponent’s sword behind the guard with his straight arm, until the tip is in front of the left side of his opponent's face, where he could hit by exending his arm, as shown by the figures. | Alexandre, qui cognoiſt tres bien le danger, voulant eviter le fort de l’eſpee contraire, chemine en travers, eſlevant & avançant le pied droit lentement, avec le genouil roide vers la Troiſieme Inſtance, au long de la meſme ligne du Quarré Inſcrit, juſqu’à ce qu’eſtant le corps ſur le poinćt de tresbucher, il entre plus viſtement en graduant la lame contraire depuis le Nombre 4. ou 5. où elle eſtoit aſſujettie, en avant; en adviſant au meſme inſtant qu’il commence à ſe pancher, de tourner ſa branche interieure horizontale, de façon qu’il en prenne & enſerre la lame contraire par deſſous, & en conduiſe ſa propre pointe circulairement vers l’Ennemi, pourſuivant d’abaiſſer le pied à terre à la lettre N ſur la meſme ligne; & auſſi quand & quand à entrer du pied gauche quelque peu circulairement, juſqu’à le planter parallel au pied droit à la lettre K, moitié dedans, moitié dehors; ſur lequel pied droit, en ſe tournant le coſté gauche un peu en devant, & le talon en gliſſant en dedans ſur la Circonference, il ſe dreſſe le corps perpendiculairement, & pourſuit par meſme voye ſon eſtocade, en graduant l’eſpee contraire par derriere la garde avec le bras roide, juſqu’à luy preſenter la pointe devant le coſté droit du viſage, retenant le pouvoir d’en faire l’execution par rigueur; comme les figures demonſtrent. |
| Circle No 4. | Cercle N.4. |
| Zachary parries the previous thrust to the inside with medium force. Alexander switches to a bent-arm thrust, by stepping forward with the left side while bending his arm, so he continues to hold his point in front of Zachary’s face. | Zacharie parant le coup de l’eſtocade precedente en dedans, avec un poids mediocre; Alexandre la change en Imbrocade, ſe mettant le coſté gauche du corps devant avec le bras courbé, en ſorte qu’il continue à luy tenir la pointe arreſtée devant le viſage.
|
| Zachary sees the tip of his opponent’s blade in front of his face and uses light force to parry it away to his left. Alexander feels this and in response, he instantly lifts his left foot and tilts the branches of his crosspiece inwards so the tip of his blade stays in front of his adversary’s face. He adjusts his next actions to the parry of his sword to the side, and by this means moves himself inside the angle of the swords by, at the same time, turning his left side forwards, setting his foot down at the letter S, the heel along the Exterior Transverse, and bending his right elbow. He continues to tilt the crossguard so much that the external branch points diagonally upwards and inwards, and slides the point of contact of his sword so the weak of his opponent’s blade is caught and trapped between the exterior branch of the crossguard and the strong of his own blade. Again, he very precisely puts the tip of his blade in front of his adversary’s eyes, with a bent arm, leaning forward, left knee slightly bent. | Zacharie ſe voyant la pointe contraire devant le viſage, il la pare en dedans du bras devers le coſté gauche, en uſant d’un poids mediocre. Ce qu’Alexandre apperçoit par le ſentiment dont il leve au meſme inſtant le pied gauche, & en tournant les branches de ſa garde en dedans, tellement que ſa pointe demeure continuellement devant le coſté droit du viſage de ſa partie adverſe; accommodant ſes aćtions à l’advenant du tranſport de ſon eſpee, & ſe mettant par ainſi dedans les angles avec le coſté gauche devant, en avançant & poſant le pied à terre à la lettre S, le talon d’iceluy ſur la traverſante exterieure, & pourſuivant à courber au meſme inſtant le bras, & à tourner les branches de ſa garde ſi avant, que l’exterieure s’en tourne diagonalement en dedans; de façon que le foible de l’eſpee contraire ſe gliſſe au fort de la ſienne entre deux la lame & la branche: dont it la prend & enſerre au meſme temps, & derechef en uſant de courtoiſie, il luy preſente la pointe devant les yeux en ligne courbe, panchant du corps en avant, avec le genouil de la jambe gauche plié. |
| Circle No 5. | Cercle N.5. |
| Zachary continues to parry further away. Alexander lets him move the two swords, putting himself further forward into the angle, right foot raised, and the crosspiece turned vertically. | Zacharie continuant à parer plus outre; Alexandre luy laiſſe emporter les eſpees, ſe mettant plus avant dedans l’angle, avec le pied droit levé, & la branche interieure de la garde tournée verticalement. |
| Zachary continues his parry, turning his opponent’s sword even further aside, dropping his arm slightly to the same side. Alexander feels this and at that same moment raises his right foot, and moves his whole right side, including his arm and sword, forward, straightening himself up, pivoting on his left foot, and twisting his wrist so the inside branch of his crosspiece points vertically upwards. Thus the tip of his sword falls slightly backwards, as the point of contact slides down the swords, until the tips are nearly together, as shown in the figure. | Zacharie continuant à parer, en deſtournant l’eſpee contraire encores plus outre, avec un petit abaiſſement du bras devers le meſme coſté; Alexandre s’en apperçoit par le ſentiment, & leve à l’inſtant meſme le pied droit, lequel il avance enſemble avec le meſme coſté, bras, & eſpee, tournant cependant la branche interieure verticalement en haut: dont la pointe s’en eſcoule avec deſgraduation des deux eſpees un peu en arriere, bien pres à egal de la pointe contraire; le tout en tournant & dreſſant le corps droit ſur la jambe gauche: comme on voit en la figure. |
| Circle No 6. | Cercle N.6. |
| Alexander disengages his blade and delivers a cut across his opponent’s face as he steps across and to the side, behind him. | Alexandre desgage ſa lame, & en donne un coup d’eſtramaçon au viſage de l’Adverſaire, en paſſant à ſon coſté, & luy venant derriere le dos. |
| Alexander follows this action, by continuing to turn his right side forwards, along with his sword arm, which he brings, at the same time, from beneath his opponents sword, by allowing his thumb, which was pressed against the crosspiece, to slide under, in such a way that his grip encircles the handle and puts the sword edge ready to cut, he raises his sword-tip up from beneath his opponent’s sword, and enters further in to the side, leaning slightly, stepping outsided the circle, and gives his opponent a cut across the face. | Alexandre pourſuit l’operation, en continuant à tourner le coſté droit devant, enſemble avec le bras de l’eſpee, laquelle il delivre au meſme tēps à la faveur du poignet de la main de deſſous l’eſpee contraire, en laiſſant gliſſer le poulce, qui eſtoit affermi contre la branche interieure, deſſous, de ſorte qu’il en entoure au meſme inſtant la poignee, & en mettant l’eſpee ſur le trenchant, il en conduit la pointe en haut par deſſus l’eſpee contraire, & en entrant plus avant à coſté avec quelque panchement du corps, allant dehors le Cercle, il en donne à ſon Contraire un coup d’eſtramaçon au viſage. |
| The actions in the three Circles No 4, 5, & 6, are shown separately, almost as if there is a short pause between them. We did this for the benefit of our learners. Because in fact the entire sequence should follow so smoothly that it would be difficult to distinguish one step from the next so there is no interruption between any two. But to keep Scholars from being confused, and to explain the real basics that they are learning, they must learn this movement in parts, slowly, so they do not become examples of the proverb: Who grasps too much, catches very little. | Les aćtions de ces Cercles N.4.5.6. ſont icy repreſentées chaſcune à part, quaſi comme s’il y intercedoit quelque petite pauſe. Ce que nous avons fait pour le regard des apprentiſs. Car autrement le tout ſe doint entreſuivre de ſi pres, qu’à grand peine y pourroit on diſtinguer le precedent d’avec le ſubſequent, tant s’en faut qu’il y aye de l’interruption entre deux. Mais pour n’embrouiller pas l’entendement des Eſcholiers, & pour leur declarer les vrais fondements de ce qu’ils apprennent, il faut que le tout ſoit monſtré par articles, ſans ſe haſter, de peur qu’il ne leur advienne ſelon le commun proverbe: Qui trop embraſſe peu eſtraint. |
| A note concerning Circle No 4. That Alexander, when moving to the bent-arm position, is not required to put his foot down exactly at the letter S on the Inside Square, since he must accomodate his appoach to the following step, according to how much he senses his sword is forced away. So it happens that sometimes he will put his foot down beside the Outside Square, and at other times even outside the Circle. This will make it easier for him to follow on to Circle No 5 and to the cut in No 6, which is shown in the figure as being exactly executed on Zachary’s head. But to perform with precision, he must keep the blade in front of Zachary’s face, before putting his foot down, and to bring it in a circular motion around to the head, at the moment when he is about to lose his balance, then step, and then, as shown in the figure, bend the right knee, put his weight on it, leaning slightly forward, with the the arm and sword extended forward at an acute angle. | Notez touchant le Cercle N.4. qu’Alexandre, en donnant la courbe, n’eſt pas tenu d’abaiſſer preciſement le pied gauche à terre ſur le coſté du Quarré inſcrit à la lettre S: car il doit accomoder ſon intrade à l’advenant, qu’il ſe ſent eſtre conduit par le tranſport des eſpees: dont il adviendra meſme aucunesfois, qu’il le plantera ſur le coſté du Quarré circonſcrit. & autresfois meſme au dehors. Ce qui luy donnera tant plus de commodité devenir à la pourſuite du Cercle N.5. & à l’eſtramaçon du 6. qui eſt repreſenté en la figure d’eſtre executé par rigeur ſur la teſte de Zacharie: mais pour jouer en courtoiſie, il luy faut preſenter la lame devant le viſage, premier que d’abaiſſer le pied en terre, & la mener circulairement outre ſa teſte, quand on commence à tresbucher. & à le planter, & puis, comme il eſt repreſenté en la figure, ployer le genouil droit & charger le corps deſſus, en panchant un peu vers le devant, avec le bras & l’eſpee eſtendus au devant en angle aigu. |
| Then, as he is leaning forward, he follows with a second cut, as follows: he lightly pushes off the ground with his left foot to straighten up, and uses this to pivot around on his right foot, so that, by raising the sword above his shoulder, keeping the hand forward and the tip raised behind him, he turns around to face his opponent, ready to strike while stepping forward with his left foot. (See Circle No 7.) Or he can put his blade in front of the right side of his opponent’s face and again raise it circularly about his opponent’s head, as he puts his foot down behind him a little off to the side. Then he again bends his forward knee to put his weight on it, with his arm and sword extended upwards at an acute angle, just as in the preceeding action, and which will be further explored in subsequent Plates, where, when the question arises, we will repeat this again, and give a more ample discussiona. | Puis eſtant ainſi avec le corps panché en avant, il pourſuivera d’en tirer encor un redoublement d’eſtramaçon, en la maniere ſuivante: c’eſt qu’il fera du pied gauche un petit pouſſement contre la terre, pour ſe redreſſer, & volter à l’aide d’iceluy ſur le pied droit, en telle ſorte, qu’en hauſſant l’eſpee par deſſus ſon eſpaule, la main quelque peu avancée, & la pointe montant en derriere le dos, il ſe tournera de front contre ſa partie adverſe, tout preſt à luy donner le coup avec l’avancement du pied gauche; ou à luy preſenter la lame devant le coſté droit du viſage, & à la monter derechef circulairement alentour de la teſte contraire, au temps qu’il plantera le pied derriere luy un peu à quartier; en apres il pliera derechef le genou de devant pour faire la charge du corps deſſus, avec le bras & l’eſpee pareillement eſtendus en angle aigu, tout ainſi qu’en l’operation precedente, & comme il en ſera parlé plus particulairement en d’autres Tableaux, où il ſera queſtion de la repeter, & d’en faire plus ample declaration. |
| Circle No 7. | Cercle N.7. |
| Alexander is behind his adversary, and does an about turn on his right foot. Zachary has also turned towards him at the same time, to defend with his sword. But before he can achieve this maneuver, Alexander cuts him across the face a second time. | Alexandre eſtant derriere ſon Adverſaire, & faiſant la volte ſur le pied droit; Zacharie s’eſt auſsi tourné devers luy au meſme temps, pour luy preſenter l’eſpee; mais avant qu’il ait parachevé l’œuvre, Alexandre luy donne encor une ſeconde touche d’eſtramaçon au viſage. |
| Here, again, we have the same second cut, which differs from the previous description only in that one was made against an enemy who had stayed still and not moved at all. But in Circle No 7, at the instant that Alexander raises his left foot and begins to turn about on his right foot, the Enemy also spins on his right foot, barely moving his left foot from its place, and bending his arm to bring his sword up and over in front of him, to put it between himself and Alexander. Alexander sees this, before he can complete the mouvement, he cuts him in the face. Or he carefully puts his blade in front of Zachary’s eyes, then sets his left foot down towards his enemy, as is shown in the image. | Voicy encor le meſme eſtramaçon redoublé, qui ne differre qu’un bien peu d’avec celuy que nous venons de deſcrire: c’eſt aſſavoir que ceſtuy-là a eſté donné ſur l’Ennemy qui ne bouge point un rien de ſa place. Mais en ce Cercle N.7. à l’inſtant qu’Alexandre commence à faire la volte du corps ſur le pied droit, en eſlevant le gauche; l’Ennemy ſe tourne pareillement ſur ſes pieds, ne bougeant qu’un bien peu de ſa place à tout le pied gauche, en avançant l’eſpee devers luy avec le bras courbe. Ce que voyant Alexandre, avant qu’il ait parachevé le mouvement, il luy donne le coup au viſage: ou bien, il luy met la lame devant les yeux en courtoiſie, plantant conſecutivement le pied gauche en terre devers l’Ennemy; comme on le voit pourtrait en la figure. |
| That is the follow-on from Circle No 4, which develops when Zachary turns the point of his adversary’s sword away from his face to the inside of his arm, after Alexander had arrived at the Third Instance, as shown in Circle No 3. Now, it is reasonable to show likewise what happens after this thrust if Zachary instead parries while his opponent is still stepping towards the Third Instance. | Voilà donc la ſuite du Cercle N.4. procedante de ce que Zacharie a deſtourné la pointe contraire de ſon viſage en dedans du bras, apres qu’Alexandre eſt arrivé à la Troiſieme Inſtance, ainſi que le Cercle N.3. demonſtre. Maintenant il eſt raiſonnable de vous repreſenter pareillement la pourſuite de ceſte meſme eſtocade, en occaſion que Zacharie la pare pluſtoſt, durant que ſa partie eſt encor en aćte de cheminer vers la Troiſieme Inſtance. |
| Circle no 8. | Cercle N.8. |
| Alexander again moves to thrust from the Third Instance, the same as in Cercle No 3. Zachary parries to the inside, but with more force than he does in Circle No 4. Thus Alexander is constrained to follow the force against his sword, moving towards the centre to L, and adjusting his left side to allow him to give hime a bent-arm thrust. | Alexandre tirant encores l’eſtocade à la Troiſieme Inſtance, tout de meſme le Cercle N.3; Zacharie la deſtourne en dedans du bras, mais avec plus de force, qu’il ne fit au Cercle N.4. Dont Alexandre eſt contraint de ſeconder le tranſport des eſpees, en allant devers le Centre juſqu’à L, & accommodant le corps avec le coſté gauche pour luy donner l’imbrocade. |
| This bent-arm thrust derives once more from the subjugation of the sword, as shown in Circle No 2. While Alexander is moving again to thrust from the Third Instance, at the instant his foot lowers down to step on the letter N, Zachary defends himself and moves the sword forcefully away to the inside. Alexander realizes this from the feel, and, tries from the beginning, to resist, and hold back against the movement of the swords, using this to quickly move his left foot across close to his right foot, as if making a fleuret [a dance move: a brief lifting of each foot on the upbeat with a forward thrust of the first on the downbeat], so the body is held upright, while raising the right foot and moving it quickly towards the centre along the Perpendicular Diameter, remembering to turn and adjust his hand according to the movement of the swords. He then leans slightly to the side and puts his weight on his right foot, which he sets down at L, and draws the left foot to the letter N, At the same moment, he bends his entire arm and turns the exterior branch of his crosspiece diagonally inwards so the opponent’s blade slides down to rest against the strong of his blade, and outside the crosspiece. At this instant, he turns his left side forward, aims the tip of his blade at his opponent’s face, carefully holding it in front of his eyes, as shown in the figure. | Ceſte imbrocade provient de l’avantage de l’aſſujettiſſement, repreſenté au Cercle N.2. Car cependant qu’il chemine derechef pour donner l’eſtocade à la Troiſieme Inſtance, à l’inſtant que le pied droit s’abaiſſe, pour ſe planter à la lettre N. Zacharie ſe defend, & luy tranſporte l’eſpee avec force au dedans du bras. Ce que recognoiſſant Alexandre par le ſentiment, il taſche du commencement, à y reſiſter, en ſe ſervant d’une petite retenue, & cependant il approche le pied gauche haſtivement bien pres de l’autre, quaſi comme un demi fleuret; dont le corps ſe dreſſe, en eſlevant le pied droit, & le portant devers le Centre le long du Diametre perpēdiculaire, ſans oublier à tourner & accommoder cependant la main à l’advenant du tranſport des eſpees; & à faire la charge du corps en panchant un peu de coſté ſur le pied droit, iceluy poſant à terre à la lettre L, & trainant proportionnellement l’autre juſqu’au point N, & en parachevant au meſme inſtant de ſe courber entierement le bras, & tourner ſa branche exterieure en dedans diagonalement, de ſorte que la lame contraire en vient à s’eſcouler, en deſgraduant, au fort de la ſienne, & au dehors de la branche; auquel inſtant il tourne le coſté gauche en devant, en aſſituant ſa pointe au viſage de l’Ennemi, & l’y tenant par courtoiſie arreſtée devant les yeux; ſuivant la figure. |
| Circle no 9. | Cercle n.9. |
| Zachary increases the force of his sword even more, to parry the preceding thrust from Circle No 3. So Alexander moves forward against this with his right foot to the Centre, thereby accomplishing the same action as above. | Zacharie augmentant encor davantage le poids de ſa lame, pour parer l’eſtocade precedente du Cercle N.3. auſsi Alexandre s’avance là deſſus avec le pied droit juſqu’au Centre, en accompliſſant derechef la meſme operation, que deſsus. |
| Here, again, is the same action, differing only in the degree of force used in defense. For at the instant Alexander put his foot down in the Third Instance, Zacharie parries his strike with even more effort than before. So Alexander, to work around the movement of the swords, must move his front foot further in towards the Centre, drawing his left foot behind him to the letter M, while performing the same actions as above, to keep the tip of his blade pointing in the face of his adversary. | Voicy derechef la meſme operation, ne differant, qu’au poids de la defenſe. Car à l’inſtant qu’Alexandre a abaiſſé le pied droit à la Troiſieme Inſtance, Zacharie a paré le coup avec plus d’effort, qu’au precedēt; dont Alexandre, pour ſeconder le tranſport des eſpees, eſt contraint d’entrer du pied droit plus avant juſques au Centre, en trainant proportionnellement le pied gauche apres juſques à l’M. en accompiſſant cependant les meſmes aćtions que deſſus, juſques à preſenter ſa pointe en ligne courbe devant le viſage de ſon Contraire. |
| Circle no 10. | Cercle n.10. |
| Alexander’s bent-arm thrust is parried even further outwards, so he lets the swords flow away by extending his arm, with the interior branch of the crosspiece vertical, and his right foot raised. | L’imbrocade d’Alexandre eſtant parée encores plus outre il laiſſe eſcouler les eſpees, en allongeant meſmes le bras, avec la branche interieure verticale, & le pied droit eſlevé. |
| Zachary sees the tip of the sword in front of his face, he continues his defense of parrying it again to the inside. Alexander percieves this through his sense of feel, and he extends his arm, along with the sword, out to the side, raising his left foot lightly off the ground and immediately setting it back down in the same place, or even a bit further out, shifting his weight back onto this foot by pushing back with his right foot and raising it off the ground. At the same time, his right arm turns so the guard moves outwards, his 7th Span against his opponent’s 4th Span, with the inside branch of the crosspiece upwards, so as to prevent his enemy from drawing into the Direct Line posture towards his face. So if he wanted to straighten his tip, he would be forced to move circularly in a bent-arm posture, to arc around this branch. This would take longer to do than to strike horizontally in a straight line. Consequently, this gives Alexander more time to percieve and respond to any movements his enemy makes. Ordinarily he would follow the moves made in this 10th Circle with with one of the actions in Circle No 11 or No 13. That is to say, he would try to hit his opponent directly in the face dropping contact with his opponent’s sword. Or he may decide to increase the force on the sword because he wants to push it further away before trying anything else. These actions, and their counters, will be explained fully in following Plates. Nonetheless, it is good to give this little warning now, so that you will remember these actions, which we will explore shortly, every time an occasion to use them presents itself. | Continuant la defenſe, & la ſuite des deux Cercles precedēts, Zacharie qui voit la pointe contraire devant ſes yeux, la pare derechef en dedans du bras. Ce qu’appercevant Alexandre par le ſentiment, il allonge le bras enſemble avec l’eſpee à ſon coſté, en eſlevant le pied gauche à fleur de terre, & le rabaiſſant derechef tout à l’inſtant au meſme endroit, ou bien un peu en dehors, en revenant droit ſur iceluy à l’aide du pied droit, qui fait en s’eſlevant un petit pouſſement contre la terre; & au meſme temps le bras droit ſe tourne avec la garde de l’eſpee en dehors, ſon Nombre 7. au Nombre 4. de l’eſpee contraire, avec la branche interieure dreſſée en haut, de ſorte qu’elle empeſche l’Ennemi de tirer en droite ligne & en un temps à ſon viſage. Car s’il y vouloit dreſſer ſa pointe, il ſeroit contraint d’aller circulairement en ligne courbe, en forme d’arc alentour de ladite branche: ce qui requiert plus de temps, que de fraper horizontalement en ligne droite: & par conſequent il donne auſſi plus de loiſir à Alexandre, pour juger, & rencontrer exaćtement la diverſité du ſentiment, que l’Ennemi luy donne. Lequel eſtant en termes de ce dixieme Cercle, ordinairement il attentera l’une ou l’autre des deux operations, du Cercle 11. ou 13. c’eſt aſſavoir qu’il taſchera de fraper ſa partie au viſage en deſtachant les eſpees; ou qu’il accroiſtra le ſentiment pour l’aſujettir à ſa fantaſie, avant que de rien attenter plus outre. deſquelles operations, & de leurs contraires, en ſera donné ſuffiſante inſtrućtion és demonſtrations ſuivantes. Toutesfois il n’eſt que bon d’en donner cependant ce petit advertiſſement, afin que toutes les fois, qu’il ſe preſentera telle ou ſemblable occaſion, il vous ſouviene de vous tenir preſt à les rencontrer, en la maniere que vous entendrez tout à l’heure. |
| In order to provide a better view of the crossed swords, Alexander is shown with his right foot and hand slightly more forward than they should be, the tip turned behind him. Which would be the preparation for striking the blow shown in Circle No 13. However, it may be that your opponent would content himself to hold the swords in this position, with a lighter contact, neither pressing, nor forcing your blade away, so that you cannot perform any of the following actions. Then you must repeat the step in with the right foot along the Perpendicular Diameter, drawing the left behind, and once again putting the tip of your blade in his face, exactly as in Circles No 8 & 9. | Pour vous mettre en veuë les eſpees croiſées, a proſpećtive du corps d’Alexandre eſt icy repreſentée avec le pied & la main droite un peu avancez, plus qu’ils ne devroyent, & la pointe tournée en arriere; qui eſt comme une preparation pour donner le coup du Cercle N.13. Que s’il advenoit cependant, que voſtre partie adverſe ſe contentaſt, de retenir les eſpees ainſi accouplées avec un ſentiment temperé, ſans pouſſer, ne ſans oſter ſa lame de la voſtre, de ſorte que vous ne pourriez venir aux operations ſuivantes; alors il faudroit reprenre l’entree du pied droit, ſuivant le Diametre perpendiculaire, en avançant le gauche, & luy preſentant derechef la pointe devant le viſage en ligne courbe, tout de meſme les Cercles N.8. & 9. |
| Circle No 11. | Cercle N.11. |
| From the previous Circle No 10, Zachary thrusts horizontally to the face. Alexander follows his movement keeping the swords in contact, in such a way that he gracefully adopts the Direct Line posture, with his sword-tip before the face. | Zacharie luy tirant une eſtocade horizontale devers le viſage, en ſuite du Cercle N.10.; Alexandre la pourſuit avec les eſpees accouplées, en ſorte qu’il prend luy meſme la droite ligne, & luy met la pointe en courtoiſie devant le viſage. |
| This follows on from the preceeding action. Zachary makes a thrust horizontally at his opponent’s face, taking his sword off of the other, and turning slightly to the outside. Alexander feels this movement as his enemy begins to pull his sword away, does not wait until he can lift it or push it away, but continuously keeps contact, so his opponent cannot circle around his guard to make his thrust to the face. As soon as his opponent’s sword moves across, he closes the Direct Line, meeting the weak of his opponent’s blade with the strong of his own, and precisely sets his tip in front of his opponent’s eyes, putting his foot down by the other one at the same instant, about one short pace apart. | C’eſt la pourſuite de la demonſtration precedente. Zacharie tire un coup de pointe horizontal vers le viſage de ſa partie, en oſtant ſa lame de deſſus la contraire, & tournant le coſté droit du corps un peu en dehors. Alexandre s’appercevant par le ſentiment de ce mouvement, que l’Ennemi commence à faire, pour deſtacher ſa lame, il n’attend pas ſi long temps, qu’il la puiſſe lever ou oſter, mais ſans l’abandonner il la pourſuit continuellement, & comme elle ne peut laiſſer de venir alentour de ſa garde, pour donner l’eſtocade au viſage; à l’inſtant qu’elle y arrive, il luy ferme la droite ligne, en accueillant le foible du fort de la ſienne, & luy mettant ſa pointe en courtoiſie devant les yeux, & abaiſſant au meſme inſtant le pied à terre à coſté de l’autre, à la diſtance d’un pas arreſté. |
| Circle no 12. | Cercle n.12. |
| Here is the final execution of the preceeding thrust. This is done by suddenly raising the right foot and stepping, with the body forward, and with the arm and sword extended, to the letter S. Continue on by putting weight on the forward knee, and pierce the head of your Adversary, who is forced to bend his arm and let his tip go up against his opponent’s sword. | Voicy la finale execution de l’eſtocade precedente; laquelle il pourſuit en eſlevant ſoudainement le pied droit, & cheminant avec le corps avancé, & avec le bras & l’eſpee eſtendus, juſqu’à la lettre S; continuant à faire la charge ſur le genou de devant, & percer la teſte à ſon Contraire, qui en eſt contraint de courber le bras, & laiſſer aller ſa poinćte en haut au gré de l’eſpee contraire. |
| Those who are well versed in this exercise, will be able to prepare and execute this thrust in one single movement. But it is better to practice as we have shown, in two parts, to instruct Novices. To whom I counsel and shall always counsel to take pains to do it a few times well, rather than repeating it often. | Ceux qui ſeront un peu verſez en l’exercice, pourront donner & executer ceſte eſtocade en un ſeul temps; mais il vaut mieux de la pratiquer, comme nous l’avons repreſentée, en deux, pour donner inſtrućtion aux Novices; auxquels je conſeille & conſeilleray touſiours de mettre pluſtoſt peine à faire bien, qu’à faire beaucoup. |
| Circle no 13. | Cercle n.13. |
| Zachary wants to force his opponent’s sword further away, following Circle No 10. Alexander will pass to the side with a double-size step, freeing his sword, and hitting him with a cut to the head. | Zacharie voulant aſſujetir l’eſpee contraire davantage, en ſuite du Cercle N.10; Alexandre luy va paſſer à coſté avec un pas double, en delivrant ſa lame, & luy en donnant un coup d’eſtramaçon à la teſte. |
| This action comes from the position shown in Circle No 10, where Zachary’s sword can be seen above the other. In this case to further force the sword away as he would like to, with more power, he increases the force on the blade. Alexander percieves this as his blade is in contact, he moves his raised foot forwards, turns his right side towards Zachary, along with his arm and the sword-guard, so that he disengages from his opponent’s sword, by moving his tip behin him in a circular motion down, around his opponent’s, and upwards. As he moves his body, stepping with his foot, he delivers a cut diagonally across the face, finishing his motion with a double-length step outside the Circle, even with the letter X, with the knee bent. | Ceſte operation provient de la demonſtration du Cercle N.10. où l’eſpee de Zacharie ſe voit deſſus l’autre: toutesfois pour l’aſſujettir à ſa fantaſie & avec plus d’avantage, il accroiſt le ſentiment. Ce qu’Alexandre appercevant par l’attouchement, il avance au meſme temps le pied, qui eſt eſlevé, en tournant le coſté droit du corps en avant, enſemble avec le bras & la garde de l’eſpee, ſi bien qu’elle ſe deſgage de l’eſpee contraire, en faiſant de ſa poinćte un circuit en arriere & alentour de la poinćte d’icelle de bas en haut, & en continuant l’advancement du corps & du pied, qui chemine, il luy porte un coup d’eſtramaçon diagonal au viſage, pourſuivant à faire avec le pied droit un pas double en ligne droite, à planter dehors le Cercle vis à vis de la lettre X, avec le genou plié, pour y faire la charge. |
| One could also make use of this action when making the cut to the face from the Third Instance. While putting the foot down at the letter N, the enemy made his defence, carrying the swords down to the inside much more forcefully than in Circles No 4, 8, & 9, so that one could not hold it with the bent arm, and one would be forced to let it go, giving it free rein. | On pourra auſſi ſervir de ceſte meſme operation, quand on ſera venu pour donner le coup de l’eſtocade à la Troiſieme Inſtance, & qu’en abaiſſant le pied droit à la lettre N, l’Ennemi aura fait ſa defenſe, en tranſportant les eſpees en dedans du bras avec plus de force, qu’il n’a fait és Cercles N.4.8.& 9. de ſorte qu’on ne le puiſſe moderer avec la courbe, & qu’on ſoit contraint de le laiſſer aller, comme à bride avallée. |
| Alexander percieves, on this occasion, the powerful force being used to parry his thrust, and makes a half pirouette with the left foot, bringing his right foot in as quickly as possible to raise it up and and bring his right side forward with his arm and sword, in the same way as above, into the angle that is open before him. He continues with the rest, the cut and the double-length step, as is shown in the figure. | Alexandre donc s’appercevant, en ceſte occaſion, de la grande force avec laquelle on luy pare ſon eſtocade, il fait une demi-fleurette avec le pied gauche, l’approchant le plus viſtement qu’il eſt possible au pied droit, pour l’eſlever, & ſe tranſporter en toute promptitude le coſté droit devant, enſemble auſſi en avançant le bras & l’eſpee, en la meſme ſorte, que deſſus, au dedans de l’angle qu’on luy ouvre: en continuant le reſte, de l’eſtramaçon, & du pas double, à l’imitation de ce qui eſt repreſenté en la figure. |
| The real blow is made severely, but in any case, nothing prevents it from being practiced carefully, simply putting the blade in front of the face, while stepping, and moving the sword about the head as the foot comes down. | Il eſt vray, que le coup y eſt executé par rigueur: toutesfois il n’y a rien qui empeſche de le pratiquer auſſi en courtoiſie; en luy preſentant la lame devant le viſage, cependant que le pied chemine, & cependant qu’il s’abaiſſe en terre, la mener circulairement outre ſa teſte. |
| That being done, one could again make a second strike, either carefully or severely, as in the example of Circle No 6, following the same instructions. | Celà fait, on le pourra redoubler encore en courtoiſie, ou en rigueur, à l’exemple de la pourſuite du Cercle N.6. ſuivant les meſmes inſtrućtions. |
| It is apparent from these examples that before one can hit the person who is holding the Direct Line posture, one must first overcome the sword. Because the large distance at the First Instance is advantageous and good for the defender, as much, in contrast, as it is difficult and inconvenient for the attacker. In fact, if you paid close attention to the demonstrations in the previous Plate V, all of Zachary’s thrusts were made from the First Instance, all of their counters were made by Alexander from the Second. As much as he never stayed in place without moving, nonetheless his hits were only begun at the instant when his enemy had closed in to the Second Instance. If someone is out of range, he is also out of danger; when at long range, he is likewise out of danger from smaller and more subtle moves. Thus is follows that, when the enemy is standing in the Direct Line posture, that one must move in closer to put him in danger, but confidently. Good foot, good eye. Believe that neither the speed of the body, nor the quickness of the arm, are nothing compared to the benefit of a good approach. Thus all the practicality of our Training is that we are always moving towards the enemy to come into the range that is most convenient and proper to the execution of our attacks. That is, if he does not bring himself into range and save us the trouble. This is what we wanted to present here, in Plate VI. More specific observations and confidence in how to proceed, shall be explained hereafter, each in its proper place. | Il appert par ces exemples, qu’il faut neceſſairement venir à l’eſpee, premier que d’attenter ſur la perſonne, qui ſe tient en ceſte poſture de la Droite ligne. Car la meſure large de la Premiere Inſtance, luy eſt avantageuſe & propre pour les defenſes, autant qu’elle eſt au contraire incommode & dangereuſe pour celuy qui la veut aſſaillir. Et de fait ſi vous avez prins bonne garde aux demonſtrations de la Table V. precedente, toutes les eſtocades de Zacharie, qu’il y eſt repreſenté d’avoir tirées de la Premiere Inſtance, elles ont eſté rencontrees par Alexandre à la Seconde. Car encores qu’il ſoit demeuré aucunesfois ſans bouger de ſa place, toutesfois les atteintes, qu’il a données, n’ont eſté commencées, ſinon à l’inſtant que l’Ennemi s’eſt avancé juſqu’à ceſte Seconde Inſtance. Car ſi celuy qui eſt hors de meſure, eſt auſſi hors de danger, auſſi qui eſt en meſure large, eſt hors du danger des plus petits & plus ſubtils mouvements. S’enſuit donc, quand l’Ennemi ſe tient en la Droite ligne, qu’il le faut aborder plus pres, pour le mettre en danger; mais avec aſſeurance, Bon pied, bon œil. Et croyez hardiment, que ny la viſteſſe du corps, ny la promptitude du bras, ne ſont rien au prix d’une bonne approche. Dont toute la Pratique de ceſtuy noſtre Exercice ſera telle, qu’on ira touſiours ſerrant l’Ennemy, juſqu’à venir à la meſure, qui ſoit convenable & juſte aux executions, qui ſe preſentent à faire; ſi ce n’eſt que luy meſme nous vienne au devant, pour nous relever de la peine. Voilà ce que nous avons voulu repreſenter en general en ce Tableau VI. Les obſervations plus particulieres, & l’aſſeurance, comment il y faut proceder, ſeront declarées cy apres, chaſcune en ſon lieu. |
| Translation by Bruce G. Hearns |
Transcription by Bruce G. Hearns |
|---|---|
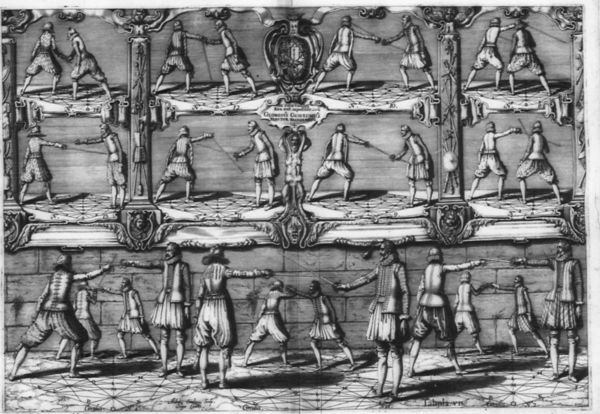
| |
| EXPLANATION OF THE ACTIONS IN THE SEVENTH PLATE | DECLARATION DES OPERATIONS DV TABLEAV SEPTIEME |
| After Zachary saw the manner in which Alexander advanced against the Direct Line posture, subjugating his adversary’s sword at the Second Instance, and all that followed thereupon, he again put himself into the same posture, but with the intention of testing Alexander’s ability as he approaches, and to perform all manner of moves against him. In the preceeding Plate, he did nothing against him, except what he had to do of necessity in his own defense. But in this one he intends to cross his opponent’s approach with several thrusts, at the beginning, in the middle, and the end of the move during which Alexander subjugates the sword. He times his counter either at the moment when Alexander raises his right foot, or when he moves towards the Second Instance, but still in balance, or when he lowers it as his body begins to fall forward, or when he puts it down, or after he is in position. Alexander, knowing nothing of Zachary’s plans, and starts again from the Direct Line posture in the same way as before, moving into the First Instance at the other end of the Circle, with his sword likewise held underneath the other. | Apres que Zacharie a veu la maniere d’Alexandre d’avancer ſes approches contre la droite ligne, en aſſujettiſſant l’eſpee contraire à la 2. Inſtance, avec tout ce qui en depend; il ſe va planter derechef en la meſme poſture, avec intention de mettre les approches d’Alexandre à l’eſpreuve, & de les travailler en toutes ſortes à luy poſsibles. Car en la Table precedente il n’avoit rien fait alencontre, ſinon ce qu’il eſtoit contraint de faire par neceſsité; pour la ſimple defenſe de ſa perſonne: mais en la preſente il ſe propoſe de traverſer l’approche de ſon contraire par pluſieurs eſtocades, tirees au commencement, à la continuation, & ſur la fin de l’aſſujettiſſement de l’eſpee: prenant le temps qu’il leve le pied droit, ou qu’il l’avance devers la 2. Inſtance, le tenant encor en balance, ou qu’il l’abaiſſe avec le tresbuchement du corps, ou qu’il le plante à terre, ou qu’il y ſoit deſia arrivé. Alexandre donc ne ſachant rien de ceſte intention, recommence à travailler ſur la droite ligne, en la meſme ſorte que devant, ſe mettant à la premiere Inſtance à l’autre bout du Cercle, avec l’eſpee ſemblablement en ligne droite parallele au deſſous de l’autre.
|
| Circle No 1. | Cercle N.1. |
| Alexander subjugates his opponent’s sword at the Second Instance to the inside of the arm. He proceeds to move there with great care, as much when raising his right foot, crossing the swords, and moving forward while sliding down the blade, as when moving the blades to take the upper hand, setting his foot down on the ground precisely in place and following with the other foot deliberately, with a circular motion, until he is once again straight on his legs, as shown here in this image. | Alexandre aſſujettit l’eſpee contraire à la Seconde Inſtance en dedans du bras; y procedant avec grande circonſpection, tant à eſlever le pied droit en accouplant les eſpees, & à l’avancer en faiſant la deſgraduation, qu’à tranſporter les lames & à en prendre deuement la ſuperiorité, en plantant le pied eſlevé à terre au lieu & avec la juſteſſe requiſe, & à pourſuivre avec l’autre lent & circulairement juſqu’a ce qu’il revienne droit ſur ſes jambes; en la forme qu’on le voit icy en figure. |
So, to subjugate his opponent’s sword at the Second Instance, he begins his work with the right foot, raising it off the ground, keeping his knee straight, at the same time he raises the tip of his sword with a small movement of the wrist, makes contact with the opponent’s sword to the inside, his 8th Span against the 3rd Span, and briefly hesitates. After which he advances his right foot towards his left side, raising the sword further for a second time with the wrist, the inside branch of the crosspiece of his guard turned sightly upwards. In such a way that he conducts the tip of his blade a little over to the left side, crossing and sliding up his opponent’s blade until his 8th Span is at least against the 4th Span, or the 5th at most. He continues to move the foot further along the same line, until his body just begins to fall forward. Then he quickly steps in and puts his foot down along the Inside Square at the letter G, then immediately raises his left foot and moves it deliberately in a circular path through the air, keeping his leg straight until he is opposite the arch of his other foot, which is on the ground. Further, to the degree his body advances with the above actions, he moves his opponent’s sword forward, with a slight roll of the wrist to force it aside, turning the inside branch of the guard vertically, and putting his left foot, currently in the air parallel to the right, down on the circumference of the Circle along the side of the Outside Square, his toes on the Oblique Diameter G-S* and his heel at the letter D. Thus the left side is turned a little forward and the heel of the right foot is on the Collateral G-M. His arm goes downwards and but slightly extended, the guard is before the right hip but slightly higher, his blade crossing his opponent’s blade at the numbers mentioned, his tip rising to the top of his opponent’s head, his body is straight and perpendicular, the muscles of his arm and his knee are tensed, his feet the proper and proportional distance apart, to have all his limbs able to move promptly and actively.
|
Et pour aſſujettir l’eſpee contraire à la ſeconde Inſtance, il commence à travailler du pied droit, l’eſlevant de terre avec le genouil roide, en faiſant monter au meſme temps par une petite accomodation du poignet de la main ſa pointe en haut, touchant l’eſpee contraire en dedans, du Nombre 3. le Nombre 8. avec quelque petite pauſe: apres laquelle il avance le meſme pied droit devers ſon coſté gauche, hauſſant encore l’eſpee pour la ſeconde fois à la faveur du poignet, avec les branches de la garde tournees un peu en dedans; de façon qu’il en conduit la pointe de ſa lame un peu de travers, croiſant & deſgraduant l’eſpee contraire en graduant la ſienne, & aſſemblant ſon Nombre 8. avec le Nombre 4. pour le moins ou 5. pour le plus: pourſuivant à avancer le pied plus outre du long de la meſme ligne, juſqu’à tant que le corps commence à tresbucher: lors il ſe haſte d’entrer, & de le planter ſur le coſté du Quarré Inſcrit à la lettre G, continuant à eſlever tout à l’inſtant le pied gauche, & à le porter lent & circulairement en l’air avec la jambe roide, juſqu’à ce qu’il vienne à l’oppoſité du creux de l’autre pied, qui eſt planté en terre. Or à meſure que le corps s’avance avec les ſuſdites aćtions, il emporte auſſi l’eſpee contraire à l’advenant, luy donnant un petit branſle du poignet de la main pour l’aſſujettir, en tournant les branches de ſa garde en dedans verticalement, & plantant le pied gauche à preſent eſlevé en l’air parallele au pied droit, ſur la circonference du Cercle, & ſur le coſté du Quarré circonſcrit, les orteils ſur le Diametre oblique C S, & le talon à la lettre D; dont le coſté gauche du corps ſe tourne un peu en devant, & le talon du pied droit en eſt tiré ſur la collaterale GM; avec le bras deſcendant & mediocrement eſtendu, la garde luy revenant à l’oppoſite de la hanche droite, un peu plus haute, ſa lame croiſant l’eſpee contraire en travers par devant ſa poitrine, & aux Nombres ſuſmentionneez, ſa point aſcendant juſqu’à la hauteur du ſommet de la teſte contraire, le corps dreſſé perpendiculairement, les muſcles du bras & des genoux tendus, les pieds en diſtance juſte & proportionée, pour avoir tous ſes membres à commandement, prompts, & aćtifs. |
| Having duly subjugated his opponent’s sword, he will find that the point of contact between the two swords will be above the two Exterior Collaterals, which cross each other on the Perpendicular Diameter at the letter M. While this action was also described in Plate VI, it was only shown as one of the background figures, and it is more fully discussed here, in this Plate, and presented as a much larger figure, to clearly show the details of the posture of the body, arm and sword, and the position of the feet in the circle, as it is now time that we take a closer look at this action. Just as the figure is larger and more detailed, our description should be more complete and precise, and readers should pay closer attention. What, after all, is more important than knowing how to attack and subjugate your opponent’s sword? Or what is more useful than to be able to approach with a distinct advantage? But as superior as this is, it is also difficult. This is one of the most important sequence of operations in our System, about which we make several important cautions, which shall be explained following this discription, and without which it would be impossible to forsee all the infinite number of countermeasures that could be made against this approach. You shall see in this Plate the more notable ones, which are made by means of circular disengagements. | Ceſt aſujettiſſement eſtant deuement accompli, il ſera trouvé que le Centre de l’attouchement des eſpees reſpondra juſtement au deſſus des deux collaterales exterieurs, qui s’entrecoupent ſur le Diametre perpendiculaire, à la lettre M. Il eſt vray que la meſme operation eſt auſſi deſcrite en la Table VI. toutesfois conſiderant, qu’elle y eſt demonſtrée par figures de moindre taille, & qu’elle devoit eſtre propoſée en ce Tableau preſent en forme plus royale, repreſentant diſtinćtement la tenue du corps, du bras, de l’eſpee, enſemble la ſituation des pieds ſur le Cercle, & qu’il eſtoit icy proprement queſtion de la mettre à l’eſpreuve; nous avons trouvé bon, que comme la figure y eſt plus grande, que auſſi les particularitez en ſoyent declarées en la deſcription plus exaćtement, & quelles s’y liſent comme en de plus gros charaćteres. Car quelle choſe plus noble, que de ſçavoir attaquer & aſſujettir l’eſpee contraire? ou quelle plus utile, que de faire ſes approches avec un ſi notable advantage? Mais autant qu’elle eſt excellente, d’autant eſt elle difficile: c’eſt l’une des plus importantes opetions [sic] de Noſtre Pratique, où il faut proceder avec la caution de pluſieurs obſervations, que ſeront declarées à la ſuite de ceſte deſcription, ſans leſquelles il ſeroit impoſſible de prevenir tant de traverſes, qui ſe pourroyent faire alencontre de ceſte approche juſqu’à un Nombre infini; dont vous en verrez en ce Tableau preſent les plus notables, qui ſe font par le moyen de la cavation. |
| One can make this subjugation against different degrees of force, according to what our adversary gives to us, because of the superior strength we have from our contact with the 8th Span against his 4th or 5th Span, before we even try to do anything with his blade. In any case one must not be complacent about having this advantage. One must take care to keep the point of contact as exactly as possible, and so diminish the power of the adversary’s sword. One must always moderate one’s own power according to the situation. If the opponent uses less force we must move the point of contact up our blade accordingly. Likewise if he increases his force, we must increase ours down the blade so the force stays the same. But if he pushes hard enough that we can feel that his blade, if we let it go, will open up his centre line with his arm and blade at an angle off to the side, then we offer no resistance, and allow his blade to fly freely off to the side and we then put ourselves inside the open angle and consequently strike him, either high, or low, according to the situation as it presents itself. | On peut faire ceſt aſſujettiſſement ſur pluſieurs differents degrez de ſentiment, que l’adverſaire nous donne, à raiſon de la grande ſuperiorité d’avoir aſſemblé le Nombre 8. avec le Nombre 4. ou 5. de l’eſpee contraire, avant que de rien attenter ſur icelle pour la tranſporter. Toutefois qu’on ne ſe fie pas tant ſur cet avantage, qu’on laiſſe de prendre garde, le plus exaćtement qu’il ſoit poſſible, à l’accroiſſement, & à la diminution de la vigueur de l’eſpee contraire. Car il faut touſiours temperer ſes forces à l’advenant. Si elle s’affoiblit, il faut que la noſtre decroiſſe pareillement; ſi elle ſe renforce, il faut que la noſtre s’augmente alencontre, pour travailler touſiours avec poids egalement proportionné. Mais s’il fait un ſi grand effort, que le ſentiment nous rapporte, qu’il s’en va forligner, & faire un angle avec le bras & l’eſpee, lors on le laiſſe aller tout du commencement, ſans nulle reſiſtence, afin qu’il s’eſcarte tant qu’il voudra, & qu’on ſe mette ce temps pendant dedans l’angle pour luy donner conſecutivement l’atteinte en haut, ou en bas, ſuivant l’occaſion qu’il preſente. |
| Likewise, it may happen that, when in the act of subjugating the opponent’s sword that he weakens his resistence and yet you continue to press with the same force, without having moderated your force at that instant to equalize with his, then you are in danger of overreaching with your blade and could be wounded if he makes a circular disengage and strikes over your arm. If he gives so much with his blade that you lose contact, and yours begins to fly too far off the line, you should immediately extend your arm and sword up at an obtuse angle towards his face with a little forward motion of the body, still staying in balance. Be aware of where his tip is aiming, either up towards your face, or under your arm, or to your side. Depending on where it is coming, you can defend by moving your body around in conjunction with your arm and sword. | Pareillement s’il advient, eſtant en aćte de faire l’aſſujetiſſement, que l’ennemi s’affoibliſſe, & que vous continuez au contraire la vigueur precedente, ſans l’avoir temperée au meſme inſtant, & à l’egal de la ſienne, vous ſerez en tresgrand danger de tresbucher de voſtre lame, & de recevoir quelque atteinte par deſſus le bras, par le moyen de la cavation. Que s’il affoiblit ſa lame ſi avant, que vous en perdiez le ſentiment, & qu’elle commence à tresbucher vous allongerez au meſme inſtant le bras & l’eſpee en angle obtus devers ſon viſage; avec un petit avancement de la partie ſuperieure du corps, le tenant cependant en balance, & en aguettant la part ou la pointe contraire tire, ſoit en haut devers le viſage, ou deſſous le bras, ou à coſté; ce que diſcernant, vous ſeconderez l’extenſion du bras & de l’eſpee avec les mouvemens du corps, ſelon qu’il ſera plus expedient pour voſtre defenſe. |
| One will discover with experience that those who are not schooled in these techniques and who do not understand the fundamental reasons for them, will usually allow an enemy to pull away, even drop the contact at will, without working against him, until they see where his point is going. Thy thus lose the proper timing, and real ability to defend themselves, when the enemy has made moves that far ahead, and he has taken such a degree of advantage, that one can no longer take the Direct Line position from him. Then all he needs to do is make a simple step, opening up the angle of approach, where he can enter, if he understands how to take the lead, and maintain his advantage by whatever opportunities present themselves. This demonstrates the vital necessity of being able to respond in time to an opponent’s movements, and the difference between letting him escape from your awareness of his movements and being instantly able to counter them, the latter being done with confidence, the former being very dangerous and impossible to do calmly. To avoid this problem, one must be able to instantly recognize the start of your opponent’s actions from the contact between swords. Having recognized these movements, then use your body, your arm, and your feet equally so they work together to help support the ability to connect with the sword. This is why we have described so thoroughly and precisely all the motions that happen together, including the body, the arms, and the legs. Such as raising the right foot from the ground, making a short pause, and then moving it forward with the knees straight to put it quickly on the ground. Likewise the step with the left foot in all its particulars. If the connection is not supported by the movement of the feet, it cannot be precise enough to detect and counter the opponents actions as they begin. | On trouvera par experience, que ceux qui ne ſont pas ſtylez en l’uſage de ceſte Pratique, & n’en comprennent encor à plein les raiſons fondamentales, permettront ordinairement à l’ennemi d’affoiblir, voire meſme de deſtacher ſon eſpee à ſa fantaſie, ſans travailler alencontre juſqu’à tant qu’ils voyent ou il dreſſe ſa pointe. Dont ils viennent à perdre le temps, & la vraye occaſion de leur defenſe; pour ce que l’ennemi quand il eſt venu ſi avant que cela, il s’eſt emparé tellement de la ſuperiorité des lames, qu’on ne luy peut d’oreſenavant clorre la droite ligne; ne reſtant autre apparence que de faire une ſimple parade, accompagnée d’une ouverture d’angle, où l’ennemi ſe peut fourrer dedans, s’il entend la maniere de prendre le temps, & de pourſuivre ſon avantage avec telle ſorte d’execution, qu’il luy viendra plus à propos. Choſe qui demonſtre bien la grande neceſſité de travailler à temps ſur les mouvmens contraires, & la difference qu’il y a de ſe laiſſer eſchapper les commencemens des occaſions hors des mains, ou de les rencontrer tout à la premiere abordee. dont l’un ſe fait avec tresgrande aſſeurance, & l’autre avec ſi extreme danger, qu’il eſt comme impoſſible d’y donner ordre. Pour eviter ceſt inconvenient, il faut recognoiſtre les commencemens des aćtions contraires par l’attouchement des eſpees; & les recognoiſſant, aſſiſter le ſentiment avec le ſecours du corps, du bras, & des pieds egalement, afin que tout aille un meſme train. C’eſt pourquoy, nous avons deſcrit ſi curieuſement & exaćtement tous les mouvemens qui vont par enſemble, tant du corps, que du bras, & des pieds: comme d’eſlever le pied droit de terre, d’en faire une petite pauſe, de l’avancer avec la jambe roide, de le planter haſtivement à terre: pareillement auſſi la demarche du pied gauche, avec toutes ſes particularitez. Car ſi le ſentiment n’eſtoit bien aſſiſté du mouvement des pieds, il ne pourroit eſtre aſſez juſte, pour recognoiſtre & rencontrer les aćtions contraires & leurs commencements. |
| When the feet land on the ground at the Second Instance, while subjugating the opponent’s sword, they must be exactly on the lines as described. Turn the body so the left side is a little more forward, and the right side slightly back, the right arm lowered and pushed slightly forward, the guard back towards the right, slightly above the hip, with the arm and guard ready to defend the side which is more exposed to danger, as we shall see by the examples in this Plate. This is to uncover the left side to the enemy, which is easier to defend as shown in Circle No 2 in the following Plate. | Ce que les pieds doivent ainſi tomber à terre à la Seconde Inſtance, & en tenant l’eſpee contraire aſſujettie, eſtre ſituez preciſement ſur les lignes que nous avons deſcrites; avec le coſté gauche du corps tourneé un peu en devant, & le bras deſcendant, & mediocrement eſtendu, la garde revenant devers le coſté droit, un peu plus haut que la hanche: c’eſt pour deſcouvrir à l’ennemi le coſté gauche, qui eſt le plus facile à defendre, ainſi qu’il paroiſtra par le Cercle 2. du ſuivant; & pour tenir le coſté droit d’autant plus arriere, avec le bras & la garde preparés à ſa defenſe, comme celuy qui eſt le plus expoſé au danger, ce qu’on verra par les exemples du Tableau preſent. |
| We begin our description with Circle No 4. The figures represent the result of two different actions, one direct, the other follows on from Circle No 2. We shall begin with the first case. | Or pour venir à ſa deſcription, nous commencerons par le Cercle 4. duquel les figures repreſentent deux differentes operations: l’une qui va de droit devant, & l’autre qui ſuit apres le Cercle 2. nous parlerons donc preſentement de la premiere. |
| Circle No 4. | Cercle N.4. |
| As soon as Alexander begins to try and cross swords, Zachary makes a thrust to the face from outside the arm. But he is surprised and wounded by Alexander who takes a step to the outside and closes the Direct Line on him. | Des qu’Alexandre commence à vouloir accoupler les eſpees; Zacharie luy tire une eſtocade en dehors du bras devers le viſage: dont il eſt luy meſme ſurprins & bleſſé par Alexandre, en deſtournant la demarche un peu en dehors, & luy fermant la droite ligne. |
| Both parties begin at the First Instance in the Direct Line posture, swords parallel. Alexander begins to move intending to subjugate his opponent’s sword when he arrives at the Second Instance. To do this, he raised his right foot, and crossed his opponent’s sword to the inside, his strong part against the weak part. Zachary makes a circular disengage under and around his opponent’s arm, then gives a determined thrust with a straight arm from outside Alexander’s arm, stepping forward with his right foot up to the letter R along the Diameter. Alexander sensesing that he has lost contact with his opponent’s sword, instantly extends his arm and sends the tip of his sword towards his opponent’s face, the tip slightly up, crossing his opponent’s sword, and, taking a step to the outside, he leans backwards, his body erect in profile, and puts his right foot down at the second intersection along the Interior Collateral C-S, while sliding the point of contact up the blade in a circular motion over his enemy’s guard, to wound him in the face. He draws his left foot up into place, to the increase the power of his thrust. This is shown in the picture of him in Circle No 4. | S’eſtans trouvez les deux parties à la Premiere Inſtance en poſture de la droite ligne, les eſpees paralleles l’une à l’autre. Alexandre commence à travailler avec intention d’aſſujettir l’eſpee contraire à la Seconde Inſtance. Et pour ce faire, ayant levé le pied droit, en touchant l’eſpee contraire en dedans, du foible le fort; Zacharie fait ſa cavation, & luy tire avec le bras roide une eſtocade reſolue devers le viſage en dehors du bras, avançant le pied droit juſqu’au point R. ſur le Diametre. Alexandre s’appercevant par le ſentiment, que l’eſpee contraire ſe commence à ſe deſtacher, il eſtend tout au meſme inſtant le bras & l’eſpee devers ſon viſage, la pointe d’icelle un peu aſcendante, en croiſant l’eſpee contraire & en deſtournant ſa demarche en dehors, avec le dos panché à l’envers, & le corps dreſſé en pourfil, il poſe le pied à terre ſur la ſeconde interſećtion de la collaterale CS. en graduant circulairement l’eſpee de ſon ennemi, & le bleſſant au viſage; & laiſſant ſuivre le pied gauche en trainant proportionnellement, pour accoiſtre la vigueur de ſon eſtocade: ainſi qu’on le voit au pourtrait de ſa figure, Cercle 4. |
| Zachary performed this circular disengage immediately after the blades made contact and as Alexander paused just after he raised his right foot. He could as well done this while Alexander was stepping to the left and forcing the swords over to the side, before Alexander reached the point of losing balance. In that case, Alexander responds in the same way. That is, he moves into the enemy by stepping along the Diameter, as far as possible, so as to control his opponent’s sword more easily, almost the same way as when forcing it aside, by crossing over top of the blade as it goes under. The more one closes the distance by moving along the Diameter, the more easily one can close off the Direct Line, and, at the same time, force his enemy’s sword out at a greater angle, leaving a safer opening to step into. | Or ainſi que ceſt cavation à eſté faite par Zacharie tout à l’inſtant, apres l’eſlevation du pied droit d’Alexandre, & de l’attouchement des deux lames, aſſavoir durant la premiere pauſe; auſſi la pourra il faire durant l’avancement du meſme pied devers le coſté gauche au commencement du tranſport de ſon eſpee, avant que le corps d’Alexandre commence à tresbucher. Cela eſtant, il ſe faudra regler encor en la meſme ſorte. C’eſt qu’on entrerera ſur l’ennemi en allant devers le Diametre, le plus qu’il ſera poſſible, afin de porter l’eſpee tant plus facilement, quaſi par maniere de jetter, en croiſant, au deſſus de celle qui fait la cavation. Car autant plus qu’on s’en approche en tirant vers le Diametre, autant plus aiſement on luy pourra fermer la droite ligne, & autant plus grand ſera l’angle, qui nous ſera ouvert pour y entrer au meſme temps, avec plus d’aſſeurance. |
| Circle No 2. | Cercle N.2. |
| At the instant Alexander begins to overbalance and his foot goes to the ground, Zachary strikes with a thrust to the face from the outside. Alexander forstalls this before he can complete his circular disengage by moving forward to the inside and sliding his blade up, keeping the arm straight and the point aimed at his face. | A l’inſtant que le pied droit d’Alexandre commence à tres-bucher vers terre; Zacharie luy va tirer une eſtocade devers le viſage en dehors du bras: dont Alexandre le previent avant qu’il ait achevé ſa cavation, en entrant plus avant dedans & graduant ſa lame; avec le bras roide & la pointe dreſſée contre ſon viſage. |
| This time, Zachary begins his circular disengagement at the moment his adversary begins to overbalance. He extends his sword with a straight arm and again aims his thrust in the Direct Line, just as before, towards his opponent’s face from outside the arm, while moving forward and stepping up to the letter V on the Diameter. As soon as Alexander feels his opponents blade weaken against his, as it goes dies away, without even waiting for the disengage, he moves his own blade forward by extending his arm, raising the tip of his sword a little towards his opponent’s face, across the opposing sword. He slides the point of contact up and steps with his right foot just inside the Inside Square. He draws his left foot up to the Exterior Collateral G-M to put himself into profile, stopping the point with precision in front of his opponent’s eyes, as shown in the figure. | Mais voicy que Zacharie commence à faire ſa cavation, au temps que le corps de ſa partie adverſe commence à tresbucher; en eſtendant l’eſpee avec le bras roide, & en tirant derechef ſon eſtocade en ligne droite, ainſi que deſſus, vers le viſage de ſa partie par dehors le bras, avançant le corps & le pied juſqu’à la lettre V. ſur le Diametre. Si toſt qu’Alexandre s’apperçoit par le ſentiment, que la lame contraire s’affoiblit, voire qu’elle s’amortit; ſans attendre qu’elle ſoit deſtachee, il avance la ſienne avec le bras eſtendu, la pointe un peu montante vers le viſage du contraire, au travers de ſa dite eſpee; icelle graduant, & entrant avec le pied droit un peu au dedans du Quarré Inſcrit; & laiſſant trainer le gauche proportionnellement derriere ſur la collaterale exterieure GM. dont il ſe met en pourfil, en arreſtant ſa pointe en courtoiſie devant les yeux de ſa partie, ſuivant la repreſentation de la figure. |
| This circular disengage occurs at the instant the opponent begins to overbalance is much more dangerous for Alexander than the preceeding one, which happens while his body is still in balance, and so consequently he has better control. This is the reason why we chose to show this second encounter in this figure, as it is the most difficult. You should also know that it is the moment Zachary will choose most often to attack with his circular disengagement. He waits just a bit, until Alexander’s foot is almost on the ground, so that he cannot put it anywhere else than at the letter G, where he expects to be able to subjugate his opponent’s sword, so the circular disengage is even more advantageous. In any case, the response remains the same, as long as one can begin to work in time, and move into profile, the same as before. | C’eſte cavation qui ſe fait à l’inſtant que la Partie commence à tresbucher du corps, eſt plus dangereuſe pour Alexandre, que la precedente, qui ſe fait durant qu’il ſe ſouſtient le corps encor en balance, & par conſequent qu’il le peut miex gouverner. C’eſt la cauſe pourquoy nous avons voulu repreſenter ceſte deuxieme rencontre en figure, comme eſtant la plus difficile. Auſſi devez vous ſçavoir que c’eſt le temps que Zacharie prendra le plus ſouvent pour tirer avec ſa cavation; que s’il attend encor d’avantage juſqu’à tant que le pied droit d’Alexandre ſoit en aćte de s’abaiſſer, de façon qu’il ne ſoit plus en ſon pouvoir de le planter autrepart, qu’à la lettre G. ou il s’attendoit d’aſſujettir l’eſpee, la cavation luy ſera, en ce faiſant, encor plus avantageuſe. Toutesfois on en fera la rencontre en la meſme ſorte, moyennant qu’on cōmence à travailler au commencement du temps, en mettant conſequemment le corps en pourfil tout de meſme qu’auparavant. |
| Circle No 3. | Cercle N.3. |
| Alexander makes his thrust powerfully. He forces the opponent’s sword and arm aside while moving into the Centre, and pushing his sword with all his strength through his opponent’s head. | Alexandre faiſant l’execution de l’eſtocade en vigueur, il force le bras & l’eſpee contraire, en entrant juſqu’au Centre, & pouſſant l’eſpee detoute ſa force à travers la teſte de ſon adverſaire. |
| This is the final part of Alexander’s thrust, from the previous Circle. He moves forward with his arm straight, sliding the point of contact up the crossed blades as he steps with his right foot into the Centre, bending the right knee and drawing the left foot behind up to the letter G, so as to put the full weight of his body leaning forwards behind the hit. Thus he will connect with his opponent’s guard hard enough to force it back, and his opponent’s arm to bend. He lets his opponent’s sword fall away to the side, and makes a large enough angle that his opponent loses all possibility of defense. | C’eſt la finale execution de l’eſtocade precedente, faite par Alexandre, en avançant le corps, graduant les lames avec le bras roide, & entrant avec le pied droit juſqu’au centre, en pliant le genouil d’iceluy, pour y faire avec l’execution du coup la charge du corps, en panchant ſur le devant; & trainant le pied gauche derriere bien pres de la lettre G. de ſorte qu’il vient rencontrer ſi rudement la garde contraire, qu’elle eſt contraint de luy ceder, & pliant le bras, & laiſſant eſcouler ſa lame à coſté; dont il ſe fait une ſi large ouverture d’angle, qu’il en perd toute apparance de ſa defenſe. |
| Circle No 4. | Cercle N.4. |
| Zachary makes his circular disengagement and aims his thrust from the outside of the arm towards the face of his adversary at the moment his sword is forced aside. So Alexander leaned backwards and stepped, and made his hit while Zachary’s sword was below his during the disengage, and followed with his left foot for for support. | Zacharie fait ſa cavation, & tire l’eſtocade en dehors du bras devers le viſage de ſa partie adverſe au temps que ſon eſpee eſt aſſujettie: dont Alexandre marché à l’envers avec le dos panché de meſme, en luy donnant l’atteinte par deſſus l’eſpee durant le temps de la cavation, l’aſsiſtant avec la pourſuite du pied gauche. |
| This circular disengage was made even later than the previous one, after Alexander subjugated his adversary’s sword, with an appropriate degree of force, as he moved over to the Second Instance, as shown in Circle No 1. Zachary made a feint so as to be able to wound him with a Direct Line thrust to the face from the outside and over his sword. He moved forward, stepping in with the right foot along Diameter almost to the letter R, following on by shifting his weight onto the forward knee, in the usual style. At the same instant that Alexander feels his opponent’s sword leave his, he extends his arm and sword towards his opponent’s face, with the tip raised up a little, and leans back, while stepping backwards with his right foot, just beyond the Diameter, near the letter E, while moving his sword in a circular motion over and across his opponent’s, so as to catch it and thrust at him. His left foot follows, bringing it up into position, sliding the contact of his sword up his opponent’s, and turning sideways, as is shown in the picture. | Voicy une cavation qui a eſté faite encor plus tard, que la precedente. Car apres qu’Alexandre tenoit l’eſpee contraire aſſujettie à la Seconde Inſtance, en la forme du Cercle 1. avec un ſentiment moderé de part & d’autre; Zacharie luy eſt venu faire une feinte pour le bleſſer en droite ligne au viſage, par dehors & par deſſus l’eſpee; en avançant le corps, & entrant du pied droit un peu par deça le Diametre, quaſi à la lettre R. pourſuivant à faire la charge du corps ſur le genouil de devant, à la mode accouſtumée. Au meſme inſtant donc qu’Alexandre s’apperçoit par le ſentiment de l’affoibliſſement de l’eſpee contraire ſe voulant delivrer de la ſienne, il luy eſtend le bras & l’eſpee devers le viſage, avec la pointe quelque peu hauſſé, marchant du pied droit à reculons avec la jambe roide & le dos panché à l’envers au delà du Diametre, & outre la lettre E. jettant au meſme temps ſon eſpee circulairement ſur l’eſpee de ſon contraire en croiſant, & luy donnant l’atteinte; laquelle il pourſuit avec le pied gauche, trainant proportionnellement apres, en graduant les eſpees, & ſe mettant en pourfil; comme il eſt demonſtré en ſa figure. |
| Circle No 5. | Cercle N.5. |
| This is the final execution of the preceding, which follows from the others. | C’eſt l’execution de la precedente, procedant en conformité des autres |
| Here Alexander executes the final part of his thrust. He keeps his arm straight, steps in along the Diameter between the letter H and the Centre, puts his weight over the forward knee, draws his left foot up behind, sliding up the blades until he strikes his opponents guard with all his strength so hard that Zachary is forced to bend his arm and let his tip fly up at an obtuse angle, as is shown in the figure. | C’eſt icy l’execution finale de la meſme eſtocade, faite par Alexandre avec le bras roide, en entrant du pied droit ſur le Diametre entre la lettre H. & le Centre: continuant à faire la charge en panchant ſur le genouil anterieur, & à trainer le pied gauche apres, en graduant les lames juſqu’a rencontrer la garde de l’ennemi, de toute ſa force ſi rudement, qu’il le contraint de courber le bras, & de laiſſer aller ſa pointe en haut en angle obtus; comme on le voit repreſenté en ſa figure. |
| Circle No 6. | Cercle N.6. |
| Zachary again tries his circular disengagement, and subsequent thrust with the same timing and form as described above, in Circle No 4. Alexander prevents this another way, by stepping further in during the circular disengage, taking the Direct Line and thrusting through the head. | Zacharie faiſant derechef le cavation, & conſequement l’eſtocade au temps & en la forme que deſſus, Cercle N.4. Alexandre le previent en une autre ſorte, ſe mettant durant le temps de la cavation dedans l’angle, en prennant la droite ligne, & luy perçant en rigueur la teſte. |
| This action also follows on from Circle No 1. As Alexander moved carefully to the Second Instance, keeping his opponent’s sword subjugated with a sensitive, light touch, enough to hold it, but not more. Then Zachary again makes his circular disengage to the outside, coming in, with his arm extended, along the diameter, stepping between the letters V & R. | C’eſt operation procede auſſi de l’avantage repreſenté au Cercle 1. Car Alexandre a eſté planté preallablement à la Seconde Inſtance, tenant l’eſpee contraire aſſujettie, avec un ſentiment mediocre & temperé des deux coſtez. Lors Zacharie luy a fait une cavation pour le bleſſer derechef au viſage par dehors l’eſpee, en entrant ſur luy avec le bras eſtendu ſur le Diametre, au milieu des lettres V. & R. |
| While this position very much resembles that of Circle No 4, this interaction is, however, different. Because as soon as Alexander feels Zachary’s blade fall away, which it must to perform the circular disengage around his arm, which also opens up an angle and leaves Zachary’s face uncovered for a moment before he can thrust. At that moment Alexander lengthens his arm in the Direct Line posture, moves into this angle, and, by stepping straight towards the enemy along the collateral, from where he had stopped his right foot before, up to the letter L, he delivers a thrust to his opponent’s uncovered face, in the same way and with the follow-through that has been described above, by putting his weight on the forward knee while leaning, and drawing the left foot up behind, almost to G, as is shown in the figure, where he has executed a powerful blow. | Il eſt vray que l’occaſion eſt toute ſemblable à celle du Cercle 4. toutefois la rencontre en eſt differente. Car dés qu’Alexandre s’apperçoit par le ſentiment, que la lame de Zacharie s’affoiblit pour ſe deſtacher, dont elle ſera forcee (pour faire la cavation) d’aller circulairement à l’entour de ſon bras, & d’ouvrir un angle avec deſcouvrement du viſage, avant qu’il puiſſe donner l’atteinte; au meſme temps Alexandre allonge le bras avec l’eſpee en ligne droite, ſe mettant dedans l’angle ſuſdit, & cheminant droitement ſur l’ennemi au long de la collaterale; ou il tenoit paravant le pied droit arreſté; le bleſſant au deſcouvert du viſage, & poſant le pied à terre à la lettre L. avec pourſuite & execution du meſme coup, à faire ainſi qu’il a eſté dit à pluſieurs fois cy deſſus, en chargeant le corps avec un panchement ſur le genouil de devant, & trainant le pied gauche proproionnellement derriere bien pres juſqu’au G. ainſi qu’il ſe voit en la figure, ou il s’en fait l’execution par rigueur. |
| Circle No 7. | Cercle N.7 |
| Zachary makes his circular disengagement, and tries his thrust to the face from the outside with a bent arm at the moment when Alexander begins to overbalance and step back to the ground. As Alexander put his foot down and straightened his tip, he changed direction and diverted his opponent’s sword, subjugating it to the outside, and putting himself into the open angle. | La cavitation eſtant fait par Zacharie, l’eſtocade tirée devers le viſage en dehors du bras en ligne courbé, au temps que le pied d’Alexandre commence à tresbucher en terre; ledit Alexandre ayant planté le pied & dreſſé ſa poinćte il en modere la courſe, & en divertiſſant l’eſpee contraire il l’aſſujettit en dehors, en ſe mettant dedans les angles. |
| We again find our two opponents at the First Instance, and Alexander begins to work the same way. To subjugate his opponent’s blade at the Second, he raised and moved his right foot, according to the instructions in Circle No 1, having forced the sword over, to the point where he begins to overbalance. At this instant, Zachary makes his circular disengagement, and gives him a bent-arm thrust from outside the arm and above the sword, to the face, stepping with his right foot along the Diameter to the letter V. | S’eſtant derechef trouvez les deux contraires à la Premiere Inſtance, Alexandre a commencé à travailler encor de meſme, pour faire l’aſſujetiſſement à la Seconde, ayant hauſſé & avancé le pied droit, ſuivant les inſtrućtions du Cercle 1. & emporté l’eſpee, juſqu’à ce qu’il vient ſur le point de tresbucher: auquel inſtant Zacharie fait la cavation, & luy porte une eſtocade courbe, en dehors du bras & par deſſus l’eſpee devers le viſage, entrant du pied droit ſur le Diametre à la lettre V. |
| Alexander once again feels the lower blade begin to disengage, at that instant he extends his arm and sword, but deliberately towards his opponent’s face, setting his right foot down at the letter G. He swiftly picks up his left. Upon percieving the bent-arm, how his enemy is folding his arm to the inside, with the interior branch of the crosspiece turned diagonally upwards, and the tip of his adversary’s sword coming at his face, he interrupts the thrust of the tip of his sword towards his opponent’s face mid-way and turns it to his own defence, crossing swords to the outside, his tip raised up and his guard lowered with his arm extended, which he does while he is moving forward and stepping in with his left side, pivoting around on his right foot, all the while putting the 5th Span of his blade against the 8th Span of his opponent. He supports his arm with his body, holding his elbow against his side, and moves beyond the Perpendicular Diameter into the open angle that he creates as he forces his opponent’s sword aside, putting his left foot down beyond the Diameter at the letter Q. Then holding his opponent’s sword down with carefully applied force, he aims his tip upwards, with his body leaning slightly forwards, and his forward knee bent, as is shown in the figure. | Alexandre s’appercevant derechef par le ſentiment, que la lame inferieure ſe commence à deſtacher, tout au meſme inſtant il allonge le bras & l’eſpee, mais lentement en ligne droite devers le viſage d’iceluy, abaiſſant le pied droit à la lettre G. & eſlevant fort haſtivement le gauche: lors s’appercevant de la courbe, & comment ſon ennemi ſe plie le bras en dedans, avec la branche interieure de la garde tournée diagonalement en haut, & la pointe venante vers ſon viſage; il arreſte la courſe de ſa pointe, qui eſtoit en train & à my-chemin de donner au viſage du contraire, dont il la deſtourne en faiſant ſa defenſe, & accouplant les eſpees par dehors le bras en croiſant, ſa pointe dreſſée en haut, & ſa garde deſcendante avec le bras eſtendu (ce qu’il fait durant l’avancement & l’entree du coſté gauche) tournant le corps ſur le pied droit en forme circulaire, de façon qu’il aſſemble durant ce meſme temps ſon Nombre 5. avec le Nombre 8. peu plus ou moins de ſa partie; & aſſiſte le bras de l’aide du corps, l’affermiſſant contre le flanc, & ſe met au dedans de la perpendiculaire & des angles qu’il s’ouvre luy meſme en deſtournant l’eſpee contraire, poſant le pied gauche à terre par deça le Diametre à la lettre Q. & tenant l’eſpee contraire en devoir avec un ſentiment temperé, ſa pointe dreſſée contremont, avec le corps un bien peu panchant, & le genouil de la jambe anterieure plié; comme il ſe voit en la figure. |
| It is worthwhile to make a few points about this last action, because it frequently happens, in almost all circumstances, that we are faced with a bent-arm attack. | Il vaut la peine de faire quelques annotations ſur ceſte derniere operation, à cauſe qu’elle vient ſouvent à propos, quaſi en toutes occurrences, où on nous preſente la courbe. |
| To begin, take the first case where the enemy makes his circular disengagement and thrust, as soon as you have raised your right foot and attacked his sword at the First Instance. The remedy to this is to advance your raised foot with a short step in a direct line, in the Circle, a little beside the Diameter, while keeping the rest of the precepts. | Et premierement poſé le cas, que l’ennemi vous en tire une en faiſant la cavation, dés que vous avez levé le pied droit, & attaqué ſon eſpee à la Premiere Inſtance. Le remede ſera d’avancer le pied, qui eſt eſlevé, d’un pas mediocre en ligne droite, en dedans du Cercle, un peu par deça le Diametre, en obſervant au reſte les meſmes præceptes. |
| For the second case, he makes his circular disengagement while you are moving your right foot towards the Second Instance, but while you can still respond. The remedy will again be to move the foot directly towards him, with a short step, and putting it down on the Exterior Transverse between the letters G and E. | Pour le ſecond, qu’il face la cavation durant l’avancement du pied droit, allant devers la Seconde Inſtance, tandis que vous l’avez encore à commandement. Le remede ſera derechef de porter le pied droitement ſur luy, en faiſant un pas mediocre, & le plantant ſur la traverſante exterieure entre les deux lettres G. E. |
| If he waits until you are just at the point of overbalancing, again, you must step to the side, as much as possible, and straighten directly against the enemy on the Collateral line before the letter G. | s’Il attend juſqu’à tant, que vous ſoyez ſur le point de tresbucher, encores faudra il deſtourner la demarche, tant qu’il ſera poſſible & la dreſſer tout droitement contre l’ennemi ſur la ligne collaterale plus avant que la lettre G. |
| He might also make his circular disengagement at the instant when the body and foot are at the point of overbalancing, in such as way that it is impossible for you to put your foot anywhere but at the letter G, as intended. This is the most dangerous moment of all. For as you overbalance with your body and your blade, they are that much more difficult to control and use for your defence. This is why we chose this moment to illustrate the Plate, as being the most advantageous for the lower blade. | Il pourra auſſi faire ſa cavation, à l’inſtant que le corps & le pied ſont deſia en aćte de tresbucher, de façon qu’il vous eſt impoſſible de divertir le pied, qu’il ne tombe à la lettre G. Selon voſtre premiere intention: que eſt le temps le plus dangereux de touts. Car d’autant que vous tresbuchez du corps & de la lame, auſſi ſont ils plus difficiles à gouverner, & à vous en ſervir pour la defenſe. C’eſt pourquoy nous avons propoſé au Tableau ce temps pour un exemple, comme eſtant le plus avantageux pour la lame inferieure. |
| Sometimes he will do his circular disengagement after his sword is subjugated as it appears in Circle No 1. Then you should once again move in a little with the right foot, and at the same time raise the left foot, move it forward in a circular motion, by pivoting on the right, and following on as previously described. | Il fera quelquefois ſa cavation apres l’aſſujettiſſement de ſon eſpee accompli en la forme du Cercle 1. Lors il vous conviendra derechef entrer quelque peu avec le pied droit, en eſlevant quant & quant le gauche, & le portant circulirement en avant, avec un tour du corps pour faire ſur le pied droit, & enſuivant au reſte la deſcription, qui en a eſté donnée. |
| Note this last one is the safest for Alexander. In this case, he is best served by the instructions for Circle No 6. Because after he reaches the Second Instance, there is no significant difference in whether Zachary comes at him with a direct line thrust or a bent-arm thrust. Because in either case, he must pass his sword in a circular move underneath the guard before he can raise the tip up to point at the face. The way in which Alexander has a care for the feel of the blade, and if he begins his work as soon as the enemy begins, by extending the arm and sword, moving his body forward, and stepping in with the right foot, he will have wounded his enemy, by putting himself inside the angles, before his opponent’s sword has finished its circular disengagement. | Or ce dernier temps c’eſt le plus ſeur de tous pour Alexandre. Et vaut mieux qu’en telle rencontre il ſe ſerve des inſtrućtions du Cercle 6. Car apres qu’il eſt venu ſi avant, que de s’eſtre mis à la Seconde Inſtance, ſoit que Zacharie luy tire ceſte eſtocade en ligne droite, ou en ligne courbe, il n’y a pas grand differēce. Car auſſi bien faut il neceſſairement, qu’il paſſe l’eſpee circulairement par deſſoubs, avant que de la remonter en haut pour vous tirer vers le viſage. De maniere que ſi Alexandre prend bon eſgard au ſentiment, & qu’il commence à travailler dés que l’ennemi commence, en allongeant le bras & l’eſpee, avançant le corps, & entrant du pied droit, il aura bleſſé l’ennemi, en ſe logeant dedans les angles, avant que l’eſpee contraire ait accompli ſa cavation. |
Furthermore, when performing this training, questions and points for debate will frequently present themselves for discussion when moving from the Second to the Third Instance. To examine these, they must necessarily be put to the test. In that case, to come straight to the points in question, which occur between the Second and Third Instance, one usually dispenses with the process of carefully moving to the Second. In the event your partner decides to be rude and try, during the initial steps (which ought to be done without any real threat, in a purely perfunctory way, because otherwise the point in question cannot be explored if the stage of subjugating the sword is not easily and quickly reached) to do a circular disengagement to try and hit to the face in the direct line attack, you cannot respond as you otherwise would, since you are not watching out while stepping.* You can, however, quickly respond with this move, by turning the left side forward. That way your face, which is the target he was aiming at, will be out of the way, and you will gain the advantage of timing and ease of execution to follow the rest of the examples of bent-arm strikes described in Circles No 7 & 8.
|
En outre comme il ſe preſentera ſouventesfois en faiſant l’Exercice, des doubtes à debattre touchant operations, qui ont leur uſage en allant de la Seconde Inſtance à la Troiſieme. Pour leſquelles examiner il eſt neceſſaire d’en faire l’eſpreuve: & qu’en tel cas, pour venir au poinćt de la diſpute, qui giſt entre la Seconde & la Troiſieme Inſtance, on ſe diſpenſe ordinairement d’aller juſqu’à la Seconde avec moins de circonſpećtion. s’Il advient donc, que la partie adverſe nous abuſe durant ce premier temps (qui devroit eſtre exempt de toutes traverſes, à cauſe que le debat ne ſe peut vuider, qu’apres l’aſſujettiſſement de l’eſpee deuement & librement accompli:) s’il nous donne donc en ce temps la quelque traverſe de cavation, pour nous toucher le viſage en droite ligne, on ne pourra faire ſi bien la rencontre en ligne droite, comme il ſeroit requis, pour n’avoir aſſez bien commené la beſogne. Vous pourrez amender ceſte inadvertence par le moyen & à l’exemple de ceſte operation preſente, en faiſant avec le coſté gauche du corps tourné en devant; dont le viſage, qui eſt le poinćt où il avoit deſtiné l’atteinte ſortira de preſence, & ſi en gaignerez vous le temps & la commodité de pourſuivre le reſte à l’exemple des courbes, ſuivant la deſcription de ces Cercles 7. & 8. |
| Likewise, it sometimes happens that you put too much effort into moving the opponent’s sword in order to subjugate it, or move your right foot too quickly, and thereupon your opponent chooses that moment to perform his circular disengagement. You cannot make use of the Direct Line because you are already committed to the move and have become unbalanced. Nevertheless, you can recover by using this counter against bent-arm attacks. | Pareillement s’il advient, que vous ayez fait trop d’effort en emportant l’eſpee contraire pour l’aller aſſujettir, ou que le pied droit ait cheminé trop viſtement; & que la deſſus la partie adverſe face la cavation; ne vous pouvant ſervir aſſez juſtement de la ligne droite, à cauſe du tresbuchement inevitable, pour la faute qui eſt deſia commiſe: elle pourra neantmoins eſtre amandée par la meſme operation de la rencontre des courbes. |
| If, through carelessness or by mistake, you find yourself overbalanced, as described above, nothing is keeping you from turning it into a stratagem to assault your opponent. You can either step forward vigorously, or harshly attack your opponents swords to give him the opportunity bend over, to try and strike your face from the outside. If this occurs, it is very easy to counter with the actions shown in Circle No 7. Because the swifter the motion you make when attacking his sword, the more you have the momentum and control to vault the left side forward, entering in with the left foot, and so regain control over the opponent’s sword as he attacks from the outside and following on as in the example, above. | Or ſi le tresbuchement dernierement dit, vous eſt arrivé par nonchalence our par meſgarde, auſſi rien n’empeſche que il ne vous puiſſe aucunefois ſervir comme d’un ſtratageme, pour abuſer le contraire; en cheminant furieuſement en avant, ou en attaquant bien rudement les eſpees, afin qu’il ait occaſion de caver, avec apparance de vous toucher par dehors au viſage. En ceſte occurrence il ſera fort facile de le rencontrer avec ceſt operation du Cercle 7. Car d’autant plus de courſe, qu’on ſe donne en attaquant les eſpees, d’autant plus a on le corps prompt & à commandement, pour ſe volter le coſté gauche devant, en faiſant l’entrade avec le pied ſeneſtre; & pour reprendre tant plus viſtement la ſuperiorité ſur l’eſpee contraire en l’affrontant par dehors, & pourſuivant à l’exemple de ce que deſſus. |
| Circle No 8. | Cercle N.8. |
| Alexander maintains his advantage, ensuring it through a light push against his opponent’s blade, then he raises his left foot and dropping the contact, gives him a thrust under the arm. | Alexandre pourſuit ſon avantage, moyennant l’aſſeurance d’un petit pouſſement ſur la lame Contraire, dont il leve le pied gauche & en deſtachant les eſpees, il luy donne l’atteinte deſſous le bras. |
| This shows the action that follows on from the previous one, in which Alexander, sensing only a light pressure from his opponent’s sword, raises his left foot while giving a small push downwards. Usually, the enemy will react by increasing the strength and force of his blade. At that instant, Alexander disengages contact with his sword, he leans back with his shoulders, brings his blade in a counterclockwise circular motion around his opponent’s arm and down, with his elbow and guard held in against his side. At the same time that he moves his left foot forward, bends the left knee, shifts his weight onto that leg, he aims the tip of his sword at the enemy’s side underneath the arm, as clearly shown in the figure. | Cecy contient la purſuite de l’operation dernierement precedente, en laquelle s’appercevāt Alexandre par l’attouchement d’un ſentimēt mediocre en l’eſpee contraire il pourſuit l’operation faiſant une petite eſlevation du pied gauche enſemble avec un petit pouſſement vers le bas. Dont il advient ordinairement que l’Ennemy en augmente la vigueur & le ſentiment de ſa lame. Auquel inſtant, deſtachant les eſpees il va pancher des eſpaules un peu à l’envers, & mener ſa pointe circulairement par maniere de jetter de haut vers le bas, s’affermiſſant le bras avec la garde de l’eſpee contre le coſté droit; avançant quand & quand un peu le pied gauche qui eſtoit eſlevé, en pliant le meſme genoil, ſur lequel il va faire la charge, enſemblement dreſſant la pointe de ſon eſpee au coſté de l’Ennemy deſſoubs le bras droićt; comme il ſe voit clairement en la figure. |
| To finish executing the movement, he again moves his left foot further forward in towards his opponent, and moves his right side forwards, drawing the right foot behind, and likewise moving his arm and sword forward in such as way as to pierce his enemy’s body through: as shown previously in Plate V, Circle No 8. | Pour en continuer l’execution, il porte derechef le pied gauche plus avant dedans vers ſon Contraire, & avance enſemblement le coſté droićt du corps, trainant le meſme pied apres, & avançant pareillement le bras avec l’eſpee en ſorte qu’il en perce le corps de ſon Ennemy tout outre: ce qui a eſté repreſenté au Tableau V. Sur le Cercle 8. |
| As much as we have divided this action into two parts, one should not make too much of this, or keep it as a clearly-defined two-step sequence as the figures shown in Circles No 7 & 8 would seem to imply. You must understand that this was divided into two parts to facilitate student’s learning the action, by breaking it down. For those who are more advanced in our training, and particularly in this action, they can execute these in a single, continuous, flowing sequence, without any noticeable break or pause between them. They must, however, be careful to disengage the sword then bring the tip down in a circular motion while they begin to move forward and while the right foot is raised. And when the move forward to step, at the same instant that they thrust, as explained above, with an extended arm, that the right foot follows behind. | Or de ce que nous avons diviſé ceſte execution en deux operations, in n’en faut pas tirer de grandes conſequences, comme ſi les temps fuſſent touſiours ſi notablement diſtinguez, ainſi que les figures des Cercles 7. & 8. ſemblent de premiere face donner à entendre. Car il faut ſcavoir, que la diviſion en a eſté faite en faveur des Diſciples, aux quels il eſt neceſſaire de donner des inſtrućtions, à chaſqun mouvement à part. Mais ceux qui ſeront un peu avancez en l’exercice, & notamment en la preſente operation, ils en pourront tirer l’execution ſans nulle pauſe entremoyenne, par la ſeule continuation des meſmes mouvements; à condition qu’ils deſtachent les eſpees, en menant la poinćte circulairement de haut vers le bas, durant qu’ils commencent à advancer le corps, & que le pied droit eſt encore eſlevé; & quand ils l’avancent pour le planter, au meſme inſtant ſera donné & achevé le coup, en la maniere que deſſus, avec extenſion du bras & de l’eſpee, le pied droićt trainant apres l’autre. |
| Circle No 9. | Cercle N.9. |
| At the very instant that Alexander begins to overbalance, Zachary disengages his sword and aims thrust at an acute angle towards his stomach, with his hand slightly raised. So Alexander draws his foot back, turning the right side outwards, with his arm and guard dropping down onto his adversary’s blade, his left foot going as far around as needed. | A l’inſtant que le corps d’Alexandre commence à tresbucher; Zacharie deſtache les eſpees, & luy tire en angle aigu devers le ventre avec la main un peu haute. Dont Alexandre retire le pied, en ſe deſtournant le coſté droit en dehors, avec le bras & la garde deſcendant ſur la lame contraire, le pied gauche allant cependant en rond à meſure que la proportion le requiert. |
| The two begin at the First Instance. Alexander has begun his attack the same as before, that is, he has crossed his opponent’s blade to the inside of the arm, while raising and moving his right foot to subjugate his opponents blade at the Second Instance just above the Diameter. While doing this, at the very instant that his body begins to overbalance, Zachary steps forward with his right foot, and disengages his sword. At the same time that he sets his foot down, a little along the Diameter near R, he bends his knee and puts his weight on it, straightens his arm, and aims his thrust at an acute angle downwards at his opponent’s lower body. He keeps his shoulder protected by his sword-guard, but his face is open. Alexander realizes, partly by sight, that his opponent’s body has begun to move forward, and partly by feel that he is about to disengage his sword. He does not complete his step with his right foot, which should go as far as the Second Instance, but instead, because his body is still enough in balance that he can change direction where his foot is going, he draws his foot back, putting his toes down on the Oblique Diameter G-I and his heel on the Circumference. At the same time that he moves his left foot circularly around to bring it up into place, he also turns his right foot, pointing his right toes towards his opponent, and by this same motion withdraws his lower right side a little back and to the outside, leaning his upper body forward, straightening and lowering his arm, so that the guard of his sword is pressing down on top of his opponent’s sword. As his opponent’s tip continues to move towards his body, he continues to withdraw the lower part of his body, while sliding the point of contact up the two blades, so that they become almost parallel, with the lower one underneath the exterior branch of the crossguard. This is what is shown by the figures. | Les deux parties s’eſtants premierement tenu ſur la Premiere Inſtance; Alexandre a commencé à travailler tout de meſme qu’auparavant, ſçavoir eſt, qu’il a touché la lame contraire avec la ſienne en dedans du bras, en eſlevant & avançant le pied droit pour faire l’aſſujettiſſement à la Seconde Inſtance par deſſoubs le Diametre. Ce que faiſant, au meſme Inſtant que le corps luy commence à tresbucher, Zacharie s’avance le corps avec le pied droićt en deſtachant ſon eſpee, & plante le pied quand & quand un peu deça le Diametre aupres de R, pliant le genouil, & panchant le corps deſſus, tirant ſon eſtocade en angle aigu avec le bras roide vers la partie inferieure du corps de ſa partie adverſe; demeurant ſon eſpaule droite couverte par la garde de l’eſpee, mais le viſage à deſcouvert. Alexandre recognoiſſant en partie à veuë d’œil, que le corps de ſon Contraire ſe commence à avancer, en partie auſſi par le ſentiment qu’il va deſtacher ſon eſpee, il ne pourſuit pas la demarche du pied droit, qui devoit aller juſqu’à la Seconde Inſtance, mais au lieu de ce faire (puis que le corps eſt encor en balance, en ſorte qu’il en peut divertir le pas) il retire le pied arriere le plantant ſur la Circonference & ſur le Diametre oblicq G I; tournoyant quand & quand le pied gauche circulairement, & le plantant en diſtance proportionelle derriere l’autre, tournant enſemblement auſſi les deux pieds, les orteils devant direćtement contre ſa partie, & au meſme moyen auſſi retirant un peu en dehors la partie inferieure du coſté droit, avec panchement de la partie ſuperieure, fait avec le bras roide en deſcendant en ſorte, qu’il vient à mettre ſon eſpee avec la garde ſur l’eſpee contraire. Et à meſure que la pointe contraire s’avance vers la partie inferieure de ſon corps, ainſi à l’advenant il s’eſloigne avec ladite partie inferieure, deſgraduant cependant les deux lames, en ſorte qu’elles viennent à ſe rendre quaſi paralleles l’une à l’autre, & celle de deſſoubs à ſe retrouver ſoubs la branche exterieure de ſa garde. C’eſt ce qui eſt repreſenté par les figures. |
| In performing this action, sometimes, because the underside of the guard is round, Zachary’s blade will slide underneath the interior branch of the crossguard. This makes no difference to this action, but to the subsequent one, which will be entirely different from that shown in Circle No 10. | Or en faiſant ceſte operation, il adviendra quelqus fois, parce que le bas de la garde d’Alexandre eſt rond, que la lame de Zacharie en gliſſera deſſoubs ſa branche interieure; ce qui ne fait pas de difference en l’operation, mais bien en l’execution qui en depend, laquelle il faudra faire en tel cas tout autrement; comme il ſera monſtré au Cercle 10. |
| Furthermore, there are three other moments when this action can be done. First, when Alexander is just raising his foot and is ready to cross swords, or they are already in contact and he is about to move it towards the Second Instance, in order to subjugate it as before. If Zachary moves at this moment by stepping with his right foot forward to the letter R, as above, Alexander will again meet his low thrust with this same action, that is, withdrawing his right foot, leaning forward, and lowering his arm, the only difference being that at this time, having not yet moved, he draws his foot straight back, and sets it back down on the Diameter in the Quadrangle, otherwise performing the rest of the movement the same as above. | Au reſte cette meſme operation peut encore eſtre pratiquée en trois autres temps; Premierement lors qu’Alexandre en eſlevant le pied s’appreſte d’accoupler les eſpees, ou qu’il les a deſia accoupleées pour les emmener & aſſujettir à la Seconde Inſtance, ainſi qu’auparavant. Car ſi Zacharie s’avance la deſſus avec le pied droit, comme il eſt dit, juſqu’à la lettre R: Alexandre rencontrera derechef ſon eſtocade avec ceſte meſme operation, aſſavoir avec le retirement du pied droit, panchement de la partie ſuperieure du corps, & abaiſſement du bras avec l’eſpee; n’y ayant que ceſte difference, que en ceſte preſente occaſion il retirera le pied eſlevé droitement arriere, & le plantera ſur le Diametre du quadrangle, procedant en tout le reſte ainſi que devant. |
| The second moment occurs when Alexander is already in the act of moving his right foot towards the Second Instance, at which point he is yet still in balance. That is when Zachary tries a thrust in the same way as before. At this time, Alexander withdraws his foot and puts it down on the Circumference where the Collateral GM crosses it, then he turns and, at the same time, draws his left foot up into place behind the other, with the same considerations as above. | Le ſecond temps ſera lors qu’Alexandre ſera deſia en aćte d’avancer le pied droit vers la Seconde Inſtance, durant qu’ils tient le corps encore en balance; & que Zacharie luy tire là deſſus une eſtocade en la meſme maniere que devant. En ceſte occaſion Alexandre retirera le pied eſlevé droićtement en arriere, le plantant ſur l’entrecoupure de la Circonference & de la Collaterale G M, en tournoyant & plantant quant & quand le pied gauche proportionnellement derriere l’autre, avec les meſmes opſervations que deſſus. |
| The third moment is the one usually used and best choice for Zachary, which is the one shown in the Circle. That is, the moment when Alexander’s weight is shifting onto his right foot and begins to overbalance. Thus, it is much more difficult for him to control his foot at that instant, than at earlier moments. | Le troiſieme temps qui eſt le plus ordinaire & le plus avantageux pour Zacharie, c’eſt celuy que la figure du Cercle nous repreſente; aſſavoir quand le pied droit d’Alexandre commence à tresbucher par la charge du corps; en ſorte qu’il luy eſt plus difficile de ſe bien gouverner en ceſt inſtant là, qu’és deux autres occaſions precedentes, où il avoit le pied plus à commandement. |
| When performing this action, one must, above all, take care to contact and subjugate the opponent’s blade by leaning over with the upper body, by which means the arm can be lowered without making any particular move of its own. Otherwise, nothing would stop the adversary from hitting from the outside over the arm at the instant it descends, because it is not possible to make two contrary motions at the same time, that is, descending and rising, or advancing and withdrawing. This can, however, be done when the body is used to lower the arm, without making any particular motion with the arm. Because even as the body leans forward, the arm remains free to move and can instantly respond to any situation, whether it be to raise it up and move it forward, or to lower it, or otherwise. As such, if the enemy tries a circular disengage to strike over the arm, one can maintain a superior position above the other sword, and not only interrupt his attack, but, what is more, wound him in the process. The reason behind this observation was explained in Plate V in the final annotation to Circle No 12. I know that action was different from this one, being done at a greater distance, nonetheless, one can make good use of the explanation of that other move. | En ceſte operation il faut ſur tout prendre garde pour deuement rencontrer & aſſujettir la lame contraire, de le faire avec & moyennant le panchement de la partie ſuperieure du corps, par lequel le bras vienne à deſcendre par compagnie ſans faire aucun mouvement particulier. Car autrement il n’y aura rien qui puiſſe empeſcher la partie adverſe de nous donner une atteinte en dehors par deſſus le bras à l’inſtant qu’il deſcend, pource qu’il ne luy eſt poſſible de faire en un meſme inſtant deux mouvements contraires, ſçavoir eſt, deſcendre & monter ou avancer & reculer enſemble. ce qu’on peut toutesfois faire quand on fait deſcendre le bras avec le corps, ſans mouvement particulier; car encores que le corps ſe panche, toutesfois le bras demeure libre pour s’accommoder au meſme inſtant à toutes occaſions, tant à monter & à avancer, qu’à deſcendre ou autrement. En ſorte que ſi l’Ennemy vient à caver & à avancer l’eſpee pour nous en frapper par deſſus le bras, on en conſervera la ſuperiorité des eſpees, que non ſeulement on luy rompra ſon entreprinſe, mais qui plus eſt, on le bleſſera luy meſme. la raiſon de ceſte obſervation eſt auſſi expliquée au Tableau V. en la derniere annotation du Cercle 12. jaçoit que l’operation en ſoit differente de celle cy, comme eſtant pratiquée de plus loing; toutesfois l’une peut grandement ſervir à l’explication de l’autre. |
| Circle No 10. | Cercle N.10. |
| Alexander takes a step towards his opponent’s sword, and hits him in the face, executing the blow by sliding up the sword and leaning forward with his arm held straight out in front. | Alexandre marche devers l’eſpee contraire, & luy donne l’atteinte au viſage, en faiſant l’execution, en graduant & panchant du corps ſur le devant avec le bras roide & avancé. |
| This is the follow-up and final execution of the previous action. Alexander steps with his right foot towards his right side, setting his foot down on the Diameter at E, quickly followed by his left foot, which he moves in a circular motion to the middle of the Quadrangle, he slides the point of contact from the centre of his blade up his opponent’s, while straightening his arm and moving his body forward, leaning in, and shifting his weight onto his bent right knee, at the same instant wounding his adversary in the face. | Voicy maintenant la pourſuite & execution de l’operation precedente: pratiquée par Alexandre en avançant le pied droit contre ſa partie à main droite, le plantant ſur le Diametre au poinćt E, avec une ſoudaine pourſuite du pied gauche, à trainer circulairement juſqu’au milieu du quadrangle, graduant enſemblement la lame contraire du centre de la ſienne, avec roidiſſement du bras & avancement du corps, panchant ſur le devant, & ſe pliant ſur le genouil droit, & ainſi bleſſant au meſme inſtant ſa partie adverſe au viſage. |
| This Alexander executes this move stepping with his right foot to the right, as long as his opponent’s blade was underneath the outside branch of his crossguard. But if, on the contrary, (which happens often enough, as noted in Circle No 9) it is the case that the opponent’s sword crosses underneath and is to the inside, the execution has to be done by stepping to the left side with his right foot, allowing his left foot to follow on with a circular motion. | Ceſte execution a eſté faite, en entrant du pied droit vers le coſté droit, pour autant que l’eſpee contraire eſtoit revenue deſſous la branche exterieure d’Alexandre: mais s’il advient au contraire (ainſi qu’il advient aſſez ſouvent, comme nous avons remarque au Cercle 9.) qu’elle ſe retrouve deſſoubs la branche interieure, il en faudra faire l’execution en marchant du pied droit vers le coſté gauche, laiſſant ſuivre & trainer le pied gauche circulairement à l’advenant. |
| In summary, we want, in this and in all other times when one performs actions sideways against an opponent’s blade, whether to the left side or the right, to subjugate the blade there. Because the more you work against it, the greater the angle you will open up, into which you can move, out of danger, and make certain of your action. | En ſomme nous voulons, qu’en ceſte & en toutes autres occaſions on pratique les executions du coſté de l’eſpee contraire, tant à droite, comme à gauche, là ou elle ſera aſſujettie: pource que d’autant plus qu’on travaillera alencontre, d’autant en fera on une plus grande ouverture d’angle, ou on ſe pourra mettre dedans hors du danger, & en aſſeurer l’execution. |
| Circle No 11. | Cercle N.11. |
| At the instant that Alexander’s body begins to overbalance, Zachary tries again to hit the stomach from an acute angle, covering his face with the guard. So Alexander, moves back and again turning, as in Circle No 9, crossing, and forcing his opponent’s blade aside by leaning forward with his upper body. | A l’inſtant que le corps d’Alexandre commence à tresbucher, Zacharie luy tire derechef en angle aigu devers le ventre, ſe couvrant luy meſme le viſage par l’entremiſe de la garde: dont Alexandre en retirant & deſtournant derechef comme au Cercle 9. va croiſer & aſſujettir la lame contraire par le moyen de la partie ſuperieure du corps à pancher ſur le devant. |
| The two adversaries begin at the First Instance with their swords held in the Direct Line position. Alexander begins to work with the intention of subjugating his opponent’s blade, as in Circle No 1. He has raised his right foot, and crossed swords with his 3rd Span against his opponent’s 8th Span and so begins to step towards the Second Instance beside the Oblique Diameter. Zachary becomes aware that Alexander’s foot is falling back to the ground as he overbalances. At that instant, he steps in, covering his face by raising and interposing his guard, moving his right foot forward to the letter V along the Diameter, at the same time making his thrust by bending his knee and leaning his body forward towards the lower part of his adversary’s body. | Les deux parties ayants, preallablement mis à la Premiere Inſtance leurs eſpees en lignes droites; Alexandre commence à travailler en intention d’aſſujettir l’eſpee contraire, tout de meſme comme au Cercle 1. Ayant donc levé le pied droit, & aſſemblé les Nombres des lames 3. contre 8. & ainſi marchant vers la Seconde Inſtance par deça le Diametre; Zacharie aguette que le pied luy viene à tomber par le tresbuchement du corps, & au meſme inſtant il entre dedans, ſe couvrant le viſage par le hauſſement & entremiſe de ſa garde, en avançant le pied droit juſques outre la lettre V ſur le Diametre, tirant egallement l’eſtocade avec pliement du genouil & panchement du corps vers la partie inferieure du corps contraire. |
| Alexander quickly perceives by his sense of feel that the blades are disengaged and seeing that Zachary is protecting his face, continues to follow the blade, crossing it from above with his own and pressing down, together with quickly withdrawing his right side, he sets his right foot down in the middle of the line G-D. He quickly follows with his left foot, bringing it into position behind and a little to the side, while leaning forward with his body, turning the exterior branch of the crossguard diagonally upwards, and sliding the point of contact up his opponent’s sword, until his 9th Span is in contact with Zachary’s 6th or 7th Span, and raising the tip of his sword, so that he is forcing the tip of his opponent’s blade down so far that his opponent's right side is uncovered, as shown in the figure. | Alexandre donc s’appercevant à temps du deſtachement des eſpees par le moyen du ſentiment, & recognoiſſant par la veuë la protećtion du viſage contraire, il continue à pourſuivre la lame, la croiſſant avec ſuperiorité de la ſienne, & enſemble retirant viſtement à coſté droit, plantant au meſme inſtant le pied droit à terre au milieu de la ligne G D; avec une ſoudaine pourſuite du pied gauche, à planter une bonne proportion, derriere l’autre un peu à coſté, panchant cependant du corps ſur le devant, & deſgraduant l’eſpee contraire, en tournant ſa branche exterieure diagonalement en haut avec la pointe de la lame en peu hauſſée, & le Nombre 9. d’icelle accouplé avec le 6.ou 7. de l’eſpee contraire, de façon qu’en aſſujettiſſant il en abaiſſe tellement la pointe, qu’il luy en deſcouvre le coſté droit du corps; comme on le voit repreſenté en la figure. |
| His adversary could try the same thrust at three other times while Alexander is in the act of stepping with his right foot from the First Instance to the Second to do the subjugation. | La meſme eſtocade pourra auſſi eſtre attentée par l’adverſaire en trois autres occaſions, durant qu’Alexandre ſera en aćte de marcher du pied droit de la Premiere Inſtance à la deuxieſme, pour faire l’aſſujettiſſement. |
| The first one is when he begins to move his raised foot towards his left side, at the instant when his foot is over the midway point, at the intersection of the two lines C-G and D-E. To parry and counter his adversary’s action, he has to let his foot drop while withdrawing it straight back to the Circumference, turning his right side outwards and quickly drawing his left foot into place to recover his balance. | Premierement lors qu’il commence à avancer le pied eſlevé vers ſon coſté gauche, à l’inſtant qu’il arrive au mitan du chemin au deſſus de l’entrecoupure des lignes CG & DE. Pour donc rencontrer & parvenir en ceſt inſtant l’operation de l’adverſaire, il faut laiſſer tomber le pied en le retirant droitement arriere juſques à la Circonference, avec un deſtournement du coſté droit en dehors; & avec ſoudaine pourſuit du pied gauche à gouverner à l’advenant. |
| Likewise, this could be performed at the instant that Alexander’s toes pass the aforesaid intersection of the lines C-G and D-E, which is a little beyond half the distance of the step, and a little before the weight of the body affects the movement of the foot. To defend against the thrust at this moment, Alexander again withdraws his foot, setting it down on the Circumference, following through with the same motion of the left foot as above. | Semblablement elle pourra eſtre pratiquée à l’inſtant que les orteils du pied d’Alexandre ſeront paſſez entre ladite entrecoupure des lignes C G, & D E, qui eſt un peu outre la moitié du chemin, & le plus avant que le pied peut aller ſans eſtre incommodé de la charge du corps. Pour ſe defendre de l’eſtocade tirée en cedit dernier inſtant, il convient à Alexandre retirer le pied eſlevé droitement en arriere, en le plantant derechef ſur la Circonference, avec la meſme pourſuite du pied gauche, que devant. |
| The third moment to again try the same move is after Alexander has moved his foot and weight over far enough that he is just about to overbalance. At this instant, Alexander must, once again, withdraw his foot to the Circumference, and follow on consequently with his left foot. | Le troiſieme inſtant pour pratiquer encore le meſme, ſera apres qu’Alexandre aura porté le pied encore plus outre ſi avant qu’il commence à tresbucher avec le tranſportement du corps: auquel inſtant Alexandre doibt derechef retirer le pied eſlevé ſur la meſme Circonference, & conſequemment pourſuivre avec le pied gauche. |
| The last possible time would be when Alexander has moved his foot so far forward as to be overbalancing, which is the most difficult time of all to respond, since he cannot withdraw his foot, but rather only turn on it. For this reason, we treat it with special attention giving it its own sequence in the Plate to show its importance. | Le dernier inſtant ſera lors qu’Alexandre aura porté le pied ſi avant, qu’il ſera venu à tresbucher tout à fait enſemble avec le corps; qui eſt l’occaſion la plus difficie de toutes à bien rencontrer, n’eſtant poſſible de retirer le pied, ains ſeulement de le tourner. Pour laquelle cauſe il nous à ſemblé expedient de la repreſenter au Tableau meſme, comme eſtant de plus grande importance. |
| Circle No 12. | Cercle N.12. |
| Alexander trains his point at his adversary’s side, by simply turning his hand, and executes the thrust by sliding the point of contact up the blades, and stepping in with his right foot. | Alexandre dreſſe ſa poinćte au coſté de l’Adverſaire, en tournant ſeulement la main, & en fait l’execution en graduant les lames, & entrant avec le pied droit dedans. |
| Alexander continues the preceding action. He raises his right foot while he turns his wrist so the exterior branch of his crossguard goes outwards and down from the vertical to contact and hold his opponent’s blade in place, which brings the tip of his own blade near to his adversary’s right side. And at the same time as he slides the point of contact of his blade along his opponent’s so the two guards meet, he moves his foot forward and enters in to the letter I. He wounds his adversary under the right armpit, by bending his right knee and leaning his body, helped by his left foot following along, and increasing the force of his thrust, so that he goes right through the body. His guard meets his opponent’s, and dominates it so much that his opponent’s tip drops to the ground, as it is shown in the figure. | Alexandre pourſuit l’operation precedente; en eſlevant le pied droit, & enſemblement tournant du poignet de la main ſa branche exterieure, de verticale qu’elle eſtoit, en dehors juſques à trouver & ſerrer la lame contraire, menant auſſi par ce meſme moyen ſa pointe en la preſence du coſté droit de l’adverſaire: & quand & quand graduant ſon eſpee, durant que le pied s’avance & entre juſqu’à la letre I. bleſſant ſa partie adverſe deſſoubs l’aixelle droite, avec pliement du genouil, & panchement du corps, aſſiſté du pied gauche en trainant apres, & augmentant la vigueur de l’eſtocade, en ſorte qu’il luy en donne à travers du corps; rencontrant la garde contraire de la ſienne, & la maiſtriſe tellement que la pointe en decline vers terre; ainſi qu’il ſe foit au pourtrait de la figure. |
| Circle No 13. | Cercle N.13. |
| Zachary aims at an acute angle towards his adversary’s stomach while his sword is being subjugated. Alexander, by turning on his toes and leaning forward, hits him with the Direct Line in his uncovered torso. | Zacharie tirant en angle aigu vers le ventre de ſon Adverſaire au temps qu ſon eſpce eſt aſſujettie; Alexandre en ſe tournant ſur ſes orteils en panchant ſur le devant, luy donne l’atteinte en droite ligne au deſcouvert de a poitrine. |
| This action proceeds from that shown in Circle No 1. At the instant that Alexander subjugates the blade at the Second Instance, Zachary enters in on Alexander, stepping forward with his right foot to just beyond the letter V beside the Diameter, aiming an acutely angled thrust with a straight arm at his lower body. Alexander feels the blade disengage and sees that his opponent’s right shoulder is uncovered. He does nothing more than withdraw the lower right side of his body (the target of the thrust) away by turning on his toes and leaning his upper body forward towards his opponent, and attacking him from the Direct Line, by straightening and extending his arm, hitting him at the nearest point, which is the uncovered shoulder. One point to consider is that Zachary’s reach is shortened to the degree that his sword is pointed off the Direct Line, aiming at an acute angle. Whereas Alexander’s lengthens because he is working along the Direct Line, increased by leaning forward, while withdrawing his lower body. This gives him enough of an advantage that he can wound his opponent without the tip of his opponent’s blade getting to him. This is also demonstrated in Plate V, where it is more fully explained and mathematically verified. | Ceſte operation procede de celle qui eſt repreſentée au Cercle 1. Car à l’inſtant qu’Alexandre accomplit l’aſſujettiſſement à la Seconde Inſtance: Zacharie luy vient entrer deſſus, en avançant le pied droit un peu outre le point V au deça du Diametre, luy tirant d’un bras roide une eſtocade en angle aigu vers la partie inferieure du corps. Alexandre qui s’apperçoit par le ſentiment du deſtachement des eſpees, & par la veue, que l’eſpaule droite du contraire ſe deſcouvre; il ne fait rien que deſtourner le coſté droit de la partie inferieure du corps (qui eſtoit la bute de l’eſtocade) en ſe tournoyant ſur ſes orteils, & enſemblement ſe panchant ſur le devant devers ſon contraire, & luy aſſenant en ligne droite, moyennant l’extenſion & roidiſſement du bras, un coup de pointe au plus prochain point d’attouchement, qui eſt en la dite deſcouverture de l’eſpaule droite. Eſtant à conſiderer que l’eſpee de Zacharie ſe racourcit à meſure qu’elle ſe depart de la droite ligne, tirant à l’angle aigu: là où celle d’Alexandre au contraire s’allonge, à raiſon qu’il en travaile en ligne droite, l’aſſiſtant meſme d’un panchement de corps, avec retirement de la partie inferieure. ce qui luy porte ſi grand avantage, qu’il atteint & bleſſe ſon Contraire, ſans que la pointe contraire puiſſe arriver juſques à luy. Ceſte demonſtration eſt auſſi repreſentée au Tableau V, où elle eſt auſſi plus amplement expliquée & verifiée par raiſons de Mathematique. |
| There are some doubts which some might raise against this, which can be resolved here and now. That is, whether the wound Alexander makes could be done against an acutely angled tip. This seems impossible, since this tip moves to the opponent’s body in the blink of an eye without stopping, the two bodies are approaching, and will immediately be so close that the lower sword will have an inevitable opportunity to wound the opponent. The answer appears in the description of the action in the following Circle. | Il faut icy reſoudre une doubte, qui pourroit eſtre propoſée alencontre; aſſavoir ſi ceſte bleſſure d’Alexandre, ſe faiſant ainſi avec panchement du corps, pourroit eſtre pratiquée avec une pointe aiguë. Ce qui ſemble ne pouvoir eſtre, à cauſe que ladite pointe paſſant en un clin d’œil le corps contraire ſans nul arreſt, les deux corps s’approcheroyent & viendroyent incontinent ſi fort en preſence que l’eſpee de deſſoubs en acquerroit l’opportunité de contrebleſſer infalliblement ſa partie contraire. La reſponce en paroiſtra d’elle meſme par la deſcription de l’operation du Cercle ſuivant. |
| Circle No 14. | Cercle N.14. |
| Alexander secures himself with his sword above his opponent’s and holds it under control, as he executes his thrust, stepping into the enemy with his left side leading. | Alexandre s’aſſeure deſſus la lame contraire, & la tenant en devoir, il fait l’execution de ſon eſtocade, en entrant deſſus l’ennemy avec le coſté gauche devant. |
| Alexander thus follows through the action he began, he steps in towards his adversary with his left foot and side forward, by turning on his right foot without any further move to make his approach. In this way, the upper body and the arm move down as they move forward, which moves the guard over top of the opponent’s blade, in a way which pushes the other tip down further the closer he moves in. As he continues to close together with the effect of leaning, at the same time he slides the point of contact up the opponent’s sword, when he puts his foot down beyond the Diameter in the middle of the line M-S, drawing up the right foot, he reinforces the force of the thrust so much that the shock of striking his opponent’s sword with his guard drives the point down almost into the ground, while pushing his tip through his opponent’s body. | Alexandre donc pourſuivant l’operation encommencée, il entre ſur ſa partie adverſe avec le pied & le coſté gauche, en ſe tournant le corps ſur le pied droit, ſans aucun autre approchement: & comme ainſi ſoit, que la partie ſuperieure du corps deſcende auſſi à l’advenant avec le bras, il conduit ſa garde deſſus la lame contraire, en ſorte que la poinćte d’icelle en eſt pouſſée vers le bas à meſure que le corps entre: dont en continuant à s’approcher davantage, & enſemblement à ſe pancher ſur le devant, au meſme temps il fait la graduation ſur l’eſpee, & plante le pied eſlevé en deça le Diametre, ſur le milieu de la ligne M S, avec pourſuite du pied droit, renforçant par ce moyen tellement la vigueur de l’execution, qu’il emporte du chocq de ſa garde le bras & l’eſpee contraire, en ſorte que la pointe en tombe quaſi à terre, en luy pouſſant l’eſtocade à travers le corps. |
| These last two actions beginning in Circle No 13 must be done very exactly in practice. Alexandre hits his opponent right at the start of his movement, as soon as he feels the disengagement of the swords, before Zachary has the ability to lean or step forward to within striking distance. This is absolutely necessary to observe. If one does not move at the exact time, and if Zachary has moved his sword and body forward however small an amount, then in that case one can no longer use the lesson of Circle No 13, since one will recieve as much as one gives. Therefore, to avoid this danger, it will be necessary to defend as in Circle No 9, turning to the right side while drawing the feet back as the turn, and following at the same time the execution of the action of Circle No 10, as previous described. | If faut tres-exaćtement obſerver en la pratique de ces deux derniers operations, qu’au Cercle 13. Alexandre à donne l’atteinte à ſon contraire tout au commencement de ſon mouvement, ſi toſt qu’il s’eſt apperceu par le ſentiment du deſtachement des eſpees, avant que le corps de Zacharie ait eu la commodité de ſe pancher ou de s’avancer pour trouver la meſure d’atteindre. Ce qui eſt du tout neceſſaire à obſerver. Car ſi on ne prend le temps juſte, & que Zacharie ait avancé l’eſpee avec le corps pour peu que ce ſoit, en ce cas on ne ſe pourra pas aider de ceſte meſme leçon du Cercle 13. car encore qu’on donnaſt, auſſi on recevroit. Pour donc eviter & prevenir le danger qu’il nous avoit appreſté, il ſera beſoing de s’en defendre à l’exemple du Cercle 9. en deſtournant le coſté droit avec retirement & tournement des pieds; en pourſuivant quand & quand l’execution du Cercle 10. ſuivant les obſervations qui en dependent. |
|
| |
| The principle to which every student must aspire in performing the actions in the Plate, is to have exact timing. This is one of the most important points of the entire system, and without this, nothing can be performed either gracefully or surely. For if Hypocrites, that Prince of Doctors, dared pronounce only with care on matters of medicine, which was difficult to observe and diagnose, even when the sypmtoms endured for days, or, at the least, hours, we have even more reason to say, how fast and difficult is the Practice of Arms, wherein we have often a moment of time, and often are presented with but an instant to decide, which is a point of time, indivisible, and without any duration. As such, there are times wherein we can find an opportunity, but few opportunities wherein we find much time. Which is why those who strive to reach this high goal to comprehend correct feel and timing, I shall warn them now, that they must not assume this is an easy thing and they must not be bored with spending a long time practising these exercises presented in this Plate VII. For beyond the confidence that they will provide in the prefection of the Theory and Practice of Arms, they may also be, in and of themselves alone, enough to become competent to enter into a fight against the greatest and toughest fighters they may find, as long as they do not play at learning to feel the sense of contact. For these others are not accustomed to having their swords crossed and in contact and even when they are closely embroiled, they always do their best to detach before they can be subjugated. Thus they do not usually present any other action than those which you see represented in this Plate, so that the time spent on these exercises could not be better used. | Le principal que le Diſciple doibt pretendre en la Pratique de ce Tableau preſent, c’eſt de prendre exaćtement le temps: qui eſt l’un des plus importants points de tout l’Exercice, & ſans lequel il n’y a rien qui puiſſe eſtre pratiqué ny avec bonne grace ny avec aſſurance. Car ſi Hippocras le Prince des Medecins a oſé prononcer que l’occaſion en medicine eſt difficile à obſerver & à prendre, laquelle y dure cependant des jours ou à tout le moins des heures entieres, à plus forte raiſon pourrons nous dire, qu’elle eſt tresſoudaine & difficile en l’Exercice des Armes, où elle ne dure ſouvent qu’un moment de temps, & ſouvent qu’elle ne s’y preſente qu’en un ſimple Inſtant, qui eſt un poinćt de temps indiviſible & ſans duree quelconque. En ſorte qu’il y a temps auquel on trouve de l’occaſion, mais bien peu d’occaſions où il ſe trouve du temps. Parquoy ceux qui taſcheront de parvenir à ce haut but de cognoiſtre & prendre juſtement les temps, je les avertis, qu’il ne l’eſtiment pas pour choſe facile, & qu’il ne leur ennuye pas de mettre un long Exercice en l’uſage des preſentes leçons de ce Tableau VII. car outre l’aſſeurance qu’elles leur donneront en la parfaite Theorie & Pratique des Armes, auſsi pourront elles eſtre quaſi ſeules tenues pour ſuffiſantes dentrer en la lice avec les plus grands & hardis tireurs d’Armes qu’ils puiſſent trouver, moyennant qu’ils ne jouent pas ſur le ſentiment. Car puis qu’ils ne ſont pas accouſtumez d’avoir les eſpees accouplées, & meſmes qu’ils s’en trouvent incontinent embrouillez, ils font touſiours leur devoir de les deſtacher avant qu’on les puiſſe aſſujettir. dont il ne ſe preſente ordinairement quaſi nulle autre operation que celles que vous voyez repreſentées en ce Tableau. de façon que le temps qu’on y mettra, ne pourra eſtre que tresbien employé. |
| Translation by Bruce G. Hearns |
Transcription by Bruce G. Hearns |
|---|---|

| |
| EXPLANATION OF THE ACTIONS IN THE EIGHTH PLATE | DECLARATION DES OPERATIONS DV TABLEAV HUICTIEME |
| Up to now we have clearly shown how to guard the right side against dangers arising from circular disengagements, we now follow with the dangers of, and counters to, thrusts from the outside line which are aimed at the left side, called Imbrocata (from the Italian term). Those who wish to keep the attacking sword at a distance, will be obliged to either withdraw in retreat or attack their opponents first, either with the Direct Line, or with a bent arm, as is shown by the examples in this Plate. The first type of thrusts which are made from the Direct Line will always need to use a circular disengagement to move to the outside of the sword, but the other sort require no preparations whatsoever. For as you move the opponent’s sword to your left side, so he can aim an imbrocata by merely following on from the movement. The former are aimed at the right side, whereas the latter are aimed at the left. Those attacks that are made from the Direct Line posture are met by closing down the opening by using the same Direct Line posture against them to counter the opponent, while those attacks made with a bent arm are countered by taking the sword and moving it off-target with a counter-bend, so that the harder the opponent pushes, the further his tip moves from his intended target. So, let us see some examples. | Puis que iuſques icy il a eſté monſtré aſſez clairement comment il faut garantir le coſté droit du danger de la cavation, il ſemble que l’ordre nous convie à traitter preſentement du danger & du remede des Imbroccades, qui pourroyent eſtre tirées vers le coſté gauche. Car ceux qui ne veulent ſouffrir qu’on leur attaque l’eſpee de loing, ſont neceſſairement obligez ou à ſe retirer en arriere ou bien à tirer les premiers ſur leurs contraires, ſoit en ligne droite, ſoit avec le bras courbe, ainſi qu’on verra par les exemples du preſent Tableau. Les premiers eſtocades qui ſe font en droite ligne, requierent touſiours l’aide de la cavation pour venir au dehors de l’eſpee; les autres n’on beſoing de preparation qui ſoit. Car ainſi qu’on emporte l’eſpee contraire à coſté, auſsi en peut on tirer des Imbroccades par la ſeule pourſuite du meſme mouvement. Celles là ſont portées vers le coſté droit du corps, celles cy vers le gauche: celles de la droite ligne ſe rencontrent pareillement en fermant la meſme droite ligne alencontre pour prevenir le contraire, celles de la courbe, en ſurprenant l’eſpee meſme d’une courbe contraire la faiſant aller à vuide, en ſorte que d’autant plus que le Contraire y employe de force, d’autant plus ſa pointe s’enſuit du poinćt d’attouchement qu’il avoit deſtiné. Or venons en aux Exemples. |
| Circle No 1. | Cercle N.1. |
| At the instant Alexander sets his foot down at G, to subjugate his opponent’s sword, Zachary moves in and aims an imbrocata at his stomach. | A l’inſtant qu’Alexandre abaiſſe le pied droit à la lettre G. pour aſſujettir l’eſpee contraire; Zacharie s’avance & luy tire une imbrocade à la poitrine. |
| The two parties have before this begun at the First Instance with swords parallel in the Direct Line posture. Alexander began his work to subjugate his opponents sword at the Second Instance along the Oblique Diameter, just the same as in the first Circle of Plate VII. As he did so, at the moment his right foot touched the ground and he drew his left foot up with a circular motion. Zachary then enters in, stepping with his right foot to the outside up to the letter S, along the Oblique Diameter, leaning forward onto the right foot, bending his arm, turning the outside branch of his crosspiece upwards and inwards to deliver the imbrocata to his opponent’s chest, then following up with his left foot onto the Quadrangle, as is shown in the picture. | Les parties y ayant preallablement eſté à la Premiere Inſtance avec les eſpees paralleles en ligne droite; Alexandre a commencé à travailler pour aſſujettir l’eſpee contraire à la Seconde Inſtance par deça le Diametre, tout de meſme qu’au Cercle N.1. du Tableau VII. En quoy faiſant, à l’inſtant qu’il abaiſſe le pied droit à la lettre G. & qu’il pourſuit circulairement avec le pied gauche; Zacharie entre ſur luy portant lepied droit dedans juſqu’à la lettre S. au deça du Diametre, ſe panchant en avant ſur le pied droit, & courbant par meſme moyen le bras, il tourne ſa branche exterieure en dedans verticalement; & ainſi il donne l’imbrocade à ſa partie adverſe en la poitrine, pourſuivant a mener le pied gauche en dehors par deça le quadrangle, ainſi que il eſt repreſenté en la figure. |
| This action is only described here to more clearly demonstrate what Zachary intends to do, so that it will be easier to understand Alexander's actions that are shown in the following Circle. | Ceſte operation n’eſt icy exprimée, que pour demonſtrer plus evidement l’intention que Zacharie pretend d’accomplir, afin qu’il ſoit plus facile de comprendre l’operation d’Alexandre, qui eſt repreſentée au Cercle ſuivant. |
| Circle No 2. | Cercle N.2. |
| Alexander seeing the imbrocata his opponent begins to aim at him, traps his opponent’s blade while turning his left side away to the outside, and puts his sword-tip in front of his opponent’s eyes. | Alexandre s’appercevant de l’Imbrocade que ſon Contraire luy commence à tirer, au meſme temps il ſurprend la lame contraire, en ſe deſtournant le coſté gauche du corps en dehors, & luy mettant ſa poinćte devant les yeux. |
| We repeat the actions of Alexander and Zachary from the start up to the moment when Zachary has begun to step forward with his right foot, bend the arm, turn his crosspiece upwards to send his imbrocata into his opponent’s chest. Alexander clearly perceives his opponent’s attack as much by the feel of the blade as by sight. At the same time that he straightens his arm, he turns the interior branch of his crossguard out and upwards as far as the top of his head, to trap his opponent’s blade from underneath, raising it up, while, turning on his feet, he moves his left side (the aim of the thrust) outwards and away from his opponent’s attack. At the same time, he aims his own blade directly at his opponent’s eyes, carefully stopping his blade, so that his opponent’s cannot advance without wounding himself in the face. This is shown by the figures. | Comme donc ces dites operations d’Alexandre & de Zacharie ſont encommencées & continuées, juſques à ce que Zacharie commēce à avancer le pied, courber le bras, mener & tourner ſa branche exterieure en dedans à la hauteur de l’eſpaule pour aſſener ſon Imbrocade en la poitrine de ſa partie adverſe: Alexandre s’apperçoit aſſez clairement de l’approche du corps de ſon cōtraire, par le ſentiment & meſmes par la veüe; que fait qu’au meſme temps en roidiſſant le bras, il tourne ſa branche interieure en dehors verticalement juſqu’à la hauteur du ſommet de ſa teſte, en ſorte qu’il en ſurpren la lame contraire par deſſoubs, & la fait monter en haut, destournant au meſme inſtant à l’aide des pieds le coſté gauche, (ou l’atteinte avoit eſté deſtinée,) en dehors, & dreſſant par meſme moyen la pointe de ſa lame droit aux yeux de ſa partie adverſe, l’arreſtant par courtoiſie, en ſorte que ſon contraire ne ſe peut avancer ſans ſe bleſſer luy meſme au viſage: ainſi qu’il eſt repreſenté par les figures. |
| Circle No 3. | Cercle N.3. |
| Zachary aims an imbrocata thrust at his opponent’s chest, stepping in and bending his arm up as high as his head, at the moment his sword is being subjugated. | Zacharie donne à ſon Contraire un coup d’Imbrocade en la poitrine, en entrant & courbant le bras à la hauteur de ſa teſte, au temps que ſon eſpee eſt aſſujettie. |
| The action in Circle No 3 comes a little later than the previous one, that is, after Alexander has stepped to the Second Instance and subjugated his opponent’s sword. At this moment, Zacharay advances on him, stepping out with his right foot into the letter S, bending his arm and turning the outside of his crosspiece upwards to the top of his head at at the same time. Thus, he gives an imbrocata thrust at his opponent’s chest by leaning his body forward, and drawing his left foot to the outside by the Quadrangle. Zachary’s actions is shown here for the same reason as Circle No 1. The only difference here is that Alexander has already moved up to the Second Instance, forcing Zachary to raise his arm higher to give his imbracata thrust from higher up and further outside. This is the situation; the counter follows. | Ceſte operation du Cercle 3. vient un peu plus tard que l’autre, aſſavoir lors qu’Alexandre eſt deſia arrivé à la Seconde Inſtance, y ayant aſſujetti l’eſpee contraire: auquel temps Zacharie s’avance ſur luy, en entrant du pied droit juſqu’à la lettre S. tournant enſemblement d’un bras courbé la branche exterieure de ſa garde verticalement juſqu’à la hauteur du ſommet de ſa teſte; donnant ainſi à ſa partie adverſe un coup d’Imbrocade en la poitrine panchant le corps, & accomodant le pied gauche pour le trainer en dehors deſoubs le quadrangle. Ceſte operation de Zacharie eſt icy repreſentée pour la meſme conſideration que la prededente Cercle 1. Auſſi elle n’en differe pas autrement, ſi ce n’eſt qu’en ce Cercle preſent Alexandre avoit les pieds deſia plantéz ſur la Seconde Inſtance, & que pour ceſte cauſe Zacharie a eſté obligé de porter la main plus haut pour donner l’Imbrocade de plus haut. Voilà l’occaſion; s’enſuit la rencontre. |
| Circle No 4. | Cercle N.4. |
| Alexander again perceives his opponent aiming an imbrocata at him after his sword has been subjugated. He turns his left side away, lowering his arm and catching his opponent’s blade, in such a way that he he leans backwards to do the move. | Alexandre s’appercevant derechef de l’Imbrocade que l’Adverſaire luy tire apres l’aſſujettiſſement, il ſe deſtourne au meſme temps le coſté gauche du corps en dehors, en baiſſant le bras & ſurprenant la lame contraire, en ſorte qu’il en fait l’execution en plongeant avec le corps panché à l’envers. |
| Just as soon as Zachary raises his foot and moves it forward, he bends his arm while turning his wrist so the exterior branch of the crossguard moves upwards to about head-height, to do his imbrocata thrust the same way as before. Alexander, who knows his opponent’s intention from the feel and movement of his sword, at once raises his right foot, spins his left side out and away and, catching his opponent’s sword with the crossguard, raises his arm up above his head and aims his point down towards his opponent’s face, putting his foot down on the line between G and L, and then puts his weight on it by learning backwards, drawing his left foot up behind into place, and executes his hit by sliding the point of contact along the blades, as is shown in the figure. | Tout auſſi toſt que Zacharie eſleve & avance le pied, courbant en haut le bras, & enſemble tournant ſa brāche exterieure en haut à l’endroit de ſa teſte, pour donner l’Imbrocade en la meſme forme que deſſus: Alexandre cognoiſſant ſon intention par le ſentiment & par les mouvements du corps de ſon contraire, eſleve au meſme temps le pied droit en l’air, deſtournant le coſté gauche du corps en dehors, & hauſſant le bras avec la garde, il eſtraint la lame contraire de ſa branche interieure, laquelle il tourne en haut au deſſus de la hauteur de ſa teſte, en dreſſant la pointe vers le bas au viſage du Contraire, & ainſi plantant le pied entre GL ſur la ligne, & ſur iceluy chargeant le corps en panchant à l’envers, meſme avec le pied gauche trainé proportionellement derriere, il pourſuit & execute ſa pointe en plongeant & graduant les eſpees de haut en bas, comme il eſt pourtrait en la figure. |
| To correctly counter these imbrocata thrusts, you must take care to move at the same instant that your opponent bends his arm, turning the exterior branch of his crossguard upwards, and thus presenting his left side. Turn your left side away, straighten your right arm, and turn the interior branch of your crossguard upwards, so as to catch your opponent’s blade. While sliding the point of contact up the blades while you wound him, make sure to keep your hand slightly above your opponent’s, so his tip will always be above your head, and so you will hit him while being certain of his sword being out of the way at an obtuse angle. | Pour prevenir juſtement ces dites Imbrocades, il faut prendre garde qu’au temps que la partie adverſe courbe le bras en tournant la branche exterieure en haut, & preſentant enſemblement le coſté gauche, de travailler au meſme inſtant juſtement au contraire, en deſtournant le coſté gauche hors de preſence avec le bras droit eſtendu, & la branche interieure de la garde tournée en haut; en ſorte que la lame contraire en ſoit ſurprinſe. Auſſi en graduant les lames durant l’execution de la bleſſure, il faut obſerver de porter tourſiours le bras avec la garde un peu plus haute que la main contraire, afin que ſa pointe vous aille au deſſus de la teſte & qu’ainſi vous luy donniez l’atteinte hors de l’angle obtus avec aſſurance. |
| Circle No 5. | Cercle N.5. |
| While Alexander is stepping from the Second Instance to the Third, Zachary moves forward and aims an imbrocata thrust at his face. So Alexander is constrained to move in against him, turning his opponent’s sword aside with his body leaning backwards, and stepping between the perpendicular Diameters, to turn in place. | Au temps qu’Alexandre chemine de la Seconde Inſtance vers la Troiſieme; Zacharie s’avance, & luy tire une Imbrocade devers le viſage: dont Alexandre eſt contraint de s’avancer pareillement alencontre, en deſtournant l’eſpee contraire avec le corps panché à l’envers au dedans des perpendiculaires, pour y faire la volte. |
| After Alexander arrived at the Second Instance, having subjugated his opponent’s sword, he intends to step to the Third and execute the attack as shown and described up to the 6th Circle of Plate VI, he has just raised his foot to take a step. Zachary again moves forward in the same way as above, moving his right foot out to the letter S, bending his arm, turning his wrist so the exterior branch of his crossguard is vertical and above his head, to give Alexander an imbrocata thrust to the face. Alexander raised his foot and moved it forward, so his body is a bit higher and slightly closer. At the very instant he realizes it is no longer possible for him to overcome his opponent with a bent arm attack that forces the tip of his opponent’s sword aside so he can deliver a downward strike, he moves likewise against him, holding his sword and arm straight out in front, upwards at an obtuse angle, he steps in between the two Diameter lines at point I, then turns his left side away, while at the same time raising his left foot and spinning it around the other so far that that his toes land on the line between R and S which helps to lean his body backwards. So his body is in the angle between the perpendicular lines, arm extended, his guard pushing his opponent’s guard and hand higher up, so that while he is in this position, he can do nothing against him. This, then, is the meaning of this figure. | Apres qu’Alexandre en aſſujettiſſant l’eſpee contraire eſt venu à la Seconde Inſtance, & qu’il commence à marcher vers la troiſieſme, en intention d’y toucher & executer en la maniere qui eſt demonſtrée par le Tableau VI. au Cercle 6. dés auſſi toſt qu’il a eſlevé le pied droit pour cheminer; Zacharie s’avance derechef en la meſme ſorte que deſſus, en portant le pied droit juſqu’à la lettre S. ſe courbant le bras, & tournant ſa branche exterieure verticalement par deſſus la hauteur de ſa teſte, pour luy donner une Imbrocade au viſage. Alexandre s’eſtant un peu hauſſé, & approché par l’eſlevation & l’avancement du pied; tout à l’inſtant il cognoiſt qu’il ne luy eſt plus poſſible de ſe prevaloir de la ligne courbe, en deſtournant la pointe contraire contremont, & aſſenant à meſme temps la ſienne en plongeant de haut en bas, parquoy au meſme inſtant, que l’adverſaire commence, il s’avance pareillemēt alencontre, avec le bras & l’eſpee roidement eſtendus en angle obtus, & plante le pied au deça le Diametre au poinćt I. en deſtournant le coſte gauche en dehors, & quand & quand eſleve le pied gauche, & le volte par derriere l’autre ſi avant, qu’il en plante les orteils ſur la ſećtion de la ligne RS. panchant le corps à l’envers, à l’aide des pieds que ſe tournent en dehors; ſe mettant ainſi le corps au dedans des perpendiculaires, avec le bras eſtendu, rencontrant & pouſſant de ſa garde la garde & le bras contaire plus haut, en ſorte qu’elle l’empeſche durant ce meſme temps, de ne pouvoir rien attenter au contraire. Voila là le ſens de la figure. |
| Circle No 6. | Cercle N.6. |
| Alexander spins around his left side while at the same time moving his sword-tip over and down, wrapping his left arm around himself while making a quick step with his left foot so as to hit his opponent in the chest. | Alexandre ſe volte le coſté gauche devant, en menant au meſme temps ſa poinćte de haut en bas, l’entortillant de ſon bras gauche avec eſlevation du pied gauche, pour executer ſa poinćte à travers la pointrine de ſon adverſaire. |
| Alexander immediately continues on from the previous action, turning his body around with his left side forward as he turns his feet, and, at the same time, turning his wrist and hand to disengage from his opponent’s blade and move his sword-tip down to point at his opponent’s chest, with his right hand held in close against his side and his left arm wrapped close across his front. At the same time, he lifts his left foot makes a short step forward to the point S, bending his knee to put his weight on it, drawing his right foot up behind from point I to the letter L on the Perpendicular Diameter, so he can easily drive his opponent backwards, as is shown in the figure. | Alexandre pourſuit ſans intermiſſion l’operation precedente, en tournant les pieds & le corps en dedans avec le coſté gauche devant, & au meſme temps, en tournant du poignet de la main la pointe de ſon eſpee de haut en bas, il abandonne la lame contraire, en ſerrant la ſienne contre ſa pointrine, icelle entortillant de ſon bras gauche; eſlevant & avançant quand & quand un bien peu le pied gauche, juſqu’à la lettre S, portant la charge du corps ſur le meſme genouil plié. le pied droit ſuivant proportionellement juſqu’à la lettre L. ſur le Diametre perpendiculaire, & dreſſant ſa pointe ſur le bas de la pointrine de ſon Contraire, en ſorte qu’il ne tient qu’à luy de le jetter à l’envers par terre, ainſi que les ſituations des figures le repreſentant. |
| Circle No 7. | Cercle N.7 |
| Once again, while Alexander is stepping with his foot towards the Third Instance, Zachary confidently aims an imbrocata thrust up towards his face, confident in his superior position. | Cependant qu’Alexandre chemine avec le pied droit devers la Troiſieme Inſtance; Zacharie luy tire derechef une Imbrocade haute devers le viſage, en prenant l’aſſeurance de la ſuperiorité. |
| Again, Alexander has reached the Second Instance, and has just raised his right foot to step over to the Third Instance at the letter N from where he intends to strike his opponent in the face. At the same time, Zachary steps forward with his right foot to the letter S, body erect, drawing his left foot up to the letter X. At the same time he bends and turns his arm inwards, the guard up above his head and, by moving the point of contact up his blade and down Alexander’s, gains superiority over his opponent, to hit him with an imbrocata thrust to the face. | Alexandre eſtant derechef arrivé à la Seconde Inſtance au poinćt G.& ayant pareillement eſlevé le pied droit pour aller à la troiſeme à la lettre N. en intention d’y donner l’atteinte au viſage de ſon Contraire: au meſme temps Zacharie marche avec le pied droit & le corps eſtendu juſqu’à S. le pied gauche revenant avec le talon levé juſqu’à la lettre X. & au meſme temps il courbe & tourne le bras dedans par deſſus la hauteur de ſa teſte, de ſorte qu’il en acquiert par l’augmentation de ſes Nombres la ſuperiorité des lames, pour donner encore à ſon Contraire un coup d’Imbrocade au viſage. |
| His sense of feel tells Alexander that his opponent has begun to dominate and is about to attack his face. He immediately redirects his foot down onto the collateral line near L, quickly lifts and moves his left foot forward, while turning his left side forward, as he turns the interior branch of the crossguard upwards, catches his opponent’s sword from beneath, and extends his right arm up above his head and to the outside, so his guard forces his adversary’s tip upwards past his head, as shown in the figure. | Alexandre s’appercevant par le ſentiment tant de la ſuperiorité que de l’intention de ſon Contraire, il divertit la demarche en mettant le pied à terre ſur la ligne collaterale pres de la lettre L, hauſſant & avançant enſemblement le pied gauche, & tournant le coſté gauche, & le bras droit eſtendu en dehors par deſſus la hauteur de ſa teſte; avec la branche interieure de ſa garde tournée contremont; dont il ſurprend par en bas la lame contraire, & en mene la poinćte par deſſus la hauteur de ſa teſte, ainſi qu’il ſe voit au pourtrait de figures.
|
| Circle No 8. | Cercle N.8. |
| Alexander has set his right foot down and, seeing he has lost the advantage, lets his blade drop, and disengages as he jumps with his left foot beside his adversary, and makes a reverse cut to his leg. | Alexandre plantant le pied droit & s’apppercevant de la ſuperiorité perdue, il laiſſe eſcouler ſa lame, & en la deſtachant il ſaute avec le pied gauche à coſté de ſon adverſaire, luy donnant un coup de revers à la jambe. |
| Alexander can feel that his adversary is still putting force on his blade, pressing it downwards, to aim an Imbroccata thrust at his face. He lifts his guard forward, and allows his wrist to flex so the tip of his sword drops away to the right. With his still-raised left foot, he leaps outside the circle, putting all his weight forward onto that foot while at the same time raising his right foot up and, while doing this, disengages his sword, allowing it to swing circularly around, upwards, and then down so that he can cut diagonally backwards across the thick of his opponent’s calf, as is shown in the figure. | Alexandre s’appercevant par le ſentiment, que ſon Adverſaire luy continue le poids de ſa lame, en pouſſant la ſienne vers le bas, pour luy donner l’Imbrocade au viſage; il en hauſſe à l’advenant la garde & en laiſſe deſcendre la pointe à l’aide du poignet de la main; ſautant du pied gauche qui eſt eſlevé vers ſa partie, en dehors au deſſoubs le Cercle, avec pareille eſlevation du pied droit, menant quand & quand la charge du corps en panchant ſur le pied gauche, & durant le meſme temps deſtachant les eſpees, & la ſienne la menant circulairemēt dehaut en bas, en ſorte qu’il en tire un coup de revers diagonal au gras de la jambe droite de ſon Contraire. ainſi qu’il eſt peint en la figure. |
| Circle No 9. | Cercle N.9. |
| He presses his advantage, pivoting around and siezing his opponent’s guard, while Zachary is trying to turn his sword on him. He puts his sword-tip into Zachary’s right armpit. | Il pouſuit ſon advantage, en voltant le corps & faiſant prinſe de la Garde Contraire, cependant que Zacharie ſe prepare à luy preſenter l’eſpee; en luy aſſenant conſequemment ſa poinćte deſſoubs l’aixelle droite. |
| This follows from the preceeding circle. Alexander takes his raised right foot quickly around with a circular move well behind his left foot which he raises at the same time off the ground. Zachary, seeing how his adversary is about to get behind him, at the same time moves his left foot, with his heel raised, over the diameter to the letter W, thus turning, so his right arm and sword are towards his opponent. While he does this Alexander grabs his guard from beneath with his left hand, moving it over his head and pulling down towards him as he leans back on his right foot. He closes his left arm against his side to hold the guard firmly in place while aiming the tip of his sword at his adversary as his left foot comes down, so that his adversary is suddenly drawn onto it, as the picture shows. | C’eſt la pourſuite du preeedent: en laquelle Alexandre mene le pied droit eſlevé d’une grande viſteſſe circulairement & fort avant par derriere le gauche, lequel il pourſuit quand & quand à eſlever en l’air: dont Zacharie recognoiſſant que ſa partie adverſe luy viendroit à gaigner la crouppe, au meſme temps il porte le pied gauche avec le talon levé au delà du Diametre à l’W, preſentant par ainſi le corps avec les pieds, le bras droit, & l’eſpee devers ſon Cōtraire. Durant lequel mouvemēt Alexandre luy empoigne la garde par deſſous, la tournant & tirant à ſoy vers le bas, avec le corps panché à l’envers ſur le pied droit, que eſt planté; s’affermiſſant le bras avec la garde de l’eſpee contre le coſté droit, en aſſenant & executant la poinćte au coſté droit de l’adverſaire avec le planter du pied gauche, en ſorte que ledit adverſaire en eſt ſurmonté tout à fait, ſelon que les figures demonſtrent. |
| It often happens, when doing the actions in Circle No 7, that Zachary will cross swords at the 6th or 7th Span with the 7th or 8th Span of his own, in order to subjugate the blade and so more easily aim his intended Imbrocata thrust. At which point, Alexander will once again bring his guard up, with the interior of his crossguard turned vertically upwards above his head while allowing his sword-tip to drop lower, and bringing his right foot closer to the Perpendicular Diameter, towards the letter N. Whereas in Circle No 8, he followed up with a reverse cut to the leg. So now, with his tip lowered even further, he will most often use a reverse-cut to the head. Likewise, instead of what was shown in Circle No 9, where he took ahold of the guard, when it sometimes happens that as his adversary turns towards him, this will not be possible to do. In that case he must execute a thrust to the face with the tip of his sword. | Or il adviendra ſouventefois en pratiquant l’operation du Cercle 7. que Zacharie en donnant la courbe, ira croiſer par en haut la lame contraire aux Nombres 6. ou 7. avec les 7. ou 8. des ſiens, pour l’aſſujettir & tirer plus aiſemēt l’execution de l’Imbrocade pretendue: Sur quoy Alexandre menera derechef la garde, avec la branche interieure tournée verticalement par deſſus la hauteur de ſa teſte en laiſſant cependant aller la poinćte plus baſſe, & menant le pied droit plus en deça le Diametre devers la lettre N. Et comme au Cercle 8. il a pourſuivy l’operation avec un coup de revers tiré à la jambe; ainſi maintenant, ſa poinćte eſtant baiſſé d’avantage, il en menera le plus ſouvent un coup de revers à la teſte. Pareillement au lieu de ce qui eſt repreſenté ſur le Cercle 9. qu’il fait prinſe de la garde, au meſme temps que ſon Contraire ſe tourne avec l’eſpee devers luy, il adviendra quelquesfois qu’il luy ſera impoſſible de ce faire; toutesfois il ne laiſſera d’executer ſur ſon Contraire, en luy tirant par le foible de l’eſpee une eſtocade en droite ligne au viſage. |
| Circle No 10 | Cercle N.10. |
| At the moment Alexander is about to reach the Third Instance, Zachary advances and again aims an Imbrocata thrust at his chest, but with his left side leading. | A l’inſtant qu’Alexandre penſe arriver à la Troiſieme Inſtance: Zacharie s’avance, & luy tire derechef une imbrocade à la poitrine, avec le coſté gauche tourné en devant. |
| After Alexander has subjugated his opponent’s blade at the Second Instance and is moving towards the Third, intending to thrust as usual. But as soon as he starts to shift his weight, Zachary again enters in, moving his right foot from the Diameter to the point S, drawing his left foot up to the letter X, with his heel raised. He moves his left side forward while bending his arm up above his head, and turning his wrist so the exterior branch of his crossguard goes upward. In this way his sword-tip is aimed straight at his opponent’s chest, ready for an outside thrust. Alexander is forced to put his foot down on the Interior Transverse by the letter M, drawing his left foot up behind. | Alexandre apres avoit aſſujetti la lame contraire à la Seconde Inſtance, il s’acheine vers la troiſieme, en intention d’y tirer l’eſtocade à la mode accouſtumée: Mais auſſi toſt qu’il en approche le pied Zacharie vient derechef entrer ſur luy, en portant le pied droit en deça le Diametre juſqu’au poinćt S. Avec pourſuite du pied gauche avec le talon levé juſques à l’X. & enſemblement avançant le coſté gauche du corps, courbant le bras par deſſus la hauteur de ſa teſte, & tournant la branche exterieure de ſa garde en haut; & par ainſi preſentant la point de ſa lame en forme d’imbrocade droit à la poitrine de ſon contraire: iceluy en eſtant forcé de planter le pied eſlevé ſur la traverſante aupres de la lettre M. le pied gauche ſuyvant proportionnellement apres. |
| This incomplete action is shown here so you can better understand Zachary’s intentions and the timing he chose to make his move as the most convenient, and how his move is forseen and countered by Alexander's actions in the following Circles. | Ceſte operation vous eſt icy repreſentée imparfaite, pour donner tant mieux à cognoiſtre l’intention de Zacharie, & le temps qu’il y choiſit pour le plus convenable; & comment elle luy ſera prevenue & annullée par Alexandre en la pourſuite de l’operation demonſtrée par les Cercles ſuivants. |
| Circle No 11. | Cercle N.11. |
| Alexander has been forced to turn the hit aside using the end of his blade, while stepping inside the angles, to prepare to turn about. | Alexandre eſt forcé à deſtourner le coup par l’entremiſe de ſa lame, en entrant dedans les angles, & ſe preparer à faire la volte. |
| Everything that was said in the last Circle about moving from one side to the other, describes the two opponents moving against each other at the same time, until Zachary leans forward, bending his arm and turning hand and sword to attack with his Imbrocata thrust. Alexander, seeing that his opponent has come in so close into range that he cannot parry him simply with a bend of his arm, as he did before in Circles No 2 and 4, puts his right foot down at the letter M. He moves his right side forward and his arm and sword against his opponent’s sword, parrying it and pushing it away, with his guard low and the tip up. At the same time, that he sweeps his left foot around and behind his other foot, setting it down by the letter S, along the Inscribed Square, he turns his left side outwards and towards his opponent, and in this way, steps in between the perpendicular diameters and the opponent’s blade, all the while keeping his eye on his opponent until the last possible moment. This is clearly shown by the figures. | Tout ce qui à eſté dit au Cercle dernier precedent, ſeſtant ainſi paſſé tant d’un coſté que d’autre, les deux Contraires s’avançent à meſme temps l’un contre d’autre, juſqu’à ce que Zacharie panche le corps ſur le devāt, courbant & tournant le bras & l’eſpee pour luy donner l’Imbrocade: Alexandre s’apperçevant que ſa partie adverſe luy eſt venue ſi avant dedans la meſure, qu’il ne le pourroit toucher avec la courbe contraire (ainſi qu’il avoit fait auparavant aux Cercles 2. & 4.) plante au meſme temps le pied à terre à la lettre M. En avançant le coſté droit du corps enſemble avec le bras & l’eſpee devers l’eſpee contraire, la deſtournant & pouſſant en dehors par l’oppoſition de la ſienne avec ſa garde baſſe & ſa pointe haute: pourſuivant quand & quand à volter le pied gauche, enſemble avec un tournoyement du coſté gauche en dehors par derriere l’autre juſqu’à bien pres de l’S. ſur le coſté du quarré inſcrit, ſe fourrant par ainſi dedans les perpendiculaires de la lame contraire, & continuant encor juſques audit dernier inſtant à regarder ſon contraire au viſage: ainſi qu’il eſt clairement demonſtré par les figures. |
| Circle No 12. | Cercle N.12. |
| He continues his about-turn to the left, keeping control of the blades. | Il fait l’aćtion de la volte, en tournant le coſté gauche, avec l’aſſeurance des lames. |
| Alexander continues the movement he started, swiftly turning his body and particularly his left side outwards, turning on his feet, his back to his opponent, so that he cannot see his face for an instant, but still keeping his arm straight with the sword pressed against his opponent’s sword, the same as before, as shown in the figure. | Alexandre continue le mouvement encommencé, en tournant viſtement le corps, & notamment le coſté gauche plus en dehors à l’aide des pieds, avec le dos devers ſa partie contraire, en ſorte qu’il ne le peut regarder en ceſt inſtant au viſage, laiſſant toutesfois cependant le bras droit avec l’eſpee appuyée contre l’eſpee adverſaire, en la meſme ſituation, qu’ils eſtoyent paravant; ainſi qu’il paroit aux figures. |
| Circle No 13. | Cercle N.13. |
| Alexander spins around, disengaging his blade, bringing the sword-tip around and down and setting his left foot down at the moment he makes his thrust. | Alexandre luy donne l’atteinte enſuite de la volte, en deſtachant les lames, & conduiſant ſa poinćte de haut en bas avec le pied gauche eſlevé, lequel il plante en faiſant l’execution. |
| Alexander continues with his action, turning his left side and feet towards his opponent, and at the same time using his wrist to move the flat of his blade around and down to hold it against his side. He wraps his left arm across his stomach and holds it there, while stepping forward and beyond the circle with his left foot and putting his weight down on it, hitting his opponent in the lower chest at the same time, so that he delivers the most power behind his thrust through his opponent’s body, enough to knock him backwards as he follows through with his right foot. This is the sense of the figure. | Alexandre pourſuivant encore la meſme operation, tourne le coſté gauche du corps & les pieds devers ſon Contraire, & au meſme temps il conduit avec le poignet de ſa main le plat de ſa lame de haut en bas alencontre de ſa poitrine; l’embraſſant & affermiſſāt avec le bras gauche, portant enſemblement le pied gauche en avant par deça le Cercle, & avançant ſur iceluy la charge du corps, donnant à ſa partie adverſe l’atteinte au bas de la poitrine: en ſorte qu’il eſt en ſa puiſſance meſme de le jetter à l’envers, en executant ſur luy ſon eſtocade à travers le corps avec pourſuite & aſſiſtance du pied droit. Tel eſt le ſens de la figure. |
| As soon as Zachary raised his guard up to head height in Circle No 11 to attack with his Imbrocata thrust, Alexander was forced to parry off to the side holding his sword and guard shoulder-high. He could also do it this way, had Zachary tried the same Imbrocat on him, but with his sword and hand going not much higher than his shoulder. More often, he would keep even lower, trying to hit the lower part of Alexander’s body. In all such situations, Alexander would defend in the same way, by bringing his guard and blade lower and forward. He must also be sure to meet all Imbrocata attacks, whether from high, or low, at about the 9th Span against his opponent’s blade, his sword-tip aimed upwards so that he cannot be hit down low along his blade, nor can his opponent go above his blade to hit high up. Following this beginning, I shall show some variations in the continuation and final execution of the hit, in a way that is very easy to understand and will not need much explanation. | Or tout ainſi que Zacharie a hauſſé ſa garde au Cercle 11. à l’egal de ſa teſte, pour tirer ſon Imbrocade; dont Alexandre a eſté contraint de la deſtourner avec le bras & la garde haute au parage de l’eſpaule: auſſi ſe pourra il faire que Zacharie entreprendra de tirer ſur luy les meſmes Imbrocades, n’allant point plus haut avec le bras & l’eſpee que ſes eſpaules; voire aſſez ſouvent, il demeurera encore plus bas, en taſchant de donner le coup en la partie inferieure du corps. En toutes leſquelles occaſions Alexandre ſe defendra touſiours en la meſme ſorte en menant auſſi ſa garde & ſa lame plus baſſe à l’advenant: & obſervant en toutes occurrences d’Imbrocades tirées ſoit de haut ſoit de bas de mettre le point 9. ou environ contre la lame adverſaire, la poinćte dreſſée contremont afin qu’il ne puiſſe eſtre touché en bas au long de ſa lame, ny en haut par deſſus. Et ſuivant ce commencement la continuation & l’execution du coup en recevront auſſi quelque changement à l’advenant; qui eſt fort facile à comprendre, & ne requiert point d’autre explication. |
| Finally, note that these three Circles, 11, 12, & 13, are not three separate actions, to be done in three parts, but rather a single sequence of three steps, shown this way for ease of the student to observe and understand the principles he must follow. As the student follows our style of fighting, they will perform these different parts one after the other so smoothly that they will come to be seen as a single fluid motion, the parts existing only in theory. | Soit obſervé en ces trois Cercles 11. 12. 13. que ce ne ſont pas trois diverſes aćtions, diſtinguées en trois temps chaſcune à part ſoy: combien que la repreſentation en ſoit ainſi faite par articles en faveur des Diſciples, pour leur demonſtrer les principales obſervations ſelon leſquelles ils ſe doivent regler. Car quand ils y ſeront ſtylez, ils pratiqueront, toute l’operation de bout en bout d’une ſi parfaite promptitude, que les parties icy repreſentées y ſeront pluſtoſt recogneues par imagination que par la veuë. |
| Here then, in these two Plates VII & VIII, we have presented the actions which will typically be used against those whose style of fighting does not involve swords in contact. As such, its usefulness is self-evident. But speaking especially about Plate VIII, I believe I should not be taken to task for the most part for these demonstrations, with these reversals of the arm, raising it up to, or even above, head-height, and making this jump from about the Third Instance to the adversary’s side, and making these spinning moves, both high and low, which appear to be strange and extreme, and, what is worst of all, to be disadvantageous to someone attempting them. To which I must respond that mistakes made while trying to follow these instructions should not be taken as a weakness of an otherwise powerful art. For, insofar as untrained students may not be able to successfully execute these moves, this does not mean the principles are not correct. Which is why, if any would criticize this system, they must show that there is some fault in the action being displayed, such as taking too long to set up, or being too awkward to perform the move as shown. To say these are extremely difficult moves means nothing if they cannot show an easier one instead, which would be appropriate in the same situations. Because everything we do is forced on us in response to our opponents moves. Because, in any case, the law of performing movements in a natural way must be held inviolable, you understand that there is nothing more compelling than necessity, which force drives all laws to be as stable as they can be. This is a general answer, which must suffice to respond to criticisms that these movements shown here are not natural, which entirely wrong. These may be difficult to put into practice at first, nevertheless, with a little practice, they become very easy to do, so that when and where they are needed, they can be done quite gracefully, and unbelievably quickly, and very successfully, not done by chance, but through skillful application of this art, grounded in rational science. These examples should not be taken as in any way unnatural, because Nature herself not only advocates these methods, but teaches us they are the answer when we are pressed to the point of being able to do nothing else, in the same way that Nature instructs a man who has fallen into the water to swim. I will say that this art does have some apparently strange moves, and is, at first, quite difficult to learn, but after some training, one will find oneself so capable, that there is not one person in the whole world who would not admit that this art is entirely in accordance with natural principles. | Or voilà donc en ces deux Tableaux VII. & VIII. les operations qui ſe preſentent ordinairement à faire contre ceux qui ſont accouſtumez à tirer des armes ſans l’uſage du ſentiment. En ſorte que l’utilité en eſt evidente d’elle meſme. Mais touchant ſpecialement le VIII. je croy qu’il ne faudra pas d’eſtre reprins en la plus part de ſes demonſtrations en ces renuerſemens du bras à porter en haut à l’egal de la teſte ou encores plus, en ce ſaut à faire depuis environ la Troiſeme Inſtance juſques à coſté de l’adverſaire, & en ces voltes du corps tant hautes que baſſes, qui ſembleront à pluſieures eſtre des mouvements eſtranges, & extremes, & qui eſt le pire de tout, deſavantageus pour celuy qui les voudroit mettre en pratique. Auxquels il faudra reſpondre, que les fautes commiſes a l’encontre des regles ne doivent prejudicier à la certitude de l’art meſme. Car encores que le diſciple malverſé n’en puiſſe venir à bout, toutesfois les preceptes n’en laiſſent pas d’eſtre juſtes. Parquoy s’ils les veulent reprendre il faut qu’il nous demonſtrent, qu’il y a de la faute en la demonſtration meſme, comme n’ayant pas le temps ou la preparation ou la commodité requiſe pour mettre en œuvre ce qu’elle monſtre. Car de dire que ce ſont des mouvements extremes, cela n’importe ſi ce n’eſt qu’ils nous en monſtrent des autres plus faciles, qui ſoyent neantmoins convenables en ces meſmes occaſions. Car tout ce que nous faiſons l’adverſaire nous y force: & partant combien que la loy de ſuivre les mouvements naturels doive eſtre inviolable, toutsfois il faut entendre que la neceſsité n’en a nulle, & qu’elle enfonce toutes loix quelques ſtables qu’elles puiſſent eſtre. Ce que nous alleguons pour une reſponce generalle, qui pourroit eſtre tenue pour ſuffiſante, encores que les mouvements icy repreſentez fuſſent contre la nature, ce qui eſt toutesfois autrement. Car encores qu’il ſoyent difficiles à pratiquer du commencement, ce neantmoins ils nous ſont rendus par l’excercice tres faciles, en ſorte qu’en lieu & temps on s’en ſert avec tres-bonne graçe, voire avec une viſteſſe incroyable, & avec un heureux ſuccés procedant non par hazard mais de la ſevreté de l’art, fondé en raiſon naturelle. Ces exemples ne doivent donc pas eſtre tenues pour choſes contre Nature, puis que c’eſt la nature meſme qui non ſeulement les avoüe, mais meſme les enſeigne, quand elle eſt reduite au point de ne pouvoir autrement; tout ainſi qu’elle monſtre à l’homme eſtant tombe en l’eau l’art de la nage; jaçoit que ledit art conſiſte en des mouvements fort eſtranges, & du commencement fort difficiles à apprendre: deſquels il ſe rend toutesfoit par l’exercice ſi capable, qu’il n’y a perſonne au Monde, qui ne confeſſe que ledit art ne ſoit du tout accordant à la Nature. |
| Translation by Bruce G. Hearns |
Transcription by Bruce G. Hearns |
|---|---|
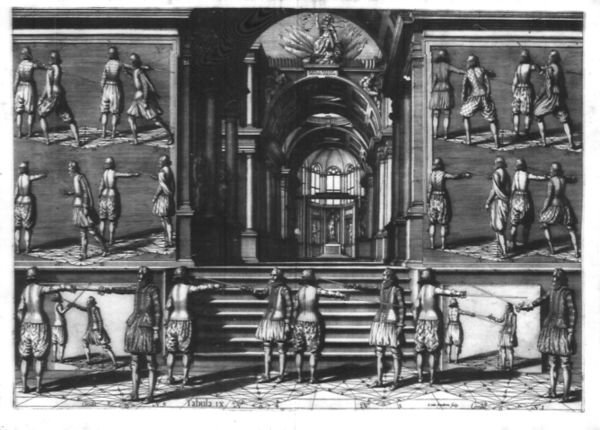
N.B., the coat of arms at the top belongs to Maurice of Nassau, Prince of Orange (1567 – 1625) who became Prince of Orange in 1618. | |
| A DISCUSSION ON THE VARIOUS DEGREES OF FORCE
to serve as an introduction to the ninth plate. |
DISCOVRS SVR LA DIVERSITE DES
poids, servant d’introdvction av tableav nevfieme. |
| It is evident from the previous demonstrations that attacks made from long range are extremely dangerous, and if they succede at all, it as much by chance as by skill. It follows that the advantage in our Art consists of the ability to close in with confidence. This cannot be done without having full knowledge of the importance of feel and sight. However, we are going to address only the former in this present Plate, not to separate the usage of one from the other, but we shall discuss the latter more fully in its proper place. In actuality, both are so tightly intertwined together that the use of one cannot even be started without the use of the other. These are the two, and only, pillars of our entire system of Training. We use sight to duly move into distance, we use feel to be more sure of it. We use sight to come to the point where we can reach out and make contact to use our sense of feeling, we use our sense of feel to execute the moves. In the way we use light to guide the eyes, we use our eyes to guide our sense of feel, and likewise our sense of feel to guide our movements. Sight is necessary at all different ranges, but Feeling can be used only when in contact, it cannot be used but at closer ranges. Nonetheless, Feeling has some excellent advantages, not only to enable us to respond against our opponent’s moves in time, but also with precision and control. This sense of feel alerts us, not only to the initial moves, but informs us of the amount of force being used, and the direction where it is going. These are things that are absolutely necessary to know, above all else, and about which sight alone can tell us so little as to be virtually useless. | Puis qu’il eſt evident par les Demonſtrations precedentes, que les coups qu’on tire de loing, ſont accompagnez d’un extreme danger, & s’ils reuſſiſſent aucunefois, que c’eſt pluſtoſt par hazard que par ſcience; il s’enſuit, que tout l’advantage de l’Art conſivte en l’aſſeurance de faire ſes approches. Ce qui ne peut eſtre pratiqué ſans avoir entiere cognoiſſance de l’importance du Sentiment & de la Veuë. Toutesfois nous ne traitterons en ce Tableau preſent que du premier tant ſeulement, non pour en ſeparer l’uſage d’avec l’autre, mais nous remettrons à parler plus amplement de la Veuë en ſon lieu propre. Car en effećt ils ſon liez touts deux ſi eſtroitement enſemble, que l’operation de l’un ne peut eſtre ne commencee ne pourſuivie ſans qu’elle ſoit à touts moments aſſiſtée de l’aſſeurance de l’autre. Car ce ſont les deux & uniques ſouſtiens de tout l’Exercice. On ſe ſert de la veuë pour venir deuëment en preſence; du ſentiment pour y eſtre plus ſeurement: par la veuë on vient au Sentiment, & par le Sentiment à l’Execution meſme; en ſorte que comme la lumiere eſt la guide aux yeux, ainſi les yeux le ſont pareillement au Sentiment & à la faculté motive. La veuë eſt neceſſaire en toutes ſortes de meſures; mais le Sentiment puis qu’il ne peut eſtre pratiqué ſinon par l’attouchement, il ne peut ſervir qu’en meſure plus eſtroite: toutesfois il ne laiſſe pas d’avoir auſſi en contreſchange des avantages fort nobles, par leſquels il nous aide & guide, non ſeulement à travailler ſur les mouvements contraires à temps, mais auſſi avec la juſteſſe & moderation requiſe. par ce que c’eſt luy qui en recognoiſt touſiours les premiers commencements, & la diverſité de l’effort, & la route de leur courſe; choſes autant neceſſaires, que nulle autre, & auſquelles la Veuë apporte ſi peu d’utilité, qu’elle n’y peut entrer en compte. |
| So now we come to the differences in Forces, which can be a considerably large number. We have, however, divided it into nine parts, or, more properly, degrees. To each of which, we have given a name to describe it, to avoid confusion, and make it more understandable. Here is the list: | Pour venir donc aux differences des Poids, encores qu’elles puiſſent eſtre en aſſez grand nombre. Nous en rapportons cependant toutes les principales à neuf eſpeces, ou à proprement parler, degrez; auxquels nous avons auſſi donné à chaſqun ſon nom propre, pour eviter confuſion, & pour les rendres plus intelligibles. Or en voicy donc la Table. |
| The First,.............Deadweight. | Le Premier,..................Mort. |
| The Second,.............Sensation. | Le Second,..............Sentiment. |
| The Third,...................Alive | Le Troiſieme,..................Vif. |
| The Fourth,.................Lively. | Le Quatrieme,.............Gaillard. |
| The Fifth,.................Livelier. | Le Cinquieme,.........Plus-Gaillard. |
| The Sixth,..............Very-Lively. | Le Sixieme,...........Tres-Gaillard. |
| The Seventh,.................Strong. | Le Septieme,...................Fort. |
| The Eighth,................Stronger. | Le Huićtieme,.............Plus-Fort. |
| The Ninth,..............Very-Strong. | Le Neufieme,..............Tres-Fort. |
| Now, to understand the meaning and, at the same time, learn how this works in practice, observe the following. | Maintenant pour en entendre le ſens, & en apprendre auſſi par meſme moyen la pratique, vous ſeres comme il s’enſuit. |
| Firstly, attack the opponent’s blade, and subjugate it, stepping from the First Instance to the Second near the Diameter, so that you arrive at the position shown in Circle No 1, subjugating the opponent’s sword, so that it is perpendicular to yours, above the letter M, almost along the the Exterior Collateral line. | Premierement attaquez la lame contraire, & l’aſſujettiſſez de la Premiere Inſtance à la Seconde au deçà le Diametre, en ſorte que vous en reveniez en la forme du Cercle 1. tenant l’eſpee contraire deuement aſſujettie, faiſant qu’elle reſponde perpendiculairement au deſſus de la lettre M, quaſi ſuivant le fil de la collaterale exterieure. |
| Being situated thusly I assure you that you can discern exactly from the feel of the blade all the nine degrees of force that this lower blade can exert on yours. And to explore them more fully, so as to leave no questions or doubts in your mind, in practice, disengage the blades as quickly as possible, pulling yours up, over, and across to the outside, so that his blade, although it springs upwards by itself, more or less, according to the degree of Force applied, cannot catch yours. As you do this, we shall show you now how to discern and name all the Forces, which are listed above. | Eſtant donc ainſi ſitué, je dis, que vous pourrez exaćtement diſcerner par le Sentiment touts les neuf degrez de Poids, que ceſt lame inferieure pourra pratiquer contre la voſtre. Et pour les examiner plus ſeurement ſans nulle reſerve de doubte, deſtachez en pratiquant les lames le plus viſtement qu’il ſoit poſſible, en oſtant la voſtre, & la jettant circulairement de deſſus la ſienne en dehors, en ſorte que la ſienne, qui ſautera d’elle meſme apres, plus ou moins à l’advenant du Poids, ne la puiſſe atteindre. Ce que faiſant, nous vous monſterons preſentement à diſcerner & à nommer touts le Poids, ainſi qu’il ſont ſpecifiez cy deſſus. |
| The First Force, that is, Deadweight. | Le Premier Poids, aſſavoir Mort. |
| This is the default Force, when the opponent’s lifeless blade presents no force against yours. This is easy to feel because in the lower blade there is no resistance, and yours would drop to the ground of the weight of its own force, if you were not holding it up. Disengaging, lifting your blade off it, the opponent’s blade will remain where it is, in the same place above the External Collateral line without moving, because there is no action in it. | C’eſt le default du Poids, quand la lame contraire ne ſe meut non plus contre la voſtre, qu’une choſe morte; ce qui vous ſera aiſé à cognoiſtre au rapport du Sentiment, par ce que la lame inferieure ne vous fait nulle reſiſtence, & meſme que la voſtre s’en va tresbucher vers le bas à faute d’appuy, ſi vous ne la ſouſtenez. En partant, en oſtant la voſtre de deſſus, elle demeurera comme morte en la meſme ſituation au deſſus de la collaterale exterieure ſans changer de place, à cauſe qu’elle n’eſtoit pas en aćtion. |
| The Second Force, which I call Sensation. | Le Second Poids, que j’appelle Sentiment. |
| This one makes a certain amount of effort, but very small, trying to raise the upper blade up, with a light feeling of force. This must be dominated and held, using the same amount of strength against it. Then, suddenly, disengaging the blades, as described above, allowing his blade to move freely, it will move from the letter M to above the Interior Collateral line, crossing the Perpendicular Diameter at the letter L, coming to rest in the direct line position pointing at your body. | C’eſt celuy qui uſe de quelque effort, mais tres-petit, taſchant d’eſlever la lame ſuperieure en haut, avec quelque peu de ſentiment. Lequel il faut dompter & arreſter, en uſant d’un pareil ſentiment alencontre: puis tout à l’inſtant, en deſtachant les lames en la maniere auparavant deſcrite, laiſſer aller la ſienne tant qu’ell pourra ce qui ne ſera, que depuis la lettre M.juſqu’au deſſus de la collaterale interieure coupant le Diametre perpendiculaire au poinćt L; & reſpondant en droite ligne ſur voſtre corps. |
| The Third Force, which I call Alive. | Le troiſieme Poids, que je nomme Vif. |
| You will recognize this likewise through the sense of feel, because the lower blade will be working harder to raise yours. So you will need to cross it lower down his blade. Then, when you again disengage your blades, the lower one will spring from the letter M, where it was held, to just above the centre of the Circle. | Vous le cognoiſtrez pareillement au rapport du ſentiment, par ce que la lame de deſſoubs travaillera avec plus d’effort pour hauſſer la voſtre; en ſorte que vous aurez auſſi beſoing d’accroiſtre à l’advenant le voſtre d’avantage. Puis en deſtachant derechef vos lames, celle de deſſous ſautera depuis le point M, où elle eſtoit aſſujettie juſtement deſſus le Centre du Cercle. |
| But it must be observed that these three proofs presume that you have both begun in the First Instance along the Diameter, with swords held parallel and in direct line, and that you subsequently moved the opposing blade out of the direct line, off to the left hand side, to the Second Instance, but without the opponent moving either his feet or his body to even the smallest degree. This is necessary to observe, to make this practice and the explanations easier, since these demonstrations depend on Natural reactions. When the opponent remains with his feet and body in this position, with the sword forced off line, he is naturally inclined to try and recover the arm and sword back to the Centre, along the Diameter. The degree to which he uses force against the upper blade will naturally result, when the blades are suddenly disengaged, in his blade springing back towards the Diametre, to a greater or lesser degree, according to the amount of force he used. Thus the Sensation Force will spring from the letter M to the letter L above the Interior Collateral line. When it feels Alive, it will spring from the same point M to above the principal Diameter. From whence it again appears that as well as with an infinite number of other considerations, that the lines drawn within our Circle are not only in accordance with Natural movements, which they also demonstrate, but also that they demonstrate the effects of Forces that result from those moves. | Or il faut obſerver, que ces trois dernieres preuves preſuppoſent que vous ayez preallablement eſté touts deux à la Premiere Inſtance ſur le Diametre avec les eſpees paralleles en ligne droite; & conſequemment que vous ayez emmené la lame contraire hors de la droite ligne à la Seconde à main gauche, ſans que le Contraire ſe ſoit pourtant en rien bougé de ladite droite ligne, ny de corps ny de pieds, pour peu que ce ſoit. Ce qui eſt du tout neceſſaire à obſerver, pour en rendre la Pratique plus facile, enſemble auſſi pour en declarer plus aiſement les raiſons, dont les demonſtrations dependent de la Nature meſme. Car quand il ſe tiendra avec les pieds & le corps en ceſte dite poſture, encores que la ſituation de l’eſpee en forligne, toutesfois elle ne laiſſe pas du s’encliner naturellement enſemble avec le bras devers le Diametre, qui en eſt comme le Centre. De maniere que ſi elle uſe de poids alencontre de la lame ſuperieure, il eſt neceſſaire, en deſtachant les eſpees, qu’elle ſaute & s’avance devers le Diametre plus ou moins à l’advenant du ſentiment qu’elle y employe. Dont le Poids de Sentiment s’en avencera depuis la lettre M, juſques à L au deſſus de la ligne Collaterale: & avec le Sentiment Vif elle ſautera depuis le meſme poinćt de la lettre M. juſques au deſſus du Diametre principal. D’où il appert derechef ainſi qu’en une infinité d’autre conſiderations, que les lignes menées dedans noſtre Cercle, ne ſont pas ſeulement accordantes avec les mouvements naturels, mais auſſi qu’elles les demonſtrent, voire auſſi qu’elles demonſtrenet les effećt des poids, dont ils ſont accompagnez. |
| But as for the rest of the Forces on the list, which include more or less extra effort than the natural tendencies, the spring which follows the disengagement of the swords will fly a further or shorter distance beyond the Diameter line. Moreover, all the jumps which pass beyond the Centre limit of the natural movements, must necessarily be unnnatural, and, at each increase of Force, each increase of the distance beyond the Diameter becomes smaller, unlike those up to the Diameter. | Mais quant au reſte des poids enſuyvants, qui ſont accompagnez d’un effort plus que naturel, le ſaut qui en procedera en deſtachant les eſpees, outrepaſſera la ligne du Diametre, plus ou moins. Or il faut que tout ce qui outrepaſſe le Centre des mouvements naturels, ſoit neceſſairement violent, & conſequemment qu’il aille touſiours en s’affoibliſſant de plus en plus, dont is s’enſuit que les ſauts qui procedent du poids de l’eſpee ſe raccourciſſent plus à l’advenant au dela du Diametre, qu’ils ne font en deça. |
| Therefore, to mark on the Perpendicular Diameter the six points where the sword will come to rest from each of the six remaining Forces, we must divide it into six unequal parts. | En ſorte que pour marquer ſur le Diametre perpendiculaire les ſix points, au deſſus d’eſquels l’eſpee contaire ſe viendra rendre à la fin de ſa courſe en chaſcun des ſix poids reſtants, il nous faudra partir inegalement en ſix parties. |
| Divide each of the two quarters of the Circumference on the far side of the Diameter into six equal parts, that is, six from C to N and likewise six more from X to N. | Partiſſez les deux quarts de la Circonference, qui ſont au delà du Diametre, chaſqun en ſix egalles parties: aſſavoir ſix depuis le C juſqu’à l’N. & pareillement ſix autres depuis l’X. juſques au bout du quadrangle, qui eſt à main droite. |
| Next run a line parallel to the Diameter from the first point marked along the Circumference, across the Perpendicular Diameter, to the first point opposite. Mark the first section point on the Perpendicular Diameter. | Puis mettez voſtre ligne parallele au Diametre principal, depuis le premier point qui ſera marqué en la Circonference, à travers le Diametre perpendiculaire, juſques au premier poinćt oppoſite: & au poinćt de la ſećtion du Diamette perpendiculaire mettez y une marque. |
| Do the same with the other points following along, connecting each point to the one opposite. | Faites en apres auſſi le ſemblable des autres points enſuyvants: en mettant touſiours la ligne d’un poinćt à l’autre, à chaſcun le ſien. |
| In this way you will mark five points along the Perpendicular Diameter, and the letter N will be the sixth. | Et par ce moyen vous trouverez cinq poinćts à marquer ſur le Diametre perpendiculaire: & la lettre N. y ſervira pour le ſixieme. |
| After this, we conventionally label each point with its own number. The first one, which is closest to the Centre, is 4. On the next one beyond that, 5. Then 6, 7, & 8 follow, so that the final point, which is on the N, will be number 9. | Apres il conviendra mettre à ceſdits poinćts à chaſcun ſon nombre: aſſavoir ſur le premier, qui eſt le plus proche du Centre 4. ſur le prochain enſuyvant 5. plus 6. 7. & 8. conſequement: en ſorte que le dernier poinćt, qui eſt marqué de l’N.ſera tenu pour le 9. |
| So, to begin the numbering, and the practical ability to discern all the different Forces, if the opposing blade lacks any sensation, so that when you disengage your sword it remains above the Exterior Collateral, where it crosses the Perpendicular Diameter at M, it is the first Force, which we call, Deadweight. | Pour venir donc, au denombrement, & à la pratique pour diſcerner touts les Poids; ſi la lame contraire manque de tout ſentiment, de ſorte qu’en deſtachant les eſpees, elle demeure immobile au deſſus de la Collaterale exterieure marquée ſur le Diametre perpendiculaire de la lettre M. c’eſt le premier Poids que nous appellons, Mort. |
| With the Second Force, which is Sensation, upon disengagement, the sword springs over to the Interior Collateral, above the letter L. | Avec le ſecond Poids, qui eſt le Sentiment, en deſtachant les eſpees, elle ſautera juſques à la Collaterale Interieure au deſſus de la lettre L. |
| With the third, which is Alive, it springs to above the principal Diameter. | Avec le tiers, qui eſt le Vif, elle ſautera juſqu’au deſſus du Diametre principal. |
| With the fourth, which is Lively, it springs to above the point marked number 4, as it is the place of the fourth level of force. | Avec le quatrieme, qui eſt Gaillard, elle ſautera juſqu’au deſſus du point marqué en ciffre 4. comme eſtant l’endroit du quatrieme poids. |
| With the fifth, Livelier, it will go to the point marked number 5. | Avec le cinquieme, Plus-gaillard, elle arrivera juſqu’au poinćt marqué en ciffre 5. |
| With the sixth, Very-Lively, it will spring to point number 6. | Le ſixieme, Tres-gaillard, ſautera juſqu’au poinćt 6. |
| With the seventh, Strong, it will spring to point number 7. | Le ſeptieme, Fort, juſqu’au 7. |
| With the eighth, Stronger, it springs to point number 8. | Le huićtieme, Plus-fort, juſqu’au poinćt 8. |
| The ninth, called Very Strong, will spring over to the ninth point, which is at the letter N. And as this is the edge of the Circle, it is also the last and the strongest of all the Forces, that we will work with. | Le neufieme, Tresfort, ſautera juſqu’au neufieme poinćt, qui eſt l’endroit de la lettre N: & comme c’eſt la borne du Cercle, auſſi eſt ce lendroit du dernier & du plus fort de tous les Poids: hors mis les Extremes. |
| When you are at the Second Instance, and you are subjugating your opponent’s sword, in the way described, you will be able to judge by the feel, which of the nine degrees of Force your opponent’s blade is pressing up with against yours. Then, the instant you disengage swords, you will name that Force: Deadweight, Sensation, Alive, Lively, Livelier, and so on, whichever it is, and you will see how well your judgement accords with how far the sword springs. Continue this exercise until you are quite capable of judging correctly each time. The most expedient way to achieve this is to practise from the Second Instance, with the advantage of having the upper blade, and the convenience of not moving. Because if the body was moving, it would diminish the ability to feel the opponent’s blade. But being stopped, one’s senses are all freer, because all there is, is the force on the blade. I would like, then, for the Student to be well-versed in these exercises to develop his judgement, and to assist him, we present the best and most convenient opportunities to learn as possible. Because the lower blade cannot always be constrained to act against the upper blade with all the different Forces, as we specified. But I would, nontheless, that the Student be able to feel them, to be able to recognize them more easily. | Eſtant donc à la Seconde Inſtance, & y tenant l’eſpee contraire aſſujettie en la forme ſuſdite, Vous jugerez par le ſentiment avec lequel de ces neuf poids la lame cōtraire travaille par deſſous contre la voſtre: puis en deſtachant les eſpees, vous nommerez le poids au meſme inſtant ſelon le jugement que vous y aurez fait, ſoit Mort, Sentiment, Vif, Gaillard, Plus-Gaillard, ou autre quel qu’il ſoit: & puis verrez ſi le jugement s’accorde au ſaut de l’eſpee. Auquel exercice il faudra continuer juſques à tant que vous en ſoyez rendu capable. Or le plus expedient pour y parvenir, c’eſt de le pratiquer du commencement à la Seconde Inſtance, avec l’avantage de la ſuperiorité, & la commodité d’avoir le corps arreſté. Car le corps eſtant en aćtion, il ne peut eſtre que le ſentiment n’en ſoit aucunement amoindri; mais eſtant arreſté, il a touts les ſens plus libres; par ce qu’il eſt tout en puiſſance. Ie veux donc que le Diſciple ſoit bonnement exercé à faire ceſdites jugements, & que pour l’y ſtyler, on luy preſente les meilleures & plus commodes occcaſions qu’il ſoit poſſible. Car la lame inferieure ne peut eſtre contrainte de travailler à la Seconde Inſtance avec tant de poids differens, comme nous venons de ſpecifier; mais je veux toutesfois qu’elles s’en ſerve en faveur du Diſciple, pour les luy apprendre à cognoiſtre plus aiſement. |
| In any case, one should not think this is never used. On the contrary, after you have subjugated your opponent’s sword at the Second Instance, if you raise your right foot and move forward so as to step and then thrust at him along the line of the Inside Square from the Third Instance, as shown in Circle No 5, then as you step forward you must duly increase your control by sliding the point of contact along the blades, so that you will have a greater advantage when you aim your hit at your opponent’s face. He will be forced, if he does not want to be hit, to increase the degree of force of his blade as you move in, even up to “Very Strong,” which is the highest degree of all, or be unable to resist your increased domination if he does not. | Toutesfois il ne faut penſer pourtant qu’ils ne viennent jamais en uſage. Car au contraire, apres que vous luy aurez tenu l’eſpee aſſujettie à la meſme Seconde Inſtance, ſi vous eſlevez conſequemment le pied droit avec avancemēt de corps pour cheminer & donner l’atteinte au long du Quarré Inſcrit à la Troiſieme Inſtance, ainſi qu’il eſt icy repreſenté au Cercle 5. Et qu’en cheminant ainſi en avant vous augmentiez deuement voſtre ſuperiorité par la graduation des eſpees, en ſorte que le coup en ſoit dreſſé avec autant d’avantage devers le viſage du Contraire; in en ſera forcé, s’il ne veut recevoir l’atteinte, d’augmenter ſon poids à l’advenant, ne pouvant reſiſter à voſtre ſuperiorité tant augmentée, s’il ne prend en aide tout le reſte des poids, meſmes juſqu’au Tres-fort, qui eſt le dernier de touts. |
| Once you are able to instantly judge and name, just from the feel, all the different degrees of Force, when standing still, free, and in a strong posture at the Second Instance, you must also practice the same, and in the same way, while you are moving, when your foot is raised to step from the Second Instance along the Inside Square towards the Third, always with the goal of performing the same strike to the head as above. At which point your adversary will be forced to defend by increasing his effort, augmenting the force. Thus you again disengage swords at the same time, in the same way as above, likewise naming the degree of force you believe it to be, to see if it still matches with your judgement. You must continue to practise until you have acquired a solid basic aptitude. Since each level of force requires a different response, as the following examples will make clear, you can be assured that this skill is the foundation of self-confidence and precision in everything else. | Or apres que vous ſerez rendu capable de juger & nommer tout à l’inſtant touts les poids au rapport du ſentiment, le corps eſtant arreſté à la Seconde Inſtance, libre, & totallement en puiſſance; auſſi faudra il conſequemment que vous alliez pratiquant le meſme, & en la meſme ſorte, durant que le corps ſera en aćtion, & que le pied droit ſera deſia eſlevé pour cheminer de la Seconde Inſtance au long du Quarré Inſcrit devers la Troiſieſme, en intention d’y donner touſiours la meſme atteinte, que deſſus. A laquelle occaſion, le Contraire ſera forcé pour ſe defendre d’accoiſtre ſon effort, en augmentant le poids. Dont vous deſtacherez derechef au meſme inſtant les eſpees en la meſme ſorte que deſſus, nommant pareillement le nom du poids ſelon ce qu’il vous en ſemble, pour voir encores ſil le ſaut en accordera avec voſtre jugement. En quoy il faudra que vous continuiez ſemblablement, juſqu’à tant que vous y ayez acquis une mediocre habitude. Car puis qu’il eſt neceſſaire d’appliquer à chaſque difference de poids differentes operations, ainſi que les exemples ſuyvants feront paroiſtre, il faut croire que ceſte habitude eſt le fondement de l’aſſeurance, & de la juſteſſ de tout le reſte. |
| Circle No 1. | Cercle N.1. |
| Showing how Alexander has subjugated his opponent’s sword to the inside, while moving from the First Instance, along the Inside Square, to the Second. | Repreſentant comme Alexandre a aſſujetti l’eſpee contraire en dedans, en allant de la Premiere Inſtance au long du Quarré Inſcrit à la Seconde. |
| Suppose the two adversaries have begun with their swords held in the Direct line posture at the First Instance. Here we see Alexander has Subjugated his opponent’s blade to the inside, at the Second Instance, stepping with his right foot along the line of the Inside Square, and following with his left foot in a circular movement, setting it down along the Outside Square, toes at the Oblique Diameter, heel at D. This procedure was explained fully in Table VII, Circle No 1. But now we must take a close look at how he must act, after he has reached this position, to take advantage of what he can discover about his opponent’s intentions from his sense of feel. Therefore, once at the Second Instance, and holding his opponent’s sword subjugated according to the proper amount of force required, he pays serious attention to the feel so as to know exactly which degree of Force his opponent is using against his blade. He may percieve that it lacks any sensation at all, as if deadweight. His immediate and subsequent actions that he uses to deal with this will be explained below, in Circle No 3. Take note that the Student must be very prudent before beginning to act, and so I must necessarily present a word of explantion about why he must be so. | Preſuppoſant que les deux Contraires ayent preallablement tenu les eſpees en droite ligne à la Premiere Inſtance; voicy conſequemment Alexandre qui à aſſujetti la contraire en dedans du bras à la Seconde Inſtance, cheminant avec le pied droit par la trace du Quarré Inſcrit, & pourſuivant circulairement avec le pied gauche, à planter ſur le Circonſcrit, les orteils ſur le Diametre oblique, & le talon ſur la lettre D. dont il n’eſt beſoing d’en expliquer maintenant la procedure, voyant qu’elle eſt amplement deſcrite au Tableau VII. Cercle 1. Mais preſentement il faut examiner comment il ſe doibt gouverner apres qu’il y ſera arrivé, pour ſe prevaloir de la cognoiſſance du Sentiment. Eſtant donc à ladite Seconde Inſtance, & tenant l’eſpee contraire aſſujettie ſelon la juſteſſe requiſe, il prend ſerieuſement garde au ſentiment pour en conoiſtre le Poids, avec quoy, la lame inferieure travaille contre la ſeinne, que s’il s’apperçoit quelle manque de ſentiment, comme eſtant morte. L’operation & la pourſuite qu’il doibt faire là deſſus, ſera tantoſt ſpecifiée au Cercle 3. Car ainſi qu’il faut une grande circomſpećtion au Diſciple avant que de la commencer, ainſi il m’est neceſſairement avant que la declarer, de vous en expoſer en un petit mot la cauſe. |
| Up until now, we have exempted our Student the need to consider the different degrees of force pressing against his sword. Because at first he would not be able to, and he had enough to do to learn to control his body, learn the footwork, and learn the arm and sword movements without adding on these extra considerations, where he would find himself completely lost in a multitude of competing considerations which are of no use to know at the beginning of training. And we have, moreover, supposed, in all the previous lessons, that when subjugating the blade at the Second Instance, and in following on, that the Adversary would constantly present him with the best possible openings, so that he would have to think of nothing more than to easily follow the lessons as shown by the figures. In this way, having arrived at the Second Instance, he would follow his path, moving on directly towards the Third Instance without any other consideration. This he can no longer begin to do, without first carefully considering what is the best course of action to follow. Because different degrees of force shall, from no on, require different actions in response, which present a danger he could not safely avoid, if he wished to proceed otherwise. We shall demonstrate this principle in Circle No 2, where we can see Alexander will undoubtedly be wounded because he did not pay enough attention to, and work appropriately with, the amount of force with which he was presented. | Iuſqu’icy nous avons diſpenſe noſtre Diſciple de travailler avec obſervation de Poids: à cauſe que du commencement il n’en eſtoit pas capable, & qu’il avoit aſſés à faire à gouverner ſeulemēt bien le corps, les demarches des pieds, & les mouvements du bras & de l’eſpee, ſans ſe mettre de premiere abord en des preceptes, où il ſe trouveroit tout incontinent embrouillé par la multitude, & encores plus par la ſubtilité, qui ne luy eſt nullement neceſſaire à l’entree de l’Exercice. Et partant nous avons preſuppoſé en toutes les leçons precedentes, qu’en aſſujettiſſant l’eſpee contraire à la Seconde Inſtance, & depuis travaillant conſecutivement, que le Contraire luy baillera touſiours les occaſions auſſi belles qu’il ſera poſſible, afin qu’il n’aye à penſer a rien, ſinon à mettre commodement en execution les leçons qui luy ſont repreſentées par les figures. En ſorte qu’eſtant venu à la Seconde Inſtance, il pourſuivra ſa demarche, en cheminant conſecutivement ſans nulle autre conſideration devers la 3. Ce qu’il ne pourra toutesfois deſormais commencer, ſans aſſeior preallablement un bon jugement de ce qui luy ſera plus convenable. Car puis que la diverſité du Poids requiert auſſi à l’advenant diverſes operations, il ne pourroit eſchapper le danger, s’il y vouloit aller autrement. Pour laquelle choſe repreſenter, nous en mettons icy un example au Cercle 2. auquel eſt demonſtré qu’Alexandre ſera bleſſé indubitablement, s’il ne travaille ſelon l’exigence du Poids, qui luy eſt preſenté. |
| Circle No 2. | Cercle N.2. |
| Alexander, at the Second Instance, has not noticed that his opponent’s blade had no force; it was Deadweight. He attempted to give a thrust from the Third Instance, but instead found himself wounded. | Alexandre n’ayant obſervé à la Seconde Inſtance le Poids de la lame contraire, qui eſtoit Morte; entreprend de luy vouloir donner l’eſtocade à la Troiſieme Inſtance: dont il ſe trouve eſtre bleſſe luy meſme. |
| Here we see Alexander, who will work against his opponent’s subjugated sword without having paid attention to how it feels. For, as he raised his foot from where it was at point G, to step over to the letter N, he has slid his sword along his opponent’s, moving the point of contact the same number of Spans up his sword, as he has along his opponent’s, from where it was subjugated, to where it is under the centre of his blade, and so move to wound his opponent in the face, as we see, for example, in Circle No 5. But because his opponent’s blade is Deadweight, that is, he feels nothing from it, at the instant he puts his foot down, Zachary can disengage the swords without Alexander noticing and hit him underneath his guard, without moving his firmly planted feet. | Voicy donc, Alexandre, qui va travailler ſur l’eſpee aſſujettie ſans prendre garde du ſentiment. Car en levant la pied droit du lieu ou il eſoit planté au poinćt G. pour aller à la lettre N. il augmente la graduation de ſon eſpee, par les meſmes nombres de l’eſpee contraire, où elle eſtoit preallablement aſſujettie, pour y mettre deſſus le Centre de la ſienne, & ainſi le bleſſer au viſage, à l’exemple de ce qui ſe voit repreſenté au Cercle 5. Mais d’autant que la lame contraire eſt morte, en ſorte qu’il n’en avoit pas de ſentiment, ſur l’inſtant qu’il plante le pied à terre, Zacharie deſtache les eſpees ſans qu’il s’en puiſſe à peine appercevoir, & luy en donne au meſme inſtant l’atteinte au deſſoubs de la garde, du lieu ou il eſtoit planté ferme a ferme. |
| Nonetheless, Alexander could give the same hit with less danger, if he, while sliding the contact along the blade, had opened up the angle and so be able to step inside it by moving his right foot forward. | Toutesfois il pourra donner le meſme coup avec moins de danger, ſi Alexandre en graduant ſon eſpee à fait quelque ouverture d’angle, & qu’il prenne bien l’occaſion de s’y fourer dedans, moyennant l’avancement du pied droit. |
| Circle No 3. | Cercle N.3. |
| Sensing that the subjugated blade is just Deadweight, he works against it accordingly, by stepping directly forward along the Interior Collateral, towards his adversary in order to wound him. | S’appercevant par le Sentiment, que a lame aſſujettie eſt Morte; il travaille deſſus ſelon l’exigence, en bleſſant & marchant droitement ſur ſon Contraire au long de la meſme Collaterale, où il eſt eſtoit planté. |
| This action shows the correct follow-on from Circle No 1, when Alexander subjugated his opponent’s sword at the Second Instance, where it remained a lifeless Deadweight. To follow on according to the needs of this situation, he moves his body by stepping forward along the Interior Collateral that runs near to Z, wounding his opponent with a straight arm thrust to the face as he does so, drawing his left foot up behind him, and thus stepping inside the angle of his opponent’s sword. Because it is held in a lifeless manner, Zachary cannot begin move it in time to make any sort of defense. It remains immobile, above the Exterior Collateral, where it was subjugated. This is what the figures are showing. | Ceſte operation demonſtre la vraye pourſuite du Cercle 1. où Alexandre tenoit l’eſpee contraire aſſujettie à la Seconde Inſtance, icelle demeurant Morte. Pour y proceder donc ſelon l’exigence de l’occaſion, il s’avance le corps en eſlevant le pied droit, du quel eſtant arrivé à la moitié du l’Inſtance, il deſtache les eſpees, plantant enſemblement le pied ſur la Collaterale interieure juſqu’aupres de Z, & bleſſant au meſme temps d’un bras roide ſon Contraire au viſage, avec proportionnelle pourſuite du pied gauche, ſe mettant ainſi dedans l’angle de l’eſpee inferieure: laquelle puis qu’elle eſtoit morte ne ſe peut mouvoir à temps pour faire aucune defenſe convenable; ains elle demeure immobile au deſſus de la Collaterale exterieure, où elle avoit eſté aſſujettie. Voilà le ſens des figures. |
| Circle No 4. | Cercle N.4. |
| He perceived that the subjugated sword resisted his to the degree called Sensation. To work against it, he stepped moving both feet over to the Diameter, and placed his sword-point precisely in front of his opponent's face. | Ayant apperceu, que la lame aſſujettie tient du Sentiment; il travaille deſſus en entrant avec les deux pieds un peu à coſté ſur le Diametre, & luy mettant ſa poinćte par courtoiſie devant le viſage. |
| Tbis action also begins by subjugating the sword, but in this case the sword resists with Sensation, the second degree of Force. Alexander feels through the contact of the swords that his opponent’s blade has Sensation. He moves his right foot forward and a little to the right side, with his body leaning slightly backwards. At the instant he overbalances, he disengages the swords, whereupon the lower sword springs according to the degree of Force, as far as the Interior Collateral, where Alexander was before, but by this time he set his foot down at the Centre of the Circle, out of his opponent’s danger zone, while again placing his sword tip exactly in his opponent’s face. He then brings his left foot up into place at H, and bends his arm to hold his tip exactly in place. This is shown by the figures. | Ceſte operation prend auſſi ſon origine de l’aſſujettiſſement de l’eſpee, en cas qu’elle tienne du Sentiment, qui eſt le ſecond Poids. Alexandre donc s’appercevant par l’attouchement des eſpees, que la lame Contraire à du Sentiment; il s’avance du pied droit un peu à coſté à main droite avec le corps panché à l’envers; & à l’inſtant qu’il commence à tresbucher, il deſtache les eſpees, dont celle de deſſoubs en ſaute ſuyvant l’effort du Poids juſqu’au deſſus de la Collaterale Interieure, où Alexandre eſtoit planté premierement, mais à preſent au meſme temps il plante le pied droit avec le corps panché en arriere ſur le Centre du Cercle (en ſorte qu’il luy eſt ſorti hors de preſence) luy mettant enſemblement la poinćte de l’eſpee devant le viſage, avec proportionnelle pourſuite du pied gauche trainant juſques à l’H. & courbant cependant le bras pour arreſter ſa poinćte par courtoiſie; ainſi que les figures demonſtrent. |
| In the actions of both these last two Circles, take great care not to drop the connection with the opponent’s sword before the right foot has reached the mid-way point to the Instance, and that at the same time as you suddenly set your foot down, to strike. If, by chance, at the moment you raise your foot up, your opponent increases the force of his blade, then you must first stop or reduce his movement it with a small push back, always assuming that the force he uses can be safely controlled. But if, as you begin, he increases the degree of Force to Lively or Very Lively, then you must follow with other actions. That is, while you are taking a whole step towards your opponent, you can allow him to lift the swords up a little, so it seems to him that he is forcing them aside, but then, at the moment your foot comes down to the ground, you dominate his sword and subjugate it once again and so be able to move inside the angle of his sword. From this position, you can work against him as opportunity presents, as will be shown in following Plates. | En toutes les deux operations de ces derniers Cercles, il faut observer de n’abandonner jamais l’eſpee contraire, avant que le pied droit ſoit arrivé à my-voye de l’Inſtance, & que lors en le plantant ſoudainement, on donne au meſme temps l’atteinte. Et s’il advient d’adventure au commencement en eſlevant le pied droit pour cheminer, que le cōtraire augmente quelque peu le poids de ſa lame, alors il la faudra premierement engourdir ou amortir avec un petit pouſſement, preſuppoſant que l’augmentation du poids de laquelle il ſe ſera ſervi puiſſe eſtre dompté avec aſſeurance. Mais s’il l’augmente du commencemēt juſques à en venir, au Gaillard ou plus Gaillard, il faudra pourſuivre l’operation autrement; aſſavoir en vous avançant avec le pied droit un pas entier devers le contraire, durant lequel vous luy laiſſerez monter un peu les eſpees, avec quelque apparence de les tranſporter, mais le redompterez, & aſſujettirez derechef à l’inſtant que mettrez le pied en terre, en vous logeant par meſme moyen au dedans de ſon angle. Et apres vous travaillerez de ce lieu là ſuyvant ce que les occaſions requerront, comme il en ſera demonſtré pluſieurs exemples à la ſuite des autres Tableaux. |
| Note again that when practicing these actions, to place the tip of the blade exactly in front of your adversary’s eyes with your body erect and your arm slightly extended, that to do this against the Deadweight degree of Force, you only need to take a short step forward with the right foot along the Interior Collateral, that against the Sensation degree of Force you move the same foot onto the Diameter at the letter H. But if opportunity presents a chance to make a forceful, direct attack, one must move from the Second Instance to the inside with a double-length step, bending the forward knee and leaning the body over it, in the usual way of other strikes, and as is shown in Circle 6. | Obſervez encor en faiſant l’exercice de ces meſmes operations, que pour mettre la poinćte de l’eſpee en courtoiſie devant les yeux du contraire avec le corps droit, & le bras mediocrement eſtendu, que ſur le Poids Mort il ne vous faut avancer qu’un pas arreſtant par le droit ſur la Collaterale Interieure; & ſur le Poids de Sentiment il faut mener le meſme pied ſur le Diametre à la lettre H. Mais s’il eſtoit queſtion de tirer à bon eſcient & d’en faire l’execution en rigueur; il faudroit s’avancer depuis la Seconde Inſtance en dedans d’un pas double, en pliant meſme le genouil anterieur, & panchant le corps deſſus, à la maniere ordinaire des autres executions, & comme il eſt repreſenté en ce preſent Tableau au Cercle 6. |
| Circle No 5. | Cercle N.5. |
| The opposing blade, while subjugated, pushes back with an Alive degree of Force. Alexander advances to the Third Instance, sliding the point of contact up the sword, and again puts his tip in his opponent’s face. | La lame aſſujettie demeurant Viſve; Alexandre s’avance à la Troiſieme Inſtance, en faiſant la graduation, & luy mettant derechef la poinćte contre le viſage. |
| This action begins the same way, in Circle No 1, where Alexander has subjugated his opponent’s blade aside at the Second Instance. However, this time the force against it is different, instead of being Deadweight, or just the Sensation degree of Force, it is pushing back with the third degree of Force, called Alive. Against this Alexander enters in against his opponent by moving along the Inside Square, and, when he is mid-way, above where the Exterior Collateral crosses the line of the Inscribed Square, keeping his body straight, he extends his arm, and slides the point of contact up the sword, so that, as he sets his foot down at point N and leans his body forward, he catches the blade with the inside branch of his crossguard, and the centre of his blade crosses the 4th or 5th Span of his opponent’s blade. As his contact slides up, he circles his tip towards the right to aim at the right side of his opponent’s head. He wounds him as he draws his left foot along the Outside Square to the letter K, while, at the same time, he turns his right foot so the heel rests along the Circumference of the Circle, as shown in the figure. | Ceſte operation prend pareillement ſon origine de celle du Cercle 1. ou Alexandre a tenu l’eſpee contraire aſſujettie à la Seconde Inſtance: toutesfois le poids en a eſté different: car au lieu qu’elle eſtoit paravant Morte, ou qu’elle n’avoit qu’un ſimple Sentiment, maintenant elle uſe de Poids Vif. Sur lequel voicy comment Alexandre travaille. Il entre ſur ſa partie adverſe enſuivant la trace du Quarré Inſcrit, & parvenant à my-voye de la Troiſieme Inſtance au deſſus de la ſećtion des lignes, il va graduer avec le corps droit & le bras eſtendu, en ſorte qu’en panchant du corps ſur le devant, & plantant le pied eſlevé au poinćt N. il ſurprend de la branche interieure de ſa garde, & par meme voye il aſſemble le Centre de ſa lame aux Nombres 4. ou 5. de la lame contraire; en dreſſant avec ladite graduation la pointe circulairement vers le coſté droit de la teſte de ſa partie; le bleſſant avec pourſuite du pied gauche à planter moitié au Quarré Circomſcrit ſur la lettre K. tournant enſemblement le talon du pied droit du Quarré Inſcrit ſur la Circonference du Cercle; ainſi qu’il eſt repreſenté en la figure. |
| Now, when performing this action, to adapt it perfectly to your opponent, great care must be taken while the right foot is making its way, before your body overbalances, and before you begin to work against his sword. If he does not change his counter, then continue on as shown by the figures. | Or en pratiquant ceſte operation, pour la bien adjuſter il faut exaćtement prendre garde, cependant que le pied droit chemine, & avant qu’il commence à tresbucher avec le corps, & devant que vous ayez commencé à travailler. Car s’il ne le change point, vous en pourſuivez la continuation en la forme que les figures repreſentent. |
| But if he increases his resistance to the Lively level of Force, with which he could move the swords enough to parry the thrust, one must apply the actions of Circle No 7. | Mais s’il alloit renforcer ſa lame juſqu’au Poids Gaillard; dont il pourroit parer l’eſtocade en tranſportant les eſpees, il y faudroit appliquer l’operation du Cercle 7. |
| If he reinforces his blade with a little less than a Lively level of Force, you only need, to keep your superiority over him, to slide the point of contact up to a stronger Span and add however much strength as required to dominate his, and then strike him the same way as before, having made his change of Force useless. | S’il la renforçoit un peu moins que Gaillard, il ne faudroit que temperer voſtre ſuperiorité alencontre, en graduant un peu vos nombres, & en renforçant l’effort de voſtre lame un petit à l’advenant pour maiſtriſer la ſienne, & luy donner encor la meſme atteinte que devant, conſideré que le changement qu’il y apporte luy eſt rendu inutile. |
| On the contrary, if it should happen, before your body begins to overbalance, that you feel him lessen the Force against your blade, it is certain the he is beginning to move his blade away, to disengage and strike you, perhaps on the right side of your blade by moving underneath the guard, then stepping forward, as he must, to enter in from your right side. Therefore, you must be careful not to continue the same steps, until you have made sure that the opponent’s sword cannot easily disengage from yours. Your right foot will be raised up, halfway through the step towards the Third Instance. By quickly turning it outwards, you can withdraw it a little to the left and adroitly turn your right side away, setting your foot down, and quickly drawing your left foot up, body leaning forwards, arm straight, tip pointing at his face, with the blade going downwards a little bit, proportionally, with the guard keeping his sword blocked, so he cannot reach underneath, and so he will be wounded in his face or the upper part of his chest. | Au contraire, s’il advient, avant que le corps vous commence à tresbucher avec le pied elevé, que le Sentiment vous die, que la lame de deſſoubs affoiblit ſon Poids, c’eſt choſe indubitable, qu’elle commence à travailler pour ſe delivrer de la voſtre, en intention de vous bleſſer, peut eſtre au coſté droit au long de voſtre lame au deſſoubs la garde, avec un pas quil doit faire en entrant ſur vous du pied droit. Pourtant en ce cas, vous vous garderez de cōtinuer la meſme demarche, ains avant que l’eſpee aſſujettie aye aucunement le loiſir de ſe deſacher de la voſtre, le pied droit eſtant preſentement eſlevé en l’air à my-voye de la Troiſieme Inſtance, en le tournant en dehors vous le retirerez un peu à gauche en eſquivant le coſté droit, & plantant ſoudainement le meſme pied à terre, avec une ſoudaine pourſuite du pied gauche, le corps panché ſur le devant, le bras roide & la pointe de l’eſpee aſſenée au viſage du Contraire, la lame deſcendant proportionnellement un peu avec la garde, en retenant touſiours la ſuperiorité, en ſorte qu’il ne puiſſe toucher par le bas, & qu’il en ſoit bleſſé luy meſme au viſage, ou en la partie ſuperieure de la poitrine. |
| But if he begins to lessen the force of his blade when you are already overbalanced and cannot avoid stepping forward, in this case set your foot down as far backwards as you can, even if you cannot avoid setting your foot down on the letter N at the Third Instance. At that point, carry on and proceed as before. | Mais s’il commençoit à vous faire ceſdits changements, au temps que le pied droit commence à tresbucher enſemble avec le corps; il vous faudroit obſerver en ce cas de le planter touſiours autant qu’il ſeroit poſſible en arriere, & quant au reſte y proceder encor en la meſme ſorte que devant: voire meſme combien que le pied fuſt venu ſi avant qu’il fuſt impoſſible de l’empeſcher de tomber à terre au poinćt N. à la Troiſieme Inſtance. |
| Circle No 6. | Cercle N.6. |
| This is the follow-on and rigurous execution of the action begun previously, by which Alexandre slides the contact of his sword up his opponent’s blade with a straight arm, driving the two guards together and back, then quickly, with the right foot, stepping up to the letter S, along the Diameter, and putting his weight on his knee, but without moving his left foot up. So his sword pierces his opponent’s head, as is portrayed by their figures. | C’est la pourſuite & execution en rigueur de l’operation dernierement precedente, faite par Alexandre en graduant d’un bras roide l’eſpee contraire, en ſorte que les deux guardes viennent à s’entredonner avec force, cheminant avec le pied droit juſqu’à l’S, qui eſt au deça le Diametre, & menant ſur le genouil d’iceluy la charge du corps, ſans nulle pourſuite du pied gauche; perçant ainſi la teſte à ſon Contraire; comme il eſt pourtrait en leurs figures. |
| Circle No 7. | Cercle N.7 |
| Alexander has moved against the Alive degree of Force from the Second Instance towards the Third, to perform the same thrust as in Circle 5. He percieves, as his foot reaches N, that Zachary has, to defend himself, increased his resistance to the Lively degree. So he steps with his other foot to W, so his left side comes around in front, and, with his arm bent, places his sword-tip before his opponent’s face. | Alexandre s’eſtant acheminé ſur le poids Vif de la Seconde Inſtance vers la Troiſieme, pour y effectuer encor la meſme eſtocade, qu’au Cercle 5. il s’apperçoit, que Zacharie augmente le Sentiment du poids Gaillard, pour ſe defendre, dont il met le pied droit en terre à la lettre N. pourſuivant avec l’autre juſqu’à l’W. en avançant le coſté gauche, & luy preſentant ſa poinćte d’un bras courbé devant le viſage. |
| Having precisely countered the Alive degree of Force and subjugated his opponent’s sword, Alexander is in the act of making his way towards the Third Instance to again perform the same strike as in Circle No 5. At the same instant that he arrives at the mid-point towards the Instance, and as he begins to slide his sword along, he senses his opponent’s blade increase to a Lively degree of Force, so as to turn aside the thrust he is aiming at Zachary’s face. Therefore, as this change begins, Alexander, while setting his foot down at the Third Instance, prevents his opponent’s sword from rising up, by adjusting the force on his own blade to match and contol the lower one. At the same time, he continues on by lifting and advancing his left foot. As he does this, feeling that his opponent’s blade is keeping the same increased amount of Force, he bends his arm so that his sword rises upwards, and turns his body slightly to bring his left side forward. As his opponent continues to try and move the swords over and force his aside, he suddenly bends his arm to the inside (i.e. drawing the right elbow back), turning the outside branch of the crosspiece upwards, which alows his opponent’s sword to spring freely too far off line, so that it comes of its own accord back into contact with the weak part against either the strong part or the centre of his own sword. In this same way, he can aim his tip precisely, straight towards his opponent’s eyes, trapping the sword from beneath with the exterior branch of his crosspiece, while spinning so his raised left foot comes inside the angle of the sword to the letter S, with his knee bent and weight forward on it. Thus, he then has but to forcibly execute the thrust, as can be seen in the portraits of the figures. | Apres le juſte aſſujettiſſement de l’eſpee contraire tenant le Poids Vif, Alexandre s’eſtant à cheminé devers la Troiſieme Inſtance pour y donner encor la meſme atteinte, comme au Cercle 5. au meſme inſtant qu’il arrive avec le pied droit à my-voye de l’Inſtance, & qu’il commence à faire la graduation, il s’apperçoit par le ſentiment, que le Sentiment de la lame contraire s’augmente en Poids Gaillard, pour deſtourner le coup, qui luy eſt dreſſé vers le viſage. Au commencement doncques de ce changement, Alexandre empeſche l’eſpee contraire de monter, en mettant le pied en terre à la Troiſieme Inſtance, & en domptant par la moderation de ſon propre poids à l’advenant de celuy de deſſoubs; pourſuivant quand & quand d’eſlever & avancer le pied gauche; durant laquelle aćtion, ſentant que le Contraire continue touſiours en a meſme augmentation de Poids qu’il avoit commencée, il s’aſſeure ſur le ſentiment de laiſſer un peu monter & tranſporter les eſpees, en ſe courbant le bras un peu en dedans vers le haut, & preſentant de meſme voye le coſté gauche peu à peu devant: & d’autant que la partie adverſe ne laiſſe pas de continuer encor à luy vouloir tranſporter & aſſujettir l’eſpee, il courbe ſoudainement le bras en dedans, avec la branche exterieure haute, en donnant à l’eſpee contraire courſe libre, en ſorte qu’elle retombe d’elle meſme avec le foible au fort & Centre de la ſienne; & que par meſme voye il luy dreſſe ſa pointe par courtoiſie droit à la veuë, en ſurprenant la lame contraire par embas avec la branche exterieure de la ſienne, ſe tournant cependant avec le pied eſlevé au dedans de l’angle, & le plantant à la lettre S. avec le genouil plié, & le corps panché deſſus: quoy qu’il n’aye tenu qu’à luy d’en faire l’execution par rigueur: ainſi qu’il eſt aiſé de recognoiſtre aux pourtraits des figures. |
| Note that, while you are allowing the swords to raise up a little, if your opponent begins to weaken his force, instead of allowing him to carry the swords across, you must once again dominate and force his sword down and away, while moving the left side and raised left foot forward and inside the angle of the sword. | Notez en laiſſant de voſtre conſentement un peu monter les eſpees, ſi l’adverſaire commençoit d’affoiblir ſon poids, qu’au lieu de luy accorder de les tranſporter, il vous faudroit la redompter & reaſſujettir derechef une autrefois, en avançant le coſté gauche & vous logeant derechef avec le pied eſlevé au dedans de l’angle. |
| Inasmuch as we have described Alexander’s actions putting his left foot down on the letter S on the Inside Square, there are also occasions which present themselves where he should move his foot the same distance, but along the Outside Square. For example, when the Opposing Force weakens, changing where he puts his foot is no longer merely desireable, but also necessary, so that when stepping forward with the right foot, the cut which must follow will be much easier. In any case, one must not decide in advance one way or the other, but respond according to the situation as it presents itself. | Or ainſi que nous venons de deſcrir l’operation d’Alexandre pour mettre le pied gauche à la lettre S. ſur le coſté du Quarré Inſcrit, auſſi il ſe preſentera des occaſions de le planter en meſme diſtance ſur le Quarré Circonſcrit; aſſavoir en cas que le Poids du Contraire ſoit un bien peu plus foible. car alors il ne ſera pas ſeulement loiſible, mais auſſi neceſſaire: & le coup d’eſtramaçon qui s’en doit enſuivre avec l’avancement du pied droit, n’en ſera que d’autant plus facile. Toutesfois il ne faut affećter ne l’un ne l’autre, ains ſimpement travailler ſelon que les occasions convient. |
| Circle No 8. | Cercle N.8. |
| While Alexander moves towards the Third Instance, to again perform the same strike, Zachary parries him, by increasing the force of his blade to Livelier, and so moves the blades to the inside. At this instant, Alexander sets his right foot down at the letter N, weighting it so as to close up with his left foot, which he sets down beside the other, then moves his right foot again, over to the letter L on the Perpendicular Diameter, shifts his weight over it, while turning his left side forward, and bending his arm so as to point his sword-tip in his opponent’s face. | Cependant qu’Alexandre s’achemine devers la Troiſieme Inſtance, pour y effectuer encores le meſme coup; Zachary le pare, en augmentant le Sentiment des lames en poids Plus-Gaillard, dont il les tranſporte en dedans. Auquel inſtant Alexandre met le pied droit en terre à la lettre N. ſe baſtant comme pour le chaſſer avec le pied gauche, le quel il met en terre parallele à l’autre, il tranſporte derechef le pied droit ſur le Diametre perpendiculaire au poinćt L. avançant ſur iceluy le corps avec le coſté gauche, & preſentant eſemblement d’un bras courbé ſa poinćte au viſage de ſon Contraire. |
| This action begins the same way as the one before, continues on the same way, to the moment Alexander begins to slide the point of contact up the blade and aim his sword-tip. To parry this, Zachary, who worked the previous Circle with the Lively degree of Force, now increases this by a degree. Against this, Alexander again begins to counter by maintaining control over his blade, pushing down and dominating so the swords cannot come upwards. Meanwhile, he sets his right foot down at the Third Instance at N, quickly following on with the left foot, which he places on the ground parallel to and beside the other, and instantly lifts his right foot, almost as if he is dancing a demi-fleurette (quick-step), stretching his body up and allowing his opponent’s sword to rise. Zachary continues to increase the force on his sword, Alexander allows the swords to be moved over bit by bit, which he avoids by moving his body to the right, with his left side slightly forward and his arm slightly bent inwards. At the instant the swords reach the point of passing over the top of his head Alexander suddenly extends his arm outwards, knowing that Zachary’s sword will spring over out of control, carried by the force behind it, as far as the Principal Diameter before he can stop it. Alexander turns the crosspiece so the exterior branch is diagonally upwards. The blades connect so that a low-numbered Span in the weak part of his opponent’s blade crosses near the guard of his own, extending beyond and so trapped behind the exterior branch of his crosspiece. He aims his tip at his opponents face, setting his right foot down at L along the Perpendicular Diameter, his weight on his bent knee, and follows this by drawing his left foot up to N. The whole is shown precisely in detail, without executing the thrust which is entirely within his ability. This can be clearly seen in the representation by the figures. | Ceſte operation à le meſme commencement que la precedente, continuant auſſi en la meſme ſorte, juſqu’à tant qu’Alexandre ſe met à faire la graduation, & à dreſſer ſa pointe; pour laquelle parer Zacharie, qui a travaillé au precedent Cercle avec le Poids Gaillard: l’augmente icy un degré plus avant. Sur lequel Alexandre travaille derechef au commencement pour luy tenir la lame en devoir, en la contrepeſant & domptant en ſorte qu’elle ne puiſſe monter; & cependant il plante le pied à la Troiſieme Inſtance au poinćt N. avec pourſuite du pied gauche, lequel il met tout ſoudainement parallele aupres de l’autre, & derechef il eſleve le droit au meſme inſtant, quaſi comme en faiſant une demi-fleurette, avec extenſion du corps. & donnant quelque permiſſion de monter à l’eſpee contraire: laquelle continuant en l’augmentation du poids, il luy conſent de tranſporter peu à peu les eſpees, leſquels il ſuit avec le corps en allant à l’advenant vers le coſté droit avec le coſté gauche un peu avancé & le bras courbe lentement en dedans: & à l’inſtant que les eſpees viennent ſur le point de paſſer l’endroit du ſommet de ſa teſte: Alexandre s’allonge le bras courbé en dehors, ſur l’aſſeurance de la continuation du poids, juſqu’au deſſus du Diametre principal, eſtant la branche exterieure de la garde tournée diagonalement en haut; le tout pour donner à l’eſpee contraire courſe libre: laquelle vient à ſe rendre avec le foible Nombre contre la garde de la ſienne, au dehors de la branche exterieure: en ſorte qu’il luy en dreſſe la pointe devant le viſage, en plantant le pied droit ſur le Diametre perpendiculaire à la lettre L, & en chargeant le corps ſur le genouil d’iceluy plié avec avancement du coſté gauche, & pourſuite du meſme pied à l’advenant, trainant juſques à l’N. Le tout ſe demonſtre par courtoisie, ſans en faire l’execution qui eſt toutesfoit en ſa puiſſance; ainſi quil ſe voit clairement en la repreſentation des figures. |
| Circle No 9. | Cercle N.9. |
| Alexander again proceeds in the same way as before from the Second Instance to the Third. Zachary turns the hit aside, moving the blades over with a Very-Lively degree of Force. Which makes Alexander place his right foot at the Centre, moving his body forward and over his knee, drawing his foot to M, and once more putting the tip of his sword before his opponent’s eyes. | Alexandre procedant encor en a meſme façon de la Seconde Inſtance vers la Troiſieme; Zacharie deſtourne le coup en tranſportant les lames avec Poids Tres-Gaillard: qui faićt Alexandre va planter le pied droit ſur le Centre, en avançant & panchant le corps deſſus, trainant le pied juſques à l’M. & mettant enſemblement (comme devant) ſa poinćte devant les yeux du Contraire. |
| In this action, there is no other difference from the two ones preceeding, except that while Alexander is in the process of extending the thrust at the Third Instance, Zachary parries to the inside with a Very-Lively level of Force, even more than before. Thereupon, Alexander controls himself again according to the principles from the previous Circle, moving his right foot along the Perpendicular Diameter over to the Centre, and leaning his body over his bent knee, following along with his left foot up to the letter M. He rapidly extends his inwardly bent arm along the Perpendicular Diameter, until it is above the Collateral, which releases his opponent’s sword to spring over until the weak part of the blade connects to the strong of his own, by which he can, in the same moment, turn his tip towards his opponent’s eyes, as we see in the figure. | En ceſte operation il n’y a nulle autre difference d’avec les deux derniers precedēts, ſinon que pendant qu’Alexandre eſt en aćtion d’allonger l’eſtocade à la Troiſieme Inſtance; que Zacharie la pare en dedans avec Poids tres-Gaillard, où il y a autant plus d’effort qu’au precedent. Là deſſus donc Alexandre ſe gouverne encore ſuyvant les obſervations du Cercle precedent, en cheminant avec le pied droit au long du Diametre perpendiculaire juſqu’au Centre, & y panche le corps à coſté deſſus le genouil plié, avec pourſuite du pied gauche revenant à la lettre M. & extenſion du bras droit courbé en dedans au deſſus du Diametre perpendiculaire, juſqu’à l’endroit de la Collaterale, moyennant laquelle, l’eſpee contraire eſt portée de ſon propre mouvement avec le foible au fort de la ſienne, de laquelle il luy en met en meſme temps la pointe devant les yeux; comme il ſe voit en la figure. |
| Circle No 10 | Cercle N.10. |
| Alexander is again mid-way to the Third Instance, and sliding the point of contact up the blade to thrust. His opponent increases the force against him and raises the blades to move them to the inside. In response, he again dominates and subjugates the blade and forces it to the side, sliding the point of contact up his blade, and as he sets his foot down at N at the Third Instance, he leans his body over it and promptly moves his left foot to just outside the Circle along the line K-N. This action can also be done against the three preceeding degrees of force, Lively, Livelier, and Very-Lively. | Alexandre eſtant derechef à my-chemin de la Troiſieme Inſtance, & y faiſant la graduation pour donner l’eſtocade; ſa partie augmente le poids & hauſſe les lames pour les tranſporter en dedans; dont au meſme temps il le redomte & raſſujettit, en luy deſgraduant la lame, & poſant le pied droit en terre à la Troiſieme Inſtance, lettre N. avec le corps panché deſſus& logé dedans l’angle des eſpees, & le pied gauche pourſuivant promptement & revenant un peu dehors le Cercle alendroit de la ligne K N. Qui eſt une operation qui ſe peut pratiquer ſur les trois precedents Poids, Gaillard, Plus-Gaillard, & Tres-Gaillard. |
| This present action also begins in Circle No 1, where Alexander held his opponent’s sword subjugated, where we presume that his opponent used, and continued to use, the Alive degree of Force. Thus Alexander begins to continue to make his way towards the Third Instance. After he has reached the mid-point on the way, he once again, as before, begins to slide the point of contact up the opponent’s blade, keeping his body from leaning forward, to again hit as he did in Circle No 5. But his sense of feel tells him that the Force of the opposing blade is increasing from the level of Alive to one of the three previous levels, that is, either Lively, Livelier, or Very-Lively, as shown, and each different action described, in the 7th, 8th, and 9th Circles, respectively. However, these levels of Force can all be responded to with the same action which we show here. That is, according to the degree to which Zachary increases the force on his blade, Alexander also increases his own, carefully allowing the swords to rise a bit, and the point of contact to slide up his opponent’s sword and down his own, so as to give the appearance that they are being moved across, meanwhile setting his right foot down at the letter N at the Third Instance. Insofar as he does this, his body moves forward while leaning in, while at the same time, by means of a slide along the blade, he again returns the point of contact back to the same Spans as before, when he previously controlled his opponent’s blade. He closes the upper right arm against his body, to further reinforce his sword, and to guard against overbalancing, and to bring his opponent’s sword back downwards and properly subjugated. With a rapid circular move, he follows on with his left foot setting it, at the proper distance, down ouside the Circle along the line K-N while moving his left side around and, with a slight lean of the body forward onto the right foot, comes inside the open angle of his opponent’s sword, which he just created. | La preſente operation prend auſſi ſon commencement du Cercle 1. où Alexandre a tenu l’eſpee contraire aſſujettie, preſupposant qu’elle uſe, & continue à uſer du Poids Vif. Dont il a commencé a cheminer conſecutivement devers la Troiſieme Inſtance; & en eſtant venu à la my-voye, il ſe met derechef ainſi que devant à graduer un peu la lame contraire avec le corps aucunement panché ſur le devant, pour donner encor l’atteinte du Cercle 5. Mais il cognoiſt par le ſentiment que le Poids de la lame contraire, ayant eſté ſeulement Vif, s’augmente juſqu’en l’un des trois dernierement precedents, aſſavoir Gaillard, Plus-Gaillard, ou Tres-Gaillard: Sur leſquels ont eſté faites és Cercles 7. 8. & 9. autant de differentes operations à chaſcun la ſienne: leſquelles peuvent cependant toutes eſtre prevenues par celle que nous mettrons icy preſentement. C’eſt aſſavoir à meſure que Zacharie ira augmentant ſon Poids; qu’Alexandre augmentera auſſi à l’adventant le ſien, avec moderation & diſcretion de laiſſer monter un petit les eſpees, avec graduation de la contraire & deſgraduation de la ſienne propre, donnant comme apparence de les laiſſer tranſporter, & mettant cependant le pied droit en terre à la Troiſieme Inſtance au poinćt N. Et d’autant qu’en ce faiſant ſon corps s’avance avec abaiſſement, au meſme temps il regaignera derechef moyennant la deſgraduation, les nombres où il tenoit preallablement l’eſpee contraire en ſubjećtion, s’affermiſſant le haut du bras au coſté droit, pour en renforcer l’eſpee d’autant d’avantage, & pour l’aſſeurer cōtre les tresbuchements, & enſemble en ramener l’eſpee contraire vers le bas ſuyvant la juſteſſe de l’aſſujettiſſement; avec ſoudaine pourſuite circulaire du pied gauche, iceluy plantant dehors le Cercle à proportion de l’autre & reſpondant ſur la ligne K N: & enſemble preſentant le coſté gauche devant, lequel il loge (par le moyen du panchemēt de la partie ſuperieure du corps, repoſé ſur le pied droit) au dedans de l’angle, qu’il s’eſt ouvert ſur l’eſpee contraire. |
| The actions which can follow from this will be seen elsewhere. | Les executions qui ſe pourront faire en ſuite de ceſte operation ſe verront autrepart. |
| It may appear that the position of Alexander’s left leg lagging behind at G is not in accord with the description we have given above. This was drawn like this deliberately to be able to clearly show the actions of the arm, hand, and sword-guard, which would not be possible, as they would be hidden, if his back were turned forward. | Or combien que la ſituation du pied gauche d’Alexandre, ſemble contrarier en la figure à la deſcription que nous en venons de faire; à raiſon qu’il y ſemble demeurer à la Seconde Inſtance au poinćt G. toutesfois il faut entendre, qu’il a eſté là pour mettre à deſcouvert les operations du bras, de la main & de la garde de l’eſpee, ce qui n’euſt eſté praticable, en cas que le dos de la figure fuſt tourné devant. |
| Circle No 11. | Cercle N.11. |
| Alexander has once again come to the mid-way point to the Third Instance, sliding his sword and turning the tip of his blade towards his opponent’s face. Zachary defends himself by increasing the degree of Force up to Strong, carrying the swords to the inside, so that Alexander, at the same time he sets his foot down at N, disengages the swords by bringing his up high, and gives his opponent a cut across the face while stepping with his left foot swiftly forward to the letter W but making sure to keep his body erect. | Eſtant encores venu à my-chemin de la Troiſieme Inſtance, graduant & tournant la poinćte de ſa lame devers le viſage de Zacharie, iceluy s’en defend par l’accroiſſement du Sentiment en poids Fort, en tranſportant les eſpees en dedans, donc Alexandre mettant au meſme temps le pied en terre à la lettre N. il deſtache les eſpees en menant la ſienne en haut; & en donne à ſon Contraire un coup d’eſtramaçon au viſage, en marchant avec le pied gauche viſtement en avant juſqu’à W. avec le corps aucunement panché en devant. |
| Here we have yet another action which likewise follows from Circle No 1 where Alexander has subjugated his opponent’s sword and is moving from the Second Instance towards the Third. His right foot has reached the mid-way point and makes the briefest of pauses at the same time that he begins to slide the point of contact along the two swords, extends his body, and aims his sword-tip towards his adversary’s face. Who, in turn, to deflect the strike, increases the level of Force against the blade to Strong. In this way, he raises the blades up and carries them across, but with the sudden force, he cannot stop his blade from reading the centre line. This is why Alexander offers no resistance, allowing the blades to follow this path, then quickly enters in, placing his right foot down at the Third Instance, and, spinning on his right toes, swiftly follows, stepping with the left foot all the way to W along the Circumference, turning his left side forwards, along with the guard and part of his right arm. As he does this, using his wrist, he swings his blade around so the tip of his sword goes backwards under his opponent’s blade, then up, overhead and, as his left foot comes down, his blade also comes down and cuts across the right side of his opponent’s head, as it is shown in the figure. | Voicy encor une autre operation, qui procede pareillement du Cercle 1. où Alexandre a tenu l’eſpee contraire aſſujettie & comme il s’eſt acheminé de la Seconde Inſtance vers la Troiſieme, en eſtant venu avec le pied droit à my-chemin, il y a fait comme une petite pauſe, & quand & quand, il y a commencé à graduer toutes les deux eſpees, eſtendant le corps & dreſſant ſa poinćte devers le viſage de ſa partie adverſe. Lequel pour deſtourner le coup, augmente le ſentiment de ſa lame en Poids Fort; au moyen duquel il eſleve & tranſporte les lames avec une ſoudaine force, dont la ſienne ne peut s’engarder de tresbucher. C’eſt pourquoy Alexandre luy donne courſe libre ſans reſiſtence, en entrant viſtement avec le pied droit à la Troiſieme Inſtance, & ſoudainement pourſuivant avec le pied gauche, en l’avançant avec le coſté gauche, & auſſi un peu le bras droit avec la garde, en jettant au meſme temps à l’aide du ſeul poignet de la main, ſa poinćte en arriere de deſſoubs l’eſpee contraire en deſſus, & par la continuation du meſme mouvement, plantant le pied gauche ſur la Circonference au poinćt W, il donne à ſon Contraire un coup d’eſtramaçon, allant par deſſus la lame & le bras au coſté droit de la teſte, avec pourſuit du pied gauche, qui ſuit & traine apres l’autre ſur les orteils; comme il eſt pourtrait en la figure. |
| Circle No 12. | Cercle N.12. |
| This circle again continues in the same way, up to the part when he moves his left foot. Instead of making the aforesaid cut to the face, because the force of the opponent’s sword has carried it further downwards, he raises his sword-tip upwards in a circular way, closing his hand and guard against the right side of his chest and wounds his opponent with the sword-tip above the arm, with his body leaning forwards. | Continuant derechef en la meſme ſorte, juſqu’à tant qu’il commence à avancer le pied gauche, au lieu, de donner le ſuſdite coup d’eſtramaçon ( à cauſe que l’eſpee contraire eſt en aćtion des tresbucher un peu plus bas) il conduit ſa poinćte circulairement en haut, s’affermiſſant la main & la garde contre la poitrine au coſté droit, & bleſſant ſa partie de poinćte au viſage par deſſus le bras avec le corps panché en avant. |
| This action accords with the preceeding one, not only in that they both begin from the same position when subjugating his opponent’s blade, but also in the Strong degree of Force with which his opponent resists against him. There is but this difference, in that, in the preceeding Cercle, Alexander set his right foot down and, while he moved his raised left foot around forwards, at the same time he disengaged his sword, bringing the sword-tip from underneath to above his opponent’s blade as it went past. But this time his adversary’s sword goes further down than in Circle No 11, giving Alexander time, in this present action, to turn his hand so the interior branch of the crossguard is upwards and hold it against his right side, slightly lower down than is shown here, as he moves his left side forward. He again sets his left foot down at W along the Outside Square, leaning slightly forwards over the bent knee, pointing the sword-tip over his opponent’s arm and sword at his adversary’s face. This action is performed with exactness, as it appears in the figure. | Ceſte operation n’eſt pas ſeulement accordante avec la precedente, en ce qu’elles prennent toutes deux leurs commencements de l’aſſujetiſſemēt des eſpees, mais auſſi meſmes en l’augmentation de poids, que revient en l’une & en l’autre juſqu’au fort. Il n’y a que ceſte difference, qu’en la precedente Alexandre plantant le pied droit & eſleveant en avant le gauche, il a deſtaché au meſme temps les lames, en menant la pointe de la ſienne de deſſoubs en deſſus la lame contraire tresbuchante: laquelle deſcend preſentement d’avantage qu’au Cercle 11. dont Alexandre ſe tourne en ceſte operation preſente la main avec la garde de l’eſpee la branche interieure en haut, & l’affermit (en menant le coſté gauche du corps devant) contre ſon coſté droit, un peu plus bas qu’il n’eſt icy repreſenté au pourtraićt, en preſentant enſemblement la pointe par deſſus l’eſpee & le bras contraire au coſté droit de la teſte de ſa partie adverſe, avec le pied gauche pour planter au poinćt W ſur le Quarré Circonſcrit, le corps panchant de meſme deſſus le geuouil d’iceluy plié. Le tout eſt pratiqué par courtoiſie; comme il appert aux figures. |
| Circle No 13. | Cercle N.13. |
| While he advances his right foot towards the Third Instance, slides his sword up his blade, and aims his point at the face of his opponent, at the instant his foot comes down at the letter N, his adversary increases the level of Force against him to Very Strong, enough to carry both the swords backwards. So, at the same time as he guides the swords overhead, he sets his left foot down beside his right, and almost chases his right foot outside the Circle to W, and leans forward while cutting to the right side of the head. | Cependant qu’il s’avance avec le pied droit devers la Troiſieme Inſtance, graduant & dreſſant ſa poinćte avec le bras ferme devers le viſage de ſon Contraire; à l’inſtant que le pied s’abaiſſe à la lettre N. ſa partie augmente le Sentiment en poids Plus fort, & luy tranſporte l’eſpee; dont au meſme temps il la mene de bas en haut en entrant du pied gauche & le plantant parallele, comme en chaſſant l’autre un peu dehors le Cercle à l’W, & enſemble donnant un coup d’eſtramçon à ſon Contraire au coſté droit de la teſte, avec le corps panché en avant. |
| This action follows from the same beginning and continuation as the previous. That is, Alexander has first subjugated his opponent’s sword at the Second Instance. From there he began to make his way to the Third, and when his right foot had reached about half-way, he began to slide the point of contact of his sword along, arm straight, by the same number of Spans to keep his opponent’s sword subjugated. Thus Zachary began to increase the force of his resistance. To which Alexander likewise at first maintained his dominance by increasing his counter-force as needed, in such a way as to keep the swords from rising up. Thus continuing the slide up the sword, with a circular motion, he aims his point at the face of his adversary as he sets his foot down at N. By this, Zachary is constrained to parry and carry the swords across to the inside by increasing the level of Force to Stronger. Thereupon Alexander, by abruptly disengaging and allowing the sword to spring over, then brings his own up, with a sudden step with the left foot, he sets it down next to his right, which, at that same moment, he raises and moves forward, almost like the quick-step dance-move, and while he does this, as he sets his foot down just beyond the Circle near W, he cuts his adversary diagnonally across the right side of his head, while leaning his body forward, as is shown in the figure. | Ceſte cy procede encor d’un meſme commencemēt & d’une pareille continuation comme la precedente: aſſavoir qu’Alexandre à premierement tenu l’eſpee contraire aſſujettie à la Seconde Inſtance: d’où il s’eſt acheminé devers la Troiſieme, & eſtant venu avec le pied droit environ le milieu, il a commencé d’avancer la graduation de ſon eſpee d’un bras roide, par les meſmes Nombres où l’eſpee contraire eſtoit aſſujettie: dont Zacharie a commencé d’augmenter ſon poids. Le quel Alexandre à pareillement domté au cōmencement, par l’augmentation de ſon contre-poids à l’advenant, en ſorte qu’il a empeſché les eſpees de monter en haut; & ainſi continuant la graduation, il a dreſſé ſa pointe circulairement contre le viſage de ſa partie adverſe, en poſant le pied à terre à la Troiſieme Inſtance au poinćt N. De quoy Zacharie eſt contraint de parer & tranſporter les lames en dedans en augmentant le Sentiment en Poids Plus fort. Là deſſus Alexandre en la deſtachant tout à l’inſtant, & la laiſſant tresbucher, mene la ſienne de bas en haut, avec une ſoudaine pourſuite du pied gauche, le plantant tout joignant l’autre, lequel quand & quand il leve & avance, cōme en forme d’une demy-fleurette, & durant icelle, il donne à ſon Contraire un coup d’eſtramaçon diagonal au coſté droit de la teſte, avec le corps preſt à pancher ſur le devant, pour planter le pied droit un peu hors du Cercle, en deça le poinćt W. comme il ſe voit en la figure. |
| Circle No 14. | Cercle N.14. |
| Alexander has passed though all the previous steps, to the moment he sets his foot down at N. Zachary parries his attack, carrying the swords over with a Very Strong degree of Force. Therefore, Alexander advances with his left foot under him, bringing his sword from underneath the other, over his head, and setting his foot down at W and leaning forward, delivers a reverse cut to the back of Zachary’s head. | S’eſtant passé encores tout le meſme juſqu’au temps que le pied droit d’Alexandre s’abaiſſe à la lettre N: Zacharie luy pare le coup, en tranſportant les eſpees avec poids Tres-fort: dont Alexandre s’avance avec le pied gauche deſſus luy, menant l’eſpee de deſſoubs l’autre au deſſus de ſa teſte, & en plantant le pied à l’W. avec le corps panché de meſme, il bleſſe le Contraire d’un coup de revers au derriere de la teſte. |
| This action likewise begins with the same steps as the preceeding ones, in the same order. Alexander is moving from the Second Instance to the Third, and at the same time gradually sliding the point of contact up the sword, when his Adversary increases the Force against him. This he overcomes by appropriately increasing his own force, and because of his superior position, prevents the swords from rising up. As he continues to slide the point of contact, keeping his arm straight and extended, he directs his sword-tip towards his opponent’s neck, while putting his foot down at N, and beginning to bring his left foot forward. As the attack comes in this way, Zachary has no option but to increase the Force of his resistance to Very Strong, so that he turns the blades aside, forcing them over to the inside. Alexander feels this, but unlike previously when he disengaged his sword and allowed his opponent’s to freely fly across, he now keeps contact as they pass overhead until they have lowered enough, before he releases Zachary’s sword to spring and overshoot down and out of the way, while bringing his own in a circular path around and over his head to strike diagonally down across the back of his opponent’s head, using his extended arm, as his left foot lands on the Outside Square at W, and his right foot spins on his toes to point forward, as is shown by the figures. | Ceſte operation a pareillement le meſme commencement, que les precedentes, & la meſme pourſuite. Alexandre allant de la Deuxſieme Inſtance vers la Troiſieme, & au meſme temps qu’il ſe met à faire lentement la graduation, le Contraire luy augement le poids. Lequel il dompte par la juſteſſe du contrepois qu’il luy oppoſe, & par l’avantage de la ſuperiorité, dont il engarde les lames de monter plus haut, & continue la graduation encommencée avec le bras roide & eſtendu, dirigeant ſa pointe circulairement vers le col de ſon Contraire, en plantant à meſme temps le pied droit à la lettre N. & pourſuivant d’avancer le gauche. Le coup eſtant porté en ceſte ſorte, Zacharies n’a point d’autre rememde pour le parer, que d’augmenter le Sentiment juſqu’au Poids Tres-fort, dont il deſtourne & tranſporte les lames en dedans. Ce que ſentant Alexandre, qui a par cy devant deſtaché les eſpees, en donnant à la contraire courſe libre, preſentement durant le tranſport, il les tient accoupleés juſqu’à tant qu’elles ſoyent aſſez deſcenduës, avant qu’il la laiſſe ſauter & tresbucher à val de route, en menant la ſienne circulairement de bas en haut par deſſus ſa teſte, & en donnant par la continuation du meſme mouvement à la teſte du Contraire par derriere un coup de revers diagonal avec le bras eſtendu, le pied gauche tombant ſur le Quarré Circonſcrit au poinćt W, & le droit ſe tournant proportionnellement à l’advenant; ainſi que repreſentent les figures. |
| In all the actions described in this Plate from Circle 11 on, Alexander has made his way from the Second Instance to the Third, intending to thrust his opponent in the face. Zachary has forseen this and parried, by raising and carrying Alexander’s sword across to the inside, intending to subjugate it, of which there is no doubt that this is the most convenient defense. In any case, he can also defend himself in another manner, that is, by increasing the force of his resistance and bringing the swords directly upwards, without any intent to carry them aside. Against this action, Alexander again attempts to dominate at first, by increasing his counter-force, intending to pursue his thrust. But if his adversary continues to increase the force of his resistance ever more to counter the hit coming at his face, raising the swords by means of Strong, Stronger, or Very-Strong levels of Force, this becomes no longer possible to dominate, nor to keep his opponent’s sword under control. Alexander allows it to escape upwards, to fly uncontrolled overhead, to an obtuse angle, while bringing his own point underneath, moving his body forward, so that he is inside the angle beneath his opponent’s sword, either with a step with the left foot or the right, as opportunity presents, and at the same time he turns the interior branch of his crossguard upwards, secures his hand against his right side and drives the sword through the right side of his opponent’s torso, with as much force and power as he can with his body. But this shall not be shown in any Plate, even one of similar actions as this. | En toutes les operations de ce Tableau depuis le Cercle 11. en avant, ou Alexandre c’eſt acheminé de la Seconde Inſtance vers la Troiſieme pour y donner à ſon Contraire l’atteinte au viſage: le coup à touſiours eſté prevenu & paré de Zacharie, en hauſſant & tranſportant l’eſpee contraire en dedans, comme avec intention de l’aſſujettir, qui eſt ſans doubte le plus convenable à ſa defenſe. Toutesfois il ſe pourra auſſi defendre en autre ſorte, aſſavoir en augmentant le poids & menant les eſpees droitement en haut, ſans intention de les tranſporter. Laquelle aćtion il convient derechef qu’Alexandre dompte en ſon premier commencement par la moderation du contrepoids, afin de pourſuivre ſa pointe. Que ſi l’adverſaire continue alors d’augmenter ſon poids encor d’avantage pour parer le coup qui luy eſt dreſſé vers le viſage, en hauſſant les eſpees avec Sentiment fort, Plus-fort, ou Tres-fort, lequel il ne ſeroit deſormais plus poſſible de dompter, ne de tenir l’eſpee contraire en devoir: il la laiſſera eſchapper en haut au deſſus de ſa teſte en angle obtus, en menant la pointe de la ſienne deſſous, avec avancement du corps, qu’il logera durant ce meſme mouvement au dedans de l’angle deſſous l’eſpee Contraire, ſoit avec la demarche du pied droit, ou du pied gauche, à meſure que l’occaſion le permet; & qu’à meſme temps il s’affermiſſe le bras, & la garde au coſté droit du corps, avec la branche interieure tourner en haut; pouſſant l’eſpee au coſté droit a travers la poićtrine de ſon contraire, donnant au deſſous du bras avec pleine force & avancement du corps, ce qui ſera repreſenté cy apres an aucuns Tableaux de ſemblables operations. |
| It may come to be that Zachary parries the thrust aimed at his face by simply raising the swords, but with less Force than we have specified, and that he contents himself to apply only a Lively, Livelier, or Very-Lively degree of Force, as in the examples shown by the 7th, 8th, and 9th Circles, where it happens that his blade will not fly up high enough. In this case, one must again slide along the blade and re-establish control, as shown in Circle No 10 against the same force. | Que s’il advenoit que Zacharie pare l’eſtocade qui luy eſt dreſſé devers le viſage en hauſſant ſimplement les eſpees, avec moins de Poids que nous ne venōs de ſepcifier, & qu’il ſe contentaſt d’y appliquer le Gaillard, Plus-gaillard, ou Tres-Gaillard, à l’exemple des Cercles 7. 8. & 9. dont il advendroit que ſa lame ne s’en fuyeroit pas aſſez viſtement; alors il la faudroit derechef deſgraduer & remettre en ſubjećtion; comme il a eſté fait & repreſenté au Cercle 10. ſur les meſmes Poids. |
| All of these examples serve to demonstrate the great importance of the sense of Feel, which is so frequently held in such little esteem by Masters of this profession. But seeing how the truth is so self-evident, they are, despite their wishes, constrained to know something about how forces act on the blade. But as soon as one attacks their blade, they feel hindered, and try by all means to deliver themselves from these straits, either by withdrawing, or by circular disengagements, or by feints, or grosser actions which are slow and take up time that they might have used to better advantage. If only they were not so enamoured of nurturing their ignorance, rather than learning to do better. At the least, as they feel hindered by the coupling of swords, they ought to consider that if they are themselves inconvenienced, that their adversary is no more free of this hindrance than they, and while some hindrances are greater than others, all these can be made more effective by following the same basic principles. And each of these hindrances can be remedied with it’s own counter move. These Masters ought to be advised they can lessen their own sense of hindrance, and increase that of their adversaries, merely by means of the sense and feel of the blade in their hand, without immediately losing their courage to desperation, for which there is no remedy except to escape as quickly as possible. This is completely the reverse of how to respond. Because experience not only demonstrates to us the importance of a sense of feeling for assessing and knowing things, but, moreso, it is a common language we can all learn, that there is nothing more sure and certain than the touch of the hand. We see that the blind know with only their sense of touch the different values of coins, and how to find their way along the streets to their intended destination. And following their example, when we find ourselves in the obscurity of darkness, we do the same. And because, in the Exercise of Arms, it is necessary to be able to discern the power or weakness of your opponent as he moves. How else do they think one could possibly understand, if not by a sense of feel through the crossing of swords and the heaviness or lightness of that touch, which is the real goal and purpose of the use of this sense. As such, it is necessary to ignore these men or to listen to them while keeping this fact in mind. By what other means would they have us know when our opponent begins to act against us, so that we can counter him, if not by the sense of feel that comes from crossing swords, where we can detect when he is about to begin because the force of his blade against our own becomes lighter? The sense of feel tells us in half the time it takes for us to see what is happening. Finally, how else would they have it, that we can work with confidence against someone, if we do not have a sense of feel by which we can know with how much force, and on which side, our opponent is attacking? Considering these points, it is easy to see that those who hold as detrimental such a useful ability are holding to false doctrines. For as soon as we have crossed swords, we can approach our opponent with confidence, because we are certain to know in good time, all the designs he would undertake against. Designs which he cannot even begin to execute, but we are already prepared against him. This is such a notable advantage, one which has been in use in the Exercise of Arms for so long, yet without these masters having been able to see it. This is a skill so obvious, so important, and so necessary, that those who have not completely learned it have no better ability than one who has never touched a weapon in his life. And through ignorance of this, they hold the belief that approaching an opponent is so dangerous that they must make use of main-gauche, or two swords, as if the sword was not entirely sufficient in and of itself for both the defence of the of the holder and causing harm to an opponent. | Toutes ces exemples demonſtrent clairement le tres-grand uſage du Sentiment, qui eſt toutesfois en ſi petite eſtime envers les Maiſtres de ceſte Profeſſion. Mais veu que la verité en eſt ſi evidente, ils ſont contraints malgré qu’ils en ayent, d’en recognoiſtre le forces. Car tout auſſi toſt qu’on les attaque la lame, ils s’en ſentent incommodez, & taſchent à la delivrer par touts moyens, ſoit en reculant, ſoit an cavant ſoit en uſant de feintes, ou meſmes de plus lourdes aćtions durant leſquelles il eſt neceſſaire qu’ils perdent touſiours autant de temps, duquel ils ſe pourroyent prevaloir à leur advantage, s’ils n’aimoyent pas de careſſer pluſtoſt leur ignorance, que d’apprendre à mieux faire. A tout le moins, puis qu’ils ſe ſentent incommodez par l’accouplement des lames, ils devroyent penſer s’ils en reçoivent quelque incommodité de leur part, qu’auſſi l’adverſaire en eſt pas libre, & puis que les incommoditez ſont plus grandes les unes que les autres, auſſi qu’elles peuvent eſtre augmentées en pourſuivant les meſmes commencements, & que elles peuvent eſtre remediés par leurs contraires. Ils devroyent adviſer à diminuer leurs propres incommodites, & à augmenter celle de leurs adverſaires par la moderation du Sentiment meſme, ſans perdre incontinent courage comme en une choſe deſeſperée, à laquelle il n’y a point de remede ſinon d’en eſchapper à touts marchez. Ce qui eſt tout au contraire. car l’experience non ſeulement nous demonſtre, que l’attouchement eſt de tres-grand importance pour le jugement & la cognoiſſance des choſes, mais qui plus eſt le commun langage nous apprend, qu’il ne peut y avoir aſſeurance plus certaine que celle qu’on touche à la main. Nous voyons que les aveugles congnoiſſent au ſeul ſentiment les differences de la monnoye, qu’à l’aide d’iceluy ils trouvent les chemins pour arriver par tout où ils pretendent; & à l’exemple deſquels quand nous nous trouvons en obſcurité, nous faiſons de meſme: & puis qu’en ceſt Exercice des Armes il eſt queſtion de diſcerner le fort & le foible des mouvements du Contraire, par quel moyen veulent ils donc qu’on les puiſſe comprendre, ſinon par le ſentiment & par l’attouchement des eſpees, & puis que le fort & le foible, ſont le propre objećt du ſentiment: en ſorte que’il eſt neceſſaire de les ignorer ou de les entendre par ceſte voye ſeule. Par quel moyen veulent ils qu’on comprenne les commencements des meſmes mouvements du Contraire, pour travailler à temps alencontre, ſinon par l’attouchement, auquel les commencements ſe deſcouvrent par leur foibleſſe, touſiours un demy temps pluſtoſt qu’ils ne ſe peuvent appercevoir à la veuë. Et finalement comment veulent ils, qu’on travaille avec aſſeurance alencontre, ſi on n’a pas l’attouchement par lequel on cognoiſſe avec quelle force, & de quel coſté l’adverſaire travaille. Par leſquelles conſiderations, il ſe voit que ceſt à fauſſes enſeignes, qu’ils tiennent pour dommageable ce qui eſt en effećt ſi Vtile. Car dés que nous avons l’attouchement des lames, nous pouvons faire nos approches deſſus l’adverſaire avec aſſeurance, puis que nous ſommes certains de ſçavoir touſiours à temps les deſſeings qu’ils voudra faire, leſquels il ne pourra tant ſeulement commencer que nous ne ſoyons deſia preparez alencontre. Advantage ſi notable, & ſi digne, que c’eſt choſe admirable, comment l’Exercice des Armes a eſté ſi longuement en vogue, ſans que les Maiſtres s’en ſoyent apperceus, eſtant choſe ſi claire, ſi ample, & ſi neceſſaire, qu’au defaut de l’avoir pratiquée, ils ſe voyent à touts moments, comme reduits à l’eſgal de ceux qui jamais n’ont manié les armes. Et pour l’ignorance de laquelle, ils tiennent les approches ſi dangereuſes, qu’ils en ſont contraints de ſe ſervir inutilement de la main gauche, ou d’Armes doubles, comme ſi l’eſpee neſtoit auſſi bien ſuffiſante à defendre la perſonne qui en uſe, comme elle eſt capable à offencer le Contraire. |
| Translation by Bruce G. Hearns |
Transcription by Bruce G. Hearns |
|---|---|
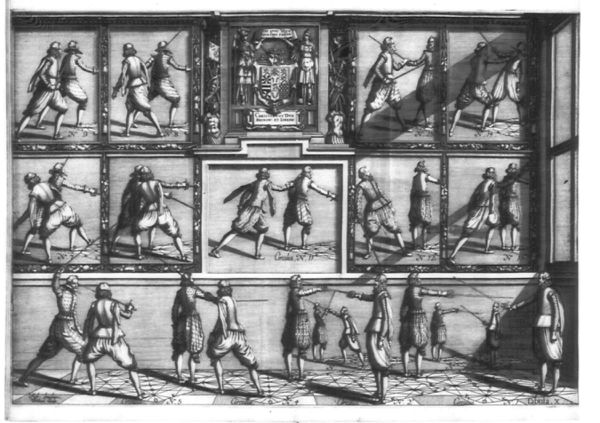
| |
| EXPLANATION OF THE ACTIONS IN THE TENTH PLATE | DECLARATION DES OPERATIONS DV TABLEAV DIXIEME |
| If it was not terribly apparent in the previous Plate just how vitally important a sense of feel is, it will be come quickly apparent in those which follow, and there are an ample number of examples. This is because it extends to all occurences when one has occasion to cross blades, as much from afar as in close, as much for the attacker as for the defendant, whether your Opponent is passive, or active, whether he is approaching or retreating, or whether he is performing the strangest moves that he knows. As such, we shall set ourselves, henceforth, to research the infinity of good and subtle inventions that Man has devised and put into practice for his defence. Just as Necessity is Mistress of the Arts, even to the point of having parrots and magpies learn to mimic human speech so far from their own nature, one must not doubt that those who are blessed with far more refined abilties, as are men, would thus have developed infinitely superior methods of self-defense. Observe that all animals have an innate desire for self-preservation, and that these employ, in times of need, all their strengths, both spiritual and physical, in their own defense. But, as we shall not dive too deeply into this labyrinth, we shall begin with situations not very much different from the preceeding actions, that is, those which follow from the subjugation of the blade at the Second Instance, just at the Oblique Diameter. Circle No 1 demonstrates the entry into distance, and the form which follows. | S’il eſt apparu par le Tableau Precedent, que le Sentiment eſt de terrible conſequence; il apparoiſtra ſemblablement bien toſt par ceux qui s’enſuivent, qu’il eſt auſſi fort ample: à cauſe qu’il s’eſtend à toutes les occurrences, où l’on a moyen de venir à l’attouchement des lames, tant de loin que de pres, tant pour l’aſſaillant, que pour le defendant, ſoit que le Contraire ſe repoſe, ou qu’il travaille, qu’il s’approche, ou qu’il recule, ou meſme qu’il ſe prevaille des mouvements les plus eſtranges, qu’il ſçauroit faire. En ſorte que nous nous allons mettre d’oreſenavant à la recerche d’une infinité de belles & ſubtiles inventions, que l’homme pourroit mettre en pratique pour ſa defenſe. Car puis que Neceſſité eſt la principale Maiſtreſſe des Arts, meſmes juſques à monſtrer aux Perroquets & aus Pies la prononciation du language humain tant eſloigné de leur Nature; il ne faut pas douter, que ceux qui ſont douëz de ſi rares qualitez, comme les hommes, n’ayent trouvé des pratiques infiniement excellentes pour ſe defendre; voyant que touts animaux ont un extreme deſir de leur propre conſervation, & qu’à icelle en temps de Neceſſité ils employent toutes leurs forces, tant corporelles, que ſpirituelles. Mais pour ne nous foncer du commencement trop avant dedans ce labyrinthe, nous commencerons par les occaſions, qui ne s’eſloignent guere des operations precedentes; aſſavoir par ce qui procede en ſuite de l’aſſujettiſſement des lames à la Seconde Inſtance en deça le Diametre: dont le Cercle N.1. en demonſtre l’entree, en la forme ſuivante. |
| Circle No 1 | Cercle N.1. |
| Alexander holds his opponent’s blade subjugated at the Second Instance, on the Diamter at the letter G. | Alexandre tient l’eſpee Contraire aſſujettie à la Seconde Inſtance en deça le Diametre à la lettre G. |
| The two opponents were previously at the First Instance, swords held parallel in the direct line posture, with Alexander’s sword beneath the other. He then began to work, raising his sword-tip, and setting his blade at the 3rd Span against the 8th Span of his opponent, at the same time raising his right foot up off the ground. He then moves the swords along the side of the Inside Square to the Oblique Diameter halfway to the Second Instance, while sliding the point of contact of the blades back so that his 8th Span comes to contact the 4th or 5th Span of his opponent and then subjgates his opponent’s blade as he sets his right foot down at the point G, at the Second Instance, drawing his left foot along using a circular path, to set it down at the Outside Square, with the toes along the Oblique Diameter, as is amply described and explained in Table VII, Circle No 1, and as is shown here in this figure. | Les deux Contraires ayants preallablement eſté à la Premiere Inſtance avec les eſpees paralleles en droite ligne, l’une au deſſus de l’autre, aſſavoir celle d’Alexandre deſſous; il a commencé à travailler, en hauſſant ſa pointe, & aſſemblant ſa lame à Nombre 3. contre le Nombre 8. de ſa partie adverſe, eſlevant au meſme inſtant le pied droit de terre; & le menant quand & quand le long du Quarré inſcrit au deça le Diametre juſquà my-chemin de la Seconde Inſtance, faiſant cependant la deſgraduation de l’eſpee contraire par la graduation de la ſienne propre, en ſorte que ſon Nombre 8. ſe vient aſſembler au 4. ou 5. des Nombres contraires, & conſequemment il en fait l’aſſujettiſſement en ces meſmes Nombres, avec plantement du pied droit eſlevé, le poſant au poinćt G. à la Seconde Inſtance, & pourſuivant circulairemēt avec le pied gauche, à planter ſur le Quarré circonſcrit, les orteils d’iceluy ſur le Diametre oblique; ainſi qu’il eſt plus amplement ſpecifié au Tabl. VII. Cercle N.1. & qu’il ſe voit icy repreſenté en la figure. |
| Circle No 2 | Cercle N.2. |
| He steps from the Second Instance to the Third, and puts the tip of his blade in front of his opponent’s face. | Il marche de la Seconde Inſtance à la Troiſieme, & y preſente la poinćte de ſa lame au viſage de ſon Contraire. |
| As Zachary is waiting for the follow-on to the previous action, Alexander advances with the right foot following the side of the Inside Square and sliding the point of contact up his sword, by the smallest number of Spans. Then Zachary immediately begins to increase his force, to defend himself. But, by sliding the point of contact up his sword Alexander has already acquired a very powerful dominance over his opponent’s sword, and continues his thrust, stepping in with the right foot to the letter N at the Third Instance, and following with his left foot to the letter K and placing his sword-tip exactly in front of his opponent’s face, as shown by the figures. | Puis que Zacharie attend la pourſuite de la precedente operation; Alexandre s’avance avec le pied droit ſuivant la trace du Quarré inſcrit, & graduant ſa lame par les moindres Nombres de la lame contraire. Dont Zacharie commence incontinent à en augmenter le poids, pour ſe defendre. Mais comme ainſi Alexandre ait acquis une tresgrande ſuperiorité par la graduation de ſa lame, il en dompte l’eſpee contraire, & pourſuit ſon eſtocade, en entrant avec le pied droit à la Troiſieme Inſtance au poinćt N. & pourſuivant avec le pied gauche à planter à la lettre K, & à mettre enſemblement ſa pointe en courtoiſie devant le viſage de l’Adverſaire; comme les figures demonſtrent. |
| Circle No 3 | Cercle N.3. |
| Alexander, wishing to complete the attack and finish the preceeding action, enters swiftly into his opponent, with his right foot moving along the line of Inside Square and driving his point firmly, so that the two guards collide forcefully, as he sets his foot down at S, and put his weight on his bent knee, leaning forward as he sends his sword through his opponent’s head. As shown in the figures. | Alexandre voulant achever l’atteinte & l’execution de l’operation precedente, il entre viſtement avec le pied droit deſſus ſon Adverſaire par le trac du Quarré inſcrit, en graduant les lames, & aſſenant ſa pointe en rigueur, de ſorte que les deux gardes s’entredonnent avec force, en plantant le pied eſlevé au poinćt S, & menant ſur le genouil d’iceluy plié la charge du ſon corps à pancher ſur le devant, en pouſſant ſa lame à travers la teſte de ſon Contraire; ſelon les figures. |
| Circle No 4 | Cercle N.4. |
| Again, he tries to perform the action from Circle No 2, while he steps towards the Third Instance. His adversary parries his strike, carrying the swords across to the inside with a Very-Strong force. So Alexander wounds him with a reverse strike to the back of his head. | Travaillant derechef pour effectuer l’operation du Cercle N.2. cependant qu’il marche devers la Troiſieme Inſtance; l’Adverſaire luy pare le coup, en tranſportant les eſpees en dedans avec poids Tres-fort: dont Alexandre le bleſſe d’un coup de revers au derriere de la teſte. |
| This actions follows from that shown in Circle No 1, where Alexander has subjugated his opponent’s blade at the Second Instance, again intending to perform action of Circle No 2. Thus, stepping with his right foot towards the Third Instance, he slides his blade with his arm straight and extended against the 5th Span of his opponent’s blade, which Span he previously held it at bay. And however much Zachary tries to parry the blow by increasing his force, nonetheless, Alexander has such superiority, that he dominates him, in such a way that the blades cannot rise up, while turning his sword-tip, with a circular motion, downwards towards the right side of his opponent’s neck, while he is moving his raised right foot towards the Third Instance at letter N, and then brings his left foot along in a circular path. By this, Zachary must employ a Very Strong degree of force to raise the blades and carry them to the inside. Which does not prevent Alexander, during this movement, from keeping the blades coupled together, and so restrain his opponent’s blade with his own beneath the other, until they have lowered enough. At that instant he disengages and allows it to fly out of control, while bringing his own out from under the other, up above his head, and ,as he sets his left foot down at W on the Outside Square, and leans his body forwards, putting his weight over his knee, he extends his arm and strikes diagonally downwards with reverse cut, to the back of his opponent’s head. This is shown in the figure. | Ceſte operation procede de celle qui eſt repreſentée au Cercle N.1. où Alexandre à aſſujetti l’eſpee contraire à la Seconde Inſtance, en intention de venir derechef à l’operation du Cercle N.2. Dont marchant avec le pied droit vers la Troiſieme Inſtance, il va graduant ſa lame avec le bras roide & eſtendu par le Nombre 5. de la lame contraire, ſur lequel il la tenoit paravant aſſujettie. Et combien que Zacharie taſche à parer le coup en augmentant le poids: Toutesfois Alexandre qui a autant de ſuperiorité, le dompte, de ſorte que les lames ne peuvent monter, tournant ſa pointe un peu circulairement deſcēdante, devers le coſté droit du col de l’Adverſaire, durant que le pied droit à preſent eſlevé ſe va planter à la Troiſieme Inſtance au poinćt N. avec pourſuite circulaire du pied gauche. Et par ainſi Zacharie eſt contraint de travailler avec un poids Tres-fort, pour hauſſer les lames & les tranſporter en dedans. Ce qui n’empeſche pas Alexandre de tenir, durant ledit tranſport, les eſpees accouplées, en retenant la contraire avec la ſienne par deſſous, juſqu’à tant qu’elle ſoit veune aſſez baſſe; auquel inſtant il la laiſſe enfuir & tresbucher, en menant la ſienne de deſſous l’autre par deſſus ſa teſte en haut, & en aſſenant diagonalement un coup de revers avec le bras eſtendu au derriere de la teſte de ſon Contraire, plantant egalement le pied gauche eſlevé ſur le Quarré circōſcrit au poinćt W, & ſur le genouil d’iceluy menant la charge du corps, à pancher ſur le devant; comme il ſe voit en la figure. |
| This reverse cut is shown being executed with full force, but when training with a friend, one stops the blow above the head of your opponent without touching him. As such, one cannot train with full speed. It also follows that the blow cannot be too difficult to parry, as we show here in the next Circle. | Ce coup de revers eſt icy repreſenté à executer en rigueur: mais quand on s’exercice en courtoiſie, on en arreſte la courſe un peu au deſſus de la teſte contraire ſans la toucher; en ſorte qu’on ne peut alors travailler avec tant de viſteſſe: dōt s’enſuit auſſi, que le coup ne ſeroit pas ſi difficile à parer, là voicy au Cercle prochain enſuivant. |
| Circle No 5 | Cercle N.5. |
| Zachary parries the preceeding reverse cut, by raising his arm and blade. At the same time, Alexander drops his point, and puts it in front of Zachary’s face. | Zacharie partant le precedent coup de revers, en hauſſant le bras & l’eſpee; au meſme temps Alexandre deſcend ſa poinćt, & la luy met devant le viſage. |
| Zachary, sees the reverse cut coming to the back of his head, as in the preceeding action. He takes a large step backwards with his left foot, quickly raising his sword to the right above his head to parry the threatening strike. Meanwhile, Alexander turns his left side inwards, his right side outwards, and draws his right arm back, so this way he brings his sword-tip in a half-circle down, around, and underneath his opponent’s blade, then aims his tip exactly at his opponent’s face, arm bent and turning his feet slightly inwards, again keeping his body leaning forward. This is shown by the figure. | Zacharie donc voyant derechef venir le meſme coup de revers devers ſa teſte, ainſi qu’en l’operation precedente; il fait un grand pas en arriere avec le pied gauche, hauſſant tresviſtement le bras avec l’eſpee par deſſus le coſté droit de ſa teſte, pour la parer devāt le coup qui le menace. Cependant Alexandre ſe tourne le coſté gauche en dedans, & le droit en dehors, retirant le bras en arriere, & par ceſte voye menant ſa pointe à demy circulairement de haut en bas deſſous la lame contraire; & a luy dreſſant en courtoiſie devant le viſage avec le bras courbe, & avec une petite entrade des deux pieds, comme auſſi avec le corps panché un peu en devant; ainſi que la figure le repreſente. |
| Circle No 6 | Cercle N.6. |
| Zachary parries the last thrust, aimed at his face, by quickly dropping his arm and sword. At the same time, Alexander takes a step in forwards with both feet, throwing his sword-arm behind, bringing the sword from beneath to above his opponent’s blade. | Zacharie parant la derniere eſtocade, qui luy eſtoit dreſsé au viſage, en deſcendant viſtement le bras avec l’eſpee; Alexandre entre au meſme temps avec les deux pieds un pas en avant, jettant le bras avec l’eſpee en arriere, de deſſous l’eſpee contraire au deſſus. |
| Zachary realizes the danger from the thrust, which had been held back, without touching his face, very quickly drops his sword down against his opponent’s blade to turn it aside. To avoid this, Alexander extends his arm, and turns his wrist, and moves his sword-tip backwards, under his opponent’s blade without touching it, while stepping forward with the left foot along the Circle, so that his toes come to be on the extreme end of the Quadrangle, his body leaning forward on his bent left knee. He then draws his right foot along, with his heel raised, on the Outside Square between the letter P and T and brings his sword from beneath to above the other, as is shown in the picture. | Zacharie recognoiſſant le danger de l’eſtocade precedente, (quoy qu’elle ait eſté retenuë, ſans luy toucher le viſage) il abaiſſe fort viſtement le bras avec l’eſpee de haut en bas devers l’eſpee contraire pour la deſtourner. Et pour ce prevenir Alexandre jette au meſme temps, en eſtendant le bras & tournant le poignet, la pointe de ſa lame à l’envers, au deſſous de la lame contraire ſans la toucher, faiſant enſemblement avec le pied gauche un pas en avant, en deça le Cercle, en ſorte que les orteils en viennent à reſpondre à l’endroit de l’extreme bout du Quadrangle, & le corps ſe panche deſſus le genouil gauche en avant, trainant conſequemment le pied droit apres avec le talon levé, ſur le Quarré circonſcrit entre les lettres P, & T, & enſemblement menant ſa lame de deſſous au deſſus de l’autre; comme il eſt montré en ſa figure. |
| Circle No 7 | Cercle N.7. |
| Alexander raises his right foot so as to lean over his left, while making a cut to the right side of his opponent’s head. | Alexandre en levant le pied droit ſe va pācher ſur le gauche, en donnāt un coup d’eſtramaçon à ſon Contraire au coſté droit de la teſte. |
| This action is nothing more than a continuation of the previous, followed on without interruption, raising the right foot in the air, leaning the body over the left leg, left arm dropping, and hitting his opponent with a cut across the right side of the head, as is shown in the figure. | Ceſte operation n’eſt autre choſe, qu’une continuation de la precedente, à pourſuivre ſans nulle interruption, en levant le pied droit en l’air, & panchant le corps en devant ſur la jambe gauche, avec le bras egalement deſcendant, & donnant à ſon Contraire un coup d’eſtramaçon au coſté droit de la teſte; comme il ſe voit en la figure. |
| Circle No 8 | Cercle N.8. |
| Next, with his right foot, he takes a good step outside the circle beside his opponent, as we have shown in the figure. After this, he leans his body forward over his right knee, and puts his sword in front of him, tip down towards the ground at an acute angle, with his arm straight. This is not shown here due to space. Nontheless, it must be performed as a means to arrive at the following action. | Apres il marche encores plus outre avec le pied droit eſlevé un bon pas en avant à coſté du corps de ſa Partie, cōme nous l’avons repreſenté icy en la figure: En ſuite de quoy il ſe panche le corps en devant ſur le genouil droit, mettant egalement l’eſpee devant luy, la pointe deſcendante juſqu’à bien pres de la terre en angle aigu, avec le bras roide. Aćtion qui n’a pas eſté icy repreſentée à faute de place; toutesfois il faut qu’elle y ſoit pratiquée pour venir à l’operation ſuivante. |
| Circle No 9 | Cercle N.9. |
| Alexander was leaning forward, his sword pointed at the ground at an acute angle, he immediately turns the tip upwards, in front of the right side of his head, by turning his wrist, and pinning it to his hip. At the same time, he twists his left side towards his opponent. He raises his left foot and pivots around on his right foot, moving so his arm and sword are in front, his hand pressed against his side and the point of his sword aimed upwards. He bringss his left hand over and around the guard. At the same time that he puts his left foot down towards his opponent, with his left knee bent, his weight on it, he executes the attack, using his body weight, against his opponent’s back. This is as demonstrated by the figures. | Eſtant Alexandre ainſi panché ſur le devant avec l’eſpee eſtendue & deſcendante en angle aigu, il en tourne tout à l’inſtant la poinćte en haut par devant le coſté droit de ſa teſte, & ce à l’aide du poignet de la main, enſemblement ſe tournant & dreſſant le corps à gauche devers ſon Contraire; avec eſlevation du pied gauche, & preſentation du bras & de l’eſpee en avant, icelle affermiſſant à ſon coſté droit avec la pointe dreſſé contre mont, & en empoignant de la main gauche la garde par deſſous; & quand & quād poſant le pied à terre devers ſa Partie, avec le genou de devant plié & le corps repoſé deſſus, au meſme temps il donne l’atteinte & en fait l’execution, moyennant la charge du corps, par le dos de ſon Contraire; ainſi que les figures le demonſtrent. |
| Circle No 10 | Cercle N.10. |
| After Alexander subjugates the sword, as he does to begin the action of Circle No 2, Zachary draws his sword away to the outside, putting it above the line S-N. So Alexander, instead of following through with his thrust, simply changes his approach. | Apres l’aſſujettiſſement de l’eſpee, comme Alexandre ſe vent mettre en devoir de commencer l’operation du Cercle N.2. Zacharie eſcarte ſa lame en dehors, la mettant au deſſus de la ligne SN. dont Alexandre, au lieu de pourſuivre l’eſtocade, ſe content d’amender ſimplement ſon approche. |
| The action in this present Circle evolves from the 1st Circle, where Alexander has subjugated his opponent’s sword at the Second Instance. After this he has wounded his opponent with a thrust at the Third, as is represented in the 2nd Circle. Now, to prevent this thrust, at the instant his feet reach the Second Instance, Zachary opens his arm and sword outwards to the right side above the Inside Square, along the line S–N. By doing this he prevents his adversary from wounding him along the line of his blade while moving from the Second to the Third Instance. Nonetheless, Alexander, still wishing to pursue his thrust, seizes from this position a new advantage, moving his right foot along the Inside Square to mid-way to the Third Instance, and bringing his left foot up, parallel to his right, along the Outside Square, as is seen in the figure. | L’operation de ce Cercle preſent depend du Cercle N.1. où Alexandre a aſſujetti l’eſpee contraire à la Seconde Inſtance; & en ſuite il a bleſſé ſoudit Contraire d’un coup d’eſtocade à la Troiſieme; ainſi qu’il eſt repreſenté ſur le Cercle N.2. Maintenant donc pour prevenir ceſte eſtocade, à l’inſtant qu’il arrive avec les pieds à ladite Seconde Inſtance, Zacharie s’eſcarte le bras & l’eſpee en dehors à la main droite deſſus le Quarré inſcrit, lignes SN. Et en ce faiſant il prévient l’Adverſaire de ne le pouvoir bleſſer au long de ſa lame en allant de la Seconde Inſtance à la Troiſieme; Alexandre voulant neantmoins pourſuivre ſon eſtocade, prend là deſſus un nouvel advantage, en allant avec le pied droit le long du Quarré inſcrit juſqu’à my-voye de la Troiſieme Inſtance, & pourſuivre avec le gauche, à planter parallel à l’autre ſur le Quarré circonſcrit; ainſi qu’il ſe voit en la figure. |
| Circle No 11 | Cercle N.11. |
| He pursues his thrust, taking a large step forward and a little outside the circle with his right foot, while, with his arm held straight, he slides the point of contact up the sword and aims the tip at his opponent’s neck. This attack is parried to the inside with a Very Strong degree of Force. He very quickly enters in against his opponent, jumping behind his back, with a reverse cut to the left side of his head. | Il pourſuit ſon eſtocade, en marchant avec le pied droit un grand pas en avant un peu en dehors le Cercle, enſemble graduant & dreſſant ſa poinćte devers le col de ſa Partie adverſe avec le bras roide. Lequel coup luy eſtant paré en dedans avec poids Violent; il entre tres-viſtement ſur ſon Contraire, en luy ſautant derriere le dos, avec un coup de revers au coſté gauche de ſa teſte. |
| This action follows on from the preceeding one, where Alexander has altered his position. Consequently, he has moved forward, while sliding the point of contact of his sword, stepping in with the right foot a good pace further on, a bit outside the Circle about the middle of the line O-Z, without lowering the swords at all, and, keeping his arm straight, moves the sword-tip around in a circle until it is aimed at the base of his adversary’s throat, who is then forced to use violent force to parry the blow, carrying the swords over to the inside. Alexander jumps in with a large step behind his opponent, turns his chest forward, while bringing his sword up passing above his head and then continuing to perform a reverse cut at the instant his left foot touches the ground and brings his right foot around to the outside. With his body leaning forward, he strikes hard to the left side of his opponent’s head, as shown. | Ceſte operation eſt la pourſuite de la precedente, où Alexandre avoit amendé ſa ſituation; & conſequement il s’eſt avancé en graduant ſon eſpee, & entrant avec le pied droit un bon bas plus outre, un peu dehors le Cercle à l’endroit du mitan de la ligne OZ. abaiſſant aucunement les eſpees, & dreſſant d’un bras roide ſa poinćte circulairement vers le bas du col de ſon Adverſaire. Lequel eſtant contraint d’uſer de Violence pour parer cedit coup, en tranſportant les eſpees en dedans: Alexandre entre un grand pas ſur luy en ſautant, & tournant la poitrine devant, & menant à meſme temps ſa lame de bas en haut par deſſus ſa teſte, & cōtinuant à en donner avec extenſion du bras un coup de revers, au meſme inſtant que le pied gauche ſe plante avec deſtournement du pied droit en dehors, pour venir derriere le Contraire, & executer ſur luy tant plus rudement, avec le corps panché, le coup aſſené au coſté gauche de ſa teſte; ſelon la figure. |
| Circle No 12 | Cercle N.12. |
| To stop his momentum after his leap, he leans backwards on his right foot, bending his knee, and draws his sword-arm behind himself, tip pointing down and forward, as presented in the image. | Pour rompre la courſe & le mouvemēt du ſaut, il ſe panche à l’envers ſur le pied droit, pliant le genouil, & retirant le bras avec l’eſpee en arriere; la pointe un peu baſſe & avancée, tirant à main droite; ainſi qu’il eſt repreſenté en la figure. |
| Circle No 13 | Cercle N.13. |
| Zachary stands motionless, stunned by the slash to the head he received. Alexander promptly raises his left foot, and steps towards his opponent, leans his body forward, and drives the sword through his back. | Zacharie demeurāt eſtonné par la vive atteinte qu’il a receuë, ſans ſe mouvoir; Alexandre leve incontinent le pied gauche, & en marche devers ſon Contraire, panchant le corps en avant, & luy pouſſant en rigueur l’eſpee à travers le dos. |
| Circle No 14 | Cercle N.14. |
| This is the follow-on from the 11th and 12th Circles. Here Zachary, perceiving that, after the leap and strike, his opponent is now behind him, turns about to the right and withdraws slightly by bringing his left foot around and putting his toes down by the Diameter, close to the letter R, turning his chest forward, raising his arm and sword up to defend himself. Because the sword, thus brought up, passes above Alexander’s head, Alexander moves forward a step with the right foot, and by leaning forward, drives his sword through Zachary’s chest. This is demonstrated by the figure. | Voicy la ſuite des Cercles N. 11. & 12. Dont Zacharie recognoiſſant que ſon Contraire luy eſt venu derriere le dos avec le ſaut & l’execution du coup precedent; il ſe retire en voltant le pied gauche à droite, & le plantant avec les orteils pres le Diametre aſſez pres de la lettre R, ſe tournant enſemblement la poitrine devant, avec le bras & l’eſpee montante, pour ſe defendre. Et puis que l’eſpee, eſtant ainſi menée, paſſe au deſſus de la teſte d’Alexandre, iceluy s’avance d’un pas avec le pied droit, & en panchant le corps, luy pouſſe la ſienne à travers la poitrine; ainſi qu’il eſt demonſtré par la figure. |
| Circle No 15 | Cercle N.15. |
| This last action again derives from the 11th and 12th Circles. For as soon as Alexander’s reverse cut hit him on the right side of his head, Zachary realized that Alexander was already behind his back, so he turns keeping his feet in place, so his body, with his arm and sword up, faces toward his opponent. At that same time Alexander steps in on him with his left foot and grabs the sword-guard from above with his left hand, then turns it outward, bringing his own guard in tight against his side, aiming the sword-tip at his opponent’s chest, exactly as shown in the image. | Ceſte derniere operation depend encor ſemblablement des Cercles N.11. & 12. Car dés qu’Alexandre luy a tiré le coup de revers au coſté droit de la teſte; Zacharie recognoit qu’il eſt deſia derriere ſon dos; dont il ſe tourne ſur les deux pieds ainſi plantez, en preſentant le corps avec le bras & l’eſpee devers ſon Contraire. Au meſme temps Alexandre luy entre deſſus avec le pied gauche, & luy empoigne par deſſus la garde de l’eſpee, avec la main gauche, & la tourne en dehors, s’affermiſſant le bras avec ſa garde au coſté, en aſſenant la pointe à la poitrine de ſon Contraire; le tout en conformité de la figure. |
| Those who my chance to contemplate the images without duly examining them, may feel they have some critique to make. They may not be easily persuaded that is practicable, when confronted with a live opponent, to use these means to get behind him, as shown. Also that this said opponent would take care not to permit this. But I would caution them, that they would but take some time to consider the opening Zachary created, the extremity of the position into which Zachary has been put, before they proudly present their case. The strike that Alexander makes can only be countered with an extremely powerful and violent parry. And such wild action cannot be conducted, nor controlled, as easily as one wishes, the opponent has benefitted from having already moved into close range, and while the swords were flying overhead, he has taken the opportunity and time to pass beyond and behind. Those who find this so very strange are those who have been trained in the traditional way, who are careful to only make a pass while they are still at long range, and upon seeing their opponent’s sword close in, withdraw out of range. What they do by chance, we perform with assurance. For we come from the sense of feel and the close range, and thereby force our opponent to counter our moves wildly, in such a way that opens to us the path for our position, from which he invariably receives a blow. | Ceux qui viendront par fortune à contempler les figures de ce Tableau, avant les avoir deuement examinées, y trouveront peut eſtre aſſez à redire. Car ils ne ſe pourront du commencement perſuader, qu’il ſoit practicable à l’homme vivant, de gaigner ainſi le derriere à ſon Adverſaire, comme elles demonſtrent; & que ledit Adverſaire devroit bien ſonger en d’autres affaires, avant que de le permettre. Mais je les adverti, qu’ils prennent premierement la patience de conſiderer l’occaſion que Zacharie en a baillée, & l’extremité en laquelle il a eſté reduit, avant que de la preſenter ſi belle. C’eſt que le coup d’Alexandre a eſté porté ſur luy avec un ſi grand avantage, qu’il luy a eſté impoſsible de le parer autrement, qu’avec violence. Et comme ainſi ſoit, que les aćtions violentes ne puiſſent eſtre conduites, ne gouvernées à ſouhait, le Contraire en a fait tellement ſon profit, qu’eſtant preallablement venu en meſure eſtroite, durant le mouvement violent, il a prins le temps de paſſer outre. Qu’ils ne trouvent celà ſi eſtrange, puis que ceux qui tirent à la mode ancienne, ſe hazardent bien de faire les paſſades, encores qu’ils ſoyent en meſure large, dé qu’ils voyent apparence que l’eſpee contraire ſortira de preſence: ce qu’ils font avec hazard, nous le monſtrons avec ſeureté; car nous venons ſur le ſentiment en meſure eſtroite, & y eſtants, nous forçons le Contraire à ſe defendre avec violence, de ſorte qu’il nous en ouvrira le chemin à noſtre poſte, ou il en recevra l’atteinte inevitable. |
| Translation by Bruce G. Hearns |
Transcription by Bruce G. Hearns |
|---|---|

| |
| EXPLANATION OF THE ACTIONS IN THE ELEVENTH PLATE. | DECLARATION DES OPERATIONS DV TABLEAV ONZIEME. |
| When doctors visit patients to diagnose illnesses, nothing gives them more trouble than the distinguishing between two similar, but different, ailments, which is why only the most learned and best experienced are not mistaken. But just as they take the feel of the pulse, which symptom is held as more significant than any other, so we do likewise in our Training. When an action occurs that is so difficult that sight alone is insufficient to properly follow what is happening, we rely then on our sense of feel to inform us and help us discover the true intent, to find in what ways his options to attack are limited, and, having found this out, we can prevent him from carrying out his desired attack. This is what, hereafter, shall be shown in this and the following Plates. If, as I say, the fabric of exercises in the 10th Plate were coarse, if they were of large movements, very easy for Alexander to perceive, the 11th shall present more subtle ones. As such, up until this point, Alexander has always subjugated his opponent’s blade at the Second Instance. Let us say that there are two means by which Zachary can interrupt this approach, the one by standing firm, which we have shown in the examples in the preceeding Plates, and the other is by retiring backwards. Here, then, Zachary will practice his withdrawals, but in all cases without disengaging swords. For we have already touched upon the topics of circular disengagements and feints, and this shall be discussed further, at another point. Now, we shall see how he tries to change the range, and how Alexander reacquires his dominance anew. | Quand les Medecins font leurs viſites pour aſſeoir un bon jugement, il n’y a choſe au Monde qui les trouble d’avantage, que la ſimilitude de l’une maladie à l’autre, qui eſt cauſe que, les plus doćtes meſmes & les mieux experimentez y ſont aucunefois trompez, en prenant l’une pour l’autre. Mais comme ils ſe tiennent en ceſte occaſion pluſtoſt au raport du poulx, qu’aux autres marques de moindre importance: ainſi en faiſons nous pareillement en noſtre Exercice; quand il s’y preſente quelque aćtion ſi difficile, que le jugement de la veüe y manque, nous nous adreſſons au Sentiment, qui nous deſcouvre le principe, d’où le mouvement eſt contraint de tirer toute ſon addreſſe, & l’intention eſtant cognue, on la peut touſiours empeſcher de ſortir l’effet qu’elle deſire. C’eſt ce qui paroiſtra doreſenavant de plus à la ſuite de nos Tables. Car ſi les occaſions de la dixieme ont eſté de groſſe eſtoffe, je di, ſi ce ont eſté de grands mouvements, & qui eſtoyent fort faciles à recognoiſtre pour Alexandre l’Onzieme vous en mettra devant les yeux des autres plus subtiles. Et comme ainſi ſoit, que juſques icy noſtre Alexandre ait touſiours taſché d’aſſujettir l’eſpee contraire à la Seconde Inſtance; diſons qu’il ya deux manieres principales pour luy rompre ceſte approche, l’une en demeurant ferme, dont nous avons propoſé les exemples aux Tableaux precedents, & l’autre en ſe retirant en arriere. Voicy donc Zacharie qui s’en va pratiquer les retirades, toutesfois ſans destaſcher les eſpees: car touchant les cavations & notamment les feintes il en a eſté parlé, & en ſera diſcouru encore autrepart. Maintenant voyons comment il taſche à luy rompre la meſure, & comme Alexandre reprend touſiours nouvel avantage. |
| Circle No 1 | Cercle N.1. |
| Alexander subjugates his opponent’s sword along the Diameter at the Second Instance. Zachary turns on his two feet, so his right side goes to the outside, and his sword arm and sword come to rest just above the side of Inside Square. | Alexandre aſſujettiſſant l’eſpee contraire au deçà le Diametre à la Seconde Inſtance; au meſme temps Zacharie ſe deſtourne ſur les deux pieds le coſté droit en dehors, en ſorte que le bras avec l’eſpee luy viennent reſpondre juſtement deſſus le coſté du Quarré Inſcrit. |
| The two opponents begin standing on the Circle at the First Instance, in the direct line posture, swords parallel, Alexander’s below the other. He begins to work against his opponent, subjugating the sword at the Second Instance, right foot on the letter G, on the Oblique Diameter. But before he can set both feet safely on the ground, Zachary spins on his toes towards the Diameter, and with a slight withdrawal of his left foot, turns his right side to the outside, a little back, and allows his extended right arm to come to rest, by means of a small slide up the blade, above and along the the side X-N of the Inside Square, with an Alive degree of Force. | Les deux Contraires s’eſtants plantez preallablement ſur le Cercle à la Premiere Inſtance en droites lignes, ſuivant la forme requiſe; l’eſpee d’Alexandre parallele au deſſous de l’autre; il commence à travailler en l’aſſujettiſſant à la Seconde Inſtance lettre G, par deça le Diametre; mais avant qu’il ait bonnement planté les pieds en terre, Zacharie ſe tourne les orteils des deux pieds devers le Diametre, & cela avec une petite retirade du pied gauche, deſtournant par ainſi le coſté droit en dehors un peu en arriere, & laiſſant aller (moyennant quelque petite deſgraduation) le bras eſtendu avec l’eſpee en droite ligne, au deſſus le coſté du Quarré Inſcrit, marqué X N, avec Sentiment Vif. |
| All of this with the intention of awaiting Alexander to once again thrust from the letter N at the Third Instance along the side of the Inside Square. Because to do this he must attack with his tip, which means the weak of his blade will pass by the strong of Zachary’s, and so Zachary would have the means to close the line and hit him instead of being hit. | Le tout en intention d’attendre en ceſte forme, qu’Alexandre luy vienne porter derechef l’eſtocade au long du Quarré Inſcrit à la Troiſieme Inſtance lettre N: car puis qu’il ſeroit contrainćt de ce faire en paſſant avec la pointe, qui eſt le foible de l’eſpee par le fort de la ſienme, il auroit moyen de luy fermer la ligne, & de donner atteinte au lieu d’en recevoir. |
| Circle No 2 | Cercle N.2. |
| Alexander follows on his action, advancing his right foot together with the left side of his body into the angle, putting his raised foot down on the Perpendicular Diameter at point L. | Alexandre pourſuivant l’operation encommencée, s’avance le pied droit enſemble avec le coſté gauche du corps au dedans de l’angle, mettant le pied eſlevé à terre au deça le Diametre au poinćt L. |
| After Zachary has almost achieved the preceeding action, and awaits his opponent to again come at him with a thrust from the Third Instance, which he reaches by stepping with his right foot along the side of the Inside Square, Alexander continues his attack, not as intended, but according to the situation, by advancing his right foot from where it was at the Second Instance, up to the letter L, along the Perpendicular Diameter, leaning forward slightly, and, notably, his left side, such that by this means he enters into the angle of his opponent’s sword, drawing his left foot behind, heel raised, up to the first section of the Exterior Collateral before the letter F, again subjugating his opponent’s sword, to then continue on with the actions shown in Circles No 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, and 13. which could nevertheless also proceed from Circle No 5, having but this sole difference of the one beginning with the right foot forward, and the other, the left. Meanwhile, be aware that here we see that Alexander has set his left foot down inside the Circle on the Interior Collateral between the letters G and I, which is done for clarity so we can see his guard. But in practice, it is best to follow the description, which is more correct. | Apres que Zacharie à parachevé la precedente aćtion, & qu’il attend que ſon Contraire luy vienne derechef tirer une eſtocade à la Troiſieme Inſtance, en cheminant du pied droit par la trace du Quarré Inſcrit: Alexandre pourſuit à travailler non pas ſelon ceſte intention, mais ſelon l’exigence, en avançant le pied droit du lieu où il eſtoit planté à la Seconde Inſtance, juſqu’à la lettre L au deçà le Diametre; avec le corps panché un peu en avant, & notamment le coſté gauche, en ſorte qu’il entre par ce moyen dedans l’angle de l’eſpee contraire, trainant le pied gauche ſur les orteils derriere juſqu’à la premiere ſećtion de la Collaterale exterieure devant la lettre F. ſujettant derechef l’eſpee contraire, pour en tirer la pourſuite des operations & executions repreſentées ſur les Cercles N.8.9.11.12.13. qui peuvent ce neantmoins proceder auſſi ſuite du Cercle N.5. n’y ayant que ceſte ſeule difference de commencer en l’un avec le pied droit devant, & en l’autre avec le pied gauche. Cependant ſoyez adverti que le pied gauche d’Alexandre eſt icy planté en la figure au dedans du Cercle ſur la Collaterale interieure entre les deux lettres G & I. ce qui a eſté fait pour mettre ſa garde en veüe. Mais en la Pratique il ſera plus expedient d’enſuivre la deſcription, d’autant qu’elle eſt plus propre. |
| Now, whereas Alexander practices this manoeuvre of entering in with the foot in Circle No 2 after his opponent has finished moving, he must also practice it at the same time that his opponent is moving, and while he is yet unable to command the situation. Which he must do by having his foot ready to follow promptly. | Or comme ceſte operation d’entrer avec le pied droit a eſté pratiqué en ce Cercle 2. par Alexandre, apres que le mouvement du Cōtraire a eſté deſia fini; auſsi la faut il pratiquer durant le meſme temps avant qu’il ſoit venu à bout de ſon intention, & durant qu’il eſt encor empeſché à former la ſituation: ce qu’il faut faire en ayant le pied prompt à le pourſuivre. |
| Circle No 3 | Cercle N.3. |
| At the same moment that Zachary is performing the aforsaid movement, Alexander very swiftly moves his right foot close to the Diameter, following it suddenly with his other foot, so that he very quickly spins it around (thus disengaging his sword) behind his right foot, such that it comes to rest across the diameter on the Circumference between W and X, and hitting his adversary with a straight-arm thrust to the head. | Durant le mouvement de l’aćtion de Zacharie dernierement dite; Alexandre s’avance au meſme temps aſſez viſtement le pied droit bien pres du Diametre, continuant à pourſuivre tout ſoudainement avec l’autre, à volter de grand viſteſſe (& ce en deſtachant les eſpees) par derriere le pied droit, de ſorte qu’il vient à tomber en terre par delà le Diametre ſur la Circonference entre W & X, en donnant l’eſtocade à ſa partie adverſe avec le bras roide à travers la teſte. |
| Before Zachary has finished this last movement, which is to turn his arm with his sword above the side of the Inside Square, and his sword comes to rest, in such as way that it looses almost all it’s sense of feeling, Alexander steps forward and enters in, keeping his sword on top, moving his right foot from where it was at the Second Instance to just near the letter R, that is on the Diameter, then, lifting his sword up from the other, spins about on his right foot, swinging his left around until it comes to rest on the Circumference between W and X. He leans backwards above his bent right knee and straightens his arm to drive a thrust through his opponent’s head, as is shown. | Avant que Zacharie ait achevé cedit dernier mouvement, qui eſt d’avoir tourné le bras avec l’eſpee au deſſus le coſté du Quarré Inſcrit, & que ſon eſpee s’en affoiblit, en ſorte qu’il en pert quaſi tout le Sentiment; au meſme temps Alexandre s’avance & entre deſſus luy, en portant le pied droit depuis la Seconde Inſtance, où il eſtoit planté, juſques bien pres du Diametre, lettre R, & oſtant ſa lame de deſſus l’autre, pourſuit tout d’un train à faire la volte à l’envers avec le pied gauche, qui tombe en terre entre W & X deſſus la Circonference avec le corps panché à l’envers deſſus le meſme genouil plié, en donnant le coup d’eſtocade avec le bras eſtendu à travers la teſte de ſon contraire, comme il eſt repreſenté en leurs figures. |
| Circle No 4 | Cercle N.4. |
| This manoeuvre does not differ much from the preceeding, just that Zachary has merely turned his body and sword, without withdrawing his left foot backwards. | Ceſte operation ne differe guerres de la precedente, ſinon que Zacharie ſe contente icy de tourner le corps & l’eſpee tant ſeulement, ſans retirer le pied gauche en arriere. |
| Because Zachary has, in the 4th Circle, decided not to step backwards, but merely turned his feet towards the Diameter, it follows then that he has not withdrawn backwards, as it the previous Circle. Thereupon Alexander advances with his right foot a bit beyond the Center along the Oblique Diameter, yet continues to immediately spin about with his left foot. As soon as he finds himself inside the perpendicular line of his opponent’s sword, he leaves it there and, with an extension of his arm, delivers a thrust to the right side of his face. He turns his right foot, which is on the the Oblique Diameter, near the letter Q, to the outside, spinning his left foot around behind him, so that he sets his toes down beyond the Oblique Diameter a little bit before where the line V-W crosses the line S-X. He puts his wieght on his bent knee, and in this way he executes the final motion of the thrust through his adversary’s head, as it appears in the portrait of the figures. | Puis que Zacharie ſe contente en ce Cercle 4. de tourner ſimplement les orteils de ſes pieds en devant vers le Diametre, ſans retirer le pied gauche, il s’enſuit donc qu’il ne ſe recule pas tant en arriere, comme au Cercle precedent: là deſſus Alexandre s’avance avec le pied droit un peu outre le Centre ſur le Diametre oblicq, en continuant tout de ſuite à volter avec le pied gauche; & d’autant qu’il ſe retrouve par ceſt advancement au dedans des perpendiculaires de l’eſpee contraire, il la quitte, & luy porte avec extenſion du bras un coup d’eſtocade au coſté droit du viſage, en tournant le pied qui eſt planté ſur le Diametre oblicq en dehors bien pres de la lettre Q, & voltant le pied gauche à l’envers en ſorte, qu’il vient à deſcendre avec les orteils par delà le Diametre un peu plus avāt que l’entrecoupure de la ligne S X, ſe chargeant le corps deſſus avec le genouil plie, & en ceſte maniere il acheve la finale execution de l’eſtocade à travers la teſte de l’Adverſaire; comme il appert au pourtrait des figures. |
| Take note that, when the opponent turns his body and sword to the outside, above the side of the Inside Square, it is usual that his blade lose all sense of feeling, or at the least, that it naturally becomes very weak. That is when one must put these last to actions into practice, but taking great care to observe that, when there remains any small amount of force in his blade, to never disengage from it, but when you have previously set your right foot down on the ground, and that the left is being already drawn up to follow. But if your opponent has skill and finesse, and when he keeps the blades in contact with a vigourous ively, Strong, or Very Strong degree of force, such that will allow him to sense your intentions, then it is not at all advisable to disengage, because he would have the means to close the line against you. One must then apply the actions which are shown in the 2nd and 5th Circle, of which the latter explanation follows, below. | Notez, quand l’adverſaire ſe deſtourne le corps avec l’eſpee en dehors, au deſſus le coſté du Quarré Inſcrit, que c’eſt alors le plus ordinaire, que ſa lame en perd le Sentiment, ou à tout le moins qu’elle s’en affoiblit fort, d’autant que la Nature meſme l’y convie. Et c’eſt alors qu’il faut mettre ces dcux dernieres operations en pratique, en obſervant fort ſerieuſement quand il y reſte quelque petit ſentiment, de ne la quitter jamais, que vous n’ayez preallablement avancé & planté le pied droit en terre, & que le gauche ſoit deſia en aćte d’en continuer la pourſuite. Mais ſi le contraire y va par fineſſe, & qu’il laiſſe les lames accouplées en bonne Vigneur Vif, fort, ou plus fort, ce que le Sentiment vous fera cognoiſtre, alors il ne vous ſera nullement loiſible d’abandonner ſon l’eſpee, par ce qu’il auroit moyen de vous fermer la ligne, mais il y faudra appliquer les operations qui vous ſont monſtrées és Cercles 2. & 5. du dernier deſquels ſuit l’explication. |
| Circle No 5 | Cercle N.5. |
| Alexander, having missed his chance to work while his opponent was moving, or if he could easily be hit himself, maintains a reasonable sense of contact, he raises his left foot from where it was placed at the Second Instance, moves it smartly forward, and places it where the Diameter crosses the Inside Square, at the letter S, and, while casting his opponent’s sword aside, turns his left side forward and inside the perpendicular lines. | Alexandre s’ayant laiſsé eſchapper l’oportunité de travailler durant le mouvement de ſa partie adverſe, ou bien que l’attouchement luy raporte, qu’il retient un raiſonnable ſentiment, il eſleve le pied gauche du lieu ou il eſtoit planté à la Seconde Inſtance, l’avance tout bellement, le plante finalement en deça le Diametre ſur le quarré inſcrit devant la lettre S, & ſe met le coſté gauche du corps (en aſſujettiſſant l’eſpee contraire) un peu d’avantage au dedans les perpendiculaires |
| After Zachary has completed this movement, we see that he has turned his body with his sword above the line of the Inside Square. His opponent has failed to make a move against him while he did so, or perhaps did not wish to because he felt himself constrained by a sufficient amount of force, or finally, because he wished to allow him to perform this move. Alexander then begins to work from where he was at the Second Instance, he raises and slowly moves his left foot forwards, before he sets his foot back on the ground by moving his left side forward, he pauses briefly, taking great care to note the force of his opponent’s sword, or if he intends to try something else. But as he feels nothing, he sets his foot down on the ground within the Inside Square, with his toes in front of the letter S. moving his left side forwards and into the angle between the two swords, his body extended, knees straight, and right foot following a bit behind beyond the letter G, as is shown in the figure. | Apres que Zacharie à conduit ce mouvement à fin, aſſavoir qu’il s’eſt tourné le corps avec l’eſpee deſſus le coſté du Quarré Inſcrit; l’adverſaire ayant failli de travailler durant le meſme temps, ou ne l’ayant pas voulu faire pour ce que il ſentoit y eſtre conſervé un Poids raiſonnable, ou finalement qu’il luy ait voulu accorder de parfaire ſon intention: Alexandre pourſuit donc à travailler de la Seconde Inſtance où il eſtoit planté, il eſleve, & avance lentement le pied gauche, & avant qu’il le laiſſe toucher la terre par l’avancement du coſté gauche, il en fait une petite pauſe, prenant ſoigneuſement garde au Poids de ſon adverſaire, s’il vouloit taſcher d’aventure à faire autre choſe; mais puis qu’il ne ſe meut point, il plante le pied en terre au dedans du Quarré Inſcrit, avec les orteils devant la lettre S. entrant du coſté gauche au dedans de l’angle des deux eſpees, le corps eſtēdu, les genoux roides, & le pied droit traināt un peu apres outre la lettre G; comme il ſe voit en la figure. |
| Circle No 6 | Cercle N.6. |
| At the very moment when Alexander is entering into the angle with his left foot and side, at the point when he is just committed to moving forward, Zachary withdraws his left foot backwards, at the same time bending his arm and lifts the guard above his head, then moves his weight back onto his front foot, and gives his opponent an imbrocata thrust to the left side of his torso. | Cependant qu’Alexandre eſt en aćtion d’entrer avec le pied & coſté gauche au dedans de l’angle, à l’inſtant qu’il commence à tomber; Zacharie ſe recule en arriere, moyennant le pied gauche, ſe courbant au meſme temps le bras de l’eſpee avec la garde par deſſus la teſte, puis il recharge le corps ſur le pied de devant, & donne à ſon Contraire un coup d’imbrocade au coſté gauche de la poitrine. |
| This action proceeds from the previous, in the time that Alexander takes to enter with his left foot, just as his body is about to fall forwards. Zacharie withdraws his rear foot backwards. While bending his arm and raising his guard above his head, he shifts his weight onto his front foot and bends his wrist to aim his tip at his opponent’s left side, as his shown in the figures. | Ceſte operation procede en ſuite de la precedente, au temps qu’Alexandre fait l’intrade du pied gauche, iceluy eſtant en train de tomber enſemble avec le corps. Zacharie donc retire le pied de derriere, en hauſſant & courbant cependāt le bras de l’eſpee par deſſus ſa teſte, & en ramenant la charge du corps ſur le pied de devant, il aſſene ſa pointe en ligne courbe au coſté gauche de ſon Adverſaire; ſuivant la repreſentation des figures. |
| If Alexander were to make his move inside without a pause before he sets his left foot down, his opponent could easily hit him with this imbrocata. Thus it is absolutely necessary to take good care of what was noted in the previous Circle. And, in fact, it is the only reason we have shown you this danger. And now here follows the counter to this. | S’il advient qu’Alexandre face l’intrade ſans pauſer avant qu’il plante le pied gauche, l’Adverſaire le pourra fort facilement toucher de ceſte imbrocade. Dont il eſt tres-neceſſaire de prendre bonne garde à ce qui eſt annoté ſur le Cercle precedent. Et de fait, c’eſt la ſeule cauſe pourquoy nous en avons voulu vous repreſenter le danger devant les yeux: duquel il s’eſuit maintenant le Contraire. |
| Circle No 7 | Cercle N.7. |
| Zachary tries to perform the same imbrocata. Alexander turns his left side away to the outside, inverting his sword-arm so the guard, and particularly the interior branch of the cross-guard is turned up above the height of his head and aiming the tip of his sword at his opponent’s face. | Zacharie voulant donner encores la meſme imbrocade; Alexandre ſe deſtourne au meſme temps le coſté gauche en dehors, renverſant le bras de l’eſpee avec la garde & notamment la branche interieure en haut par deſſus la meſure de la teſte; en mettant ſa pointe devant le viſage du Contraire. |
| Here we see the same actions as in the previous circle, but in this case, as Alexander moves his left foot, before he sets it on the ground, he pauses briefly, as we cautioned before. Thus his opponent did no know when to begin to move to attack him in the same way as before, with a bent-arm because he could not instantly feel his move. To interrupt Zachary’s strike, he sets his foot down suddenly along the line M-S, while twisting to withdraw his left side, he leans back on his right leg. Keeping his arm straight, he turns the interior branch of his crossguard upwards above his head, so that he catches his opponent’s blade, and puts his sword-tip precisely in front of his face, needing only to execute the finish, as is shown by the figures. | C’eſt icy encores la meſme operation du Cercle precedent, toutesfois Alexandre en avançant le pied gauche, avant qu’il le laiſſe toucher à terre, il en a fait une petite pauſe, ſelon l’advertiſſement, que nous venons d’en donner. Dont ſa partie adverſe n’a ſceu commencer pluſtoſt à ſe mouvoir pour le bleſſer derechef en la meſme ſorte en ligne courbe, qu’il ne s’en ſoit apperceu tout au premier Inſtant par le ſentimēt: & pour luy rompre le coup, il met tout ſondainement le pied à terre ſur la ſećtion de la ligne M S, retirant enſemble le coſté gauche, & ſe panchant à l’envers ſur le pied droit avec le bras roide, en tournant & hauſſant la branche interieure de ſa garde plus haut que ſa teſte, de ſorte qu’il en enſerre la lame Contraire, & luy met la pointe par courtoiſie devant le viſage, ne tenāt qu’à luy d’en faire l’execution; comme il eſt repreſenté par les figures. |
| Note how Zachary has bent his arm to thrust his imbrocata, so Alexander bent his own arm to be able to defend against it, while at the same time attacking with his sword-tip inverted. | Notez comme Zacharie ſe courbe le bras en dehors, pour tirer ſon Imbrocade, qu’Alexandre courbe le ſien au contraire pour faire ſa defenſe, luy oppoſant au meſme temps la pointe renverſéé. |
| Circle No 8 | Cercle N.8. |
| This is a follow-on from Circle No 5. Alexander leans forward onto his front foot, leaving the other behind raising his heel so he rests on his toes. Then at the same time that he moves his left foot forward to the letter S, he seizes his opponent’s hilt. By disengaging the blades he moves his sword-tip against his opponent’s chest. | Ceſt icy une pourſuite du Cercle 5. Alexandre ſe va pancher ſur le pied de devant, en laiſſant trainer un bien peu l’autre apres ſur les orteils; ce qu’eſtant fait, il s’avance quand & quand le pied gauche avec le milieu ſur la lettre S, en faiſant prinſe de la garde contraire, moyennant le deſtachement des lames deſquelles il conduit la poinćte de la ſienne contre la poitrine de l’adverſaire. |
| This action follows on from Circle No 5 where Alexandre has entered into the angle between the swords, with his foot very close to the letter S. He then leans the left side of his body forward onto this left foot, and draws the other foot along behind. At the same time, he raises his left hand between, and as high as, the two swords, the same way as Alexandre does in Circle No 10. Having done this, he immediately skips his left foot over, so the middle is on the letter S, and and that the same time lifts his sword from the other so that he can grab the hilt from above, and pull it towards himself while turning the interior branch of the crossguard upwards. He draws his right foot up to where the line crosses the collateral G-M while at the same time holding the guard against his side with the crosspiece vertical and sets his sword-tip exactly against his opponents chest, as is shown in the figure. | Ceſte opearation procede en ſuite du Cercle 5. où Alexandre eſt entré dedans l’angle avec le pied gauche devant bien pres de la lettre S. Maintenant donc il ſe va pancher le coſté gauche du corps en avant ſur le meſme pied, en ſorte que l’autre traine un peu derriere, hauſſant au meſme temps le bras & la main gauche entre deux & à l’egal des eſpees, comme il eſt repreſenté par la figure d’Alexandre au Cercle N.10. Ce qu’ayant fait, tout à l’inſtant il s’avance le pied gauche comme en ſantelant avec le milieu ſur la lettre S, & à ce meſme temps il oſte ſon eſpee de deſſus l’autre, dont il fait prinſe de la garde par en haut, la tire à ſoy en tournant la branche interieure en haut, menant le pied droit en ſuite de l’autre juſqu’à l’entrecoupure de la collaterale G M. s’affermiſſant au meſme temps la garde contre les coſtes avec la branche interieure verticale, & la pointe preſantée par courtoiſie à la poitrine de l’adverſaire: comme les figures repreſentent. |
| During the time it takes for Alexander to perform this action, leaning over his left foot and raising his hand and arm ready to grasp the hilt, he must above all pay attention to the feel of the blades, so that he may immediately perceive if the force from his ennemy’s blade weakens, or if he begins to withdraw his blade, possibly moving his body backwards, as well. In which case, he could not effectively grab the hilt. On the contrary, he must instead move his right side forward with his arm and sword at the same time so as to hit his opponent’s face. | En ceſte operation au temp qu’Alexandre s’avance pour ſe pancher ſur le pied gauche, & qu’il hauſſe le bras & la main pour faire preparation de la prinſe, il faut qu’il obſerve ſur toutes choſes le Sentiment des lames, afin qu’il ſe puiſſe touſiours appercevoir à temps, ſi l’Ennemy n’affoiblit pas la ſienne, ou s’il ne la retire point en arriere, meſme avec reculement du corps. Car en ce cas là la prinſe de la garde ne pourra ſortir a effet. Au contraire il faut alors avancer le coſté droit, enſemble le bras & l’eſpee pour toucher au meſme temps au viſage. |
| Circle No 9 | Cercle N.9. |
| This is another follow-on from Circle No 5, which happens as soon as Alexander has begun to move his upper body forward onto his left foot. Zachary increases the force of his blade, to push Alexander’s aside as Alexander is bringing his right foot up behind. As soon as he realizes from the feel that his opponent’s blade will escape overhead out of his control, and thus will close off any approaches from the right side, he moves his left foot along the middle of the line of the Inside Square, where he puts his weight on his bent knee, and sets his sword-tip against his adversary’s right side. | C’eſt encor une autre pourſuite du Cercle 5. Dés qu’Alexandre commence à approcher la partie ſuperiure du corps en avant, pour ſe charger ſur le pied gauche; Zacharie augmente le ſentiment de ſa lame, en uſant de force pour tranſporter celle d’Alexandre, ſur quoy Alexandre approche durant le meſme temps le pied droit, & d’autant qu’il recognoiſt par le ſentiment, que la lame contraire s’en va luy eſchapper par deſſus, & icelle affermiſſant contre ſes coſtes au coſté droit, en marchant du pied gauche deſſus le milieu du Quarré Inſcrit, où il fait la charge du corps deſſus avec le genouil plié, en aſſenant ſa pointe au coſté droit de l’adverſaire. |
| This action also follows from Circle No 5. As soon as Alexander begins to move his left side and to lean over his left foot which is already set on the ground, his opponent increases the amount of force on his blade. Against this, Alexander at first resists, as he brings his right foot up behind him. But as his adversary continues to increase the force against his blade until it is enough to move them both to the side. Alexander recognizes from the feel that this force has become powerful enough, that if he suddenly lets them go, they will fly overhead and far off centre. So he quickly pulls his own blade off his opponent’s and presses his guard against his right side, while moving his left foot to the middle of the line N-X. He shifts his weight onto his left foot, then bends his knee while he moves his right foot in a circular motion to the letter M along the Perpendicular Diameter and at the same time wounds his opponent under the right armpit. This is shown by the figures. | Ceſte operation procede auſſi du Cercle 5. Des qu’Alexandre commēce à avancer le coſté gauche, pour ſe pancher ſur le meſme pied qui eſt deſia planté; en ce meſme temps ſon Contraire luy augmente le poids de ſa lame: à quoy Alexandre fait un peu de reſiſtence au commencement, en approchant le pied droit; mais puis que l’Averſaire continue à l’augmenter de plus en plus, juſqu’à uſer de force pour tranſporter les lames; & qu’Alexandre cognoiſt par le Sentiment, qu’ell s’en va forligner d’elle meſme par deſſus & outre ſa teſte, voire & qu’elle y fera un aſſez grand Angle; il la laiſſe enfuir, en oſtant & affermiſſant la ſienne a ſon coſté droit avec la garde, avançant enſemblement le pied gauche ſur le milieu de la ligne NX, où il ſe charge & pance le corps deſſus avec le genouil plié cependant, le pied droit pourſuit en forme circulaire, juſqu’au Diametre perpendiculaire, lettre M. & cependant il bleſſe ſa partie adverſe en l’aixelle droite; ſuivant la repreſentation des figures. |
| Circle No 10 | Cercle N.10. |
| This one also follows from Circle No 5. Here Zachary waits to see what happens. Alexander moves his left side forwards, at the same time that he lifts his right foot onto his toes, and draws it up behind him, he raises his left arm and hand level with and between the two blades, as is shown by the figures. | Voicy qui procede encor du Cercle 5. quand Zacharie en attend la pourſuite, Zacharie s’avance le coſté gauche du corps, entrainant quand & quand le pied droit apres ſur les orteils, & hauſſant au meſme temps le bras & la main gauche à l’egal & entre les deux lames; comme il eſt repreſenté en la figure. |
| Circle No 11 | Cercle N.11. |
| In this one, we continue on, where Alexander skips his left foot to the letter S, and, then he leans his body forward, in such a way that his right foot is raised up as it follows on. At the same time, he puts his hand over top of both blades and seizes his opponent’s hilt, as is shown by the figures. | Ceſt la continuation du precedent: où Alexandre s’avance par un petit ſaut avec le pied gauche ſur la lettre S, panchant le corps ſur le devant, en ſorte que le pied droit s’eſleve quand & quand en haut en ſuite de l’autre, & au meſme temps en portant la main par deſſus le long des deux lames, il fait prinſe de la garde contraire, commes les figures demonſtrent. |
| Circle No 12 | Cercle N.12. |
| Alexander continues the previous action, taking a large about-face step, swinging his already-raised right foot all the way around behind his adversary. He then leans back onto his right foot, raises his left fott, and pulls the guard that he is grasping in his hand upwards. Meanwhile, he presses his own guard gainst his right side, and the tip of his sword against the right side of his opponent, as can be seen by the figures in the image. | Alexandre pourſuit à continuer la precedente operation, voltant un grand pas à l’envers, avec le pied droit qui eſtoit j’à eſlevé, en ſorte qu’il le plante meſme derriere le corps de l’adverſaire, puis il ſe va pancher à l’envers ſur le meſme, en eſlevant le pied gauche, & attirant à ſoy vers le haut la garde qu’il tient en prinſe, affermiſſant cependant la ſienne au coſté droit, & ſa pointe au coſté droit de la poitrine de ſon contraire, comme il ſe voit aux figures. |
| Circle No 13 | Cercle N.13. |
| This is the final execution of the movement which follows from the preceeding actions. That is, Alexander steps forward, putting his left foot down in between his opponent’s feet, shifting his weight onto it, bending his knee, and leaning his body forward, while driving his thrust through his opponent’s body, as it is shown by the figures. | Ceſt la derniere continuation & execution en ſuite des precedēts: aſçavoir qu’Alexandre s’avāce, & entre avec le pied gauche vers le contraire, juſqu’à le planter entre les deux pieds d’iceluy, en faiſant la charge deſſus avec le genouil plié & le corps panché de meſme, & donnant par meſme voye le coup d’eſtocade à ſon homme à travers le corps; ainſi qu’il appert aux figures. |
| What is most noteworthy and special in this Plate as compared to the others, is the maner of putting oneself in between the angles, on which the moves which follow depend. Inasmuch as there are an infinite number of possible opportunities and it is impossible to show each and every variation of sequences, in any case, it is quite certain that Zachary will not know of any way to counter against any move which is similar to the the ones shown here. As soon as he opens the angle, however much or little, as long as there is an angle, Alexander should be ready to enter in, not to throw himself recklessly in do-or-die desperation, but with prudence, and with such sensibility, that his adversary cannot make the least move, without his being fully aware of it, so that he can unrestrainedly hit with a mortal blow, as shown in Circles No 3 & 4. Even if he has created an opening by pushing with his blade, Alexander does not step in with either his right or left foot, unless the opening is large enough and he can see a sufficient opportunity. This he does nonetheless with the same adroitness and care as before, being very careful above all, not to throw away the advantageous position he worked to gain, with an ill-advised rush. And after he has stepped, in, before he puts his advantage to effect, either by seizing his opponent’s guard, or by executing a strike, he always takes the same care. In sum, he is never in haste, but waits until his preparations are complete and he is ready to put an end to this undertaking, as long as he keeps the true timing, so that the opportunity does not escape from him, nor does he act too soon and thus do all his work in vain. When he proceeds deliberately, he is better able to be on his guard, and his adversary can do nothing that cannot be easily interrupted, nor can his adversary do anything much to disrupt him, and he himself is always able to change his actions, according to the situation. | Ce qui eſt le plus notable & ſpecial en ce Tableau preſent par deſſus les autres, c’eſt la maniere de ſe mettre dedans les angles, avec les ſuites qui en dependent. Car encores que les occaſions ſoyent infinies, & qu’il ſoit impoſsible de repreſenter touts les changements qui pourroyent ſurvenir un à un, toutesfois il eſt certain que Zacharie ne ſçauroit rien pratiquer en telle occaſion avec eſpees touchantes, qui ne puiſſe aiſement ſe raporter à ces meſmes leçons que nous en avons propoſées. Car dés qu’il ouvre l’angle, ſoit grand, ſoit petit, moyennant que ce ſoit un angle, Alexandre ſe prepare pour y entrer, non pourtant qu’il ſe precipite là dedans à corps perdu, comme pour mourir ou vaincre à la deſeſperade. Mais c’eſt avec prudence, & avec telle obſervation du Sentiment, que l’adverſaire ne peut faire à la moindre faute à l’obſerver pareillement de ſa part, qu’il n’en ſoit incontinent touché d’une mortelle atteinte, comme il ſe voit és Cercles 3. & 4. Et meſme apres qu’il l’aura ouvert avec bon ſentiment, Alexandre ne laiſſe pourtant de s’y loger dedans avec le pied droit ou gauche devant, ſelon que l’ouverture eſt grande & l’opportunité qu’il en trouve. Ce qu’il fait cependant avec la meſme adreſſe & circonſpećtion qu’auparavant, ſe gardant ſur tout de prodigner ſes mouvements par une viſteſſe mal adviſée. Et apres qu’il eſt entré dedans, avant que de mettre l’advantage en œvre, ſoit à faire prinſe de la garde contraire, ou execution de pointe ou de taille, que ce ſoit touſiours avec la meſme prudence. Somme, que jamais il ne ſe haſte juſqu’à tant que toutes les preparations ſoyent faites, & qu’il ſoit venu ſur le point de mettre fin à l’entreprinſe. Si lors s’en eſt le vray temps, afin que l’occaſion ne luy eſchappe hors des mains, non point devant afin qu’il ne ſe travaille en vain. Car quand il y va lentement, il eſt mieux ſur ſes gardes, & n’y peut rien arriver de par l’Adverſaire qui le puiſſe grandement mettre en deſordre, par ce qu’il ne fait rien luy meſme qu’il ne puiſſe touſiours changer à temps, quand l’occaſion ſe change. |
| Translation by Bruce G. Hearns |
Transcription by Bruce G. Hearns |
|---|---|

| |
| EXPLANATION OF THE ACTIONS IN THE TWELFTH PLATE. | DECLARATION DES OPERATIONS DV TABLEAV DOUZIEME. |
| We follow here, in this twelfth plate, the example of those who are concerned with fortifications. After they have taught to their students the form of ideal designs, they then briefly show them how, in practice, these must be adapted to the particulars of each place. Moreover, it is impossible to have site exactly one would wish. Thus, we do the same for our System, because we have already explained the manner of entering into the sword-angles, which is one of the points of the greatest importance, we shall now show the versatility of this move and the multiplicity of circumstances in which the scholar can prevail. Such contemplation will be very useful and very easy for them, considering the small number of precepts to keep in mind on which we can build, and which dominate even against the most unusual moves. To do this, we propose to examine a few particular examples, where Zachary opens up the angle in diverse ways, of which none are particularly strange. And in fact he allows opportunities of all sorts. Some ones which consist of a simple defence, others which include attempts to attack. At some times he will completely open up the angle, at other times he will do no more than prepare to. But all with such moves as he hopes will will create confusion by their novelty. But why, then, do this? These situations are useless to learn, because they are so rare, you say? On the contrary, the strangest situations are those that are most necessary to learn. For your enemy will not fail to perform any strange action, if he thinks it will confuse and confound you. Furthermore, whether or not he performs these moves with the same intent and the same follow-on exactly as we show here, nevertheless, you will find yourself often enough in similar situations such as these by chance one way or another. Therefore, be prepared for everything. For in the practice of Arms, after a mistake is made, there is neither valid excuse nor available recovery. | Nous enſuivons en ce Tableau XII. l’exemple de ceux qui traitent les matieres des fortifications. Car apres qu’ils ont enſeigné les figures regulieres, ils ſe contentent de monſtrer briefvement à leurs diſciples, qu’en la Pratique il les faut accommoder ſelon les particularitez de chaſcune place; d’autant qu’il eſt impoſſible de les avoir touſiours à ſouhait. Ainſi donc pour faire le meſme en noſtre Exercice, puis que nous venons de declarer la maniere d’entrer dedans les angles, qui eſt un de points de plus grande importance; monſtrons maintenant combien l’uſage en eſt ample, & comme l’Eſcholier s’en pourra prevaloir en pluſieurs occurrences. Contemplation qui luy ſera tresutil, & tresaggreable, conſiderant que le petit Nombre de ſes preceptes eſt baſtant à tenir en devoir voire & à dompter meſme des mouvements ſi extraordinaires. Pour ce faire nous propoſerons icy quelques particularitez d’exemples, ou Zacharie luy fait l’ouverture de l’angle en diverſes manieres, & aucunes d’icelles bien eſtranges. Et de fait il luy en donne des occaſions de toutes ſortes; les unes qui conſiſtent en ſimple defenſe, les autres conjointes avec intention d’offenſer; tantoſt il ouvre l’angle tout à fait, tantoſt il n’en fait que la ſeule preparation; le tout avec de tels mouvements, qu’il eſpere luy en troubler le jugement par la nouveauté meſme. Mais quoy donc? Direz vous, ce ſont des occaſions inutiles, pour ce qu’elles ſont rares? Au contraire, le plus eſtranges ſe ſont les plus neceſſaires. Car l’Ennemy ne manquera pas à faire une aćtion eſtrange, s’il penſe qu’il vous en mettra en deſordre; & d’autrepart combien qu’il ne les face pas avec la meſme intention, & en la meſme ſuite qu’elles ſont icy repreſentées, toutesfois on ſe retrouve aſſez ſouvent en telles & ſemblables ſituations par les changements des occaſions de part & d’autre. Soyons donc preparez à tout. Car au fait des Armes, apres que la faute eſt commiſe, il n’y a ny remede ny excuſe valable. |
| Circle No 1 | Cercle N.1. |
| Alexander, has subjugated his opponent’s sword at the Second Instance, has stepped with his foot to the Third, in such a way that his left foot is in the process of following along, with the intent to wound his opponent with the length of his blade. At this very moment, Zachary turns his right side to the outside, raising his arm and sword to an obtuse angle above the Inscribed Square X-N, holding it with some force. Alexander sees this, he allows his own tip to rise up, lowering and closing his elbow against his side, and setting his left foot on the ground inside the Quadrangle at the letter O. | Alexandre ayant ſujetté l’eſpee contraire à la Seconde Inſtance, & puis marché avec le pied droit à la Troiſieme, en ſorte que le pied gauche eſt deſia en train à pourſuivre l’autre, avec intention de bleſſer le Contraire au long de ſa lame; en ce meſme temps Zacharie ſe deſtourne le coſté droit en dehors, hauſſant le bras & l’eſpee en angle obtus au deſſus le coſté du Quarré Inſcrit X N, retenant le poids en force. Dequoy s’appercevant Alexandre il laiſſe aller au meſme temps ſa pointe contremont, en abaiſſant & affermiſſant la coude à ſon coſté, & mettant le pied gauche à terre dedans le Quadrangle à la lettre O. |
| After Alexander has subjugated his opponent’s blade moving from the First to the Second Instance along the Diameter at G, and taken a step with his right foot along the side of the Inside Square to the letter N, intending to slide the point of contact up his opponent’s blade to give him a thrust to the face, he draws his left foot along the path following the other. At this time, Zachary turns his toes forward towards the diameter, without leaving his Quadrangle, in such a way that his right side is withdrawn a quarter turn, bringing his extended arm with his sword up into an obtuse angle along the side of Inscribed Square, X-N, with some force, so that the thrust to the face which his adversary had thought to give him is diverted aside. At the same time, Alexander drops his arm and guard down, while his sword-tip comes up, and he closes his elbow against his right side to protect himself, and he sets his left foot down inside the Quadrangle at the letter O, while keeping his body erect. This is shown by the figures. | Apres qu’Alexandre a ſujetté l’eſpee contraire, de la Premiere Inſtance à la Seconde au deça le Diametre lettre G. & ayant conſequemment cheminé avec le pied droit par la trace du Quarré Inſcrit juſqu’à la Troiſieme à la lettre N, pour en graduant l’eſpee contraire luy donner une eſtocade au viſage, dont le pied gauche eſt deſia en train de cheminer apres l’autre : à ce meſme temps Zacharie ſe tourne les orteils en devant vers le Diametre ſans bouger de ſon Quadrangle, en ſorte que le coſté droit du corps s’en retire à quartier, menant le bras eſtendu avec l’eſpee en haut en angle obtus au deſſus le coſté du Quarré Inſcrit X N avec poids de force; de façon que l’eſtocade, que l’adverſaire luy penſoit donner au viſage, en eſt divertie : Au meſme temps Alexandre s’abaiſſe le bras & la garde, & avec la pointe dreſſée contrement il ſe l’affermiſt coſté droit pour defenſe de la partie inferieure de ſa perſonne, mettant enſemblement le pied gauche à terre, dedans e Quadrangle à a lettre O, avec le corps eſtendu; comme les figures demonſtrent. |
| Circle No 2 | Cercle N.2. |
| Alexander raises his right foot in the air, while forcing his opponent’s sword down a little, which (while setting his foot down on the ground before the letter S) he subjugates it, turning his left side forward, and leaning his body even further forward on the same foot inside the angle, while simultaneously drawing his left foot along up to the letter N. | Alexandre eſleveant le pied droit en l’air, abaiſſe enſemble quelque peu l’eſpee de ſon Contraire, laquelle (en plantant le meſme à terre devant la lettre S) il aſſujettit, avançant le coſté gauche, & panchant du corps ſur le devant encores ſur le meſme pied au dedans de l’angle, entrainant quand & quand le pied gauche derriere juſqu’à la lettre N. |
| As soon as Alexander has completed the preceeding action, he pauses briefly, so as to see if his adversary will try to work against him, so he can counter it. But as soon as he sees him waiting, he follows on, moving forward and raising himself with his right foot while lowering the swords with his sense of contact and likewise turning his left side forward, in such a way that the instant his foot lands on the ground in front of the letter S, and his weight comes down on it, he subjugates his opponent’s blade, then leans his body onto the forward foot, drawing his left foot along behind up to the letter N. Thus he puts himself inside the angle of the swords, and inside the lines of his ennemy; As is evident in the portrait of the figures. | Alexandre dés qu’il à parachevé l’aćtion precedente, fait une petite pauſe, afin que ſi l’adverſaire taſche d’avēture à travailler deſſus, il y puiſſe donner order. Mais quand il le voit attendre, il pourſuit, en avançant & hauſſant le corps avec le pied droit, & abaiſſant enſemble un peu les lames au rapport du Sentiment, avec pareil advancement du coſté gauche; en ſorte qu’à l’inſtant que le corps deſcend, & que le pied droit tombe à terre devant la lettre S, il aſſujettit l’eſpee de l’adverſaire, ſe panchant du corps ſur le devant, & entrainant le pied gauche derriere juſqu’au point N. Dont il ſe met par ainſi dedans l’angle, & au dedans des perpendiculaires de l’ennemy; comme il eſt evident au pourtrait des figures. |
| Circle No 3 | Cercle N.3. |
| Alexander continues the movement by leaning further forward, while raising his left hand between them over the swords. Then, he simultaneously moves forward, shifts his weight entirely onto his right foot, raises his left foot, reaches his left hand above the blades to seize the whole of his opponent’s guard and moves his left side leaning still further forward, as we see portrayed in the figure. | Alexandre continuant l’operation encommencée, ſe panche un peu davantage, hauſſant tout d’un temps en avant ſa main gauche entre deux & à l’egal des lames, puis il s’avance quand & quand en ſautant du pied droit, eſlevant en ſuite le pied gauche, & prenant enſemble par deſſus le long des lames la garde du Contraire avec ſa main gauche, le coſté gauche du corps panché encor davantage; ainſi qu’on le voit pourtrait en la figure. |
| Circle No 4 | Cercle N.4. |
| Alexander follows on from the previous movements, stabbing his opponent’s right side with the sword-tip. | Alexandre pourſuit les operations precedentes, donnant à ſon contraire un coup de pointe au coſté droit par le fil de ſa lame. |
| Here the movement carries on, where Alexander suddenly takes his already raised left foot and makes a sudden large circular step outside the Circle, off to the side of his opponent. This he follows with a similar very quick circular move of his right foot, in a volte, taking a large step behind his left foot, he traps his opponent’s sword as he turns his opponent’s hand and pushes the guard away, which creates the opening to stab his opponent’s right side along the line of the blade, as his shown in the figure. | Ceſt encor la continuation du precedent, ou Alexandre pourſuit ſoudainement à faire un grand pas circulaire avec le pied gauche, qui eſtoit deſia eſlevé, au dehors du Cercle à coſté de l’adverſaire; pourſuivant pareillement en cercle avec l’autre pied, aſſavoir le pied droit, qu’il avance & volte de pareille viſteſſe, faiſant un grand pas derriere le pied gauche, pouſſe & tourne cependant le bras & la garde contraire au loing, & luy donne par le fil de la lame un coup de pointe au coſté droit; comme il eſt repreſenté en la figure. |
| Circle No 5 | Cercle N.5. |
| Alexander completes the final execution of the movement by pushing his thrust with full force through his opponent’s body. | Alexandre faiſant la finale execution pouſſe ſon eſtocade au travers le corps de ſon Contraire de pleine force. |
| This is the final follow up to the previous moves, done by Alexander immediately raising his left foot and stepping into his opponent, putting his weight down on it, and thereby pushing his thrust with full force through his opponent’s body. | C’eſt la derniere ſuite de la continuation precedente, fait par Alexandre en eſlevant tout à l’inſtant & avançant le pied gauche devers ſon Contraire, en faiſant la charge du corps deſſus, & luy pouſſant par ainſi l’eſtocade à travers le corps de pleine force. |
| Circle No 6 | Cercle N.6. |
| This action stems from Circle No 1, in the case when his opponent puts more force behind his blade. Thus Alexander continues to work against his opponent, taking a large, deliberate step straight forward with his right foot, moving his body in closer to his sword, and being very attentive to the feel, so to be aware if perchance his opponent comes to change the force he is using and so change the resuting actions as well. | Ceſt aćtion prend ſon origine du Cercle 1. à condition, qu’il y ait plus de poids en la lame contraire. Dont Alexandre pourſuit à travailler, en faiſant un grand pas tout droit en avant lentement avec le pied droit, s’approchant le corps plus pres de ſon eſpee, & prenant fort ſerieuſement garde au ſentiment, ſi daventure le Contraire venoit à changer le poids, pour changer auſſi l’operation. |
| Circle No 7 | Cercle N.7. |
| This continues from the preceeding Circle, where Alexander takes a further large, deliberate step with his left foot, straight forwards, out beside his adversary. After which he raises his right foot and brings it up near to the left one. As he feels that his opponent’s sword still resists with the same degree of force, he turns on the ball of his left foot, to face him. | C’eſt la continuation du precedent, ou Alexandre marche encor un autre grand pas tout droit en avant & lentement avec le pied gauche à coſté de l’adverſaire; pourſuivant apres à eſlever & avancer le pied droit, lequel il joint tout pres de l’autre; & comme il ſent que la lame contraire continue encor au meſme poids, il ſe tourne ſur le pied gauche qui eſt planté tout droit contre luy pour le regarder.
|
| Circle No 8 | Cercle N.8. |
| Alexander carries on the preceeding actions and, entering in towards his opponent, he aims the tip of his blade into his right side, thrusting with full force. | Alexandre pourſuit les operations precedents, & entrant devers le Contraire luy aſſene ſa pointe au coſté droit, l’executant de pleine force. |
| Continuing to feel the same degree of force against his blade, Alexander carries on his actions, disengaging the swords (so the other passes over his head) and at the same instant he enters in towards his opponent with the right foot, which was raised and ready, while aiming his sword-tip at the right side, and then driving it in with full force and his body leaning behind it, in accordance with the figures. | Continuant le meſme Sentiment des lames, Alexandre pourſuit l’operation, en deſtachant les eſpees (dont l’eſpee contraire luy paſſe par deſſus la teſte) & au meſme inſtant il entre devers le Contraire avec le pied droit, qui eſtoit deſia preparé, luy aſſenant la pointe au coſté droit, & l’executant à pleine force avec le corps panché de meſme; le tout en conformité des figures. |
| Circle No 9 | Cercle N.9. |
| Alexander has finished the actions of Circle No 1, and sees his adversary increase the degree of force resisting his blade. After he releases the sword to fly overhead, he wounds his opponent in the right side with his sword-tip. | Alexandre ayant achevé les operations du Cercle 1. voyant que l’adverſaire luy reſiſte en augmentant le poids, apres avoir laiſſé eſchapper l’eſpee contraire il le bleſſe d’un coup de pointe au coſté droit. |
| This is an action which follows from Circles 1 & 2. Alexander has finished the movement in Circle 1. to the point where he has raised his right foot intending to force down and subjugate his opponent’s blade, as in Circle 2. His adversary resists by greatly increasing the degree of force against his blade, enough to move the swords back. To which Alexander lifts his sword from on top, allowing the other to fly freely overhead from the intensity of the force, and at the same time enters in to the angle, by advancing his right foot, which he sets down where the line crosses the segment S-X. He wounds his opponent’s right side by a strike with his sword-tip and finishes the move with his body leaning forward, and left leg drawn up appropriately behind him, as his shown in the figure. | C’eſt icy une operation qui procede en ſuite des Cercles 1. & 2. Alexandre ayant achevé celle du Cercle 1. apres avoir eſlevé le pied droit pour abaiſſer, & conſequemment pour aſſujettir l’eſpee contraire à l’exemple du Cercle 2. l’Adverſaire luy fait reſiſtance, en augmentant le Poids, & uſant de force pour tranſporter les lames. Qui fait qu’Alexandre en oſte ſon eſpee de deſſus, laiſſant enfuir l’autre, qui luy paſſe outre la teſte par la vehemence de la force, & entrant au meſme temps dedans l’angle par advancement du pied droit, qu’il plant à la ſećtion de la ligne S X, il le bleſſe d’un coup de pointe au coſté droit, & en fait la finale execution avec le corps panché en avant, le pied gauche trainant proportionnellement derriere; comme il eſt repreſenté au pourtrait de ſa figure. |
| Circle No 10 | Cercle N.10. |
| Zachary resists by increasing the force against his blade. Alexander slides the point of contact down the blade to prepare the next move. | Zacharie faiſant reſiſtance hauſſant le poids des lames, Alexandre deſgradue les lames & ſe prepare à l’execution ſuivante |
| This action likewise begins from Circle 2, in which Alexander is shown lowering and subjugating his opponent’s blade. Against which Zachary has tried to resist by raising and increasing the force against the blade, however, with a little less than in the previous Circle. So Alexander leans a bit further forward, while making a quick step with his right foot up to the letter S, and with his left hand seizes his opponent’s guard, then slides the point of contact down along the entire length of the blade in such a way that he pulls away as he keeps his grip on the guard, holding it out to the left. He turns his right side forward, raising his left foot, and raises his opponent’s guard up high, while turning the tip of his own blade away behind his back. Thus, he is prepared to perform the following moves, as we can see him making ready in the image. | Ceſte operation prend ſemblablement ſon origine du Cercle 2. auquel Alexandre eſt repreſenté abaiſſant & aſſujettiſſant la lame cōtraire: à quoy Zacharie à voulu faire reſiſtance, en hauſſant & accroiſſant le poids des lames, toutesfois avec un peu moindre effort, qu’au Cercle dernier precedent. Dont Alexandre ſe panche un peu davantage, faiſant au meſme temps avec le pied droit un petit ſaut en avant à la lettre S, & avec la main gauche prend la garde contraire, enluy deſgraduant la lame entier, de ſorte qu’il ſe retire & s’affermit le bras de l’eſpee avec la garde au coſté gauche, en tournant le coſté droit devant avec le pied gauche eſlevé, pouſſant enſemblement ſon bras gauche, qui tient l’eſpee contraire en haut, & conduiſant la pointe de la ſienne contremont par derriere le dos. Voilà comme il s’eſt preparé le corps pour venir conſequemment à l’operation ſuivante; comme on l’y voit tout appreſté en la figure. |
| Circle No 11 | Cercle N.11. |
| This follows on from the last. Alexander, leaps with a large, circular, forward step with his left foot outside the Circle to a point almost behind his adversary, to whom he gives, by leaning forward with his body and bringing his right foot smoothly around through the air in circular motion, setting it down behind the other, a reverse cut to the thick part of his opponent’s left leg, while pressing his opponent’s arm and sword down and pinning them against his left side, as is portrayed in the figure. | C’eſt la ſuite du prēcedent. Alexandre ſaute avec le pied gauche un grand pas circularement en avant au dehors du Cercle à peu pres derriere l’adverſaire; auquel il donne (en panchant du corps ſur le devant, & continuant à mener circulairement le pied droit en l’air derriere l’autre) un coup de revers au gras de la jambe gauche, pouſſant enſemblement vers le bas le bras & l’eſpee contraire, laquelle il s’affermiſt à ſon coſté gauche; ainſi qu’il eſt pourtraićt en la figure. |
| Circle No 12 | Cercle N.12. |
| Alexander continues with the same sequence. He suddenly moves backward and sets his foot down right behind himself, then rocks back onto it, leaning backward and lifing his left foot. As he does, he pulls his opponent’s hand and sword off to his left, and draws his own sword back to his right side, as we see represented in the figure. | C’eſt la continuation de la meſme ſuite, faite par Alexandre, en retirant & plantant ſoudainemēt le pied droit en arriere, ſur lequel il ſe redreſſe & ſe panche à l’envers, en eſlevant le pied gauche, & retirant à ſoy le bras & l’eſpee contraire, meſme auſſi la ſienne, laquelle il conduit à coſté de ſa perſonne à main droite, la pointe tournée vers le bas; comme on le voit repreſenté à la figure. |
| Circle No 13 | Cercle N.13. |
| Here, Alexander executes his strike, and pierces his oppnent with a straight arm through the body. | Alexandre execute icy ſon coup, & perce ſa partie d’un bras roide au travers du corps. |
| And here is the final move. Alexander steps with his left foot forward into his opponent, & leaning his body, he drives his sword, with a straight and extended arm, through his opponent’s body. | En voicy le finale execution. c’eſt qu’Alexandre marche avec le pied gauche deſſus ſon homme, & en panchant le corps de meſme, il luy pouſſe d’un bras roide & eſtendu l’eſpee au travers du corps. |
| Circle No 14 | Cercle N.14. |
| Alexander subjugated his opponent’s sword. Zacharie tries to wound his opponent by disengaging his blade. Alexander perceives this move and swiftly follows, sliding his tip along and again subjugates it. | Alexandre ayant aſſujetti l’eſpee contraire, Zacharie taſche de bleſſer ſa partie en deſtachant ſa lame, Alexandre s’en apercevant le pourſuit vivement & graduant ſa pointe l’aſſujettiſt derechef. |
| Alexander has previously subjugated his opponent’s sword at the Second Instance at the letter G, along the Diameter, according to our precepts and required form. Zachary tries to circularly disengage his blade, which is subjugated underneath the guard, and raise it over Alexander’s, to wound him from above his arm. Alexander feels it is about to disengage, follows it quickly before that can happen, turning it down and outside of the intended path. He does this with his wrist, turning and sliding the point of contact up to the centre of his opponent’s sword, so it cannot escape, at least until the two swords have been raised up at an obtuse angle. Then, with his body upright, he enters in with his left foot forward as he again slides the point of contact up the sword to dominate his opponent’s sword, setting his foot down on the Diameter at the letter Q, bearing the weight of his body on it, over his bent knee, inside the perpendicular lines, as it appears in the figure. | Alexandre ayant preallablement aſſujetti l’eſpee contraire à la Seconde Inſtance lettre G, au deça du Diametre, ſelon les preceptes & en la forme requiſe. Zacharie taſche à luy paſſer circulairement ſa lame, qui eſt aſſujettie par deſſous la garde, pour bleſſer par deſſus le bras. Dont Alexandre, qui recognoiſt au Sentiment, qu’elle commence à ſe vouloir deſtacher de la ſienne, la pourſuit vivement avant qu’elle ſe ſoit delivrée, en tournoyant par le bas & en dehors la meſme chemin q’uelle s’en alloit prendre; ce qu’il fait avec le poignet de la main, tournant & graduant ſa pointe un peu devers le Centre de l’eſpee contraire, afin qu’elle ne luy puiſſe eſchapper, juſqu’à tant que les deux eſpees ſoyent conduites en haut en angle obtus; Lors il entre avec le corps eſtendu, le pied gauche devant, en faiſant derechef deſgraduation en aſſujettiſſant l’eſpee contraire, & plantant le meſme pied au deça le Diametre à la lettre Q, menant la charge du corps deſſus ayant le genoil plié, au dedans des perpendiculaires, ainſi qu’il paroit à la figure. |
| This same action can be done, even if Alexander has not yet done more than set his right foot down at the Second Instance, before his left foot has come into place, and the subjugation of his opponent’s blade is but half done. However, in this latter case, one will not have the leisure to set the left foot down at the Second Instance, before one must increase the size of his step, and move in one up motion to the letter Q, keeping in mind all the same particulars as above. | Ceſte meſme operation ſe pourra pratiquer, moyennant qu’Alexandre n’ait encor planté que le pied droit à la Seconde Inſtance, avant que le gauche y ſoit arrivé, & que l’aſſujettiſſement ne ſoit qu’à demi fait. Toutsfois en ce dernier cas on n’aura pas le loiſir d’aller planter le pied gauche en terre à la Seconde Inſtance, ains il faudra en aggrandir la demarche, & entrer tout d’un train juſqu’à la lettre Q, en obſervant touſiours le meſmes particularitez que deſſus. |
| Circle No 15 | Cercle N.15. |
| This is the follow-on from the preceeding action. Alexander momentarily raises his left foot, making little or no forward motion. He leans on it, moves his left side forward, at the same time disengaging his sword, and seizing hold of his opponent’s guard with his left hand, which he pulls towards himself. He puts the tip of his sword on his adversary’s right side, as the figures demonstrate. | Voicy une ſuite de l’operation precedente. aſſavoir qu’Alexandre eſleve tout à l’inſtant un peu le pied gauche avec peu ou point d’avancement, ſe panchant deſſus, le coſté gauche du corps avancé, en deſtachant au meſme tēps les eſpees, & faiſant prinſe de la garde contraire avec ſa main gauche, laquelle il retire à ſoy, en aſſenant ſa pointe au coſté droit de l’edverſaire; comme les figures demonſtrent. |
| In this action, which proceeds from Circle No 14, where Alexander held his opponent’s blade subjugated with his left foot forward, he follows in Circle No 15 by disengaging the swords while at the same time seizing his opponent’s guard. Note that he could also do the step in with his right foot, and performing the consequent seizure and follow-on without disengaging the blades, as shown in Circles No 2, 3, 4, and 5. | En ceſte opration precedente du Cercle 14, où Alexandre tient l’eſpee contraire aſſujettie avec le pied gauche devant; laquelle il a pourſuivie au Cercle 15. en deſtachant les eſpees, & faiſant au meſme temps prinſe de la garde contraire. Notez qu’il peut auſſi pratiquer la meſme intrade avec le pied droit, en faiſant conſequemment la prinſe avec le ſuite annexées ſans quitter les lames en conformié de ce qui eſt repreſenté es Cercles 2. 3. 4. 5. |
| This is similar to Circle No 2, when Alexander had his right foot forward, but in any case, nothing impedes him from following on as from Circle No 14 disengaging his sword, seizing his opponent’s guard, and giving his a thrust in the stomach, as is shown in Circle No 15. | Semblable eſt du Cercle N.2. combien qu’Alexandre y ait le pied droit devant, toutesfois rien n’empſche qu’il n’en puiſſe auſſi tirer la ſuite du 14. en deſtachant les eſpees, à faire prinſe, & luy preſenter l’eſtocade à la poitrine; comme il eſt monſtré au Cercle N.15. |
| The usefulness of seizing the space inside the angle is so obvious, it should require no further proof. Anyone who has entered inside will always have twice the advantage, with regard to timing and distance. For he cannot be hit in a single beat, because he has passed the tip of his opponent’s sword, yet he has not given up the ability to attack however he wishes to. And if his enemy begins to draw back his sword to thrust, he can feel it and wound his enemy before he can pull it far enough, because he is in position, and outside his enemy’s line, and thus has the advantage. Also, note that those who fence in the old style, because they know no better, try to open up the angle, to beat the opposing sword aside. What we do with our sword, they want to do with their left hand. But this is their fault, because, since they always remain face to face against their opponents in a straight line, how is it possible for them to safely open up the angle, when we consider how this is the opposite of the direct line, and cannot happen except when one line crosses the other. This is why they do not know how to engage their enemy’s swords without uncovering their own side at the same time. That is why Alexander always approaches by moving to the side. Because he knows his enemy does not know how to parry the slightest strike without creating an angle. But if he does not create a large enough opening for them, there is nothing that stops him from executing his strike. And if not, he only needs to step inside the angle. | L’uſage de ſaiſir les angles eſt ſi manifeſte, qu’il n’en faut pas demander des preuves. Car celuy qui eſt entré dedans, a touſiours double avantage au regard du temps & de la meſure. Dont il ne peut eſtre touché au Premier Inſtant, par ce qu’il a paſſé la pointe contraire, & pourtant il ne laiſſe pas d’avoir la commodité luy meſme de travailler à touts moments, ſi bon luy ſemble. & ſi l’Ennemy commence à vouloir ramener ſa pointe, il a le ſentiment qui l’advertit de le bleſſer au meſme temps avant qu’il en ſoit venu à bout de ſorte qu’il a l’ennemi en preſence, eſtant luy meſme dehors, tant il a d’avantage. Auſſi voit on que ceux qui tirent à la veille mode, à faute de ne ſçavoir mieux, ils taſchent d’ouvrir les angles pour battre l’eſpee contraire. Ce que nous faiſons avec l’eſpee meſme, ils le veulent faire avec la main gauche. mais c’eſt leur faute. car puis qu’ils demeurent touſiours viz à viz de leurs contraires en ce droite ligne, comment leur ſeroit il poſſible de bien ouvrir les angles, conſideré que l’angle ceſt tout le contraire de la ligne droite, & qu’il n’y en a peut avoir, ſinon que l’une des lignes ſoit miſe en travers de l’autre. Et c’eſt la cauſe pourquoy ils ne ſçauroyent engager les eſpees des Ennemis, qu’ils ne ſe deſcouvrent auſſi de leur coſté pareillement. Voilà donc pourquoy Alexandre a fait touſiours ſes approches en allant de travers. Pour ce qu’il ſçait que l’Ennemi ne ſçauroit parer le moindre coup ſans faire angle. Car s’il ne fait point aſſez d’ouverture, il n’y a rien qui l’empeſche de faire l’execution; & ſi au contraire, il ne tient qu’à luy d’entrer dedans l’angle. |
| Translation by Bruce G. Hearns |
Transcription by Bruce G. Hearns |
|---|---|
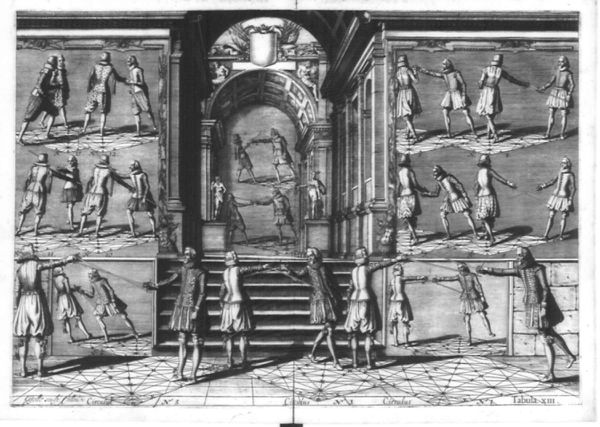
| |
| EXPLANATION OF THE ACTIONS IN THE THIRTEENTH PLATE. | DECLARATION DES OPERATIONS DV TABLEAV TREIZIEME. |
| It could be that, instead of presenting his sword in a direct line posture, as was performed by Zachary in the preceeding plates, he changes his approach, and presents to you in the way shown here, in Plate XIII, Circle No 1, not moving far from the same posture, except that he holds his hand a little higher, and his tip little lower. In such a way that he can only see his blade through his guard. In this case, it is inadvisable to try and contact his blade according to the previous instructions, to carry it over and subjugate it at the Second Instance. This is because it would be impossible to do without uncovering the upper part of one’s own body far too much. Which is why, to address the problem of carrying the blade away from this position, refer to the instructions in Plate XIX. For the present, I shall show you how you may thrust against this posture, along his blade, and hit under his arm, where he is the most vulnerable. This is because the shoulder, face, and chest remain covered by the wall made by his guard. Thus, in order to avoid the strong of his blade, and to duly work against the weak, here are the actions Alexander must perform, which, as general principles, will serve you well. | Il ſe pourra faire, qu’au lieu de preſenter l’eſpee en droite ligne, comme il a eſté pratiqué par Zacharie aux Tables precedentes, qu’il changera d’avis, & vous la preſentera à la façon qu’il eſt icy pourtrait en ce Tableau XIII. ſur le Cercle N.1. ne s’eſloignant gueres de la meſme poſture, ſinon qu’il tient la main un peu plus haute, pour ſe couvrir le viſage, & la pointe un peu baſſe, en ſorte qu’il ne la puiſſe voir luy meſme, ſi ce n’eſt à travers la garde. En tel cas, il ne ſeroit pas expedient de vouloir trouver ſa lame ſuivant les inſtrućtions precedentes, pour l’emmener & aſſujettir en dedans du bras à la Seconde Inſtance; à cauſe qu’il ſeroit impoſsible de le faire ſans ſe deſouvrir par trop ſoy meſme en la partie ſuperieure du corps. Parquoy s’il eſt queſtion de l’emmener, voyez-en les inſtrućtions au Tableau XIX. Pour le preſent, il vous ſera monſtré, comment vous luy pourrez tirer ſur ceſte poſture au long de ſa lame un coup de pointe ſous le bras, où il ſe deſcouvre le plus; à raiſon que l’eſpaule, la poitrine, & le viſage luy demeurent couverts du rempart de la garde. Afin d’eviter doncques le fort de ſon eſpee, & pour travailler deuëment ſur le foible, voicy les operations d’Alexandre, qui vous ſerviront de preceptes. |
| Circle No 1 | Cercle N.1. |
| Zachary presents his sword to his opponent with his arm high and his tip low. Against which Alexander approaches with his left foot forward at the First Instance, and covers his opponent’s sword with his guard. | Zacharie preſente l’eſpee à ſon adverſaire, avec le bras haut & la pointe baſſe; ſur quoy Alexandre s’approche du pied gauche à la Premiere Inſtance, & ſe va pancher en devant ſur le meſme, couvrant la lame contraire avec ſa garde. |
| Zachary has placed himself in the circle inside his quadrangle, right foot on the circumference at X and left foot on the Pedal Line at Z, body extended upright, and presents his sword at his opponent above the Diameter, with his hand raised up, in such a way as to cover his face with his guard, allowing his tip to point downwards by bending his wrist, in order to strike at his opponent. Alexander approaches, with his left foot forwards, which he sets down at the First Instance on the letter C, keeping his body leaning backwards, and in one motion, circles his sword over to the inside line, down from an obtuse to an acute angle, then continuing the movement around until he has once again brought it upwards to the right hand side, as he shifts his body over his left foot, and finally allows his thumb to slide off and around under the crossguard so that it raises up. After a brief pause, he allows his blade to drop and leans forward, lifting his trailing right foot for balance, extending his arm so his guard covers the end of his opponent’s blade at the 1st or 2nd Span, crossing a bit above it, as the figures demonstrate. | Zacharie s’eſtant planté ſur le Cercle dedans ſon Quadrangle, le pied droit à la Circonference lettre X, & le gauche ſur la ligne Pedale Z, le corps eſtendu perpendiculairement, preſente l’eſpee à ſon Contraire, au deſſus du Diametre, avec le bras eſtendu vers le haut, de façon qu’il ſe couvre le viſage de ſa garde, laiſſant deſcendre la pointe vers le bas à l’aide du poignet de la main, pour attendre ſa partie. Là deſſus Alexandre s’approche premierement du pied gauche, qu’il plante à la lettre C en Premiere Inſtance, retenant le corps panché à l’envers, & menant par meſme voye l’eſpee circulairement de haut en bas en dedans du bras, d’angle obtus en angle aigu; dont par la continuation de meſme mouvement il la ramene derechef en haut à main droite, en ſe dreſſant le corps ſur le meſme pied gauche, & finalement ſe laiſſe eſcouler le poulce de deſſus la brance interieure de la garde, où il eſtoit affermi, en deſſous, de ſorte qu’elle en vient à ſe dreſſer contrement; laiſſant par ainſi deſcendre ſa lame, & panchant tellement du corps ſur le devant, avec le pied de derriere eſlevé & le bras eſtendu, que de ſa garde il couvre la lame contraire avec un petit arreſt, à 1 ou 2 Nombres tout contre la pointe, la croiſant un peu de biais vers le haut; comme les figures demonſtrent. |
| During the time he is moving his guard above the tip of his opponent’s sword, he should pause briefly, as we said: to always be read to adjust to any action or change his opponent may make while he is performing this move, so, being on guard, he cannot surprise you. | Au temps qu’on porte ſa garde par deſſus la pointe contraire, il faut bien adviſer de le faire avec le petit arreſt, que nous venons de dire: & ce pour eſtre touſiours preſt à rencontrer toutes les aćtions, que l’adverſaire pourroit pratiquer durant le meſme temps. autrement il ne faudra pas à nous ſurprendre, ſi nous ne ſommes bien ſur nos gardes. |
| Circle No 2 | Cercle N.2. |
| Alexander continues his action, by making contact with his guard against the tip of his opponent’s sword and sliding it up as he steps in with his right foot a little beyond the letter H, following in so as to raise his left foot up, thrusting along his opponent’s blade under his arm and into his right side. | Alexandre pourſuit l’operation encommencée, joignant ſa garde au foible & à la pointe de l’eſpee contraire, laquelle il va graduer en entrant avec le pied droit un peu outre la lettre H, à pourſuivre & eſlever tout d’un train le pied gauche en l’air, & luy donner un coup d’eſtocade au coſté droit deſſus le bras par le fil de ſa lame. |
| Since Zachary is doing nothing more than waiting, Alexander continues with his action, maintaining contact with the tip of his opponent’s blade at the 1st or 2nd Span, trapping it beneath the external branch of his crossguard by sliding the point of contact up the blade. As he straightens his arm, he lowers his sword-tip, and as moves his right foot forward along the Diameter between the centre and the letter H, he continues to lean forward, raising his left foot into the air, so that he enters into the angle which he has created by turning his opponent’s sword aside to the outside and behind himself with the external branch of his crossguard, which he is using to trap the blade. By the same means, his bladepasses over his opponent’s, and he makes a straight arm thrust into his opponent’s right side, below the armpit, as is shown by the figures. | Puis que Zacharie ne fait rien que attendre, Alexandre commence à pourſuivre l’operation, accouplant par en haut ſa garde à la pointe de l’eſpee contraire à 1 out 2 Nombres, la ſurprennant par deſſous avec ſa branche exterieure, en uſant de graduation, abaiſſe enſemblement ſa pointe avec le bras eſtendu, & avance le pied droit ſur le Diametre entredeux le centre & la lettre H; continuant à ſe pancher en devant avec le corps tout eſtendu, & le pied gauche eſlevé en l’air par la meſme continuation, de ſorte qu’il entre du coſté droit dedans l’angle, qu’il s’eſt ouvert luy meſme, en deſtournant l’eſpee contraire arriere de ſoy en dehors avec l’aide de la branche exterieure, dequoy il la tient enſerrée, & par meſme voye il le bleſſe par deſſus le fil de ſa lame, luy donnant l’eſtocade d’un bras roide au coſté droit deſſous le bras; ſelon qu’il eſt repreſenté en la figure. |
| Circle No 3 | Cercle N.3. |
| This follows on from the previous, performed by Alexander without pause, by turning his right foot around to the inside, and spinning the other around so his toes come onto the part of the line L-S just beyond the Perpendicular Diameter. He puts his weight on his left foot and leans further backwards, knee and arm bent, continuing to turn his opponent’s blade aside with the exterior branch of his crossguard, and thereby increasing the power of his thrust, as the figures show. | Ceſt la continuation de la precedente, pratiquée par Alexandre tout de ſuite ſans perdre temps; en tournant le pied droit à l’envers, & voltant l’autre de meſme à tout les orteils ſur la ſećtion de la ligne LS par delà le Diametre; ſur lequel il ſe va charger & pancher le dos plus outre, le genou plié, & le bras courbé, en continuant à deſtourner la lame contraire encores davantage au moyen de ſa branche exterieure, & augmenter par ainſi la vigueur de ſon eſtocade; comme on le voit repreſenté. |
| Circle No 4 | Cercle N.4. |
| To end the action, Alexander drives his sword-tip further by entering in, stepping with his right foot to the letter V along the Diameter, where he puts his weight onto it, bending his knee and and increasing the full power of his thrust, forcing it through his opponent’s body, so that the two guards come together, but without releasing the blade, so that he forces the tip down to an acute angle, and, as it appears in the portrait of the figures, forces it backwards towards Zachary’s right foot, who, off-balance, has already raised it into the air. | Pour mettre fin à l’execution, Alexandre pourſuit ſa pointe à marcher & entrer tout d’une tire avec le pied droit ſur le Diametre lettre V, où il ſe charge deſſus le meſme genou plié, ravivant la vigueur de ſon eſtocade à pleine force, & la pouſſant à travers le corps du Contraire, en ſorte que les deux gardes ſe rencontrent, ſans luy relaſcher pourtant ſa lame, dont il pouſſe la pointe en angle aigu vers le bas, & l’enforce tellement, qu’il le jette à l’envers, comme il appert aut pourtrait des figures, au pied droit de Zacharie, eſtant deſia eſlevé en l’air à faute de reſiſtance. |
| Circle No 5 | Cercle N.5. |
| The two adversaries began by establishing their position at the First Instance on the Circle, in direct line postures. Alexander, having set his blade parallel to and beneath the other, steps and subjugates his opponent’s blade along the Oblique Diameter at the Second Instance. His opponent then raises his extended arm up to an obtuse angle, so that he covers his face with his guard, allowing his sword-tip to drop downwards. From here the same operations proceed, performed by Alexander, up to the end, as described as follows. | Les deux Contraires s’eſtans preallablement plantez ſur le Cercle à la Premiere Inſtance en droites lignes; Alexandre ayant mis ſa lame parallele au deſſous de l’autre, il marche & aſſujettit le Contraire en deçà le Diametre à la Seconde Inſtance; iceluy hauſſaunt le bras eſtendu en angle obtus, de ſorte qu’il ſe couvre le viſage avec ſa garde, laiſſant deſcendre la pointe à bas; dequoy procedent derechef les meſmes operations, à pratiquer & continuer par Alexandre juſqu’à la finale execution en la maniere qu’il s’enſuit plus particulierement. |
| After Zachary established his direct line posture in his quadrangel on the Pedal Line Z and presented his sword, Alexander likewise established his position in the opposite Quadrange, right foot along the Circumference at the letter C, his left along his Pedal Line, and brought his sword up parallel to and beneath the other. That done, he then began to perform the actions which lead to this Circle, stepping with his right foot over to the letter G, on the Oblique Diameter at the Second Instance, drawing his left foot up, and subjugating his opponent’s sword. At this instant, his opponent raises his arm up high, covers his face with his guard, and sets his sword-tip low, as the figures demonstrate. | Apres que Zacharie s’eſt planté ſur le Cercle dedans le Quadrangle Z, preſentant l’eſpee en droite ligne; & qu’Alexandre s’eſt planté pareillement alencontre au Quadrangle oppoſite en Premiere Inſtance, le pied droit à la Circonference lettre C, & le gauche ſur la ligne Pedale, portant l’eſpee en droit ligne parallele au deſſous de l’autre. Cela fait il a pourſuivi à pratiquer les aćtions de ce Cercle preſent, marchant avec le pied droit en deçà le Diametre, à la Seconde Inſtance lettre G, à pourſuivre conſequemment du pied gauche, & y aſſujettir l’eſpee de l’adverſaire, qui eſleve à ce meſme inſtant le bras en haut, ſe couvrant le viſage de ſa garde avec la pointe baſſe; comme les figures demonſtrent. |
| Thereupon Alexander performs the actions as in Circles No 2, 3, & 4, as follows. | Là deſſus Alexandre pourſuit à pratiquer les operations des Cercles N.2.3.4. ſelon qu’il s’enſuit. |
| While Zachary is raising his arm and the guard of his still-subjugated sword to cover his face and before he can finsh this movement, Alexander moves forward and steps with his right foot to the centre of the Circle, and then his left foot raised in the air, he slides the point of contact up the blades, so as to hit his opponent with his sword-tip on the right side, beneath the weapons, keeping in mind all the previous considerations explained in Circle No 2. | Durant que Zacharie ſe hauſſe le bras & la garde de ſon eſpee qui eſt aſſujettie, pour s’en couvrir le viſage, avant que le mouvement ſoit àchevé, Alexandre s’avance & marche avec le pied droit ſur le centre du Cercle, en continuant à eſlever le pied gauche en l’air, & graduer le lames, de façon qu’il atteint l’averſaire d’un coup de pointe au coſté droit deſſous les armes, y obſervant toutes les meſme conſiderations, qui en ont eſté ſpecifiées au Cercle N.2. |
| Now, if Zachary’s movement, that is, to raise the arm and guard, had been completed, Alexander would not have been able to do the same the thing again. But the best and the surest way is to move first. | Or combien que le mouvement de Zacharie, aſſavoir de hauſſer le bras & la garde euſt eſté conduit à fin, Alexandre n’euſt pas laiſſé pourtant de faire encor la meſme choſe; mais c’eſt le meilleur & le plus ſeur de prendre le temps meſme. |
| The follow-up to this action is that Alexander turns instantly about swinging his left foot around his right foot and behind him, a little beyond the letter Q along the Diameter. He leans back onto it, knee bent, and for the rest follows the particulars described in Circle No 3. | La ſuite de ceſte operation c’eſt, qu’Alexandre ſe volte tout à l’inſtant le pied gauche par derriere & alentour le pied droit, un peu outre la lettre Q par delà le Diametre, ſe panchant à l’envers deſſus le meſme, à tout le genou plié, & obſervant au reſte les particularitez de l’aćtion repreſentée au Cercle N.3. |
| After which he continues on, turning and stepping to the letter W on the circumference, shifting his weight onto that foot and thus he increases the power of his thrust right through his enemy’s body, as done in Circle No 4. | Ce qu’eſtant fait, il pourſuit l’operation juſqu’à la Circonference lettre W, où il ſe charge le corps deſſus, & par meſme voye augmente ſon eſtocade à pleine force à travers le corps de l’Ennemi, en conformité du Cercle N.4. |
| When Alexander, as he is portrayed here, has subjugated his opponent’s blade at the same time as his opponent raises his guard to cover his face, he can also enter in with his right foot following the line of the same Interior Collateral from where it was at the letter G, up to the letter Q, following with the left foot, and so wounding his adversary, just the same as before, under the arm by sliding the point of contact up the blades, and, by leaning forward to put himself inside the angle of the sword, which he has trapped and turned away, outside and behind him. | Quand Alexandre fait l’aſſujettiſſement, comme il eſt icy pourtrait, au meſme temps que l’Adverſaire ſe hauſſe le bras avec la garde, pour ſe couvrir le viſage, Il peut auſsi entrer avec le pied droit par la trace de la meſme Collaterale interieur, où il eſt planté, juſqu’à la lettre Q, en pourſuivant du pied gauche, & bleſſant ſa partie adverſe, tout de meſme qu’auparavant, deſſous le bras moyennant la graduation des lames, ſe mettant par l’avancement du corps panché, au dedans l’angle de l’eſpee contraire, laquelle il a ſurprinſe & deſtournée en dehors arriere de ſoy. |
| So, after Alexander has successfully performed this action in divers ways, without his adversary discovering a counter to it, notwithstanding that he has done his best to turn the sword aside in several sorts of ways, this said adversary comes to persuade himself that he can do the same to Alexander, as long as he presents the same posture. Thus he requests that Alexander do this, to test the premise. | Or apres qu’Alexandre a parachevé ceſte operation à diverſes fois, ſans que l’Adverſaire y ait ſceu donner remede, nonobſtant qu’il ait fait ſon devoir à la divertir en pluſieurs ſortes; ledit Adverſaire ſe va perſuader, qu’il en fera tout le meſme à Alexandre, moyennant qu’il luy preſente ſans plus l’eſpee en la meſme poſture. Dont il le requiert amiablement de ce faire, pour en voir la preuve. |
| Alexander, not wishing to refuse this challenge, adopts the posture in the A-C Quadrangle, right foot on the letter C, left foot on the Pedal Line, holding his sword as was presented to him in Circle No 1. To attack against this, Zachary sets his left foot down at the First Instance on the letter X in the opposing Quadrangle, and consequently will lean forwards raising his left foot in the air behind him, and covering his opponent’s sword from above, as he has seen Alexander do in the aforesaid Circle No 1. | Par ainſi donc Alexandre ne le voulant eſconduire, ſe va mettre le premier en poſture ſur le Quadrangle AC, le pied droit à la lettre C, & l’autre ſur la ligne Pedale, tenant l’eſpee tout de meſme, qu’elle avoit eſté preſentée par le Contraire au Cercle N.1. Pour travailler donc alencontre Zacharie ſe met le pied gauche en Premiere Inſtance à la lettre X au Quadrangle oppoſite, & conſequemment ſe va pancher ſur le devant, en eſlevant le pied de derriere en l’air, & couvrant de par enhaut l’eſpee contraire, cōme il a veu faire à Alexandre audit Cercle N.1. |
| To perform the strike, Zachary advances his right foot, to thrust to Alexander’s side underneath his arm, as we see in Circle No 2. But, at the same time that he drops the tip of his sword underneath the guard and the arm, Alexander, keeping the swords in contact, turns the guard and his arm in a circular motion downwards and outside to the right, allowing his sword-tip to rise up against his opponent, so that he crosses and subjugates his opponent’s sword, and thus interrupts his intent, as is shown in Circle No 6. | Pour continuer l’operation Zacharie s’avance avec le pied droit, pour luy donner l’eſtocde au coſté deſſous les armes, comme on le voit repreſenté au Cercle N.2. mais au meſme temps qu’il luy deſcend ſa pointe ſous la garde & le bras, Alexandre, tenant les eſpees accouplées, ſe tourne circulairement le bras & la garde en dehors à main droite vers le bas, laiſſant monter ſa pointe au contraire, dont il va croiſer & aſſujettir l’eſpee contraire, en ſorte qu’il luy rompt le deſſein, comme il eſt repreſenté au Cercle N.6. |
| After that, he continues a follow on to finish, stepping with his right foot forward along the diameter to E, where he puts his weight against the weak of the blade, hitting with the same thrust to the right side that his opponent intended, as it appears in Circle No 7. | Qui plus eſt, Il en fait la pourſuite juſqu’à l’execution, marchant avec le pied droit en avant ſur le Diametre à la lettre E, où il ſe charge le foible, & tirant le meſme coup d’eſtocade au coſté droit de l’Adverſaire, qu’il avoit penſé à tirer ſu luy, comme il appert au Cercle N.7. |
| And so Alexander once again readies himself on the Circle, in the A-C Quadrangle, presenting his sword in the straight-line posture. Zacharie sets himself against him at the First Instance in the opposite Quadrangle, then steps with his right foot to the Second Instance, along the Oblique Diameter, with his toes on the letter S and heel at W, and subjugates Alexander’s sword. Alexander has raised his arm and guard up high, covering his face, so Zachary finds himself in the same situation as Alexander, portrayed in Circle No 5. | Alexandre ſe va planter autrefois ſur le Cercle dedans le Quadrangle AC, luy preſentant l’eſpee en droite ligne: Zacharie ſe met alencontre au Quadrangle oppoſite en Premiere Inſtance avec l’eſpee parallele au deſſous; puis marche avec le pied droit à la Second par delà le Diametre lettre S, pourſuivant à avancer le pied gauche, les orteils ſur le Diametre oblic, & le talon à la lettre W, & aſſujettir l’eſpee d’Alexandre; qui eſleve au meſme temps le bras avec la garde en haut, s’en couvrant le viſage; de façon que Zacharie s’en retrouve par delà le Diametre en la meſme ſituation qu’Alexandre eſt pourtrait au Cercle N.5. |
| Circle No 6 | Cercle N.6. |
| Following the previous described action, Zachary tries to strike his adversary under the arm, by moving his right foot forward to the centre of the Circle, and spinning his left forward behind him. At which point Alexander breaks his strike, turning his arm and guard to the outside, dropping down and subjugating the sword. | En ſuite de l’operation dernierement deſcrite Zacharie taſche à frapper l’Adverſaire deſſous le bras, en avançant le pied droit ſur le Centre du Cercle, & voltant le gauche à l’advenant derriere. Dequoy Alexandre luy rompt le coup, ſe tournant le bras & la garde en dehors de haut à bas, de ſorte qu’il luy aſſujettit l’eſpee. |
| Thus, Zachary subjugates his opponent’s sword at the Second Instance. At the same time, his adversary raises his arm and guard up to cover his face, sword-tip pointing down. In this way, Zachary works against him, allowing his point to descend, and sliding the point of contact up the swords, advancing his right foot to the centre of the Circle, intending to spin his left foot around behind, and by this motion to wound his opponent from beneath the sword. Because he is doing this close in, that is, at the Second Instance, Alexander moves his left foot a little backwards out of the Quadrangle, where he shifts his weight a little backwards onto it, and drawing his other foot along behind. Without disengaging the blades, Alexander brings his wrist down in a circular motion, while turning his arm and guard to the outside and to the right. Thus he traps and subjugates his opponent’s sword, as shown by the figures. | Faiſant donc Zacharie l’aſſujettiſſement de l’eſpee contraire à la Seconde Inſtance, & que l’Adverſaire ſe hauſſe au meſme temps le bras avec la garde, dont il ſe couvre le viſage, avec la pointe deſcendante: En ſemblable Zacharie travaille au meſme temps alencontre, laiſſant deſcendre ſa pointe, & graduant les lames, en avançant le pied droit juſqu’au Centre du Cercle, avec intention de volter le pied gauche alenvers, & de bleſſer par meſme voye ſon Contraire au coſté droit deſſous les armes. Et puis qu’il fait le tout de fort pres, aſſavoir de la Seconde Inſtance, Alexandre ſe retire au meſme temps le pied gauche un peu en arriere au dehors du Quadrangle, où il fait la charge du corps deſſus à pancher vn peu alenvers, & pourſuivre de l’autre pied à l’advenant; enſemble ſe tournant (ſans deſtacher les lames) le bras droit avec la garde de l’eſpee à l’aide du poignet circulairement de haut à bas en dehors & à main droite: dont il enferme & aſſujettit par en haut l’eſpee contraire; enſuivant le pourtrait des figures. |
| Circle No 7 | Cercle N.7. |
| Alexander presses his attack, using his wrist to turn his arm together with the interior branch of his crossguard upwards in such a way as to catch and seize his opponent’s blade with the other branch of his crossguard. He then steps forward with his right foot up to the letter E and turns the trapped blade behind him as he slides the point of contact up the blade. He leans onto his right foot, drawing his left foot behind him a little bit forwards. He wounds his adversary with a hit from his sword-tip in the right side underneath the armpit, the very sort of thrust Zachary had thought to do, now turned back on him, as evidenced and demonstrated by the figures. | Alexandre pourſuit ſon advantage, en tournant le bras, & enſemblement la branche interieure de ſa garde contremont à l’aide du poignet, de façon qu’il accueilt & enferme avec l’autre branche la lame contraire, laquelle il pourſuit à destourner arriere de ſoy, & à graduer en marchant avec le pied droit à lettre E, où il fait la charge du corps deſſus, laiſſant trainer le pied gauche un peu à l’advenant, & bleſſant de meſme ſa partie adverſe d’un coup de pointe au coſté droit deſſous l’aixelle, de ſorte qu l’eſtocade que Zacharie avoit pourpenſée à Alexandre, elle retombe ſur luy meſme; comme il eſt evident par la demonſtration des figures. |
| Circle No 8 | Cercle N.8. |
| Zachary again tries to execute the same attack, taking aim at Alexander from the Second Instance, to wound him underneath the arm. Alexander again prevents him, and subjugates his blade, just the same as in Circle No 6 and consequently, having straightened up after leaning backwards, he seizes the sword with the interior branch of his crossguard, sliding the point of contact up the blade, and setting his sword-point precisely in front of Zachary’s eyes, just as the figures show. | Zacharie taſchant à executer encores la meſme entreprinſe, à tirer ſur Alexandre de la Seconde Inſtance, pour le bleſſer deſſous le bras; Alexandre le previent derechef, & luy aſſujettit la lame, tout de meſme qu’au Cercle N.6. & conſequemment s’eſtant redreſsé le corps, qui eſtoit panché un peu en arriere, il la va graduer & enfermer par deſſous avec ſa branche interieure, luy mettant la pointe en courtoiſie devant les yeux; ainſi que les figures demonstrent. |
| Circle No 9 | Cercle N.9. |
| This is the final step of the preceeding action, performed with determination by Alexander, who steps with his right foot along the Diameter to the letter E, where he leans his body onto it, sliding the point of contact up the swords with his arm extended out straight, so that the two guards crash together and his opponent is forced to bend his arm and allow the raised sword-tip to drive through his head with full force, as is represented by the figures. | Ceſt la finale execution de la precedente, pourſuivie en rigueur par Alexandre, à marcher avec le pied droit ſur le Diametre lettre E, où il ſe panche le corps deſſus, en graduant les lames d’un bras roide & eſtendu, de ſorte que les deux gardes ſe rencontrent ſi rudement, que le bras du Contraire en eſt forcé à ſe plier, & laiſſer monter ſa pointe en haut, en recevant le coup à pleine force à travers ſa teſte, comme il eſt repreſenté par leurs figures. |
| Circle No 10 | Cercle N.10. |
| Here, Zachary makes the same attempt to wound his adversary in the same way as above. Alexander has again subjugated the blade as in Circle No 6, but instead of moving backwards, he has advanced with his right foot along the Diameter at letter E, where he leaned his body over it, inside the angle, and follows by drawing his left foot after him in a circular motion, while disengaging his sword, so that he makes a backwards cut to the right side of his opponent’s head, as is shown in the figures. | Voicy Zacharie qui a fait encor la meſme preuve, pour bleſſer l’Adverſaire en la meſme ſorte que deſſus: Alexandre luy aſſujettit derechef la lame en conformité du Cercle N.6. mais au lieu de reculer, is s’eſt avancé avec le pied droit ſur le Diametre lettre E, où il ſe panche le corps deſſus au dedans de l’angle, pourſuivant à trainer circulairement le pied gauche apres, & deſachant au meſme temps les eſpees, en ſorte qu’il luy donne un coup de revers au coſté droit de la teſte; comme les figures demonſtrent. |
| Circle No 11 | Cercle N.11. |
| Zachary again wishes to perform the same attack on Alexander underneath the arm, from the Second Instance, but is once again trapped through the same action as in Circle No 6. Then Alexander, having trapped and subjugated his blade, continues to work against him, stepping with his right foot a little outside the Circle, between the letters D & F, following along in a circular motion with his left foot, and sliding the point of contact down the blade towards the tip, by giving a light push downwards with his wrist and lowering his arm, at which point he leaves it there, lifting his own, carrying it over his head with a movement of his elbow, spinning his left foot around behind the other, and exactly striking his adversary’s left ear, as is seen in the figure. | Zacharie retournant à vouloir donner encore la meſme atteinte à Alexandre deſſous le bras de la Seconde Inſtance, il y eſt derechef attrapé moyennant l’operation du Cercle N.6. dont Alexandre luy ayant enfermé & aſſujetti la lame, continue à travailler, en marchant avec le pied droit vn peu au dehors du Cercle entre deux les lettres D & F, pourſuivant circulairement avec le pied gauche, & deſgraduant avec ſa lame devers la pointe contraire, y faiſtant vn petit pouſſement deſſus avec le bras deſcendant & à l’aide du poignet, dequoy il amortit le ſentiment, & au meſme inſtant il en oſte la ſienne, la menant par deſſus ſa teſte par le mouvement du coude, en voltant le pied gauche derriere l’autre, & preſentant en courtoiſie un coup de taille à l’oreille gauche de ſon Adverſaire; comme il ſe voit en la figure. |
| If Alexander had wanted to deliver a more severe blow, he would have spun the left foot around a good deal further, and then added another with his right foot, with which he would have repeated the same blow, again spinning the left foot around, and by this means, have found himself behind his enemy, placing himself entirely out of reach of any danger. But here, he puts his left foot right behind the other in order to control the motion of his body and his sword, so that he can keep the blow precise, which he would not be able to easily do otherwise. | Si Alexandre euſt voulu donner le coup en rigueur, il euſt volté le pied gauche un grand pas plus outre, y adjouſtant par apres encor un autre avec le pied droit; dequoy il redoubleroit le meſme coup, en voltant derechef le pied gauche, & par ce moyen viendroit à gaigner le derriere de l’Ennemi, ſe mettant totalement à l’abri de touts dangers: mais qu’il plante icy le pied gauche droitement derriere l’autre, c’eſt pour en moderer la courſe du corps & de l’eſpee, afin qu’il puiſſe retenir le coup en courtoiſie, ce qu’il ne pourroit faire autrement, ſinon à grand peine. |
| Circle No 12 | Cercle N.12. |
| It is Zachary’s pleasure to once again test the proposition, which is once again nullified by the same action as in Circle No 6. This time Alexander follows up by stepping with his right foot along the Diameter to letter E, and at the same time that leans his upper body forward over it, he lifts his left foot in the air, and seizes his opponent’s hand and guard with his left hand reaching over the crossed swords and pulls it towards him so that his opponent’s sword-tip lowers towards the ground, as is shown by the figure. | Zacharie ſe plait à repeter encor la meſme preuve, qui luy eſt derechef annullée par la meſme operation du Cercle N.6. dont Alexandre pourſuit à travailler en marchant avec le pied droit ſur le Diametre lettre E, où il ſe panche la partie ſuperieure du corps un peu en avant, eſlevant quand & quand le pied gauche en l’air, & faiſant prinſe de la garde contraire avec la main gauche, à porter par deſſus le long des deux lames croiſées, la retirant devers ſoy en ſorte que la pointe contraire s’en abaiſſe devers la terre; comme la figure demonſtre. |
| Circle No 13 | Cercle N.13. |
| Alexander carries on, by bringing his left foot, already raised in the air, onto the Perpendicular Diameter at the letter M, then right away spins his right foot around behind himself and, setting it down just outside the Circle near the letter W, he leans back on it, and again raising his left foot and stepping towards his adversary on the point Q, he shifts his body forward onto it, bends his knee, and hits his opponent on the right side beneath the arm, driving through his body, as is shown in the figure. | Alexandre pourſuit l’operation, en menant le pied gauche, qui eſt ià eſlevé, en deça le Diametre à la lettre M, & voltant tout de ſuite le pied droit derriere au dehors du Cercle bien pres de l’W, ſur lequel il ſe va pancher à l’envers, en eſlevant derechef, & cheminant avec le gauche devers l’Adverſaire au point Q, où il ſe charge le corps deſſus en avant à tout le genou plié, luy donnant l’atteinte au coſté droit deſſous le bras & la pouſſant à travers le corps; comme il eſt repreſenté en la figure. |
| Seeing how effectively each time Alexander has parried Zachary’s attempt to strike under his arm, and how he did this in such a way as to control the blade and then confidently made so many effective strikes, Zachary then decides to imitate him, and arranges with Alexander to have him attack with the actions shown in Circles Nos 1, 2, 3, 4, & 5, convinced he cannot fail to perform the same actions, that is, the subjugate, and wound him, in the same various ways that Alexander has done. | Voyant donc qu’Alexandre a destourné ſi avantageusement & à tant de fois l’entreprinſe de Zacharie, qui eſtoit de le bleſſer ſous le bras; de ſorte qu’il luy a gaigné la lame, & en a tiré tant d’executions ſi avantageuſes, meſme qu’il a fait le tout avec ſi grande aſſeurance; Zacharie ſe propoſe de le vouloir imiter, & ſe fait accroire, que ſi Alexandre le vouluſt derechef attaquer avec les operations de Cercles N.1.2.3.4.5. qu’il ne manqueroit pas à luy rendre pareille, c’eſt aſſavoir de l’aſſujettir, & le bleſſer conſequement en telles & ſemblables ſortes, qu’il a veu pratiquer à Alexandre. |
| To arrive at a result, they reset themselves in the direct-line posture on the Circle at the First Instance. And Alexander, who has set his blade beneath the other to perform the subjugation stepping with his right foot to the Second Instance, in the same way, and in the same conditions as Circle No 5. followed by raising his right foot to step and wound his opponent under the arm, as in Circle No 2. So Zachary parries the strike, bringing his blade circularly around his opponent’s to the right hand side to trap it, and subjugate it, as in Circle No 6. | Pour en venir à l’effećt, ils ſe vont remettre ſur le Cercle à la Premiere Inſtance en droites lignes. Et Alexandre, qui a mis ſa lame deſſous, à faire l’aſſujettiſſement, en cheminant avec le pied droit à la Seconde Inſtance, en la meſme ſorte, & avec les meſmes circonſtances comme au Cercle N.5. pourſuivant à travailler en eſlevant le pied droit pour bleſſer l’Adverſaire en conformité du Cercle N.2. deſſous le bras. Dont Zacharie en deſtourne le coup, menant ſa lame circulairement à la main droite alentour de l’eſpee contraire, pour l’enfermer, & aſſujettir comme au Cercle N.6. |
| Circle No 14 | Cercle N.14. |
| At the same time that Zachary works to drop his arm, intending to cross over and subjugate his opponent’s blade, Alexander moves his raised right foot forward from the Second Instance to the letter Q on the Oblique Diameter, turning his tip around under his opponent’s arm over the blade and drawing his left foot up to the letter H while placing his tip exactly in front of his opponent’s eyes. However quickly Zachary tries to bring his arm and sword back over his opponent’s to defend himself, he is too late. As is shown in the figure. | Au meſme temps que Zacharie travaille à deſcendre le bras, pour croiſer & aſſujettir la lame contraire; Alexandre s’avance avec le pied droit, qui eſtoit eſlevé, de la Seconde Inſtance, en deçà le Diametre à la lettre Q, tournoyant ſa pointe par deſſous le bras contraire au deſſus de la lame, & entrainant le pied gauche à la lettre H, & enſemblement luy preſentant la pointe devant les yeux en courtoiſie. Et combien que Zacharie ſe ramene derechef le bras & l’eſpee en haut pour ſe defendre, toutesfois il y vient trop tard; comme on le voit au pourtrait de la figure. |
| Circle No 15 | Cercle N.15. |
| This is the finish, where Alexander extends his arm with the sword, advancing his right foot along the Interior Collateral about as far as the letter V on the Diameter, where he leans onto it, at the same time drawing his left foot up to the letter M on the Perpendicular Diameter, so that the guards smash together with so much force that his opponent’s arm and sword are forced to bend upwards, driving the thrust through the head. As is shown in the figure. | C’eſt l’execution de la precedente, où Alexandre eſtend le bras avec l‘eſpee, s’avançant le pied droit ſur la ligne collaterale interieure en deçà le Diametre pres la lettre V, où il ſe va pancher deſſus, entrainant quand & quand le pied gauche juſqu’au Diametre perpendiculaire lettre M, dont les gardes ſe rencontrent d’une telle violence, que le bras & l’eſpee contraire en ſont forcez à ſe plier & à monter la pointe en haut, luy pouſſant l’eſtocade à travers la teſte; comme il eſt en la figure. |
| So now Zachary, confused at seeing his plans so frustrated so many times, beaten when he expected to triumph. But because his action was begun at the Second Instance, he begins to suspect that he had perchance begun to work from too close. Thus he requests another chance to start again at the First Instance, as in Circle No 1. This Alexander accords to him and the both set themselves on the Circle in the same way, and Alexander proceeds as in Circle No 2. So Zachary again seeks to subjugate his blade by circling around the arm and guard. Alexander again gets himself out of trouble moving his sword-tip from beneath he arm, and sets it exactly in front of Zacharys face, as in Circle No 14. | Voilà maintenant Zacharie tout confus de ſe voir tant de fois furſtré en ſon entreprinſe, voire qu’il en a eſté vaincu luy meſme au lieu de vaincre. Mais puis que l’operation a eſté commencée à la Seconde Inſtance, il entre en ſoupçon d’avoir travaillé par adventure de trop pres: dont il requiert à recommencer derechef à la Premiere Inſtance, ſuivant le Cercle N.1. Ce qu’Alexandre luy accorde, & ſe vont mettre touts deux ſur le Cercle ſuivant la meſme repreſentation, & Alexandre à pourſuivre comme au Cercle N.2. Dont Zacharie luy veut derechef aſſujettir la lame par le tour du bras & de la garde. Alexandre luy deſrobbe encor ſa pointe par deſſous le bras, & la luy met en courtoiſie devant le viſage, comme au Cercle N.14. |
| In sum, to see how Alexander does the actions in Circle No 6, by which he captures and subjugates his opponent’s sword, it seems there is nothing easier. This is because he works from a good foundation. And even though the swords do not always make contact in the same place, at the same Spans, nevertheless the choice of thrust, cuts, and holds which follow are entirely his own. He may freely take whichever pleases him. He will completely upend those ignorant or foolhardy imitators who have the temerity to to copy what they have seen done three or four times by a well trained and able man. From which they can gain only a sense of shame and confusion, when they try to test him, and find all their intentions frustrated at every moment, because they do not know the depth of this science, nor how difficult it is, nor the time, well worth the effort, which it requires to learn, nor the amount of study to bring to the subtleties of these examples. Gentlemen both presumptuous and ridiculous, who, having learned but two or three points, convince themselves that they fully understand the techniques, and that they can deal with any situation with the little that they know. They have no consideration of the full expanse, of the infinity of variation which dailly presents itself in training. Because each one has his own way of striking, different from all others, just as each hour, each minute, each instant changes from one to the next. So I can say, comparing the chamber, where debates are resolved with words, to the promenade where questions are settled with victory in arms, that just as [in logical discourse] arguments are subjected to critiques, critiques to ripostes, ripostes to secondaries, secondaries to tertiaries until all evidence the adversaries wish to examine has been discussed, so in the performance of arms there is no stroke, either ordinary, or well examined, or completely grasped, or so secret, or so amazing, that it does not have a counter. As such one must never be too confident of any particular strike. What is good on one occasion will fail in another. It may be the best attack in the world, but nothing prevents someone from defending against it. It should not be that strange if common fencers are always unsure, given that their training, not being founded on general sciences, should fail to prepare them to face all situations, and so it must follow that much of the result of their workings depends in great measure on fortune, where the path of wisdom is closed to them. | En ſomme à voir faire à Alexandre l’operation du Cercle N.6. par laquelle il enferme & aſſujettit l’eſpee contraire, il ſemble, qu’il n’y ait rien plus facile. c’eſt pour autant qu’il travaille avec fondement. Et encores que les eſpees ne s’accouplent pas touſiours aux meſmes endroits, & à meſmes Nombres; toutesfois le chois des eſtocades, coups de taille, & prinſes, qui s’en enſuivent, ne depend que de ſa ſeule elećtion; il en prendra librement celle, qui luy viendra le plus à gré. Tout au rebours en ſera il de ces ignorants & hardis entrepreneurs d’imiter temerairement tout ce qu’ils auront veu pratiquer trois ou quatre fois à vn homme adroit & bien fondé: dequoy ils ne peuvent raporter que honte & confuſion, quand il eſt queſtion d’en venir aux preuves, ſe voyants fruſtrez à touts moments de leurs intentions, à faute de ne cognoiſtre pas l’amplitude de ceſte Science, ne combien elle eſt difficle, le temps qu’elle requiert & merite pour l’apprendre, ne l’eſtude qu’il faut apporter à la ſubtilité de ſes demonſtrations. Gents preſomptueux & ridicules; qui n’ayants apprins, que deux ou trois pointilles, ſe ſont accroire, que rien ne leur manque, ſur l’aſſeurance qu’ils ont de faire ſervir à toutes occaſions le peu qu’ils en ſavent; ſans conſiderer la grande eſtendue, voire l’infinité des variations, qui ſe preſentent journellement en la Pratique; par ce que chaſcun a ſa propre maniere à tirer differemment des autres, voire que les heures, les minutes, les inſtants touſiours ſe changent. Dont je puis dire, en faiſant compariſon du bureau, où les debats ſe finiſſent par paroles, avec le parquet où les queſtions ſe terminent par la victoire des armes, que comme les accuſations ſont ſujettes aux exceptions, les exceptions aux repliques, le repliques aux duplications, triplications, & finalement à toutes les Inſtances que la partie adverſe voudra faire; ainſi au fait des armes il n’y a aucun trait tant ordinaire, tant bien examiné, tant priſé, tant ſecret, ne tant admirable, que n’ait ſon contraire; de ſorte qu’il ne faut jamais fier en aucun trait particulier; tout ce qui eſt bon en l’une des occaſions, eſtant faux en l’autre: ſoit aſſailli le mieux du monde, rien n’empeſche qu’il ne ſoit encore mieux defendu. Dont ſi les vulgaires en demeurent eſtonnez, il ne faut pas le trouver eſtrange; attendu que leur pratique, n’eſtant pas fondée en ſcience generale, qui ſoit baſtante à les preparer contre toutes occurrences, il s’enſuit de neceſſité, que les iſſues de leurs entreprinſes dependent en partie du ſort de la Fortune, qui domine par tout, où la Prudence eſt forcloſe. |
For further information, including transcription and translation notes, see the discussion page.
| Work | Author(s) | Source | License |
|---|---|---|---|
| Images | courtesy of Reinier van Noort | Thibault.zip | |
| Translation | Bruce G. Hearns | Wiktenauer | |
| Transcription | Bruce G. Hearns | Wiktenauer |
Additional Resources
- Howden, Matthew. "Comparison of Thibault’s Circle and the Leiden Circle". Sworded Contemplations. April, 2008. Retrieved 08 February 2015.
- Majár, János and Zoltán Várhelyi. "Thibault and Science I. Measure, Distances and Proportions in the Circle". Acta Periodica Duellatorum 2(1): 67-104. 2014. doi:10.1515/apd-2015-0014.
- Thibault, Gérard. Academy of the Sword. Trans. John Michael Greer
- 1st edition. Highland Park, TX: Chivalry Bookshelf, 2006. ISBN 978-1891448409
- 2nd edition. London: Aeon Books, 2017. ISBN-978-1-190465-884-9
References
- ↑ de la Verwey, Herman Fontaine. "Gerard Thibault and his Academie de l'Espée," Quaerendo VIII (1978) pp.288, 297
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 de la Verwey, Herman Fontaine. "Gerard Thibault and his Academie de l'Espée," Quaerendo VIII (1978) p.289
- ↑ de la Verwey, Herman Fontaine. "Gerard Thibault and his Academie de l'Espée," Quaerendo VIII (1978) p.297
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 de la Verwey, Herman Fontaine. "Gerard Thibault and his Academie de l'Espée," Quaerendo VIII (1978) p.288
- ↑ de la Verwey, Herman Fontaine. "Gerard Thibault and his Academie de l'Espée," Quaerendo VIII (1978) p.288-289
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 de la Verwey, Herman Fontaine. "Gerard Thibault and his Academie de l'Espée," Quaerendo VIII (1978) p.290
- ↑ de la Verwey, Herman Fontaine. "Gerard Thibault and his Academie de l'Espée," Quaerendo VIII (1978) pp.289-290
- ↑ de la Verwey, Herman Fontaine. "Gerard Thibault and his Academie de l'Espée," Quaerendo VIII (1978) p.294
- ↑ de la Verwey, Herman Fontaine. "Gerard Thibault and his Academie de l'Espée," Quaerendo VIII (1978) pp.294-296
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 de la Verwey, Herman Fontaine. "Gerard Thibault and his Academie de l'Espée," Quaerendo VIII (1978) p.296
- ↑ de la Verwey, Herman Fontaine. "Gerard Thibault and his Academie de l'Espée," Quaerendo VIII (1978) pp.296, 310
- ↑ Thibault, Gérard. Academy of the Sword. Trans. John Michael Greer. Highland Park, TX: The Chivalry Bookshelf, 2006. pp 1-2.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||