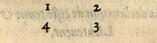|
|
You are not currently logged in. Are you accessing the unsecure (http) portal? Click here to switch to the secure portal. |
Difference between revisions of "Henry de Sainct Didier"
m (offend -> attack) |
m (minor changes in jeu de paume.) |
||
| Line 2,543: | Line 2,543: | ||
| ''The following is a treatise on exercise and certain points required to know the tennis, for all those who love it, written by the Author, since it requires the same steps and to know the same strikes of fencing, as will be seen by this treatise, and the Author because of the affinity and friendship they have together, leads to alert and give instruction to the unlearned, which do not understand the terms of this exercise, and not for the learned and skillful.'' | | ''The following is a treatise on exercise and certain points required to know the tennis, for all those who love it, written by the Author, since it requires the same steps and to know the same strikes of fencing, as will be seen by this treatise, and the Author because of the affinity and friendship they have together, leads to alert and give instruction to the unlearned, which do not understand the terms of this exercise, and not for the learned and skillful.'' | ||
| − | The author having considered that tennis and fencing are closely related, as stated above, and whoever is able to play | + | The author having considered that tennis and fencing are closely related, as stated above, and whoever is able to easily play tennis would also have learned to throw sword strikes, and so is the opposite, but the one that is better than the other is fencing because it preserves the health and honor of those who are afraid of losing them. Anyone could ask why fencing and tennis are related. The Author responds and says that the same strikes that one throws from fencing to overcome his enemy in times of peace or to win money or some celebration, which are: |
# Right-hand | # Right-hand | ||
| Line 2,549: | Line 2,549: | ||
# Thrust | # Thrust | ||
| − | It is true that one of the | + | It is true that one of the aforementioned strikes must be removed, which is the thrust, and only two will remain which are: |
# Right-hand | # Right-hand | ||
# Reversal | # Reversal | ||
| − | The reason why I remove the thrust is | + | The reason why I remove the thrust is that the racket has no point, and thus one would not be able to make a thrust. |
It is true that sometimes we strike and beat down with the racket when the ball comes straight to the face or higher, which is that we return the ball, and we beat it down with the racket when it comes from high or to the face keeping it straight, and leaning neither on the right nor left, and yet in the game of tennis, there are only the aforementioned two strikes, right-hand and reversal. But it is necessary to multiply them properly to 4 targets, from high and low, for example right-hand from below, and right-hand from above, reversal from below, and reversal from above, and thus it is necessary to be very dexterous and graceful to know how to strike because we strike at each other as we do with fencing. And knowing how to strike skillfully, we must observe the words of our ancestors who are skilled tennis players, who said whoever leaps to forsake the volley, will never be an esteemed player; it is necessary to take heed here, which is that when you can volley, you should never wait for a leap. The reason is that with a leap, several accidents can occur, yet on the volley, never, if one is well trained, and is safe. | It is true that sometimes we strike and beat down with the racket when the ball comes straight to the face or higher, which is that we return the ball, and we beat it down with the racket when it comes from high or to the face keeping it straight, and leaning neither on the right nor left, and yet in the game of tennis, there are only the aforementioned two strikes, right-hand and reversal. But it is necessary to multiply them properly to 4 targets, from high and low, for example right-hand from below, and right-hand from above, reversal from below, and reversal from above, and thus it is necessary to be very dexterous and graceful to know how to strike because we strike at each other as we do with fencing. And knowing how to strike skillfully, we must observe the words of our ancestors who are skilled tennis players, who said whoever leaps to forsake the volley, will never be an esteemed player; it is necessary to take heed here, which is that when you can volley, you should never wait for a leap. The reason is that with a leap, several accidents can occur, yet on the volley, never, if one is well trained, and is safe. | ||
Revision as of 14:43, 22 October 2021
| Henry de Sainct Didier | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Born | 1530s (?) Pertuis, Provence |
| Died | after 1584 Paris, France (?) |
| Occupation | Fencing master |
| Patron | Charles IX of France |
| Influences | |
| Influenced | Salvator Fabris (?) |
| Genres | Fencing manual |
| Language | Middle French |
| Notable work(s) | Les secrets du premier livre sur l'espée seule (1573) |
| Translations | Traducción castellano |
| Signature | |
Henry de Sainct Didier, Esq. was a 16th century French fencing master. He was born to a noble family in Pertuis in the Provence region of France, son of Luc de Sainct Didier. Sainct Didier made his career in the French army, ultimately serving 25 years and seeing action in Piedmont, Italy from 1554 - 1555. He wrote of himself that he "lived his whole life learning to fight with the single sword" and eventually "reached a point of perfection" in his art. Apparently he became a fencing master of some renown, for in ca. 1573 he secured a royal privilege for a period of ten years for treatises on a number of weapons, including the dagger, single sword, double swords, sword and buckler, sword and cloak, sword and dagger, sword and shield (both rotella and targe), and greatsword. Unfortunately, only his treatise on the single sword, titled Les secrets du premier livre sur l'espée seule ("Secrets of the Premier Book on the Single Sword") and printed on 4 June 1573, is known to survive; it seems likely that the others were never published at all.
Contents
Treatise
Illustrations |
by John Tse | |
|---|---|---|
| THE TREATY CONTAINING THE SECRETS OF THE FIRST BOOK ON THE SWORD ALONE, MOTHER OF
all weapons, which includes sword and dagger, cape, targe, buckler, rondel; two-handed swords, and dual-wielding swords with portraitures that show the weapon in hand for throwing strikes to defend and attack at the same time, both offensively and defensively, which is very useful and advantageous to become a skillful noble and disciples of Mars; written for the art, order, and practice. Written by Provencal Gentleman Henry de Saint Didier. DEDICATED TO THE MAJESTY OF THE MOST CHRISTIAN KING CHARLES THE NINTH. PARIS, Printed by Jean Mettayer, and Matthurin Challenge, and is sold at Jean Dalier, on the Saint Michel bridge, at the sign of the White Rose, 1573. WITH THE PRIVILEGE OF THE KING. |
TRAICTE CONTENANT LES SECRETS DU PREMIER LIVRE SUR L’ESPEE SEULE, MERE DE
toutes armes, Qui sont espée dague, cappe, targue, bouclier, rondelle, l’espée deux mains & les deux espées, avec ses pourtraictures, ayans les armes au poing pour se deffendre & offencer à un mesme temps des coups qu’on peut tirer, tant en assaillant qu’en deffendant, fort utile & profitable pour adextrer la noblesse, & suposts de Mars : redigé par art, ordre & pratique. Composé par Henry de Sainct Didier Gentilhomme Provençal. DEDIÉ À LÀ MAJESTE DU ROY TRESCHRESTIEN CHARLES NEUVIESME. À PARIS, Imprimé par Jean Mettayer, & Matthurin Challenge, & se vend chez Jean Dalier, sur le pont Sainct Michel, à l’enseigne de la Rose blanche, 1573. AVEC PRIVILEGE DU ROY. | |
| LETTER TO THE KING.
SIRE, It does not please me to say how many are to be praised for those who strive, as they say, to help or even perfect the nature of reducing confusion to order, and in such a way that the face of it appeared rough, sick, and inaccessible; was made easy, accessible, and approachable by them. Even though the only harm that results from confusion and disorder, and among other things that are proper to the Gentlemen make them quite recommendable. Why would I turn my pen elsewhere to show you that to restore a battle that is in disarray, to put it back in its previous order, that a leader must be familiar with two things. To make certain decisions to save time and the place, where and when to stop the broken ranks and by a feint to divert the enemies, while the remaining troops reform and regroup. That decision cannot be acquired, even the reason for it cannot be believed without the second point that I the leader must make is truly necessary, which is having the experience of things, from which arises the aforementioned decision. SIRE, whoever wants to put art or doctrine back in order to avoid confusion lest in the end it will be wasted, decision is required, arising from the experience seen through the exercise of the art which I have from having served in battle, very much for your grandfather as well as for your Majesty, for twenty years in Piedmont and elsewhere. I can justly attribute to myself having used my life to experience such arms, so much so that accumulating such evidence may have allowed me to to perfect the art and the practice of them. So seeing how confused and disordered they have been and are for today by everyone shown and practiced, have in my mind figured some model or idea, which as an example, I make sure that the order will not only be good so the art that consists of it will be completely restored, and will reach closer to perfection which I have longed for, both because of my powerlessness and extreme poverty (the enemy of good spirits) as well as to be prevented from serving you, kept hidden and buried among my papers in my office where the Muses after martial efforts made me, and hope that will keep me company. But I now have the desire to give you a most humble and pleasant service, far from the zeal that all my life I have had to fencing and to those who enjoy them and who make a profession of them have allowed little, that in this time when Mars gives us some respite, I have not been emboldened to present myself to your Majesty, something not worthy of such a great Monarch, but very suitable for the exercise of a common man, both in war and in peace, namely a treatise on the sword alone, mother of all weapons, that I wrote according to my opinions, which contains six points that I declare had never been organized and their proofs, both by reason and by effect attached to the end. SIRE, this here will contain this little work, which is like a summary or collection of the first book that I still have beside me. If your Majesty appreciates this, with God giving me the grace to live, I hope by means of your Majesty to later enlighten others. Therefore, you who is first and foremost to drive skill to the nobility, I thought you who is the patron of fencing worthy of this treatise, begging you most humbly where and when it would be reputed by other, to please take my ardent affection, which for a long time has been dedicated to offer you the most humble and pleasant service in payment for employing me for something of which this concerns, and I will be more than happy with endless opportunity and will, more than great to pray to the Sovereign Rector of the Universe to give you a long and happy life, and for the boundary of your Empire to only be the Sea.
|
EPISTRE AU ROY.
SIRE, Je ne m’amuseray à vous descrire combien sont à louer ceux qui taschans (comme l’on dit) ayder voire parfaire la nature, ont reduit les choses confuses en ordres, & de telle sorte que ce que de primeface sembloit rude, malaisé, & inaccessible, a esté par eux rendu aisé, traictable, & facile à aborder. Veu mesmement que le seul mal qui provient de la confusion & desordre des choses, et entre autres de celle qui sont propres aux Gentils-hommes les rendent assez recommandables. Parquoy tourneray ailleurs ma plume à vous remonstrer, que pour restaurer une bataille qui est en derroute, & la remettre en son pristin[1] ordre, il est besoin à un chef avoir deux choses bien familieres. Assavoir le jugement, pour gaigner le temps & le lieu, où & quand il faut arrester les rancs rompus & par une fainte cargue amuser les ennemis, pendant que le reste des troupes se rassemble & reserre. Lequel jugement ne se peut acquerir, voire la raison d’iceluy ne se peut croire sans le second poinct que je dy au chef estre fort necessaire, qui est l’experience des choses, de laquelle naist le jugement susdit. (SIRE) quiconque veut remettre quelque art ou doctrine en son ordre ou la tirer de la confusion, de peur qu’en fin elle ne se gaste, il est requis qu’il soit fourny de jugement, nay de l’experience veue par lexercice dudit art, ce que je ne dy sans cause car ayant fait service au faict des armes, tant à voz ayeux, comme aussi à vostre Majesté, par l’espace de vingtcinq ans en Piedmont & ailleurs. Je me puis justement attribuer avoir usé ma vie à l’expérience desdites armes, tellement qu’une si longue preuve peut avoir en moy engendré quelque perfection de l’art & pratique d’icelles. De sorte que voyant combien confusément, & avec mauvais ordre elles ont esté & sont pour le jourd’huy par tout le monde monstrées, & pratiquées, ay en mon cerveau figuré quelque patron ou idée, suivant laquelle comme exemplaire, je me fay fort que l’ordre en sera non seulement bon, ains l’art qui y consiste sera du tout restauré, & atteindra plus prés sa perfection, lequel j’ay par longs jours, tant à cause de mon impuissance & extreme pauvreté (ennemie des bons esprits) comme aussi pour estre empesché à vostre service, tenu caché & ensevely parmy mes papiers en mon cabinet, où les Muses aprés les efforts martiaux m’ont fait, & espere que me feront compaignie. Mais maintenant le desir que j’ay de vous faire treshumble & tresagreable service, loinct le zelle que toute ma vie j’ay eu aux armes, & à ceux qui les aiment, & qui en font profession, n’ont peu permettre, qu’en ce temps (ou Mars nous donne quelque relasche) je ne me sois enhardy presenter à vostre Majesté, chose non digne d’un tel & si grand Monarque, mais fort propre pour l’exercice d’un commun père, tant des armes que de paix, scavoir, un traicté sur l’espée seule, mere de toutes armes, que j’ay composé suivant mon petit jugement, dans lequel sont contenus six poincts, par cy aprés declarez, avec un ordre, non encores jamais usité, & la preuve d’iceluy, tant par raison que par effait attaché au bout. Voyla (SIRE) que contiendra, à present ce petit œuvre, qui est comme un sommaire ou recueil du premier livre que j’ay encores par devers moy. Parquoy si vostre Majesté prent quelque goust à cestuy cy, Dieu me donnant la grace de vivre, j’espere par le moyen de vostredite Majesté en mettre par cy aprés d’autres en lumiere, Donc cestuy (qui est le premier & principal pour adextrer la noblesse) j’ay pensé digne de vous, qui estes le protecteur, & soustien des armes, desquelles il traicte, vous suppliant plusque treshumblement, là & quand il seroit reputé autre vous plaise prendre mon ardente affection, laquelle de long temps a esté dediée à vous offrir treshumble, & tresagreable service, en payement m’employant à quelque chose, qui concerne iceluy, & je me tiendray plus que tresheureux avec perpetuelle occasion & volonté, plus que grande de prier le souverain Recteur de l’univers vous donner treslongue, & tresheureuse vie. Et pour borne de vostre Empire la seule Mer Occeane. | |
| Your most humble, and obedient servant, Henry de S. Didier, Provencal Gentleman. |
Vostre treshumble, & obeïssant serviteur, Henry de S. Didier, Gentilhomme Provençal. | |
| The following six points are required to understand and above all else to best execute the secrets of the sword alone and all other weapons that are dependent.
The first is how many types of steps there are in the art of said fencing, how to choose the best, and to explain why. |
S’ensuivent les secrets de ceste espée seule, & de toutes les autres armes qui en dépendent, pour lesquels entendre, & sur tout mieux executer, six poinct sont requis.
Le premier est combien de desmarches il y a en tout l’art desdites armes, & eslire la meillleure, & en donner raison. | |
| The second: how many guards and placements there are in fencing, to choose the best, and explain the reason. | Le second, combien de gardes, & situations y a ausdittes armes & eslire la meilleure, & par quelle raison. | |
| The third: how many strikes the aggressive enemy can attack the defender and to give the same explanation. | Le troisiesme, de combien de coups l’ennemy aggresseur peut offencer le deffendeur & en donner pareille raison. | |
| The fourth: how many distinct targets can be listed for the strikes on a person, both in attacking as well as in defending. | Le quatriesme, en combien de lieux propres se peuvent adapter lesdits coups sur la personne, tant en assaillant, qu’en deffendant. | |
| The fifth is namely for all those who make or will make it their profession by teaching fencing: being able to defend and attack at the same time some strike or strikes that one can throw, and thus if they do not know how can they teach their disciples. | Le cinquiesme, sçavoir, à tous ceux qui font, ou feront, cy aprés profession de monstrer audites armes : soy deffendre & offencer à un mesme temps de quelque coup ou coups qu’on peut tirer, & par ainsi s’ils ne les sçavent comment les pourront ils monstrer à leurs disciples. | |
| By the sixth point, which is the last, we will see a great secret which is to decide which strike that the attacker can throw on the defender and will be given an explanation. | Par le sixiesme poinct, qui est le dernier on verra un grand secret, qui est de juger du coup que l’assaillant peut tirer sur le deffendeur & en sera donné raison. | |
| Regarding the first point, which is to know how many steps there are, I answer that there are no more than two because we have no more than two feet. | Quand au premier poinct, c’est à sçavoir combien il y a de desmarches, je respond qu’il n’y en a[2]que deux, par ce que nous n’avons que deux pieds. | |
| Some stand on the right foot, others on the left foot, however none give good reasons for one step or the other. But rest assured when he must take the sword in hand, knowing which of the two steps is better, more certain, and more effective is necessary to keep to execute the art. | Les aucuns se tiennent sur le pied droict, les autres sur le pied gauche, toutefois en donnent bien peu de raisons, soy tenant sur l’une ou sur l’autre desmarche. Mais pour estre bien asseuré quand il est besoing de mettre l’espée au poing, faut sçavoir laquelle desdites deux desmarches est la meilleure & la plus certaine & superlative & en icelle comme dit est se faut tenir pour executer ledit art. | |
| As for me I favor with experience and proof that the step which is done by standing on the left foot initially in putting sword in hand is better and more effective, both for attacking and for defending. How little that our previous demonstrators keep to either on one or the other, give very little reason. Because of this I will conclude that there are no more than two steps in the entire art to start this off. | Quant à moy je soustiens avec l’esperience & preuve la desmarche qui se faict, soy tenant sur le pied gauche, pour la premiere foys, en mettant l’espée au poing, est la plus certaine & meilleure, tant pour l’assaillant que pour le deffendant. Combien que peu de noz encestres demonstrateurs s’y tiennent, & soy y tenant, tant sur l’un que sur l’autre, en donnent bien peu de raison. À ceste cause je concluray qu’il n’y a que deux desmarches en tout l’art, pour bien commencer iceluy. | |
| And in order to effectively follow the teachers and imitate them, one must choose the better of two good things, and of two bad things to avoid both if possible and if not at least avoid the worse; and in doing so I advise all said adherents to take the better of the two steps, which is the one where you stand on the left foot initially with weapons in hand to make one of the three drawings. | Et pour bien suivre les doctes, & les immiter, faut de deux choses bonnes choisir la meilleure, & de deux mauvaises, eviter les deux, si faire se peut, sinon la pire, & en ce faisant, je conseille à tous lesdits suppots de prendre la meilleure desdites deux desmarches, qui est celle qu’on se tient sur le pied gauche pour la premiere fois, en mettant les armes au poing, faisant un desdits trois desgainements. | |
| The following are the declaration and reasons of the six points.
The first reason is that there are no more than two steps, the one on the right foot and the other on the left foot. |
Sensuivent cy aprés les declarations & raisons desdits six poincts.
La raison du premier est qu’il n’y a que deux desmarches, l’une se fait sur le pied droit, & l’autre sur le pied gauche. | |
| As for me I believe that the left foot is the best because one can be free to take more time and move farther than on the step of the right foot, and therefore to attack effectively and to defend better, as will be seen later in the section on the strikes. | Quant à moy je dy soy tenant sur le pied gauche est le meilleur, par ce que y estant on a liberté de prendre plus de temps, & grande course, que sur la desmarche du pied droict & par consequent de bien assaillir, & de beaucoup mieux se deffendre, comme se verra cy aprés à l’ordre des coups. | |
| This is the reason why we know that stepping with the left foot is better than that of the right foot. | Voyla la raison pourquoy la desmarche qu’on faict sus ledit pied gauche, est meilleure que celle dudit pied droict. | |
The second is knowing how many guards and placements there are of said fencing. I say that there are no more than three guards and three principal placements.
|
La seconde est sçavoir combien de gardes & situations il y a ausdites armes. Je dis qu’il n’y a que trois gardes, & trois assituations principalles.
| |
| Some demonstrators, when they define the guards, start at the top. As for me, I start on the bottom, since everything begins at the foundations. For example, learned people do not start by teaching advanced level sciences; neither do masons start on the buildings when they construct houses; they start on the foundations. And so I start on the low guard which is the foundation to guarding effectively. | Les aucuns demonstrateurs, quand ils definissent lesdites gardes, accommencent à la haute. Quant à moy, je commence à la basse, attendu que toutes choses se commencent aux fondements. Comme pour exemple, les gens doctes ne commencent à monstrer les sciences aux hautes, ne les maçons quand ils viennent à commencer à bastir les maisons, ne commencent pas à la tuille, ains au fondement. Et par ainsi je commence à la basse, qui est le fondement qu’on doit bien garder. | |
| It is true that this low guard can itself generate two other lows: one on the right side and the other on the left side. | Bien est vray, que de ceste garde basse, s’en peut engendrer deux autres basses, l’une est sur le costé droit, l’autre sur le costé gauche. | |
| This one which is the right side leaves the natural form and domain of the original one and participates on the right side. | Celle qui se fait sur le costé droit, elle se faict laissant la nature, & proprieté de leurditte mere, & participer sur le costé droict. | |
| The one which is the left side also leaves the natural form of its said originator and participate on the left side. | Celle qui se fait sur le costé gauche, elle se fait aussi laissant la nature, & estre de saditte mere, & participer du costé gauche. | |
| These two guards created by the low is often done for drawing some ignorant strikes who makes either a high right-hand or high thrust; because we cannot use another strike, which we easily can trick and hit the attacking enemy who would be surprised, and would not consider the mistake that could come from being on the two imagined guards. But the original low guard is the most effective, so therefore there are no more than three guards as stated. | Cesdites deux gardes engendrées de ladite basse, elle se font bien souvent pour attirer quelque coup des ignorans, qui fera un maindroict, ou un estoc haut ; car autre coup on ne peut, sur lesquels facilement on peut attraper & toucher l’ennemy assaillant qui sera estourdy, & ne considerera l’accident qui peut venir, estant sur sesdittes deux gardes faintes. Mais la garde basse leur mere est la plus certaine, de sorte qu’il n’y a que trois gardes, comme dit est. | |
The third point that one must know is how many strikes the attacking enemy can attack the defender. As for me I say that the attacker and defender can attack with no more than three strikes. Which are:
|
Le troisiesme poinct est qu’il faut scavoir de combien de coups l’ennemy assaillant peut offencer le deffendant. Quant à moy, je dy que l’assaillant & deffendant ne se peuvent offencer que de trois coups. Qui sont,
| |
| It is true that they can be multiplied in six distinct targets on the human body, which must be well-protected, such as as a good tennis player must protect the goal[3] well so that the ball of the opposing party does not hit it. So too must a good fencer be careful that one of the three strikes do not hit the six targets that can be adapted as stated, which will be seen later. | Bien est vray qu’ils se peuvent multiplier en six lieux propres sur corps humain, qui faut bien garder, tout ainsi qu’un bon joueur de paulme faut qu’il garde bien l’es,[4] que lesteu[5] de partie adverse ne le touche. Aussi faut il qu’un bon tireur d’armes garde bien qu’un desdits trois coups ne touchent aux six lieux ausquels se peuvent adapter comme dit est, dont se verront cy apres. | |
| It should be noted that fencing and tennis are related, and whoever knows how to play tennis well will be able to strike well easily and early in fencing. | Faut noter que les armes, & la paulme sont cousins germains, & qui scaura bien jouer à la paulme, facilement & tost scaura bien tirer des armes. | |
| The fourth point is that attacking and defending can attack with no more than three said strikes: it is true that they can be multiplied and adapted as have been promised above at six distinct targets on a person, either in attacking or in defending, and whoever knows the means to defend and attack with the three strikes at the same time when multiplied can know a hundred strikes, which is above and will be defined later. | Le quatriesme poinct est, que l’assaillant & deffendant ne se peuvent offencer que desdicts trois coups : bien est vray qu’ils se peuvent multiplier, & adapter comme avons promis si dessus en six lieux propres sur la person ne, soit en assaillant, ou en deffendant, & qui scaura le moyen de soy deffendre, & offencer à un mesme temps, comme ce peult, desdicts trois coups, qui sont cy dessus & seront si aprés definis, estant multipliez il en scaura cent. | |
The following are the names of the six distinct targets where one can and must throw the three strikes which are:
|
Sensuivent les noms desdits six lieux propres, ou fault, & se peuvent tirer les susdicts trois coups, c’est à dire,
| |
| The first strike and target is a low right-hand to the left leg of the defender. | Le premier coup & lieu, est un maindroict, de bas au jarret gauche du deffendant. | |
| The second strike and target is a low reversal to the right leg of the defender if he is right; and if he left, it will be done at his left leg. | Le second coup & lieu, est un renvers, de bas au jarret droict du deffendeur, s’il est droictié, & s’il est gauché, se fera au jarret gauche. | |
| The third target, the right-hand, is multiplied once from above on the left side of the defender. | Le troisieme lieu, ledict maindroict est multiplié une fois d’hault sur le costé gauche du deffendant. | |
| The fourth target is a high reversal at the right shoulders of the defender, multiplied once. | Le quatriesme lieu est un renvers d’hault sur l’espaulle droicte du deffendant, estans multiplié une fois. | |
| The fifth target is the left nipple, to which the attacking Lieutenant throws a thrust to the Provost, which is the third strike. | Le cinquiesme lieu, est le tetin gauche, auquel le Lieutenent assaillant tirera un estoc au Prevost, qui est ledict troisieme coup. | |
| The sixth and final target, is the right nipple of the Provost to which the Lieutenant throws a thrust, which is the third strike, being multiplied once like the Right-Hand and the Reversal. | Le sixiesme & dernier lieu, est le tetin droict dudict Prevost auquel le Lieutenent tirera un estoc, qui est ledict troisiesme coup, estant multiplié une fois comme ledict Maindroict, & Renvers. | |
| The end of the six targets, which is also the end of the fourth point. | Fin desdicts six lieux, qui est aussi la fin du quatriesme poinct. | |
| The fifth is that it is necessary to be defending and attacking at the same time with the three strikes, adapting and throwing at the targets, both in attacking and in defending observing the time that is required. All of which will then be shown and declared at length in the instruction of the sword alone. | Le cinquiesme est, qu’il fault sçavoir soy deffendre & offencer à un mesme temps desdits trois coups, adaptez & tirez aux susdits lieux, tant en assaillant qu’en deffendant observant bien le temps qui est requis. Dont le tout sera cy aprés monstré & declaré au long à l’instruction de ceste espée seule. | |
| The sixth and last point is one of the good ones that is required to know in all of the art, which is to decide which strikes could be thrown, both in attacking and in defending, because being able to decide easily will be provide a remedy; otherwise it will be hard. And to do this we must look at the sword point and never lose sight of it and in doing so, we will easily decide which strike we will find to defend and attack at the same time, as promised. | Le sixiesme & et dernier poinct est un des bons qui soit requis de sçavoir en tout l’art, qui est juger du coup qui se peut tirer, tant en assaillant qu’en deffendant, car le jugeant facilement on y trouvera son remede, autrement non. Et pour ce faire faut regarder la pointe de l’espée, & ne la perdre jamais de veue, & en ce faisant, facilement on jugera du coup, le jugeant on trouvera moyen de soy deffendre & offencer, comme j’ay promis à un mesme temps. | |
| The reason to decide the strikes is that the outside, which is the sword point, directs and leads by the inside, which is the will and knows not the sword point, which is the outside, to be so skillful as the observation, and therefore the observation of deciding the strike and gaining time. The observation and the gained time could succeed and precede the outside, which is the strikes that the Lieutenant could throw at the defending Provost, and there we can find the remedy. | La raison pour juger d’un desdits coups est que l’exterieur, qui est ladite pointe de l’espée, se conduit & meine par l’interieur, qui est la volonté, & ne scauroit la pointe de l’espée, qui est l’exterieur, estre si habile que la veue, & par consequent la veue fait juger du coup, & gaigner le temps. La veue & le temps gaignées peuvent succeder & prealler[6] ledit exterieur, qui est l’un desdits coups que le Lieutenant peut tirer sur le Prevost deffendant, & par là on peut trouver son remede. | |
| This is the end and the declaration of the sixth and last point, which is truly necessary to know in order to understand this weapon and everything else on the same subject.
Following the aforementioned six points, someone named Fabrice and Jules came to see me once with some of his people, because they had heard talks of me, and they were told that I was writing a book on fencing and that I had dedicated it to the King. Avaricious and willing to know even more of fencing than they knew, they begged me to show them the book, which I refused until his said Majesty had seen it, and then seeing their good will knowing that they had not come to chatter to try to see the contents of the book, I am excited to discuss with them some points contained in fencing and asked them certain questions, which we will be able to see later, along with their responses, by which we can easily judge who best touches the goal of the true definition and demonstration of said fencing. |
Voicy la fin & declaration du sixiesme & dernier poinct, qui est necessaire de scavoir à tous, pour l’intelligence de ceste arme, & de toutes les autres qui sont du mesme subjet.
Suyvant les dessusdits six poincts, un nommé Fabrice[7] & Jule, me vindrent une fois voir, avec quelques uns de leur païs, par ce qu’ils avoient ouy parler de moy, & leur avoit on dit que je composois un livre sus les armes & que je l’avois dedié au Roy. Eux cupides & volontaires, de sçavoir encores plus ausdites armes qu’ils ne sçavoient, me prierent de leur monstrer ledit livre, ce que je leur fis refus, (jusques à ce que ladite Majesté l’eust veu) & alors voyant leurs volontez bonnes, & qui n’estoient venus à moy pour eux jacter, ains pour tascher à voir le contenu dudit livre, cela m’esmeut de discourir avecques eux quelques poincts contenuz ausdites armes, & leurs fis certaines interrogations, qu’on pourra voir cy aprés avec leurs responses, par lesquelles on pourra facillement juger qui touche mieux au but de la vraye definition, & demonstration desdites armes. | |
| And so I come attacking Fabrice first, and say to him, "Sir Fabrice, before discussing presently with you about none other than fencing, I want to know how many strikes the attacking enemy can attack the defender. And yet with your grace, I pray you tell me." | Et alors je me viens atacquer premierement audit Fabrice, & luy dis Seigneur Fabrice, avant que tirer à present avec vous, ny avec autre ausdites armes, je veux sçavoir de combien de coups l’ennemy assaillant peut offencer le deffendant. Et pourtant, de grace vous prie, le moy dire. | |
| And so responding Fabrice said that there are many blows, blows in Neapolitan is what is called strikes in French. And hearing this response uttered by Fabrice the Author answered that this answer is infinite and vague. Responding again Fabrice asked, "Sir why do you say that my answer is impertinent?" | Et alors respondit ledit Fabrice & dit, de plusieurs bottes, bottes en napollitain vaut autant à dire que coups en françois. Et encores oyant ledit Autheur cette response proferée par ledit Fabrice, estre infinie et incertaine. Respondit encore ledit Fabrice & dist seigneur pourquoy dictes vous que ma reponse est impertinente. | |
| Responding Saint Didier says that every answer with infinite points are vague, so to this said answer of many blows from Fabrice is impertinent. | Respond ledit de Sainct Didier & dit que toute response infinie n’a point de certitude, à ceste cause ladite response qu’a ledit Fabrice respondu de plusieurs bottes est impertinente. | |
And so Fabrice saw that I was shaking my head, meaning that he did not answer me pertinently. Fabrice comes to his senses and gives another answer and says that there are five blows that the attacking enemy could attack the defender: And again I told him to define them, and this time he says:
And hearing this answer uttered by Fabrice when he said the above five Blows. |
Et alors ledit Fabrice voyant que je remuois la teste, signifiant par là qu’il ne m’avoit respondu pertinement. Va ledit Fabrice un petit reprendre ses esprits, & feit autre response, & dit que de cinq bottes l’ennemy assaillant pouvoit offencer le deffendant : Et encores je luy dis definissez les, & à ceste heure il dit d’un,
Et oyant ceste responce proferée par ledit Fabrice, quand il dit cy dessus de cinq Bottes. | |
| So the Author, without pause responded to him and said that these two answers that he responded is wrong, whereas one is a response that is plural, the other is singular. The plural is worthless given the reason above; the singular which is when he said above about there being five blows is also impertinent. The reason is because there are too many and thus some must be removed. | Alors le dit Autheur, sans bien peu d’intervalle luy respondit & dit que telles responses contenoient deux chefs, par lesquels il avoit mal respondu, attendu qu’il y a une response qui est plurielle, & l’autre singuliere. La plurielle ne vaut rien, la raison est cy dessus donnée, la singuliere qui est quand il a dit cy dessus de cinq bottes n’est aussi pertinente. La raison par ce que il en y a trop & par ainsi en faut oster. | |
| Fabrice, seeing that I said that we must remove some of the strikes of the blows, replied to know of my true definition and secret and said to me, "Sir S. Didier, why have you said these responses that I said above that of the many blows and of the five blows are incorrectly answered by me?" | Voyant ce, ledit Fabrice, que je dits qu’il falloit oster quelques coups desdites bottes, me repliqua pour scavoir de moy la vraye definition & secret, & me dit, Seigneur de S. Didier, pourquoy avez-vous dit que les responses, que je dy cy dessus, de plusieurs & de cinq bottes n’estoient par moy bien ne deuement respondues ? | |
| Responding a second time the Author, and saying that truly such above responses are worthless, at least the plural, as has been defined above, and will be shown as an example next. | Respond derechef ledit Autheur, & dit que veritablement telles susdites responses ne valloient rien, au moins la plurielle, comme a esté definy cy dessus, & sera monstré cy aprés comme par exemple. | |
| If one would speak and interrogate a camp master and asked him how many times the enemy can come up to a camp, and he answered from several, I would say that such a response would be uncertain and therefore impertinent, whereas when we ask such aforementioned questions to a camp master or any other masters, they must be certain of their responses. Otherwise they are not fit to rule or govern a camp nor a republic, since it is necessary to be sure of how many times the enemy can come up to a camp; to that end that we can put as many as a hundred, for the preservation and protection of it. | Si on disoit & interrogoit un maistre de camp, & on luy demandast de combien d’advenues l’ennemy peut venir sur un camp, & qu’il respondit de plusieurs : Je dy que telle response seroit incertaine, & par consequent n’est pertinente, attendu que quand on fait telle susdittes interrogations à un maistre de camp ou autres, tels doivent estre certains de leurs responses. Autrement ne sont dignes de regir ne gouverner un camp, ne republiques, attendu qu’il faut estre certain de combien d’advenues l’ennemy peut venir sur un camp, à celle fin qu’on y puisse mettre autant de centinelles, pour la conservation & garde d’iceluy. | |
| And to answer and conclude to what was said above we need to know how many strikes the enemy can attack us, to know how to remedy and defend our body and honor, like a camp master who has a camp of a hundred or fifty thousand men because it is in our specific interest. As for me, I say with the learned that what can be done with less is better than what can be done with more. Because of this I will remove two of the five blows that Fabrice have because I say they are redundant, which is Fendente and Imbrocatta, and so remain no more than three, which is defined above and will be next. | Et pour respondre & conclure, à ce que dessus est dit nous avons autant de besoin de scavoir de combien de coups l’ennemy nous peut offenser, pour scavoir à iceux remedier & deffendre nostre corps & honneur, comme un Maistre de camps qui a un camp de cent ou cinquante mille hommes car c’est nostre interest particulier. Quant à moy je dis avec les doctes que ce qui ce peut faire avec peu est meilleur que ce qui ce fait avec beaucoup. À ceste cause j’osteray deux desdites cinq bottes que tient le dit Fabrice par ce que je les dy estre superflus, qui sont Fendant, & Imbronccade, & n’en demeurera plus que trois, qui sont cy dessus par moy definis, & seront cy apres. | |
| The following is the declaration and reason why the Author removes Fendente against the opinion of Fabrice and Jules and many others, who nevertheless always put them in the list of the strikes.
The reason why I first removed Fedante is because it cannot actually be done. Because any Fendente that is true must hold and must not leave the top and middle of the thing you want to slash. I know of no man, as long as I have practiced in all the sciences or arts, that having a sword in hand, cutlass, or another weapons that can properly slash with whatever strikes that he can do, will not participate either on one side or the other, which gives up the middle. And yet if such a strike is thrown in the right side, is not Fedente but is Right-Hand, and if kept on the left side, it is not Fendente but will be a Reversal. |
S’ensuit la declaration & raison cy aprés pourquoy ledit Autheur oste ledit Fendant, contre l’opinion desdits Fabrice & Julle, & plusieurs autres, ce neantmoins de tout temps les ont mis & mettent au ranc desdits coups.
La raison pourquoy j’oste premierement ledit Fendant est par ce qu’il ne se peut faire proprement. Car tout Fendant qui est propre faut qu’il tienne & ne laisse le sommet & meillieu de la chose qu’on veut fendre. Or est il que je ne sache homme, tant soit il exercé en toutes sciences ou arts, qu’ayant une espée au poing, couttellats, ou autres armes à ce propres à fendre, que quelque coup qu’il puisse faire, ne participe ou d’un costé ou d’autre, laissant le meillieu. Et pourtant si tel coup tiré participe du costé droict, n’est Fendant, ains Maindroict, & s’il tient plus du costé gauche, n’est aussi Fendant, mais sera un Renvers. | |
| This is the reason why Fendente is removed by the Author: of the number of blows that were held by Fabrice, and in it remains no more than four. | Voyla la raison pourquoy ledit Fendant est osté par ledit Autheur : du nombre desdites cinq bottes que tient le susdit Fabrice, & n’en demourera plus que quatre. | |
| This is also why the author declared that he removed Imbrocatta from the number of the five blows.
The reason is because Stoccata and Imbrocatta are both the same, like grapejuice green and green grapejuice, which are also the same. Because by asking for one or the other, one will never admit that they are the same. As such, a Stoccata and an Imbrocatta are the same thing since it is only the point that differs. And by removing the Fendente and Imbrocatta as stated, there will remain no more than three of the strikes that are above declared in the third point. |
Cy aprés est aussi declaré pourquoy ledit autheur oste ladite Imbronccade du nombre desdites cinq bottes.
La raison, par ce qu’Estoccade & Imbronccade, c’est tout un, comme verjus verd, & verd verjus,[8] c’est aussi tout un. Car en demandant l’un ou l’autre, on ne vous apportera jamais que le mesme. Aussi une Estoccade, & une Imbronccade, c’est une mesme chose, attendu que cest tousjours la pointe qui faict la faction. Et par ainsi ostant comme dit est, le Fendant & imbronccade, n’en demoureront plus que lesdits trois coups qui sont cy dessus declarez audit troisiesme poinct. | |
| Here is the end of every requirement to know and to understand for whoever wants to be skillful in fencing.
To truly understand fencing and discover the art, order and pratice of it, he must imagine three personas: the first is the Author, the second the Lieutenant, the third the Provost. The Author will describe all of the orders that the Lieutenant and the Provost must fulfill in the art of the sword alone, which follows next and is now commencing. END. |
Voicy la fin de tout ce qui est requis & necessaire de scavoir & entendre à un chacun, qui veut estre adroit ausdites armes
Pour bien donner entendre lesdites armes, & discourir de l’art, ordre & pratique d’icelle, il a fallu feindre trois personnages : lLe premier c’est l’Autheur, le second le Lieutenant, le troisiesme le Prevost. Par l’Autheur sera descrit cy aprés tout l’ordre que doit tenir ledit Lieutenant & Prevost en l’art de ceste espée seule, laquelle s’ensuit cy aprés & le commencement d’icelle. FIN. | |
| To the King.
By the Gentleman Stephen of Guette. SIRE, it is all but certain that men are made |
Au Roy.
Par Estienne de la Guette, gentilhomme. SIRE, il est tout certain que les hommes sont faits | |
| Sonnet to the author by Sir L'Aigle.
I already see, Sainct Didier, the intuition of your beautiful book |
Sonnet à l’auteur, par Monsieur de l’Aigle.
Je voy ja, Sainct Didier, au flair de ton beau livre | |
Illustrations |
by John Tse | |
|---|---|---|
| The following is how one must be planted to put the sword in hand, both in time of peace and in times of war, with the steps, guards, drawings, and placements required in this art, which is truly necessary to those who wish to practice fencing.
Four footprints are placed below the Lieutenant's and the Provost's feet which are marked number 1, and another 2, and another 3, and another 4, which serves the Lieutenant and Provost and everyone else to teach how one must skillfully make all the steps, drawings, guards, and placement of the weapons effectively as imagined in this rectangle. |
Sensuit cy aprés comment il se fault planter pour bien mettre l’espée au poing, tant en temps de paix qu’en temps de guerre, avec les desmarches, gardes, desgainements, & assituations requises en cest art, qui sont fort necessaires à ceux qui veulent exercer lesdites armes.
Cy aprés quatre semelles mises & assituées au dessous des pieds du Lieutenent & Prevost, dont à l’une est cotté en chiffre 1, & à l’autre 2, & à l’autre 3, & l’autre 4, qui servent au Lieutenent & Prevost, & à tous autres, monstrans comment il faut bien & dextrement faires toutes les desmarches, desgainements, gardes, & assituations aux armes faignant un tel quadriangle, | |
| The position and general plan to make the first step and the first, second, and third drawings, which is necessary to know both for the attacking Lieutenant as well as for the defending Provost and all those who love fencing, carrying the sword on their side.
Here follows the declaration of this position and plan for the Lieutenant. And to do this the Lieutenant first must have the feet together thus placed, keeping the left foot in the footprint marked close to number 1 and the right foot in the other footprint where it is marked number 2, keeping the right hand on the sword hilt and the left hand on the sword's scabbard, showing that he wants to teach the Provost how this must be made, as shown above at the portraiture of the Lieutenant marked number 1 behind the hat. The end of what the Leiutenant needs to do. The declaration of the plan and position of the Provost. And to do this the Provost needs to have the feet together, keeping the left foot in the footprint marked above at number 1 and the right foot in the other footprint marked above at number 2, keeping the right hand on the sword hilt and the left hand on the scabbard, showing that he is ready to make the necessary first step, as shown by the Lieutenant, which is the first, second, and third drawings, as marked above at its portraiture and figure in number 2. This is the end and declaration of the first plan for the Provost. |
Tenue & plan general, pour faire la premiere desmarche & le premier, second, & tiers desgainements, qui sont necessaires scavoir, tant pour le Lieutenent assaillant, que pour le Prevost deffendant, & à tous autres qui aiment les armes, portans espée en leurs costez.
Icy ensuit la declaration de ceste tenue & plan pour le Lieutenent. Et pour ce faire faut que cestuy premier Lieutenant soit à pied joinct, ainsi placé, tenant le pied gauche dans une semelle, où il y a cotté auprés en chiffre 1, & le pied droict dans l’autre semelle, où il y a auprés cotté en chiffre 2, tenant la main droicte à la garde de son espée, & la main gauche au fourreau de l’espée, monstrant par cela qu’il veut monstrer au Prevost comment il faut qu’il face par cy aprés : comme est monstré cy dessus à la pourtraicture dudit Lieutenent cotté en chiffre au derriere du chappeau 1. La fin de ce que doit faire à present ledit Lieutenent. La declaration du plan & tenue pour ledit Prevost. Et pour ce faire est besoin que ledit Prevost soit à pied joinct, tenant le pied gauche dans une semelle où est cotté au dessous icelle en chiffre 1, & le pied droict dans une autre semelle où est cotté au dessus en chiffre 2, tenant la main droicte à la garde de l’espée, & la main gauche au fourreau d’icelle, monstrant qu’il est prest à faire ce que est necessaire en ceste premiere desmarche, comme luy a monstré ledit Lieutenent, qui est le premier, second, & tiers desgainement, comme est cotté cy dessus à sa pourtraiture & figure en chiffre 2. Voyla la fin & declaration dudit premier plan pour ledit Prevost. | |
| The guard to execute the first step and the first and second drawings for the Lieutenant and Prevost.
And to do the first step for the Lieutenant, he must have the feet together as shown above at the first portraiture marked number 1, and being there he must pull the right foot back on the footprint marked number 3 below, which is the first step. And at the same time, put the sword in hand, for the first drawing carry the sword hilt higher than the right shoulder, placing the sword point straight at the left nipple, content 1, keeping the left hand right of the face, as shown above at the portraiture of the Lieutenant marked number 3 behind the collar. This is the end of the first drawing for the Lieutenant. The following is the second drawing for the Lieutenant. For the second drawing for the Lieutenant, he must have the feet together like so as shown above at the first portraiture marked number 1. And to execute this said second drawing, he must move the right foot a little apart in the air, remove it from the footprint marked 2, carrying the sword hilt, drawing it higher than the shoulder, and the placement of this as above content 1. And in an instant pass the sword above the head, extending strongly the arms, keeping the sword hilt higher than the right shoulder, and placing the sword point at the Provost's left nipple, as shown in the portraiture at number 3. The end of the second drawing for the Lieutenant. This is the declaration for the first and second drawings for the Provost, which is to know how to put the sword in hand as taught by the Lieutenant. And to do this the Provost must remember how he has was placed above at the first plan marked number 2, which is with the feet together, and from there the Provost must make the first drawing by pulling the right foot on footprint 2 back to the footprint marked number 3, which is also the first step, and at the same time put the sword in hand, carrying the sword hilt higher and a bit farther than the right shoulder, placing the sword point straight at the left eye to be on high guard, and keeping the left hand right of the left nipple to deflect the sword point of said Lieutenant if by fortune he wants to advance further, as shown above in the portraiture marked number 4. This is the end of the first drawing of the Provost. The following is the second drawing for the Provost. And to effectively execute the second drawing, the Provost must have the feet together as shown in the portraiture marked number 2, and from there the Provost must pull the right foot out of the footprint where it was in number 2, putting it down a bit, and making the second drawing which is that he must carry the sword hilt in middle guard, and the point straight at the left nipple. And to begin the third drawing, he must pass the sword above the head, extending strongly the arms, and carrying the sword hilt higher and a bit farther than the right shoulder, placing at the same time the sword point straight at the Lieutenant's left eye, and the left hand is kept right of the left nipple, as shown above in the first drawing and as shown at the portraiture marked behind the back of the person marked number 4. The end of the first and second drawings for the Provost. After having shown this said first plan above, being to make the first and second drawings for the Lieutenant and the Provost, stay for the demonstration of the third drawing, after which one will be able to see the guard and position to and to be able to execute and do it. |
Garde pour faire, & executer ladite premiere desmarche, premier & second desgainement, pour le Lieutenent & Prevost.
Et pour faire ledit premier desgainement pour ce Lieutenent, est besoing qu’il soit à pied joinct, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa premiere pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre 1, & y estant, faut qu’il tire le pied droict arriere sur la semelle où est cotté au dessoubs d’icelle en chiffre 3, qui est pour la premiere desmarche. Et à un mesmes temps, mettre l’espée au poing, pour ledit premier desguainement portant la garde de l’espée aussi haut que l’espaule droite, assituant la pointe de l’espée droit le tetin gauche, contant 1, tenant la main gauche droict le visage, comme est monstré si dessus à la pourtraiture dudit Lieutenant, cotté en chiffre au derriere du col 3. Voyla la fin du premier desgainement pour ledit Lieutenent. Sensuit le second desgainement pour ledit Lieutenent. Pour le second desgainement pour ledict Lieutenent, faut qu’il soit ainsi placé à pied joinct, comme est monstré cy dessus, à la premiere pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre 1. Et pour executer cedit second desgainement est besoin, & faut qu’il tienne le pied droit un peu à quartier en l’air, l’ostant de la semelle où est cotté 2, portant la garde de l’espée, la desgainant aussi haute que l’espaule & la situation d’icelle comme dessus contant 1. Et à un instant passer l’espée par dessus la teste, estendant fort le bras, allant pauser ladicte garde de l’espée aussi haute que l’espaulle droitte, assituant la pointe de l’espée au tetin gauche du prevost, comme est cotté à sadite pourtraiture en chiffre 3. La fin du second desgainement pour ledit Lieutenent. Cy aprés est declaré le premier & second desgainement pour ledit Prevost, qui est pour scavoir bien mettre les armes au poing, comme luy monstre ledit Lieutenent. Et pour ce faire fault que ledit Prevost se souvienne comme il estoit placé cy dessus à sondit premier plan cotté en chiffre 2, qui est à pied joinct, & y estant, faut que cedit Prevost, pour faire cedit premier desgainement qu’il tire le pied droict qu’il a sur la semelle cottée 2, arriere sur la semelle où est cotté en chiffre 3, qui est aussi pour la premiere desmarche, & à un mesme temps mettre l’espée au poing, portant la garde de l’espée aussi hault, & un peu d’avantage que l’espaulle droict assituant la poincte de l’espée, estant sur ceste garde haulte, droit l’œil gauche, tenant sa main gauche droict son tetin gauche pour détourner la pointe de l’espée dudit Lieutenent, si par fortune la vouloit advancer davantage, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture cotté en chiffre 4. Voyla la fin de ce premier desgainement pour ledit Prevost. Sensuyt pour iceluy Prevost le second desgainement. Et pour bien executer le second desgainement, fault que ledit Prevost soit à pied joinct, comme est monstré a sadite pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre 2, & y estant, faut que cedit Prevost tire le pied droict hors de la semelle où il estoit, qui est cotté en chiffre 2, la posant un peu à cartier, faisant ledit second desgainement, qui est qu’il faut porter la garde de l’espée en garde moyenne, & la pointe droit le tetin gauche. Et pour commencer ce tiers desgainement, faut passer l’espée par dessus la teste, estendant bien fort le bras que tient icelle, & porter la garde de l’espée aussi haut, & un peu davantage que laditte espaulle droicte, assituant à un mesme temps la pointe de l’espée droict à l’œil gauche dudit Lieutenent, & la main gauche la tenant droict son tetin gauche, comme est dit cy dessus au premier desgainement, & comme est monstré à sadite pourtraiture cotté en chiffre au derriere du dos 4. La fin du premier & second desgaignement pour ledit Prevost. Aprés avoir monstré cy dessus, estant sur ledit premier plan, pour faire le premier & second desgainement pour le Lieutenent & Prevost, reste à monstrer le troisiesme desgainement, dont cy aprés on verra la garde & tenue pour executer & faire iceluy. | |
| The guard and position to start making the third drawing for the demonstrating Lieutenant at the defending Provost.
This third drawing for the Lieutenant is to be done with the feet together, as stated above and shown at the general plan, keeping the left foot on the footprint marked number 1 below, and the right foot at the footprint marked 2, and in order to effectively start this said third drawing, the Lieutenant must remove the right foot from the footprint marked 2 and carry it forward in the air, making the first drawing, which can be seen above at its place in content 1, and while keeping the foot in the air, turn the sword hilt, the back of the hand down and the nails high, placing the sword point straight at the belly, keeping the left hand behind, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 5 behind the hat. The end of the start of the third drawing for the Lieutenant. The third drawing for the Provost starts by having the feet together as shown above in the plan of the Provost marked number 2, keeping the left foot in the footprint marked near number 1, and the right foot in the other footprint marked 2, and to start and do the third drawing, the Provost must put the right foot which is on the footprint marked 2 a bit up in the air. And doing the first drawing that has been made by the Provost above in content 1. And to complete this said drawing, he must turn the nails on the sword hand upwards, content 2, placing the sword point straight at the eyes, keeping the left hand behind, as shown above at the portraiture and figure marked number 6 behind the bonnet. This is the end of the beginning of the third drawing for the Provost. |
Garde & tenue pour commencer à faire troisiesme desgainement pour le Lieutenent demonstrateur, au Prevost deffendeur.
Ce troisiesme desgainement pour ce Lieutenent, il se fait estant à pied joinct, comme est dit cy dessus, & monstré audit plan general, tenant le pied gauche sur la semelle où est cotté au dessous en chiffre 1, & le pied droict à la semelle où est cotté 2, & pour bien commencer cedit troisiesme desgainement, faut que ledit Lieutenent oste le pied droict de ladite semelle, où est cotté 2, & la porter en avant en l’air, faisant le premier desgainement, voy en son lieu cy dessus, contant un, & tenant tousjours le pied en l’air, tournant la garde de l’espée, le dessus de la main en bas, & les ongles en haut, assituant la pointe de l’espée droict au ventre, tenant la main gauche derriere, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture cotté en chiffre au derriere du chappeau 5. La fin du commencement dudit troisiesme desgainement pour le Lieutenent. Le troisiesme desgainement pour ledit Prevost, il se commence & se faict estant à pied joinct, comme est monstré cy dessus au plan dudit Prevost, cotté en chiffre 2, tenant le pied gauche dans une semelle, où est cotté en chiffre auprés 1, & le pied droict dans une autre semelle où est cotté 2, & pour commencer & faire ledit troisiesme desgainement faut que le Prevost mette le pied droict qui est sur la semelle cotté 2 un peu à cartier en l’air. Et faisant le premier desgainement qu’a faict ledit Prevost cy dessus contant 1. Et pour parachever cedict desgainement fault tourner la main de l’espée les ongles en hault, contant 2, assituant la pointe de l’espée droit à la veue, tenant la main gauche derriere, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture & figure cotté en chiffre au derriere du bonnet 6. Voila la fin du commencement dudit troisiesme desgainement pour ledit Prevost. | |
| The last of the third drawing for the Lieutenant and the Provost that is left to declare its properties and significance below as portrayed and completed here.
In order to be effective and graceful to complete the third drawing for the Lieutenant, the Lieutenant must do the plan portrayed above where he keeps the right foot forward in the air after having made the first and second drawing marked in number 5 in order to complete this drawing, which is to leave the right foot over the footprint marked number 3 in this portraiture, turning the back of the hand holding the sword hilt up, as done by the Lieutenant marked number 3 since the artist made a mistake with this one. Yet the Lieutenant is to keep his left hand, making sure that he keeps it well under his sword arm as shown at the portraiture number 7. The last of the final third drawing for the Lieutenant. And in order to complete the third drawing for the Provost, he must come to be on the same plan as the above marked number 5 as shown with the preceding Provost, who keeps the right foot in the air, keeping the back of the hand holding the sword hilt up, and to complete this said third drawing, the Provost must pull the right foot back from the air as stated above and leave it on the fooprint marked number 3 at the portraiture, turning the nails on the sword hand down, placing the sword point straight at the face or better yet the left eye, and keeping the left hand right on the shoulder, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 8. This is the last and final said third drawing for the Provost. |
La fin du troisiesme desgainement pour le Lieutenent & Prevost, que voicy pourtraits & parachevez, reste à declarer cy dessous leurs proprietez & significations
Pour bien, & avec grace parachever ledit troisiesme desgainement pour ce Lieutenent, faut estant sur le plan cy dessus pourtraict, où il tient le pied droict[14] en avant en l’air ayant fait ledit premier & second desgainement, cotté en chiffre, 5, est besoin que ledit Lieutenent, pour parachever ce desgainement, qu’il pause ledit pied droict qu’avoit en l’air, sur la semelle où est cotté à ceste pourtraiture en chiffre 3, retournant la garde de l’espée le dessus de la main en haut, comme fait le Lieutenent où est cotté en chiffre 3, car le pourtrayeur a faict faute à cestuy cy[15]. Mais cestuy Lieutenent icy tient bien sa main gauche, attendu qu’il la tient soubs le coude du bras de l’espée, comme est monstré à sa pourtraiture cotté en chiffre 7. La fin du parachevement dudit troisiesme desgaignement pour ledit Lieutenent. Et pour le parachevement dudit troisiesme desgainement pour ledit Prevost, faut aussi qu’il vienne à faindre estre sur le mesme plan cy dessus cotté 5, en chiffre à l’autre precedent Prevost, lequel tient le pied droict en l’air, tenant la garde de l’espée le dessus de la main en haut, & pour le parachevement de cedit troisiesme desgainement, faut que ledit prochain Prevost tire son pied droict arriere qu’avoit en l’air, comme est dit cy dessus, & le pauser sur la semelle où est cotté à sa pourtraiture en chiffre 3, tournant la main qui tient l’espée les ongles en bas, assituant la pointe de l’espée droict la face, ou l’œil gauche, qui est le mieux, & tenant la main gauche droict son espaulle, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture cotté en chiffre 8. Voyla la fin & parachevement dudit troisiesme[16] desgainement pour ledit Prevost. | |
| General position for both the attacking Lieutenant as well as for the defending Provost, in order to execute the art, order, and practice contained in the sword alone.
In order to show and declare this general position for the Lieutenant, he needs to place his feet together for all strikes, to keep the left foot roughly in the footprint marked number 1, and the right foot in the other footprint also marked on number 2, keeping the right hand at the sword hilt, and the left hand on the scabbard, showing to the Provost how he must do so, as shown above at the portraiture, marked number 9. The end of the position and plan for the Lieutenant. The following is the plan and position that the defending Provost must do as instructed by the Lieutenant. And similarly to do this, the Provost is to place his feet together, keeping the left foot in the footprint marked number 1, and the right foot in the other footprint marked number 2, keeping also his sword on his left side and his right hand open, showing with this gesture that he is ready to take the sword, and to do what the Lieutenant would say, the Provost also is keeping his left hand on his side, showing that he is nimble, and not far to put the sword in hand, and to do as the Lieutenant does marked in number 9, and the Provost must do, and follow everything that is written here, and as is also written at the portraiture and figure marked at number 10. The end of the position and plan for the Provost. |
Tenue generalle, tant pour le Lieutenent assaillant, que pour le Prevost deffendant, pour executer l’art, ordre & pratique contenu en ceste espée seule.
Pour monstrer & declarer ceste tenue generalle pour le Lieutenent, est besoing, & faut à tous coups qu’il soit ainsi placé à pied joinct, ou à peu prés, tenant le pied gauche dans la semelle où est cotté en chiffre 1, & le pied droict dans une autre semelle où est cotté aussi en chiffre 2, tenant la main droicte à la garde l’espée, & la main gauche au fourreau d’icelle, monstrant au Prevost comment il doit faire, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre 9. La fin de ceste tenue & plan pour ledit Lieutenent. S’ensuit le plan & tenue que faut que ledit Prevost deffendant fasse, estant instruit par ledit Lieutenent. Et pour ce faire faut pareillement, que ledit Prevost soit ainsi placé à pied joinct, tenant le pied gauche dans une semelle où est cotté en chiffre 1, & le pied droict en l’autre semelle, où est cotté en chiffre 2, tenant aussi son espée au costé gauche, & sa main droicte ouverte, monstrant par ce signe qu’il est prest à prendre l’espée, & faire ce que ledit Lieutenent luy dira, ledit Prevost tient aussi sa main gauche à son costé, signifiant qui la tient preste, & n’est gueres loin pour mettre l’espée au poing, & faire comme fait ledit Lieutenent cotté en chiffre 9, & cedit Prevost doit faire, & suivre tout ce qui est escrit icy, &[17] comme est aussi escrit à sa pourtraiture, & figure cotté en chiffre 10. La fin de la tenue & plan pour ledit Prevost. | |
| Postion and guard of the first strike of the sword alone, for the Lieutenant, which is a low right-hand at the leg of the Provost, thrown by the Lieutenant, and defended by the Provost, as will be seen after the first strike.
And to do this the Lieutenant is to have the feet together as shown above in the portraiture of the Lieutenant marked number 9, pull the right foot back a little apart, and in drawing his sword will take the sword hilt higher than his shoulder, placing the point straight at the Provost's left nipple, keeping the left hand below the arm, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 11 behind the bonnet. Written for the first guard and position for the Provost, in order to begin the section on the sword alone. And to do this, the Provost must have his feet together as portrayed above marked in number 10. And the Provost having made one of the three drawings, is to remain in the high guard, having pulled the right foot back, keeping the sword hand a bit higher than the right shoulder, placing and aiming the sword point straight at the chin, and keeping the left hand right of his nipple, ready to do whatever is necessary, and will be willing afterwards as shown above at the portraiture and figure of the Provost marked number 12 behind the hat. The end of this first guard for the Provost. |
Tenue & garde du premier coup de ceste espée seule, pour le Lieutenent, qui est un maindroit de bas au jarret du Prevost, tiré par le Lieutenent, & deffendu par le Prevost, comme se verra cy aprés au premier coup.
Et pour ce faire le Lieutenent estant à pied joinct, comme est monstré cy dessus à la pourtraiture dudit Lieutenent cotté en chiffre 9, cedit Lieutenent tirera le pied droict arriere, un peu à cartier, en desgainant son espée, portera la garde d’icelle, en un mesme temps, aussi haute que son espaulle, assituant la pointe droit le tetin gauche du Prevost, tenant la main gauche au dessous du bras, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture cotté en chiffre au derriere du bonnet 11. Escrit pour la premiere garde & tenue pour ledit Prevost, pour commencer l’ordre de ceste espée seule. Et pour ce faire, faut que ledit Prevost soit à pied joinct comme est pourtrait cy dessus, cotté en chiffre 10. Et cedit Prevost ayant fait un desdits trois desgainemens, est demouré sur la garde haute, ayant tiré le pied droict arriere, tenant la main qui tient l’espée, un peu plus haute que l’espaulle droicte, assituant & visant la pointe de l’espée droict le menton, & tient ledit Prevost la main gauche droit son tetin, preste à faire ce que conviendra, & sera besoin cy aprés comme est monstré cy dessus à la pourtraiture & figure dudit Prevost cotté en chiffre au derriere du chappeau 12. La fin de ceste premiere garde pour ledit Prevost. | |
| This guard is almost similar to the one before, hardly different yet it will serve as another one to make and execute the first strike of the sword alone for the Lieutenant and Provost.
In order to declare this guard for the Lieutenant, he must have his feet together to pull the right foot[18] back a little apart, carrying the sword hilt higher than the right shoulder, placing the sword point straight at the throat; the guard of the Lieutenant above marked in number 11 is the same, but the placement isn't because he places the point at the left nipple, whereas this one states it is at the throat, keeping the left hand under the sword arm, as shown below at the portraiture marked on number 13. This is the purpose of this guard for the Lieutenant. The Provost being such that the feet were together and having pulled the right foot back while having remained on the left foot, having made one of the three drawings, and having carried the sword hilt a little higher than the right shoulder by keeping the back of the sword hand up and the nails down as he should, unlike the Lieutenant, as expected since the painter made an error with all of the future Lieutenants because they should be keeping the nails of the sword hand down and keeping them high, but the Provost does this better, and also keeping the left hand above the left lap, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 14. This is the end of the second position, which serves as another one for said defending Provost. |
Cette garde est presque semblable à la sudite, il n’y a guere de difference, & pourtant ne serviront que d’une, pour faire, & executer ledit premier coup de ceste espée seule, pour le Lieutenent & Prevost.
Pour declarer ceste garde, pour ce Lieutenent, faut estant à pied joinct tirer le pied droit[19] arriere un peu à cartier, portant la garde de l’espée aussi haute que l’espaulle droicte, assituant la pointe de l’espée droict à la gorge, la garde du Lieutenent cy dessus cotté en chifffre 11, est de mesmes, mais la situation non, par ce qu’il assitue la pointe de son espée droict le tetin gauche, & cestuy comme est dit à la gorge, tenant sa main gauche au desoubs le bras de l’espée, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre, 13. Voyla la raison de ceste garde pour le Lieutenent. Cedit Prevost estant ainsi à pied joinct a tiré le pied droit arriere, & est demouré sur le pied gauche, ayant fait un desdits trois desgainements, & a porté la garde de l’espée un peu plus haut que l’espaulle droitte, tenant le dessus de la main que tient l’espée en haut, & les ongles en bas, comme il doit, & le dit Lieutenent ne fait, ainsi attendu que le peintre a fait faute à tous lesdits plus prochains Lieutenens, car ils devroient tenir les ongles de la main de l’espée en bas[20], & les tiennent en haut, mais cedit Prevost fait mieux que lesdits, & tient aussi sa main gauche au dessus du giron gauche, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre 14. Voicy la fin de ceste seconde tenue, qui ne sert que d’une pour ledit Prevost deffendeur. | |
| The following is the first strike of the sword alone for the attacking Lieutenant against the defending Provost.
And to do this, this said Lieutenant must have taken the step and one of the drawings, staying on the left foot as the portraiture above marked number 13, and in order to execute this first strike of the sword alone, the Lieutenant will advance the right foot, being on the guard marked 13, and will throw a low right-hand at the Provost's left knee, raising the sword hilt almost as high as the left shoulder, lowering the sword point well down to do this said right-hand at the leg more perfectly, and keeping the left hand as shown above at the portraiture of the Lieutenant marked number 15. This is the end of the first strike of the sword alone for the attacking Lieutenant against the defending Provost. Next is to declare how the Provost will have defended his knee and will have thrown a right-hand at the Lieutenant's arms. And to do this, the Provost being on his left leg, having made one of the three drawings, guards, and placement, and staying on the guard marked number 14 above, the Provost to properly execute, defend, and attack at the same time this said low right-hand, pulls his left foot back and throws a right-hand at the Lieutenant's sword arm, and unlike other ignorant demonstrators who crosses sword against sword when a strike comes from below, which is fine because by that he defends himself; but this strike is better because he defends himself and attacks thereby doing two good things, I recommend that you take the better one, as the Provost also does in executing this said strike, keeping the left hand as shown at the portraiture marked number 16. This is the defense of the low right-hand at the knee defended by the Provost against the Lieutenant. |
Sensuyt le premier coup de ceste espée seule pour le Lieutenent assaillant, contre le Prevost deffendant.
Et pour ce faire, faut que cedit prochain Lieutenent ayant fait la desmarche, & un desdits desgainemens, estant demouré sur le pied gauche, comme est sur la pourtraiture cy dessus cotté en chiffre 13, & pour faire & executer ce premier coup de ceste espée seule, ledit Lieutenent advancera le pied droit, estant sur ladite garde cotté 13, & tirera un maindroit de bas au jarret gauche du Prevost, haussant la garde de l’espée aussi haulte presque l’espaulle gauche, baissant bien la pointe de l’espée en bas, pour faire plus perfectement cedit maindroit au jarret, tenant la main gauche, comme est monstré cy dessus à la pourtraiture dudit Lieutenent cotté en chiffre 15. Voicy la fin du premier coup de ceste espée seule, pour le Lieutenent assaillant, contre le Prevost deffendant. Cy aprés est declaré comment le Prevost a deffendu son jarret, & a tiré un maindroit sur le bras du Lieutenent. Et pour ce faire, ledit Prevost estant sur le pied gauche, ayant fait un des trois desgainements, gardes & assituations, estant demouré sur la dite garde cotté en chiffre cy dessus 14, a ledit Prevost pour bien executer, deffendre, & offencer, à un mesme temps cedit maindroit de bas, tire son pied gauche arriere, & a tiré un maindroit sur le bras de l’espée dudit Lieutenent, & non comme ont fait aucuns demonstrateurs ignorans qui croisent l’espée contre espée, quand un coup vient de bas, cela est bon, car par là on se deffend : mais ce coup est meilleur, car par iceluy on se deffent, & si on offence, & par ainsi de deux choses bonnes, je vous conseille de prendre la meilleure, comme cedit Prevost tient aussi en executant cedit coup, tenant sa main gauche, comme est monstré à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre, 16. Voila la deffence dudit maindroit de bas au jarret deffendu par le Prevost contre ledit Lieutenent. | |
| The following is the first counter and continuation of the first strike, which is for the attacking Lieutenant and for the defending Provost.
And to do this, the Lieutenant being again on the right foot, having thrown the low right-hand at the knee, while the Provost threw a right-hand at the sword arm at the same time as shown above at the Lieutenant on number 15 and the Provost on 16. The Lieutenant being again on the right foot, seeing himself about to be struck by a right-hand on the sword arm, immediately lifts and carries his sword high and throws a back-hand on the side of the Provost's right shoulder, keeping the Lieutenant's fingernails of the right hand to face left, and his left hand is keeping right of his face, as shown above at the portraiture marked behind the collar in number 17. The end of the first counter of the first strike of the sword alone for the Lieutenant. Next will be declared the defense of the first counter and continuation for the Provost against the Lieutenant. And to evade and to guard himself against this first continuation, which is a high back-hand, having thrown a right-hand at the Lieutenant's arms , as shown above at the portraiture of the Lieutenant marked number 15 and at the Provost who executed the right-hand marked number 16, the Provost being on the right foot to guard and to defend this said first counter, will cross the Lieutenant's sword with the strong on weak, presenting a thrust to the Lieutenant's face, keeping the Provost's left hand near his left nipple, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 18. The end of the first counter and continuation for the Provost against the Lieutenant, being effectively defended by this. |
Sensuit la premiere opposite & suitte, du premier coup, qui est pour le Lieutenent assaillant, & pour le Prevost deffendant.
Et pour ce faire, le Lieutenent, estant encores sur le pied droit, ayant tiré ledit maindroit de bas au jarret, le Prevost luy a tiré à un mesme temps un maindroit sur le bras de l’espée, comme est cotté cy dessus audit Lieutenent en chiffre 15, & au Prevost 16. Cedit Lieutenent estant encores sur le pied droit, se voyant frappé d’un maindroit sur le bras de l’espée, a incontinent monté & porté sont espée en haut, & tiré un arrieremain sur le costé de l’espaulle droite du Prevost, tenant ledit Lieutenent, sa main droite les ongles des doids regardant du costé gauche, & sa main gauche la tenant droit son visage, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre au derriere de son col 17. La fin de la premiere opposite du premier coup de ceste espée seule, pour ledit Lieutenent[21]. Cy aprés sera declaré la deffence de la premiere opposite & suitte pour le Prevost, contre ledit Lieutenent. Et pour evader & se garder de ceste premiere suitte, qui est un arrieremain d’haut, ayant tiré un maindroit sur le bras dudit Lieutenent, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre dudit Lieutenent 15, & au Prevost qui execute ledit maindroit, cotté en chiffre 16, ledit Prevost estant sur le pied droit, pour se garder & deffendre de cestedite premiere opposite, croisera l’espée dudit Lieutenent, du fort le foible, luy presentant un estoc au visage dudit Lieutenent, tiendra ledit Prevost sa main gauche auprés de son tetin, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre 18. La fin de la premiere opposite & suitte pour ledit Prevost, s’estant bien deffendu d’icelle, contre ledit Lieutenent. | |
| The following is the second counter and continuation for the Lieutenant and the Provost of the first strike of the sword alone, which is a right-hand.
And to complete this second continuation by the Lieutenant, he must still be on the right foot and having made the second counter and continuation, having seen the Provost defending himself, the Lieutenant again for this second continuation steals away[22] his sword below the Provost's sword hilt and throws a high right-hand at the Provost, keeping the back of the sword hand down and the nails up, and the left hand right of his face, as shown above at the portraiture and figure marked number 19. The end of the second continuation of the first strike for the Lieutenant. Next will show how the Provost must defend himself of the second counter and continuation thrown by the attacking Lieutenant. And to guard himself effectively, the Provost must watch the Lieutenant's sword point, and when he steals away below the Provost's sword hilt to throw the high right-hand at him, the Provost not removing the step of the right foot, will cross the right-hand that is thrown at him by the Lieutenant with the strong on weak and will present a thrust to the Lieutenant's face, keeping the left hand right upon his shoulder, as shown above at the portraiture and figure marked number 20. This is the end of the second counter and continuation of the first strike for the Provost. |
Sensuit la seconde opposite & suitte pour le Lieutenent & Prevost du premier coup de ceste espée seule, qui est un maindroit.
Et pour bien faire & parachever ceste seconde suitte par ledit Lieutenent, faut qu’il soit encores sur le pied droit, & ayant fait la dite seconde opposite & suitte, ayant veu que ledit Prevost s’est deffendu, a ledit Lieutenent encores pour ceste seconde suitte desrobbé son espée par dessous la garde de l’espée du Prevost, & a tiré un maindroit d’hault sur ledit Prevost, tenant le dessus de la main que tient l’espée en bas, & les ongles en hault, & la main gauche droit son visage, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture & figure, cotté en chiffre 19. La fin de ceste seconde suitte dudit premier coup pour le Lieutenent. Cy aprés sera monstré comment le Prevost se doit deffendre de ladite seconde opposite & suitte, tirée par ledit Lieutenent assaillant. Et pour s’en bien garder, ledit Prevost doit regarder la pointe de l’espée dudit Lieutenent, & quand il l’a desrobbé par desous la garde de l’espée dudit Prevost, comme il doit, pour luy tirer un maindroit d’hault, ledit Prevost ne s’ostant sur la desmarche du pied droit, comme il est, croisera ledit maindroit que luy a tiré ledit Lieutenent du fort le foible, & luy presentera un estoc au visage dudit Lieutenent, tenant sa main gauche droit son espaule, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture & figure, cotté en chiffre, 20. Voici la fin de ceste seconde opposite & suitte de cedit premier coup pour ledit Prevost, | |
| The following two portraitures show the guard and position to make the second strike for the Lieutenant and the Provost in this section of the sword alone.
To do this said guard for the Lieutenant effectively he must have his feet together as shown above in the general position of the Lieutenant marked number 9, which is to demonstrate how one must make all of the guards which is required for fencing. And to do this guard for the Lieutenant, being thus placed as stated, he needs to pull his right foot back a little apart under the right side and at the same time put the sword in hand, carrying the sword hilt a little higher than the right shoulder which is the high guard, placing the sword point straight at the eyes, keeping the left hand above the left thigh, as marked at the portraiture number 21. The end of the guard for the Lieutenant. The following is the writing of the guard and position for the Provost. And to do this the Provost likewise is to have the feet together, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 10, and in order to make the low guard effectively the Provost needs to pull the right foot back in drawing to carry the sword hilt above his left lap, placing the sword point straight at the Lieutenant's braies, and also keeping the left hand right of the left nipple, as shown above at the portraiture and figure marked number 22 behind the bonnet. The end of the guard and position for the Provost. |
En ces deux pourtraitures qui sensuivent est monstrée la garde & tenue pour faire le second coup pour le Lieutenent & Prevost, suivant l’ordre de ceste espée seule.
Pour bien faire cestedite garde pour le Lieutenent faut qu’il soit à pied joinct, comme dit est cy dessus, à la tenue generalle dudit Lieutenent, où est cotté en chiffre 9, qui est pour monstrer comment faut faire toutes les gardes, qui sont requises à toutes les susdites armes. Et pour faire ceste garde icy pour ledit Lieutenent est besoin, estant ainsi placé comme dit est, qu’il tire le pied droict arriere un peu à cartier sus le costé droict, & à mesme temps mettre l’espée au poing, portant la garde de l’espée un peu plus haute[23] que l’espaulle droicte qui est en garde haute, assituant la pointe de l’espée droict à la veue, tenant sa main gauche sus la cuisse gauche, comme est cotté en chiffre à sa pourtraiture 21. La fin de ceste garde pour ledit Lieutenent. Sensuit l’escrit de la garde & tenue pour ledit Prevost. Et pour ce faire ledit Prevost estant pareillement à pied joinct, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture cotté en chiffre 10, faut pour bien faire ceste garde basse que ledit Prevost tire le pied tire le pied droict arriere en desgainant portant la garde de l’espée sus son giron gauche, assituant la pointe de l’espée droict à la braye dudit Lieutenent, tenant aussi sa main gauche droict le tetin gauche, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, & figure cotté en chiffre au derriere de son bonnet 22. La fin de ladite garde & tenue pour ledit Prevost. | |
| The following is the second strike of the sword alone on this section, which is a low reversal at the Provost's right knee, thrown by the Lieutenant and properly defended by the Provost.
And to do this, the Lieutenant remaining on the right foot having made and thrown the first and second counters, is to execute and make the second strike by advancing with the left foot and throwing a back-hand at the Provost's right knee, keeping the left hand right of his face, as shown above at the portraiture and figure marked 23. This is the end of the second strike for the Lieutenant. The Lieutenant pretends to not know the remedy of the reversal, but he does as will be seen afterwards; because he does not want to defend himself, therefore not making the remedy, waiting for him to show the Provost how he has to do it. Here will be declared the second strike of the sword alone for the Provost, which is a reversal on the Lieutenant's sword elbow. And to do this, having made the first guard and drawing while being under the left foot, in order to execute this strike when the Lieutenant advanced his left foot to throw a low back-hand at the Provost's knee, the Provost pulls back his right foot and throws a reversal at the elbow of the Lieutenant's sword arm instead of going for the sword as done by the ignorant, keeping the left hand above the left lap, as shown above at the portraiture and figure marked number 24 behind the collar. The end of the second strike which is a reversal under the elbow of the Lieutenant's sword arm, thrown by the Provost. |
Sensuit le second coup de ceste espée seule, suivant l’ordre d’icelle, qui est un renvers de bas au jarret droict du Prevost, tiré par le Lieutenent, & deffendu proprement par le Prevost.
Et pour ce faire, le Lieutenent estant sur le pied droict ayant faict & tiré ladite premiere & seconde opposite, & pour executer & faire cedit second coup advance le pied gauche, & tire un arriere main au jarret droict du Prevost, tenant la main gauche droict son visage, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture & figure cotté en chiffre 23. Voila la fin dudit second coup pour le Lieutenent. Cedit Lieutenent feint ne scavoir le remede de cedit renvers, mais il le fait comme ce verra cy aprés : car il ne se veult deffendre, ne faire le remede, attendu qu’il montre audit Prevost, comment il doit faire. Cy aprés sera declaré le second coup de ceste espée seule, pour ledit Prevost, qui est un renvers sur le coude de l’espée du Lieutenent. Et pour ce faire ledict Prevost ayant faict la premiere garde & desgainement estant sus le pied gauche pour executer ce coup quand ledit Lieutenent a advancé le pied gauche pour luy tirer un arrieremain de bas au jarret, le Prevost a tiré le pied droict arriere, & a tiré un renvers sur le coude du bras de l’espée dudit Lieutenent, & n’est allé à l’espée comme font un tas d’ignorans tenant la main gauche sur le giron gauche, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa portraiture & figure cotté en chiffre au derriere du col, 24. La fin du second coup qui est un renvers sus le coude du bras de l’espée dudit Lieutenent, tiré par cedict Prevost. | |
| The following is the counter and continuation and declarations of the second strike, which is a low reversal at the Provost's left knee thrown by the Lieutenant.
And to do this the Lieutenant remains on the left foot, seeing himself about to be struck on the elbow of the sword arm as stated at the other said figures marked 23 and 24, immediately this Lieutenant is to make his first counter or continuation and pulls up his right hand for a high thrust, as he should do, keeping the sword hilt with the fingertips facing left and keeping the left hand right of his shoulder, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 25. This is the end of the first counter of the strike for the Lieutenant. Here will be shown the declaration of the first counter or continuation of the second strike, which is a low reversal at the Lieutenant's knee and a reversal at the elbow, thrown by the Provost marked number 23 and 24 above for the Lieutenant and for the Provost. And to defend himself from the second counter or continuation, which is a right-hand or high thrust thrown by the Lieutenant, it is necessary that the Provost being on the step of the left foot, crosses the Lieutenant's sword with the strong on weak, and presents him a thrust to the Lieutenant's face, keeping the fingernails on the hand of the sword hilt up and the left hand under the elbow of the sword arm, as shown above at the portraiture and figure marked number 26. This is the end of the first counter of the second strike for the Provost. |
Sensuivent les opposites & suittes, & declarations d’icelles dudit second coup, qui est un renvers de bas au jarret gauche du Prevost tiré par le Lieutenent.
Et pour ce faire ledit Lieutenent estant sur le pied gauche, se voyant touché sur le coude du bras de son espée comme dit est aux autres susdites figures, cotté en chiffre, 23, & 24, incontinent se prochain Lieutenant a faict ceste premiere opposite, ou suitte, & est remonté d’un main droict, ou estoc d’haut, comme il pouvoit & a faict, tenant la garde de l’espée la pointe des doids regardant le costé gauche, & tenant la main gauche droict son epaulle, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre 25. Voyla la fin de la premiere opposite dudit second coup pour le Lieutenent. Cy aprés sera monstré la declaration de la premiere opposite ou suitte dudit second coup, qui est un renvers de bas au jarret pour ledict Lieutenent, & un renvers sur le coude, tiré par ledict Prevost cotté en chiffre cy dessus, pour ledict Lieutenent 23. & pour ledict Prevost 24. Et pour se deffendre de ceste seconde opposite ou suitte, qui est un main droit ou estoc de hault tiré par ledict Lieutenent, est necessaire que ledict Prevost estant sur la demarche du pié gauche, il croise de son espée celle dudict Lieutenent, du fort le foible, & luy presenter un estoc au visaige dudit Lieutenent, tenant la garde de l’espée les ongles de la main d’icelle en hault, & la main gauche au dessoubs le coude du bras de l’espée, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture & figure cotté en chiffre 26. Voila la fin de la premiere opposite dudict second coup pour ledict Prevost. | |
| Declaration of the second counter of the second strike for the Lieutenant and the Provost.
And to do this, the Lieutenant needs to be under the step of the right foot to steal away his sword under the Provost's sword hilt, and to throw again either a high reversal or high thrust for the second counter and continuation of his choice on the right side, keeping the nails on sword hilt facing left, and the left hand straight at his face, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 27. The end of the second counter for this Lieutenant on the second strike. Declaration of the second counter for the defending Provost against the Lieutenant. And to do this the Provost needs to also be under the right foot and that he crosses and strikes down with the strong on weak of the attacking Lieutenant's sword, which is the second continuation, keeping the sword hilt and fingertips down, and presenting a thust to his left nipple, and also keeping the left hand right of the left nipple, as shown above at the portraiture and figure marked number 28. This is the end of the second counter for the Provost starting with low reversal at the Lieutenant's knee, then defended and cut at the arms by the Provost, as shown at length with the portraitures above the strikes. And if some Lieutenants or Provosts are left-handed, they must observe the same step, guard, and placement, if they want to be good and perfect to demonstrate fencing. |
Declaration de la seconde opposite dudit second coup pour le Lieutenent & Prevost.
Et pour ce faire faut & est besoin, que le Lieutenent susdict estant sus la démarche du pied droict desrobera son espée par desoubs la garde de l’espée du Prevost, & tirera encores un renvers ou estoc d’hault pour la seconde opposite & suitte à son chois sus le costé droict, tenant la garde de son espée ses ongles regardant du costé gauche, & la main gauche droict son visaige, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa portraiture cotté en chiffre, 27. La fin de la seconde opposite pour le Lieutenent provenante du second coup. Declaration de la seconde opposite pour le Prevost deffendant contre ledict Lieutenent. Et pour ce faire est besoing que ledict Prevost soit aussi sus le pied droict & qu’il croise & rabbate du fort le foible, l’espée dudit Lieutenent assaillant, qui est ceste seconde suitte, tenant la garde de l’espée & le bout des doids que tient icelle en bas, & luy presenter un estoc au tetin gauche, tenant aussi la main gauche droit le tetin gauche, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture & figure cotté en chiffre, 28, Voicy la fin de la seconde opposite pour le Prevost provenante du renvers de bas au jarret pour le Lieutenent, & deffendue & tiré sur le bras par le Prevost, comme est monstré tout au long aux portraitures cy dessus aux coups. Et si c’est qu’aucuns Lieutenens, ou Prevosts soient gauchiers, fault qu’ils observent la mesme dessusdite desmarche garde & assituations, s’ils veullent bien & parfaictement monstrer lesdites armes. | |
| The following guard and position of the third strike, which is a high right-hand for the attacking Lieutenant against the defending Provost.
And to do this the Lieutenant needs to have done the steps and drawings, and having remained on the left foot in low guard, keeping the sword hand and the cutting edge down and the point placing a bit above the Provost's braies, keeping also this said Lieutenant's left hand right of his chin, as shown above at the portraiture and figure marked number 29 behind the hat. End of the guard and position for the Lieutenant. The following is the guard and position of the third strike for the defending Provost. And to do this, the Provost must also be on the left foot having done the step, and having remained on the left foot in high guard, keeping the sword hilt and the back of the hand up, and let the sword be flat so that it can remain high there, otherwise such guard would be imperfect, and he must place the sword point straight at the left eye, which is the high guard and keeping the left hand right of the stomach, as shown above at the portraiture and figure marked number 30. This is the end of the guard and position for the Provost in order to execute and defend against the third strike of the sword alone from the Lieutenant |
Sensuit la garde & tenue du troisiesme coup, qui est un maindroit d’hault pour le Lieutenent assaillant contre le Prevost deffendant.
Et pour ce faire est besoin que ledit Lieutenent aye fait une desdites desmarches & desgainement, & soit demouré sur le pied gauche, en garde basse, tenant la main de l’espée le trenchant en bas, & la pointe l’assituant un peu au dessus la braye du Prevost, tient aussi cedit Lieutenent la main gauche droict son menton, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture & figure, cotté en chiffre au derriere du chapeau 29. Fin de la garde & tenue pour ledit Lieutenent. Sensuit la garde & tenue dudit troisiesme coup pour ledit Prevost deffendeur. Et pour ce faire, faut que ledit Prevost soit aussi sur le pied gauche ayant fait ladite desmarche, & soit demouré sur le pied gauche en garde haute, tenant la garde de l’espée, le dessus de la main que tient icelle en haut, & que icelle espée soit plaine, tellement que un de y puisse demourer dessus, autrement telle garde seroit imperfaite, & fault qu’il assitue la pointe de l’espée droict l’oeil gauche, qui est la garde haulte & tient aussi sa main gauche droict son estomac, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa portraiture & figure cotté en chiffre 30. Voila la fin de la garde & tenue pour ledit Prevost pour executer & deffendre ledit troisiesme coup de ceste espée seule contre ledit Lieutenent. | |
| The third strike of the sword alone for the Lieutenant and the Provost is a high right-hand that follows the section of the distinct targets.
And to do this, the attacking Lieutenant demonstrating this must, as have been stated many times, be on the step of the left foot as marked above at the portraiture of the Lieutenant, not this one but the other marked number 29. And to do this said third strike, which is a high right-hand at the Provost's left shoulder, the Lieutenant must advance the right foot and throw a right-hand at the defending Provost's left shoulder, keeping the sword hand up[24], and his left hand right of the chin as shown above at the portraiture marked number 31. Next is the declaration and defense of the third strike which is a high right-hand thrown by the attacker and defended by the Provost. And to do this the Provost needs to be on the step of the left foot, having made one of the three drawings in high guard, as shown in the figure of the defending Provost marked number 30. And to effectively execute and defend against the high right-hand of the third strike, the Provost following the section of the true teachings of the sword alone, must pull the left foot back, cross the sword of the attacking Lieutenant with strong on weak, that is to say from the hilt to near the middle of the Lieutenant's sword, keeping the nails of the sword hand up, throwing a thrust straight at the Lieutenant's chin, and keeping the left hand right of the nipple as shown above at the portraiture and figure marked 32. The end of the third strike for the Provost. |
Le troisiesme coup de ceste espée seule pour le Lieutenent & Prevost est un maindroit d’hault suivant l’ordre des susdits lieux propres.
Et pour ce faire, fault que ledit Lieutenent assaillant demonstrateur, comme avons dit en plusieurs lieux, estant comme dit est sur la desmarche du pied gauche, comme est cotté cy dessus à la pourtraiture dudit Lieutenent, non à ceste icy, mais aux autres, cotté en chiffre 29. Et pour cedit troisiesme coup, qui est un maindroit d’hault sur l’espaulle gauche dudit Prevost, faut que ledit Lieutenent advance le pied droit, & tirer un maindroit sur l’espaulle gauche dudit Prevost deffendeur, tenant le dessus de la main que tient l’espée en hault[25], & sa main gauche droit son menton : comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture cotté en chiffre, 31. Si aprés est la declaration & deffence dudit troisiesme coup qui est un main-droit d’ault, tiré par ledit assaillant, & deffendu par ledit Prevost. Et pour ce faire est besoin[26] que ledit Prevost soit sur la desmarche du pied gauche, ayant fait un desdits trois desgainements en garde haulte, telle qui est figuré audit Prevost deffendeur, marqué en chiffre 30. Et pour bien executer & deffendre audit Prevost cedit maindroit d’hault troisiesme coup, suivant l’ordre de la vraye demonstration de ceste espée seule, faut que ledit Prevost tire le pied gauche arriere, croise de son espée celle dudit lieutenent assaillant du fort le foible, c’est à dire d’auprés la garde de l’espée, un peu plus hault, & au milieu de l’espée dudit Lieutenent, tenant la main que tient l’espée, les ongles en hault, assituant & tirant un estoc droit le menton dudit Lieutenent, & tient sa main gauche droit son tetin comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, & figure, cotté en chiffre, 32. La fin dudit troisiesme coup pour ledit Prevost. | |
| The following is the first counter and continuation for the Lieutenant and the Provost, for the third strike of the sword alone.
To do this first counter and continuation for the third strike effectively, which is a high right-hand the Lieutenant must be under the right foot having thrown the right-hand against the Provost, as shown in the figure and portraiture number 31 above. And in an instant in order to execute and make the first counter and continuation effectively the Lieutenant must steal away his sword in passing a back-hand below the Provost's sword hilt, and throw a high reversal or high back-hand at the Provost's left shoulder, as shown above in the figure of the Lieutenant, marked number 33. The end of the counter and continuation of the third strike for the Lieutenant. The following is the defense of the first counter and continuation of the third strike for the Provost against the Lieutenant. And to do this, this said Provost must be on the right foot. And when the Lieutenant steals away and passes his sword underneath the Provost to throw a back-hand at his right side of the sword, the Provost holding firm on the right foot to defend this continuation will cross his sword on the attacking Lieutenant's sword, strong on weak, as defined above many times at the other counters and continuations, keeping the nails on the sword hand down, presenting a thrust at the Lieutenant's stomach, and also keeping his left hand right of his nipple, as shown above at the portraiture and figure marked number 34. The end of the first counter of the third strike for the Provost. |
Sensuit la premiere opposite & suitte pour le Lieutenent & Prevost, pour ledit troisiesme coup de l’espée seule.
Pour bien faire ceste premiere oposite & suitte pour ledit troisiesme coup qui est un maindroit d’hault fault que ledit Lieutenent soit sus le pied droit ayant tiré ledit maindroit contre le Prevost, comme est cotté en sa figure & pourtraiture cy dessus en chiffre 31. Et à un mesme instant pour bien executer & faire ceste premiere opposite & suitte fault que ledit Lieutenent desrobe son espée en passant un avant-main par dessoubs la garde de l’espée du Prevost, & luy tirer un renvers ou bien arriere-main d’hault sur l’espaule gauche du Prevost, tenant les doids de la main de son espée vers le costé gauche & la main gauche droit le menton, pour rabbatre d’icelle la pointe de l’espée du Prevost, comme est monstré cy dessus en la figure dudit Lieutenent, cotté en chiffre, 33. La fin de l’opposite & suitte du troisiesme coup pour le Lieutenent. Sensuit la deffence de la premiere opposite & suitte dudit troisiesme coup pour le Prevost contre ledit Lieutenent. Et pour ce faire, faut que ledit prochain Prevost soit sur le pied droit. Et quant ledit Lieutenent desrobera & passera son espée par desoubs celle du Prevost pour luy tirer un arriere-main sur le costé droit de l’espée, le Prevost soy tenant ferme sur le pied droit pour deffendre ceste suite ledit Prevost croisera de son espée l’espée dudit Lieutenent assaillant, du fort le foible, comme est definy cy dessus en plusieurs lieux aux autres opposites & suittes, tenant la main que tient l’espée les ongles en bas, luy presentant un estoc à l’estomac dudit Lieutenent, & tient aussi sa main gauche droit son tetin, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa portraiture & figure cotté en chiffre 34. La fin de ceste premiere opposite dudit troisiesme coup pour le Prevost. | |
| The second counter and continuation of the third strike for the Lieutenant and the Provost.
And to effectively do the second counter and continuation of the third strike for the Lieutenant, the Lieutenant must be on the right foot and with the Lieutenant sword having reversaled, with the step of the same right foot, he will pass and steal away his sword below the Provost's sword hilt and throw the second counter and continuation with a fore-hand<re>read: right-hand</ref> on the Provost's left shoulder, keeping the nails on the sword hand facing left and the left hand right of the face, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 35. The end of the second counter and continuation of the third strike for the Lieutenant. Next will show and declare the second and last counter and continuation of the third strike for the Provost. And to do this, the Provost must step as mentioned above, which is on the right foot, and to defend himself from that said counter or continuation, the Provost must cross the attacking Lieutenant's sword near the hilt to a bit higher than the Lieutenant's middle of the sword with strong on weak, keeping the sword hilt and the nails holding it up, presenting a thrust to the Lieutenant's face, and also keeping the Provost's left hand right of his nipple as shown above at the portraiture marked number 36 behind his back. This is the end of the second and last counter of the third strike, which is a high right-hand for the Lieutenant marked 35, and defended by the Provost marked 36. |
Seconde opposite & suitte dudit troisiesme coup pour le Lieutenent & Prevost.
Et pour bien faire ceste seconde opposite & suitte dudit troisiesme coup pour ledit Lieutenent, fault & est necessaire que ce present Lieutenent soit sur le pied droit, & estant l’espée dudit Lieutenent sur le renvers, en ceste mesme desmarche du pied droit, passera & desrobera son espée par desous la garde de l’espée du Prevost & tirera pour ceste seconde opposite & suitte un avant-main[27] sur l’espaule gauche du Prevost, tenant la main que tient l’espée, les doids regardant vers le cotté[28] gauche & la main gauche droit le visaige, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture cotté en chiffre 35. La fin de la seconde opposite & suitte dudit troisiesme coup pour ledit Lieutenent. Si aprés sera monstré & declaré la seconde & derniere opposite & suitte dudit troisiesme coup pour ledict Prevost. Et pour ce faire, fault que ledit Prevost soit sur la desmarche que dessus est dit, qui est sur le pied droit, & pour la deffence de ceste-dicte opposite ou suitte, faut que ledit Prevost croise l’espée dudit Lieutenent assaillant d’auprés la garde, un peu plus hault au milieu de l’espée dudit Lieutenent, qui est du fort le foible, tenant la garde de l’espée, & la main que tient icelle les ongles en hault, presentant un estoc au visaige dudit Lieutenent, & tient aussi ledit Prevost sa main gauche droit son tetin comme est monstré cy dessus à sadite pourtraiture cotté en chiffre au derriere du dos, 36. Voicy la fin de la seconde & derniere opposite dudit troisiesme coup, qui est un maindroit d’hault pour ledit Lieutenent cotté 33, & deffendue par cedit Prevost cotté 36. | |
| The following is the declaration, guard, and positioning of the fourth cut, which is a high reversal on this section of the sword alone for the Lieutenant and the Provost, and everything that must be done.
And to do this, the Lieutenant must have the feet together to first make one of the two drawings as stated, and here is where the Lieutenant places his right foot, which demonstrates the difference from where the left foot is placed, and the Lieutenant keeps the sword hilt upon the right lap in low guard placing the sword point straight at the Provost's lap, keeping the left hand opposite of his chin, as shown above at the portraiture and figure of the Lieutenant, marked in number 37. This is the end of the position and guard for the attacking Lieutenant, which is to begin to throw the fourth strike. The following is also the reason of the portraiture and the position for the defending Provost, who after having made one of the three drawings the Provost has also remained on the step of the right foot in middle guard, keeping the sword hilt straight and higher than the right shoulder, placing the sword point at the Lieutenant's left nipple, and keeping the left hand right of his stomach, as shown above at the portraiture marked in number 38. This is the end of the guard for the Lieutenant for throwing the fourth strike against the Provost. |
Sensuit la declaration, garde & tenue du quatriesme coup, qui est un renvers d’hault suivant l’ordre de ceste dicte espée seule pour le Lieutenent & Prevost, & de tout ce qu’il faut qu’ils fassent.
Et pour ce faire, fault que ce present Lieutenent estant à pied joinct a faict un desdits deux desgainemens premiers susdits, & à cestuy icy s’est mis ledit Lieutenent sur le pied droict, pour monstrer la difference qu’a à l’endroit d’iceluy qui se fait sur le pied gauche, & tient cedit Lieutenent la garde de son espée sur le giron droit, en garde basse assituant la pointe de l’espée droit le giron du Prevost, tenant la main gauche vis à vis de son menton, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture & figure dudit Lieutenent, cotté en chiffre 37. Voila[29] la fin de la tenue & garde pour le Lieutenent assaillant, qui est pour commencer à tirer le quatriesme coup. Sensuit aussi la raison de la pourtraiture, & tenue pour ledit Prevost deffendeur, qui est aprés avoir fait un desdits trois desgainements, est ledit Prevost demouré aussi sur la desmarche du pied droict, en garde moyenne, tenant la garde de l’espée droite, aussi haut que l’espaulle droite, assituant la pointe de l’espée au tetin gauche dudit Lieutenent, tenant sa main gauche droit son ventre, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture cotté en chiffre, 38. Voyla la fin de la garde pour ledit Lieutenent, pour tirer ledit quatriesme coup contre le Prevost. | |
| This will show and declare the fourth strike of the sword alone, which is a high reversal, multiplied for the attacking Lieutenant against the defending Provost.
And to execute it, the Lieutenant must be on the right foot, advances the left foot, and throws a reversal on the Provost's right shoulder, pretending to throw a thrust to his face, keeping the left hand right of his chin, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 39. This is the end of the fourth strike for the Lieutenant. Next is the defense of the fourth strike for the defending Provost, which is a high reversal thrown by the agressive Lieutenant. And to do this, the Provost is to be on the right foot in middle guard, as shown above at the portraiture and figure number 38, and he must pull his right foot back and cross his sword at the Lieutenant's sword, strong on weak, on the reversal, which is the fourth strike thrown by the Lieutenant, keeping the nails on the sword hand down and therefore the back of the hand up, and presents a thrust at the Lieutenant, also keeping the left hand right on his shoulder, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 40 behind the collar. This is the end of the fourth strike for the defending Provost. |
Cy aprés sera monstré & declaré le quatriesme coup de ceste espée seule, qui est un renvers d’hault, estant multiplié pour le Lieutenent assaillant, contre le Prevost deffendant.
Et pour l’executer, faut que cedit Lieutenent, estant sur le pied droict avance le pied gauche, & tirer un renvers sur l’espaulle droicte du Prevost, ayant fait semblant de luy tirer un estoc au visage, tenant sa main gauche droict son menton, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture cotté en chiffre 39. Voyla la fin du quatriesme coup pour le Lieutenent. Aussi aprés est monstré la deffence dudit quatriesme coup pour le Prevost deffendeur, qui est un renvers d’hault, tiré par ledit Lieutenent agresseur. Et pour ce faire, faut que ledit Prevost estant sur le pied droict en garde moyenne, comme est cotté cy dessus à sa pourtraiture & figure en chiffre 38, faut qu’il tire le pied droict arriere, & croiser de son espée l’espée dudit Lieutenent, du fort le foible, sur ledit renvers, quatriesme coup tiré par ledit Lieutenent, tenant la main que tient l’espée les ongles en bas, & par consequent le dessus en haut, & presenter un estoc audit Lieutenent, tenant aussi sa main gauche droict son espaulle, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture cotté en chiffre au derriere du col 40. Voyla la fin dudit quatriesme coup pour ledit Prevost deffendeur. | |
| The following is the first counter and continuation of the fourth strike for the attacking Lieutenent against the defending Provost.
And to do this, this Lieutenant must remain on the step of the left foot and at the same instance that he throws the high reversal, he steals away his sword below the Provost's and throws a high right-hand at the Provost as the first counter, being as stated on the left foot, keeping the nails on the sword hand up and the left hand right of his chest, as shown above at the portraiture and figure marked number 40. The end of the first counter for the demonstrating Lieutenant. This is the defense of the first counter of the fourth strike for the Provost against the Lieutenant. And to do this, this said Provost must be on the step of the left foot and when the Lieutenant throws a high right-hand at him, in order to counter the Provost needs to cross and beat down at the same time, and without a moment to waste, be strong on weak, turning the fingernails on the sword hilt up to present a thrust at the Lieutenant's throat or eyes, keeping the left hand right of his nipple as shown above at the portraiture marked number 42. This is the defense of the first counter, derived from the fourth strike for the Provost. |
Sensuit la premiere opposite & suitte dudit quatriesme coup pour le Lieutenent assaillant, contre le Prevost deffendant.
Et pour ce faire, faut que ce present Lieutenent soit, & demeure sur la mesme desmarche du pied gauche, & à un mesme instant qu’il aura tiré ledit renvers d’haut, desrobera son espée, par dessous celle du Prevost, & tirera pour la premiere opposite un maindroit d’hault sur ledit Prevost, estant comme dict est sur le pied gauche, tenant la main de l’espée les ongles en haut, & la main gauche droit sa poitrine, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture & figure, cotté en chiffre 40. La fin de la premiere opposite pour le Lieutenent demonstrateur. Icy aprés est monstré la deffence de la premiere opposite du quatriesme coup pour le Prevost, contre ledit Lieutenent. Et pour ce faire, faut & est besoing que ledit prochain Prevost soit sus la desmarche du pied gauche, & quand ledit Lieutenent luy tirera un maindroit d’hault, pour opposite est besoin que le Prevost croise & rabate à un mesme temps, & sans bien peu d’intervalle l’espée dudit Lieutenent, du fort le foible, tournant la garde de l’espée les ongles de la main que tient icelle, en haut, & presenter un estoc à la gorge, ou à la veue dudit Lieutenent, tenant la main gauche droict son tetin comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre 42. Voyla la deffence de la premiere opposite, provenant dudit quatriesme coup pour ledit Prevost. | |
| The following is the second and last counter for the fourth strike, which is a high reversal, and will also begin on the left foot for this attacking Lieutenant and defended by this Provost.
And to do this, this Lieutenant in order to execute the second counter effectively must, without leaving where he's currently planted which is on the left foot, steal away the sword below the Provost's and throw a high reversal, which is the proper strike, keeping the sword hand up and the left hand right of the chin, as shown above at the portraiture and figure marked number 43 behind the bonnet. After having declared the second counter by the attacking Lieutenant, stay to perform and declare the second counter for the defending Provost. And to do this, the Provost must be on the left foot, and at the same time without a moment to waste after having thrown and defended the first counter and continuation, return to cross and beat down the second counter which is the high Lieutenant's reversal, and also must be strong on weak, keeping the nails of the sword hand down, and presenting a thrust to his neck, keeping the left hand below the sword arm as shown next to this writing at the portraiture and figure marked number 44. This is the end of the defense of the second counter of the fourth strike for the Provost. |
Sensuit cy aprés la seconde & derniere opposite dudit quatiresme coup, qui est un renvers d’hault, & sera aussi maintenant sur le pied gauche pour ceste opposite, pour ce present Lieutenent assaillant, & deffendue aussi par ce present Prevost.
Et pour ce faire, faut que ce present Lieutenent, sans s’oster de la desmarche où il est à present planté, qui est sur le pied gauche, pour bien executer ceste seconde opposite, faut qu’il desrobe l’espée par dessoubs celle du Prevost, & tirer un renvers d’hault, comme son susdit coup propre, tenant le dessus de la main qui tient l’espée en hault, & la main gauche droict le menton, comme le tout est figuré cy dessus à sadite pourtraiture & figure, cotté en chiffre au derriere du bonnet 43. Aprés ayant declaré la seconde opposite par ledit Lieutenent assaillant. Reste à traiter & declarer ceste seconde opposite pour le Prevost deffendant. Et pour ce faire, faut que le Prevost soit sur le pied gauche & à un mesme temps sans bien peu d’intervalle aprés ayant tiré & deffendu ladite premiere opposite & suitte, qu’il retourne croiser & rabatre ceste seconde opposite que tire ledit Lieutenent sus un renvers d’hault, & faut que soit aussi du fort le foible, tenant les ongles de la main que tient l’espée en bas, & luy presenter un estoc à la gorge, tenant aussi sa main gauche au desous le bras de l’espée comme est monstré tout ce qui est dit à cedit prochain escrit à sadite pourtraiture & figure, cotté en chiffre 44. Voicy la fin de la deffence de la seconde opposite dudit quatriesme coup pour le Prevost. | |
| The following is the position and guard for the attacking Lieutenant and for the defending Provost to execute and throw a high thrust which is the fifth strike.
And to do this the Lieutenant is to have the feet together as stated in the first plan, which is necessary for doing the first low guard effectively, he then pulls the right foot back while drawing the sword, to carry the hilt right of the left lap, cutting edge down, placing the point straight more or less at the braies, and also keeping the left hand right of the nipples as shown above at this portraiture of the Lieutenant marked number 45 behind the top of the collar. This is the end of the guard and position to make the fifth strike for the sword alone, following the section for the Lieutenant. Next is declared the guard and position for this said Provost to defend himself from the fifth strike which is the thrust thrown by the Lieutenant. And to do this the Provost is to also have the feet together to do this said guard and position, he then must pull his right foot back and do one of the three drawings and carry the sword hilt a bit higher than the right shoulder to be in high guard, keeping the back of the sword hand up, placing the sword point at the Lieutenant's mouth, and also keeping the left hand right of the chest as shown and can be seen above at the portraiture marked number 46. This is the end of the position and guard for this said Provost to defend and guard himself from the thrust, the fifth strike, thrown by the attacking Lieutenant. |
Sensuit la tenue & garde pour le Lieutenent assaillant, & pour le Prevost deffendant, pour executer, & tirer un estoc d’haut, pour le cinquiesme coup.
Et pour ce faire, ce Lieutenent estant à pied joint comme est dit à un desdits premiers plans, fault pour bien faire ceste premiere garde basse, qu’il tire le pied droit arriere, en desgainant l’espée, & porter la garde d’icelle droit le giron gauche, le tranchant en bas, assituant la pointe droit la braye ou à peu-prés, tenant aussi sa main gauche droit son tetin comme est monstré cy dessus à la prochaine pourtraiture dudit Lieutenent, cotté en chiffre au derriere du haut de son collet 45. Voila la fin de la garde & tenue pour faire ledit cinquiesme coup de ceste espée seule, suivant l’ordre pour le Lieutenent. Si aprés est declaré la garde & tenue pour ledit prochain Prevost, pour soy deffendre dudit estoc cinquiesme coup tiré cy aprés par le Lieutenent. Et pour ce faire, cedit Prevost estant aussi à pied joint pour faire ceste susdite garde & tenue, faut qu’il tire le pied droit arriere, & face un desdits trois desgainemens, & porte la garde de l’espée un peu plus haut que l’espaulle droite, & soy mettant en garde haute, tenant la main que tient l’espée le dessus d’icelle en haut, assituant la pointe de l’espée à la bouche dudit Lieutenent, tenant aussi sa main gauche droit la poictrine comme est monstré & se peult voir cy dessus à sadite pourtraiture cotté en chiffre 46. Voici la fin de la tenue & garde pour ledit prochain Prevost, pour soy deffendre & garder dudit estoc, cinquiesme coup, que tirera cy aprés le Lieutenent assaillant. | |
| The following is the fifth strike which is a high thrust with the right-hand, following the section of the sword alone for the attacking Lieutenant against the defending Provost.
And to do this, this Lieutenant must be on the left foot as shown above at the other portraiture marked 45, then advances the right foot and throws a thrust at the Provost's nipples, turning the nails and sword hilt up and the left hand right of his face as apparently shown by this writing for the portraiture, marked number 47 behind the back of the head. This is the fifth strike fo the sword alone, thrown by the attacking Lieutenant. The following is the defense for the fifth strike, which is a high thrust, made from a high right-hand by the defending Provost against the attacking Lieutenant. And to do this, the Provost must be on the right foot, then pulls the left foot back, beats down and crosses the Lieutenant's sword with his own, strong on weak, which is to say to be near the middle guard, with the sword point a bit higher, the nails up, presenting a thrust to the Lieutenant straight to his face, and keeping the Provost's left hand right of his left nipple, as shown by the portraiture and figure marked number 48 above. And if the Provost is left-handed and the right-handed Lieutenant shoots a thrust at him, he must advance the right forward, and cross the Lieutenant's sword, strong on weak as can be seen by the example and exercise against a left-hander. It is true that if the Provost is left-handed, the Lieutenant or whoever must adapt to the left-handed Provost to teach him, that is to say that he needs to be left-handed and make the first step be with the feet together and pulls the left foot on the footprint marked at the first portraitures 4, and leaves the footprint marked 1, strange as it seems. The end and declaration of the fifth strike for the Lieutenant and the Provost when one or the other is left-handed. |
Sensuit le cinquiesme coup, qui est un estoc d’hault sur le maindroit, suivant l’ordre de ceste espée seule pour le Lieutenent assaillant, contre le Prevost deffendant.
Et pour ce faire, faut que ce prochain Lieutenent estant sur le pied gauche comme est cotté cy dessus à l’autre pourtraiture en chiffre 45, advancer le pied droit, & tirer un estoc au tetin gauche du Prevost, tournant la garde de l’espée les ongles en hault, & la main gauche droit son visaige comme est monstré appertement tout ce que est dit par cest escript à sadicte pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre au derriere du sommet de sa teste 47. Voila le cinquiesme coup de ceste espée seule, tiré par ledit Lieutenent assaillant. Sensuyt la deffence dudit cinquiesme coup, qui est un estoc d’hault, participant du maindroit d’hault pour ledit Prevost deffendant, contre ledit Lieutenent assaillant. Et pour ce faire, faut que ledit Prevost estant sur le pied droit, tire le pied gauche arriere, & rabate & croise l’espée dudit Lieutenent de la sienne, du fort le foible, c’est à dire, d’auprés de la garde, au millieu, un peu plus haut vers la pointe de l’espée, les ongles[30] en hault, presentant un estoc audit Lieutenent droit son visage, tenant ledit Prevost sa main gauche droit son tetin gauche, comme le tout est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture & figure cotté en chiffre 48. Et si ledit Prevost est gaucher, faut que ledit Lieutenant droiturier luy tire cest estoc, advançant le pied droit arriere, & croisera l’espée dudit Lieutenent, du fort le foible, comme se pourra voir par exemple & praticque contre un gaucher. Bien est vray que si le Prevost est gaucher, ledit Lieutenent ou autre se doit adapter au Prevost gaucher à la demonstration, c’est à dire, qu’il se doit faire gaucher, & faire la desmarche premiere estant à pied joint, & tirer le pied gauche sur la semelle cotté aux premieres pourtraitures, 4, & laisser la semelle où est cotté, 1, vaccue[31] comme se peult voir & en son lieu. La fin & declaration dudit cinquiesme coup, pour ledit Lieutenent & Prevost combien que l’un ou l’autre soit gaucher. | |
| The following is the first counter and continuation of the fifth strike which is the high thrust thrown by the attacking Lieutenant against the defending Provost.
And to do this, the Lieutenant must be on the step of the right foot to do this counter and continuation a little after he has thrown the thrust, the fifth strike with the right-hand, the Lieutenant steals away his sword below the Provost's sword hilt that he has thrown at this Lieutenant, for the first counter and continuation another on the reversal, which is on the Provost's right side, keeping the left hand right of the nipple as shown above at the portraiture and figure marked number 49. And if the Lieutenant is left-handed, he must throw the strike at the opposite of what is described, holding the opposite step of the counter and continuation, that is to say that if the Lieutenant throws a right-handed reversal, the Provost if left-handed would have to beat it down with a right-hand using his left hand. The end of the counter for the Lieutenant. Next will be declared the defense of the first counter and continuation of the fifth strike for the Provost against the agressive Lieutenant. And to do this, the Provost is to also be on the right foot while the Lieutenant steals away his sword to throw the first counter at him which is a high thrust on the right. The Provost seeing this, being on his right foot crosses his sword on that of the Lieutenant with strong on weak, keeping the back of the sword hand up and presenting a thrust to his neck, keeping the left hand right of his left nipple as shown above at the portraiture and figure marked number 50. This is the end of the counter for the Provost. |
Sensuit la premiere opposite & suitte dudit cinquiesme coup, qui est sur l’estoc d’hault, tiré par le Lieutenent assaillant, contre le Prevost deffendant que voicy.
Et pour ce faire, faut que cedit Lieutenent estant sur la desmarche du pied droit pour faire ceste presente opposite & suitte un peu de temps aprés qu’il a eu tiré ledit estoc cinquiesme coup sur le maindroit, a ledit Lieutenent desrobé son espée par dessous la garde de l’espée du Prevost, & a tiré cedit present Lieutenent, pour la premiere opposite & suitte un autre sur le renvers, qui est sur le costé droit du Prevost, tenant la main gauche droit le tetin comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture & figure, cotté en chiffre 49, Et si ledit Lieutenent est gaucher, faut qu’il tire les coups tout à l’opposite de ce qu’a esté tiré cy dessus, tant de la desmarche que ladite opposite & suitte, c’est à dire, que si ledit Lieutenent tiroit un renvers estant droiturier, faudroit que le Prevost s’il estoit gaucher le rabatit d’un maindroit de la main gauche. La fin de ceste opposite pour ledit Lieutenent. Si aprés sera declaré la deffence de ceste premiere opposite & suitte dudit cinquiesme coup pour ledit Prevost, contre ledit Lieutenent agresseur. Et pour ce faire, ledit Prevost estant aussi sur le pied droit, ledit Lieutenent voudra desrober son espée pour luy tirer ceste premiere opposite qui est un estoc d’hault sur le costé droit. Cedit Prevost voyant ce, estant sur ledit pied droit a croisé de son espée celle dudit Lieutenent du fort le foible, tenant la main que tient l’espée le dessus de la main en haut, & luy a presenté un estoc à la gorge, tenant la main gauche droit son tetin gauche comme est monstre cy dessus à sa pourtraiture & figure cotté en chiffre 50. Voyla la fin de cestedite opposite pour ledit Prevost. | |
| The following is the second counter and continuation of the fifth strike fo the sword alone, which is a high thrust for the attacking Lieutenant and for the defending Provost.
In order to declare and understand the second counter and continuation for this Lieutenant effectively, he must be on the step of the right foot, as he had been when he threw the fifth strike, the high thrust, passing his sword to steal away the back-hand below the Provost's sword hilt, and in an instant the Lieutenant for the second continuation throws again his choice of a high thrust or high right-hand at the defending Provost's left side, keeping the back of the sword hand down, the nails up, and the keeping left hand right of the nipple as shown above at the portraiture and figure marked number 51. The end of the second counter for the Lieutenant. Next is declared the protection and defense of the second counter of the fifth strike, which is to guard this said Provost further against the Lieutenant. And to do this, the Provost needs to be on the step of the right foot, cross and beat down the attacking Lieutenant's sword, strong on weak, on the right-hand otherwise called the fore-hand, and by this means will defend and ward the Provost from the second counter and continuation, thrown by the Lieutenant, and when all is done the Provost will present a thrust to the Lieutenant's face, keeping the sword hilt and the nails on the hand holding it up, and the left hand right of the left nipple, as shown above at this portraiture marked number 52 behind his hat. The end of the second counter and continuation of the fifth strike, which is a high thrust with the right-hand, defended by the Provost against the demonstrating Lieutenant. |
Sensuit la seconde opposite & suitte dudit cinquiesme coup de ceste espée seule, qui est un estoc d’hault pour le Lieutenent assaillant, & pour le Prevost deffendant.
Pour declarer, & bien donner à entendre ceste dite seconde opposite & suitte pour ledit prochain Lieutenent, faut qu’iceluy soit sur la desmarche du pied droit, comme il estoit quand il a tiré ledit estoc cinquiesme coup d’hault, passant son espée en la desrobant sur un ariere-main par desoubs la garde de l’espée du Prevost, & à un instant ledit Lieutenent pour ceste seconde suitte tirera encores un estoc ou maindroit d’hault à son chois sur le costé gauche du Prevost deffendeur, tenant la main que tient l’espée le dessus d’icelle en bas, & les ongles en hault, & la main gauche la tenant droit son tetin comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture & figure cotté en chiffre 51. La fin de la seconde opposite pour ledit Lieutenent. Si aprés est declaré la tuition[32] & deffence de la seconde opposite dudit cinquiesme coup, de laquelle ce doit garder ledit plus prochain Prevost contre ledit Lieutenent. Et pour ce faire, est besoin que ledit Prevost, estant sur la desmarche du pied droit, croise & rabate l’espée dudit Lieutenent assaillant, du fort le foible, sur un maindroit autrement appellé avant-main, & par ce moyen deffendra & evitera ledit Prevost ladite seconde opposite & suitte, tirée cy dessus par ledit Lieutenent, & tout cela fait presentera ledit Prevost un estoc au visaige dudit Lieutenent, tenant la garde de son espée les ongles de la main que tient icelle en hault, & la main gauche droit le tetin gauche, comme est monstré cy dessus à sadite prochaine pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre au derriere de son chappeau 52. La fin de la seconde opposite & suitte dudit cinquiesme coup, qui est un estoc d’hault sur le maindroit, deffendu par ledit Prevost contre ledit Lieutenant demonstrateur. | |
| This is the guard and position of the Lieutenant and the Provost for the sixth strike the thrust, multiplied at the sixth distinct target on the defender.
One must declare this next guard and position to make and execute the thrust, which is the sixth and last strike and target, being as stated multiplied in several strikes and counters of the sword alone above. And this is multiplied on the right side. One could begin to pull the left foot but will have to multiply the strikes, or execute them with a feint. But to begin this said guard by the Lieutenant the sixth strike, he will keep himself on the right foot in middle guard, keeping the back of the sword hand up, placing the sword point straight at the Provost's eyes, and the keeping the left hand right of the chin, as shown at the portraiture marked number 53 behind the collar. One must note for left-handers to defend this said high thrust effectively, it is necessary that he keeps the left foot and crosses the sword with strong on weak for defense, as will be seen after the subsequent strike. The end and declaration fo the position and guard by the Lieutenant. The following is the declaration of the guard and position for the Provost, to prepare to defend from the high thrust, which will be thrown after by the Lieutenant against the Provost, the sixth and last strike being mulitplied as stated at the sixth target. This said guard and position for the Provost, which must be on the right foot like the Lieutenant, is how one can keep on the left foot and advance the right foot, but at the last strike and target being multiplied, we will perform the guard which is being done on the right foot. To do this, the Provost will be on the right foot in low guard, keeping the nails on the sword hand down, placing the sword point straight at the Lieutenant's stomach, and keeping his left hand right of the nipple, as we can see above at the portraiture and figure marked number 54 near the plume of the bonnet. One must note that all left-handers who follow the instruction that I put, both for the Lieutenant and also the Provost must make the opposite step, and similarly the drawings and the strikes are also the opposite of right-handers, and those who strive to follow these said reasons will improve. Because experience will make them improve. This is the end of the position and guard for the Provost to defend himself from the sixth strike, which had been thrown by the demonstrating Lieutenant. |
Voicy la garde & tenue du Lieutenent & Prevost pour l’estoc sixiesme coup, estant multiplié au sixiesme lieu propre sur le deffendeur.
Faut declarer ceste garde & tenue prochaine, pour faire & executer l’estoc sixiesme & dernier coup & lieu, estant comme dit est multiplié en plusieurs coups & opposites de ceste espée seule cy dessus. Et à cestui cy est multiplié sur le costé droit. On le pourroit commencer à tirer sur le pied gauche, mais faudroit multiplier les coups, ou les executer avec une fainte. Mais à cestedite garde, pour commencer par ledit Lieutenent cedit sixiesme coup, il se tiendra sur le pied droit en garde moyenne, tenant le dessus de la main que tient l’espée en hault, assituant la pointe de l’espée droit la veue du Prevost, & la main gauche la tenant droit son menton, comme est monstré à sa pourtraiture cotté en chiffre au derriere du col 53. Fault noter que le gaucher pour bien deffendre cedit estoc d’hault, il est necessaire qu’il se tienne sur le pié gauche, & croiser l’espée du fort le foible, pour la defendre, comme se verra cy aprés aux coup qui ensuivent. La fin & declaration de la tenue & garde par cedit Lieutenent. Sensuit la declaration, de la garde & tenue pour ledit Prevost,pour se preparer à deffendre dudit estoc d’hault, qui sera tiré cy aprés par le Lieutenent contre le Prevost, au sixiesme & dernier coup, estant multiplié comme dit est au sixiesme lieu. Cestedite garde & tenue pour ledit Prevost est, qu’il faut estre sur le pied droict, comme ledit Lieutenent, combien qu’on se peut tenir sur le pied gauche, & avancer le pied droit, mais à ce dernier coup & lieu estant multiplié, nous traicterons de la garde qui se fait estant sur le pied droict. Pour ce faire, ledit Prevost sera sur le pied droict en garde basse, tenant la main que tient l’espée les ongles en bas, assituant la pointe de l’espée droit l’estomac dudit Lieutenent, & sa main gauche la tenant droit le tetin, comme on peut voir cy dessus à sa pourtraiture & figure, cotté en chiffre, auprés du panache de son bonnet 54. Fault noter que tous les gauchers qui ensuyvent l’instruction que je mets, tant pour le Lieutenent que Prevost facent la desmarche à l’opposite, & les desgainemens semblables, & les coups aussi à l’opposite d’iceux droicturiers, & se trouveront fort bien ceux qui tascheront à suyvre cesdictes raisons. Car l’experience leur fera trouver bonnes. Voila la fin de ladite tenue & garde pour le Prevost, pour soy deffendre du sixiesme coup, qui sera cy aprés tiré par le Lieutenent demonstrateur. | |
| The following is the sixth and last strike and target of the sword to be multiplied, which is a high thrust on the reversal thrown by the attacking Lieutenant against the defending Provost.
And to do this, this Lieutenant must be on the guard and said step shown above at the portraiture marked number 53. This Lieutenant being on the right foot as stated will pretend to make a thrust at the Provost's left side on the right foot, and in an instant will advance the left foot, stealing away his sword below the Provost's sword hilt, and throwing a thrust at his right, keeping the sword hilt and the fingertips on the hand holding it facing left, and keeping the left hand right of his left nipple, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 55 behind the collar of the Lieutenant. The end and declaration of the sixth and last strike of the sword alone for the attacking Lieutenant. After having performed the sixth and last strike of the sword alone for the attacking Lieutenant, also stay to perform the defense of it for the defending Provost. And to do this, the Provost is to be on the right foot as shown at the portraiture being on his guard marked number 54, pulling it back and crossing his sword on the attacking Lieutenant's sword, beating down and defending the thrust with strong on weak - defining again strong on weak which is that he must cross all strikes near the sword hilt at the middle of the enemy's sword - and in doing this the Provost will present a thrust to the attacking Lieutenant's chest, keeping the back of the sword hand up and the left hand below the sword elbow, as shown above at the portraiture marked 56. The end and the declaration of the defense of the sixth and last strike for the defending Provost against the attacking Lieutenant. |
Sensuit le sixiesme & dernier coup & lieu de ceste espée seule, estant multiplié, qui est un estoc d’hault sur le renvers tiré par le Lieutenent assaillant, contre le Prevost deffendant.
Et pour ce faire, faut que ce prochain Lieutenent estant sur ladite garde, desmarche, que dessus est dit & monstré à sadite pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre 53. Cedit prochain Lieutenent estant sur le pied droit, comme il est dit, fera semblant de tirer un estoc au costé gauche du Prevost sur ledit pied droit, & à un instant advancera le pied gauche, desrobant son espée, par dessous la garde de l’espée du Prevost, & luy tirera un estoc au costé droit, tenant la garde de l’espée, & la main que tient icelle la pointe des doids regardant le costé gauche, & sa main gauche la tient droit son tetin gauche, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa portraiture cotté en chiffre au derriere du collet dudit Lieutenent 55. La fin & declaration de cedit sixiesme & dernier coup de ceste espée seulle pour le Lieutenent assaillant. Aprés ayant traité dudit sixiesme & dernier coup, de ceste espée seulle pour ledit Lieutenent assaillant. Reste à traiter aussi de la deffence d’iceluy pour le Prevost deffendant. Et pour ce faire, ledit Prevost estant sur le pied droit, comme est monstré à sadite pourtraiture estant en sa garde où est cotté en chiffre 54, le tirera arriere & croisera de son espée celle dudit Lieutenent assaillant, rabatant & deffendant ledit estoc du fort le foible, declarant encores qui est le fort le foible, c’est qu’il faut croiser tous coups d’auprés de la garde de l’espée au milieu de l’espée de l’ennemy, & voila du fort le foible, & ce fait ledit Prevost presentera un estoc à la poitrine dudit Lieutenent assaillant, tenant la main que tient l’espée le dessus d’icelle en haut, & la main gauche dessous le coude du bras que tient l’espée, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture cotté en chiffre, 56. La fin & declaration de la deffence dudit sixiesme & dernier coup pour ledit Prevost deffendant, contre ledit Lieutenent assaillant. | |
| The following is the first counter and continuation of the sixth and last strike being multiplied, which is a high thrust for the attacking Lieutenant and defended by the Provost.
This is shown by the author Henry d S. Didier what the Lieutenant must do to effectively attack the Provost with the last strike and target of the sword alone, following the art and order of this. And to do this, the Lieutenant is to be on the left foot, having thrown the sixth strike as shown above at the portraiture marked number 55. His sword being on the back-hand and to execute the first counter effectively, this Lieutenant will steal away his sword below the Provost's sword hilt, and will throw at him a thrust on the right-hand for the first counter, turning the nails on the sword hand up and the left hand right of his face, to protect against the Provost's sword point as shown above at the portraiture and figure marked number 57 behind the collar of the Lieutenant. The end of the first counter and continuation of the sixth strike and target for the attacking Lieutenant. This is the defense of the first counter and continuation for the Provost of the sixth strike, which is a high thrust being multiplied and thrown by the attacking Lieutenant and defended by the Provost, as will be seen by the writings after the author directs and teaches, as it should be defended from the thrust. And to do this, the Provost must remain firm and stable on the step of the left foot, and for the defense and conservation of the counter, which will be a thrust the Provost will cross his sword on the Lieutenant's sword with strong on weak coming from the side of a right-hand, carrying the nails on the sword hand up and presenting a thrust to the Lieutenant's face, keeping also the Provost's left hand right of the left nipple, as shown above at the portraiture marked 58. This is the end and defense of the first counter and continuation of the sixth and last strike for the defending Provost. |
Sensuit la premiere opposite & suitte dudit sixiesme & dernier coup, estant multiplié, qui est un estoc d’hault pour le Lieutenent assaillant, & deffendu par le Prevost que voicy.
Icy est monstré par Henry de S. Didier auteur, comment cedit Lieutenent doit faire pour bien assaillir le Prevost, sur cedit dernier coup & lieu de cestedite espée seulle, suivant ledit art & ordre d’icelle. Et pour ce faire, cedit Lieutenent estant sur le pied gauche, ayant tire ledit sixiesme coup comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture cotté en chiffre 55. Son espée estant sur l’arieremain, & pour bien faire & executer ceste premiere suitte, ce Lieutenent prochain desrobera son espée par desous la garde de l’espée du Prevost, & luy tirera un estoc sur le maindroit pour ceste premiere opposite, tournant la main que tient l’espée les ongles en haut, & sa main gauche droit son visaige, pour obvier à la pointe de l’espée du Prevost comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture & figure cotté en chiffre au derriere du col dudit Lieutenent 57. La fin de la premiere opposite & suite de ce sixiesme coup & lieu pour ledit Lieutenent assaillant. Ici aprés est la deffence de ceste premiere opposite & suitte pour ledit Prevost dudit sixiesme coup, qui est un estoc d’hault estant comme dit est multiplié & tiré par ledit Lieutenent assaillant, & deffendu par le Prevost[33], comme sera veu par cest escript cy aprés dont ledit auteur le conduit & monstre, comme il se doit deffendre de cedit estoc. Et pour ce faire, ledit Prevost doit demourer ferme & stable sur la desmarche du pied gauche, & pour la deffence & conservation de cestedite opposite, qui sera un estoc le Prevost croisera de son espée, l’espée dudit Lieutenent du fort le foible venant du costé d’un maindroit, portant les ongles de la main que tient l’espée en haut presentant un estoc au visaige dudit Lieutenent, tenant aussi ledit Prevost sa main gauche droit le tetin gauche, comme est monstre cy dessus à sa pourtraiture cotté en chiffre 58. Voyla la fin & deffence de la premiere opposite & suitte du[34] sixiesme & dernier coup, pour ledit Prevost deffendeur. | |
| This is the second and last counter and continuation of the sixth strike being multiplied, which is a high thrust on the reversal, coming from the thrust on the Lieutenant's right-hand executed against the Provost.
And to do this, this said Lieutenant must be on the left foot and his sword at the first counter, which is a right-hand or thrust, as shown at the portraiture marked 57. And to execute the second and last counter for the Lieutenant, he must steal away his sword below the Provost's sword hilt and throw another thrust on the back-hand, keeping the back of the sword hand up, his left hand right of the face to defend against the Provost's sword point if in case he drives it more forward, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 59 behind the hat. This is the end of the second and last counter and continuation for the attacking Lieutenant against the defending Provost. The defense of the second counter or continuation of the sixth and last strike of the sword alone, which is a high thrust on the reversal for the defending Provost against the attacking Lieutenant. And for the defense of this said counter and continuation for the Provost, he must be on the left foot, and he need to cross the Lieutenant's sword, strong on weak, which is near the hilt at the middle of the sword as stated above several times, and present a thrust at the Lieutenant's left nipple or at the eye, having the nails on the sword hand down, and the left hand right of his stomach which is below the sword elbow, as shown in the portraiture marked number 60 behind the hat. This is the end of the six said strikes, being multiplied at the distinct targets, as stated above, with counters and continuations, both for the attacking Lieutenant as well as for the defending Provost. |
Icy est la seconde & derniere opposite & suitte, dudit sixiesme coup, estant multiplié, qui est un estoc d’hault,sur le renvers, venant dudit estoc sur le maindroit pour le Lieutenent, contre le Prevost, dont la voicy executée.
Et pour ce faire, faut que cedit prochain Lieutenent, estant sur le pied gauche, & son espée sur ladite premiere opposite, qui est sur le maindroit ou estoc d’icely, comme est monstré à sa pourtraiture cotté 57. Est besoing, & faut pour executer ceste seconde & derniere opposite, pour ce Lieutenent, qu’il desrobe son espée par dessoubs la garde de l’espée du Prevost, & tirer un autre estoc sur ledit arrieremain, tenant la main que tient l’espée le dessus en haut, & sa main gauche droite le visage, pour deffendre la pointe de l’espée du Prevost, si la poussoit plus avant, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre au derriere du chappeau 59. Icy est la fin de ceste seconde & derniere opposite & suitte, pour le Lieutenent, assaillant, contre le Prevost deffendant. La deffence de ceste seconde opposite ou suitte, dudit sixiesme, & dernier coup de ceste espée seule, qui est un estoc d’hault, sur le renvers, pour le Prevost deffendant, contre ledit Lieutenent assaillant. Et pour la deffence de cestedite opposite & suitte, pour ledit Prevost, faut qu’il soit sur le pied gauche, & y estant doit croiser de son espée celle dudit Lieutenent, du fort le foible, qui est auprés de la garde, au milieu de l’espée comme a esté dit cy dessus en plusieurs lieux, & presente un estoc au tetin gauche, ou à l’oeil dudit Lieutenent, ayant la main que tient l’espée les ongles en bas, & la main gauche droit son estomac, qui est par dessous le coulde du bras, que tient l’espée comme est monstré en sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre au derriere du chapeau 60. Voicy la fin des six susdits coups, estans multipliez ausdits lieux propres, comme a esté dit cy dessus, avec ses opposites & suittes, tant pour ledit Lieutenent assaillant, que pour le Prevost deffendant. | |
| Here are the guard and position to make two good and subtle strikes in the manner of a triangle or a rectangle for the attacking Lieutenant against the defending Provost.
And to do this, this Lieutenant having done one of the three drawings with his step remaining on the left foot which is planted and resting on the footprint which is marked number 1 and is in middle guard, placing the sword point straight at the Provost's left nipple, keeping the left hand over the left lap as marked number 61 above at the portraiture behind his hat. And if he is left-handed, he must keep his right foot on the triangle if wants to execute and make the principal strike well as will be seen later, and he will keep the same guard if he is attacking as marked at the portraiture of the right-handed Lieutenant on number 61. This is the end of the guard and position of the Lieutenant to execute the triangle against the defending Provost. The following is the declaration, guard, and position of the triangle for the defending Provost. And to do this, this Provost must be on the left foot, keeping this foot on the corner of the triangle marked number 1 at the portraiture, having made one of the drawings with the proper step and the Provost is to remain in high guard, keeping the back of the sword hand up, placing the point straight at the Lieutenant's left eye, and the left hand right of his nipple, swiftly deflecting the sword point of said attacking Lieutenant, as shown above number 62 at the pourtraiture. The end of the guard and position of the defending Provost. |
Icy est monstré la garde & tenue pour faire deux bons & subtils coups, en mainiere de triangle, & quadriangle, pour le Lieutenent assaillant, contre le Prevost deffendant.
Et pour ce faire, ce present[35] Lieutenent ayant faict un desdits trois desgainements, avec sa desmarche à ce propres est demouré sur le pied gauche lequel est planté & pausé sur la semelle du triangle où est cotté en chiffre 1 & est en garde moyenne, assituant la pointe de l’espée droit le tetin gauche du Prevost, tenant la main gauche sur le giron gauche comme est cotté cy dessus en chiffre à sa pourtraiture au derriere de son chapeau 61. Et s’il est gauché, faut qu’il tienne son pied droit sur ledit triangle, s’il veut bien executer & faire le principal coup, comme se verra cy aprés, & se tiendra en mesme garde, s’il est assaillant, comme est cotté en chiffre à cestedite pourtraiture dudit Lieutenent droictié 61. Voyla la fin, garde & tenue pour ledit Lieutenent, pour executer ledit triangle, contre le Prevost deffendant. Sensuit la declaration, garde & tenue dudit triangle, pour ledit Prevost deffendeur. Et pour ce faire, faut que le susdit prochain Prevost soit sur le pied gauche, tenant iceluy pied sur le coin du triangle, où est cotté en chiffre à sadite pourtraiture 1, ayant fait un desdits desgainements, avec la desmarche à ce propre, & est demouré cedit Prevost en garde haute, tenant le dessus de la main que tient l’espée en haut, assituant la pointe de l’espée droit l’oeil gauche dudit Lieutenent, & la main gauche droit son tetin, preste à destourner la pointe de l’espée dudit Lieutenent assaillant, comme est figuré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre 62. La fin de la garde & tenue pour ledit Prevost deffendant. | |
| The following is what the attacking Lieutenant must do to execute a very effective and subtle strike, imagining on the ground a triangle, desiring to use it against the defending Provost, and doing well to have both its portrait and figure under his feet.
And to begin well, the Lieutenant will advance the right foot that was kept back at the portraiture marked number 61 on the footprint near the corner of the triangle marked number 2, and throw a thrust at the Provost's face, keeping the nails on the sword hand up, and the left hand right of his face as apparently shown here at the portraiture of the Lieutenant marked number 63. This is how to throw a thrust which will serve as a start to being to do this said triangle for the Lieutenant. The following is how the Provost need to defend himself from the thrust, thrown by the Lieutenant on the figure and manner of the triangle. And to do this, the Provost having made the drawing, guard, and placement to get to the portraiture marked number 62, the Provost then pulls the left foot back, and having placed upon the footprint marked number 2, and crosses the Provost's sword coming upon the thrust thrown by the Lieutenant, strong on weak, which is declared in several places including the strikes as well as on the counters and continuations, turning the nails on the sword hand up, and presenting a thrust to the Lieutenant's face, keeping the left hand right and below the thigh as shown above at the portraiture marked number 64[36]. This is the end and the defense of starting the first strike thrown by the Lieutenant against the Provost. |
Sensuit comment il faut faire, pour executer un fort bon & subtil coup, faignant en terre un triangle par le Lieutenent assaillant, le voullant faire contre le Prevost deffendant, dont ont tous deux soubs leurs pieds le portrait & figure d’iceluy pour le bien faire.
Et pour le bien commencer, ce Lieutenent advancera le pied droit qu’il tenoit arriere, à ladite pourtraiture cotté en chiffre 61, sur la semele où est auprés du coin du triangle où il y a cotté en chiffre 2, & tirer un estoc au visaige du Prevost, tenant la main que tient l’espée, les ongles en haut, & la main gauche, droit son visaige, comme est monstré apertement icy à ceste pourtraiture de ce Lieutenent cotté en chiffre 63. Voila comment doit tirer ledit Lieutenent un estoc qui servira d’espion pour commencer à faire cedit triangle. Sensuit comment le Prevost se doit deffendre dudit estoc, tiré par ledit Lieutenent sur une figure en manière de triangle. Et pour ce faire, ledit Prevost ayant fait ladite desmarche, garde, & assituation qu’a fait à sadite pourtraiture cotté en chiffre 62, a cedit Prevost tiré le pied gauche arriere, & l’a mis sur la semelle, où est ou doit estre cotté en chiffre 2, & a croisé cedit Prevost l’espée venant sur un estoc, tiré par ledit Lieutenent, du fort le foible, lequel est declaré en plusieurs lieux, tant desdits coups que aux opposites & suittes, tournant la main que tient l’espée, les ongles[37] en haut, & presenter un estoc au visaige dudit Lieutenent, tenant sa main gauche droit & dessus la cuisse, comme est cy dessus à sa pourtraiture cotté en chiffre 64[38]. Voila la fin & deffence du commencement & premier coup que tirera ledit Lieutenent contre ledit Prevost. | |
| And for the first counter and continuation of the triangle for the attacking Lieutenant against the defending Provost, the Lieutenant does a high thrust or high reversal.
To do this counter and continuation well for the Lieutenant, he must have his left foot on the footprint of the triangle marked number 1 in the portraiture, advance the right foot on the footprint marked number 3, and pass the sword point below the Provost's sword hilt, having made and thrown the strike, and throw a high thrust on the Provost's right side for the first counter and continuation, keeping the nails on the sword hand down, and the left hand right of the nipple, as shown at the portraiture marked number 65. The end of the first counter and continuation of the triangle for the attacking Lieutenant against the defending Provost. The following is the defense of the first counter and continuation for the Provost against the Lieutenant. And to do this the Provost must watch the Lieutenant's point when it would pass below the sword hilt in order to throw either a high thrust or high reversal at the Lieutenant's choice, wait for the attack, and for the conservation of the first counter and continuation of the triangle made by the Lieutenant, the Provost needs to cross the Lieutenant's sword, strong on weak, being on the right foot, and to present a thrust at the Lieutenant's face, keeping the back of the sword hand up, and the left hand right of the nipple, as shown above at the portraiture, marked number 66. This is the end and defense of the first counter of the triangle for the Provost. |
Et pour la premiere opposite, & suitte dudit triangle, pour le Lieutenent assaillant, contre le Prevost deffendant, il se fait sur un estoc ou renvers d’hault, pour le Lieutenent.
Pour bien faire ceste premiere opposite & suitte, pour ledit Lieutenent, faut ayant le pied gauche sur la semelle du triangle, où est cotté aux pourtraitures susdites en chiffre 1, advancer le pied droit sur la semelle où est cotté, ou doit estre 3, en chiffre, & passer la pointe de l’espée par dessous la garde de l’espée du Prevost, ayant fait & tiré le susdit coup, & tirer un estoc d’haut sur le costé droit du Prevost, pour ceste premiere opposite & suitte, tenant la main que tient l’espée les ongles en bas, & la main gauche droit le tetin, comme est monstré à sadite pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre, 65. La fin de la premiere opposite & suitte dudit triangle, pour le Lieutenent assaillant, contre le Prevost deffendant. Sensuit la deffence de la premiere opposite & suitte, pour ledit Prevost contre ledit Lieutenent. Et pour ce faire, faut que ledit Prevost regardant la pointe de l’espée dudit Lieutenent, quand elle passera par dessous la garde de son espée, pour luy tirer un estoc d’haut, ou renvers, au chois dudit Lieutenent, attendu qu’il est assaillant, & pour la conservation de ceste premiere opposite & suitte de cedit triangle, fait par le Lieutenent, est besoin que ledit Prevost croise l’espée dudit Lieutenent, du fort le foible, estant sur son pied droit, & presenter un estoc au visage dudit Lieutenent, tenant la main que tient l’espée le dessus d’icelle en haut, & la main gauche droit le tetin, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre 66. Voila la fin & deffence de la premiere opposite dudit triangle pour ledit Prevost. | |
| The following is the second counter and continuation which is a high thrust or high right-hand, originating from the triangle strike for the attacking Lieutenant against the defending Provost.
And the Lieutenant again for the second counter of the triangle, if the Lieutenant sees that the Provost defends against the first counter and throws a back-hand as marked number 66 at the Provost, and if he is skillful; the Lieutenant staying on the same right foot step steals away his sword below the Provost's sword hilt by a back-hand, and feints a back-hand at the Provost's cuisse, raising at the same time his sword up, and to execute the second counter he crosses the Provost's sword strong on weak and presents a thrust to the body or the face, shifting the right foot which is on the corner of the triangle or number 3 and puts it on the footprint marked 2, keeping the nails of the sword hand up and the left hand right of the face, as shown at the portraiture marked number 67 behind the hat. This is the end for the Lieutenant against the Provost. The following is the reverse of the second counter and continuation for the Provost. And to do this, the Provost must be on the left foot having made his step, as stated above at the figures of the three drawings, marked number 2 and 4, also as shown above at portraiture 62 of the Provost, and to guard the strike thrown by the Lieutenant well in the manner and fashion of the triangle, the Provost needs to watch the Lieutenant's sword point and never lose sight of it, and when the Lieutenant advances his right foot to throw a high thrust or high reversal, the Provost must cross these strikes, strong on weak, and present a thrust at the face, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 64, and to make and execute the second counter for the Provost, he will be on the right foot and cross the thrust coming on the reversal thrown by the Lieutenant, strong on weak, keeping the nails on the sword hand up, presenting a thrust at the Lieutenant's face, and keeping the Provost's left hand right of the braies, as marked number 68 above. This is the end and defense of the strike for the Provost. |
Sensuit la seconde opposite, & suitte, qui est un estoc ou maindroit d’hault, provenant dudit coup du triangle pour le Lieutenent assaillant, contre le Prevost deffendant.
Et encores cedit Lieutenent pour ceste seconde opposite dudit triangle, si ledit Lieutenent voit que ledit Prevost se soit deffendu de ceste susdite premiere opposite, faite & tirée sur l’arrieremain, comme est cotté audit Prevost en chiffre 66. & qu’il soit adroit. Ce present Lieutenent ayant demouré sur la mesme desmarche du pied droit desrobbera son espée, par dessous la garde de l’espée du Prevost, par un arrieremain, & fera semblant de tirer un arrieremain à la cuisse du Prevost, montant à un mesme instant son espée en haut, & pour executer ceste seconde opposite, croisera l’espée du Prevost du fort le foible, & luy presentera un estoc au corps ou au visaige, changeant le pied droit, qui estoit sus le coin du triangle, où est cotté en chiffre 3, & le mettre sur la semelle où est cotté 2, tenant la main de l’espée les ongles en haut & la main gauche droit le visaige, comme est monstré à sa pourtraiture au derriere du chappeau cotté en chiffre 67. Voila la fin pour le Lieutenent contre le Prevost. Sensuit le contraire de ceste seconde opposite & suitte pour ledit Prevost. Et pour ce faire, faut que ledit Prevost estant sur le pied gauche ayant fait sa desmarche, comme est dit cy dessus ausdites figures desdits trois desgainemens, cotté en chiffre 2, & 4 & comme est aussi monstré cy dessus à la pourtraiture dudit Prevost 62, & pour se bien garder de cedit coup tiré par ledit Lieutenent, en maniere & façon de triangle, est besoin que ledit Prevost regarde bien la pointe de l’espée dudit Lieutenent, & ne la perde jamais de veue & quand le Lieutenent susdit advancera son pied droit pour tirer un estoc ou renvers d’hault, faut que ledit prochain Prevost croise iceux coups, du fort le foible, & luy presenter un estoc au visaige, comme est monstré cy dessus à sadite pourtraiture cotté en chiffre 64, & pour faire & executer ceste seconde opposite, pour cedit Prevost, il sera sur le pied droit & croisera l’estoc venant sur le renvers qu’aura tiré ledit Lieutenent, du fort le foible, tenant la main que tient l’espée, les ongles en haut presentant un estoc au visaige dudit Lieutenent, & tiendra sa main gauche ledit Prevost droit la braye, comme est cotté cy dessus en chiffre 68. Voila la fin & deffence dudit coup, pour ledit Prevost. | |
| Position and guard of the first strike in order to execute the rectangle for the Lieutenant and the Provost.
It must be noted that to execute the rectangle for the Lieutenant, he must have the left foot on the corner of the rectangle marked number 1, having made one of the three drawings with his step, and be in a low middle guard, the cutting edge down, the sword point straight at the belly, and keeping the left hand right of the stomach, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 69. This is the end of the guard and position for the Lieutenant in order to begin and execute the rectangle against the defending Provost. Definition, guard, and position for the defending Provost to guard and defend himself from the rectangle thrown by the attacking Lieutenant against the defending Provost. And to do this, the Provost must be on the left foot, placing his foot on the footprint marked number 1 on the rectangle, being in middle guard having made his step, drawing as stated above in the several places, keeping the back of the sword hand up and therefore the nails down, and the left hand over the left lap, as shown above at the portraiture and figure marked number 70. Next we will show a very effective strike for the attacking Lieutenant and for the defending Provost in the manner of the rectangle and everything that is required to know it for the Lieutenant and Provost and therefore other adherents as well. |
Tenue & garde du premier coup, pour executer & faire le quatriangle pour le Lieutenent & Prevost.
Faut bien notter que pour faire & executer cedit quatriangle pour le Lieutenent, faut qu’il aye le pied gauche sur le coin dudit quatriangle, cotté en chiffre 1, ayant fait un desdits trois desgainemens, avec sa desmarche, & à ceste garde faut qu’elle soit moyennement basse, le trenchant de l’espée en bas, & la pointe de l’espée droit le ventre, tenant la main gauche droit l’estomac, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre 69. Voila la fin garde & tenue pour ledit Lieutenent, pour commencer, faire & executer le quatriangle, contre le Prevost deffendant. Definition, garde & tenue pour ledit Prevost deffendant, pour se garder & deffendre dudit quatriangle tiré par ledit Lieutenent assaillant, contre le Prevost deffendant. Et pour ce faire, faut que ledit Prevost soit sur le pied gauche, dont iceluy pied sera mis sur la semelle, où est cotté en son quatriangle en chiffre 1, estant en garde moyenne ayant fait sa desmarche, desgainement que dessus est en plusieurs lieux dit, tenant la garde de l’espée le dessus de la main que tient icelle en haut, & par consequent les ongles d’icelle main en bas, & la main gauche sur son giron gauche, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture & figure, cotté en chiffre 70. Si aprés sera monstré un fort bon coup pour le Lieutenent assaillant, & pour le Prevost deffendant, en maniere de quatriangle & tout ce que y est requis scavoir par lesdits Lieutenens & Prevosts, & par consequent aux autres suppots. | |
| The first strike and continuation of the rectangle for the Lieutenant and the Provost.
And to do this well, the Lieutenant needs to have done one of the drawings while moving the left foot on the footprint marked number 1 for the first strike, and to execute this strike the Lieutenant must advance the right foot on the footprint marked number 2, and throws a steep high thrust, keeping the nails on the sword hand up, and the left hand over the right lap, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 71 behind the hat. This is how the Lieutenant must begin to make a strike in the manner of the rectangle, imagined as such on the ground. The following is how the Provost must defend himself from the strike that is made and thrown by the Lieutenant, imagined and represented by a rectangle on the ground, as shown above. And to do this, the Provost must be on the left foot as shown and stated above at the first position. And to defend this rectangle strike made by the Lieutenant well, which is either a high thrust or high right-hand. The Provost pulls the left foot on the footprint of the rectangle marked number 1 and pause it on the corner of the triangle marked number 3, and crosses the Lieutenant's sword, strong on weak, deflecting the rectangular right-hand or thrust thrown by the Lieutenant, and presents a thrust straight at the Lieutenant's left, keeping the nails on the sword hand up, and the left hand in front of his braies, as shown above at the portraiture of the Provost, marked number 72. This is what the Provost needs to do to defend himself from the rectangle thrown by the attacking Lieutenant. |
Premier coup & suitte du quatriangle, pour le Lieutenent & Prevost.
Et pour le bien faire, est besoin pour le premier coup que le Lieutenent, ayant fait un desdits desgainements demoure sur le pied gauche, qui est sur la semelle cotté en chiffre 1, & pour executer ce coup faut que cedit Lieutenent advance le pied droit sur la semelle où est cotté en chiffre 2, & tirer un roide estoc d’hault, tenant la main que tient l’espée les ongles en haut, & la main gauche sur son giron droit, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre au derriere du chapeau 71. Voila comment il faut que ledit Lieutenent commence à faire ce coup, en maniere de quatriangle, le feignant ainsi estre en terre. Sensuit comment il faut que ledit Prevost se deffende de ce coup, fait & tiré par ledit Lieutenent, faignant & figurant un quatriangle en terre, tel que cestuy cy dessus. Et pour ce faire, faut que ledit Prevost soit sur le pied gauche, comme est monstré & dit cy dessus à sa premiere tenue. Et pour bien deffendre cedit coup, fait comme dit est, en quatriangle, par ledit Lieutenent, sur un estoc ou maindroit d’haut. Ledit Prevost tirera ledit pied gauche, de la semelle dudit quatriangle, où est cotté en chiffre 1, & pausera le pied gauche sus un petit coin du triangle, où est cotté en chiffre 3, & croisera l’espée dudit Lieutenent, du fort le foible, detournant le maindroit ou estoc, tiré par ledit Lieutenent en quatriangle, comme dit est, presentant par ledit Prevost un estoc, droit l’oeil gauche dudit Lieutenent, & tiendra la main que tient l’espée les ongles en haut, & la main gauche droit sa braye, comme est monstré cy dessus à la portraiture dudit Prevost, cotté en chiffre 72. Voila ce que doit faire ledit Prevost, pour soy deffendre dudit quatriangle, tiré par ledit Lieutenent assaillant. | |
| The first counter and continuation of the rectangle for the Lieutenant and the Provost.
And in order to continue to execute the first counter or continuation of the rectangle for the Lieutenant, he again needs to make a continuation seeing if the Provost is skillful and not ignorant and waiting if he defended himself well, the Lieutenant needs to steal away his sword below the Provost's sword hilt and take the left foot on the footprint marked number 3. In passing a right-hand, throwing the body a little back, and removing the right foot on the place marked number 2.[39] And as shown above at the portraiture marked number 73 behind the hat. This is what the Lieutenant must do for the first counter as required for the rectangle strike. The following is the defense of the first counter and continuation of the rectangle for the defending Provost against the attacking Lieutenant. And to do this, the Provost must have the left foot on the corner of the triangle marked number 1 and the right foot on the footprint also marked number 2. And for the defense of the first counter, the Provost is to be on the right foot to cross the Lieutenant's sword, strong on weak, and present a thrust to his face, keeping the back of the sword hand up and keeping the left hand right of his nipple as shown above at the portraiture and figure marked number 74. This is what the Provost must do to guard himself from the counter thrown by the Lieutenant. |
Premiere opposite & suitte du quatriangle pour le Lieutenent & Prevost.
Et pour continuer, faire executer ceste premiere opposite ou suitte dudit quatriangle pour le Lieutenent, est encores besoing qu’il face une suitte, voyant que ledit Prevost a esté adroit, & non ignorant, attendu qu’il s’est bien deffendu, à ceste cause doit ledit Lieutenent[40] desrober son espée par desous la garde de l’espée du Prevost, & mettre le pied gauche sur la semelle où est cotté en chiffre 3. En passant un maindroit, tirant un peu le corps en arriere, & oster le pied droit du lieu où estoit cotté en chiffre 2[41]. Et comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture cotté en chiffre au derriere du chapeau 73. Voila que doit encores faire ledit Lieutenent, pour la premiere opposite, comme est requis en cedit coup de quatriangle. Sensuit la deffence de ceste premiere opposite & suitte, de cedit quatriangle pour ledit Prevost deffendant, contre le Lieutenent assaillant. Et pour ce faire, faut que ledit Prevost soit sur le pied gauche, sur le coin de son triangle, où est cotté en chiffre 1, & le pied droit sur la semelle où est cotté aussi en chiffre 2. Et pour la deffence de cestedite premiere suitte, estant ledit Prevost sur le pied droit, a croisé l’espée dudit Lieutenent, du fort le foible, & luy a presenté un estoc à son visage, tenant la main que tient l’espée le dessus d’icelle en haut, & la main gauche la tient droit le tetin, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, & figure cotté en chiffre 74. Voila que doit faire ledit Prevost, pour se garder de cestedite opposite, qu’a tiré ledit Lieutenent jusques icy. | |
| The following is the completion of the rectangle which is a high right-hand or high thrust thrown by the Lieutenant against the Provost.
To complete the rectangle for the Lieutenant against the Provost, the Lieutenant must have the right foot on the footprint marked number 4 and the left foot on the footprint marked 3, stealing away his sword below the Provost's sword hilt and throwing a high right-hand or high thrust to complete the rectangle, keeping the nails on the sword hand down and the left hand right of his face, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 75. This is the completion of the strike made in the fashion of a rectangle for the Lieutenant against the defending Provost. The following is the defense and completion of the strike with two continuations in the fashion of a rectangle for the defending Provost against the attacking Lieutenant. And to do this, the Provost for the first continuation must be on the right foot, crossing and beating down the high reversal or high thrust thrown by the Lieutenant, strong on weak, keeping the nails on the sword hilt down, and throwing a high thrust at the Lieutenant's left as shown above at the other portraiture and figure marked number 74. And for the second counter and continuation which is to complete the rectangle, the Provost must also be on the right foot and carefully watch the Lieutenant's sword point in every discourse of the rectangle, and cross the Lieutenant's sword who is making the second counter which is a high right-hand or high thrust coming from the strong on weak, keeping the nails on the sword hand up and presenting a thrust to the Lieutenant's face while keeping the left hand at his nipple as shown above at the portraiture marked number 76. The end of the rectangle for the Provost. After having written the above for all of the art, order, and practice of the sword alone and defining all the requirements; both in attacking as well as for defending, next I intend to write and show four very effective and subtle grabs that one can do, both in attacking as well as in defending as will be seen later at their portraitures. |
Sensuit le parachevement dudit quatriangle, qui est sur un maindroit ou estoc d’hault, tiré par ledit Lieutenent, contre le Prevost.
Pour bien parachever cedit quatriangle pour ledit Lieutenent contre le Prevost, faut que ledit Lieutenent, ayant le pied droit sur la semelle cotté en chiffre 4, & le pied gauche sur la semelle cotté 3, desrobera son espée par dessous la garde de l’espée du Prevost, & tirera un maindroit ou estoc d’haut, pour parachever ledit quatriangle, tenant ledit Lieutenent la main de l’espée les ongles en bas, & la main gauche droit son visage, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre 75. Voicy le parachevement dudit coup, fait en façon de quatriangle, pour ledit Lieutenent, contre le Prevost deffendant. Sensuit la deffence & parachevement dudit coup, avec ses deux suittes, en facon de quatriangle pour ledit Prevost deffendant, contre ledit Lieutenent assaillant. Et pour ce faire, faut que ledit Prevost pour la premiere suitte, estant sur le pied droit, croise & rabate ledit renvers ou estoc d’hault tiré sur iceluy par ledit Lieutenent, du fort le foible, tenant la garde de l’espée les ongles de la main que tient icelle en bas, tirant un estoc d’hault, à l’oeil gauche dudit Lieutenent, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture & figure cotté en chiffre aux autres pourtraitures 74. Et pour ceste seconde opposite & suitte, qui est le parachevement de cedit quatriangle, ledit Prevost faut aussi qu’il soit sur le pied droit, & regarde bien la pointe de l’espée dudit Lieutenent, en tout le discours dudit quatriangle, & croise l’espée dudit Lieutenent faisant cestedite seconde opposite, qui est un maindroit ou estoc d’hault provenant d’iceluy du fort le foible, tenant la main que tient l’espée, les ongles en hault presentant audit Lieutenent un estoc à son visaige tenant la main gauche à son tetin, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture cotté en chiffre 76. La fin dudit quatriangle pour ledit Prevost. Aprés avoir traicté cy dessus de tout l’art, ordre & praticque de ladite espée seulle, & defini tout ce que y est requis, tant en assaillant que en deffendant, j’ay bien voulu cy aprés traicter & monstrer quatre fort bonnes & subtilles prinzes qui se peuvent faire, tant en assaillant que en deffendant comme se verra cy aprés à leurs pourtraitures. | |
| Next is the plan and position of the attacking Lieutenant to show and make the first grab against the Provost.
And to do this, this said Lieutenant being on the left foot, having made as stated his step, guard, and placement at the earlier aforementioned plans, and from there he must be on the right foot in middle guard, keeping the nails on the sword hand down and the left hand right of the face to be ready to beat down a high thrust that could from the Provost or any other defender, because all thrusts can be defended and deflected at the hand; but one not to stop them as the point is in the air and far from the force from which it proceeds from. And everything that is in the air is easy to deflect as needed, if it so happens that the Provost advances his point further as shown above at the portraiture marked number 77 behind the collar. The end of the guard and position for the attacking Lieutenant to show the Provost how to do the first grab. The following is the guard and position for the Provost to defend from the first grab against the Lieutenant as will be seen after at the portraiture following number 90. And to do this guard, the Provost is required to do the same step, guard, and placement as stated above, one of the drawings, having pulled the right foot back and remain on the left foot in high guard, keeping the nails on the sword hand down, placing the point straight at the Lieutenant's left eye, keeping also the left hand right of his nipple, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 78 behind the hat[42]. The end of the guard and position for the defending Provost. |
Cy aprés est monstré & declaré le plan, & tenue du Lieutenent assaillant, pour monstrer à faire la premiere prinse, contre le Prevost.
Et pour ce faire, faut que cedit prochain Lieutenent soit sur le pied gauche, ayant fait comme dit est, sa desmarche, garde & assituation susdite, aux premiers plans, & à ceste cy faut qu’il se tienne sur le pied droit, en garde moyenne, tenant la main de l’espée les ongles en bas, & la main gauche droit le visage, pour estre plus prés à rabatre d’icelle un estoc d’haut[43], s’il advenoit que ledit Prevost, ou autre deffendeur luy tirast, car tous estocs sont aisez à deffendre, & à detourner de la main : mais qu’on ne les faille, attendu que la pointe est en l’air, & loin de la force dont elle procedde[44], qui est de son tireur. Et tout chose qui est en l’air est facille à detourner. comme il est prest à faire, s’il advenoit que le Prevost avançast sa pointe davantage, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre au derriere du col 77. La fin de la garde & tenue pour ledit Lieutenent assaillant, lequel veut monstrer au Prevost à faire la premiere prinse. Sensuit la garde & tenue pour le Prevost, pour se deffendre de la premiere prinse contre ledit Lieutenent, comme ce verra cy aprés à la portraiture que s’ensuit en chiffre, 90. Et pour ceste garde, est requis que ledit Prevost aye fait mesme desmarche, garde & assituation, que dessus est dit, à un desdits desgainements, ayant tiré le pied droit arriere, & soit demouré sur le pied gauche, en garde haulte, tenant la main que tient son espée les ongles en bas, assituant la pointe d’icelle droit l’oeil gauche dudit Lieutenent, tenant aussi la main gauche droit son tetin, comme est monstré cy dessus à sadite pourtraiture cotté en chiffre au derriere de son chappeau 78[45]. La fin de ladite garde & tenue pour ledit Prevost deffendant. | |
| In the next two portraitures are shown the first strike which is a high right-hand or high thrust thrown by the Lieutenant against the Provost for doing the first grab of the sword alone.
And to do this the Lieutenant having made his step, guard, and placement as stated, is to remain on the left foot and to execute this strike which is a high right-hand or high thrust, this said Lieutenant advances his right foot and throws his choice of either a right-hand or thrust against the Provost, keeping the nails on the sword hand up and the left hand right of his nose as shown at the portraiture marked number 79 behind the collar. This is the end of the strike that the Lieutenant needs to throw to make the first grab of the sword alone. The following is the protection and defense of the first strike for the Provost in order to prepare himself to make the first grab seen in the later portraitures. And to do this the Provost must also have made his step and drawing, remaining in high guard, as shown above at the portraiture of the Provost marked number 78, being on the left foot and to defend himself from the high right-hand or high thrust thrown by the Lieutenant, in order to show that the first grab could be made, and make on the strikes the Provost is to be on the left foot, pulling the right foot back and crossing the Lieutenant's sword, strong on weak, raising a bit the point of his sword up, the left hand right of the Lieutenant's face, keeping the nails on the sword hand up and the left hand right of the nipple, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 80 behind the head feather[46]. This is the end of how the Provost defends the strike against the Lieutenant. These two portraitures is to show using the attacking Lieutenant to the defending Provost, how they and everyone must do the first grab of the sword alone, and next will be the counter-grab so that anybody can observe all that is said and whoever follow this without omitting anything, he will never find surprises nor offenses and if he find them, he must admit it is not the fault of the Author nor of the art, but instead his own, having committed the fault so that whoever recognizes his fault such as this can be said to be learned as long as you can educate and understand. I caution to you all adherents of Mars that the art and science of fencing was not drafted by the Author to be abused, but instead for defending your honor and health because anyone who breaks this rule will dishonor the Author and the art, however the sages dominate the stars and ill will. |
En ces deux pourtraitures suivantes, est monstré le premier coup, qui est un maindroit ou estoc d’hault, tiré par le Lieutenent, contre le Prevost pour faire la premiere prinse de ceste espée seule.
Et pour ce faire, cedit Lieutenent ayant fait sa desmarche, garde & assituation susdite, est demouré sur le pied gauche, & y estant pour executer ce coup, qui est un maindroit, ou estoc d’haut, cedit prochain Lieutenent a advancé le pied droit, & a tiré un maindroit ou estoc à son chois contre le Prevost, tenant la main que tient l’espée les ongles en haut, & la main gauche droit son nez, comme est monstré à sa pourtraiture cotté au derriere du col en chiffre 79. Voila la fin du coup que doit tirer ledit Lieutenent au Prevost pour faire la premiere prinse de ceste espée seule. Sensuit la tuition & deffence du premier coup pour le Prevost, pour se preparer à faire la premiere prinse que verrez cy aprés aux pourtraitures. Et pour ce faire, faut que ledit Prevost ayant aussi fait sa desmarche, desgainement, est demouré en garde haute, telle qui est figuré cy dessus à la portraiture dudit Prevost cotté en chiffre 78, estant sur le pied gauche, & pour se deffendre de cedit maindroit ou estoc d’haut que luy a tiré ledit Lieutenent, pour luy monstrer que la premiere prinse ce peut faire, & fait sur lesdits coups, cedit Prevost estant sur ledit pied gauche, a tiré le pied droit arriere & a croisé l’espée dudit Lieutenent, du fort le foible, haussant un peu la pointe de son espée en haut, & la main gauche droit le front du Lieutenent, tenant la main de l’espée les ongles en haut & la main gauche droit le tetin, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture cotté en chiffre au derriere du sommet de la teste 80[47]. Voila la fin comment le Prevost a deffendu le coup susdit contre ledit Lieutenent. Par ces deux pourtraitures qui sensuivent, est monstré par le Lieutenent assaillant au Prevost deffendant, comment faut qu’il face & tous autres, la premiere prinse de ceste espée seulle, & en aprés luy sera monstré de contreprinses, de sorte, que quiconques observera tout ce que dit est, & ce qui sensuit cy aprés sans rien obmettre, il ne se trouvera jamais surprins ne offencé, & s’il se treuve, faudra qu’il confesse que n’est la faute de l’Auteur ne de l’art, ains la sienne, ayant commis la faute, de sorte que qui cognoit sa faute tel ce peult dire estre docte attendu que de soymesmes se pourra instruire & reprendre. Je vous advertis tous suppots de Mars que cedit art & sciences des armes n’ont esté redigé par l’Auteur pour en abuser, ains pour conserver vostre honneur & santé, car quiconque fera autrement la reigle ne faudra à l’Auteur ne à l’art, ains à celuy qui en abusera, & pourtant les sages dominent les astres & mauvaises volontez. | |
| First strike thrown as a high right-hand or high thrust for the first grab by the Lieutenant and nearly executed by the Provost as shown here.
And to do this, the Lieutenant needs to have made his said step, guard, and placement, being on the left foot, he must advance the right foot as shown at the figure and portraiture as stated in number 79. And also this said Lieutenant, being on the left foot advances his right foot and throws a high thrust or high right-hand at the Lieutenant[48], keeping the nails of the sword hand up, and keeping also the left hand right of his stomach and below the sword arm, as shown at the portraiture marked number 81. This is the end of the strike thrown by the Lieutenant to show the Provost how to do the first grab of the sword alone. Next we will show and declare how the Provost will need to do the first grab against his Lieutenant. And to do this, the Provost being on the left foot when the Lieutenant throws a high right-hand or high thrust, the Provost pulls his left foot back and crosses his sword, strong on weak, with the Lieutenant's sword, turning his nails on the sword hand up. And at the same time without a moment to waste, advances his left foot forward strongly, and with his left hand grabs the sword hilt and pretends to twist it to take it from him, as will be seen later keeping the sword point straight at the forehead as shown above at the portraiture and figure marked number 82. This is the end of the first grab, nearly executed for the defending Provost against the Lieutenant. |
Premier coup, tiré sur le maindroit, ou estoc d’hault, pour la premiere prinse par le Lieutenent, & presque executée par le Prevost, comme icy est monstré.
Et pour ce faire, est besoin que cedit Lieutenent ayant fait sadite desmarche, garde, & assituation, estant sur le pied gauche, fault qu’il advance le pied droit, comme est monstré à sa figure & pourtraiture susdite, cotté en chiffre, 79. Et aussi cedit prochain Lieutenent, estant sur le pied gauche cy dessus, a advancé le pied droit, & a tiré un estoc d’hault, ou un maindroit au Lieutenent[49], tenant la main que tient l’espée les ongles en hault, & tient aussi cedit Lieutenent, sa main gauche droit son estomac, au dessous du bras de son espée, comme est monstré à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre 81. Voyla la fin du coup qu’a tiré ledit Lieutenent, pour monstrer au Prevost à faire la premiere prinse de ceste espée seule. Cy aprés sera monstré & declaré, comment le Prevost doit & peut faire la premiere prinse, contre son Lieutenent. Et pour ce faire, ledit Prevost estant sur le pied gauche, quand ledit Lieutenent a tiré ledit maindroit, ou estoc d’hault ; comme il peut, cedit Prevost a tiré ledit pied gauche arriere, & a croisé de son espée, du fort le foible, l’espée dudit Lieutenent, tournant la main que tient l’espée les ongles en haut. Et à un mesme instant, sans bien peu d’intervalle, a advancé son pied gauche, fort advant, & luy a prins de sa main gauche la garde de l’espée, & fait semblant de luy donner le tour, pour la luy faire quitter, comme se verra cy aprés tenant la pointe de l’espée droit le front comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture & figure, cotté en chiffre 82. Voicy la fin de la premiere prinse, presque executée pour ledit Prevost deffendeur, contre ledit Lieutenent. | |
| The first grab and strike shown by the Lieutenant and executed by the Provost as shown here.
And for the Lieutenant to show what he must do to the Provost and execute the first grab effectively, the Lieutenant must be on the left foot and have advanced his right foot while throwing a high right-hand or high thrust against the defending Provost. And being surprised that the Provost took away his sword, the Lieutenant is forced to pull back his right foot and stay on his left foot, keeping his hand in front of his nipple, ready to defend against the Provost's sword point, and keeping his left hand against his left leg as shown at the portraiture marked number 83 behind the collar. This is everything that the Lieutenant must do to show the Provost what he must do to execute all of the first grab of the sword alone. The following is the first grab and its execution for this said Provost against the Lieutenant. And to do this the Provost must have made the first step, guard, and placement as stated; which is to say to be on the left foot while the Lieutenant throws either a high right-hand or high thrust and advances his right foot to execute the first grab for this said Provost, then pulling his left back back and crossing the Lieutenant's sword, strong on weak, raising a bit the sword point up and at the same time without a moment to waste the Provost is advancing the left foot and with the left hand grabbing the Lieutenant's sword hilt, twisting the top down and taking the sword from him, carrying it under the arms, presenting the sword point straight at the Lieutenant's mouth, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 84. This is the end of the first grab, demonstrated by the Lieutenant and executed by the Provost. |
Premiere prinse, monstrée par le Lieutenent, & à ce coup aussi monstrée par iceluy, & executée par le Prevost comme est monstré icy.
Et pour bien monstrer icy par ce Lieutenent, comment il fault que le Prevost face, & execute ceste premiere prinse, est besoin, & faut que ce Lieutenent soir sur le pied gauche, & y estant advancer le pied droit & tirer un maindroit, ou estoc d’hault, à l’encontre du Prevost deffendant. Et estant surprint[50] du Prevost qui luy a osté son espée, a esté ledit Lieutenent contraint de retirer son pied droit, & demourer sur le pied gauche, & tenir sa main gauche devant son tetin, la tenant preste à deffendre la pointe de l’espée du Prevost, & tient aussi cedit Lieutenent sa main gauche contre sa cuisse gauche, comme est monstré à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre au derriere du col 83. Voila tout ce qu’a fait ledit Lieutenent, pour monstrer au Prevost comment il faut qu’il face, pour executer du tout ladite premiere prinse de cestedite espée seule. Sensuit la premiere prinse, & execution d’icelle, pour ledit prochain Prevost, contre ledit Lieutenent. Et pour ce faire, faut que ledit Prevost, ayant fait sa premiere desmarche, garde, & assituation susdite, c’est à dire, estant sur le pied gauche, ledit Lieutenent luy a tiré un maindroit, ou estoc d’haut, comme il pouvoit, advançant son pied droit & pour faire & executer cestedite premiere prinse pour cedit prochain Prevost, a tiré son pied gauche arriere, & a croisé l’espée dudit Lieutenent, du fort le foible, haussant un peu la pointe de l’espée en haut, & à un mesme instant, sans bien peu d’intervalle, a ledit Prevost advancé le pied gauche, & avec la main gauche, a prins la garde de l’espée dudit Lieutenent, tournant le dessus d’icelle en bas, donnant le tour, pour luy faire quitter l’espée, & la porter sous le bras, presentant la pointe de l’espée droit la bouche dudit Lieutenent, comme est monstré cy dessus à sadite pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre 84. Voyla la fin, & demonstration dudit Lieutenent, & l’execution de ladite premiere prinse, pour cedit Prevost. | |
| The next grab that must be done is the counter-grab as shown here by the Lieutenant to the Provost.
And to do this, the Lieutenant being on the left foot, having thrown a steep high right-hand or high thrust at the Provost's left side and at the same time having turned to advance the left foot and having grabbed the Provost's sword hilt below his arms, and when just about to twist it, the Provost makes the counter-grab which is the just the same as stated, demonstrated, and shown above at the portraiture marked number 85 behind the collar. This is the end of the counter-grab for the Lieutenant. The following is the counter-grab for the Provost against the attacking Lieutenant. And to do this, the Provost will also be on the left foot in high guard, and when the Lieutenant will advance the right foot to throw either a high right-hand or high thrust, the Provost will pull the left foot back and will cross the right-hand or thrust thrown by the Lieutenant, strong on weak, and when he will see that the Lieutenant will advance the left foot to come and take the sword hilt to make the grab, the Provost seeing this at the same time will advance the left foot and also grab the Lieutenant's sword hilt with his left hand by passing it below the sword arm, turning the back of the hand down and having grabbed it, will pretend to twist his hand to remove the sword point as shown above at the portraiture of the Provost marked number 86 behind the collar. The end of the counter-grab for the Provost against the Lieutenant. The figures and portraitures that follow show how the counter-grab marked number 85 and 86 are executed both for the Lieutenant as well as for the Provost, so that the Lieutenant having followed the Author, removed the Provost's sword and the Provost also having done the same following his part as instructed to remove the Lieutenant's sword, so next we will see that the Lieutenant has the Provost's sword and the Provost has the Lieutenant's sword as marked number 87 and 88 at the portraitures of the Lieutenant and the Provost. |
À prinse faut faire contreprinse, comme est icy monstré par ce Lieutenent au Prevost.
Et pour ce faire, le Lieutenent estant sur le pied gauche, tirera un roidde[51] maindroit, ou estoc d’ault sur le costé gauche dudit Prevost, & à un mesme instant tournera advancer le pied gauche, & prendra la garde de l’espée dudit Prevost venant par dessous son bras, & voulant donner le tour, le Prevost a fait la contreprinse qui est tout de mesme comme luy avoit dit & monstré, comme est cy dessus à sa portraiture, cotté en chiffre au derriere de son col 85. Voila la fin pour faire ceste contreprinse pour le Lieutenent. Sensuit la contreprinse pour le Prevost, contre ledit Lieutenent assaillant. Et pour ce faire, ledit Prevost sera aussi sur le pied gauche, en garde haute, & quand ledit Lieutenent advancera le pied droit, pour tirer un maindroit ou estoc d’hault, comme il peut à son chois, le Prevost tirera le pied gauche arriere, & croisera ledit maindroit ou estoc, tiré par ledit Lieutenent, du fort le foible, & quand il verra que ledit Lieutenent advancera le pied gauche pour luy venir prendre la garde de l’espée pour faire ladite prinse, ledit Prevost ce voyant à un mesme instant advancera le pied gauche, & prendra aussi la garde de l’espée dudit Lieutenent avec sa main gauche, la passant par dessous le bras, de l’espée, tournant le dessus de la main en bas, & l’ayant prinse faira semblant de tourner icelle main pour luy oster l’espée du poin, comme est monstré cy dessus à la pourtraiture dudit Prevost, cotté en chiffre au derriere du col 86. La fin de la contreprinse pour le Prevost, contre le Lieutenent. Aux figures & pourtraitures qui sensuivent, est monstré comment ladite contreprinse cottée 85 & 86 est executée, tant pour le Lieutenent que pour le Prevost, de sorte que ledit Lieutenent ayant bien observé la volonté dudit auteur, a osté l’espée du tout au Prevost & aussi le Prevost ayant fait le mesme, observant de sa part ce qu’il devoit, a osté l’espée audit Lieutenent, de sorte qu’on verra cy aprés que le Lieutenent a l’espée du Prevost, & le Prevost a l’espée du Lieutenent, comme est cotté en chiffre cy aprés aux pourtraitures du Lieutenent 87, & au Prevost 88. | |
| The following is a counter-grab shown below by the Lieutenant and executed by the Provost.
And to do this, the Lieutenant being on the left foot as stated, will advance the right foot, throwing a high right-hand or high thrust at the Provost, and again at the same time advance the left foot and take the Provost's sword below his right arm, turning the left hand, and giving a twist to make him leave the sword, and seeing that the Provost is quick and skillful in doing one to him at the same time, the Lieutenant have stepped his said left foot back, and keeping the Provost's sword below his left hand and immediately puts the right hand back on the swordgrip, pretending to put back the swordgrip as shown at the portraiture above marked number 87 behind the head. This is the end of the counter-grab executed by the Lieutenant against the Provost. The following is an effective counter-grab for the Provost corresponding with the counter-grab above made by the Lieutenant. And to do this, this said next Provost will also be on the left foot in high guard, and when the Lieutenant will advance the right foot as instructed to throw a high right-hand or high thrust, the Provost will pull the left foot back and will cross the Lieutenant's sword strong on weak, beating down the high right-hand or high thrust and when he will see that the Lieutenant will advance the left foot to take the sword hilt to make the grab, the Provost will advance the left foot at the same time as him and the Provost will take the Lieutenant's sword hilt below his sword, turning the back of the left hand down as shown above at the portraiture of the Provost marked number 88. This is the end of the counter-grab for the Provost against the Lieutenant. |
Sensuit une contreprinse, monstrée cy dessous par le Lieutenent, & exécutée par le Prevost.
Et pour ce faire, le Lieutenent estant sur le pied gauche, comme dit est, advancera le pied droit, tirant un maindroit ou estoc d’hault sur le Prevost, & à un mesme temps de rechef advancera le pied gauche, & prendra l’espée dudit Prevost par desous son bras droit, tournant la main gauche, donnant un tour pour luy faire quiter l’espée, & voyant que le Prevost a esté prompt & habile de luy en faire autant à un mesme temps, cedit Lieutenent a desmarché sondit pied gauche arriere, & tenant l’espée dudit Prevost dessous son bras gauche, & incontinent a remis la main droite à la poingnée de l’espée, faisant semblant de remettre l’espée au poin comme est monstré à sa pourtraiture cy dessus cotté en chiffre au derriere de sa teste 87. Voyla la fin de la contreprinse executée pour le Lieutenent contre le Prevost. Sensuit une fort bonne contreprinse pour le Prevost, correspondante à la contreprinse cy dessus faicte par ledict Lieutenent. Et pour ce faire, ledit prochain Prevost sera aussi sur le pied gauche, en garde haute, & quand ledit Lieutenent advancera le pied droit, comme il doit & peult, pour tirer un maindroit ou estoc d’hault, ledit Prevost tirera le pied gauche arriere, & croisera l’espée dudit Lieutenent du fort le foible, rabatant ledit maindroit ou estoc d’hault qu’il a tiré, & quand il verra que ledit Lieutenent advancera le pied gauche, pour luy prendre la garde de l’espée, pour faire la prinse, le Prevost advancera le pied gauche à un mesme temps comme luy, & prendra ledit Prevost la garde de l’espée dudit Lieutenent par dessous son espée tournant ledit Prevost le dessus de la main gauche en bas comme est monstré cy dessus à la pourtraiture dudit Prevost cotté en chiffre 88. Voyla la fin de la contreprinse, pour ledict Prevost, contre ledict Lieutenent. | |
| The position and guard of the second grab for the Lieutenant against the Provost.
And to do this, the Lieutenant having made one of the drawings while remaining on the left foot in low guard, placing the sword point straight at the braies of his disciple the Provost who is in middle guard, the Lieutenant then keeps the cutting edge of the sword down and the left hand right of his chest as shown above at the present portraiture of the Lieutenant marked number 89 behind the collar. The end and definition of this low guard for the attacking Lieutenant. After having written the guard and position of the Lieutenant above, stay to read the guard and position for the defending Provost. The Provost, after having made his step, guard, and placement, remains on the left foot in middle guard, keeping the hilt even higher than the right shoulder and the fingertips that is holding the sword down, placing the sword point straight at the Lieutenant's left eye, and the keeping left hand upon the left thigh, and all the other who would want to be in this guard will maintain this gesture as the Provost has shown above at the portraiture marked number 90. The end of the guard and position for the Provost. Next the Lieutenant will show the Provost how he must make the second grab and the Lieutenant will begin to do this. |
Tenue, & garde de la seconde prinse, pour le Lieutenent, contre le Prevost.
Et pour ce faire, le Lieutenent ayant fait un desdits desgainements est demouré sur le pied gauche, en garde basse, assituant la pointe de son espée droit la braye du Prevost, son disciple, luy faisant faire & tenir en garde moyenne, & tient cedit Lieutenent le trenchant de l’espée en bas, & la main gauche droit sa poitrine comme est monstré cy dessus à la presente pourtraiture du Lieutenent, cotté en chiffre au derriere du col 89. La fin & definition de ceste garde basse pour le Lieutenent assaillant. Aprés avoir traité cy dessus de la garde & tenue dudit Lieutenent. Reste à traiter de la garde & tenue pour ledit Prevost deffendant. Le Prevost susdit, aprés avoir faire sa desmarche, garde & assituation, est demouré sur le pied gauche, en garde moyenne, tenant la garde aussi haute que l’espaule droite, & la pointe des doids de la main, que tient l’espée en bas, assituant la pointe de l’espée droit l’oeil gauche dudit Lieutenent, & la main gauche la tiendra sur sa cuisse gauche, &[52] tous les autres qui se voudront tenir sur ceste garde, se tiendront, & feront la geste[53] comme cedit Prevost comme est monstré cy dessus à a sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre 90. La fin de la garde & tenue pour ledit Prevost. Cy aprés le Lieutenent monstre au Prevost, comme il doit faire la seconde prinse, & pourtant ledit Lieutenent commence à ce faire. | |
| The second grab for the demonstrating Lieutenant against the defending Provost.
And to do this the Lieutenant will be in low guard on the left foot as stated, placing the sword point straight at the braies or the Provost's belt as stated and marked above at their portraitures number 89 and 90. And to execute this second grab for the Lieutenant who is the attacking demonstrator, being in the low guard as stated, he will advance the right foot, pretending to throw a high right-hand or thrust coming from him. The Provost seeing the strike charged at him, will block it, crossing and beating down the Lieutenant's sword and so the Lieutenant will advance the left foot and will throw a back-hand at his head. The Provost will want to beat down again at his sword, so the Lieutenant will advance the left foot at an instant and will take the sword hilt with his left hand and will present a thrust at his stomach as shown at the portraiture marked number 91 behind the collar. This is the end of the second grab and demonstration for the Lieutenant against the Provost. The following is what the Provost must do to make the second grab against the Lieutenant. And to do this, the Provost also will also be on the left foot in middle guard as shown above at the portraiture in number 90. The Lieutenant having thrown his choice of a high right-hand or high thrust, the Provost pulls the left foot back and crosses and beats down the Lieutenant's sword, strong on weak, and seeing that he was tricked by the Lieutenant's step and grab, this said Provost seeing the trickery, signals with his left hand that he wants to turn away and beat down the thrust at him, and can attack the Lieutenant as shown above at the next said portraiture and figure marked number 92 behind his head. The end of the second grab made by the Lieutenant at the Provost and how he dealt with it. |
Seconde prinse pour le Lieutenent demonstrateur, contre le Prevost deffendeur.
Et pour ce faire, le Lieutenent fera, & se mettra comme dit est, en garde basse, sur le pied gauche, assituant la pointe de l’espée comme dit est, droit la braye ou ceinture du Prevost comme est cotté en chiffre cy dessus à leurs pourtraitures 89 & 90. Et pour faire, & executer ceste seconde prinse pour cedit Lieutenent, qui est assaillant demonstrateur, estant sur la garde basse, que dit est, advancera le pied droit, faisant semblant de tirer un maindroit ou estoc d’hault, provenant d’iceluy. Le Prevost se voyant ainsi chargé d’un tel coup, se vouldra deffendre, croisant & rabatant l’espée dudit Lieutenent & alors cedit Lieutenent advancera le pied gauche, & luy tirera un arrieremain sur sa teste. Le Prevost le vouldra rabatre de rechef de son espée, alors cedit Lieutenent advancera le pied gauche à un instant, & luy prendra la garde de son espée avec sa main gauche & luy presentera un estoc à son estomac, comme est monstré à sa pourtraiture cotté en chiffre au derriere de son col 91. Voicy la fin de la seconde prinse, & demonstration d’icelle, pour ledit Lieutenent, contre le Prevost. Sensuit se que doit faire ledit Prevost, pour la seconde prinse contre ledit Lieutenent. Et pour ce faire, ledit Prevost estant aussi sur le pied gauche, en garde moyenne comme est cotté cy dessus à sa pourtraiture en chiffre 90. Le Lieutenent ayant tiré un maindroit ou un estoc d’hault, à son obtion, le Prevost a tiré le pied gauche arriere & a croisé & rabatu l’espée du Lieutenent, du fort le foible, & voyant qu’il a esté circonvenu par la desmarche & prinse susdite dudit Lieutenent, ledit prochain Prevost voyant ladite circonvention, fait signe de sa main gauche qu’il veult detourner & rabbatre l’estoc que luy veult, & peult tirer ledit Lieutenent, comme est monstré cy dessus à sadite pourtraiture & figure plus prochaine cotté en chiffre au derriere de sa teste 92. La fin de la seconde prinse qu’a fait ledit Lieutenent, au susdit Prevost, & ce qu’a peu faire icelluy. | |
| The second grab shown by the Author to the Lieutenant and executed by him against the Provost, so that he can do this to another.
And to do this, this said Lieutenant must have been on the right foot, advancing the left foot, and throwing a high right-hand or high thrust at the Provost, stealing away with a reversal, passing the sword below the Provost's sword hilt, and at the same time, advancing the left foot and crossing the Provost's sword, strong on weak, and having taken his sword hilt with the left hand, hold it and pull so that he will be forced to leave it, seeing the point in front of him, and so will anyone else when we do the same to them as shown above at the portraiture marked number 93 behind the collar. This is the end of the second grab shown and executed by the Lieutenant at the Provost. And the Provost seeing that he is surprised and pressed, obviates the accident and danger that could happen to him, is forced to let go of the sword and pull the right foot back, readying the right and left hand to beat down a thrust that the Lieutenant would throw at him. But he won't since he is only doing so to show him how he could do this to another, imitating well everything about the grabs that the Lieutenant has shown him, as shown above at the portraiture of this said Provost marked number 94 behind the collar. This is how the Provost must face and do the second grab against the Lieutenant. Next that will be shown by the portraiture and the writing is how after the Lieutenant having shown the Provost, the Provost will do the same to him, because anything that is necessary to know needs to be shown to truly understand it. |
Seconde prinse monstrée par l’Auteur au Lieutenent, & executée par iceluy, contre le Prevost, à celle fin qu’il en puisse faire autant à un autre.
Et pour ce faire, faut que cedit prochain Lieutenent, estant sur le pied droit avance le pied gauche, & tire un maindroit, ou estoc d’haut, sur le Prevost, le desrobant sur le renvers, passant l’espée par dessoubs la garde de l’espée du Prevost, & à un mesme instant, & temps advancera le pied gauche, & croisera l’espée du Prevost, du fort le foible, & luy prendra la garde de l’espée avec la main gauche, la tenant, faut tirer, & ainsi sera contraint de quitter icelle, voyant la pointe devant soy, & ainsi feront tous les autres quand on leur fera de mesme comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre au derriere du col 93. Voyla la fin de ceste seconde prinse monstrée & executée par le Lieutenent au Prevost. Et le Prevost se voyant ainsi surprins & pressé obviant à l’accident & danger qui peut advenir, est contraint de quitter l’espée & tirer le pied droit arriere, se preparant de la main droite & gauche, de rabatre l’estoc, que ledit Lieutenent luy veut tirer. Mais il n’a garde : car il ne le fait que pour luy monstrer comment il en pourra faire autant à un autre, imitant bien tout ce que luy a monstré ledit Lieutenent, ausdites prinses, comme est monstré cy dessus à la pourtraiture dudit prochain Prevost, cotté en chiffre au derriere du col 94.
Cy aprés sera monstré par pourtraicture & escrit, comment le Lieutenent ayant monstré audit Prevost, le Prevost luy en fait autant, car ce n’est rien de scavoir qui ne le scait monstré. Page | |
| The second grab as shown and executed by the Lieutenant and now executed by the Provost against his Lieutenant as shown here.
The following is a demonstration of how the Lieutenant would show the Provost to make the second grab of the sword alone, and to do that this said Lieutenant must be on the right foot, and having thrown a steep high right-hand or high thrust at the Provost's left shoulder, he advances the left foot and seeing the speed and being surprised by his ability and the instruction that was executed by the Provost, the Lieutenant is forced to pull back his said right foot and let his right hand go from his sword, and with the left hand to beat down the Provost's sword, the Lieutenant had to be careful if he wanted the Provost to not have made this grab, but in the end he chose to be ignorant so that the Provost could be able to make this said grab at him, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 95 of the Lieutenant behind the bonnet. This is how the Lieutenant loses his sword, seeing that the Provost having done this well as had been shown above. The following is a demonstration of what the Provost needs to do to remove the Lieutenant's sword, copying point by point what he demonstrated at the aforementioned grabs. And to do this, the Provost having made one of the four drawings, guards, placements and remaining on the left foot, and seeing that the Lieutenant has thrown a steep high right-hand or high thrust, the Provost having good understanding and memory of what the Lieutenant had done and shown, he does the same to the Lieutenant; the Provost unrestrained and without pause crosses his sword with the Lieutenant strong on weak, and presents a thrust at the throat or somewhere around there to force him to leave his sword as shown above at the portraiture and figure of the Provost marked number 96 behind the hat. This is the end of the second grab executed by the Provost against the Lieutenant his instructor, having shown him how it is done. |
Ceste seconde prinse, a esté monstrée & executée par ledit Lieutenent, & à present est executée par le Prevost contre son Lieutenent comme est monstré icy.
Sensuit icy la demonstration comment ce Lieutenent veut monstrer & de fait monstre, à faire au Prevost ceste seconde prinse sur l’espée seulle, & pour ce faire ledit prochain Lieutenent, estant sur le pied droit, a tiré un roide maindroit ou estoc d’hault sur l’espaulle gauche du Prevost, advançant le pied gauche, & voyant la promptitude & surpinse que par son moyen, & instruction qu’a executé le Prevost, le Lieutenent a esté contraint de retirer sondit pied droit, & quitter son espée qu’avoit à sa main droite, & de la main gauche rabattre l’espée du Prevost, ce Lieutenent se fust bien gardé s’il eut voulu que le Prevost ne luy eut fait ceste prinse, mais il a faint d’estre ignorant à celle fin que ledit Prevost luy fist cestedite prinse, comme est monstré cy dessus à la pourtraiture dudit Lieutenent cotté en chiffre au derriere de son bonnet 95. Voila comment ledit Lieutenent a quitté son espée, voyant que le Prevost a bien faict comme luy avoit monstré cy dessus. Sensuit la demonstration comment le Prevost doit faire, pour oster l’espée audit Lieutenent imitant de point en point ce que luy mesme luy a monstré & fait aux susdites prinses. Et pour ce faire, le Prevost ayant fait un desdits quatre desgainemens, gardes & assituations, & demourant sur le pied gauche, & voyant que ledit Lieutenent luy a tiré un roide maindroit ou estoc d’haut, ledit Prevost ayant bon entendement, & souvenance de ce que luy avoit fait et monstré ledit Lieutenent ayant le coeur de mesme, a ledit Prevost incontinent & sans intervalle croisé de son espée celle dudit Lieutenent du fort le foible, & luy a presenté un estoc à la gorge ou à peu prés qu’a esté la cause que luy à quitté son espée comme est monstré cy dessus à la pourtraiture & figure dudit Prevost, cotté en chiffre au derriere du chappeau 96. Voicy la fin de ceste seconde prinse executée par ledit Prevost contre ledit Lieutenent son instructeur, luy ayant monstré comme il debvoit faire. | |
| The following is the guard and position to make the third grab for the Lieutenant against the Provost.
And to do this the Lieutenant having made one of the four drawings that he wanted, remaining on the left foot in middle guard, keeping the fingertips on the sword hand down, the placement straight at the Provost's left nipple, keeping the left hand upon the left thigh, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 97 behind the hat. This is the end of the guard and position for the Lieutenant to prepare to make the third grab against the Provost. Next is to show the guard and position for the Provost. The guard of the Provost that he must be in is the same drawing as stated above, and remaining on the left foot initially, and seeing that the Lieutenant keeps himself in middle guard, the Provost is to keep himself in high guard, placing the sword point straight at the Lieutenant's left eye, keeping the nails on the sword hand down, and he must really keep the sword flat so that a dice can stay on it without falling on one side or the other, so that the two quillons of the sword will be as high as the other, and so the sword must be in high guard and middle, otherwise we hold it false, incongruent, and not so good; otherwise the quillons of the sword would be falsely invented as shown above at the portraiture marked number 98 behind the head. This is the end of the guard and position for the Provost to throw the first strike for the third grab. |
Sensuit la garde & tenue pour faire la troisiesme prinse pour le Lieutenent, contre le Prevost.
Et pour ce faire, cedit Lieutenent ayant fait un desdits quatre desgainements tel qu’il luy a pleu, est demouré sur le pied gauche, en garde moyenne, tenant la main que tient l’espée la pointe des doids en bas, l’assituant droit le tetin gauche du Prevost, tenant la main gauche sur la cuisse gauche, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre au derriere du chapeau 97. Voila la fin, de la garde & tenue pour ledit Lieutenent, pour se preparer à faire ceste troisiesme prinse contre le Prevost. Cy aprés est monstré la garde & tenue pour ledit Prevost. La garde dudit Prevost est qu’il faut qu’aye fait mesme desgainement, que dessus est dit, à un desdits desgainements, & soit demouré sur le pied gauche, pour la premiere fois, & voyant que ledit Lieutenent se tient en garde moyenne, cedit Prevost se tiendra en garde haute, assituant la pointe de l’espée droit l’oeil gauche dudit Lieutenent, tenant la main que tient l’espée les ongles en bas, & faut qu’il tienne bien l’espée plaine, qu’un dé puisse demourer dessus, sans qu’il puisse choir d’un costé ou d’autre, & ainsi les deux quillons de l’espée seront aussi hault l’un que l’autre, & ainsi faut que soit ladite espée en ladite garde haute, & moyenne, autrement on la tient faulse, & commet incongruité, & n’est si bien, estans autrement lesdits quillons de ladite espée seroient faulsement inventez comme est monstré cy dessus à sadite pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre au derriere de sa teste 98. Voila la fin de la garde & tenue pour ledit Prevost, pour tirer le premier coup pour la troisiesme prinse. | |
| The following is the first strike to make and to demonstrate the third grab for the Lieutenant and the Provost.
And to do this the Lieutenant must be on the left foot, having made everything that is required as stated, such as the aforementioned steps and one of the three drawings. And to execute this said strike, he will advance the right foot and will throw a high thrust at the left Provost's shoulder, keeping the sword hilt somewhat up, keeping the nails on the sword hand down, and the left hand upon the right nipple, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 99. And to execute this said third grab, the Lieutenant must advance the left foot and at the same time take the defending Provost's sword, extending strongly the left arm and passing it above the right, keeping the back of the hand up, giving a twist below the arms or elbow, and presenting a wholly unrestrained thrust at the Provost's face, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 99. This is the end of the third grab for the Lieutenant against the Provost. The following is the defense of the first strike to make and to execute the third grab for the Provost against the Lieutenant. And to do this, the Provost has also made one of the drawings, guards, and placements, with the aforementioned step, and remaining on the left foot, and the Provost seeing that the Lieutenant at the same time has thrown a high right-hand, the Provost being on the left foot pulls it back, and crosses the sword where the Lieutenant has thrown a high right-hand or high thrust, and defending himself this way the Provost, beating it down strong on weak, keeping the back of the sword hand down, placing the point straight at the Lieutenant's face, also keeping the left hand right and above the right thigh as shown above at the portraiture marked number 100. The end of the defense and protection of the strike, for preparing to make the third grab for the defending Provost. |
Sensuit le premier coup, pour faire & monstrer la troisiesme prinse, pour le Lieutenent, & Prevost.
Et pour ce faire, faut & est necessaire que cedit Lieutenent soit sur le pied gauche, ayant fait tout ce qui y est requis, c’est à dire, comme la desmarche susdite, & un desdits trois desgainements. Et pour executer cedit coup advancera le pied droit, & tirera un estoc d’haut, sur l’espaulle gauche du Prevost, tenant la garde de l’espée mediocremement haute, tenant les ongles de la main que tient l’espée en bas, & la main gauche sur le tetin droit, comme est monstré cy dessus à sadite pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre 99. Et pour executer cestedite troisiesme prinse, faut à un mesme instant que ledit Lieutenent sans advancer le pied gauche, prenne l’espée du Prevost deffendant, estendant fort le bras gauche, le passant par dessus le droit, tenant le dessus de la main en haut, donnant le tour par dessous le bras ou coude, & presentant tout incontinent un estoc au visage du Prevost, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture cotté en chiffre 99. Voila la fin de la troisiesme prinse pour ledit Lieutenent contre le Prevost. Sensuit la deffence de ce susdit premier coup, pour faire & executer ladite troisiesme prinse pour le Prevost contre le Lieutenent. Et pour ce faire, ledit Prevost aura ainsi fait un desdits desgainements, gardes, & assituations, avec la desmarche susdite, & demoure sur le pied gauche, & voyant ledit Prevost, que ledit Lieutenent à un mesme temps luy a tiré un maindroit d’haut, ledit Prevost estant sur le pied gauche, l’a tiré arriere, & a croisé l’espée, par laquelle ledit Lieutenent luy a tiré un maindroit, ou estoc d’haut, & la deffendu ledit Prevost par ce moyen, le rabatant du fort le foible, tenant la main que tient l’espée le dessus d’icelle main en bas, assituant la pointe droit le front dudit Lieutenent, tenant aussi sa main gauche droit & sus sa cuisse droite comme est monstré cy dessus à sadite pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre, 100. La fin de la deffence & tuition de cedit coup, pour ce preparer à faire cestedite troisiesme prinse, pour ledit Prevost deffendant. | |
| The third grab shown and executed by the Lieutenant against the Provost, so that the Provost can figure out how to do this in the future, and consequently afterwards maybe for others as well.
And at an instant without pause to gain time, having thrown the right-hand or thrust as stated and shown above at the other portraitures marked and numbered 99 at the aforementioned Lieutenant and 100 at the Provost, the Lieutenant must take the Provost's sword with his left hand, turning the back of the hand down and the palm up, holding it flat with the fingers spread, leaning it against the arms below the elbow, raising it up so to force him to let go of it and having lost momentum, presenting a thrust to the Provost's face, and in doing so will force him to leave the sword, as shown above at the portraiture of the Lieutenant marked number 101 behind the collar. The end of the third grab for the Lieutenant against the Provost. The following is how the Provost must face the Lieutenant who is showing him what he needs to do. And to do this, the Lieutenant having made as stated several targets above and discouraged, which is what the Provost needs to have done as he has one of the guards and drawings above, and is remaining on the left foot and the Provost seeing that the Lieutenant has advanced a step to throw a high right-hand or high thrust, which is the strike, having grabbed the Provost's sword and forced him to let go, seeing that the Lieutenant is presenting a thrust to his face, by which the Provost keeps his left hand right of his left nipple, reading to beat down and deflect the Lieutenant's sword that he could thrust at his face, as shown above at the portraiture of this said Provost marked number 102 behind the bonnet. This is the end of the third grab made and executed by the Lieutenant and what the Provost did, being thus surprised by his master the Lieutenant. |
Troisiesme prinse monstrée, & executée par ce Lieutenent, contre le Prevost, à celle fin que le Prevost luy en sache, & puisse faire autant à l’advenir, & par consequent puis aprés à quelques autres.
Et à un instant sans bien peu d’intervalle pour gaigner le temps, ayant tiré ledit maindroit ou estoc comme dit est, & monstré cy dessus aux autres pourtraitures, cotté en chiffre, non à ce Lieutenent mais au susdits 99, & au Prevost 100, faut que cedit Lieutenent prenne l’espée du Prevost avec sa main gauche, tournant le dessus d’icelle main en bas & le creux en haut, la tenant plate, les doids estandus, l’apuyant le long du bras, par dessous le coude, haulsant bien haut pour la luy faire quitter, & faire perdre du poin, comme il fait, presentant un estoc au visaige dudit Prevost, & en ce faisant sera contraint de quitter l’espée, comme est monstré cy dessus à la pourtraiture dudit Lieutenent cotté en chiffre au derriere du col 101. La fin de la ladite troisiesme prinse pour ledit Lieutenent, contre le Prevost. Sensuit ce que faut que le Prevost face, ledit Lieutenent luy monstrant comment il a fait. Et pour ce faire, ledit Lieutenent ayant fait comme dit est en plusieurs lieux, cy dessus & discouru, qui est que ledit Prevost doit avoir fait, comme il a une des gardes & desgainemens cy dessus, & est demouré sur le pied gauche & voyant ledit Prevost que ledit Lieutenent a advancé une desmarche pour luy tirer un maindroit ou estoc d’hault, & que tout à un coup, luy a prins l’espée dont cedit Prevost a esté contraint de la quitter voyant que ledit Lieutenent luy presentoit un estoc au visaige, parquoy ledit Prevost tient sa main gauche droit le tetin gauche, preste pour rabattre & detourner d’icelle l’espée dudit Lieutenent qui est un estoc ou doit estre au visaige, comme le tout est monstré cy dessus à la pourtraiture dudit prochain Prevost cotté en chiffre au derriere du bonnet 102. Voyla la fin de la troisiesme prinse faicte & executée par ledict Lieutenent & de ce qu’a peu faire ledict Prevost, estant ainsi surprins par ledit Lieutenent, son maistre. | |
| The third grab shown above by the Lieutenant to the Provost and is executed by the Provost here, as evidenced.
And to do this, the Lieutenant having thrown a high right-hand or high thrust at him and advancing the right foot, having made the strikes, step, guard, and placement that he wanted without restraint as shown above, the Provost has executed the grab so diligently that the Lieutenant is forced to let go of the sword. And seeing that the Provost wants to thrust his belly, the Lieutenant as stated is forced is to let go of his sword and with the left hand ready to beat down the Provost's sword as shown above at the portraiture marked number 103. This is the end of the counter-grab that the Provost has done at the Lieutenant, as evidenced. The following is what the Provost must do to execute the third grab against the Lieutenant. And to do this, the Provost will be on the step of the left foot when the Lieutenant throws his choice of a high right-hand or high thrust at the Provost's left shoulder or left nipple. But to stop whichever strike that he may throw, the Provost needs to pull his left foot back and cross the Lieutenant's sword, dropping the point over the Lieutenant's arms, and without pause take with the Lieutenant's sword with his left hand, with the back of the hand raised up so that it passes below the elbow to make him lose the sword, presenting a thrust at his stomach as shown above at the portraiture of the Provost marked number 105 behind the collar. This is the end of the third grab for this said defending Provost against the Lieutenant. Next we will be showing the position and guard for the Lieutenant and the Provost to make and execute the fourth and last grab of the sword alone. There are others, but those have been omitted.[54] |
Troisiesme prinse, monstrée cy dessus par ledit Lieutenent au Prevost, & est icy executée par le Prevost, comme appert.
Et pour ce faire, le Lieutenent luy ayant tiré un maindroit, ou estoc d’hault, advançant le pied droit, ayant fait comme est monstré cy dessus en plusieurs coups, la desmarche, garde & assituation, telle que luy a pleu, & incontinent, le Lieutenent ayant tiré ledit maindroit, ou estoc d’hault, le Prevost a tellement deligenté qu’il a executé cestedite prinse, dont ledit Lieutenent a esté contraint de quitter l’espée. Et voyant que le Prevost luy vouloit tirer un estoc au ventre, ledit Lieutenent comme dit est, luy a esté forcé de quiter son espée, & de la main gauche faisant semblant de rabatre l’espée du Prevost comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre 103. Voyla la fin de la contreprinse qu’a fait ledit Prevost audit Lieutenent comme il appert. Sensuit cy aprés comment doit faire le Prevost, pour executer ladite troisiesme prinse contre ledit Lieutenent. Et pour ce faire, ledit Prevost estant sur la desmarche du pied gauche, ledit Lieutenent tirera un maindroit, ou estoc d’hault, à sa liberté, sur l’espaulle gauche dudit Prevost, ou au tetin gauche. Mais pour annuller quelque coup qu’il puisse tirer, faut & est besoin que ledit Prevost tire le pied gauche arriere, & croise de son espée, celle dudit Lieutenent, du fort le foible & sus ce mesme pied droit à un mesme instant passera ledit Prevost, l’espée par dessous l’espée dudit Lieutenent, laissera tomber la pointe dessus le bras dudit Lieutenent, & sans intervalle prendra de sa main gauche l’espée dudit Lieutenent, du plat de sa main haussera en haut l’ayant passée par dessous le coude pour la luy faire perdre de la main, luy presentant un estoc à son ventre comme est monstrée cy dessus à la pourtraiture dudit Prevost, cotté en chiffre au derriere du col 105. Voyla la fin de la troisiesme prinse pour ledit prochain Prevost deffendeur contre ledit Lieutenent. Cy aprés sera monstrée la tenue, & garde, pour le Lieutenent & Prevost, pour faire & executer la quatriesme & derniere prinse de ceste espée seule. Il en y a d’autres mais à l’autre impression ne sera rien obmis ne laissé.[55] | |
| The position and the guard of the fourth and last grab for the attacking Lieutenant against the defending Provost.
And in order to effectively perform the aforementioned guard and fourth grab for the Lieutenant, he must have made the step, drawing, and guard above at one of the drawings. And the Lieutenant needs to be on the left foot in high guard, keeping the back of the sword hand up and nails down, placing the sword point straight at the Provost's mouth, keeping the left hand upon the left lap, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 105. The end of the guard to make a strike, to execute the fourth grab for the Lieutenant. Next he will be showing the guard and position to defend a high right-hand or high thrust thrown by the Lieutenant against the Provost to make the fourth grab. To do this, the Provost must also have made one of the three drawings and be on the left foot while keeping himself in middle guard, which is best, keeping the back of the sword hand up, placing the point straight at the Lieutenant's left nipple, and the left hand right upon the lap, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 106. This is the end of the description and position for the Provost. |
Tenue & garde de la quatriesme, & derniere prinse, pour le Lieutenent assaillant, contre le Prevost deffendant.
Et pour bien traiter de ceste susdite garde & quatriesme prinse pour le Lieutenent, faut qu’il aye fait ainsi la desmarche, desgainement, & garde, que dessus, à un desdits desgainements. Et à cestuy cy est besoing que ledit Lieutenent soit sur le pied gauche, en garde haute, tenant le dessus de la main que tient l’espée en haut, & les ongles en bas, assituant la pointe de l’espée droit la bouche du Prevost, tenant la main gauche sur son giron gauche, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre 105. La fin de la garde pour faire un coup, pour executer ceste quatriesme prinse pour le Lieutenent. Il sera cy aprés monstré la garde & tenue, pour deffendre un coup, qui sera un maindroit, ou estoc d’hault, tiré par ledit Lieutenent, contre le Prevost, pour faire la quatriesme prinse. Pour ce faire, faut qu’il aye aussi fait un desdits trois desgainements, & estant sur le pied gauche, se tiendra ledit Prevost en garde moyenne, qui est la plus superlative, tenant le dessus de la main que tient l’espée en haut, assituant la pointe d’icelle droit le tetin gauche dudit Lieutenent, & la main gauche droit son giron, comme est monstré cy dessus en sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre 106. Voila la fin de la description, & tenue pour ledit Prevost. | |
| The high right-hand or high thrust thrown by the Lieutenant and defended by the Provost that will have to be repeated at the Lieutenant to execute the fourth grab against the Provost.
And to do this, this said Lieutenant must be on the left foot in high guard as shown above at the other portraiture marked number 105, seen in his place. And to execute this strike which at the Lieutenant's choice is either a high right-hand or high thrust, he will advance the right foot and throw a steep thrust at the Provost's face, keeping the sword hilt even higher than the right shoulder and the back of the sword hand down, and the left hand in front of his chin as shown above at the portraiture marked number 107. The end of the strike for the attacking Lieutenant. The way to defend the Provost at the aforementioned high right-hand or high thrust thrown by the Lieutenant so that afterwards he then execute the fourth grab. And to do this, this said Provost must be on the left foot in middle guard as shown above at the portraiture marked number 106. And for the defense of this high right-hand or high thrust thrown by the Lieutenant, this said Provost needs to pull the left foot back and cross his sword with that of the Lieutenant, be it a high right-hand or high thrust, strong on weak, just like we did above at any one of the other said counters and continuations; and present a thrust to the Lieutenant's face, keeping the back of the sword hand down and the nails up, and the left hand right of his nipple, placing the sword point straight at the Lieutenant's mouth as shown and done above at the portraiture of the Provost marked number 108 behind the collar. This is how the Provost effectively guards the aforementioned strike thrown by the Lieutenant. Next we will show the fourth and last grab which is very subtle to make his adversaries let go of his weapons, which will be in the middle of a high right-hand or high thrust that will be thrown and will be served to tell us whether they are ignorant or knowledgeable. Because if he is ignorant and clumsy, it will easily be done at him, and if he is skillful, he must feint as will be seen later in time at the declaration of the Lieutenant, who will do this to show the Provost. |
Maindroit ou estoc d’haut, tiré par le Lieutenent, & deffendu par le Prevost, que faudra reiterer au Lieutenent, pour executer la quatriesme prinse contre le Prevost.
Et pour ce faire, faut que cedit prochain Lieutenent estant sur le pied gauche, en garde haute comme est monstré cy dessus à son autre pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre 105, voy en son lieu. Et pour executer ce coup, qui est un maindroit, ou estoc d’hault, au chois dudit Lieutenent, advancera le pied droit, & tirera un roide estoc au visage du Prevost, tenant la garde de l’espée aussi haute que l’espaulle droite, & le dessus de la main que tient l’espée en bas, & la main gauche au devant son menton, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre 107. La fin de cedit coup pour ledit Lieutenent assaillant. Moyen de soy deffendre, au Prevost de ce susdit maindroit, ou estoc d’hault, tiré par ledit Lieutenent, pour puis aprés executer ladite quatriesme prinse. Et pour ce faire, faut que ledit prochain Prevost estant sur le pied gauche, en garde moyenne, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre 106. Et pour la deffence de cedit maindroit, ou estoc d’hault, tiré par ledit Lieutenent, est besoin, & faut que cedit prochain Prevost tire le pied gauche arriere, & croise de son espée celle dudit Lieutenent, soit maindroit, ou estoc d’haut, du fort le foible, tout ainsi comme on a fait cy dessus à une desdites opposites & suittes, & presenter un estoc au visage dudit Lieutenent, tenant le dessus de la main que tient l’espée en bas, & les ongles en hault, & la main gauche droit son tetin, assituant la pointe de l’espée droit la bouche dudit Lieutenent comme est monstré & fait cy dessus à la pourtraiture dudit Prevost, cotté en chiffre au derriere du col 108. Voyla comment ledit Prevost s’est bien gardé de ce susdit coup, tiré par ledit Lieutenent. Cy aprés sera monstré ladite quatriesme, & derniere prinse, qui est fort subtile, pour faire quitter les armes à son adversaire, qui sera moyennant un maindroit, ou estoc d’hault, qu’on tirera, qui servira d’espion pour apporter ignorance ou scavoir. Car s’il est ignorant, & mal adroit, facilement se pourra faire, & s’il est adroit faut faire une fainte comme se verra cy aprés en son lieu à la declaration du Lieutenent, qui la fera pour la monstrer au[56] Prevost. | |
| The fourth grab shown by the attacking Lieutenant to the defending Provost, as clearly shown and written below.
And to do this, the Lieutenant being on the left foot as shown above at the portraiture of the aforementioned position and the guard marked number 105, advanced the right foot and throws a high right-hand or high thrust on the Provost's left to test, as stated and shown above at the portraiture of the Lieutenant marked number 107, and the Lieutenant seeing that the Provost has defended the high right-hand or high thrust, this said Lieutenant in order to make the grab steals away his sword with a right-hand below the Provost's sword, and let his sword drop above the Provost's arms, turning the nails of the sword hand up, and with the left hand near the tip take the Provost's sword. With this the Lieutenant tells the Provost, "Listen, if I wanted to lower and press my left hand down you would be forced to let go of your sword, as you can do to me and in fact will do," as will be seen after provided that you do as shown above at this said portraiture and figure of the Lieutenant marked number 109. This is the end of the fourth and last grab for the demonstrating Lieutenant against the defending Provost. The following is what the Provost can do when he does not know how to counter-grab. For every grab there is a counter-grab which he did not do above but later will with the knowledge given to him by the Lieutenant. And to do this, this said Provost being on the left foot in middle guard as shown above at the portraiture marked number 106 at the Provost to learn to make the aforementioned grab, having pulled the left foot back and remains on the right foot, and having crossed the high right-hand or high thrust that the Lieutenant has thrown, but the Lieutenant having circumvented him by stealing away with a right-hand to get the grab through and the Lieutenant having rendered the point to let go of the Provost's sword, and had he wanted to, he would have taken the sword but decided to leave it alone. Nevertheless the Provost having been tricked as shown above the portraiture marked number 110. The end of what the Provost can do against his instructor the Lieutenant. |
Quatriesme prinse monstrée par le Lieutenent, assaillant, au Prevost deffendant, comme voicy clairement monstré, & cy dessous par escrit declaré.
Et pour ce faire, le Lieutenent estant sur le pied gauche, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, à la tenue & garde susdite cotté en chiffre 105, a advancé le pied droit, & a tiré un maindroit ou estoc d’haut pour espion, sur le costé gauche du Prevost, comme est dit & monstré cy dessus à la pourtraiture du Lieutenent cotté en chiffre 107, & voyant ce Lieutenent que le Prevost s’est deffendu de ce maindroit ou estoc d’hault, a cedit prochain Lieutenent pour faire ceste prinse desrobé son espée, d’un maindroit par dessous l’espée du Prevost, & luy a laissé tomber ce Lieutenent son espée dessus le bras du Prevost, tournant les ongles de la main que tient l’espée en haut, & avec la main gauche prend l’espée du Prevost, auprés de la pointe. Ce fait, ce Lieutenent parle au Prevost & luy dit, escoute si je voulois baisser & peser ma main gauche en bas tu serois contraint de quitter ton espée, comme tu me pourras faire, & de fait le feras, comme se verra cy aprés moyennant que tu face comme est monstré cy dessus à ladite prochaine pourtraiture & figure dudit Lieutenent, cotté en chiffre 109. Voila la fin de ladit quatriesme & derniere prinse pour ledit Lieutenent demonstrateur contre le Prevost deffendeur. Sensuit ce qu’a peu faire ledit Prevost, ne scachant aucune contreprinse. Car à toute prinse il y a une contreprinse, ce qu’il n’a fait cy dessus, mais cy aprés il le fera moyennant l’intelligence que luy a donné ledit Lieutenent. Et pour ce faire, ledit prochain Prevost estant sur le pied gauche, en garde moyenne, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture cotté en chiffre 106, a ledit Prevost pour apprendre à faire ceste susdite prinse, tiré le pied gauche arriere & demouré sur le pied droit, & a croisé le maindroit ou estoc d’hault, que luy a tiré ledit Lieutenent, mais ledit Lieutenent l’ayant circonvenu par un maindroit desrobé, pour parvenir à sadite prinse, a ledit Lieutenent rendu ledit Prevost à l’extremité de quitter son espée, & s’il eust voulu, il la luy eust fait perdre de la main mais la luy a encores laissée. Toutefois ledit Prevost a fait comme il a peu estant circonvenu comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture cotté en chiffre 110. La fin de ce qu’a peu faire ledit Prevost contre ledit Lieutenent son instructeur. | |
| The fourth and last grab executed by the defending Provost against his demonstrator the Lieutenant, as it appears at the portraitures showing him what to do above.
And to do this, the Lieutenant must be on the left foot as stated above, and while advancing the right foot he will throw a high right-hand or high thrust of his choice as shown above at the other portraitures of the Lieutenant marked number 107 and the Lieutenant next having thrown one of the strikes, the Provost does the same as above. The Lieutenant having done as appears at the portraiture marked number 109 but with this grab the Lieutenant is forced to let go of his sword and must use his left hand to beat down the Provost's sword, who would throw a thrust as appears at the portraiture above marked number 111 behind the collar. The end of what the Lieutenant does to having shown the Provost how he must make this grab. The following is the execution of the fourth and last grab of the sword alone for the Provost against the Lieutenant his said demonstrator. And to do this, this said Provost must be on the left foot and when he sees that the Lieutenant or another attacker will throw a high right-hand or high thrust, having advanced the right foot, the Provost will pull his left foot back, and at the same time steal away his sword below the Lieutenant's sword hilt, and without a moment to waste, let the sword point fall on the Lieutenant, and the Provost will forcefully take the Lieutenant's sword point with the left hand and pass and lower it, so it will force the Lieutenant to let go of his sword as shown above at the portraiture of the Provost marked number 112. This is the end of the fourth and last grab of the sword alone, both by the attacking Lieutenant as well as for the defending Provost. Next we will be showing some particularly good and subtle strikes extracted from the aforementioned strikes of the sword alone which I call the subtleties that can and will be done both for attacking as well as for defending. |
Quatriesme & derniere prinse, executée par le Prevost deffendeur contre le Lieutenent son demonstrateur, comme icy appert par ces pourtraitures, luy monstrant ce que luy a fait cy dessus.
Et pour ce faire, faut que ce Lieutenent soit sur le pied gauche, comme dessus est dit, & advançant le pied droit tirera un maindroit ou estoc d’hault, à son chois, comme est monstré cy dessus à d’autres pourtraitures du mesme Lieutenent cotté en chiffre 107, & ayant ce Lieutenent prochain tiré un desdits coups, ce Prevost luy a fait de mesme que dessus. Ledit Lieutenent luy a fait comme appert à sa pourtraiture cotté en chiffre 109, mais à ceste prinse icy, ledit Lieutenent a esté contraint de quitter son espée & de sa main gauche veut rabatre l’espée du Prevost, lequel luy veut tirer un estoc, comme appert à sa pourtraiture cy dessus cotté en chiffre au derriere du col 111. La fin de ce qu’a fait cedit Lieutenent ayant monstré au Prevost comment faut qu’il face ceste prinse. Sensuit l’execution de ceste quatriesme & derniere prinse de cestedicte espée seulle pour le Prevost contre ledit Lieutenent sondit demonstrateur. Et pour ce faire, faut que ledit prochain Prevost, soit sur le pied gauche, & quant il verra que ledit Lieutenent ou autre assaillant, tirera un maindroit ou estoc d’haut, advançant le pied droit, ledit Prevost tirera son pied gauche arriere, & à un mesme temps, desrobera son espée, par dessous la garde de l’espée dudit Lieutenent, & avec un bien peu d’intervalle, laissera tomber la pointe de l’espée sur celle dudit Lieutenent, & incontinent prendra ledit Prevost la pointe de l’espée dudit Lieutenent avec sa main gauche, & la passera & baissera en bas, & ainsi sera contraint ledit Lieutenent de quitter sadite espée, comme est monstré cy dessus à la pourtraiture dudit Prevost cotté en chiffre 112. Voici la fin de cestedit quatriesme & derniere prinse de ladite espée seulle, tant par ledit Lieutenent assaillant que pour ledit Prevost deffendant. Cy aprés seront monstrez quelques bon & subtils coups particuliers extraits des susdits coups de ladite espée seule que j’appelle les subtilitez qui se peuvent faire & font, tant en assaillant qu’en deffendant. | |
| The guard and position to make and execute the subtleties of the sword alone both for the attacking Lieutenant as well as for the defending Provost.
And to do this, the demonstrating Lieutenant having made one of the drawings, step, guard, and placement; must be on the left foot in high guard, keeping the sword even higher than the right shoulder, the the back of the hand up, and the nails down, placing the sword point at the Provost's face, and the left hand below his sword arm, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 113 behind his bonnet. The end of the position and guard for the attacking Lieutenant. The following is the definition, guard, and position for the Provost. And to do this, the Provost must have made one of the drawings as he pleases, and having kept himself on the left foot in low guard, keeping the sword hilt upon the left knee, placing the point straight at the belt or the Lieutenant's braies, the cutting edge down, and the left hand right of the left nipple, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 114. The end of the guard for the Provost. |
Garde & tenue, pour faire & executer les subtilitez de ceste espée seule, tant pour le Lieutenent assaillant, que pour le Prevost deffendant.
Et pour ce faire, faut que ce Lieutenent demonstrateur, ayant fait un desdits desgainements, desmarche, garde, assituation, il sera sur le pied gauche, en garde haute, tenant la main de l’espée aussi haute que l’espaulle droitte, & le dessus d’icelle en haut, & les ongles en bas, assituant la pointe de l’espée au visage du Prevost, & la main gauche dessous son bras de l’espée, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre au derriere de son bonnet 113. La fin de la tenue & garde pour ledit Lieutenent assaillant. Sensuit la definition, garde & tenue pour ledit Prevost. Et pour ce faire, faut que ledit Prevost face un desdits desgainements, tels qu’il luy plaira, & se tienne sur le pied gauche, en garde basse, tenant la garde de son espée sur le genoil gauche, assituant la pointe d’icelle droit la ceinture, ou braiette dudit Lieutenent, le tranchant en bas, & la main gauche droit le tetin gauche, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre 114. La fin de ladite garde pour ledit Prevost. | |
| The first strike which is a low right-hand thrown by the Lieutenant against the Provost, which serves as intelligence gathering to report whether he is ignorant or knowledgeable.
And to do this, the Lieutenant being on the left foot in high guard as shown above at the guard and position of the subtlety marked number 113. And to execute the subtlety well for the demonstrating Lieutenant, the Lieutenant will advance the right foot and will throw a low right-hand at the leg, which serves as intelligence gathering to report whether the one against is ignorant or knowledgeable; because if he is ignorant he will cross the sword against sword, and if he is knowledgeable he will throw a right-hand at the sword arm. But it is good to see this Provost is ignorant so he crosses with the Lieutenant's sword; show the Provost the mistake that he made by beating down his sword and he throw a right-hand at the arms as will be done later. But at this strike he crosses the sword, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 115. This is how the Lieutenant throws a low right-hand at the knee to determind the ignorant. The following is the defense of the strike for the Provost. And to do this, the Provost must have made the same guard and placement above as shown at the portraiture of the Provost marked number 114. And to defend the strike of the right-hand at the knee thrown by the Lieutenant, the Provost being ignorant like many demonstrators, pulls the left foot back and crosses his sword with the Lieutenant's sword, which isn't necessarily ignorance, but he totally is since he left the proper and took the unsuitable, which as stated and shown above at the portraiture marked number 116. This is how the Provost defends himself from the first strike thrown by the Lieutenant. He defends himself with what he knows due to human nature as shown many times because he would do the same even without having learned the art. |
Premier coup, qui est un maindroit de bas, tiré par le Lieutenent, qui sert d’espion, pour raporter ignorance ou scavoir, contre le Prevost.
Et pour ce faire, ledit Lieutenent estant sur le pied gauche en garde haute comme est monstré cy dessus à sa dite garde, & tenue desdites subtilitez cotté en chiffre 113. Et pour faire, & bien executer cestedite subtilité pour le Lieutenent demonstrateur, advancera ledit Lieutenent le pied droit, & tirera un maindroit de bas au jarret, qui servira d’espion, pour raporter ignorance ou scavoir de celuy contre qui tel coup sera tiré, car s’il est ignorant, croisera espée contre espée & s’il est scavant il tirera un maindroit sur le bras de l’espée. Mais il est bon à veoir que ce Prevost est ignorant, attendu qu’il croise de son espée celle dudit Lieutenent : monstrera au Prevost la faute qu’il a fait, attendu qu’au lieu qu’il a rabbatu de l’espée, devoit tirer un maindroit sur le bras, comme il fera cy après. Mais à ce coup il croise l’espée, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre 115. Voicy comme ledit Lieutenent a tiré un maindroit de bas, au jarret, pour voir l’ignorance. Sensuit la deffence de ce coup pour ledit Prevost Et pour ce faire, faut que ledit Prevost aye fait mesme desmarche garde, & assituation, que dessus est monstrée, à la pourtraiture dudit Prevost, cotté en chiffre 114. Et pour se deffendre de ce coup, qui est un maindroit de bas au jarret, à luy tiré par ledit Lieutenent, Ledit Prevost estant ignorant comme beaucoup de demonstrateurs, a tiré le pied gauche arriere, & a croisé de son espée l’espée dudit Lieutenent, qui n’est à presumer ignorance, mais l’estre tout à fait, attendu qu’il a laissé le propre, & prend l’impropre, qui est dit & monstré cy dessus à sadite pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre au derriere dudit Prevost 116. Voyla comment ledit Prevost se deffent de ce premier coup, tiré par ledit Lieutenent. Mais il s’en deffend comme il l’entend, & comme le monstrent plusieurs, suivant la nature humaine car elle en fait autant sans avoir jamais aprins aucun art. | |
| The guard and position for the Lieutenant and the Provost for the Lieutenant to show to the Provost what he must do henceforth and not like what he did at the previous strike.
And to do this, the Lieutenant must also have made one of the three drawings of his choice, and the Lieutenant having remained on the left foot in middle guard, placing the sword point straight at the left nipple, keeping the back of the sword hand up, and the left hand below the sword arm, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 117. The end of the guard of the Lieutenant to execute the subtlety, following the ignorance that the Lieutenant saw of the Provost marked number 115 and 116. The following script is for knowing the position and guard of the Provost for the Lieutenant to execute the subtlety, and showing it to the Provost, as will be seen later at the next strike. And to do this, this said Provost must have also made the step as was done above this said Lieutenant, his demonstrator, and one of the drawings, and having remained on the left foot in high guard, keeping even higher the sword hilt and the back of the sword hand up, placing the point straight at the face, keeping the left hand right of his nipple, as shown above at the portraiture of the Provost above marked number 118. This is the end of the guard and position for the Provost. |
Garde & tenue pour le Lieutenent & Prevost, pour monstrer par ce Lieutenent au Prevost, comment il faut qu’il face desormais, & non comme il a fait au precedent coup.
Et pour ce faire, faut aussi que cedit Lieutenent aye fait un desdits trois desgainements, lequel luy aura pleu, & ce fait ledit Lieutenent est demouré sur le pied gauche, en garde moyenne, assituant la pointe de son espée droit le tetin gauche, tenant le dessus de la main que tient icelle en haut, & la main gauche dessous le bras de l’espée, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre 117. La fin de la garde dudit Lieutenent, pour faire & executer ladite subtilité, suivant l’ignorance qu’a veu ledit Lieutenent audit Prevost, cotté en chiffre 115, & 116. Sensuit l’escript pour scavoir faire la tenue & garde, dudit Prevost pour executer ladite subtilité, par ledit Lieutenent, la monstrant au Prevost, comme se verra cy aprés au prochain coup. Et pour ce faire, faut que ledit prochain Prevost aye fait aussi la desmarche qu’a fait cy dessus ledit prochain Lieutenent, son demonstrateur, & un desdits desgainemens, & soit demouré sur le pied gauche, en garde haute, tenant aussi la garde de l’espée, & le dessus de la main que tient icelle, en haut, assituant la pointe droit la face, tenant sa main gauche, droit son tetin, comme est monstré cy dessus à la pourtraiture dudit Prevost, cotté en chiffre 118. Voyla la fin, garde, & tenue, pour ledit Prevost. | |
| The first strike of the subtlety, which is the first strike of the sword alone, shown here by the Lieutenant and executed by the Provost.
The Lieutenant, to effectively make and show the Provost the right-hand, the first strike of the order of the sword alone and of the subtlety, must be on the left foot and advance the right foot while throwing a low right-hand at the Provost's knee, keeping his left hand right of his face as shown above at the portraiture marked 119. The end of the first strike which is a low right-hand thrown by this said Lieutenant and defended by the Provost and executed wherever it is necessary.
And to do this, the Provost being in high guard as shown above at the other said portraiture marked number 118 that the Provost has now seen, the Lieutenant having thrown a low right-hand at his knee, the Provost recognizing this strike that he had done wrong to beat down the sword, and that only the step enough to guarantee himself from the right-hand, and so at this strike the Provost pulls the left foot back, and at the same time while defending, throws the right-hand coming from the high guard at the Lieutenant's sword arm and presents again a thrust at the Lieutenant's braies, keeping the sword hilt high enough and the nails up, and the left hand right of the left nipple, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 120. The end of this subtlety for the Provost and everything that he must do, following the instructions of the author and of his said Lieutenant. |
Premier coup de ladit subtilité, qui est sur le premier coup de ladite espée seulle, icy monstrée par ce Lieutenent & executée par ce Prevost.
Ce present Lieutenent, pour bien faire & monstrer au Prevost cedit maindroit, premier coup de l’ordre de ladite espée seulle, & de cestedite subtilité, faut, estant sur le pied gauche, qu’il advance le pied droit, & tire un maindroit de bas au jarret du Prevost, tenant sa main gauche droit le visaige, comme est monstré[57] cy dessus, à sa pourtraiture cotté en chiffre 119. La fin de ce premier coup qui est un maindroict de bas, tiré par cedit prochain Lieutenent & deffendu par le Prevost, & executé par iceluy, là ou il faut. Sensuit tout ce que faut que face cedit Prevost pour soy deffendre & offencer, à un mesme temps, de cedit maindroit de bas au jarret, tiré par ledit Lieutenent contre cedit Prevost. Et pour ce faire, le Prevost estant en garde haute, comme est monstré cy dessus à sadite autre pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre, 118, a maintenant cedit Prevost ayant veu, que ledit Lieutenent luy avoit tiré un maindroit, de bas au jarret gauche, ledit Prevost à ce coup congnoissant qu’il avoit mal fait de rabattre de l’espée, & que la seulle desmarche suffisoit à le garantir de ce maindroit, & à ce coup cedit Prevost en tirant le pied gauche arriere, à un mesme temps deffendu, cedit maindroit venant de sadite garde haute, sur le bras de l’espée du Lieutenent, & presente encores un estoc, à la braye dudit Lieutenent, tenant la garde de l’espée assez haute & les ongles d’icelle main en haut & sa main gauche droit le tetin gauche, comme est monstré cy dessus à sadite pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre 120. La fin de ceste subtilité pour ledit Prevost & de tout ce qu’a fallu qu’il aye fait, suivant l’instruction dudit auteur & de sondit Lieutenent. | |
| The low guard and position to execute the second strike of the subtlety, which is a low reversal, being on the right foot, will serve to gather information to report whether ignorant or knowledgeable, both for the attacking Lieutenant as well as for the defending Provost.
To skillfully and effectively execute the second subtlety for the Lieutenant, he must have made one of the drawings and to throw the second strike the Lieutenant must be on the right foot in low guard, the cutting edge of the sword down, the sword hilt upon the right lap, placing the sword point straight at the Provost's right thigh, keeping the left hand right of his braies as shown above at the portraiture marked number 121. The end of the declaration of the guard for the Lieutenant. The following is the declaration of the guard and position for the Provost. And to do this, the Provost must have made the same step, drawing, and nearly the same guard, that he keeps himself, and be on the right foot, keeping the sword hilt upon the right thigh, placing the sword point straight at or around the Lieutenant's braies, keeping the cutting edge of the sword down, and his left hand kept near close to his belt, the fingertips near the braies as shown above at the portraiture marked number 122. The end and position for the Provost. |
Garde & tenue basse, pour executer & faire le second coup desdites subtilitez, qui est un renvers de bas, estant sur le pied droit, lequel servira d’espion, pour rapporter ignorance ou scavoir, tant pour le Lieutenent assaillant, que pour le Prevost deffendant.
Pour bien & adextrement executer cestedite seconde subtilité pour cedit Lieutenent, faut qu’il aye fait un desdits desgainemens, & pour tirer ce second coup faut que ledit Lieutenent soit sur le pied droit, en garde basse, le trenchant de l’espée en bas, et la garde de l’espée sur son giron droit, assituant la pointe de l’espée droit la cuisse droite du Prevost, tenant sa main gauche droit sa brayette, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre 121. La fin de la declaration de la garde pour ledit Lieutenent. Sensuit la garde & tenue pour ledit Prevost, & declaration d’icelle. Et pour ce faire, faut que ledit Prevost aye fait mesme desmarche & desgainement, & presque garde, & qu’il se tienne, & soit sur le pied droit, tenant la garde de l’espée sur sa cuisse droite, assituant la pointe de l’espée droit la braye dudit Lieutenent, ou à peu prés, tenant le trenchant de l’espée en bas, & sa main gauche la tient auprés de sa ceinture, la pointe des doids auprés de la braye comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre, 122. La fin & tenue pour ledit Prevost. | |
| The second strike which is a low reversal will serve to gather information to better execute the second subtlety for the Lieutenant against the Provost.
And to do this, the Lieutenant must be on the right foot in low guard as shown above at the other portraitures marked at the Lieutenant in number 121. And being on this step and guard, he pretends to throw a thrust at the Provost's face and at the same instant advances the left foot and throws a back-hand at the Provost's right knee, keeping the sword hilt a bit high and keeping the left hand below the sword arm as shown above at the portraiture marked number 123 behind his bonnet. The end of the strike which is a low reversal, which will serve to gather information for the Lieutenant to report back ignorance and not knowledge, as he has done. The following is what the Provost does to defend against the low reversal throw by the Lieutenant. And to do this, the Provost being also on the right foot in low guard as shown at the portraiture marked number 122, and at this strike of the Lieutenant having advanced the left foot to throw a low back-hand at the Provost's knee, which seeing him charge it, the Provost pulls the right foot back and crosses his sword with that of the Lieutenant, which is ignorant, as done daily by all of the ignorant demonstrators; but the skilled and the learned no longer does this, because he must gain time in everything, and especially in the art of fencing, as will be seen later; and the Provost keeps his left hand right of his chest as shown at the portraiture marked number 124. The end of the false strike that this said Provost has done because he has took the unsuitable and improper strike. |
Le second coup, qui est un renvers de bas, qui servira d’espion pour mieux faire & executer la seconde subtilité, pour le Lieutenent, contre le Prevost.
Et pour ce faire, faut que ce Lieutenent soit sur le pied droit, en garde basse comme est cotté cy dessus aux autres pourtraitures, & cotté à celle dudit Lieutenent en chiffre 121. Et estant sur icelle desmarche, & garde, face semblant de tirer un estoc au visage du Prevost, & à un mesme instant advancera le pied gauche, & tirer un arrieremain au jarret droit du Prevost, tenant la garde de l’espée un peu haute, & tenir la main gauche au desous le bras de l’espée comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre au derriere de son bonnet 123. La fin de ce coup, qui est un renvers de bas, qui sert d’espion pour ledit Lieutenent, pour rapporter ignorance, comme il fait, & non scavoir. Sensuit ce que fait ledit Prevost, pour la deffence de cedit renvers de bas, tiré par ledit Lieutenent. Et pour ce faire, le Prevost estant aussi sur le pied droit en garde basse, comme est monstré à sadite pourtraiture cotté en chiffre 122, & à ce coup ledit Lieutenent ayant avancé le pied gauche, pour tirer un arrieremain de bas au jarret du Prevost, lequel se voyant chargé d’iceluy, a tiré ledit Prevost, le pied droit arriere, & a croisé de son espée celle dudit Lieutenent, comme ignorant, & comme font encores pour le jourd’huy aucuns ignorans demonstrateurs, mais les adroits & doctes ne le font plus au moins doibvent faire, car il faut gaigner le temps en toutes choses, & principallement en cest art des armes, comme sera monstré cy aprés & tient cedit Prevost sa main gauche droit sa poictrine, comme est monstré à sadite pourtraiture cotté en chiffre 124. La fin du coup faux, qu’a fait ledit prochain Prevost car il a laissé le propre & prins l’impropre. | |
| The second strike which is a reversal at the Provost's arms thrown and executed by this Lieutenant against the Provost, showing that he could do so, and without beating down on the sword, as he has does at the coming portraitures.
And to do this, the Lieutenant being on the right foot in low guard as stated and shown above marked number 121. And the Lieutenant being on the right foot having pretended to throw a thrust at the Provost's face, advances the left foot to pretend to throw a back-hand at the knee, the Provost would want to beat down sword against sword as he normally does. The Lieutenant seeing this, winds back his sword and throws a back-hand at the sword arm's elbow, keeping the left hand below the sword arm, as shown above at the portraiture marked 125 behind his bonnet. The end of the reversal executed and shown by the Lieutenant to the Provost. The following is what the Provost does. The Provost being on the right foot in low guard as shown at the portraiture marked 122, the Provost pulls his right foot back, throws a reversal at the Lieutenant's arms, and should not have crossed his sword with that of the Lieutenant, as he had done returning to beat down the aforementioned strike which is how the Lieutenant throws a reversal at his sword elbow, and keeping the Provost's left hand right of his left nipple, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 126 behind his collar. The following is another very effective and subtle strike, leaving the reversal at the arms, and coming with a thrust to the chest, crossing the Provost's sword with the strong on weak, as shown here by the author at the Provost and consequently the Provost will have learned from the Lieutenant. |
Second coup qui est un renvers sur le bras du Prevost tiré & executé par ce prochain Lieutenent contre le Prevost, monstrant que luy en pouvoit faire autant, & non rabattre de l’espée, comme il a fait cy dessus aux prochaines pourtaitures.
Et pour ce faire, cedit Lieutenent estant sur le pied droit en garde basse, comme est dit & monstré cy dessus cotté en chiffre 121. Et estant ledit Lieutenent sur ledit pied droit faira semblant de tirer un estoc au visaige dudit Prevost & advançant le pied gauche faira semblant de tirer un arieremain au jarret, le Prevost le vouldra rabattre comme il a fait espée contre espée. Ce Lieutenent voyant ce, remontera son espée, & tirera un arrieremain sur le coude du bras de son espée, tenant sa main gauche au dessous le bras de son espée, comme est monstré cy dessus à sadite pourtraiture au derriere de son bonnet, cotté en chiffre 125. La fin de ce renvers executé, & monstré par ledit Lieutenent au Prevost. Sensuit qu’a fait ledit Prevost. Ledit Prevost estant sur le pied droit, en garde basse, comme est cotté à sadite pourtraiture en chiffre 122, devoit ledit Prevost en tirant son pied droit arriere, tirer un renvers sur le bras dudit Lieutenent, & non croiser de son espée celle dudit Lieutenent, comme il a fait retournant rabbatre comme au susdit coup qui est la cause que ledit Lieutenent luy a tiré un renvers sur son coude, au bras que tient son espée, & tient cedit Prevost sa main gauche droit son tetin gauche, comme est monstré cy dessus à sadite pourtraiture cotté en chiffre, au derriere de son col 126. La fin de ce qu’a fait ledit Prevost contre ledit Lieutenent, pour la deffence de cestedite seconde subtilité. Sensuit un autre fort bon & subtil coup, laissant le renvers sur ledit bras, & venant d’un estoc au ventre, croisant du fort le foible, l’espée dudit Prevost comme est monstré icy par l’auteur au Prevost & par consequent le Prevost l’apprendra dudit Lieutenent. | |
| Another very effective and subtle strike for the Lieutenant against the Provost, leaving the back-hand at the elbow and throwing a thrust at the stomach, as shown here.
To effectively execute the strike as a thrust, which is a subtle and very effective strike, the Lieutenant needs to be on the right foot, and being there he will advance the left foot and will pretend to throw a low back-hand at the Provost's knee, the Provost will think to beat it down so the Lieutenant will advance the left foot and instead of striking the arm, as he has done at the previous strike, he will cross the strong of his sword at the middle of the Provost's sword, and will present a thrust at the belly and will keep his left hand below the elbow of the sword arm, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 127 behind the plume of his hat. This is what the Lieutenant does to effectively execute and show the strike in the manner of the thrust at the Provost. The following is what the Provost must do for the last strike of the sword alone. And this last said Provost of the entire treatise, being on the right foot, having seen that the Lieutenant wants to throw a low back-hand at the knee, the Provost pulled back his right foot and thought to throw a back-hand at the Lieutenant's sword arm, as was shown by the above portraiture of the Provost marked number 125, yet here the Provost has found himself frustrated by the execution of the reversal which he thought he was he doing well until the Lieutenant beat him down, strong on weak, and presented a thrust at him, but this was done by the Lieutenant to show the Provost that he can make two of the aforementioned strikes - the reversal and thrust - and so the last Prevost, is to keep his left hand right of his nipple to beat down the Lieutenant's sword since he was crossed strong on weak and cannot defend against a thrust other than with his left hand, as shown above at the portraiture marked number 128 near the plume of his bonnet. This is the end and the defense of the strike for the last Prevost against the Lieutenant, and every other content of in the treatise of the sword alone as stated, mother of all fencing. Made and written by Henry de Saint Didier, Squire, Provencal Gentleman. Next is a treatise written by the Author about tennis and how it relates to fencing, with the points and reasons that will be declared later. |
Autre fort bon, & subtil coup pour le Lieutenent contre le Prevost, laissant ledit arrieremain sur le coude & tirer un estoc au ventre, comme est monstré icy.
Pour bien faire & executer cedit coup en estoc, qui est un coup subtil, & fort bon, est besoin, & faut que cedit Lieutenent soit sur le pied droit, & y estant advancera le pied gauche, & fera semblant de tirer un arrieremain de bas au jarret du Prevost, le Prevost le pensera rabattre alors le Lieutenant advancera le pied gauche et au lieu de tirer sur le bras, comme il a fait au coup precedent, croisera du fort de son espée au milieu de l’espée du Prevost, & luy presentera un estoc au ventre, & tiendra sa main gauche au dessous le coude du bras de son espée, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture, cotté en chiffre au derriere du pennache de son chappeau 127. Voila ce que doit faire ledit Lieutenent pour bien executer & monstrer cedit coup en facon d’estoc au Prevost. Sensuit ce que doit faire le Prevost pour le dernier coup de ceste espée seule. Et ledit prochain & dernier Prevost, de tout cedit traité, estant sur le pied droit, a veu que le Lieutenent luy vouloit tirer un arrieremain de bas au jarret, ledit Prevost a tiré le pied droit arriere, & pensant tirer un arrieremain sur le bras de l’espée dudit Lieutenant, comme luy avoit esté monstré par luy cy dessus à la pourtraiture dudit Prevost, auquel est cotté en chiffre 125, & icy le Prevost s’est trouvé frustré de ladite execution de sondit renvers, qu’il pensoit bien faire attendu que ledit Lieutenant luy a rabatu, du fort le foible, & luy a presenté un estoc, mais cecy a esté fait par ledit Lieutenent monstrant au Prevost qu’il peut faire les deux susdits coups renvers estoc susdits, & tient cedit dernier Prevost sa main gauche droit le tetin pour rabbattre l’espée dudit Lieutenent, attendu que la luy a croisée du fort le foible, & ne la peut deffendre qu’il ne tire un estoc, si ce n’est de sadite main gauche, comme est monstré cy dessus à sa pourtraiture cotté en chiffres auprés du pennache de son bonnet 128. Voicy la fin & deffence de cedit coup pour ce dernier Prevost, contre ledit Lieutenent, & de tous les autres contenuz en ce traité de ceste espée seule, comme dit est, mere de toutes armes. Fait & composé par Henry de Sainct Didier, Escuyer, Gentilhomme Provencal. Sensuit cy aprés un traité composé par l’Auteur, qui est de la paulme avec les armes, avec les points & raisons cy aprés declarez.
| |
Illustrations |
by John Tse | |
|---|---|---|
| The following is a treatise on exercise and certain points required to know the tennis, for all those who love it, written by the Author, since it requires the same steps and to know the same strikes of fencing, as will be seen by this treatise, and the Author because of the affinity and friendship they have together, leads to alert and give instruction to the unlearned, which do not understand the terms of this exercise, and not for the learned and skillful.
The author having considered that tennis and fencing are closely related, as stated above, and whoever is able to easily play tennis would also have learned to throw sword strikes, and so is the opposite, but the one that is better than the other is fencing because it preserves the health and honor of those who are afraid of losing them. Anyone could ask why fencing and tennis are related. The Author responds and says that the same strikes that one throws from fencing to overcome his enemy in times of peace or to win money or some celebration, which are:
It is true that one of the aforementioned strikes must be removed, which is the thrust, and only two will remain which are:
The reason why I remove the thrust is that the racket has no point, and thus one would not be able to make a thrust. It is true that sometimes we strike and beat down with the racket when the ball comes straight to the face or higher, which is that we return the ball, and we beat it down with the racket when it comes from high or to the face keeping it straight, and leaning neither on the right nor left, and yet in the game of tennis, there are only the aforementioned two strikes, right-hand and reversal. But it is necessary to multiply them properly to 4 targets, from high and low, for example right-hand from below, and right-hand from above, reversal from below, and reversal from above, and thus it is necessary to be very dexterous and graceful to know how to strike because we strike at each other as we do with fencing. And knowing how to strike skillfully, we must observe the words of our ancestors who are skilled tennis players, who said whoever leaps to forsake the volley, will never be an esteemed player; it is necessary to take heed here, which is that when you can volley, you should never wait for a leap. The reason is that with a leap, several accidents can occur, yet on the volley, never, if one is well trained, and is safe. The accident that can happen to the volley is to crack the wood of the racket, but this is not an accident, instead it is a fault committed by the one who made the wood and not from the inside of the racket to the ball. For this reason I want to warn those who are not yet sure of the leap, who practice the volley, because it should never be done, but they are the ones who fail it, and if it is necessary, we still have recourse to the leap, and yet who can, must always take the volley, and not the leap. Next will be declared the points which are necessary in the game and exercise of tennis which must be observed. The first requirement of one who wants to attack another, consequently is to take leaded shoes or else heavy heels and wear them for two or three hours before starting his game; after the time passes, one will take off these said heavy heels and be content with his own shoes, or he wears light slippers which are sufficient, and in doing so he will find that he is more ready and skillful than those who will not do so, for experience is the master of all arts. The second requirement is to demand and choose the primary racket that is lightest in the hand. Just as all of fencing requires a light sword and a heavy dagger, tennis also must have a light racket and a weighted ball, weighing not too much nor too little, because everything that is too much or too little is worthless. The third point requires that we have to watch that when we are playing tennis is to have another racket other than the one we want to use, and tell the opposing party to throw the racket to see which will be in or out, and then when they say to throw your own if he lets you, throw the bad one and not the good one for the reason that will be declared later, and if he wants to throw his own, let him throw it away because throwing it weakens the cord, wasting it since the cords are loosened, and thus it will not be able to serve as well as it had before. One could say that he will ask for another, but respond to this that it is possible to not be able to find as good in the hand as the one that had been previously found that he did not want to keep because very often a racket is an advantage just as a good sword is also an advantage that one will overcome his enemy. The fourth point, having carefully observed all that is said, that remains is on which step it is necessary to take to effectively perform the art of tennis, and to serve the ball well on the roof, and give a wicked game as much as possible throughout the game. I say that as good practice for all the strikes being multiplied and to serve well, it is necessary to keep on the left foot initially and almost always while doing a pirouette on it: look for the ball on the side it will travel. Some might say, "I don't know where the ball will go and cannot decide." One should consider when deciding where the ball will be hit by their opposing party, observe him and decide where he wants to hit it is fine. But I'll give one that's better and the apparent reason. The aforementioned judgment is often deceptive because by observing him, one cannot truly figure out what the inside wants to do and execute which is to direct and cast the ball. I only want to decide based on where the opposing party can cast it. Do not observe him because he will deceive you, but instead look closely at the ball being served. And never lose sight of the ball because whoever is outside direct and leads without being misled by the inside which is the will of your opposing party; and yet being sure of your hand, without fail you will easily defeat your opponent without observing him; however if you look at him you will think that he casts the ball at you in the opposite direction of his gaze yet the inside will be entirely different, and nevertheless, you could be deceived by looking at your opposing party, so you will never be looking at the ball. And it is this argument that I have made of fencing where you must look at the sword point and not at the intent of the man. I do not put these said reasons for those who already understand them, but on the contrary for those who do not understand them. I was kind enough to speak of tennis because a brave man who is one of the good players came to see me two or three times only, and having learned effectively two or three strikes, he increased his skill almost by fifteen; and the brave man throws a forehand and reversal very gracefully, and thus tennis and fencing, as stated have a great affinity. END. |
Sensuit un traité sur l’exercice, & certains points requis de scavoir au jeu de la paulme, pour tous ceux qui l’aiment, composé par ledit Auteur, attendu que y est requis mesme desmarche, & scavoir, mesmes coups que ausdites armes, comme ce verra par iceluy traité, & la fait ledit Auteur à cause de ladite affinité & sympatie qu’ils ont ensemble, joint pour bailler advertissement, & instruction aux indoctes, & qui n’entendent les termes de cedit exercice, & non pour les doctes & adroits.
Ledit auteur ayant consideré, que la paulme, & les armes, sont cousins germains bien proches, comme a esté dit cy dessus, & qui scaura bien jouer à ladite paulme facillement auroit aprins à tirer coups d’espée, & à l’opposite, mais l’un vaut mieux que l’autre, qui sont les armes, car elles conservent la santé & honneur de ceux qui ont peur de la perdre. Quelqu’un pourroit dire, pourquoy lesdites armes, & ceste paulme sont cousins germains ? L’Auteur respond à cela, & dit, que de mesmes coups que on tire ausdites armes pour vaincre son ennemy au temps de paix ou de guerre, d’autant aussi de mesmes coups on peult vaincre sa partie adverse quant il veut faire quelque partie pour luy gaigner son argent, ou quelque banquet, qui sont.
Bien est vray, qu’il faut oster un desdits coups, qui est l’estoc, & n’en demeurera que deux qui sont.
La raison pourquoy j’oste ledit estoc est, attendu que la raquette n’a point de pointe, & par ainsi on n’en scauroit faire un estoc. Bien est vray, que quelques fois, on fait quelque coup, & rabat on de la raquette, quand l’eteuf vient droit le visage ou plus haut, qui est qu’on detourne l’eteuf, & on le rabat de la raquette quand il vient d’hault, ou au visage la tenant droite, & non penchante ne du costé droit, ne du costé gauche, & pourtant à cedit jeu de paulme il n’y a que lesdits deux susdits coups, maindroit & renvers. Mais il les faut multiplier proprement en 4 lieux, d’hault & de bas, comme par exemple, maindroit de bas, & maindroit d’haut, renvers de bas & renvers d’hault & par ainsi les faut bien dextrement & avec grace les sçavoir tirer car ils se tirent tout ainsi que font ausdites armes. Et les sachant bien adextrement tirer fault bien observer le dit de nos ancestres, bons joueurs de paulme, (qui dient,) qui par le bond delaisse la vollée, jamais bon joueur estimé ne sera, c’est à dire qui fault prendre icy un bon advertissemens, qui est que quant on peut prendre la volée, jamais ne faut s’attendre au bond. La raison par ce qu’à un bond, il peut intervenir plusieurs accidens, & à la volee, jamais, si on est si bien exercé, & qui soit seur. L’accident que peut advenir à ladit volee, c’est de rabatre du bois de la raquette, mais cela n’est accident, ains c’est une faute commise par celuy qui donne du bois, & non du dedans de la raquette à l’esteuf. À ceste cause je veux advertir ceux qui ne sont encores seurs du bond, qui s’exercent à ladite volee, car elle ne faut jamais mais se sont ceux qui la faillent, & si on la faut, on a encores recours audit bond, & pourtant qui peut, faut toujours prendre ladite volée, & non ledit bond. Cy aprés seront declarez les poincts qui sont fort necessaires en cedit jeu, & exercice de la paulme, qui faut bien observer. Le premier est requis à un qui veut assaillir un autre, & faire partie de consequence, de prendre des soulliers avec des mulles plombees, ou bien pesantes, & les porter deux ou trois heures, avant que commencer sa partie, ce temps passé, tel vient à laisser cesdites mulles pesantes & se contante de ses soulliers, ou il se fait bailler des chaussons legers, qui soyent bien à son point, & en ce faisant, tel ou tels se trouverons plus dispos & adextres que ceux que ne le feront, l’experience est la maistraisse de tous arts. Le second est requis en se jeu de demander le premier des raquettes & choisir la meilleure & qui soit legere & bien à la main. Car tout ainsi que ausdites armes est requis une espée legere, & une dague pesante, aussi à la paulme faut avoir une raquette legere & l’eteuf pesant, pesant (inquant[58]) ne trop, ne trop peu, car toute chose ou il y a trop, ou trop peu ne vault rien. Le troisiesme point est requis, & fault bien regarder que quant on sera dedans le jeu de paulme d’avoir une autre raquette que celle dequoy on se veux aider, & dire à la partie adverse, jettons la raquette, pour voir qui sera dedans ou dehors, & alors dira jettez la vostre, s’il te donne liberté jette la meschante, & non la bonne, & pour cause que sera cy aprés declarée, & s’il veult jetter la sienne, laisse la luy jetter car la jettant les cordes s’afoiblissent, s’afoiblissant elle se gaste, attendu que les cordes se destendent, & par ainsi elle ne pourra servir cy bien quelle eut fait auparavant. On pourroit dire, on en demandera un autre, responce, à ce possible n’en pourra trouver si bien à la main que celle qu’avoit trouvé auparavant que n’a voulu contregarder, car bien souvent une raquette est le gain de la partie, comme une bonne espée est aussi le gain que on vaincra son ennemy. Item le quatriesme, ayant bien observé tout ce que dit est, reste à scavoir sur quelle desmarche, il se faut tenir pour bien executer ledit art de ladite paulme, & pour bien servir l’eteuf sur le toit, & donner mauvais jeu le plus qu’on pourra tout le long du jeu. Je dis que pour le bien pratiquer tous lesdits coups, estans multipliez & pour bien servir, il se faut tenir sur le pied gauche pour la premiere fois, & presque tousjours en faisant la pirouette sur icelluy : cherchant l’eteuf du costé qu’il ira. Quelqu’un pourroit dire je ne scay pas où ira l’eteuf, & n’en puis juger. Fault consideré qu’aucuns quand ils jugent de l’eteuf où il sera tiré par leur partie adverse, le regardant à la veue, & par la jugent où il le veult tirer, cela est fort bon. Mais j’en donneray un qui sera meilleur, & la raison apparente. Ce jugement susdit est souvent deceptif car par la veue, on ne peut juger seurement ce que l’interieur veult faire & executer, qui est de conduire & jetter l’esteuf. Je dy que pour bien juger de l’esteuf où partie adverse le pourra jetter, ne le fault regarder à sa veue car il te decepvra par icelle mais bien regarde l’esteuf que auras servi, & ne le pers jamais de veue car ledit esteuf, qui est l’exterieur est conduit & mené sans fallace par l’interieur, & volonté de ta partie adverse, & pourtant estant bien seur de ta main, sans faulte vaincras ta partie adverse aisément, & non regardant la veue, car la regardant tu penseras qu’il te jette l’esteuf à l’opposite de son regard, & son interieur sera tout autrement, & pourtant voila, regardant la veue de tadite partie adverse, tu pourras estre deceu, & regardant l’eteuf ne le seras jamais. Et c’est l’argument que j’ay dit ausdites armes, qui fault regarder la pointe de l’espée, & non la veue de l’homme. Je ne mets cesdites raisons pour ceux qui les entendent, mais au contraire pour ceux qui ne les entendent. J’ay bien voulu parler de la paulme par ce que le brave qui est un des bons joueurs en icelle m’est venu voir deux ou trois fois seullement, & ayant bien aprins deux ou trois coups, il a augmenté son adresse presque de quinze, & tire ledit brave un avantmain & arrieremain de fort bonne grace, & par ainsi la paulme & lesdites armes, comme dit est, ont une grande affinité. FIN. | |
| Friendly reader,
Whoever among you buy these books from and won't find in them the name and initials of the Author written by his hand, such books are not to be sold by their will, for this reason, he asks you to have them brought to his house, and he will give you back the money that they cost you, telling him who have sold them to you, and if he will give you as much what he will bring, which will cost you nothing, and besides you will show the author and will declare the contents of him, which will cost you nothing to have recourse in justice against those who such books will have sold and will please him. |
Amy lecteur.
Qui d’entre vous acheptera de ces livres, & n’y trouvera le nom surnom & paraffe de l’Aucteur escrit de sa main, tels livres ne seront vendus par la volonté d’iceluy, à ceste cause, il vous prie les luy faire apporter en sa maison, & il vous rendra l’argent qu’ils vous auront cousté, luy disant qui vous les aura vendus, & si vous en donnera autant, que luy en apporterez, qui ne vous cousteront rien, & outre vous monstrera ledit auteur & declarera le contenu d’iceluy, qui ne vous coustera rien pour avoir recours par justice à l’encontre de ceux qui tels livres auront vendus & luy ferez plaisir. | |
| FRIENDLY READER,
The author is cognizant that fencing and law are two virtues most required to acquire the friendship of Kings, Princes, and Lords, even of Ladies. For this reason the Author preferred to choose and follow the art and practice of this than of the law: not that he abandoned them completely; but in this were practiced for the space of thirty years and after many long days, God bestowed him the grace with which he dedicated and in fact presented this treatise to one of the greatest Christian Monarchs under heaven. And by his command took with his Highness fencing, and with my Lord the Duke of Guise and others of his court, of which the Author has praised and praises God, who has made him well and fortunate and with favor of His said Majesty. Because of this, he once again took courage and daring, after being privileged by the Lord to have it printed, and put in light for the relief and satisfaction of his nobility and for public good. There may be some who may slander against the Author for the reasoning of the treatise and other little discourse, and advices made on the exercises and tennis. The Author has not dealt with what was said, for those who are skillful and have experimented and who understand the real terms, which are required in the two exercises; but good for those who do not understand them, that is to say fencing and tennis. For this reason the Author requests that the Readers only to take it in good faith and to excuse him. And do not look at the language nor to the letter nor the skin[59] of it, because at times it can find itself, for such things will contradict itself and will want to slander what he does not know and does not know how to do, and having wanted and spoken to the Author who may discuss with you for an explanation, and effectively show the treatise's contents, of which the contradictors, if any are found, may be satisfied, if the wise and their thoughts are determined and facts will not do it, thus they will address the Author who will be able to make them satisfied with the reason for his explanations. This treaty finished printing on June 4, 1573. |
AMY LECTEUR.
L’auteur cognoissant que les armes, & les loix, sont deux vertus plus requises, à faire acquerir l’amitié des Roys, Princes, & Seigneurs, mesmes des Dames. À ceste cause ledit Auteur a mieux aymé choisir & suivra l’art & pratique d’icelles, que desdites loix : non que du tout il les aye abandonnées : mais en icelles s’est exercé l’espace de trente ans, & aprés ses longs jours, Dieu luy a fait la grace qu’il a dedié, & de fait presenté cedit traité, estant à un des plus grands Monarques Chrestiens, qui soit soubs le ciel. Et par son commandement ay tiré avec son Altesse ausdites armes, & avec Monseigneur le Duc de Guise, & autres de sa court, dont l’Auteur en a loué & loue Dieu, qui luy a fait ce bien qu’il a eu cest heur & faveur de sadite Majesté. À ceste cause a derechef prins courage & hardiesse, aprés le privilege par ledit Sieur à luy donné, de le faire imprimer, & mettre en lumiere pour le soulagement, & contentement de sa noblesse, & bien public. Il en pourra avoir quelques uns qui pourront calomnier contre ledit Auteur, pour raison dudit traité, & autres petits discours, & advertissement qu’a fait sur l’exercice & jeu de la paulme. Ledit Auteur n’a traitté de ce que dit est, pour ceux qui sont adroits, & experimentez, & qui entendent les vrais termes, qui sont requis ausdits deux exercices ; mais bien pour ceux qui ne les entendent, c’est à dire des armes & de la paulme. À ceste cause l’Auteur prie les Lecteurs, ne le vouloir prendre que en bonne part, & l’excuser. Et ne regarder au langage, ne à la lettre & escorce d’icelle, ains au temps que y peult consister, car tel y contredira, & y vouldra calomnier qu’il n’en à sceu & n’en scavroit faire aultant, & ayant veu & oy parler ledit Auteur qui vous pourra discourir par raisons, & monstrer par effait le contenu dudit traité, dont lesdits contredisans (si aucuns s’en treuvent) se pourront trouver contens, les saiges & arestez en paroles & en faits ne le feront, ains s’adresseront à l’Auteur qui les pourra rendre contens par la raison de son dire. Cedit traité a esté achevé d’imprimer le 4 de Juing, 1573. | |
| PRIVILEGE OF THE KING.
King Charles of France by the grace of God. To our friends and foes, the people on the courts of Parliament, Bailiffs, Officials, Provosts, or their Lieutenants, and to all our justices and officers, and to anyone who wishes to be included, salutations and blessings. Our dear and good friend Provencal Gentleman Esquire Henry S. Didier, we have heard that he wrote certain books that he had dedicated to us in the manner of fencing, namely on the sword alone, the sword and dagger, sword and cape, sword and rondel, sword and targe, sword and buckler, two-handed sword, dual-wielding swords, and dagger alone, written for the art, order, and practice with the means to defend and attack at the same time with strikes that can be thrown both in attacking as well as in defending, which is very useful and notable for making skillful youths which similarly he will write for all of the weapons he would like to glady have printed and illuminated. However as something that he could only do with great expense and fees, he fears that after having incurred the expenses, no printer nor booksellers nor anyone else, to his serious detriment and damage, would reprint them if he did not have our permission and special privilege. To that end, we have humbly implored and requested him to provide this letter as necessary. We desire with these causes as much as possible for us to treat every people with knowledge to the maintenance and advancement of things that are useful and beneficial to the public. So to encourage everyone to more willingly strive to do the same, having audited S. Didier, we have granted by those present that he can be free to have the all of the books written by him on the same subjects mentioned above printed by any printer as he sees fit. And to that end, whoever the printers chosen will be in charge of the books, will be compensated for the fees as is acceptable for doing this effect. We have continued to inhibit and defend all other booksellers and printers in our Kingdom, land, and lordship of our obedience, that during the terms of ten consecutive years following to be counted from the day and date to its said books will have been printed, they cannot print neither large, small, nor any other form whatever form it takes, and do not sell the above said books, which will have been printed by no other than by him or those who will be in charge of said S. Didier, on pain of arbitrary fine, confiscation, and loss of all said books. If we mandate you, we commit and enjoin by those presents and to each of you in right be, if as it will belong to him, that according to our granted permissions and will, you make or have made express inhibitions and defenses by us on the penalties mentioned above, and other than that will be imposed on all printers and booksellers remaining in your rights and jurisdictions that by afterwards, none of them other than the one who will have charge and express commission of said by S. Didier, do not print nor put for sale during the time of ten years the books above mention and if after the orders made you find any offenders proceed against them by condemnation of said penalties and otherwise also that will be done according to the requirements of the cases, because such is our pleasure, and because of the contents in those aforementioned present will be able to deal in several and various places. We want the vidimus[60] of these to be made under royal seal or collated by one of our notaries and secretaries done either as this present original and that by putting a brief or extracting the content in its said present at the beginning of the aforementioned books they are held as it should be, signaling to all the aforementioned booksellers and printers and others like them. Given in Paris on the twenty third day of January in the year of the Lord one thousand five hundred and seventy-three of the thirteenth reign[61]. Thus signed for the King by Brulart[62] and sealed on a simple yellow wax queue[63] |
PRIVILEGE DU ROY.
Charles par la grace de Dieu Roy de France. À noz amez & feaux, les gens tenans noz courts de Parlements, Baillifs, Senechaux, Prevosts, ou leurs Lieutenents, & à tous noz justiciers & officiers, & à chacun d’eux, si comme à luy appartiendra, Salut & dilection[64]. Nostre cher & bien amé Henry de S. Didier Escuyer, gentilhomme Provençal, nous a fait entendre qu’il compose certains livres qu’il nous a dediez, sur la maniere de tirer des armes, à scavoir de l’espée seule, espée & dague, espée cape, espée rondelle, espée targue, espée bouclier, espée à deux mains, les deux espées, & la dague seule, redigez par art, ordre & pratique, avec moyen de soy deffendre & offencer en un mesme temps, des coups qu’on peut tirer, tant en assaillant, qu’en deffendant, fort utilles & notables pour adextrer la jeunesse, lesquels & semblablement tous ceux qu’il composera pour le fait des armes, il desireroit volontiers faire imprimer & mettre en lumiere. Toutefois estant chose qu’il n’a peu faire qu’avec grands fraits & despens, il craint qu’aprés y avoir esposé lesdits fraits, aucuns imprimeurs, ou libraires, & autres ne les feist à son grand detriment, & dommage, rimprimer, s’il n’avoit de nous permission, & privilege special. À ceste fin nous ayant humblement fait supplier, & requerir luy vouloir sur ce pourvoir de noz lettres à ce necessaires. Nous à ces causes desirans, en tant qu’il nous sera possible, favorablement traiter toutes personnes de bon scavoir, à l’entretenement & advencement des choses utiles, & profitables au public. Afin que chacun plus volontiers s’esvertue de faire le semblable, avons audit de S. Didier permis & octroyé, permettons & octroyons par ces presentes, qu’il puisse & luy soit loisible faire imprimer par tel imprimeur que bon luy semblera, lesdits livres cy dessus mentionnez, ensemble tous ceux qui seront par luy composez, sur le mesme subjet. Et à fin que celuy ou ceux desdits imprimeurs, qui auront charge de luy, de ce faire, ayant moyen d’eux recompenser des fraits, qu’il conviendra faire pour cest effet. Avons inhibé & defendu, inhibons & deffendons à tous autre libraires & imprimeurs de cestuy nostre Royaume, pais terres & seigneurie de nostre obeissance, que durant le temps & terme de dix ans ensuivans, consecutifs, à conter du jour & date qu’à sesdits livres auront esté imprimez, il n’ayent à imprimer, ne faire imprimer, ne grande, petite, ou autre forme, quelle qu’elle soit, ne vendre les dessusdits livres, qui auront esté imprimez par autres que par celuy ou ceux qui auront charge dudit de S. Didier, sur peine d’amende arbitraire, & de confiscation, & perte de tous lesdits livres. Si voulons & vous mandons, commettons & enjoignons par ces presentes, & à chacun de vous en droit soy, si comme à luy appartiendra, que selon & ensuivant noz permissions octroy & vouloir, vous faites ou faites faire expresses inhibitions & deffenses de par nous sur les peines cy dessus indites, & autre que verrez estre à imposer à tous imprimeurs & libraires demourans en voz destroits, & juridictions, que par cy aprés eulx, n’aucuns d’eux, autre que celuy qui aura charge & commission expresse dudit de S. Didier, pour ce faire n’ayent à imprimer ne faire imprimer, mettre n’exposer en vente, durant ledit temps de dix ans lesdits livres cy dessus mentionez & si aprés lesdits commandemens faits vous trouvez aucuns contrevenans à iceux procedez à l’encontre d’eux par condemnation desdites peines & autrement aussi que verrez estre à faire selon l’exigence des cas, car tel est nostre plaisir, & parce que du contenu en cesdites presentes l’on pourra avoir affaire en plusieurs & divers lieux. Nous voulons qu’au vidimus[65] d’icelles fait soubs scel royal ou collationné par l’un de noz notaires & secretaires fait soit adjousté comme à ce present original & que en mettant par brief ou extrait le contenu en sesdites presentes au commencement desdits livres elles soient tenues pour deuement signifiees à tous libraires & imprimeurs dessusdits & autres qu’il appartiendra. Donné à Paris le vingtroisiesme jour de Janvier l’an de grace mil cinq cens soixante & treize de nostre regne le treziesme. Ainsi signé par le Roy Brullart[66] & seellées sur simple queue de cire jaulne. |
For further information, including transcription and translation notes, see the discussion page.
| Work | Author(s) | Source | License |
|---|---|---|---|
| Illustrations | |||
| Translation | John Tse | ||
| Transcription | Olivier Dupuis | FFAMHE |
Additional Resources
- Hyatt, Robert Preston and Wilson, Devon. "The Single Sword of Henry de Sainct Didier." Masters of Medieval and Renaissance Martial Arts. Ed. Jeffrey Hull. Boulder, CO: Paladin Press, 2008. ISBN 978-1-58160-668-3
- Sainct Didier, Henry de. The Single Sword of Henry de Sainct-Didier (Traicté Contenant Les Secrets Du Premier Livre Sur L'Espée Seule). Trans. Robert Preston Hyatt and Devon Wilson. Boulder, CO: Paladin Press, 2009. ISBN 978-1581607048
- Slee, Chris. Secrets of the Sword Alone. LongEdge Press, 2014. ISBN 978-0646926353
References
- ↑ Pristin : ancien, antérieur
- ↑ Insertion du « a ».
- ↑ The "es" is a wooden board placed in the back wall of the tennis court which, if hit by a volley, is scored immediately. In modern tennis, this board is replaced by a grid.
- ↑ « L'es », habituellement orthographiée « ais », désigne une planche de bois placée dans le mur du fond de la salle de jeu de paume qui, si elle est touchée par un coup de volée, donne le point immédiatement. Dans le jeu de paume moderne, cette planche est remplacée par une grille. Il est possible que cet « ais » ait donné le terme anglais d'« ace » que les étymologies modernes confondent avec l'« as » du jeu de carte. Voir la définition d' « ais » de l'Encyclopédie de Diderot et d'Alembert.
- ↑ L’esteuf : ancien nom pour la balle.
- ↑ précéder. « Préaller » subsiste en français sous la forme « préalable ».
- ↑ Il s’agit très probablement du maître d’arme italien Fabris Salvator de Padoue (1544-1617). Voir la note sur Fabris Salvator de Vigeant p. 162 et aussi les références à ses publications (Vigeant p. 55-56)
- ↑ Version alimentaire de l’adage « blanc bonnet et bonnet blanc ».
- ↑ Transcription la plus sûre du texte : « gran d erre »
- ↑ Serviteur du grand prêtre venu arrêter Jésus au Mont des Olivier et dont l’oreille coupée a été immédiatement guérie. Selon la lecture du passage, il est parfois pris pour celui qui soufflète Jésus.
- ↑ Un des anciens nom de l’abeille.
- ↑ Sens incertain ; peut-être s'agit-il d'une mauvaise graphie de « filial ».
- ↑ drillant : étincellant, brillant (dictionnaire de Nicot).
- ↑ Correction du texte d’origine donnant « peid ».
- ↑ Cette correction sur les images d'Henri de Saint-Didier indique que celles-ci ont été réalisées avant la version finale du texte.
- ↑ Le « o » de troisiesme est curieusement placé en exposant.
- ↑ Suppression du doublement de l'esperluette.
- ↑ Dupuis states the original says left but is incompatible with the rest of the text and the engraving.
- ↑ Proposition de correction de l’édition originale qui donne « gauche », en incohérence avec la gravure et le texte plus bas qui confirme que la posture du Lieutenent est identique à celle de la section précédente où c’était bien le pied droit qui était reculé.
- ↑ Deuxième remarque de l'auteur sur les gravures montrant que le texte a été retouché après réception des gravures. À comparer avec une remarque similaire faite dans le i.33.
- ↑ Correction du texte d’origine donnant « Leiutenent ».
- ↑ In modern fencing, dérobement is a fencing term for disengage.
- ↑ Correction de l'édition originale qui omet lors d'un changement de page le début du mot « haute »
- ↑ The position of the hand illustrates the fingers down, in opposition to the text.
- ↑ La position de la main illustrée a les doigts au-dessus, en opposition avec le texte.
- ↑ Proposition de correction pour « bessoin »
- ↑ Proposition de correction pour « avan-main »
- ↑ Proposition de correction pour « couté »
- ↑ Proposition de correction pour « Vola ».
- ↑ Proposition de correction pour « ongle »
- ↑ Sens inconnu.
- ↑ La tuition est un synonyme de « garde », « défense », très souvent employé à cette époque pour appuyer le mot « défense ».
- ↑ Proposition de correction pour « Provost »
- ↑ Proposition de correction de « du–sixiesme »
- ↑ Proposition de correction pour « persent ».
- ↑ The triangle represented here is not correct. The one marked 65 seems to better reflect the proposed movement.
- ↑ Proposition de correction pour « le ongles ».
- ↑ Le triangle représenté ici n'est pas correct, celui cotté 65 paraît rendre mieux compte du déplacement proposé.
- ↑ Dupuis thinks 75 represents this correct and that 73 is incorrect.
- ↑ Proposition de correction pour « Lieutent ». La marque indiquant une contraction a probablement été omise.
- ↑ On pourrait compléter : « ...et le mettre en 4 ». L'illustration 73 est incorrecte puisque le pied gauche est resté sur la semelle 1 et n'est pas placé sur la semelle 3 (à gauche) comme demandé ; la position des pieds de l'illustration 75 correspond à ce qui aurait dû être représenté.
- ↑ The Provost shown at the portraiture does not correspond to the text since he is on the right foot
- ↑ Proposition de correction pour « dh’aut »
- ↑ Sic.
- ↑ Le prévôt représenté ici ne correspond pas au texte puisqu'il se tient sur le pied droit.
- ↑ The Provost of 80 isn't on the left foot as written but is coherent with 78.
- ↑ Le prévôt de la figure 80 n’est pas sur le pied gauche comme écrit et mais reste cohérent avec la figure 78.
- ↑ It is meant to read as Provost here.
- ↑ Il faut évidemment lire ici « Prevost ».
- ↑ Proposition de correction pour « suprint »
- ↑ Sic.
- ↑ Suppression du doublement de l'esperluette dans « sa cuisse gauche, & & tous ».
- ↑ Sic. Au XVIe siècle, le genre des mots était encore indécis.
- ↑ The author is announcing here another edition to augment his book which has never has been written.
- ↑ L’auteur annonce ici une prochaine édition augmentée de son oeuvre qui n’a a priori jamais eu lieu.
- ↑ Proposition de correction pour « ou ».
- ↑ Proposition de correction pour « mostré »
- ↑ Du latin médiéval « inquinatum » signifiant « pour combien »
- ↑ lit. bark or shell, outer layer. Idiom similar to "Don't judge a book by its cover.
- ↑ A vidimus is a certified copy of an earlier act
- ↑ of King Charles IX
- ↑ It must be either Pierre or Jean Brûlart who both served on Parliament
- ↑ If the seal is appended to the document with a strip of parchment, it is called a "queue". If there is a double strip, it is then called a "double queue".
- ↑ Dilection : attachement, amour pur.
- ↑ Un vidimus est la copie certifiée d'un acte antérieur.
- ↑ Il doit s'agit de Pierre ou Jean Brûlart (tout deux avait une charge au Parlement) qui signe pour le roi.