|
|
You are not currently logged in. Are you accessing the unsecure (http) portal? Click here to switch to the secure portal. |
Pedro de Heredia
| Pedro de Heredia | |
|---|---|
| Occupation |
|
| Nationality | Spanish |
| Movement | Esgrima común |
| Genres | Fencing manual |
| Language | Middle French |
| Notable work(s) | Book of Lessons |
| Principal manuscript(s) |
|
Pedro de Heredia was a 17th century Spanish governor of a region in Belgium and captain of cavalry from 1615-1645.
Contents
- 1 Treatises
- 1.1 Preface
- 1.1.1 Section 1 - How one must accommodate the body to get into a good posture.
- 1.1.2 Section 2 - The four principle guards of the single sword.
- 1.1.3 Section 3 - Counterguards to the aforementioned.
- 1.1.4 Section 4 - It is also important to know how our body can operate.
- 1.1.5 Section 5 - The most notable points of warning that must be observed in several places.
- 1.1.6 Section 6 - Knowing which is the correct[2] or false edge of the sword.
- 1.1.7 Section 7 - Four ways of passing.
- 1.1.8 Section 8 - Knowing which are the kind of times.
- 1.1.9 Section 9 - Which kind are being in and out of measure.
- 1.1.10 Section 10 - How to win the measure.
- 1.1.11 Section 11 - What is the strong and the weak of the sword.
- 1.1.12 Section 12 - Understanding when one is on guard with advantage.
- 1.1.13 Section 13 - Some definitions of words that are noted to understand fencing.
- 1.2 Single Sword Play
- 1.2.1 Chapter 1 - Simple lessons of the single sword.
- 1.2.2 Chapter 2 - The discard[3].
- 1.2.3 Chapter 3 - Double lessons of the single sword.
- 1.2.4 Chapter 4 - Feints.
- 1.2.5 Chapter 5 - Spread[4] and remedies.
- 1.2.6 Chapter 6 - The passes.
- 1.2.7 Chapter 7 - Times and counter-times.
- 1.2.8 Chapter 8 - Lessons on sword attack.
- 1.2.9 Chapter 9 - On the use of the free hand.
- 1.2.10 Chapter 10 - On sword-taking and its remedy.
- 1.2.11 Chapter 11 - The gainings[5] or the subjections of the sword.
- 1.2.12 Chapter 12 - Slashes[6], reversals[7], and their remedies.
- 1.2.13 Chapter 13 - Single sword play in mathematics form.
- 1.2.14 Chapter 14 - Discourse and warning of the single sword play, both for winning land and other required subtleties.
- 1.2.15 Chapter 15 - Rule to avoid being surprised on the time of the foot.
- 1.2.16 Chapter 16 - Single sword play against sword and dagger.
- 1.2.17 Chapter 17 - On the short sword.
- 1.2.18 Chapter 18 - On the use of the cloak.
- 1.2.19 Chapter 19 - The grapples of the single sword.
- 1.2.20 Chapter 20 - Against the left-hander.
- 1.3 Sword and Dagger Play
- 1.3.1 Chapter 1 - First the dagger parries.
- 1.3.2 Chapter 2 - The simple lessons of sword and dagger.
- 1.3.3 Chapter 3 - The feints of the said sword and dagger play.
- 1.3.4 Chapter 4 - On the beats of both sword and dagger.
- 1.3.5 Chapter 5 - On the long play.
- 1.3.6 Chapter 6 - The double intentions.
- 1.3.7 Chapter 7 - The passes and their remedies.
- 1.3.8 Chapter 8 - The spreads.
- 1.3.9 Chapter 9 - On times and counter-time.
- 1.3.10 Chapter 10 - The encroachment.
- 1.3.11 Chapter 11 - The advancing[8] on the long and short play.
- 1.3.12 Chapter 12 - On the breaking.[9]
- 1.3.13 Chapter 13 - The slashes of the sword and dagger play.
- 1.3.14 Chapter 14 - Binding and unbinding.
- 1.3.15 Chapter 15 - Subjugation, disengagement, and avoidance of engagement.
- 1.3.16 Chapter 16 - Lessons of dagger cuts.
- 1.3.17 Chapter 17 - How one can throw the sword out of the hand.
- 1.3.18 Chapter 18 - On the left foot.
- 1.3.19 Chapter 19 - Against the left-hander.
- 1.3.20 Chapter 20 - Discourse and warning of the sword and dagger play.
- 1.3.21 Chapter 21 - Know who has more advantage being in a mountainous place, he who holds the top or the bottom.
- 1.3.22 Chapter 22 - Know who has more advantage, the left-hander or the right-hander.
- 1.3.23 Chapter 23 - Rule against those withdrawing that we want to catch off guard while you pursue.
- 1.3.24 Chapter 24 - Know who has more advantage, the sword and cape or the sword and dagger.
- 1.3.25 Chapter 25 - Warning how a little man needs to control a big man.
- 1.3.26 Chapter 26 - The grapples of the sword and dagger.
- 1.3.27 Chapter 27 - The guard takes against dagger cuts.
- 1.4 Copyright and License Summary
- 1.1 Preface
- 2 Additional Resources
- 3 References
Treatises
Illustrations |
Transcribed by | |
|---|---|---|
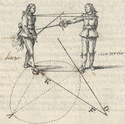
| The strong will be from the back half for defense. And the weak for offense from the point until the middle.
The sword can also be divided into three as you see above. As for the guards on which I want to rest my foundation, I stand with the common opinion of those who have made a profession of handling arms well that there are four guards, in the order that they are consecutively attributed; which nevertheless can be reduced to two, joining the first and second in one, and the third and fourth in the other. So let's say before going over what it is to be perfectly on guard. To be on guard consists of two things, namely: the accommodation of the body and that of the sword. |
||
For further information, including transcription and translation notes, see the discussion page.
| Work | Author(s) | Source | License |
|---|---|---|---|
| Illustrations | |||
| Transcription | Lionel Lauvernay, Olivier Dupuis, Philippe Errard, Didier de Grenier | Livre des Lecons |
Additional Resources
References
- ↑ According to Lauvernay, "fourniment" is the powder case of arquebusiers and musketeers (sometimes extended to all the equipment carried). The word is only used once to indicate a place on the body, probably a bit below the shoulder.
- ↑ Droit can mean "right" (as in not left or not wrong) or "correct" (as in not incorrect) or "true" (as in not false). All are likely acceptable.
- ↑ Credits to Alan Bloniarz for providing context to the word "garatusa".
- ↑ Écarté is the French word for the Italian technique "inquartata".
- ↑ Gannance is a loanword derived from the Spanish word "ganancia", which means "gain". It is used to describe a situation where your blade is used to restrict the opponent's blade movement. Credit to Tim Riviera for the explanation.
- ↑ Cortelade is a cut from outside to inside (right to left for a right hander). The Spanish word "cortar" simply means "to cut".
- ↑ Rever is a cut from inside to outside (left to right for a right hander).
- ↑ Chassement means "chasing". In this case, it is the back foot chasing the front. In modern fencing, this is known as advancing.
- ↑ Crèvement means "to burst or to puncture." In the treatise, it is used to describe breaking guards.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||