|
|
You are not currently logged in. Are you accessing the unsecure (http) portal? Click here to switch to the secure portal. |
Difference between revisions of "Augsburg Group"
| Line 2,566: | Line 2,566: | ||
* [[Rainer Welle|Welle, Rainer]] (in German). ''…vnd mit der rechten faust ein mordstuck - Baumanns Fecht- und Ringkampfhandschrift''. Herbert Utz Verlag, 2014. ISBN 978-3831643776 | * [[Rainer Welle|Welle, Rainer]] (in German). ''…vnd mit der rechten faust ein mordstuck - Baumanns Fecht- und Ringkampfhandschrift''. Herbert Utz Verlag, 2014. ISBN 978-3831643776 | ||
* [[Rainer Welle|Welle, Rainer]] (in German). ''"…und wisse das alle höbischeit kompt von deme ringen". Der Ringkampf als adelige Kunst im 15. und 16. Jahrhundert.'' Pfaffenweiler: Centaurus-Verlagsgesellschaft, 1993. ISBN 3-89085-755-8 | * [[Rainer Welle|Welle, Rainer]] (in German). ''"…und wisse das alle höbischeit kompt von deme ringen". Der Ringkampf als adelige Kunst im 15. und 16. Jahrhundert.'' Pfaffenweiler: Centaurus-Verlagsgesellschaft, 1993. ISBN 3-89085-755-8 | ||
| − | * [[Grzegorz Żabiński|Żabiński, Grzegorz]] and [[Bartłomiej Walczak|Walczak, Bartłomiej]]. '' | + | * [[Grzegorz Żabiński|Żabiński, Grzegorz]] and [[Bartłomiej Walczak|Walczak, Bartłomiej]]. ''Codex Wallerstein: A Medieval Fighting Book from the Fifteenth Century on the Longsword, Falchion, Dagger, and Wrestling''. Boulder, CO: [[Paladin Press]], 2002. ISBN 978-1-58160-585-3 |
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 18:46, 26 August 2022
| Augsburg Group | |
|---|---|

| |
| Bauman Fechtbuch, ff 20v - 21r | |
| Author(s) |
|
| Compiled by | |
| Illustrated by |
|
| Date | ca. 1470s |
| Genre | |
| Language | Early New High German |
| State of Existence | Original hypothetical; several fragmentary copies exist |
| Manuscript(s) |
Libr. pict. A.83 (ca. 1510s)
|
| Concordance by | Michael Chidester |
| Translations | |
The Augsburg Group is a series of 15th and 16th century German manuscripts that describe a common set of techniques and seem to have originated in the area of Augsburg, Germany. It has been suggested that these treatises define a local martial arts tradition native to that city, which would be a subset of the mainstream German style. The first two components of the Bauman Fechtbuch are the oldest entry in the group, and it's possible that the later treatises are dependent on it, particularly that of Albrecht Dürer. However, this issue is complicated by the fact that the first grappling section of the Glasgow Fechtbuch, which is comprised of material not drawn from Bauman, contains much of the remainder of Dürer's work.
Despite the existence of several fencing manuals describing these teachings, there are few known masters of this tradition. Despite attempts by a few modern writers to connect Albrecht Dürer to the Marxbrüder fencing guild, there is no evidence suggesting that he was anything but a master painter, and it seems unlikely that he practiced the techniques in his book.[1] In fact, the only known master whose connection to the tradition is certain is Antonius Rast, a former Captain of the Marxbrüder who left a partially-completed fencing manual upon his death in 1549. This manuscript was later acquired and completed by Paulus Hector Mair, and it seems to have influenced his own writings to some extent.
Contents
Treatises
The Wrocław Codex 1246 disappeared during World War Ⅱ and cannot presently be integrated into this concordance. Fortunately, Friedrich Dörnhöffer referenced this text extensively in his 1909 edition Albrecht Dürers Fechtbuch. In the transcription, he included notes where the text of the Codex 1246 differs from that of the MS 26-232; those notes have been preserved in this compilation, indicated by footnotes with the abbreviation Br.
While the Berlin Picture Book contains a wealth of high-quality illustrations, it draws on multiple sources aside from the Augsburg tradition including Hans Talhoffer's writings and a series of anonymous sword and buckler images. Because of this, images which don't overlap other works in the tradition can't be verified as belonging to it and thus are omitted here.
Images |
Images |
Augsburg Version Ⅰ (1470s) |
Glasgow Version (1508) |
Vienna Version (1512) |
Augsburg Version Ⅱ (1553) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
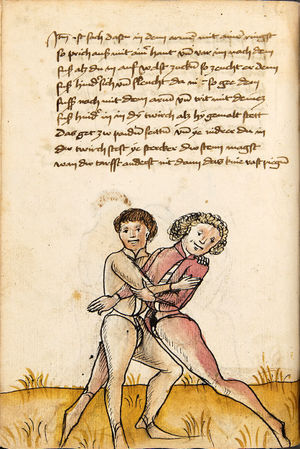
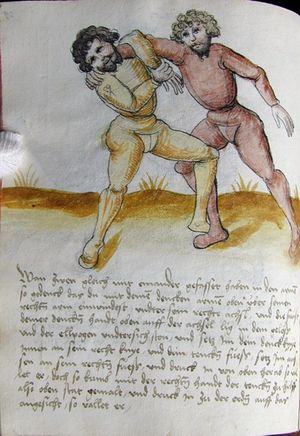
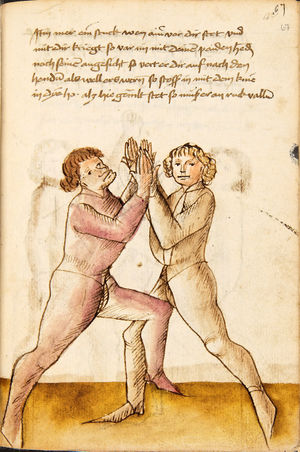
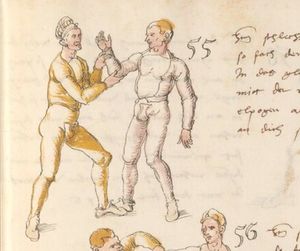
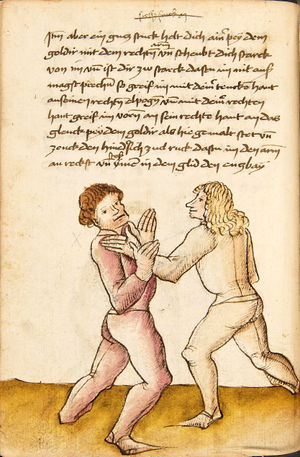
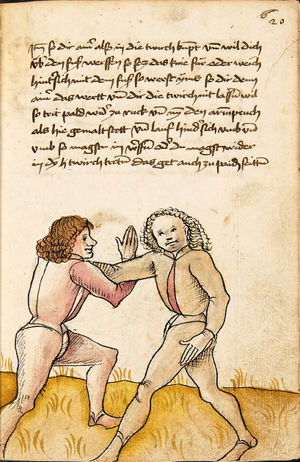
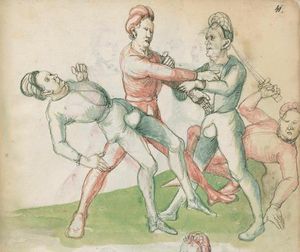
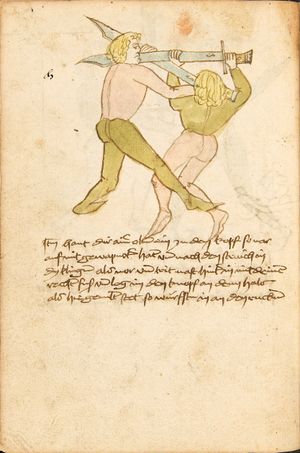
| The First Lesson of Wrestling
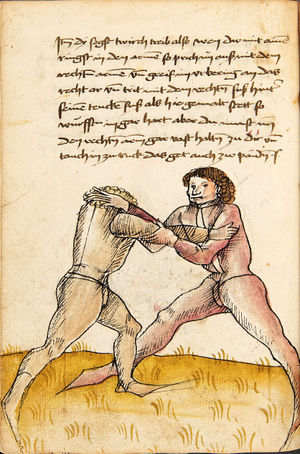
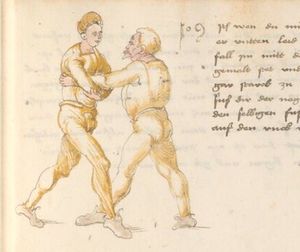
Item, mark that the wrestling will have three sorts, Strength, Measure, and Agility. The Strength thus is that everyone shall necessarily go low in the Balance and shall set himself strongly on the earth. The Measure thus is that you know to correctly position your hands and feet in all stances as that you hereafter will. The Agility thus is that you well forefend all stepping-behind, pulling and striking, arm-breaks, that you therein all things have good thought quickly to turn, and all times hinder, and fall in the balance. |
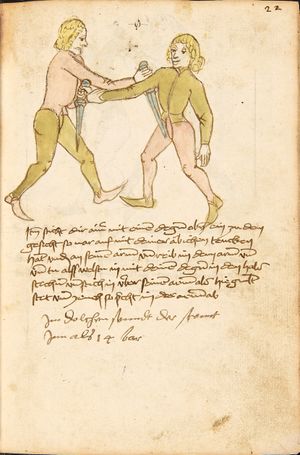
[15r] Von ringen dy erst ler
Item zu mercken das das Ringen will haben dreyerlay / sterck / masß / vnd phentikait / dy sterck also zwprauchen Das ain yeder nider sol gen in der wag vnd sich starck soll seczen auf dy erden Dy masß also das du dein hent vnd füsß wist recht zw schicken in allen stäntten alstu her nach woll ...en wirst Dy phentikait also dastu woll für sechst all hinter trit zucken vnd stossen armm prüch dastu dar Inn güt gedächtnüsß habst allew ding pald zw wenten vnd alzeit swären vnd In dy wag vallen |
|||||
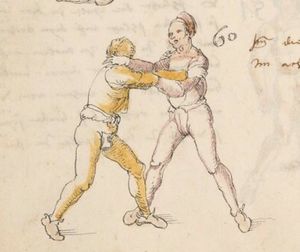
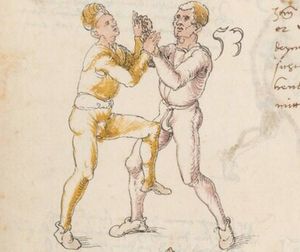
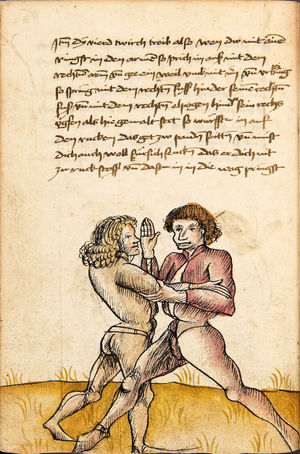
| The Second Lesson of Wrestling
Also you shall know that every Weak one you should wrestle Before as with Strength, and an Equal one should you wrestle With as with Measure, and a Strong one should you wrestle After as with Agility. Thus when you wrestle with a Weak one, then you may not worry before him if you have Measure and Agility and set yourself in a balanced stance. What you then seek, thwart or open, arm-breaks, combat-techniques, mortal-techniques, or other techniques, they may he then not well defend otherwise than fleeing-from and evasion. |
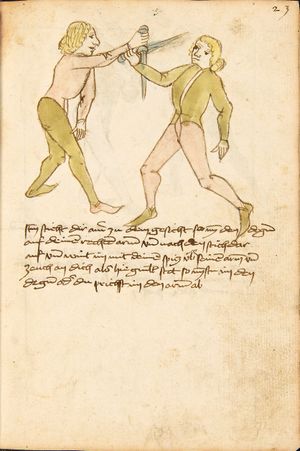
Dy ander ler von Ringen
Auch so soltu wissen dastu einen yeden krancken vor solt ringen alz mit sterck vnd einen gleichen mitt solt Ringen als mit masß vnd einen starcken nach solt Ringen als mit phentikait Also wen du mit einem krenckeren Ringst so darfstu dich nit vor Im psorgen hastu masß vnd phentikait vnd seczt dich in ein stäte wag wastu dan suchst twirch oder plösß armm prüch kampf stuck mord stuck oder ander stuck dy mug er dir dann nit woll weren anderst dan ausß fliechen vnd ausweichen |
|||||
| If you then wrestle with an Equal one, then see also that you well beware before pulling, stepping-behind, and arm-breaking, and before other misleading that are performed, thus that you stand in the balance, and find Strength with Measure, and all times hinder him in setting and in working off. Thereafter you may also overcome Agility with Measure. | [15v] Ringstu dan mit einem gleichen so sich auch Dastu dich woll pewarst vor zucken hinter treten vnd armm prüchen vnd vor anderen verfüren das thů also dastu dich stät in der wag vnd sterck mit masß vinden last vnd alzeit swärlich in in seczt vnd in ab arbaiczt dar nach magstu in auß phen- tikait über eylen mit masß | |||||
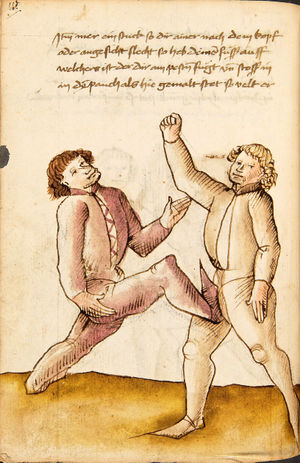
| The Third Lesson of Wrestling
If you wrestle with a Strong one, then beware yourself thus where he attacks you or falls, so see that you set yourself low fast and strike out his arms with the bear-strikes, and with other techniques also break out, and give very much way before him, and see if you may mislead him and overcome him with Agility, that you catch his foot or such under-steps that you throw him, as you will then find with more techniques and counters hereafter depicted and written. |
dy drit Ler ic
Ringstu mit einem starcken so pewar dich also wo er dich an greift oder velt so sich dastu vast nider seiczt vnd ym sein arm mit dem peren stosß auß stost vnd mit anderen stucken auch auß prechst vnd gar vil vor im weichst vnd stich ob dw in mit phentikait verfüren vnd über eylen mügst dastu im ein füß er wischst oder sünst vnter treczt Dastu in werfst alstu Dann mit mer stucken vnd pruchen her nach inn gemell vnd inn geschrift vinden wirst |
|||||
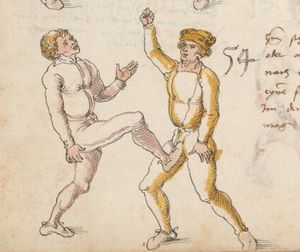
| Not More Than a Preface
Yet so is every Weak wrestler in earnest an Equal to a Strong one if he has taken advantage of Agility and Measure, combat-techniques and mortal-techniques, but with social wrestling so the Strong one has yet advantage at all times, so the Art becomes praised before knights and soldiers ahead of all things. |
Nit mer dan ein vorred
Doch so ist ein yeder krancker Ringer im ernsten einem starcken zwgleichen hat er pehentikait vnd masß kampf stuck vnd mord stuck enpfor genomen aber mit gesellen ringen so hacz der starck alzeit enpfor doch so wirt dy künst gelopt vor ritter vnd knechten für allew ding etc |
|||||
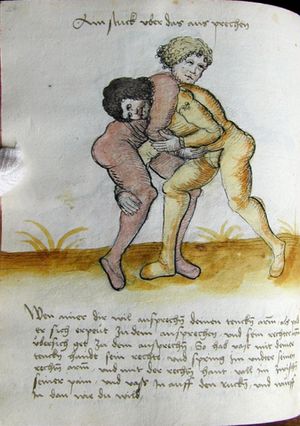
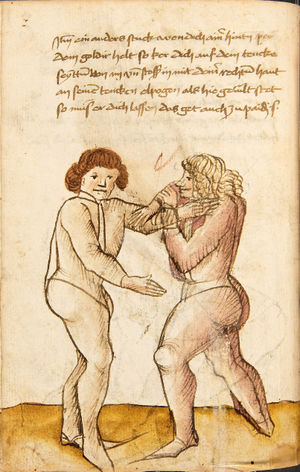
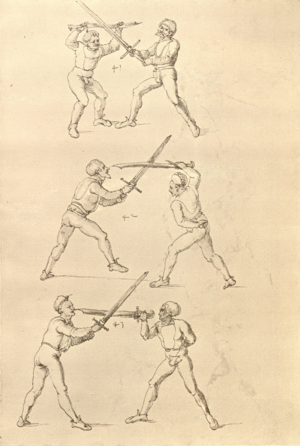
| [35v] Der Standt zum Ringen | ||||||
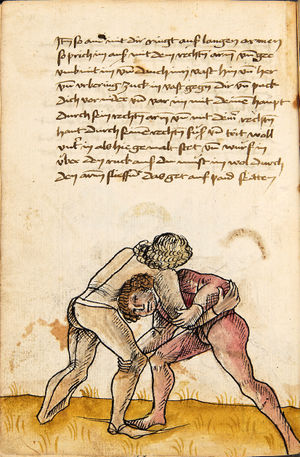
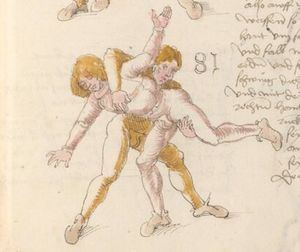
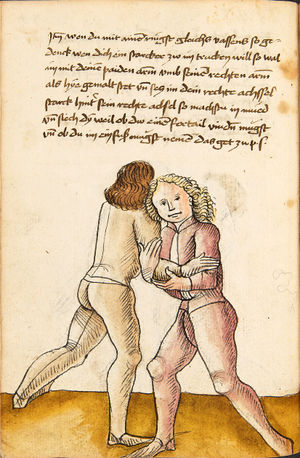
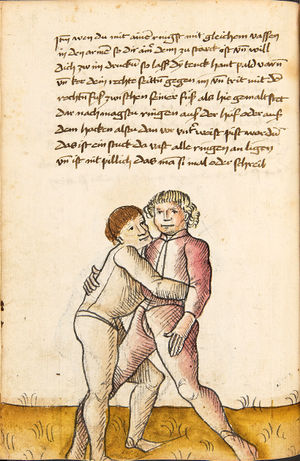
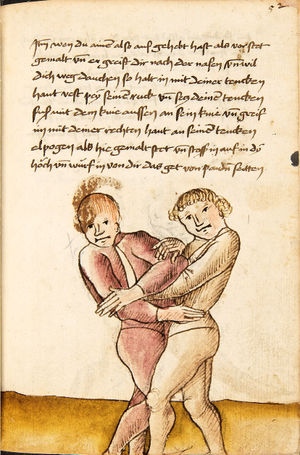
| daz erst stuck
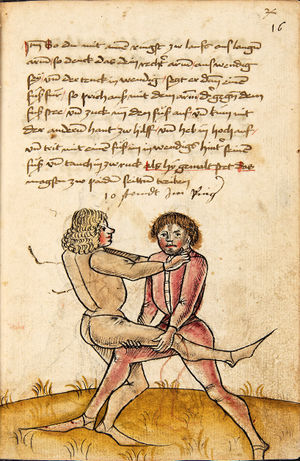
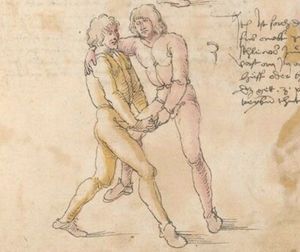
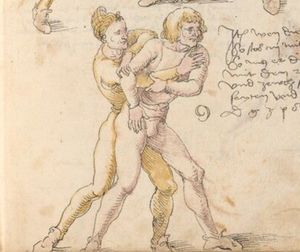
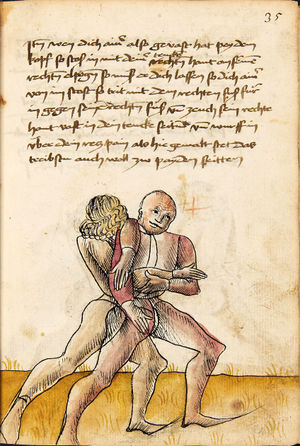
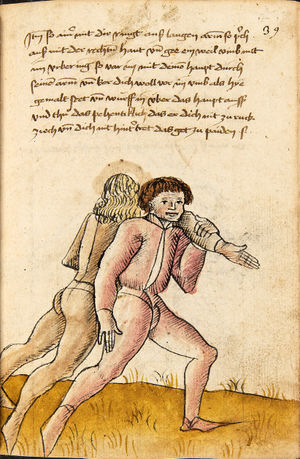
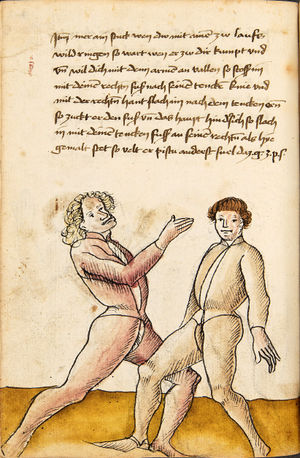
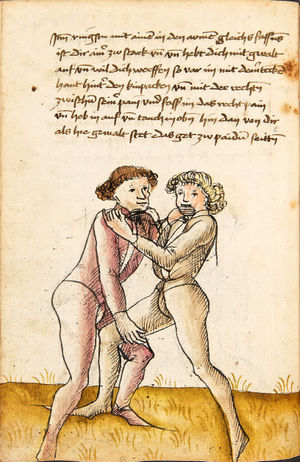
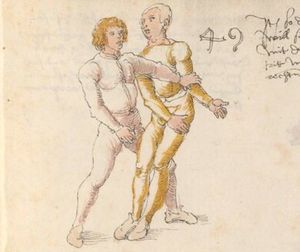
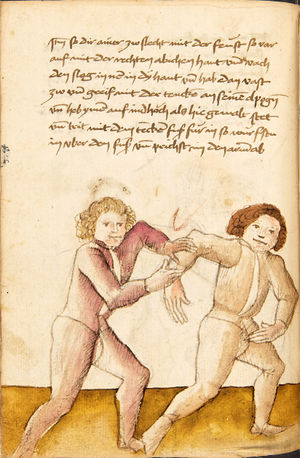
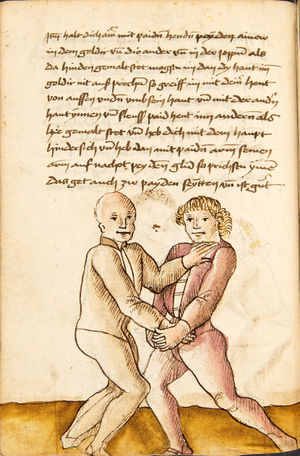
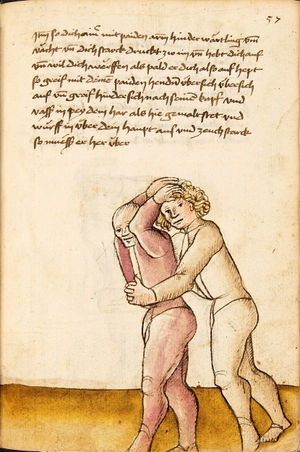
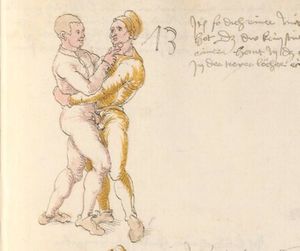
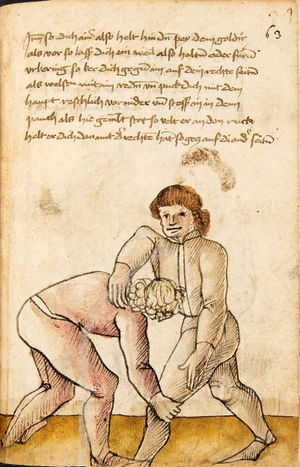
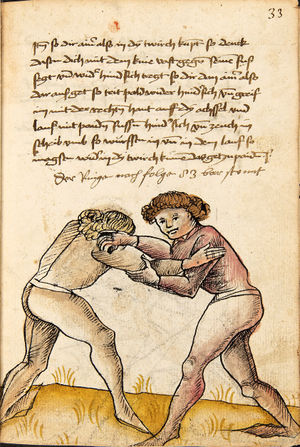
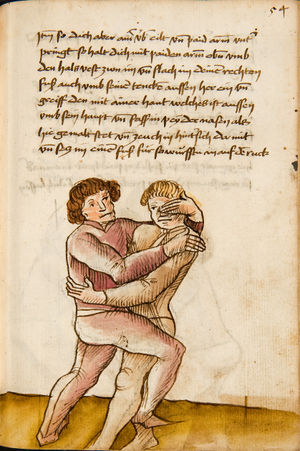
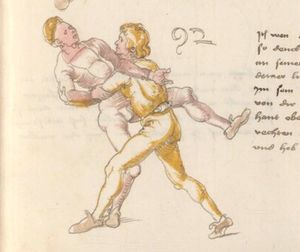
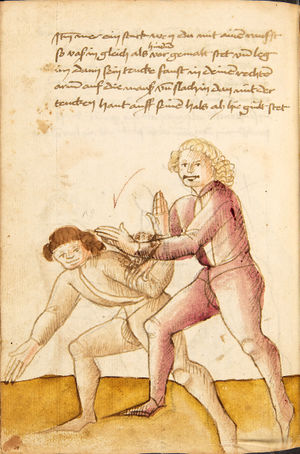
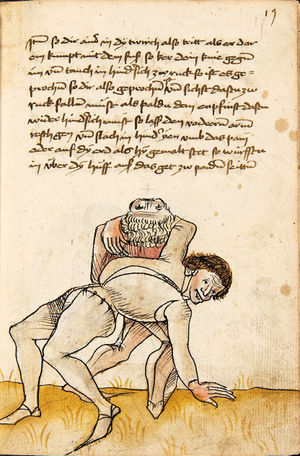
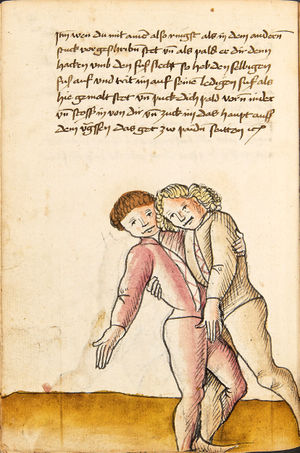
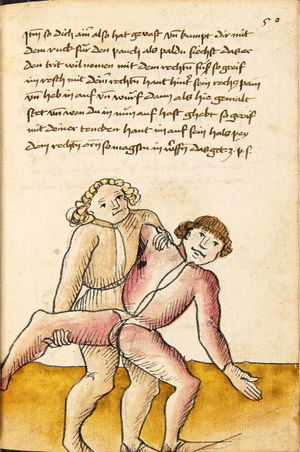
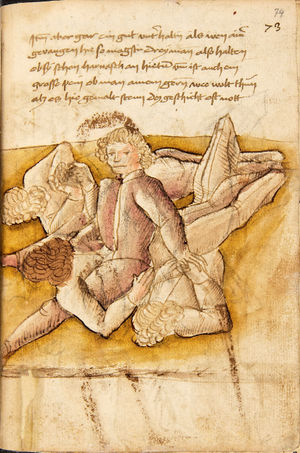
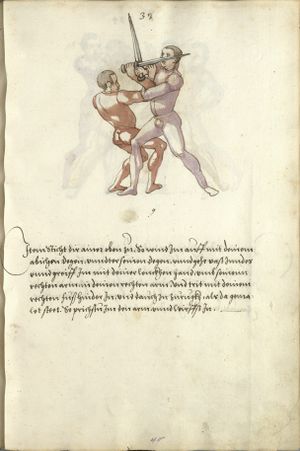
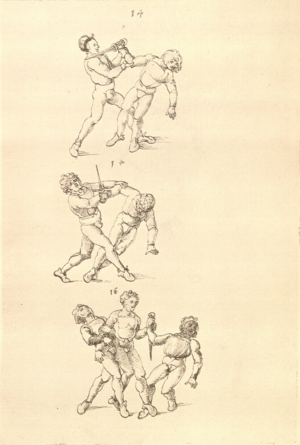
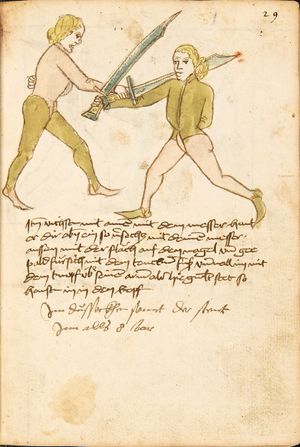
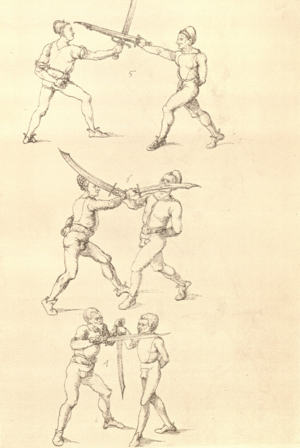
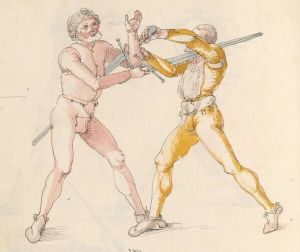
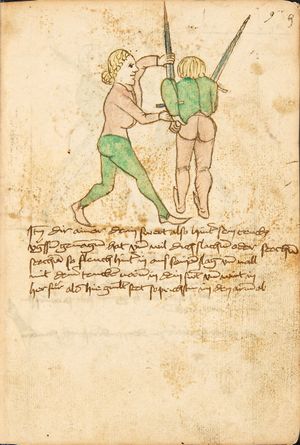
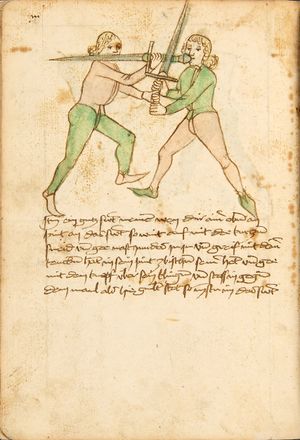
[16r] Item / So du mit ainem ringst zw laufen aus langen armen / so denck das dein rechter armm auswendig sey / vnd der tenck in wendig / seczt er dann einen füß für / so prich auß mit dem armm der gegen dem fuß stee vnd zuck im den füß auf vnd küm mit der anderen hant zw hilff vnd heb in hoch auf / vnd trit mit einem füß im inwendigs hinter seinen füß vnd tauch in zw ruck / als hy gemalt stet / Das magstu zw paiden seitten treiben Paulus Hector Mair's hand: 10 stenndt Im Ringen |
[13r-a] 1 Item so du mit einem ringst zu laus1 (Zulaufs) eins langen armen, do denck, daz dein rechter arm auswendig sei und der linck inwendig. Sezt er den einen fus für (vor), so prich aus2 mit dem arm, der gegen dem fus stett, und zuck im den fus auff und kum mit der ander[n] hand zu hielff und heb in hoch auff und trit mit einem fus im inwendig hinter sseine[n] fus und tauch in zurück, as (als) do gemolt stett. Daz gett zu peden Seiten. 1 Br. crossed out and corrected "zu Land". 2 Br. einem. |
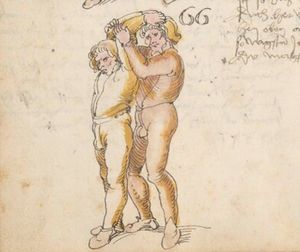
[21r] Nºr
Item so du mit ainem Ringest. in langen armen. so gedennck das dein rechter arm außwendig sey. vnnd der lenckh Innwendig. seczt Er den ainen fuß für. so prich jn auß mit dem arm. der Im gegen dem fuß ste. vnnd zuckh Im den fuß auff. vnnd kum mit der anndern hannd zuhilff. vnd heb jn hoch auff. vnnd trit Im mit einem fuß jnnwendigs hinder seinen fuß. vnd dauch[2] jn zurugkh. als da gemalet steet. Das geet zu baiden. wiltdu das prechen. so zuckh den fuß hindersich. 24 stenndt jm Ringen | ||||
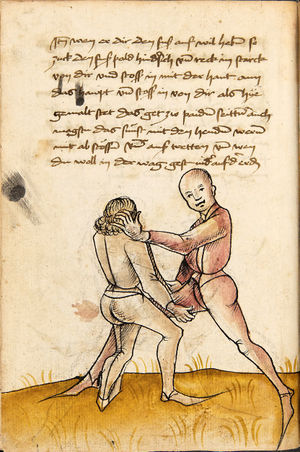
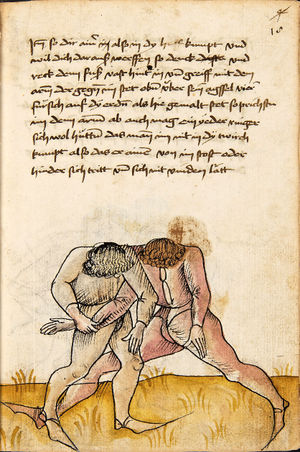
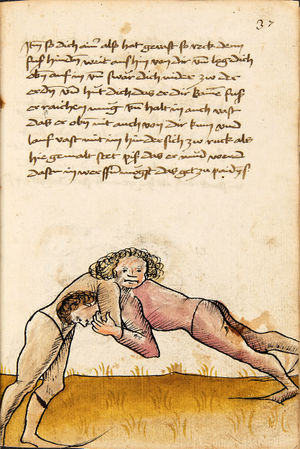
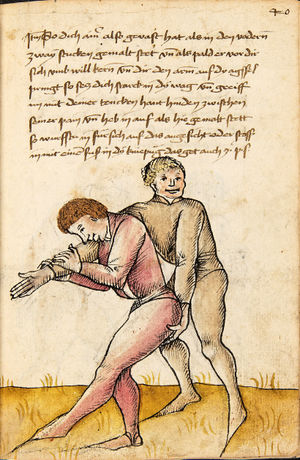
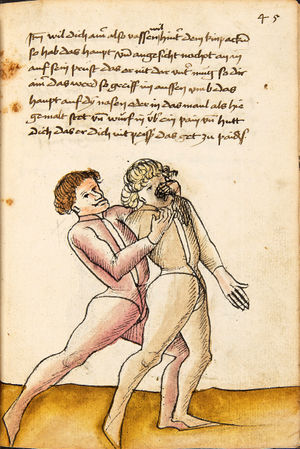
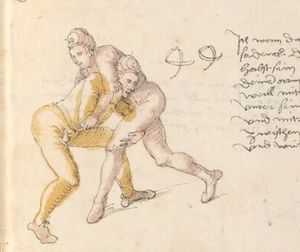
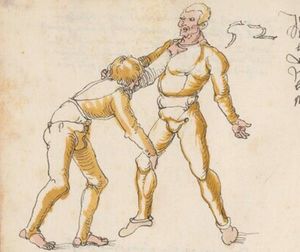
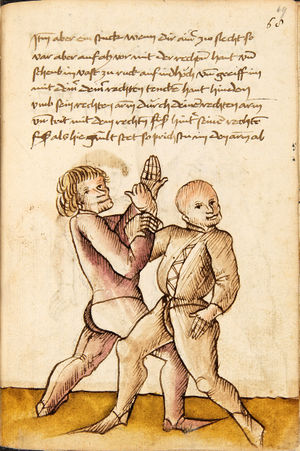
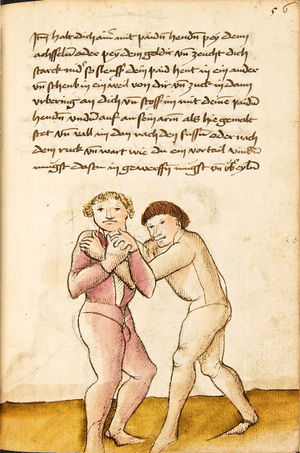
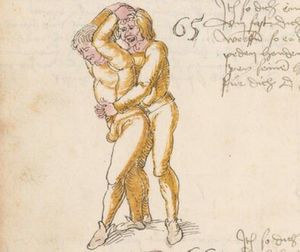
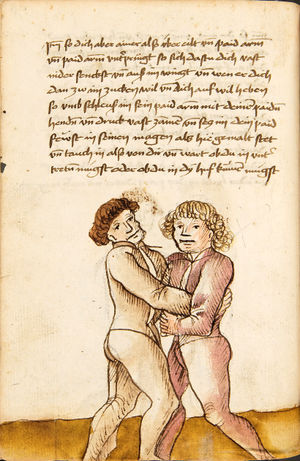
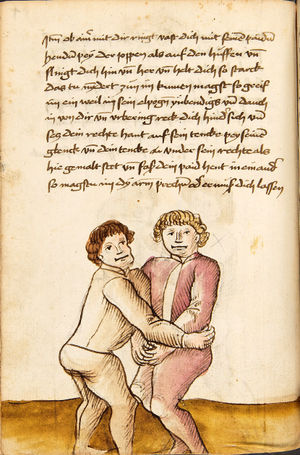
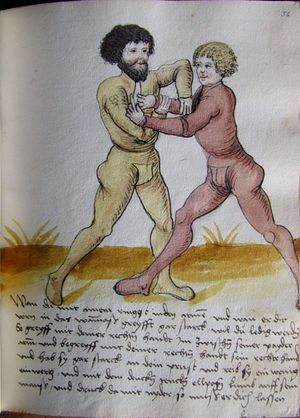
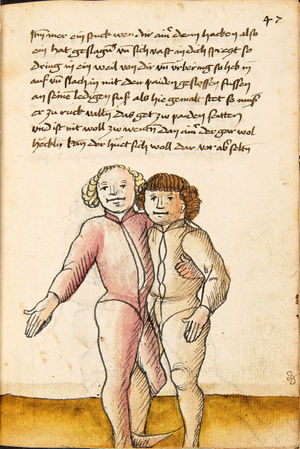
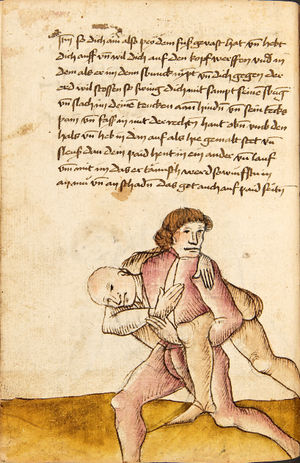
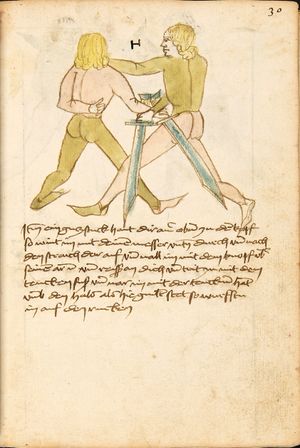
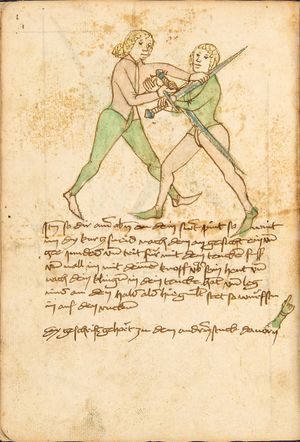
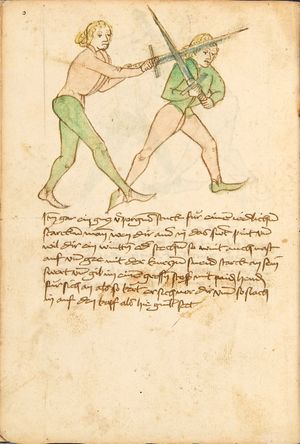
| [16v] Item wen er dir den fuß auf wil heben so zuck den fuß pald hindersich vnd reck im starck von dir vnd stosß in mit der hant ann das hawpt vnd stosß in von dir als hye gemalt stet das get zw paiden seitten auch magstu das sünst mit den henden weren mit ab stössen vnd auß tretten vnd wen du woll in der wag gest nider auf der erden | [13r-b] 2 Item wen er dir den vus (fuss) auff heben will, so czuck in hinder sich und streck in starck von dir und stos in mit der hand andaz (an das) haubt, in mos (maß) as (als) hie gemolt stett. D. g. z. p. S. (das geht zu beiden Seiten). — Auch magstu (magst du) das sunst wenden mit hant abstossen oder austretten und wen du woll in der wog (Wage) gerst (gehst) auf die erd. | |||||
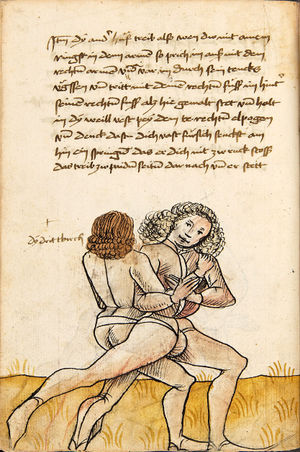
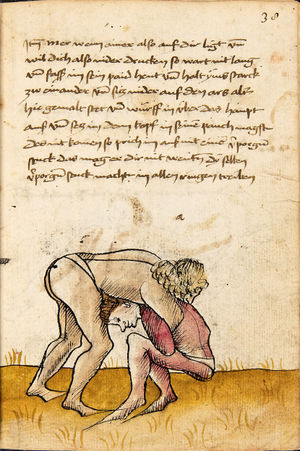
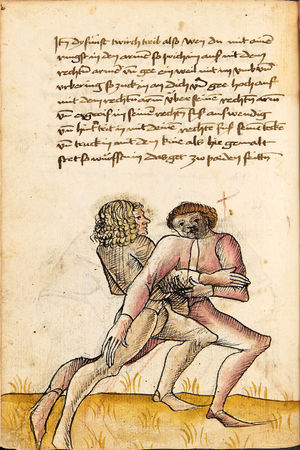
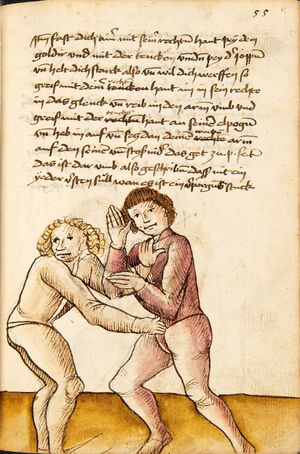
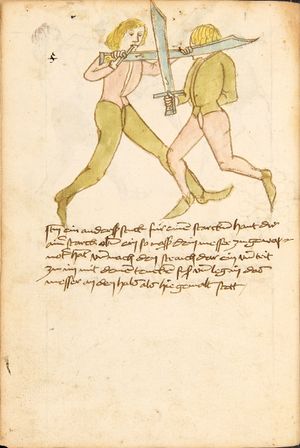
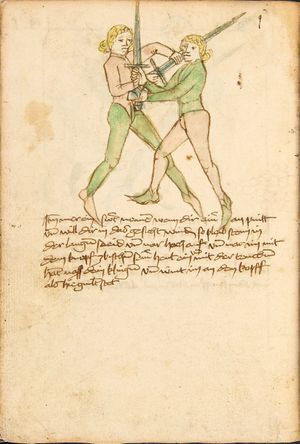
| [17r] Item ist sach das dich ainer über eilt vnd dir denn fuß auf zucht so wart dastu den fuß pald reckst vnd sleusß ymen zwischen seiner fusß vnd halt dich vast an in als hye gemalt stett also magstu woll in dy hüff kummen vnd in den hacken vnd magst in dar aus werffen das get auch zw paiden seitten vnd magst auch woll ein verporgens stuck treiben ob er not tüt | [13r-c] 3 Item ist sach1, daz dich einer ubereilt (übereilt) und dir den fus auffzuckt, so reck den vür (vor) pald und schleus imen (ihn) zwischen sein fus2 und halt dich vast (fest) an in, as (als) hie stett; also magstu (magst du) woll in die hüff oder hocken kumen, doraus zu werfen. Daz gett z. p. s. (zu beiden Seiten). Auch magstu ein verporgen stück treiben, thut es nott.
1Br. Sorg. 2Br. und stehe vor ihme zwischen sein fueß. |
|||||
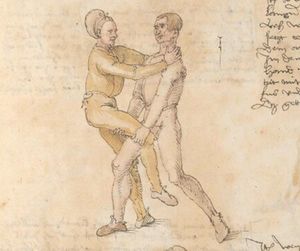
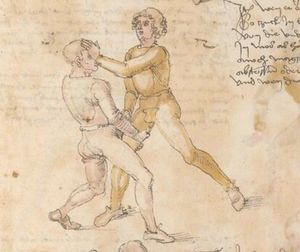
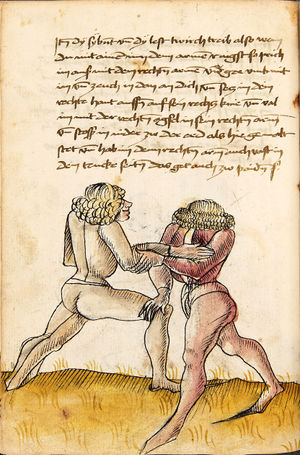
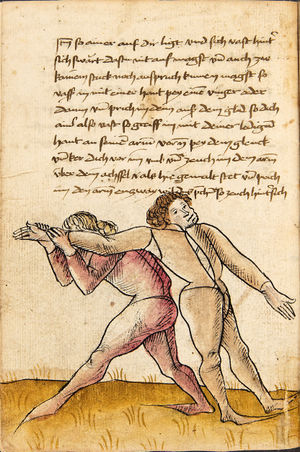
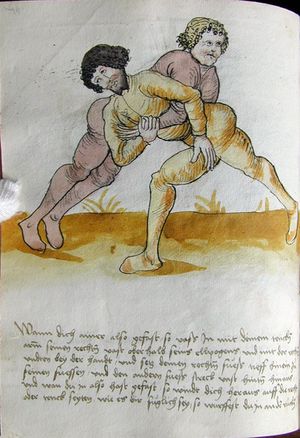
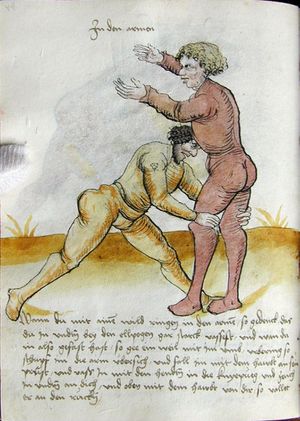
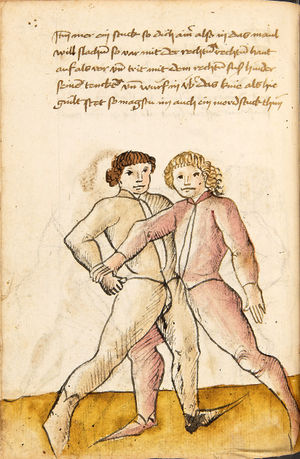
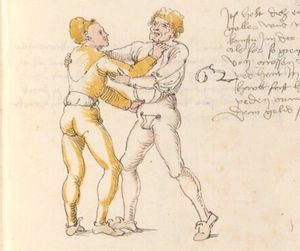
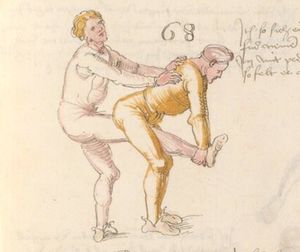
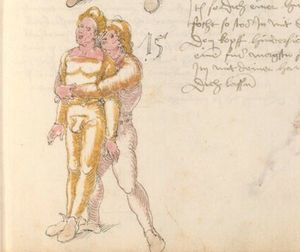
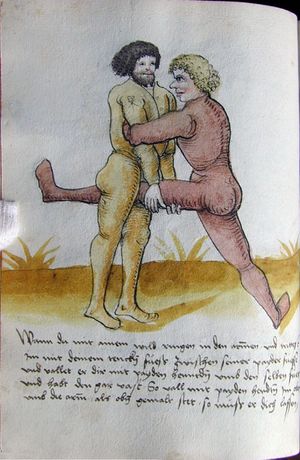
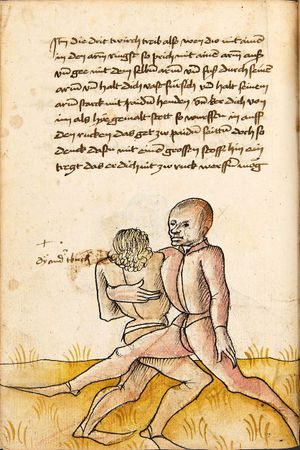
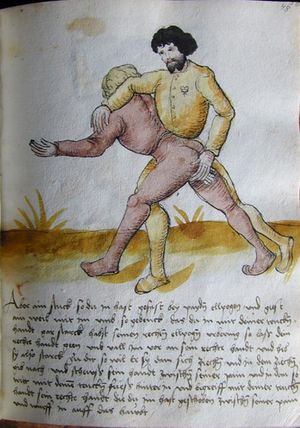
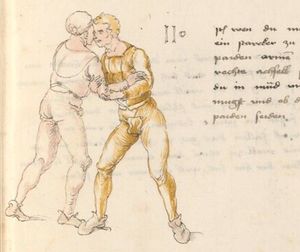
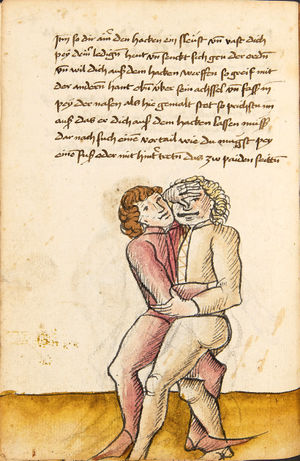
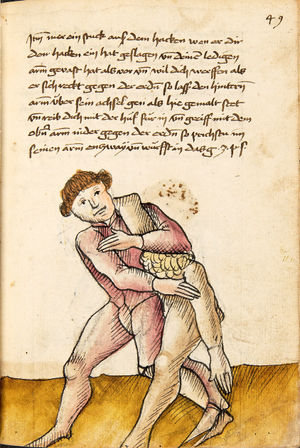
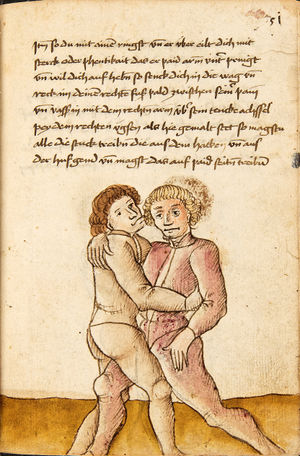
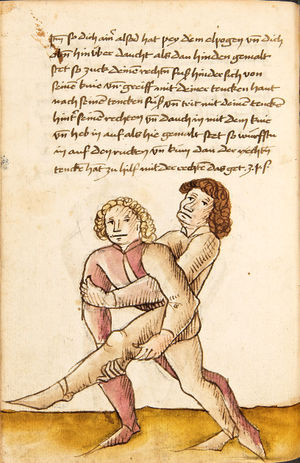
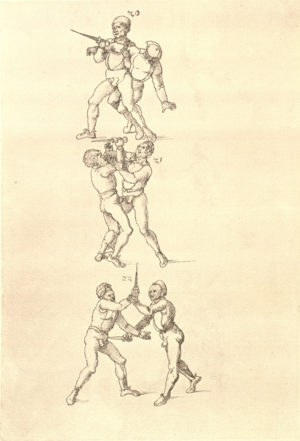
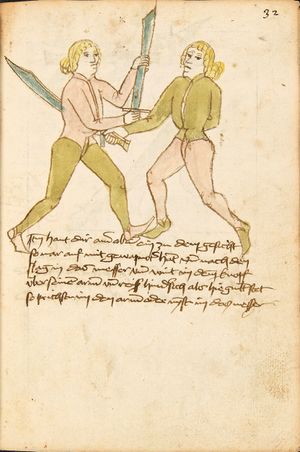
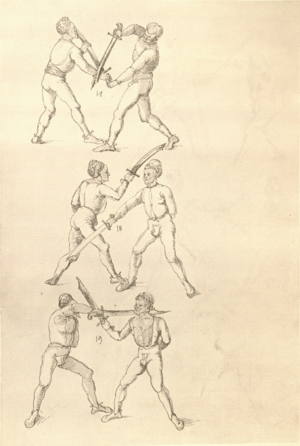
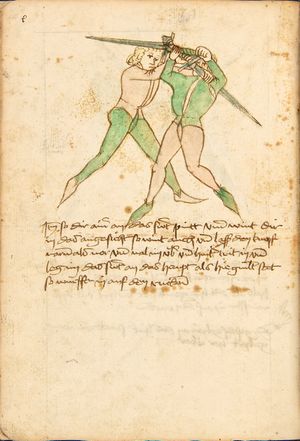
| [17v] Item ist sach dastu in denn armm mit ainem ringst so prich auß mit ainer hant vnd var im nach dem fuß alz du im auf welst zucken so zeucht er denn fuß hindersich vnd fleucht da in so gee dem fusß nach mit dem armm vnd trit mit deinez fuß hinder in in dy twirch alz hy gemalt stett Das get zw paiden seitten vnd ye nidrer du in der twirch stest ye stercker dw stenn magst wan dw tarfst anderst nit dann das knie vast piegen | [14r-a] 4 Item ist sach daz du ringst mit einem in langen armen, so prich aus mit einer hant und far (fahre) im nach eim fus, als (als wenn) du in auf wolst zucken, so zeucht er den fus hinder sich domitt zu flihen, so ge (geh) dem fus noch (nach) mit dem arm und trit mit deinem fus hinder im in die zwirch (Zwerchstellung), as (als) hie gemolt ist. D. g. zu p. s. (das geht zu beiden Seiten). Und nidrer (je niederer) in der zwirch stest (stehst), je sterker du sten (stehen) magst und darfst änderst nit den daz knie fast (fest) piegen. | [21v] 2 Item so du mit ainem Ringest. vnnd auß hast geprochen. vnnd wildt Im den fuß auff zuckhen. vnnd Er fleucht hindersich mit dem fuß. so gee dem fus nach mit dem arm. vnnd trit mitt deinem fuß hinder In. vnnd wirff In vber das knie. alls da gemalet steet. Das geet vonn baiden seitten. vnnd haist die erst tbirch.[3] ~ | ||||
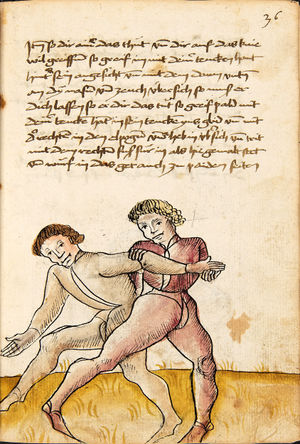
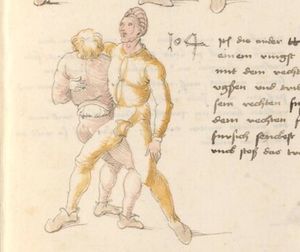
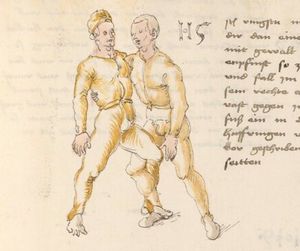
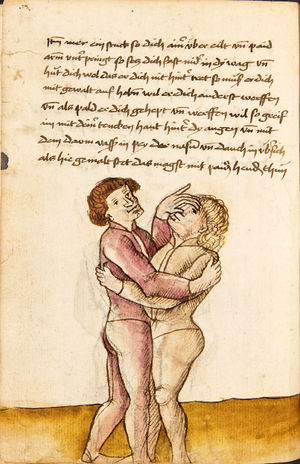
| [18r] Item so dir ainer in also in dy huff kumpt vnd wil dich dar auß werffen so denck dastu vnd reck denn fuß vast hinter in vnd greiff mit dem armm der gegen im stet oben über sein agssel vier fürsich auf dy erden als hie gemalt stet so prichstu im denn armm ab auch mag ein yeder ringer sich wol hütten das mann im nit in dy twirch kumpt also das er ainen von im stost oder hinder sich tritt vnd sich nit vinden lätt | [14r-b] 5 Item so dir einer also in die zwirch kumt und will dich doraus werfen, so reck den fus fast (fest) hinter sich, indes greif mit dem arm, der gegen im steet, oben über sein agsell vier für (vor) sich auf die erden, als hie stet, so prichstu (brichst du) im den arm ab. Auch mag ein jder (jeder) ringer sich woll hüten, daz man im nit in die zwirch kumt, also du magst in hinder sich oder von dir stossen las dich kein winden.1
Item die trit zwirch treib also: wen du mit einem in langen armen ringst, so prich mit einer hant aus und ge (geh) mit demselben arm und fus durch seinen arm starck mit peyden und ker (kehre) dich von im, als hie stett, so würstu (statt: wirfst du) in uf den rucken. D. g. z. p. s. (das geht zu beiden Seiten). 1Br. schreibt am Schlüsse ganz sinnlos bein windten. |
|||||
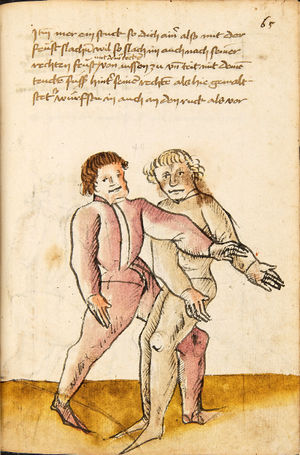
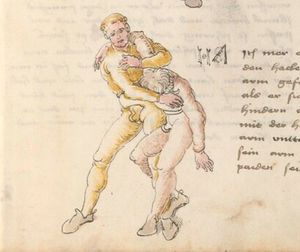
| [18v] Item dy ander hüf treib also wen dw mit ainem ringst in denn armen so prich im auß mit dem rechten armen vnd var im durch sein rn tencks ügssen vnd tritt mit deinem rechten füsß im hinter seinen rechten fusß alz hie gemalt stet vnd halt in dy weill vest pey dem te.rechten elpogen vnd denck dastu dich vast fürsich senckst am hin ein springen das er dich nit zw ruck stosß das treib zw paiden seiten dar nach vnd er stett | [14r-c] 6 Item aber (noch einmal) zu der tritten zwirch treibs also: wen. du mit einem ringst in langen armen, so prich im aus mit dem rechten arm und far (fahr) im unter sein lingke ügssen (Achsel) und trit mit deinem rechten füs hinder seinen rechten füs, als hie stett, und halt in fest pey seinen rechten elpogen (Ellbogen) und streck dich am einhin springen fast (fest) für (vor) sich, daz er dir den ruck (Rücken) nit ab gewin. Daz g. z. p. s., dornoch er stett. | [22v] 4 Item die drit tbirch. prich Im auß. vnnd gehe Im mit deiner rechten hand vnnd fuß. durch seinen rechten arm. so wirffstu In vber deinen fuß. alls da gemalet steet. vnd gehet zu baiden seitenn. ~ | ||||
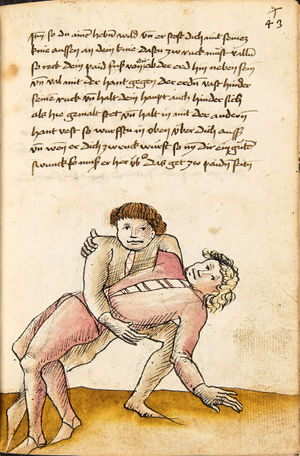
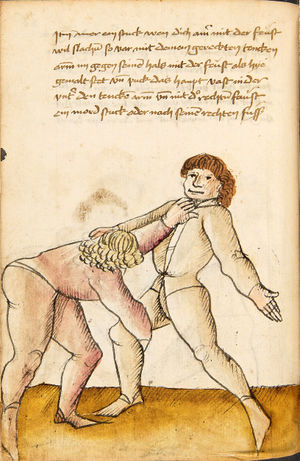
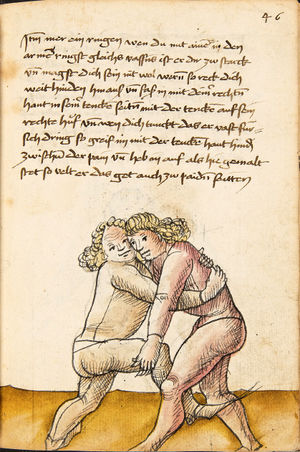
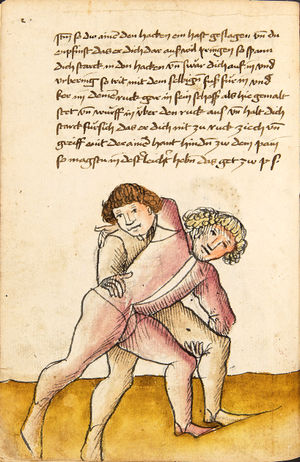
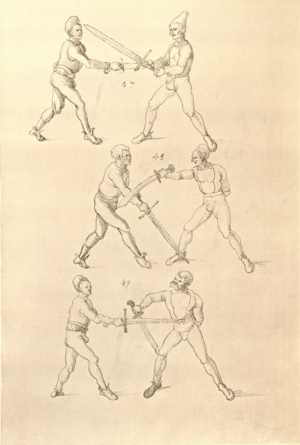
| [34r] Item so dir ainer also mit dem armen über wil vallen nach dem füss so secz dich in dy wag vnd druck in von dir mit denn armen so er dich dann also von im stost so greiff im mit der rechten hant auf seinen hals pey dem rechten oren vnd zeuch vast hintersich als hie ge malt stet vnd hütt dich das er dich nit hinter tret vnd das er dir mit dem haupt nit durchgee da get zu p.s. | [15r-a] 7 Item so dir einer also mit dem arm über will vallen (fallen) noch dein füs, so secz dich in die wog und dauch1 in von dir mit dem arm. So er dich dan (dann) also von im stest (stößt), so greif im mit der rechten hant auf den hals pei dem rechten arm und zeuch fast hinder sich, als hie gemalt stett. Und hüt dich, daz er dich nit hinter trett und daz er dir mit dem haubt nit durch ge (gehe). Daz g. zu p. s.
1Br. daweg. |
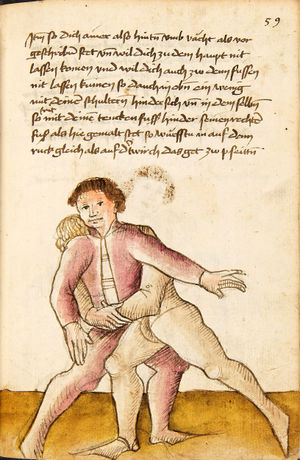
|||||
| [32r-a] 59 Item so dir einer mit den armen will uberfallen nach dem fuß, so sez dich in die wag und dauch in von dir mit den armen. So er dich dan also von im stost, so greiff im mit der rechten hant auf den hals pei dem rechten arm und zeuch fast hinder sich und hutt dich, das er dich nit hinder tret und das er dir mitt dem haupt nit durch ge. | ||||||
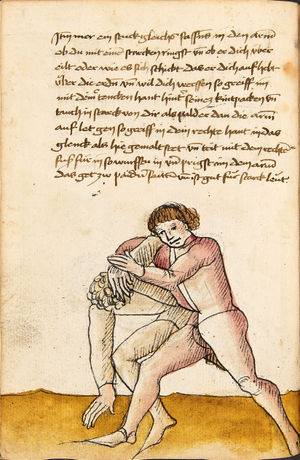
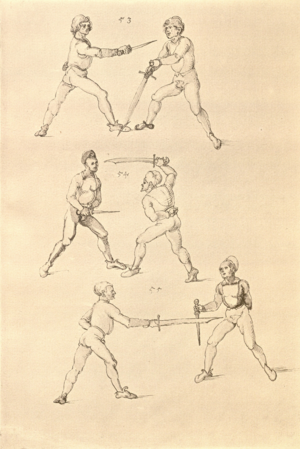
| [34v] Item dy segst twirch treib also wen du mit ainem ringst in den armen so prich im auß mit dem rechten armen und greif im urbering an daß recht or und trit mit dem rechten fuß hinter seinem tencken fuß alß hie gemalt stett so würfstu in gar hart aber du must im den rechten armen gar vast halten zu dir und tauch in zuruck daß get auch zu paiden s. | [15r-b] 8 Item die VI zwirch treib also: wen du mit einem ringst in armen, so prich im aus mit dem rechten arm und greif im über ruck an daz recht or (Ohr) und trit mit deinem rechten fus hinter seiner (statt seinem) lincken, als hie stett, so würfstu (wirfst du) in gar hart. Aber du must in gar hart pei dem rechten arm halten und dauch in zuruck. D. g. z. p. s. | [24v] 8 Item die sibennt tbirch prich auß. vnnd gehe vmb mit Ihm vrbäring. greiff Im mit deiner rechten hanndt. an seyn rechts or. vnnd trit Im mit deinem fuß. vnnd an seinen lennkchen. als da gemalet steet. vnnd dauch jn vonn dir. Das geet zu baiden seitten. ~ | ||||
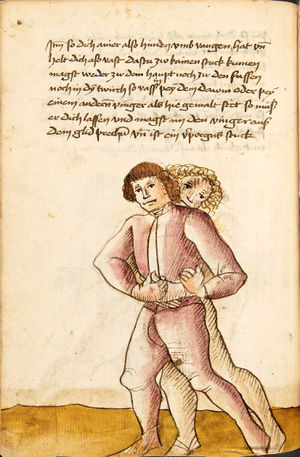
| [32r-b] 60 Item die sechst zwirch ist for geschriben im achten stuck. | ||||||
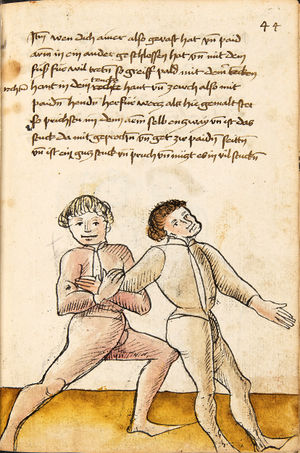
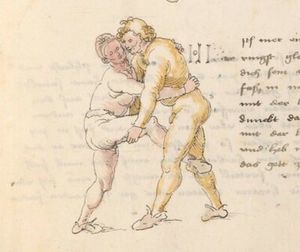
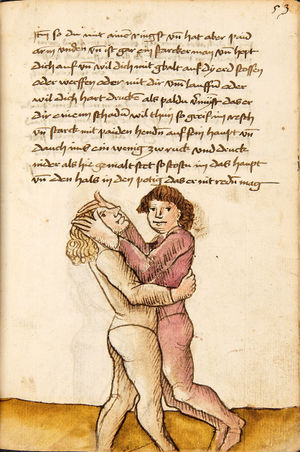
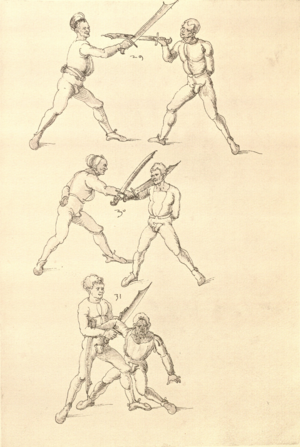
| [35r] Item wen dich ainer also gevast hat pey dem kopf so stoß in mit deiner tencken hant an seinem rechten elpogen so muß er dich lassen so dich ainer von im stost so trit mit dem rechten fuß für in gegen seiner rechten füß vnd zeuch sein rechte hant vast in dein tencke seiten vnd wurff in über dein recz pain als hie gemalt stet das treibstu auch woll zw paiden seitten | [15r-c] 9 Item wen dich einer also gefast hat pei dem kopf, so stos in mit deiner lincken hant an seinen elpogen; so mus er dich lassen. So dich einer von im stost, so trit mit dem rechten fus für (vor) in gegen seinen rechten und zeuch sein rechte hant vast (fest) in dein lincke seiten und würf in über dein rechtes pei[n] (Bein), als hie stett. D. g. z. p. s. | [25r] 9 Item hat dir ainer außgeprochen. vnnd will dir in ein tbirch geen. vnnden oder oben. so greiff Im mit deiner hanndt an seinen Elenbogen. vnnd stoß In von dir. wilt Er dir das wern. so halt In starckh bey seinem arm. vnnd trit für In. als da gemalet steet. | ||||
| [32r-c] 61 Item wen dich einer also hott pei dem kopff, so stos in mit deiner lincken hant an seinen elpogen, so mus er dich lassen. So dich einer stost von im, so trit mit dem rechten fus für (vor) in gegen seinen rechten fus und zeuch sein rechte hant fast in dein lincke seiten und wurff in über dein rechtes pein. D. g. z. p. s. | ||||||
| [35v] Item dy sybent vnd dy lest twirch treib also wenn du mit ainem inn denn armen ringst so prich im auß mit dem rechten armen vnd gee vmb mit im vnd zeuch in dan an dich vnd secz im dein rechte hant aussen auff sein rechcz knie vnd val im mit der rechten agsel in sein rechten armen vnd stosß in nider zw der erd als hie gemalt stet vnd hab im denn rechten armen auch vast in dein tencke seiten das get auch zw paiden seiten. | [16r-a] 10 Item die VII und die lezt zwirch treib also: wen du mit einem in den armen ringst, so prich im aus mit dem rechten arm und ge (geh) um mit im und zeuch in dan an dich und sez (setze) im dein rechte hant aussen auf sein rechtes knie und fall im mit der rechten achsel in sein rechten arm und stos in nieder zu der erden, als hie stett, und hab (halt) im den rechten arm vast in deine lincke Seiten. D. g. z. p. s. | |||||
| [36r] Item so dir ainer das thüt vnd dir auf das knie wil greiffen so greif im mit deiner tencken hant hinter sein angesicht vnd mit dem dawm vnten an dy nasen vnd zeuch übersich so muß er dich lassen so er dir das tüt so greif pald mit deiner tencken hant in sein tencken yns glid vnd mit der rechten in den elpogen vnd heb in übersich vnd trit mit dem rechten fuß für in als hie gemalt stet vnd würf in das get auch zw paiden seiten | [16r-b] 11 Item so dir einer daz thut und dir will uf daz knie greifen, so greif im mit deiner lincken hant hinter sein angesicht und mit dem daumen unten an die nasen und zeuch über sich, so mus er dich lassen. So er dir daz thut, so greif bald mit deiner lincken hant in sein lincke ins glid (Glied) und mit der rechten in den elpogen und heb in über sich und trit mit dem rechten fus für in, als hie stet. D. g. z. p. s. | |||||
[36v] Item so ainer mit dir ringt auß langen armen so prich im auß mit dem rechten armen vnd gee vmb mit im vnd dauch im vast hin vnd her vnd vrbering zuck in vast gegen dir vnd puck dich vor nider vnd var im mit deinem haupt durch sein rechten armen vnd mit deiner rechten hant durch seinen rechten füß vnd trit woll vnter in als hie gemalt stet vnd würf in über den ruck auf du müst im wol durch den armen fliessen das get auf paid seitten |
[16r-c] 12 Item so einer mit dir ringt aus langen armen, so prich im aus mit deinem rechten arm und ge um mit im und dauch in fast hin und her und über ring (plötzlich) zuck in fast gegen dir und puck (bücke) dich foreri (vorn) nider und far im mit deiner (statt: deinem) haubt durch seinen rechten arm und mit deiner rechten hant durch sein rechten fus und trit woll unter in, als hie stet, und wirf in über dein ruck (Rücken). Aber du must im woll durch sein arm schüfen (schlüpfen). Daz get z. p. S. |
[26r] 11 Item Ringestu mit ainem. vnnd Er will dich in kain tbirch kommen lassen. so prich Im auß. vnnd gehe ein weil vmb mit Im. ubaring zuckh In an dich. vnnd var Im mit deine(m) rechten arm. durch sein rechts pain. vnnd mit deinem haupt durch sein rechte vchsen. vnnd heb In auff. als da gemallet steet. Das gehet zu baiden seitten | ||||
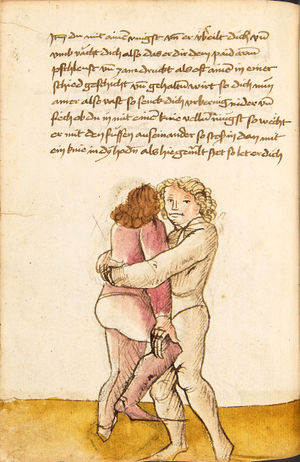
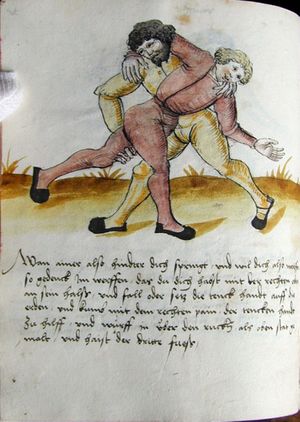
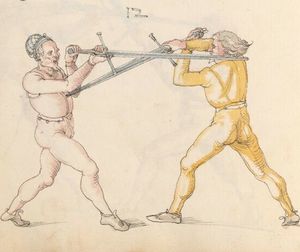
| [37r] Item so dich ainer also hat gevast so reck denn fuß hinden weit aus hin von dir vnd leg dich oben auf in vnd swär dich nider zw der erden vnd hüt dich das er dir kainen fuß er raichen müg vnd halt in auch vast das er oben nit auch von dir kum vnd lauf vast mit im hindersich zw ruck als hie gemalt stet piß das er müd werd dastu in werffen mögst das get zu paiden seiten. | [17r-a] 13 Item so dich einer also gefast hat, so reck ser (sehr) die füs hinder sich und leg dich oben uf in und sper dich nieder zu der erden und hüt dich, daz er dir keiner (!) fus erreichen müg und halt in fast, daz er oben nit von dir kün (könne), und lauf fast mit im hinder sich zu ruck, als hie stett, pis (bis) er müt (müde) würt (wird), so magstu in den (dann) werfen. Daz get z. p. s. | |||||
| [37v] Item so sich ainer also auf dich legt vnd sich hinden vast hin ausß spreiczt vnd dich hart druckt so thü als welstu im nach den füssen greiffen vnd nach dem rucken vnd swing in auch hin vnd her als vil du magst vnd vrbe- ring so vasßim sein paid hent zw ein ander vnd halt dy starck pey den elpogen oder sünst vnd sleuf dan mit dem haupt aus im vnd wint dich hinter im vmb als welst an den ruck vallen vnd streck dich als hie gemalt stet das get z.p.s. | [17r-b] 14 Item so sich einer also auf dich legt und sich fast (fest) hinder sich spert, dich fast zu trucken (drücken), so tu, as (als) wolstu (wolltest du) im noch dem fus greifen und noch dem rucken, und swing (schwing) in hin und her, als vill (viel) du magst, und uberring und vaß (faß) im sein ped (beide) hend zu einander und halt die starck pei den elpogen oder sunst im schlos dan mit dem haubt auff in und wind dich hinter im um, als wolst an ruck fallen, und streck dich, als hie stett. Daz gett zu peden sehen. | [25v] 10 Item so dich ainer also vbereylt. so reckh deinen fuß hinden weytt hinauß. vnnd leg dich schwer auff in pruch. so sich ainer also auff dich schwert. so faß Im baid hend zu: samen. vnnd wind dich auß Im. als wellest auff den Rugken fallen. als da gemalet steet. ~ | ||||
| [38r] Item mer wenn ainer also auf dir ligt vnd wil dich also nider drucken so wart nit lang vnd fasß im sein paid hent vnd halt yms starck zw einander vnd sicz nider auf den ars als hie gemalt stet vnd würff in über das haupt auß vnd secz im denn kopf in seinen pauch magstu des nit komen so prich im auß mit einem verporgen stuck das mag er dir nit wenten dy selben verporgen stuck machtu in allen ringen treiben | [17r-c] 15 Item wen einer also auf dir leit (liegt) und dich also nider trückt, so wart nit lang und fas im sein peid arm und halt ims (sie ihm) starck zu einander und siez (sitz) nider auf den ars, als hie stett, und wurf in über das haubt und setz im den kopf in sein pauch. Magstu des nit kumen, so prich im aus mit einem verporgnen stück. Das mag er dir nit wenden. Die selben verporgenen stück magstu in allen ringen treiben. | |||||
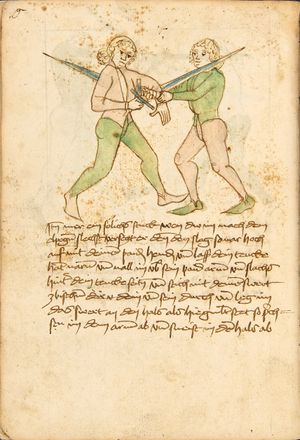
| [38v] Item so ainer auf dir ligt vnd sich vast hinter sich swärt dastu nit auf magst vnd auch zw kainem stuck noch auspruch kumen magst so vasß in mit einer hant pey einem vinger oder daum vnd prich im denn auß dem glid so dich ainer also vast so greiff im mit deiner ledigen hant an seinen armen voren pey dem glenck vnd ker dich vor im vmb vnd zeuch im den armen über dein achssel als hie gemalt stet vnd prich im den armen enczway wildus prechen so zeuch hintersich | [18r-a] 16 Item so einer auf dir ligt und sich fast hinter sich schwert, daz du nit auf magst und auch zu keinem stück noch pruch kumen magst, so fas (faß) in mit einer hant pey einem finger oder daumen und prich im den aus dem glid. So dich einer also fast (faßt), so greif in mit deiner ledigen hant an seinen arm foren (vorn) an das glenk oder pey dem glenck und ker (kehr) dich von im um und zeuch im den arm über die agsell, als hy stett, und prich im den arm entzwei; wiltus (willst du's) brechen, so zeuch hinder sich. | |||||
| [39r] Item so ainer mit dir ringt auß langen armen so prich auß mit der rechten hant vnd gee ein weil vmb mit im vrbering so var im mit deinem haupt durch seinen armen vnd ker dich woll vor im vmb als hye gemalt stet vnd würff in über das haupt ausß vnd thü das pehentiklich das er dich nit zu ruck ziechen vnd dich nit hinter tret das get zu paiden s. | [18r-b] 17 Item so einer mit dir ringt aus langen armen, so prich aus mit der rechten hant und ge ein weil mit im um, ubering so far im ein mit deinem haubt durch seinen arm und ker dich wol von im um, als hie stett, und würf in über daz haubt. Und du (tu) daz phendiglich (behendiglich), daz er dich nit zuruck zich und dich nit hinder trett. D. g. z. p. s. | |||||
| [39v] Item So du mit ainem ringst in langen armen so prich im auß mit deinem rechten armen vnd gee ein weil vmb mit im vnd zeuch in starck hin vnd her vnd vrbering so ker dich vor im vmb vnd zeuch im denn rechten armen auß dein rechte agssel vnd greiff zw mit deiner rechten hant im voren in das glenck als hie gemalt stett vnd würff in also das get auf paiden seitten | [18r-c] 18 Item so du mit einem ringst in langen armen, so prich im aus mit deinem rechten arm und ge einweil mit im um und geh mit im hin und her in schterck (Stärke) und übering so ker dich von im um und zeu (zeuch) im seinen rechten arm auff dein rechte agsel und greif zu mit deiner rechten hant im forn in daz glenck, als hy stett. Daz gett zu beden Seiten, also wurf in. | |||||
| [40r] Item So dich ainer also gevast hat als in den voderen zwayen stucken gemalt stet vnd als pald er vor dir sich vmb will keren vnd dir den armen auf dy agssel pringt so secz dich starck in dy wag vnd greiff im mit deiner tencken hant hinden zwischen seiner pain vnd heb in auf als hie gemalt stett so wurfstu in fürsich auf das angesicht oder stosß in mit einem fuß in dy kniepüg das get auch z.p.s. | [19r-a] 19 Item so dich einer also gefast hat, als in den vordern zweien ringen stett, und als pald er sich von dir kert und dir dein arm auf sein agsell pringt, sosez dich starck in die wag und greif im mit deiner lingken hand hinden zwischen sein pein und heb in auf (zu ergänzen: als) hie stett, so würfstu in für (vor) sich auf daz angesicht oder stos in mit eim fus in die knie püg (Kniebeuge). D. g. z. p. s. | |||||
| [40v] Item so du mit ainem ringst in langen armen so prich im auß mit deinem rechten arm vnd var zw stund damit an seinen rechten elpogen vnd fasß inn denn armen starck in dem paid hend vnd schlaipf dy hent paid her für an seinem armen pisß an das glenck vnd zuck in starck nach dir vnd ker dan dein tecke seitten gegen im an sein rechten elpogen als hye gemalt stet vnd prich im den arm das get.z.p.s. | [19r-b] 20 Item so du mit einem ringst in langen armen, so prich aus mit der rechten hant und far zu stunt (zur Stund) damit deinen arm in sein rechten elpogen und fas im den arm starck in dein peid hend und slaipf die hend ped herfür an seinen arm pis an das gelenk und zuck in starck an dich und ker den dein lingke seiten gegen im an sein rechte seiten an elpogen als hie stett, und prich im dem arm. D. g. zu p. s. | |||||
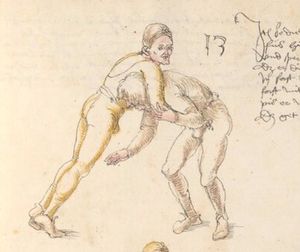
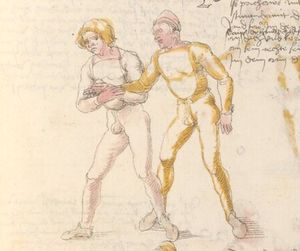
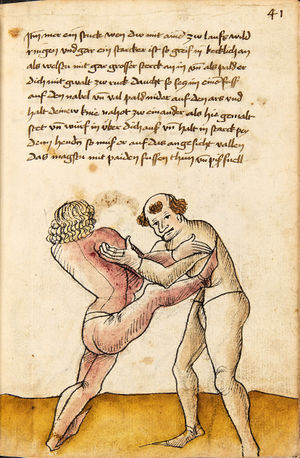
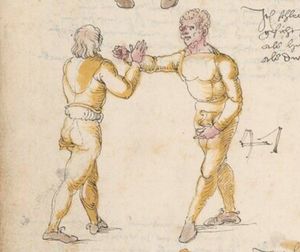
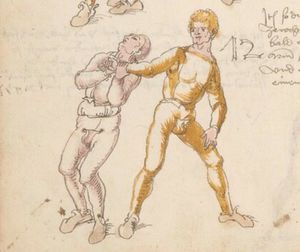
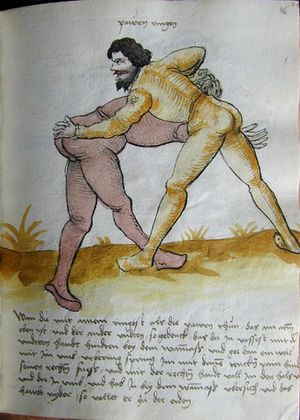
| [41r] Item mer ein stuck wen dw mit ainem zw laufs wild ringen vnd gar ein starcker ist so greif in kecklich an als welstu mit gar grosser sterck an in vnd als pald er dich mit gwalt zw ruck daucht so secz im einen fusß auf den nabel vnd val pald nider auf den ars vnd halt deinew knie nahot zw einander als hie gemalt stet vnd würf in über dich auß vnd halt in starck pey denn henden so muß er auf das angesicht vallen das magstu mit paiden fussen thun vnd piß snell | [19r-c] 21 Item wen du mit einem zu lauf wilt ringen, so er fast (sehr) starck ist, greif in kecklich an, als wölst mit grosser sterck mit im ringen, und als pald er dich mit sterck zuruck daucht, so sez im einen fus auf den pauch und fall bald nider auf den ars und halt deine knie zu einander und wirf in uber dich hinaus und halt in starck pei den henden, so mus er uff daz angesicht fallen. Daz gett zu peden seiten. | [23r] 5 Item so dir ainer in die tbirch trit. so peug das knie. oder trit hin: dersich. so dir ainer das erwert. so trit bald wider zurugkh. vnnd nymb Im den arm pruch. alls da gemalet steet. das gehet zu baiden seitten. | ||||
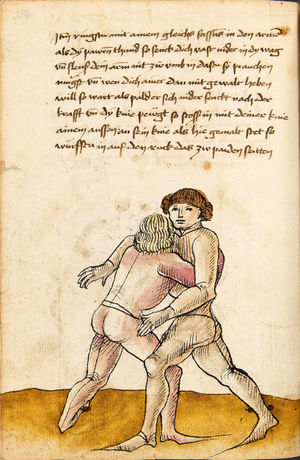
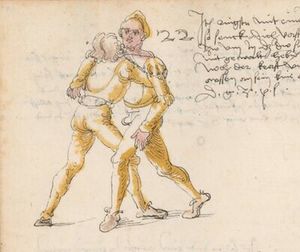
| [41v] Item ringstu mit ainem gleichs fassens in den armen als dy pawren thund so senck dich vast nider in dy wag vnd sleuß dein armen nit zw vmb in dastu sy prauchen mügst vnd wen dich ainer dann mit gewalt heben will so wart als pald er sich nider senckt nach der krafft vnd dy knye pewgt so stosß in mit deiner knie ainem aussen an sein knie als hie gemalt stet so würfstu in auf den ruck das zw paiden seitten | [20r-a] 22 Item ringstu mit einem gleichs fassens in den armen als die pauren, so senck dich vast (fest) nider in die wag und schleus dein arm nit zu um in, daz du sie prauchen mügst, und wen dich don (dann) einer mit gewalt heben will, so wart, as (als) bald er sich nider senkt noch der krast (verschrieben für: kraft) und die pein peugt, so stos in mit deinem knie aussen an sein knie, als hie stett, so wurfstu in auf den rucken. D. g. z. p. s. | [26v] 12 Item Ringestu mit ainem gleichs vassen. vnnd Er ist dir zu starckh. so wart. alspald Er dich heben will. Das du Ihm deine khnie aussen an sein knie seczt. so wirffstu Ine darüber. al da gemalet steet. Das gehet zu baiden seiten. | ||||
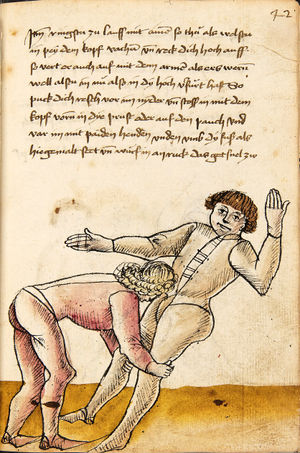
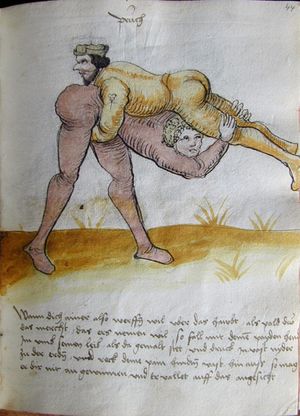
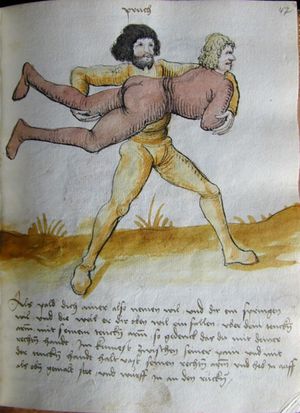
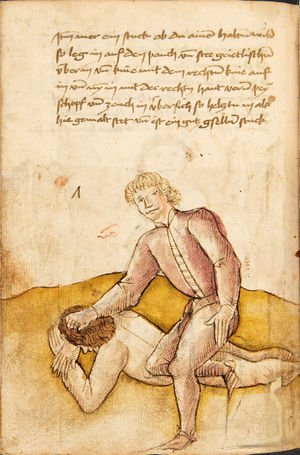
[42r] Item ringstu zu lauss mit ainem so thü als welstu in pey dem kopf vachen vnd reck dich hoch auff so vert er auch auf mit dem armen als ers weren woll alstu in nü also in dy hoch verfürt hast So puck dich resch vor im nyder vnd stosß in mit dem kopf voren in dye prust oder auf den pauch vnd var im mit paiden henden vnden vmb dy fuß als hie gemalt stet vnd würf in an ruck das get snel zw |
[43v] In den armen
Wann du mit aine~ wild ringen in den arme~ / so gedenck / das du in vndtñ beÿ den ellpogen gar starck vassest / vnd wan du in also gefast hast / so gee ein weil mit im vmb / vrbering so schupf im die arm vbersich / vnd fall im mit dem hawbt an sein prust / vnd vaß In mit den hendtñ in die knyepu~eg / vnd zeuch in vndtñ an dich / vnd oben mit dem hawbt von dir / so vallet er an den ru~ckñ / |
[20r-b] 23 Item ringstu zu laufs mit einem, so tu, als wolstu in pei dem kopf fassen, und reck dich hoch auf, so fert (fährt) er auch auf mit dem arm, als woll ers weren (wehren); und so du in in die hoch verfürst (verführst), puck (bück) dich resch von im nider und stoß in mit dem kopf foren (vorn) an die prust oder pauch und far im mit peden henden unden die füs, als hie stett, und wirf in auf den rucken. Daz gett zu peden sehen. |
[32v] 24 Item Ringestu mit ainem gar starcken. vnnd magst jme nit ausprechen. so stoß Jm die arm mit den [p]ern[4] stossen ab. vnnd lauff Im mit dem kopff in den pauch. vnd mit baiden armen vmb die kniepug. als da gemalet steet. so stossestu In auff den Rugken. wilt du das prechen. so wart wann Er sich puckht. vnnd will dich stossen. so stoß In mit deinem knie vnnder das maull.
[In another hand] Enndt der Ringen | |||
| [42v] Item mer ain stuck wen dw mit ainem zw laufs wild ringen so wart wen er zw dir kunpt vnd vnd wil dich mit denn armen an vallen so stosß im mit deinem rechten fuß nach seinem rechten knie vnd mit der rechten hant slach im nach dem tencken armen so zuckt er den fuß vnd das haupt hindersich so slach in mit deinem tencken fusß an seinen rechten als hye gemalt stet so velt er pistu anderst snel daz.get.zu.paiden.seiten. | [20r-c] 24 Item ringstu mit einem zu laufs, so wart, wen er zu dir kumt und will dich mit den armen an fallen, so stos im noch (nach) seinem lingen knie mit deinem rechten fus und mit deiner rechten hant schlach (schlag) im noch seinen lingken arm, so zeuchts er den fus und daz haubt hinder sich, so schlag in mit deinem lincken fus an sein rechten, als hie stett, so velt (fällt) er, pistu (bist du) änderst schnell. D.g. z.p.s. | |||||
| [43r] Item so du ainen heben wild vnd er stost dich mit seinez knie aussen an dein knie dastu zw ruck müst vallen so reck dein paid fuß von dir ob der erd hin neben sein vnd val mit der hant gegen der erden vast hinder seinen ruck vnd halt dein haupt auch hinder sich als hie gemalt stet vnd halt in mit der anderen hant vest so wurfstu in oben über dich ausß vnd wenn er dich zw ruck würft so nym dir ein güten swunck so muß er her über das get zw paiden seitn | [21r-a] 25 Item so du einen heben willt und stost dich mit seinem knie aussen an dein knie, daz du zurück must fallen, so streck dein peid füs von dir ob der erd hin neben sein und fall mit der hant gegen der erd fast hinder seinen ruck und halt dein haubt auch hinder sich, als hie ste[tt] , und halt in mit der andern hant fast, so würfstu in oben über dich aus. Und wenn er dich zu ruck wirst (statt: wirft), so nim dir einen guten schwung, so mus er her. Daz g. z. [p. s.]. | |||||
| [43v] Item mer ein stuck gleichs fassens in den armen ob du mit einem starcken ringst vnd ob er dich vber eilt oder wie es sich schickt das er dich auf hebt über die erden vnd wil dich werffen so greiff im mit deiner tencken hant hinter seinez kinhpacken vnd tauch in starck von dir als pald er dan die armen auf let gen so griff in dein rechte hant indas glenck als hie gemalt stet vnd trit mit dem rechten fuß für in so wurfstu in vnd prigst im dem armen das get zw paiden seitten vnd ist gut für starck leüt | [21r-b] 26 Item ein stück gleich fassens in den armen. Ringstu mit einem starcken und er dich übereilt oder wie es sich schickt, daz er dich auf hebt über die erden und will dich werfen, so greif im mit deiner lincken hant hinter sein kinpacken (Kinnbacken) und dauch in starck von dir. Als bald er den die arm auf gest (statt: lässt) gen,1 so greif in dein rechte hant in daz glenck, als hie stett, und trit mit dem rechten füs für in, so wurffstu in und, wiltu (willst du), so prichstu in den arm. D. g. z. p. s.
1Br. so bald er die arm aufhebt. |
|||||
| [44r] Item wen dich ainer also gevast hat vnd paid armen in ein ander geschlossen hat vnd mit dem füß für wil treten so greiff pald mit deiner tencken rechten hant in dein tencke hant vnd zeuch also mit paiden henden herfür wercz als hie gemalt stet so prichstu im denn armen selb enczway vnd ist das stuck da mit geprochen vnd get zw paiden seitten vnd ist ein gucz stuck vnd prüch vnd nüczt es in vil stucken | [21r-c] 27 Item wen dich einer also gefast hat und ped arm in einander geschlossen und mit dem fus für will tretten, so greif bald mit deiner rechten hant in dein linck hant und zeuch also mit peden henden herfür, als hie stett, so prichstu in den arm entzwey und ist daz forder stück mit prochen (gebrochen). Daz g. z. p. s. | |||||
| [44v] Item ringstu mit ainem in den armen gleichs fassens ist dir ainer zw starck vnd vnd hebt dich mit gwalt auf vnd wil dich werffen so var im mit deiner tencken hant hinter den kinpacken vnd mit der rechten zwischen seiner pain vnd fasß im das recht pain vnd heb in auf vnd tauch in oben hin dan von dir als hie gemalt stet das get zw paiden seitten | [22r-a] 28 Item ringst mit einem in den armen gelichs (gleichen) vassens (fassens), ist dir einer zu starck und hebt dich mit gewalt auf und will dich werfen, so far im mit deiner lincken hant hinder den kinpacken und mit der rechten zwischen sein pein und faß im daz recht pein und heb in auf und dauch in oben hinder sich von dir, als hie stett. Daz gett zu peden sehen. | |||||
| [45r] Item wil dich ainer also vassen wil hinter dem kinpacken so hab das haupt vnd angesicht nachot an in auf sein prüst das er nit dar vnter müg so dir ainer das werd so greiff im aussen vmb das haupt auf dy nasen oder in das maul als hie gemalt stet vnd würf in über ein pain vnd hutt dich das er dich nit peisß das get zu paiden seiten. | [22r-b] 29 Item will dich einer hinder dem kinpacken, so hab (halte) daz haubt nohent (nahe) an in auf sein prust, daz er nit dorunder (darunter) müg. So er dirs werts (wehrt), so greif im aussen um daz haupt auf die nasen oder in das maull, als hie stett, und wirf in über dein pein und hüt dich, daz er dich nit peis (beisse). Daz g. z. p. s. | |||||
| [44r] Pru~ch
Wann dich ainer also werffñ wil vber das hawbt / als pald dw° das merckst / das ers nemen wil / so fall mit deine~ payden hend[tñ] Im vmb seinen leib / als da gemalt stet / vnd druck in vast nÿder zu der erdñ / vnd reck deine pain hindtñ vast hin auß / so mag er dir nit an gewinnen / vnd Er vallet auff das angesicht |
[22r-c] 30 Item ein pruch über daz, so dich einer über den kopf will werfen. Als bald du entpfindest, daz ers nimt, so vall (fall) im mit peden henden um den leib, als hie stett, und zück in gar fast nider zu der erd und reck dich vast hinden aus, so mag er dir nit abgewinen. |
|||||
| [44v] Wann dich ainer also gefast / so vaß In mit deinem tenckñ arm~ seinen rechtñ vast oberhalb seins ellpogens / vnd mit der rechtñ vndten beÿ der handt / vnd setz deinen rechtñ fueß tieff hinein zu seinen fuessen / vnd den andern fueß streck vast hintñ hinaus / vnd wan du in also hast gefast / so windt dich heraus auff die recht oder tenck seÿten / wie es die fuglich sey / so wurffest du in an de~ rückñ / | [23r-a] 31 Item wen dich einer also hat gefast mit peden henden um den leib und truckt dich nider zu der erden, so fas mit deinem lincken arm seinen rechten fast1 oberhalb seines elpogen und mit der rechten unden pey der hand und sez deinen rechten fus tieff hinein zu seinem füs und den andern reck flux hinder sich hnaus (hinaus). Und wen du in also hest gefast, so wind dich auf dein rechte seiten heraus, als ob du an den ruck wollest fallen, so wurstu (statt: würfstu) in. D.g. zu p.s.
1Br. seine rechte faust. |
|||||
| [45r] Wann du mit ainem wild ringen / so gedenck das du mit deiner tenckñ handt / begreiffest sein tencke bey dem ellpogen / vnd wan du in also gefast hast / so hab in gar starck / vrbering / so zuck in an dich / vnd setz den rechtñ fueß hinter in / vnd stoß In mit deinem rechtñ ellpogen oben auff die prust / so vallet er vber das pain / | [23r-b] 32 Item so du mit einem ringst, so ergreif mit deiner linken hant sein linge (linke) pei seinen elpogen, und wen du in also hast gefast, so halt in starck und ge ein weill mit im um, urbring so spring mit deinem rechten füs tief hinder seinen lingen und1 mit dem rechten arm stos in sein linge prust, so felt er über daz recht pein.
1Br. umb. |
|||||
| [45v] pru~ch
Als pald ainer das vorgeschriben stuck treiben wil / vnd wil dich in die prust stossen mit dem selben ellpogen / so gedenck das du in begreiffest beÿ dem rechtñ arm~ / vnd ker dich vmb als oben gemalt stet / so prichst du im den arm~ ab / wil du gerñ / |
[23r-c] 33 Item den pruch über daz stück. Als pald er daz stück nemen bill (will) und will dich in die prust stossen mit seiner rechten hand oder mit dem elpogen, also bald begreiff im seine[n] rechten arm und heb in über dein lincke agsell, doch daz du in habst mit deiner rechten hant vornen pei den glenck und mit der anderen pey seinem elpogen und inI, wo du wilt, oder prich im den arm ab.1 1Br. den gar ab |
|||||
| [38r] Pruch
Wann dich ainer also werffen wil / auß dem drittem fueß / so gedenck / das du im den tenckñ fueß nit lassest / als oben stat gemalt / vnd heb In hoch auff / vnd tritt hintersich / vnd leg zu an den ruckñ / so prichst du im den trittñ fueß / |
[24r-a] 34 Item ein anders stück über daz, wen dich einer hat also gefast und will den trutten fues (Trudenfuß) machen. Als pald du sein entpfindzt (empfindest), das ern (er ihn) nemen will, so las in nit zu der erden und heb in hoch auf und würf in auf den ruck und gee fast ersling1 (ärschling) und las im sein lincken fues nit zu seinem (!) rechten hant kumen und hab in gar fast, so ist das stück ganz. D. g. z. p. s. 1Br. erstling. |
|||||
| [38v] Wan zwen gleich mit einander gefasset haben in den arme~ so gedenck das du mit deine~ dencken arme~ oben vber seinen rechtñ arm einwindest / vndter sein rechte achsl / vnd die faust deiner denckñ handt oben auff der achsel lig in dem gelõß vnd der ellpogen vndtersich ston / vnd setz Im dein denck knÿe innen an sein recht knÿe / vnd dein tenckñ fueß / setz im aussen an sein rechtñ fueß / vnd druck in von oben herab / so vallet er / doch so kumb mit der rechtñ handt der tenckñ zu hilff also oben stat gemalt / vnd druck in zu der erdñ auff das angesicht / so vallet er / | [24r-b] 35 Item den schwunck.1 Wenn du mit einem wilt ringen in den armen, so gedenck, daz du in mit deinem linck arm seinen rechten ausprechst und mit dem ausprechen wind im hin ein mit deiner lincken hant auf sein rechte agsell und stand ein wyll (Weil) vor im schill (still); urbering so kum mit deiner rechten hand deiner lincken zu hilf forn pey dem glenck und spring mit deinem lincken pein hinder sein rechtes pein und trey (drehe) in flux noch (nach) dem zirkel, so wirstu (wirfstu) in auf den rucken. D. g. z. p. s.
1Br. Zwanckh. |
|||||
| [39r] Wan dich ainer also gefasset hat / vnd wil dich werffen / als das vorder stuck gesagt hat / so merck wan er dir hat eingewunden / vnd wil mit der rechtñ der tenckñ zu hilff kumeñ / so gedenck das mit der tenckñ handt im kumest an sein rechtñ ellpogen / vnd spring mit deinem tencken fueß / fu~r sein rechtñ fueß / vnd hab im mit der rechtñ handt sein tenckñ arm~ / vnd wurff in vbe° den fueß / oder vber die hu~ff / | [24r-c] 36 Item den pruch über daz stück. Wen du mit einem ringst in den armen, alß vor (vorher) geschriben stett, als bald er dir einwint und mit seiner rechten hand der lincken zu hilf will kumen, so fall mit deiner lincken hant an seinen rechten elpogen und spring mit deinen (!) lincken pein tieff hinder sein füs und wurf in über die hüff, oder tu also: wen er den schwung will machen, so spring im bald ein in die hüff und würf in darüber. | |||||
| [39v] Wen zwen gleich mit einander gefasset haben / wie vor auch stet geschribñ / so gedenck das du mit deine~ tenckñ arm~ obñ vber seinen rechtñ arm~ einwindest / vndter sein rechte achsl vnd die faust oben auff der achsel lig in dem gele~ß / vnd der ellpogen vndtersich stee / vnd setz dein tenckñ fueß zwischen seiner pain / vnd setz dein tencks knye Im auff seine~ tenckñ wadl / vnd kumb mit deine~ rechtñ arm~ od~ handt der tenckñ zehilff / vnd druck vast vndtersich zu d~ erdñ iñdes gleichñ mit dem knye / als obñ stat gemalt / so vallet er / | [25r-a] 37 Item aber ein stuck. Wen du in hast also in dem schwung und in also um trest (umdrehst), so hab in gar fast und truck in zu der erden mit deinem lincken arm und mit dem rechten und schreit zwischen sein pein mit deinem lingen vorn hinein und sez inen (ihn) vorn hinder seinen rechten fus und an den enckell und fall mit deinem lingen knie im inwendig in sein knie, so feit (fällt) er an den ruck oder spring im ein und nim die d hüff. | [27r] (Similar) 13 Item Ringestu gleichs vassens. vnnd ainer ist dir zue starckh. vnnd zuckht dich auff von der erden. so greiff Im bald mit deinem obern arm vnnden an seinen halß. vnnd dauch In von dir. vnnd faß dein baid hennd zusamen. vnnd zeuch Ine herfür. vnnd trit für mit einem fuß. so würffestu In. vnnd prichest Im den arm. als da gemalet steet. das gehet zu baiden seitten | ||||
| [40r] Wann du In nu also hast gefasset / vnd in also nÿder pringest zu der erden / als das vorder stuck sagt / wolt es dir aber nit gei~en geen / so spring Im mit der hu~ff ein / vnd wurff In vber die hu~ff :. | [25r-b] 38 Item aber ein stück, das heist die hüstI. Wen du mit einem ringst, als die pauern thun, das (daß) ein arm unden ligt und der ander oben, so gedengk, daz dein lincker arm unden seinem rechten lig und dein rechter ob seinen lincken und ge mit im ein weill um und urwering so spring mit deinem lingken pein vor im um für (vor) seinen kinken (linken), doch daz in (ihm) dein ars in sein schoß kum, und würf in über dy hüff, als hy stett. | |||||
| [40v] der pruch vber die vndter hu~ff
Wann dir ainer ein springt / vnd wil dir die vndter hu~ff nemen so gedenck / wan er fu~r springt vnd wil dir neme~ die hu~ff / so senck dich nyder / vnd fall Im mit deinem dencken knye in sein rechknye pu~eg / so mag er dich nit auff hebñ / darnach mach was du wild / |
[25r-c] 39 Item der pruch über die hüff. Wen dich einer also will werffen und springt dir für mit der hüff, als bald senck dich nider hinder seinen rucken und fall im mit deinem lincken knie in sein lingk knie püg1 (Kniebeuge), so felt (fällt) er an den rücken. Und alle stück, dy aus der hüff getriben werden, dy gend (gehen) zu peden seyten. 1Br. püch. |
|||||
| [41r] Fu~r das auß prechñ
Wann du mit ainem gleich gefasset hast / in den arme~ / vnd er wil dir auß prechen mit der rechtñ handt / so gedenck das du mit der tenckñ handt sein rechte hant starck habst / vnd dring vbersich mit dem ellpogen / vnd schreit mit dein[em] tenckñ fueß vorñ starck hinein / vnd wurff In vber das tenck pain / so vallet Er / als obñ stet gemalt / |
[26r-a] 40 Item aber gar einst guz1 (gutes) stück für (dafür), wen dir einer will aus prechen deinen lincken arm. Als bald er den arm über geid (geht) und will aus prechen, so denck, daz du mit deinem lincken arm seinen über sich pringst, doch daz der elpogen über sich ste (stehe), und spring mit deinem lincken fus vür (vor) sein lincken fus und würf in über dy hüff. 1Br. guetes. |
|||||
| [41v] Ain stuck vber das aus prechen
Wen ainer dir wil ausprechñ deinen tenckñ arm~ / als pald er sich erpeu~t zu dem ausprechen / vnd sein rechter arm~ vbersich get / zu dem ausprechñ / So hab vast mit deiner tenckñ handt sein rechte / vnd spring im vndter seinen rechtñ arm~ / vnd mit der rechtñ hant / vall im zwischñ seiner pain / vnd vaß In auff den ruckñ / vnd wu~rff in dan wie du wild / |
||||||
| [26r-b] 41 Item mer ein stück wider die (statt: das) aus prechen.1 Wen dir einer aus will prechen den lincken arm, als bald er sich erpeut (erbietet) zum ausprechen und sein rechten arm übersich peut, so halt im2 fast (fest) mit deiner lingken hant sein rechte und spring im under sein rechten arm und mit der rechten hant vall (falle) im zwischen sein pein und stoß in auf den rucken und würff in, wie du willt.
1Br. armbrecher. 2Br. in. |
||||||
| [42r] Noch ain pessers ausprechñ
Wann dir ainer wil ausprechñ den rechtñ oder tenckñ arm~ / als pald er sich darzu erpewt / zu dem außprechñ / so scheus im den selben arm~ ein an seinen hals / vnd spring Im fu~r / vnd wurff In vber die hu~ff / das get auff pede seÿttñ / |
[27r-a] 42 Item noch ein fessers1 (statt: fessen, Fassen) für daz ausprechen. Wen dir ausprechen will dein lincken arm, als pald er sich erpeutt zu dem aus prechen, so vall (falle) mit deiner hant im um den hals und spring im ein und würff in über dy hüff. Daz get z. p. s. 1Br. ein besseres. |
|||||
| [42v] Ain pruch vber das ober huff ringen /
Wann dich ainer hat beÿ dem haubt / vnd wil dich werffen vber die hu~ff / vnd springet dir fu~r / mit seinem tenckñ fueß / vnd wil dich werffen vber die hu~ff / als pald er dich also hat gefast / so wind dein rechtñ arm~ herauß / den du hindtñ auff seinem rucken hast / vnd mit deiner tenckñ handt kum deiner rechtñ handt zu hilff / vorn in dem glenck / oder peÿ d~ faust / vnd stos Im dan mit dem tenckñ ellpogñ in sein prust so vallet er vber das recht pain / |
[26r-c] 43 Item ein pruch über daz hüff ringen. Wen dich einer hat pey dem kopff und wül dich werfen uber dy hüff und spricht springt dir ein mit seinem, rechten pein, als pald er dich also hat gefast, so wind deinen lingen arm heraus, den du hinden auff seinen ruck hast, und mit deiner rechten hant kum der lincken zu hilff voren (vorn) in daz glenck (Gelenk) und stoß in mit deinen elpogen in sein prust, so velt (fällt) er über daz ling pin (Bein). |
|||||
| [43r] In den armen
Wan du mit ainem ringest in den armen / so gedenck das dw° im mit deiner rechtñ hant habst seinen tenckñ ellpogen / vnd setz dich in die huet / vnd gee ein weil mit vmb / vnd halt In vast beÿ dem ellpogen / vrbering so zuck In an dich / vnd wurff in auff deinen ruckñ / vnd kumb Im tieff vndter seine~ tenckñ arm~ / vnd mit d~ tenckñ handt / vall im zwischñ seiner pain / der rechtñ zu hilff vnd wurff In dan vber auß / |
[27r-b] 44 Item wenn du mit einem ringst mit den armen, so denck, daztu (dass du) im mit deiner rechten hant habst sein lincken elpogen; urwering1 so prich deinen arm seinen rechten aus und ge (gehe) ein weill mit im um, urbering so spring im ein unter seinen lincken arm mit deinem kopff und mit deiner lincken hant vall im zwischen sein pein und faß in auff den ruck und würff in. 1Br. urbeling. |
|||||
| [43v] In den armen
Wann du mit aine~ wild ringen in den arme~ / so gedenck / das du in vndtñ beÿ den ellpogen gar starck vassest / vnd wan du in also gefast hast / so gee ein weil mit im vmb / vrbering so schupf im die arm vbersich / vnd fall im mit dem hawbt an sein prust / vnd vaß In mit den hendtñ in die knyepu~eg / vnd zeuch in vndtñ an dich / vnd oben mit dem hawbt von dir / so vallet er an den ru~ckñ / |
[27r-c] 45 Item wen du mit einem in den armen ringst, so denck, daz tu (du) in unden pey dem elpogen fast (fassest) gar starck, und ge (gehe) ein weill mit im um, urbering so schüpff (schieben, werfen) im dy über sich und fall im mit dem kopff unden an seinen pauch und mit dein peden henden fall im unden an dy füs und würff in über den kopff aus.1 1Br. adds: Diß stuckh gefeit dem Sebast. Khrößl gar wol. NB. |
|||||
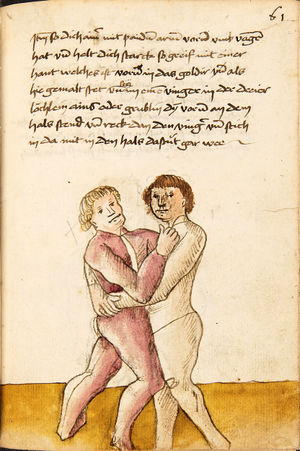
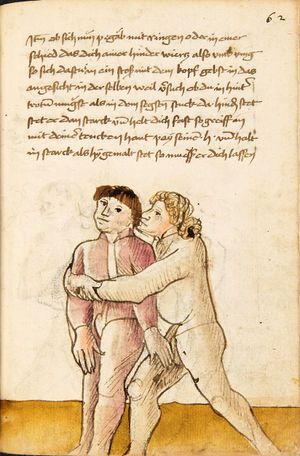
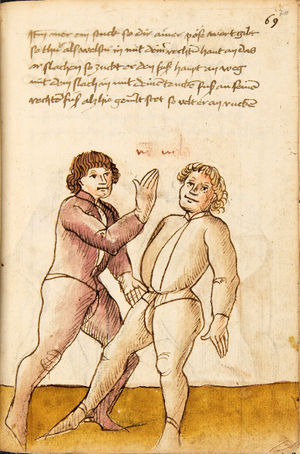
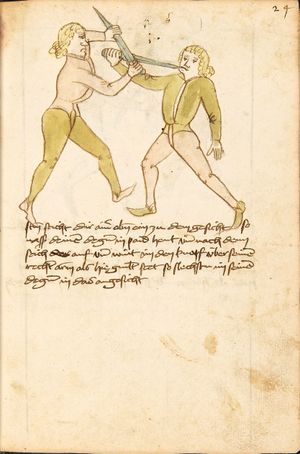
| [63v] Item ein anders stuck wen dich ainer hinten pey dem goldir helt so ker dich auf dein tencke seytten von im vnd stosß in mit deiner rechten hant an seinen tencken elpogen als hie gemalt stet so müs er dich lassen das get auch zu paiden.seiten. | [28r-a] 46 Item helt dich ein (einer) hinden pei dem goller, so ker (kehre) dich auff dein kingk (linke) seiten von im und stos in mit deiner rechten hant in seinen lingen elpogen, so mus er dich lassen. D. g. z. p. s. | |||||
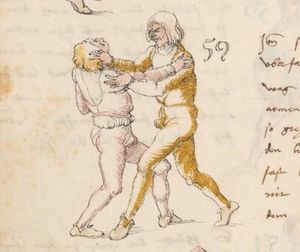
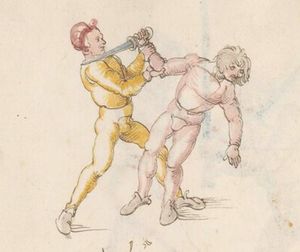
| [64r] Item mer ein stuck ist dastu mit ainem kriegst vnd vor im stest so lege dein hent auf deinen pauch vnd dy recht oben slecht er dir dan zu mit der fäust gegen dem gesicht so var auf mit deiner rechten hant vnd slach im zu seiner feüst mit offenr hent als hie gemalt stet | [28r-b] 47 Item schlecht (schlägt) dir einer mit der feust (Faust) zu dem gesicht, so far auff mit deiner rechten hant, als hie stet, so magstu (magst du) in dan woll werffen, als du hernoch vyndest (findest). | |||||
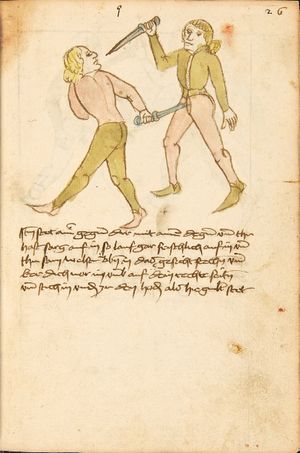
| [64v] Item mer ein stuck so dich ainer also in das maul will slachen so var mit der rechten rechten hant auf als vor vnd trit mit dem rechten fuß hinder seinen tencken vnd würf in über das knie als hie gmalt stet so magstu im auch ein mord stuck thün | [28r-c] 48 Item so dich einer in daz maull will schlahen, so far mit deiner rechten hant auff for (wie vorher) und trit mit deinem rechten füs hinden (statt: hinter) seinen lingken und würff in über daz pein oder knie , als hie stett, und magst ein verporgen stück treiben. | |||||
| [65r] Item mer ein stuck so dich ainer also mit der feüst slachen wil so slach im auch nach seiner rechten feüst mit deiner tencken von aussen zu vnd trit mit deinem tencken füsß hinter seinen rechten als hie gemalt stet so würfstu in auch an den ruck als vor | [29r-a] 48 Item so dich einer in daz maull will schlahen, so far mit deiner rechten hant auff for (wie vorher) und trit mit deinem rechten füs hinden (statt: hinter) seinen lingken und würff in über daz pein oder knie , als hie stett, und magst ein verporgen stück treiben. | |||||
| [65v] Item mer ein stuck wenn dir ainer nach dem ange- sicht slecht mit der feüst so vach den slag in dein rechte hant vnd stosß in auf den elpogen mit deiner tencken hant als hie gemalt stet so prichstu im den armen | [29r-b] 50 Item schlecht dir einer mit der faust noch dem gesicht, so foch (fange) den schlag in dein rechte hant und stos in auff den elpogen mit deiner lingen hant, als hie stett, so prichstu (brichst du) im den arm entzwei. | |||||
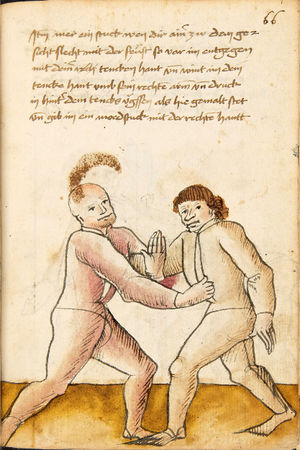
| [66r] Item mer ein stuck wen dir ainer zw dem ge- sicht slecht mit der feüst so var im entgegen mit deiner rech tencken hant vnd wint im dein tencke hant vmb sein rechten armen vnd druck in hinter dein tencks ügssen als hie gemalt stet vnd gib im ein mordstuck mit der rechten hantt | [29r-c] 51 Item schlecht einer mit der feust nocht (!) (nach) dir, so far im entgegen mit deiner lingen hant und wind im dein hant um sein rechten arm und trück in hinter dein linge ügsen (Achsel), als hie stet. Du magst auch ein verporgen stück treiben. | |||||
| [66v] Item mer ein stuck wen dich ainer mit der feüst wil slachen so var mit deinem gereckten tencken armen im gegen seinen hals mit der feüst als hye gemalt stet vnd puck das haupt vast nider vnter den tencken armen vnd mit der rechten faüst ein mord stuck oder nach seinem rechten füsß | [30r-a] 52 Item wenn dir einer zu schlecht (schlägt) so far im mit deiner lingen feust gegen seinen hals, als hie stett, und puck (bücke) daz haubt fast under den lingen arm und far im mit der rechten hant noch seinem lingen pein oder noch (nach) einem verporgen stück. | |||||
| [67r] Item mer ein stuck wen ainer vor dir stet vnd mit dir kriegt so var im mit deinen paiden henden nach seinem angesicht so vert er dir auf nach den henden als well ers weren so stosß in mit dem knie in dye hoch• alz hie gemalt stet so müß er an ruck vallen | [30r-b] 53 Item kriegt' ayner mit dir und furchst, er woll schlagen, so far im auf mit deinen paiden henden nach seinem angesicht, so fert er auch auf nach deinen henden und lest sich verfuren (verführen), so stoß in mit einem knie in die h1[öden].
1Br. hoden, als hie gemalt stet, so muß er an ruck Valien |
|||||
| [67v] Item mer ein stuck so dir ainer nach dem kopf oder angesicht slecht so heb deinen füsß auff welchers ist der dir am pesten fügt vnd stosß in in dy pauch als hie gemalt stet so velt er | [30r-c] 54 Item schlecht dir einer nach den kopff oder angesicht, so far mit den henden nach dem schlag und stoß in mit einem fuß in den pauch, so erwerstu (erwehrst du) im den schlag, daz er dir nit schaden mag. | |||||
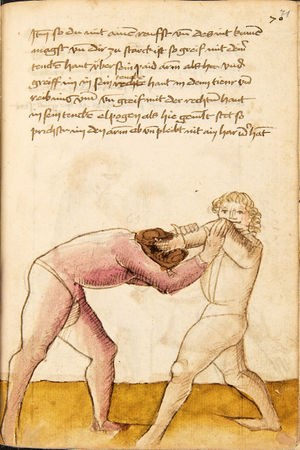
| [68r] Item mer ein stuck wen dir ainer nach dem maul slecht mit der feüst so var auf mit deiner tencken hant vnd vach den slag in das glenck vnd greif mit den vingeren vmb sein armen vnd greif mit der rechten hant vnden nach seinem elpogen alz hie gemalt stet vnd zeuch dan so prichstu im den armen ab | [31r-a] 55 Item schlecht dir einer nach dem maul, so fach den schlag auff dein lincke hand in das glenck und greiff und greiff (!) im mit der rechten hant unden nach dem elpogen, als hie gemalt stet, und zeuch fast an dich, so prichstu (brichst du) im den arm. | |||||
| [68v] Item so dir ainer zw slecht mit der feüst so var auf mit der rechten abichen hant vnd vach den slag innen in dy hant vnd hab dan vast zw vnd greif mit der tencken an seinen elpogen vnd heb ymen auf indy höch als hie gemalt stet vnd trit mit dem tencken fuß für in so würfstu in vber den füß vnd prichst im den armen ab | [31r-b] 56 Item schlecht dir einer nach dem [maul], so fach den streich auff dein rechte hant und greiff mit deiner lincken hant an seinen elnpogen und heb ime[n] auf in die hoch und trit mit de[m] lincken fuß fur, so wirfstu in uber [den] fuß und prichst im den arm. | |||||
| [69r] Item aber ein stuck wenn dir ainer zw slecht so var aber auf alz vor mit der rechten hant vnd scheub in vast zu ruck auf indy höch vnd greiff in mit deiner deiner rechten tencken hant hinden vmb sein rechten armen dürch deinen rechten armen vnd trit mit dem rechten fuß hinter seinen rechten fuß als hie gemalt stet so prichstu im den armen ab | [31r-c] 57 Item schlecht dir einer zu dem ang[esicht], so fach den schlag auf deyn rechte [hant] und stoß in fast zu rucken auf [in die] hoch und greyff mit deiner lincken [hant] hinden umb sein rechten arm und [trit] mit dem rechten fuß hinder sein [rechten], so wirfst in und prichst im den [arm]. | |||||
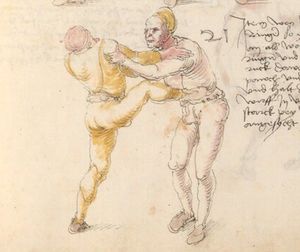
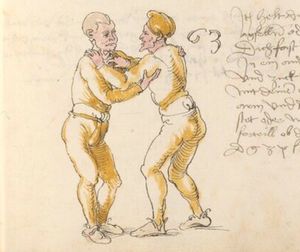
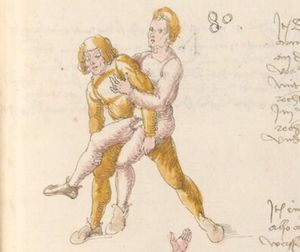
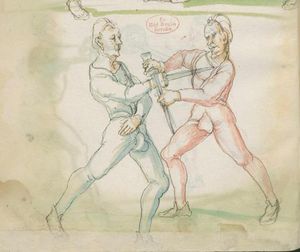
| [33v] Item dy fünft twirch treib also Wen du mit ainem ringst in den armen so prich im auß nit dem rechten armen vnd gee ein weil mit im vmb vnd vrbering so zuck in an dich vnd gee hoch auf mit dem rechten armen über seinen rechten armen vnd ergreif im seinen rechten fuß auswendig vnd hinter trit in mit deinem rechten fuß seinen tencken vnd truck in mit dem knie als hie gemalt stet so würfstu in das get zw paiden seitten | [33r-a] 58 Item die funft zwirch treib also. Wen du mit einem ringst in den armen, so prich im aus mit den rechten arm und gee ein weil mit im umb und urbering so zuck in an dich und gee hoch auff mit deinem rechten arm und ergreiff im sein rechten fus auswendig und hinder trit in mitt deinem rechten fuß sein lincken und truck in mit dem knie. G. z. p. s. | [24r] 7 Item die sechst[5] tbirch. wenn du mit ainem Ringest. so prich Im auß. vnnd gehe ein weil vmb mit Im. vnnd schlach Im mit deinem rechten fuß. hinder seinen lenckhen fuß. alls da gemalet steet. so wirffestu In auff den Rugkhen. das gehet zu baiden seitten. | ||||
| [55v] Item halt dich ainer mit paiden henden pey den ainew in dem goldir vnd die ander vnden in der joppen als da hinden gemalt stet magstu im dan dy hant imm goldir nit auß prechen so greiff im mit deiner hent von aussen vnden vmb sein hant vnd mit der andern hant ynnen vnd sleusß paid hent inn anderen als hie gemalt stet vnd heb dich mit dem haupt hindersich vnd heb dan mit paiden armen seinen armen auf nachot pey denn glid so prichstu ymen das get auch zw payden seytten vnd ist güt | [33r-b] 62 Item helt dich einer mit der rechten hant pei dem goller und mit der lincken unden pei der jopen, kanstu (kanst du) im der hant in dem goller nit aus prechen, als vor (vorher), so greiff im mit deiner lincken hant von aussen um sein hant, nimm und schleus ped hent in ein ander und heb dich mit dem haubt fast hinder sich, so heb dornoch mit deinen peden armen sein arm fast über sich nohett (nahe) pey dem gelid (glied), so pristu (brichst du) im daz. D. g. zu. p. s. | |||||
| [56r] Item halt dich ainer mit paiden henden pey denn achsseln oder pey dem goldir vnd zeucht dich starck nider so sleusß dein paid hent in ein ander vnd scheub in ein weil von dir vnd zuck in dann vrbering an dich vnd stosß im mit deinen paiden henden vnden auf an sein armen als hie gemalt stet vnd vall im dan nach den fussen oder nach dem ruck vnd wart wie du ein vortail vinden mügst dastu in gewerffen mügst vnd über eylen | [33r-c] 63 Item halt dich einer mit peden henden pei den agselln oder pei dem gelenck und zeuch dich fast nider, so schleus dein ped hend starck in ein ander und scheub in ein weill von dir und zuck in den urwering an dich und stos in mit deinen peden henden unden an an (!) sein arm und vall im noch (nach) seinen füssen, als hie stet, oder noch dem ruck und wart uff deinen forteill (Vorteil), ob du in urwering mügst werffen. D. g. z. p. s. | |||||
| [56v] Item aber ein gucz stuck helt dich ainer pey dem goldir mit dem rechten armen vnd scheubt dich starck von im vnd ist dir zw starck dastu im nit auß magst prechen so greif im mit deiner tencken hant auseinen rechten elpogen vnd mit deiner rechten hant greif im voren an sein rechte hant an das glenck pey dem goldir als hie gemalt stet vnd zenck den hindersich zuck ruck dastu im den armen an reckst vnd stoß ymen in dem glid den enczbay | [34r-a] 64 Item helt dich einer mit dem lincken arm und scheubt dich fast von im, daz du im nit kanst ausprechen, greiff im mit deiner rechten hant an seinen lincken elpogen und mit der lincken greiff im vorn in daz gelenck, as (als) hie stet, und zeuch den hinder sich zu ruck, daz du im den arm aus rechkest, (reckst) und stos im von unden das glid entzwei.. D. g. z. p. s. | |||||
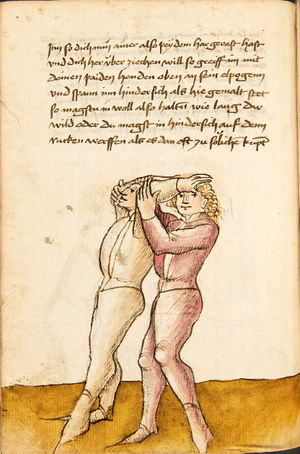
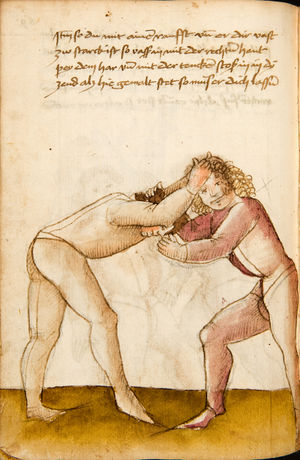
| [57r] Item so dich ainer mit paiden armen hinder wärtling vmb vächt vnd dich starck druckt zw im vnd hebt dich auf vnd wil dich wërffen als pald er dich also auf hept so greif mit deinen paiden henden übersich übersich auf vnd greif hindersich nach seinem kopf vnd vasß in pey dem har als hie gemalt stet vnd würff in über dein haupt aus vnd zeuch starck so müesß er her über | [34r-b] 65 Item so dich einer mit peden henden hinderwertlich (hinterrücks) um fast, dich truckt, auff hebent und will dich werffen, so er dich hebt, als pald greiff mit dein peden henden auff hinder sich und fas in starck pey seinem har und wurff in über dein haubt für dich. D. g. z. p. s. | [31r] 21 Item hat dich ainer mit baiden armen hinden vmbfangen. vnnd helt dich starckh. vnnd hebt dich auff. vnnd will dich zu kainem stuckh kommen lassen. so greiff mit baiden armen hochiber dem haupt. vnnd vaß in starckh bey dem haar. vnnd zeuch vasst. als da gemalet steet. so wirffestu In vber das haupt. auß. wiltdu das prechen. so greiff jme mt baiden hennden an sein Elpogen. vnnd zeuch sy hin: dersich. so wirffestu In auff den rugkhen. | ||||
| [57v] Item so dich nün ainer also pey dem har gevast hast vnd dich her über ziechen will so greiff im mit deinen paiden henden oben an sein elpogenn vnd spann inn hindersich als hie gemalt stet so magstu in woll also halten wie lang dw wild oder du magst in hindersich auf denn rucken werffen als es dan oft zu sölichem kumpt | [34r-c] 66 Item so dich einer also pei dem hor (Haar) hat und will dich her über zihen, so greiff in mit dein peden hen (statt: henden) oben an sein elpogen und zeuch in hinder sich, so magstu in halten, wie lang du wilt. Du magst in auch auf den rucken werffen. | |||||
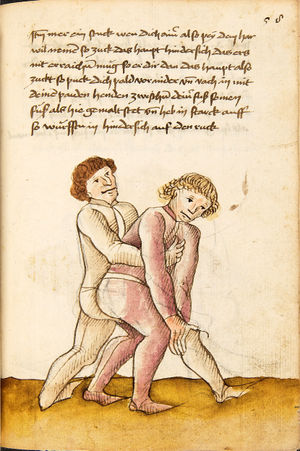
| [58r] Item mer ein stuck wen dich ainer also pey dem har wil nemen so zuck das haupt hindersich das ers nit erraichen müg so er dir dan das haupt also zuckt so puck dich pald vor nider vnd vach in mit deinen paiden henden zwischen deiner fuß seinen füß als hie gemalt stet vnd heb in starck auff so würfstu in hindersich auf den ruck | [35r-a] 67 Item wen dich einer also pey dem har will nemen, so zuck daz haubt hinder sich, daz er dich nit erreich. So du entpfindest, daz dir einer daz haut (!) (Haupt) also tzogt (zuckt), pug (bück) dich behendicklich und var mit peden henden zwischen dein pein nach seinen füs und heb in starck auf, so würstu (wirfst du) in hinder sich auff den rucken. | |||||
| [58v] Item so du nun ainenn also hintersich gevast hast vnd er wil dich pey dem har hin über ziechen oder wil dich pey dem fusß ergreiffen als pald er dich pey deinem fusß ergreift so stosß in mit deinen payden henden hinden auf denn ars als hie gemalt stet so velt er fürsich auf das maul | [35r-b] 68 Item so sich einer also pugt (bückt) und will dir den fus nemen und so palt er den fus fast, so stoß in mit peden henden starck uff seinen rucken, so felt er auff daz antlitz. | |||||
| [59r] Item so dich ainer also hinten vmb vächt als vor geschriben stet vnd wil dich zu dem haupt nit lassen komen vnd wil dich auch zw denn fussen nit lassen kumen so dauch in oben ein wenig mit deinen schulteren hindersich vnd in dem selben so trit mit deinem tencken fusß hinder seinen rechten fuß als hie gemalt stet so würfstu in auf denn ruck gleich als auf der twirch das get zw paiden.seitten | [35r-c] 69 Item so dich einer hinden umfast und helt dich fast, dastu weder kopff noch fus wenden magst, so dauch in oben mit deinen schultern hinder sich. In dem selben so trit mit deinem lincken fus hinter seinen rechten, so würstu (wirfst du) in auf den rucken. D. g. z. p. [s]. | [30v] 20 Item hat dich ein starckher hinden mit baiden armen vmb: fangen. so stoß jn mit dem haupt vnnder das angesicht. vnnd trit mit einem fuß hinder In. vnnd senckh dich vrbe ring nider. als da gemalet steet. so wirffestu jn auff den. rugkhen. vnnd geet von baiden seitten. ~ | ||||
| [59v] Item so dich ainer also hinden vmb vangen hat vnd helt dich also vast dastu zw kainen stuck kumen magst weder zw dem haupt noch zw den fussen noch in dy twirch so vasß in pey dem dawm oder pey einem anderen vinger als hie gemalt stet so müß er dich lassen vnd magst im den vinger auß dem glid prechen vnd ist ein verporgns stuck | [36r-a] 70 Item so dich einer hinden um fangen hat und halt dich so starck, daz du zu keinem stück kumen kanst, so fas in pei dem daumen oder finger, so mus dich desmols lassen, will er nit, daz si im ab prochen werden. | [31v] 22 Item hat dich ainer hinden vmbfanngen. vnnd helt dich starckh. vnnd seczt sich in die wag. vnnd will dich gar zue kainem stuckh khommen lassen. so senckh dich resch nider als wellestu dich von Im reiben. vnnd vaß jm ein Glid als da gemalet stett. so prichstu dich von Im. das stuckh mag man in allen ringen treiben. ~ | ||||
| [60r] Item so du ainen also vmb vangen hast so halt in vast vnd secz dich gewiß in dy wag vnd hütt deins kopf vnd deiner fuß vnd vor der tbirch vnd sleus auch dein feust über einander das er kainen vinger er- greiffen mög vnd ob er nün ain vinger oder dawm ergriff vnd peügt dirn zuruck so gib im pald nach vnd greiff mit deiner anderen hant zw voren in sein glenck vnd ker dich vor im vmb vnd zeuchs auf dein achssel als hie gemalt stet so stostu im den arm ab das get auch von paiden seiten | [36r-b] 71 Item so dir einer also dy finger will prechen, so gib im bald noch und greiff im mit der andern hand vorn noch seiner hant pei dem gelenck und tre (drehe) dich vor im um und zeuch im den arm uber dein agsell und stos im den ein zwei. D. g. zu peden s. | |||||
| [60v] Item so es dich also schickt in den ringen oder in anderen ringen das dich ainer also gevast hat denn armen über dy achssel als hinden ge- malt stet wen dw siechst das er sich naigt nach dem armen so zuck in starck hinder sich zu ruck als hie gemalt stet oder stosß in mit einem fuß hinden in den rucken das in vil stucken nücz | [36r-c] 72 Item so dir einer den arm uber die agsell zeucht und will den abstossen und so bald er sich dornoch neigt, so zuck den arm starck hinder sich, so mus er fallen und, ob du willt, magstu in mit einem fus in den ruck stossen. | |||||
| [61r] Item so dich ainer mit paiden armen voren vmb vangen hat vnd helt dich starck so greif mit einer hant welches ist voren in das goldir vnd als hie gemalt stet vnd secz im einen vinger in der dreier löchlein ains oder grublein dy voren an dem hals stend vnd reck dan den vinger vnd stich in da mit in den hals dastüt gar wee | [37r-a] 73 Item so dich einer mit peden armen starck umfangen hat, daz du kein stück treiben magst, so greif im mit einer hant in daz goller und trück in mit einem finger in der treyen löcher eins. | |||||
| [61v] Item du mit ainem ringst vnd er übereilt dich vnd vmb vächt dich also das er dir dem paid armen pschleust vnd zam druckt als oft ainen in einer schied geschicht vnd gehalten wirt so dich nün ainer also vast so senck dich vrbering nider vnd siech ob du in mit einem knie vellen mügst so weicht er mit den füssen auseinander so stoß in dan mit ein knie in dy hoden als hie gemalt stet so lest er dich | [37r-b] 74 Item so dir einer ped arm über fast, als oft scheidensweis geschicht, so senck dich fast in die wog und tu, als wölstu in hinder tretten, so weicht er mit den füssen fast aus ein ander, so stos in den mit einem knie an die hoden, so wirstu ledig. | |||||
| [62r] Item ob sich nün pegäb mit ringen oder in einer schied das dich ainer hinder wiercz also vmb ring so sich dastu in ein stoß mit dem kopf gebst in das angesicht in der selben weil versuch ob du in hinter treten mügst als in dem segsten stuck da hinden stet stet er dan starck vnd helt dich fast so greiff in mit deiner tencken hant pey seinem.hoden. vnd halt in starck als hy gemalt stet so müesß er dich lassen | [37r-c] 75 Item so dich einer hinderwertlich ob deinen armen um focht, so stos im mit dem kopf in daz angesicht, mach in den kopff hindersich zucken und hinder tritt in mit einem fus. Magst sein aber nit bekumen, so greiff im mit deiner hant noch den hoden, so mus er dich lassen. | |||||
| [62v] Item so es sich füegët dastu gevangen wurczt oder gehalten als das dich ainer mit seiner tencken hant hinten pey dem goldir fassät vnd dich starck helt so ker dich gegen im auf dein rechte seiten vnd gee durch mit deinem rechten armen vnd greiff mit der tencken hant in sein tencker hant voren in das glenck vnd mit dem rechten auf in dy höch über seinen elpogen vnd trit für mit dem rechten fuß als hie gemalt stet | [38r-a] 76 Item fast dich einer hinden pei dem goller, so ker dich gegen in auff dein rechte Seiten und ge durch mit deinem rechten arm und greiff mit der lincken hant forn in das glenck und mit der rechten auf seinen elpogen und trit fur mit dem rechten fus. | [30r] 19 Item vasset dich ainer bey dem Goller. vnnd vnden bey der Joppen. so greiff Im mit deiner linckhen hand vorn in das glenckh. vnnd reib Im die hand vmb. vnnd secz Im deinen rchten arm oben auff seinen arm. vnd dauch nider. alls da gemalet steet. so prichstu Im den arm ab. vnnd gehet vonn baiden seitten. ~ | ||||
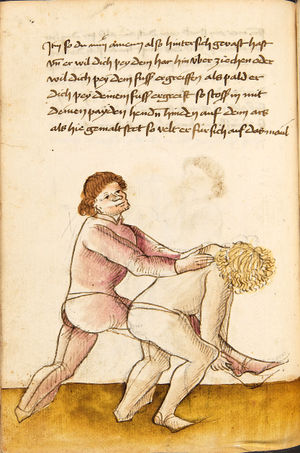
| [63r] Item so dich ainer also helt hinden pey dem goldir als vor so lasß dich ein weil also halten oder füren vrbering so ker dich gegen im auf dein rechte seiten als welstu mit im reden vnd puck dich mit dem haupt reschlich vor nider vnd stosß in in denn pauch als hie gemalt stet so velt er an den ruck helt er dich dan mit der rechten hant so gecz auf di ander seiten | [38r-b] 77 Item helt dich einer hinden pei dem goller, urwering ge um auff dein rechte seiten und puck dich vom nider und stoß in mit dem kopff in den pauch, so felt er an den rucken. Helt er dich den (dann) mit der lingken hant, so ker dich auff die andere seiten. | |||||
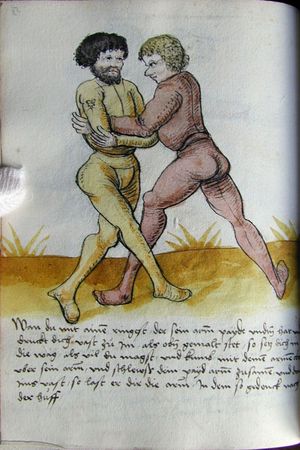
| [36r] Der Stant darauß geen zway stuck | [38r-c] 78 Item merck dy Stent, wie du dich zum ringen schicken solt. Ringstu mit einem in den armen, so vas mit deiner rechten hant ausserhalb seiner lincken und mit der lingcken inerhalb seiner rechten und ste gleich mit deinen peinen und senck dich nider und wellichen fus du einen für den andern sezt, so pistu (bist du) verlorn. Pis (sei) stet1 (stät) in deinen tritten und schnell mit deinen dingen, so gelingt dir dester (desto) pas (besser). 1Br. und stehe. |
|||||
| [36v] So du mit ainiem ringen wilt / vnd du mit ainem gleich gefast hast in den armen / vrbering so prich Im seinen tenckñ arm~ aus / vnd fal im mit deiner rechten handt an sein rechte / vnd mit der linckñ handt an sein rechtñ elpogen / als dan oben gemalt stet / vrbering so zuck in vnd schwing in vor dir hin / vnd schlag In mit deinem tenckn fueß / vndtñ an seinen enckl / so valt er an den ruckñ / das get zu paydñ seyttñ: | [39r-a] 79 Item so du mit einem ringst geleichs fassens in den armen, so gedenck, daz du mit deiner lincken hant habst seinen rechten elpogen und mit deiner rechten hant prich im aus sein lincke hant und kum mit der rechten hant deiner lincken zu hilff und begreiff do mit seiner rechten hant vorn pei dem gelenck. Und wen du in also hast gefast, so zuckt (!) in urwering vor dir hin und schlach in mit deinem lincken fus an seinen rechten fus py (bei) dem enckell, so felt er an den ruck. D. g. z. p. s. | |||||
| [37r] Wen dich ainer also swingen wil / vnd wil dich werffen / als dan vor stat gemalt / in dem selbigen schwingen / spring mit deinem tencken pain Im hindter seine pain / an seiner rechtñ seÿttñ / vnd fall im mit deinem paÿden henden / vndten an sein payde payn / als oben stat gemalt / so wurfst du in wie du wilt / | [39r-b] 80 Item den pruch über stück mit rinen (! Ringen) in den armen. Als pald du den (dann) sichst, daz er forn an dy hant fallen will, so zuck als pald von im hin dan und spring und spring (!) mit deinem lincken fus tieff hinder sein rechten und mit dein lincken arm vall im vorn um den pauch1 und mit der rechten hand unden pei seinen füs und heb in auf und würff in. D. g. z. p. s.
1Br. leib pauch. |
|||||
| [37v] Wan ainer also hindter dich springt / vnd wil dich also werffen so gedenck Im werffen / das du dich habst mit der rechten oben an sein halß / vnd fall oder setz die tenck handt auff die erden / vnd kumb mit dem rechten pain / der tencken handt zu hilff / vnd wurff in vber den ruckñ / als oben stat gemalt / vnd haist der dritte fueß / | [39r-c] 81 Item ein anderen pruch. Wen dich einer also auf zuckt und und (!) will dich werffen, so vall im mit deiner lincken hant um seinen hals, halt in gar starck und fall mit der rechten hant auff die erden. Und so er dich werffen will, so schwing dich flugs um undre (unter) seinen pauch und mit deinem lincken fus kum deiner rechten hant zu hilff, so würstu (wirfst du) in über den rucken aus. Daz magstu zu peden seiten treiben an sorg (ohne Sorge), dustu (tust du) im anders recht. Es get zu peden seiten und daz stuck heist man den traten fus. | |||||
| [20r] Item so dir ainer also in die twirch kumpt vnd wil dich über den fuß werffen so secz das knie für oder weich hintersich mit dem fuß so werst yms so dir denn ainer das wertt vnd dir die twirch nit lassen wil so trit pald wider zu ruck vnd nym den armpruch als hie gemalt stett vnd lauf hindersich vmb vnd vmb so magstu in werffen oder du magst wider in dy h twirch treten das get auch zu paiden seitten | [40r-a] 82 Item so dir einer also in die zwirch kumt, will dich über die fus werffen, so sez daz knie für oder weich hinter dich mit dem fus, so werstu (wehrst du) ims (ihm es). So man dir den werd (wehrt) und dir die zwirch nit lest (lässt), so trit pald wider zuruck und nim denn arm pruch und lauff hinder sich um und und (!), so würffstu in oder magst wider in die zwirch tretten. D. g. z. p. s. | |||||
| [20v] Item dy vierd twirch treib also wen dw mit ainem ringst in den armen so prich im auß mit dem rechten armen vnd gee ein weil vmb mit im vnd vr...ing so spring mit dem rechten fusß hinder seinen rechten fuß vnd mit dem rechten elpogen hinder sein rechs ügsen las hie gemalt stet so würfstu in auf den rucken das get zw paiden seitten vnd müst dich auch woll fürsich sencken das er dich nit zw ruck stosß vnd dastu in in die wag pringst | [40r-b] 83 Item die 4 tzwirch treib also. So du mit einem ringst inn langen armen, so prich aus mit dem rechten arm und ge ein weill mit im um. Urbering spring mit deinem rechten fus hinder seinen rechten füs und mit deinem rechten elpogen ge under sein rechte ügsen, so würstu (wirfst du) in auf den ruchk. D. g. z. p. s. | [23v] 6 Item die vierdt tbirch treib also. wenn du mit ainem Rin: gest. so prich auß. vnnd gehe ein weyl vmb mit Im. vnnd vrbering[6] ruckh in an dich. vnnd stoß In mit deinem rechten Elbogen vnnder sein rechte yechsen. vnnd trit mit deinem rechten fuß. hinder seinen fuß. als da gemalet stehet. Das gehet zu baiden seitten. ~ | ||||
| [33r] Item so dir ainer also in dy twirch kumpt so denck dastu dich mit dem knie vast gegen seinem fuß seczt vnd wider hindersich treczt so dir dan ainer also dar außget so trit pald wider hindersich vnd greif im mit der rechten hant auff dy achssel vnd lauf mit paiden fussen hindersich vnd zeuch in scheib vmb so würfstu in vnd in dem lauf so magstu wider in dy twirch kumen das get zu paiden.seiten.
Paulus Hector Mair's hand: Der Ringen nach folgen 83 bar stennt |
[40r-c] 84 Item so dir einer also in zwirch kumt, so gedenck, daz du dein knie fast gegen seinen füs sezt und wider hinder sich tretzt (tretest). So dir den einer also voraus trit, so trit bald wider hinder sich und greiff im mit deiner rechten hant auff die agsell und lauff mit peden füssen hinder sich und zeuch in scheub (schief) um, so wurstu (wirfst du) in und in dem lauff magstu wider in die zwirch kumen. D. g. z. p. s. | |||||
| [41r-a] 85 Item so dir einer noch dem fus greift, in auff zu heben, so vall im behendiglich um den hals mit der lingken hand und und (!) kum zu hilff mit der rechten in daz gelenck und zeuch vast unter sich, so mus er dich lassen. | ||||||
| [46r] pawrn ringen
Wan du mit ainem ringest als die pawrn thu~n / das ain arm~ oben ist / vnd der ander vndten / so gedenck / das du in vassest mit d~ vndtern handt hindten beÿ dem wam~aß / vnd gee dan ein weil mit im vmb / vrbering spring im mit deine~ tenckñ pain hind[ter] seinen rechtñ fueß / vnd mit der rechtñ handt vall im den hals v[?] vnd dre In vmb / vnd hab In beÿ dem wam~aß vbersich / vnd das hawbt nÿder / so vallet er zu der erden / |
[41r-b] 86 Item wen du mit einem ringst, als die pauern thun, daz din linger arm unden ist und der recht oben, so fas in mit deiner linken hand hinden pei der jopen, halt in starck und gen (!) (geh) ein weill mit im um; urwering spring im mit deinem lincken pein hinter seinen rechten fus und mit der rechten hant vall im um den hals und tre in um und heb pei der jopen hoch auff und den kopff nider, so felt er. |
|||||
| [46v] Wann du mit ainem ringest / so gedenck das du mit deiner rechten handt begreyffest sein tencken ellpogen / vnd wan du in also starck gefast hast / vrbering so spring Im mit deinem tenckñ fueß hindter sein tencks pain / vnd mit deiner rechten hant / vall Im vber sein tenckñ arm~ / vnd nym in in der knyepu~eg / als oben gemalt stet / vnd wurff in vber dein tenck pain / | [41r-c] 87 Item so du ringst, gedenck mit deiner rechten hant sein elpogen zu ergreiffen, vas (fasse) in starck. Urbering so spring mit deinem rechten fus hinter sein rechten und mit deiner lincken hant vall im über sein rechten arm und nim in in der knie püg und werff in uber dein linx (linkes) pein. | |||||
| [47r] pruch
Als pald dich ainer also nemen wil / vnd dir ain springen wil / vnd die weil er dir oben wil ein fallen / vber dein tenckñ arm~ / mit seinem tenckñ arm~ / so gedenck das du mit deiner rechtñ handt Im kumest zwischen seiner pain / vnd mit der tenckñ handt halt vast seinen rechtñ arm~ / vnd heb in auff als obñ gemalt stet / vnd wurff in an den rückñ / |
[42r-a] 88 Item so bald dich einer also nimt und dir ein springt, so stos in mit deiner rechten hant in sein lincke seiten flux von dir oder in dem sprung, den er auff dich tut, so greiff in mit deiner rechten hant zwischen sein pein vorn hinein und heb in auff oder wirff in über die hüff. |
|||||
| [47v] pawrn ringen
Ain stuck / wan du mit ainem ringest in den arm~ / als die pawrñ thu~n / das ain arm~ vndtñ ligt vnd der ander oben / So gedenck / das du in vassest mit deiner rechtñ handt sein tenckñ ellpogñ / vnd setz dich in die mag [!] / vrbering / so zuck deinen tencken arm herauß / aus seinem rechtñ arm~ / vnd vber wurff in vber seinen tenckñ arm~ / vnd vall Im mit paÿdñ hendtñ an sein tencke knyepu~g zwischñ Euren paÿdñ / vnd wurff in dan / |
||||||
| [53v] Item so dich aber ainer also über eilt vnd paid armen vnd paid armen vnterpringt so sich dastu dich vast nider senckst vnd auß im winczt vnd wen er dich dan zw im zucken wil vnd dich auf wil heben so vmb schleuß im sein paid armen mit deinen paiden henden vnd druck vast zammen vnd secz im dein paid fewst in seinen magen als hie gemalt stet vnd tauch in also von dir vnd wart ob du in vnter treten mügst oder ob du in dy huf kümmen mügst | [42r-b] 89 Item wen du mit einem ringst, daz dein lincker arm hinder seinen rechten leit (liegt) und der recht oben, und so ir ped eins gleichen legers sint und so dich bedunckt, daz dir der linck arm werden müg, so zuck in flux aus im und dein rechten behalt an seinen lincken underhalb seins elpogens, tre (drehe) in üux um und über fall mit deiner kincken (linken) hant sein rechten arm und greiff im in die knie püg und werff in. | |||||
| [54r] Item so dich aber ainer über eilt vnd paid armen vnter pringt so halt dich mit paiden armen oben vmb den hals vest zwn im vnd slach im deinen rechten fuß auch vmb seinen tencken aussen her ein vnd greiff den mit ainer hant welches ist aussen vmb sein haupt vnd fasß in pey der nasen als hie gemalt stet vnd zeuch in hintersich da mit vnd secz im einen fuß für so würfstu in auf den ruck | ||||||
| [54v] Item ob ainer mit dir ringt vast dich mit seinen paiden henden pey der joppen als auf den hüffen vnd slingt dich hin vnd her vnd helt dich so starck das tu nydert zün im kumen magst so greif im ein weil in sein elpogen ÿnbendigs vnd dauch in von dir vnd vrbering reck dich hindersich vnd secz dein rechte hant auf sein tencke pey seinem glenck vnd dein tencke vnder sein rechte als hie gemalt stet vnd faß dein paid hent in einander so magstu im dy armen prechen oder er müß dich lassen | ||||||
| [55r] Item fast dich ainer mit seiner rechten hant pey dem goldir vnd mit der tencken vnden pey der joppen vnd helt dich starck also vnd wil dich werffen so greif mit deiner |
||||||
| [49v] Wann du mit ainem wild ringen in den arm~en / vnd trittest im mit deinem tenckñ fueß zwischen seiner payder fuesse / vnd vallet er dir mit paÿden henntdñ vmb den selben fues vnd habt den gar vast / So vall mit payden hendtñ Im obñ vmb die arm~ / als obñ gemalt stet / so muß er dich lassen / | [42r-c] 90 Item so du in armen ringst und tritzt im mit deinem lincken füs zwischen sein pein und er ergreift dir in1 mit peden henden und, so er starck helt, fall im mit peden henden oben um sein arm, so mus er dich lassen.
1Br. und ergreiffst du in. |
|||||
| [51v] Ein pawrn ringñ
Wann mit aine~ du ringen wilst in den arme~ / als die pawrn thu°n / das ain arm vndtñ ligt / vnd der ander oben / so gedenck das du mit dem arm~ / oder mit der handt / die vndtñ ligt In hindtñ beÿ dem wam~aß vast habst / vnd setz die and[er] handt Im vndtñ an sein pauch / vrbering so heb in ab au[ff] in die hõch / als oben gemalt stet / so wurffest du in wan du wild / |
[43r-a] 91 Item ein guz (gutes) stuck einem starcken. Wen du mit einen also ringst, so denck, das dein paid arm unten lig[en], und gee ein weil mit im umb. Die weil du mit im umb gest, so sez im die recht hant unten an seinen pauch und heb in auf und gee ein weil mit im umb und wurff in dan uber das linck pain. |
|||||
| [49r] pruch
Merck / wan Er dir auß pricht vnd wil den selbñ stoß thu~n / vnd so pald Er dich stoß / so stos auch / so prichest du im das stuck / Oder spring fu~r mit der hu~ff / vnd begreyff in beÿ dem hawbt / oder vall Im zwischñ seiner pain / als oben gemalt v stet / so prichst du ims / oder wurffest In / |
[43r-b] 92 Item wen du mit einem wilt ringen in den armen, so denck, das du habst mit deiner rechten hant an seinen lincken elpogen. Urbering kum mit deiner lincken hant der rechten zu hilf und greiff in sein lincke forn ins glenck und ruck in flugs vor dir hin dan und vall im mit deiner lincken hant oben um sein rechten arm und mit deiner rechten hant aussen an seinen lincken fuß und heb in auf und wurf in. |
|||||
| [50r] Das heckeln
Wann dich ainer also hat gefast peÿ dem pain / als vor gemalt ist / vnd hast dich geledigt / In dem so wend dich vor im vmb / vnd begreyff in beÿ dem hals / vnd kumb mit der anderñ hant der anderñ zu hilff / vnd druck in vast zu der erdñ / vnd b vberdring in / doch solt du des fueß nit vergessñ in dem vmbkerñ / als obñ gemalt stet / So kumb mit deine~ fueß / Im zwischñ seiner pain / vnd wind deine~ fueß Im vmb seine~ / vnd hab in vast / vnd heb mit deine~ fueß / den seinen hindtñ hoch auff / so vellt er an den ru~ckñ / |
[43r-c] 93 Item wen du mit einem wilt ringen in den armen, so denck, das du im zu den oberen huff ringen1 mit deinem rechten armen umb den halß und mit deinem rechten fuß kum im zwischen sein pain und um[b] schlag im deinen rechten fuß sein linkes pain und urbering dring in dan, so velt er an den ruck. 1Br. ringest. |
|||||
| [50v] Aber ain gu~t stuck / wan mit ainem gleich gefast hast in den arme~ / so merck am Erstñ / das du mit deiner tenckñ han[t] habst seinen tenckñ ellpogen / oder auff welche seytñ du dan d[as] stuck treibñ wilds / treibst du es auff die tenck seÿtñ / so spr[ing] mit deinem rechtñ fueß / hindter in auff die tenck seÿttñ / als oben gemalt stet / vnd mit der andern / der andern zu hilff vnd wind seine~ arm~ vmb / vnd schleuff mit dem hawb vnd[ter] dem arm~ hinein / vnd vall im mit der rechtñ handt im vmb sein diech / vnd mit der anderñ handt / an das tenck[e] pain / so wurffest du in / wie du wild / | ||||||
| [51r] pruch
Wan dich ainer also werffñ wil / als vor geschribñ stet / vnd so er nach dir wil greyffñ / so lueg ob sein fueß stee zwischñ deiner fu~eß / Stet er zwischñ deiner pain / so greyff nach dem selbñ fu~eß / vnd heb in auff / so vallet er an den ru~ckñ als obñ stet gemalt |
||||||
| [69v] Item mer ein stuck wen dir ainer zu dem maul wil slachen so var auf mit der rechten hant vnd vach den slag auf denn armen vnd stosß in dann mit deiner tencken hant vnden an sein ügssen als hie gemalt stet so stostu in auf den ruck | [44r-a] 94 Item Schlacht dir einer zu dem maul, so vach den schlag auf dein rechte hant und stoß in mit deiner lincken hant unten an sein uchßen (Achsel) und lauf vast und stoß in hindersich, so muß er vallen. | |||||
| [70r] Item mer ein stuck so dir ainer pöse wort gibt so thü als welstu in mit deiner rechten hant an das or slachen so zuckt er den fuß haupt an weg mit dem slach in mit deinem tencken fuß an seinen rechten fuß alz hie gemalt stet so velt er an rucken | [44r-b] 95 Item Schlacht dir einer zu dem maul, so vach den schlag auf dein rechte hant und stoß in mit deiner lincken hant unten an sein uchßen (Achsel) und lauf vast und stoß in hindersich, so muß er vallen. | |||||
| [70v] Item so du mit ainem raufst vnd er dir vast zw starck ist so vasß in mit der rechten hant pey dem har vnd mit der tencken stoß in in dy zend alz hie gemalt stet so müs er dich lassen | [44r-c] 96 Item so du mit einem rauffest, der dir zu starck ist, so vaß in mit der rechten hant pei dem har und mit dem (!) lincken stoß in in die zenn (Zähne), so muß er dich laßen. | |||||
| [71r] Item so du mit ainem raufst vnd des nit kumen magst vnd dir zu starck ist so greif mit deiner tencken hant über sein paid armen als hie vnd greiff im in sein |
[45r-a] 97 Item rauffstu dich mit einem und er ist dir zu starck und magst sein nit uberkumen, so greiff mit deiner lincken hant uber sein paid arm und (greif) im in sein lincke hant in sein finger und reib ims umb und greiff im mit der rechten hant an seinen lincken elpogen, so prichst du im den arm ab und im pleibt nit ein har in der hant. | |||||
| [71v] Item mer ein stuck wen du mit ainem raufst so vaß in gleich als hinden vor gemalt stet vnd leg im dann sein tencke faust in deinen rechten armen auf die maußvnd slach in dan mit der tencken hant auff seinen hals alz hie gmalt stet | [45r-b] 98 Item wen du mit einem rauffst, so vaß in, als hinden am negsten gemalt stet, und leg im dan sein lincke faust in deinen rechten arm auf die mauß und schlag in dan mit der lincken hant auf seinen (hals) als hie gemalt stet. | |||||
| [53r] Wan dich ainer hat gefast mit paÿdñ arme~ als obñ gemalt stet / das du freÿ steest / vnd so er dich zu Im druckt / vnd haltet dich vast / so setz dich in die wag / vnd wan dich bedu~nckt / das du gar wol in der wag seyest / vnd dein arm~ in der hõche habest vrbering so dree dich vor Im vmb / gar starck / vnd vall mit der tenckñ handt Im vmb sein hals / vnd dru~ck In da mit zu der erdñ / so vallet er gar liederlich / | [45r-c] 99 Item wen dich einer also hat gevast und druckt dich [vast] zu im, so dre dich flugs umb auf die lincken seitten und dring nach, so velt (fällt) er an den ruck oder vall im an die huff oder in den hacken. Das treib dann, [als] vor an geschriben stet. | |||||
| [53v] Ain pruch vber den standt / wan dir ainer payd arm~ vber den pauch hat gefast / so far Im mit deinem rechtñ am~ ÿnnen vmb den hals / vnd mit dem tenckñ arm~ aussen vmb den hals / als obñ gemalt stet / vnd druck In vast von dir / so muß er dich lassen / | [46r-a] 100 Item ein pruch uber die stant. Wen dir einer paid arm umb den pauch hat gevast, so far im mit deinem rechten arm unten umb den halß und mit dem lincken außen umb den halß und truck in vast von dir, so muß er dich lassen. | |||||
| [54r] Wan dw mit aine~ ringest in den arme~ / so gedenck / das du in erwischest mit deiner rechtñ handt peÿ seiner tenckñ hand[t] vorñ in dem glenck / vnd hab in starck / Vrbering so vall mit deiner tenckñ handt der rechtñ zu hilff / vnd nym Im sein tenckñ ellpogñ / vnd druck In mit der rechtñ handt von dir / vn[d] mit der tenckñ zu dir / vnd schreÿt mit deine~ tenckñ pain fu~r als obñ gemalt stet / so vallet er vber das pain | [46r-b] 101 Item wen du mit einem ringst in den armen, so gedenck, dastu in erwischt mit deiner rechten hant pei seinem lincken vorn im glenck und halt in starck, urbering vall mit deiner lincken hant der rechten zu hilff und nim im sein lincken elpogen und truck mit der rechten hant von dir und mit der rechten zu dir und schreitt mit deinem lincken pain fur (vor), so vellt (fällt) er über das pain. | |||||
| [54v] Wan du mit ainem ringest / der dir einfallet vorn in das wam~aß / als obñ gemalt stet / so senck dich in die wag / vnd stoß Im mit deiner tenckñ handt sein recht auß darnach mit der rechtñ / sein tencke handt / so wirdest du ledig / von im / | [46r-c] 102 Item wen dir einer mit paiden henden in die joppen felt, so stoß mit deiner lincken hant an sein rechte und mit der rechten an sein lincke, so muß er dich lassen. Oder faß sein lincke hant in sein rechte und uber mit deinem lincken elpogen uber seinen lincken arm pey dem glenck und raiß umb nach deiner lincken seitten, so muß er lassen. | |||||
| [55r] Wan dich ainer beÿ dem hawbt hat / vnd druckt dich vndt° sich / so setz dich in die wag / vnd kumb mit deine~ paydñ hendtñ im vndtñ an sein ellpogen inwendig / vrbering / so schewb sein arm~ von einander / so wirdest du von Im ledig / | [47r-a] 103 Item ein auß prechen. Wen dich ainer hat pei dem kopf, so senck dich nider auf die erden, so latt (läßt) er dich gen (gehen) und tritt mit deinem lincken pain im hinder seinen rechten fuß und vall im umb sein pain und werff in what.1
1Br. weg. |
|||||
| [55v] [No text] | ||||||
| [56r] Wan du mit ainem ringest inden arme~ / vnd wan er dir vorn in das wam~aß greyfft gar starck / wil du ledig werdñ So greyff mit deiner rechtñ handt Im zwischñ seiner payder arm~ / vnd begreyff mit deiner rechtñ handt sein rechte hand[t] vnd hab sÿ gar starck an dein prust / vnd reib sÿ ein wenig einwertz / vnd mit dem denckñ tenckñ ellpogñ kumb auff sein mauß / vnd druck da mit nyder / so muß er dich lassen | ||||||
| [19v] Item die drit twirch treib also wen dw mit ainem in den armen ringst so prich mit ainem armen auß vnd gee mit dem selben armen vnd fuß durch seinen armen vnd halt dich vast fürsich vnd halt seinem armen starck mit paiden henden vnd ker dich von im als hye gemalt stett so wurfstu in auff den rucken das get zw paiden seitten doch so denck dastu mit einem grossen stosß hin ein treczt das er dich nit zw ruck werffen mög
dy ander tbirch |
[47r-b] 104 Item die ander twirch treib also. Wen du mit einem ringst mit langen armen, so prich im auß mit dem rechten arm und far im durch sein lincke ugßen (Achsel) und tritt mit deinem rechten fuß im hinder sein rechten fuß und halt in die weill vest pei dem rechten fuß (durchstrichen) elpogen und denck, das du dich fast fur sich senckest im hinan springen, das er dich nit zuruck stoß. Das treib zu paiden seiden, darnach und er [stett]. | [22r] 3 Item die annder tbirch prich auß mit dem rechten arm. vnnd var Im durch sein lenckhe yechsen. vnnd trit mt deinem rechten fuß hinder seinen rechten fuß. alls da gemalet steet. so würffstu Jn auff den Rugkhen. Das geet zue baiden seitten. ~ | ||||
| [19r] Item so dir ainer in dy twirch also tritt als er dar ein kumpt mit dem fuß so ker dein knie gegen im vnd tauch in hindersich zw ruck so ist es ge- prochen so dir also geprochen ist vnd sichst dastu zw ruck fallen müst als paldu dan enpfinst dastu wider hindersich müst so lasß den vodreren armen resch gen vnd slach in hinder yen vmb das pain oder auf dy erd als hy gemalt stet so würfstu in über dy hüff auß das get zw paiden seitten | [47r-c] 105 Item so dir einer in die twirch tritt und als er darein kumpt mit dem fuß, so ker ker (!) dein knie gegen im und dauch in hinder sich zuruck, so ist es geprochen. So dir also geprochen ist und sichst, das du zuruck valien must, als pald du enpfinst (empfindest), das du wider hinder sich must, so laß den vodern arm resch gen (gehen) und schlag in hinden umb das pain oder auf die erd, als hie gemalt stet, so wurfst du in uber dich. Als (Alles) das g. z. p. s. | |||||
| [48r] Wan dich ainer beÿ dem hawbt hat / vnd druckt dich vndt° sich / so setz dich in die wag / vnd kumb mit deine~ paydñ hendtñ im vndtñ an sein ellpogen inwendig / vrbering / so schewb sein arm~ von einander / so wirdest du von Im ledig / | [48r-a] 106 Item wen du mit einem wild ringen in den armen, so hab im sein rechten elpogen mit deiner lincken hant gar vast und urbernig (!) so prich im mit deiner rechten hant sein lincke auß und vall mit der rechten hant im an sein rechte und hab da pei und gee ein weill mit im umb. So er will die hant an sich zucken, so gib im flugs nach mit deiner rechten hant und scheubs ims zwischen die pain und mit deiner lincken hant vall im aussen umb das pain in sein rechte hant und heb im auf, als da gemalt stett. | |||||
| [48v] Aber ain stuck / wan du mit ainem gleich hast gefasset / So gedenck das du In starck habst beÿ dem ellpogen / als obñ gemalt stet / vrbering so prich im sein tenckñ arm~ auß / vnd stos mit deiner rechtñ handt im oben in den rechtñ arm~ an die mauß / das er sich verdert / darnach so vall mit der rechtñ handt Im zwischñ seiner pain / vnd heb In auff / vnd wurff in wie du wild / | [48r-b] 107 Item wen du mit einem wild ringen in den armen, so hab in mit deiner lincken hant sein rechten elpogen und urberling (!) so prich im seinen arm auß mit deiner rechten hant (ausgestrichen) und stoß im auf sein rechte mauß mit deiner rechten hant im zwischen sein pain und mit der rechten unten an sein lincken fuß, so velt er an seinen rucken. | |||||
| [52r] Aber ain pawrn ringen
Wan du mit aine~ gefast hast / das ain arm~ vndtñ ligt / vnd der ander obñ / als die pawrn thu~n / wan du dan aine~ werffen wilst / so gedenck / das du mit dem arm~ der vndtñ ligt In mu~gst vassen aussen am pain peÿ den hosñ / vnd mit der andern handt vorn im wam~aß / vrbering so gee mit im vmb in dem rad / vrbering so zuck In her vmb auff die ander seÿttñ / vnd wu~rff in vber das pain / |
[48r-c] 108 Item wen du mit einem wilt ringen, so denck, das lincker arm unten lig und der ein oben seines lincken, so gee mit im umb und stoß in mit deiner lincken hant unten an den ars und urberling so heb in auf und gee mit im umb, das er tamisch wirtt, und wurff in uber das linck bain. |
|||||
| [52v] Wan du mit aine~ ringest / der sein arm~ paÿde vndtñ hat vnd druckt dich vast zu im / als obñ gemalt stet / so setz dich in die wag / als vil du magst / vnd kumb mit deine~ arme~ ob[ñ] vber sein arm~ / vnd schlewß dein paÿd arm~ zusame~ / vnd druck ims vast / so last er dir die arm~ / In dem so gedenck nach der hu~ff / | [49r-a] 109 Item wen du mit einem wild ringen in den armen und er unten leid (liegt) mit seinen armen umb den pauch, so fall im mit deinen armen uber sein arm, als hernach gemalt stet, und druck im sein arm mit den armen gar starck zu und gee mit im umb; und welcher fuß dir der nagst (nächste) ist, so schreit mit deinen painen hind[er] den selbigen fuß und dring in dar uber, so muß er auf den ruck vallen. | |||||
| [45v] Item wen du mit ainem ringst gleichs vassens so ge- denck wen dich ein starcker zw im trucken will so wal im mit deinen paiden armen vmb seinen rechten armen als hye gemalt stet vnd secz im dein rechte achssel starck hinter sein rechte achsel so machstu in müed vnd siech dy weil ob dw einen fortail vinden mügst vnd ob du im ein fuß mügst nemen das get zw p.s. | [49r-b] 110 Item wen du mit einem ringst gleichß vassens, so den [dich] ein starker zu im drucken will, so vall im mit dein[en] paiden armen umb sein rechten arm und sez im [dein] rechte achsell starck hinder sein rechte achsel, so [mach] du in müd und sich die weill, ob du einen forteill (Vorteil) [finden] mugst und ob du einen fuss nemen künst. Das get [zu] paiden seiden. | |||||
| [46r] Item er ein ringen wen du mit ainem in den armen ringst gleichs vassens ist er dir zw starck vnd magst dich sein nit wol weren so reck dich weit hinden hinauß vnd faß in mit deiner rechten hant in seiner tencken seiten mit der tencken auf sein rechte hüf vnd wen dich tunckt das er vast für sich dring so greif im mit der tencken hant hinder zwischen der pain vnd heb in auf als hie gemalt stet so velt er das get auch zw paiden seitten | [49r-c] 1011 Item mer ein ringen. Wen du mit einem in dem [armen] ringst gleichß vassens, ist er dir zu starck und [magst] dich sein nit erweren, so reck dich weit hin auß [und] faß in mit deiner rechten hant in sein lincke [seitten] mit der lincken auf sein rechte hüff und wen [dich] dunckt, das er vast für sich dring, so greiff im mit der lincken hant hinden zwischen die pain und heb in auf, als hie gemalt stett, so vellt er. Das gett zu paiden seiden. | |||||
| [46v] Item wen du mit ainem ringst mit gleichem vassen in den armen so dir ainer denn zu starck ist vnd will dich zw im drucken so lasß dy tenck hant pald varen vnd ker dein rechte seitten gegen im vnd trit mit dem rechten fuß zwischen seiner füß als hie gemalt stet dar nach magstu ringen auß der hüf oder auß dem hacken alstu dan vor vnter weist pist worden das ist ein stuck da vast alle ringen anligen vnd ist nit pillich das man si mal oder schreib | [50r-a] 1012 Item wen du mit einem ringst gleichß vaßens in den armen, so dir einer den (dann) zu starck ist und wil dich zu im drucken, so laß die linck hant farn und ker di recht seitten gegen im und trit mit dem rechten fuß zwischen sein fuß. Darnach magstu ringen auß dem huff oder auß dem hacken, alstu (wie du) vor (vorher) gelessen hast. Das ist ein stuck, da (!) vast alle ringen an ligen, und get auf peid seitten. | |||||
| [47r] Item mer ein stuck wen dir ainer denn hacken also ein hat geslagen vnd sich vast in dich spreczt so dring in ein weil von dir vnd ürbering so heb in auf vnd slach in mit den paiden geslossen fussen an seinen ledigen fuß als hie gemalt stet so müß er zu ruck vallen das get zw paiden seitten vnd ist nit woll zw wenten dan ainer der gar wol hëckln kann der hüet sich woll dar vor aber seltn | [50r-b] 1013 Item mer ein stuck. Wen dir einer den hacken ein hat geschlagen und sich vast zu dir spreizt, so tring (dränge) in ein weill von dir und urberling so heb in auf und schlag im mit den paiden fussen an seinen ledigen fuß, so muß er zuruck fallen. Das get zu paiden seiden und ist nit woll zu thun; dann einer, der woll hacklen kan, der hut sich woll davor aber selten. | [28r] 15 Item als pald du ainem den hackhen hast eingeschlagen. so wart ob du Im den geschlossen fuß herfür mögst pringenn. als da gemalet steet. so wirffstu In auff den Rugkhenn vnnd gehet zu baiden seitten. will Er dir den fuß nit lasse(n) so treib ein verporgens stuckh. vnnd wirff In vber die huff. Das geht zu baiden seitten. | ||||
| [47v] Item so dir ainer en hacken ein sleüst vnd vast dich pey deiner ledigen hent vnd senckt sich gen der erden vnd wil dich auß dem hacken werffen so greif mit der anderen hant oben über sein achssel vnd fasß in pey der nasen als hie gemalt stet so prichstu im auß das er dich auß dem hacken lassen müsß dar nach such einen vortail wie du mügst pey einem fuß oder mit hinter treten das zw paiden seitten | [50r-c] 1014 Item so dir einer den hacken einschlecht und vast dich pei deiner ledigen hant, sanckt (senkt) sich gen der erden und wil dich auf den hacken werffen, so greiff mit der andern hant oben uber sein achsel und faß in pei der nassen, so prichstu im auß, das er dich auß dem hacken lassen muß. Darnach such einen forteil, wie du mugst, pei einem fuß oder mit hinter tretten. Das get zu paiden seiden. | |||||
| [48r] Item ringstu mit ainem in den armen gleichs vassens so dir ainer dan zw starck ist vnd wil dich mit ge- walt zw in rucken als paldu des enpfinst so zuck den rechten armen auß im vnd val im mit der tencken armen über sein rechte achsel vnd ker dein tencken seitten vast gegen im vnd slach im dein tencken fuß ein in den hacken als hie gemalt stet so magstu aber alle hüfringen vnd hinter treten als vor geschriben stet das gat als zu paiden seiten | [51r-a] 1015 Item ringstu mit einem gleiches fassens, so dir dan einer zu starck ist und will dich mit gewalt zu im rucken, als paldu (alsbald du) des enpfinst, so zuck den rechten arm auß im und fall im mit dem lincken arm uber sein rechte achsel und ker dein lincke sei[ten] vast gegen im und schlag im dein lincken fuß ein in die hacken, so magstu uber [alle] huff ringen und hinter tretten treiben, [als] vorgeschrieben stet. Das gat auch alles zu [paiden] seitten.1
1Br. Das geb Gott zue baiden tayll. |
[27v] 14 Item ist dir ainer zu starckh. vnnd will dich mit gwaldt heben. so schleuß Im den hackhen ein. vnd sich ob du jm den arm mögest ergreiffen. oder würff In auß der huff. so dir ainer den hackhen ein schleust. so heb In mit deiner handt auff. vnnd schlach jn mit deinem geschlossen fuß an seinen ledigen fuß. als da gemalet steet. | ||||
| [48v] Item wen du mit ainem also ringst als in dem anderen stuck vorgeschriben stet vnd als pald er dir denn hacken vmb den fuß slecht so heb den selbigen fuß auf vnd trit im auf seinen ledigen fuß als hie gemalt stet vnd puck dich pald voren nider vnd stosßin von dir vnd zuck in das haupt auff dein ügssen das get zw paiden seitten etc. | [51r-b] 1016 Item wen du mit einem ringst, als in de[n] andern stucken geschriben stet, und als pald er dir den hacken umb den fuß schlecht, so heb denselbigen fuß auf und trit im auf sein ledigen fuß und pu[ck] dich pald voran nider und stoß in von dir und zuck im das haubt auß den [achsen]. Das get zu paiden seiden. | [28v] 16 Item alspald du empfindest. das dir ainer den hackhen ein schleust. so tritt Im für auff seinen ledigen fuß. mitt baiden geschlossen füessen. vnnd dauch jn oben hindan. von dir. als da gemalet steet. so wirffestu In darauß. vnnd gehet zu baiden seitten ~ | ||||
| [49r] Item mer ein stuck auß dem hacken wen er dir den hacken ein hat geslagen vnd deinen ledigen armen gevast hat als vor vnd wil dich werffen als er sich reckt gegen der erden so lasß den hinteren armen über sein achsel gen als hie gemalt stet vnd reib dich mit der hüf für in vnd greiff mit dem oberen armen nider gegen der erden so prichstu im seinen armen enczway vnd würfst in das get.zu.paiden.seiten. | [51r-c] 1017 Item mer ein stuck auß dem hacken. Wen er [die] (dir) den hacken ein hat eingeschlagen und deinen [ledich] arm gefast hat, als vor, und wil dich wer[ffen], als er sich reckt gegen der erden, so laß den hindern arm uber sein achselen und reib dich mit der huff fur in und greiff mit dem [oberen] arm unten gegen der erden, so prichstu im sein arm enzwey und wurfst in. Das get zu paiden seiden. | [29r] 17 Item ist dir ainer so starckh. Das du Im den hackhen nit ge. nemen magst. so greiff Im Innen auff mit deinem vn: dern arm. hech in sein obern. vnnd secz Im die huff jnn seinen pauch. vnnd zeuch an. als da gemalet steet. das get zu baiden seitten. ~ | ||||
| [49v] Item so dw ainem den hacken ein hast geslagen vnd du enpfinst das er dich dar auß wil pringen so spann dich starck in den hacken vnd swär dich auf in vnd vrbering so trit mit dem selbigen fuß für in vnd ker im deinen ruck gar in sein schosß als hie gemalt stet vnd würff in über den ruck aus vnd halt dich starck fürsich das er dich nit zu ruck ziech vnd greiff mit der ainen hand hinden zw dem pain so magstu in dester leichter heben das get zw paiden.seiten. | [52r-a] 1018 Item so du einem den hacken ein hast geschlagen und du enpfinst, das er dich darauf will pringen, so span dich starck an den hacken und schwer dich auf in und urberling so trit mit dem selbigen fuß fur in und ker im deinen ruck gar in sein schoß und wurf in uber den ruck auß und halt dich starck für sich, daß er dich nit zuruck ziech, und greif mit der einen hant hinden zu dem pain, so magstu in dester leichter heben. Das get zu paiden seiden. | [29v] 18 Item Ringestu mit ainem starckhen. vnnd will dich nitt einlassen in die hueff. oder in den hackhen. so prich jm auß mit einem arm. vnd zuckh jn an dich. vnnd var Jm vber die Achsell auß. vnnd schleuß Im den arm vmb den halß. vnnd greiff Im mit der anndern hanndt hinden nach seinem pain. vnnd heb In als da gemalet steet. das gehet zu baiden seitten. | ||||
| [50r] Item so dich ainer also hat gevast vnd kumpt dir mit dem ruck für den pauch als paldu siechst das er den trit wil nemen mit dem rechten füß so greif im resch mit deiner rechten hant hinter sein rechcz pain vnd heb in auf vnd würf dann als hie gemalt stet vnd wen du in nün auf hast ghebt so greif mit deiner tencken hant im auf sein hals pey dem rechten oren so magstu in werffen das get.zu.paiden.seiten. | [52r-b] 1019 Item so dich einer also hat gefast und kumpt dir mit dem ruck fur den pauch, also pald du sichst, das er den trit wil nemen mit dem rechten fuß, so greiff im resch mit der rechten hant hinter sein rechtes pein und heb in auf und wurf in dan. Und wen du in dan auf hast gehebt, so greif mit deiner lincken hant im auf seinen hals pei dem rechten or und so magstu in werffen. Das get auch zu paiden seiden. | |||||
| [50v] Item so dich ainer also pey dem fuß gevast hat vnd hebt dich auff vnd wil dich auf den kopf werffen vnd in dem als er nu denn sbunck1 nympt vnd dich gegen der erd wil stossen so swing dich mit sampt seinem sbung vnd slach im deinen tencken armen hinden vmb sein tencks pain vnd fasß in mit der rechten hant oben vmb den hals vnd heb in dan auf als hie gemalt stet vnd sleuß dan dein paid hent in ein ander vnd lauf vmb mit im das er tämisch werd so würfstu in an mü vnd an schaden das get auch auf paid seiten
1swunck |
[52r-c] 1201 Item so dich einer also pey dem fuß gefast hat und hebt dich auf und wil dich auf den kopf werffen und indem als er in dem sbunck (Schwung) kumpt und dich gegen der erd wil stossen, so schwing dich mit sampt seinem schwung und schlag im deinen lincken arm hinden umb sein linckes pain und faß in mit der rechten hant oben umb den hals und heb in den auf und - schleuß dan dan (! dein) paid hend in einander und lauf umb mit im, das er tamisch werd, so wurfst du in an müe (ohne Mühe) und an schaden. Das g. z. p. s.
1Br. 1020. |
|||||
| [51r] Item so du mit ainem ringst vnd er vber eilt dich mit sterck oder phentikait das er paid armen vnter pringt vnd wil dich auf heben so senck dich in die wag vnd reck im deinen rechten fuß pald zwischen seiner pain vnd vasß in mit dem rechten arm über sein tencke achssel pey dem rechten ügsen als hie gemalt stet so magstu alle die stuck treiben sie aus dem hacken vnd aus der huf gend vnd magst das auf paid seiten treiben | ||||||
| [51v] Item mer ein stuck so dich ainer über eilt vnd paid armen vnter pringt so secz dich fast nider in dy wag vnd hüt dich wol das er dich nit hinter tret so müß er dich mit gewalt auf heben wil er dich anderst werffen vnd als pald er dich gehept vnd werffen wil so greif im mit deiner tencken hant hinter dy augen vnd mit dem daum vasß in pey der nasen vnd dauch in übersich als hie gemalt stet das magst mit paiden henden thün | ||||||
| [52r] Item wen du ainen also auf gehebt hast als vor stet gemalt vnd er greift dir nach der nasen vnd wil dich weg dauchen so halt in mit deiner tencken hant vest pey seinem ruck vnd secz deinen tencken fuß mit dem knie aussen an sein knie vnd greif im mit deiner rechten hant an seinen tencken elpogen als hie gemalt stet vnd stosß in auf in dy höch vnd würf in von dir das get von paiden seitten | ||||||
| [52v] Item so dich ainer alsod hat pey dem elpogen vnd dich oben hinüber daucht als dan hinden gemalt stet so zuck deinen rechten fuß hinder sich von seinem knie vnd greiff mit deiner tencken hant nach seinem tencken füß vnd trit mit deinem tencken hinter seinen rechten vnd dauch in mit dem knie vnd heb in auf als hie gemalt stet so würfstu in auf den rucken vnd küm dan der rechten tencken hant zu hilf mit der rechten das get.zu.paiden.seiten. | ||||||
| [53r] Item so du mit ainem ringst vnd hat aber paid armen vnden vnd ist gar ein starcker man vnd hept dich auf vnd wil dich mit gbalt1 auf dy erd stossen oder werffen oder mit dir vmb lauffen oder wil dich hart drucken als paldu vermÿnst das er dir einenn schaden wil thün so greif im resch vnd starck mit paiden henden auf sein haupt vnd dauch ims ein wenig zw ruck vnd druck nider als hie gemalt stet so stostu im das haupt vnd den hals in den potig das er nit reden mag
1gwalt (see "tbirch", "zbischen") |
[32r] 23 Item Ringestu mit ainem. vnnd Er ist dir zu starckh. vnnd pringt dir baid arm vnnder. vndd hebt dich mit gewaldt. alspald du des empfindest. das Er dich vber die Erd vringt[7] so greiff Im mit baiden henden auff sein haupt. vnnd dauch ein wenig hindersich. vnnd stoß dann nider zu der Erden. als da gemalet steet. so prichstu jm den halß ab. | |||||
| [72r] Item ob sein not tüt dastu müst zwen gevangen halten vngepunden so faß sy also nym den ainen pey dem rechten armen als in dem nagsten stuck da hinden gemalt stet vnd den anderen pey dem tencken als sy hie gemalt sten so helcztu sy an sorg als lang das man dir zu hilf kumpt | ||||||
| [72v] Item ein pesser stuck ob dw zwen halten wild oder füren so zu versten dastu gesellen genüg hast dy sy dirs nötten helfen vnd die selben gesellen ander auch vachen müsten so vasß sy also alz hie gemalt stet so fürstu sy an sarg ein halbe meil vnd hieten sy holt paid harnasch an | ||||||
| [73r] Item du solt mercken ein gut stuck vnd vnterhalten als wen ein starcker velt vnd wie in ainer halten sol so ainer auf der erd ligt auf dem angesicht so zeuch im seinen tencken armen hinder hin auß vnd trit im mit deinem tencken füß auf dy maus vnd slach im dy faust für dein schinpain als hie gemalt stet so helcztu in vnd er schon harnasch an hiet | ||||||
| [73v] Item mer ein stuck ob du ainen halten wild so leg in auf den pauch vnd stee grietlischen über in vnd knie mit dem rechten knie auf in vnd nym in mit der rechten hant voren pey schöpf vnd zeuch in übersich so helcztu in als hie gemalt stet vnd ist ein gut gsellen stuck | ||||||
| [74r] Item aber gar ein gut vnterhalten als wen ainer gevangen hie so magstu drey mann also halten ob sy schon harnasch an hietn vnd ist auch ein grosse pein ob man ainem geren wee wolt thün alz es hie gemalt stenn den geschicht oft nott |
Images |
Images |
Translation (from the Augsburg Ⅱ) |
Augsburg Version Ⅰ (1470s) |
Berlin Version (1510s) |
Vienna Version (1512) |
Augsburg Version Ⅱ (1553) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Note, one holds you by the collar and stabs after your face.
So grasp with your left hand, over his left wrist and with your right on his elbow and stretch the arm, and thrust in on the arm against the joint, as there stands depicted. So break the arm off. |
[41v-b] [No text] | [33r] 25 Item halt dich ainer bey dem Goldir. vnnd sticht dir nach dem angesicht. so greiff mit deiner linckhen hand. vber sein lencke in das glenkh. vnnd mit deiner rechten an seinen Elpogen vnnd reckh jm den arm an. vnnd stoß jm den arm wider das Glid. als da gemalet steet. so prichstu jm den arm ab.
[16 stendt im dolchen][8] | ||||
| Note, one holds you by the collar and will thrust at you, so wind with your right inverted hand up and under his dagger and step with the right foot behind him, as there depicted stands . So throw him on the back and take the dagger. | [41r-b] [No text] (Similar) | [33v] 26 Item halt dich ainer bey dem Goldir. vnnd will dich stechen so wind mit deiner rechten abichen[9] hannd vnden auff. vnder seinen Degen. vnnd tritt mit dem Rechten fuß hinder jn als da gemalet steet. so wirffestu jn auff den Ruckhenn vnnd nymest jm den Degen. | ||||
| Note, one runs at you with a dagger and stabs after your face. Then wind with your right turned hand up under his dagger and grab him with your hand on his elbow, and wind on, as there depicted stands, and step forward so you take the dagger and break his arm. | [55r-b] [No text] | [66v-b] 15 | [34r] 27 Item laufft ainer auff dich mit ainem degen. vnnd sticht dich nach dem gesicht. so wind mit deiner rechten abichenn handt auff vnndter seinen Degen. vnnd greiff jm mit dei,,ner hand an seinen Elpogen. vnnd wind auff als da ge,,malet steet. vnd trit für. so nymbstu Im den Degenn. vnnd prichest jm den arm. | |||
| Note, one stabs you above after the face. So wind with your left hand up behind his dagger and grab him with your right hand on his elbow, as there stands depicted. So wrench the dagger from him and break the arm off. | [44v-b] [No text] (Similar) | [66v-a] 14 | [34v] 28 Item stich dir ainer oben nach dem angesicht. so windt mit deiner lenckhen hanndt auff. hinder seinen Degen vnnd greiff Im mit deiner rechten handt. an seinen El,,pogen. als da gemalet steet. so reibstu Im den Degenn auß. vnnd prichest jm den arm ab. | |||
| Note, one stabs after your stomach. So fall in with your left inverted hand on his dagger and wind in around and grab him with your right hand after his elbow, as there stands depicted. So you take his dagger and break his arm. | [64v-b] [No text] | [35r] 29 Item sticht dir ainer nach dem pauch. so fall Im mit deiner lenckhen abichen handt. auff seinen degen. vnnd wind jms vmb. vnnd greiff jm mit der rechten hand nach seinem El,pogen. als da gemalet steet. so nymbstu jm den Degenn. vnnd prichest jm den arm. | ||||
| Note, one stabs after your breast. So grasp your dagger in the right hand and fall in on his dagger and grab him with your left hand below on his dagger, and wind in over your dagger from the hand, as there stands depicted. | [28v] Item sticht dir ainer mit langem degen nach der prust als franczoschisch, so var auf mit deiner tencken abichen hant unten an seinen degen und leg im deinen degen auf seinen rechten arm und prich im den degen darüber auß, als hie gemalt stet. | [48r-b] [No text] (Similar) | [35v] 30 Item sticht dir ainer nach der prust. so vaß deinen Degen in die rechten handt. vnnd vall Jm auff seinen Degen. vnnd greiff jm mit deiner linckhen handt. vnnden an seinen Degen. vnnd wind yinen vber deinen Degen auß der hannd. als da gemalet stett. ~ | |||
| Note, one stabs you with the dagger above in to the face. The drive up with your turned left hand and on his arm and pull his arm and do as you would stab with your dagger on his neck, and stab in over his arm, as here depicted stands, and pull, so you break his arm off. | [22r] Item sticht dir ainer mit dem degen oben ein zu dem gesicht, so var auf mit deiner äbichen (verkehrten) tencken hant und an seinen arm und reib (dreh) ihn den arm und tu, als welstu in mit deinem degen in den hals stechen, und stich in über seinen arm, als hie gemalt stet, und zeuch, so pricht im der arm ab. | [38v-a] [No text] (Similar) | ||||
| Note, one stabs you from above at the neck. So grasp your dagger outwards on your arm and wind up under his dagger and grab him with your left hand on his elbow and wind and step with your foot inside, as there stands depicted. So break his arm off and throw him. | [22v] Item sticht dir ainer oben zu dem gesicht, so vaß deinen degen auf dein rechte hant und var auf damit und vach den stich darauf und greif mit deiner tencken hant an seinen elpogen und heb auf, als hie gemalt stet, so prichst du im den arm und nimst im den degen. | [36r] 31 Item sticht dir ainer oben anch dem halß. so vaß deinen Degen. aussen auff deinen arm. vnnd wind Im auff vnder seinen Degen. vnd greiff Im mit deiner linckhen handt. an seinen Elpogen. vnnd wind vmb. vnnd tritt mit einem fuß hir In. alls da gemalet steet. so prichstu Im den arm ab. vnnd wirffest In. | ||||
| Note, one stabs after your neck. So wind in up with your inverted dagger below on his dagger and fall in with the point under his arm, so you wrench his dagger from the hand, as there stands depicted. | [23r] Item sticht dir ainer zu dem angesicht, so nim den degen auf deinen rechten arm und vach (fang) den stich darauf und wint im mit deinem spicz über seinen arm und zeuch an dich, als hie gemalt stet, so nimstu im den degen oder du prichst im den arm ab. | [37r-b] [No text] | [36v] 32 Item sticht dir ainer zu. nach dem halß. so wind jm vff mit deinem abichen Degen, vnden an seinen Degen. vnd vall Jm mit dem spicz vber seinen arm. so reibstu jm den tegen auß der hanndt. als da gemalet steet. ~ | |||
| Note, one stabs to you from above. So wind on in with your inverted dagger under his dagger and go quickly meanwhile and grab him with your left hand. around his right arm, on your right arm, and step with your right foot behind him and shove him backwards, as stands depicted. So break his arm and throw him. | [50r-b] [No text] | [37r] 33 Item sticht dir ainer oben zu. so wind Jm auff mit deinem abichen Degen. vnndter seinen Degen. vnnd gehe vast jnndes vnnd greiff Jm mit deiner lenckhen hand. vnmb seinenn rechten arm. in deinen rechten arm. vnd trit mit deinem rechten fuß hinder In. vnd dauch jn zurugkh. als da gema: let steet. so prichstu Im den arm. vnnd wirffst In. | ||||
| Note, one stabs you from above down to the neck. So stab against him from below around his arm, grab with your left hand forward around the point and press his arm firmly to the earth as stands depicted. How you will break this: So take your dagger in the left hand and stab him in the neck. | [23v] Item sticht dir ainer oben zu dem gesicht, so stich mit deinem degen von unden auf mit abicher hant umb seinen rechten arm und var mit deiner tencken hant vorn an spicz und zeuch nider zu der erden, als hie gemalt stet, so helcztu (hältst du) in mit gewalt. Wildu ledig werden, so nim deinen degen in die tenck hant und stich in. | [55v-b] [No text] (Similar) | [37v] 34 Item sticht dir ainer oben nider. zu dem halß. so stich vnden gegen Im auff vmb seinen arm. vnnd greiff mit deiner linckhen hanndt vorn vmb den spicz. vnnd druckh jme den arm vast zu der erden. als da gemalet steet. wiltdu das prechen. so nymb deinen degen in die lennckhen hanndt. vnnd stich jn In den halß. ~ | |||
| Note, one stabs at you above in to the face. Then grasp your dagger in both hands and catch the stab on it and wind the pommel in over his right arm, as here depicted stands, so you strike his dagger in his face. | [24r] Item sticht dir ainer oben ein zu dem gesicht, so vaß deinen degen in paid hent und vach den stich auf und wint im den knopf über seinen rechten arm, als hie gemalt stet, so slechstu in seinen degen in das angesicht. | [57v-b] [No text] | ||||
| Note, one stabs you from above after the neck. So grasp your dagger with 1armed hand and catch the stab thereon and go fast meanwhile and wind your point over his arm. So you break the dagger from him as there stands depicted. 1 One hand on the handle and one hand on the blade. |
[38r] 35 Item sticht dir ainer oben nach dem halß. so vaß deinenn Degen zu gewappneter handt. vnnd vach den stich darauff vnnd gehe vast jnndes. vnnd wind jm deinen spicz. vber seinen arm. so prichstu jm den Degen auß. als da gemalet steet. ~ | |||||
| Note, one stabs you after the neck. So drive up with 1armed hand with the dagger and catch the stab thereon and shove in his dagger over the head and pull him down to the earth. As stands depicted. 1One hand on the handle and one hand on the blade. |
[24v] 8 Item sticht dir ainer oben ein zu dem gesicht, so vaß deinen degen in paid hent, als vor, und vach den stich darauf und lauf vast hinter sich zuruck mit im und dauch ymen (ihn) über seinen kopf an den hals, als hie gemalt stet, so zeuchstu in auf dy erden. | [37v-a] [No text] | [38v] 36 Item sticht dir ainer nach dem halß. so var auff mitt ge. wappneter hand mit dem Degen. vnnd vach den stich darauff. vnnd dauch jm seinen Degen vber das haupt. vnnd zeuch in nider zu der Erden. als da gemalet steet. | |||
| Note, one stabs to your face, then catch the stab, as before, and release your left hand and grasp his right arm and pull his arm on your back, as here depicted stands, so you bind him with the dagger. | [25r] Item sticht dir ainer zu dem gesicht, so vach den stich, alz vor, und laß dein tencke hant und faß im seinen rechten arm und reib in von dir nider gegen deine rechte seiten und verbürff (?) den degen und stich in über sein agsel und zeuch in an dich und reib im den arm auf den rucken, als hie gemalt stet, so pincztu in mit dem degen. | [64v-a] [No text] | ||||
| Note, one stabs above to your face. Then grasp your dagger on your right arm and catch the stab thereon and thrust in with the left hand on his elbow from you, that he turns around before you, and grasp him by a foot with your dagger, as here depicted stands, so you throw him. | [25v] Item sticht dir ainer oben zu dem gesicht, so vaß deinen degen auf den rechten arm und vach den stich darein und stoß in mit der tencken hant an seinen elpogen von dir, das er sich vor dir umker, und faß in pey einem fuß mit deinem degen, alz hie gemalt stet, so wurfstu in. | [43r-a] [No text] (Similar) | ||||
| Note, one stands against you with a dagger and you have attended him, then run very quickly on in and as if you will stab above to his face, and turn yourself around before him on your right side and stab him below to the testicles, as here stands depicted. | [26r] Item stet ainer gegen dir mit ainem degen und thu (du) hast sarg (sorg) auf in, so lauf gar festlich auf in und, sam (wie wenn) welstu oben in das gesicht stechen, und ker dich vor im umb auf dein rechte seiten und stich in unden zu den hoden, als hie gemalt stet. | [47r-b] [No text] (Similar) | ||||
| Note, one stabs you above to your face, then strike him with the left hand outside on his right hand, then he stabs himself in the testicles, and then stab him with your dagger above in to his neck, as depicted here stands. | [26v] Item sticht dir ainer oben zu dem gesicht, so slag in mit deiner tencken hant außen auf sein rechtew hant, so sticht er sich selb in dy hoden und stich in dann mit deinem degen oben ein zu dem hals, als hie gemalt stet. | [38r-b] [No text] (Similar) | ||||
| Item, one stabs you below to the stomach with the false stab, then grasp your dagger in both hands and fall in above on his dagger and grasp his right with your left hand and turn yourself speedily around before him, and pull him over your shoulder, so you break the arm off. | [27r] Item sticht dir ainer unden zu dem pauch den wälschen stich, so vaß deinen degen in paid hent und val im oben auf seinen degen und vaß mit deiner tencken hant sein rechte und ker dich reschlich umb vor im und zeuch in über die agsel, so prichstu im den arm ab. | [36v-b] [No text] (Similar) | ||||
| Note, one stabs at you below to the stomach. Then grasp your dagger in both hands and fall in on the stab and drive in with your dagger against your right side, and lift over you in the air, as here depicted stands, so you wind the dagger from his hand. | [27v] Item sticht dir ainer unden zu dem pauch, so vaß deinen degen in paid hent und vall im auf den stich und treib in mit deinem degen gegen dein rechte seiten und heb über sich auf in dy höch, als hie gemalt stet, so wincztu im den degen aus der hant. | [39r-a] [No text] | ||||
| Note, one stabs above to your face. Then drive up with your turned left hand and break the stab out and stab in with the dagger between his legs and lift him up, as here depicted stands, so you throw him on the back. | [28r] Item sticht dir ainer oben ein zu dem gesicht, so var auf mit deiner abichen tencken hant und prich im den stich auß und stich in mit deinem degen zbischen der pain und heb in auf, als hie gemalt stet, so würfstu in auf den rucken. | [40r-b] [No text] | ||||
| Note, one stabs after you below at the stomach. So fall in with your inverted hand with the dagger on his dagger and wind in up high and step with your right foot behind him as stands depicted. So throw him on the back. | [64r-a] [No text] | [39r] 37 Item stich dir ainer vnnden nach dem pauch. so vall Jym mit deiner Abichen handt mit dem Degen. auff seinen Dege(n) vnnd wind in auff in die höch. vnd trit mit deinem recht(en) fuß hinder In. als da gemalet steet. so wirffstu jn auf den Ruckhen. | ||||
| Note, you are held by two by each arm and the third will stab you. So you hold fast by the two and thrust with your dagger with a foot in the groin and step behind one with a foot and throw him on the back and thrust the third with a 1fatal technique as stands depicted. So you are free and come from them all three without harm. 1 Literal translation is “death-technique” |
[41r-a] [No text] | [39v] 38 Item halten dich zwen bey den armen. vnnd der drit will dich stechen. so halt dich vesst bey den zwayen. vnd stoß den mit dein Degen mit einem fuß in die hoden. vnd hinder tritt den ainen mit ainem fuß. vnnd wirf in auff den, rugken. vnnd stoß den dritten mit ainem merstuckh, als da gemalet steet. so wirstu ledig. vnnd kumbst von jnen allen dreyen one schaden. ~ | ||||
| [66v] 14
15 16 |
||||||
| [67r] 17
18 19 |
||||||
| [67v] 20
21 22 |
Images |
Images |
Augsburg Version Ⅰ (1470s) |
Berlin Version (1510s) |
Vienna Version (1512) |
Augsburg Version Ⅱ (1553) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [40r] 39 Item hawt dir ainer oben nach dem kopff mit einem messer so wind abichen auff mit deinem Degen vnder das messer vnnd wind Im den Degen vmb seinen arm. vnd greiff Im mit deiner linkchen hannd an seinen Elpogen. vnnd trit mit einem fuß für In. als da gemalet steet. so prichstu Im den arm. vnnd wirffst In. ~ | ||||||
| [40v] 40 Item hawt dir ainer nach dem kopff mit einem messer. so wind abichen auff. mit dem Degen. vnd nach den straich darein. vnnd vall Im mit deinem abichen lenckh(en) arm. vber seinen rechten arm. vnder dem vchsen. als da gemalet steet. so magstu In stechen. vnd das Messer nemen. ~ | ||||||
| [91r] 53
54 55 |
||||||
| [92r] 56
57 58 |
Images |
Images |
Augsburg Version Ⅰ (1470s) |
Berlin Version (1510s) |
Vienna Version (1512) |
Augsburg Version Ⅱ (1553) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [73r] 1
2 |
||||||
| [74r] 3
4 |
||||||
| Item; one hews at you with a messer after your head. So parry, your thumb on the flat of your messer, and catch the strike on the nail, as stands depicted there, so you may thereafter work what you will, as you find hereafter. | [75r-a] 5 | [41r] 41 Item hawt dir ainer zu. mit einem messer nach dem kopff. so versecz deinen daum auff die flach deines messers. vnnd vach den straich auff den Nagel. als da gemalet steet. so magstu darnach arbaiten was du wilt. als du hernach finden wirst. ~ | ||||
| Item; You fight with one with the messer; he hews in at you above, so parry with your messer outwards with the flat on the nail and go quickly before you with the left foot and fall in with the pommel over his arm, as stands depicted here, so you hew him in the head. | [29r] Item vichstu (fichst du) mit ainem mit dem messer, haut er dir oben ein, so versechcz (versetz) mit deinem messer außen mit der fläch auf den nagel und gee pald für sich (vorwärts) mit dem tencken fuß und vall im mit dem knopf über seinen arm, als hie gemalt stet, so haustu in in den kopf. | [83r-b] 30 | [41v] 42 Item so du verseczt hast als vor steet. so trit fürsich mit deinem linckhen fuß. vnd vall Im vber seinen arm. mit deinem messer. so hawstu In vber den kopff. als da gemalet steet. deß geleichs mag der auch vber fallen der geschlagen hat. welcher ee kumbt. der velt vber. | |||
| Item; one more good technique. One hews to you down from above, so catch the strike on the nail, as before, and go with the left foot meanwhile and thrust his right hand with your left hand toward the earth and hew in over his head, as is depicted here. | [29v] Item mer ein gucz stuck. Haut dir ainer zu von oben nider, so vach (fange) den slag auf den nagel, als vor, und gee mit dem tencken fuß indes und stoß in mit deiner tencken hant sein rechte nider zu der erden und hau in über den kopf, als hie gemalt ist. | [84r-a] 32 | [42r] 43 Item hawt dir ainer oben zu dem kopff. so versecz mit der flech. als vor. vnd trit fürsich mit dem linckhen fueß. vnnd greiff Im mit deiner linckhen hand. vorn auff sein rechte. vnnd stoß Ims nider zu der Erden. vnnd haw In durch den kopff. als da gemalet steet. ~ | |||
| Item; one more good technique. One hews at you above to the head, so wind in through below with your messer and catch the strike thereon, and fall in with the pommel over his arm and wrench on yourself, and step forward with the left foot, and drive in with the left hand around his neck, as here stands depicted, so you throw him on his back. | [30r] Item mer ein gucz stuck. Haut dir ainer oben zu den kopf, so wint im mit deinem messer unten durch und vach den straich darauf und vall im mit dem knopf über seinen arm und reiß an dich und trit zu mit dem tencken fuß und var im mit der tencken hant umb den hals, als hie gemalt stet, so wurfstu in auf den rucken. | [84r-c] 34 | ||||
| Item; one more good technique. When one hews down from above, so wind through below with your messer and run on in and drive with your left hand high over his right arm and grasp it behind the armpit, and stab with your messer through between you and him on his neck, as stands depicted here. | [30v] Item mer ein gucz stuck. Wen ainer oben nider haut, so wint unten durch mit deinem messer und lauf in ein und var mit deiner tencken hant hoch über seinen rechten arm und vaß hinter das ugssen (Achsel) und stich mit deinem messer zbischen dir und im durch an sein hals, als hie gemalt stet. | [85r-a] 35 | [42v] 44 Item hawt dir ainer nach dem kopff. so wind Im durch mit deinem messer. vnnd rechk dich lanckh hinein. vnd vall Im mit deinem linckhen arm abichen vmb seinen arm. vnnd schlach jn vnder dein vchsen. vnnd stich jm mit deinem messer zwischen dein vnnd sein durch. an seinen halß. als da gemalt steet. ~ | |||
| Item, one hews above to you above in to the head, so parry yet with the flat and on the nail and send his messer away, so that he must strike, and when he then will strike, then seek the nearest and pull the arm off, as stands depicted here. | [31r] Item haut dir ainer oben ein zu dem kopf, so versecz aber mit der fläch und auf den nagel und dauch im sein messer an wege, das er slachen müße, und wen er den (dann) slachen wil, so such die nachent (Nähe) und zeuch im den arm ab, als hie gemalt stet. | [82r-b] 27 | ||||
| Item; another technique for a strong one. One hews in above strongly, so grasp your messer with the armed-hand and catch the strike thereon and step forward in with your left foot and lay in the messer on his neck, as stands depicted here. | [31v] Item ein anders stuck für einen starcken. Haut dir ainer starck oben ein, so vaß dein messer zu gewapnoter hant und vach den straich darein und trit zu im mit deinem tencken fuß und leg im das messer an den hals, als hie gemalt stet. | [77r-b] 12 | [43r] 45 Item hawt dir ainer oben nach dem kopff. so vaß deyme messer zu gewappneter handt. vnndt lauff Im vnnder den schlag. vnnd wind Im mit dem spicz an seinen halß. vnnd hinder trit In mit deinem lenckhen fuß. als da gemalet steet. so wirffstu In auff den Rugkhen. ~ | |||
| Item; one hews above to you to your face, so drive up with the armed-hand and catch the strike on the messer and wind in the pommel over his arm and wrench behind you, as stands depicted here, so you break the arm or take the messer. | [32r] Item haut dir ainer oben ein zu dem gesicht, so var auf mit gewapnoter hant und vach den slag in das messer und wint im den knopf über seinen arm und reiß hinder sich, als hie gemalt stet, so prichstu im den arm oder nimst im das messer. | [77r-a] 11 | ||||
| Item; one hews above in to the head, so drive up with the armed-hand and catch the strike on the blade, as before, and step fast behind him with your right foot and lay in the pommel on his neck, as stands here depicted, so you throw him on his back. | [32v] Item haut dir ainer oben ein zu dem kopf, so var auf mit gewapnoter hant und vach den straich in dy klingen, als vor, und trit vast hinter in mit deinem rechten fuß und leg im den knopf an den hals, als hie gemalt stet, so würfstu in an den rucken. | [78r-b] 15 | ||||
| Item; one runs quickly on you, so do as you will hew him after the head, and turn yourself completely around before him, and hew him long on his arm, as stands depicted there. | [85r-b] 36 | [43v] 46 Item laufft dich ainer Resch an. so thue als wellestu Im nach dem kopff hawen. vnnd ker dich vbering vmb vor Jm. vnnd haw Im lannckh anch seinem arm. als da gemalt steet. ~ | ||||
| [75r] 5
6 7 |
||||||
| [76r] 8
9 10 |
||||||
| [77r] 11
12 13 |
||||||
| [78r] 14
15 16 |
||||||
| [79r] 17
18 19 |
||||||
| [80r] 20
21 22 |
||||||
| [81r] 23
24 25 |
||||||
| [82r] 26
27 28 |
||||||
| [83r] 29
30 31 |
||||||
| [84r] 32
33 34 |
||||||
| [85r] 35
36 37 |
||||||
| [84r] 38
39 40 |
Images |
Images |
Augsburg Version Ⅰ (1470s) |
Berlin Version (1510s) |
Vienna Version (1512) |
Augsburg Version Ⅱ (1553) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [87r] 41
42 43 |
||||||
| [44r] 47 Item hastu ein messer. vnnd einer schlecht mit einem schwert. auff dich. so wind jm mit der fläch lannckh ein. vnnd trit zu mit deinem lenckhen fuß. vnnd faß jne mit der handt bey seinem rechten Elpogen. vnd wind vff als da gemalt steet. vnnd geet auß dem Degen | ||||||
| [88r] 44
45 46 |
[44v] 48 Item wind auff als vor. vnnd vall Im mit dem messer vber. vnnd trit mit deinem lenckhen fuß hinder In. vnd mit dem arm vmb den halß. so wirffstu In auff den Rugken. vnnd hawst. oder stichst In. als da gemalet steet. | |||||
| [89r] 47
48 49 |
||||||
| [90r] 50
51 52 |
Images |
Images |
Augsburg Version Ⅰ (1470s) |
Berlin Version (1510s) |
Vienna Version (1512) |
Augsburg Version Ⅱ (1553) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reach
Item. When you fence with someone and come against their sword such that you both have bound up, extend both your sword and your arm far away from yourself and place yourself in the scales with your body low so that you have reach and measure in your sword so that you can defend anything that is your necessity to deal with. Reach means that you stand behind your sword and extend yourself. Measure means that you stand low (as is pictured here) and make yourself small in body, so that you are great in sword. |
[3r] Leng.
Item so du mit ainem vichst und zu im kumst an das swert, das ir paid an hapt gepunden, so reck dein arm und dein swert lanck von dir und secz dich mit dem leib nider in dy wag und sich, das du leng und maß in dem swert habst, so magstu arbaiten weren alles, das dain notturft ist. Dy leng das ist, dastu hinter deinem swert stest und reckst dich; dy maß ist, dastu nider stest, als hie gemalt stet, und mach dich klain mit dem leib, so pistu groß im swert. |
[32v-a] [No text] | [45r] 49 Item vichst du mit ainem in dem langen schwert. so pind Im oben lanckh an. vnd pring Im leng vnd maß ann das schwert. vnd gewin Im schwech vnd sterckh an. vnd bleib am schwert. vnd empfind ob Er schwach oder starckh sey. vnd ob er bleiblich oder vnbleiblich sey. Ist Er bleiblich vnd schlecht nach den plössen. so nymb vor vnd nach. vnd gehe jnndes mit der arbait. als du vnnderweist bist,
[In a later hand, difficult to read] 24 stende jm langen [schwert?][10] | |||
| Measure
Item. As you bind up against their sword, slash in long at their face using your point and wind in at their face using your short edge (as is pictured here), so you can wrench in with your pommel or weapon in hand or thrust into their face. |
[3v] Maß.
Item alstu (wenn du) ainen an pinczt (bindest) an das swert, so slach im lanck ein mit dem ort zu dem gesicht und wint im mit der kurczen sneid ein in das angesicht, als hie gemalt stet, so magstu im ein reissen mit dem knopf oder mit gewapneter hant in das gesicht stoßen. |
[65r-b] 12 (Similar) | [45v] 50 Item pindstu ainem an das schwert. Vnnd gewinst Iyme schwech vnd sterckh an. so trit bald für mit dem lenckhenn fuß. ein solschen trit, vnnd wind Im auff seiner lincken seitten oben ein nach dem halß, als da gemalet steet. vert Er auff vnnd wert den stich. so treib den fäler | |||
| Weak
Item. If you bind someone up against your sword, then see if they are soft or hard. If they are hard, then wind into their face as was written before. But if they are soft, then seek the weak of their sword and wind over to your right side (as is pictured here), then you can snap at their face and seek their openings. |
[4r] Swech.
Item so du ainen an pinczt an das swert, so wart, ob er waich oder hert sey. Ist er hert, so wint im in das angesicht, als vor geschriben stet. Ist er aber waich, so such dy swech seines swercz (Schwertes) und wint im über auf dein tencke seiten, als hie gemalt stet, so magstu im nach den kopf snappen und dy pleß (Blöße) suchen. |
[25v-b] [No text] | [46r] 51 Item pintstu an das schwert. Vnnd empfindest das Er schwach ist. so wind deinen knopf duch deinen rechten arm. das dein kurcze schneid auf sein schwert komme. als da gemallet steet. so magstu Im das schwert an den hals winden. oder den fäler treiben | |||
| Strong
Item. If you hew in from above into the opponent's sword and they hold strong, then rise up into the air with your sword against their sword back toward the weak of their sword and your hilt stays against their sword and wind the short edge against their throat (as is pictured here), then you can draw them to the ground with power. |
[4v] Sterck.
Item haustu ainem oben ein in das swert und er helt starck wider, so var auf in dy hoch mit deinem swert hinder sich an seinem swert gegen sein swech und das dein gehilcz an seinem swert ste und wint im dy kurcz sneid an den hals, als hie gemalt stet, so magstu in mit gewalt auf dy erden ziechen. |
[32r-b] [No text] | [46v] 52 Item pindestu ainem an. Vnnd empfindest das Er starckh ist. so gehe Inndes. vnnd wind auff. das dein kurcze sneid an sein schwert komb. vnnd empfind mer. ist Er dann aber starckh. so gehe mit deinem schwert in sein schwech. vnnd wind Im das schwert an den hals. vnnd zeuch jne vmb als da gemalet steet. | |||
| Before
Item. If you bind someone up against your sword and they slash in strongly at your head, parry them with your short edge and force into them so that they must strike. Then if they strike on the other side, lay your sword against their left shoulder (as is pictured here), then strike them in their ear. This is called being situated inside and also called the before. |
[5r] Vor.
Item so du ainen in das swert pinczt (bindest) und er slecht dir starck ein zu dem kopf, so versecz in mit der zurczen (kurzen) sneid und dring in in, so muß er slachen. Slecht er den zu der andern seiten, so lege im dein swert anf sein tencke agssel, als hie gemalt stet, so slechstu im an ein or. Das haist eingelegt und haist vor. |
[61r-b] 4 | [47r] 53 Item pindestu ainem an. vnnd empfindest das Er nit pleib lich ist. wenn Er dir dann nach der plöß schlecht. so trit Inndes vnnd wind Im dein kurcze schneid an das Or. als da gemalt steet. das haist vor. vnd reckh dich wol vnd biß beheindt. | |||
| After
Item. If someone hews in at you strongly from above, be careful and parry the hew with the short edge. Then if they are as swift and cut before you can get situated inside, allow them to hew freely and fall upon their sword with your short edge (as is pictured here), then bind them up and strike them in the ear and go forwards. |
[5v] Nach.
Item so dir ainer oben starck ein haut, so wart und versecz im dy heu mit der kurczen sneid. Ist er dan als pehent und haut ee, wen du im ein magst legen, so laß in frey hauen und vall im mit der kurczen sneid auf sein swert, als hie gemalt stet, so pincztu in und slechst in an das or und ge fur sich. |
[31v-a] [No text] | [47v] 54 Item pindestu ainem an. vnnd Er trit behennd zu dir vnnd schlecht dir nach der vordern plöß. so gee Inndes vnd wind Im dein kurcze schneid. oben an sein or. als vor oben auff sein schwert. das haist nach. vnd reckh dich wol. als da gemalet steet. | |||
| Feeling Indes
Item. If the opponent binds into your sword and winds into your face or conducts other techniques, then wind out as well and go swiftly forwards into them and as soon as they will employ something, fall strongly into their arms and shove them back as is pictured here, such that you thrown them on their back. |
[6r] Fülen ynndes.
Item so dir ainer in das swert pint und will dir in das angesicht winden oder ander kunst treiben, so wint auch aus und gee reschlich für sich in in und, als pald er etwas arbaitten will, so vall im starck in sein armen und stoß im zuruck, als hie gemalt stet, so wurfstu in an den rucken. |
[48r] 55 Item so du ainem pintst. der nit pleiblich ist, vnd den plösenn nach schlecht. als vor. vnnd wenn du den vor vnd nach nymbst[11]so gehe vast Inndes. vnnd pleib vest mit deiner kurczen sneid an seinem schwert. vnnd stoß jm zu rugkh als da gemalet steet. so mag Er zu kainer arbait mehr khommen. | ||||
| Item. If you bind someone up and they wind in at your face, then wind in as well and stand firm in the winding and on their sword and feel like this so that you do not allow them to come away from your sword, so that they cannot come to any work. This is the greatest measure of the sword and stand strong in scales[12] as is pictured. | [6v] Item so du ainen anpinczt und er wint dir ein zu dem gesicht, so wint im auch ein und stee vest in der winden und empfind an seinem swert als so, dastu in nit von deinem swert last komen, das er zu kainer arbait mag komen. Das ist die größt maß dez swercz und stee starck in der wag, als gemalt stet. | [24v-a] [No text] | [48v] 56 Item pindestu ainem an. vnnd empfindest das Er pleiblich ist. so vest auff dein rechten seiten. vnd bleib steen. als da gemalet steet. vnnd kumb jm nit von dem schwert. so empfindestu was Er arbaiten will. ~ | |||
| Item. If you bind up into the opponent's sword and they wind in at your face with their short edge, then you as well wind up high in the air and when they rise up and will parry it, hew a suddenly retracted cut at their elbows with your long edge (as is pictured here). | [7r] Item pincztu ainem in das swert und er wint dir ein zu dem gesicht mit seiner kurczen sneid, so wint auch hoch auf in dy hoch und, wen er auf vert und wil das verseczen, so hau im einen verzuckten hau nach seinen elpogen, alz hie gemalt stet. | [32r-a] [No text] | [49r] 57 Item so du ainem oben an pindest. als vor. so windt Im baldt nach der schwech. vert Er denn auff. vnd wils wern. so trit zu mit dem linckhen fuß. vnnd haw Im einen verzuckhten haw. mit der lanngen schneid nach seinem Elpogen. alls da gemalet steet. so magstu den faler treiben. oder stuckh. | |||
| Item. When you have hewn at the opponent's elbow (as was previously pictured), if they then parry that hew, shove their sword sword down with your hilt and with [both] your pommel and with both of your arms fall across them and lay your short edge against their throat and draw it (as pictured here). | [7v] Item so du ainem nach dem elpogen hast gehauen, als da hinden gemalt stet, verseczt er denn (dann) den hau, so stoß im sein swert nider mit deinem gehilz und vall im mit dem knopff und mit paiden armen über und leg im dy kurcz sneid an den hals und zeuch in, als hie gemalt stet. | [7r-b] [No text] | [49v] 58 Item ein stuckh auff das das [sic!] vorder. so du ainem nach dem Elpogen schlechts. der verseczt dir den straich. so pleib vest ann seinem schwert. vnnd stoß jm sein schwert nider mit deinem gehilcz. vnd vall jm mit deinem knopff vber. vnd schlach jn mit der kurczen schneid auff den kopff. vnd leg jm dann das schwert an den halß. als da gemalet steet. ~ | |||
| Item. One more play. When you suddenly retract toward their elbows and they parry the cut, remain standing with your sword against theirs and lunge forwards with your right foot as if you will strike on their other side and slice out toward their left ear (as is pictured here). This is called the coupling to the outside. | [8r] Item mer ein stuck. Wen du im nach dem elpogen siechst und er vercezt (versetzt) den hau, so pleib sten mit deinem swert an den seinen und trit für mit dem rechten fuß, als welstu im zu der andern seiten slachen, und sneid im auß nach seinen tencken oren, als hie gemalt stet. Das haist die ausser mynn. | [25r-a] [No text] | [64r-b] 10 | [50r] 59 Item verseczt dir ainer den halben haw nach dem Elpogenn. vnnd ist nit pleiblich am schwert. vnd weicht hinder sich. so trit zu mit dem rechten fuß. vnnd bleib an seinem schwert stet. vnnd wind Im dein kurcze schneid. an sein lenckhes Or. als da gemalet steet. das haist die ausser mynn. oder der ausschnit. ~ | ||
| Item. One more such play. When you suddenly retract toward their elbows and they parry the strike, rise up high with both of your hands and let your left hand pass and drop across both of their arms and slap it back toward your left side and thrust through between yours and theirs with your own sword and lay your sword against their throat (as is pictured here), then you break off their arm and sever their throat. | [8v] Item mer ein solichs stuck. Wen du im nach dem elpogen siechst, verseczt er den den slag, so var hoch auf mit deinen paiden henden und laß dein tencke hand varen und vall im über sein paid armen und slachs hinter dein tencke seiten und stich mit deinem swert zbischen (zwischen) dein und sein durch und leg im das swert an den hals, als hie gemalt stet, so prichstu im den arm ab und sneist (schneidest) im den hals ab. | [13v] [No text] | [65r-a] 11 | [50v] 60 Item verseczt dir ainer den halben haw mer als vor. vnd bleibt starckh am schwert. so wind hoch auff. vnnd vall Im Inwendig mit deinem lenckhen arm lanckh vber sein baid arm. vnd vach Im sein schwert vnder dein vchsen. vnnd zuckh dein schwert vber dein haubt. vnd verwinds. vnnd Im nach dem gesicht. als da gemalet steet. oder stich Im vnden durch an seinen hals. | ||
| Item. When they have caught your sword under their armpits in this way and will extend to slash or stab you, then flee behind them away from their strike and fall forward into your sword with your left and wind it forwards right there (as is pictured here) so that you break off their arm. | [9r] Item dir ainer dein swert also hinter sein tencken vgssen (Achsel) gevangen hat und wil dich slachen oder stechen stechen (!), so fleuch hinter in aus seinen slag und vall mit deinem tencken (Hand?) voren in dein swert und wint in herfür, als hie gemalt stet, so prichstu im den arm ab. | [12r-b] [No text] | [63r-b] 8 | [51r] 61 Item so dir ainer dein schwert vnder das vchsen hat gefangenn als vor. vnnd will dich stechen oder hawen. so fleuch mit deinem rechten fuß hinder In. vnnd greiff mit deiner lenckh(en) handt vber sein Achsel. in dein schwert klingen. vnnd wind auff in die höch. als da gemalet steet. so wirstu ledig. vnnd prichst jm den arm ab.
[directly under the right figure, probably added later, difficult to read] mit dem fuß [beins?] [ferfing?] hinder[13] seinen [lingkhen?] [very faintly written] fus | ||
| Item. If someone has struck at your elbow and grasped your sword with their left hand as before and will thrust through between you and them toward your throat as before, then clasp their sword's blade into your left hand and lay that against their throat (as is pictured here) and lunge in behind, then you throw them on their back.[14] | [10r] Item so dir ainer nach dem elpogen hat geschlagen und vächt (fängt) dir dein swert mit seiner tencken hant, als vor, und wil zbischen (zwischen) dir und in durchstechen nach deinen hals, als vor, so vach sein swercz klingen in dein tencke hant und leg ims selb an seinen hals, als da hie gemalt stet, und hinter trit in, so würfstu in auf den rucken.
Dy geschrift gehört an das hinter stuck, iene gehört herüber. |
[10v-a] [No text] | [51v] 62 Item vbereylt dich ainer, vnd pring dir das schwert an dei nen halß. als vorsteet. so vach seinen spicz in dein lenckh(e) hand. vnnd wend Innen an sein lenckhs or. vnd trit mit deinem linckhen fuß. hinder seinen rechten. als da gemalet steet. ~ | |||
| Item. If someone binds against your sword, wind in your short edge at their face and indes, go and lunge forwards with your left foot and fall across their hands with your pommel and clasp your blade into your left hand and lay it against their throat (as is pictured here), then you throw them on their back.[15] | [9v] Item so dir ainer an dein swert pint, so wint im dy kurcz sneid nach dem angesicht ein und gee inndes und trit für mit dem tencken fuß und vall im mit deinem knopf über sein hent und vach dein klingen in dein tencke hant und leg ims an den hals, als hie gemalt stet, so würfstu in auf den rucken.
Dy geschrift gehört zu dem andern stuck davorn. |
[31v-b] [No text] | [60r-a] 1 | [52r] 63 Item nun merckh besunder. pindt dir ainer an. vnd enpfindst vnnd bleibt starckh. vnnd wil[s] dich nit nach dem Elpogen schlage(n) lassen. so laß deinen knopff. vnd vall Im vber sein schwert damit. vnnd greiff mit deiner hand in dein klingen. so schlechstu In auff den kopff. als da gemalet seet. ~ | ||
| Item. If someone binds against your sword and winds into your face, then you wind as well and let your pommel pass as before and fall across them and lunge behind them and lay your sword against their head (as is pictured here), then you throw them on their back. | [10v] Item so dir ainer an das swert pint und wint dir in das angesicht, so wint auch und laß den knöpf varen, als vor, und val im über und hinter trit in und leg im das swert an das haupt, als hie gemalt stet, so würfstu in auf den rucken. | [60r-b] 2 | [52v] 64 Item so du vber bist gefallen als vor steet. so leg Im die klingen an seinen halß. vnnd trit mit deinem lenckhen fuß weytt hinder In. als da gemalet steet. vnnd wind hoch auff. so wirffstu In auff den Rugkhen. vnd stoß das schwert In jn | |||
| Item. If someone winds in into your face, them immediately grab your sword's blade with your left hand and stab them across their sword and into their testicles (as is pictured here). This is quite a good remarkable play. | [11r] Item wint dir ainer ein in das gesicht, so greif bald mit deiner tencken hant in dein swercz klingen und stich über sein swert in zu seinen hoden, als hie gemalt stet. Das ist gar ein gucz namhaftes stuck. | [9v-a] [No text] (Similar) | [64r-a] 9 | [53r] 65 Item so du ainen anpindest. vnd empfindest das Er bleiblich ist. vnd will dich vom schwert nit lassen. so greiff mit deiner lincken hand in dein klingen. vnnd stich jn vber sein schwech nach den hoden. als da gemalet steet. vnd bleib nahent Ihin schwert. das Er dir nit darauß gehe. | ||
| Item. A good sword disarm. When someone binds you up against their sword, wind up with your short edge and Indes, enter them firmly and grasp into their bind between their hands with your left hand and go across their blade with your pommel and shove toward their mouth (as is pictured here), then you take their sword. | [11v] Item ein gucz swert nemen. Wen dir ainer oben an pint an das swert, so wint auf mit der kurczen sneid und gee vast inndes in in und greif mit deiner tencken hant in sein pint zbischen sein hent und gee mit dem knopf über sein klingen und stoß in gegen dem maul, als hie gemalt stet, so nimstu im das swert. | [30r-a] [No text] | [53v] 66 Item steestu in den anpinden uner ist so hoch das du jm nit vber magst. so greiff Im mit deiner lencken hand zwischen seine hend in das pint. vnnd var Im mit deinem knopff auff an seinem schwert. nach der schwech. vnd stoß Ihne mit dem knopff in das angesicht. als da gemalet steet. | |||
| Item. Quite a good obscure device for a particularly strong man. When someone binds into your sword and will wind in or thrust, wind up firmly as well and go strongly against their sword with your short edge and give them a great shove onwards with both hands. If they are turned away before you, strike them upon the head (as is pictured here). | [12r] Item ein anderes swert nemen. Wen dir ainer an pint und wil dir ein winten zu dem gesicht, so greif bald mit deiner tencken hant in paid swercz klingen und zeuchs auf dein tencke seiten und gee mit deinem gehilcz unden an sein hant und dauch über sich, als hie gemalt stet, so nimstu im das swert. | [30v-b] [No text] (Similar) | [54r] 67 Item pindt dir ainer an. vnnd ist so stett in dem enpfinden. das Er dich gar nit vom schwert will lassen. so greiff mit deiner lencken hand mitten in baid schwerts klingen. vnnd secz Im dein pind vnden an sein hend. vnnd wind auff als da gemalet steet. so nymbstu Im das schwert. | |||
| Item. Quite a good obscure device for a particularly strong man. When someone binds into your sword and will wind in or thrust, wind up firmly as well and go strongly against their sword with your short edge and give them a great shove onwards with both hands. If they are turned away before you, strike them upon the head (as is pictured here). | [12v] Item gar ein gucz verporgenes stuck für einen iedlichen starcken mann. Wen dir ainer in das swert pint und wil dir ein winten oder stechen, so wint auch vast auf und gee mit der kurczen sneid starck an sein swert und gib im einen großen stoß mit paiden henden für sich an, so kert er sich vor dir und so slach in auf den kopf, als hie gemalt stet. | [54v] 68 Item so du ainem anpindest. der stät in dem enpfinden ist. vnnd will sich nit verfüeren lassen. so secz Im dein baid armen an seinen rechten arm. vnd stoß jn starckh von(n) dir. so kert Er sich dir vmb. das du In on alle nine auff den kopff schlechts. als da gemalet steet. | ||||
| Item. One more good sword disarm. When someone binds you up against their sword, immediately pass into the bind with your right hand past their sword between both of their hands and pull toward yourself and with your left hand push away the cross of their sword and thrust the pommel into their face (as is pictured here). | [13r] Item mer ein gucz swert nemen. Wen dir ainer an pint an das swert, so var pald mit deiner rechten hant in sein swert zbischen seiner paider hent in das pint und zeuch an dich und scheub mit deiner tencken mit dem creucz sein swert an weg und stoß in mit dem knopf in das maul, als hie gemalt stet. | [27v-a] [No text] | [55r] 69 Item pindt dir ainer oben starckh an. vnnd will dich vbertring(en) so greiff Im mit der rechten a bichen handt in sein pint. vnnd stoß Im sein schwert oben weg. mit deinem Kreucz. vnd ruckh starckh an dich. vnnd trit mit dem lencken fuß hinder In. vnnd stoß jn mit dem knopff jns maul. als da gemalet steet. | |||
| Item. One more sword disarm. When someone binds you up and will wind into your face, remain engaged with your long edge and rise up high and with your pommel pass in between their hands and with your left hand clasp your blade and wind against their head (as is pictured here). | [13v] Item mer ein swert nemen. Wen dir ainer an pint und wil dir in das gesicht winden, so pleib sten in der langen sneid und var hoch auf und var im mit dem knopf zbischen sein hent ein und mit der tencken hant vaß dein klingen und wint im an den kopf, als hie gemalt stet. | [62r-b] 6 | [56r] 71 Item pindt dir ainer starckh an. vnnd vert hoch auff. vnd will dich vbertringen. so laß deinen knopff. vnnd ynnen zwischen seiner hend in das pind. vnd greiff jnn dein klingen. vnnd trit für. vnd wind Im das schwert an den halß. als da ge. malet steet. so nymbstu Im das schwert. vnd wirffst jn.
| |||
| [66r-a] 13 | ||||||
| Item. One more sword disarm. When someone binds against your sword, bind in strongly as well and duck it back behind you and let your left hand pass and [reach] past their sword over their right arm [and] grab between their hands and pull backwards (as is pictured here). | [14r] Item mer ein swert nemen. Wen dir ainer an das swert pint, so pint in auch starck ein und dauch in hinder sich zuruck und laß dein tencke hant varen und greif im über sein rechten arm in das swert zbischen seiner hent und zeuch hinter sich, als hie gemalt stet. | [55v] 70 Item pindt dir ainer oben starckh an. vnnd windt dir hoch nach dem haupt. so greiff jm mit deiner lenckhen hand vber seinen arm abichen. in sein pind. vnd ruckh starckh an dich. als da gemalet steet. sy nymbstu Im das schwert. vnd schlechst In. | ||||
| Item. A good play. When someone binds against your sword, swiftly wind in and with your pommel, drop over and with your left hand, grab your blade and with your left foot, lunge in behind and lay your sword against their throat and pull them onto their back and thrust your sword into them (as is pictured here). | [14v] Item ein gut stuck. Wenn dir ainer an das swert pint, so wint im reschlich ein und val mit dem knopf über und greif mit der tencken hant in dein klingen und trit mit dem tencken fuß hinder in und leg ims swert an hals und zeuch in an rucken und stichs swert in in, als hie gemalt stet. | [62r-a] 5 | ||||
| [63r-a] 7 | ||||||
| Item. One more sword disarm. When someone binds against your sword, bind in strongly as well and duck it back behind you and let your left hand pass and [reach] past their sword over their right arm [and] grab between their hands and pull backwards (as is pictured here). | [7v-a] [No text] (Similar) | [56v] 72 Item pindt dir ainer oben starckh an. vnnd bleibt stät in dem enpfinden. so wirff Im deinen knopff hinder sein gehilcz vnnd greiff Im mit deiner lenkchen handt an seinen rechten Elpogen. vnnd wind auff. vnnd trit mit dem rech(ten) fuß für. als da gemalet steet. so prichestu jm den arm ab. vnnd wirffst in. | ||||
| Item. A good play for someone strong. When you bind someone up against your sword, act as if you will wind into their face and thrust firmly against their sword with your cross and rise up high and let your sword go, dropping over your head and cast yourself down around both their feet (as is pictured here), then you throw them. | [21r] Item ein gucz stuck fur einen starcken man. Wenn du mit ainem an pinczt an das swert, so thu, als welstu im in das angesicht winden, und stoß mit deinem creucz (Kreuz) vast an sein swert und var hoch auf und laß dann dein swert vallen über dein haupt und vall im unden um paid füß, als hie gemalt stet, so wurfstu in. | [16v-a] [No text] | ||||
| A good sword disarm. When someone binds against your sword, with your left hand slip in both sword's blades and with both your pommel and your right hand go down through their sword and pull backwards (as is pictured here), then you take their sword. | [21v] Item ein gucz swert nemen. Wenn dir ainer an das swert pint, so val im mit deiner tencken hant in paid swercz klingen und gee mit dem knopf und mit der rechten hant unten durch sein swert und zeuch hinter sich, als hie gemalt stet, so nimstu im das swert. | [20r-b] [No text] (Similar) | [61r-a] 3 (Similar) |
For further information, including transcription and translation notes, see the discussion page.
| Work | Author(s) | Source | License |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cod. Ⅰ.6.4°.2 Images | Universitätsbibliothek Augsburg | Universitätsbibliothek Augsburg | |
| Libr. Pict. A.83 Images | Staatsbibliothek zu Berlin | Staatsbibliothek zu Berlin | |
| Reichsstadt Nr. 82 Images | Stadtarchiv Augsburg | WikiMedia Commons | |
| Translation (dagger) | Chuck Wyatt and Cory Winslow | Wiktenauer | |
| Translation (messer) | Cory Winslow | Wiktenauer | |
| Translation (messer) | Christian Trosclair | Wiktenauer | |
| Augsburg Version Ⅰ | Friedrich Dörnhöffer | Die Ringkunst des deutschen Mittelalters | |
| Glasgow Version | Dierk Hagedorn | Hammaborg Historischer Schwertkampf | |
| Berlin Version | Jens P. Kleinau (with Dierk Hagedorn) | Hans Talhoffer ~ A Historical Martial Arts blog by Jens P. Kleinau | |
| Vienna Version | Friedrich Dörnhöffer | Die Ringkunst des deutschen Mittelalters | |
| Augsburg Version Ⅱ | Werner Ueberschär | Schwertbund Nurmberg e.V. |
Additional Resources
- Dörnhöffer, Friedrich (in German). "Albrecht Dürers Fechtbuch". Jahrbuch der Kunsthistorischen Sammlungen des Allerhöchsten Kaiserhauses. Vienna: 1909. pp 300-462.
- Dörnhöffer, Friedrich (in German). Albrecht Dürers Fechtbuch. Vienna: F. Tempsky, 1910.
- Ott Jud; Dürer, Albrecht; Auerswald, Fabian von; Petter, Nicolaes; Paschen, Johann (in German). Chronik alter Kampfkünste: Zeichnungen und Texte aus Schriften alter Meister entstanden 1443-1674. Weinmann, 2003. ISBN 978-3878920311
- Hagedorn, Dierk (in German). Albrecht Dürer. Das Fechtbuch. VS-Books, 2021. ISBN 9783932077500
- Hagedorn, Dierk and Daniel Jaquet. Dürer's Fight Book: The Genius of the German Renaissance and his Combat Treatise. Barnsley, UK: Greenhill Books, 2022. ISBN 978-1-784438-703-7
- Strauss, Walter L. The complete drawings of Albrecht Dürer. New York: Abaris Books, 1974. ISBN 0913870005
- Welle, Rainer (in German). Albrecht Dürer und seine Kunst des Zweikampfes : auf den Spuren der Handschrift 26232 in der Albertina Wien. Kumberg: Sublilium Schaffer, Verlag für Geschichte, Kunst & Buchkultur, 2021. ISBN 9783950500806
- Welle, Rainer (in German). …vnd mit der rechten faust ein mordstuck - Baumanns Fecht- und Ringkampfhandschrift. Herbert Utz Verlag, 2014. ISBN 978-3831643776
- Welle, Rainer (in German). "…und wisse das alle höbischeit kompt von deme ringen". Der Ringkampf als adelige Kunst im 15. und 16. Jahrhundert. Pfaffenweiler: Centaurus-Verlagsgesellschaft, 1993. ISBN 3-89085-755-8
- Żabiński, Grzegorz and Walczak, Bartłomiej. Codex Wallerstein: A Medieval Fighting Book from the Fifteenth Century on the Longsword, Falchion, Dagger, and Wrestling. Boulder, CO: Paladin Press, 2002. ISBN 978-1-58160-585-3
References
- ↑ J. Christoph Amberger. "The Death of History: Historic European fighting arts in the Mis-information Age". Fencers Quarterly Magazine. Retrieved 12 October 2010.
- ↑ dauchen : drücken, niederdrücken.
- ↑ Im Fechten gibt es den Zwerhau, der in dieser Handschrift als Twir bezeichnet wird, in anderen Quellen aber auch Twirch geschrieben wird, von zwerch = schräg, quer. Zum einen würde diese Bedeutung in Verbindung mit dem Ringen hier keinen wirklichen Sinn ergeben, zum anderen wäre die Schreibweise mit „b“, auch wenn dieses stimmlos gesprochen werden kann, äußerst ungewöhnlich. Im Rheinischen Wörterbuch findet sich dagegen der Begriff Pirch = Pferch = Einzäunung. Diese Bedeutung ergibt im Ringen mehr Sinn und könnte hier evtl. mit „Umklammerung“ übersetzt werden.
- ↑ der erste Buchstabe (p) ist nicht sauber geschrieben. pern stossen = Bärenstoß?
- ↑ es fehlt die „fünfft tbirch“, Dafür hat das Stück zwischen der drit und der vierdt tbirch keine Nummerierung.
- ↑ 5. plötzlich, unversehens.
- ↑ hier zu lesen als: fringt = ringt.
- ↑ The addition is difficult to read on the document, but results from the Table of Contents
- ↑ von äbich: abstehend, verkehrt (Deutsches Wörterbuch of the Brothers Grimm)
- ↑ The following pictures are marked with numbers underneath. As on the original the numbering is difficult to read, it was omitted in the transcription of the plays.
- ↑ das „b“ bei „nymbt“ wurde nachträglich aus vermutlich ursprünglich „y“ verbessert
- ↑ alt: fulcrum
- ↑ das „h“ ist über das vermutete „g“ geschrieben
- ↑ Text from subsequent image, per the statement "This passage belongs to the previous device, those belong hereafter."
- ↑ Text from subsequent image, per the statement "This passage belongs to the other devices before."