|
|
You are not currently logged in. Are you accessing the unsecure (http) portal? Click here to switch to the secure portal. |
Johannes Lecküchner
| Johannes Lecküchner | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Born | ca. 1430s Nuremberg, Germany |
| Died | December 31, 1482 Herzogenaurach, Germany |
| Occupation |
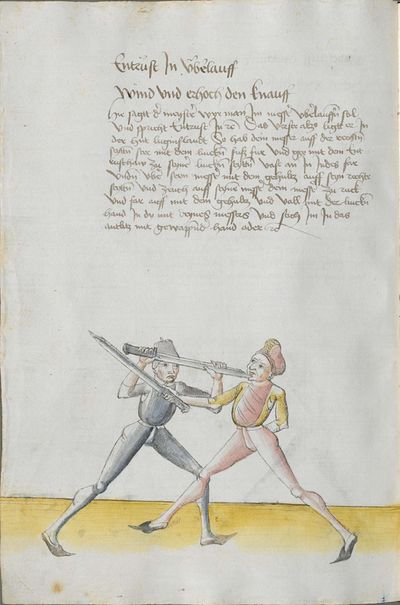
|
| Alma mater | University of Leipzig |
| Influences | Johannes Liechtenauer (?) |
| Genres | Fencing manual |
| Language | Early New High German |
| Notable work(s) | Kunst des Messerfechtens |
| Archetype(s) |
|
| Manuscript(s) |
MS E.1939.65.354 (1533)
|
| Concordance by | Michael Chidester |
| Translations | |
| Signature | |
Johannes Lecküchner (or Hans Lebkommer; ca. 1430s – 1482) was a 15th century German cleric and fencing master. He was born in the Nuremberg area, and in 1455 he was inscribed at the University of Leipzig. In 1457, he received the title of baccalaureus, and he was consecrated as a Catholic acolyte in 1459. At some point before creating his first manuscript in 1478, Lecküchner was consecrated as a priest. From 1480 until his death on December 31, 1482, he was employed as a communal priest in Herzogenaurach, Germany.[1] Lecküchner dedicated his fencing manual to Philip "the Upright" of Wittelsbach, Elector Palatine of the Rhine, but the nature of his connection to the duke remains unclear.[2]
Some 19th century scholars assumed that Lecküchner's name was a corruption of "Liechtenauer" and a reference to Johannes Liechtenauer, the grand master of the best-known German tradition. However, biographical information from historical records, as well as the colophon in the manuscript itself, thoroughly disproves this theory. Lecküchner's system of Messer fencing does, however, seem to be closely related to the long sword teachings of Liechtenauer from earlier in the century. His teachings are organized in a similar fashion using similar terminology, and often his Recital (Zettel) is nearly identical to that of Liechtenauer; he quotes or paraphrases the Lew gloss in many places, but it's unknown whether he had access to other teachings from the Liechtenauer tradition as well.
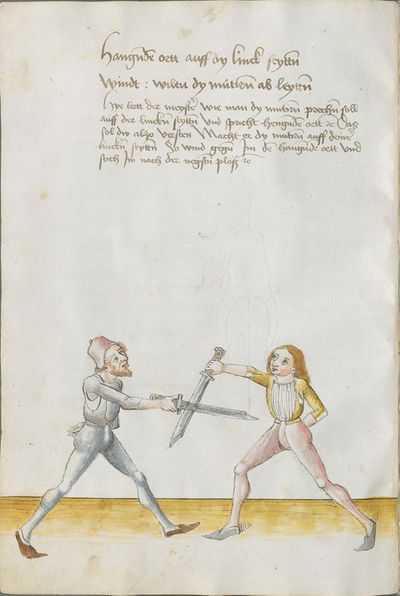
Two potential autograph copies of Lecküchner's treatise are preserved: the Cod. Pal. Germ. 430, completed between 1478 and 1482, and the Cgm 582, completed on 19 January 1482 (the year of his death).[3] The Cgm 582 mentions in the last paragraph that a previous draft had been produced which has sometimes been presumed to be a reference to the CPG 430, but since that is clearly a polished work for a client rather than a draft, it's more likely to be a lost third manuscript. This lost draft was probably the source for the shorter version included by Hans von Speyer in the MS M.I.29 in 1491, as well as those by Gregor Erhart in 1533, Paulus Hector Mair in the 1540s, and Lienhart Sollinger in 1556.
Preceding the treatises of Lew and Lecküchner in the MS M.I.29 are brief notes by a Magister Andreas explaining equivalences in concepts and terminology between the two,[4] perhaps indicating that by this time Lecküchner's teachings had been integrated into the Liechtenauer school of fencing. This notion is further supported by the appearance of Lecküchner's Recital alongside Liechtenauer's in Marxbrüder captain Peter Falkner's treatise of ca. 1495.
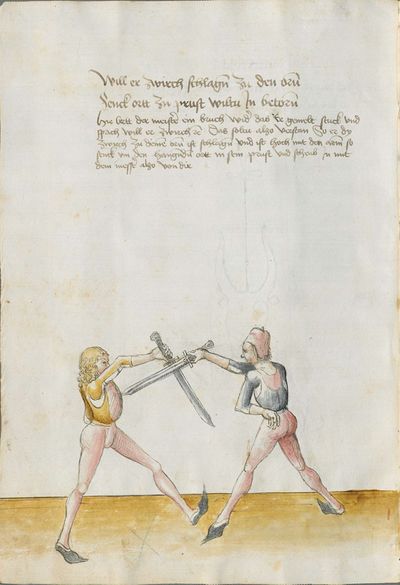
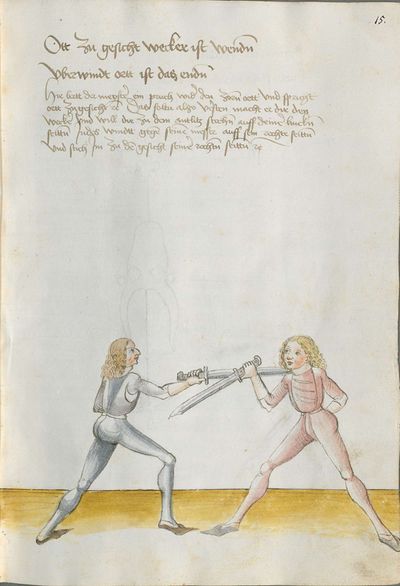
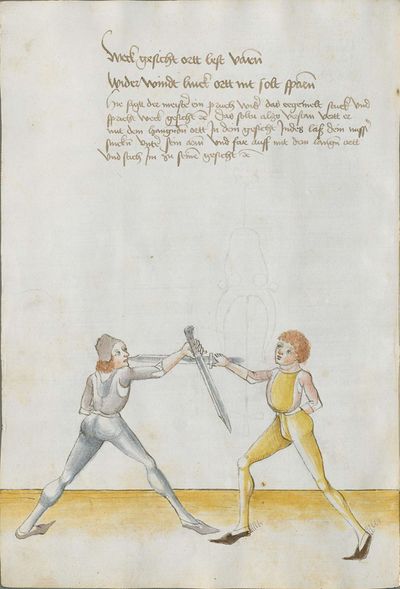
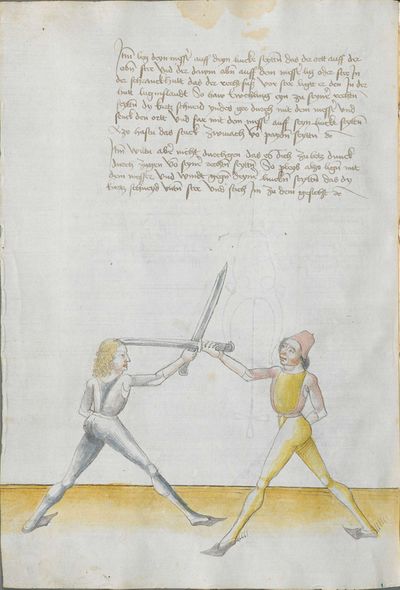
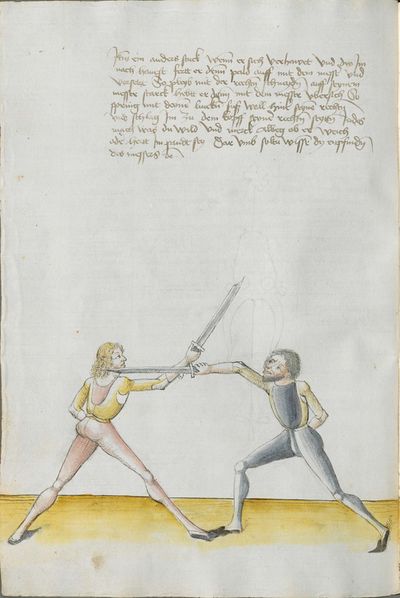
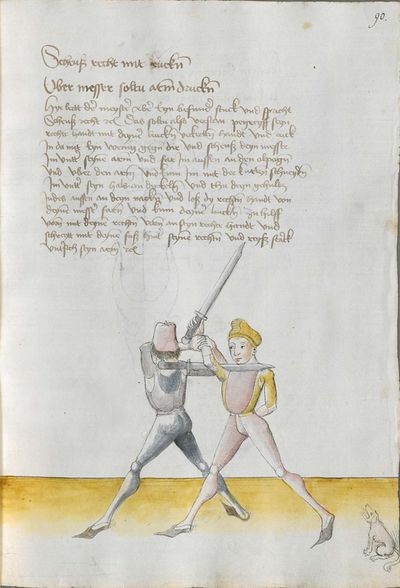
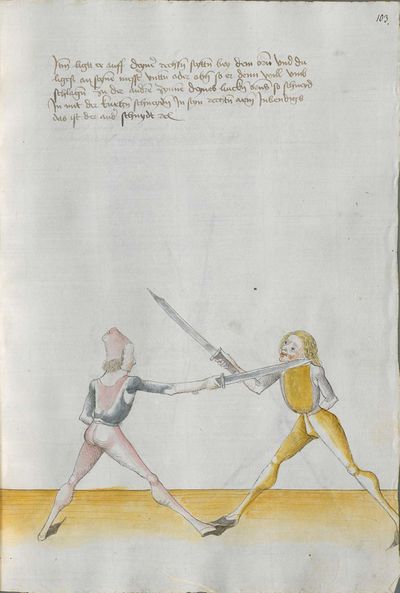
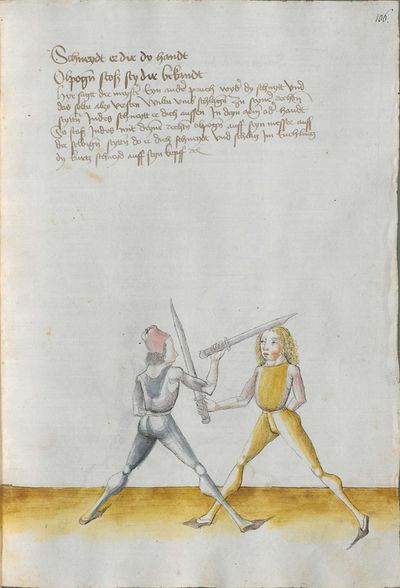
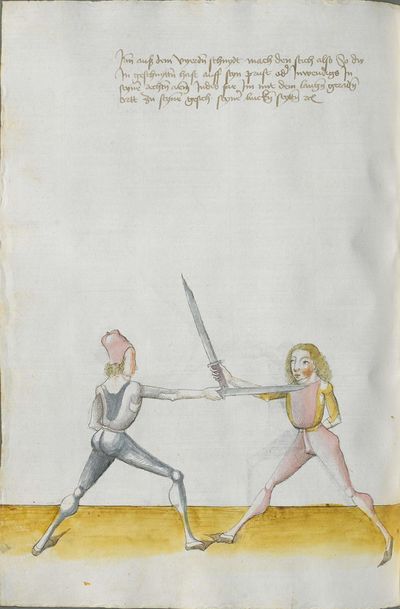
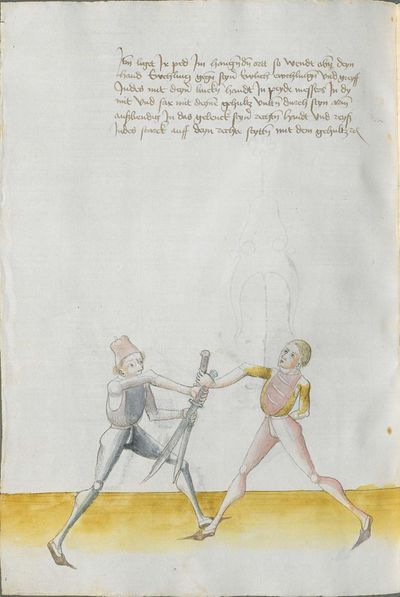
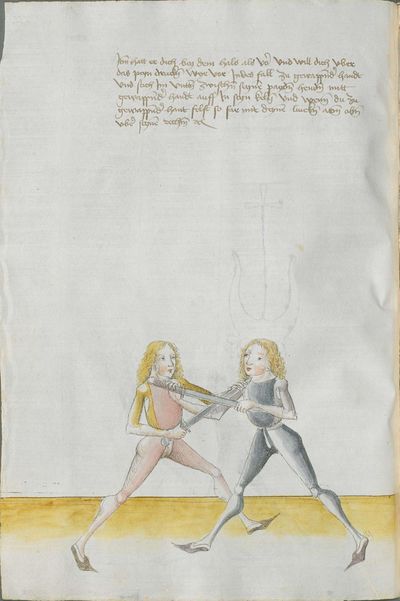
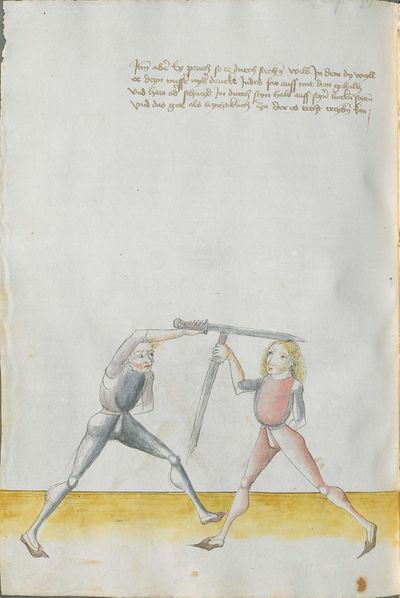
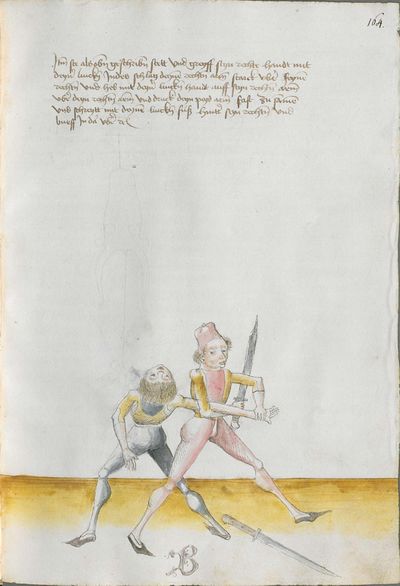
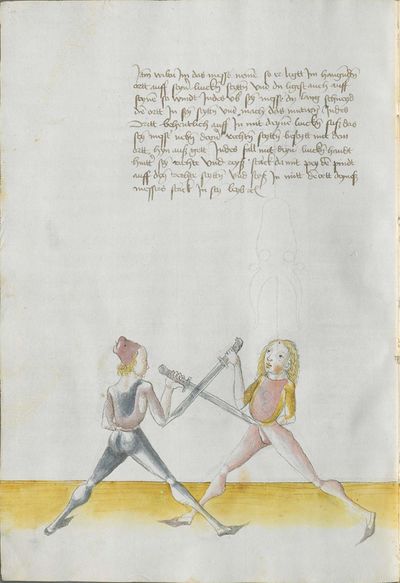
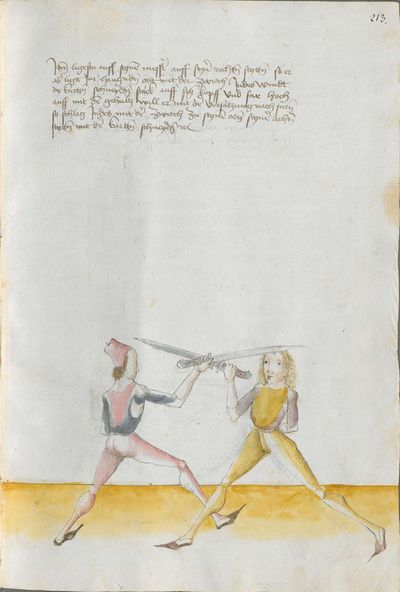
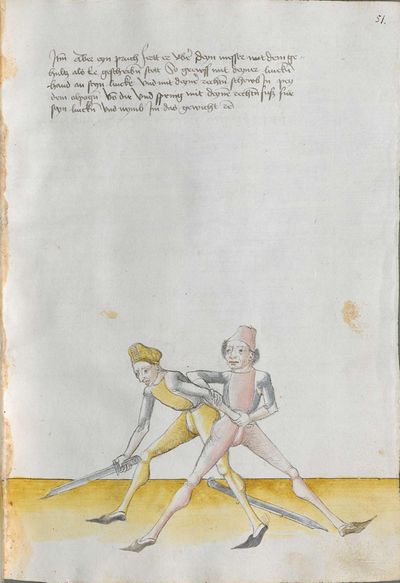
One final note of interest is that in 1531, printer Christian Egenolff published a fencing anthology entitled Der Allten Fechter gründtliche Kunst, and included a brief treatise on the Messer attributed to a certain Master Hans Lebkommer. This is either a misspelling or alternate rendering of "Lecküchner"; the text appears to be a brief summary of Lecküchner's teachings, intermingled with the Messer teachings of Andre Paurenfeyndt (uncredited). Since there is no indication that it was actually written by Lecküchner (who was long dead by that time), and in order to avoid confusion here, this otherwise anonymous treatise can be found on the Lebkommer page.
Contents
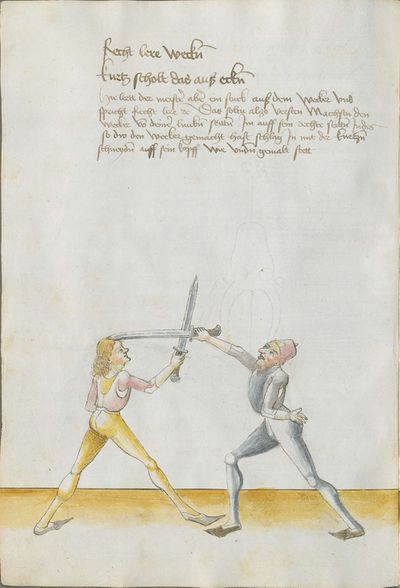
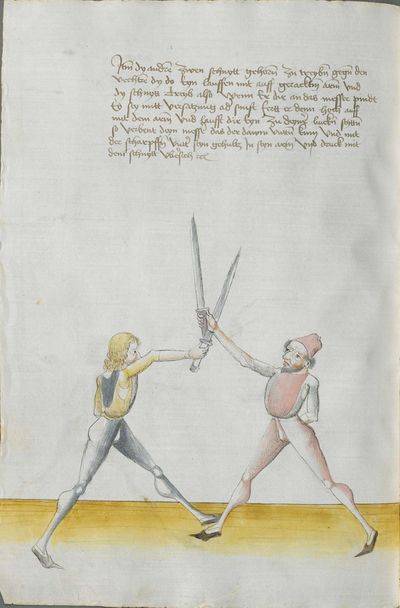
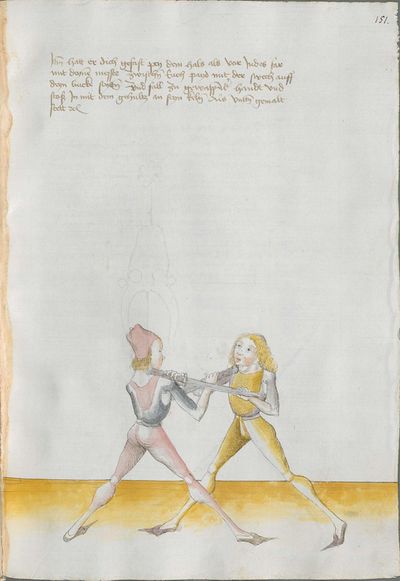
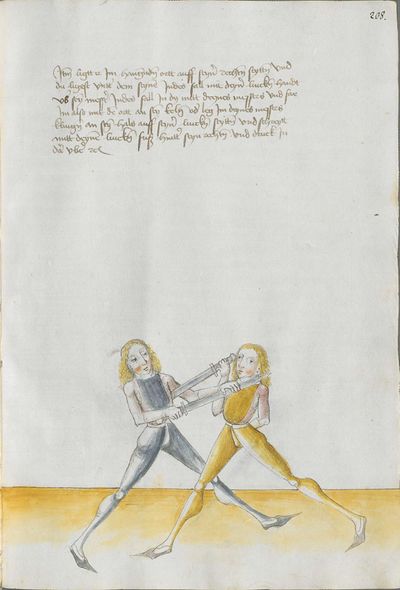
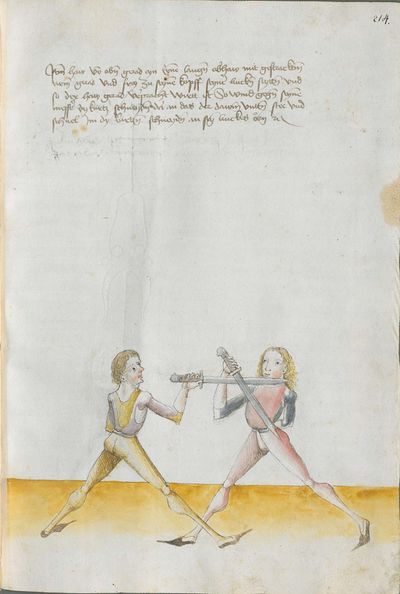
Treatise
The two manuscripts whose creation seems to have been personally overseen by Lecküchner contain a number of substantial differences, some of which can be interpreted as corrections in the later edition and others which are less explicable. In this compilation, they're treated as mutually-authoritative and translated separately; it's possible that a future version of this article will merge the translations together and describe the differences in footnotes. Both of these manuscripts were prepared late in Lecküchner's life based on one or more lost earlier versions. The Salzburg version seems likely to be a faithful copy of one of those versions, so it is presented in the first transcription column to illustrate how the text expanded over time.
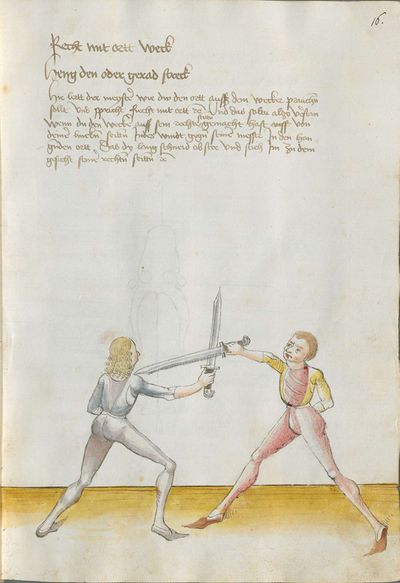
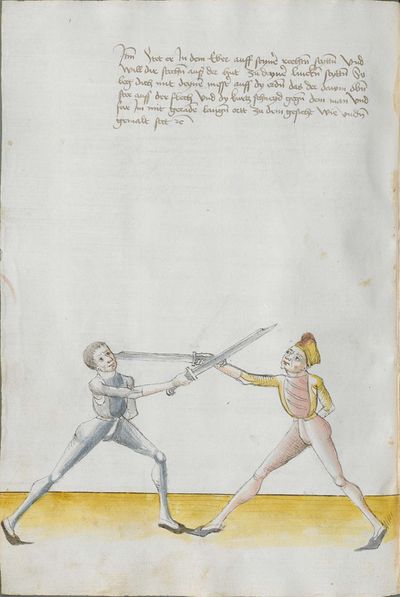
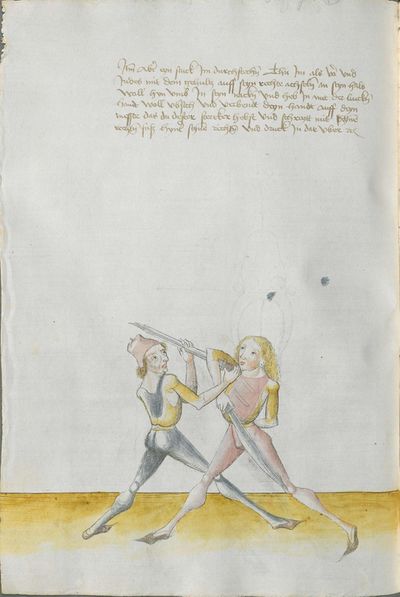
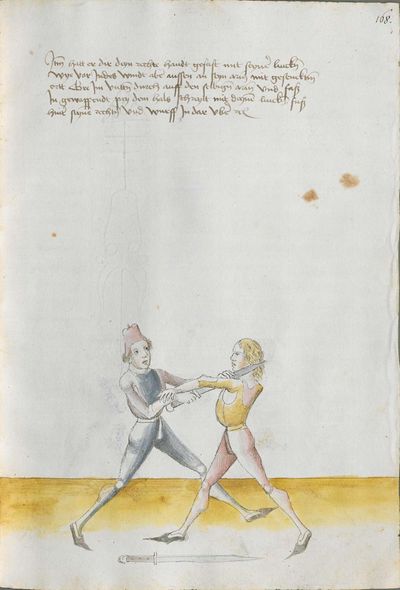
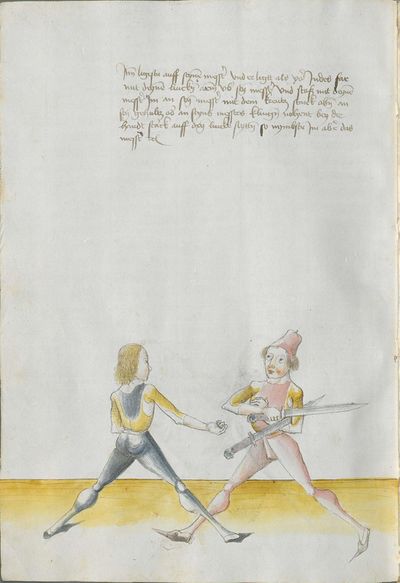
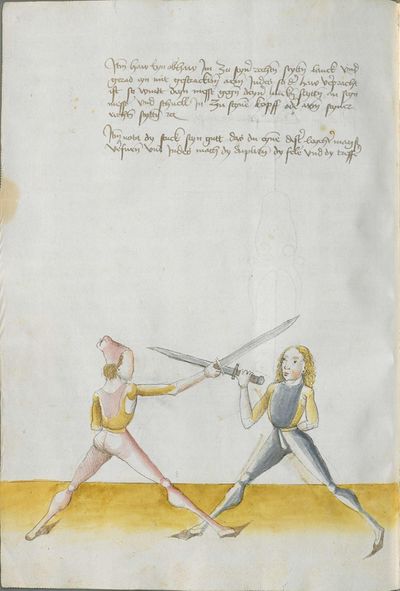
The typical Wiktenauer style is to break up the Recital into verses in a standard fashion according to their rhyme scheme. In the case of Lecküchner, however, the Recital is already broken into discrete lines in most extant copies, but the precise separation varies from copy to copy. The format of the various copies has therefore been preserved in this table in order to allow comparison (even though that means leaving the Vienna version completely un-separated). In the translation, the verses that are common to multiple copies are rendered in red text, while the verses that are unique to Munich version Ⅰ appear in black text.
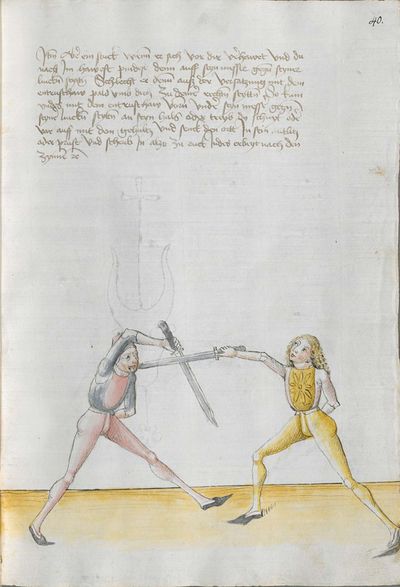
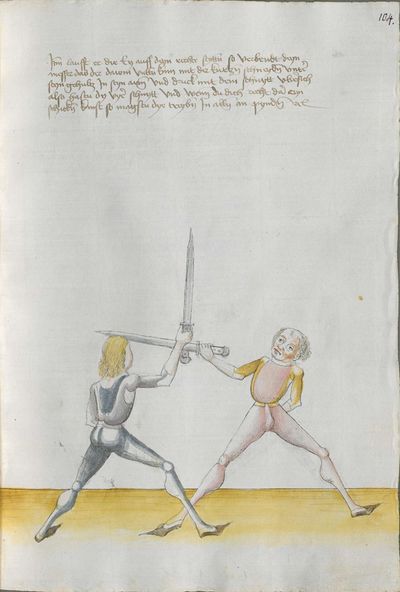
- To view a version of this table without illustrations and including a transcription of the Augsburg version of the Lew long sword gloss for reference, see Johannes Lecküchner/No illustrations.
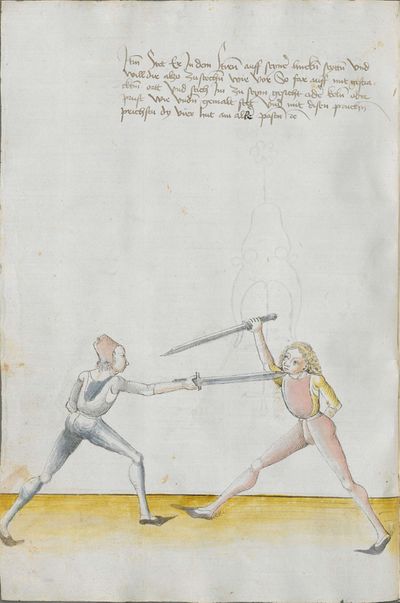
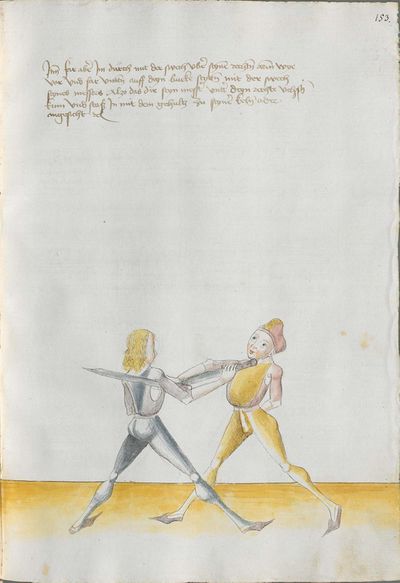
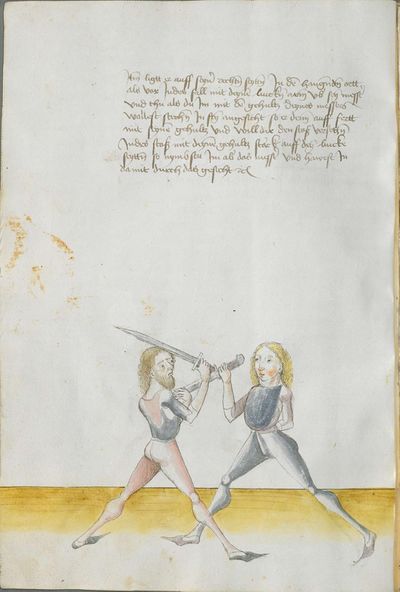
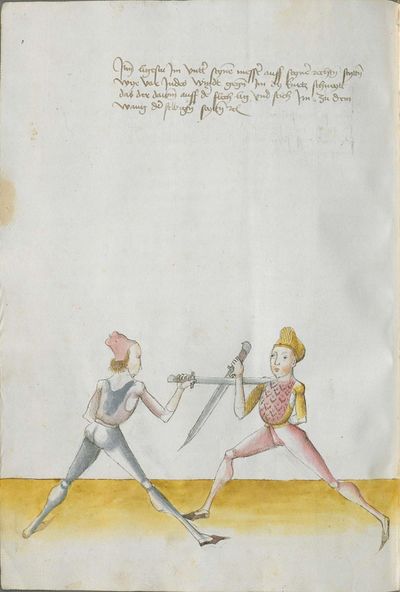
Illustrations |
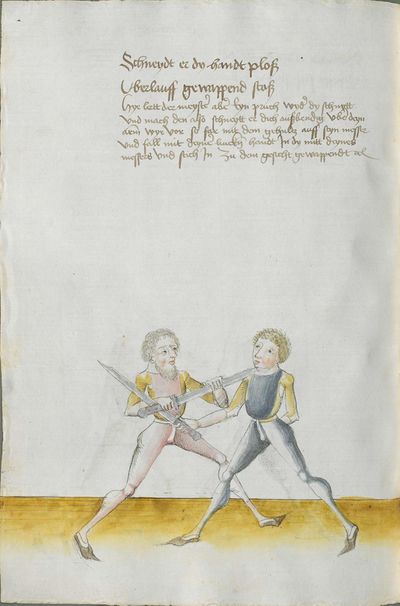
Partial Translation (from the Heidelberg) |
Draft Translation (from the Munich) |
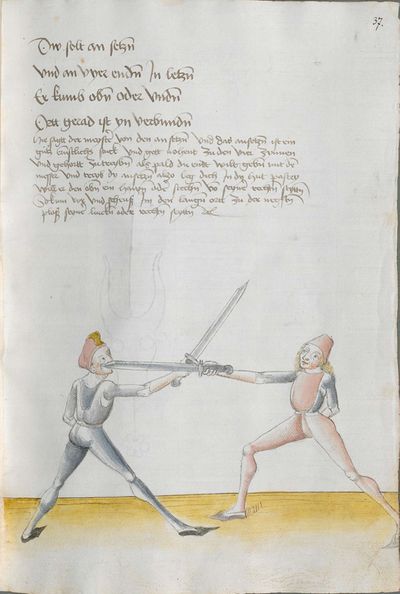
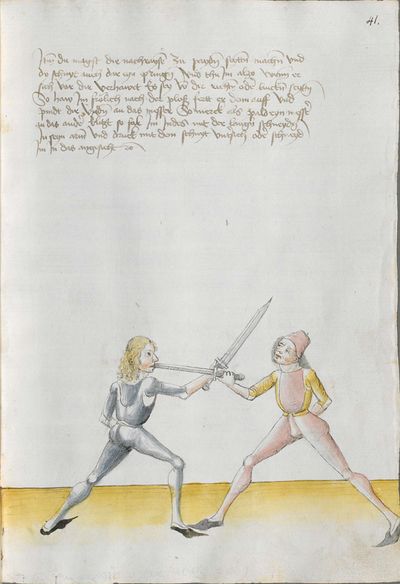
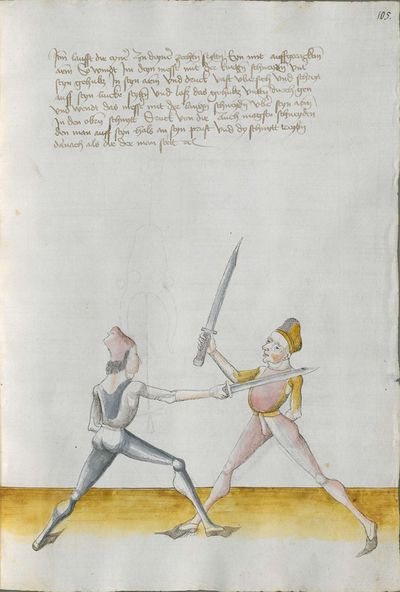
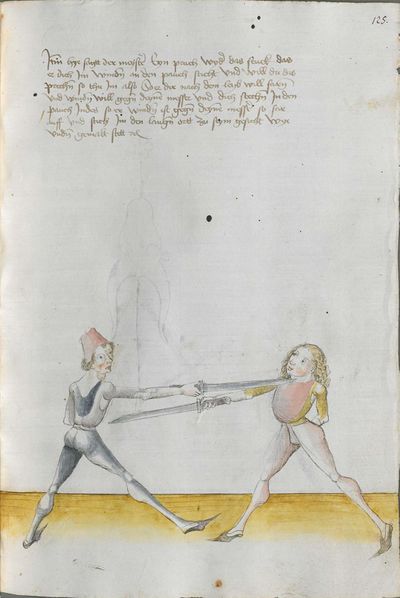
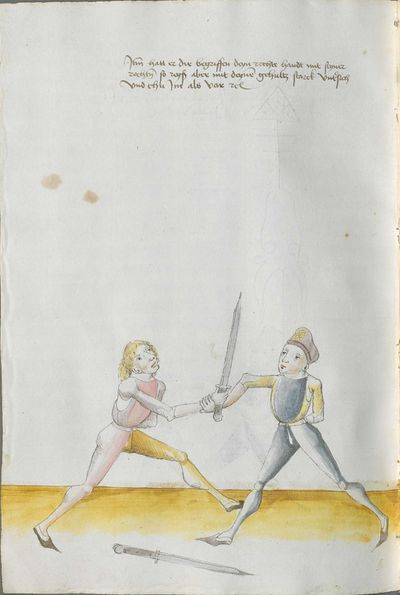
Salzburg Version (1491) |
Heidelberg Version (1478) |
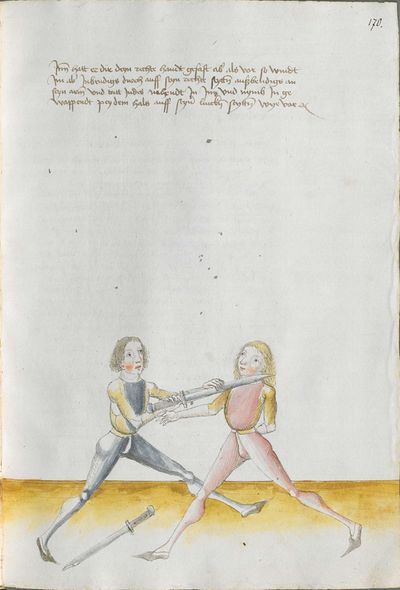
Munich Ⅰ Version (1482) |
Vienna Version (1512) |
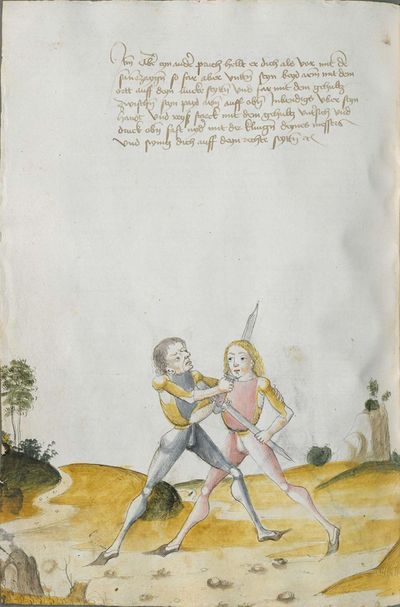
Glasgow Version (1533) |
Dresden (Mair) Version (1542) |
Vienna (Mair) German Version (1550s) |
Munich (Mair) Version (1540s) |
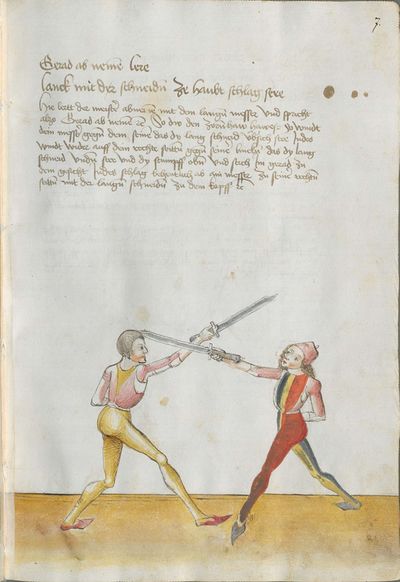
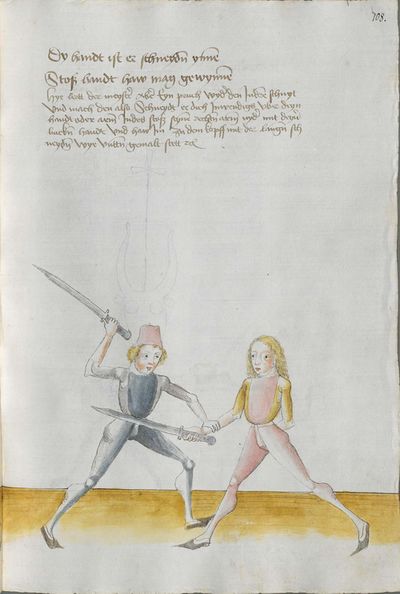
Vienna (Mair) Latin Version (1550s) |
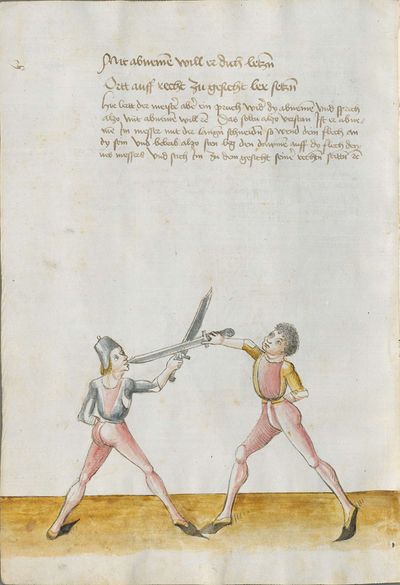
Munich Ⅱ Version (1556) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
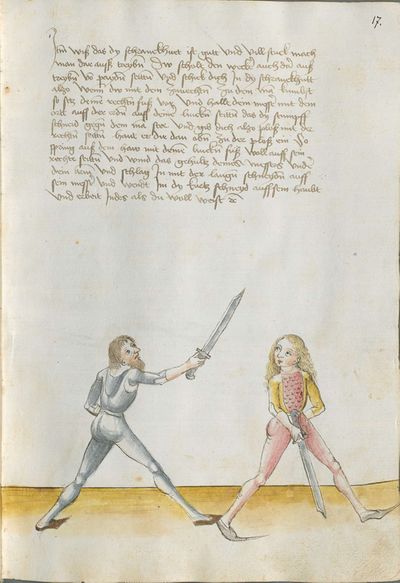
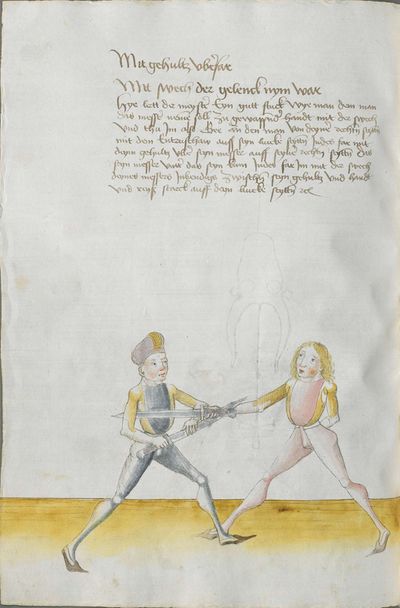
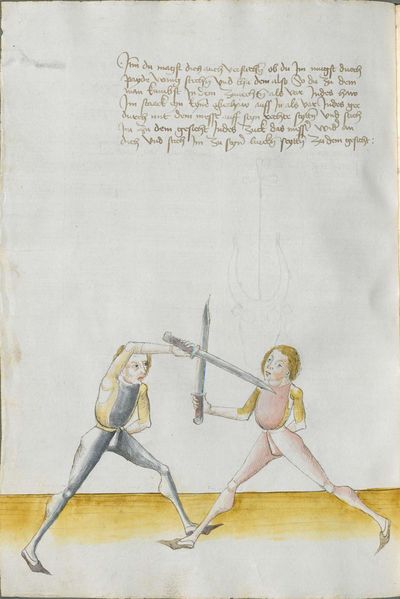
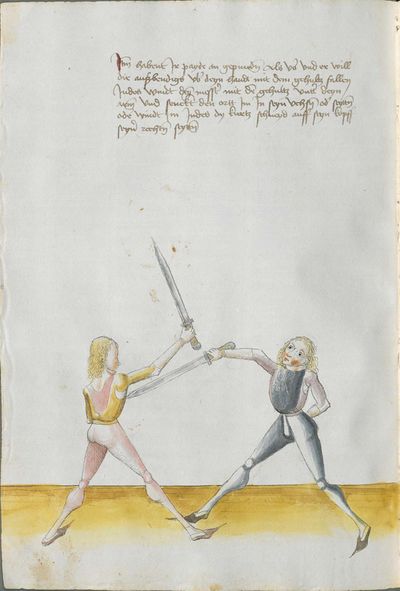
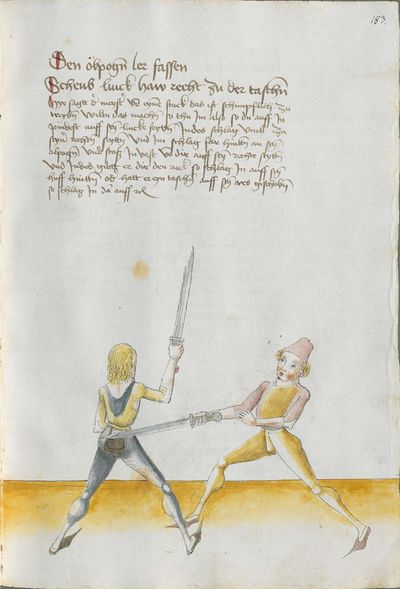
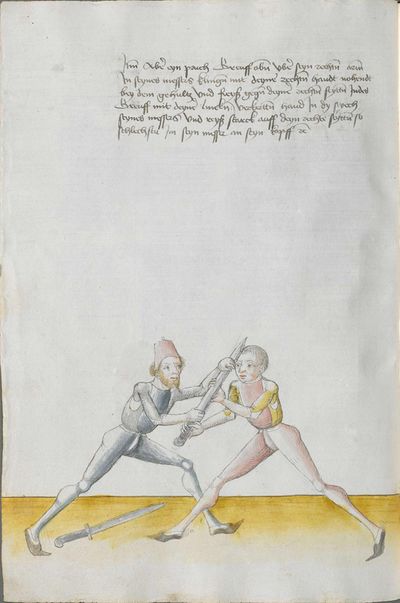
[1] This is the art and charter on the Messer of Sir Hans Leckuchner of Nürnberg, which he did and put together himself, the text and the explanation of it. |
This is the art and charter on the Messer of Sir Hans Leckuchner of Nürnberg, which he did and put together himself, the text and the explanation of it to His Highness Prince and Duke Philip, Count Palatine of Rhein, Arch-Cup-bearer and Prince Elector, and Duke in Bavaria. |
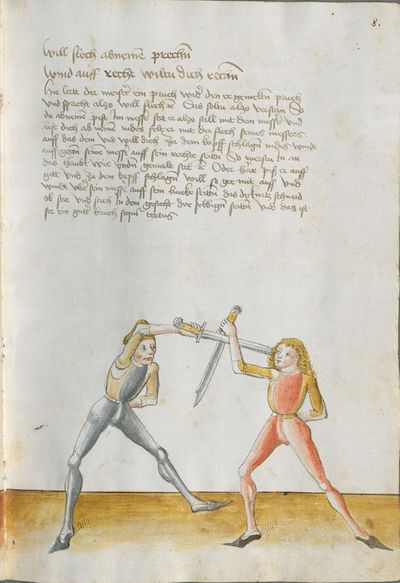
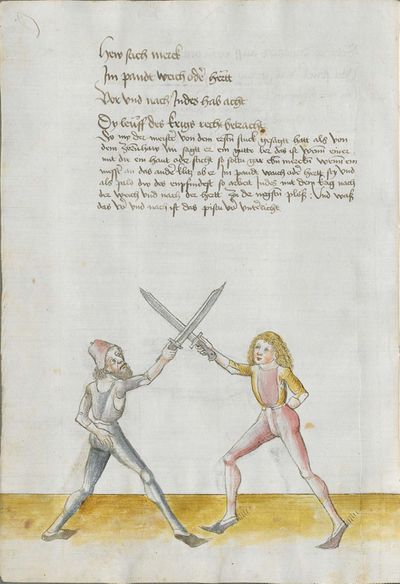
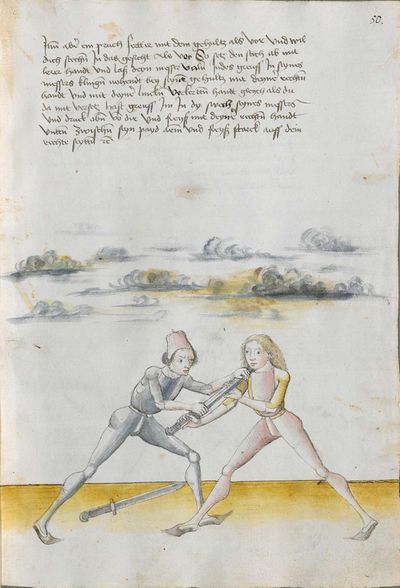
[2r.1] DAs ist herrn hansen Lecküchnerß von Nûrnberg künst und zedel ym messer dy er selbs gemacht und getichtt hatt den text und dÿ auslegüng daruber etc |
[1r.1] Das ist herr hannsen Lecküchner von Nurenberg künst vnd zedel ym messer dy er selbs gemacht vnd geticht hatt Den Text vnd dy auslegung dar über Dem hochgeporen fursten vnd herren hertzogen philippen phaltzgraffen Bey reyn Ertzdruckseß vnd kurfürst vnd hertzog yn Bayern etc |
|||||||||
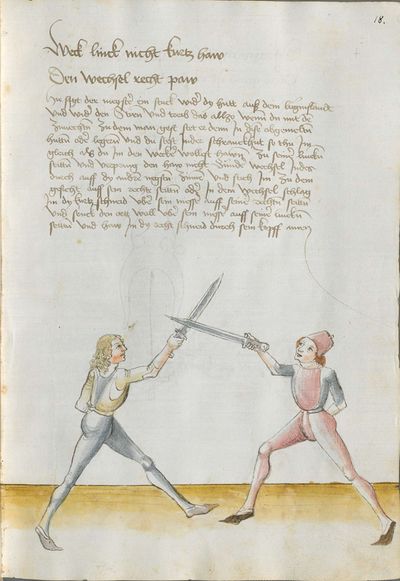
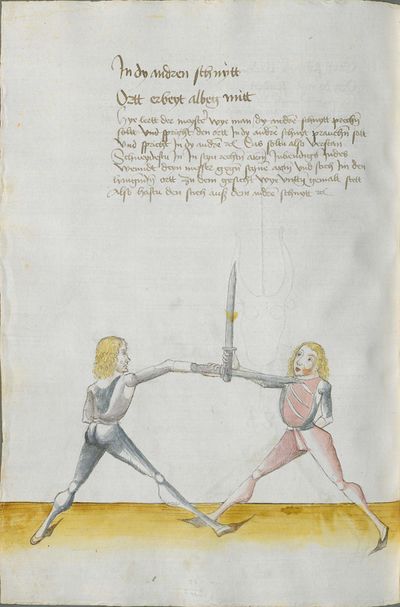
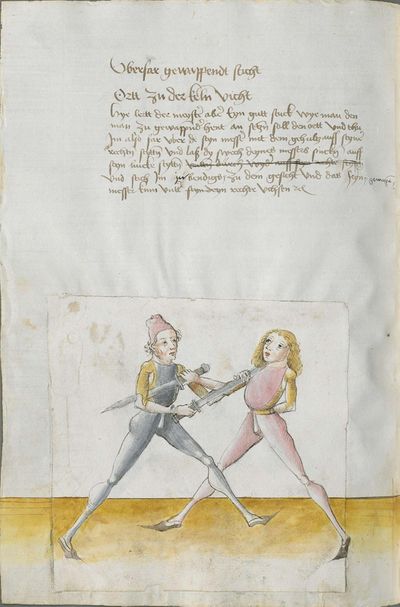
[2] |
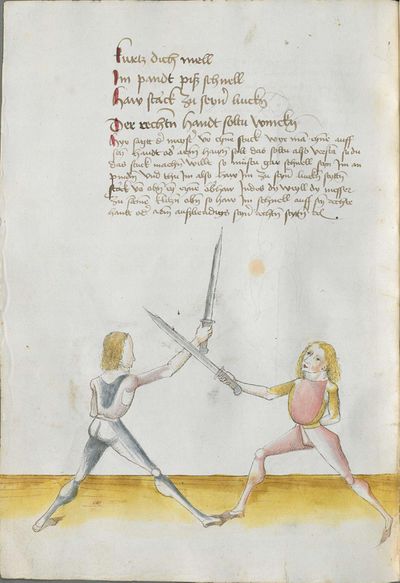
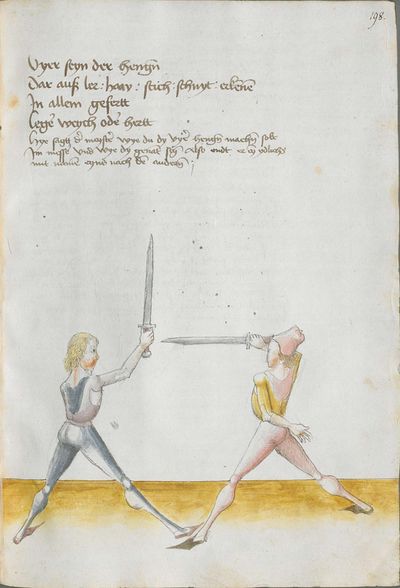
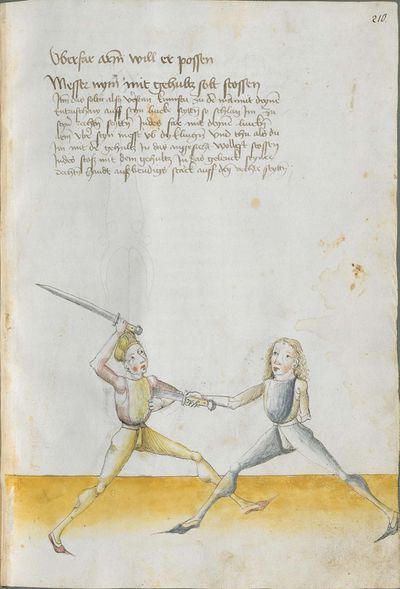
The foreword Pay attention on the following Here begins the foreword on the Messer and states that who wants to fight well with the Messer, should learn the proper art and obey to this art and skill written below. This way, he will be able to stand with the rightful art in front of the princes and lords, and his art will be better rewarded to him than to other masters who do not know these things and cannot perform them. Namely, there are many masters of the sword who do not know the art of the Messer and cannot excogitate it properly. Who is able to perform this thing and this art, there are numerous serious elements by which he can beat the masters well and skillfully force them so that they must let themselves be beaten, thrust, led, thrown and held against their wish. |
[46r] [O]B du wilt achten Hie hebt sich an die vorred im messer vnd saget wer will leren vechten im messer daß er sol leren recht künst vnd sich geben vff disse artt vnd künst So mag er wil besten mit rechter künst vor fursten vnd vor hend Im sol billicher siner künst baß gelonett werden dan andern meinstern die deß dings nit wissen vnd sich nit künden schicken wan eß sint viel meinster deß schwertz die nit wissen von der art deß messers noch recht vszenden mugen Wer sich in disse ding vnd art schicken kan der vint viel ernstlicher stueck do mit er die meinster wol mag vff wecken vnd künstlich beschliessen daß sie sich an dancken schlagen stoßen furen werffen halten muessen losßen etc Sequitur textus |
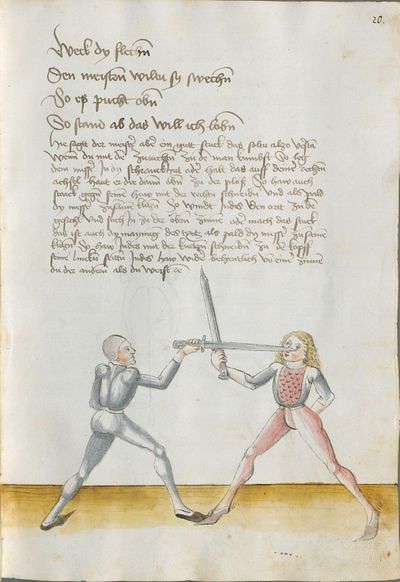
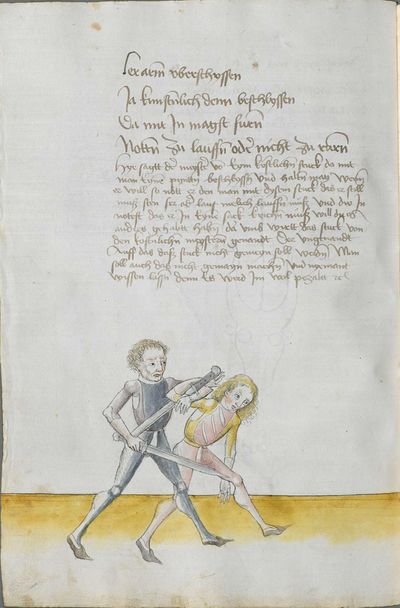
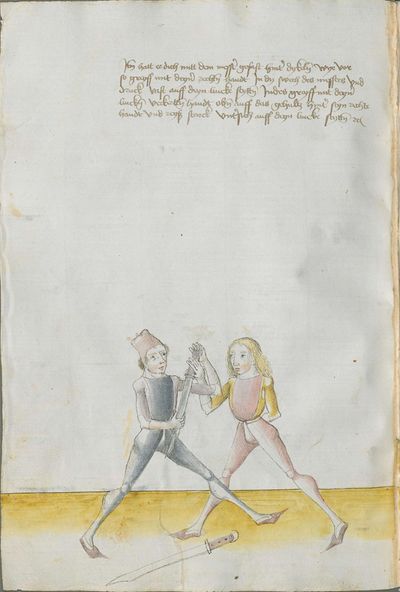
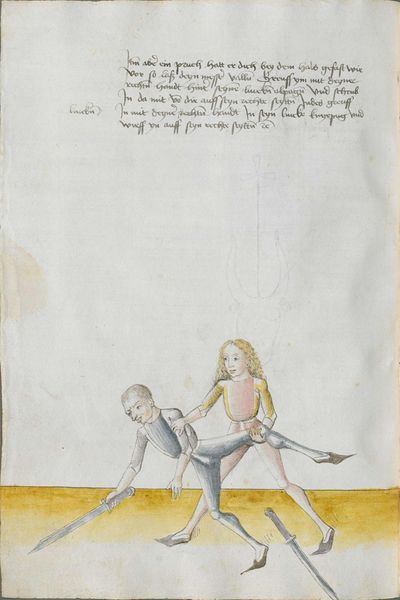
[2r.2] ¶ Dye vor red. Ob dw wild achten Hye hebt sich an dy vor rede ym messer und sagtt wer woll vechten ym messer das er soll lerenen [2v.1] rechte kunst und sich geben auff dyse nach geschriben art und kûnst so mag er wol pestan mitt rechter kunst vor fuersten und vor herren ym soll aych pillicher seyner kunst paß geluenet werden den anderen meysteren dye dyser dinck nicht wyssen und sich nicht dar eyn kunnen schicken wann eß syn vill meysteren des swercz dye nicht wyssen von der artt deß messers noch rechtt aussynnen mugen wer sich aber yn dyse ding und artt schicken kann der findt vill ernestlicher stuck da mit er dy meyster wol mag uff wecken und kunstenlichen weschlyssen daß sy sich an danck schlagen stossen fueren werffen halten mussen lassen Sequitur textus |
[1r.2] Dy vor rede [O]B dw wilt achten Hye hebt sich an dy vor rede ym messer vnd sagt wer woll vechten ym messer Das er schül lernen rechte kunst vnd sich geben auff dyse nachgeschriben artt vnd kunst So mag er woll westan mit rechter kunst vor fursten vnd vor herren ym sol auch pillich seyner kunst paß gelōnet werden den anderen meysteren des dings nicht weysen vnd sy nicht dar eyn kunnen schicken wenn es seyn vill meyster des Swertz dy nicht wissen von der art des messers noch recht auß synnen mügen wer sich yn dyse ding vnd art schicken kan der syndt vill ernnstlicher stück do mit er dy meyster woll mag auff becken vnd kunstenlich weschlissen Das sy sich an danck schlagen stossen furne werffen halten müß lassen; |
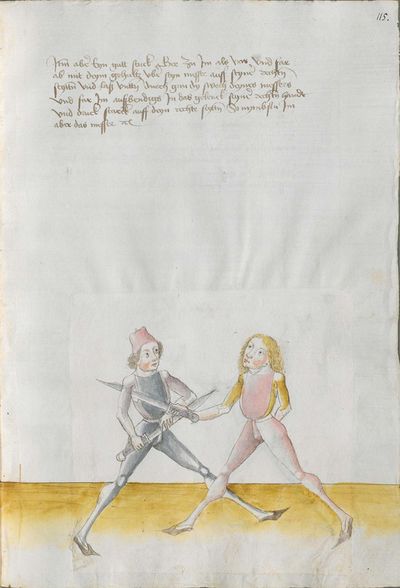
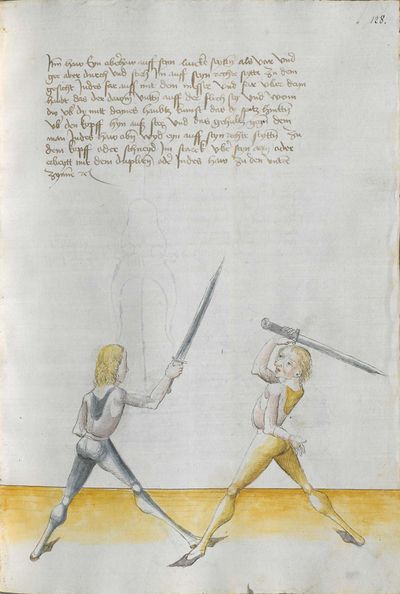
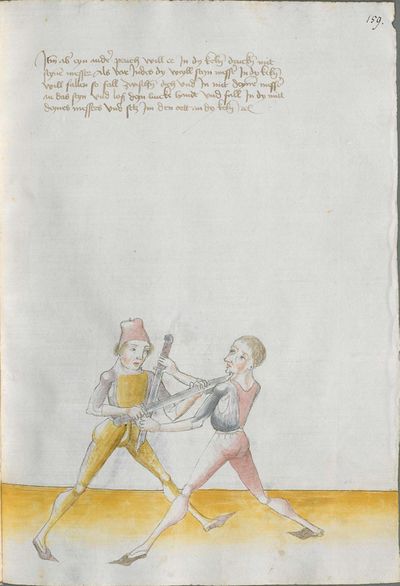
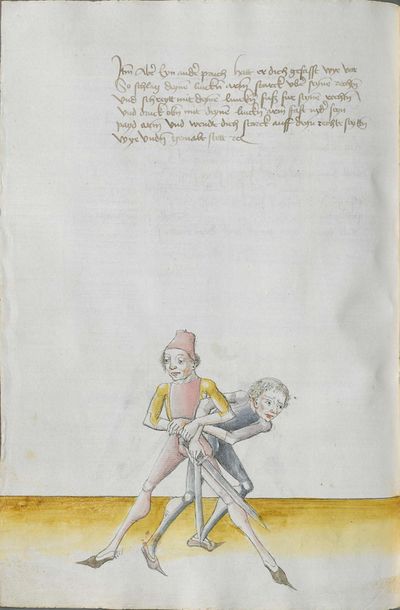
[97r.1] ob du wilt achten messer wechten So lernn dingk das dich zieret zu schimpff vnd zu ernst hofieret / do mit du erschreckest / vnd die meyster kunstlich erweckest / Hie hebt sich an Im messer vnd sagt wer wil leren Im messer das er soll lerer recht kunst so mag er wol bestan mit rechten kunst vor fůrsten vnd vor heren Man sal auch billichen sein kunst bas gelonet werden den anderen / Maystern dy des dinges nit wissen von den art des messers noch recht auß synnen můgen / wer sich in diesse dich schiecken kan da seind vil kunstlich stuck / do mit er die meyster wol mag auff wecken vnd kunstlich beschlissen das sy sich an dancken schlachen stossen sweren werffen halten můssen lassen |
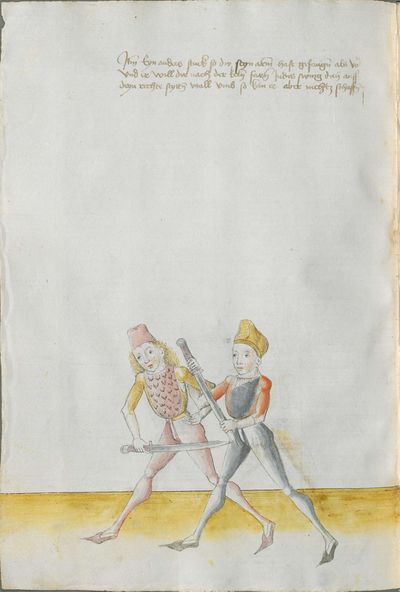
[138r] Der zetel des Duseggen Fechtens Ob du Nimpst acht Wellicher will Lernen Fechten Inn Duseggen. der soll Lernen rechte Kumst / vnnd sich geben auf dise Nachgeschribne Art. So mag Er wol bestan vor fursten vnnd herzen. Im soll auch seinner Kunnst billich bas gelonnt werden dann anndern Mai= [138v.1] stern die des dinngs nit wissen. Vnnd. sy nit kinden darem schicken wann es seind vil Maister des schwerts die nichts wissen der Art des duseggen. noch recht auszinnen mögen. Wer sich Inn diese dinng vnnd art schicken kann. der finndt vil ernnstliche stuckh dar Inn er die Maister wol mag aufwecken. vnnd kunnstlich beschliessen. das sy sich on danck schlagen. stossen. fieren. werffen vnnd hallten muessen lassen. |
||||||
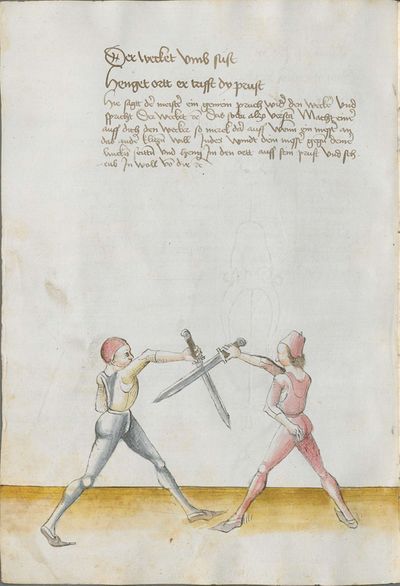
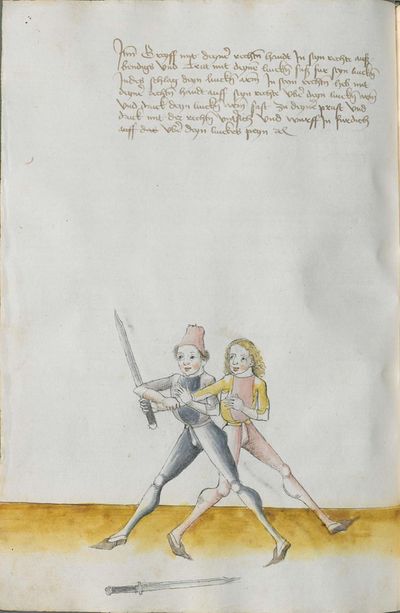
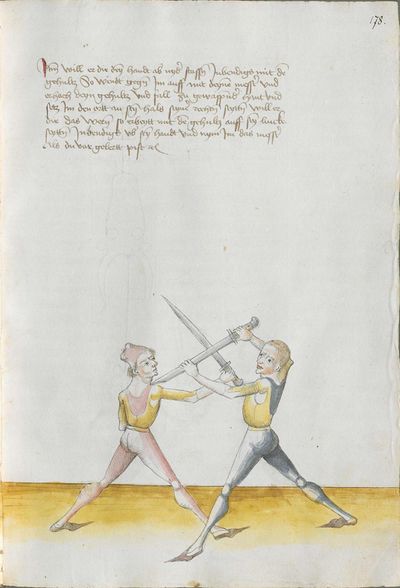
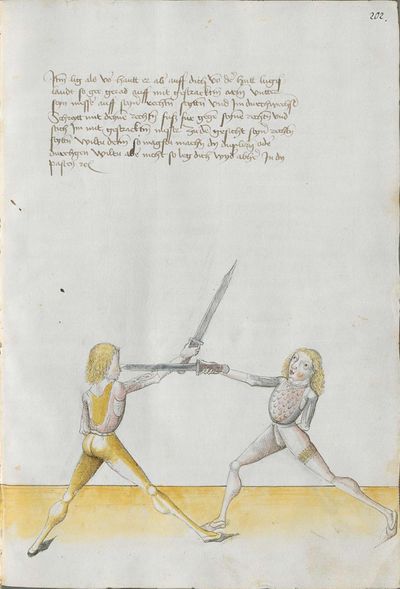
[3] |
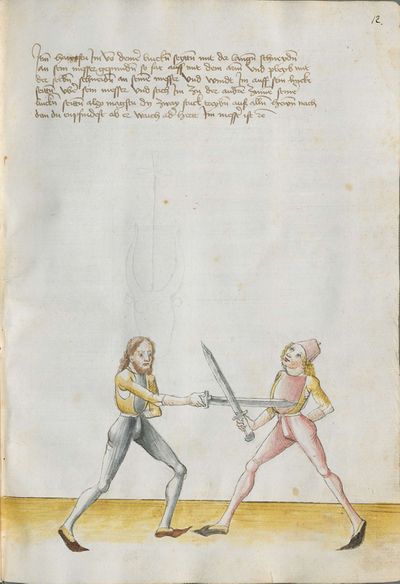
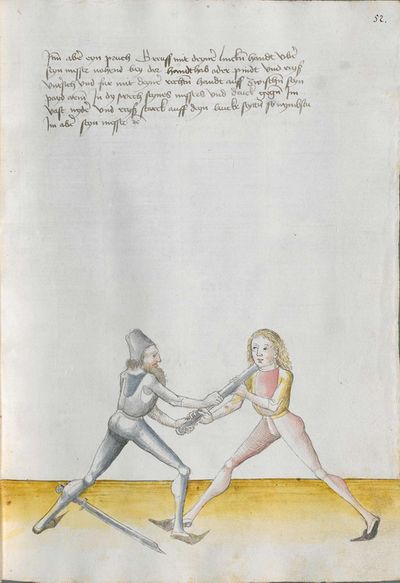
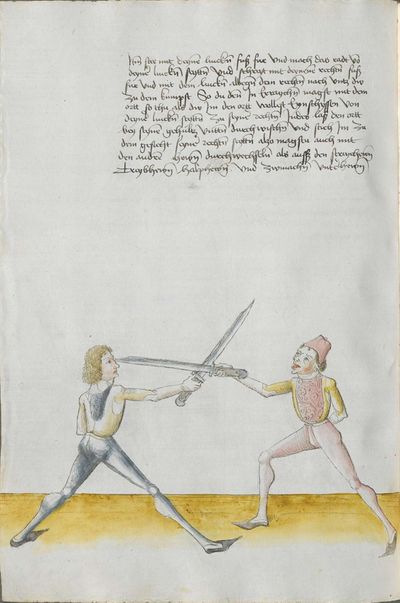
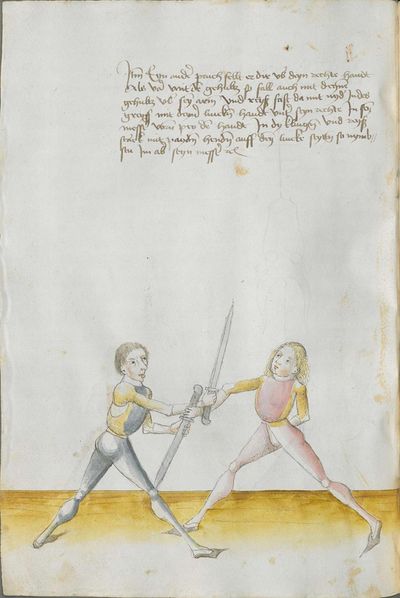
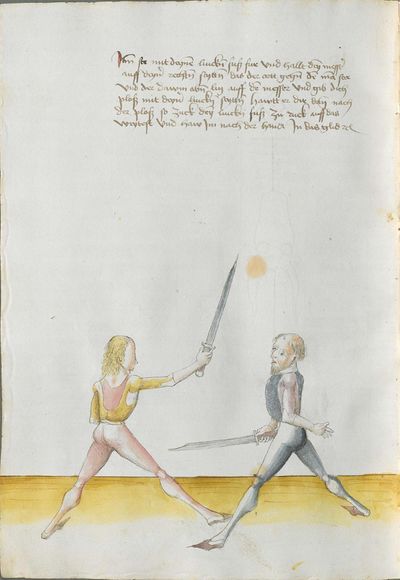
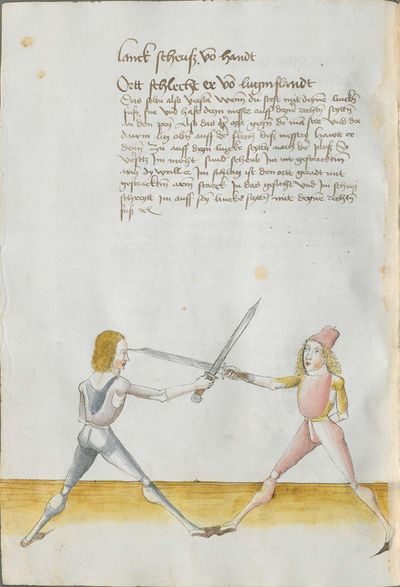
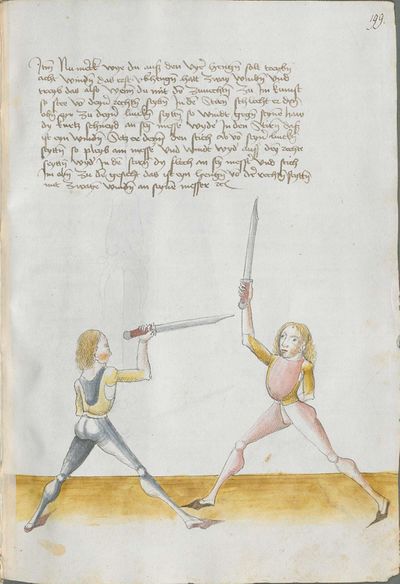
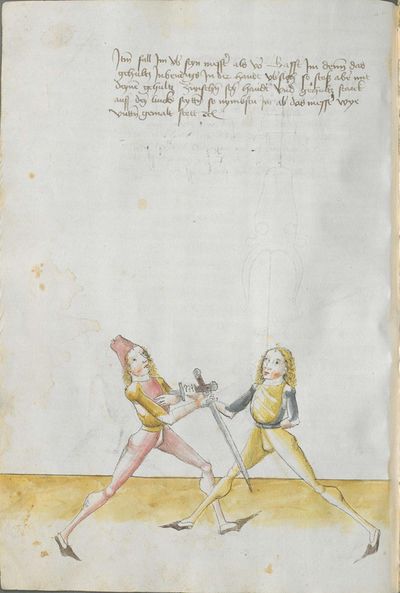
Who displaces only Here the master ended the foreword and now he gives you a good teaching. Understand it this way: when you come to a man in the Zufechten, you should not stand still with the Messer and wait for his strokes. That is because the swordsmen who only want to displace are beaten a lot, because as they try to displace, they cannot perform any rightful art and this way, as they do not want to do anything but displace and they want to look at other men’s strokes and work, they are beaten and weakened in spite of their entire art. |
[46v.1] Wer mir versetz So nue der meinster gendet hat die vorred Nü git er dir eyen gutten lere die verste also wan du mit dem zuevechten zue dem man kümpst So soltu nit stil stan mit dinen messer vnd sienen haulben noch warten wan die vechter die nuer wellen versetzen die werdent sere geschlagen dan die wiell sie versetzen mogen sie keÿn rechtt künst triben vnd so sie anders nit thuen wellen dan versetzen vnd vff ander luet schleg vnd arbeit wollen sehen So werdent sie geschlagen vnd geschmecht by allen Iren kuensten etc |
[2v.2] Wer newer verseczet [3r.1] So nw der meyster geendet hatt dy vor der nw gibt er dir eyn gute ler dy verste alzo wen dw mit dem zw vechten zw dem man kumbst so soltu nicht stil sten mit dem messer und seynen hewen nach warten wan dy vechter dy newer wollen verseczen dy werden ser geschlagen wan dy weyll sÿ verseczen můgen sy kayn rechte kunst treyben und so sye anderß nicht thün wöllen dann verseczen und auff ander lewtt schleg und arbaytt newer wöllen sehen so werden sye geschlagen und geschwechtt pey allen yren künsten |
[1r.3] Wer newer versetzet So nw der meyster geendet hatt dy vor rede nw gibt er dir ein gutte ler dy verste alzo Wenn dw mit dem zwuechten ze dem man kumbst so soltu nicht stil sten mit dem messer vnd seynen heẅen nach wortten wenn dy vechter dy newer wellen versetzen dy werden ser geschlagen wann dy weil sy versetzen mügen sy [1v.1] kain rechte kunst treyben vnd so sy anders nicht thun wollen dan versetzen vnd auff ander lewt schleg vnd erbeyt wollen sehen So werden sy geschlagen vnd geswecht bey allen iren kunsten. |
[97r.2] So ym der meister verendet dy vor red Nün gibt er dir ein gutte lere dy vorstehe also wen du zu vechten mit dem man kumst / so soltu nit still sthen mit den messer vnd seynen hew noch warten wen dy vechter dy mit wellen versetzen / dy werden ser geschlagen won(?) dy weyl sy versetzen můgen sy kein recht kunst treyben můgen vnd so sy anders nit thun wellen sehen so werden sy geschlagen vnd geschwecht bey allen iren kunsten |
[138v.2] Wer vil versetzt Item hie merckh ain gute Ler. Wann du zu dem Mann kumpst. so soltu nit still stan mit deinnem Duseggen / auch nit auf seinnen haw harzen. noch warten. wann die fechter die nur wöllen versetzen. mogen zu kainner rechten Arbait nit kummen. dann die da versetzen vnnd auf annder leut schleg vnnd arwait warten. die werden geschlagen. vnnd geschmecht bey allen Iren kunsten. |
||||||
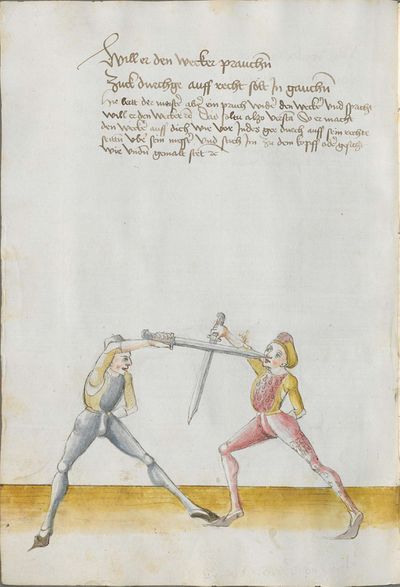
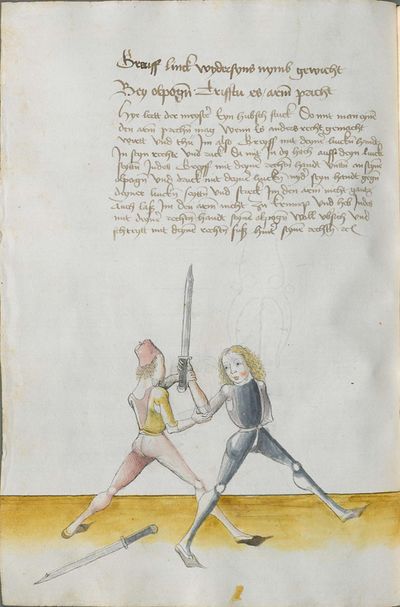
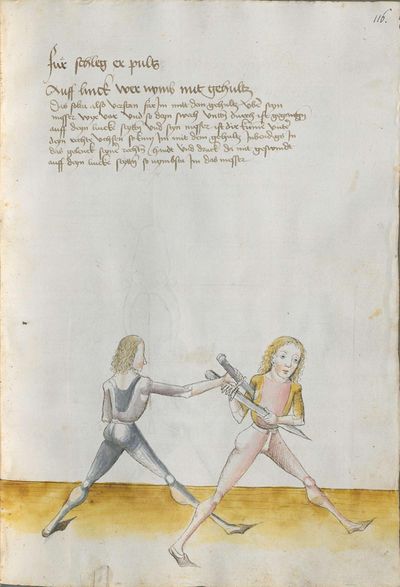
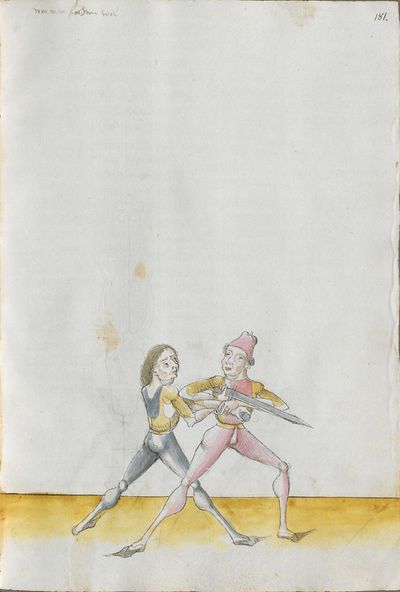
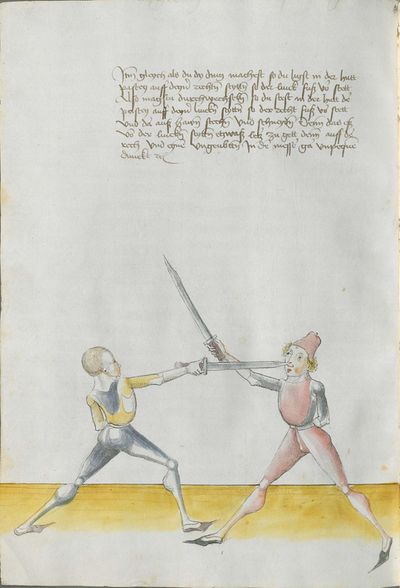
[4] |
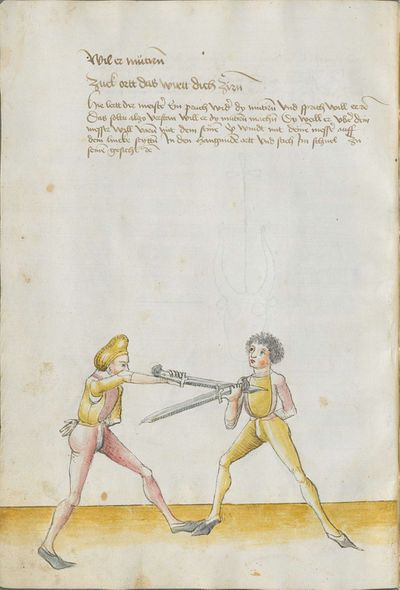
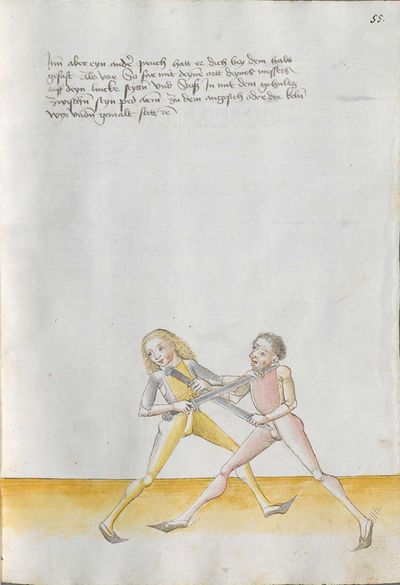
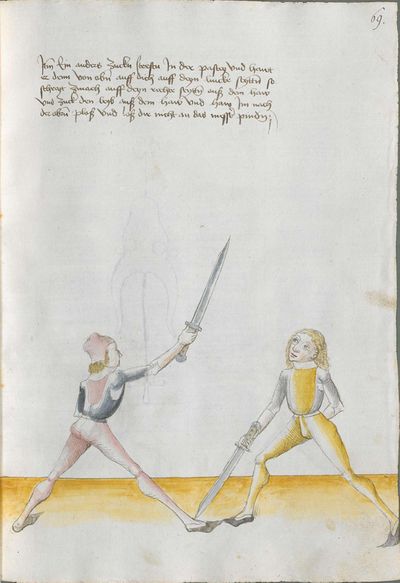
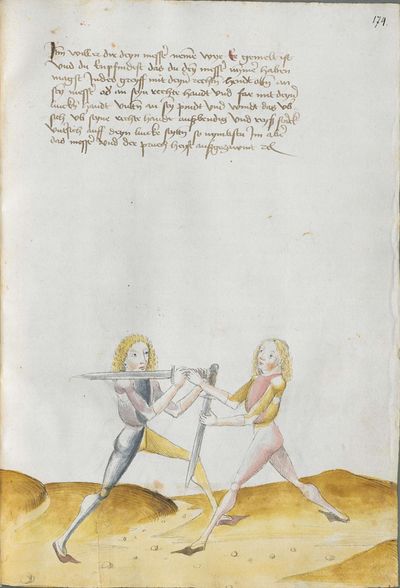
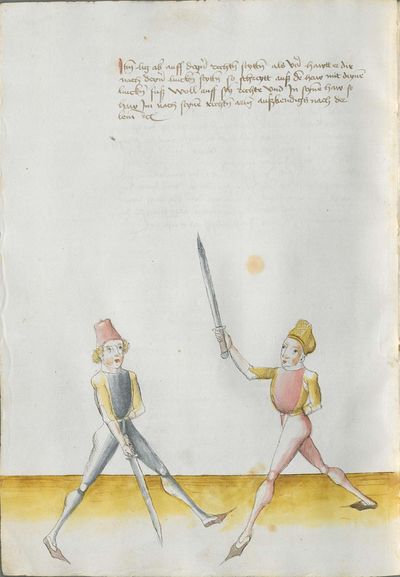
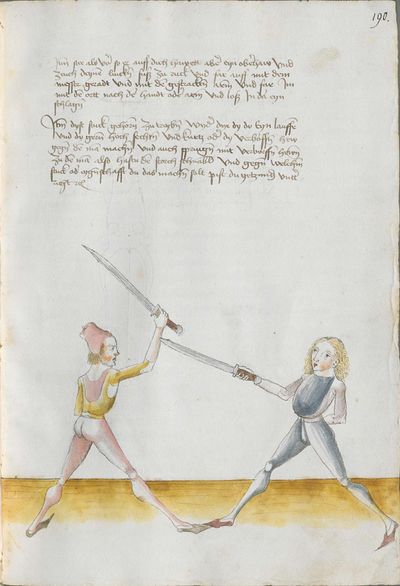
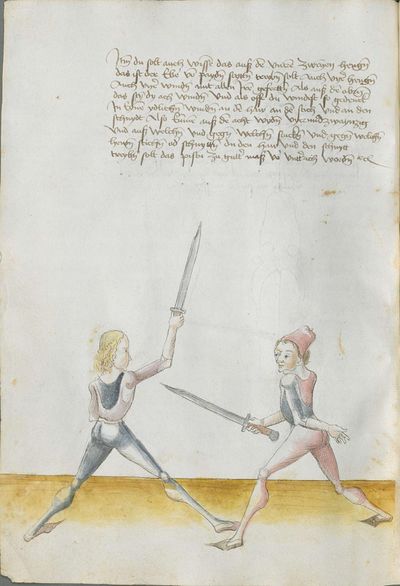
“Simultaneously,” “before” and “after,” these words Here the master states and announces the base of the Messer fencing and says: “simultaneously,” “before” and “after,” etc. You should understand it this way that you should learn properly before all other things these two things, that is the “before” and the “after” and the “strong” and the “weak,” and the word “simultaneously,” as the base of the entire art of fencing comes therefrom. And if you learn and understand these things properly, and additionally you do not forget the word “simultaneously” in all the elements you have performed, you can be well a good master of the Messer and you can teach the princes and lords so that they stand well with the rightful art in friendly and in serious combat. |
[46v.2] Indes / vor / vnd noch / die wort Hie saget der meinster vnd meldett den gruent des messers vechten vnd sprichtt Indeß vor vnd noch etc Daß soltu also verstan daß du vor allen dingen recht vernemen solt die zweÿ ding dz ist daß vor vnd noch vnd die schwech vnd sterck vnd daß wort indeß wan darueß kuemptt aller gruentt aller der künst deß messers vechtens vnd [47r.1] wen dü die ding recht vernÿempst vnd verstoest vnd zue vor an daß wortt Indes nit vergist In allen stuecken die du triben bist So magstu wol eyen guetter meinster deß messers sin vnd magst fuersten vnd heren leren dz sie mit rechter kuenst woll besten In schÿmff vnd In ernst ~ |
[3r.2] Yndeß vor und nach dy wortt Hye sagt der meyster und meldt [3v.1] den gruntt deß messer vechtenß und spricht ÿndes vor und nach etc Daß soltu alzo verstan daß dw vor allen dingen recht vernemen sollt dy czwen dyng daß ist daß vor und daß nach und dy swech und dy sterck und daß wortt yndeß wann dar auß kumbt aller grund aller der künst deß vechtenß und wenn dw dy ding recht vernymbst und verstest und zw vor an deß worcz yndeß nicht vergist yn allen stucken dy dw treyben pist So magst dw wol eyn gutter meyster deß messerß seyn und magst leren fursten und herren daß sy mit rechter kunst wol bestan yn schympff und yn ernest etc |
[1v.2] Yndes / vor / vnd /nach / dy wortt Hye sagt der meyster vnd melt den grundt des messers vechtens vnd spricht yndes vor vnd nach etc Das soltu alzo verstan das dw vor allen dingen recht vernemen solt dy zway ding das ist das vor vnd nach. vnd dy swech vnd dy sterck vnd das wort yndes wann dar auß kumbt aller grundt aller der kunst des vechtens vnd wenn dw dy ding recht vernymbst vnd verstest vnd zwvoran des wortz yndes nicht vergist yn allen stucken dy dw treyben pist So magstu woll eyn gutter meyster des messers sein vnd magst fursten vnd herren leren das sy mit rechter kunst wol bestann yn schimpff vnd yn ernnst |
[97r.3] Indes vor vnd noch dy wort sein aller kunst
ein hort Schwech vnd sterck prieff weyslich
so du wilt vechten kunstlich / Hie sagt der meister vnd melt den grund des messers vechten vnd spricht Indes vor vnd noch etc / das saltu verstan also / das du vor allen dingen recht vernemen solt dy zwen ding das ist das vor vnd noch vnd dy schweche vnd sterck vnd das wort Indes |
[139r.1] Inndes vor vnnd nach Item hie findstu den Grund des Duseggen fechtens. das wort Indes. vnnd das vor vnnd nach. das soldu versteen. allso das du vor allem dinngen. recht vernemmen solt die zwaydinng. das ist das vor. vnnd das Nach. vnnd die schwech vnnd sterckhe vnnd das wort Indes. wann darausz kumpt aller Grvnnd des Duseggen fechtens vnnd wann du die dinng Recht vernimpst vnnd versteest vnnd zuuoran das wort Indes. so magstu wol ain guter Maister des Duseggen sein vnnd magst Fursten vnnd herzen lernen. das synnt rechter Kunst wol bestan Inn schiimpff vnnd Inn Ernnst. |
||||||
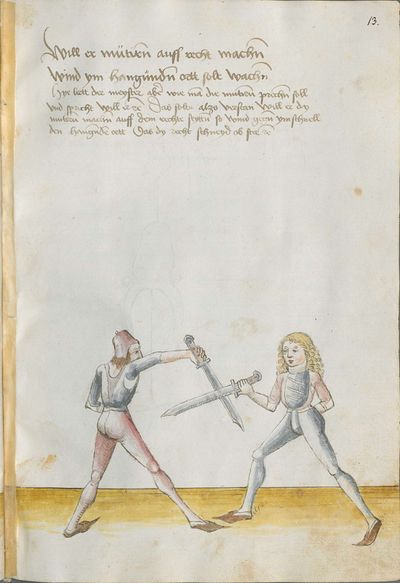
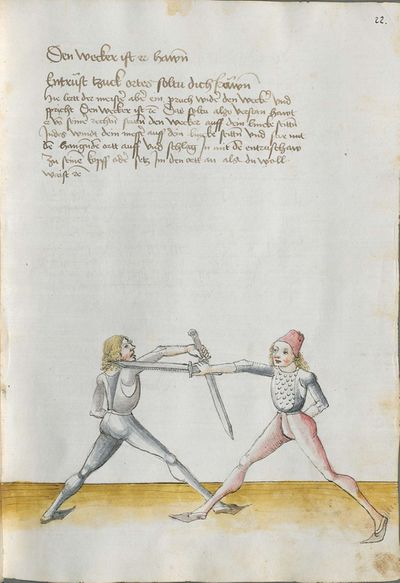
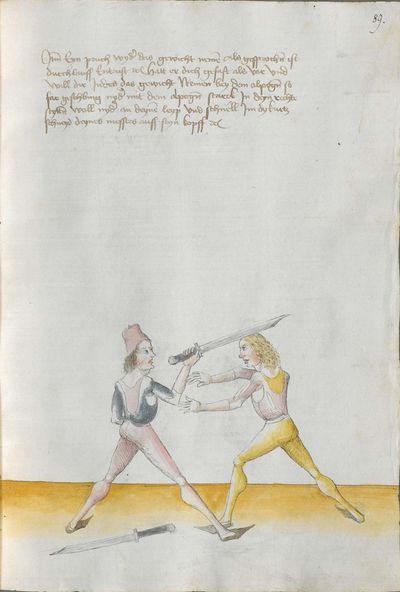
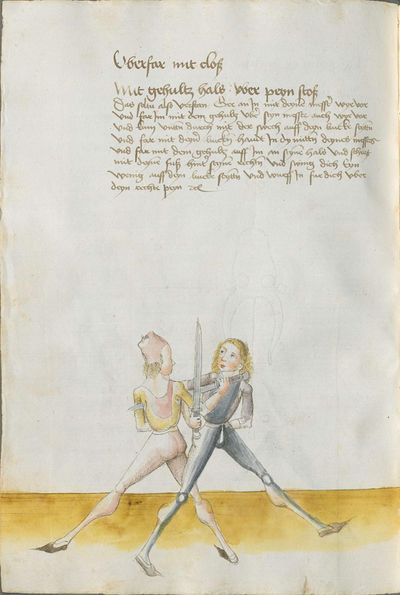
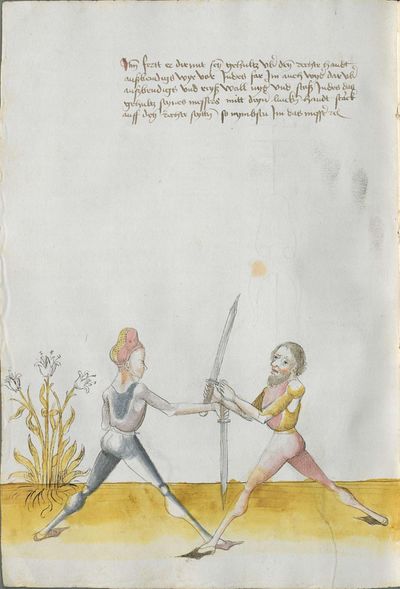
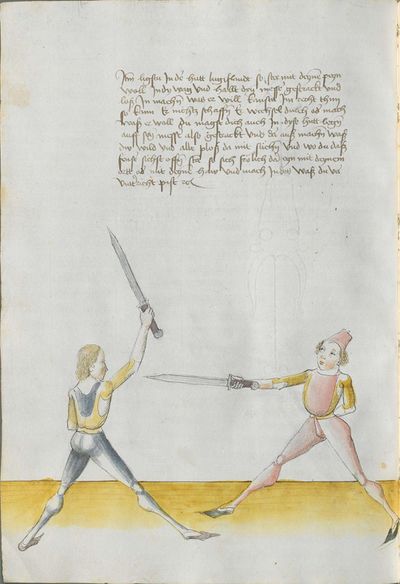
[5] |
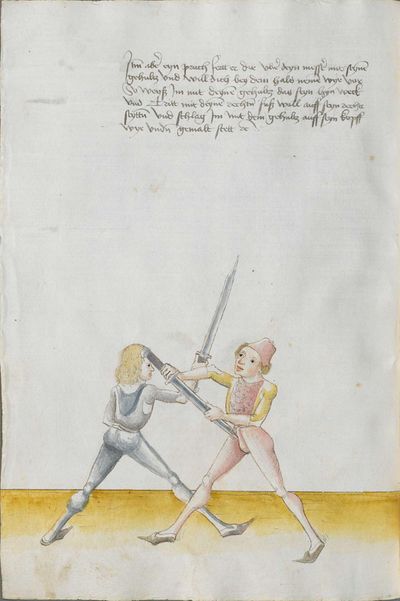
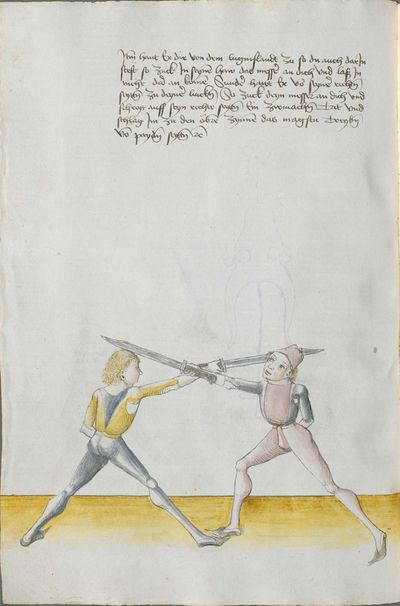
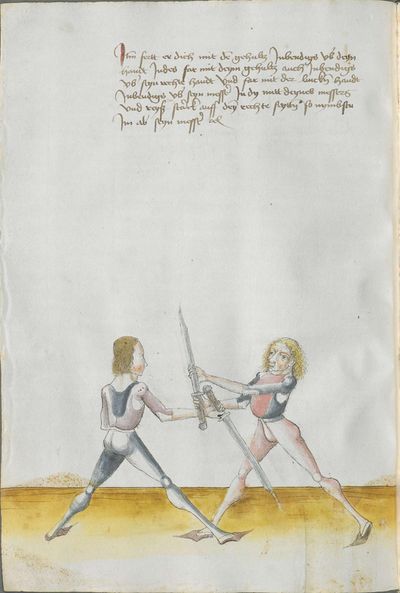
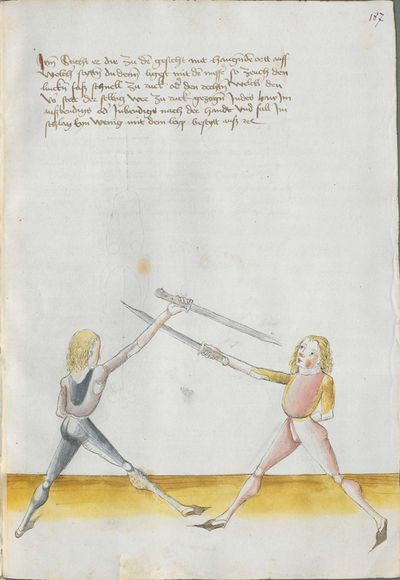
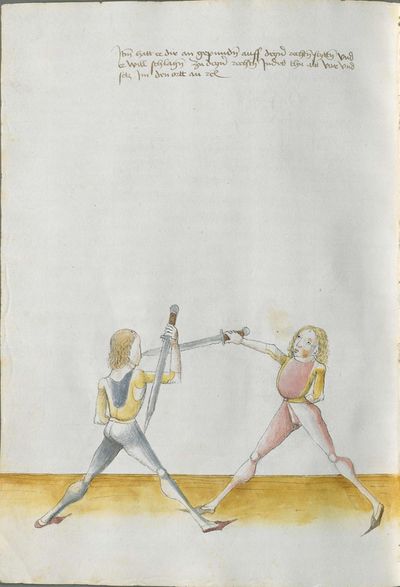
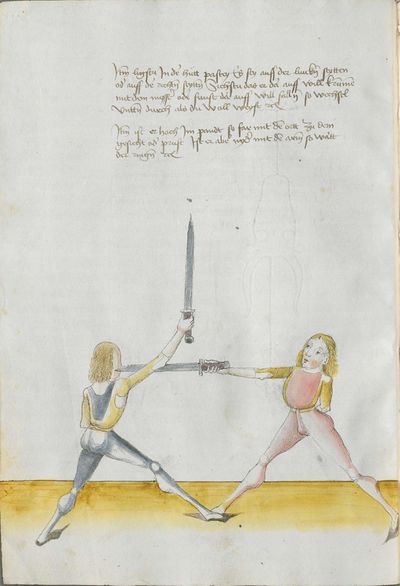
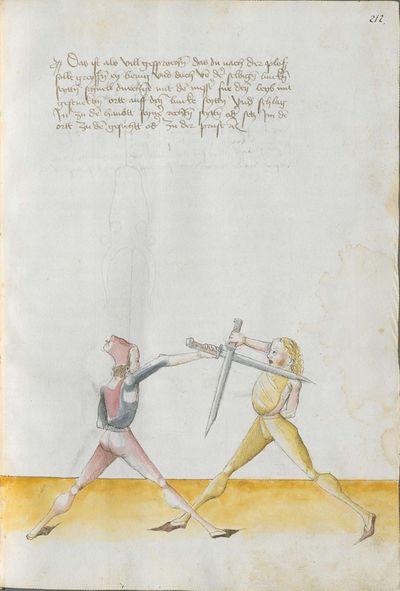
Then, the “before” is that if you are coming with a stroke sooner than he so that he has to displace. So work “simultaneously” skillfully with the Messer in front of you or with other elements and do not let him come to any work afterwards. This way, you have acquired the “before.” |
[47r.2] das vor Item daß vor ist so du e kuempst mit dem haulb dan er daß er dir versetzen mueß So arbeytt Indes behendeglich mit dem messer fur dich vnd loß in darnoch zu keyner arbeytt kuemen also hastu Im an gewuenden daß vor etc |
[3v.2] Item daß vor ist do dw ee kumbst mit dem haw den er daß er dir verseczen müß So erbayt yndeß behentlich fuer dich mit dem messer oder mit andern stucken und laß yn dar nach zw kayner erbait kummen [4r.1] alzo hastu ym an gebunnen daß vor |
[1v.3] Item das vor ist. So dw ee kumbst mit dem haw dann er das er dir versetzen muß So erbayt yndes behendiklich mit dem messer fur dich oder anderen stücken vnd laß yn dar nach zw keyner erbeit kummen alzo hastu ym an gebunen das vor |
[139r.2] Das vor Item das vor Ist so du Ehe kumpst Mit dem Duseggen oder mit dem haw dann er. das er dir versetzen muosz. so ar= [139v.1] bait Indes behenndigclich mit dem Duseggen fur dich oder sunnst mit anndern stuckhen vnnd lasz In darnach zu kainner arbait kummen also hastu Im abgenommen das vor. |
|||||||
[6] |
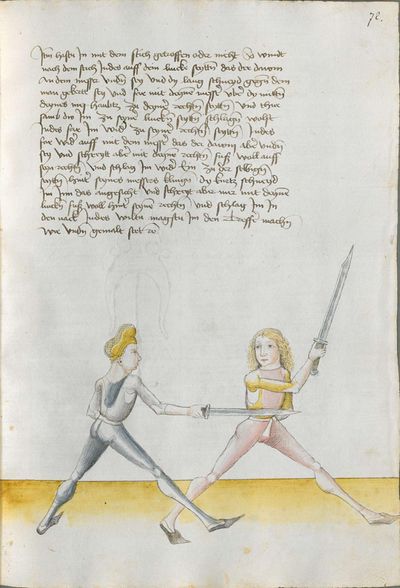
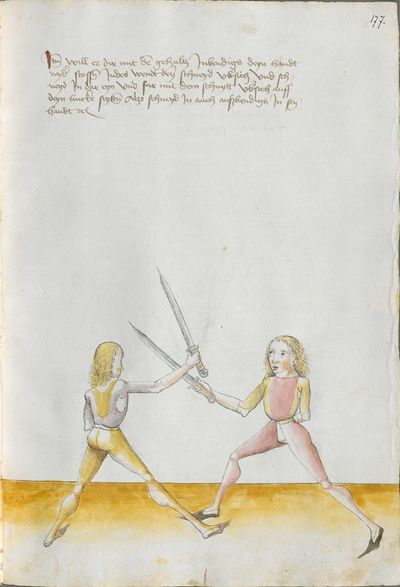
And if he comes sooner than you with the work or with the stroke and you have to displace it, work “simultaneously” skillfully with the Messer or otherwise with the elements. This way, you take the “before” from him with your “after,” and this is called the “before” and “after.” |
[47r.3] das noch Item wan er E kuempt mit dem haulb den du vnd Im das versetzen muest So arbeytt Indeß behendeglich mit dem messer oder suenst mit stuecken So nyembstu Im daß vor mit dem noch vnd das heist das vor vnd das noch ~ |
[4r.2] Item wenn er ee kumbt mit der erbat oder mit dem haw denn dw daß dw ym verseczen mûst So arbayt yndeß behentlich mit dem messer oder sünst mit stucken so nymbstu ym daß vor mit dem nach und daß hayst daß vor und nach |
[1v.4] vnd wenn er ee kumbt mit der erbeyt oder mit dem haw denn dw vnd ym das versetzen müst So erbeyt yndes behendicklich mit dem messer oder sunst mit stucken So nymbstu ym das vor mit dem nach vnd das heyst das vor vnd nach |
[139v.2] Das nach Item das nach Ist Wann er kumpt mit der arbait oder mit dem haw dann du. vnnd Im das versetzen muost. so arbait Indes behenndiglich mit dem duseggen oder sunnst mit stuckhen. so Nimpst du Im das vor mit dem nach. |
|||||||
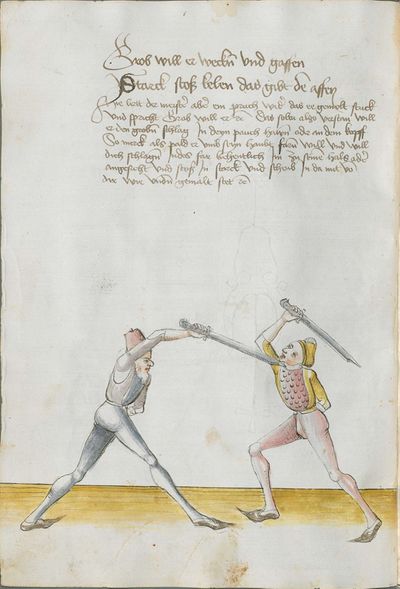
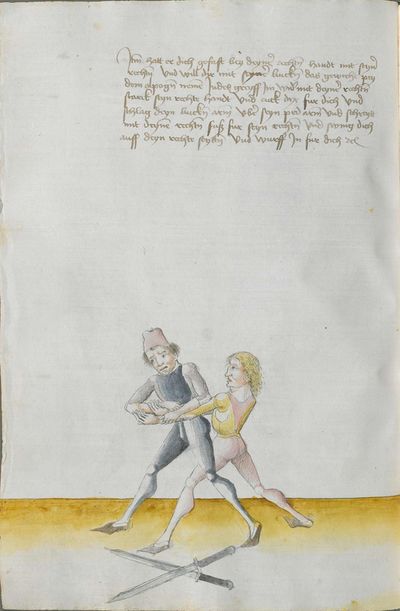
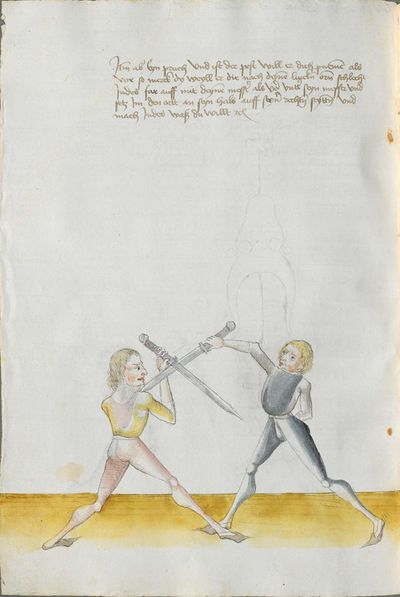
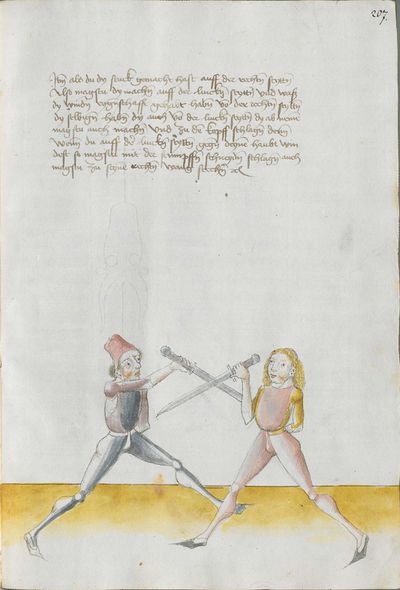
[7] |
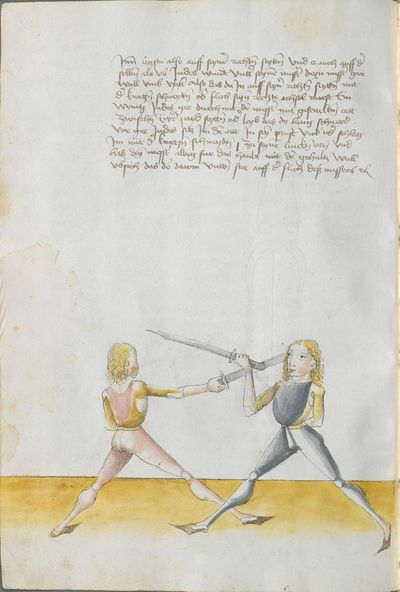
Then, you should also know before all other things the “weak” and the “strong” of the Messer. Be aware that from the hilt to the middle of the Messer there is the “strong” and from the middle down to the point there is the “weak.” And how you should fence therefrom, you find written afterwards, and also what the word “simultaneously” is. |
[47r.4] schvech vnd sterck Item du solt auch vor allen dingen wissen die schwech vnd sterck des messers Nu merck von dem gehultz biesß an die mitte des messers das ist die sterck Vnd von der mit biß an das ortt das ist die schwech vnd wie du dar vß vechten solt daß |
[4r.3] Item dw solt auch vor allen dyngen wyssen dy swech und dy sterck deß messerß nw merck von dem gehülcz piß an dy mitte deß messerß daß ist dy sterck und von der mitten uncz an den ortt daß ist dy swech und wye dw dar auß vechten sollt daß findestu her nach geschriben und waß daß wortt ynder ist etc |
[1v.5] Item dw solt auch vor allen dingen wissen dy swech vnd dy sterck des messers nw merck von dem gehültz piß an dy mitten des messers das ist dy sterck vnd von der mitten vntz an den ortt das ist dy swech vnd wye dw dar auß vechten scholt das vindest dw her nach geschriben vnd was das wort yndes ist |
[139v.3] Die schwech vnd sterckh Item du solt Auch vor allen dinngen Wissen die schwech vnnd sterckh des Duseggen. Nun merckh vonn dem gehultz bisz an die mitte des duggseggens ist die sterckh vnnd von der mitte bis an den Ortt das ist die schwech. vnnd wie du darausz fechten sollt das sindstu hernach geschriben. vnnd was das wort Indes ist. |
|||||||
[8] |
Learn six strokes Here teaches the master how one should hold himself in the Messer fencing and how one should prepare to it. And firstly, you should fence with one hand with the Messer and you should have the other one on the back. If you want to fight with the empty hand, as in Messer-taking, grasping, clenching the arms etc., you should turn the hand from the back to the chest when you want to perform something on him on the inside over the arm. |
[47r.5] Sechs heulb lere Hie lert der meinster wie man sich schuecken sol in dem vechten deß messers vnd wie man sich darin schuecken sol vnd zuem ersten soltu mit eyner hant fechten mit dem messer vnd die ander vff dem ruecken halten Ob du aber willt mit lerer hant vechten als mit messer nemen vber grieffen arm beschlueßen etc So soltu die hant von dem rueck vff die bruest wenden waß du wiltt Inlbendig uber den arm triben etc |
[4r.4] Sechs hew lere Hye lert der meyster wye man sych halten sol yn dem vechten deß messerß und wye man sich dar eyn sol[5] schicken und züm ersten söltu mit eyner hendt vechten mit dem messer und dy ander soltu auff dem rück haben ob dw aber wild mit lerer hand vechten alz mit messer nemen ubergreiffen arm beschlyssen etc So solt dw dy hand von dem rück auff dy prust wenden waß dw ym wild ynbendig vber den armen treyben etc |
[1v.6] Sechs hew lere Hye lert der meyster wye man sich halten sol yn dem vechten des messer vnd wye man sich dar ein sol schicken vnd zum ersten So soltu mit eyner hendt vechten mit dem messer vnd dy ander soltu auff dem ruck haben ob dw aber wildt mit lerer handt vechten alz mit messer nemen vber greffyen arme beschlissenSo soltu dy handt von dem ruck auff dy prust wenden waß dw ym wildt ynbendig vber den arme treyben |
[97r.4] Wan lernt der meyster wye man sich halten soll In dem vechten des messers vnd wÿ man sich dar ein sol schicken vnd zum ersten soltu mit eynem haue vechten mit dem messer vnd dy ander hand soltu auff dem rucken behalten Ob du aber mitt lerer hand woldest vechten also mit messer nemen vber greyffen am schissen etc. so soltu dy hand von dem ruck auff dy brust wenden was du wilt Innewing vber dem arm treyben |
[140r.1] Wie du fechten solt Mit ainner hanndt
Item Inn das Duseggen Fechten schickh dich also. zum ersten soltu mit ainner hannd fechten. mit deiner wehr vnnd die annder auf dem Ruckhen hallten. Aber wann du willst mit Leerer hannd fechten. als mit Duseggen nemmen. vbergreyffen. arm beschliessen. so soltu die hannd vonn dem Ruckhne auf die prust wennden. was du wild Innwenndig vber den arm treyben. |
||||||
[9] |
Secondly, the six hidden strokes are described and mentioned in the text, from that many good elements come, if one can perform them right and know how to prepare them skillfully. And how you should perform them with three elements, you will be taught afterwards. |
[47v.2] Item zu dem andern So werdent im text Sechs verborgen haulb gemelt vnd beruerett auß dem kuemen vil guetter stueck were sie recht triben kan vnd In die wiße kunstlich sich zu schicken vnd wie du sie triben solt mit triehen stuecken daß wierstu hernach enttruechtt etc |
[4v.2] Item zw dem andren so werden yn dem text Sechß verporgen hew ge merckt und peruertt auß den kummen vill gutten stuck wer sye recht treyben kan und sich yn dye wayß kunstenlich zw schicken vnd wye dw dye treyben sölt mit dreyen stucken daß wirst hyne nach unter richt etc Sequitur textus |
[2r.2] Item ze dem anderen so werden yn dem text sechs verporgen hew gemelt vnd werutt auß dem kummen vil gutter stuck wer sy recht treyben kann vnd sych yn dy weyß kunstenlich zw schicken vnd wye dw dy treyben solt mit dreyen stucken das wirstu her nach vnterricht. |
[97r.5] Item zu dem andern so werden Im text sechs forogen hewe gemelt vnd berurt auß dem komen vil gutt stůck wer ssy recht kan vnd sich wust kunstlichen schicken vnd wie du dy treyben solt mit knÿenen [!] stucken das wirstu her noch vnter richt |
|||||||
[10] |
The Zornhau, Wecker Here the master names the six hidden strokes, as each is called with its name, so that you can learn the elements in a better way. And he says that the first is called the Zornhau, the other the Wecker, the third the Entrüsthau, the fourth the Zwinger, the fifth the Geferhau and the sixth is called the Wincker. These are the six elements and are the main elements, as you will see afterwards. |
[47v.3] Zorn haulb / wecker haulb / Hie nennet der meinster die sechs verborge~ haulb wie sie heissent mit namen vff daß du die stueck aller bast vernemen magst vnd sprichtt daß der erst heist der zorn haulb der ander der wecker d |
[5r.1] Czoren haw wecker Hye nendt der meyster dy sechs verporgen hew wye yczlicher mit namen hayst auff daß dw dy stuck dester paß vernemen mügst und spricht daß der erst hayst der czoren haw der ander der wecker der dridt der entrust haw der feyert der czwinger fünft der gefer haw und der sechst hayst der wincker daß seyn sechß stuck und seyn der hawbt stuchk alz dw her nach horen wirst etc Sequitur textus |
[2r.3] Zoren haw vecker Hye nendt der meyster dy sechs verporgen hew wye yetzlicher mit namen heyst auff das das dw dy stück dester paß vernemen mügst vnd spricht das der erst heyst der zoren haw Der ander der wecker der dritt der entrusthaw der vyerdt der zwinger Der funft der gefer haw vnd der sechs hayst der wincker Das seyn sechs stuck vnd seyn der hawbt stuck alz dw her nach hōren wirst; |
[97r.6] Zorn hau wecker / entrist / hartzwinger [!] / gefer mit wincker hie nennet der meyster dyr sechs verborgen hewe wie ein iglicher mit namen heysset auff das / das du dir [!] die stuck aller bast vernemen magst vnd spricht das der pest heysset der zornhaw / der ander der wecker / der dritt der entrist haw / der vierd der zwinger / der fůnft der geferhaw / der sechst der wincker / das seÿnd sechs stuck vnd seind der hewp stuck als du her noch horen wirdest |
[140r.2] Die sechs hew Zornhaw |
||||||
[11] |
The Bastei, displace Here the master lists the other main elements: these are seventeen. The first are the four guards-they are referred to as the text says: the Bastei. |
[48r.1] die pasteÿ / versetz / Hie zelt der meinster die andern haubt stueck der sint l sieben zehen daß erst das sint die vier leger die werdent berürett do der text spricht die pasteÿ |
[5r.2b] Dy pasteyn, versecz Hye czelt der meyster dy andren hawbt stuck der seyn sybenczehen daß erst Das erst seyn dy vyer leger dy werden peruert so der text sprich dy pasteyn du |
[2r.4] Dy pasteyn versetz Hye zelt der meyster dy anderen hawbtstuck Der seyn sibenzehen Das erst seyn dy vyer leger dy werden werürt So der text spricht dy pasteyen |
[97r.7] Dy pasteÿ versetz vber reys vber lauf vnd ab setz
denn wechsel durch ruck lauff dy ab schneidt vnd
druck Ab lauff durch gee bogen dy were nÿme
hend dy wind ghen plessen schlach dy streych
lere verdrossen. Hye zelt der meyster dy andern stůck / der seind sybenzehen / Das erst das seind dy vier leger dy werden berůrt so text spricht dye pastey |
[140v.1] Hernach volgent die Anndern Siben zehen hauptstuckh.
[140v.2] Die vier Leger |
||||||
[12] |
Then, the other element is called displacing-it is referred to as the text says: displace. |
[48r.2] Item daß ander stueck heist das versetzen das wuertt berutettruerett so der text spricht versetz ~ |
[5v.2] Item daß ander stuck haysset daß verseczen daß wirtt peruertt so der text sprich versecz |
[2v.2] Item das ander stuck heysset das versetzen das wird beruert So der text spricht versetz |
[97r.8] Item das ander stuck heysset das versetzen das wird berůrt so der text spricht versetz / |
[140v.3] Versetzen. |
||||||
[13] |
Then, the third are the drawing after-it is referred to as it is said: drawing after. |
[48r.3] Item daß dritt syndt dz noch reissen das wurtt bereiret so der text sprich noch reiß ~ |
[5v.3] Item daß drit seyn dy nach raysen daß wirtt peruert So der text spricht nachrayß etc |
[2v.3] Item Das dritt seyn dy nachreysen das wirt beruert So gesprochen wirtt vberlauff dy nachraysen |
[97r.9] Item das dritt sein dy noch reyssen das wůrt berůrt so der text spricht Noch reyß / |
[140v.4] Nachraisen |
||||||
[14] |
Then, the fourth are overrunning-it is referred to as it is said: run over. |
[48r.4] Item daß vierd sint die vberlauffen dz wurt beruerett do der text sprichtt vberlauff ~ |
[5v.4] Item daß vyerd seyn dy uberlauffen dy werden peruert so gesprochen wirt uberlauff dye etc |
[2v.4] Item das viert sein dy vberlauffen das wirt berütt So gesprochen wirtt vber lauff dy |
[97r.10] Das vierd seind die vber lauffen das w b s d t s. vber lauffen |
[140v.5] Oberlauffen. |
||||||
[15] |
Then, the fifth are setting off-it is referred to as it is said: set off. |
[48r.5] Item daß fünfft sint die ab setzen dz wurt berüret do der text sprichtt absetz ~ |
[6r.1] Item daß fünft seyn dy abseczen daß wirtt peruert so gesprochen wirt absecz |
[2v.5] Item Das funft seyn dy absetzen das wirtt berütt so gesprochen wertt absetz |
[97r.11] Item das fůnft seind dy absetzen d w b s d t s absetzen |
[140v.6] Absetzen. |
||||||
[16] |
Then, the sixth are changing through-the master refers to it as he says: change through. |
[48r.6] Item daß sechst daß sint die duerch wechschell daß wuertt beruerett so der text spricht wechschell durch ~ |
[6r.2] Item daß segst syn dy durchwechsel daß peruert der meyster so er spricht wechsel durch |
[2v.6] Item das sechst sein dy durch vechselen das berütt der meyster so er spricht vechsel durch |
[97r.12] Item das sechst sein dy durch wechsel das berurt der meyster so er spricht wechsel durch |
[140v.7] Durchwechslen |
||||||
[17] |
Then, the seventh is called twitching-it is referred to as he says: twitch. |
[48r.7] Item die siebende heist dz zuecken dz wuertt beruerett so er sprichtt zueck ~ |
[6r.3] Item daß sybent haysset daß czucken daß wirt peruert so er spricht czuck |
[2v.7] Item das sybent heyst das zucken das wirtt berurtt So er spricht zuck |
[97r.13] Item das sibent heysset das zucken d w b s d t spricht zůck |
[140v.8] Zuckhen. |
||||||
[18] |
Then, the eighth are running through-they are referred to as it is said: run through. |
[48r.8] Item daß achst sint die duerch lauffen dz ist so er spricht lauff durch etc ~ |
[6r.4] Item daß acht daß syn dy dürchlauffen und dy werden peruert so gesprochen wirt lauff durch |
[2v.8] Item Das acht sein dy durchlauffen dy werden werütt so gesprochen wirtt lauff durch |
[97r.14] Item das viii. sein dy durchlauff etc. lauff durch |
[140v.9] Durchlauffen. |
||||||
[19] |
Then, the ninth are cutting off or the four cuts-it is referred to as it is said: cutting off. |
[48r.9] Item daß Nünde sint die ab schniden oder die vier schnit dz wuert berueret so gesprochen wuerde ab schnide etc ~ |
[6r.5] Item daß newndt daß seyn dy abschnydt oder veÿer schnydt daß wirt peruert so gesprochen wirtt dy abschnydt |
[2v.9] Item das newndt sein dy abschnidt oder dy vier schnidt das wirtt beruret so gesprochen wertt dy abschnidt |
[97r.15] Item das .ix. sein dye abschneide oder dy vir schnit d w b s d t s. dy abschneid |
[140v.10] Abschneyden. |
||||||
[20] |
Then, the tenth is called pressing the hands-it is referred to as he says: press. |
[48v.1] Item daß zehende heist die hend drueck dz wuertt so er spricht druck ~ |
[6r.6] Item daß zehendt daß hayst dy hend drucken daß wirt peruert so er spricht druck |
[2v.10] Item das zehendt heyst dy hendt drücken das wirt beruret so er spricht druck |
[97r.16] Item .x. heysset dy hentrucken d w b s er spricht druck |
[140v.11] Henndtruckhen. |
||||||
[21] |
Then, the eleventh are running off-it is referred to as he says: run off. |
[48v.2] Item daß elfte sind die ab lauffen dz wurt beruerett so er sprichtt ab lauff ~ |
[6r.7] Item daß eylfft syn dy ablauffen daß wirt peruert so er spricht ablauff |
[2v.11] Item das eylfft sein dy ablauffen das wirdt berütt So er spricht ablauff |
[97r.17] Item das xi. sein dÿ ablauffen d w b s er s ab brüff |
[140v.12] Ablauffen. |
||||||
[22] |
Then, the twelfth are taking over-it is referred to as he says: take over. |
[48v.3] Item daß zwelffte sint die benemen dz wuertt berüret so der text spricht benÿm ~ |
[6v.1] Item daß se czbelfft seyn dy pnemen daß peruert unß der meyster So er spricht pnym |
[2v.12] Item das zwelfft seyn dy pnemen das wirdt perütt so er spricht pnym |
[97r.18] Item das xii. sein dy benemen d w etc benÿmen |
[140v.13] Benemben. |
||||||
[23] |
Then, the thirteenth are going through-it is referred to as he says: go through. |
[48v.4] Item daß xiij daß sint die duerch gen dz wuertt so er sprichtt durch ge ~ |
[6v.2] Item daß dreyzehent seyn dy durchgen daß wirtt peruert so er spricht durchgee |
[2v.13] It[em] das dreyzehent das sein dy durchgen vnd das wirtt berut so er spricht durchge |
[97r.19] Item das xiii. sein dy durch ghen d w etc durch ghe |
[140v.14] Durchgeen. |
||||||
[24] |
Then, the fourteenth is called the bow-it is referred to as he says bow. |
[48v.5] Item daß xiiij sint die bogen dz wurt so er spricht bogen |
[6v.3] Item daß virzehent heyst der pogen daß wirt peruert So er spricht pogen |
[2v.14] Item das virzehent heyst der pogen das wirt beruert so er spricht pogen |
[97r.20] Item das xiiii heysset der bogen d w b s er s bogen |
[140v.15] Bogen |
||||||
[25] |
Then, the fifteenth is called taking the Messer-it is referred to as it is said: take the defense. |
[48v.6] Item daß xv heist dz messer nemen dz ist so er sprichtt were nÿm ~ |
[6v.4] Item daß fünftzehent heyst daß messer nehmen daß wirt perüert so gesprochen wirt wer nymb |
[2v.15] Item das funftzehent heyst das messer nemen das wirt beruett so er so gesprochen wirtt wer nymb |
[97r.21] Item das xv heysset das messer nemen d w b s er s wirt vernym |
[140v.16] Duseggen nemen. |
||||||
[26] |
Then, the sixteenth are the hangings-they are referred to as it is said: hang. |
[48v.7] Item das xvj daß die hengen dz ist so er sprichtt henge |
[6v.5] Item daß sechzehent daß seyn dy hengen dy werden peruertt So gesprochen wirtt heng |
[3r.1] Item das sechzehndt sein dy hengen dy werden berüert so gesprochen wirt heng |
[97r.22] Item das xvi sein dÿ henge d w b s er s heng |
[140v.17] Henngen |
||||||
[27] |
Then, the seventeenth are winding with the Messer-the master refers to it for us as he says: wind against the openings. Thus, you have the main elements which are twenty-three. |
[48v.8] Item dz xvij sint die wenden im messer So er spricht wende gegen den plosßen also hastu dz der haubt stueck sintt zeh drÿvndzwentzig ~ |
[6v.6] Item daß sybentzehent daß syn dy wynden yn dem messer daß peruert unß der meyster So er spricht wynd gen den plossen alzo hastu daß der haubtstuck seyn dreÿ und czwaynczyg. Sequitur. |
[3r.2] Item das sibzehendt sein dy winden yn dem messer das beruert vns der meyster so er spricht wind gen den plössen Also hastu der hauptstuck sein dreyundzaynzig etc |
[97r.23] Item das xvii sein dy winden Im messer das berůrt vnß der meyster so er spricht wind den blossen also hastu das der hawpt stuck sein .xxiii |
[140v.18] Winden /. |
||||||
[28] |
What is turned against you As the master divided the Messer fencing into the different techniques and described each of them with a name. Now he begins to speak about the first part of the division, that is about the Zornhau. And one is to know that the Zornhau Ort breaks all the strokes from above but is still nothing else but a simple peasant stroke. |
[48v.9] Was vff dich wurt gericht So der meinster des messer vechten in die stueck geteilt hatt vnd eyn yttlichs mit namen genant hatt Nu hebt er an zue sagen von dem ersten glyett der teÿllüng als von dem zorn haulb ~ |
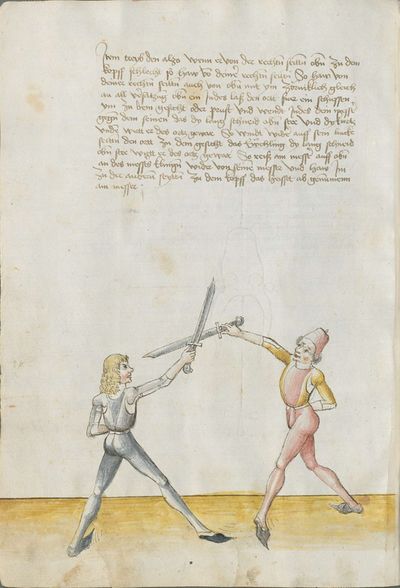
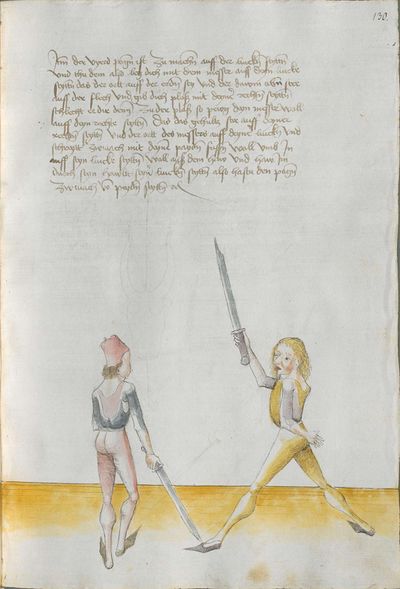
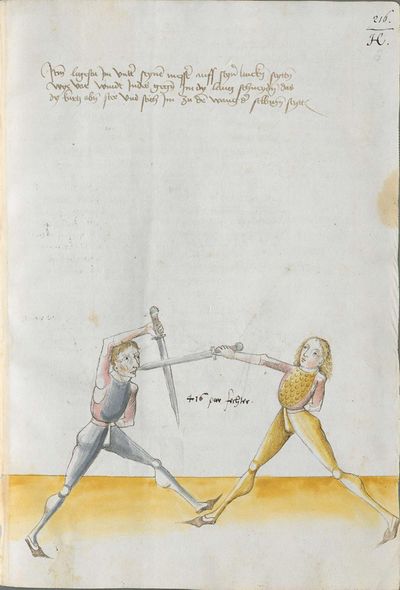
[7r.1] Waß auff dich wirtt gericht So der meyster daß vechten deß messerß yn dy stuck getaylt hatt und eyn yetlichß mit namen genent hatt \ Nw hebt er an zw sagen von dem ersten glid der taylung alz von dem zoren haw und ist zw wyssen daß der czoren haw mit dem ortt pricth all öberhew und ist doch eyn schlechter paweren schlag |
[3r.3] Was auf dich wirt gericht So der meister das vechten des messers yn dy stuck geteylt hat vnd eyn ytlichs mit namen genent nw hebt er an ze sagen von dem ersten glid der tailung als von dem zorenhaw vnd ist zw wissen das der zorenhaw mit dem ortt bricht all ōberhaw vnd ist doch eyn schlechter pawren schlag |
[97r.24] was
auff dich wirt gericht zorn haw ort das
gar bericht wiltu In beschmehen [!] am
messer lere abnemen So der meyster das vechten des messers In dy stuck geteylt hat vnd ein yiglichs mit namen genenet Nun hebt er an von dem ersten gelyrt zu sagen der teylungk als von dem zornhaw vnd ist zu wissen das der zornhaw mit dem ort bricht alle ober hew vnd ist doch ein schlicht pawren haw schlag |
[141r.1] Der Zornhaw mit Seinnen stuckhen Was auf dich wirt gericht |
||||||
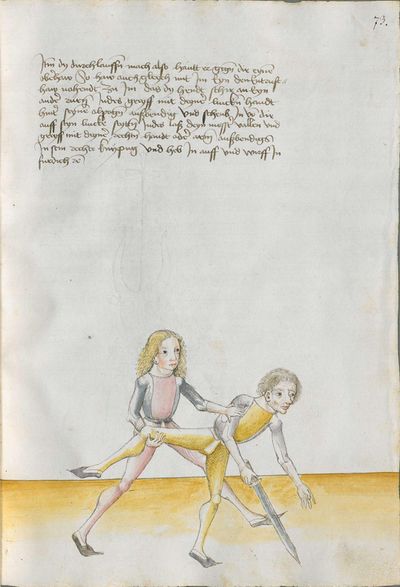
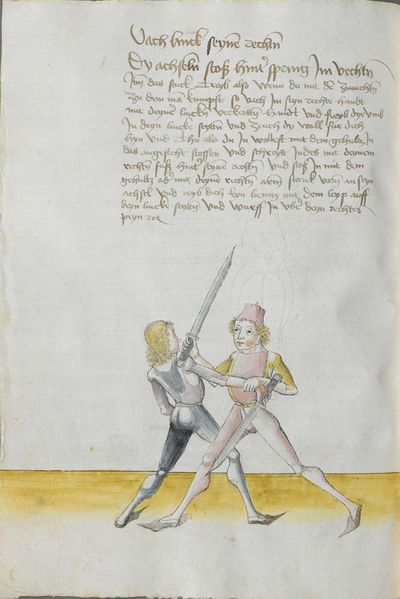
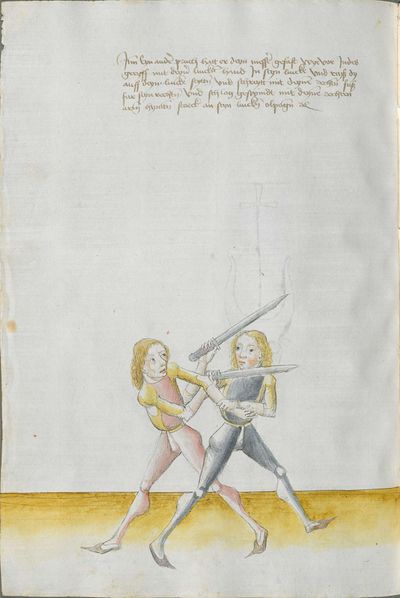
[29] |
Then, do it this way: when he strikes from above from the right side to the head, strike from your right side[6] also from above angrily[7] above together to displace him. Then Let “simultaneously” your point shoot forwards towards his face or the chest and “simultaneously” turn your Messer against his, so that the long edge stands above and the short edge is below. If he becomes aware of the point, wind again the point on his left side towards the face, so that always the long edge is above. If he becomes aware of the point, pull up the Messer on the upper Messer’s blade against his Messer and strike to him at the other side to the head. This is called taking away on the Messer. |
[48v.10] Item den tribe also wan er von der rechten syten oben zue dem koppff schlecht So haulb von diner rechten syten auch von oben mit Im zorniclichen glich an al versatzüng [49r.1] oben In Indeß loß den ortt fur In schuessen Im zue dem gesiecht oder brust vnd wend Indes din messer gegen dem sinen dz die lang schnide oben ste vnd die kurtz vntten wuertt er dz orttz gewar so wende wider vff sin lincken siten den ort zu dem gesicht dz euechling die lange schnid oben ste wurtt er dz ortz geware so rieß im messer vff an das messers clingen wider von sinen messer vnd haulb im von zu der andern siten zu dem kopff dz heist ab genomen Im messer etc |
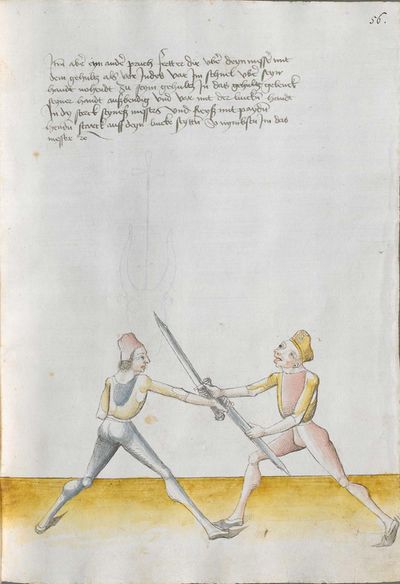
[7r.2] Item treyb den alzo wenn er von der rechten seytten oben zw dem kopff schlecht so haw von deyner rechten seytten auch von oben mit ym zörnycklich gleych an alle versaczung oben eyn yndes laß den ort gerichtes füer eyn schyssen zw dem gesichtt [7v.1] oder prust und wendt deyn messer gegen dem seynen daß dy lang sneydt oben stee und dy kurcz unten wirt er deß orcz gebar so wyndt wyder auff seyn lincke seytten den ort zw dem gesicht daß ewchling dy lang schneyd oben stee wirt er deß orcz gewar so reysß am messer uff oben an deß messerß klingen von seynem messer und haw ym zw der andren seytten an seyneß messerß klyngen wyder zw dem kopff daß heysset abgenumen etc |
[3v] Item treyb den alzo wenn er von der rechten seitten oben zu dem kopff schlecht so haw von deiner rechten seitten So haw von deiner rechten seitten auch von oben mit ym zōrniklich gleich an all versatzung oben ein Indes laß den ortt fuer ein schiessen ym zu dem gesicht oder prust vnd wendt Indes dein messer gegen dem seinen das dy lang schneid oben stee vnd dy kurtz vnden wirtt er des ortz gewar So windt wider auff sein lincke seiten den ortt zu dem gesicht das Ew̄chling dy lang schneid oben stee wirtt er des ortz gewar So reiß am messer auff oben an des messers klingen wider von seinem messer vnd haw Im zu der anderen seytten zu dem kopff das heisset ab genommenn am messer; |
[97r.25] Item treyb den also wan er von der rechten seytten oben zu dem kopff schlecht so haw von deyner rechten seyten auch von oben mit Im zornniglichin gleych an alle versatzung ob Im Indes loß den ort fůr In schissen Im zu dem gesicht oder brust vnd wind Indes dein messer ge kegen dem sein das dy lang schneid oben stee vnd dy kurtz vnden wurt er des orts gesneid gewar so wind wider auff dy lincken seytten den ort zu dem gesicht das euchling dy lang oben stee / wirt er des orts gewar so reyss am messer auff an des messers klingen wider von seinem messer vnd haw Im zu der ander seytten zu dem kopff das heyst abgenomen Im messer |
[141r.2] Den zornhaw mach also. Wann er von der rechten seiten oben zu dem kopf schlecht. so haw von deiner Rechten seitten auch von oben mit Im zornigklich gleychem on alle versatzung. Indes lasz den ort fur dich einschiessen. Im zu dem gesicht. oder der prust. vnnd winnd Indes. dein Duseggen. gegen dem seinnen. das die Lanng schneid oben stee. vnnd die kurtz vnnde. Wirt er des ort gewar. so wind wider auf sein linnckhe seiten. den Ort zu dem gesicht. das alweg. en die lanng schneid oben stee. Wirt er des orts widerumb gewar. so Reyss. am Duseggen auf. an des Duseggen klinngen wider von seinnem Duseggen. vnnd haw Im zu der anndern seitten. zum kopff. das haist abgenomme Im Duseggen. |
||||||
[30] |
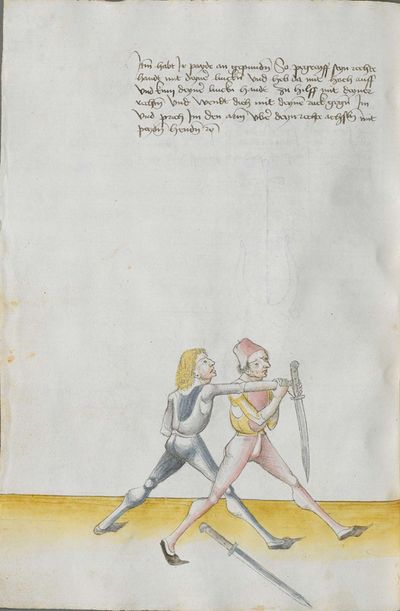
The Zornhau Ort is turned against you Here the master teaches the break against the Zornhau Ort, and the text states: The Zornhau Ort, etc. You should understand it this way: if he delivers the Zornhau with the Ort against you, strike to his hand on the wrist inside of his same hand. |
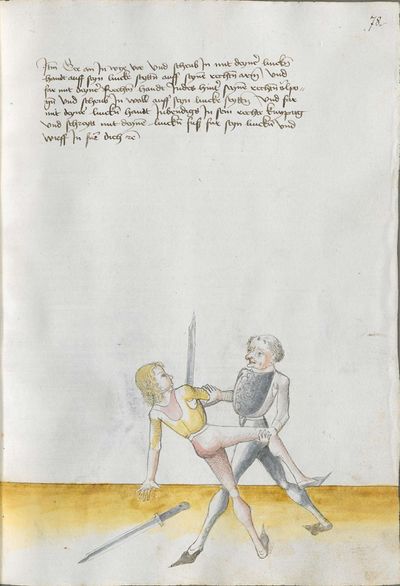
[4r] Zorenhaw ortt auff dich gericht Hie lertt der meyster dy pruch wider den zorenortt vnd spricht der text zoren haw ortt etc Das soltu alzo verstan Macht er den zorenhaw auff dich mit dem ortt so haw Im nach seiner handt In das gelenck Inbendigs auff sein Eẅerliche handt etc |
||||||||||
[31] |
Then, if he delivers the Zornhau Ort to you and wants to thrust at your face, lower your Messer with straight arm and lower the point to his chest and push him well back and put the left leg well back. |
[4v] Item macht er auff dich den zorenhaw mit dem ortt vnd will dir zu dem gesicht stechen So senck dein messer nider mit gestracktem arme vnd senck Im den ortt auff sein prust vnd scheub In woll ze ruck vnd setz das linck pain woll zu rück etc |
||||||||||
[32] Then, if he strikes from above his right side, strike also angrily together with him and turn the point to the face against the Messer, so that the right edge is above. If he becomes aware of the thrust, let your point “simultaneously” go down and go between you and him high with it and strike to his right side from above to the head with the long edge etc. |
[49r.2] ein anders Item hautt er von siner rechten achsell So haulb auch zorniclich glich mit Im In vnd wend den ortt zu dem gesicht gegen sinen messer dz die recht schnid oben ste wurtt er dz stichs gewar So loß den ortt Indes vnten sencken vnd far zwueschen dich vnd Im do mit gesencktem ortt vff vnd haulb im zue der rechten siten oben zu dem kopff mit der langen schniden ~ |
[7v.2] Item hawt er von seyner rechten achseln so haw auch zornyklich mit ym eyn und wendt den ortt zw dem gesicht gegen seynem messer daß dy recht schneyd oben stee wirtt er deß stichß gewar so laß den ortt yndeß unter sincken und par czwischen dich und yn da mit auff und haw ym zw seyner rechten seytten oben zw dem kopff mit der langen schneyden etc |
[97r.26] Item hewet er von .s. r. achsel so haw auch zorninglich mit Im ein vnd wend den ort zu dem gesicht gegen seinem messer das dy recht schneid oben sthee / wirt er des gestichs gewar so los den ort In des vnd schencken vnd far zwischen dich vnd Im do mit gesenckem ort auff vnd haw Im zu der rechten seytten oben zů dem kopff mit der rechten langen schneiden |
|||||||||
[33] |
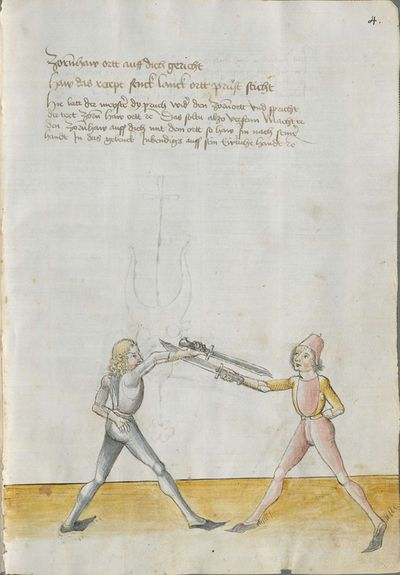
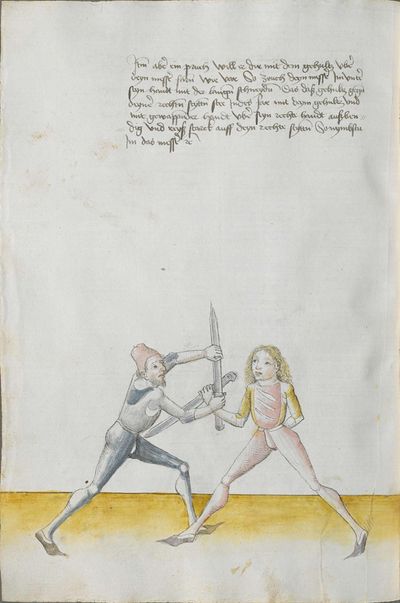
You should lower through the point Here the master teaches an element: when you have done the Zornhau Ort, lower the point down between you and him in front of your body and strike to him with the cross stroke and with the long edge to his right ear. |
[5r] Den ortt soltu durch sencken Hie lertt der meister ein stuck so dw den zorenhaw gemacht hast mit dem ortt so laß den ortt nider sencken vnd var zwischen dich vnd In fur dein leib vnd schlag In mit der zwirch vnd mit der langen schneiden zu seinen rechten oren etc |
||||||||||
[34] |
If he wants to strike crosswise to the ears Here the master teaches a break against the element described above and says: If he wants to strike crosswise, etc. You should understand it in this way: If he is stroking the cross stroke to your ears and is high with the arms, lower the hanging point into his chest and push him with the Messer from you. |
[5v] Will er zwirch schlagen zu den oren Hie lertt der meister ein bruch wider das Ee gemelt stuck vnd sprich will er zwirchen etc Das soltu alzo verstan So er dy zwirch zu deinen oren ist schlagen vnd ist hoch mit den arme so senck ym den hangenden ortt in sein prust vnd scheub In mit dem messer alzo von dir |
||||||||||
[35] Then, you can also do it with the short edge and also strike or you can strike to the head with the Entrüsthau, as soon as you let the point sink, it all goes right, so that you can perform it rightfully. |
[8r.1] Item auch magstu daß thun mit der kurczen schneyden vnd auch alzo schlagen oder mit dem entrusthaw magstu zw dem kopff hawen alz offt dw den ort lest alzo sincken daß get alleß recht zw so dw daß recht treyben kanst |
[97r.27] Item auch magstu das mit der kůrtzen schneiden vnd auch also schlahen oder mit dem entrist mustu zu [97v.1] dem kopff hawen / als offt du ein ort last sincken das ghet alles recht zů / so du das recht treyben kanst / |
||||||||||
[36] You can also do the doubling in it, which is also quite good in the work. |
[8r.2] ¶ Auch magstu dy dupliren dar eyn machen daß ist auch gar gut yn dy erbat |
[97v.2] auch magstu dy dupliren dar In ist gar gut zu der arbeytt |
[141v.1] Vom dupliern Auch magstu die Duplieren darein mache ist auch gar guot zu der arbait. |
|||||||||
[37] |
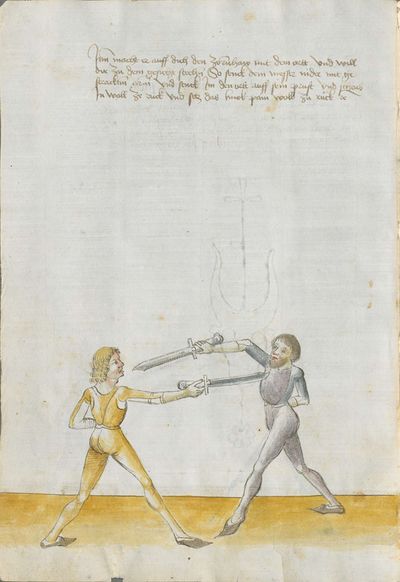
From the Zornhau, learn to deliver low to the right Here the master teaches an element that you should deliver out of the Zornhau, and says: From the Zornhau learn, etc. You should understand it this way: if you have done the Zornhau on him, you should lower the point and you should go with the lowered Messer with the arm high between you and him, so that the hilt is standing above. Then, “simultaneously” bend your hand and strike with the short edge in his face or cut through his face with the short edge. |
[6r] Auß zorenhaw ler gesenckt auff recht treyben Hie lertt der meister aber ein stuck das dw auß dem zorenhaw treiben solt vnd sprich auß zorenhaw lere etc Das soltu alzo verstan so dw den zorenhaw auff In gemacht hast So soltu den ortt aber sencken vnd schalt mit gesencktem messer hoch mit dem arme zwischen dich vnd In faren das das gehultz obersich stee Indes verbendt dein handt vnd schlag Im dy kurtz schneid In sein gesicht oder schneid In durch sein antlitz mit der kurtzen schneiden etc |
||||||||||
[38] |
If he has bound with the short edge Here the master teaches a breaking against the element described above, and he says: If he wants with the short edge, etc. You should understand it this way: if he wants to cut or strike at you with the short edge to your face, as it is described before, wind “simultaneously” the point against his Messer and thrust at his face on his right side. |
[6v] Kurtz mit schneiden ist er pinden Hie lertt der meister ein bruch widr das ee gemelt stuck vnd spricht kurtz will mit schneiden etc Das soltu alzo verstan will er dich mit er kurtzen schneiden dich In dein antlitz schneiden oder schlagen wie vor gesagt Ist So windt Im Indes den ortt auff gegen seinem messer vnd stich Im zu dem gesicht seiner rechten seitten etc |
||||||||||
[39] |
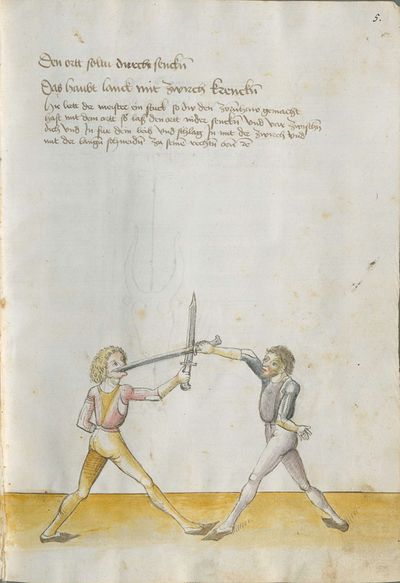
Learn to directly take away Here the master teaches the taking away with the long Messer and says: Directly to take away, etc. If you strike the Zornhau, wind your Messer against his one, so that the long edge is standing above itself. “Simultaneously” wind again to your right side against his left side, so that the long edge is below and the blunt one is above, and thrust straight at his face. “Simultaneously” strike skillfully along the Messer to his right side with the long edge to the head. |
[7r] Gerad ab nemen lere Hie lertt der meister abnemen mit dem langen messer vnd spricht alzo Gerad ab nemen etc So dw den zorenhaw hawest so windt dein messer gegen dem seinen das dy lang schneid übersich stee Indes windt wider auff dein rechte seitten gegen seiner lincken das dy lang schneid vnden stee vnd dy stumpff oben vnd stich Im gerad zu dem gesicht Indes schlag behentlich ab am messer zu seiner rechten seitten mit der langen schneiden zu dem kopff etc |
||||||||||
[40] |
If he has taken away straight on the Messer Here the master teaches the breakings against the takings away and says: On the Messer straight, etc. You should understand it this way: if he takes away on you with straight Messer, as it is stated above, “simultaneously” step aside to your right side well away out of his stroke and remain standing still, and strike to him with the long edge of your Messer on his head. Or turn your Messer against his one, so that the long edge is standing upwards, and thrust to his face or strike with the short edge to his face. |
[7v.1] Am messer geradt ist er abnemen Hie lertt der meister dy pruch widr dy abnemen vnd sprich am messer gerad etc Das soltu alzo verstan So er abnybt auff dich mit geradem messer wie vor gesagt ist Indes trit beseit auff dein rechte seitten woll auß seinem schlag vnd beleib alzo sten vnd schlag In mit der langen schneiden deines messers auff sein kopff oder wendt dein messer gegen dem seinen das dy lang schneid ob stee vnd stich Im zu seinem gesicht oder schlag Im dy kurtz schneid In das antlitz. |
||||||||||
[41] Then, if he takes you away on the Messer, turn your Messer with the back of your Messer a bit on his one and strike at him from above to the opening, so that you strike through his head, amen. |
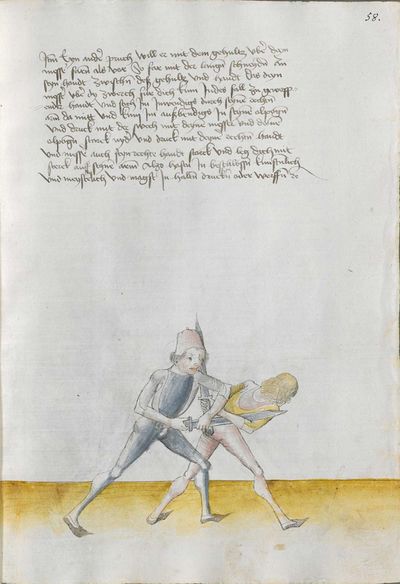
[49r.3] ein anders Item nÿmpt dir eyner ab am messer So wind din messer mit dem rueck dines messers anwenig auff dz sin vnd haulb im oben noch der ploß so schlechstu In duerch den kopff |
[8r.3] Item nymbt dir eyner ab am messer so wendt deyn messer mit dem ruck deyneß messerß eyn wenick auff daß seyn und haw ym oben nach der ploß so schleghstu yn durch den kopff amen |
[97v.3] Item nympt dir eyner ab am messer so wend dein messer mit dem ruck diesses ein wenig auff das sein vnd haw Im noch der ploesse so schlechstu In durch den kopff |
[141v.2] Item nimpt dir ainner ab an dem Duseggen. so wirff dein Duseggen mit dem ruckh ain wennig auff den seinnen vnnd haw Im oben nach der plöss. so hawstu In durch den kopff. |
||||||||
[42] |
Then, or drive with the flat of your Messer on his Messer during the taking away and strike to his head with the long edge. And notice, as you fall with the flat on his Messer, that you hit it cleanly. “Simultaneously” go high with the long edge and strike to his head, as it is depicted below. |
[7v.2] Item oder far Im mit der flech auff sein messer Im abnemen vnd schlag In zu seinem haubt mit der langen schneiden vnd merck So du mit der flech auff sein messer vellest das du seẅberlich dar auff stossest Indes far auff mit der langen schneiden vnd schlag In zu dem kopff wie vnden gemalt stet etc |
||||||||||
[43] Then, another breaking against the taking away: “Simultaneously” as he takes away, step sideways away from the stroke and work to his next opening with the stroke. |
[49r.4] Item eyn ander bruch wider die ab nemen Indes so er ab neÿmpt So drett besitz vß dem haulb oder schlag vnd arbeÿtt im zu der nesten ploß mit dem haulb ~ |
[8r.4] Item eyn ander pruch wyder dy ab nehmen yndeß so er ab nymbdt so drit peseytt auß dem schlag vnd erbat ym zw der negsten plöß mit dem haw |
[97v.4] Item ein ander bruch wider dy abnemen Indes so er abnÿmpt so trytt besutz auß dem schlag vnd arbeyt zu der recht ploes mit dem haw |
[141v.3] Ein pruch wider Die abnemmen Item trit bey seytz Ausz dem schlag vnnd Arbait Im zu der rechten plosse / mit ain haw. |
||||||||
[44] Then, another breaking: “simultaneously” as he takes away, thrust at his face. |
[49r.5] Item eyn ander bruch Indeß so er ab nÿmpt Stich im zue dem gesichtt etc textus |
[8r.5] Item aber eyn pruch yndeß so er abnymbt stich ym zw dem gesicht etc. |
[141v.4] oder mit ain stich Im abnemmen zu dem gesicht. |
|||||||||
[45] |
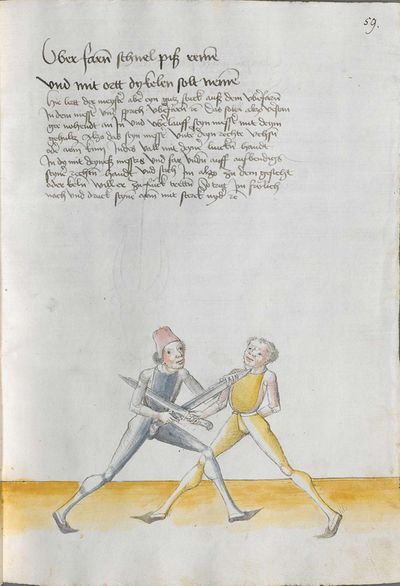
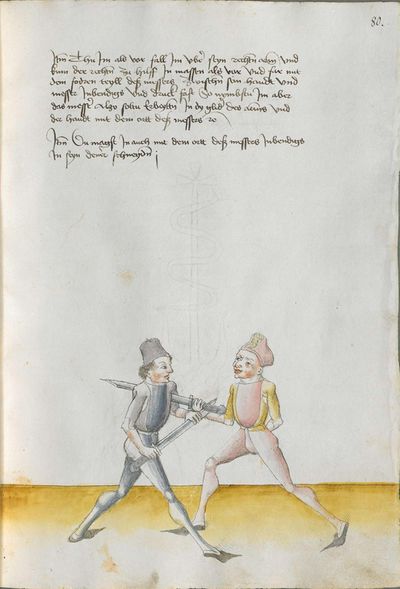
If you want to break the taking away with the flat of the Messer Here the master teaches a breaking against the breaking described above and says: If you want the flat, etc. You should understand it this way: if you have taken away on the Messer and he stands still with the Messer and lets you take away and if “simultaneously” he falls with the flat of his Messer on your one, and wants to strike you to the head, “simultaneously” wind against his Messer on his right side, so that you touch him at the head, as it is depicted below. Or, wait till he goes high and wants to strike to the head-then, go also high and wind over his Messer to his left side, so that the short edge is standing above, and thrust to the face to the same side. This is a very good breaking. The text follows. |
[8r] Will flech abnemen prechen Hie lertt der meister ein pruch wider den ee gemelten pruch vnd spricht alzo will flech etc Das soltu alzo verstan So du abnemen pist Im messer stet er alzo still mit dem messer vnd lest dich ab nemen indes felt er mit der flech seines messers auff das dein vnd will dich zu dem kopff schlagen indes windt auff gegen seinem messer auff sein rechte seitten So ruerstu In an das haubt wie vnden gemalt stet etc Oder harr piß er auff gett vnd zu dein kopff schlagen will so gee mit auff vnd windt vber sein messer auff sein lincke seitten das dy kurtz schneid ob stee vnd stich In dem gesicht der selbigen seitten vnd das ist ser ein gutter bruch sequitur textus |
||||||||||
[46] |
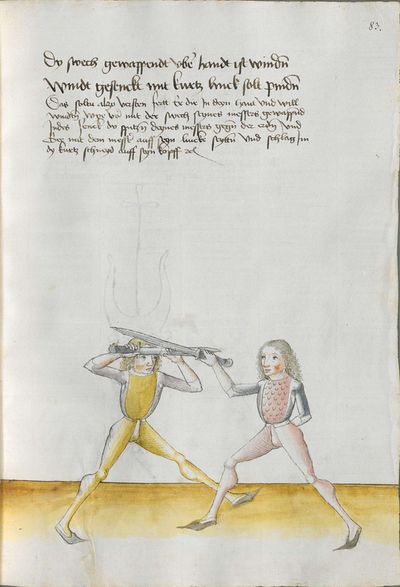
If he wants to hurt you with taking away Here the master teaches a breaking against the takings aside and says: If he wants with taking aside, etc. You should understand it this way: if he has taken away on the Messer with the long edge, wind your flat on his one, and remain standing there. Then, put the thumb on the flat of your Messer and thrust to his face of his right side. |
[8v] [10]Mit abnemen will er dich letzen Hie lertt der meister aber ein pruch wider dy abnemen vnd sprich alzo mit abnemen will etc Das soltu alzo verstan Ist er abnemen Im messer mit der langen schneiden so wend dein flech an dy sein vnd beleib alzo sten leg den dawmen auff dy flech deynes messers vnd stich Im zu dem gesicht seiner rechten seitten etc |
||||||||||
[47] |
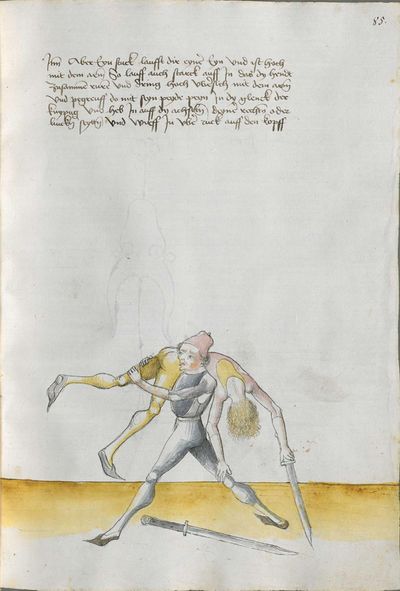
If he sets the point to the face to the right Here the master teaches a breaking against the breaking described above and says: If he sets to the face, etc. You should understand it this way: if you want to take away and he wants to break it with the point, as it is described above, lower your point with a straightened arm and put the left foot well back and thrust straight to his throat or chest. |
[9r] Setzt er zugesicht auff recht ortt Hie lertt der meister ein pruch widr den ee gemelten pruch vnd spricht Setzt er zu gesicht etc Soltu das alzo versten so du wild abnemen Ist er dir das prechen mit dem ortt wie ee gemelt ist so senck deinen ortt lanck auß gestracktem arme vnd setz den lincken fuß woll hinden hin auß vnd stich In geradt auff sein gurgel ader[11] prust etc |
||||||||||
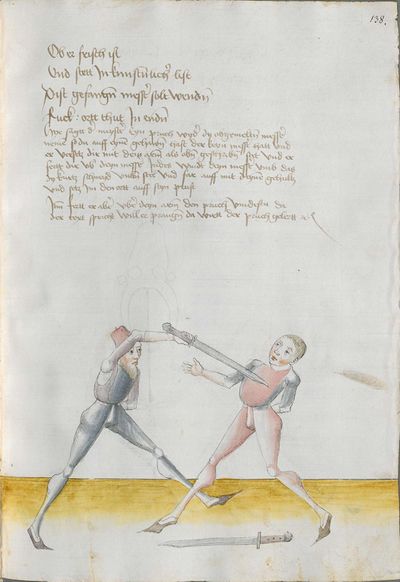
[48] Strike, thrust, notice Now, the master has said about the first element, that is about the Zornhau. Now he says a good teaching, that is, if one strikes or thrusts together with you, you should notice well, as one Messer sparks on the other, whether he is “soft” or “hard” in the binding. And as soon as you realise this, work “simultaneously” in the “war” according to the “soft” and to the “hard” to the next opening. |
Strike, thrust, notice Now, the master has said about the first element, that is the Zornhau. Now he says a good teaching, that is, if one strikes or thrusts together with you, you should notice when one Messer touching the other, whether he is “soft” or “hard” in the binding. And as soon as you realise this, work “simultaneously” in the “war” according to the “soft” and to the “hard” to the next opening. |
[49r.6] Haulb / stich / merck So nuen der meinster von dem ersten stueck hat gesaget als von dem zorn haulb Nu saget er eyn gut lere dz ist wan eÿner mit dir zue haulbt oder sticht So soltu eben mercken wan eyn messer an daß ander glitz ob er Im bandt wiechtt oder hart ist vnd als bald du daß entpfindest So arbeÿtt Indes mit dem krÿeg noch der weich vnd noch der hartt zu der nesten ploß / |
[8v.1] Hew stich merck So der meyster von dem ersten stuck hat gesagt alz von dem czornhaw Nü sagt er eyn gutte ler daß ist wen eyner mit dir eynhawet oder sticht So soltu gar eben mercken wen eyn messer an daß ander kliczt ob er ym pandt waych oder hert sey und alz pald dw daß empfindest so erbayt yndeß mit dem kryeg nach der waych und nach der hert zw der negsten plöß |
[9v.1] Hew stich merck So nw der meister von dem ersten stuck gesagtt hat als von dem zorenhaw nu sagtt er ein gutte ler das ist wenne einer mit dir ein haut oder sticht so soltu gar eben mercken wenne ein messer an das ander klitz ob er Im pandt waich oder hertt sey vnd als pald dw des empfindest so arbeit Indes mit dem krig nach der weich vnd nach der hertt zu der negsten plöß: |
[97v.5] Hewe stich merck Im band weych oder hart
vor vnd nach Indes hab acht dy lauff des kriegs
recht bewacht / So mir der meyster von dem ersten stuck hat gesagt als von dem zornhaw so sagt er ein gutte lere wenn eyner mit dir Im haw oder Im stich leÿt / so saltu eben merken wen ein messer an das ander glitzt ob er Im band weych oder hart seÿ / vnd als bald dü das entpfindest so arbeyt Indes mit dem kriegk noch der weych vnd noch der hert zu der nechste ploese |
[142r] Die waiche vnd die herte Haw stich merckh Item wann ainner Mit dir einhawt oder sticht. so soltu eben merckhen. wann ain Dusegg ann dem anndern glitz. ob er Im bannd waich oder hert sey vnnd als bald du das empfindst. so arbait Indes mit dem krieg nach der waich vnnd nach der hert. zu der nechsten Plosse / |
||||||
[49] Know that if you can work properly with the “war” and you lead it well, he is hardly able to escape from you You can do your work on him, so that he is hardly able to come from you without having been beaten. And what is “before” and “after,” you have heard before, and what is the “war” you will be taught afterwards. The text follows. |
And what is “before” and “after,” you have been taught before. |
[49v.2] Wiß wan du mit dem kryeg recht arbeyten kanst vnd den rechtt fuerest So kan er dir hart engen du machst im arbeit machen dz er küm von dir vngeschlagen kümen mag Vnd waß dz vor vnd dz noch ist dz hastü vor gehortt vnd waß der krieg ist wuerstu hernoch entrichtt etc |
[8v.2] ¶ Wyß wenn dw mit dem krig recht erbaytten kanst und den recht füerst so kann er dir hartt entgen dw macht dwu ym erbat machen daß er kawm von dir vngeschlagen kumen mag und waß daß vor und daß nach ist daß hastu vor gehort und [9r.1] waß aber der kryeg ist daß wirstu hyn nach unterricht etc Sequitur textus |
[9v.2] Vnd waß das vor vnd nach ist das pistu vor unterrichtt |
[97v.6] biß wan du mit dem krieg recht arbeyten kanst vnd den recht furest so kan er dir hart entghen du magst Im arbeyt machen das er kawm von dir vngeschlegen kumen mag vnd wiß das vor vnd nach ist das hastu vor gehört was aber der krieg ist das wirstu hernach entricht |
|||||||
[50] The “war” dissolve Here the master says what the war is and what one should perform therefrom towards the four peaks, that is to the four openings. Now, it is to be known that the war are the “windings” in the Messer and the work therefrom with the point to the four openings. This is called the “war”. |
The “war” dissolve Here the master teaches what the “war” is and what one should work therefrom towards the four peaks, that is to the four openings. Now, it is to be known that the “war” are the “winding” in the Messer and the work therefrom with the point to the four peaks. This is called the “war”. |
[49v.3] Den krieg vff los Hie saget der meinster waß der krieg vnd waß man darüß triben sol zü den fuer zinnen daß ist zu den viern plossen Es ist ze wissen daß der krieg ist die vier wenden im messer vnd die arbeyt darvß mit dem ortt in die vier zÿnnen dz heißt der krieg |
[9r.2] Den kryg vff loß Hye sagt der meyster waß der kryeg ist und waß man dar ausß treyben soll zw der vyer czynnen daß ist zw den vyer plössen Nw ist zw wyssen daß der kryg syn dy wynden ym messer und dy arbayt ym messer dar auß mit dem ortt zw der vyer czynnen daß hayst der kryeg |
[10r.1] Den krig auff löß Hie lertt der meister was der krig sey vnd was man darauß treyben sol zu den vier zinnen Das ist zu den vier plössen Nu ist zu wissen Das der krieg sein dy winden Im messer vnd dy arbeit dar auß mit dem ortt zu den vier zinnen Das heist der krieg |
[97v.7] Der krieg auff loß
oben nÿder wart der bloeß / Hie sagt der meyster was der krieg ist vnd was man dar auß treyben sol zů den vier zynnen das ist zu dem [!] vier blossen / Nun ist zu wissen das die g krieg ist die vierd winden Im messer vnd dy arbeyt dar auß mit dem ort zu dem [!] vier zynnen das heysset der krigg / |
[142v.1] Der Krieg Den krieg auf losz Item hie merckh Was der krieg ist vnnd was man darausz treiben soll. zu den vier zinnen. das ist zu den vier Plossen. es ist zu wissen das der krieg ist die vier winden. Im Duseggen. vnnd die arbait darausz mit dem Ort. Inn die vier Zinnen. das haist der krieg. |
||||||
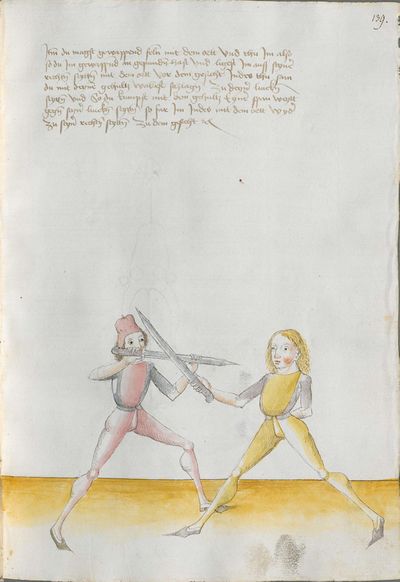
[51] Now, you should perform the war this way: if you strike the Zornhau together with him, as soon as he displaces, go high with the arm and wind him the point on his Messer from above to the face to his left side. If he sets the thrust aside, go to the lower peak to his right side and set him the point on. If he follows your Messer with the displacement, seek another peak with the point, downwards to the left side. If he becomes aware of the point, seek the fourth peak with the point, to the face to his right side. And when you want to prepare for the war, you should cleverly understand to always go high with the arm in front of the head, and sink the point to the peaks. |
Now, perform the war this way: if you strike the Zornhau on him, as soon as he then displaces, go high with the arm and wind him the point on his Messer from above to the face on his left side. If he displaces the thrust aside, go high to the other side to the other peak under his right arm on the chest. In case he follows the thrust, work to the next opening that you can find. |
[49v.4] Nu den krieg trib also wan du mit im zuhauelbest den zorn haulb als bald er den versetz So far vff mit dem arm wind im den ortt an sin messer oben In zue dem gesichtt siner lincken siten Setz er den stich ab So far in in die vnttern zÿnnen vff sin rechte siten vnd setz im den ortt an folget er dan dinen messer noch mit der versatzüng So stich mit dem ortt die [50r.1] die andern zÿnnen vntten vff die linck siten wurtt er deß ortz gelbar so stich die vierde zynnen mit dem ortt zu dem gesicht vff siner rechten siten vnd wend du dich in den krieg wil legen So soltu dich weißlich versehen dz du alllbegen mit dem arm vff farest in die hoege fur daz haupt vnd senck den ortt vff die zinnen |
[9r.3] ¶ Nü den kryeg soltu alzo treyben wenn dw mit ym eyn hawest den czorenhaw alzo pald er denn verseczt So far auff mit dem armen wyndt ym den ortt an seyn messer oben eyn zw dem gesicht seyner lincken seytten Seczt er denn den stich ab so far yn dy unteren czynnen auff seyn rechte seytten und secz ym den ortt an volgt er denn deynem messer nach mit der versaczung so suech mit dem ortt dy andern [9v.1] czynnen unten auff der lincken seytten wirtt er deß orcz gewar so süech dy vyertten czynnen mit dem ortt zw dem gesicht auff seyner rechten seytten und wenn dw dich alzo yn den kryg wild legen so soltu dich weyslich versehen daß dw albegen mit dem armen auff farest yn dy hoch fuer daß hawbtt und senck den ortt auff dy czynnen |
[10r.2] Nu den krig treib alzo wenne du mit Im ein hawest den zorenhawvnd als pald er den versetz So var auff mit dem arme windt Im den ortt an sein messer oben ein zu dem gesich seiner lincken seitten setzt er denn den stich ab So var auff dy anderen seitten auff dy andren zinnen unter seinem rechten arme auff dy prust volgt er denn aber dem stich nach So arbeit zu der negsten plöß dy du vinden magst etc |
[97v.8] Nun den krieg treyb also / wen du mit Im ein hewest den zorhaw [!] als bald er den versetzt so far auff mit dem arm vnd in den ortt an sein messer oben Im zu dem gesicht .Sn lis. setzt er den stich ab so far In dy vntter zynnen auff sein recht seytten vnd setz Im den ort an schlach slech er deinem messer noch mit der versatzung so stich mit dem ort In dy andernn zynnen vnnd auff dy lingken seytten wirt er des ort gewar so stich dye vierden zynnen mit dem ort zu dem gesicht auff sein rechten seyten / vnd wan du dich also in dem krieg wilt legen so soltu dich weyslich besehen das du albÿeg mit dem arm auff farest In dy hoehe fur das hawpt vnd senck den ort auff dy zynnen |
[142v.2] Item den krieg mach also. Wann du mit Im ein hawest. den zornhaw. als hab er den versetzt. so far auf mit dem arm. vnnd winnd Im den Ort an seinnem Duseggen oben ein zu dem gesicht seinner linncken seitten. setzt den stich ab. so far Inn die vnndern [143r.1] Zinnen seinner rechten seitten Vnnd setz Inn den Ort an. volgt er dann deinnem Duseggen nach mit der versatzunng so stich mit den Ort zu der anndern zinnen. vnnden auf die linnckh seitten. wirt er des orts gewar. so stich die vier zinnen mit dem Ort zum gesicht auf seinner rechten seitten. Vnnd wann du dich also Inn den krieg wildt Legen so soltu dich weyszlich fursehen. das du alwegen mit dem arm auf farest Inn die höche fur das haupt. vnnd sennckh den Ort fur die zinnen. |
||||||
[52] I tell you that if you have practiced the war and its properties with prudence, your adversary will be weakened from above and from below. The text follows. |
[50r.2] So wuertt dir din widersach von dir geschmechtt von dir wan du den krieg recht triebst ~ |
[9v.2] ¶ Ich sag dir so dw denn mit dem krÿg und mit seyner aygenschafft fertig pist treyben und mit fursichtikaytt so wirtt deyn wydersach oben und unten geswecht etc Sequitur textus |
[97v.9] Ich sag dir so du dem mit dem krieg vnd mit seyner eygen schafft bist vnd den treyben mit fursichtikeyt so wer drey widersach oben vnd vnden geschmecht(?) |
[143r.2] Ich sag dir so du dann den krieg vnnd sein aigenschafft prauchst vnnd treibst mit fursichtig kait so wirt dein widersacher oben vnnd vnnden geschmecht vonn dir /. |
||||||||
[53] There are four peaks Here the master says that you in the Zufechten, that is, while you come to the man, should not strike to his Messer, but you should diligently attack the four peaks. |
There are four peaks Here the master teaches that you in the Zufechten, that is, while you come to the man, should not strike to his Messer, but you should remember the four peaks. |
[50r.3] Vier sint der zinnen
Nu saget der meinster von den vier zÿnnen |
[9v.3] Vyer seyn der czynnen
Nw sagt der meyster daß dw ym [10r.1] zw vechten so dw zw dem man kumbst söltu mit nicht dem man nach dem messer hawen Sünder dw sölt dich fleysig remen der vyer czynnen |
[10v.1] Vier sein der zinnen
Hie lertt der meister Das dw Im zuuechten So dw zu dem man kumbst soltu nicht dem man nach dem messer hawen Sunder dw solt dich fleyssig remen der vier zinnen |
[143r.3] Vier sennd der zinnen [143v.1] Auszlegung der vier Zinnen Item wann du Mit em zufechten zu dem Mann kumpst. so soltu mit nichten dem Mann nach der wehr hawen. sonnder du solt gar fleyssig achtunng haben auf die vier zinnen. |
|||||||
[54] The first one is the right side, the other is the left side also above the belt of the man. |
The first one is the right side above the belt, the other is the left side also above the belt. |
[50r.4] Die erst zynne ist die recht siten vnd die ander die lincke siten als oberthalbt der gurttell des mans |
[10r.2] dy erst czynnen dy ist dy erst rechtt seytten und dy ander dy linck seytten alz od oberhalb der gurttel der gurtel deß manß |
[10v.2] die erst das ist dy recht seitten oberhalb der gurtel Dy ander dy linck seytten auch oberhalb der gurtel |
[143v.2] Die ersten zwu Zinnen Die erst zinn ist die Erst recht seiten. vnnd die annder zinnen das ist die linnckh seitten als oberhalb der gurtel des Manns./ |
|||||||
[55] The two other peaks are the left side and the right one below the belt of the man. |
The two other are below the belt of the man. |
[50r.5] die andern zwueo vndern zÿnnen dz ist uff der rechten siten vnd vff der lincken siten niderthalbt der gurttell / des mans |
[10r.3] dy andren czwü czynnen daß ist dy lynck seytten und dy recht nyderhalb der gurtel deß mannß |
[10v.3] dy anderen zwō sein vnderhalb der gurtel desmans |
[144r.1] Die anndern zwen Zinnen Item die anndern zwu Zinnen. dz ist die Linnckh seitten vnnd die recht vnnderhalb der gurtel des Mans. |
|||||||
[56] Take one of the openings and do not pay attention to what he does against you. Strike to it bravely; in case he displaces, strike quickly to the other peak, to the next opening that you can acquire. You should also wait for the body of the man and not for the Messer. The text follows. |
Take the peaks with no fear and do not pay attention to what he does against you. Strike to it bravely; in case he displaces, strike quickly to the other peak, to the next opening that you can acquire. |
[50r.6] Nüem nÿme dir der zÿnnen eyne fuer vnd ach nit waß er gegen dir vicht haulb dar zue kuenlich versetz er dir dan so haulb schell zu der andern zynnen zue der nesten die du gehaben magst also soltu vß warten deß liebs des mans vnd nichtt deß messers ~ |
[10r.4] nymb dir der czynnen eyne fuer und acht nicht waß er gegen dir vichtt haw dar zw kuenlich verseczt er dir denn so haw schnel zw der andren czynnen zw der negsten dy dw gehaben magst alzo soltu auß warten deß leybß des manß und nicht deß messers etc Sequitur textus |
[10v.4] nymb dir der zinnen eine fur vnd acht nicht was er gegen dir vicht haw dar zu kunniklich versetzt er dir dan So haw schnel zu der anderen zinnen der negsten ploß die dw gehaben magst etc |
[144r.2] Nimb dir der Zinnen aine fur. vnnd acht nit was er gogen dir Ficht. haw darzu redlich / versetzt er dir dann. so haw schnel zu der anndern zinnen dir du gehaben magst. allso soltu auswarten. des Manns leyb vnd nit des Duseggen. |
|||||||
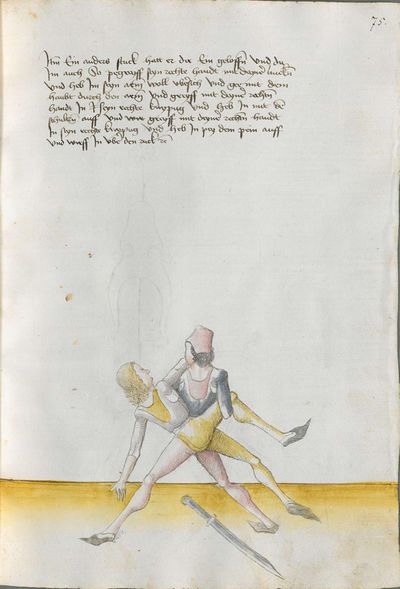
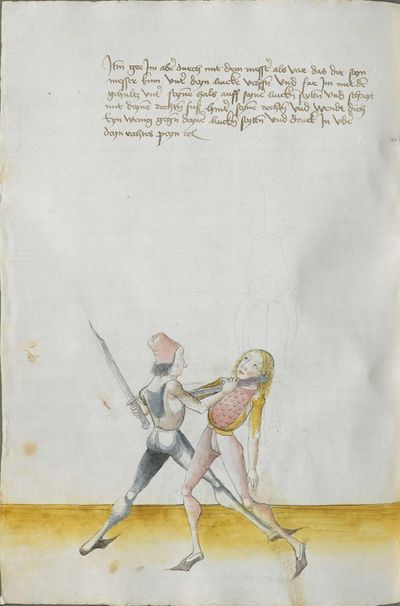
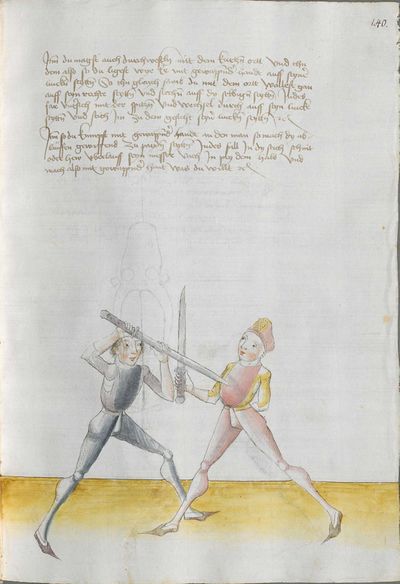
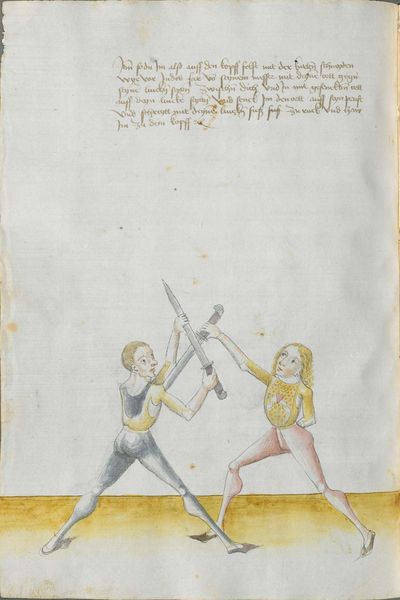
[57] If you have grasped that Here the master says that if one strikes to you honestly and you want to take revenge on him and break skillfully the peaks, so that you can beat him at his own game, be it pleasant or painful to him, perform the doubling against the “strong” of the Messer and the mutating against the “weak.” I tell you for the truth that he is hardly able to guard himself against the strokes and is hardly able to come to the strokes before your strokes. |
If you have grasped that Here the master says that if one strikes to you honestly and you want to take revenge on him and break skillfully the peaks, perform the doubling against the “strong” of the Messer and the mutating against the “weak.” I tell you for the truth that he is hardly able to defend himself against the strokes and is hardly able to come to the strokes. |
[50r.7] Hastu daß vernümen Hie sagett der meinster von eyner ernstlichen Inhaulbüng als von den zynnen wie du dich regchen soltt vnd saget der meinster hie von dem dupliren ~ |
[10r.5] Hastü daß vernümmen Hye sagt der meyster ob dir eyner ernestlich eyn hawett wiltu dich denn rechen an ym und dy czynnen kunstenlich prechen daß dw yn uber seynen danck magst schlagen eß sey ym lyeb oder laydt so treyb dy dwpliren gegen der sterck deß messerß und daß mutiren gegen der swech Ich sag dir fuer war daß er dich hartt vor schlegen hutten kann und vor deynen schlegen hart zw schlegen kummen mag etc |
[11r.1] Hastu das vernummen Hie sagt der meister ob dir einer ernnstlich ein hawett wiltu dich den rechen an Im vnd dy zinnen kunstenlich prechen So treib dy dupliren gegen der sterck des messers vnd das mutiren gegen der swech Ich sag dir furbar das er sich hartt vor schlegen schützen mag vnd hart zu schlegen kummen kan |
[97v.10] Hastu
das vernůmen dy zynnen seind gewnen wiltu
dich rechen die vier zynnen kunstlich brechen oben
dupliren do niden gantz müteren Hie sagt der meyster ob eyner ernstlichen Innen hewet wiltu dich dann rechen an Im vnd dy zynnen kunstlichen brechen das du vber sein danck magst hawen oder schlahen es sey Im lieb oder leyt So treyb dy duplir gegen der sterck des messers / vnd das mutieren gegen der schwech ich sag dir ver war das er sich hart vor schlegen huten mag vnd fur deinen schlegen hart zu schlagen kumen mag |
[144r.3] Hastu das vernommen Item wann dir ainner Ernstlich einnhawt. wildu dich ann Im Rechen vnnd die zinnen kunstlich prechen das du In vber seinn dannckh magst schlachen. es sey Im lieb oder laid. so treib das dupliern gegen der sterckh des Dusegens. vnnd dz Mutieren gögen der schwech. Ich sag dir fur war. das er von deinnen schlegen hart vngeschlagen kummen kann |
||||||
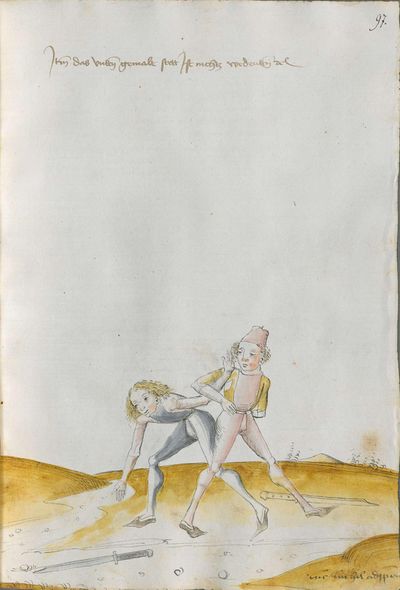
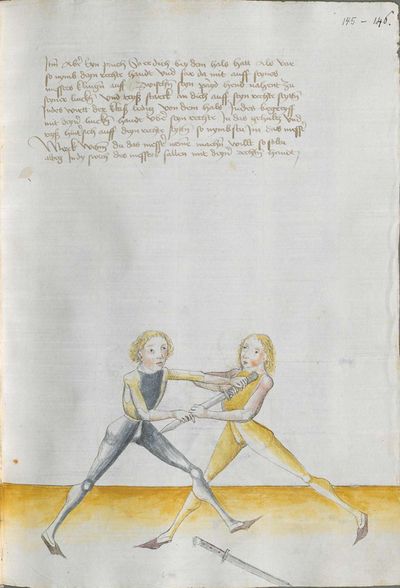
[58] |
Then, if you strike to him from your left side and bind him on his Messer with the long edge, go quickly high with the arm and remain standing on the Messer and strike to him behind the blade of his Messer with the blunt edge. |
[11r.2] Item hawstu ym von deyner lincken seytten zw und pyndest ym an seyn messer mit der langen schneyden so far pald auff mit dem armen und pleyb alzo sten am messer und schlag yn hynter seyneß messerß klyngen mit der stümpffen schneyden etc |
[11r.2] Item hawstu Im von deiner lincken seitten vnd pindest Im an sein messer mit der langen schneiden so far pald auff mit dem arme vnd pleib alzo sten an dem messer vnd schlag Im hintter seines messers klingen mit der stumpffen schneyden etc |
[97v.12] Item gewestu Im von der .l. s. zu vnd bindest Im an sein messer mit der langen schneiden so far bald auff mit dem arm vnd blayb also stan an dem messer l vnd schlach hinder seines messers klingen mit der stumpfen schneiden |
||||||||
[59] |
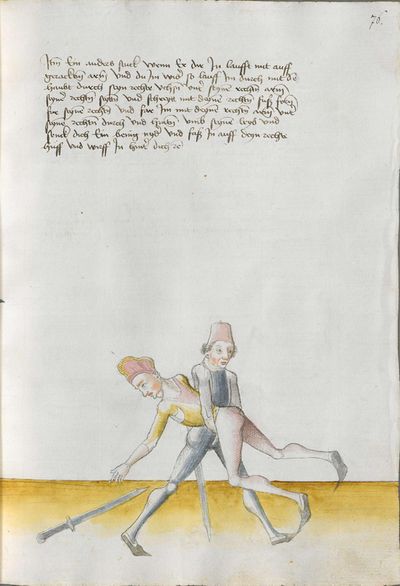
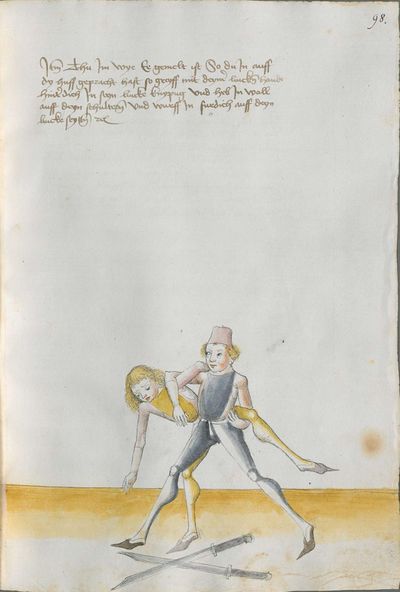
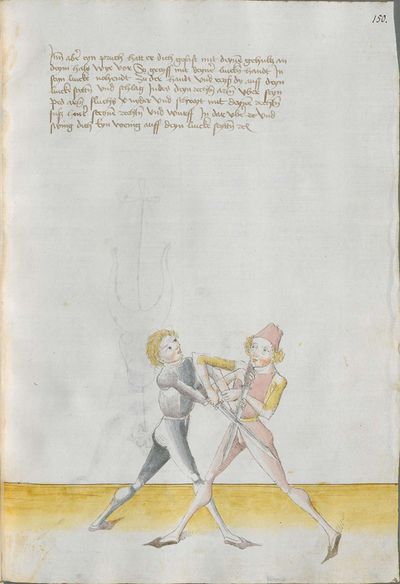
Then, perform the doubling this way: if he strikes to you from above coming from his right shoulder, so strike from your right with strength the same way as he from above to the head. If he displaces the stroke with the strength, wind the hilt under your right arm and go quickly high with the arm and strike him with the long edge behind the blade of his Messer to the head. |
[50v.2] Item daß düpliren mach also wan er dir oben zue haulbett von siner achsell So hauch von diner rechten achsell mit im glich starck zu dem kopff versetz er dan den haulb mit sterck So wind daß gehultz vntter den rechten arm vnd far balde vff mit dem arm vnd schlag in dan mit der langen schniden hinder sin messers klingen vff den kopff ~ |
[10v.2] Item daß dwpliren treyb also wenn er dir oben zw hawet von seyner rechten achsel so haw auch von deyner rechten mit ym geleich starck oben zw dem kopff versecz er denn [11r.1] den haw mit sterck so wendt daß gehultz unter deyn rechten armen und far pald auff mit dem armen und schlag yn mit der langen schneyden hynter seyneß messerß klingen auff den kopff |
[11v.1] Item das dupliren treyb alzo wenne er dir oben zu hawet von seiner rechten achsel So haw auch von deiner rechten mit Im gleich starck oben zu dem kopff versetz er denn den haw mit sterck So wendt das gehultz vnder dein rechten arme vnd far pald auff mit dem arme vnd schlag In mit der langen schneyden hinter seines messers klingen auff den kopff |
[97v.11] Item das duplieren treyb also wan er dir oben ein hewt von seiner rechten achsel / so haw auch von seyner rechten achsel mit Im gleych starck oben zu dem kopff / versetzt er den den haw mit stercke so wind das gehultz vnder den rechten arm vnd far bald auff mit dem arm vnd schlach In dem mit dein lange schneiden hinder seines clingen aff auff den ckropff |
[144v.2] vnnd das Durplieren treib. allso Wann er dir oben zu hawt. vonn seinner Rechten Achsel. so haw auch vonn deinner Rechten achsel mit Im gleich starckh zu dem kopff / versetzt er dann den haw mit sterckh / so wind des gehultz vnnder den rechten Arm vnnd far bald auf mit dem Arm vnnd schlag In mit lannger schneidin hinnder seinns duseggen klinngen auf den kopff. /. |
||||||
[60] |
Then, it was said about the doubling. Now, it is said about the mutating that you should perform it this way: if you strike to him from your right shoulder strongly from above and he displaces and is “weak in the Messer,” wind to him on your left side on to his Messer and go with it well high with the arms. Then, hang the point to him from above over his Messer and go with the arm high over his Messer, and thrust at him to the other peak. |
[50v.3] Item Hie saget der meinster von dem mutiren vnd tribe also wan du von diner rechten achsell oben In starck haulbest versetz er dan vnd ist wiech im messer So wende vff din lincken siten vff sin messer vnd far do mit woll vff mit den armen vnd heng im den ort oben vber sin messer vnd far do mit dem arm vber sin messer vnd stich im zue der andern zynnen ~ |
[11r.3] Item Nw gesagt ist von dem dwpliren und wye man daß treyben söl nw wirt gesagt von dem mutiren und daß mütiren treyb alzo wenn dw ym von deyner rechten achseln oben starck eyn hawest verseczt er und ist waych ym messer so wynd auff deyn lincke seytten an seynz messer und far wöl auff mit dem armen und heng ym den ortt oben uber seyn messer und far da mit [11v.1] dem armen auff uber seyn messer und stich ym zw der anderen czynnen etc |
[11v.2] Item nü gesagt Ist von den dupliren Nu wirtt gesagt von den mutiren dy soltu treyben als vnden gemalt stat vnd das mutiren treyb alzo wenne dw Im von deiner rechten achsel oben starck ein hawest versetz er vnd ist waich Im messer So windt Im auff dein lincke seytten auff sein messer vnd far da mit woll auff mit dem arme vnd heng Im den ortt oben vber sein messer vnd far da mit dem arme auff vber sein messer vnd stich Im zu der andren zinnen etc |
[97v.13] Item nůn ist gesagt von dem dupliren vnd wie man das treyben solt / Nun wirt gesugt [!] von dem mutiren treybs also / wan du von deyner achsel oben In starck hewest versetz er vnd ist weych Im messer so wind auff dein .l. s. auff sein messe [!] vnd far do mit wol auff mit dem arm vnd heng Im den ort oben vber sein messer vnd stich Im zu der andern zynnen |
[144v.3] Das Mvnndiern Item das Mvndiern treib also wann du von deinner rechten Achsel oben. ein starckh hawest. versetzt en vnnd ist waich Im Duseggen. so winnd auf dein Linncken seiten auf sein Dusegen. vnd[145r.1] far damit wol auf mit dem arm. Vnnd henng Im den Ort oben vber seinn duseggen. vnnd stich Im zu der anndern zinnen. |
||||||
[61] |
Then, have you bound from your left side with the long edge at his Messer: go high with the arm and remain with the same edge at his Messer and wind to his left side over his Messer and thrust at him to the other peak of his left side. This way you can perform the two elements from all the strokes after you have feeled whether he is “soft” or “hard” “on the Messer.” |
[11v.2] Item hastu ym von deyner lincken seytten mit der langen schneyden an seyn messer gepunden so far auff mit dem armen und pleyb mit der selbigen schneyden an seynem messer und stich zw der andren czynnen alzo magstu dy czway stück treyben auß allen hewen nach dem dw enpfindest ob er waych oder hertt ym messer ist etc Sequitur textus |
[12r] Item hawestu Im von deiner lincken seytten mit der langen schneyden an sein messer gepunden so far auff mit dem arme vnd pleyb mit der selben schneiden an seinem messer vnd windt Im auff sein lincke seitten vber sein messer vnd stich Im zu der andren zinnen seiner lincken seitten alzo magstu dy zway stuck treyben auß allen hewen nach dem du empfindest ob er waich oder hertt Im messer ist etc |
[97v.14] Item hewestu Im von der .l. s. mit der langen schneiden an sein messer gebunden an seynem messer vnd stich zu der andern zynnen also magstu dy zwey stuck treyben aus allen hewen noch dem du empfindest ob er weych oder hert Im messer ist etc |
||||||||
[62] |
If he wants to mutate Here the master teaches a breaking against the mutating and and speaks: If he wants, etc. You should understand it this way: if he wants to do the mutating, at the moment when he wants to go over your Messer with his own one, wind with your Messer to your left side in the hanging point and thrust at him quickly to his face. |
[12v] Wil er mütiren Hie lertt der meister Ein pruch wider dy mutiren vnd sprich will er etc Das soltu alzo verstan will er dy mutiren machen Dy weill er vber dein messer will varen mit dem seinen So windt mit deinem messer auff dein lincke seitten In den hangunden ortt vnd stich Im schnel zu seinem gesicht etc |
||||||||||
[63] |
If he wants to do the mutating to the right Here the master teaches how one should break the mutating and speaks: If he wants, etc. You should understand it this way: if he wants to do the mutating to your right side, wind against him quickly the hanging point so that the right edge is above. |
[13r] Will er mütiren auff recht machen Hye lertt der meyster aber wie man die mutiren prechen soll vnd spricht will er etc Das soltu alzo verstan will er dy mutiren machen auff dein rechte seytten so wind gegen ym schnell den hangenden ortt Das dy recht schneyd ob stee etc |
||||||||||
[64] |
The hanging point to your left side Here the master teaches how one should break the mutating on the left side and speaks: The hanging point, etc. You should understand it this way: if he does the mutating on your left side, wind against him the hanging point and thrust at him to the next opening. |
[13v] Hangenden ortt auff dy linck seytten Hye lertt der meyster wie man dy mutiren prechen soll auff der lincken seytten vnd spricht hengenden ortt etc Das sol dw alzo versten Macht er dy mutiren auff deiner lincken seytten So wind gegen Im den hangenden ortt vnd stich Im nach der negsten plöß etc |
||||||||||
[65] |
If you have deflected the mutating in the hanging point Here the master teaches a breaking against the mutating and says: The mutating in, etc. You should understand it this way: if you have wound against the mutating and you are in the hanging point, go “simultaneously” to his face with the long point and thrust at him into the face. |
[14r] Dy mütiren ym hangenden ortt pisz ab leytten Hie lertt der meyster aber ein pruch wider dy mutiren vnd spricht alzo Dy mutiren ym etc Das soltu alzo versten So dw nü gewunden hast wider dy mutiren vnd ligst In dem hangenden ortt Indes far Im zu dem gesicht mit dem langen ortt vnd stich Im Inn das gesicht etc |
||||||||||
[66] |
Do the Wecker skillfully Here the master has explained and told about the first chapter with his characteristics. Now he commences to the other chapter and says: Do the Wecker skillfully, etc. |
[50v.4] Weck vff behend Hie saget der meinster von eymen haupt stueck vnd von [51r.1] eynen haulb vnd ist genat der wecker haulb der ander |
[11v.3] weck aüff behendt So nw der meyster daß erst stuck auß gelegt hat und erczelt mit seyner eygenschafft nw hebt er an [12r.1] daß ander stuck und spricht weck auff wehendt etc |
[14v.1] Wēck auff behendt So nw der meyster das erst capitel auß gelegt hatt vnd erzeltt mit seiner eygenschafft Nw hebtt er an das ander capitel vnd spricht weck auff behendt etc |
[97v.15] Weck auff behend den ort zů gesicht wend /
wer mit schritten wol weckt / vil hewe er ser schreckt So nůn der meister hat vnderzelt mit seiner eygenschafft Nůn hebt er an das ander stůck weck auff behend / |
[145r.2] Der weckher haw mit seinnen stuckhen Weckh auf behennd |
||||||
[67] |
Now notice that the Wecker is one of the four displacements against the four guards, as with it one obtains the Stier and the Eber, and the strokes from below. |
[12r.2] ¶ Nw merck daß der wecker ist der vyer verseczen eyneß wyder dy vyer leger wann do mit gewynt man den stiren und den eber und dy unterhew etc |
[14v.2] Nü merck Das der wecker ist der vier versetzen eyns wider die vier leger wann da mitt gewindt man den stiren vnd den eber vnd dy vnterhew etc |
[97v.16] Nun merck das der wecker ist der vier versetzen eins wider dy vier leger do mit gewinnet man den stieren vnd den eber vnd dy ander hew |
[145r.3] Nun merckh Das der wecker haw Ist der vier versetzen ainns wider die vier Leger. wann damit pricht man den Stier. den Eben vnnd die vnnderhaw |
| ||||||
[68] |
Then, perform the Wecker this way: when you come to a man with the Zufechten and he stands against you and holds his Messer in front of the head in the guard of the Stier on his left side, put your left foot forwards and have your Messer on your right shoulder or in the Schrankhut at the right leg and leap with the right foot well to your right side and strike to him with the right edge well on his Messer. “Simultaneously” wind the point into his face. |
[51r.2] Item den wecker tribe also wan du mit dem zu vechten zu dem man kümpt Stett er dan gegen dir vnd hebt dz messer vor din kopff in der hut deß stiers vff siner lincken siten So setz dinen lincken fus fur und heb din messer vff diner rechten achßell oder in der schranckhutt by dinen rechten beyn vnd spring mit dinen rechten fus wol vß vff din rechten syten vnd schlag in mit der rechten schniden wol vff sin messer Indes wind im den ortt In daß gesichtt |
[12r.3] Item den wecker mach alzo wenn dw mit dem zw vechten zw dem man kumbst stet er den gegen dir und hellt seyn messser fuer den kopff yn der hut deß stiren auff seyner lincken seytten So secz den lincken fueß fuer und hab deyn messer auff deyner rechten achseln oder yn der schranckhut pey deynem rechten payn und spring mit dem rechten fues wol auff deyn rechte seytten und schlag yn mit der rechten schneyden wol auff seyn messer yndeß wendt ym den ortt in daß gesicht etc |
[14v.3] Item Den wecker mach alzo wenn dw mit dem zuuechten zu dem man kumbst stet er denne gegen dir vnd helt sein messer für den kopff In der hutt des stiren auff seiner lincken seitten so setz den lincken füß fur vnd hab dein messer auff deiner rechten achsel oder In der schranck wey dem rechten pein vnd spring mit dem rechten fuß woll auff dein rechte seitten vnd schlag In mit der rechten schneyden wol auff sein messer Indes windt Im den ort In das gesicht etc |
[97v.17] Item denn wecker mach also wan du mit dem zu vechten zu dem man kumest steet er den gegen dir vnd helt sein messer fur dem kopff Inder hůt des stieres auff sein .l. s so setz den lincken fuß fur vnd hab das messer auff d. r. a. oder In lincken der schranck hůt bey dem rechten beyn vnd spring den rechten fuß wol auff dein recht seyten vnd schlag In mit der langen schneyden wol auff sein messer Indes wend Im den ort In das gesicht |
[145v.1] Item den weckherhaw Mach allso wann du mit dem zufechten zum Mannd kumpst. steet er dann gogen dir vnnd hellt den Duseggen vornnen fur den kopff In der hut des Stiers auf seinner Linnckhen seitten so setz dein Linncken fuosz fur. vnnd halt dein Duseggen auf deiner Rechten achsel. oder Inn der. schrannckhut. bey deinnem rechten pain. vnnd sprinng mit deinem rechten fuosz wol auf dein rechte seitten vnnd schlag In mit Lannger schneid wol auf seinn Duseggen. Indes winnd Im den Ort Inn das Gesicht. |
||||||
[69] |
The Wecker turns the point to the face Here the master teaches a breaking against the Zornhau Ort and speaks: The point to the face, etc. You should understand it this way: if he does the Wecker against you and wants to thrust to your face on your left side, “simultaneously” wind against his Messer on his right side and thrust to his face on his right side. |
[15r] Ortt zu gesicht wecker ist wenden Hie lertt der meyster ein pruch wider den zoren ortt vnd spricht ortt zu gesicht etc Das soltu alzo versten macht er dir den wecker vnd will dir zu dem antlitz stechen auff deiner lincken seitten Indes windtt gegen seinem messer auff sein rechte seitten vnd stich Im zu dem gesicht seiner rechten seitten etc |
||||||||||
[70] |
Learn to do the Wecker to the right Here the master teaches an element from the Wecker and speaks: Learn to the right, etc. You should understand it this way: if you do the Wecker from your left side against him on his right side, “simultaneously” as you have done the Wecker, strike against him with the short edge to his head, as it is depicted below. |
[15v] Recht lere wecken Hie lertt der meister aber ein stuck auß dem wecker vnd spricht Recht lere etc Das soltu alzo versten Machstu den wecker von deiner lincken seitten Im auff sein rechte seitten Indes so dw den wecker gemacht hast schlag In mit der kurtzen schneyden auff sein kopff wie vnden gemalt stett |
||||||||||
[71] |
Do the Wecker with the point to the right Here the master teaches how you should use the point from the Wecker, and speaks: To the right with the point, etc. And you should understand it this way: if you have done the Wecker on his right side from your left side, “simultaneously” wind against his Messer in the hanging point, so that the long edge is above and thrust to the face on his right side. |
[16r] Recht mit ortt weck Hie lertt der meyster wie dw den ortt ausß dem wecker prauchen sollt vnd spricht Recht mit ortt etc Vnd das soltu alzo verstan wenn du den wecker auff sein rechte seitten gemacht hast auff von deiner lincken seitten Indes windt gegen seiner messer In den hangenden ortt Das dy lang schneid ob stee vnd stich Im zu dem gesicht seiner rechten seitten etc |
||||||||||
[72] |
Do the Wecker, let the point go to the face Here the master states a breaking against the element described above and speaks: Do the Wecker, to the face, etc. You should understand it this way: if he thrusts with the hanging point to your face, “simultaneously” let your Messer go down below his arm and go high with the long point and thrust to his face. |
[16v] Weck gesicht ortt lest varen Hie sagt der meister ein pruch wider das eegemelt stuck vnd spricht weck gesicht etc Das soltu alzo verstan vertt er mit dem hangenden ortt In dein gesicht Indes laß dein messer sincken vnter sein arme vnd far auff mit dem langen ortt vnd stich Im zu seinem gesicht etc |
||||||||||
[73] |
Then, know that the Schranckhut is good and one can perform many elements therefrom. |
[51r.3] Item daß die schranckhüt güt ist vnd vil stueck mag man dar vß triben |
[12r.4] Item wyß daß dy schranckhut güt ist und vil stuck mag man dar auß treyben |
[17r.1] Item wiß das dy schranckhuet ist gutt vnd vill stuck mach man dar ausß treyben |
[97v.18] Item wiß das dy schranck hůt gůt ist vnd stuck mag man dar treyben |
[145v.2] Von der schrannckhut Item merckh das die Schrannckhut. guot ist vnnd vil stuckh mag man darausz treiben. |
||||||
[74] You should also perform the Wecker therefrom on both sides and perform the Schranckhut this way: When you come with the Zufechten to the man, put your left foot forwards and hold your Messer with the point to your right side on the ground and the long edge be turned upwards on the Messer, and expose yourself with the left side. If he strikes to you from above to the opening, leap out of the stroke with your right foot well to the right side and wind the hilt of the Messer under your arm and strike to him with the long edge to his Messer and turn the blunt edge to his head. |
You should also perform the Wecker therefrom on both sides and perform the Schranckhut this way: if you come with the Zufechten to the man, put your right foot forwards and hold your Messer with the point on the ground on your left side, so that the blunt edge is against the man. And expose yourself with the right side. If he strikes from above to your opening, leap out of the stroke with your left foot well to his right side and wind the hilt of your Messer under your arm and strike with the long edge on his Messer and turn the short edge on his head and work “simultaneously” as you know it well. |
[51r.4] vnd den wecker soltu dar vß triben von beiden siten Nuer in die schranckhuett schick dich also Wan du mit dem zu vechten zu dem man kümpst so setz dinen lincken fus fur vnd halt din messer mit dem ort vff diner rechten siten vff der erden dz die stümpff schnid oben gewendet sy am messer vnd gib dich also ploß mit der lincken syten haut er dan dir zu der ploß oben In so spring vß den haulb mit dem rechten fus wol uff die rechte siten vnd wind dz gehultz dz messers vntter din arm vnd schlag in mit der kurtzen schniden vff sin haubtt |
[12r.4] ¶ Und den wecker soltu dar [12v.1] auß machen von payden seytten nw yn dy schranckhütt schick dich alzo Wenn dw mit dem zw vechten zw dem man kümbst so secz deyn lincken fues fuer und hallt deyn messer mit dem ortt auff deyner rechten seytten auff der erden daß dy lang schneyd oben gebendt sey am messer und gib dich alzo ploß mit der lincken seytten hawtt er dir den zw der plöß oben eyn so spring ausß dem haw mit dem rechten fueß wol auff dy recht seytten und wynd daß gehulcz deß messerß unter deyn armen und schlag ym mit der langen schneyden auff seyn messer und wendt ym dy stumpff schneyd auff seyn hawbt |
[17r.2] Dw scholt den wecker auch dar auß treyben von payden seitten vnd schick dich In dy schranckhutt alzo wenne dw mit dem zuuechten zu dem man kumbst so setz deinen rechten fuß vor vnd hallt dein messer mit dem ortt auff der erden auff deiner lincken seitten das dy stumpff schneid gegen dem man stee vnd gib dich alzo ploß mit der rechten seitten haut er dir dan oben zu der ploß ein So spring auß dem haw mit deinem lincken füß woll auff sein rechte seitten vnd wind das gehultz deines messers vnder dein arme vnd schlag In mit der langen schneyden auff sein messer vnd wendt Im dy kurtz schneyd auff sein haubt vnd erbeit Indes als du woll weist etc |
[97v.19] vnd den wecker soltu do ausß nemen zu beyden seytten nůn In dy schranck hůt schick dich wen du mit dem zu wechten zu dem man kumest so setz dein lincken fůß fur vnd halt dz messer mit dem ort auff d. r. s. auff der erden das dy stumpff schneid oben gewend sey am messer vnd gib dich also plos mit der l. s. hawet er dir den zu der plosse oben ein so spring auß dem haw mit dem rechten fůß wl [!] auff dy r. s. vnd wind das gehůltz des messers vnd den arm vnd schlag Im mit der kürtzen schneiden auff sein messer vnd wend Im dy stumpff schneiden auff sein hawpt vnd arbeyt Indes also do wol weyst |
[145v.3] vnnd den wecker soltu darausz treiben von baiden seitten Nunn Inn die schrannckhut schickh dich also wann du mit dem zufechten zu dem Mann kompst. so setz den linncken fuosz fur. vnnd halt dein Duseggen mit dem Ort auf deinner Rechten seiten auf der Erden. das die kurtz schneid oben stee an dem Duseggen. vnnd gib dich also plosz ander linncken seitten hawt er dann zu der plosz oben ein. so spring ausz dem haw mit dem rechten fuosz. wol auf dein Rechte seitten vnnd wennd das [146r.1] gehultz des Duseggen vnnder dein Arm vnnd schlag. In mit der kurtzen schneid auf seinn Duseggen bey der hannd. vnnd wind Im die stumpff schneide auf sein haupt vnnd arbait Indes als du wol bericht bist seinner nechsten plösse zu. |
||||||
[75] Then, assume the Schranckhut on the left side this way: if you come with the Zufechten to the man, put your right foot forwards and hold your Messer with the point at your left side on the ground, so that the short edge is above on the Messer. And expose yourself with the right side. If he strikes to your opening, step with your left foot well out of the stroke to your left side and strike at him while stepping with the short edge over his Messer near the hand and turn the long edge to his head or thrust at his face as before. |
Then, perform the Schranckhut on your right side in this way: when you come with the Zufechten to the man, put your left foot forwards and hold your Messer with the point to your right side so that the point is on the ground and the short edge is against the man, and expose yourself with the left side. Then, step with your right foot well out of the stroke to your right side and strike to him with the short edge on his Messer close to the hand. Then, turn the long or the short edge on his head or thrust to his face as before. You can also perform the Wecker to the Stier, as it is depicted below. |
[51r.5] Item Also schick dich in die schranckhutt zu der lincken siten wan du mit dem zu vechten zu dem man kümpst so setz din rechten fus für vnd halt dein messer mit dem ortt [51v.1] nahent diener lincken siten vff der erden dz die kürtz schnid im messer oben sy vnd gib dich mit der rechten siten ploß haut er dir dan zu der ploß So schrit mit dinen lincken fuß wol vß dem haulb vff din lincke siten vnd schlag in mitten der kurtzen schniden uber sin messer by der hant vnd wind im die lang schnid vff sin hauptt oder stich im zu dem gesicht |
[12v.2] Item alzo schick dich yn dy schranckhut zw der lincken seytten wenn dw mit dem zw vechten zw dem man kümbst so secz den rechten fuß fuer und hallt deyn messer mit dem ort neben deyner lincken seytten uff der erden daß dÿ kurcz schneyd [13r.1] an dem messer oben stee und gib dich mit der rechten seytten ploß hawt er dir den zw der plöß so schreyt mit dem lincken füß wol ausß dem haw auff deyn lincke seytten und schlag yn mit yn dem schrit mit der kurczen schneyd uber seyn messer pey der hand und wendt ym dy lang schneyd uff seyn hawbt oder stich ym zw dem gesicht alz vor etc |
[17v] Item alzo schick dich In dy schranckhuet deiner rechten seitten wenn du mit dem zuuechten zu dem man kumbst So setz deinen lincken fuß für vnd halt dein messer mit dem ortt auff deiner rechten seitten das der ortt auff der erden stee vnd dy kurtz schneid gegen dem man stee vnd gib dich mit der rechten lincken seitten ploß vnd schreyt mit deinem rechten füß woll auß dem haw auff dein rechte seitten vnd schlag In mit der kurtzen schneiden auff sein messer nohendt bey der handt vnd wendt Im dy lang oder kurtz schneyd auff sein haubt oder stich Im zu dem gesicht als vor auch magstu den wecker treyben auff den stir wie vnden gemalt ist etc |
[97v.20] Also schick dich In dy schranck hůt zů d. l. s. wan du mit dem zu vechten zů dem man kumest so setz den rechten fuß fur vnd halt dein messer mit dem ort neben deiner l. s. auff das dy kurtz schneiden an dem messer oben sthee vnd gib dich mit der rechten seitten ploß / hewt er dir den zu ploese so schreyt mit dem lincken fuß wol auff den haw auff deyner lincken seytten vnd schlach In mit den schritt mit der kůrtzen vber sein messer wend durch vnd wind In dy lange schneiden vber sein hewpt vnd schach sach [!] Im zu dem gesicht als vor etc |
[146r.2] Item schickh dich aber Inn die Schrannckhut so zu der linncken seiten wann du mit dem zufechten zu dem Man kumpst. so setz dein rechten fuosz fur. vnnd halt dein Duseggen mit dem ort neben deinner linncken seitten auf der Erden. das die kurtz schneid oben stee. vnnd gib dich mit der Rechten seitten plosz. hawt er dir dann zu der plosz so schreit mit deinnem linncken fuosz. wol ausz dem haw auf linncken seitten vnnd schlag In mit der kurtzen schneid vber sein Duseggen bey der hannd. vnnd winnd Im die Lanng scheide auf sein haupt. oder stich Im zu dem gesicht als vor. |
||||||
[76] |
Do not do the Wecker to the left, strike short Here the master states an element against the guard from the Luginsland and against the Stier. And perform it in this way: when you come with the Zufechten to the man and he stands in these guards or stances announced above, and you stand in the Schranckhut, do as if you wanted to strike the Wecker to him to his left side, but do not deliver the stroke. Instead, “simultaneously” change through to the other next peak and thrust at his face to his right side, or as you change, strike the short edge over his Messer to his right side and let the point fall well over his Messer to his left side, and strike with the right edge through his head. Amen. |
[51v.2] Weck linck / nicht kürtz haulb Hie saget der meinster eyn bruch wider die hut lueginßland vnd vß dem stier den bruch trib also wan du mit dem zu vechten zu dem man gest Stot er dan In den obgemelten hutten oder leger eynem vnd stest in der schranckhutt So thün glich alß dü im den wecker wollest haulben zu siner lincken siten vnd verspring den haulb nicht Sünder wechsell Indeß durch vff die andern nesten zynnen vnd stich Im zu dem I gesichtt vff sin rechte siten oder im dem wechschell so schlag im die kurtz schnid vber sin messer vff siner lincken siten vnd haulb im die recht schnid durch sin kopff ~ Sequitur textus |
[13r.2] Weck linck nicht kürcz haw Hye sagt der meyster eyn prüch wyder dy hut auß dem luginsland und auß dem stiren den pruch treyb alzo wenn dw mit dem zw vechten zw dem gest stet er den yn dysen ob gemelten hutten eyner und dw stest yn der schranckhuet so thw sam dw ym den wecker wollest hawen zw seyner lincken seytten und verpring den haw nicht sunder wechsel yndeß [13v.1] durch uff dy andern negsten czynnen und stich ym zw dem gesicht oder ym wechsel so schlag dy kurcz schneyd uber seyn messer auff seyner rechten seytten und senck den ort wol uber seyn messer uff seyner lincken seytten und haw ym dy recht schneyd durch seyn kopff amen Sequitur textus |
[18r] Weck linck nicht kurtz haw Hie sagt der meyster ein stuck wider dy hutt auß dem lüginslandt vnd wider den Stiren vnd treib das allzo wenne du mit dem zuuechten zu dem man gest stet er denn In disen obgemelten hutten oder legeren vnd du stest Inder schranckhut so thu Im gleich als du Im den wecker wollest hawen zu seiner lincken seitten vnd verpring den haw nicht Sünder wechsel Indes durch auff dy andren negsten zinnen vnd stich Im zu dem gesicht auff sein rechte seitten oder In dem wechsel schlag Im dy kurtz schneid vber sein messer auff seiner rechten seitten vnd senck den ortt woll vber sein messer auff seiner lincken seitten vnd haw Im dy recht schneid durch sein kopff amen |
[97v.21] Weck
linck nit kurtz hew der wechsel recht pruch Hie sagt der meister eynen bruch dy hůt In lůginßland vnd auß dem styren / den bruch treyb also wan du mit dem zuvechten zu dem man gheest stat er Im messer der obgnanten hůt oder leger eyner / vnd [98r.1] du steest in der schranck hůt / so thů gleych ob du welest In dem messer hawen zu seiner lincken seyten / vnd verspring den hew nit / sunder verwechsel In des durch auff dy nechsten anderen zynnen / vnd stich Im zu dem gesicht auff sein r. s. oder In den wechsel so schlach Im dy kurtz schneid vber sein messer auff der rechten seyten vnd senck den ort wol vber sein messer auff sein lincken seytten vnd haw Im dy recht schneyd durch sein kopff |
[146r.3] Weckh Linck nit kurtz haw [146v.1] Item aber ain gut stuckh Inn der hut Luginslannd oder Inn dem Stier den pruch treib allso wann du mit dem zufechten zum Mann geest. steet er dann Inn disen obgemellten hutten. oder leger ainnem vnnd du steest Inn der schrannckhut. so thu gleych alls du Inn den weckher wolest hawen. zu seinner linncken seitten vnnd verpring den haw nit sonnder wechsel Indes durch auf die annder nechst zinnen vnd stich In zum gesicht auf sein rechten seitten. oder Inn dem wechsel. so schlag In mit der kurtzen schneid vber seinnen Duseggen. auf sein rechten seitten vnnd sennckh den Ort wol vber sein Duseggen auff seinner linncken seitten. vnd haw Im dir recht schneid durch seinnen kopf. |
||||||
[77] |
If he has done the Wecker to the left with changing through Here the master teaches a breaking against the changing through in the Wecker and speaks: Changing through to the left, etc. You should understand it this way: if he wants to change through in the Wecker from his right side to your right and does as if he wanted to strike to your left side, “simultaneously” as he changes through and thrusts at your face to your right side, remain standing with the Messer and thrust at him with the long direct point in a stretched manner to the face. And put the rear foot far outside so that you are able to reach further. |
[18v] Durchwechsel linck ist er wecken Hie lertt der meister ein pruch wider das durchwesseln Im wecker vnd spricht durchwechsel linck etc Das soltu alzo verstan wenn er durchwechsen will Im wecker von seiner rechten seitten auff dein rechte vnd thut Sam er wöll hawen zu deiner lincken seitten Indes wechselt er durch vnd stich dir zu dem gesicht deiner rechten seitten So pleib alzo steen mit dem messer vnd stich Im mit dem langen geraden ortt gestrackt zu dem gesicht vnd den hin dersten fuß setz weidt hin auß auff das das du dester weitter raichen mugst etc |
||||||||||
[78] |
Strike the Wecker to the left Here the master states a good element. If one stands in the guard of the Luginsland or in the Stier or so, and strikes to you from the Luginsland, rest in the Schranckhut on your left side and strike to him with the blunt edge to his Messer and “simultaneously” go high with the arm and change through and thrust at his face or chest to his left side. |
[52r.1] den wecker linck haulb Hie saget der meinster aber eyn gut stuck in der hat lugeßlant oder in den stier oder so er vff dich schlecht vß dem luginßlant So lig in der schranckhutt vff diner lincken siten vnd haulb die stümpff schnid vff sin messer Indes far hoch vff mit dem arm vnd wechschell im durch vnd stich im zu dem gesichtt oder brust vff siner lincken siten |
[13v.2] Den wecker linck haw Hye sagt der meyster aber eyn gutt stuck so eyner stet yn der huet luegynsland oder yn dem Stiren oder so er auff dich schlecht ausß dem luginsland So lig yn der schranckhut uff deyner lincken seytten und haw dy stumpff schneyd auff seyn messer yndeß far hoch auff mit dem armen und wechsel ym durch und stich ym zw dem gesicht oder prust auff seyner lincken seytten etc |
[19r.1] Den wecker linck haw Hie sagt der meister aber ein gut stuck So einer stet in der hut lunginslandt oder In dem Stiren oder so er auff dich schlecht ausß dem luginslandt So lig in der schranckhut auff deiner lincken seitten vnd haw Im dy stumpff schneid auff sein messer Indes far hoch auff mit dem arme vnd wechsel Im durch vnd stich Im zu dem gesicht oder prust auff seiner lincken seitten. |
[98r.2] Den
Wecker linck haw durch wechsel do mit
haw hie sagt der meister aber ein gut stuck In der hůt lugimßland [!] oder in dem styeren oder so er auff dich schlecht auß dem lugimßland [!] so lyg In der schranck hůt auff d. l. s. vnd haw dy stumpffe schneyden auff sein messer In des far hoch auff mit dem arm vnd wechsel Im durch vnd stich Im zu dem gesicht oder brust auff s. l. s. |
[146v.2] Den weckher linck haw Item mer ain gut stuckh Inn der hut luginsland oder Inn dem Stier oder so er auf dich schlecht ausz dem luginslannd. so lig Inn der schrannckhut. auf der linncken seitten vnnd haw die stumpff schneid [147r.1] auf sein Duseggen. Indes far hoch auf Mit dem Arm. vnnd wechsel Im durch vnnd stich Im zum gesicht oder der prust auf sein lincke seitten. |
| |||||
[79] Then, if you want to try him, let “simultaneously” your Messer with the point to his left side and strike to him again to his left side with the long or the blunt edge. |
Then, if you want to try him, let ”simultaneously“ your Messer with the point to your left side and strike to him again to his right side with the sharp or the short edge. |
[52r.2] ein anders Item Wiltu In baß versuchen so loß im dz messer mit dem ortt uff din lincken siten sencken vnd haulb im wider vff die rechte siten mit der scharpffen oder stümpffen schniden uff sin lipt ~ |
[14r.1] Item wiltu yn paß versuechen So laß yndeß deyn messer mit dem ortt auff seyn lincke seytten und haw ym starck wyder eyn auff seyn lincke seytten mit der langen schneyden oder stumpffen etc |
[19r.2] Item wiltu In paß versüchen so laß Indes dein messer mit dem ortt auff dein lincke seitten vnd haw Im wider ein auff sein rechte seitten mit der scharpffen oder kurtzen schneid etc |
[98r.3] Item wiltu Im baß vnd haw Im wider auff dy r. s. mit der schwechsten oder stumpfen schneyden |
|||||||
[80] |
If he strikes the Wecker from the left and wants to save the point Here the master teaches a breaking against the changing through from the Wecker, if he wants to do the Wecker from his left side to your right side, and speaks: If he strikes the Wecker from the left, etc. You should understand it this way: if he strikes the Wecker from his left side to your right side and “simultaneously” wants to change through to your left side, remain directly with your Messer to his left side and thrust at his with the direct point or Messer to the throat or the face, as it is depicted below. |
[19v] Weckt linck ortt will er helen Hie lertt der meister ein pruch wider das durchwechslen auß dem wecker So er den wecker machen wil von seiner lincken seitten auff dein rechte seitten vnd spricht weckt linck etc Das soltu alzo verstan haut er von seiner lincken seitten den wecker auff dein rechte seitten vnd will Indes durchwechslen auff dein lincke seitten so peleib geradt mit deinem esser auff seiner lincken seitten vnd stich Im mit geradem ortt oder messer zu der kelen oder antlitz wie vnden gemalt stett etc |
||||||||||
[81] Do the Wecker to the flats Here the master states a good element that you should perform this way: if you come to the man with the Zufechten, put your Messer on your right side in the Schranckhut or hold it on your right shoulder. If he strikes to you from above to the opening, strike also firmly against his stroke with the right edge. And as soon as the Messers spark together, wind “simultaneously” to the face with the point and thrust at him to the upper peaks. Or do the element that is also meant in the text: as soon as the Messers spark together, strike “simultaneously” with the short edge to the head to his left side. And “simultaneously” strike skillfully to the other opening to his right side. “Simultaneously” skillfully again to the other lower peak of his left side, “simultaneously” again to the upper peak of his right side, etc. |
Do the Wecker to the flats Here the master states a good element that you should understand this way: if you come to the man with the Zufechten, put your Messer in the Schranckhut or hold it on your right shoulder. If he strikes to you from above to the opening, strike also firmly against his stroke with the right edge. And as soon as the Messers spark together, wind “simultaneously” the point to the face and thrust at him to the upper peaks. Or do the element that is also meant in the text: as soon as the Messers spark together, strike “simultaneously” with the short edge to the head to his left side. And strike “simultaneously” again skillfully from one peak to the other, as you know it. |
[52r.3] Weck die flech Hie saget der meinster aber ein gut stueck dz soltu also verstan wan du mit dem zu vechten zu dem man kümpst oder halt daß vff diner rechten achsell haut er dir dan oben zu der ploß so haulb auch starck gegen sinem haulb mit der rechten siten schniden vnd als balde die messer zu samen glitzen So wind [52v.1] Indes den ortt zu dem gesichtt vnd stich im inder obern zÿnnen oder mach s daß stueck dz auch die meÿnung deß text ist ~ |
[14r.2] Weck dy flechen Hye sagt der meyster aber eyn gut stuck daß soltu alzo treyben wenn dw mit dem zwvechten zw dem man kümbst so leg deyn messer uff deyn rechte seytten yn dy schranckhüett oder hallt daß auff deyner rechten achsel hawt er dir dann oben zw der plöß so haw starck gegen seynem haw mit der rechten schneyden und alz pald dy messer zwsammen kliczen [14v.1] So wynd yndeß zw dem gesicht den ort und stich ym zw der obreren czynnen, oder mach daß stuck daß ist auch dy maynung deß textz alz bald dy messer zw sammen kluczen so haw yndeß mit der kurczen schneyden zw dem kopff yndeß pehendtlich haw zw der andren czynnen auff seyn rechte seytten yndeß pehentlich wyder zw der anderen unteren czynnen seyner lincken seytten yndeß wyder zw der oberen czynnen seyner rechten seytten etc |
[20r] Weck dy flechen Hie sagtt der meister aber ein gutt stuck das soltu alzo verstan wenne du mit dem zuuechten zu dem man kumbst So leg dein messer In dy schranckhut oder halt das auff deiner rechten achsel haut er dir danne oben zu der plöß So haw auch starck gegen seinen haw mit der rechten schneiden vnd als pald dy messer zusammen klitzen So windt Indes den ortt zu dem gesicht vnd stich In zu der ōbren zinnen oder mach das stuck das ist auch dy maynung des textz als pald dy messer zusammen klitzen So haw Indes mit der kurtzen schneiden zu dem kopff seiner lincken seitten Indes haw wider behentlich von einer zinnen zu der anderen als du weist etc |
[147r.2] Weckh dir flechen Item das soltu allso versteen Wann du mit dem zufechten zu dem Mann kumpst so leg dein Duseggen Inn die schrannckhut. oder halt In auf der Rechten Achsel. hawt er dann oben zu der plösz so haw auch starckh gegen seinnem haw mit der Rechten schneid vnnd bald die Duseggen zusammen glitzen. so wind Indes den Ort zum gesicht. vnnd stich Im zu der obern zinnen welliche dir werden mag. |
|||||||
[82] |
He does the Wecker around so Here the master states a common breaking against the Wecker and speaks: He does the Wecker, etc. You should understand it this way: if one does a Wecker on you, notice, as one Messer is going to spark on the other, “simultaneously” wind your Messer against your left side and hang the point to his chest and push him well from you. |
[20v] Der wecket vmb süst[13] Hie sagtt der meister ein gemein pruch wider den wecker vnd spricht Der wecket etc Das soltu alzo verstan Macht einer auff dich den wecker so merck dar auff wenne ein messer an das ander klitzen will Indes windt dein messer gegen deiner lincken seitten vnd heng Im den ortt auff sein prust vnd scheub In woll von dir etc |
||||||||||
[83] |
If he is going to expose himself with the Wecker Here the master teaches another breaking against the Wecker and speaks: With the Wecker, etc. You should understand it this way: if he has done the Wecker on you, notice, as he has stroke against your Messer, “simultaneously” twitch your Messer towards you and let the point go down towards your left side and strike to him over his Messer directly to his head, as it is depicted below. |
[21r] Mit wecker will er placken Hie lertt der meister ein anderen pruch wider den wecker vnd spricht mit wecker etc Das soltu alzo verstan Ist er den wecker auff dich machen so merck dar auff So er gegen deinem messer ist hawen Indes ku tzuck dein messer gegen dir vnd senck den ortt gegen deiner lincken seitten vnd haw Im vber sein messer geradt auff sein kopff wie vnden gemalt stet etc |
||||||||||
[84] |
If he wants to use the Wecker Here the master teaches a breaking against the Wecker and speaks: If he wants to use the Wecker, etc. You should understand it this way: if he does the Wecker on you as above, “simultaneously” go through to his right side over his Messer and thrust at him to the head or face, as it is depicted below. |
[21v] Will er den wecker prauchen Hie lertt der meister aber ein pruch wider den wecker vnd spricht will er den wecker etc Das soltu alzo verstan So er macht den wecker auff dich wie vor Indes gee durch auff sein rechte seitten vber sein messer vnd stich Im zu dem kopff oder gesicht wie vnden gemalt stet etc |
||||||||||
[85] |
If he has struck the Wecker Here the master teaches a breaking against the Wecker and speaks: If he has done the Wecker, etc. You should understand it this way: if he strikes the Wecker from his right side to your left side, “simultaneously” wind your Messer to your left side and go with the hanging point high and strike to him with the Entrüsthau to his head. Or, set him the point on, as you know it well. |
[22r] Den wecker ist er hawen Hie lertt der meister aber ein pruch wider den wecker vnd spricht Den wecker ist etc Das soltu alzo verstan hawt er von seiner rechten seitten den wecker auff dein lincke seitten Indes windt dein messer auff dein lincke seitten vnd far mit dem hangenden ortt auff vnd schlag In mit dem entrusthaw zu seinem kopff oder setz Im den ortt an als du woll waist etc |
||||||||||
[86] Do the Wecker to the flat roughly with commoners Here the master states a good element against these who cannot fight or against the “peasant strokes.” And do it this way: if one strikes to you with a great peasant stroke, and wants to strike you honestly through the head with the Messer, hold your Messer in the Schranckhut or at the shoulder or at the knee, so that the point is against the face of the man. And as you stand then in a stance, you can use the element, and do it on him this way: if he strikes to you, strike also together with him between the Messer and the man with the long edge. And as soon as the Messers spark together, go around the head with the Messer, and strike him to the neck. If you do not want to hurt him hard, strike to his arm. If it occurs at a “Fechtschul” tournament, strike to his stomach to his left side, roughly and peasantly, so that he feels it well. The text follows. |
Do the Wecker to the flat roughly with commoners Here the master states a good element against these who cannot fight or against the “peasant strokes.” And do it this way: if one strikes to you with a great peasant stroke, and wants to strike you honestly through the head, hold your Messer in the Schranckhut or at the right shoulder or at the knee, so that the point of your Messer is against his face. And as you stand then in a stance, you can use the element, and do it on him this way: if he strikes to you, strike also together with him between the Messer and the man with the long edge. And as soon as the Messers spark together, go “simultaneously” to your left side around the head towards your right side with your Messer, and strike him to the neck. If you do not want to strike to his neck or head, strike to his left arm or to the stomach to his left side, roughly and peasantly, so that he feels it well. |
[14v.2] Weck dy flech grob mit doben Hye sagt der meyster eyn gut stuck wyder dye dy nicht vechten kunnen oder wyder dy paweren straych und macht daß alzo hawt eyner auff dich mit eynem grossen pawren schlag und wyll dich durch den kopff ernestlich hawen mit dem messer so haltt deyn messer aber yn der schranckhüt [15r.1] oder pey der achsel oder ob dem knÿ daß dy spicz gegen dem antlicz stee deß manß und wye dw den yn eynem stant stest so magstu daß stuck prauchen und thw ym alzo hawt er auff dich so haw gleych mit ym eyn czwischen messer und man mit der langen schneydern und alz pald dy messer zw sammen kliczen so far umb den kopff mit dem messer und haw ym zw dem halz wiltü yn nicht hart wünden so schlag yn auff den armen ist aber daß auff eyner vechtschullz so schlag yn yn den pawch auff seyner lincken seytten grob und pewrisch daß erß wol enpfindt etc Sequitur textus |
[22v] Weck dy flech grob mit doben Hie sagtt der meister ein guttes stuck wider dy die nicht vechten kunnen oder wider dy pawrenstraich vnd mach das alzo haut einer auff dich mit einem grossen pawrenschlag vnd will dich ernnstlich durch den kopff hawen So halt dein messer in der schranckhutt oder pey der rechten achsel oder neben dem knye das dy spitz seines messers gegen Seinem[14] antlitz stee vnd wie du denn In eynem standt stest so magstu das stuck prauchen vnd thu Im alzo hautt er auff dich so haw auch gleich mit Im eyn zwischen messer vnd man mit der langen schneiden vnd als pald dy messer zu sammen klitzen So far Indes gegen deiner lincken seitten vmb den kopff auff dein rechte seitten mitt deynem messer vnd haw Im zu dem hals will du Im nit zu dem hals oder kopff hawen so schlag In auff den lincken arme oder In den pauch seiner lincken seitten grob vnd pewerisch das er seyn woll empfindt etc |
[98r.4] ¶ Weck dye schleg dye schleg grab mit daber stand ab ober bleyb oben Hie sagt der meister ein gut stuck wider die / dy nit vechten kunnen oder wider die paweren streych vnd mach das also / hewt eyner auff dich mit eynem grossen paweren streich vnd wil dich schlahen durch den kopff / so halt dein messer In der schranck hůt oben bey der rechten achsel ober [!] neben dem knye das dy spitz deynes messers gegen Im Ins antlitz stee vnd wie du dann In eynem stand stest so magstu das stuck brauchen vnd thůn Im also / hew er auff dich / so haw auch gleych mit Ime In starck zwischen messer vnd nym mit der langen schneiden vnd als bald dy messer zu samen glitzen / so far in des gegen der lincken seyten mit dem messer vnd haw Im zu dem haltz wiltu Im nit zu dem halß hawen oder zu dem kopff so haw Im auff den lincken arm Ist das es aber auff eynem rechten stůl(?) so schlach In vmb den bauch s. l. s. grob vnd beweys das er das wl [!] entpfindet |
[147v] Weckh die flech grob mit doben Item aber ain gut stuckh Wider die puffel schleg vnnd das mach allso. hawt amer auf dich mit ainnem grossen pauren straich vnnd will dich Ernstlich durch den kopff hawen. so halt dein Duseggen Inn der schrannckhut. oben bey der Rechten Achsel oder neben dem knie. das der spitz deinnes Duseggen gegen seim[15] angesicht stee [wie du damit dein stand stest]. so magstu das stuckh prauchen. vnnd thu Im also. hawt Er auf dich so haw auch gleich mit Im ein zwischen Duseggen. vnnd dem Man. mit der lanngen schneidin. so bald die Duseggen zusammen glitzen. so far Indes gegen deinner linncken seitten. vmb den kopff auf dein Rechte seitten. mit dem Duseggen vnnd haw Im zu dem hals. wiltu In nit zu dem kopff schlagen. so schlag In auf seinen linncken arm oder wo du hin wildt. |
|||||||
[87] |
Learn to set off with the bow Here the master teaches a breaking against the element announced above and speaks: With the bow, etc. You should understand it this way: if he wants to strike around his head and wants to strike to your neck, bend under his Messer and displace with the bow if you want.[16] “Simultaneously” wind over his Messer to his right side and “simultaneously” step behind him and strike to his head. |
[23r] Mitt pogen ler abetzen Hie lertt der meister ein pruch widr das ee gemelt stuck vnd spricht mit pogen etc Das soltu alzo versten So er vmb sein haubt will hawen dich an deinen halß schlagen will so pewg auff vnder seyn messer vnd versetz mit dem pogen ob du wildt Indes windt vber sein messer auff seiner rechten seitten vnd trit Indes hintter In vnd schlag In zu seynem kopff etc |
||||||||||
[88] |
If he wants to do the Wecker and look roughly Here the master teaches a breaking against the element announced above and speaks: If he wants to roughly, etc. You should understand it this way: if he wants to strike a rough stroke to your stomach or to your head, notice, as soon as he wants to go around his head and wants to strike to you, go “simultaneously” skillfully to his neck or face. And thrust at him and push him with it from you, as it is depicted below. |
[23v] Grob will er wecken vnd gaffen Hie lertt der meister aber ein pruch widr das ee gemelt stuck vnd spricht Grob will er etc Das soltu alzo verstan will er den groben schlag In deyn pauch hawen oder an dein kopff So merck als pald er vmb seyn haubt faren will vnd will dich schlagen Indes far behentlich Im zu seinem hals oder angesicht vnd stoß In starck vnd scheub In da mit von dir wie vnden gemalt stet etc |
||||||||||
[89] |
Do the Wecker politely with squinting Here the master teaches a nice element from the Wecker and speaks: Do the Wecker politely, etc. You should understand it this way: do the Wecker from your right side to his left side and “simultaneously,” as soon as one Messer sparks on the other, turn your hand always against his Messer, so that the short edge touches him slightly on his left side. “Simultaneously” let your point go down towards the ground and go between yourself and him high to your left side and strike to him to his right side, with the short or the long edge to the head. Or, thrust, cut or do what you want. |
[24r] Weck hōflich mit wincken Hie lertt der meister ein hübsch stuck auß dem wecker vnd spricht weck hōflich etc Das soltu alzo verstan Mach den wecker von deiner rechten seitten auff sein lincke seitten Indes als pald ein messer auff das ander klitz So wendt dein handt Ewchling gegen seinem messer Das dy kurtz schneid In ein wenig rür auff seiner lincken seitten Indes senck den ortt gegen der erden vnd far zwischen dich vnd In auff gegen deiner lincken seitten vnd schlag In auff seiner rechten seitten dy kurtz oder lang schneiden auff sein kopff oder stich schneid vnd thu was du wild etc |
||||||||||
[90] Notice the weak Then, the master states an element against the “weak” in the displacement and perform it this way: if you have “bound” him firmly with the Wecker on his Messer, and he is “weak in the binding”, wind “simultaneously” your Messer to his right side and take him by his neck. And come to help your right hand with the left one on the “binding,” and as you have pressed him a bit down, let the left hand go from the Messer, and hold him firmly with the right one. If he raises his Messer with the “strong,” strike to him again quickly below his Messer to his head or neck. |
Notice the weak Then, the master states an element against the “weak“ in the displacement and perform it this way: if you have bound him firmly with the Wecker on his Messer, and he is “weak in the binding,” wind “simultaneously” your Messer to his right side and take him by his neck. If he raises his Messer with the “strong,” strike to him again quickly below his Messer to his head to his right side. |
[52v.2] der schwech nim war Hie saget der meinster eyn stueck wider die die schwach in versatzüng sint Vnd tribe dz also so du Im mit dem wecker starck vff sin messer bindest Ist er dan schwach im pand so wende Indeß vff sin rechten siten din messer vnd nÿm In bÿ dem hals vnd küm diner rechten siten zu hilff vnd so du In ein wenig nider getruck hast mit den messer so loß din lincken hant wider von dem messer vnd halt In mit diner rechten hant fest hebt er dan mit der sterck uff sine messer so haulb im wider schnell vntter sin messer zu sinem haupt oder hals |
[15r.2] Der swech nymb war Hye sagt der meyster eyn stuck wyder dye swach yn der versaczung sÿn und treyb daß alzo so dw ym mit dem [15v.1] wecker starck auff seyn messer pyndest ist der den swach ym pant so wyndt yndeß auff seyn rechte seytten deyn messer und nymb yn pey dem halz und kum der rechten zw hilfft mit der lincken an daß pandt und so dw yn eyn wenick nyder gedruckt hast so laß dy lincken hant wyder von dem messer und hallt yn mit der rechten vest hebt er den mit der sterck auff seyn messer so haw ym wÿder snel unter seyn messer zw seynem hawbt oder halz |
[24v.1] Der swech nymb war Hie sagt der meister ein stuck wider die swach In der versatzung sein vnd treib das alzo So dw Im mit dem wecker starck auff sein messer pindest ist er denne swach Im pandt So windt Indes auff sein rechte seitten deyn messer vnd nymb In bey dem hals hebt er den mit der sterck auff sein messer So haw Im wider schnel vnder sein messer zu seinem haubt auff seyner rechten seitten |
[98r.5] der schwech
nym war / den halß nym vngefar hie sagt der meister ein stück wider dye schweche dy in der versetzungk sein vnd treyb das also / so du Im mit dem wecker starck auff sein messer bindest / ist der er dann schwach Im band / so wind Indes aff auff sein r. s. dein messer vnd nym Im bey dem hals vnd kum der rechten seyten zů hulff mit deyner lincken hand / Indes bind vnd so du In eyn wenigk nyder von dem messer gedruckt hast mit deinem messer so las dy linck hand wyder von dem messer vnd halt Im mit der rechten hand feste / halt de er dan mit der sterck auff sein messer so haw Im wider schwell [!] vnder sein messer zu sein haüpt oder hals |
[148r.1] Der schwech Nymb war Item aber ain gut stückh Wider die / die schwach Inn der versatzunng seind vnnd treib das also. so du Im mit dem wecker haw starckh auf sein duseggen pindest. Ist er dann schwach Im bannd. so wind Indes auf sein rechten seitten seins Duseggens vnnd Nimb In bey dem hals vnnd kum der Rechten hannd zu hilff. mit deinner linncken hinden an das pannd. vnnd so du In ain wennig Nider getruckht hast. mit dem Duseggen. so lasz dein linncke hannd wider vonn dem Duseggen vnd halt Im mit der rechten hannd veest. hellt er dann mit der sterckh auf sein Duseggen. so haw Im wider schnell auf sein haupt oder hals. |
||||||
[91] If he is so “strong” and you want to wind to the neck, work quickly with the “weak” to the other next peak. |
If he is so “strong” that you cannot perform this element, work quickly with the “weak” to the next peak of the other side. |
[52v.3] ist er aber also starck so du zu dem hals winden wiltt So arbeit mit der schwech schnell zu der andern nesten zÿnnen |
[15v.2] ¶ Ist er aber sterck so dw zw dem halz wynden wild so erbayt mit der swech schnel zw dem negsten andren czynnen etc |
[24v.2] ist er aber als starck das du das stuck nicht treyben kanst So erbeit schnel mit der swech zu der negsten plöß eyner andren zynnen |
[98r.6] Ist er aber als starck so thu zu dem hals winden wilt / so arbeit mit der schweche schnell zu der rechten andern zynnen |
[148r.2] Ist er aber zu starckh. so arbait mit der schwech Im zu den vnndern zwu zinnen. |
||||||
[92] Then, you should know that you cannot have one for long with the Messer on his neck with one hand. That is why notice that as soon as you work towards his throat, thrust at him to his face or do as it is stated above. |
Then, you should know that you cannot hold one for long with the Messer on his neck with one hand. That is why notice that as soon as you work towards his throat, thrust at him to his face. |
[15v.3] Item dw solt wyssen daß dw eynem nicht lang magst pey dem halz mit eyner hand ym messer halten dar umb merck alz pald dw ym nach dem halz arbayttest alzo pald stich ym zw dem gesicht oder thw alz oben stet |
[24v.3] Item Du solt wissen das du nit lang magst eynen halten mit dem messer bey dem hals mit eyner handt dar vmb merck als pald du Im nach dem hals arbeittest als pald stich Im zu dem gesicht etc |
[98r.7] Item du solt wissen das du eynen nit lang bey dem hals magst haben mit eyner hand Im messer dar vmb merck als bald du Im nach dem hals arbeÿsest [!] als bald stich Im zu dem gesicht oder thu also oben stadt / |
[148r.3] auch soltu wissen das du ainnem nit lanng bey dem hals magst hallten mit ainer hand am Duseggen. |
|||||||
[93] As when you go to the throat, the meaning is not that you should hold him there for long, but that you also deceive them and “simultaneously” do what you want. [The text] follows. |
[15v.4] ¶ wann so dw zw dem halz ferst ist dy maynung nichtt daß dw yn da lang halten sölt sünder [16r.1] daß dw yn auch verfuerest und yndeß machest waß dw wild etc Sequitur |
[98r.8] wan so du Im zu dem halß ferst mit dem messer ist dy meynung nit so du im lang haben solt / sunder das du In do mit verfurest vnd indes machestu was du wilt |
[148r.4] dann so du zu dem hals ferst mit dem Duseggen. Ist die Warnnung nit das du Inn lanng hallten sollest. sonder das du In verfierest darmit vnd Indes machest was du wildt. |
|||||||||
[94] The Entrüsthau takes Here the master commences to speak about the third element in the Messer and explains it with its features and speaks: the indignation etc. Now notice that the Entrüsthau breaks the guard from the Luginsland and all the strokes that are struck from above downwards. And perform it this way: |
The Entrüsthau takes Here the master commences to speak about the third element and paragraph in the Messer and explains it with its features. Now notice that the Entrüsthau breaks the guard from the Luginsland and all the strokes that are struck from above downwards. And perform it this way: |
[52v.4] der entrüest nÿmpt Hie saget der meinster von dem entrusch haulb Nü merck den entruest haulb |
[16r.2] dEr entrüst nymbt Hye hebt der meyster an zw sagen von dem tritten stück ym messer und erlewttert daß mit seyner aygenschafft und sprich der entrust etc Nw merck der entrüsthaw pricht dy hüt vom lüginsland und alle hew dy von oben nyder gehawt werden und treyn den alzo |
[25r.1] Der entrüst nymbt Hier heb der meister an zu sagen von der dritten stuck vnd capitl Im messer vnd erlewttert das mit seiner eygenschafft Nu merk der entrusthaw pricht dy hut vom luginslandt vnd alle hew dy von oben nyder gehawt werden vnd treibt den alzo |
[98r.9] Der
Entrist nympt / was von oben dar
kumpt / Hie hebt der meister an zu sagen von dem dritten stuck Im messer vnd erleutert das mit seyner eygenschafft vnd spricht der entrist etc Nun merck den entrist hewe bricht du [!] hůt von lüginß land vnd alle hewe dy von oben nyder gehawen werden vnd treyb den also / |
[149r.2] Der entristhaw mit Seinnen stücken
[149r.3] Item merckh der Enntristhaw. pricht die hut Luginslannd vnnd alle hew die von oben nidergehawen werden. den haw mach also |
||||||
[95] If you come to him with the Zufechten and he stands against you and holds his Messer with the stretched arm above the head in the guard and waits for you, notice, as you come close to him, put your left foot forwards and hold your Messer to the ground, so that the flat is against your torso on your right side. If he steps to you and endangers you with a stroke, you should go “before” and leap with the foot well to your right side. And while leaping turn your Messer with the hilt in front of your head, so that the thumb is downwards. And strike to him with the blunt edge to his left side to the upper peak. However, if he comes sooner with the stroke than you, leap with the right foot and with the displacement described above out of the stroke well to your right side and strike to him with the Entrüsthau long from the arm to his head. |
if you come to him with the Zufechten and he goes against you and holds his Messer with the stretched arm over the head in the guard Luginsland, and waits for you, notice, as you come close to him, put your left foot forwards and hold your Messer to the ground, so that the flat is against your torso on your right side. If he steps to you and endangers you with a stroke, you should go “before” and leap with the foot well to your right side. And while leaping turn your Messer with the hilt in front of your head, so that the thumb is downwards. And strike to him with the blunt edge to his left side to the upper peak. However, if he comes sooner with the stroke than you, leap with the right foot and with the displacement described above out of the stroke well to your right side and strike to him with the Entrüsthau long from the arm to his head. |
[53r.2] wan du mit dem zu fechten zu dem man kümpst fertt er dan gegen dir vnd helt sin messer mit vff gerechtten arm vber dz haubtt in der hutt vnd wartt vff dich So merck wan du nahent zu im kümpst So setz din lincken fus fur vnd halt din messer vff der erden dz die flech gegen dem lieb stee an diner rechten syten drit er dan zu dir vnd dreulbett dir zu schlagen So soltu vor kumen So spring mit dem fuß woll vff din rechten siten vnd im sprüng wende din messer mit dem gehultz fur din haueptt dz der thuem vntten ste vnd schlag inn zu mit der stümpffen schniden den zu siner lincken siten zu der obern zÿnnnen kümpt er abe ee mit dem haulb wan du So spring mit dem rechten fuß vnd mit der vor geschribenen versatzüng vß dem haulb woll vff din rechten siten vnd schlag in mit dem entruescht haulb langck vß dem haulb arm zu sinen hauptt ~ Sequitur textus |
[16r.3] wenn dw mit dem zw vechten zw dem man gest stet er denn gegen dir und helt seyn messer mit auff geracktem armen uber daß hawbt yn der hüt und wart auff dich so merck wenn dw nohent zw ym kümbst so secz deynen lincken fuß fuer und hallt deynn messer auff der erden daß dy flech gen dem leyb stee an deyner rechten seytten drit er den zw dir und tzawet dir [16v.1] zw schlagen so soltu vor kummen und spring mit dem fuß woll auf deyn rechtne seytten und ym sprung wendt deyn messer mit dem gehulcz fuer deyn hawbt daß der dawm unten stee und schlag ym zw mit der stumpffen schneyden zw seyner lincken seytten zw der oberen czynnen kumbtt er aber ee mit dem haw den dw so spring mit dem rechten fuß und mit der vorgeschriben versaczung auß dem haw wol auff deyn rechte seytten und schlag yn mit dem entrusthaw lanck auß dem armen zw seyner haubt |
[25r.2] wenne du mit dem zuuechten zu dem gest vertt er denn gegen dir vnd helt sein messer mit ausgeracktem arme vber das haupt In der hut luginslandt vnd wartt auff dich So merk wenn du nohent zu Im kumbst So setz deinen linken fuß fur vnd halt dein messer auff der erden das dy flech gegen deinem leibe stee an deiner rechten seitten tritt er denn zu dir vnd drött dir zu schlagen so soltu vor kummen vnd spring mit dem fuß woll auf dein rechte seitten vnd Im sprung wendt dein messer mit dem gehultz fur dem haubt das der dawm vnden stee vnd schlag Im zu mit der stumpffen schneyden zu seiner lincken seytten zu der obren zinnen kumpt er aber Ee mit dem haw den du so spring mit dem rechten fuß vnd mit der vor gestriben[17] versatzung auß dem haw wol auff dein rechte seytten vnd schlag In mit dem entrusthaw lanck auß dem arme zu seinem haubt etc |
[98r.10] ¶ wan du mit dem zü vechten zu dem man geest ffert er denn gegen dir vnd helt sein messer mit auff gereckten arm vber hawpt in der hüt vnd wart auff dich / So merck so du nahent zu Im kumest so setz dein lincken fuß für vnd halt dein messer auff der erden das dy fleche gegen dem leyb stee an deyner rechten seyten / tryt er dann zu dir vnd trewet dir zu schlahen / so soltu f vor kumen / so spring mit dem fuß wol auff dein rechten seyten vnd Im sprung wend dein messer mit dem gehültz für dein hawpt das dir der arm vnden stee vnd schlach In mit stumpffen schneyden zů der l. s. zu der obernn zynnen / kompt er aber seyner ee mit dem haw den thu / so spring mit dem rechten vnd mit dem vorgeschriben spring auß dem haw wol auff dy rechten seyten vnd schlag In mit dem entrist haw lang auß dem arme zu seinem hawpt |
[149r.4] wann du mit zufechten zum Mann kumpst. fert er dann gegen dir vnnd hellt sein weher mit aufgerecktem arm vber sein haupt Inn die hut vnnd wart auf dich. so merckh wann du nahent zu Im kumpst. so setz deinnen lincken fuosz fur. vnnd halt dein Duseggen auf der Erden das die flech gogen dir stee an deinner Rechten seitten trit er dann zu dir vnnd treuwet dir zuschlagen. so spring mit dem linncken fuosz wol auf dein rechten seitten. vnnd Im sprunng wennd dein Duseggen mit dem gehultz fur dein haupt. das der dawm vnnden stee. vnd schlag Im zu seinner linncken seitten zu der obern zinnen. |
||||||
[96] |
Do the Entrüsthau to the strong It is to be known that when you strike to him with the Entrüsthau, you should do it with the “strong” of your Messer. If he displaces, go high with the “strong” of your Messer to the “weak” of his Messer. If you grasp with the “strong” his “weak,” you should mutate to him over his Messer to the other peak from above to the neck. In case you cannot come to this, work from the doubling behind the blade of his Messer and strike to his head. If he is too strong in the displacement, so that you cannot come to these elements, work with the crosspiece or with the “guarding nail” and push his Messer with it aside, and strike with the Entrüsthau to the other peak. |
[53v.1] Ruest zu der sterck Hie saget der meinster wan dü mit dem entruesch haulb zu haulbest daß soltu thun mit sterck dineß messers versetz er dan So far vff mit der sterck dineß messers noch der schwech sines messers So du begriffest mit der sterck sin schwech So soltu mütiren Im vber sin messer zu der anderen zynnen oben zu dem hals Aber so dü nit dar zü kümen magst So arbeit vß dem duppliren hinder sins messers clingen vnd schlag im zu dem kopff Ist er aber mit der versatzung so starck dz du zu dem stueck nit kümen magst So arbeit mit dem crutz oder mit dem werenagell Stoß sin messer do mit hÿn wegck vnd schlag in mit dem entruscht haulb zu der anderen zÿnnen ~ |
[16v.2] Ruest zw der sterck Eß ist zw wyssen wenn dw ym mit dem entrusthaw zwhawest daß soltu thun mit sterck deyneß messers versecz er den so far uff mit der sterck deyneß messerß nach der swech seyneß messers So dw pegreuffest [17r.1] mit der sterck seyn swech so soltu mutiren ym uber seyn messer zw der andren czynnen oben czben zw dem halz so dw aber nicht dar zw magst kummen so erbat auß dem dwpliren hynter seyneß messers klyngen und schlag ym zw dem kopff Ist er aber mit der versaczung zw starck daß dw zw den stucken nicht kummen magst so erbayt mit dem krawcz oder wernagil stoß seyn messer da mit hyn weck und schlag yn mit dem entrusthaw zw der anderen czynnen etc |
[25v] Rust zu der sterck Es ist zu wissen wenne dw Im mit dem et entrusthaw zu hawest das soltu thun mit sterck deines messers versetzt er denn so far auff mit der sterck deynes messers nach der swech seines messers So du pegreuffest mit der sterck seyn swech so soltu mutiren Im vber sein messer zu der andren zinnen oben zu dem hals so du aber nicht dar zu kummen magst So erbeyt auß dem dupliren hinter seynes messers klingen vnd schlag Im zu dem kopff Ist er aber mit der versatzung zu starck das du zu den stücken nicht kummen magst so erbeyt mit dem kreutz oder mit dem wernagel vnd stoß Im sein messer da mit hyn weck vnd schlag Im mit dem entrusthaw zu der andren zynnen etc |
[98r.12] Rust
zu der starck / dein arbeyt do mit merck Es ist zu wissen wan du In mit dem ernsthaw [!] zu hewest das saltu thun mit stercke deynes messers / versetzt er dan / So far aüff mit der stercke deynes messers / so saltu mutieren Im vber sein messer zu der andern zynen ader zu dem hals / So du aber nit dar zu kommen magst / so arbeyt auß dem dupliren hinder seynes messers cling vnd schlag Im zu dem kopff Ist er ober mit der versetzung zu starck das du zu dem stuck nit kommen magst / so arbeyt mit der kurtzen oder mit dem wernagel stoß sein messer da mit hinweck vnd schlag In mit dem entristhaw zu der andern zynnen |
[149v.1] Rist zu der sterckh Item es ist zu wissen Wann du Im mit dem Entristhaw zu hawest. soltu es thun mit sterckh deinnes Duseggens. versetzt er dann so far auf mit sterckh deinnes Duseggen nach der schwech seines dussegen so begreifstu mit der sterckh seinn schwech. Indes Muttier Im vber sein Duseggen zu der anndern zinnen. oben zu dem hals aber so du mit zukummen magst. so arbait mit dem Duplieren hinder seinnes duseggen klingen vnnd schlag. In zu dem kopff. ist er aber mit der versatzunng zu starckh. das du zu den stucken nit kummen magst so arbait mit dem Creytz oder wehr nagel. vnnd stosz sein Duseggen. damit wegck vnnd schlag In mit dem Entristhaw zu der anndern zinnen. |
||||||
[97] |
Do the Entrüsthau to the peaks Here you are taught that you should always remember the four peaks, so that you can have the man the surer and you can strike to him bravely. And do not strike to the Messer, as you were taught before. If one comes to you in the Zufechten and stands against you in the guard of the Luginsland, leap with the right foot against him well to your right side and strike to him with Entrüsthau to the upper peak. If he displaces, strike quickly to the lower peak of his right side-that is, strike the stroke from one peak to the other and if you want to be successful, you should strike with every Entrüsthau to another peak. If he displaces, strike quickly to the upper peak of his right side-that is, strike the stroke from one side to the other and if you want to be successful, you should leap far with every Entrüsthau to the side, and move well around with your arm. This way, you have the man the surer and you can give a good stroke to his head. “Simultaneously” you should pay attention that you hold your shield, that is, the displacement, well in front of your head. |
[17r.2] Rust zw den czynnen Hye wirst gelertt daß dw dich fleyssig solt remen der vyer czynnen so magstu den man dester gewyser haben und den künstenlichen zw hawen und nicht haw zw dem messer alz dw den vor unterricht pist wenn [17v] eyner mit dem zw vechten zw dir kumbt stet er denn gegen dir ynn der hüt luginslandt So spring mit dem rechten fuß gegen ym woll auff deyn rechte seytten und schlag yn mit dem entrust haw zw der öberen czynnen versecz er den so schlag aber pald zw der unteren czynnen seyner rechten seytten alzo haw den haw von eyner czynnen zw der anderen und wildw daß dir geling so soltu mit yetlichen entrust haw zw den oberen czynnen schlagen versecz er den so schlag aber pald zw der oberen czynnen seyner rechten seytten alzo haw den haw von eyner czynnen zw der anderen und wildw daß dir geling so soltu mit ytlichem entrusthaw weyt auß springen auff eyn seytten und mit dem armen gib dich wol hyn umb so hastu den man dester gewyser und magst ym an seyn haubt eyn gute ruer geben yndeß soltu dich pebaren daß dw deyn schilltt daß ist dy versaczung soltu woll fuer deyn hawbt etc Sequitur textus |
[26r] Rüst zu den zynnen Hie wirst gelertt das du dich fleyssig solt remen der vyer zynnen So magstu den man dester gewiser haben vnd dem kunelich zu hawen vnd nicht haw zu dem messer als du den vor vnterricht pist wenne einer mit dem zuuechten zu dir kumbt stet er danne gegen dir yn der hut luginslandt So spring mit dem rechten fuß gegen Im woll auff deyn rechte seytten vnd schlag In mit dem entrusthaw zu der obren zynnen versetzt er den so schlag aber pald zu der vndren zynnen seyner rechten seytten alzo haw den haw von eyner zynnen zu der andren vnd wiltu das dir geling so soltu mit ytlichem entrusthaw zu der obren zynnen schlagen versetzt er denn So schlag aber pald zu der obren zynnen seyner rechten seytten alzo haw den haw von eyner seytten zu der andren vnd wiltu das dir geling so soltu mit ytlichen Entrusthaw weyt auß springen auff eyn seytten vnd mit dem arme gib dich woll hyn vmb So hastu den man dester gewyster vnd magstu Im an seyn haubt woll eyn gutte Rür geben Indes soltu dich pewaren das du dein schilt das ist dy versatzung woll fur dein haubt haltest etc |
[98r.11] Rust zu
dem zynnen kumpstu dar ein dir wirtt gelingen Hie wirstu gelert das du dich fleyssen reyme der vier plösen oder zynnen so magstu den man dester gewisser haben vnd dem künlich zu hawen vnd nit haw zu dem messer als du vor vndericht bist wan einer mit dem züüechten zu dir kumpt / stet er dann gegen dir in der hůt luginßland So spring mit dem rechten fuß gegen Im wol auff dein r. s. vnd schlach bald zu der andern zynnen seyner rechten seyten also haw den haw von eyner zynnen zu der andern hand vnd wiltu das dir geling / so saltu mit etlichen entrist haw zu der oberen zynnen schlahen / versetzt er aber das / so schlach aber bald zu der oberen zynen s. r. s also haw den haw von eyner seyten zu der andern / vnd wiltu das dir geling so soltu mit etlichen entrist haw weyt auß springen auff ein seiten mit dem arm gib dich wol hin vmb so hastu den man des gewisser / vnd magst Im an sein hawpt ein gute růer geben Indes soltu dich bewaren das du den schild dz ist dy vorsetzung wl [!] für dein hawpt habst oder haltest |
[149v.2] Rust zu den Zinnen [150r.1] Item hie wirst Gelert das du dich fleyssen solt der vier plössen oder zinnen so magstu den Mann dester gwiser haben Im auch gar kecklich zu hawen vnnd nit haw dem duseggen zu. als du dann vor vnnderricht bist. Wann ainner mit dem zufechten zu dir kumpst. steet er dann gegen dir Inn der hut luginslannd. so spring mit dem rechten fuosz gegen Im wol auf sein rechte seitten vnnd schlag Im mit dem Enntrusthaw zu der obern zinnen. versetzt er dann so schlag aber bald zu der vnndern zinnen seinner Rechten seitten. also haw den haw vonn ainner zinnen zu der anndern. vnnd wiltu das dir geling. so soltu mit Jetlichem Entrusthaw soltu weit ausz sprinngen. auf ain seit. vnnd mit dem arm gib dich wol hinnumb. so hastu den Man dester gewiser vnnd magst Im an sein haupt ain gute Ruor geben. Indes soltu dich bewaren. das du den schildt. das ist die versatzunng wol fur dein haupt haltest. |
|||||||
[98] |
The feint deceives Here the master teaches how one should feint with the Entrüsthau, as with the feints the masters who want to displace only and who strike to one’s Messer are duped a lot. |
[53v.2] Feler verfueret Hie saget der meinster wie man mit dem entrusch haulb fellent sol wan mit dem feller werdent die meinster sere gepluet die do nuer versetzen willentt [54r.1] vnd haulben noch dem messer des mans vnd nichtt zu den zÿnnen des mans |
[18r.1] Feler verfüret Hye lert der meyster wye man mit dem entrüsthaw felen solt wann mit denn feleren werden dy meyster ser geplewtt dye dy newer verseczen wöllen und hawen nach dem messer deß manß und nicht ni zw den czynnen deß mannß |
[26v.1] Feler verfuret Hie lertt der meyster wie man mit dem entrusthaẅ felen soltt wenne mit den feleren werden dy meyster ser geplewet dye dy newer versetzen wollen vnd hawen nach dem messer des manß |
[98r.13] ffeller ver fuert dye
zÿnnen Nach wunschlicher rieret Hie beret der meister wie man mit dem entristhaw felent sol / wan mit dem feler werden dy meister sere geplend dy do mit versetzen wellen vnd hawen noch dem messern des mans vnd nit zu den zynnen des mans |
[150r.2] Feler verfieret Item merckh wie man mit dem Entrusthaw felen soll wann mit dem feler werden die Maister seer betriebt. die damit versetzen wollen vnnd hawen nach dem Duseggen des Mans. vnnd nit nach der plosse des Manns. |
||||||
[99] |
Now, perform the feint this way: do as if you wanted to strike with the Entrüsthau to the upper peaks of his left side, and while striking, as you are close to the Messer, stike to him to the other peak of his right side to the head. |
[54r.2] Nu den feller tribe also thün sam du wollest haulben mit dem entruest haulb zu der obern zÿnnen siner lincken siten vnd im haulb So du nahent by dem messer bist so haulb im zu der andern zÿnnen siner rechten siten zu dem hauptt ~ |
[18r.2] Nw den feler treyb alzo Thu samb dw ym wöllest hawen mit dem entrusthaw zw der oberen czynnen seyner lincken seytten und ym haw so dw nohent pey seynem messer pist so haw ym zw der anderen czynnen seyner rechten seytten zw dem haubt etc Sequitur textus |
[26v.2] Nu den feler treyb alzo Thu als sam du yn wollest hawen mit dem entrusthaw zu den obren zynnen seyner linken seytten vnd ym haw So du nohent bey dem messer pist So haw ihm zu der andren zynnen seytten seyner rechten seytten zu dem haubt etc |
[98r.14] Nun den feller treybt also thu sam dü welest hawen mit dem entrist haw zu den oberen zynnen s. l. s. vnd Im haw so du nohent bey dem messer bist so haw Im zu der andern seyten s. r s zu dem hawpt |
[150v.1] Der feler Item den feler mach allso thu als Dam du wollest hawen mit dem Entrusthaw zu der obern zinnen seinner linncken seitten vnnd Imm haw so du nachent bey dem Duseggen bist so haw Im zu der anndern zinnen seinner Rechten seitten zu dem haupt. |
||||||
[100] |
If you feint in a double manner Then, you should understand it this way: hold your Messer on your right side, so that the point is on the ground and the thumb is below on the flat of the Messer. And when he is high in the Luginsland and you have noticed that he let himself be deceived easily and follows eagerly with the displacement, go high in front of your body with the Messer and let the point hang towards the ground and go with the Messer above your left shoulder till over the middle of your head, so that the point goes out over the back and the hilt is against the man. And do as if you wanted to strike to his left side and “simultaneously” strike to his right ear with the Entrüsthau. |
[54r.3] Ob du fellest zwiffach Daß soltu also verstan halt din messer vff diner messer vff diner rechten siten dz der ortt vff der erden ste vnd der thum vntten an der flech des messers vnd so er dan hoch luett Im luginßlant vnd du hast gemerck daß er sich luechtiglich verfuren lest vnd gern der versatzung noch gett So far vff fur din lieb mit dem messer laß den ortt hangen gegen der erden vnd far mit dem messer vber din lincke achschell vntz vber die mit dines hauptes dz der ortt vber rueck hynueßgee vnd daß gehultz gegen dem man ste vnd thunsam du zu wollest schlagen zu siner lincken syten Indeß schlag in zu dem rechten oren mit dem entruest haulb ~ |
[18r.3] Ob dw felest czwiüach Item daß soltu alzo verstan haltt deyn messer auff deyner rechten seytten [18v.1] daß der ortt auff der erden sey undt der dawm unter auff der flech deß messers und so er den hoch ligt ym luginsland und dw hast gemerckt daß er sich leychtiklich verfuren lest und gerne der versaczung nach get so far auff fuer deyn leyb mit dem messer laß den ort hangen gegen der erden und far mit dem messer uber deyn lincke achsel und uber dy mit deynes hawbcz daß der ortt uber ruck hyn auß gee und das gehulcz gegen dem man stee und thw sam dw yn wöllest schlagen zw seyner lincken seytten yndeß schlag yn zw dem rechten oren mit dem entrusthaw |
[27r] Ob du felest zwiuach Item du solt das alzo verstan halt deyn messer auff deyner rechten seytten das der ortt auff der erden sey vnd der dawm vnden an der flech des messers vnd so er denn hoch ligt Im lunginslandt vnd hast gemerckt das er sich leichtiklich verfuren lest vnd gerne der versatzung nach gett so var auff fur deyn leyb mit dem messer vnd laß den ort hangen gegen der erden vnd var mit dem messer vber deyn linke achselen vntz vber dy mit sey deynes haubtz das der ortt vber ruck hyn auß gee vnd das gehultz gegen dem man ste vnd thu sam du In wollest schlagen zu seyner lincken seyten yndes schlag In zu dem rechten oren mit dem entrüsthaw etc |
[98r.15] Ob du
felest zwifach / dy schneyd mit mach / das saltu also verschtan / halt dein messer auff dein r. s / das der ort auff der erden sey vnd der dawm vnten [98v.1] an der flech des messers / vnd so er do nach leyt Im lüginsland vnd du hast gemerckt das er sich leychtlich verfuren lost vnd gegen der versetzung laufft / so far auff für dein leyb mit dem messer vnd loß den ort hengen gegen der erden vnd far mit dem messer vber dein l. a. vntz voer dy mitte deines haupt das der ort vber růck hinaus ghee vnd das gehültz gegen dem man stee vnd thu sim [!] du wellest zu schlahen zu s. l. s In des schlach In zu dem rechten ore mit dem entristhaw |
[150v.2] Ob du felest zwifach Item das soltu Also versteen. hallt dem Duseggen auf deinner rechten seitten. das der Ort auf der Erden stee. vnnd der dawm vnnden stannd an der flech. des duseggens vnnd so er dann hoch leit Im luginslannd vnnd hast gemerckt das er sich leychtlich verfieren last. vnnd geren der versatzunng nach geet. so far auf mit dem leyb vnnd lasz den Ort hanngen. gegen der Erden. vnnd far mit dem Duseggen vber [151r.1] sein rechte achsel. vnnden vber die Mitte deinnes hals das der Ort vberzuckh hinnausz gee. vnnd das gehultz gegen dem Mann stee. vnnd thu samm du Im wollest schlagen seinner linncken seitten zu. Indes schlag zum rechten arm. mit dem Entrusthaw. |
||||||
[101] |
Then, if you want to do the feint to the right, do this way: stand with the left foot forwards as above. While you lead your Messer in front of your body, step with the right foot to your left one and menace him as if you wanted to strike to his left side. Then, nod with the upper part of your body towards his left side for a moment and “simultaneously” step with your left foot towards his right side and strike with the Entrüsthau to his right ear. “Simultaneously” go high with the Messer and do as if you wanted to strike to his left side and nod a bit with the body to his left side. “Simultaneously” step with your right foot behind his right one and strike again to his right side with the doubling and strike the short edge behind the blade of his Messer to his face. “Simultaneously” step again around him and go high with the Messer as above, and step with the left foot well behind his right one and strike to his neck. “Simultaneously” go high and step behind him and strike to his stomach-this is called the hitter. “Simultaneously” even step around him well and strike again to his neck. |
[18v.2] Item wiltu den feler recht machen so thu ym alzo stee mit dem lincken fuß fuer alz vor so dw nw daß messer fuer deynen leyb ferwest so schreytt mit dem rechten fuß zw deynem lincken und traw ym alz dw wollest zw seyner lincken seytten schlagen und wenck mit dem obren tayl deyneß leybs [19r] gegen seyner lincken seytten dy weyl yndeß schreyt mit dem lincken fuß auff seyn rechte seytten und schlag yn mit dem entrusthaw zw dem rechten oren yndeß far auff mit dem messer und thu aber sam dw wöllest schlagen auff seyn lincke seytten und wenck eyn wenick mit dem leyb uff seyn lincke seytten yndeß schreyt aber mit dem rechten fusß hynter seynen rechten und schlag yn wyder zw der rechten seytten eyn mit dem dupliren und schlag ym dy kurcz schneyd hynter seyneß messerß klingen yn daß an gesichtt yn deß schreytt nach paß umb yn und far aber auff mit dem messer alz vor und schreytt mit dem lincken füß wol hynter seynen rechten und schlag yn ynn seyn genick yndeß far aber auff und schreyt aber hyn hynter und schlag yn ynn den pauch daß hayst der treffer yndeß umbschreyt yn gar und haw ym [19v.1] wyder zw dem nack etc |
[27v] Item wiltu den feler recht machen so thu Im alzo stee mit deynem lincken fuß fur als vor So du nw das messer fur deynen leib furest So schreyt mit dem rechten fuß zu deynen lincken vnd dro ym als du wollest zu seyner lincken seytten schlagen vnd wenck mit dem obren teyl deynes leybs gegen seyner lincken seytten dy weyll yndes schreit mit deynem lincken fuß auff seyn rechte seytten vnd schlag In mit dem entrusthaw zu seynen rechten oren yndes far auff mit dem messer vnd thu aber samm du In wollest schlahen auff seyn lincke seytten vnd wenck eyn wenig mit dem leyb auff seyn lincke seytten Indes schreyt aber mit deyner rechten fuß hinter seynen rechten vnd schlag In wider zu der rechten seytten eyn mit dem dupliren vnd schlag Im dy kurtz schneid hinter seynes messers klingen In das angesicht Indes schreit nochpaß vmb In vnd far aber auff mit dem messer als vor vnd schreyt mit dem lincken fuß woll hinter seynen rechten vnd schlag In In seyn genick Indes var aber auff vnd schreyt aber hinter yn vnd schlag Im in den pauch das heist der treffer Indes vmbschreyt In gar vnd haw Im wider zu dem nacken etc // |
[98v.2] Item wiltu den veler recht mochen so thü Im also / stee mit dem lincken vor als vor so schreit mit dem rechten fuß zu deiner lincken vnd thun Im als wellestu In zw s. l. s. schlahen vnd weck mit dem obern teyl deines leybes gegen se. l. s. die weil In des schreyt mit deinem lincken fuß auff s. r s / vnd schlag Im mit dem entristhaw zu dem rechten ore In des far auff mit deinem messer vnd thün aber sam wolestu In schlahen auff sein lincke seyten vnd wenck ein wenig mit dem leyb auff sein lincke seyten Indes schreyt aber mit deynem rechten fuß hinder sein rechten vnd schlach Im wider zu der rechten seyten ein mit dem dupliren vnd schlach Im dy kurtze schneid hinder seines messers klingen In des angesicht In des schreyt nach bas vmb vnd far aber auff mit dem messer als vor / vnd schreyt mit dem lincken fuß wol hinder sein rechten vnd schlach In In sein genick In das var f auff vnd schreyt ab hin hinder vnd schlach Im auff dy bruch / das heysset der treffer Indes Ingar [!] vnd haw Im das wider zu dem noch |
[151r.2] Mer von dem Feler Item wiltu den Feler machen. so thuo also. stannd mit dem linncken fuosz fur. alsz vor. so du Nun den Duseggen vor deinnem leyb fierst. so schreit mit dem rechten fuosz zu seinem linncken vnnd treib In also als wollestu zu seinner Rechten seitten schlagen. vnnd wennck mit dem obern thail deinnes leybs zu seinner linncken seitten. Indes schreit mit deinnem linncken fuosz auf sein rechten vnnd schlag In mit dem Entristhaw zu dem rechten arm. Indes far auf mit deinnem Duseggen vnnd thu aber als wollestu schlagen auf sein linncken seitten vnnd wennck ain wenig mit dem leyb auff sein linncken seitten. vnnd Indes schreit aber mit deinnem Rechten fuosz hinder seinnen rechten. vnnd schlag Im wider zu seiner rechten seitten mit dem Dupliern vnd schlag Im die kurtz schneidin hinder seinnes Duseggen klingen In das angsicht. Indes schreit nach vas vmb In. vnnd far auf mit dem Duseggen. als vor. schreit mit dem linncken [151v.1] fuosz wol hinnder seinnen rechten Vnnd schlag In Inn sein geinckh Indes far auf schreit aber hin hinndert vnnd schlag In Inn den pauch vnd das haist der treffer Indes vmb schreit In gar vnnd haw Im wider zu dem nackh. |
|||||||
[102] |
Then, if you do not want to perform this element announced above, cut him with the doubling through his face. Or, if he wants to go “simultaneously” from the binding, cut him firmly to the next opening. |
[19v.2] Item wiltu dyser stuck nicht treyben so schneyd yn mit dem dupliren durch daß maull oder will er yndeß gen auß dem pandt so schneyd yn starck yn dy negsten ploß etc Sequitur textus |
[28r.1] // Item wiltu disß stuck Eegemelt nicht treyben So schneyd In mit dem dupliren durch das gesicht mit dem dupliren oder will er yndes gen auß dem pandt so schneyd In starck yn dy negsten ploß etc |
[98v.3] Item wiltu desse stůck nit treyben so schlah Im mit dem dupliren durch das maul / oder wil er Indes gheen auß dem band so scnit [!] Im starck in dy rechte ploes |
[151v.2] vnnd wiltu diese stuckh nit treiben so schneid In mit dein Dupliern durch das maul oder will er Indes geen ausz dem pand so schneid In starckh Inn die nechst plosse die du finndest |
|||||||
[103] |
If he wants to do the Entrüsthau and measure to the peaks Here the master teaches a breaking against the feints and Entrüsthaue and speaks: If he wants to, etc. You should understand it this way: if he wants to do feintswith the Entrüsthau, you should break it with the Sprechfenster, that is with the long point, and seek the openings with it in a masterly way, as you know it well. |
[28r.2] Will er zu den zynnen Rüsten vnd messen Hie lertt der meyster eyn pruch wider dy veler vnd entrusthew vnd spricht will er zu etc Das soltu alzo verstan will er mit den rusthewen feler machen So soltu das prechen mit dem sprechuenster das ist mit dem langen ortt vnd dy plöß da mit meysterlich süchen als du den woll weyst etc |
||||||||||
[104] The Zwinger breaks, Here the master says about the fourth element and chapter that is called the Zwinger. Perform it this way: if you come with the Zufechten to the man, put your left foot forwards and hold your Messer on the ground with the point, so that the thumb is below on the Messer. If he strikes from above to the head, turn your Messer and strike against his stroke with the blunt edge long from the stretched arm from above over his Messer to his face. If he defends against it cleverly, and falls with this, and changes through below, remain with the long point long in front of his face, so that he is able to do nothing and cannot come through below. |
The Zwinger breaks Here the master says about the fourth element and chapter that is called the Zwinger. Perform it this way: if you come with the Zufechten to the man, put your left foot forwards and hold your Messer on the ground with the point, so that the thumb is below on the Messer. If he strikes from above to the head, turn your Messer and strike against his stroke with the blunt edge long from the stretched arm from above over his Messer to his face. If he defends against it cleverly, and falls with this, and changes through below, remain with the long point long in front of his face, so that he is able to do nothing and cannot come through below. |
[54v.1] Der zwinger yn pricht Hie saget der meinster von dem vierden stueck dz do heissett der zwinger Den tribe also wan du mit dem zuüechten zu dem man kümpst So setz dinen lincken fus für vnd halt din messer an der erden mit dem ortt dz der thuem vnten ste vff dem messer haut er dan von oben ze dem haupt So verwind din messer vnd haulb gegen sinen haulb In mit stümppfer schniden lang vß dem gestrackten arm oben vber sin messer im zu dem gesichtt were er aber als luestig vnd felett mit dem haulb vnd wechschelt vntten durch So blytt mit dem langen ortt lang vß gestrackten arm vor sin gesichtt so mag er nit Schaffen noch schaden vnd kan dir vntten nichtt woll durch kumen ~ |
[19v.3] dEr czwynger eyn pricht Hye sagt der meyster von dem vyerden stuck daß do heysset der czwynger den treyb alzo wenn dw mit dem zw vechten zw dem man kumbst so secz deynen lincken fuß fuer und halt deyn messer uff der erden mit dem ort daß der dawm unter sey uff dem messer hawt er dan von oben [20r.1] zw dem hawbt so verbendt deyn messer und haw gegen seynem haw eyn mit stumpffer schneyden lanck auß gestracktem armen oben uber seyn messer ym zw dem gesicht Wer er aber alz listig und felet mit dem haw und wechslet unten durch so pleyb mit dem langen ort lanck auß gestrackten armen vor seym gesicht so mag er nicht schaffen noch schaden und kann dir unten nicht wol durch kumen etc |
[28v] Der zwinger eyn pricht Hie sagt der Meyster von dem virden stuck vnd capitel das da heysset der zwinger den treyb alzo wenn du mit dem zuuechten zu dem man kumbst So setz deynen lincken fuß für vnd halt deyn messer auff der erden mit dem ortt das der dawm vnden sey auff dem messer haut er denn von oben zu dem haubtt so verbendt deyn messer vnd haw gegen seynen haw eyn mit der stumpffen schneyden lanck außgestrackten arme oben vber seyn messer Im zu dem gesicht Wer er aber als listig vnd felet mit dem vnd wechslet vntten durch so pleyb mit dem langen ortt lanck vor seym gesicht so mag er nichtz schaffen vnd kan vnden nicht durch kummen etc |
[98v.4] Der zwinger ein bricht
so der piffel schlecht vnd sticht / wer wechsel wil treyben
der zwinger wil In vertreyben Hie von sagt der meister von dem werden stuck das do heysset der zwinger dem [!] treybt also / wan du mit dem züüechten zu dem man kümest so setz dein lincken fuß fur vnd halt dein messer auff der erden mit dem ort das dein daüm vnden seÿ auff dem messer hawt er dann von oben zu dem hawpt / so wend dein messer vnd haw gegen seinem haw ein / mit stumpffer schneiden vnd mit langen gestracken arm oben vber sein mesß Im zu dem gesicht / wer er aber also listig vnd felet mit dem haw vnd wechselt durch / so bleyb mit dem langen ort lang auß mit starckem arm vor seinem gesicht / so mag er nit schaffen oder schaden vnd kan dir vnden nit wol durch kumen |
[151v.3] Der zwinngerhaw Mitt seinnen stuckhen. Der zwinnger einbricht [152r.1] Item den zwinnger Mach allso wan du mit dem zufechten zu dem Mann. kumpst. so setz deinnen linncken fuosz fur vnnd hallt dein Duseggen. an der Erden mit dem ort. das dein dawmen vnden sey auf deImem[19] duseggen hawt er dann von oben zu dem haupt. so verwend dein duseggen vnnd haw gegen seinnem haw mit ausz gestracktem arm. oben vber sein Duseggen zu dem gesicht ist er aber so listig vnnd fellt mit dem haw vnnd wechslet vnnden durch. so bleib mit lanngen Ort. lanng mit ausz gerecktem arm vor seIm [20] gesicht. so mag er nichts schaffen noch schaden. vnd kann dir vnnden. nit wol durch kummen |
||||||
[105] Then, you can break this with the Zwinger when one wants to thrust at you from the Eber. And this goes from both sides, and if you want otherwise, from above. |
[54v.2] ein anders Item du magst mit dem zwinger dz brechen [55r.1] So dir eÿner will zu stechen vß dem eber vnd dz gatt von beÿden syten zue wiltu dich dan sünst vben ~ |
[20r.2] Item dw magst mit dem czwynger daß prechen so dir eyner wil zw stechen auß dem eber und daß gett von payden seytten zw wildw dich anderß sunst uber etc |
[98v.5] Item du magst mit dem zwinger dz wol brechen so dir eyner wil zu schtechen auß dem eber vnd das gat von beyden seyten zu / wiltu dich sunst ̈vben |
[152r.2] vnnd magst mit dem zwinger das prechen. so dir ainer will zustechen ausz dem Eber vnnd das geet von baiden seitten. wiltu dich annderst sunst geben. |
||||||||
[106] |
The Geferhau with its point Here the master speaks about the Geferhau, the fifth element and chapter. You should do it this way: if one stands in the guard of the Bastei, and as you come with the Zufechten to him, put your left foot forwards and hold your Messer with the stretched arm high above your head in the guard of the Luginsland. Then, leap to him with the right foot and strike with the long edge from above, and remain with your arm high and move your point downwards to his face or chest. |
[55r.2] Der gefer mit siner artt Hie sagett der meinster von dem fuenfften stueck als von dem gefer haulb den soltu also machen lig eÿner in der huett der pasteÿn vnd so du mit dem zu fechten zu im kümpst So setz din lincken fus fur vnd halt din messer mit vß gestrecktem arm hoch vber din hauptt Inder huett lueginßlantt vnd spring zu ym mit dem rechten fus vnd haulb mit der langen schniden oben In vnd pleyb mit dem arm hoch vnd senck Im den ortt vnter stich ze synen gesicht oder bruest etc Sequitur textus |
[20r.3] dEr gefer mit seyner artt Hye sagt der meyster von dem funften [20v.1] stueck alz von dem geferhaw den soltu alzo machen ligt eyner inder hut der pasteyn und so dw mit dem zwvechten zw ym kumbst so secz deynen lincken fues fuer und halt deyn messer mit auff gerackten armen hoch uber deyn hawbt yn der hut luginsland und spring zw ym mit dem rechten fuß und haw mit der langen schneyden oben eyn und pleyb mit dem armen hoch und senck ym der ort untersich zw seynem gesicht oder prust etc |
[29r] Der gefer mit seyner artt Hie sagtt der meyster von dem gefer von dem fünften stuck vnd capitel den soltu alzo machen ligt eyner In der hut pasteyn vnd so du mit dem zuuechten zu Im kumbst so setz deynen lincken fuß für vnd halt deyn messer mit aufgerecktem arme hoch vbersich vber deyn haubtt In der hut luginslandt vnd spring zu Im mit dem rechten fuß vnd haw mit der langen schneyden oben eyn vnd pleyb mit dem arme hoch vnd senck Im den ortt vntersich zu seynem gesicht oder prust etc |
[98v.6] Des gefer mit seiner art Das angesicht vnd brust verwart Hie sagt der meister von dem fünfften stuck als von dem geferhaw den soltu also machen / leyt eyner Inder hůt der pastey vnd so du mit dem zu vechten zu im kumest / so setz dein lincken fuß fur vnd halt dein messer mit auß geracktem arm hoch vber dein hawpt In der hüt luginsland vnd spring zů Im mit dem rechten fuß vnd haw mit der langen schneyden oben ein vnd bleyb mit dem arm hoch vnd senck Im den ort vnder sich zu seinem gesicht oder brust |
[148v.1] Der Beferhaw mit Seinnen stucken [148v.3] Befer haw mit seiner art [148v.2] Item den Beferhaw Mach allso. ligt ainner Inn der hut der pastey vnnd du mit dem zufechten zu Im kumpst. so setz dem linncke fuosz fur vnnd halt dein Duseggen mit ausz gestrecktem arm hoch vber dein haupt Inn der hut luginslannd vnnd sprinng zu Im mit dem rechten fuosz vnnd haw mit der lanngen schneidin oben ein bleib mit dem arm hoch vnnd sennckden ort vnndersich zu seinn gesicht oder seinner prust |
||||||
[107] |
Strike the Geferhau Then, you should deliver the element this way: if he stands against you in the Luginsland, as you come to him, strike against his Messer. If he goes high and wants to set the stroke aside, “simultaneously” let your point go down forwards and change through and thrust to his right side at the face with the stretched arm, and “simultaneously” do what you prefer. |
[55v.1] Gefer haulb Daß stueck soltu also tryeben ligt er gegen dir im lügeinßlant So du zu Im kümpst So haulb gegen sinem messer isst ist er hoch vnd will den haulb ab setzen Indes loß dÿn ortt foren nider sencken vnd wechsell durch vnd stich Im vff sin rechten syten zu dem gesichtt mit gestrackten armen Indeß mach waß dir eben ist |
[20v.2] Gefer haw Item daß stuck soltu alzo treyben ligt er gen dir ym luginslandt so dw zw ym kumbst so haw gegen seynem messer ist er hoch und wil dir den haw abseczen yndeß laß deyn ort foren nyder sincken und wechsel durch und stich ym auff seyn rechte seytten [21r.1] zw dem gesicht mit gestracktem armen yndeß mach waß dir eben ist etc |
[29v] Gefer haw Item das stuck soltu alzo treyben ligtt er gegn dir Im luginslandt So du zu Im kumbst So haw gegen seinem messer Ist er hoch vnd will den haw ab setzen Indes laß deyn ortt faren nyder sincken vnd wechsel durch vnd stich ym auff seyn rechte seytten zu dem gesicht mit gestracktem arme Indes mach waß dir eben ist etc |
[98v.7] Resterhaw [!] durch wechsel
Indes schaw Item das stuck also treyben leyt er gegen dir Im luginsland / so du zu Im kumest so haw gegen seinem messer Ist er hoch vnd wil haw absetzen In des laß dein ort nider sincken vnd wechsel durch vnd stich Im auff sein recht seyten zu dem gesicht mit gestrackten arm In des mach was dyr eben ist etc |
[148v.4] Beferhaw [149r.1] Item das stuckh mach Allso Ligt er Im luginslannd gegen dir. so haw gegen seinem duseggen. Ist er hoch vnnd will den haw absetzen so lasz Indes dein ort vornen nider senncken vnnd wechsel durch vnnd stich Im auf sein rechten seitten zu dem gesicht mit gestracktem arm Inndes mach was du wildt. |
||||||
[108] |
You should shoot the Wincker Here the master speaks about the sixth element that is called the Wincker and is one of the main elements in the Messer and strikes well the “free fighters” who displace freely, and is a new stroke and element in the Messer, and is peculiar and good. |
[55v.2] Den wincker soltu erstrecken Hie sagett der meinster von dem sechsten stueck dz do heissett der wincker vnd ist der haubt stueck eyns im messer vnd gehoerett woll vff die frÿen vechtern die da frÿ versetzen vnd ist eyn nulber haulb vnd stueck im messer [56r.1] Vnd ist seltzam Vnd guet |
[21r.2] dEn Wyncker soltu erstrecken Hye sagt der meyster von dem sechsten stuck daß da heysset der wyncker und ist der hawbtstuck eyneß ym messer und geret woll auff dy freyvechter dy frey verseczen und ist eyn newer haw und stuck ym messer und ist setlzam und gut |
[30r.1] Den wincker soltu erstrecken Hie sagt der meyster von dem sechsten stuck das do heisset der wincker vnd ist der hauptstuck eyns ym messer vnd geret woll auff dy freyfechter dy frey versetzen vnd ist eyn newer haw vnd stuck ym messer vnd ist seltzam vnd gutt |
[98v.8] Den wincker soltu her
strecken vnd dy meister do mit erwecken / zwifach
er wincken zu der rechten von der lincken hie sagt [der meister von dem sechsten stuck das do heisset der][21] wincker vnd ist der hewpt stuck eins Im messer vnd gerecht wol auff dy freÿ fechter dy frey versetzen vnd ist ein můtter [!] haw vnd stuck Im messer vnd ist seltzam vnd gůt |
[152r.3] Der winnckerhaw Mit seinnen stuckhen Den winncker solltu erstrecken |
||||||
[109] |
If you want to do the element, do to him this way: stand with your left foot forwards and hold your Messer on your right shoulder. If he stands in the Luginsland, strike from your right shoulder with the stretched arm long to him with the long edge. And as you strike wind against his Messer and strike to his head with the short edge. “Simultaneously” let your Messer go down towards your body and go through “simultaneously” to your left side with the lowered point and strike to his head towards his left side with the short edge. |
[56r.2] Wiltu dz stueck machen So ste mit dinem lincken fuß fur vnd halt deyn messer vff diener rechten achsell Stott er dan In lügenßlant So haulb von dÿner rechten achsell mit gestracken arm zu Im lang In mit der langen schniden Vnd im we haulb so wende gegem synem messer vnd schlag in vff dz haupt mit der kurtzen schniden Indes loß dyn messer sencken fur dynen lieb dan ge durch Indes vff dyn lincken syten mit gesencktem ortt vnd schlag In vff den kopf vff syner rechten siten mit der kürtzen schniden ~ |
[21r.3] ¶ wiltu daß stuck machen so thw ym alzo stee mit deynem lincken fuß fuer und halt deyn messer auff deyner rechten achseln stet er denn ym luginslandt so haw von deyner rechten [21v.1] achseln mit gestracktem armen zw ym lanck eyn mit der kurczen schneyden und ym haw so wyndt gegen seynem messer und schlag yn auff daß hawbt mit der kurczen schneyden yndeß laß deyn messer sincken fuer deyn leyb und ge durch yndeß auff se deyn lincke seytten mit gesencktem ortt und schlag yn auff den kopff auff seyner rechten seytten mit der kurczen schneyden etc |
[30r.2] wiltu das stuck machen So thu Im alzo stee mit deynem lincken fuß fur vnd halt deyn messer auff deyner rechten achsl stet er dan Im luginslandt So haw von deyner rechten achsel mit stracktem arme zu Im lanck eyn mit der langen schneyden vnd Im haw so windt gegen seynem messer vnd schlag In auff das haubt mit der kurzen schneyden yndes laß deyn messer sinken fur dein leib vnd ge durch Indes auff deyn lincke seytten mit gesenckten ortt vnd schlag In auff den kopff auff seyner rechten seytten mit der kurtzen schneyden etc |
[98v.9] wiltu das stuck machen so thun Im also Stee mit deinem lincken fuß für vnd halt dein messer auff deiner rechten achsel / steet er dann Im luginsland so haw von deiner rechten seyten achsel mit gestracken arm zu Im lang In mit der langen schneiden vnd Im haw so ferwend gegen seinem mesß vnd schlach In auff das hawpt mit der kurtzen schneiden Indes laß dein mesß sincken fur dein leyb den ghe durch Indes laß auff dein lincken seyten mit gesencktem ort vnd schlach In auff den kopff auff sein rechten seitten mit der kurtzen schneiden |
[152v.2] Item den wincker haw Mach allso. stee mit deinnem linncken fuosz fur. vnnd halt dein Duseggen auf deinner Rechten Achsel. steet er dann Im luginslannd. so haw von deinner rechten Achsel mit geschrenncktem arm zu Im mit der lanngen schneidin vnnd Im haw winnd gegen seinnem Duseggen. vnnd schlag In auf das haupt. mit der kurtzen schneidin. Indes lasz dein duseggen sincken fur dein leyb. dann gee durch Indes auf dein lincken seitten mit gesencktem Ort vnnd schlag In auf den kopff. auf seiner lincken seitten mit der kurtzen schneidin. |
||||||
[110] |
Then, put your Messer on your left side, so that the point remains on the ground and the thumb is above on the Messer, or stand in the Schranckhut, so that the right foot is forwards. If he stands in the guard of the Luginsland, strike always to his right side with the short edge. “Simultaneously” go through with the Messer and lower the point and go with the Messer to his left side. This way, you have the element in a double manner from both sides. |
[56r.3] Ein ander stueck Item leg dyn messer vff dyn lincken syten dz der ortt vff der erden ste vnd der thum oben vff dem messeg [!] lig oder ste in der schranckhutt dz der rechtt fuß vor ste lyett er dan in der hut lueginßlant So haulb eÿchling In zue siner rechten syten die kuertz schnid Indes gee dürch mit dyem messer vnd senck den ortt vnd far mit dem messer vff syn lincken siten also [56v.1] hastu dz stueck zwyffach von beyten seÿten |
[21v.2] Item leg deyn messer uff deyn lincke seytten daß der ortt uff der erden stee und der dawm oben auff dem messer lige oder stee yn der schranckhutt daß der recht füß vor stee ligt er den ynder hut luginsland so haw ewchling eyn zw seyner rechten seytten dy kurcz schneyd yndeß gee durch mit dem messer und senck den ortt und far mit dem messer uff seyn lincke seytten alzo hastu daß stuck czwiuach von [22r.1] paeden seytten etc |
[30v.1] Item leg deyn messer auff deyn lincke seytten das der ortt auff der erden stee vnd der daum oben auff dem messer lig oder stee In der schranckhutt das der recht fuß vor stee ligtt er den In der hutt luginslandt So haw Ewchling eyn zu seyner rechten seytten dy kurtz schneid yndes gee durch mit dem messer vnd senck den ortt vnd far mit dem messer auff seyn lincke seytten alzo hastu das stuck zwiuach von payden seytten etc |
[98v.10] Item leg dein mesß auff d. l. s. das der ort auff der erden stee vnd der dawm oben auff dem mesß layt oder stehe in der schranckhut das der recht fuß var stee leyt er dann in der hůt luginsland so haw vrplich Im zu der r. s. dy kurtz schneid In des ghe durch mit dem mesß vnd senck den ort vnd far mit dem messer auff sein l. s also hastu das stuck zwiüach von beyden seyten |
[152v.3] Item leg dein Duseggen auf dein linncke seiten das der ort auf der Erden stee. vnnd der dawm oben auf der wehr/ [153r.1] Lig oder stee Inn der schrannckhut das der Recht fuosz vor stee. leit er dann Inn der hut luginslannd. so haw Im ein zu seiner rechten seitten. die kurtz. schneidin. Indes gee durch mit deinnem duseggen. vnnd senckh den Ort vnnd far mit dem Duseggen auf sein lincken seitten. also hastu das stuckh zwifach von baiden seitten. |
||||||
[111] |
Then, if you do not want to go through, so that it is the last thing for you to go through from his right side, remain standing with the Messer and wind towards your left side, so that the short edge is below, and thrust at him at the face. |
[56v.2] Item wiltu aber nicht durch gin dz eß dich zueletz duenck durch zu gen von syner rechten syten So blib also lÿgen mit dem messer vnd wind geger sÿner lincken syten dz die kuertz schnid schnid vnten ste vnd stÿch Im zue dem gesicht etc |
[22r.2] Item wiltu aber nicht durchgen daß eß dich zw lecz dunckt durch zw gen von der rechten seytten so pleyb alzo ligen mit dem messer und wynd gegen deyner lincken seytten daß dy kurcz schneyd unten stee und stich ym zw dem gesicht etc |
[30v.2] Item wiltu aber nicht durchgen das er dich zu letz dunck durch zugen von seyner rechten seytten So pleyb alzo ligen mit dem messer vnd windt gegen dyner lincken seytten das dy kurtz schneyd vnten stee vnd stich Im zu dem gesicht etc |
[98v.11] Item wiltu aber nit durch gehn das es dich zu letz duncket es sey durch zu ghen von s. r. s so bleyb also lygen mit dem mesß vnd wind gegen d. l. s das dy kurtz schneid vnden stee vnd stych Im zu dem gesicht |
[153r.2] wiltu aber nit von der rechten seitten. so bleib also. ligen mit dem duseggen. vnnd wind gogen deiner lincken seitten das die kurtz schneid vnndern stee. vnnd stich Im zu dem gesicht. |
||||||
[112] |
Wind to the left in hitting You should understand it this way: if he stands against you in the Luginsland, strike from your right shoulder directly from above an upper stroke to him with the long or stretched arm to his left side. Now notice, in the stroke, as the stroke goes to the head, “simultaneously” wind towards his Messer, so that the short edge is below, and do not complete the stroke. Instead, in the stroke, let your point go down and go down through with your Messer to your left side and strike to him with the short edge to the head. “Simultaneously” wind your Messer towards you and strike to him to the same side to the head with the long edge, and “simultaneously” do what you prefer. This element can also be done on both sides. |
[56v.3] Winck linck ym treffen Daß soltu also verstan Stott er gegen dir in lügenßlant So haulb von dÿner rechten achßell gerad oben In zu Im In eynem ober haulb mit langem ortt gestracktem arm zu syner lincken syten Nu merck Im haulb dÿweill der haulb nach dem kopf get Indeß wind gegen synenm messer dz die kuertz schnid vnten stee vnd verend den schlag nicht sünder In dem schlag loß den ortt sincken vnd ge vnten duerch mit dem messer vff din lincken syten [57r.1] vnd schlag In mit der kurtzen schniden vff den kopff Indes wind din messer gegen dir vnd schlag in vff die selbigen syten vff den kopff mit der langen schniden Indes mach wz dir eben ist dz stueck gat auch zue beÿden seyten ~ |
[22r.3] Winck linck ym treffen Daß soltu alzo verstan stet er gegen dir ym luginsland so haw von deyner rechten achsel gerad oben eyn zw ym Ee eyn oberhaw mit langen gestracktem armen zw seyner lincken seytten Nw merck ym haw dy weyl der haw nach dem kopff gett yndeß wynd gegen seynem messer daß dy kurcz schneyd oder stumpff schneyd unten stee und verendt den schlag nicht sünder [22v.1] ym schlag laß den ort sincken und gee unter durch mit dem messer auff deyn lincke seytten und schlag yn mit der kurczen schneyden uff den kopff ynder wenndt deyn messer gegen dir und schlag yn auff der selbigen seytten auff den kopff mit der langen schneyden yndeß mach waß dir eben ist daß stuck get zw zw payden seytten etc |
[31r] Windt linck ym treffen Das soltu alzo verstan stet er gegen dir Im luginslandt So haw von deyner rechten achsel gerad oben eyn zu Im eynen oberhaw mit langem oder gestracktem arme zu seyner lincken seytten Nu merck ym haw dy weill der haw nach dem kopff gett yndes windt gegen seynen messer das dy kurtz schneyd vnden stee vnd verendt den schlag nicht Sunder yn dem schlag laß den ortt sincken vnd ge vntten durch mit dem messer auff deyn lincke seytten vnd schlag In mit der kurtzen schneyden auff den kopff yndes wendt deyn messer gegen dir vnd schlag In auff der selbigen seitten auff den kopff mit der langen schneyden Indes mach waß dir eben ist Das stuck gett auch zu zue peyden [Sic] seytten seytten etc |
[98v.12] winck linck Im treffen haw recht wiltu
In effen das saltu also versteen Steet er gegen dir Im luginsland so haw von dein r a. gerad oben In zu Im In ein eber öber haw mit langem ader gestracktem arm zu s. l. s. Nun merck Im haw / dy weyl der haw noch dem kopff ghet Indes wind gegen seinem mesß das dy kurtz schneid vnden stee vnd verwend den schlag mit [!] sunder In dem schlachen los dein ort sincken vnd ghe vnden durch mit dem mesß auff dy lincken seyten vnd schlach In mit der kurtzen schneiden auff den kopff Indes wend dein mesß gegen dir vnd schlach In auff dy selbigen seyten auff den kopff mit der langen schneiden Indes mach was dir eben ist / das stuck gat auch zu beyden seyten |
[153r.3] Winck linck Im treffen Item das soltu also Verst on. steet er gegen dir Im luginsland. so haw von deinner Rechten Achsel gerad oben ein zu Im einen oberhaw mit der lanngen schneid oder mit gestracktem arm. zu seinner linncken seitten Nun merckh Im haw. dieweil der haw nach dem kopff geet. so wind gegen seinnem duseggen das die kurtz schneid vnden stee. vnnd verwend den schlag mit svnnder In dem schlag lasz den ort lincken vnnd ge vnnden durch mit dem duseggen. auf dein lincken seitten. vnd schlag In mit der kurtzen schneid Indes mach was dir eben ist. das stuckh [153v.1] geet auch zu baiden seitten. |
||||||
[113] |
Then, as you strike with the long edge to his right side to his head, “simultaneously” wind your Messer towards yourself and go high with the arm and thrust at his face to his right side. “Simultaneously” wind again towards him to his right side and thrust to his right side again to his face. |
[57r.2] ein anders Item so du haulbest mit der langen schniden vff syner rechten syten noch seÿnem hauptt Indes wind gegen dir din messer vnd far vff mit dem arm vnd stich im zu dem gesichtt syner rechten syten Indes wind wider gegen Im vff syn rechten seyten vnd stich Im vff syn rechte syten wider zu dem gesicht ~ |
[22v.2] Item so dw hawest mit der langen schneyden auff seyner rechten seyttenn nach seynem hawbtt yndeß wyndt gegen dir deyn messer und far auff mit dem armen und stich ym zw dem gesicht seyner rechten seytten yndeß wyndt wyder gegen ym auff deyn rechten seytten und stich ym auff seyner rechten seytten wyder zw dem gesicht etc Sequitur textus |
[31v] Item so du hawest mit der langen schneyden auff seyner rechten seytten nach seynem haubt Indes windt gegen dir dein messer vnd var auff mit dem arme vnd stich Im zu dem gesicht seyner rechten seytten Indes windt wider gegen Im auff sein rechte seytten vnd stich auff seyner rechten seytten wider zu dem gesicht etc |
[98v.13] Item so du hewest mit der langen schneiden auff s. r. s. noch saynem kopff Indes wind gegen dir dein messer vnd far auff mit dem arm vnd stich Im zu dem gesicht s. r. s. Indes wind wider gegen Im auff dein r. s vnd stich Im auff s. r. s zu dem gesicht |
[153v.2] vnnd so du hawest Mit der lanngen schneidin zu seinner rechten seitten nach seinnem haupt. so wind dein duseggen gegen dir vnnd far auf mit dem arm vnnd stich Im zu dem gesicht seinner rechten seitten. Indes winnd wider auf sein rechten seitten. vnnd stich Im aber zu seinnem gesicht. |
||||||
[114] |
If you want to deceive the masters Here the master speaks about the element that is called the Wincker and speaks: If you want… the masters, etc. You should understand it this way that this element goes rightfully to anyone who displaces in a crooked manner or wrongly, then this element has its priority.[22] |
[57r.3] Wiltu die meinster pleulben Hie saget der meinster von dem stueck dz do heÿssett [57v.1] der wincker vnd spricht wiltu die meinster plulben daß soltu also verstan dz daß stuck recht zu gett vff eym ÿttlichem er versetz kruem oder schlechtt So hat dz stuck synen fur ganck vnd were dem stuck rechtt kan thun der schlecht gar viell luede ~~ |
[22v.3] Wiltu dy meyster plewen Hye sagt der meyster von dem stuck daß do heysset der wincker und spricht wiltu dy meyster etc das soltu alzo verstan daß daß stuck recht zw gett auff eynem ytlichen er versecz krump oder schlecht so hatt daß stuck seynen fuerganck und wer dem stuck rechtt kann thun der schlecht gar vil lewt |
[32r.1] Wiltu dy meister plewen Hie sagt der meyster von dem stuck das da heyst der wincker vnd spricht wiltu dy meystr etc Das soltu alzo verstan das daß stuck recht zu get auff eynem ytzlichen er versetz krump oder schlecht So hatt das stuck seinen furganck |
[98v.14] Wiltu die meyster plewen des
winckers soltu dich frewen was kemp krump
oder schlecht das ist dem wincker alles recht Hie sagt der meyster von dem stuck das do heyset der wincker vnd spricht wiltu dy meister etc das saltu also versten das • das stuck recht zů get auff ein yeglichen er versetzt krump oder schlecht so hat das stuck seynen fur gang vnd wer dein stuck recht kan thun der schlecht gar vil leuwt |
[153v.3] Wiltu die Maister plewen Item das soltu also Verstan. das des stuckh recht zu geet. auf ain Jetlichen. er versetzt krum oder schlecht. so hat das stuck seinnen vorganng. vnnd wer dem stuckh recht kann thun der schlecht gar vil lewt. |
||||||
[115] |
Do to him this way: if he displaces in a crooked manner, strike from your right shoulder from above a free upper stroke to his Messer and as you strike, turn your Messer before one sparks on the other, and go high with the arm and strike the short edge to his head. |
[57v.2] Item thün Im also versetzt er kruem So haulb von oben s von dyner rechten achsell oben vff sin messer eyn fryehen ober haulb vnd im haulb verwind din messer E dz eyns an dz ander glickett vnd far mit dem arm hoch vff vnd schlag Im die kuertze schnid vff syn kopff |
[23r.2] und thw ym alzo verseczt er krump so haw von deyner rechten achsel oben auff seyn messer eyn freyen oberhaw und ym haw so verbendt deyn messer dan dw daß seyn ruerest und far mit dem armen hoch auff und schlag ym dy kurcz schneyd uff seyn kopff |
[32r.2] Thu Im alzo versetzt er krump so haw von deyner rechten achsel oben auff sein messer eynen freyen oberhaw vnd Im haw So verbendt dein messer Ee den das eyns an das ander klitzet vnd var mit dem arme hoch auff vnd schlag Im dy kurtz schneyd auff sein kopff etc |
[98v.15] Item thůn also ver setzt er krump So haw oben von deiner r. achsel oben auff sein mesß Ee dan das ein an das ander glitztt vnd vfar mit dem arm hach auff vnd schlach Im haw die kurtz schneid auff sein kopff |
[153v.4] vnnd das stuckh mach also. versetzt er krumb so haw vonn oben deiner rechten Achsel oben auf sein duseggen. ain freyen oberhaw. vnnd Im haw verwennd deinnen duseggen. Ee das ains an das annder kumpt. vnd far mit dem Arm hoch auf vnnd schlag Im dein kurtzen schneidin auf den kopf. |
||||||
[116] |
Then, if you have not hit him, as it is already stated, with the stroke, go with the point against your left side and thrust at his throat or chest, or take away on the Messer, as you know it well. |
[57v.3] hastu In nit getroffen mit dem haulb So far mit dem ortt vff dyn lincke syten vnd stich im zu der kellen oder bruest oder nÿm ab vff dem messer als du dan woll weÿst ~ |
[23r.3] ¶ hast yn nicht getroffen mit dem haw so far mit dem ortt [23v.1] auff deyn lincke seytten und stich ym czw der kelen oder prust oder nymb ab auff dem messer etc |
[32v] Item hastu In nicht getroffen als yetzund gesagt ist mit dem haw So far mit dem ortt gegen deiner lincken seytten vnd stich Im zu der kelen oder prust oder nymb ab auff dein messer als du woll weist etc |
[98v.16] hast In nit getroffen mit dem haw So far mit dem ort auff auf die lincken S. vnd stich Im zů der kelen oder brust oder nim ab auff dem messer alß du wol weyst |
[153v.5] hastu In nit getroffen mit dem haw. so far mit dem ort auf dein [154r.1] linncke seitten. vnnd stich Im zu der Kelen oder prust. oder Nimb ab auf dem Duseggen. als du dann wol bericht bist. |
||||||
[117] |
You should praise the four guards It is to be known that the master has stated and explained the six strokes or chapters. Now he speaks here about the seventh chapter and main element. And first about the four stances in the Messer, which one can consider and defend himself from them with the rightful art. |
[57v.4] Vier leger soltu ab senden [58r.1] So nü der meinster gesagt vnd vß gerichtt hatt die sechs haulb Nu sagett er von andern hauptt stuck vnd zu dem ersten saget er von den viern legern im messer do von halten mag vnd sich mit rechter kuenst daruß weren ~ |
[23v.2] Vyer leger solt absynnen So nw der meyster gesagt und außgericht hatt dy sechß hew nw sagt er von den andren hawbt stuck und czwm ersten wirt gesagt von den vyer legeren ym messer da von man halten solt und sich mit rechter kunst dar auß sol weren |
[33r.1] Vier leger soltu mynnen Saend[23] So nẅ der meyster gesagt hat vnd außgericht dy Sechs hew oder capitel nẅ sagt er hie von dem sibenden capitel vnd haubtstuck vnd zu dem ersten von den vier legern im messer Da von man halten mag vnd sich mit recht kunst dar auß weren |
[98v.17] Vier
leger soltu absinen Im mesß vechten wiltu gewinen
pastey vnd luginsland Stier vnd eber sig dir
beckand So mir der meyster gesagt vnd auß gericht hat die sechst hew nün sagt der meister aber von der den andern hawpt stucken zu dem ersten sagt er von vier legeren Im mesß do von man halten mag vnd sich mit rechter kunst dar auß weren |
[154r.2] Die vier Leger Vier leger soltu absynnen Item so Nun die sechs hew Imm Duseggen ausz gelegt vnnd erklert worden seinnd. so volgen Nun hernach die anndern Siben zehen hauptstuck. vnnd erstlich vonn der vier legern Inn dem duseggen. darausz man sich mit rechter Kunnst wehren kann. |
||||||
[118] |
Then, the first stance or guard is called the Bastei. Assume it this way: put your left[24] foot forwards and hold your Messer with the stretched arm in front of you with the point on the ground, so that the short edge is above. |
[58r.2] der erst leger Item dz erst leger oder hutt heÿssett die pastein Schick dich in die also Setz dynen lincken fus vor vnd halt din messer mit gestracktem arm vor dir mit ortt vff der erden dz die kurtz schnid oder stümpff schnid oben stee ~ |
[23v.3] Item daß erst leger oder hut dy heyst dy pasteyn und schick dich yn dy also secz deynen lincken fuß fuer und halt [24r.1] deyn messer mit gestracktem armen vor dir mit dem ort uff der erden daß dy kurcz schneyd oder stumpff oben stee etc |
[33r.2] Item Das erst leger oder hüt heysset dy pastey Schick dich in dy alzo Setz deinen rechten füß vor vnd halt dein messer mit gestracktem arme vor dir mit dem ortt auff der erden das dy kurtz schneyd oben stee etc |
[98v.18] Item das erst leger oder hůt heysset dy pasteÿ schick dich also setz deinen [rechten fuß vor vnd halt dein messer mit gestracktem][21] [99r.1] arm vor dir mit dem spitz auff der erden das dye kurtz schneid oder stumpf schnid oben stee |
[154v.1] Die Pastey Item das erst Leger oder hut haist die Pastey darein schickh dich also. setz deinnen linncken fuosz fur vnnd halt deinnen Duseggen. mit gestracktem Arm vor dir mit dem ort auf der erden. die kurtz schneid oben. |
||||||
[119] |
Then, the other guard or stance is the Luginsland—assume it this way: put your left[25] foot forwards and hold your Messer with the stretched arm high in in front of your head and the long edge or the sharp edge stands against the man. |
[58r.3] der ander Item die ander hutt oder leger heÿst der lugginßlant darin schick dich also Setz Dinen Lincken fus vor vnd halt din messer mit vff gestrecktem arm hoch fur din hauptt vnd die lang oder kurtz scharff schnid fur vnd ste also inder hut lueginßlantt ~ |
[24r.2] Item dy ander hut oder leger heyst der luginsland dar eyn schick dich alzo secz deynen lincken fuß fuer und hallt deyn messer mit auff geracktem armen hoch fuer deyn hawbt und dy lang schneyd oder dy scharpff schneyd fur und stee alzo ynn der hüt etc |
[33v.1] Item dy ander hut oder leger ist der luginslandt schick dich dar ein alzo setz deynen rechten fuß für vnd halt dein messer mit aufgerecktem arme hoch fur dein haubt vnd dy lang schneid oder scharpff schneid gegen dem man stet als oben gemalt stett da du ein handt gemalt sichst |
[99r.2] Item die ander hůt oder leger heyst der lüginsland dar In sick schick dich also setz dein lincken fuß fur vnd halt dein mesß mit auff gerecktem arm hoch fur dem kopff hawpt die lang oder scharff schnid fur vnd stee also In der hut |
[154v.2] Der luginslannd Item die annder hüt oder leger haist der luginslannd darein schickh dich also. setz deinnen linncken fuosz fur. vnnd hallt dein duseggen mit auf gerecktem arm hoch fur. dein haupt. das die lang schneid fur gee. stee also Inn der hut. |
||||||
[122] The fourth guard is called the Eber. Assume it this way: hold your Messer at the right leg on the right side with the hilt at the hip, so that the blunt edge is above and the point is forwards against the face of the man. |
Then, assume the Eber this way: put your left foot forwards and hold your Messer at the right leg on the right side with the hilt at the hip, so that the blunt edge is above and the point is forwards against the face of the man. |
[58v.1] Item die vier hut heyßt der eber in die schick dich also Setz din lincken fus vor vnd halt din messer bÿ dem rechten beyn vff der rechten syten mit dem gehultz nebent der huefft dz die stümpff schnid oben ste vnd der ortt for sich vff ste dem man zu dem gesichtt ~ |
[24r.4] Item dy vyerdt hut hayst der eber yn dy schick dich alzo halt deyn [24v.1] messer bey dem rechten payn auff der rechten seytten mit dem gehultz neben der hüff daß dy stumpff schneydt oben stee und der ortt fur sich auff stee dem man gegen dem gesicht etc |
[33v.2] Item In den Eberer Schick dich alzo setz deinen lincken füß fur vnd halt dein messer bey dem rechten payn auff der rechten seytten mit dem gehultz neben der hüff das dy stumpff schneid oben stee vnd der ortt fursich auff stee dem man zu dem gesicht |
[99r.4] Item die vierd hůt heist der Eber dar In schick dich also setz dein lincken fuß fur / vnd halt dein messer bey dem fůß auf der rechten seyten mit dem gehiltz das dy stumpf schnid oben stee vnd der ort für sich auff stee dem man zů dem gesicht |
[155r.2] Der Eber Item die viert hut oder Leger haist der Eber darein schickh dich also. setz deinnen lincken fuosz fur vnd halt dein duseggen bey dem rechten pain auf der rechten seitten. mit dem gehultz neben der hufft. das die kurtz schneid oben stee. vnnd der Ort fursich auf stee dem Mann zu dem gesicht. |
||||||
[123] Then, you should also perform the guard from the left side with the Messer. And assume the guard this way: hold your Messer at your left side at the left hip, so that the long edge is turned upwards and the point stands upwards against the face of the man. The text follows. |
Then, you should also perform the Eber from the left side with the Messer. And assume the guard this way: hold your Messer at your left side at the hip, so that the long edge is turned upwards and the hilt is a bit lowered towards the ground and the point stands upwards against the face of the man, as it is depicted below. |
[58v.2] Item du magst die hutt vß der lincken siten auch triben mit dem messer Vnd schick dich also halt din messer nebent diner lincken syten vnttersich vff nebend diner lincken huefft dz die lang schnid oben gewind sy vnd der ortt vbersich ste dem man zu den aügen oder gesichtt ~ |
[24v.2] Item dw magst dy hut ausß der lincken seytten auch treyben mit dem messer und schick dich yn dye alzo haltt deyn messer neben deyner lincken seytten untersich auff dy lincken huff daß dy lang schneyd oben gewendt sey und der ort ubersich stee dem man zw dem gesicht etc Sequitur textus |
[33v.3] Item du solt den Eber treyben auch von der lincken seytten mit dem messer vnd schick dich In dy hutt alzo halt dein messer neben deiner lincken seytten neben bey der huff das dy lang schneyd oben gewendt sey vnd das gehultz sey eyn benigß gesenckt gegen der erden vnd der ort vbersich stee dem man zu dem gesicht wie vnden gemalt stet etc |
[99r.5] Item du magst die hut auß der lincken seyten auch treyben mit dem mesß vnd schick dich also halt dein mesß neben deiner lincken seyten vnder sich auff dy neben deiner lincken huft das dy lang schnid oben wend vnd der ort vber sich stee dem man zu dem gesicht |
[155r.3] so magstu die hew von der lincken seitten auch treiben. vnnd schickh dich allso darein hallt dein duseggen neben deinner linncken seitten vntersich neben deinnen lincken hufft das die lanng schneid oben gewennt sey. vnd der Ort vnndersich stee. dem mann zu dem gesicht. |
||||||
[120] Then, assume the Stier this way: put your left foot forwards and hold your Messer on the left side with the hilt in front of your head, so that the short edge is against you and the point against the face. |
The fourth guard is called the Stier. Assume it this way: stand with your left foot forwards and hold your Messer on the right side with the hilt in front of your head, so that the short edge is against you and the point against the face. |
[58r.4] Im stier ~ Item Inden stÿer schick dich also Ste mitt dinem lincken fus fur vnd halt din messer zu der lincken syten mit dem gehultz fur dz hauptt dz die kuertz schnid gegen dir stee vnd halt im den ortt gegen dem gesicht ~ |
[24r.3] Item yn den stiren schick dich alzo stee mit deynem lincken fuß fuer und hallt deyn messer zw der lyncken seytten mit dem gehulcz fur daß hawbt daß dy kurcz schneyd gegen dir stee und hallt ym den ortt alzo zw dem gesicht etc |
[34r.1] Die vierdt hut heysset der Stir Schick dich In den also stee mit deynem lincken fuß fur vnd halt deyn messer zu der lincken seytten mit dem gehultz fur das haubt das dy kurtz schneyd gegen dir stee vnd der ortt zu dem gesicht etc |
[99r.3] Item In den stieren schick dich also In der hut stee mit deinem lincken fuß fur vnd halt dein messer zu der lincken seyten mit dem gehyltz fur das hewpt das dy kurtz schneyd gegen dir stee vnd halt Im den ort gegen dem gesicht |
[155r.1] Der Stier Item die drit hüt oder leger haist Der Stier darein schickh dich allso. setz deinnen linncken fuosz fur. vnnd halt dein duseggen zu deinner linncken seitten mit dem gehultz fur dein haupt. das dir kurtz schneid gegen dir stee. vnnd halt den Ort zu dem gesicht |
||||||
[121] |
Then, assume the Stier on the other side side as it is depicted below. |
[34r.2] Item In den Stiren auff der andren seytten Schick dich wie vnden gemalt stet etc |
||||||||||
[124] You should love the four displacements, Here the master speaks about the eighth chapter or element. These are the four displacements that break the four guards. |
You should refrain from the four displacements Here the master speaks about the eighth chapter or element. These are the four displacements that break the four guards. |
[58v.3] Die versetzen soltu mynnen Hie saget der meinster von dem achsten stueck dz sintt die vier versetzen die selbigen die brechen [59r.1] die fuer hutt |
[24v.3] vÿer verseczen soltü mynnen [25r.1] Hye sagt der meyster von dem achten stuck daß syn dy vyer verseczen dy selber prechen dy vyer huet |
[34v.1] Vier versetzen soltu ab synnen Hie sagt der meyster von dem achten capitel oder stuck Das seyn dye vier versetzen dy selben prechen dy vier hüt Nu soltu wissen das dy vier versetzen synd die vier hütt Das sein dy vier versetzen dy selben prechen dy vier hutt |
[99r.6] Die versetzen soltu
nemen / wiltu die leger bezwingen vor versetzen
dich hat huet versetzen dick den man muwet Hie sagt der meyster von den achten stucke das da sin[d] die vier versetzen die selben brech die vier leger / |
[155v.1] Die vier versetzen Wenden soltü die versetzen Item das sennd die Vier versetzen dieselben prechen die vier hut. |
||||||
[125] |
Now you should know that there are four displacements and know that no displacement against the four guards belongs here because the four strokes which break the four guards. |
[59r.2] Nu soltu wissen wz die vier versetzüng syntt Vnd wiß dz keyn versetzen wider nichtt wider die vier hut gehortt dan die vier haulb brechen die vier hutt ~ |
[25r.2] ¶ Nw soltu wissen waß dy vyer verseczen syn und wyssen daß kayn verseczen nicht wyder dy vyer huet gehort den dy vyer hew prechen dy vyer hüt |
[34v.2] Nu soltu wissen bas dy vier versetzen sindt vnd wiß das keyn versetzen wider dy vier hutt gehortt den dy vier hew dy prechen dy vier hutt |
[99r.7] Nun soltu wissen / was die vier versetzen sind vnd wiß das keyn versetzen nich wider die vier hůt gehore dan die vier hew brechen die wier hůtt |
[155v.2] Nun soltu wissen. das kain versetzen mit nichten. wider die vier hutten gehoren dann die vier haw prechen die vier hutten. |
||||||
[126] |
Then, the first stroke is the Wecker. It breaks the guard from the Stier. |
[59r.3] Item der erst haulb ist der wecker der bricht die hut vß dem stÿer ~ |
[25r.3] Item daß erst daß ist der wecker der pricht dy hut auß dem stiren etc |
[34v.3] Item der erst haw ist der wecker Der pricht dy hut auß dem Stiren |
[99r.8] Item der erst hew ist der wecker der bricht die hůt auß dem stieren |
[156r.1] Item der erst haw ist der Weckerhaw der pricht die hutt ausz dem Stier |
||||||
[127] |
The other is the Entrüsthau. It breaks the guard from the Luginsland. |
[59r.4] Item der ander haulb ist der entruest haulb brichtt die hut luginßlant ~ |
[25r.4] Item daß ander ist der entrusthaw der pricht dy hut vom luginslandt |
[34v.4] Der ander ist der entrußthaw der pricht dy hut vom luginslandt |
[99r.9] Item der ander hew ist der entrist hew der bricht die hůt luginsland |
[156r.2] Der annder haw Ist der Entrusthaw. der pricht dir hut luginslannd. |
||||||
[128] |
Then, the third is called the Zwinger. It breaks the guard from the Eber. |
[59r.5] Item der dritt ist der zwinger oder schierler der brichtt die hut vß dem Eber ~ |
[25r.5] Item der drit hayst der czwynger der pricht dy hut auß dem eber |
[34v.5] Item der dritt heysset der zwinger der pricht dy hut auß dem eber |
[99r.10] Item der drit hew ist der zwinger der bricht die hůt auß dem eber |
[156r.3] Der drit haw Ist der Zwinnger der pricht die hutt ausz dem Eber |
||||||
[129] Then, the fourth is the Geferhau. It breaks the guard that is called the Bastei. How you should perform the elements, you have been taught to a great degree before, as the strokes are dealt with, and how one should break the four guards with them. |
Then, the fourth is the Geferhau. It breaks the guard that is called the Bastei. How you should perform the elements, you have been taught to a great degree before, as the strokes are dealt with, and how one should break the four guards. |
[59r.6] Item der vierd ist der geferre haulb oder scheÿttler der bricht die hut der pastein vnd wie du die stueck triben solt dz biestu woll vntterichtt da die haulb gezellt werden vnd wie man die vier hut brechen soll ~ |
[25r.6] Item daß vyerd ist der geferhaw der pricht dy hut dy do hayst pasteyn wye dw dy stuck treyben solt daß pistu zw guter maß wol unterricht da forne da man dy hew erczelet und wye man dy vyer hut da mit prechen söl |
[34v.6] Item der vierd ist der geferhaw der pricht dy hut dy da heyst dy pastey wie du dye stuck treyben solt das pistu zu gutter maß woll unterricht Da vorne da dy haw erzelt werden vnd wye man dy vier hutt prechen soll |
[99r.11] Item der vierd hew ist der gefer hew der bricht die hůt die do heysset die pastey wie du die stuck trieben solt das bistu zů gutter mosse wol vnder richt do vornen da dye hewe erzelt werden vnd wie man die vier hůtt brechen soll |
[156r.4] Der viert haw Ist der Gefererhaw der pricht die hut der Pastey vnnd wie du die stuckh. treiben solt. das bistu wol vnnderricht worden. davon die hew gezelt werden. vnnd wie man die vier huten prechen soll. |
||||||
[130] |
Then, the text also speaks: Mind yourself not to displace. This to say that you should not displace a lot, if you do not want to be ashamed and beaten otherwise, as you have been taught before. |
[59r.7] Item sprichtt auch der textt vor versetzen hutt dich dz ist also viell geredt dz du nit viel versetzen solt ~ |
[25r.7] Item eß spricht der text von verseczen [25v.1] dich huet etc Daß ist alz vil geredt daß dw nicht vil verseczen solt wil dw anderß nicht geschendt und geschlagen werden alz dw denn vor unterrichtt pist etc |
[34v.7] Item Es spricht auch der text vor versetzen hutt dich Das ist als vill geredt das du nicht vill versetzen sollt willtu anders nicht geschendt vnd geschlagen werden als du den vor unterricht pist etc |
[99r.12] Item spricht auch der dg[?]t vor versetzen hut dich daß ist also vil goed das du nit vil versetzen solt wiltu anderß nit verschmecht vnd geschlagen werden alß du vor vnder richt bist |
[156r.5] auch spricht der text vor versetzen hiet. dich. das Ist so vil geredt. das du nit solt versetzen |
||||||
[131] |
If the Eber and the Stier intend to defend themselves Here the master teaches a breaking against the Eber and the Stier and speaks: If...intend, etc. You should understand it this way: if he stands in the Eber on his left side and wants to thrust at you to your right side, go with long stretched point “simultaneously” to his face, and fall with the rear foot well outside, so that you hit him at his face. And you should know that the breakings with the long point are better than these announced above from the strokes, as the strokes cannot protect themselves on their own against the long point and they are broken with it. |
[35r] Vermeynt sich Eber stir zu weren Hie lertt der meyster pruch wider den eber vnd den stiren vnd spricht vermeynt sich etc Das soltu alzo verstan stet er Im eber auff seiner lincken seitten vnd will dir stechen auff dein rechtn seytten So far mit langen gestracktem ortt Im Indes zu seym gesicht vnd vall mit dem hindresten fuß woll hinauß So trifstu In in das antlitz vnd du solt wissen das die pruch mit dem langen ortt pesser seyn denne dy vor gemelten auß den hewen worvmb dy hew kunnen sich selbst vor dem langen ortt nich bebaren sy werden da mit geprochen etc |
||||||||||
[132] |
Then, if he stands in the Eber on his right side and wants to thrust at you from the guard to your left side, put the Messer on the ground so that the thumb is above on the flat and the short edge is against the man, and go with the ready long point to his face, as it is depicted below. |
[35v] Item Stet er In dem Eber auff seyner rechten seytten vnd will dir stechen auß der hut zu deyner lincken seytten So leg dich mit deynem messer auff dy erden das der dauwm oben stee auff der flech vnd dy kurtz schneyd gegen dem man vnd far Im mit geradem langen ortt zu dem gesicht wie vnden gemalt stet etc |
||||||||||
[133] |
Then, if he stands in the Stier on his right side and wants to thrust at you from the same guard, “simultaneously” go readily high and thrust at his face with the long point, as it is depicted below. |
[36r] Item stet er in dem Stiren auff seyner rechten seytten vnd will dir zu stechen auß der selbigen hut Indes var aber gerad auff vnd stich Im zu dem gesicht mit dem langen ort wie vnden gemalt stet etc |
||||||||||
[134] |
Then, if he stands in the Stier on his left side and wants to thrust at you as before, go high with the stretched point and thrust at his face or throat or chest, as it is depicted below. And with these breakings you break the four guards always in the best way. |
[36v] Item Stet Er In dem Stiren auff seyner lincken seytten vnd will dir alzo zu stechen wie vor So far auff mit gestracktem ortt vnd stich Im zu seym gesicht oder kelen oder prust wie vnden gemalt stet vnd mit disen pruchen prichstu dy vier hut am aller pasten etc |
||||||||||
[135] |
You should set on Here the master speaks about the settings on and the setting on is a good honest element and it goes close to the four peaks. And it should be performed as soon as you want to finish with the Messer, and perform the settings on this way: assume the guard of the Bastei, and if he wants to strike or thrust from above from his right side, come “before” and shoot the long point to his next opening of his left or right side. |
[59r.8] Du solt an setzen ~ Hie saget er von an setzen vnd dz ist die ansetzen ist ein gut gantz erntstlich stuck vnd gat nahentt die vier zÿnnen vnd gehorett ze triben als bald du endt willt geben mit dem messer vnd trib die an setzen also leg dich in die huett des stÿer oder des ebers wil er dan oben In haulben oder stechen von syner rechten syten so küm vor vnd schuß im den langen ortt In zu der nesten ploß siener lincken syten vnd wart allbegen dz du im an setzest ~ |
[25v.2] dw sölt an seczen Hye sagt der meyster von dem [26] stuck alz von den anseczen und daß ist eyn gucz ernestlichß stuck und gat nohent den vyer czynnen und gehort zw treyben alz pald dw end wild geben mit dem messer und treyb dy anseczen alzo leg dich yn dy hut deß stiren oder deß eberß will er [26r.1] den oben eyn hawen oder stechen von seyner rechten seytten so kum vor und schewß ym den langen ort eyn zw der negsten plöß seyner lincken seytten und wart albeg daß dw ym an seczest etc |
[37r] Dw solt an setzen Hie sagtt der meyster von den an setzen vnd das ansetzen ist ein gutz ernnstlichs stuck vnd gett nohent zu den vier zynnen vnd gehortt zu treyben als pald du endt wilt geben mit dem messer vnd treyb dy ansetzen alzo leg dich In dy hut pastey will er den oben ein hawen oder stechen von seyner rechten seytten [Sic] Sokum vor vnd scheuß Im den langen ortt zu der negsten ploß seyner lincken oder rechten seytten etc |
[99r.13] Du solt an setzen an vier
end In letzen er kum oben oder vnden ort
gerad ist Im verbunden Hie sagt der meyster von dem ansetzen vnd das ansetzen ist ein gantz ernstlich stuck vnd gar nochent der vier czinnen vnd gehert zů treiben als bald du end wilt geben mit dem mesß vnd trib dy ansetzen also leg dich In die hůt des stierns oder des ebers wil er dan oben In hawen oder stechen von s. r. s. so kum vor vnd schuß Im den langen ort Im zu der nesten pleß s. l. s. vnd wart alwegen das du Im ansetzest |
[156v.1] Du sollt ansetzen Item das ansetzen ist ain gut Vnnd ernstluch stuckh. vnnd geet nachent den vier zinnen. vnnd gehort zu treiben alszbald du ennd wildt geben mit dem Duseggen. vnnd treib die ansetzen also. leg dich Inn die hut des Stiers oder Ebers. will er dann einhawen oder. steest vonn seinner Rechten seitten. so kum vor. vnnd scheusz Im den lanngen ort ein zu der nechsten plosse seiner linncken seitten. vnnd wart alweg das du Im ansetzest. |
||||||
[136] |
Then, if he strikes from above from his left side, come “before” with the displacement and shoot the long point long to his right side to the next opening. |
[59v.2] Item hautt er dir von oben In von sÿner lincken syten So küm vor mit diner versatzung vnd schuß im den ortt lang in zu syner rechten syten ~ |
[26r.2] Item oder hawt er dir von oben eyn von seyner lincken seytten so kum vor mit der versaczung und schewß ym den ort lanck eyn zw seyner rechten seytten zw der negsten plöß |
[37v] Item haut er von oben eyn seyner lincken seytten Sokum vor mit der versatzung vnd scheuß Im den ortt lanck eyn zu seyner rechten seytten zu der negsten plöß etc |
[99r.14] Item hawt er von oben In von s. l. s. So kum vor mit der versetzung vnd schuß Im den ort lang... |
[156v.2] Item hawt er dann von oben ein Vonn seinner linncken seitten. so kum vor mit deiner versatzunng vnd scheusz Im dem lanngen Ort ein zu seiner rechten seitten. |
||||||
[137] |
Then, if he strikes at you from below from his right side, shoot the point long to him to the next opening of his left side. |
[59v.3] Item hautt er dir von vntten vff von syner rechten syten So schuß im den ortt lang eyn zu der nesten ploß syner lincken seytten ~ |
[26r.3] Item hawt er dir von unten auff von seyner rechten seytten so schewß ym den ortt lanck eyn zw der negsten plöß seyner lincken seytten etc |
[38r] Item haut er dir denn von vnden auff seyn rechte seytten so scheuß Im den ortt linck eyn zu der negsten ploß seyner lincken seytten etc |
[99r.15] ...In zu der mesten [!] pleß s. l. s. |
|||||||
[138] |
Then, or if he strikes to you from below from his left side, shoot the point long to him to the lower opening of his right side. If he becomes aware of the shoot and displaces, remain with the Messer on his one, and work skillfully to the next opening. |
[60r.1] Item oder haulbt er zu von vntten vff von syner lincken siten So schuß im den ortt lang eyn zu der vntter ploß siner rechten syten wurtt er deß schuß geware vnd versetzt so plÿb mit dem messer vff seÿnem vnd arbeÿtt behendeglich zu der nesten ploß ~ |
[26r.4] Item oder hawt er dir zw von unden auff von seyner lincken seytten so scheuß den ortt lanck eyn zw der unteren plöß seyner rechten seytten wirt er deß schuß gebar und verseczt so pleyb mit dem messer auff seynem und arbayt pehentlich zw der negsten plöß etc |
[38v.1] Item oder hawt er dir zu von vnden auff von seyner lincken seytten So scheuß Im den ortt lanck ein zu der vndren ploß seyner rechten seytten wirtt er deß schuß gewar vnd versetzt So pleyb mit dem messer auff seynem vnd erbeyt behentlich zu der negsten ploß etc |
[99r.16] Item hewt er von vnden auf von s. l. s. so schuß Im den langen ort zů der vndern ples s. r. s. wirt er des schus gewar vnd versetzt So pleyb mit dem messer auf seinem meser vnd arbeyt behend klichen zů der nesten plesin |
[157r.1] Item oder hawt er dir Von vnden auf von seinner lincken seitten so scheusz Im den lanngen ort ein zu der vnndern plosse seinner rechten seitten. wirt er des schusz gewar vnnd versetzt. so bleib mit dem Duseggen. auf dem seinnen vnnd arbait behenndigclichen zu der nechsten plossen. |
||||||
[139] |
Then, you should also know that as soon as you come together in the Zufechten, and as soon as he only raises his Messer and wants to strike around, you should fall in the point and thrust at the next opening. |
[60r.2] Item du solt auch wissen als bald als ir zu samet kümpt im zuvechten vnd als bald er sin messer nuet hebt vnd vmb schlagen will also bald soltu in den ortt fallen vnd stech nach der nesten ploß |
[26r.5] Item dw solt auch daß wyssen alz pald [26v.1] Ir zwsammen kumbt und alz pald dy er seyn messer newer hebtt und umb schlagen will alz pald soltu yn den ortt fallen und stechen nach der negsten ploß |
[38v.2] Item du solt auch wissen als pald Ir zu sammen kumbt Im zuuechten vnd als pald er seyn messer newer hebt vnd vmbschlagen will alzo pald soltu In den ortt fallen vnd stechen nach der negsten ploß |
[99r.17] Item du solt auch wissen als bald Ir zu samen kumpt Im zuüechten vnd als bald er sein messer vir hept vnd vmb schlachen wil also bald soltu In den ort fallen vnd stehen [!] noch der nesten pleß |
[157r.2] Item du solt wissen Allsbald Ir zusammen kumpt Im zufechten. vnnd alsbald er sein duseggen erhept. vnnd vmb schlagen will alsbald soltu Im den ort fallen. vnnd stechen nach der nechsten plosze / |
||||||
[140] |
If he does not want to go with the Messer, you should go yourself with your Messer. And as often as you end a stroke, fall “simultaneously” in the point. If you can perform the settings on properly, he is hardly able to go without injury from you. The text follows. |
[60r.3] wil er aber mit dem messer nicht geen vnd als vfft du ein schlag endest als vfft fall indeß in den ortt kanstu die absetzen recht triben So mag er sich hartt regen oder wegen er müß dir eyn ruer loßen |
[26v.2] ¶ will er aber nicht mit dem messer gen So soltu selbß gen mit deynem messer und alz offt dw eyn schlag endest alz offt fall yndeß yn den ortt kanstu dy anseczen rechte treyben so kann er sich hart regen oder wegen er mueß dir eyn fedren lassen etc |
[38v.3] will er aber mit dem messer nicht gan so soltu selbst mit deynem messer gen vnd als offt du eyn schlag endest als offt vall Indes In den ortt kanstu dy ansetzen recht treyben so kann er an schaden hartt von dir kummen sequir textus; |
[99r.18] wil er aber mit dem mesß nit geen vnd als oft du ein schlag endest also oft falle In den ort vnd kanstu dy absetzen So mag er sich hart rechen oder wegen er muß dir ein růr lassen |
[157r.3] will er aber mit dem duseggen nit gan. so merckh als offt du ain schlag endest. also offt fell Indes den ort kanstu die ansetzen recht treiben so mag er sich hart regen oder wegen. er muosz dir ain Fur lassen |
||||||
[141] Learn to draw after Here the master speaks about the tenth and element, that is the drawing after, which are numerous and diversified, and should be practiced with great care against the “free fighters,” who fight with long free strokes and do not know the rightful art of the Messer and against those who cannot do much in the rightful art but still believe that they know a lot, although they know nothing. And against those who strike to the stomach and grab at the openings for the sake of being praised. The drawing after should also be done against those who withdraw from the man or deliver strokes that miss. |
Learn to draw after Here the master speaks about the ninth chapter and element, that is the drawing after. They are numerous and diversified, and should be practiced with great care against the “free fighters,” who fight with long free strokes and do not know the rightful art of the Messer. And they deliver strokes that miss and strike to the breakings and to the sides and who withdraw from the man. |
[60r.4] Lere noch reisen [60v.1] Hie saget der meinster von dem Nuende stueck dz ist dz noch reÿssen der ist viel vnd mangeleÿ vnd gehortt zue triben mit grosser fuersichtikeÿtt gegen den frÿen vechtern die vß frÿhen langen haulben fechtnt vnd sünst von künst deß messers nicht halten Vnd zu den die nicht viel künnen in rechter künst vnd sie doch meÿnen sie wissen vil wie woll sie nicht wissen vnd wider die die dem man noch dem buch haulben oder schlagen vnd griffen nach den plasen von ruemes wegen auch gehoret die noch ryesen vff die die vor dem man sich abzehent mit dem messer oder sich vorhaulben |
[26v.3] lEr nach raysen Hÿe sagt der meyster vonn dem zehenten newden stuck daß ist daß nach reysen daß ist vil und manigerlay und daß gehortt zw treyben mit grosser fursichtikayt gegen den freyfechteren dy ausß [27r.1] langen freyen hewen fechten und suest von rechter kunst deß messerß nicht halten und zw den dy nicht vill kunnen in rechter kunst und si doch maynen si wyssen will wye wol si nichtz wyssen und wÿder dye dy dem nach nach dem pauch schlagen und greuffen nach den plössen von romeß wegen auch gehoren dy nachraysen auff dye dy sich vor dem man abczyhent oder sich verhawen etc |
[39r.1] Ler nachraysen Hie sagtt der meyster von dem newden capitel vnd stuck das ist das nachrayßen der ist vill vnd manigerlay dy gehōren zu treyben mit grosser fürsichtikeyt gegen den freyuechteren dy auß langen freyen hewen vechten vnd sunst von rechter kunst des messers nicht halten vnd die sich verhawen vnd schlagen nach den peuchen vnd nach den seytten vnd dy sy vor dem man abzyhen |
[99r.19] ler noch reyssen Inw[?] wer dye schnid thů weysen
ort(?) weych ler die machen mit kunsten soltu dich besachen Hie sagt der meyster von dem newende stuck das ist das noch reyssen der ist vil vnd mancherleÿ vnd geheren zu triben mit grosser verschtikeit gegen den freyfechtren die auß langen freygen hewen vechten vnd sünst von kunst des messers die nicht halten vnd zů den die nicht vil kumen In rechter kunst vnd sy doch meynen sy kynnen vil wie wol sy nicht wissen vnd wider dye die dem man noch dem bauch schlagen vnd grieffen noch der plesen von růmß wegen auch geheren die nach reysen auf die die sich vor dem man ab zeychen zechen mit dem messer ader sich verhewen |
[157r.4] Der nachraysen [157v] Zwu schneyden Item der nachraisen Send vil vnd mancherlay vnnd gehoren zutreiben mit grösser fursichtigkait. gegen den freyen Vechtern die ausz lanngen frewen hewen fechten. vnnd sunst von kunst des duseggen nichts hallten vnnd zu den. die nit vil finden. Inn rechter Kunst. vnnd sy doch mainnen sy wissen vil. die weil sy nit wissen. vnnd wider die / die dem Mann nach dem pauch schlagent vnd greiffen nach der plosse von Koms wegen. auch gehoren die nachraisen auf die / die sich vor dem Mann. abziechen mit dem Duseggen. oder sich verhawn. |
||||||
[142] |
And do the drawing after this way: if you come with the Zufechten to the man, put your left foot forwards and stand in the guard of the Luginsland and see what he does against you. If he strikes from above long from his right shoulder to you, make sure he does not reach you with the stroke and notice, in the moment as he lets his Messer go down towards the ground with the stroke, leap with the right foot and strike to him from above to the opening of his right side sooner than he comes high again with the Messer. |
[60v.2] Ein noch reisen Item daß noch rÿßen ist wan du mit dem ze vechten zu dem man kümpst so setz dÿnen lincken fus fur vnd ste in der hut luginßlant vnd sich oben waß er gegen dir tribt oder vichtt hautt er dan oben lang in von syner rechten achßell So wartt dz er dich mit dem haulb mit erlange Nu merck die will er sin messer vnttersich mit dem haulb let gen gegen der erden So spring mit dem rechten fus zu vnd haulb im oben ze der ploesß syner rechten syten [61r.1] E wan er mit dem messer kümptt So ist er gar gnaulb gesclagen ~~ |
[27r.2] Item daß erst stuck auß dem nachraysen wenn dw mit dem zw vechten zw dem man kumbst so secz deynen lincken fuß fuer und stee ynder hut luginsland und sich eben waß er gen dir vicht hawt er dir dann oben lanck eyn von seyner rechten achseln So wart daß er dich nicht mit dem haw erlang und merck dy weyl er seyn messer untersich mit dem haw lest gen gegen der erden so spring mit dem rechten fuß zw und haw ym oben zw der plöß seyner rechten [27v.1] seytten ee wenn er mit dem messer auff kumbt so ist er gar genawen geschlagen etc |
[39r.2] vnd mach das nachraysen alzo wenne du mit dem zuuechten zu dem man kumbst so setz deynen lincken fuß für vnd stee In der hutt luginslandt vnd sich eben was er gegen dir vicht hawt er dir den von oben lanck eyn von seyner rechten achsel so wartt das er dich mit dem haw nicht erlang vnd merck dy weil er seyn messer vntersich mit dem haw lest gen gegen der erden so spring mit dem rechten fuß zü vnd haw Im oben zu der ploß seyner rechten seytten Ee wenn Er mit dem messer wider auff kumpt etc |
[99r.20] Item das noch reyssen ist wen du mit dem züuechten zů dem man kämest So setz deinen l. fuß fur vnd stee In der hut luginsland vnd sich eben was er gegen dir trib oder vicht hawt er dan lang In vonn s. r achsel So wart das er dich mit dem haw nit er lang vnd merck die wil er sein messer vnder sich mit dem haw lat gan gegen der erden So spring mit dem r. fuß zů vnd hew Ime oben zů der pleß s. r. s. Ee wan er mit dem mesß kompso ist er gar genaw geschlagen |
[158r.1] Item das nachraisen Ist Wann du mit dem zufechten zu dem Mann kumpst. so setz dein linncken fuos fur In der hut luginslannd. vnnd sich was er gogen dir treibt. hawt er dann obenn lanngein von seinner rechten Achsel. so wart das er dich mit dem haw gegen der Erden lasz geen. spring mit dem rechten fuos hinfur. vnd haw Im oben zu der plosz seinner rechten seitten Ehe. wann er mit dem duseggen kumpt. so ist er gar gnach geschlagen. |
||||||
[143] |
Then, another element. If he delivers a stroke that misses and you strike to him “after,” and he goes quickly high with the Messer and displaces, remain firmly with the right edge on his Messer. If he raises his Messer, leap with you left foot well behind his right one and strike to his head to his right side. “Simultaneously” do what you want to do. |
[27v.2] Item eyn anderß stuck wenn er sich verhawet und dw ym nach hawest fert er den pald auff mit dem messer und verseczt so pleyb mit der rechten schneyden auff seynem messer starck hebt er dann mit dem messer ubersich so spring mit deynem lincken fuß wol hynter seynem rechten und schlag ym zw dem kopff seyner rechten seytten yndeß mach waß dw wild etc |
[39v.1] Item ein anders stuck wenne er sich verhawet vnd dw Im nach hauest fertt er denne pald auff mit dem messer vnd versetzt So pleyb mit der rechten schneyden auff seynem messer starck hebtt er denne mit dem messer vbersich So spring mit deynem linken fuß woll hinter seynen rechten vnd schlag Im zu dem kopf seyner rechten seyten Indes mach waß du wild |
[99r.21] Item ein ander stuck wan er sich verhewt vnd du Im nach hewest So wirt er bald auff mit dem mesß vnd versetzt So pleyb mit mit [!] der rechten schniden auff sein mesß vbersich So spring mit dem lincken fuß wol hinder seynen rechten vnd schlach Im zů dem lopf [!] s r. s. Indes mach was du wilt |
[158r.2] Ein nachraisen so Sich ainner verhawt Item ainannders stuck Wann er sich verhawt. vnnd du Im nach hawest. steet er dann bald auf mit dem duseggen. vnnd versetzt. so bleib mit der rechten schneidin auf seim [sic] duseggen starckh. hebt er dann mit dem duseggen vbersich. so sprinng mit deinnem lincken fuos wol hinder seinen Rechten. vnnd schlag Im zu seinner rechten seitten. seinnes kopfs Indes mach was du wilt |
|||||||
[144] |
And notice always whether he is “soft” or “hard” in the binding. That is why you should know the “feeling of the Messer.” |
[27v.3] und merck albeg ob er waych oder hert ym pandt seyn dar umb soltu wyssen dye enpfynden ym messer |
[39v.2] vnd merck albey ob er weich oder hertt im pandt sey Dar vmb soltu wissen dy enpfinden des messers etc |
[99r.22] Merck allwegen ob er wech oder hert Im band sich dar nach vmb soltu wissen die enpfindung des messers |
[158v.1] Ob er waich oder hert ist. Item merckh alwegen ober waich oder hert sey pand darumb soltu wissen die empfindung des Duseggen. wie offt gemelt ist. |
|||||||
[145] |
Then, an element: if he delivers a stroke that misses in front of you, and you strike at him “after,” and then you bind on his Messer towards his left side. If he strikes then from the displacement with the Entrüsthau quickly around you to your right side, come “simultaneously” with the Entrüsthau forwards under his Messer against his left side to his neck. Or, perform the cuts, or go high with the hilt and lower the point to his face or chest and push him backwards. “Simultaneously” work towards the peaks. |
[27v.4] Item aber eyn stuck wenn er sich vor dir verhawet und dw nach hawest pyndest dan uff seyn messer gegen seyner lincken seytten schlacht er dann auß der versaczung mit dem entrusthaw pald umb dich zw deyner rechten seytten so kumb yndeß mit dem entrusthaw foren unter seyn messer gegen seyner [28r.1] lincken seytten an seynen halz oder treybn dy schnydt oder far auff mit dem gehultz und senck den ort yn seyn antlicz oder prust und schewb yn alzo zw ruck yndeß erbat nach den czynnen etc |
[40r] Item aber ein stuck wenne er sich vor dir verhawet vnd du nach Im hawest pindest denn auf seyn messer gegen seyner lincken seytten Schlecht er denne auß der versatzung mit dem entrusthaw pald vmb dich Zu deiner rechten seytten So kum yndes mit dem entrusthaw vorne vnder seyn messer gegen seyner lincken seytten an seyn hals oder treyb dy schnyt oder var auf mit dem gehultz vnd senk den ortt In sein antlitz ader[27] prust vnd scheub In alzo zu ruck Indes erbeyt nach den zynnen etc |
[99r.23] Item aber ein stuck wan er sich aber vor dir verhewt vnd du nach Im hewest pindest dan auff seyn mesß gegen s. l. s. schlecht er dan auß der versetzung mit dem entristhew bald vmb dich zů d. r. s So kume In des mit dem entristhew bald vmb dich zů s. r. s. So kum Indes mit dem entristhew faren vnder sein mesß gegen sein lincken seyten an sein halß oder treyb die schnid oder far auf mit dem gehiltz vnd senck den ort In sein angesicht oder brust vnd scheyß [!] In also zů ruck Indes arbeyt nach den zinen |
[158v.2] Mer ain nachraisen So sich ainner Verhawt Item wann er sich vor dir verhawt vnd du Im nachhawest. pindstu dann auf sein duseggen gegen seinner lincken seitten. vnnd er schlecht bald vmb. ausz der versatzung mit dem Entrusthaw. zu deinner rechten seitten. so kum Indes. mit. vornen vnden sein Duseggen. gegen seinner lincken seitten. an seinnen hals. vnnd treib die schnit oder far auf mit dem gehultz. vnnd senckh den Ort In sein gesicht oder prust. vnnd scheub In also von Ruckh. Indes arbait nach den vier zinnen. |
|||||||
[146] Then, a drawing after: if you stand in the guard of the Bastei and he falls with his Messer on yours before you raise it, remain below “on the Messer” and raise up. If he wants to strike at you “on the displacement” or wind in “on the Messer,” do not let him come away “from the Messer” and work “simultaneously” to the next peak. |
[28r.2] Item aber eyn nachreysen ligstu ynder hut pasteyn felt er den mit dem seyn messer uff daß deyn ee den dw uff kumbst so peleyb alzo unten auff dem messer und heb ubersich wil er dir den an der versaczung eyn hawen oder am messer eyn wynden so laß yn von dem messer nich ab kummen erbayt yndeß zw den negsten czynnen |
[99r.24] Item aber noch ein reÿssen listu in der hůt pasteÿ felt er dan mit seynem mesß auff das dein ee dan dw auff kumst So bleyb also auf deim mesß vnd heb vbersich wil er dan an(?) der versatzug In hawen oder an dem mesß an winden So laß Im von dem mesß nit abkumen vnd volg Im dar an nach vnd arbeyt Indes dar nach zů der nesten pleß oder zinen |
[159r.1] Ein annders nachraisen Item mer ain Nachraisen. ligstu In der hut der Pastey. fellt er dann mit seinnem duseggen. auf den deinen. Ee dann du auf kumpst. so bleib also vnnden auf dem duseggen. vnnd heb vbersich. will dir dann an der versatzung einhawen oder andem Duseggen ein winden. so lasz In von dem duseggen nit abkumen vnd volg Im daran nach Indes arbait nach der nechsten plosse. |
|||||||||
[147] |
Then, an element: assume the guard of the Bastei, stand with your left foot forwards, and if he wants to strike from his right side to the Messer, “simultaneously” avoid the stroke with the Messer on his right side and thrust at him with the stretched arm over his Messer. |
[28r.3] Item aber eyn stuck leg dich yn dy hut pasteyn und stee mit eynem lincken fuß fuer will er dir den von seyner rechten seytten hawen auff daß messer yndeß weych auß dem haw mit dem messer auff seyn rechte seytten und stich ym mit gestracktem armen uber seyn messer |
[40v.1] Item aber ein stuck leg dich In dy hut pastey stee mit deynem lincken fuß fur will er dir den von seyner rechten seytten hawen auff das messer Indes weich auß dem haw mit dem messer auff seyn rechte seytten vnd stich Im mit gestracktem arme vber seyn messer vnd schreyt mit dem rechten peyn hyn nach |
[99r.25] Item aber ein stuck lůg In der hůt pasteÿ Vnd stee mit deinem lincken fuß für wil er dir dan von s r s hewen auf das messer Indes weÿch auß dem hew mit dem mesß auff sein recht seyten vnd stich Im mit den gestrackten arme vber sein messer |
[159r.2] Mer ain nachraisen Item leg dich Inn die hut der Pastey vnd stee mit deinem lincken fuosz fur. will er dir dann von seiner rechten seitten einhawen. so weich ausz dem haw mit dem Duseggen auf sein rechten seitten. vnnd stich Im mit [159v.1] gestracktem armen vber sein Duseggen. |
|||||||
[148] |
If he is skilled and displaces the stroke, go high skillfully with the stretched arm, wind to his Messer the point firmly at his face. |
[28r.4] ¶ ist eyner alzo pehendt [28v.1] und verseczt den stich yndeß far auff mit gestracktem armen behendlich wyndt auff seyn messer ym den ort starck zw dem gesicht |
[40v.2] Ist er als behend vnd versetzt den stich Indes far auff behendlich mit gestracktem arme windt auff seyn messer Im den ort starck zu dem gesicht etc |
[99r.26] ist er also behend vnd versatzt den stich Indes var auf mit gestrackten arm behendicklichen wind auf sein mesß Im den ort starck zů dem gesicht |
[159v.2] Versetzt dir den stich. so far Indes. auf mit gestracktem arm. behendigclich vnnd wind auf sein Duseggen mit dem ort starckh zu dem gesicht. |
|||||||
[149] Then, you can do the drawing after on both sides and also bring cuts to it. And do him this way: if he delivers a stroke that misses in front of you, be it from the right or the left side, strike to him merrily to the opening. If he goes high and binds you from below on the Messer, notice as soon as one Messer sparks on the other, go “simultaneously” with the long or sharp edge to his arm, and press with the cut downwards, or cut “simultaneously” through his face. |
Then, you can do the drawing after on both sides and also bring cuts to it. And do him this way: if he delivers a stroke that misses in front of you, be it from the right or the left side, strike to him merrily to the opening. If he goes high and binds you from below on the Messer, notice as soon as one Messer sparks on the other, go “simultaneously” with the long edge to his arm, and press with the cut downwards, or cut through his face. |
[61r.2] Item du magst die noch ryssen zu beÿden syten triben vnd die vnd die schnitt darin bringen vnd thuen im also wan er sich vor dir verhaulbett eß sy von der rechten oder lincken syten So haulb im frelich noch der ploß fertt er dan vff pindt dir vntten an daß messer Somerck als bald eyn messer an dz ander glitzett So fall im ÿndes mit langen oder scharffen schniden vff sin arm vnd trueck mit dem schnid vndesich oder schnid im mit indas dem indaß gesichtt |
[28v.2] Item dw magst dy nachraysenn zw payden seytten machen und dy schnydt auch dar eyn pringen und thw ym alzo wenn er sich von dir verhawet eß sey von der rechten oder von der lincken seytten so haw ym frolich nach der ploß wie fert er dan auff und pyndt dir unten an daß messer So merck alz pald eyn messer an daß ander kliczet so fal ym yndeß mit der langen oder scharpffen schneyden auff seyn armen und druck mit dem schnydt untersich oder schneyd yn mitt dem yndes yndaß angesicht etc |
[41r] Item du magst die nachraysen zu payden seytten machen vnd dy schnyt auch dar eyn pringen vnd thu Im alzo wenne er sich vor dir verhawet Es sey von der rechten oder linken seytten So haw Im frōhlich nach der ploß fertt er dann auff vnd pindt dir vnden an das messer So merck als pald eyn messer an das ander klitzt so fal Im Indes mit der langen schneyden In seyn arme vnd druck mit dem schnyt vntersich oder schneyd Im In das angesicht etc |
[99r.27] Item du magst die nach reyss auff beyden seiten triben vnd die schnid dar In bringen vnd thů Im also wan er sich vor dir ver hewt es sig von der rechten oder lincken seyten so haw Im frellich noch der plesse ver er dan auf vnd bind dir vnden an das messer So merck als bald dein mesß an das ander gliczet So val Im In des mit dem der langen oder scharffen schniden auff sein arm vnd druck mit dem schnid vnder sich oder schnid In mit dem In das angesicht |
[159v.3] Nachraisen von baiden Seitten Item du magst Die Nachraisen. vonn baiden seitten treiben. vnnd thu Im allso / wann Er sich vor dir verhawt. es sey von der rechten oder linncken seitten. so haw Im frolich nach. der plöss / fert er dann auf / vnnd pindt dir vnnden an den duseggen. so merck als bald ain. duseggen an den anndern glitz. so fall Im Indes mit lannger oder scharpffer schneidin auf sein Arm vnd truckh mit dem schnit vnndersich oder schneid In Inn das angesicht / |
||||||
[150] |
If he wants to sway around the head Here the master teaches a drawing after and speaks: Around the head, etc. You should understand it this way: if he remains in the horizontal stance on his left side against your right, and wants to strike around his head to your left side, remain “simultaneously” with your Messer and go readily down and strike to his neck, as it is depicted below. |
[41v] Umb das hawbt will er gagen Hie lertt der meyster aber eyn nachraysen vnd sprich vmb das haubtt etc Das soltu alzo verstan ligt er In der zwirch auff seyner linken seytten gegen deyner rechten vnd will vmb seynen kopff schlagen zu deyner linckn seytten Indes pleyb mit deynem messer alzo ligen vnd var gerad nyder vnd haw In durch seyn hals wie vnden gemalt stett etc |
||||||||||
[151] |
If the duffers deliver strokes that miss You should understand it this way: if one wants to strike to your stomach, and wants to leap away with it, notice, as soon as he goes down with the stroke, strike to his head, as it is depicted below. |
[42r] Verhawen sy sich dy Iüflappen Dasoltu alzo verstan will dich ainer In deynen pauch schlagen vnd will da mit hin weck springen so merk als pald er mit dem haw nyder gett So schlag Im nach seynem haubt wie vnden gemalt stet etc |
||||||||||
[152] |
Bowing with the shield to the right should defend you Here the master teaches how one should displace the drawing after and speaks: Bowing with, etc. You should understand it this way: if you have delivered a stroke that missed to your right side, you should go with bowing under his Messer, so that the thumb is below on your Messer and the hilt is against your left side. If he wants to draw after, catch the stroke on the flat on your Messer, so that the short edge is against him. |
[42v] Pogen mit schilt recht dich solt bebaren Hier lertt der meyster wie man dy nachraysen versetzen sol vnd spricht pogen mit etc Daß soltu alzo versten hastu dich verhauet auff dein rechte seytten so soltu mit dem pogen faren vnder seyn messer daß der dawm vnten stee an deynem messer vnd das gehultz gegen deyner lincken seytten will er alzo nach raysen so vach den schlag auff dy zwirch deines messers das dy kurtz schneid gegen Im stet etc |
||||||||||
[153] |
Overwind the bowing, learn to thrust at the cheek You should understand it this way: if he wants to go high with the bowing and displace the drawing after, wind “simultaneously” over his Messer to his right side and thrust with the point to his right cheek to his right side. |
[43r] Pogen vberwindt wang ler stechen Das soltu alzo versten will er auff faren mit dem pogen vnd versetzen dy nachraysen Indes windt vber sein messer auff sein rechte seytten vnd stich Im mit dem ortt nach dem rechten wang seyner rechten seytten etc |
||||||||||
[154] |
If he wants to enjoy the overwinding with the point Here the master teaches a breaking against the counter-breaking and you should understand it this way: if he winds to your right ear and wants to thrust at your cheek as before, “simultaneously” go with the hilt over his “weak” of the Messer and strike or thrust at his face. |
[43v] Vberbintten mit ortt will er possen Hie lertt der meyster eyn pruch wider den widerpruch vnd solt das alzo versten windt er dir zu deynen rechten oren vnd will dich zu dem wang stechen wie vor Indes far mit dem gehultz vber seyn swech des messers vnd schlag oder stich Im zu seym angesicht etc |
||||||||||
[155] |
You should bow to the left You should understand it this way: if you have delivered a stroke that missed to yout left side and he wants to attack you after, go with the bowing under his Messer, so that the long edge is against him, as it is depicted below. |
[44r] Auff linck solstu auff pÿgen Das soltu alzo verstan hastu dich verhawen auff dein lincke seytten vnd er will dir nachraysen so far auff mit dem pogen vnter seyn messer das dy lang schneyd gegen Im stee wie vnden gemalt stett etc |
||||||||||
[156] |
Wind the point to the left to the bowing You should understand it this way: if he goes against you with the bowing from his left side, work against him with the war to his ear of his left cheek and wind to his left side, so that the thumb is inside against you and the long edge is below, and thrust at his face or where you want. |
[44v] Windt ortt linck auff pogen Das soltu alzo versten gett er gegen dir mit dem pogen von seyner lincken seytten So erbeyt Im mit dem krig zu seynen oren des lincken wangs vnd windt auff sein lincke seytten das der dawmen Innen stee gegen dir vnd dy lang schneyd vnden vnd stich Im Zu seynem antlitz oder wo du hyn wild etc |
||||||||||
[157] |
If he winds and lets the point show Here the master teaches a breaking against the breaking announced above. If he winds to your face as above, strike “simultaneously” high with the lowered point with the long edge to his face or thrust at his throat. |
[45r] Windt er vnd lest ortt schawen Hie lertt der meyster eyn pruch wyder den Eegemelten pruch windt er dir zu dem angesicht wye for So haw Indes vbersich mit gesenktem ortt mit der langen schneyden In seyn gesicht Oder stich In zu der kelen etc |
||||||||||
[158] |
If he wants to strike as before You should understand it this way: if he strikes to you face as announced above, or he wants to thrust at it, remain standing and thrust with the long point with the stretched arm at his face, thus he is not able to reach you with his stroke. |
[45v] Will er als vor hawen Das soltu alzo versten hawt er dir zu dem gesich als Eegemelt ist oder will dich dar eyn stechen so pleyb alzo sten vnd stich In mit dem langen ortt mit gestracktem arme In das angesicht So kann er dich mit seynem haw nicht erlangen etc |
||||||||||
[159] |
Overrun the lower hurt Here the master speaks about the tenth chapter, that is about the overrunning, and speaks: Overrun, etc. Understand it this way: if you come with the Zufechten to the man and he strikes to you from below, do not displace it but notice, as his lower stroke or half-stroke goes to you, strike to him from your right shoulder from above long and shoot the point long to his face, and set on to him, so that he is not able to reach you from below. If he goes from below high and displaces, remain with the long edge firmly on his Messer and “simultaneously” go high with the arm, wind and hang the point to his face. Amen. |
[61r.3] Vber lauf die vnder raem Hie saget der meinster von dem zehenden stueck als von dem vberlauffen vnd spricht vberlauffen Daß verste also wan du mit dem ze vechten [61v.1] ze dem man kümpst hautt er dir dan vntten zue daß vesetz im nicht Sünder merck wan syn vntter haulb oder halb haulb gegen dir gegent So haulb im von diner rechten achßell von oben lang in vnd schus im den ortt lang in zue dem gesicht vnd setz im an So kan er dich vntten nicht gereÿchen fertt er dan von vntten vff vnd versetzt So plyb mit langen ortt oder schniden starck vff sin messer vnd indes far vff mit dem arm wind vnd henge im den ortt zue dem gesichtt ~ |
[28v.3] uber lauff dy unteren ram Hye sagt der meyster von dem eylften zehenden stuck alz von dem uberlauffen und spricht uberlauff etc Daß vernymb alzo wenn dw mit dem zw vechten zw dem man kumbst hawt er dir dan unten zw daß versecz ym nicht sunder merck wenn seyn unterhew oder halphew gegen dir genen so haw ym von deyner rechten achsel von oben lanck eyn und scheuß ym den ort lanck eyn czw dem gesicht und secz ym an so kann er dich unten nicht der raychen fert er dan von unten auff und ferseczt so pleyb mit der langen oder scharpffen schneyden starck auff seynem messer und yndeß far auff mit dem armen wynd und heng ym den ort zw dem gesicht amen Sequitur textus |
[46r] Vberlauff dy vntren ram Hie sagtt der meyster von dem zehnden capitel als von dem vberlauffen vnd spricht vberlauff etc Das verstee alzo wenne du mit dem zuuechten zu den man kumbst hautt er dir danne vntten zu das versetz nit Sunder merck wenn seyn vnterhew oder halphew gegen dir gen So haw Im von deyner rechten achsel von oben lanck eyn vnd scheuß Im den ortt lanck zu dem gesicht vnd setz Im an so kann er dich vnden nicht erraichen fertt er denn von vntten auf vnd versetzt so pleyb mit der langen schneyden starck auff seynem messer vnd Indes far auff mit dem arme wind vnd heng Im den ortt Zu dem gesich Amen |
[99r.28] Vber lauff
Die vnder ram mit sterck vnd In bescham Ist die versatzung
dar bracht ortt wind kurtz biß bedacht Hye sagt der meyster von den zehen stucken als von dem vber lauff vnd spricht vber lauf das [verstee also wan du mit dem zuüechten][21] [99v.1] Zu dem man kumest hewet er dir dan vnden zu dem versetz Im nicht Sunder merck wan sein vnderhaw oder happhaw gegen dir geyn So haw Im von deyner r. s. von oben lanck zů Im vnd schuß Im den ortt lang Im zu dem gesicht vnd setz Im an so kan er dich vnden nit erreychen fert er dan von vnden auf vnd versetzt So pleyb mit dein langen oder scharffen schniden starck auff sein messer vnd indes far auff mit dem arm wind vnd heng Im den ortt zu dem gesicht |
[160r] Das vberlaüffen Vberlauff die vnder kam Item das vberlaüffen Merckh allso. wann du mit dem zufechten zu dem Man kumpst. hawt er dir vnnden zu. so versetzt nit. svnder merckh wie sein vnnderhaw oder halb haw gegen dir geet. so haw Im von deinner rechten Achsel oben lanng ein. vnd scheutz Im den Ort lanng ein zu dem gesicht / vnnd setz Im an. so kann er dich nit anrieren / fert er dann von vnnden auf / vnd versetzt. so bleib mit starcker oder scharpffer schneidin auf seinnem Duseggen. vnd far Indes auf mit dem Arm. wind. vnd heng Im den ort zu dem gesicht. |
||||||
[160] Strike the Entrüsthau to him, overrun Here the master says how one should overrun in the Messer and speaks: Strike the Entrüsthau to him, etc.
|
Strike the Entrüsthau to him, overrun Here the master says how one should overrun in the Messer and speaks: Strike the Entrüsthau to him, etc.
|
[61v.2] Entruest in vberlauff Hie saget der meinster wie man mit dem messer vber lauffen sol vnd spricht entruest etc |
[29v.1] Entrust yn uberlaüff Hye sagt der meyster wye man ym messer uberlauffen söl und spricht entrust yn etc |
[46v.1] Entrüst in vberlauff Hie sagtt der meyster wye man Im messer vberlauffen sol vnd spricht Entrust In etc |
[99v.2] Entrust In vber lauff / wind vnd erhog
den knopf Hie sag der meyster wie man Im mesß vber lauffen soll vnd spricht Entrust In etc |
[160v.1] Entrist In vberlaüff wind vnnd erhoch den knopff Item hie findstu Wie man ausz dem Entrist vberlauffen soll. |
||||||
[161] Understand it this way: if he stands in the guard of the Luginsland, hold your Messer on the right side, stand with the left foot forwards and go with the Entrüsthau to his left side, quickly to him. “Simultaneously” go from below above his Messer with the hilt to your left side and pull your Messer on his Messer back, and go high with the hilt, and strike witht the left hand in the middle of your Messer. Then, thrust at his face with the armed hand or “simultaneously” hit him with a “thunderstroke” to his head or go with the “weak” downwards to his lower peaks. |
Understand it this way: if he stands in the guard of the Luginsland, hold your Messer on the right side, stand with the left foot forwards and go with the Entrüsthau to his left side, quickly to him. “Simultaneously” go from below over his Messer with the hilt to his righ side and pull your Messer on his Messer back, and go high with the hilt, and drop your left hand onto the middle of your Messer. Then, thrust at his face with the armed hand or so. |
[61v.3] Daß verste also ligt er in der hut lueginßlant so hab din messer vff diner rechten siten Ste mit dinem lincken fus vor vnd ge mit dem entrueest haulb ze syner lincken siten vast an In Indes far vnten vff uber sin messer mit dem [62r.1] gehueltz vff sin rechten syten vnd zueck vff sin messer din messer ze rueck vnd far vff mit dem gehultz vnd fal mit der lincken hant in die mit dines messers vnd stich im in dz antluetz mit gewoppnetter hantt / oder indes schlag im den dimessers schlag vff sin hauptt oder far im mit der schwech wider zu der vndern zÿnnen ~ |
[29v.2] daß verstee alzo ligt er yn der hut luginsland so hab deyn messer auff der rechten seytten stee mit dem lincken fuß fur und gee mit dem entrusthaw zw seyner lincken seytten fast an yn yndeß far unten uber seyn messer mit dem gehulcz auff seyn rechte seytten und czeuch uff seynem messer deyn messer zw ruck und far auff mit dem gehuelcz und fal mit dem lincken hant yn dy mit deyneß messerß und stich ym yn daß antlicz mit gewapender hant oder yndeß schlag ym den donnerschlag auff seyn hawbt oder far ym mit der swech nyder zw der unteren czynnen |
[46v.2] Das verste alzo ligtt er In der hut luginslandt So hab dein messer auff der rechten seytten stee mit dem lincken fuß fur vnd gee mit dem Entrusthaw zu seyner lincken seytten vast an In Indes far vnden vber seyn messer mit dem gehultz auf seyn rechte seytten vnd zeuch auff seynem messer dein messer zu ruck vnd far auff mit dem gehultz vnd vall mit der lincken hand In dy mit deynes messers vnd stich Im In das antlitz mit gewappender hand oder etc |
[99v.3] Das verstee also lit er In der hůt Im luginsland so hab dein messer auf d. r. s. stee mit dem lincken fůß fůr vnd fast an In Indes far vnden In sein mesß mit dem gehiltz auff sein r. s. vnd zuch auff sein messer dein messer zu ruck vnd far auff mit dem gehiltz vnd fal mit der lincken hand zů In die mitte deynes messers vnd stich Im In das antlitzt mit gebogneder(?) hand oder Indes schlach Im mit der schweche wider zu der vnderen zinnen |
[160v.2] vnnd thu Im also. ligt er Inn der hut luginsland / so heb dein Duseggen auf der rechten seitten. vnnd stee mit dem lincken fuosz vor. vnnd gee mit dem Entristhaw zu seinner lincken seitten fast an In / Indes far vnnden vber sein Duseggen mit dem gehultz auf sein rechten seitten vnd zuckh auf sein duseggen dein Duseggen. zuruckh vnnd far auf mit dem gehultz. Indes fall mit der lincken hand Inn die mit deinnes Duseggen. vnd stich Im Inn das angesicht mit gewappneter hand. oder schlag Im Indes den dunnerschlag auf sein haupt. oder far Im mit der schwech nider zu der vndern zinnen / | ||||||
[162] |
Overrun with the striking point You should understand it this way: as you have gone over his Messer, as it is stated before, and you have pulled your Messer towards yourself, strike in the middle of your Messer with your left hand and turn the right hand on your Messer around, so that the thumb stands above, and strike to him with the hilt at his head. Then, step “simultaneously” with the right foot well behind his right one and step with your left foot also well behind him and strike to him with no displacement with the hilt at his stomach. “Simultaneously” step behind him once again and strike to him with the hilt at his neck. |
[47r] Vberlauff mit schlagendem ortt Das soltu alzo verstan so Du vber faren pist seyn messer als vor geschriben stet So du deyn messer alzo an dich zogen hast so vall In dy mit deynes messers mit deyner lincken handt vnd wendt dy recht an deynem messer vmb das der dawm vbersich stee vnd schlag In mit dem gehultz auff sein kopff vnd schreyt Indes mit dem rechten fuß woll hinter seynen rechten vnd schreyt mit deynem lincken fuß auch woll hinter In vnd schlag In an alle versatzung mit dem gehultz In seynen pauch Indes hintertrit In noch paß schlag In den mit dem gehultz In seynen nacken etc |
||||||||||
[163] |
If you want to get through with overrunning Here the master says how you should overrun the man and grab at the neck and throw. And you should understand it this way: go to the man as before from your right side to his left, and “simultaneously” wind firmly with the hilt over his Messer and come to help to your right hand. Then, go with the left hand in the “weak” of your Messer blade and go to his throat to his left side. Then, press him firmly with the hand or arm below his throat and step with your left leg behind his right leg and push him over it. |
[62r.2] Wiltu dich uber lauffens mossen Hie saget der meinster wie du im solt vberlauffen den man by dem hals vohen vnd werffen vnd solt dz also versten ge ze dem man als vor von diner rechten syten ze syner lincken syten Indeß wind starck aber mit dem gehultz vber sin messer vnd küm der rechten hant zu hilff vnd far mit der lincken hant in die schwech dines messers clingen vnd far im in den hals syner lincken siten vnd druck in mit dem elnbogen starck vntter sin hals vnd schrit mit dem rechten peyn hintter syn rechtes peyn oder mit dinen lincken [62v.1] hinter sin rechtes beyn vnd stoß Im also darueber |
[29v.2] Wiltu dich uberlauffenß mössen Hye sagt der meyster wye dw solt ym uberlauffen den man pey dem halß vahen und werffen und solt daß alzo verstan gee czw dem man alz vor von deyner rechten seytten czw seyner lincken seytten yndeß wyndt starck aber mit dem gehultz uber seyn messer und kum der rechten hand zw hilff und far mit der lincken hant yn dy swech deyneß messerß und far ym an den halz seyner lincken seytten und druck yn mit den ölpogen starck unter seyn halz und schreyt mit dem rechten payn hynter seyn rechteß payn oder mit dem lincken hynter seyn rechteß peyn und stoß yn dar uber etc Sequitur textus |
[47v] Wiltu dich vberlauffens moessen Hie sagtt der meyster wie du solt vberlauffen den man vnd pey dem hals vahen vnd werffen vnd solt das alzo verstan Ge zu dem man als vor von deyner rechten seytten zu seyner lincken Indes windt stark aber mit dem gehultz vber seyn messer vnd kum der rechten handt zu hilff vnd far mit der lincken hand In dy swech deyneß messers klingen vnd var Im an den hals seyner lincken seytten vnd druck In mit der handt oder arme starck vnter seynen hals vnd schreyt mit deynem linken peyn hinter seyn rechteß peyn vnd stoß In alzo dar vber etc |
[99v.4] Wiltu dich vber lauffenß mossen hal vach über bein ler stossen / Hie sagt der meister wie du Im solt uber lauffen den man bey dem hals fahen vnd werffenn vnd salt daß also verstan gee zu dem man als von deiner r. s. zů der l. sayten Indes wind aber starck mit dem gehiltz über sein messer vnd kumme der rechten hand zu hilf vnd far mit der lincken hand In die schweche deynes messers klingen vnd far Im an dem halß seiner lincken seytten vnd druck In mit dem elenbogen starck vnder sein haltz vnd schreyt mit dem rechten beyn hynder sein rechten fůß oder mit deiner lincken hinder sein rechts bein vnd stoß Im also dar über |
[160v.3] Wiltü dich vberlauffens massen Item das soltü Allso verstan Gee zu dem Mann als vor. von deinner rechten seitten. zu seinner linncken. Indes wind starckh. [161r.1] Mit dem gehultz vber sein duseggen Kum der rechten hannd zu hilff. vnnd far mit der linncken hannd Inn die schwech deinnes Duseggen klingen. far Im an den hals. seinner lincken seitten truckh In mit dem Elenpogen starckh vnnder seinnen hals. vnnd schreit mit dem Rechten pain vnnder sein rechts pain. vnnd stosz In also daruber |
||||||
[164] |
Turn your edge Here the master states a breaking against the verses announced before and their elements. And first of all, against the first two verses, as he speaks: Strike the Entrüsthau to him, etc. |
[62v.2] Din schnid wendt Hie saget der meinster wider die egmelten versz vnd ir stueck vnd zuem ersten wider die ersten verß do er spricht etc |
[30r.2] Deyn schneyd wendt Hye sagt der meyster pruch wyder dy wye ee gemelten verß und yren stuck und zum ersten wyder dy ersten czwen verß so er spricht Entrust yn etc |
[48r.1] Deyn schneyd wendt Hie sagtt der meyster ein pruch wider dy Eegemelten verß vnd yre stuck vnd zum ersten wider dy ersten zwen verß so er sprich Entrust In etc |
[99v.5] Dein schnid wend schnid mit ortt
biß behend will er ringen vnd drucken stoß ring
wer ler zucken Hie sagt der meister stuck In der die egemelten verß vnd Im ersten stuck wider die zwen ersten werß do der text sprich |
[161r.2] Dein schneyde wend Hernach volgent Die pruch vber die vorhemellten versz. vnnd Ire stuckh |
||||||
[165] |
Then, do the first breaking this way: if he goes high with the hilt over your Messer back as it is announced before, and wants to thrust at your face with the armed hand with the short point, “simultaneously” as he goes high with the hilt to your Messer, windt your edge over against him and cut him with the long edge over his hand and press firmly downwards to his left side. |
[62v.3] der erst bruch Item den ersten bruch mach also fert er dir mit dem gehultz vber din messer vnd fertt vff dynem messer vff ze rueck vnd wil dich mit gewopnetter hant mit dem kurtz ortt in daß gesicht stossen Indes die wil er mit dem gehultz vff fertt vff dynen messer Indes wind si din schnid vbersich gegem Im vnd schnid im mit der langen schniden vber sin hant vnd druck fast vber sich vff syn lincken syten ~ |
[30v.2] Item den ersten pruch mach alzo fert er dir mit seym gehultz uber deyn messer und fert mit auff deynem messer auff zw rueck und will dich zu mit geboppender hant mit dem kurczen ort yn daß gesicht stossen yndeß dy weil er mit dem gehulcz uber fertt auff deynem messer yndeß wendt deyn schneyden ubersich gegen ym und schneyd yn mit der langen schneyden uber seyn hand und druck fast untersich auff deyn lincke seytten etc |
[48r.2] Item den ersten pruch mach alzo fertt er dir mit dem gehultz vber dein messer auff zu ruck wie vor gemelt ist vnd will dich mit geboppender hand mit dem kurzen ortt In das gesicht stossen Indes dy weill er mit dem gehultz auff fertt auff deynem messer Indes wendt dein schneydt vbersich gegen Im vnd schneyd Im mit der langen schneyden vber seyn hand vnd druck vast vndersich auff seyn lincke seytten etc |
[99v.6] Item den bruch mach also fert der entrist In Item // wil er dir mit dem gehiltz uber dein messer auff an dein messer auf zů ruck vnd will dich mit gewoper hand mit dem kurtzen ort in das gesicht stossen Indes die wil er mit dem gehiltz auf fert auf dein messer Indas wend dein schnid ubersich vnd schnid gegen Im vnd schnid In mit der langen schniden uber sein hand vnd druck vast vndesich auf deyne lincke seytten |
[161v.1] Der erst pruch Item den ersten Pruch Mach also. fert Er dir mit dem gehultz vber dein duseggen. vnnd will dich mit gewappneter hannd mit dem kurtzen ort Inn das gesicht stössen. Indes dieweil er mit dem gehultz auf fert auf dein duseggen. so wind dein schneid vber sich gegen Im. vnnd schneid In mit der lanngen schneidin vber sein hannd vnnd truckh fast vnndersich auf sein lincken seitten |
||||||
[166] |
Then, another breaking: if he goes with the hilt as before and wants to thrust at your face with the armed point, wind your Messer against your left side so that the long edge is above and “simultaneously” lower your point to his chest and push him “simultaneously” with the thrust firmly backwards. Amen. |
[62v.4] der ander ~ Item eyn ander bruch fertt er dir mit dynem gehultz als vor vnd will dich mit gewoppneter ortt in daß gesichtt stossen So wind din messer [63r.1] gegen syner lincken syten dz die lang schnid oben ste Indes senck din ortt vff sin brust vnd im stich schüb in ze rueck ~ |
[30v.3] Item eyn ander pruch fert er dir mit [31r.1] dem gehulcz alz vor und wil dich mit geboppenden ort yn daß gesicht stechen so wynd deyn messer gegen deyner lincken seytten daß dy lang schneyd oben stee yndeß senck den ort auff seyn prust und ym stich scheub yn da mit zw ruck amen etc |
[48v] Item ein ander pruch fertt er dir mit dem gehultz als vor vnd will dich mit gep gebappendem ortt In das gesicht stechen so windt deyn messer gegen deyner lincken seytten das dy lang schneyd ob ste Indes senck deyn ortt auff seyn prust vnd scheub In Indes mit dem stich stark zu ruck etc |
[161v.2] Der annder Pruch Item fert er dir Mit dem gehultz als vor vnnd will dich mit dem Ort Inn das gesicht stossen. so wind dein duseggen. gegen seinner linncken seitten. das die lanng schneid oben stee. Indes senckh dein ort auf die prust. vnnd Im stich scheub In zuruckh. |
|||||||
[167] |
[No text] |
[49r] [No text] |
||||||||||
[168] |
[No text] |
[49r] [No text] |
||||||||||
[169] |
Then, a breaking: if he goes with the hilt as before and wants to thrust at your face as before, set the thrust aside with the empty hand and drop your Messer. “Simultaneously” grab the blade of his Messer close at his hilt with your right hand, and also with your left turned hand, as you have displaced with it. Grab the “weak” of his Messer and press upwards from you and pull with your right hand below between both his arms and pull firmly to your right side, so that you take his Messer. |
[63r.2] ander bruch Item eyn ander bruch fertt er dir mit dem gehultz als vor vnd will dich stechen in dz gesicht als vor So setz den stich ab mit lerer hant vnd loß din messer fallen Indes griff in sins messers clingen nohent by synen gehultz mit diner rechten hant vnd mit dyner lincken verkerten hant glich als du do mit versetzt hast griff im in die schwech sines messers vnd druck oben von dir vnd riß mit der rechten hant vnten nider zwuschen synen beÿden armen vnd riß starck vff din rechte seyten So nÿmpstu Im daß messer ~~ |
[31r.2] Item aber eyn pruch fert er dir mit dem gehulcz alz vor etc und will dich stechen yn daß gesicht alß vor so secz den stich ab mit lerer hand und laß deyn messer fallen yndeß greuff yn seyneß messerß klingen nohent pey seym gehulcz mit deyner rechten handt und mit deyner lincken verckerten hand gleich alz dw da mit versecz hast greuff yn dy swech seyneß messerß und druck oben von dir und reyß mit der rechten hand unter nyder czwischen seyner payden armen starck auff deyn rechte seytten so nymbstu ym seyn messer etc |
[50r] Item aber ein pruch fertt er mit dem gehultz als vor vnd wil dich stechen In das gesicht als vor So setz den stich ab mit lerer handt vnd laß deyn messer valen Indes greuff in seynes messers klingen nohendt bey seynem gehultz mit deyner rechten handt vnd mit deyner lincken verkertten handt gleych als du da mit versetz hast greuff Im In dy swech seynes messers vnd druck oben von dir vnd Reyß mit deyner rechten handt vntten zwischen seyn payd arme vnd Reyß starck auff dein rechte seytten etc |
[162r.1] Der drit Pruch Item will er dich Inn das Gesicht stossen. als vor. so setz den stich ab mit lerer hand vnnd lasz dein duseggen fallen. Indes greiff In seins duseggen klingen nachent bey seinnem gehultz mit der rechten hannd vnnd mit deinner linncken verkerten hand thu gleich als du versetzen wöllest / vnnd greiff Im Inn die schwech seines duseggens. vnnd truckh oben von dir vnnd Reysz mit der rechten hannd vnnden nider zwischen seinnen baiden Armen. auf sein rechten seitten. so Nimbstu Im den duseggen vnnd magst In auch werffen. |
|||||||
[170] |
Here the master states breakings against the other two verses and elements, as: If he wants to fight hand-to-hand, etc. |
[31v.1] Item hye sagt der meyster pruch wyder dy andere czwen verß und stuck alz wildu dich etc |
[50v.1] Hye sagtt der meyster pruch wider dy andren zwen verß vnd stuck als will er ringen etc |
|||||||||
[171] |
Then, do the first breaking this way: if he goes over your Messer with the hilt and comes with the armed hand on your neck and wants to push you through his right or left leg, break it this way. Grab with your right hand from behind at his elbow and push him well to your right side, and grab with your left hand between both his arm well at his throat to his right side. Then, step with your left foot well behind his left one and throw him over your left hip. |
[31v.2] Item den ersten pruch mach alzo fertt er uber deyn messer mit dem gehulcz und kumbt mit gewappender hand an deyn halz und wil dich drucken uber seyn rechteß oder linckeß payn so prich daß alzo greuff mit der rechten handt hynter an seyn olpogen und scheub yn wol auff seyn rechte seytten und greuff mit deyner lincken hand czwischen seynen payden armen wol hyn auff an seyn halz seyner rechten seytten und schreyt mit deynem lincken fuß wol hyner seynen lincken und wirff yn uber deyn lincke huff etc |
[50v.2] Item den ersten pruch mach alzo fertt er vber deyn messer mit dem gehultz vnd kumbt mit gebappender handt an deyn hals vnd will dich drucken vber deyn rechteß oder linckeß peyn So prich das alzo Grewff mit deyner rechten handt hynden an seyn olpogen vnd schewb In woll auff deyn rechte seytten vnd greuff mit deyner lincken handt zwischen seyn payd arme woll hyn auff an seyn hals seyner rechten seytten vnd schreytt mit deynem lincken fuß woll hynter seynen lincken vnd wirff In vber deyn linke huff etc |
[162r.2] Der viert Prüch Item fert er vnder dein Duseggen mit dem gehultz vnnd kumpt dir an deinnen hals. vnnd will dich trucken vber sein rechten oder linncken fuosz. so prich das also. greiff mit der rechten hannd. hinnden In sein Elenpogen. vnnd scheub In wol auf sein rechten seitten. vnd greiff [162v.1] mit deinner linncken hannd Zwischen seinne beed Arm wol hinausz. an seinnen hals. seinner rechten seitten vnnd schreit mit deinnem lincken fuosz wol hinnder seinnen lincken. vnnd wirff In vber die linckh huff. |
||||||||
[172] |
Then, another breaking: if he goes over your Messer with the hilt, as it is stated before, grab with your left hand at his left one and with your right push him at the elbow from you. Then, leap with your right foot to his left and deprive him of his balance. |
[31v.3] Item aber eyn pruch fert der uber deyn messer mit dem gehulcz alz ee geschriben stet so greuff mit deyner lincken hand an seyn lincke und mit deyner rechten scheub yn von dir und spring mit deynem rechten fuß fur seynen lincken und nym ym daß gewicht etc |
[51r] Item aber ein pruch fertt er vber deyn messer mit dem gehultz als Ee geschriben stett So grewff mit deyner lincken hand an seyn lincke vnd mit deyner rechten schewb In pey dem olpogen von dir vnd spring mit deynem rechten fuß für seyn lincken vnd nymb Im das gewicht etc |
[162v.2] Der funfft Prüch Item ainannderer Pruch. fert er vber dein Duseggen mit dem gehultz. als oben geschriben steet so greiff mit deiner linncken hannd an sein lincke. vnnd mit der rechten scheub In von dir. Indes. spring mit deinnem Rechten fuosz fur seinnen lincken vnd Nimb Im das gewicht. |
||||||||
[173] |
Then, another breaking: if he goes with the hilt as before, grab with your left hand in his right arm close at the hand and pull it downwards on you. “Simultaneously” hit with your right arm firmly over his left one and press both arms well to your body. Then, step with your right foot to his both feet and swing to your left side. |
[32r.1] Item aber eyn pruch fert er mit dem gehulcz alz vor etc So greuff mit deynem lincken hand yn seyn rechten armen nohend pey der hand und ruck den untersich an dich yndeß schlag deynen rechten armen starck uber seynen lincken und druck seyn payde armen wol an deyn leyb und trit mit dem rechten fuß fuer seyn payde und swyng dich uff deyn lincke seytten etc |
[51v] Item aber eyn pruch fertt er mit dem gehultz als vor so grewff mit deyner lincken hand In seyn rechten arme nohend bey der handt vnd ruck den vbervntsich vntersich an dich Indes schlag deynen rechten arme starck vber seynen lincken vnd druck sy beyde arme woll an deyn leyb vnd tritt deynen rechten fuß fur seyn peyde vnd swing dich auff deyn lincke seytten etc |
[162v.3] Der sechst Pruch Item mer ain Pruch. fert Er mit dem gegultz als vor. so greiff mit deinner lincken hannd In seinnen rechten arm nachent [163r.1] bey der hannd vnnd ruckh den Vndersich an dich. Indes schlag deinnen rechten arm starckh vber sein linncken vnd gee durch seinne beed arm/ wol an seinnen leib. vnnd trit mit dem rechtne fuosz wol fur seinne bed fusz. vnnd schwing dich auf dein lincken seitten. so wirfstu In. |
||||||||
[174] |
[32r.2] Item helt er dich alz vor so greuff mit deyner rechten handt czwischen seyn payd armen von unden uff yn seynß messers klyngen nohend bey dem gehultz yndes greuff auff deyn prust czwischen seyn messer mit deyner lincken verkerten hand yn dy swech seynes messers und reyß starck auff deyn rechte setten etc |
[163r.2] Der sibent pruch Item helt Er dich Alls vor. so greiff mit deiner rechten hannd zwischen seinne baid Arm von vnnden auf Inn seinnen Duseggen. nachent bey dem gehultz. Indes greyff auff. sein prust zwischen seinnem duseggen. mit der linncken verkerten hannd In die schwech seinnes Duseggen vnnd Reysz starckh auf dein rechtne seitten. |
||||||||||
[175] |
Then, another breaking: grab with your left hand over his Messer close to the handle or bind and pull down and go high with your right hand between his both arms in the “weak” of his Messer and press towards him firmly down. Then, pull firmly to your left side, so that you take his Messer. |
[32r.3] Item aber eyn ander pruch greuff mit deyner lincken hand uber seyn messer nohend pey der hand hab und reyß untersich und far mit deyner rechten hand uff czwischen seyn pede arem yn dy swech seyneß messerß und druck gegen ym fast nyder und reyß starck [32v.1] auff deyn lincke seytten so nymbstu ym aber daß messer etc |
[52r] Item aber eyn pruch Greuff mit deyner lincken handt vber seyn messer nohend bey der handthab[28] oder pindt vnd reyß vntersich vnd far mit deyner rechten handt auff zwischen seyn payd arme In dy swech seynes messers vnd druck gegen Im vast nyder vnd reyß starck auff deyn lincke seytten so nymbstu Im aber seyn messer etc |
[163r.3] Der Acht pruch Item greyff mit deinner lincken hand vber sein duseggen. nachent bey dem hefft darmit vnndersich. vnnd far mit deinner rechten hanndt auf zwischen seinne baid arm Inn die schweche seinnes Duseggen. [163v.1] vnnd truckh gegen Im fast. Nider vnnd reisz starckh auf sein lincken seitten. so nimbstu Im den duseggen. |
||||||||
[176] |
Then, another breaking: grab above over his right arm in the blade of his Messer with your right hand close at the hilt and pull towards your right side. “Simultaneously” grab with your left turned hand in the “weak” of his Messer and pull firmly to your right side, in that way you strike his Messer at his head. |
[32v.2] Item aber eyn pruch greuff oben uber seynen rechten armen yn seynß messerß klyngen mit deyner rechten hand nohent zw dem gehulcz und reyß gegen deyner rechten seytten yndeß greuff mit deyner lincken verckerten hand yn dy swech seyneß messerß und reyß starck auff deyn rechte seytten so schlegstu ym seyn messer an seyn kopff etc |
[52v] Item aber eyn pruch Greuff oben vber seyn rechten arme In seynes messers klingen mit deyner rechten handt nohendt bey dem gehultz vnd Reyß gegen deyner rechten seytten Indes Greuff mit deyner lincken verkertten hand In die swech seynes messers vnd reyß stark auff deyn rechte seytten so schlechstu Im seyn messer an seyn kopff etc |
[163v.2] Der Nevndt Prüch Ainn annderer Pruch greiff oben vber sein rechten Arm Inn seinnes Duseggen klingen. mit deinner rechten hannd. nachent zu dem gehultz vnnd Reyst gogen deiner rechten seitten. Indes greiff mit deinner linncken verkerten hand. Inn die schwech seinnes duseggen. vnnd Reysz. starckh auf dein rechten seitten. so schlechstu Im seinnen Duseggen an seinnen kopff. |
||||||||
[177] Then, another breaking: if he stands as before and has you at the throat as before, and you grab at his Messer over his right arm and you feel that he is too strong for you and you cannot pull the Messer to your right hand, “simultaneously” grab with your left hand behind his right hand at the hilt and pull downwards firmly to your left side. |
[32v.3] Item aber eyn ander pruch stet er alz vor und hat dich pey dem halz alz vor und dw greufft ym yn seyn messer uber seyn rechten armen und dw enpfyndest daß er dir zw starck ist und daß messer nicht reyssen kanst auff deyn rechte seytten yndeß greuff mit deyner lincken hand hynter seyn rechte hand an daß gehulcz und reyß unter sich starck auff deyn lincke seytten etc |
[163v.3] Der Zehend Prüch Item fert Er als vor Vnd hat dich aber bey dem hals. vnnd du greyffest Im Inn sein Duseggen. vber seinnen rechten [164r.1] Arm. vnnd du aber empfindest. das Er dir zu starckh. ist. das du Im sein duseggen nit kanst reissen. auf sein rechten seitten. so greiff mit deinner linncken hannd hinder sein rechte an das gehultz. vnnd Reisz vnnder sich starckh auf dein lincke seiten. so nimbstu Im den Duseggen. |
||||||||||
[178] |
Then, a breaking: if he goes over your Messer as before and holds you at your neck as before, go high with your left hand behind his right one between his hands and hilt, and press with it firmly to your right side and turn quickly to the side announced before. |
[32v.4] Item aber eyn ander pruch fert er uber deyn messer alz vor und helt dich pey dem halz alz vor so far auff mit deyner [33r.1] lincken hand hynter seyn rechte czwischen seyn hand und gehulcz und druck da mit starck auff deyn rechte seytten und wend dich geswynd auff dy ee gemelt seytten etc |
[53r] Item aber eyn pruch fertt er vber deyn messer als vor vnd hellt dich bey dem hals als vor So far auff mit deyner lincken handt hynter seyn rechte zwischen seyn hendt vnd gehultz vnd druck da mit starck auff deyn rechte seytten vnd wendt dich geswindt auff dy Eegemelt seytten etc |
[164r.2] Der Anlfft Pruch Item fert Er uber dein Duseggen als vor / so far auf mit deinner lincken hannd sein rechte zwischen seinner hand. vnnd gehultz vnnd truckh damit starckh auf sein rechte seitten. vnnd wind dich geschwind auf dein Ergemellte seitten. so hastu In. aber gewunnen / |
||||||||
[179] Then, if he holds you as before, thrust at him between both his arms with the “weak” over his right arm at the joint and raise with the hilt firmly to his left arm at the joint of the elbow and press from above downwards firmly to his right side. The text follows. |
[63r.3] Item helt er dich als vor So stich im indes zwuschen sin beid arm mit der schwech vber syn rechte arm in dz geleng vnd heb mit dem gehultz starck vff sin lincken arm bÿ dem gelenckg deß elnbogens vßwendig vnd druck von oben nider starck vff syn rechten seyten ~ Sequitur textus |
[33r.2] Item helt er dich alz vor so stich ym yndeß czwischen seyn pede armen mit der swech uber seynen rechten armen yn daß gelenck und heb mit dem gehulcz starck auff seynen lincken armen pey dem gelenck deß olpogenß und druck von oben nyder starck auff seyn rechte seytten etc Sequitur textus |
[164r.3] Der zwelfft prüch Item hellt Er dich als vor. so stich Im Indes seinne baid Arm mit der schwech vber sein rechte arm. Inn das gelaich. vnnd heb mit [164v.1] dem gehultz starckh auf sein lincken Arm bey dem gelaich des Elenpogens. auszwenndig vnnd truckh von oben nider starckh auf seinn rechte seitten |
|||||||||
[180] |
Then, he has you at your neck as before: grab with your left hand forwards to his left one and push your Messer under his right arm to his chest and turn yout right hand around. Then, press him firmly on his left arm with the Messer and turn his left hand with your left one well around and step with your right foot to his both ones. Then, swing to your left side and throw him on the face. This way he is clenched, and step with your left foot on the hilt of the Messer in the measure and form, as it is depicted below. |
[53v] Item hatt er dich bey dem hals als vor So grewff mit deyner lincken handt vorne an seyn lincke vnd stoß Im deyn messer vnter seyn rechten arme auff seyn prust vnd vmbker deyn rechte handt vnd druck In fast an seyn lincken arme mit dem messer vnd reyb seyn lincke handt mit deyner lincken wol vmb vnd schreyt mit deynem rechten fuß fur seyn payd vnd Swing dich auff deyn lincke seytten vnd wirff In auff das antlitz So ist er beschlossen vnd Tritt mit deynem lincken fuß auf das gehultz des messers in mäß vnd gestalt wie das vnden gemalt stat etc |
||||||||||
[181] |
Then, another breaking against the counter-breaking. If he wants to do the breaking against the holding with the foot, and he is about to throw himself on his back, grasp the Messer and strike at him as he turns around to his right arm, so that he cannot stand up well. If you want, step with both feet on the Messer, with each foot on the end.[29] This element serves for the combat, as an armoured man is thrown and clenched, so that he is not able to stand up. You should keep this element in secret and not show it to anyone, as one should not strew the roses for the swine.[30] |
[54r] Item aber eyn pruch wyder den wyderpruch will er den pruch machen wyder das halten mit dem füß vnd ist sich vmb werffen auff seynen ruck So grewff In das messer vnd schlew In Inn dem vmbwenden seynen rechten arme dar eyn So kann er nicht woll auff stan wiltu Z so tritt mit peyden fussen auff das messer mit ytzlichem fuß auff eyn ortt Das stuck das dynet dem kampff So eyn geharnischter man geworffen wirtt vnd alzo beschlossen wirtt mag er nicht mer auff sten Das stuck soltu haben verporgen vnd nyemant weysen wann dy Rosen sol man nicht fur dy Seẅ Streuwen etc |
||||||||||
[182] |
Then, if he has grabbed you at the neck as before and wants to push you over the leg, go with the short-point to him between his both arms and set the point on his throat, as it is depicted below. |
[54v] Item hatt er dich bey dem hals gefast als vor vnd will dich vber das peyn drucken als vor So far Im mit dem kurtzen ortt zwischen seyn ped arme vnd setz Im den ortt an seyn kelen wye vnden gemalt stet etc |
||||||||||
[183] |
Then, another different breaking: if he has grabbed you at the neck as before, go with your point of your Messer to your left side and hit him with the hilt between both his arms at the face or the throat, as it is depicted below. |
|||||||||||
[184] |
Then, another breaking: if he goes over your Messer with his hilt and wants to take you at the neck as before, push his hilt away with yout hilt and step with your right foot well to his right side and strike to him with the hilt at his head, as it is depicted below. |
[55v] Item aber eyn pruch fertt er dir vber deyn messer mitt seynem gehultz vnd will dich bey dem hals nemen wye vor So weyß Im mit deynem gehultz das seyn hyn weck vnd Tritt mit deynem rechten fuß woll auff seyn rechte seÿtten vnd schlag Im mit dem gehultz auff seyn kopff wye vnden gemalt stett etc |
||||||||||
[185] |
Then, another different breaking: if he goes over your Messer with the hilt as before, “simultaneously” go quickly over his hand close to his hilt at the joint of his hand on the outside. Then, go with the left hand to the “strong” of his Messer and pull with both hands firmly to your left side, so that you take his Messer. |
[56r] Item aber eyn ander pruch fertt er dir vber deyn messer mit dem gehultz als vor Indes var Im schnel vber seyn handt nohendt zu seym gehultz In das gehultz gelenck seyner handt außbendig vnd var mit der lincken handt In dy sterck seyneß messers vnd Reyß mit payden henden starck auff deyn lincke seytten So nymbstu Im das messer etc |
||||||||||
[186] |
Then, another breaking: if he has grabbed you at the neck as before, drop your Messer. Grab him with your right hand behind his left elbow and push him with it from you to his right side. “Simultaneously” grab him with your left hand in his left knee-bending and throw him to his right side. |
[56v] Item aber ein pruch hatt er dich bey dem hals gefast wie vor so laß deyn messer vallen Greuff ym mit deyner rechten handt hinter seynen lincken olpogen vnd scheub In da mit von dir auff seyn rechte seytten Indes greuff In mit deyner lincken rechten handt In seyn lincke knyepug vnd wirff yn auff seyn rechte seytten etc |
||||||||||
[187] |
Then, another different breaking: if he has grabbed you at the neck as before, drop your Messer and go with your right hand behind his left elbow and grab with your right hand in the middle of his body on his right side, and with your left hand in the middle of his left side. Then, lift him firmly up and turn him around on your chest and throw him with the head to the ground, as it is depicted below. |
[57r] Item aber ein ander pruch hatt er dich bey dem hals gevast als vor so loß deyn messer vallen vnd var mit deyner rechten handt hinter seynen lincken olpogen vnd grewff mit deyner rechten handt In dy mit seynes leybs auff seyner rechten seytten vnd mit deyner lincken hand In dy mitt seyner lincken seytten vnd heb In starck auff vnd dree In auff deyner prust vmb vnd wirf In mit dem kopff auff dy erden wie vnden gemalt stett etc |
||||||||||
[188] |
Then, another breaking: if he wants to go with the hilt over your Messer as before, pull your Messer under his hand with the long edge, so that the hilt is against your right side. “Simultaneously” go with your hilt and with the armed hand over his right hand from outside and pull firmly to your right side, so that you take his Messer. |
[57v] Item aber ein pruch will er dir mit dem gehultz vber deyn messer faren wie vor So zeuch deyn messer Im vnter seyn handt mit der langen schneyden Das daß gehultz gegen deyner rechten seytten stee Indes far mit deym gehultz vnd mit gewappender handt vber seyn rechte handt außbendig vnd reyß starck auff deyn rechte seytten So nymbstu Im das messer |
||||||||||
[189] |
Then, another breaking: if he wants to go with the hilt over your Messer as before, go with the long edge on his hand between the hilt and the hand, so that your Messer comes over the horizontal in front of you. “Simultaneously” take to the armed hand and thrust at him on the inside through his arm with it. Then, come on the outside to his elbow and press with the “weak” with yout Messer and your elbow firmly down, and press with your right hand and Messer also his right hand firmly. Then, lay down firmly on his arm. This way you have clenched him skillfully and masterly and you can hold, press or throw him. |
[58r] Item Eyn ander pruch will er mit dem gehultz vber deyn messer faren als vor So far mit der langen schneyden an seyn handt zwischen deß gehultz vnd handt Das deyn messer vber dy zwerch fur dich kum Indes fall zu gewappender handt vnd stich Im Inwendigs durch seynen rechten arme da mitt vnd kum Im außbendigs In seynen olpogen vnd druck mit der swech mit deynem messer vnd deynem olpogen starck nyder vnd druck mit deyner rechten handt vnd messer auch seyn rechte handt starck vnd leg dich mit sterck auff seynen arme alzo hastu In beschlossen kunstenlich vnd meysterlich vnd magst In halten drucken oder werfen etc |
||||||||||
[190] |
Then, another breaking: if he wants to go over with the hilt as before, go “simultaneously” with your left hand on the inside over his Messer and take to the armed hand in the middle of your Messer and go with the “weak” from outside on his joint of the hand, and press firmly in the joint to your right side, so that you take his Messer. |
[58v] Item aber eyn pruch will er dir mit dem gehultz vber faren wie [Sic] far Indes far mit deyner lincken handt Inbendigs vber seyn messer vnd fall zu gewappender handt in dy mit deyneß messers vnd far Im mit der swech außbendigs In seyn gelenck der handt vnd druck vast In das gelenck auff deyn rechte seytten so nymbstu Im das messer etc |
||||||||||
[191] |
Pass over, aim quickly Here the master teaches a good element from going over in the Messer and speaks: Going over, etc. You should understand it this way: go close to him and overrun his Messer with your hilt, so that his Messer comes under your right shoulder or arm. “Simultaneously” fall with your left hand in the middle of your Messer and go up beneath and outside his right hand and thrust at his face or throat. If he wants to withdraw, step merrily after him and press his arm down with force. |
[59r] Vberfaren schnel piß remen Hie lertt der meyster aber eyn gutz stuck auß dem vberfaren In dem messer vnd sprich vberfaren etc Das soltü alzo verstan gee nohendt an In vnd vberlauff seyn messer mit deym gehultz alzo das seyn messer vnter deyn rechte vchsen oder arme kum Indes vall mit deyner lincken handt In dy mit deyneß messers vnd far vnden auff ausbendigs seyner rechten handt vnd stich Im alzo zu dem gesicht oder kelen will er zu Rück tretten So tritt Im frōlich nach vnd druck seynen arme mit sterck nyder etc |
||||||||||
[192] |
Go over firmly, cut the joint Here the propagator of the art teaches another element from the overrunning with the hilt and speaks: Go over firmly, etc. You should understand it this way: if you go over his Messer with your hilt, go down through, so that his Messer comes under your right shoulder. Then, go on the outside to the joint of his hand and press towards the ground quickly down, so that you take his Messer. |
[59v] Vberfar starck schneyd das glenck Hie lertt der merer der kunst Ein anders stuck auß dem vberlauffen mit dem gehultz vnd sprich vberfar starck etc das soltu alzo versten ferstu Im vber sein messer mit deym gehultz So far Im vnden durch das seyn messer vnder deyn rechte vchsen kum vnd far Im außbendigs In das gelenck seyner handt vnd druck gegen der erden geswindt nyder So nymbstu Im das messer etc |
||||||||||
[193] |
If you want to start the Messer taking Here the propagator of the art teaches an element from the above depicted art and speaks this way: Messer taking, etc. You should understand it this way: go with the hilt on the outside over his Messer and let then your “weak” go down inside, and go with the hilt from outside to the joint of his hand. Then, swing “simultaneously” to your right side and pull firmly with the hilt on it, as it is depicted below, so that you take his Messer. |
[60r] Messer nemen wilt begynnen Hie lertt der Merer der kunst aber Ein stuck auß der Ee gemelten artt vnd spricht alzo Messer nemen etc Das soltu alzo verstan far Im mit dem gehultz außbendigs vber seyn messer vnd laß den dy swech sincken Inwendigs nyder vnd far Im mit dem gehultz außwendigs In das gelenck seyner handt vnd Swing dich Indes auff deyn rechte seytten vnd Reyß starck mit dem gehultz dar auff wie vntten gemalt stett etc so nymbstu Im das messer; |
||||||||||
[194] |
The Messer taking with one hand Here the propagator of the art teaches how one should take the other’s Messer with one hand, and when one has one hand only or is lame in the left hand, so that he even though can take the other’s Messer quickly and with force. Understand it this way: go across with your Messer to his left side close to his hilt, so that the long edge is against the man. “Simultaneously” drop your Messer over the head and go with your right hand on the outside over his hand. Wind over them, so that they come outside again and “simultaneously” pull with it firmly with the one hand to your right side, so that you take his Messer easily without any trouble. |
[60v] Messer nemen mit eyner hendt Hie lertt der merer der kunst wye man aynen eyn messer nemen solt mit eyner hendt vnd ob eyner halt nicht mer hett wenn Eýn handt oder lamb wer In der lincken handt das Er dennich Eynem seyn messer nemen mocht schnell mit gewallt Das verstee alzo Gee auff mit der zwirch mit deynem messer auff seyn lincke seytten nohendt an seyn gehultz Das dy lang schneyd gegen dem man stee Indes laß deyn messer fallen vber das haubt vnd var mit deynen rechten handt Im außbendig vber seyn handt vberbindt dye Das sy wyder außbendig kum Indes Reyß da mit starck mit der eyn hendt auff deyn rechte seytten So nymbstu Im gar lyderlich an alle nott seyn messer etc |
||||||||||
[195] |
Learn to pull with an empty hand towards yourself Here the master and the propagator of the art teaches a good element that works also with an empty hand. If you come to him as before, drop your Messer and go over his arm as before. Then, wind the arm around so that his right hand comes under your right shoulder and your right hand on his elbow, and the left arm is stroke over his right arm. Then, press his right arm firmly to your body or chest and hold him as it is depicted below. If you want to throw him, step with your left leg in front of his both legs and throw him over it. Or, fall on your arse, so that he falls on his face and cannot stand up unless you let him cordially stand up. |
[61r] Mit lerer handt ler an dich rucken Hye lertt der meyster vnd der merer der kunst aber eyn gutz stuck das gett zu auch mit lerer handt So dw zu Im kumbst wye vor So laß deyn messer fallen vnd far aber vber seynen arme wye vor vnd windt den arme vmb das dir seyn rechte handt kum vnter deyn rechte vchsen vnd deyn rechte handt auff seynen olpogen vnd der linck arme wer geschlagen vber genß rechten arme vnd druck seynen rechten arme starck an deynen leyb oder prust vnd halt In wye vnden gemalt stet wiltu In aber werffen so schreyt mit deynem lincken peyn fur d seyn pede peyn vnd wirff In dar vber oder vall auff den arß so fellt er auff seyn antlitz vnd kan nicht auff stan den du last In gerne auff sten etc |
||||||||||
[196] |
If he also goes, go over Here the master teaches a breaking against the going over with the hilt and speaks: If he goes, etc. You should understand it this way: if he goes with the hilt over your Messer as before, go also with your hilt “simultaneously” over his right hand on the outside and pull firmly the hand to your right side. Then, turn with your body to his left arm and pull his hand with the Messer well to your chest. Then, strike your left arm over his right elbow and take his Messer. Or, step with the left foot in front of his both ones and throw him over it. |
[61v] Fertt er auch vberfar Hye lertt der meyster Eyn pruch wyder dy vberfaren mit dem gehultz vnd spricht fertt er etc Das soltu alzo verstan fertt Er mit dem gehultz vber deyn messer wye vor So far auch mit deym gehultz Indes vber seyn rechte handt außbendigs vnd Reyß starck dye handt auff deyn rechte seytten vnd wendt dich mit dem leyb an seynen lincken arme vnd reyß Im seyn handt mit dem messer woll zu deyner prust vnd schlag deynen lincken arme vber seynen rechten olpogen vnd nymb Im alzo das messer oder schreyt mit dem lincken fuß fur seyn payde vnd wirff In dar vber etc |
||||||||||
[197] |
Learn to set off Here the master says how one should set off in the Messer, be it strokes or thrusts. If you come with the Zufechten to him, and he stands against you as if he wanted to thrust, put your left foot forwards, assume the guard of the Eber on your right side against him, and expose yourself with the left side. If he thrusts at your opening, wind with your Messer on your left side against his thrust, so that the short edge comes on his Messer and set with it aside, so that the point stands against his face or against his body. Then, thrust at his face or chest. |
[63v.1] Die absetzen lere Hie saget der meinster wie man sol absetezen im messer Es sihent heulb oder stich wan du mit dem ze vechten zu dem man kümpst stelt er dan gegen dir als weller stechen So setz dinen lincken fus fur vnd leg dich gegen im in die hut des ebers zu diner rechten syten vnd gib dich ploß mit diner lincken siten stich er dan dich zu der ploß So wind mit dinem messer vff din lincke syten gegen synem stich die kurtz schnid an sin messer küm vnd versetz do mit ab dz der ort gegen sinen gesicht ste oder gegen dem lib vnd stich zu dem gesicht oder zu der bruest ~ |
[33r.3] [D]y abseczen lere Hye sagt der meyster wye man sol ym messer abseczen eß seyn hew oder stich merck wenn dw mit dem zwvechten [33v.1] zw ym kumbst stelt er sich dan gegen dir alz woll er stechen so secz deynen lincken fuß fuer und leg dich gegen ym yn dy hut deß eberß zw deyner rechten seytten und gib dich ploß mit deyner lincken seytten sticht er dir den zw der ploß so wynd mit deynem messer auff deyn lincke seytten gegen seynem stich daß dy kurcz schneyd an seyn messer kum und secz da mit ab daß deyn ort gegen seym gesicht stee oder gegen dem leyb und stich ym zw dem gesicht oder zw der prust etc |
[62r] Sy absetzen lere Hie sagtt der meyster wye man soll Im messer absetzen Es seyn hew oder stich Wenn du mit dem zuuechten zu Im kumbst stelt Er sich den gegen dir als woll Er stechen vnd setz deynen lincken fuß fur leg dich gegen [Sic] Im In dy hut des Ebers zu deyner rechten seytten vnd gib dich ploß mit der lincken seytten sticht Er dir denn zu der ploß So windt mit deynem messer auff deyn lincke seytten gegen seynen stich das dy kurtz schneyd an seyn messer kumb vnd setz da mit ab das der ortt gegen seynem gesicht stee oder gegen dem leyb vnd stich Im zu dem gesicht oder prust etc |
[99v.7] Die absetzen etc Hie sagt der meister wie man Im messer sal absettzen es sigen hew oder stich wen du mit dem zuüechten zů Im kumest stelt er sich dan gegen dir alß wol er stechen So setz dein lincken fuß fur vnd leg dich gegen Im die hutt des ebers zů deiner r. s. vnd gib dich Ime ploß mit d. l. s. schlecht er dir dan zů der plesse So wend mit dem mesß auff d. l. s. gegen seinem stich das die kurtz schnid an sein mesß komm vnd setz do mit ab das der ortt gegen seinem gesicht stee oder gegen den lib vnd stich Im zů dem gesicht oder brust |
[164v.2] Das absetzen Die absetzen Leer Item merckh wie Mann soll absetzen Im Duseggen. es seien haw oder stich. vnnd machs allso. wann du mit zufechten zu dem Mann kumpst. stellt er sich dann gogen dir als woll er stechen. so setz. deinnen lincken fuosz fur vnnd leg dich gogen Im. Inn die hut des Ebers zu deinner rechten seitten. vnnd gib dich plosz mit deiner lincken seitten sticht. [165r.1] er dich oben zu der plösz. so winnd Mit deinnem Duseggen. auf dein linncken seitten gogen seinnem stich. die kurtz schnein an sein Duseggen. vnnd setz dennt ab. das der Ort gegen seinem gesicht stee. oder gegen dem leyb. vnnd stich zu dem gesicht oder prust. |
||||||
[198] Then, another element: if you stand on your right side in the Eber and he strikes to your left side from above to the opening, and wind with it to your left side against his stroke, so that the hilt comes in front of the head to the Stier. Then, step with the right foot forwards and thrust at his face or chest. You can perform these elements on both sides from the four guards. |
Then, another element: if you stand on your right side in the Eber and he strikes to your left side from above to the opening, go high with the Messer and wind with it to your left side against his stroke, so that the hilt comes in front of the head to the Stier. Then, step with your foot forwards and thrust at his face or chest. You can perform these elements on both sides from the four guards. |
[63v.2] eyn anders Item eyn ander stuck wan du stest zu dyner rechten syten in dem eber hautt er dir zu der lincken siten oben zu der ploß So far vff mit dem messer vnd wind do mit vff die lincke seyten [64r.1] gegen synen haulb dz dz gehultz vor dz hauptt kuem in den stier vnd schrit mit dem fus zu vnd stich im zu dem gesicht oder brust die stich magstu triben vß den viern legern ~ |
[33v.2] Item eyn anderß stuck wenn dw stest zw deyner rechten seytten yn dem eber haut er dir dan zw der lincken seytten oben zw der plöß und wynd da mit auff deyn lincke seytten gegen seynem haw daß daß gehultz fuer daß haubt kum yn den stiren und schreyt mit dem rechten fuß zw und stich ym zw dem gesicht oder prust dy stuck magstu auch treyben von payden seytten auß dysen legeren etc |
[62v] Item Ein anders stück wenn du stest zu deyner rechten seytten In dem Eber hawtt er dir denn zu der lincken seytten oben zu der plöß so far auff mit dem messer vnd windt da mit auff deyn lincke seytten gegen seynen haw Das daß gehultz fur das haubt kum In der Stiren vnd schreyt mit deym füß fur zu vnd stich Im zu dem gesicht oder prust Dy stuck magstu treyben von payden seytten auß den vyer legren etc |
[99v.8] Item ein ander stuck wan du steest zů d. r. s. In dem eber hewt er dir dan zů der lincken seiten oben zů der plose So far auff mit dem mesß vnd wind do mit auf die l. s. gegen seinem hew das das gehiltz fur das haupt kum In den stieren vnd schrit mit dem fuß zů vnd stich Im zů dem gesicht oder brust die stuck magstu triben auß den vier legeren |
[165r.2] Ein annders absetzen Item wann du steest zu seinner Rechten seitten In dem Eber. hawt er dir dann von der linncken seitten oben zu der Plose. so far auf mit dem Duseggen vnnd wind damit auf dein lincke seitten. gegen. seinnem haw. das des gehiltz fur. das haupt kum In den stier. Indes schreit mit dem rechten fuosz hinein vnnd stich Im zu dem gesicht oder prust / die stich magstu treiben ausz den Vier legern. |
||||||
[199] |
Changing through, this element Here the master speaks about the changing through and speaks: Change through, etc. |
[64r.2] Dürch wechsel daß stuck Hie saget der meinster von dem durch wechschelln vnd spricht durch wechseln dz stueck etc~ |
[34r.1] [D]Urchwechseln daß stuck Hye sagt der meyster von dem dürchwechselen und spricht durchwechseln daß stuck etc |
[63r.1] Durchwechsel das stuck Hye sagtt der meyster von dem durchwechsel vnd spricht Durchwechsel das etc |
[99v.9] Durch wechsel das stuck etc |
[165r.3] Das durchwechszlen [165v.1] Dürchwechsel das stückh |
||||||
[200] |
Now it is to be known that the changing through are numerous and various. You can do them from all the strokes against the fighters who strike to the Messer and not to the peaks of the man. Now, you should perform the changing through with great care so that one does not set on against you while you change through. |
[64r.3] Nu ist zu wissen dz der durch wechschell vil sint vnd mangeleÿ du mag die triben vß allen haulben gegen den vechtern die do haulben zu den messern vnd nit zu den zÿnnen des manes Nu den durch wechschell soltu triben mit grossem fursichtiglich oder fursichtikeytt dz man dir nit absetz die will due duerch wechscheltt ~ |
[34r.2] nw ist zw wyssen daß der durchwechseln vil ist und mangerlay dy magstu treyben auß allen hewen gegen den vechteren dy do hawen zw dem messer und nicht zw den czynnen deß manß nw den durchwechseln soltu treyben mit grosser fursichtikayt daß man dit nicht an secz dy weyl dw durchwechselst |
[63r.2] Nu ist zu wissen das der durchwechsel vill sind vnd mancherlay du magst dy machen auß allen hewen Gegen den vechteren Dy do hawen zu den messeren vnd nicht zu den zynnen des mannes Nu den durchwechsel soltu treyben mit grosser fursichtikeyt das man dir nicht ansetz Dy weyll dw durchwechselt etc |
[99v.10] Item ist zů wissen das der dürch wechsel vil sind vnd mancherleÿ die magstu triben auß allen hewen gegen dem vechter die do hewen zu den messern vnd nit zu den zinnen des manß Nün durchwechsel soltu triben mit grosser virsichtikeyt das man der nit ansetz dir wil du durch wechselst |
[165v.2] Item der durchwechsel Ist vil vnnd Manckerlay / vnnd magst die treiben ausz allen hewen. gegen den Fechtern die da hawen zu dem Duseggen. vnnd nit zu der plösse des Mans. du solt aber en durchwechsel treiben mit aller. fursichtigkait. das man dir nit ansetz. die weil du durchwechszlest. |
||||||
[201] |
Then, perform the changing through this way: if you come with the Zufechten to the man, strike at him from above long to the head. If he strikes then against you to the Messer and not to the body, let the point change through below while striking before he binds you on the Messer, and thrust at him to the other peak. If he is aware of the thrust and goes with the Messer after the stroke with the displacement, change through to the other side. Perform it always when he follows your Messer with the displacement. You should perform it on both sides. |
[64r.4] durch wechsel mach [64v.1] Item den durch wechsell trib also wan du mit dem zubechten zu dem man kümpst So haulb im oben lang in zu dem kopff haut er dan gegen dir zu dem messer vnd nit zu dem lib So loß den ortt mit dem haulb vnten durch wechsell ee er dir in daß messer pÿndt vnd stich zu der andern zÿnnen wurtt er dan dz stichs gewar vnd fert mit dem messer dem stich noch mit der versatzüng so wechsell aber durch zu der andern syten daß tribe also wan er dir noch dem messer fertt mit der versatzüng dz soltu triben zü peÿden seyten ~ |
[34r.3] Item den durchwechseln treyb alzo wen dw mit dem zw vechten zw dem man kumbst so haw ym oben lanck eyn zw dem kopff hawt er dan gegen dir zw dem messer und nicht zw dem leyb so laß den ort mit dem haw unter durchwischen ee er dir an daß [34v.1] messer pyndet und stich ym zw der andren czynnen wirt er dan deß stichß gewar und fert mit dem messer dem stich nach mit der versaczung so wechsel aber durch zw der andren seytten daß treyb albeg wenn er dir nach dem messer fert mit der versaczung daß soltu treyben zw payden seytten etc |
[63v] Item den durchwechsel Treyb alzo wenn du mit dem zuuechten zu dem man kumbst So haw Im von oben lanck Eyn zu dem kopff hawtt er dann gegen dir zu dem messer vnd nicht Zu dem leyb So loß den ortt mit dem haw vntten durchwechselen Ee er dir an das messer pindet vnd stich Im Zu der andren zynnen wirtt er denn das stichs gewar vnd fertt mit dem messer dem stich nach mit der versatzung So wechsel aber durch Zu der andren seytten das treyb albegen wenn Er dir nach dem messer vertt mit der versatzung Das soltu treyben zu payden seytten etc |
[99v.11] Item den durchwechsel trib also wan du mit dem züechten zů dem man kümest So hew Im Indes lang Im zů dem kopf hewet er dan gegen dir zu dem messer vnd nit zů dem dein lib So loß den ortt vnden durchwechsel ee er dir an das messer bindet vnd stich Im zů der anderen zinnen wirtt er dan das stichß gewar vnd fert mit dem messer vnd [!] stich noch mit der versatzung So wechsel aber durch zů der anderen seitten vnd treyb alwegen wan er dir nach dem mesß fert mit der versatzung das saltu triben zů beyden seiten |
[165v.3] Item den durchwechsel treib Allso Wann du mit dem zufechten zu dem Mann kumpst. so haw Im oben. lanng ein dem kopff / hawt er dann gogen dir zu dem duseggen. vnnd nit zu dem leyb. so lasz den ort mit dem haw vnnden. durchwechslen. Er dir an den duseggen pindt. vnnd stich Im zu der anndern plösz wirt er dann des stichs gewar / vnnd fert. mit dem duseggen dem stich nach mit der versatzung. so wechsel zu der andern seitten. das treib also. wann Er dir nach dem Duseggen fert. mit der versatzung das solltu treiben zu baiden seitten. |
||||||
[202] |
Then, another changing through: if you come with the Zufechten to him, set your left foot forwards and hold the long point against his face. If he strikes at you from above or from below to the Messer and wants to strike it away or bind on it, “simultaneously” let the point go down through below, and thrust at him to the other side. You can do it against all the strokes. |
[64v.2] aber eyns Item aber eyn durch wechschell wan dü mit dem man zubechten zu dem man kümpst So setz dynen lincken fus for vnd halt im den langen gegen dem gesicht haut er dir dan von oben oder von vntten zu dem messer vnd wil dir daß weg schlagen oder darin bÿnden Indes loß den ortt vnttersich durch sincken vnd stich im zu der andern zÿnnen in vnd dz magstü thün gegen allen haulben |
[34v.2] Item aber eyn durchwechsellen wen dw mit dem zw vechten zw ym kumbst so secz deynen lincken fuß fuer und halt ym den langen ort gegen dem gesicht hawt er dir den von oben oder von unden zw dem messer und wil dir daß hyn weck schlagen oder dar an pynden yndeß laß den ort untersich durchsincken und stich ym zw der anderen seytten eyn und daß magstu thun gegen allen hewen |
[64r.1] Item aber Ein durchwechselen wenn du mit dem zuuechten zu Im kumbst So setz deynen lincken fuß fur vnd halt Im den langen ortt gegen dem gesicht haw er dir denn von oben oder von vnten zu dem messer vnd will dir das weck schlagen oder dar an pinden Indes laß den ortt vntersich durch sincken vnd stich Im zu der andren seytten Eyn das magstu thun gegen allen hewen etc |
[99v.12] Item aber ein ander durch wechsel wan du mit dem züuechten zu dem man kümest So setz dein lincken fuß fur vnd halt Im den langen ortt gegen dem gesicht hewt er dir dan von oben ader von vnden zů dem mesß vnd wil dir das messer weck schlagen ader an binden Indes loß den ortt vndersich sincken vnd stich z Im zu der anderen seytten das magstu thůn gegen allen hewen etc |
[166r.1] Ein annders dürchwechszlen Item wann du Mitt dem zufechten zu dem Mann kumpst. so setz deinnen Lincken fuos fur / vnnd halt Im den lanngen Ort zu dem gesicht. hawt Er dir dann von oben oder vnnden zu dem duseggen / vnnd will dir das hinnweckh schlagen oder daran pinden. so lasz Indes dein ort vnndersich durch sincken. vnnd stich Im zu der anndern seitten. das magstu thun gegen allen hewen. |
||||||
[203] |
Then, a good teaching Then, notice a good teaching and the third element. If he has displaced or has bound otherwise on your Messer, and he does not hold his point on the Messer against your face or the opening of your body, and lets his point go out sideways at you to the side, change through merrily. But if he remains with the point against the face or against the openings, do not change through, but remain on the Messer and work with it to the next opening, so that he is not able to draw after to you or set on. |
[64v.3] eyn gut lere Item eyn gut lere Vnd daz tridt stueck mach gere eben wan er dir versetz hat oder sünst an [65r.1] din messer hat gebünden helt er dan am messer sin ortt nicht gegen dem gesichtt oder bloß dines libes vnd lest den ortt nebent sich besitz vß gon vff eyn syten So wechsel im frelichen durch plibet er aber mit dem ortt gegen dem antluetz oder gegen den ploßen So wechsell im nicht durch sünder plyb im messer vnd arbeytt im do mit zu der nesten ploß So mag er dir nit noch reÿßer oder an setzen etc |
[34v.3] Item eyn gutte ler daß dritt stuck merck gar eben da wenn er dir verseczt hat oder sunst an deyn messer hat gepunden hellt er den am messer seyn ort nicht [35r.1] gegen dem gesicht oder ploß deyneß leybß und lest den ort neben dir peseyt außgan uff dy seytten so wechsel ym kunlich durch pleybt er aber mit dem ort vor dem gesicht oder gegen den plössen so wechsel ym nicht durch sunder peleyb am messer und erbatt ym da mit zw der negsten plöß so mag er dir nich nach geraysen noch an seczen etc Sequitur textus |
[64r.2] Item Ein gutte ler [64v] Item Ein gutte ler vnd das dritt stuck merck gar eben wenn Er dir versetzt hatt oder sunst an deyn messer hatt gepunden helt er den am messer seyn ortt nicht gegen deynem gesicht oder plöß deynes leybs vnd lest den ortt neben dir y beseytz auß gan auff Eyn seytten So wechsel Im frolich durch pleybt er aber mit dem ortt gegen dem antlitz oder gegen den plossen So wechsel Im nicht durch Sunder pleyb am messer vnd erbeyt Im da mit zu der negsten ploß So mag er dir nicht nachraysen noch ansetzten etc |
[99v.13] Das dritt stuck etc merck gar eben wan er dir versetzt hat ader sunst an das messer gebunden helt er dir dan an mesß seynen ortt nit gegen deynem gesicht oder plese dines libes vnd last den ortt neben sich beseitz auf gen auff ein seytten So wechsel Im nit durch ferlichen durch bript [!] er aber mit dem ortt gegen deim antlitz oder gegen der plossen So wechsel Im mit [!] durch sunder blib am messer vnd arbeyt Im do mit zů der nesten pleß So mag er dir nit nach reyssen ader ansetzen |
[166r.2] Mer ain durchwechsel Item wann Er dir versetzt Hawt. oder sunst an dein duseggen. gepvnden hat. hellt er dann am duseggen. sein ort gegen deinnem gesicht oder prust deines leibs nit. vnnd lest den ort neben sich beyseytz. auszgeen auf ain seitten. so wechsel Im frolich durch. bleibt er dann mit dem Ort. gegen dem angesicht oder gegen den plossen. so wechsel Im nit durch sonder bleib am dusegen vnd Arbait Im damit zu der nechsten plosse. so mag er dir nit nachraisen oder ansetzen. |
||||||
[204] If you want to strike long from the left from below Here the master teaches how one should change through in the Messer from long straight strokes from below from both sides and firstly to the left side. Notice, go to him with strokes from below from your left side, so that the right foot goes forwards and the left one follows the right and the feet come together while stepping. And strike the strokes from a straightened arm long. Thus, if you come in the Zufechten to him, do as if you wanted to shoot the point to his right side at the face, and “simultaneously” change through from below close at the hilt and thrust at his face to his left side. |
If you want to strike long from the left from below Here the master teaches how one should change through in the Messer from long straight strokes from below from both sides and firstly from the left side, so that the right foot goes forwards and the left one follows the right and the feet come together while stepping. And strike the strokes from a straightened arm long. Thus, if you come in the Zufechten to him, do as if you wanted to shoot the point to his right side at the face, and “simultaneously” change through from below at the hilt and thrust at his face to his left side. |
[65r.2] Wiltu linck lang vnter haulben Hie leret der meinster durch wechsell man sol im messer vß langen geradnen vnter haulben von beiden siten zu vor vß von der lincken siten dz der recht fus fur ste vol ge zu im in vntter haulben vnd der linck dem rechten noch volget also dz die fus in schritten zu samen kümen vnd haulb die heulb vß gestrackten arm lanckg in So du dan im zu vechten zu im kümest So thun glich als du im den ortt in wollest schissen zu siner rechten siten zu dem gesicht Indes wechsches vntten durch [65v.1] bÿ dem gehueltz vnd stich im in sin angesichtt vff siner lincken syten ~ |
[35r.2] Wiltu linck lanck unterhawen Hye lert der meyster wye man durchwechsellen solt ym messer auß langen geraden unterhewen von payden seytten zw vor auß zw der lincken seytten Nota gee zw ym yn unterhewen von deyner lincken seytten daß der recht fuß vor gee und der linck dem rechten nachvolg alzo daß dy fuß yn schritten zw sammen kummen und haw dy hew außgerackten armen lanck eyn so dw den yn dem zw vechten czw ymb kumbst so thw geleich [35v.1] alz dw ym den ort wollest eyn schyssen zw seyner rechten seytten zw dem gesicht yndeß wechsel unten durch nohent bey dem gehulcz und stich ym yn seyn angesicht auff seyner lincken seytten etc |
[65r] Wiltu linck lanck vnter hawen Hye lertt der meyster wye man durchwechslen soll Im messer auß langen geraden vnterhewen von payden seytten zu vor auß von der lincken seytten das der recht fuß vor gee vnd der linck dem rechten nachvolg alzo das dy fuß Im schreytten zusammen kummen vnd haw dy hew außgestracktem arme lanck Eyn so dw denn In dem zuuechten zu Im kumbst so thu gleych als du Im den ortt wollest Eyn schyssen zu seyner rechten seytten zu dem gesicht Indes wechsel vntten durch bey dem gehultz vnd stich Im In seyn angesich seyner lincken seytten |
[99v.14] Wiltu lincken etc Hie lertt der meister wie einer durch sol wechseln sol im mesß auß langem gracktem vnderhewen von beyden seytten zů st vor auß von der lincken seiten das der recht fuß for stee oder gee zů Im Im vnder hawen vnd der linck dem rechten nach volg also das die fuß Im schritten zů samen kumen vnd hew die hew auß gestackten arm lang In So du dan Im dem ortt In schiessenn wiltt zu s. r. s. zu dem gesicht Indes wechsel vnden durch bey dem gehiltz vnd stich Im in sein angesicht auf s. l. s. |
[166v.1] Wiltu linckh lang vnder hawen Item solltu verrer Durchwechslen Ausz Lanngen geraden vnnderhawen. von baiden seitten. zuuoraus von der linncken seitten. das der recht fuosz vor stannd volg zu Im Inn vnnderhewen. also das die fuesz Im schrit zusammen kumen vnnd haw. die hew gestrackten armen. lanng ein. so du dann Im zufechten zu Im kumpst. so thu gleich als du Im den Ort wollest einschiessen. vnnden durch zu seinner rechten seitten zu dem gesicht / Indes wechsel vnnden durch bey dem gehultz vnnd stich In Inn das angesicht auf seinner linncken seitten. |
||||||
[205] From the left let shoot long to the right Here the master teaches a good element from the strokes from below announced before and says: From the left long, etc. |
From the left let shoot long to the right Here the master teaches a good element from the strokes from below announced before and says: From the left long, etc. |
[65v.2] linck lanck loß recht in schussen Hie lert der meinster aber eyn guet stuck vsz dem gemelten vntter haulb vnd spricht wiltu linck lanck etc |
[35v.2] Linck lanck laß recht eyn schvessen Hye lert der meyster aber eyn gutt stuck auß dem ee gemelten unterhewen und spricht linck lanck etc |
[65v.1] Linck lanck laß recht eyn schyessen Hie lertt der meyster aber Eyn gutt stuck auß den Eegemelten vnterhewen vnd spricht linck lanck etc |
[99v.15] Linck lang etc aber ein gut stuck auß dem gemelten vnder hew vnd spricht wiltu linck lang etc |
[166v.2] Linckh. lang lasz recht einschiessen [167r.1] Item mer ain guts stuckh ausz Den vnnderhawen. |
||||||
[206] You should understand it this way: go to him with a stroke from below from your left side to his right side with the straightened arm and with a twofold step as before, so that the thumb is above on the flat of the Messer and the blunt edge goes forwards. Then, if you come to the man, shoot the long point directly to his face, so that the thumb is above. If you have not hit him with the point, remain standing with the Messer and wind your Messer to your left side on his Messer, so that the short edge is above and the right edge is below. Then, step well to his right side with the left foot, and step well around him and thrust at his face. If you want, do “simultaneously” the doubling to his right side behind the blade of his Messer. You can hit him with it, but before you hit him you should do a double feint. |
You should understand it this way: go to the man with the strokes from below from your left side to your right side with the straightened arm and with a twofold step as before, so that the thumb is above on the flat of the Messer and the blunt edge goes forwards. Then, if you come to the man, shoot the long point directly to his face, so that the thumb is above. If you have not hit him with the point, remain standing with the Messer and wind your Messer to your left side on his Messer, so that the short edge is below and the right edge is above. Then, step well to his right side with your left foot, and step well around him and thrust at his face. If you want, do the doubling to his right side behind the blade of his Messer. You may hit him with that. |
[65v.3] dz stuck mach Daß stueck soltu also verstan ge vff den man mit vnter haulben von diner lincken siten zu siner rechten siten mit gestracktem arm vnd mit eynem zwieffachen drÿtt als for dz der thum oben ste vff der flech des messers vnd die stümpff schniden vor ge So du dan zu dem man kümpt so schueß im den langen ortt gerad In zu dem gesicht dz aber der thüm oben sy hastü in dan mit dem ort nicht getroffen So blib also sten mit dem messer vnd winde din messer vff din lincke syten an sin messer dz die kurtz schnid vnten ste vnd die rechte oben vnd dritt wol vff sin rechte mit dim lincken fus schrit woll vmb in vnd stich im noch dem gesicht wiltu dan so magstu Indes dupliren zu siner rechten Hinder sins messers clingen auch machstu den treffer [66r.1] darin machen du solt aber vor dem treffer machen ein zwiffachen feller ~ |
[35v.3] daß soltu also verstan gee auff yn yn eynem unterhaw von deyner lincken seytten zw seyner rechten seytten mit gestracktem armen und mit eynem czwiuachen trit alz vor daß der dawm oben auff der flech lig deß messerß und dy stumpff schneyd for gee so dw dan zw dem man kumbst so scheuß ym den langen ort gerad eyn zw dem gesicht daß der dawm oben stee hastu yn dan mit dem ort nicht getroffen so pleyb alzo stan mit dem messer und wind deyn messer uff [36r.1] deyn lincke seytten gegen seynem messer daß dy kurcz schneyd oben stee und dy recht schneyd unden und trit wol auff seyn rechte seytten mit dem lincken fuß schreyt wol auff seyn rechte und stich ym zw dem gesicht wiltu den so mach yndeß daß dupliren zw seyner rechten seytten hinter seyneß messerß klyngen auch magstu den treffer dar eyn machen dw solt aber vor dem treffer machen eyn czwiuachen feler |
[65v.2] Das soltu alzo verstan Gee auff den man In vnterhewen von deyner lincken seytten zu deyner rechten seytten mit gestracktem arme vnd mit Eynem zwiuachen tritt als vor das der dawm oben stee auff der flech deß messers vnd dy stumpff schneyd vor gee So du denn d zu dem man kumpst So scheuß Im den langen ortt geradt Eyn zu dem gesicht Das aber der dawmen oben stee hastu In denn mit dem ortt nicht getroffen So pleyb alzo sten mit dem messer vnd windt deyn messer auff deyn lincke seytten auff seyn messer das dy kurtz schneyd vntten stee vnd dy recht schneyd oben stee vnd Tritt woll auff seyn rechte seytten mit deynem lincken fuß schreytt woll vmb In vnd stich Im zu dem gesicht d wiltu denn so mach das dupliren zu seyner rechten seytten hinter seynes messers klingen auch magstu den treffer dar Eyn machen; |
[99v.16] das soltu also versteen gee auf den man mit vnderhewen von deiner l. s. mit gestrackten arm vnd Im zuüechten trit also vor dz der thume oben stee auf die schle fleche des messers vnd die stumpf schnid vor gee So du dan zu dem man kumest So schnid In mit dem langen ort gerad Im zu dem gesicht das aber der thům oben sey hastu In dan mit dem ort nit getroffen So pleyb mit dem ort sten mit dem mesß das die kurtz schnid vnden stee vnd rechten schnid obenn stee vnd drit wol auff seyn r. s. mit dem lincken fuß schrit wol vmb Im Indes duplieren zů s. r. s. hinder seinß messers klingen auch magstu den treffen dar In machen du [100r.1] solt aber den treffer machen ein triffach feller |
[167r.2] vnnd mach das also. gee auf den Man. mit vnnderhewen. von deinner linncken seitten. zu seinner rechten. mit gestrackten armen. vnnd mit ainnem zwifachen trit. als vor. das der daum oben stee. auf der flech des Duseggens vnnd die kurtz schneid vorstee. so du dann zu dem Mann kumpst. so scheusz Im den lanngen Ort gerad ein zu dem gesicht. das aber der dawm oben sey / hastu In dann mit dem ort nit getroffen. so bleib also stehen mit dem duseggen. vnnd wind dein duseggen auf dein linncke seitten an sein duseggen. das die kurtz schneid vnnden stee. vnnd dir recht schneid oben Indes trit mit dem lincken fuosz auf sein rechten. seitten. schreit wol vmb In vnnd stich Im zu dem gesicht. Wiltu dann so magstu duplieren zu seinner rechten seitten. hinnder seinnes duseggen klingen. auch magstu ain treffen darein machen. oder ain zwifachen feler. |
||||||
[207] |
Who can do the wheel Here the master speaks about the element that is called the wheel and speaks: Who can do the wheel, etc. |
[66r.2] Wer das Rad kan machen Hie saget der meinster von dem stuck dz do heist daß rade Vnd spricht were dz rad kan machen ~ |
[36r.2] Wer daß rad kan machen Hye sagt der meyster von dem stuck daß do heysset daß rad und spricht wer daß rad etc |
[66r.1] Wer das radt kann machen Hie sagtt der meyster von dem stuck Das do heysset das radt vnd spricht wer das Radt etc |
[100r.2] wer das rad etc Hie der meister wer das rad will machen etc |
[167r.3] Das Rad Wer das Rad kam machen |
||||||
[208] |
You should understand it this way: if you want to do the wheel, strike at him from your right shoulder a direct driving stroke with the stretched arm and stand with the left foot forwards and go with the point above yourself so that the blunt edge is above. And let it go away from above from your right shoulder well behind yourself and again high from below, so that the point is always against the man. And do as if you wanted to shoot the point at his face to his left side and “simultaneously” go high with the point and change through to his right side at the face. |
[66r.3] Daß soltu also verstan wiltu dz rad machen So haulb zu Im von diner rechten syten eyn geraden trib haulb mit gestracketn arm vnd ste mit dem lincken fus vor vnd far mit dem ortt vbersich dz die stümpff schnid oben ste vnd loß oben von deyner rechten achsell woll hinter sich ab gen vnd von vnten wider vff also dz der ort albwegen gegen dem man ge vnd thun als du im den ortt gegen dem gesicht wollest schuessen zu siner lincken siten Indes far vff mit dem ortt vnd wechsell durch zu siner rechten siten zu dem gesicht ~ |
[36r.3] daß soltu alzo verstan wiltu daß rad machen so haw zw ym von deyner rechten achsel eyn geraden treybhaw mit gestracktem armen und stee mit dem lincken fuß fur und far mit dem ort [36v.1] ubersich daß dy stumpff schneyd oben stee und laß oben von deyner rechten achsel wol hyntersich abgen und von unten wyder auff alzo daß albeg der ort gegen dem man stee und thu sam dw ym den ort zw dem gesicht wollest schyssen zw seyner lincken seytten yndeß far auff mit dem ort zw seyner rechten seytten zw dem gesicht |
[66r.2] Das soltu alzo verstan wiltu das radt machen So haw zu Im von deyner rechten achsel Eyn geraden treyb haw mit gestrackten arme vnd stee mit dem lincken füß fur vnd far mit dem ortt vbersich das dy stumpff schneyd oben stee vnd laß oben von deyner rechten achsel woll hintersich abgen vnd von vntten wider auff alzo das albeg der ortt gegen dem man gee vnd thu als dw Im den ortt zu dem gesicht wolltest schyssen zu seyner lincken seytten Indes far auff mit dem ortt vnd wechsel durch zu seyner rechten seytten zu dem gesicht etc |
[100r.3] das soltu also verstenn wiltu das rad machen So hew zu Im vonn deiner r. s achselen Ein graden trib hew mit gestracktem arm vnd drit mit dem lincken fůß fůr vor mit dem ortt über sich das die stümpf schnid über sich stee vnd laß oben von deiner rechten achselen wol hinder sich ab gen vnd von vnder sich auf also das alwegen der ortt gegen dem man gee vnd thů alß du Im den ortt gegen dem angesicht wolest schiessenn zů seyner lincken seytten Indes var auf mit dem ortt vnd wechsel durch zů sein r. s. zu dem gesicht |
[167v.1] Item wiltu das Rad machen So thu Im also. haw zu Im vonn deinner rechten Achsel. ain geraden treib haw mit gestracktem arm. vnnd stee mit deinnem lincken fuosz vor. vnnd far mit dem Ort vbersich. das die kurtz schneid oben stee. vnnd lasz oben von deinner rechten Achsel wol hinnder sich abgeen vnnd von vnnden wider auff / das allweg der ort gegen dem Mann stee. vnnd thu als wollestu Im den Ort gegen seinner linnckhne seitten einschiessen. Indes far auf vnnd wechsel durch zu seinner rechten seitten. zu dem gesicht. |
||||||
[209] Then, stand with your left foot forwards and do the wheel from your left side and step with your right foot forwards and with the left foot always follow the right one till you come to it. When you can reach him with the point, do as if you wanted to shoot the point from your left side to his right side and “simultaneously” let the point sway through down at his hilt and thrust at his face to his right side. Thus, you can also change through with the other strokes, as from the strokes from below, and driving strokes. The text follows. |
Then, stand with your left foot forwards and do the wheel from your left side and step with your right foot forwards and with the left foot always follow the right one till you come to it. When you can reach him with the point, do as if you wanted to shoot the point from your left side to his right side and “simultaneously” let the point sway through down at his hilt and thrust at his face to his right side. Thus, you can also change through with the other strokes, as from the strokes from below, driving strokes, half-strokes and twofold strokes from below. |
[66r.4] eyn ander stueck // Item Ste mit dinem rechten fus fur Vnd mach dz rad von diner lincken siten vnd schrit mit dynem rechten fus fur vnd mit dem lincken [66v.1] alwegen dem rechten noch vntz du zu dem man kümpst So du dan in errauechen magst mit dem ortt So thuen du als wollest den ort eyn schuessen von diner lincken syten zu siner rechten siten Indes loß den ort bÿ sinem gehultz vntten durch wueschen vnd stich im zu dem gesicht siner rechten syten also magstu auch mit dem andern haulben durch wechschell als vß den streich haulben vnd zwiffach vnter haulben |
[36v.2] Item stee mit deynem rechten fuß fuer und mach daß rad von deyner lincken seytten und schreyt mit deynem rechten fuß und mit deynem lincken alzeit dem rechten nach uncz dw zw ym kumbst so dw yn den eraychen magst mit dem ort so thu alz dw ym den ort wollest eyn schyssen von deyner lincken seytten zw seyner rechten seytten yndeß laß den ort pey dem gehultz unten durch wischen und stich ym zw dem gesicht seyner rechtten seytten alzo magstu auch mit den anderen hewen durch wechselen alz auß den straych hewen treybhewen etc Sequitur textus |
[66v] Item stee mit deinem lincken fuß fur vnd mach das radt von deyner lincken seytten vnd schreyt mit [Sic] deynenem [Sic] rechten fuß fur vnd mit dem lincken albegen dem rechten nach vntz dw zu dem kumpst So du denn In Erraychen magst mit dem ortt so thu als dw Im den ortt wollest Eynschyssen von deyner lincken seytten zu seyner rechten Indes laß den ortt bey seynem gehultz vntten durchwischen vnd stich Im zu dem gesicht seyner rechten seytten alzo magstu auch mit den andren hewen durchwechselen als ausß den streychewen Treybhewen halphewen vnd zwiuachen vnterhewen |
[167v.2] Ein annders stückh Vonn dem Rad. Item stee mit deinnem Rechten fuosz vor. vnnd vmach das rad von deinner lincken seitten. Indes volg mit dem lincken schennckel hinnach. vnnd thu als wollestu. Im den ort einschiessen. von deinner linncken seitten zu seinner rechten Indes lasz den ort bey seinnem gehultz vnnden durchwischen. vnnd stich Im zu dem gesicht. seinner rechten seitten. also magstu mit dem vnnderhewen. durchwechslen. als ausz den straichhewen. vnnd zwifachen vnnderhewen. |
|||||||
[210] Twitch from the hits Here the master says how one should twitch in the Messer and know that twitching is also one of the main elements and twitchings are numerous and various, and they are to be performed against the masters who bind firmly on the Messer with the displacement and also against those who remain standing “on the Messer” and wait whether one wants to get away from them. If you want to dupe and deceive such masters, do the twitching against him. |
Twitch from the hits Here the master says how one should twitch in the Messer and know that twitching is also one of the main elements and is numerous and various, and they are to be performed against the masters who bind firmly on the Messer and are strong in the displacement. If you want to dupe and deceive such masters, do the twitching against him. |
[66v.2] Zueck die treffen Hie saget der meinster wie man im messer zuecken sol Vnd wiß dz zuchcken ist auch der haupt stueck eins der ist auch vil vnd mancheleÿ vnd gehoertt zu triben vff die meinstern die starck an das messer pinden vnd starck in der versatzüng sin vnd auch gegen den die im messer stan plyben vnd warten ob man sich [67r.1] vor im wil ab zyehen oder verhaulben wiltu die selbigen meinster tueschen vnd effen So mag die zuecken gegen im also |
[37r.1] Czuck dy treffen Hye sagt der meyster wye man ym messer czucken söl und wiß daß daß czucken ist auch der haubtstuck eynß und der czucken ist vil und manigerlay und gehoren zw treyben gen den meysteren dy starck an daß messer pynden mit der versaczung und auch gegen den dy am messer sten peleyben und warten ob man sich vor yn wöl ab hawen wil dw dy selben meyster teuschen oder effen so mach dy czucken gegen yn alzo |
[67r.1] Zuck dy treffen Hie sagtt der meyster wye man Im messer zucken soll vnd wiß das daß zucken ist auch der haubtstuck Eynes vnd ist vill vnd manchlay vnd gehoren zu treyben gegen den meystren dy starck an das messer pinden vnd starck In der versatzung sindt wiltu dy selbigen meyster effen vnd Teuschen So mach dy zucken gegen In also |
[100r.4] Zück die etc sten also mach die zucken gegen den die starck Im messer bleyben |
[168r.1] Das Zuckhen Zückh die treffen Item der zückhen seind vil Vnd Mannicheerlay vnd gehoren zutreiben gegen den Maistern. die starckh an den duseggen pinden. vnnd starckh Inn der versatzung send vnd auch gegen den die am duseggen stehen bleiben. vnnd warten. ob man sich vor In well abziechen oder verhawen. wiltu die Maister teuschen. vnd effen. so mach die zucken gegen Im also. |
||||||
[211] Bind with the Entrüsthau on his Messer on his left side and “simultaneously” strike with the same stroke to his right side and as the Messers spark together, “simultaneously” twitch back with the arm and do a thrust from the stroke, and thrust in the twitching to his left side at the face. |
Bind with the Entrüsthau on his Messer on his left side and “simultaneously” strike with the same stroke to his right side and as the Messers spark together, “simultaneously” twitch a little back with the arm and do a thrust from the stroke, and thrust in the twitching to his left side at the face. |
[67r.2] pind mit dem entruest haulb an sin messer vff siner lincken siten vnd wan die messer zu samen glitzen Indes zueck mit dem arm eyn wenig zue ruck vnd mach vß dem haulb eyn streich vnd stich im zuecken vff sin lincke siten zu dem gesicht |
[37r.2] ¶ pynd mit dem entrusthaw gegen ym an seyn messer auff seyn lincke seytten yndeß haw mit dem selben haw zw seyner rechten seytten und wen dy messer zw sammen czkliczen yndeß [37v.1] czuck mit dem armen zw rück und mach außdem schlag eyn stich und stich ym czucken ym auff seyn lincke seytten zw dem gesicht |
[67r.2] pindt mit dem Entrusthaw an seyn messer auff seyner linckn seytten Indes haw mit dem selben haw zu seyner rechten seytten vnd wenn dy messer zusammen klitzen Indes zuck mit dem arme Eyn benigs zu ruck vnd mach auß dem schlag Eyn stich vnd stich Im zucken auff seyn lincke seytten zu dem gesicht etc |
[100r.5] bind mit dem antristhew an sin mesß auff sein l. s. Indes hew mit dem selben haw Zu s. r. s. vnd wan die messer zü samen glitzen Indes zuck mit dem arm ein wenigk zu ruck auf s. l. s. zu dem gesicht |
[168r.2] pind mit dem Entrusthaw an sein duseggen auf seiner linncken seiten. Indes. haw mit dem selbigen haw zu seinner rechten seitten. vnnd wann die Dusegen zusammen glitzen. so zuckh mit dem Arm. ain wenig zuruckh. vnnd mach ausz dem schlag ain stich auf sein linncke seitten zu dem gesicht. |
||||||
[212] Then, if you want, let the Messer go through and strike at him again with the blunt or the sharp edge at his right side to the upper peak. And what the going through is, you will be taught afterwards. |
Then, if you want, let the Messer go through and strike at him again with the blunt or the sharp edge at his right side to the upper peak. And what the going through is, you will be taught afterwards. And make sure that you do the going through according to my meaning, as I have stated them to be different in the Messer than in the sword. |
[67r.3] Wiltu dan so loß das messer durch gan vnd schlag im wider In mit der stümpffen oder scharffen schniden zu siner rechten siten vff sin obern zÿnnen vnd wz dz duerch gen ist dz wuerstu her nach enttichtt vnd sich eben dz du die durch gen machest noch mÿner meÿnug wan ich die ym messer anders betuett dan Im schwertt |
[37v.2] ¶ wiltu den so laß daß messer durchgen und schlag ym wyder eyn mit der stumpffen oder scharpffen schneyden zw seyner rechten seytten auff dy öbren czynnen etc und waß daß durchgen ist deß wirst hyn nach unterricht |
[67v] Item wiltu so laß das messer durchgen vnd schlag Im wider Ein mit der stumpffen oder scharpffen schneyden zu seyner rechten seytten auff dy obren zynnen vnd waß das durchgen ist das wirstu hin nach vnterricht vnd sich eben das du dy durchgen machest nach meyner maynung wann Ich dy In dem messer anders bedewtten pin dann Im swertt etc |
[100r.6] wiltu dan So loß das messer durch gen vnd schlag Im wider In mitt der stumpffen oder scharffen schniden zů s. r. s. auf die oberen zinnen vnd was das durch gen ist das wirstu hernach vnder recht vnd sich eben das du die durch geng machest nach meyner meynüg |
[168r.3] wiltu dann so lasz den Duseggen. durchgeen. vnnd schlag Im wider ein mit der kurtzen oder scharpfen schneidin zu seiner Rechten seitten. auf die obern plosse. vnd was das /. [168v.1] durch geen ist. das wirstu hernach bericht Vnnd sich oben das du die durchgeen machest nach meinner Mainnung. wann ich die Im duseggen annderst bedeut dann Im schwert |
||||||
[213] |
Then, strike to him from the right side from above firmly to the head. If the goes to it and wants to displace, twitch your Messer to yourself before he binds on it and thrust at his other peak of the other side. Do it in all the hittings of the Messer. |
[67r.4] ein anders Item Haulb im von der rechten siten oben In starck zu dem kopff fert er dar vnd will versetzen so zueck din messer an dich e er dan an pindt vnd stich Im nach der andern zÿnnen der andern siten dz thun In allen treffen des messers ~ |
[37v.3] Item haw ym von der rechten seytten oben starck eyn zw dem kopff fert er dar und wil verseczen so czuck deyn messer an dich ee wan er dar an pyndet und stich ym zw der andren czynnen der andren seytten daß thu yn allen treffen deß messerß etc |
[68r] Item haw Im von der rechten seytten oben starck zu dem kopff fertt er dar vnd will verstetzen So zuck dein messer an dich Ee wenn Er dar an pindet vnd stich Im zu der andren zynnen der andren seytten das thu In allen treffen das messers etc sequir aliud notabile |
[168v.2] Ein annder Zückhen Item haw Im von der Rechten seitten. oben starckh ein zu dem kopff. fert er dar / vnnd will versetzen. so zuckh dein duseggen an dich Ee wann er daran pindes. vnnd stich Im zu der ander zinnen seinner linncken seitten. das thu Inn allem treffen des duseggen. |
|||||||
[214] Then, if he has bound on your Messer and stands against you on the Messer and waits whether you want to pull back, do as if you wanted to pull back and do as if you wanted to twitch, and remain on the Messer and twitch your Messer till the middle of the blade towards yourself. Then, thrust on the Messer again quickly at the face or chest. |
Then, if he has bound on your Messer and stands against you and waits whether you want to pull back and [do] as if you wanted to twitch, and remain on the Messer and twitch your Messer till the middle of the blade towards yourself. Then, thrust on the Messer again quickly at the face or chest. And if you want to twitch, you always have to wind your Messer against his one, so that the long edge is above, as you have heard it before. |
[67r.5] ein anders Item hat er an din messer gebünden vnd stat er dan gegen dir am messer vnd wartt ob du dich wellest ab ziehen So thun als ob du dich [67v.1] Wellest ab ziehen vnd also du wellest zuecken vnd blib im messer vnd zueck din messer vntz an die mitt der clingen an dich vnd stich am messer wider in pald zu dem gesichtt oder brust So du also wilt zucken So müstu din messer alwegen winden gegen sinem dasz die lang schnid oben ste als du vor gehortt hast ~ |
[37v.4] Item hat er an deyn messer gepunden und stet er den gegen dir am messer und wart ob dw dich wollest abczyhen so thu alz dw dich wollest abczyhen und thu alz dw wollest czucken und pleyb am messer und czuck deyn [38r.1] messer uncz an dy mit der klingen an dich und stich am messer wyder eyn pald zw dem gesicht oder prust |
[68v.1] Item hatt er an deyn messer gepunden vnd stet er dann gegen dir vnd wartt ob du dich wollest ab zyhen vnd als du wollest zucken vnd pleyb am messer vnd zuck deyn messer vntz an dy mit der klingen an dich vnd stich am messer wider Eyn pald zu dem gesicht oder prust vnd So du wilt zucken So mustu deyn messer albeg winden gegen dem seynen das dy lang schneyd oben stee als du vor gehōrtt hast etc |
[168v.3] Mer ain anders Zucken Item hat er dir an dein Duseggen. gepvnden. vnnd steet daran still vnnd wart ob du dich wollest abziechen. so thu gleich als wollest. abziechen oder vom duseggen zuckhen / zuckh aber nit. sonder bleib dar= [169r.1] an stehen. vnnd zuckh dein duseggen. Mit der klinngen an dich. vnnd stich am duseggen wider bald ein zu dem gesicht oder prust. so du allso wildt zucken. so magstu dein duseggen allweg wennden gegen dem seinnen / das die lanng schneid oben stee. alls du vor gehort hast. |
|||||||
[215] |
Then, if you do not hit him rightly with the thrust, work with the doubling or with other good elements. |
[38r.2] Item drifst dw yn nicht recht mit dem stich so arbayt mit dem dupliren oder mit andren stucken etc |
[68v.2] Item Trifstu In nicht recht mit dem stich so erbeyt mit dem dupliren oder mit andren gutten stucken etc |
[169r.2] Ainn annders stückh trifstu In nit recht mit dem stich. so arbait mit dem duppliern oder anndern guten stucken zu Im behenndigclich ein |
||||||||
[216] |
Then, another twitching. If you stand in the Bastei and he strikes from above at you to your left side, step in a twofold manner to your right side out of the stroke and twitch your body out of the stroke. Then, strike at his upper opening and do not let yourself be bound on the Messer. |
[38r.3] Item eyn anderß czucken steestu ynder pasteyn und hawt er den von oben auff dich auff deyn lincke seytten und so schreyt dw czwiuach auff deyn rechte seytten auß dem haw und czuck den leyb auß dem haw und haw ym nach der oberen ploß und laß dir nicht an daß messer pynden |
[69r] Item Ein anders zuckn steestu In der pastey vnd hawt er denn von oben auff dich auff deyn lincke seytten so schreyt ziuach auff deyn rechte seytten auß dem haw vnd zuck den leyb auß dem haw vnd haw Im nach der obren ploß vnd loß dir nicht an das messer pinden; |
[169r.3] Einn zückhen so Du Inn der Pastey steest. Item steestu Inn der Pastey / hawt Er dann von oben auf dein linncken seitten. so schreit du zwifach auf dein rechten seitten. vnnd zuckh den leyb ausz dem haw. vnnd haw Im nach der obern plosse / vnd merckh das du dir nit an dein duseggen pinden lassest |
||||||||
[217] |
Then, if he strikes at you from the Luginsland and you also stand it in, twitch your Messer to yourself while he strikes and do not let him come on it. Instead, if he strikes from his right side to your left one, twitch your Messer to yourself and step to his right side with a twofold step and strike at his upper peaks. You can perform it on both sides. |
[38r.4] Item haut er dir von dem luginsland zw so dw auch dar ynnen stet so czuck yn seynem haw deyn messer an dich und laß yn nicht dar an kommen sunder hawt er von seyner rechten seytten zw deyner lincken so czuck deyn messer an dich und schreyt auff seyn rechte seytten eynen czwiuachen trit und schlag yn zw den obren czynnen daß magstu treyben von payden seytten |
[69v] Item haut Er dir von dem luginslandt zu so du auch dar In stest so zuck In seynem haw das messer an dich vnd laß In nicht dar an komen Sunder hawt Er von seyner rechten seytten zu deyner lincken So zuck deyn messer an dich vnd schreyt auff seyn rechte seytten Ein zwiuachen Trit vnd schlag Im zu den ōbren zynnen das magstu Treyben von payden seytten etc |
[169v.1] Ein zuckhen so du Inn dem luginslannd steest. Item hawt er dir von Im luginsland zu vnnd du auch dar Innen steest. so zuckh ausz seinnem haw. dein duseggen. an dich. vnnd lasz In nit daran kumen svnnder hawt Er von seinner rechten seitten zu deinner linncken. so zuckh dein duseggen. an dich vnnd schreit auf seinn rechte seitten. ain zwifachen trit. vnnd schalg Im zu der obern plosse / das magstu treiben zu baiden seitten |
||||||||
[218] |
Then, if he has bound you on the Messer on your left side and wants to strike around to the other peak, do not displace. Instead, strike to the other peak and step in a twofold manner away to his right side and strike at his neck or at his head. |
[38v.1] Item hat er dir an daß messer gepunden auff deyner lincken seytten und will er umb schlagen zw der andren czynnen So versecz ym nicht sunder schlag zw der andren czynnen und trit czwiuach auß auff seyn rechte seytten und schlag ym zw dem nacken oder auff daß hawbt |
[70r] Item havtt er dir an das messer gepunden auff deyner lincken seytten vnd will Er vmb schlahen zu der andren zynnen so versetz Im nicht Sunder schlag zu der andren zynnen vnd Tritt zwiuach auß auff seyn rechte seytten vnd schlag Im zu dem nacken oder auff das haubtt etc |
[169v.2] Ein zücken ausz dem Anpund Item hat Er dir an dein duseggen gepunden. Auff deinner linncken seitten. vnnd will sich vmb schlagen zu der anndern zinnen. so versetzt Im auf dein rechten seitten. vnnd schlag In zu dem Rackh oder auf das haupt |
||||||||
[219] |
Then, a quite good twitching. If you want to do it, do it this way: if you stand in the guard of the Luginsland and he has bound you on your Messer on your left side and wants to strike around to your right side, twitch your Messer towards yourself and raise the hilt to the head, so that the short edge is against you, and let the point go down to your left side. Then, set the point in his throat or chest and push him with it backwards. |
[38v.2] Item aber gar eyn gucz czucken und ist eyn guldenß stuck wiltu daß machen so thue ym alzo stest dw ynder hut luginsland und hat er dir an deyn messer gepunden auff deyner lincken seytten und will er umb schlagen zw deyner rechten seytten so czuck deyn messer an dich daß dy kurcz schneyd gegen dir stee und laß den ort nyder sincken an deyner lincken seytten ab und secz ym den ort an seyn kelen oder prust und scheub yn da mit zw ruck etc |
[70v] Item aber gar Ein gutz zucken wiltu das machen so thu Im also stestu In der hut luginslandt vnd hatt er dir an deyn messer gepunden auff deyner lincken seytten vnd Er will vmb schlagen zu deyner rechten seytten So zuck deyn messer an dich vnd Erhöch das gehultz fur das haubtt das dy kurtz schneyd gegen dir stee vnd laß den ortt nyder sinken an deyner lincken seytten ab vnd setz Im den ortt In seyn kelen oder prust vnd scheub In da mit zu ruck etc. |
[170r.1] Einn annders Zuckhen Item merckh ain gar guott. Ernnstlichstuckh / wiltu das machen so thu Im also / steestu Inn der hut luginslannd / vnnd hat er an dein duseggen gepvnnden. auf deinner linncken seitten. vnd will vmb schlagen zu seinner rechten seitten so zuckh dein duseggen ann dich vnnd erhoch das gehultz fur dein haupt. das die kurtz schneid gegen dir stee. vnd lasz den Ort nider sennckhen. an deinner linncken seitten ab. vnnd setz Im den ort Inn sein keel oder prust / vnnd stosz In allso damit zuruckh. |
||||||||
[220] |
If the gate stands open Here the master teaches how one should work with the point and how to twitch in the feints, and speaks: If stands open, etc. You should understand it this way: go crosswise close to the man to his left side and do as if you wanted to strike to his right side. Go over your head so that you come above the middle of your head so that the point comes out backwards and the hilt is against the man. Then, strike again to his left side, and as you surely come to his left side to the Messer, do not strike to his Messer so that you hit it. Instead, do as if you wanted to hit it and “simultaneously” twitch your Messer close at his crosspiece towards yourself, and thrust at his face to his right side, so that the short edge is below and the thumb lies on the flat. |
[71r] Stet offen dy pfortt Hie lertt der meyster wye man mit dem ortt Erbeytten vnd zucken soll In dy feler vnd spricht stet offen etc Das sol dw also verstan Gee mit der zwirch nohendt an den man zu seyner linckn seytten vnd Thu samb[32] dw wolst schlagen zu seyner rechten seytten vnd far vber deyn haubtt so dw kumbst vber dy mit deynes haubtz das der ortt hinden hin auß gett vnd das gehultz gegen dem man stee So schlag wyder zu seyner lincken seytten So du schir zu seyner lincken seytten zu dem messer kumbst so haw nicht zu seynem messer das dw das Treffest Sunder Thu samb dw es Treffen wollest Indes zuck nohendt bey seynem kreutz deyn messer an dich vnd stich Im zu seynem antlitz auff seyner rechten seytten das dy kurtz schneyd vntten stee vnd der dawmen auff der flech lig etc |
||||||||||
[221] |
Strike your flat to the Luginsland The sense or the meaning of the text you should understand this way: if he stands in the guard of the Luginsland, strike from your right shoulder with the flat against his Messer, so that the long edge is against you. And as you strike, step with your right foot well to his right side to his right foot and strike equally to his Messer. And as the Messers are surely to spark together, “simultaneously” twitch your Messer to yourself with the hilt against your left side, and thrust the point firmly with no displacement rudely at his face to his right side. |
[67v.2] Haulb din flech zuem lueginßlant Die meÿnüng des text Soltu also verstan Stat er in der hut lüginßlant So haulb von diner rechten siten oder achschell mit der flech gegen sinem messer dz die lang schnid gegen dir ste vnd im haulb so schrit mit dinem rechten fus woll vff sin rechten siten zu sinem rechten fus vnd haulb glich zu sinem messer vnd so die messer schier zu samen glitzen Indes zueck din messer an dich mit [68r.1] gehultz gegen diner lincken siten vnd stich im den ortt strack an alle versatzüng grob zu dem gesicht siner rechten siten |
[38v.3] Haw deyn flech zum luginslandt Daß solt dw alzo verstan stet er yn der hut luginslandt so haw von deyner rechten achseln mit der flecht gegen seynem messer daß dy lang schneyd gegen dir stee und ym haw so schreyt mit deynem rechten fuß wol auff seyn rechte seytten zw seynem rechten fuß und haw gleich zw seynem messer und so dy messer schir zw sammen wellen kliczen yndeß czuck deyn messer an dich mit dem gehulcz gegen deyner lincken seytten und stich ym den ort starck und grob zw dem gesicht seyner rechten seytten |
[71v.1] Haw deyn flech zum luginslandt Senesu[33] dy maynung des Textz soltu alzo verstan stett er In der hutt luginslandt so haw von deyner rechten achsel mit der flech gegen seynem messer das dy lang schneyd gegen dir stee vnd Im haw So schreyt mit deynem rechten fuß woll auff seyn rechte seytten zu seynem rechten fuß vnd haw gleych zu seynem messer vnd So dy messer Schir zu sammen wollen klitzen Indes zuck deyn messer an dich mit dem gehultz gegen deyner lincken seytten vnd stich Im den ortt starck an alle versatzung grob zu dem gesicht seyner rechten seytten vnd merck das du Im Stich ym nachschreytest deynen lincken fuß mit deynem rechten das der schritt zwiuach wer etc |
[170r.2] Haw dein flech zum lüginsland [170v.1] Item das soltu allso Verstan. steet Er. Inn der hut luginslannd. so haw von deinner rechten Achsel oder seitten. mit flech gegen seinnem Duseggen. das die lanngschneid gegen dir stee. vnnd Im haw so schreit wol auf sein rechten seitten. mit deinnem Rechten fuosz zu seinem rechten schennckel. Indes haw gleich zu seinnem duseggen. vnnd so die duseggen schier zusammen glitzen. so zuckh dein Duseggen an dich mit dem gehultz gegen deinner linnckhen seitten. vnnd stich Im den ort starckh on alle ver versatzung zu dem gesicht seinner rechten seitten. |
|||||||
[222] |
And make sure that you step after your left foot with your right foot as you thrust, so that the step is twofold. |
[68r.2] vnd merck daß dü im stich Im noch schritteßt dinen lincken fus mit dinen rechten dz der schrit zwieffach wer ~ |
[39r.2] ¶ und merck daß dw ym stich ym nach schreytest deynen lincken fuß mit deynem rechten alzo daß der schrit czwiuach wer etc |
[71v.2] vnd merck das du Im Stich ym nachschreytest deynen lincken fuß mit deynem rechten das der schritt zwiuach wer etc |
[170v.2] vnnd merckh das du Im stich nach schreitest. mit deinnem linckhen fuosz vnnd mit dem Rechten auch hinnach / damit der trit zwifach wird. |
|||||||
[223] |
Then, whether you have hit him with the thrust or not, wind after the thrust “simultaneously” to your left side, so that the thumb is below on the Messer and the long edge is turned against the man. And go with your Messer over the middle of your head to your right side and do as if you wanted to strike at his left side. “Simultaneously” go again to his right side and “simultaneously” go again high with the Messer so that the thumb is below. And step with your right foot well to his right one and strike again at him to the same side behind the blade of his Messer, with the short edge to his face. And step well with your left foot behind his right one and strike at his neck. “Simultaneously,” if you want, you can hit him. |
[68r.3] ein anders Item hastu In mit dem stich troffen oder nit so wind noch dem stich indes vff sin lincke siten dz der thuem an dem messer am vnten sy vnd die lang schnid gegen dem man kerett vnd far mit dem messer vbor die mit dines hauptes zu der rechten siten vnd thuen starck zu der lincken siten schlagen wellest Indes far im wider zu siner rechten siten Indes far wider vff mit dem messer dz der thun aber vntten sÿ vnd schritt aber mit dinem rechten fus wol vff sin rechten vnd schlag im wider In zu der selbigen siten Hinder sins messers klingen die kuertz schnid im in daß an gesicht vnd schrit aber mere mit dinem lincken fus wol hinter sin rechten vnd schlag In in den nack wiltu dan so muestu den treffer auch gar wol darin machen ~ Sequitur textus |
[39r.3] Item hastu yn mit dem stich getroffen oder nicht so wynd nach dem stich yndeß auff deyn lincke seytten daß der dawm an dem messer unten sey und dy [39v.1] lang schneyd sey gegen dem man gekert und far mit deynem messer uber dy mit deyneß haubcz zw deyner rechten seytten und thu samb dw ym zw seyner lincken seytten schlagen wollest yndeß schlag ym wyder zw seyner rechten seytten yndeß far wyder auff mit dem messer daß der dawm aber unten sey und schreyt aber mit deynem rechten fuß woll auff seyn rechten und schlag ym wyder eyn zw der selben seytten hynter seyneß messerß klingen dy kurcz schneyd ym yn daß angesicht und schreyt aber mer mit deynem lincken fuß woll hynter seynem rechten und schlag yn yn den nack wiltu denn so magstu den treffer dar eyn auch machen etc |
[72r] Item hastu In mit dem stich getroffen oder nicht So windt nach dem stich Indes auff dein lincke seytten das der dawm an dem messer vnden sey vnd dy lang schneyd gegen dem man gekertt sey vnd far mit deynem messer vber dy mitten deynes mes[34] haubtz zu deyner rechten seytten vnd thue samb dw Im zu seyner lincken seytten schlagen wolst Indes far Im wider zu seyner rechten seytten Indes far wider auff mit dem messer das der dawm aber vnden sey vnd schreytt aber mit deynem rechten fuß woll auff seyn rechten vnd schlag Im wider Ein zu der selbigen seytten hinter seynes messers klingen dy kurtz schneyd Im Inn das angesicht vnd schreyt aber mer mit deynem lincken fuß woll hinter seynen rechten vnd schlag Im In den nack Indes wiltu magstu Im den Treffer machen wie vnden gemalt stet etc |
[170v.3] Item hastu In Mit dem stich troffen oder nit so wind Indes nach dem stich auf sein. linncke seitten. das der daumen an an dam duseggen vnnden stee. vnnd die lanng schned gegen dem Mann stee Indes schlag Im zu seinner rechten seitten. vnnd far wider auf mit dem Duseggen / das der dawn aber vnnden ste. vnnd schreit mit deinnem rechten fuosz wol auf sein rechten seitten Indes schlag Im. wider ein zu derselben seitten hinnder seinnes Duseggen klingen die kurtz schneid Inn sein angesicht. auch magstu den treffer wol darein machen. |
|||||||
[224] If he is strong Here the master speaks about a main element, that is about the running through and how one should run through the other. |
If he is strong Here the propagator of the art speaks about a main element, that is about the running through and how one should run through the other. |
[68v.1] Ob er starck ist Hie saget der meinster aber von eynem haubt stuck als vom durch laufen vnd wie man durchlauffen sol |
[39v.2] Ob er starck ist Hye sagt der meyster aber von eynem haübtstuck alz von dem dürchlaüffen und wye man den man dürchlauffen söl |
[72v.1] Ob er starck ist Hie sagtt der merer der kunst aber von Eynem haubtstuck als von dem durchlauffen vnd wye man dem man durchlauffen soll |
[100r.7] Aber starck ist /etc |
[171r.1] Das dürchlaüffen Ob er Starckh ist |
||||||
[225] Now notice that the running through and hand-to-hand combat belong against the masters who rush in eagerly and are high with the arms and displacement, and want to push you over with force. |
Now notice that the running through and hand-to-hand combat is to be performed against the masters who rush in eagerly and are high with the arms and displacement, and want to push you over with force. |
[68v.2] Nu merck die durchlauffen vnd die ringen gehoren gegen den meinstern die gern eyn lauffen vnd hoch vff mit den armen vnd in versatzung ligen vnd die dich mit sterck wollen vber tringen |
[40r.2] ¶ nw merck dy dürchlaüffen und dy ryngen dy gehören gegen den meysteren dy geren eyn lauffen und hoch auff mit dem armen und versaczung lygen und dye dich wollen mit sterck uber dryngen |
[72v.2] Nu merck dy durchlauffen vnd dy ringen dy gehoren den meysteren zu treyben dy gerne Ein lauffen vnd hoch auff mit den armen vnd versatzung ligen vnd dy dich mit sterck wellen vber dringen etc |
[100r.8] Nün merck das die durch laufffen vnd die ringen die geheren den meystern die gern Im lauffen vnd hoch auff mit dem arm vnd In versatzungen ligen vnd die dich mit stercke wellen übertringen |
|||||||
[226] Now, do the running through this way: if he strikes against you with an upper stroke, strike also together with him the Entrüsthau closely, so that the hands touch surely on each other, and “simultaneously” grab with your left hand behind his elbow on the outside and push him from you to his left side. “Simultaneously” drop your Messer and grab with your right hand or arm on the outside at his right knee-bending and lift him up and throw him away from you. |
Then, do the running through this way: if he strikes against you with an upper stroke, strike also together with him the Entrüsthau close to him, so that the hands touch surely on each other, and “simultaneously“ grab with your left hand behind his elbow on the outside and push him from you to his left side. “Simultaneously” drop your Messer and grab with your right hand or arm on the outside at his right knee-bending and lift him up and throw him in front of you. |
[68v.3] Nu die durchlauffen mach also haut er gegen dir ein ober haulb so haulb auch glich mit im in den entruest haulb nahent dz bÿ die hend an eynnandern rueren Indes griff mit diner lincken hant hinder sin elnbogen vszwendig vnd schuebe In von dir vff syn lincken siten Indes s laß din messer fallen vnd grÿff mit diner rechten hant oder arm vßwendig in sin knue buege heb in vff vnd wuerff in etc |
[40r.3] nw dy dürchlaffen mach also hawt er gegen dir mit eynem oberhaw so haw auch gleych mit ym eyn den entrusthaw nohent daß schir dy hend an eyn ander rüeren yndeß greüff mit deynem lincken hand hynter seynen ölpogen aüßbendigß und scheüb yn von dir auff seyn lincke seytten yndeß laß deyn messer fallen und greuff mit deyner rechten hand oder armen außbendigß yn seyn rechte knyepueg [40v.1] heb yn auff und wirff yn von dir etc |
[73r] Item dy durchlauffen mach also hautt er gegen dir eynen oberhaw So haw auch gleych mit Im Eyn den Entrusthaw nohendt zu Im das dy hendt schir an Eyn ander rüren Indes greyff mit deyner lincken handt hinter seynen olpogen außbendig vnd scheub In von dir auff seyn lincke seytten Indes laß deyn messer vallen vnd greyff mit deyner rechten handt oder arme außbendigs In sein rechte knÿpug vnd heb In auff vnd wirff In furdich etc |
[100r.9] Nůn die durch lauffen mach also hawt er gegen dir ein ober haw So hew auch glich mit Im In nider(?) entrist hew nohen das die hend bey an einander rieren Indes grif mit deyner lincken hand hinder seynen ellenbogen auswendig vnd scheyb In von dir auf sein lincken seytten Indes loß dein mesß vallen vnd griff Im mitt deyner rechten hand oder arm auß wendig in sein rechte knipuge heb In auf vnd wirff in |
[171r.2] Item das durchlauffen Mach all. so hawt Er gegen dir ain oberhaw. so haw auch gleich mit dem Entristhaw. das baid hend an ainannder kumen Indes. greiff mit deinner lincken hand hinder seinnen Elenpogen auszwendig. vnnd scheub In von dir auf sein lincken seitten Indes lasz dein duseggen falle. vnnd greiff mit deinner rechten hannd auszwenndig Inn sein kniepuge. heb In auf. so wirfstu In. |
||||||
[227] |
Then, if you both have bound, grab his right hand with your left one and raise with it high, and come to help your left hand with your right hand. Then, turn with your back against him and break his arm over your right shoulder with both hands. |
[68v.4] ein anders [69r.1] Item habt ir beide an gebünden So begriff sin rechte hant mit diner lincken vnd heb do mit hoch vff vnd kum diner lincken hant zu hilff mit diner rechten vnd wind dich mit dem ruck gegen im vnd brich im den arm vber din rechten ab achsel mit peÿden henden |
[40v.2] Item habt Ir payde an gepünden so pegreuff seyn rechte hand mit deyner lincken und heb da mit hoch aüff und kümb deyner lincken hand zw hilff mit deyner rechten und wendt dich mit dem ruck gegen ym und prich ym den armen uber deyn rechte achsel mit payden henden etc |
[73v] Item habt Ir payde an gepunden So pegreyff seyn rechte handt mit deyner lincken vnd heb da mit hoch auff vnd kum deyner linckn handt zu hilff mit deyner rechten vnd wendt dich mit deynem ruck gegen Im vnd prich Im den arme vber deyn rechte achseln mit payden henden etc |
[100r.10] Item habt ir beyd an gebunden So begriff sein recht hand mit deiner lincken hand vnd heb do mit hoch auf vnd kümpt mit deiner lincken hand zů hilff vnd wend dich mit deim ruck gegen im vnd brich im den arm über dein rechte achsel mit beyden henden |
[171v.1] Einn durchlauffen Ausz dem anpvnnd. Item hapt Ir baid Ainannder angepvnden. so begreiff sein rechte hannd. mit deinner linncken. vnnd heb hoch vbersich auf. Indes kum deinner lincken hannd zu hilff mit deinner rechten. vnnd wennd dich mit dem Rucken gegen Im vnnd prich Im den Arm vber dein rechten achsel mit baiden hennden. |
||||||
[228] |
Then, if you both have bound as before, grab with your right hand at his right one and come to help your right hand with your left hand forwards at the joint, and turn your left shoulder against his right arm. Then, raise it high above it and break his arm over your left shoulder. And take care that the elbow comes always on the shoulder, and do it as it is depicted below. |
[74r] Item habtt Ir an gepunden wy vor So greyff mit deyner rechten handt In seyn rechte vnd kum deyner rechten mit deyner lincken zu hilff vorne bey dem gelenck vnd wendt deyn lincke achsel gegen seym rechten arme vnd heb den hoch dar vber vnd prich Im den arme vber deyn lincke achsel vnd maß dich das der olpogen albeg auff dy achsel kum vnd mach das wye vntten gemalt stett etc |
||||||||||
[229] |
Then, if he has run into you and you against him, grab his right hand with your left one on the inside and turn it from you. Then, raise his arm well high and “simultaneously” run with the head through his arm to his right side, and put his right arm with your left hand on the neck and over your left shoulder. Then, rise well high with the neck and with the shoulders and break his arm firmly over it. |
[69r.2] ein anders Item hat er dir ein gelauffen vnd du im wider so begriff im sin rechten hant mit diner lincken Inwendig vnd rieb die von dir vnd heb im den arm woll vff Indes lauff mit dem hauptt durch sin arm vff siner rechten siten vnd rueck im sin rechten arm mit diner lincken hant vff din nack vnd vber din lincken achsell vnd erheb dich woll vff mit dem nack vnd mit den schultern vnd brich im den arm starck darvber ~ |
[40v.3] Item hat er dir eyn geloffen und dw ym wyder so pegreuff seyn rechte hand mit deyner lincken ynbendigs und reyb dy von dir und heb ym den armen wol auff yndeß lauff mit dem haubt dürch seyn armen auff seyner rechten seytten und ruck ym seyn rechten armen mit deyner lincken hand auff deyn nack und uber deyn lincke achsellen und erheb dich woll auff mit dem nack und mit den schülteren und prich ym den armen starck dar uber etc |
[74v] Item hatt er dir Eyn geloffen vnd dw Im wider so pegreuff sein rechte hand mit deyner lincken Inbendigs vnd reyb dye von dir vnd heb Im den arme woll auff Indes lauff mit dem haubt durch sein arme auff seyner rechten seytten vnd ruck Im seyn rechten arme mit deyner lincken handt auff den nacken vnd vber deyn lincke achseln vnd Erheb dich woll auff mit dem nack vnd mit den schultern vnd prich Im den arme starck dar vber |
[171v.2] Ainn annders Durch lauffen Item Ist Er dir Eingelauffen. vnnd du Im Wider so begreiff sein rechte hannd mit deinner linncken Innwendig vnd reib die von dir. vnnd reib Im den arm wol auf. Indes lauf mit deinnem haupt durch sein arm. auf sein rechten seitten. vnnd ruckh Im den Arm mit deiner lincken hand auf den nackh vnnd vber dein lincken achsel er heb dich wol auf mit dem Rackh vnnd mit den schultern. vnnd prich Im den arm starckh Dariber. |
|||||||
[230] |
Then, another element: if he has run into you and you have also done so, grab his right hand with your left one and lift his arm well above you. Then, go with the head through the arm and grab with your right hand at his right knee-bending, and lift him up with the shoulders. Then, grab with your right hand in his right knee-bending and lift him up at the leg and throw him over the back. |
[69r.3] ein anders Item ein anders hat er dir in gelauffen vnd du im auch So begriff sin rechte hant mit diner lincken vnd heb im sin arm wol vber sich vnd gee mit dem haupt durch den arm vnd griff mit der rechten hant in sin rechte knuegbueg vnd heb in mit den schultern pÿ dem beyn vff vnd würff in vber din rueck vff den kopff ~ |
[40v.4] Item eyn anderß stuck hat er dir eyn geloffen und dw ym auch so pegreuff [41r.1] seyn rechte handt mit deyner lincken und heb ym seyn armen wol ubersich und gee mit dem haubt dürch den armen und greuff mit der rechten handt yn seyn rechte knyepug und heb yn mit den schultren und pey den payn aüff und wirff yn uber den ruck auff den kopff |
[75r] Item Ein anders stuck hatt er dir Ein geloffen vnd du Im auch So pegreyff seyn rechte handt mit deyner lincken vnd heb Im seyn arme woll vbersich vnd gee mit dem haubt durch den arme vnd greyff mit deyner rechten handt In I seyn rechte knypug vnd heb In mit den schultern auff vnd wir greyff mit deyner rechten handt In seyn rechte knypug vnd heb In pey dem pein auff vnd wirff In vber den ruck etc |
[172r.1] Mer ainn durchlauffen Item Ist dir Einnge lauffen vnnd du Im auch. so begreiff dein rechten hannd mit deinner lincken. vnd heb Im sein arm wol. wol.[35] vbersich. Indes gee mit dem haupt durch sein arm. vnnd greiff mit der rechten hannd Inn sein rechten kniepug. heb In mit der schultern bey dem bain. vnnd wirff. In vber dein rucken auf den kopff. |
|||||||
[231] |
Then, an element: grab with your left hand in his right one and turn it from you to your left side. Then, step with your right foot behind his right one and grab with your right hand from the front around his body and throw him forwards over the hip of your right leg. |
[69r.4] ein anders stuck [69v.1] Item aber eyn stueck griff in mit der lincken hant in sin rechte vnd rieb dir die von dir in din lincke siten vnd schrit mit dinem rechten fus hinder sin rechten vnd griff mit diner rechten hant vorn vmb sin lip vnd wurff in for dich vber die huefft dines rechten peins ~ |
[41r.2] Item aber eyn anderß stuck greuff ym mit der lincken hand yn seyn rechte und reyb dy von dir yn deyn lincke seytten und schreyt mit deynem rechten fuß hynter seynen rechten und greüff mit deyner rechten hand voren umb seyn leyb und wirff yn furdich uber dy huff deyneß rechten paynß etc |
[75v] Item aber Ein stuck Greyff mit der lincken hand In seyn rechte vnd reyb dy von dir In deyn lincke seytten vnd schreytt mit deynem rechten fuß hinter seynen rechten vnd greyff mit deyner rechten handt vorne umb seyn leyb vnd wirff In furdich vber dy hüff deynes rechten peyns; |
||||||||
[232] |
Then, another element: if he runs into you with the stretched arm and you do against him, run him through with the head through his right shoulder under his right arm on his right side, and step with your right foot in front of his right one. Then, go with your right arm under his right one and around his body from behind and lower your stance a bit, and grab him on your right hip and throw him behind yourself. |
[69v.2] ein ander stuck Item eyn ander stuck wan er dir in lauffett mit vf gerechten armen vnd du im wider so lauff im durch mit dim haupt vntter sin rechten arm siner rechten vnd schritt mit dinem rechten fus vorn fur sin rechten vnd far im mit dinem rechten arm vnter sin rechten durch vnd hinten vmb sin lib vnd senck dich eyn wennick nider vnd faß in vff din rechten huefft vnd wurff in hinder dich ~ |
[41r.3] Item eyn anderß stuck wenn er dir eyn laüfft mit auff geracktem armen und dw ym wyder so lauff ym durch mit dem haubt unter seyn rechten armen zw seyner rechten seytten und schreyt mit dem rechten fuß voren fur seynen rechten und far ym mit dem rechten armen unter seyn rechten armen [41v.1] durch hynten umb seyn leyb und senck dich eyn benig nyder und faß yn auff deyn rechte hüff und wirff yn hynterdich etc |
[76r] Item Ein anders stuck wenn Er dir In laufft mit auff geracktem arme vnd du Im wider so lauff Im durch mit dem haubt durch seyn rechte vchsen vnter seynen rechten arme seyner rechten seytten vnd schreytt mit deynem rechten fuß forne fur seynen rechten vnd far Im mit deynem rechten arme vnter seynen rechten durch vnd hinten umb seynen leyb vnd senk dich Ein benig nyder vnd faß In auff deyn rechte hüff vnd wirff In hinter dich etc |
||||||||
[233] |
Then, if one runs into you to your right side and is high with the arms, and you are also, hold your Messer at his one and go with the hilt over his right hand and turn yourself to him with your left side towards his right one. And leap with your left foot in front of his right one and go with the arm well around his body from behind, and lower your stance a bit. Then, catch him on your left hip and throw him forwards on his face. Or, let him fall on your Messer, as you certainly know. |
[69v.3] ein anders Item laüfft dir eyner eyn zu diner rechten siten vnd ist hoch mit dem arm vnd du auch so halt din messer zu dem seynen vnd far im mit dem gehultz vber sin rechte hant vnd wind dich an In mit diner lincken siten an sin rechte vnd spring mit dem lincken fus fur sin rechten vnd far mit dem arm wol hinten vmb [70r.1] sin lib vnd senck dich ein wenig nider vnd fas in vff din lincke huefft vnd wurff in fur dich vff sin antzlutz oder laß in In din messer fallen als du woll weÿst ~ |
[41v.2] Item laüfft dir eyner eyn zw deyner rechten seyten und ist hoch mit dem armen und du auch so halt deyn messer zw dem seynen und far ym mit dem gehulcz uber seyn rechte hand und wendt dich an yn mit deyner lincken seytten an seyn rechte und spring mit deynem lincken fuß fuer seyn rechten und far mit dem armen hynter wol umb seyn leyb und senck dich eyn wenig nyder und faß yn auff deyn lincke huff und wirff yn furdich auff seyn antlicz oder laß yn ynn deyn messer fallen |
[76v.1] Item laufft dir Eyner Ein zu deyner rechten seytten vnd ist hoch mit dem arme vnd du auch So haltt deyn messer zu dem seynen vnd far mit dem gehultz vber seyn rechte handt vnd wendt dich an In mit deyner lincken seytten an seyn rechte vnd spring mit deynem lincken fuß fur seynen rechten vnd far mit dem arme hinten woll vmb seyn leyb vnd senck dich Ein wenig nyder vnd faß In auff deyn lincke hüff vnd wirff In furdich auff seyn antlitz vnd oder laß In Ein[36] deyn messer vallen als dw woll weyst etc |
||||||||
[234] |
Then, if he is too strong for you, so that you cannot throw him easily over your hip, go with the hilt of your Messer firmly on the nape of his neck and pull with it to your right side, so that you throw him certainly.
|
|||||||||||
[235] |
Then, if one runs into you and holds his Messer and his arms low, grab with your left turned hand in his right one on the inside and leap with your right foot behind his right one. Then, go with your right hand from the front around his neck and throw him over the right hip. |
[41v.3] Item wenn er dir eyn laüffet und helt seyn messer nyder und dy hand so greuff mit deyner lincken verkerten hand seyn rechte ynbendig und spring mit dem rechten fuß hynter seynen rechten und far mit dem rechten armen voren umb den halz und wirff yn alzo uber [42r.1] dy rechten huff etc |
[77r] Item wenn dir Eyner Ein lauffet vnd hellt seyn messer nyder vnd dy handt So greyff mit deyner lincken verkerten handt In seyn rechte Inbendig vnd spring mit deynem rechten füß hinter seynen rechten vnd far mit deynem rechten arme vorne vmb seyn hals vnd wirff In alzo vber dy rechten huff; |
|||||||||
[236] |
Then, if you have grabbed him on the outside at his right arm with your right hand, pull his right one firmly with your right one, and go with the left hand around his neck on the outside and throw him over your left leg or hip. |
[42r.2] Item hastu den aüßwendigß gefast bey seyner rechten handt mit deyner rechten so czeüg sere seyn rechte mit deyner rechten auff deyn prüst und far mit der lincken hand ausser umb seyn halz und wirff yn uber deyn linckeß payn oder huff etc |
[77v.1] Item hastu In außbendig gefast bey seynem rechten arme mit deyner rechten handt so zeuch sere seyn rechte mit deyner rechten vnd far mit der lincken handt aussen vmb seyn leyb hals vnd wirff In vber deyn linckes peyn oder huff; |
|||||||||
[237] |
Then, if one runs into you on the Messer and holds his hand low, go with your hilt on the outside up over his arm over the right hand, and press with it firmly down. Then, pull it well to your chest and grab him with the left hand at his right elbow and leap with the left foot in front of his right one and push him over it. |
[42r.3] Item wenn dir eyner eyn lauffet ym messer und ist nyder mit der handt so far mit dem gehultz aussen ym oben uber seyn armen uber dy rechten handt und drück da mit nyder und zeüch dy woll auff deyn prust und faß in mit der lincken hand bey seynen rechten ölpogen und spring mit dem lincken fuß fur seynen rechten und drück yn also dar uber etc |
[77v.2] Item wenn dir Eyner Ein lauffett Im messer vnd ist nyder mit der handt so far mit deynem gehultz aussen Im oben vber sein arme vber dy rechten handt vnd druck do mit nyder vnd zeuch dy da mit woll auff deyn prust vnd faß In mit der lincken handt bey seynem rechten olpogen vnd spring mit dem lincken fuß fur seyn rechten vnd druck In also dar vber; |
|||||||||
[238] |
Then, go to him as before and push him with your left hand to his left side on his right arm and go with your right hand “simultaneously” behind his right elbow and push him well to his left side. Then, go with your left hand on the inside to his right knee-bending and step with your left foot in front of his left one and throw him in front of you. |
[78r] Item Gee an In wye vor vnd scheub In mit deyner lincken handt auff seyn lincke seytten auff seynen rechten arme vnd far mit deyner Rechten handt Indes hinter seynen rechten ōlpogen vnd scheub In woll auff seyn lincke seytten vnd far mit deyner lincken handt Inbendigs In sein rechte knypug vnd schreytt mit deynem lincken fuß fur seyn lincken vnd wirff In für dich etc |
||||||||||
[239] |
Then, the text speaks: The joints you should, etc. If you come to him in the Zufechten, fall with the left hand on the inside from above over his Messer and grab “simultaneously” with your left hand down to your Messer in the middle of it. Then, go firmly with your Messer on his one on the outside, and leap with the entire body “simultaneously” to his left side, in this way you take his Messer. |
[42r.4] Item der text spricht der glider etc daß soltu alzo verstan wenn dw zw ym kümbst ym zwvechten und er zw dir so fall ym mit der lincken handt [42v.1] ynbendigs oben uber seyn messer und greuff mit deyner lincken hand unten an deyn messer yn dy mit deyneß messerß und far starck mit deynem messer an seyn messer und spring mit ganczem leibn yndeß auff deyn lincke seytten so nymbstu ym daß messer |
[78v] Item der text spricht der glider soltu etc Wenn dw zu Im kumbst Im zuuechten So fall Im mit der lincken hend Inwendigs oben vber seyn messer vnd greyff Indes mit deyner lincken hand vntten an deyn messer In dy mit vnd far starck mit deynem messer an das seyn außbendig vnd spring mit gantzem leyb Indes auff seyn lincke seytten so nymbstu Im das messer |
|||||||||
[240] |
Then, go on him as before and go with your left arm over his Messer. “Simultaneously” go with your left hand in the middle of your Messer and let the point go out on your left side. Then, go from inside with the hilt on his hand and leap to your left side, in that way you take his Messer. |
[79r] Item Gee an In als vor vnd far mit deynem lincken arme vber seyn messer Indes far mit deyner lincken handt In dy mitt deynes messers vnd laß den ort auff deyner lincken seytten hyn auff gan vnd far Im Inwendigs mit dem gehultz an seyn handt vnd spring auff deyn lincke seytten So nymbstu Im seyn messer; |
||||||||||
[241] |
Then, if he strikes at you, leap with the bowing under his Messer and grab with your left hand over his Messer. Then, grab “simultaneously” your Messer with your left hand in the middle, and raise the point to his right side, and press into his wrist of his right hand with the sharp edge, in that way he has to drop the Messer. |
[42v.2] Item hawt er auff dich so spring mit dem pogen unter seyn messer und greuff mit deyner lincken hand aber uber seyn messer und faß yndeß deyn messer mit der lincken hand in der mit und heb den ort auff seyn rechten seytten und drück yn ynn daß gelenck seyner rechten hand mit der scharpfen schneyden so müeß er daß messer fallen lassen etc |
[79v] Item hawtt er auff dich So spring mit dem pogen vnter sein messer vnd greyff mit deyner lincken handt aber vber seyn messer vnd faß Indes dein messer mit deyner lincken handt In der mit vnd heb den ortt auff seyn rechte seytten vnd druck In Inn das gelenck seyner rechten handt mit der scharpffen schneyden so muß Er das messer fallen lassen; |
|||||||||
[242] |
Then, do him as before: fall over his right arm and come to help the right hand in the reach as before, and go with the front part of the Messer between his and the Messer on the inside and press firmly, in that way you take his Messer. This way you should work in the joints of the arm and the hand. |
[42v.3] Item thue ym alz vor fall ym uber seyn rechte armen und kumb der rechten zw hilff yn maß alz vor und far mit dem fodren teyl deß messerß czwischen seyn hand und messer und druck fast so nymbstu ym aber daß messer [43r.1] alzo soltu erbaytten yn dy glider deß armens und der handt etc |
[80r.1] Item Thu Im als vor fall Im vber seyn rechten arme vnd kum der rechten zu hilff In massen als vor vnd far mit dem fodren teyll deß messers zwischen sein handt vnd messer Inbendigs vnd druck fast So nymbstu Im aber das messer alzo soltu Erbeytten In dy glider des armes vnd der handt mit dem ortt deß messers etc |
|||||||||
[243] |
Then, you can also cut with the point of the Messer on the inside into his palm. |
|||||||||||
[244] Then, a Messer-taking. Do him as before: if you have come with the left hand to help your Messer, go down with the pommel or the hilt from on his right side on the inside above over the hand to the joint and pull firmly to your right side, in that way you take his Messer. |
Then, a Messer-taking. Do him as before: if you have come with the left hand to help your Messer, go down with the hilt, go through below to his right side, and on the outside go up over his right hand and pull firmly to your right side, in that way you take his Messer again. |
[43r.2] Item aber eyn messer nemen thu ym alz vor so dw deynem messer zw hilff pist kummen mit der lincken hand so far untersich mit dem knauff oder gehulcz auff seyn rechte seytten ynbendigß oben uber dy hand ynn daß glenck und reyß starck auff deyn rechte seytten So nymbstu ym aber daß messer |
[80v] Item aber Eyn messer Nemen Thu Im als vor So du deynem messer zu hilff piß kummen mit deyner lincken handt so far vntersich mit dem gehultz vntten durch auff seyn rechte seytten außbendigs far oben vber seyn rechte handt vnd reyß starck auff deyn rechte seytten So nymbstu Im aber seyn messer etc |
|||||||||
[245] |
Then, go to the man as before and go over his Messer with your left hand and fall in the middle of your Messer as before. Then, go with the hilt on the inside over his hand and pull to your right side. |
[81r] Item Gee an man wye vor vnd far vber seyn messer mit deyner lincken handt vnd fall In dy mitten deynes messers wye vor vnd far mit dem gehultz Inbendigs vber seyn handt vnd Reyß auff deyn rechte seytten etc |
||||||||||
[246] |
Then, strike the Entrüsthau at his right side, and “simultaneously” fall with the armed hand to the same side, and go with your hilt up over his arm. Then, go outside over his arm and wind his hand with your hilt firmly to his right side above, in that way you take his Messer. |
[81v] Item haw Im den Entrusthaw zu seyner rechten seytten Indes fall zu gewappender hant zu der selbigen seytten vnd far mit deynem gehultz oben vber seyn arme vnd far Im aussen vber seyn arme vnd windt mit deym gehültz seyn handt starck auff seyn rechte seytten vbersich so nymbstu Im das messer etc |
||||||||||
[247] |
Then, an element: fall with your left hand over his right on the inside and pull it to your left side. Then, drop your Messer, and “simultaneously” grab with the right hand in his knee-bending and throw him in front of you. |
[43r.3] Item aber eyn stück fal mit deyner lincken hand uber seyn rechte ynbendigß und ruck dye yn deyn lincke seytten und laß deyn messer fallen yndeß greuff mit der rechten hand yn seyn rechte knyepug und wirff yn alzo furdich etc |
[82r.1] Item aber Ein stuck fall mit deyner lincken handt vber seyn rechte Inbendigs vnd ruck dy In deyn lincke seytten vnd laß dein messer vallen Indes greyff mit der rechten handt In seyn rechte knypüg vnd wirff In fur dich etc |
|||||||||
[248] |
Then, as you have found the joints of the hand with the “weak” of the Messer and the point, you can also find them with the hilt of the Messer on the outside and inside, and you can take his Messer, as you have been taught above. |
[82r.2] Item als du dy glenck der handt mit der swech des messers vnd des ortz ersicht hast alzo magstu dy auch ersuchen mit dem gehultz des messers außbendigs vnd Inbendigs vnd das messer Im alzo nemen als du oben vnterricht pist; |
||||||||||
[249] |
Armed wind the weak through to the hand Here the master teaches a good element and a Messer-taking and speaks: Armed wind through, etc. You should understand it this way: strike with the Entrüsthau close to him at his left side and strike around to his right side. “Simultaneously” fall to the armed hand and wind the “weak” over on the inside to the joint of his hand and wind through over his hand and press it firmly to your right side, in that way you take his Messer. |
[82v] Bewappent durchwind swech zu handt Hie lertt der meyster aber Eyn gutz stuck vnd Eyn messer nemen vnd spricht Bewappent durchwindt etc Das soll du alzo verstan haw mit dem Entrusthaw nohent zu Im Eyn zu seynen lincken seytten vnd schlag vmb zu seyner rechten seytten Indes fall zu gewappender hant vnd wind dy swech oben hyn Eyn Inbendigs in das gelenck seyner handt vnd windt dürch vber seyn handt vnd druck dy fest auff deyn rechte seytten so nymbstu Im seyn messer etc |
||||||||||
[250] |
If he has wound the armed weak over the hand You should understand it this way: if he goes into your hand and wants to wind as before with the “weak” of his Messer in the armed way, lower “simultaneously” the point of your Messer towards the ground and go with the Messer to his left side, and strike the short edge onto his head. |
[83r] Dy swech gewappendt vber handt ist winden Das soltu alzo versten fertt Er dir In deyn hant vnd will windten wye vor mit der swech seynes messers gewappend Indes senck dy spitzen deynes messers gegen der erden vnd Gee mit dem messer auff seyn lincke seytten vnd schlag Im dy kurtz schneyd auff seyn kopff etc |
||||||||||
[251] |
If he strikes short and goes eagerly It is to be known that the propagator of the art states a counter-breaking against the breaking announced above and speaks: if he strike short, etc. You should understand it this way: if he goes with the hanging Messer to your left side and wants to strike at your head with the short edge, fall “simultaneously” quickly in the armed hand and thrust at his face or chest. And go rapidly close to him. |
[83v] Kurtz schlecht er vnd gett mit lust Saend[39] Das der mezer der kunst setz Ein wider pruch wider den Eegemelten pruch vnd spricht kurtz schnel schlecht er etc das soltu also verstan Gett er mit hangenttem messer auf deyn lincke seytten vnd will dich mit der kurtzen schneyden auff deyn kopff schlagen So fall Indes schnel In dy gewappendt handt vnd stich Im zu dem gesicht oder prust vnd Gee vast nohend zu Im etc |
||||||||||
[252] |
[172r.2] Das abschneiden Schneyd ab die herten [172v.1] Item das Ist ain Pruch Wider die vberwinnden des duseggens vnnd treib das also Wann du zu Im ficht ausz vnnderhewen. oder ligst gegen Im Inn dem Eber fellt er dir dann mit seim duseggen auf den deinnen. Ee wann du mit dem duseggen auf kumest. so bleib vnnden am duseggen. vnnd heb mit der kurtzen schneidin fast vbersich. truckht Er dann vast nider. so streich vnnden mit dem Duseggen an seins duseggen klinngen hindersich ab. vnnd haw Im bald wider oben ein zu dem gesicht. |
|||||||||||
[253] |
[172v.2] Das henndtruckhen Das mach also Wann er dir einlaufft. zu deinner lincken seitten. mit auf gereckten armen. so verwend dein duseggen mit der. lanngen schneidin vnnder sein gehultz In sein arm vnnd truckh fast vbersich. vnnd schreit damit auf sein rechten seitten. Indes wind den knopff mit vnnder durch. vnnd kum mit dem Duseggen nit von seinen armen. vnd wind den duseggen ausz dem vndern schnit Inn den obern vber sein Arm. mit der lanngen schneidin. |
|||||||||||
[254] Run through, strike the Entrüsthau, |
Run through, strike the Entrüsthau Here the master teaches a running into with the Entrüsthau and do him this way: go with the Entrüsthau to the man firmly, so that the thumb is below on the Messer on the flat and strike to his right side to the head with the blunt edge. Then, pull firmly to him with the hilt, so that the hands touch each other, and “simultaneously” drop your Messer and grab his hand at the joint, in which he has the Messer, and turn it around and take the balance at the elbow. Then, leap into the scale, and throw him over your left leg or hip. |
[70r.2] Durch lauff entruest Hie lert der meinster ein In lauffen mit dem entruest haulb vnd thün Im also ge mit dem entruest haulb an den man starck dz der thümen vnten ste am messer vff der flech vnd haulb im noch der rechten siten zu dem kopff mit der stümpfen schniden vnd ruck fast an In mit dem gehultz dz die hende an eynander rüren Indeß loß din messer fallen vnd begriff sin hant bÿ dem gelenck darin er daß messer hatt vnd rieb die vmb vnd nyem dz gewichtt pÿ dem elnbogen vnd spring in die woge vnd wuerff in vber din lincken beyn oder heufft ~ |
[43r.4] Dürchlauff entrust Hye lert der meyster eyn eynlaüffen mit dem entrusthaw und verste den text alzo gee mit dem entrusthaw an den man starck daß der dawm unten stee am messer auff der flech und haw ym zw der rechten seytten zw dem kopff mit der stümpffen schneyden und ruck fast an yn mit dem gehulcz daß dy hend an eyn ander rueren yndeß laß deyn messer fallen und pegreuff seyn hand pey dem gelenck dar yn er daß messer hat und reyb dye umb und nymb daß gebicht bey dem ölpogen und spryng yn dy wag und wirff yn uber deyn linckeß payn oder ölpogen etc |
[84r] Durchlauff entrust Hie lertt der meyster Eyn Eynlauffen mit dem Entrusthaw vnd thu Im also Gee mit dem Entrusthaw an den man starck das der dawm vntten stee am messer auf der flech vnd haw Im zu der rechten seytten zu dem kopff mit der stumpffen schneyden vnd ruck fast an In mit dem gehultz das dy hendt an Eyn ander ruren Indes laß deyn messer fallen vnd pegreyff seyn handt bey dem gehultz gelenck Dar In Er das messer hatt vnd Reyb dy vmb vnd nymb das gewicht bey dem olpogen vnd spring In dy wag vnd wirff In vber deyn linckes peyn oder huff |
[173r] Das ablaüffen Ablauff enntrist Item haw Im zu der rechten seitten Zum kopff mit dem Entristhaw. das der daum vnnden stee am Duseggen. auf der fleche. vnnd mit der kurtzen schneid truckh fast an In mit dem gehultz. das die hennd anainannder Fierent. Indes lasz dein duseggen fallen. ergreiff dz gelaich seinner hannd dar Inn Er den duseggen hat reib die vmb vnnd Nimbs gewicht mit dem Elenpogen. sprinng Inn die wag. vnd wirff In vber dein linckhs pain. |
|||||||
[255] Then, if you want to do another element, let your left arm hang, and hit with your left shoulder at his elbow from behind and pull with your right hand his right one to your chest and press with the right hand his right one firmly over your chest, and leap firmly to your right side. |
Then, if you want to do another element, let your left arm hang, and as you have grabbed his right arm on your chest, hit with your left shoulder and press with your right hand on his right arm firmly over your chest, and leap firmly to your right side. |
[70v.1] Item wiltu dz ander stuck machen So loß din lincken arm fallen hangen vff din brust so stoß mit diner lincken achseln vnd truck mit der rechten hant sin rechte arm vast vber din bruest vnd spring strack vff din rechten siten |
[43v.2] Item wiltu daß ander stuck machen so laß deyn lincken armen hangen und stoß mit deyner lincken achsel hynten an seynen olpogen und czeüch mit deyner rechten hand seyn rechte auff deyn prust und druck mit der rechten handt seyn rechte fast uber deyn prust [44r.1] und spring starck auff deyn rechten seytten etc |
[84v] Item wiltu das ander stuck machen So laß deyn lincken arme hangen So du In gefast hast seynen rechten arme auff deyn prust so stoß mit deyner lincken achsel vnd druck mit deyner rechten handt seyn rechten arme fast vber deyn prust vnd spring starck auff deyn rechte seytten etc |
||||||||
[256] Then, an element: if one runs into you and holds his arms high, run also firmly to him, so that the hands come together, and rush high upwards with the arms and “simultaneously” drop your Messer and go down with the arm and grab with them both his legs in the joints of the knee-bending and raise him on the shoulder of your right side, and throw him over the back on the head. |
Then, an element: if one runs into you and holds his arms high, run also firmly to him, so that the hands come together, and rush high upwards with the arms and grab with them both his legs in the joints of the knee-bending and raise him on the shoulder of your right or left side, and throw him over the back on the head. |
[70v.2] Item laüfft dir eyner In vnd ist hoch mit dem arm So lauff aüch starck vff in dz die hend zu samen rüren vnd dring hoch vber h sich mit dem indes loß din messer fallen vnd far vnttersich mit den armen vnd begriff do mit sin peÿden henden beÿn in die geleng ob der knue buege vnd heb in vff die achsell diner rechten oder limcken [!] siten vnd wurff in vber rueck vff den kopff |
[44r.2] Item aber eyn stuck laüfft dir eyner eyn und ist hoch mit den armen so laüff auch starck zw ym daß dy hend zw sammen rüeren und dring hoch ubersich mit dem armen yndeß laß deyn messer fallen und far untersich mit den armen und pegreuff da mit seyn pede payn yn dy gelenck der gelenck der knyepüg und heb yn auff dy achsel deyner rechten seytten und wirff yn uber ruck auff den kopff etc |
[85r] Item aber Ein stuck laufft dir einer Eyn vnd ist hoch mit dem arme So lauff auch starck auff In das dy hendt zusammen ruren vnd dring hoch vbersich mit dem arme vnd pregreuff do mit seyn peyde peyn In dy glenck der knypug vnd heb In auff dy achselen deyner rechten oder lincken seytten vnd wirff In vber ruck auff den kopff |
||||||||
[257] |
Then, grab with your left hand your right one and drop your Messer, and wind with your left one his right one well around to your left side, and step with your right foot towards his right one. Then, strike your right arm firmly over his right one and press firmly “simultaneously” to your right side and swing to your left side, and throw him over the right leg. |
[70v.3] ein anders Item laufft dir eyner In zu diner rechten syten so begriff sin rechten hant mit diner lincken verkerten hant indes schrit mit dinem rechten fus wol vff syn rechten vnd far mit diner linckent hant hant vnder din rechten elnbogen vßwendig vber sin arm mit der rechten hant vnd zueck mit beÿden henden sin rechten arm vff din brust vnd zwing dich starck vff din lincken siten vnd schrit mit dinem rechten fus fur sinen rechten vnd wuerff in vber din rechtes beyn ~ Sequitur texus |
[44v.2] Item greuff mit deyner lincken hand yn seyn rechte und laß deyn messer fallen und wynd mit deyner lincken seyn rechten umb woll yn deyn lincke seytten und schreit mit deynem rechten fuß fur seynen rechten und schlag deyn rechte armen starck uber seynen rechten und druck starck yn deyn rechte seytten und swyng dich auff deyn lincke seytten und burff yn uber daß recht payn etc |
[85v] Item Greyff mit deyner lincken handt dein rechte vnd laß deyn messer vallen vnd windt mitt deyner lincken seyn rechte woll vmb In deyn lincke seytten vnd schreytt mit deynem rechten füß fur seynen rechten vnd schlag deynen rechten arme starck vber seynen rechten vnd druck starck Indes In dein rechte seytten vnd swing dich auff dein lincke seytten vnd wirfst yn vber das recht peyn etc |
||||||||
[258] Then, an element: if one runs into you to your right side, grab his right hand with your left turned hand, and “simultaneously” step with your right foot well to his right one, and go with your right hand under his right elbow above his arm with the right hand. Then, pull his right arm with both hands to your chest and swing firmly to your left side and throw him over your right leg. And this is an element by Master Andreas of armoured combat.[40] |
Then, an element: if he runs into you to your right side, grab his right hand with your left turned hand, and “simultaneously” step with your right foot well onto his right one, and go with your right hand under his right elbow on the outside over his arm. Then, pull his right arm with both hands to your chest and swing firmly to your left side and step with your right foot to his right one and throw him over your right leg. |
[44r.3] Item aber eyn stuck laufft dir eyner eyn zw deyner rechten seytten so pegreüff seyn rechte hand mit deyner lincken verkerten handt yndeß schreyt mit deynem rechten fuß wol auff seyn rechte und far mit deyner rechten hand unten seyn rechten olpogen uber seyn armen mit der rechten hand und czeüg mit payden henden seyn rechten armen auff deyn prust und swing dich starck auff deyn lincke seytten [44v.1] und wirff yn uber deyn rechteß payn und daß ist meyster andreß stuck von chamb |
[86r] Item aber eyn stuck laufft er dir eyn zu deyner rechten seytten so pegreuff seyn rechte handt mit deyner lincken verkerten handt Indes schreytt mit deynem rechten füß woll auf seyn rechten vnd far mit deyner rechten handt vnter seyn rechten olpogen außbendigs vber seyn arme vnd zeuch mit peyden henden seyn rechten arme auff deyn prust vnd swing dich starck auff deyn lincke seytten vnd schreytt mit deynem rechten fuß fur seynen rechten vnd wurff In vber deyn rechtes peyn etc |
|||||||||
[259] |
Then, grab with your right hand in his right one on the outside and step with your left foot to his left one. “Simultaneously” strike your left arm into his right one, lift with your right hand to his right over your left arm and press your left arm firmly to your chest and press with the right downwards and throw him in front of you over your left leg. |
[44v.3] Item greuff mit deyner rechten hand seyn rechte außwendigß und trit mit deynem lincken fuß fur seynen lincken yndeß schlag deynen lincken armen yn seynen rechten und heb mit deyner rechten hant auff seyn rechte uber deynen lincken armen und druck den lincken armen fast zw deyner prust und druck mit der rechten untersich und wirff yn furdich uber deyn linckeß payn etc |
[86v] Item Greyff mit deyner rechten handt In seyn rechte außbendigs vnd Tritt mit deynen lincken füß fur seyn lincken Indes schlag deyn lincken arme In seyn rechten heb mit deyner rechten handt auff seyn rechte vber deyn lincken arme vnd druck deyn lincken arme fast zu deyner prust vnd druck mit der rechten vntersich vnd wirff In furdich auff das vber deyn linckes peyn etc |
|||||||||
[260] |
If he takes the balance Here the master states a breaking against the verses as it is stated: Run through, strike the Entrüsthau, etc. And he speaks: Take the balance, etc. |
[71r.1] Nimpt er daß gewicht Hie saget der meinster eyn bruch wider die verß als gesprochen ist durch lauff enttruest ~ vnd spricht nymb dz gewiecht etc |
[45r.1] Nÿmbt er daß gebicht Hye sagt der meyster eyn pruch wyder dy verß alz gesprochen ist durchlauff entrust etc und spricht der wyder nymbt er etc |
[87r.1] Nymbt er das gewicht Hye sagtt der meyster Eyn pruch wyder dy verß als gesprochen ist Druchlauff Entrust etc Vnd spricht nymb das gewicht etc |
[173v.1] Einn pruch wider das obgeschriben stuckh. Nimpt Er das gewicht |
|||||||
[261] |
You should do the breaking this way: if he falls to your right hand with his right turned hand and wants to take the balance with the left hand at your elbow, “simultaneously,” as you feel that he grabs your right hand with his right, “simultaneously” grab skillfully with your right one also in his right one and grab with your left hand also in his right elbow and leap with your left foot in front of his right one and do the element that he wanted to do on you and be skillful. |
[71r.2] Item den bruch soltu also machen fellet er dir in dyn rechte hant mit siener rechtem [!] verkerten hant vnd wil dir dz gewiecht mit diner lincken by dÿnem elnbogen nemen Indes diewiell du entpfindest dz er dyn recht hant griefft mit syner rechten Indes begriff behendiklich mit dyner rechten auch in syne rechte vnd griff mit der lincken hant auch an syn elnbogen vnd spring mit dynem lincken fus fur sinen rechten vnd mach dz stuck dz er dir hat wellen machen beß schnell vnd behend etc |
[45r.2] Den pruch soltu alzo machen fellt er dir yn deyn rechte hant mit seyner rechten verckerten hand und wil dir daß gebicht mit der lincken bey deynem ölpogen nemen yndeß beyl dw enpfindest daß er deyn rechte hant greuft mit seyner rechten yndeß greuff behentlich mit deyner rechten auch seyn rechte und greuff mit der lincken hand auch an seynen rechten ölpogen und spring mit deynem lincken fuß fuer seynen rechten und mach daß stuck daß er dir hat wollen machen und piß schnel und pehendt etc |
[87r.2] Den pruch soltu also machen Vellt er dir In deyn rechte handt mit seyner rechten verkertten handt vnd will dir das gewicht mit der lincken pey dem olpogen nemen Indes weyl du empfindest Das er deyn rechte handt Greyfft mit seyner rechten Indes greyff behentlich mit deyner rechten auch In seyn rechte vnd Greyff mit deyner lincken handt auch an seynen rechten olpogen vnd spring mit deynem lincken fuß fur seyn rechten vnd mach das stuck das er dir hatt wollen machen vnd piß behendt etc |
||||||||
[262] |
Then, a breaking: if he wants to grab you as [before], go with your hilt over his hands and fall with the left hand in the middle of your Messer and assume an armed stance with your left arm and Messer firmly on his arm. Then, press and pull firmly to your right side, and step with your left foot in front of his right one. |
[71r.3] ein ander bruch [71v.1] Item eyn ander bruch will er dir fassen als vor so far mit dynem gehultz uber sin hant vnd fal mit der lincken hant In die mit dyneß messers vnd leg dich mit dem lincken arm vnd messer gewoppnet starck vff syn arm vnd drück vnd rieß starck vff din rechte syten vnd schrit mit dynen lincken fus fur synen rechten ~ |
[45v.1] Item aber eyn pruch will er dich fassen alz vor so far mit deym gehulcz uber seyn hant und fal mit der lincken hand yn dy mit deyneß messerß und leg dich mit dem lincken armen und messer geboppend starck auff seyn armen und druck und reyß starck auff deyn rechte seytten und schreyt mit dem lincken fuß fuer seyn rechte etc |
[87v] Item aber eyn pruch will er dich fassen als so far mit deynem gehultz vber seyn handt vnd fall mit der lincken handt In dy mit deynes messers vnd leg dich mit dem lincken arme vnd messer gewappend starck auff seyn arme vnd druck vnd reyß starck auff deyn rechte seytten vnd schreytt mit deynem lincken fuß fur seyn rechten etc |
||||||||
[263] |
Then, if he has grabbed your right hand with his right turned one, and wants to take the balance at your elbow, “simultaneously” let your hilt go down over his hand towards the ground, and grab with your left hand below his hand in your hilt of the Messer in order to help your right hand. Then, pull with both hands firmly downwards and strike through his head. |
[71v.2] eyn ander Item hat er dir dyn rechten gefast mit dyner rechten verkerten vnd wil dir by dem elnbogen dz gewiechtt nemen Indes loß dÿn gehultz vber syn hant sincken gegen der erden vnd griff mit dyner lincken hant vnter syn hant In dÿn gehultz des messers dyner rechten zu hilff vnd riß mit peyden henden starck vntter sich vnd haulb im durch syn kopff ~ |
[45v.2] Item hat er deyn rechte hant gefast mit seyner rechten verkerten und wil dir bey dem olpogen daß gebicht nemen yndeß laß deyn gehulcz uber seyn hant sincken gegen der erden und greuff mit deyner lincken hant unter seyn handt yn den gehulcz deß messerß deyner rechten zw hiff und reyß mit payden henden starck untersich und haw ym durch seyn kopff etc |
[88r.1] Item hatt er dir deyn rechte handt gefast mit seyner rechten verkertten vnd will dir pey dem olpogen das gewicht nemen Indes laß deyn gehultz vber seyn handt sincken gegen der erden vnd Greyff mit deyner lincken handt vnter seyn handt In deyn gehultz des messers deyner rechten zu hilff vnd reyß mit payden henden starck vndersich vnd haw Im durch seyn kopff etc |
||||||||
[264] Then, a breaking: if he has grabbed you as before and “simultaneously” while he wants to take the balance at your elbow, go skilfully down with your elbow firmly down and to your body and hurry with your Messer to his head etc. The text follows. |
Then, a breaking: if he has grabbed you as before and “simultaneously” wants to take the balance at your elbow, etc. You find this element as this one that stands before. |
[71v.3] aber eyn bruch Item aber eyn bruch hat er dich gefast als vor Indes wil er dir dyn gehultz nemen bÿ dem elnbogen so far geswind nider mit dem elnbogen starck vnd wol nider vnd an din lib vnd schnell [72r.1] In mit dynem messer vff syn koppff ~ |
[45v.3] Item aber eyn prüch hat er dich gefast alz vor yndeß weyl er dir daß gebicht will nemen bey dem ölpogen so far geswynd nyder mit deynem ölpogen [46r.1] starck woll nÿder und an deyn leÿb und schnel yn mit deynem messer auff seÿn kopff etc Sequitur textus |
[173v.2] Item hat Er dir dein rechte hannd Allso gefast vnd. will dir dz gewicht nemmen bey dem Elenpogen. so far geschwind nider mit dem Elennpogen starckh an dein leib. Indes schlag Im mit deinem duseggen. zu seinem haupt. |
||||||||
[265] |
Grab left in the opposite manner, take the balance Here the master teaches a nice element with that one can break one`s arm if it is done otherwise properly. And do him this way: grab with your left hand into his right one and pull with it high to your left side. “Simultaneously” grab with your right hand below at his elbow and press with your left one below his hand towards your left side, and do not stretch him the arm completely, and do not let his arm be too crooked, either. Then, “simultaneously” lift his elbow with your right hand well upwards and step with your right foot behind his right one. |
[88v] Greuff linck wydersyns nymb gewicht Hye lertt der meyster Eyn hubsch stuck Do mit man eynen den arme prechen mag Wenn Es anders recht gemacht wirtt vnd thü Im also Greyff mit deyner lincken handt In seyn rechte vnd ruck Da mit In dy höch auff deyn lincke seytten Indes Greyff mit deyner rechten handt vntten an seynen olpogen vnd druck mit deyner lincken nyder seyn handt gegen deyner lincken seytten vnd streck Im den arme nicht gantz auch laß Im den arme nicht zu krump vnd heb Indes mit deyner rechten handt seynen olpogen woll vbersich vnd schreytt mit deynem rechten fuß hinter seynen rechten etc |
||||||||||
[266] |
Then, a breaking against taking the balance, as it was stated: Run through, strike the Entrüsthau. If he has grabbed you as before and “simultaneously” wants to take the balance at your elbow, go well downwards with the elbow firmly to your right side, quickly downwards to your body and flick the short edge of your Messer on his head. |
[89r] Item Eyn pruch wyder das gewicht nemen als gesprochen ist durchlauff Entrust etc Hatt er dich gefast als vor vnd will dir Indes das gewicht Nemen bey dem olpogen so far geschbing nyder mit dem olpogen starck In deyn rechte seytten woll nyder an deynen leyp vnd schnell Im dy kurtz schneyd deynes messers auff seyn kopff etc |
||||||||||
[267] |
Then, if he has grabbed you at your right hand with his right one and wants to take the balance with his left one at your elbow, “simultaneously” grab against with your right one firmly at his right hand and pull it towards yourself. Then, strike your left arm over his both arms and step with your right foot in front of his right one and swing to your right side and throw him in front of you. |
[89v] Item hatt er dich gefast bey deyner rechten handt mit seyner rechten vnd will dir mit seyner lincken das gewicht pey dem olpogen nemen Indes greyff Im wider mit deyner rechten starck seyn rechte handt vnd ruck dye fur dich vnd schlag deyn lincken arme vber seyn ped arme vnd schreytt mit deynem rechten fuß fur seyn rechten vnd swing dich auff deyn rechte seytten vnd wurff In fur dich etc |
||||||||||
[268] |
Shoot right with pulling Here the master teaches a special element and speaks: Shoot right, etc. You should understand it this way: grab his right hand with your left turned hand and pull it with it a bit to yourself and shoot your Messer under his arm and go outside on his elbow and over his arm. Come with the short edge below his neck on his throat, and put your hilt “simultaneously” outside on the nape of your neck and let your right hand go from your Messer and come to help your left one forwards with your right one forwards on his right hand. Then, step with your foot behind his right one and pull his arm firmly downwards. |
[90r] Scheuß recht mit rucken Hie lertt der meyster aber Eyn besunder stuck vnd spricht Scheuß recht etc Das soltu also verstan pegreyff seyn rechte handt mit deyner lincken verkertten handt vnd ruck In da mit Eyn wenig gegen dir vnd scheuß deyn messer Im vntter seynen arme vnd far Im aussen an den olpogen vnd vber den arme vnd kum Im mit der kurtzen schneyden Im vntter seyn hals an dy kelen vnd thu deyn gehultz Indes aussen an deyn nacken vnd loß dy rechten handt von deynem messer faren vnd kum deyner lincken zu hilff vorne mit deynem rechten vorne an seyn rechte handt vnd schreytt mit deynem fuß hinter seynen rechten vnd reyß starck vntersich seyn arme etc |
||||||||||
[269] Learn to shoot over the arms Here the master speaks about a skillfull element with which one can bind and clench and hold one. And when one wishes, one forces the man with this element that he must stand still. And when you want to do it, so that he must run quickly or slowly-thus, he must do it. And you also force him so that he himself has to crawl into a bag, if you want to have it done. That is why the element is called by masters the “Hidden Grab,” as one should not make this element common and should not let anyone know it. Thus, this element is well-paid. |
Learn to shoot over the arms Here the master speaks about a skillfull element with that one can bind, clench and hold one, when one wishes, so that one forces the man with this element that he must stand still or run. And you force him that he has to crawl into a bag, if you want to have it otherwise. That is why the element is called by skilled masters the Unnamed, as this element should not become common. One should also not make it common or let any-one know it, thus it will be well-paid to him. |
[72r.2] Ler arm vber schussen Hie saget der meinster von eynem kuestlichem stueck do mit man eynen bynden vnd bescluessen mag vnd halten vnd wan er will so noet er den man mit dissem stueck dz er still mueß stan vnd wan du wilt machen dz er sere oder gemach sol lauffen also mueß er thun du nottest In auch mit dyssem stueck dz er selbs In eynen sack mueß kryechen wiltu es anders gehet haben daruemb so wuertt daß stueck von koestlichen meinstern der verborgen griff genant vff dz dz man stueck nit gemeyn sol machen vnd neyman [72v.1] sol loßen wissen den dz stueck werd gar woll bezalt |
[46r.2] Ler armen uberschyssen Hye sagt der meyster von eynem kunstenlichen stuck da mit man eynen pynten und beschlyssen und halten mag und wenn er will so nöt er den man mit dysen stuck daß er still muß stan und wenn dw wild machen daß er ser oder gmelich söl lauffen alzo muß er thuen dw nötest yn ach mit dysem stuck daß er selbs yn eyn sack muß krychen so dw eß gehabt wild haben und darumb wirt daß stuck von den meystern genandt der verporgengriff [46v.1] auff daß daß man daß stuck nicht gemayn sol machen und nymant sol lassen wyssen denn daß stuck wer wol peczalt |
[90v] Ler arme vberschyssen Hye sagtt der meyster von Eym kunstlichen stuck da mit man Eynem pyntten[43] beschlyssen vnd halten mag wenne er will so nott er den man mit dysem stuck das er still muß sten ser oder lauf melich lauffen[44] müß vnd dw In notest das er In Eynen sack krichen müß will du es anders gehabtt haben dar vmb wirtt das stuck von den kostenlichen[45] meysteren genandt Der vngenandt auff[46] das daß stuck nicht gemayn soll werden Man soll auch das nicht gemayn machen vnd nyemant wissen lassen denn Es werd Im wol pezaltt etc |
||||||||
[270] It is also a pity that careless men or masters would know this element, who make this element common because of the wish to be famed, so that they are praised by people thanks to it. |
Then, you should not spread the element depicted above to the careless men or masters who want to spread this element out of wicked will, so that they are praised by the other. “As one should not throw noble pearls or roses for the swine, so that they are not profanated and trampled down into the mud by them.”[47] |
[72v.2] Es ist auch schad dz luechtfertig luede oder meinster dz wissen sollen die dz stuck gemeyn machen von rüembs wegen dz sie dar durch gelobt sollend werden ~ |
[46v.2] Eß ist auch schad daß leichtfertig lewt oder meyster daß stuck sollen wyssen dy daß stuck gemayn machen von römeß wegen daß sy dar durch gelobt wellen werden von den leutten |
[91r.1] Item du solt das Ee gemalt stuck nicht offenbaren leychfertigen lewtten oder meystern dye durch Römß willen das stuck gemayn mochten machen auff das/das sy von andren gelobt sollen berden wanne man soll dy edlen margaritten oder rosen nicht fur dy sweyn strewen Das sy durch dy selbigen nich vngeertt werden vnd getretten In das kott |
||||||||
[271] Now, it you want to do the element, do him this way: if he runs into you in the Messer, drop your Messer and turn your right hand and grab with it at his right one and turn the hand downwards around and with your left hand. And with your left hand grab him with it at the right elbow and leap with the left foot forwards and raise his right hand up and hit it above your left arm and lift him up with it. |
Now, it you want to do the element, do him this way: if he runs into you in the Messer, drop your Messer or hold it in your right hand, and grab with your right turned hand into his right one on the outside, and turn the hand downwards around. And with your left hand grab him at his right elbow and leap with your left foot in front of his right one and lift his right hand up with your right hand. If you still have your Messer in your hand, raise the same right hand up with the crosspiece of your Messer and hit it over your left arm and raise it with it upwards and press firmly down with your left hand. |
[72v.3] ein ander stuck Item wiltu dz stuck machen so thun Im also wan er dir In laufft im messer So loß din messer vallen vnd verkere din rechte hant vnd begriff do mit syne rechte vßwendig vnd rib die hant vbersich vmb vnd mit diner lincken hant fas in do mit dynem rechten elnbogen vnd spring mit dynem lincken fus for vnd heb sin rechte hant vff vnd stos die mit dynem lincken arm vnd heb in do mit vbersich vff |
[46v.3] Item wiltu daß stuck machen so thue ym alzo wenn er dir eyn lauffet ym messer so laß deyn messer fallen und verker deyn rechte hand und pegreuff da mit seyn rechte und reyb dy hand untersich umb und mit deyner lincken handt faß yn da mit bey dem rechten olpogen und spring mit dem lincken fuß fuer und heb seyn rechte hand auff und stoß dye uber deynen lincken armen und heb yn da mit ubersich auff |
[91r.2] Nu will du das stuck machen So thu Im alzo wenn Er dir Eyn lauffett In dem messer So laß deyn messer vallen oder behaltz In deyner rechten handt vnd Greiff mit deyner rechten verkerten handt In seyn rechte außbendig vnd reyb dy handt vntersich vmb vnd mit deyner lincken hand faß In bey seynem rechten olpogen vnd spring mit deynem lincken fuß fur seynen rechten vnd heb seyn rechte handt auff mit deyner rechten handt hastu aber deyn messer noch In deyner hendt so heb dy selbig seyn rechte handt auff mit dem kreutz deynes messers vnd stoß dye vber deyn lincken arme vnd heb In da mit vbersich auff vnd druck starck nyder mit deyner lincken handt |
||||||||
[272] If he is very strong, grab with your right hand from above at his right shoulder and acquire the balance on him, in that way you can lead, strike, throw and hold him and do what you want. |
Or, if he defends firmly, grab with your right hand from above at his right shoulder and acquire the balance on him, so that you can lead, throw, strike, hold or force him as you wish. Namely, you have this element, as it is depicted above before. |
[72v.4] ob aber er starck were so griff mit dyner rechten hant oben vff syn rechte achsell vnd gewind im die woge ab so magstu In furen schlagen werffen vnd halten ~ |
[46v.4] ¶ ob er aber ser starck wer so greuff mit deyner rechten hand oben auff seyn rechte achsel und gebyn ym dy wag an so magst yn furen schlagen werffen und halten und thuen waß dw [47r.1] wild etc |
[91r.3] Ob aber er so starck wer So greyff mit deyner rechten handt oben auff seyn rechte achsel vnd Gebyn Im dy wag an so magstu In furen werffen schlagen halten nötten wye du willt alzo hastu das stuck wye oben vor gemalt stett etc |
||||||||
[273] |
Then, if you come to the man, grab him as it is stated before, and as you have grabbed him, fall “simultaneously” close to him on your arse, and as you fall, turn your back on his right side and hold him firmly. You can also play board games, eat and drink, so that he cannot stand up unless you let him cordially up, otherwise he has to rot under you. |
[91v] Item So du zu dem man kumbst so faß In wye Ee geschriben stett vnd So du In also gefast hast So fall Indes neben In auff deyn ars vnd Im fall wendt deynen ruck an seyn rechte seytten vnd hallt In vest auch magstu Im pretspilen Essen vnd Trincken das er nicht auff mag stan denne du lost In gerne auff Sunst must er vntter dir erfaulen etc |
||||||||||
[274] Then, if you do not want to drop your Messer, as you have done the element announced above, go to him with the Entrüsthau or with an upper stroke and go precisely to him, so that the hands touch together. “Simultaneously” go with the hilt high over his right arm to the joint of the hand with the cross, and raise his hand with the hilt over your left arm. |
[72v.5] aliud Item wiltu aber din messer vallen loßen so thun dz egemelt stück wilt machen so ge an in mit dem entruest haulb oder mit eynen ober [73r.1] haulb gnaülb an In dz die hend zue samen rüren Indes far vff mit dem gehultz vber sin rechte arm in dz glenck der hend mit dem kruetz vnd heb sin hant mit dem gehultz vber din lincken arm ~ |
[47r.2] Item wiltu aber deyn messer nicht fallen lassen so dw daß ee gemelt stuck pist machen so gee an yn mit dem entrusthaw oder mit eynem oberhaw und gee genaw an yn daß dy hend zw sammen rueren yndeß far mit dem gehulcz auff uber seynen rechten armen yn daß gelenck der handt mit dem kreucz und heb seyn hand mit dem gehulcz uber s deyn lincke armen etc |
||||||||||
[275] Then, if you want to throw him into a bag, so secretly appoint two men with your bag, who stay behind the people. Then, grab him as it is announced before and tell the two to raise the bag and press him firmly and make him crawl to it. If he does not want to crawl into, grab with your right hand on the outside at his right knee-bending and throw him into it in the name of God. |
Then, if you want to throw him into a bag with the element announced before, so secretly appoint some men who have a hidden bag with them at the swordsmanship competitions and stand behind the people. Then, grab him as it is depicted before, and as you have brought him in the scale, lead him with force to these who stand with the bag and make him crawl to it. If he does not want to do it voluntarily, when they hold the bag open, grab with your right hand at his right leg close at the bone on the outside and lift him with it high to your right side and step with your left foot in front of his left one and throw him in the name of God into the bag and then do to him what you want. |
[47r.3] Item wiltu yn ynn eynen sack schyben so pestel heymlich czwen mit deynem sack dye hinter dem volck stenen und faß yn alz ob gemelt ist und hayß dy czwen den sack auff haben und druck yn fast und nöt yn daß er daß eyn krich wil er aber nicht dar eyn krychen so greuff mit deyner rechten hand außwendigß yn seyn rechte kynepug und wirff yn eyn gotteß namen dar eyn etc. |
[92r] Item wiltu In Inn eynen Sack schyben mit dem Eegemelten stuck So pestell heymlich Etlich dy Eynen sack verporgen pey In haben auff der schull Dy hintter dem volck stenn vnd faß In als Ee gemelt ist vnd So du In Inn dy wag gepricht hast So für In mit gewallt Da dye mit dem sack stenn vnd hayß In dar Eyn krychen will er das nicht williklich thun So denn dy den sack auff halten So greyff mit deyner rechten handt In seyn rechteß peyn nohent bey dem knochen[48] außbendigs vnd heb In da mit auff auff deyn rechte seytten vnd schreytt mit deynem lincken fuß fur seyn lincken vnd wurff In In nammen gottes In den sack vnd Thu Im darnach wye du willt etc |
|||||||||
[276] If you do not want to throw him, keep your Messer and make him do as you wish with it. |
[47v.1] Item wiltu yn aber nit werffen So pehallt deyn messer und nöt yn da mit wye dw wild etc |
|||||||||||
[277] Then, another clenching: as you come together in the Zufechten, grab him above his right arm with your left hand, and as you grab, go with your Messer below his right arm and fall with the left hand in the middle of the blade, and go with it to his elbow from behind. Then press firmly down and step exactly to him and raise with your right hand firmly up with the Messer, in that way he is clenched again. |
Then, another clenching: as you come together in the Zufechten, grab him above his right arm with your left hand, and as you do it, go with your Messer below his right arm and fall with the left hand in the middle of the blade of your Messer, and go with it to his right elbow from behind. Then press firmly down and step exactly to him and raise with your right hand firmly up with the Messer, in that way he is clenched again. |
[47v.2] Item eyn anderß peschlyssen so ir ym zw vechten zw sammen kumbt so greuff ym uber seyn rechten armen mit deyner lincken hand yn dem griff far mit deynem messer unter seynen rechten armen und fal mit der lincken hand yn dy mit der klyngen und far da mit ym yn seyn olpogen hynten und druck mit sterck nyder und trit genaw an yn und heb mit deyner rechten hand ser ubersich mit dem messer alzo ist er aber peschlossen etc |
[92v] Item Eyn ander beschlyssen So Ir Im zuuechten zu sammen kumpt So greyff Im vber seyn rechten arme mit deiner lincken hantt In dem far mit deynem messer vnter seyn rechten arme vnd fall mit der lincken handt In dy mit deynes messers klingen vnd far do mit Im In seinen rechten olpogen hyntten vnd druck mit der sterck nyder vnd Tritt genaw an In vnd heb mit deyner rechten handt ser vbersich mit dein messer alzo ist er aber beschlossen etc |
|||||||||
[278] Then, another clenching with the Messer. Do as before and press the arm on the outside firmly down and turn to him with your left side as before. If he is strong, so that you cannot press him down and you cannot come to the element, turn again your right side quickly to him to his right side, and wind on the inside up with the hilt to the joint of the elbow, so that the hilt comes outside under the arm to the elbow and the weak of the Messer comes to the hand. And lay with the body firmly on his arm and take his hand and do not let him from the clench and step with your right foot behind his right one and push him over it. |
[47v.3] Item eyn anderß peschlyssen aber mit dem messer Thu ym alz vor und druck ausbendigß den armen fast nyder und wendt dich an yn mit deyner lincken seytten alz vor ist er den starck daß dw yn nicht nyder drucken kanst und zw dem stuck nicht kumen magst so wendt dich wyder schnel gegen ym deyn rechte seytten an seyn rechte und wynd ynbendigß [48r.1] auff mit dem gehulcz yn daß gelenck deß ölpogenß daß daß gehulcz aussen unter den armen kum an den olpogen und dy swech deß messerß kum an dy handt und gib dich mit dem leib fast an seyn armen und nymb seyner handt war und lauß yn nicht auß dem schloß und schreyt mit deynem rechten fuß hyn ter seynem rechten und druck yn dar ueber etc |
|||||||||||
[279] Then, another clenching: fall over his right arm with your left one and grab “simultaneously” below in the middle of your Messer and go with the hilt below through his arm in the joint of the elbow and turn your left side on his right one and press firmly downwards and step close to him, so that he cannot come out from the binding. This way you have locked and closed him. |
Then, another clenching: fall over his right arm with your left one and grab “simultaneously” below in the middle of your Messer and go with the hilt below through his arm in the joint of the right elbow on the outside and turn your left side on his right one and press with the hilt with the armed hand quickly from above downwards and step close to him, so that he cannot come out from the binding. This way he is locked and closed. |
[48r.2] Item eyn ander peschlossen fall ym aber uber seyn rechten armen mit deynem lincken und greuff yndeß aber unter yn dy mit deyneß messerß und far mit dem gehulcz unten durch seyn armen yn daß gelenck deß olpogenß und wendt deyn lincke seytten an seyn rechte und druck fast nyder und trit nohent an yn daß er auß dem pandt nicht kummen mag alzo hastu yn aber verrygelt und verschlossen etc |
[93r] Item Eyn ander beschlyssen fall Im vber seyn rechten arme mit deynem lincken vnd greyff Indes aber vntten In dy mitten deynes messers vnd var mit dem gehultz vntten durch seyn arme In das gelenck des rechten olpogens außbendigs vnd wendt deyn lincke seytten an seyn rechte vnd druck mit dem gehultz zu gewappender hantt fast oben nyder vnd Tritt nohendt an In das er auß dem pandt nicht kummen mig[49] alzo ist er verigelt vnd verschlossen etc |
|||||||||
[280] |
Learn to pull the hand to the chest Here the master teaches a skillful holding and element, and as you fall on your arse while doing the element, you can hold the man so that he cannot stand up. And the element is called the Unnamed and is one of the best elements and is to be performed against the strong men. |
[73r.2] Ler hand ze brust reiben Hie saget der meinster eyn kostlich haltüng vnd stuck vnd so dü wollest in vff den ars so magstu den man halten dz er nicht vff mag sten vnd dz stuck heiszt der vngenant vnd ist der besten stuck eÿns vnd gehorett zu triben gegen den starcken ~ |
[48r.3] Ler hand zw prust reyben Hye lert der meyster eyn konstenlich halten und stuck und so dw fellest yn dem stuck auff deyn arß so magstu den man halten daß er nich auff mag stan und daß stuck hayst der ungelnant und ist der peste stuck eyneß und gehort zw treyben gegen den starcken |
[93v] Ler handt zu prust reyben Hye lertt der meyster Eyn kostenlich halten vnd stuck vnd So du felst In dem stuck auff deyn ars So magstu den man halten das er nicht auff mag sten vnd das stuck heysset der vngenant vnd ist der pesten stuck eyns vnd gehortt zu Treyben gegen den starcken wye hernach geschriben stett etc |
||||||||
[281] Then, if you want to do the element, do him this way: strike at his left side with the Entrüsthau and “simultaneously” pull close to him on his hilt with your [Messer]. “Simultaneously” drop your Messer and grab with your right turned hand at his right one and turn it around and turn around with your left side on his right one, and step with the left foot in front of his right one and pull the arm to your chest and strike the left arm over his right arm and lie down with the entire strength on it, and leap to your right side, in that way you break his arm. |
Then, if you want to do the element announced before, do it this way: strike at his left side with the Entrüsthau and “simultaneously” pull close to him on his hilt with your Messer. “Simultaneously” drop your Messer and grab with your right turned hand at his right one and turn around with your left side on his right one, and step with your left foot in front of his right one and pull his arm to your chest and strike your left arm over his right arm and lie down with the entire strength on it, and leap to your right side, so that you break his arm, as it is depicted before. |
[73r.3] ein anders Item wiltu dz stueck machen so thun im also haulb zu syner lincken syten mit dem entruest haulb Indes [73v.1] ruck nahent an in an syn gehultz mit dyenem Indes loß din messer fallen vnd griff mit dyner verkerten hant sin rechte hant vnd wind dich vmb vnd wind dich mit dyner lincken siten an sin rechten vnd trett mit dem lincken fus vor sin rechte vnd ruck den arm vff din brust vnd schlag dyn lincken arm vber syn rechten arm vnd leg dich mit gantzer starck daruff vnd spring vff din rechte syten so brischstu im den arm |
[48v.2] Item wiltu daß stuck machen so thu ym alzo haw zw seyner lincken seytten mit dem entrusthaw yndeß ruck nohent an yn an seyn gehulcz mit deynem yndeß laß deyn messer fallen und greuff mit deyner rechten verkerten hand seyn rechte hand und wendt dy umb und wendt dich mit deyner lincken seytten an seyn rechten und trit mit dem lincken fuß [49r.1] fur seyn rechte und ruck den armen auff deyn prust und schlag den lincken armen uber seynen rechten und leg dich mit ganczer sterck dar auff und spring auff deyn rechte seytten so prigstu ym den armen |
[94r.1] Item wiltu das Eegemelt stuck machen So thu Im also haw zu seynen lincken seytten mit dem Entrusthaw Indes ruck nohent an In an seyn gehultz mit deynem messer Indes loß deyn messer fallen vnd Greyff mit deyner rechten verkertten handt In seyn rechte vnd wendt dich vmb mit der lincken seytten anseyn rechte vnd Tritt mit deynem lincken fuß fur seynen rechten vnd Ruck seyn arme auff deyn prust vnd schlag deynen lincken arme vber seyn rechten arme vnd leg dich mit gantzer sterck dar auff vnd spring auff deyn rechte seytten So prichstu Im den arme etc wye danne vor gemalt stett; |
||||||||
[282] Then, if you want to throw him and hold so that he cannot stand up, “simultaneously” as you have turned on your right side, fall on the arse on the ground, so that he has to fall with you, and he falls on his face. You can also give him a dagger in his left hand as he lies at you and let him thrust, but he cannot do anything to you if you can hold him correctly and perform the element correctly. |
Then, if you want to throw him and hold so that he cannot stand up, “simultaneously” as you have turned on your right side, fall on your arse on the ground, so that he has to fall with you, and he falls on his face close to you. This way he cannot stand up until you let him cordially up, and do to him as it is depicted below. |
[49r.2] ¶ wiltu yn den werffen und halten daß er nicht auff mag stan yndeß so dw dich pist wenden auff deyn rechte seytten yndeß fal auff den arß an dy erden so muß er mit dir fallen und felt auff seyn angesicht dw magst ym auch dy weill er ligt eyn degen yn seyn lincke handt geben und erlaub ym zw stechen er mag dir nichtz thuen so dw yn recht kanst halten und daß stuck recht treyben |
[94r.2] Item wiltu In den werffen vnd So hallten das er nicht auff kann stan Indes so dw dich pist wenden auff deyn rechte seytten Indes vall auff deyn ars auff dy erden So müß er mit dir fallen vnd fellt auff seyn antlitz neben dich also kan er nicht auff sten den du lost In gerne auff vnd Thu Im wye vntten gemalt stett etc |
|||||||||
[283] |
Grab his right to the left Then, perform the element this way: when you come to the man in the Zufechten, grab his right hand with your left turned hand and turn it around to your left side, and pull it well towards yourself. And do as if you wanted to hit im with the hilt at the face, and “simultaneously” step with your right foot behind his right one and hit him with the hilt or with your right arm firmly to the front of his shoulder. Then, turn a bit with the body to your left side and throw him over your right leg. |
[73v.2] Vach linck sinen rechten Hie saget der meinster von eynem gutten stuck dz tribe also wan du mit dem zu vechten zu dem man kümpst so vahe im sin rechte hant mit diner lincken verkerten hant vnd rib die vmb vff dyn lincken siten vnd zuch die woll vmb sich dich oder vor dich heyn vnd thun sam dü wollest mit dem gehultz in dz angesicht stossen Indes schrit mit dynem rechten fus hinter synen rechten vnd stoß in mit dym gehultz oder mit dym arm [74r.1] starck vorn an sin rechte achsell vnd rib dich eyn wenig mit dem lib vff din lincken syten vnd wurff in vber dz recht peyn ~ |
[49r.3] Vach linck seynen rechten Item daß stuck treyb alzo wenn dw mit dem zwvechten zw ym kummest so fach ym seyn rechte hand mit deyner lincken verkerten hand und reyb dy umb yn deyn lincke seytten und czeug dy woll fur dich [49v.1] hyn und thu sam dw yn wollest mit dem gehulcz yn daß angesicht stossen yndeß schreyt mit deynem rechten fuß hynter seynen rechten und stoß yn mit dem gehulcz oder mit deynem armen starck foren an seyn lincke achsellen und reyb dich eyn wenig mit dem leyb auff deyn rechte seytten und wirff yn uber daß rechtt payn etc Sequitur textus |
[94v] Vach linck seynen rechten Item das stuck Treyb also wenn du mit dem zuuechten zu dem man kumpst so vach Im seyn rechte handt mit deyner lincken verkertten handt vnd Reyb dye vmb In deyn lincke seytten vnd zeuch dy woll fur dich hyn vnd Thu als du In wollest mit dem gehultz In das angesicht stossen vnd schreytt Indes mit deynem rechten fuß hinter seynen rechten vnd stoß In mit dem gehultz oder mit deynem rechten arme starck vorne in seyn achsel vnd reyb dich Eyn benig mit dem leyp auff deyn lincke seytten vnd wurff In vber deyn rechtes peyn etc |
||||||||
[284] |
If he want to hit the shoulder Here the master states a breaking against the element announced before and speaks: The shoulder, etc. You should understand it this way: if he has grabbed your right arm with his left one and has stepped with the right foot behind your right one and wants to hit your shoulder, “simultaneously” as he wants to hit, take your left hand and go with it behind to his elbow and push him away from you to his left side. Or, strike your left arm firmly from above over his right one and turn firmly to your right side. |
[74r.2] Die achsell wil er stossen Hie saget der meinster ein stuck wider das egemelt vnd spricht also daß soltu also verstan hat er den rechten arm gefangen mit dem lincken vnd ist mit dem rechten geschritten hinder dynen rechten vnd wil dyn achsell stossen Indes so er stossen will so far do mit dyner lincken hant an syn elbogen vnd schub in von dir vff syn lincken syten oder sclach dyn lincken arm starck von oben vber syn rechte vnd schrit mit dem lincken fus fur syn rechten vnd wind dich starck vff din rechte syten |
[49v.2] Dy achselen will er stossen Hye sagt der meyster eyn pruch wyder daß ee gemellt stuck und spricht alzo dy achsel etc Daß soltu alzo verstan hat er deyn rechten armen gefangen mit seynem rechten und ist mit dem rechten fuß geschriten hynter deynen rechten und will deyn achselen stossen yndeß so er stossen will so nymb deyn lincke hand und far da mit hynten an seyn ölpogen und scheub yn von dir auff seyn lincke seytten oder schlag deyn lincken armen starck [50r.1] von oben uber seyn rechte und schreit mit deynem lincken fuß fur seyn rechte und wendt dich starck auff deyn rechte seytten Sequitur textus |
[95r] Dy achselen will er stossen Hye sagtt der meyster Eyn pruch wyder das obgemelt stuck vnd spricht also Dye achselen etc Das soltu also verstan hatt er deynen rechten arme gefangen mit seynem lincken vnd ist mit dem rechten fuß geschritten hinter deynen rechten vnd will deyn achsel stossen Indes so er stossen will So nymb deyn lincke handt vnd far Im da mitt hyntten an seyn olpogen vnd scheub In von dir auf seyn lincke seytten oder schlag Im deyn lincken arme starck oben vber seynen rechten vnd wendt dich starck auff deyn rechte seytten etc |
||||||||
[285] |
Then, another breaking: if he has grabbed you as before, strike your left arm firmly over his right one and step with your left foot in front of his right one and press his both arms from above firmly down with your left arm. Then, turn firmly to your right side, as it is depicted below. |
[95v] Item aber Eyn ander pruch hatt er dich gefasst wye vor So schlag deynen lincken arme starck vber seynen rechten vnd schreytt mit deynem lincken fuß fur seynen rechten vnd druck oben mit deynem lincken arme fast nyder seyn payd arme vnd wendt dich starck auff deyn rechte seytten wye vnden gemalt stett etc |
||||||||||
[286] |
If he strikes at you from the right Here the master speaks about a good element and speaks: If he strikes at you, etc. You should understand it this way: go stretched to him with an Entrüsthau and grab his right arm with your left arm or hand. Then, turn it around and drop your Messer and go from below through his arm, and strike your right arm on the outside in the joint of the elbow. Then, pull his elbow to your chest and lie down firmly with the body on it. If you want to throw him, step with your right foot behind his right one. |
[74r.3] Haut er vff dich rechtens Hie saget der meinster aber von eynem gutten stuck vnd spricht haut er vff dich etc Das soltu also verstan Gee starck vff in mit dem entruest haulb vnd vahe syn rechten arm mit dynem lincken arm oder hant vnd kere dich vmb vnd loß din messer fallen vnd far ym vnten durch den arm vnd schlag ym den rechten arm vßwendig indaß gelenck des elnbogens vnd ruck syn[50] elnbogen an din brust vnd leg dich starck mit dem lib darüff wiltu yn dan werffen so schrit mit dynem rechten fus hinder sin rechten vnd wurff yn daruder [!] ~ |
[50r.2] Haüt er aüff dich rechtenß Hye sagt der meyster aber von eynen guten stuck und spricht haut er auff dich etc Daß soltu alzo verstan gee gestrackt auff yn mit dem entrusthaw und vach seyn rechten armen mit deynem lincken armen oder hand und ker ym dye umb und laß deyn messer fallen und far ym unten durch den armen und schlag ym deyn rechten armen ausbendigß yn daß gelenck deß ölpogenß und ruck seyn ölpogen an deyn prust [50v.1] und leg dich starck mit dem leyb darauff wiltu yn den werffen so schreit mit deynem rechten fuß hynter seynen rechten fueß etc Sequitur textus |
[96r] Haut er auff dich rechtens Hye sagtt der meyster von Eynem gutten stuck vnd spricht hautt er auff dich etc Das soltu also verstan Gee gestrackt auff In mit Eynen Entrußthaw vnd vach seynen rechten arme mit deynem lincken arme oder handt vnd ker dy vmb vnd laß deyn messer vallen vnd far Im vntten durch den arme vnd schlag Im deynen rechten arme außbendig In das gelenck des olpogens vnd ruck seyn olpogen an deyn prust vnd leg dich starck mit dem leypp dar auff wiltu In werffen so schreytt mit deynem rechten füß hinter seynen rechten etc |
||||||||
[287] If he wants in the fight Here the master states a breaking against the element announced before and speaks: If he wants, etc. |
If he wants in the fight Here the master states a breaking against the element announced before and speaks: If he wants, etc. |
[74v.2] Wil er im vechten Hie saget der meinster eyn bruch wider dz egemelt stuck vnd spricht also Wil er Im vechten etc |
[50v.2] Will er ym vechten Hye sagt der meyster eyn pruch wyder daß ee gemelt stuck und spricht alzo will er etc |
[96v.1] Will er ym vechten Hye sagtt der meyster Eyn pruch wyder das Eegemelt stuck vnd spricht will er etc |
||||||||
[288] You should understand it this way: if he falls with his left hand on your right one and wants to go with his right arm through from below through your right one, and wants to strike it on the outside in the joint of the elbow, “simultaneously” let your Messer go and pull your right hand out of his right one downwards, and go through under his arm from below. Then, go from behind above his right arm with your right hand and press his hand under your right shoulder on your body, and turn your left side on his right one, and fall with your left hand from above over his left shoulder and swing to your right side. |
You should understand it this way: if he falls with his left hand on your right one and wants to go with his right arm through from below through your right arm, and wants to strike it on the outside in the joint of your elbow, “simultaneously” drop your Messer and pull your right hand out of his right one downwards, and go through under his right arm from below. Then, go from behind over his right arm under your right shoulder and press his hand on your body, and turn your left side on his right one, and fall with your left arm or hand from above over his left shoulder and swing to your right side or fall on your arse and hold him, and sit at him, as it is depicted below. |
[75r.2] Daß soltu also verstan felt er dir mit dyner lincken hant in dyn rechte hant vnd mit syner rechten Wil er vnten durch faren durch dyn rechten vnd wil dir dan schlagen vßwendig in das gelenck des elnbogens Indes loß dyn messer fallen vnd din rechte hant reiß vber syn rechten vnttersich vnd far vnter synem rechten arm durch vnd far hinden vber syn rechten arm mit dyner rechten hant vnd druck syn hant vntter syn v rechten vschen an din lib vnd wind dyn lincke syten an syn rechte vnd fal mit diner rechten lincken oben vber syn lincke achschell vnd schwing dich vff dyn rechte syten ~ |
[50v.3] daß soltu alzo verstan felt er dir mit seyner lincken yn deyn rechte handt und mit seyner rechten will er unter durch faren durch deyn rechten und wil dir den schlagen außwendigß yn daß glenck deß ölpogenß yndeß laß deyn messer und deyn rechte hand reyb auß seyner rechten untersich und far unter seyn rechten armen unten durch [51r.1] und far hynter uber seyn armen mit deyner rechten hand und druck seyn hand unter deyn rechte vchsen an deyn leyb und wendt deyn lincke seytten an seyn rechte und fal mit deyner lincken hand oben uber seyn lincke achsel und swyng dich auff deyn rechte seytten etc |
[96v.2] Das soltu alzo verstan Fellt er dir mit seyner lincken handt an deyn rechte vnd will mit seynem rechten vntten durch faren durch deyn rechten arme vnd will dir den außbendigs schlahen In das gelenck deynes olpogens Indes laß deyn messer fallen vnd reyb deyn rechte hand auß seyner rechten vntersich vnd far vnter seynen rechten arme vntten durch vnd far hintten vber seyn rechten arme vntter deyn rechte vchsen vnd druck seyn handt an deyn leyb vnd wenck deyn lincke seytten an seyn rechte vnd fall mit deynem lincken arme oben v oder handt oben vber seyn lincke achselen vnd swing dich auff deyn rechte seytten oder fall auff deyn ars vnd halt In vnd sitz neben Im wye vntten gemalt stett |
||||||||
[289] |
Then, what is depicted below, does not mean anything. |
[97r.1] Item das vntten gemalt stett Ist nichtz wedeutten etc |
||||||||||
[290] |
This does not [mean anything?] |
[97r.2] Hic nihil ad implevit |
||||||||||
[291] |
Then, he grabs you with his left turned hand in your right [arm] and wants to strike his right [arm] over your right [arm] in the joint of the elbow as before. “Simultaneously” be skilled and drop your Messer and pull your right hand free from his left one on the inside, and go from below through his left arm with the stroke behind with your right arm over his left one, firmly from above downwards. Then, turn your right side on his left one and throw him firmly over your right hip. |
[75r.3] alliud Item griefft er dir mit dÿner lincken verkerten hant in dyn rechte vnd wil syn rechten vber din rechten in daß gelenck des elnboges [75v.1] als vor indes boeß behendenn vnd loß dyn mesß fallen vnd rieß din rechte hant Inlbendigks vß syner lincken vnd far vnten durch syn lincken arm mit dem schlag hinden mit dienem rechten arm vber syn lincken starck von oben nider vnd wind din rechte syten an syn lincke vnd wurff in starck vber dyn rechte huefften |
[51r.2] Item greuft er dir mit seyner lincken verkerten hand und will seyner rechten schlagen uber deyner rechten yn daß gelenck deß ölpogenß alz vor yndeß piß behendt und laß deyn messer fallen und reyß deyn rechte handt ynbendigß auß seyner lincken und far unten durch seyn rechten armen mit dem schlag hynten mit deynem rechten armen uber seynen lincken starck von oben nyder und wendt deyn rechte seytten an seyn lincke und wirff yn starck uber deyn rechte huff etc |
[97v] Item Greyfft er dir mit seyner lincken verkertte handt In deyn rechte vnd will seynen rechten schlagen vber deyn rechten In das gelenck des olpogenß als vor Indes piß behendt vnd loß deyn messer fallen vnd reyß deyn rechte handt Inwendigs auß seyner lincken vnd far vntten durch seyn lincken arme mit dem schlag hintten mit deynem rechten arme vber seynen lincken starck von oben nyder vnd wendt deyn rechte seytten an seyn lincke vnd wurff In starck vber deyn rechte huff etc |
||||||||
[292] |
Then, do him as it is depicted behind: as you have brought him on the hip, grab with your left hand behind yourself in his left knee-bending and lift him well on your shoulders and throw him in front of you to your left side. |
[98r] Item Thu Im wye Ee gemelt ist So du In auff dy huff gepracht hast so greyff mit deyner lincken handt hinter dich In seyn lincke knypug vnd heb In woll auff deyn schulteren vnd wurff In furdich auff deyn lincke seytten etc |
||||||||||
[293] |
Then, another arm-breaking: if he grabs you with his left hand as before, and wants to strike his right [arm] over your right [arm] on the outside, “simultaneously” turn your Messer with the “short” edge against him and let “simultaneously” the already mentioned edge fall quickly with the lowered point to his left elbow and go with the Messer between you both and with the edge from below through his right arm, and come with your left hand in the middle of your Messer. Then, press with it firmly on the outside of his right firmly down and turn with your left side into his right one and throw him over your left leg. |
[51r.3] Item aber eyn ander pruch greufft er dir mit seyner lincken hand alz vor [51v.1] und will mit seyner rechten schlagen uber deyner rechten außbendingß alz vor yndeß wendt deyn messer mit der kurczen schneyden gegen ym und laß yndeß dy ee gemelt schneyden mit gesencktem ort an seynen lincken ölpogen schell ablaytten und far mit dem messer czwischen euch payden mit der klyngen unten durch seyn rechten armen und kum mit deyner lincken hand yn dy mit deyneß messerß und druck da mit außbendigß seynen rechten armen fast nyder und wendt dich mit deyner lincken seytten an seyn rechte und wirff yn uber deyn linckeß payn |
[98v] Item aber Eyn ander pruch Greyfft er dir mit seyner lincken handt als vnd will seynen rechten schlagen vber deyner rechten außbendigs Indes wendt deyn messers mit der kurtzen schneyden gegen Im vnd loß Indes dy Ee gemelten schneyden mit gesencktem ortt an seynen lincken olpogen schnell ableytten vnd far mit dem messer zwischen Euch payd mit der klingen vnden durch seyn rechten arme vnd kum mit deyner lincken hand In dy mitten deynes messers vnd druck do mit außbendigs seynen rechten arme fast nyder vnd wendt dich mitt deyner lincken seytten an seyn rechte vnd wirff In vber deyn linckes peyn etc |
|||||||||
[294] Then, if he grabbed you with his left hand as [before] and wants to strike his right one over, also as before, “simultaneously” lower your hilt well above his left hand and come with your left hand to help your right hand down on your hilt. Then, pull with your both hands firmly downwards and strike through his head strongly, and step “simultaneously” with the left foot back. |
Then, if he grabbed you with his left hand as before, “simultaneously” lower your hilt well over his left hand and come with your left hand to help your right hand down on the hilt. Then, pull with your both hands firmly downwards and strike at his head, and step “simultaneously” with your left foot back. |
[51v.2] Item hat er dich gefast mit seyner lincken hand alz und will seyner rechten uberschlagen auch alz vor yndeß senck deyn gehulcz woll uber seyn lincke handt und kum mit deyner lincken hand deyner rechten zw hilff unten an deyn gehulcz und reyb mit deynen payden henden starck untersich und haw [52r.1] yn durch den kopff starck und schreyt yndeß mit dem lincken fuß zw ruck |
[99r.1] Item hatt er dich gefast mit seyner lincken handt als vor Indes senck deyn gehultz woll vber seyn lincke handt vnd kum mit deyner lincken handt deyner rechten zu hilff vntten an dem gehultz vnd reyß mit deynen peyden henden starck vntersich vnd haw Im zu dem kopff vnd schreytt Indes mit deynem lincken fuß zu ruck |
|||||||||
[295] You should also know that you should be quick in these breakings announced above, so that he does not bring you in the scale. The text follows. |
You should also know that you should be quick with these breakings announced before, so that he does not bring you in the scale. |
[52r.2] ¶ Dw solt auch wyssen daß dw yn dysen obgemelten pruchen gar schnel solt seyn daß er dich nicht yn dy wag pring etc Sequitur textus |
[99r.2] Du solt auch wissen das dw mit dysen Eegemelten bruchen schnell seyn sollt das er dich nit In dy wag pring etc |
|||||||||
[296] Right with left, learn to clench the arms Here the master speaks about a clenching and speaks: Right with left, etc. You should understand it this way: if he strikes a stroke from above at you, and you strike against him the Entrüsthau together with him and come close to him, so that the hands come together. “Simultaneously” hold the right arm firmly on his right one so that your hand is always on his one, and strike “simultaneously” your left arm above his right one in the joint of the elbow of his right arm on the outside. Then, go with the left hand from inside on your right arm lie down with the chest on his arm, so that his elbow comes on your chest, and press firmly with your both hands, in that way he is clenched. |
Right with left, learn to clench the arms Here the master speaks about a clenching and speaks: Right with left, etc. You should understand it this way: if he strikes a stroke from above at you, strike against him the Entrüsthau and come close to him, so that the hands touch. “Simultaneously” hold your right arm firmly on his right one so that your hand is always on his one, and strike “simultaneously” your left arm in the joint of his elbow of his right arm on the outside. Then, go with the left hand from inside on your right arm lie down with the chest on the same arm, so that his elbow comes on your chest, and press firmly with your both hands, so that he is clenched. |
[76r.1] Recht mit linck lern arm beschlissen Hie saget der meinster aber von eynem beschuesß vnd spricht recht mit linck etc Dz soltu also verstan haut er vff dich eyn ober haulb vnd haulb mit ym glich In mit eynem Entrüst haulb vnd küm nohent an In dz die hend zu samen ruren Indes halt din rechten arm starck an sinen rechten dz din hant euchling an siner ste vnd schlag indes din lincken arm vber sin rechten Indaß gelenck des elnbogen sins rechten arm vßwendigs vnd far mit der lincken hant Inlbendig an dinem rechten arm vnd leg dich mit der brust vff den selbigen arm also dz sin elnbogen an sin bruest kümen vnd druck in mit dinem peiden henden also ist er aber beschlossen ~ |
[52r.3] Recht mit linck ler armen peschlyssen Hye sagt der meyster aber von eynem beschlyssen und spricht recht mit linck etc daß solltu alzo verstan hawt er auff dich eyn oberhaw und haw mit ym gleich eyn mit eynem entrusthaw und kum nohend an yn daß dy hend zwsammen rueren yndeß hallt deyn rechten armen starck an seynen rechten daß deyn hand euchlyng an der seyner [52v.1] stee und schlag yndeß deynen lincken armen uber seynen rechten yn daß gelenck deß ölpogenß seyneß rechten armeß außbendigß und far mit der lincken hand ynbendigß yn deyn rechten armen und leg dich mit der prust auff seynen armen daß seyn olpogen an deyn prust kwm und druck fast mit deynen payden henden alzo ist er aber peschlossen etc |
[99v] Recht mit linck ler arme beschlyssen Hye sagtt der meyster aber von eynem beschlyssen vnd spricht Recht mitt linck etc Das soltu also verstan haut er auff dich Eynen oberhaw So haw gegen Im den Entrusthaw vnd kum nohent an In das dy hend zusammen ruren Indes halt den rechten arme starck an seynen rechten das deyn handt Ewchling an seyner stee vnd schlag Indes deyn lincken arme In das gelenck seynes olpogens seynes rechten armes außbendigs vnd far mitt der lincken handt Inwendigs auff deynen rechten arme vnd leg dich mit der prust auff den selbigen arme also das seyn olpogen an deyn prust kum vnd druck vast mit deynen peyden henden also ist er aber beschlossen etc |
||||||||
[297] |
Then, another clenching: grab with your left hand above his right arm well to the elbow and with the same left hand go on the outside behind his arm, and take your Messer in the middle with your left hand and let the point come out sideways at your left side. Then, step with your right foot behind his right one, and hit him with your Messer or arm to his right shoulder. Then, press his right arm with your left hand firmly to your left side, and throw him over your right leg. Or, put the hilt on the nape of the neck on his neck on his right side. |
[76r.2] Item Aber eyn beschluessen griff mit diner lincken hant vber sin rechten arm Wol zu dem elbogen vnd mit der selbigen hantt [76v.1] far hÿnab vßwendig vnter sin arm vnd nÿm mit diner lincken din messer in der mitten vnd loß den ortt besitz nebent diner lincken hynuß ge vnd schrit mit diner rechten fus hinter synem rechten vnd stos in also mit dinem messer oder arm vff sin rechten achsell vnd druck mit diner lincken hant sin rechten arm vast in dim lincke siten vnd wurff im vber din rechte peyn oder leg im daß gehultz an den hals siner lincken siten oder vff siner rechten siten leg im dz gehultz in sin genueck hinten ~ |
[52v.2] Item aber eyn peschlyssen greuff mit deyner lincken hand uber seyn rechten armen wol zw deym ölpogen und mit der selbigen lincken hand far hyn ab außbendigsß unter seyn armen und nym mit deyner lincken hand deyn messer yn der mit und laß den ortt peseytt neben deyner lincken seytten hyn auß gan und schreyt mit deynen rechten fuß hynter seynen rechten und stoß yn alzo mit deym messer oder armen auff seyn rechte achsel und druck mit deyner lincken hand seynen rechten armen fast yn deyn lincke seytten und wirff yn uber deyn rechteß payn oder leg ym daß gehulcz an den halz [53r.1] seyner lincken seytten oder auff seyner rechten seytten leg ym daß gehulcz yn seyn genick hynden etc |
[100r] Item aber eyn beschlyssen Greyff mit deyner lincken handt vber seynen rechten arme woll zu dem olpogen vnd mit der selben lincken handt far hyn ab außbendigs hinter seyn arme vnd nym mit deyner lincken deyn messer In der mitten. vnd laß den ortt beseyt neben deyner lincken seytten hyn auß gan vnd schreytt mit deynem rechten fuß hynter seynen rechten vnd stoß In also mit deynem messer oder arme auff seyn rechte achselen vnd druck mit deyner lincken handt seynen rechten arme fast In deyn lincke seytten vnd wurff In vber deyn rechtes peyn oder leg Im das gehultz an den hals In seyn genick auff seyner rechten seytten etc |
||||||||
[298] |
Then, go through him with the Messer as before, so that his Messer comes under your left shoulder, and go with the hilt under his throat to his left side. Then, step with your right foot behind his right one and turn a bit to your left side, and push him over your right leg. |
[100v] Item gee Im aber durch mit dem messer als vor das dir seyn messer kum vnter deyn lincke vchsen vnd far Im mit dem gehultz vnter seynen hals auff seyner lincken seytten vnd schreyt mit deynem rechten fuß hinter seynen rechten vnd wendt dich Eyn wenig gegen deyner lincken seytten vnd druck In vber deyn rechtes peyn etc |
||||||||||
[299] |
If he has clenched you Here the master teaches a breaking against the clenching announced before and speaks: If he has clenched you, etc. You should understand it this way: if he has grabbed you with the left arm in the joint of your right elbow on the outside and with his right [hand] under your right [arm] and has grabbed your arm on his chest and wants to press you with it over the back, “simultaneously” stand warlikely against him and let your Messer go down to your left shoulder. Then, grab with your left hand in his arm close to the shoulder, and step with your right foot behind his right one, and turn around to your left side, and throw him over your right foot. |
[76v.2] Beschlossen so er dich halt Hie lert der meinster ein bruch wider die egemelt beschlussen vnd spricht beschlusß Daß soltu also verstan hat er dir griffen mit dem lincken arm Indas gelenck dines rechten elnbogens vßwendig vnd mit siner [77r.1] rechten vnder diner rechten vnd hat din arm vff sin brust gefast vnd will dich do mit vber ruck drucken Indes ste strittes gegen im vnd loß din messer sencken nider in din lincke vschen vnd griff mit diner lincken hant in sin arm nohent by der achsell vnd schrit mit dinem rechten fus hinter sinen rechten vnd rib dich vmb vff din lincke siten vnd wurff in vber din rechten fus ~ |
[53r.2] Beschlossen so er dich hatt Hye lert der meyster eyn pruch wyder dy ee gemelten peschlysssen und spricht peschlossen so er etc. Daß soltu alzo verstan hat er dir gryffen mit dem lincken armen yn daß glenck deyneß rechten ölpogenß außbendigß und mit seyner rechten Ist unter deynen rechten und hat deyn armen auff seyn prust gefast und will dich da mit uber ruck drucken yndeß stee streytteß gegen ym und laß deyn swertt messer sincken nyder yn deyn lincken uchsen und greuff [53v.1] mitt deyner lincken hand yn seyn armen nohent bey der achsel und schreyt mit dem rechten fuß hynter seyn rechten und reyb dich umb auff deyn lincke seytten und wirff yn uber deyn rechten fuß etc |
[101r] Beschlossen so er dich hatt Hye lertt der meyster Ein pruch wyder dy Eegemelten beschlissen vnd spricht beschlossen so er dich etc Das soltu alzo verstan hatt er dir griffen mit dem lincken arme In das Glenck deynes rechten olpogen außbendigs vnd mit seyner rechten vnter deynen rechten vnd hatt deyn arme auff deyn prust gefast vnd will dich da mit vber ruck drucken Indes stee streyteß gegen Im vnd loß deyn messer sincken nyder In deyn lincke vchsen vnd Greyff mit deyner lincken handt In seyn arme nohendt bey der achsel vnd schreytt mit deynem rechten fuß hinter seynen rechten vnd reyb dich vmb auff deyn lincke seytten vnd wirff In vber deyn rechten fuß etc |
||||||||
[300] |
Then, another breaking: if he has grabbed you with his right [arm] under your right one and stroke with his left [hand] in your right elbow as before, fall “simultaneously” in the middle of your Messer with your left hand and go high with the blade and go with your hilt above his both arms. Then, step with the left foot in front of his left one and press with the hilt firmly from above downwards, and with your left arm push firmly his shoulder down and throw him over your left leg. |
[77r.2] ein ander bruch Item Aber eyn bruch hat er dich gefast mit siner rechten vnter sinen rechten vnd mit siner lincken geschlagen In dinen rechten elnbogen als vor so fal in die mit dines messers mit diner lincken hant vnd far vff mit der klingen in die hohe vnd far mit dinen gehultz vber sin beide arm vnd schrit mit dem lincken fus fur sin lincken vnd druck mit dem gehultz starck von oben nider vnd mit dem lincken arm schub starck by siner achsell vff sin lincke siten vnd wuerff in vber din linckes peynd |
[53v.2] Item aber eyn ander pruch hat er dich gefast mit seynem rechten unter deynen rechten und mit seyner lincken geschlagen yn deynen rechten olpogen alz vor so fal yn dy mit deynß messerß mit deyner lincken hand und far auff mit der klyngen yn dy hoch und far mit deym gehulcz uber seyn ped armen und schreyt mit dem lincken fuß fur seynen lincken und druck mit dem gehulcz starck von oben nyder und mit deynen lincken armen scheub starck pey seyner achsel auff seyn lincke seytten und wirff yn uber deyn linckeß payn |
[101v] Item aber eyn pruch hatt er dich gefast mit seynem rechten vntter deynen rechten vnd mit seyner lincken geschlagen yn deynen rechten olpogen als vor So fall In dy mit deynes messers mit deyner lincken handt vnd far auff mit der klingen In dy höch vnd far mit deynem gehultz vber seyn peyde arme vnd schreyt mit dem lincken fuß fur seynen lincken vnd druck mit dem gehultz starck von oben nyder vnd mit deynem lincken arme scheub starck seyn achselen nyder vnd wurff yn vber deyn linckes peyn |
||||||||
[301] Then, another different breaking: if he grabs as before, grab with your left hand from below at your hilt to help the right hand and pull firmly downwards as you have been taught before and strike at him through his head from above. The text follows. |
Then, if he has grabbed you as [before], hit with your left hand into his right elbow well to his right side and strike with your Messer to his head. |
[77r.3] Item Aber eyn ander bruch grifft er also vor so griff mit diner lincken hant vnten an din gehultz der rechten zu hillff vnd riß starck vndersich als du vor vntterricht bist vnd haulb im durch den koppff ~ |
[53v.3] Item aber eyn ander pruch greufft er alz vor so greuff mit deyner lincken hand unten an deyn gehulcz der rechten zw hilff und reyß starck untersich alz dw vor [54r.1] unterricht pist und haw yn durch seyn kopff von oben etc Sequitur textus |
[102r] Item hatt er dich gefast als so stoß mit deyner lincken handt seynen rechten olpogen woll auff seyn rechte seytten vnd schlag In mit deynem messer auff seyn kopff etc |
||||||||
[302] Do not forget the cuts Here the master speaks about the cuts and their peculiarities, and states that the cuts are four. The first two, the two from above, are to be performed against the fighters who go from the bind and who eagerly strike around with the Messer to the other side. Break it before with the cut in this manner: if he binds you on your Messer with displacing or else to your left side and with it strikes quickly around with the Entrüsthau or else to your right side, leap out of the stroke with the left foot to his right side and fall with the sharp or long edge above over his arm and press him with the cut from you. You should do this. |
Do not forget the cuts Here the master speaks about the cuts and their peculiarities, and states that they are four. The first two, that is the two from above, are to be performed against the fighters who go from the bind and who eagerly strike around with the Messer to the other peaks. The cut breaks it this manner: if he binds you on your Messer with displacing or else to your left side and then he strikes quickly around with the Entrüsthau or else to your right side, leap out of the stroke with the left foot to his right side and fall with the sharp edge over his arm and press him with the cut from you. You should always do this when he strikes from the displacement. |
[77v.1] Nit vergiß der schnit Hie saget der meinster von den schnitten vnd von iren eygenschafft vnd spricht dz der schnitt vier sigen die zwyn ersten die zwin oben gehoren zu triben gegen den vechtern die vß dem pand gan vnd die do gern mit dem messer vmb sclagen zu der andern siten vnd b dz bricht er mit dem schnitt also wan er dir versetz oder sunst an din messer pindt zu diner lincken siten vnd schlag do mit bald vmb mit dem entrusch haulb oder sust zu diner rechten siten so spring vmb vß dem haulb mit dinem lincken fus vff sin rechte siten vnd fal im mit der scharpfen schniden oder mit der langen schniden vber sin arm vnd druck in mit dem schnitt von dir dz soltu alwegen triben wan er vß der versatzung schlechtt ~ |
[54r.2] Nicht vergiß der schnydt Hye sagt der meyster von den schnytten und von iren eygenschaften und spricht daß der schnydt vyer seyn zwm ersten dy czwy oberen gehoren zw treyben gegen den vechteren dy auß dem pandt genen und dy geren mit dem messer umb schlagen zw der anderen seytten und daß prich ee mit dem schnydt alzo wenn er dir mit den verseczen oder sunst an deyn messer pyndt zw deyner lincken seytten und schlecht da mit pald umb mit dem entrusthaw oder sust zw deyner rechten seytten so spryng auß dem haw mit dem lincken fuß auff seyn rechte seytten und fall ym mit der scharpffen oder langen schneyden oben uber seyn armen und druck yn mit dem schnydt von dir daß soltu treyben |
[102v] Nicht vergyß der schnytt Hye sagtt der meyster von den schnytten vnd von Iren eygenschafften vnd spricht das Ir vyer seyn dy zwen ersten als dy zwen obren gehoren zu Treyben gegen den vechternn dy auß dem pandt gen vnd dy mit dem messern gerne vmb schlagen zu den andren zynnen das prichtt der schnytt also wenn Er dir mit dem versetzen oder sunst an deyn messer pyndett zu deyner lincken seytten vnd schlecht er denne d paldt vmb mitt dem entrusthaw oder sunst zu deyner rechten seytten so spring auß dem haw mit dem lincken fuß auff seyn rechte seytten vnd fall Im mit der scharphen schneyden vber seyn armm vnd druck In mit dem schnyt von dir das soltu albogen treyben wenne er auß der versatzung schlecht etc |
[100r.11] Nit vergiß der schnid etc Hie spricht der meyster dar der schnid vier sind die zwen ersten die zwo oben keren zů tribenn gegen dem vechtern die auß dem band gen vnd die gern mit dem messer vmb schlagen zu der andren seytten vnd daß bricht er mit dem schnid also wan er dir mit dem versetzen oder sunst an dein messer kümpt oder bindt Zu deyner lincken seytten vnd schlacht mit bald vmb mit dem entrist hew oder sunst zů deyner rechten seytten So spring auß dem haw mit dem lincken füß auf sein recht seytten vnd fall Im mit der scharffen schniden oder mit der langen schniden über sein arm vnd druck In mit dem schnid von dir du solt ob triben wan er auß der versatzung schlecht |
|||||||
[303] |
Then, if he lies to your right side at the ear, and you lie on his Messer from below or from above, as soon as he wants to strike around to the other peak of your left ear, cut with the short edge into his right arm on the inside. This is the other cut. |
[77v.2] Item lig er vff siner rechten siten bÿ den oren vnd list vff sinem messer es sy vnten oder oben so er wil dan vmb schlagen zu der andern zÿnnen dines lincken ores so schnid im mit der kurtzen schniden in sin rechten arm Inlbendigs dz ist der ander schnitt |
[54v.1] Item ligt er dir auff deyner rechten seytten bey dem oren und dw ligst auff seynem messer eß sey unten oder oben so er denn will umb schlagen zw der anderen czynnen deyneß lincken orenß so schneyd yn mit der kurczen schneyden yn seyn rechten armen ynbendigß daß ist der andere schnydt |
|||||||||
[304] |
Then, the two other cuts are to be performed agains the fighters who run in with high stretched arm and perform the cuts this way: if he binds you on the Messer, be it with displacing or else, and he then goes high with the arm and runs into you to your left side, turn your Messer so that the thumb is below and [cut] with the sharp [edge] under his hilt to his arm, and press upwards while cutting. |
[54v.2] Item dy czwen unteren schnydt gehoren zw treyben gegen den vechteren dy dy do eyn lauffen mit auff gerecktem armen und dy schnydt treyb alzo wenn er dir an daß messer pyndet eß sey mit versaczung oder sunst fert er dan hoch auff mit dem armen und lauffet dir zw deyner lincken seytten so verbendt deyn messer daß der dawm mit der scharpffen schneyden unter seynem gehulcz yn seynn armen und druck mit dem schnydt ubersich |
[78r.1] Item die zwin vntern schnitt gehoren ze triben gegen den fechtern die do In lauffen mit vff gerechten armen vnd die schnit dribe also wan er dir an dz messer pindt es sÿ mit versatzung oder sust fertt er dan hoch vff dem arm vnd laufft dir zu diner lincken siten so verwind din messer dz der thüm vnten küm vnd mit der scharpffen schniden vnter sin gehultz in sin arm vnd druck mit dem schnitt vber sich ~ |
[103v] Item dy andren zwen schnytt gehoren zu treyben gegen den vechtren dy do Eyn lauffen mit auff geracktem arme vnd dy schnytt Treyb also wenn Er dir an das messer pindt Es sey mitt versatzung oder sunst fertt er denn hoch auff mit dem arme vnd laufft dir Eyn Zu deyner lincken seytten so verbent deyn messer das der dawm vntten kum vnd mit der scharpffen vntter seyn gehultz In seyn arme vnd druck mit dem schnytt vbersich etc |
[100r.12] Item die zwen vnder schnidt geheren zů triben gegen den vechtern die do inn lauffen mit auf gerecktem arm die schnid trib also wan er dir an das messer bindt es sig mit versatzung oder sunst fert er dan hoch auf mit dem arm vnd lauft dir zů deiner lincken seytten So verwend dein messer das der thaüm vnden stee oder kume vnd mit der scherpfe vnder sein gehiltze in sein arm vnd druck mit dem schnid über sich |
|||||||
[305] |
Then, if one runs into you to your right side, turn your Messer so that the thumb is below and come with the short edge under his hilt to his arm. And press upwards while cutting. Thus, you have the four cuts and if you can perform them well, you are able to perform them in all the bindings. |
[78r.2] Item laufft er dir In vff din rechten siten so verwind din messer dz der thum vnten kum mit der stümpfen oder kurtzen schniden vnder sin gehultz In sin arm vnd druck mit dem schnitt vber sich also hastu die vier schnitt vnd wan du dich rechtt darin schicken wilt so magstu die triben im messer im schwertt ~ |
[54v.3] Item laufft er dir eyn auff deyn rechte seytten so verbend deyn messer daß der dawm unter kum mit der kurczen oder [55r.1] stumpffen schneyden unter seyn gehulcz yn seyn armen und druck mit dem schnydt ubersich alzo hast dy vyer schnydt und wenn dw dich recht dar eyn schicken wild so magstu dy treyben ym messer und ym swertt |
[104r] Item laufft er dir Ey auff deyn rechte seytten so verbendt deyn messer das der dawm vntten kum mit der kurtzen schneyden vnter seyn gehultz In seyn arme vnd druck mit dem schnytt vbersich also hastu dy vyer schnytt vnd wenne du dich recht dareyn schicken kanst so magstu dye treyben In allen an pynden etc |
||||||||
[306] If he wants to pull from the binding Now the master speaks how you should change one cut into the other one, and speaks: If he wants, etc. Notice it this way: if one runs into you to your left side with the arm stretched high, turn your Messer with the long edge under his hilt to him arm and press firmly upwards and step with it to his right side. Then, wind the pommel through downwards with the Messer from his arm and turn the Messer from the cut from below into the one from above over his arm with the long edge. |
If he wants to pull from the binding Here the master speaks how one should change one cut into the other one, and speaks: If he wants, etc. You should understand it this way: if you have bound one on his right side and you both assume the hanging point on the same side, “simultaneously,” as he strikes around, cut into his arms upwards with the short edge and “simultaneously” turn your Messer around on his arm and cut the upper cut over the same arm. |
[78r.3] Wil er vs dem pand rucken Hie saget der meinster Wie du eyn schnitt in den andern wechseln solt vnd spricht [78v.1] wil er vß etc daß merck also wan eyner dir in laufft zu diner lincken siten mit vff gerechten arm so verwind so verwind [!] din messer mit der langen schniden vntter sin gehultz in sin arm vnd druck fast vber sich vnd schrit do mit vff sin rechten siten vnd wend den kopff mit vnten durch mit dem messer von sinem arm vnd wind dz messer vß den vnten schnit in den obern vber sin arm mit der langen schniden ~ |
[55r.2] Will er auß dem pandt rucken Nw sagt der meyster wye dw eyn schnydt yn den anderen wechsellen solt und spricht will er auß etc daß merck alzo wenn dir eyner eyn laufft zw deyner lincken seyten mit aufgerecktem armen so verbend deyn messer mit der langen schneyden unter seyn gehulcz ym yn seyn arm und druck fast ubersich und schreyt do mit auff seyn rechte seytten und wynd den knauff mit unten durch mit dem messer von seynen armen und wend daß messer auß dem unteren schnydt yn den oberen [55v.1] uber seyn armen mit der langen schneyden |
[104v] Will er auß dem pandt rucken Hye sagtt der meyster wye man Eyn schnyt In den andren wechselen solt vnd spricht will er auß etc Das soltu alzo verstan wenne dw eynem an gepunden hast auff seyner rechten seytten vnd Ir ligett ped Im hangenden ortt auff der selbigen seytten Indes so er vmb schlech schneyd In an seyn arme vbersich mit der kurtzen schneyden Indes wendt deyn messer vmb auff seynen arme vnd schneyd Im den obren schnyd vber den selbigen arme etc |
[100r.13] Will
er auß dem band etc Spricht der meister wil er auß dem band etc Das merck also wann dir einer in lauft zů deiner lincken seytten mit auf gerecktem arm so verwend dein messer mit der langen schniden vnder sein gehiltz in sein arm vnd druck vast über sich vnd schrait do mit auf sein r.s. vnd wend dein knopf do mit vnden durch mit dem messer von seinem arm vnd wind das messer auß dem vnderen schnid in den oberen schnid uber seyn arm mit der langen schniden |
|||||||
[307] |
Then, if one runs into you to your right side with the stretched arm, wind your Messer with the short edge under his hilt into his arm, and press firmly upwards and step to his left side, and let the hilt go through below. Then, turn your Messer with the long edge over his arm into the cut from above and press from yourself. You can also cut the man into his neck or his chest, and thereafter deliver the cuts according to as the man stands. |
[78v.2] Item laufft er dir In zu diner rechten siten mit vff gerechten arm so wind im din messer mit der kurtzen schniden vnder sin gehultz in sin arm vnd truck vast vber sich vnd schrit vff sin lincke siten vnd las dz gehultz vnten durch gen vnd wend dz messer mit der scharppen schniden vber sin arm in den schnitt druck von dir ouch magstu im die hend schlagen oder trucken etc |
[55v.2] Item laufft er dir eyn zw deyner rechten seytten mit auff geracktem armen so wynd ym deyn messer mit der kurczen schneyden unter seyn gehulcz yn seyn armen und druck fast ubersich und schreyt auff seyn lincke seytten und laß daß gehulcz unten durch gen und wendt daß messer mit der scharpffen schneyden uber seyn armen yn den schnydt druck von dir auch magstu ym dy hend schlagen oder drucken |
[105r] Item laufft dir eyner zu deyner rechten seytten Eyn mit auffgeracktem arme So windt Im deyn messer mit der kurtzen schneyden vnter seyn gehultz In seyn arme vnd druck vast vbersich vnd schreyt auff seyn lincke seytten vnd loß das gehultz vntten durch gen vnd wendt das messer mit der langen schneyden vber seyn arme In den obren schnytt Druck von dir auch magstu schneyden den man auff seyn hals an seyn prust vnd dy schnytt treyben darnach als dir der man stett etc |
[100r.14] ¶ Item lauft er dir zu der r. s. mit auf gerackten arm So wind Im dein messer mitt der kurtzen schnid vnder sein gehiltz In sein arm vnd druck vast übersich vnd schnid auf sein linck seytten vnd loß das gehiltz vnden durch gen vnd wend dein messer mit der scharffen schniden uber sein arm In dem schnid druck von dir auch magstu Im die hand schlagen oder drucken |
|||||||
[308] |
If he wants to cut the hand Here the propagator of the art states how one should break the cuts and speaks: The hand, etc. You should understand it this way: if he cuts into your right arm on the outside, “simultaneously” keep your hilt and hand on his sword [sic!] and grab with your left hand from above into his hilt behind his hand and pull firmly to your right side. |
[105v] Dy handt will er schneyden Hye sagtt der Merer der kunst wye man dy schnytt prechen soltt vnd spricht dy handt etc Das soltu also verstan Schneydt er dir In deyn rechten arme außbendigs Indes laß deyn gehultz vnd handt auff seyn swertt vnd greyff mit deyner lincken handt oben In seyn gehultz hynter seyner handt vnd reyß starck auff deyn rechte seytten etc |
||||||||||
[309] |
If he cuts into your hand Here the master states another breaking against the cuts and you should understand it this way: if you want to strike around to his right side, and he “simultaneously” cuts outside into your arm or hand, hit “simultaneously” with your right elbow into his Messer to the same side into which he cuts, and strike always the short edge on his head. |
[106r] Schneydt er dir dy handt Hye sagtt der meyster Eyn ander pruch wyder dy schnytt vnd das soltu alzo versten wiltu vmb schlagen zu seyner rechten seytten Indes schneytt er dich aussen In deyn arme oder handt So stoß Indes mit deynem rechten olpogen auff seyn messer auff der selbigen seytten do er dich schneydt vnd schlag Im Euchling dy kurtz schneyd auff seyn kopff etc |
||||||||||
[310] |
If he cuts to the hand opening Here the master teaches a breaking against the cuts and do it this way: if he cuts on the outside to your arm as before, go with the hilt on his Messer and fall with your left hand in the middle of your Messer and thrust at his face in the armed manner. |
[106v] Schneydt er dy handt ploß Hye lertt der meyster aber Eyn pruch wyder dy schnytt vnd mach den also schneytt er dich außbendig vber deyn arme wye vor so far mit dem gehultz auff seyn messer vnd fall mit deyner lincken handt In dy mitt deynes messers vnd stich In zu dem gesicht gewappendt etc |
||||||||||
[311] |
If he cuts from inside, go throught with the weak You should understand it this way: if he cuts from inside into your right arm, wind your Messer against his one, so that the long edge is above and the short one is against you. Then, let the point go down towards the ground and go with the weak below through to his right side with the short edge to his Messer. Then, strike “simultaneously” to his head to the same side with the long edge. |
[107r] Schneydt Inwendig / swech durchge Das soltu also verstan schneydt Er dich Inwendigs In deynen rechten arme so wind deyn messer gegen dem seynen das dy lang schneyd oben stee vnd dy kurtz gegen dir vnd senck den ortt gegen der erden vnd gee mit der swech vntten durch auff seyn rechte seytten mit der kurtzen schneyden auff seyn messer vnd haw In Indes Zu seynen kopff der selbigen seytten mit der langen schneyden etc |
||||||||||
[312] |
[No text] |
[107v] [No text] |
||||||||||
[313] |
If he has cut the hand inside Here the master teaches a breaking against the cut from inside, and do it this way: if he cuts from inside to your hand or arm, “simultaneously” push his right arm down with your left hand, and strike at his head with the long edge, as it is depicted below. |
[108r] Dy handt ist er schneyden ynnen Hye lertt der meyster aber Eyn pruch wyder den Indren schnyt vnd mach den also Schneydt er dich Inwendigs vber deyn handt oder arme Indes stoß seynen rechten arme nyder mit deyner lincken handt vnd haw Im zu dem kopff mit der langen schneyden wye vntten gemalt stett etc |
||||||||||
[314] |
Wait the inner cut to the hand Here the master teaches another breaking against the cut on the inside and do it this way: as he cuts into your arm on the inside, “simultaneously” let your Messer go down and change the long point through to his right side, and thrust at his face to the same side. If you do not hit him with the long point, step close to him and wind the hanging point at his face to the same side. |
[108v] Inwendig handt mit schneyden wirtt Hye lertt der meyster aber Eyn pruch wyder den Inbendigen schnytt vnd mach den also So er dich schneyt In deynen arme Inbendigs Indes laß deyn messer Sincken vnd wechsel Im den langen ortt durch auff seyn rechte seytten vnd stich Im zu dem gesicht der selbigen seytten Trifstu In nicht mit dem langen ortt so tritt nohendt In Inn vnd windt Im den hangenden ort Zu seynem gesicht der selbigen seytten etc |
||||||||||
[315] |
Learn to turn your edge Here the master states an element from the cuts and speaks: Your edge, etc. You should understand it this way: as you have done the cut to his right side, “simultaneously” wind your Messer against his one and thrust at him with the hanging point at his face from above to the same side above his arms. |
[109r] Deyn schneyd ler wenden Hye sagtt der meyster Eyn stuck auß den schnytten vnd spricht deyn schneyden etc das soltu also verstan So du den schnytt auff seyner rechten seytten gemacht hast Indes windt deyn messer gegen dem seynen vnd stich In mit dem hangenden ortt zu dem gesicht oben zu der selbigen seytten vber seynen arme etc |
||||||||||
[316] |
In the other cuts Here the master teaches how one should use the point in the other cuts and speaks: In the other, etc. You should understand it this way: if you cut into his right arm on the inside, “simultaneously” turn your Messer against his right arm and thrust the hanging point into his face, as it is depicted below. Thus, you have the thrust from the other cut. |
[109v] In dy andren schnytt Hye lertt der meyster wye man / dy andrenschnytt prechen Soltt vnd spricht / den ortt In dy andren schnyt prauchen solt vnd spricht In dy andren etc Das soltu also verstan Schneydestu In In seyn rechten arme Inbendigs Indes wenndt deyn messer gegen seynen arme vnd stich Im den hangenden ortt zu dem gesicht wye vntten gemalt stett also hastu den stich auß dem andren schnytt etc |
||||||||||
[317] |
Then, from the third cut do the thrust this way: as you cut with the long edge from below upwards to the side or to the arm to his right side, “simultaneously,” as the hilt of your Messer is at its highest, let the point go down under his shoulder or chest. |
[110r] Item auß dem dritten schnytt mach den stich also Su dw mit der langen schneyden von vnden auff schneydest dy seytten oder den arme auff seyner rechten seytten Indes so du auff das hochst kumest mit dem gehultz deyneß messers Indes senck Im den ortt vntter seyn vchsen oder prust etc |
||||||||||
[318] |
Then, from the fourth cut do the thrust this way: as you have cut to his chest or from inside to his right arm, “simultaneously” go with the long direct point to his face to his left side. |
[110v] Item auß dem vyerden schnydt mach den stich also So dw In geschnytten hast auff seyn prust oder Inwendigs In seynen rechten arme Indes far Im mit dem langen geraden ortt zu seynen gesich seyner lincken seytten etc |
||||||||||
[319] |
Showing the sun Here the master speaks about an element that is called the sun showing. Do it this way: if he strikes at you or you at him, and as the Messers spark together, go with the hilt of your Messer above his Messer on his right side, and step with your left foot behind his right one. Then, grab with your left hand behind on his shoulder of his left side, and pull him firmly towards you, and go with the hilt and the crosspiece of your Messer under his throat, and press his throat firmly against the nape of the neck. This is called the sun showing in the Messer. |
[78v.3] Das sünnen zeichen Hie saget der meinster von eÿnem stuck dz heist er dz sünnen zeÿchen Daß mach also haut er zu dir oder du zu Im vnd so die messer zu samen glitzen so far mit dinem gehultz dines messers vber sin messer vff siner rechten siten vnd schrit mit dem lincken fus hinter sinen rechten vnd griff mit diner lincken hant hinten an sin achsell siner lincken siten vnd druck in fast zu dir vnd far mit dem gehultz vnd crütz dines messers vnter sin hals vnd druck sere gegen dem nack dz heisset im messer dz sünnen zeÿchen ~ |
[55v.3] Daß swnnen czaÿgen [56r.1] Hye sagt der meyster von eynem stuck daß hayst er daß sunnen czaygen daß mach alzo haut er zw dir oder dw zw ym und so dy messer zw sammen kliczen so far mit dem gehultz deyneß messerß uber seyn messer auff seyner rechten seytten und schreit mit dem lincken fuß hinter seyn rechten und greuff mit deyner lincken hand hynten an seyn achsel seyner lincken seytten und ruck yn fast zw dir und far mit dem gehulcz und kreucz deyneß messerß unter seyn halz und druck sere gegen dem nack daß hayst ym messer daß sunnen czaygen etc Sequitur textus |
[111r] Das sunnen zaygen Hye sagtt der meyster von Eynen stuck das heyst das sunnenzaygen das mach also hawtt er zu dir oder du Zu Im vnd so dy messer zu sammen klitzen so far mit deym gehultz deynes messers vber seyn messer auff seyner rechten seytten vnd schreytt mit deynem lincken füß hinter seynen rechten vnd greyff mit deyner lincken handt hyntten an seyn achselen seyner lincken seytten vnd ruck In vast zu dir vnd far mit dem gehultz vnd kreutz deynes messers vntter seynen hals vnd druck Im seyn kelen ser gegen dem nack das heysset Im messer das sunnenzaygen etc |
||||||||
[320] |
If he feels for Here the master states a breaking against the sun showing and do it this way: if he has gone with the hilt above your Messer under your neck, and with the left [hand] from behind to your left shoulder, drop your Messer and go with your right hand through his both arms, or between his both arms, and go with your right hand to his right arm from behind to the elbow. Then, pull with it firmly towards your right side and go with your left hand from outside under his right elbow to help your right hand, and turn your left side to his right one, and push with both hands with the entire force to your right side. This way, you will get his right arm clenched above your left one, and also his Messer. |
[79r.2] Ob er dast Hie saget der meinster eyn bruch wider dz sünnen zeychen vnd spricht vber tast etc Daß soltu also verstan ist er dir mit sinem [79v.1] gehultz gefaren vber din messer vnter dinem hals vnd mit der lincken hinten an din lincke achsel so loß din messer fallen vnd far mit diner rechten hant durch sin peide arm oder zwuschen sin beide arm vff vnd far mit der rechten hant vber sin rechten arm hinden an dem elnbogen vnd zuch do mit starck gegen diner rechten siten vnd far mit diner lincken hant vßwendig vnter sin rechten elnbogen diner rechten hant zu hilff vnd wind din lincke siten an sin rechte vnd schub mit peiden henden mit gantzer karfft vff din recht siten so kümpt dir sin rechten arm geschlossen vber den lincken vnd auch sin messer also hastu den verborgen griff genant gemacht ~ |
[56r.2] Ob er tast [56v.1] Hye sagt der meyster eyn pruch wyder daß sunnen czaygen und spricht ob er tast etc Daß soltu alzo verstan ist er dir mit seym gehulcz geforen uber deyn messer unter deynen halz und mit der lincken hand hynten an deyn lincke achsel so laß deyn messer fallen und far mit deyner rechten hand durch seyn pede armen oder czwischen seyne payden armen auff und far mit der rechten hand uber seynen rechten armen hynter an den ölpogen und czeug da mit starck gegegn deyner rechten seytten und far mit deyner lincken hand außbendigß unter seynen rechten olpogen deyner rechten handt zw hilff und wendt deyn lincke seytten an seyn rechte und scheub mit peden henden mit ganczer krafft auff deyn rechte seytten so kumbt dir seyn rechter armen geschlossen uber deyn lincken und auch seyn messer alzo hastu den verporgenen griff gemacht etc |
[111v] Ob er dast[53] Hye sagtt der meyster Eyn pruch wyder das sunnezaygen vnd mach den also ist er dir mit dem gehultz gefaren vber deyn messer vntter deynen hals vnd mit der lincken hyntten an deyn lincke achselen so laß deyn messer fallen vnd far mit deyner rechten handt durch seyn peyde arme oder der zwischen seyn payd arme vnd far mit der rechten handt auff seyn rechten arme hyntten an den olpogen vnd zeuch do mit starck gegen deyner rechten seytten vnd far mit deyner lincken handt außben digs vntter seynen rechten olpogen deyner rechten handt zu hilff vnd wendt deyn lincke seytten an seyn rechte vnd scheub mit payden henden mit gantzer krafft auff deyn rechte seytten vnd so kumt dir seyn rechter arme beschlossen vber deynen lincken vnd auch seyn messer wye es vntten gemalt stett etc |
||||||||
[321] |
Then, if he has grabbed you with the hilt as before, and wants to do the sun showing, go with your Messer under his both arms to your left side, so that the point goes outside behind, and assume the armed hand, and go high with the hilt and with the right arm. Then, turn with your chest a bit backwards and “simultaneously” hit with your hilt firmly to his right elbow on the outside and step with your left foot in front of his right one and go with the hilt firmly above his right elbow, so that the point is above, and the hilt is towards the ground, on the inside to his arm and press firmly from above downwards with the armed hand to your right side. |
[79v.2] alliud Item hat er dich mit dem gehultz gefast als vor vnd will dir aber dz sünnen zeychen machen so far mit dem messer vntter sin beide arm vff din lincke siten dz der ortt hinden vssen ge vnd fal zu gewopenter hant vnd far vff mit dem gehultz vnd far vff mit dem rechten arm vnd wenck mit der prust eyn wenig zu ruck Indes stos mit dinem gehultz starck an sin elnbogen vswendig [80r.1] vff din recht siten vnd schrit mit dem lincken fus fur sin rechten vnd far mit dem gehultz starck vber sin rechten dz der ortt oben ste vnd dz gehultz gegen der erden vnd druck starck von oben nider mit gewopenter hant vff dim [!] rechten siten ~ |
[56v.2] Item hat er dich mit dem gehulcz gefast [57r.1] alz vor und will dir aber daß sunnen czaygen machen so far mit deynem messer unter seynen payden armen auff deyn lincke seytten daß der ortt hynter dich außhyn gee und fal zw gewoppender handt und far auff mit dem gehultz und mitt deym rechten armen und wenck mit der prüst eyn benig zw ruck yndeß stoß mit deym gehulcz starck an seynen lincken olpogen außbendigß auff deyn rechte seytten und schreyt mit dem lincken fuß fuer seyn rechten und far mit dem gehulcz starck uber seynen rechten daß der ort oben stee und daß gehulcz gegen der erden und druck starck von oben nyder mit geboppender handt auff deyn rechte seytten etc |
[112r] Item hat er dich mit dem gehultz gefast als vor vnd will dir aber das sunnenzaygen machen so far mit deynem messer vntter seyn payd arme auff deyn lincke seytten das der ortt hynden auß hyn gee vnd fall zu gewappender handt vnd far auff mit dem gehultz vnd mit dem rechten arme vnd wenck mit der prust eyn wenig zu ruck Indeß stoß mit deynem gehultz starck an seynen rechten olpogen außbendig vnd schreytt mit dem lincken fuß fur seynen rechten vnd far mit dem gehultz starck vber seynen rechten olpogen das der ortt oben stee vnd das gehultz gegen der erden Inbendigs an seynen arme vnd druck starck von oben nyder mit gewappen der handt auff deyn rechte seytten etc |
||||||||
[322] |
Then, another different breaking: if he holds you as before with the sun showing, go under his both arms with the point to your left side and go with the hilt between his both arms upwards on the inside above his hand, and pull firmly with the hilt downwards and press firmly downwards with the blade of your Messer and swing to your right side. |
[80r.2] ein ander bruch Item aber eyn ander bruch hat er dich mit dem sunnen zeichen so far vber vnter sin beid arm mit dem ortt vff sin lincke siten vnd far mit dem gehultz zwuschen sin beide arm vff oben Inlbendig vber sint hant vnd riß starck mit dem gehultz vntersich vnd druck oben fast nider mit der klingen dines messers vnd schwing dich vff din rechten siten ~ |
[57r.2] Item aber eyn ander pruch hellt er dich alz vor mit dem sunnen czaygen so far aber under seynen payden armen mit dem ortt auff deyn lincke seytten und far mit dem gehulcz czwischen seynen payden armen auff oben ynbendigß uber seyn hand und reyß starck mit deym [57v.1] gehulcz untersich und druck oben fast nyder mit der klyngen deyneß messerß und swyng dich auff deyn rechte seytten etc |
[112v] Item aber eyn ander pruch hellt er dich als vor mit dem sunnenzaygen so far aber vntten seyn beyd arme mit dem ortt auff deyn lincke seytten vnd far mit dem gehultz zwischen seyn payd arme auff oben Inbendigs vber seyn handt vnd reyß starck mit dem gehultz vntersich vnd druck oben fast nyder mit der klingen deynes messers vnd swing dich auff deyn rechte seytten etc |
||||||||
[323] |
Then, another different breaking: is he has grabbed you with the sun showing as before, notice “simultaneously” at the moment as he goes with the left arm to your left shoulder, do not let him come around you with the arm. Instead, as he wants to rush against you and stretches his arm, “simultaneously” go with the point of your Messer with the weak between his both arms high to the joint of the elbow of his right arm. Then, go with the hilt and with the strong of your Messer from below high on the inside to the joint of his left elbow, and turn with your right side to his left one, and step with your right foot in front of his right one. Then, press rapidly to your left side. Thus, you have grabbed and locked him, so that you can lead him where you want without his wish, and you can also throw him so that he cannot stand up. And you can sit at him and play board games, eat and drink, in that way he has to rot unless you let him cordially stand up. |
[57v.2] Item aber eyn ander pruch hatt er dich mit dem sunnen czaygen gefast alz vor so merck yndeß dy weyl er fert mit dem lincken armen nach deyner lincken achsel So laß yn umb dich mit dem armen nichtt kummen sunder weyl er tasten wil gegen dir und seynen armen streckt yndeß far mit dem ort deyneß messerß mit der swech czwischen seynen payden armen auff ynn daß gelenck deß olpogenß seyneß rechten armenß und far mit dem gehulcz und mitt der sterck deyneß messerß von unten auff außbendigß yn daß gelenck seyneß lincken olpogenß und wendt dich mit deyner rechten seytten an seyn lincke und schreyt mit dem rechten fuß fur seyn rechten und druck geswyndt auff deyn lincke seytten alzo hastu yn aber gefangen und verrigeltt daß dw yn fueren magst wo dw hyn wild uber seynen danck und magst yn auch werffen daß er nicht [58r.1] auff mag stan Und magst do neben ym syczen und ym pret spilen essen oder trincken so muest er erfaulen den dw lyest yn geren auff stan etc |
[113r] Item aber eyn ander pruch hatt er dich mit dem sunnenzaygen gefast als vor So merck Indes dy weyll er fertt mit dem lincken arme nach deyner lincken achsel so laß In vmb dich mit dem arme nicht kummen Sunder weyll er tasten will gegen dir vnd seynen arme streckt Indes far mit dem ortt deynes messers mit der swech zwischen seyn payd arme auff In das gelenck des olpogens seynes rechten armes vnd far mit dem gehultz vnd mit der sterck deynes messers von vntten auff Inbendigs In gelenck seynes lincken ōlpogens vnd wendt dich mit deyner rechten seytten an seyn lincke vnd schreyt mit deynem rechten fuß fur seynen rechten vnd druck geswindt auff deyn lincke seytten also hast In aber gefangen vnd verigelt das du In furen magst wo dw hyn wildt vber seyn danck[54] vnd magst In auch werffen das er nicht auff mag stan etc |
|||||||||
[324] Then, if he holds you as before in the sun showing, go with the Messer with the armed hand to your left side as before, but sooner than he has grabbed your shoulder. “Simultaneously” as he stretches the arm against you, go high with the hilt between his both arms in front of his joint of the left elbow or the hand and turn your left side to his right one, and step with your left foot to his right one. [Then, pull with the hilt] his right arm or hand firmly down, and press with the blade of your Messer and with your elbow to his right shoulder firmly from you. Then, lay down with your arm and chest on the same shoulder. |
Then, if he holds you as before in the sun showing, go with the Messer with the armed hand to his left side as before, but sooner than he has grabbed your shoulder. “Simultaneously” as he stretches the arm against you, go high with the hilt between his both arms and turn your left side to his right one, and step with your left foot in front of his right one. Then, pull with the hilt his right arm or hand firmly down, and press with the blade of your Messer and with your elbow to his right shoulder firmly from you. Then, lay down with your arm and chest on the same shoulder. |
[58r.2] Item hellt er dich alz vor ym sunnen czaygen so far aber mit dem messer mit gewappender handt auff deyn lincke seytten alz vor nw ee er deyn achsel pegriffen hatt yndeß weill er den armen gegen dir streck yndeß far auff mitt dem gehulcz czwischen seyn ped armen yn seyn gelenck deß lincken olpogenß oder der handt und wendt deyn lincke seytten an seyn rechte Und schreyt mit deynem rechten fuß lincken fuß für seyn rechten armen oder handt starck nyder und druck mit deyneß messerß klyngen und mit deynem olpogen seyn rechte achsellen starck von dir und leg dich mit deynem armen und prust starck auff dy selbigen achsellen etc |
[113v] Item helt er dich als vor ym sunnenzaygen so far aber mit dem messer mit gewappender handt auff seyn lincke seytten als vor nun Ee er deyn achsel pegryffen hatt Indes weyll er den arme gegen dir streckt Indes far auff mit dem gehultz zwischen seyn payd arme vnd wendt deyn lincke seytten an seyn rechte vnd schreytt mit deynem lincken füß für seyn rechten vnd reyb mit dem gehultz seyn rechten arme oder handt starck nyder vnd druck mit deynes messer klingen vnd mit deynem olpogen seyn rechte achselen starck von dir vnd leg dich mit deynem arme vnd prust auf dy selben seytten achselen etc |
|||||||||
[325] |
Then, if he has grabbed you as before, again in the moment when he wants to grab to your shoulder as before, go with your right arm outside firmly above his left on the outside to the joint and the elbow to his left side, and step with the left foot behind his right one and push him over it. |
[58v.1] Item hatt dich eyne gefast alz vier vor dy weill er aber greuffen wil nach deyner achselen alz vor So far mit deynem rechten lincken armen aussen starck uber seynen lincken außbendigs yn das gelenck und olpogen auff seyn lincke seytten und schreyt mit dem lincken fuß hynter seynen rechten und druck yn dar uber |
[114r] Item hatt er dich geuast als vor dy weyll er aber greyffen will nach Deyner achselen als vor so far mit deynem rechten arme aussen starck vber seyn lincken außbendigs yn das gelenck vnd olpogen auff seyn lincke seytten vnd schreytt mit dem lincken fuß hinter seyn rechten vnd druck In dar vber etc |
|||||||||
[326] |
Go over with the hilt Here the master teaches a good element how one should take the Messer from a man with the armed hand with the weak. And do him this way: go to the man from your right side with the Entrüsthau to his left side. “Simultaneously” go with your hilt above his Messer on his right side, so that his Messer comes under your one, and “simultaneously” go with the weak of your Messer on the inside between his hilt and his hand, and pull firmly to your left side. |
[114v] Mit gehultz vberfar Hye lertt der meyster Eyn gutt stuck wye man dem man das messer nemen soll zu gewappender handt mit der swech vnd thu Im also Gee an den man von deyner rechten seytten mit dem Entrusthaw auff seyn lincke seytten Indes far mit deym gehultz vber seyn messer auff seyner rechten seytten das seyn[55] messer vntter das seyn kum Indes far Im mit der swech deynes messers Inbendigs zwischen seyn gehultz vnd handt vnd reyß starck auff deyn lincke seytten etc |
||||||||||
[327] |
Then, another good element: go to him as before and go with your hilt above his Messer on his right side, and let the weak of your Messer go down through, and go on the outside in the joint of his right hand, and press firmly to your right side, in that way you take his Messer. |
[115r] Item aber Eyn gutt stuck Gee zu Im als vor vnd far aber mit deym gehultz vber seyn messer auff seyner rechten seytten vnd laß vntten durch gan dy swech deynes messers vnd far Im außbendigs In das gelenck seyner rechten handt vnd druck starck auff deyn rechte seytten So nymbstu Im aber das messer etc |
||||||||||
[328] |
Go over, thrust in the armed manner Here the master teaches another good element how one should set on the point with the armed hand to a man, and do him this way: go above his Messer with the hilt on his right side and let the weak of your Messer go down to his left side, and thrust him on the inside at his face, so that his Messer comes under your right shoulder. |
[115v] Vberfar gewappendt sticht Hye lertt der meyster aber Eyn gutt stuck wye man den man zu gewappender hent an setzen soll den ortt vnd thu Im also far vber de seyn messer mit dem gehultz auff seyner rechten seytten vnd laß dy swech deynes messers sincken auff seyn lincke seytten vntten dürch wyder auff seyn rechte seytten vnd stich Im jnnbendigs gewappen zu dem gesicht vnd das seyn messer kum vntter seyn deyn rechte vchsen etc |
||||||||||
[329] |
If he moves to the stroke You should understand it this way: go with the hilt over his Messer as before, so that your weak comes through downwards to your left side, and his Messer comes under your right shoulder. Then, go with the hilt on the inside into the joint of his right hand and press with it quickly to your left side, in that way you take his Messer. |
[116r] Für schleg er pultz Das soltu also verstan far Im mitt dem gehultz vber seyn messer wye vor vnd so deyn swech vntten durch ist gegangen auff deyn lincke seytten vnd seyn messer ist dir kummen vnter deyn rechte vchsen so kum Im mit dem gehultz Inbendigs In das gelenck seyner rechten handt vnd druck da mit geswindt auff deyn lincke seytten so nymbstu Im das messer |
||||||||||
[330] |
Go over with the hilt You should understand it this way: go to him with your Messer as before and go with the hilt above his Messer also as before, and come through down with the weak to your left side. Then, go with your left hand in the middle of your Messer and go with the hilt to him on his neck, and step with your foot behind his right one, and swing a bit to your left side, and throw him forwards over yout right leg. |
[116v] Vberfar mit cloß Das soltu also verstan Gee an In mit deynem messer wye vor vnd far Im mit dem gehultz vber seyn messer auch wye vor vnd kum vntten durch mit der swech auff deyn lincke seytten vnd far mit deyner lincken handt In dy mitten deynes messers vnd far mit dem gehultz auff Im an seynen hals vnd schreyt mit deynem fuß hinter seynen rechten vnd swing dich Eyn wenig auff deyn lincke seytten vnd wurff In fur dich vber deyn rechte peyn etc |
||||||||||
[331] |
You should pull to him Here the master teaches another element how one should grab one at one’s hand, and do him this way: as you go with your hilt over his Messer as before, pull with your hilt on his Messer backwards, so that the weak of your Messer comes to his right hand. And “simultaneously” fall with your left one in both Messers, and also with your right hand from above in both Messers, and press with both hands firmly. Then, turn your left side to his right and do what you want. |
[117r] Zu Im soltu rücken Hye lertt der meyster aber Eyn stuck wye man Eynen vahen[56] solt bey seyner handt vnd thu Im also So du mit deynem gehultz vberfersst seyn messer wye vor So zeuch mit deynem gehultz auff seynem messer zü ruck das dy swech deynes messers kum auff seyn rechte handt vnd fall yndes mit deyner lincken In payde messer vnd auch mit deyner rechten oben In payde messer vnd druck mit peden henden vast zü vnd wendt deyn lincke seytten an deyn rechte vnd mach was du willt etc |
||||||||||
[332] |
If you want to run off Here the master teaches a main element and states how you should run off in the Messer and speaks: if you want to run off, etc. |
[80r.3] Wiltu ab lauffen Hie lert der meinster aber eyn haupt stuck vnd sagett wie du im messer salt ab lauffen vnd spricht wiltu abe lauffen |
[58v.2] Wiltu ablauffen Hye lertt der meyster aber eyn hawbt stuck und sagt wye dw ym messer absolt lauffen und spricht wiltu ablauffen etc. |
[117v.1] Wiltu ab lauffen Hye lertt der meyster aber Eyn haubtstuck vnd sagtt wye du Im messer ab solt lauffen vnd sprich wiltu ab etc |
[100r.15] Wiltu ablauffen etc |
|||||||
[333] |
You should understand it this way: if you come in the Zufechten to him, and you have close to him with the binding, and then you want to run off with the Messer, you should weave with it, as the women do when they unspool the yarn on both sides. And do as if you wanted to sit down with the Messer, and let the Messer go off from both sides, so that the thumb is always down on the flat of the Messer. And as you see that he follows your Messer with the displacement, do “simultaneously” a feint on the side on which you can have the man in the surest manner, in that way you hit him. |
[80r.4] dz soltu also verstan wan du im zubechten zu im kümpst vnd hast nicht zu im mit dem anbinden wiltu dan ab lauffen mit dem messer so soltu do mit [80v.1] werffen als die fraulben wan sie dz garn ab haspeln von beiden siten vnd thün glich als wollest nider sitzen mit dem messer vnd loß dz messer von beiden siten ab gen doch dz der thüm alwegen vnten ste vff der flech des messers vnd wan du dan sihest dz er dinem messer noch get mit der versatzüng Indes mach eyn feller vff welcher siten du den man an dem gewisesten meinest zu haben so trifstu in |
[58v.3] Daß soltu alzo verstan wenn dw ym zw vechten zw ymb kumbst vnd hast nohent zw ym mit dem an pynden wiltu den ablauffen mit dem messer so soltu da mit bayffen alz dy frawen wenn si daß garen abwynten oder wayffen [59r.1] von payden seytten und thue gleich alz dw nyder seczen wollest und laß daß messer von payden seytten abgen doch daß der dawm albegen unten stee auff der flech deß messerß und wenn dw den stigst daß er deynem messer nach gett mit der versaczung yndeß mach eyn feler auff welcher seytten dw den man am gebisten mogst zw haben so triffest dw yn |
[117v.2] das soltu alzo verstan wenne du Im zuuechten zu Im kumbst vnd hast nahendt zu Im mit dem anpinden wiltu denn ablauffen mit dem messer so soltu da mit bayffen[57] als dy frawen wan sy das garnn ab haspelen[58] von payden seytten vnd thu geleych als dw nyder wollest setzen mit dem messer vnd laß das messer von payden seytten abgen dach[59] das der dawmen albeg vntten stee auff der flech des messers vnd wenne dw denn Sichst das er deynem messer nach gett mit der versatzung Indes mach Eyn feler auff welch seytten du den man am gewisten meynst zu haben so triffestu In // |
[100r.16] laufe also verste wann du Im zuüechten zü Im kumpst vnd hawest noch zů Im mit dem an binden wiltu dan ab lauffen mit dem messer So soltu do nit beyssen alß die frowen thůn wenn sey garn haspelen von beyden seytten vnd thů glich alß du nider wolest sincken mit dem mesß von beyden seytten ab gen dach das der thaum vnden stee auf der schlec fleche des messers vnd wan du sichst das er deynem messer nachget mit dem versetzung Indes mach ein feler auf welcher seytten du dem man am gewsten haben magst So drifstu In |
|||||||
[334] Then, or as you run off from both sides,“simultaneously” as you have run off from above, strike quickly to one of the the lower peak, and “simultaneously” strike quickly again to the upper peak. |
Then, or as you run off from both sides, “simultaneously” as you have run off, strike quickly to the lower peak, and “simultaneously” strike quickly again to the upper peak. Or, strike the point at his chest and strike “simultaneously” skillfully to the previous peak. |
[80v.2] oder so du ablauffest von beiden siten Indes so du oben ab gelauffen bist also bald schlach zu der vntern zynnen Indes schlag pald wider ze der obern zynnen oder schlag im den ortt in sin brust vnd schlag indes behend ze der vorigen zÿnnen ~ |
[59r.2] ¶ oder so dw ablauffest von payden seytten yndeß so dw oben abgelauffen pist alzo pald schlag zw der unteren czynnen eyner yndeß schlag pald wyder zw den oberen czynnen |
[118r.1] // Item oder so du ablauffest von payden seytten Indes so du abgeloffen pist alzo pald schlag zu der untteren zynnen Indes schlag pald wyder zu der obren zynnen oder schlag Im den ortt In seyn prust vnd schlag Indes nohendt zu der forigen zynnen etc |
[100r.17] oder so du ablauffest von beyden seytten Indes so du abgelauffen bist also bald schlag zů der vnderenn zinnen Indes schlag bald wider zů der oberen zinnen ader schlag im den ortt In sein brust vnd schlag Im Indes behend zů der vorigen zinnen |
|||||||
[335] |
If he is in the hanging point Here the master teaches how one should assume the hanging point and what to do from it in both guards. And assume the hanging point on both sides as it is depicted below. |
[81r.3] Ligt er im hangenden ort |
[59r.3] Ligt er ym hangettem ortt |
[118r.2] Ligt er ym hangenden orcht Hye lertt der meyster wye man sich legen solt In den hangenden ortt vnd dar auß machen sol auff payden legeren vnd schick dich In den hangenden ortt auff payden seytten wye vntten gemalt stet etc |
[100r.18] ligt er Im langenden [!] ortt etc |
[174r.1] Das benemen Ligt Er Im hanngenden ort |
||||||
[336] |
Then, here the master speaks about a main element, that is about the taking over. |
[80v.4] Hie saget der meinster aber ein halbpt stuck dz ist von dem bnÿmen |
[59r.4] Hye sagt der meyster aber von eynem haubtstuck daß ist von den pnemen ym [59v.1] messer |
[118v.1] Item hye sagtt der meyster aber von eynem haubtstück das ist von dem pnemen |
||||||||
[337] |
Now notice that the taking over in the Messer is while you come together in the Zufechten and you both stand in the hanging point. |
[80v.5] Nu merck dz benemen im messer dz ist wan ir im ze vechten ze samen kümptt vnd so ir beid |
[59v.2] ¶ merck daß pnemen ym messer ist wenn Ir ym zw vechten zw sammen kumbtt und so Ir payde |
[118v.2] Nu merck das pnemen Im messer ist wenne Ir Im zuuechten zusammen kumpt vnd so Ir payde |
||||||||
[338] |
If he stands against you in the hanging point on your right side and you stand as well on his right side in the hanging point, and you both stand againt each other and are in binding, go with the crosspiece to his left side on his Messer and push his Messer to his right side with your Messer. “Simultaneously” step well around to his left side with your right foot and strike with the blunt edge at his head. |
[81r.2] Item ligt er gegen dir ym hangenden ortt vff diner rechten siten vnd du ligst auch vff diner rechten siten im hangenden ort vnd so ir also ligent gegen eynander also stint ym band so far mit dem gehultz vff sin lincke siten an sin messer vnd schub mit dinem messer sin messer vff sin rechte siten wol vnd schrit Indes wol vmb vff sin lincke siten mit dinen rechten fus vnd schlag yn mit der stümpfen schniden an syn kopff |
[59v.4] Item ligtt er gegen dir ym hangattem ortt auff deyner rechten seytten und dw ligest auch auff seyner rechten seytten auch ym hangattem ortt und so ir alzo ligtt gegen eyn ander und alzo seit ym pandt so far mit dem kreucz oder gehultz auff seyn lincke seytten an seyn messer und scheub mit deynem messer auff seyn rechte seytten woll und schreit yndeß wol umb auff seyn lincke seytten mit deynem rechten fuß und schlag yn mit der stumpfen [60r.1] schneyden an seyn kopff Sequitur textus |
[118v.3] ligtt Im hangenden ortt wye oben gemalt ist ligtt er gegen dir Im hangenden ortt auff deyner rechten seytten vnd dw ligest auch auff seyner rechten seytten Im hangenden ortt vnd so Ir also ligtt gegen Eyn ander vnd also seyt Im pandt so far mit dem kreutz auff seyn lincke seytten an seyn messer vnd scheub mit deynem messer seyn messer auff seyn rechte seytten vnd schreytt Indes woll vmb auff seyn lincke seytten mit deynem rechten füß vnd schlag In mit der stumpffen schneyden an seyn kopff etc |
[174v.1] Item Ligt Er dir Also an deinner rechten seitten. vnnd du Im gegen der seinnen angepvnnden hast. so far mit dem Creutz oder gehultz an sein linncken seitten am Duseggen. scheubs zur rechten Indes schreit wol zu seinner linncken mit dem fuos. vnnd schlag In mit der kurtzen schneid |
|||||||
[339] |
Then, if you stand on his left side on his Messer in the hanging point, go with the crosspiece or the hilt to his right side on the blade of his Messer, and push his Messer to his left side. “Simultaneously” step with your left foot forwards to his right side and strike at his head with the long edge. |
[80v.6] ligt im hangenden ort ligstu dan vff [81r.1] siner lincken siten an sinem messer so far mit dem crutz oder gehultz vff sin rechte siten an sin messers klingen vnd schub im also sin messer vff sin lincke siten Indes schrit mit dinem lincken fus vff sin rechte siten vnd schlag im zu dem kopff mit der langen schniden |
[59v.3] ligtt ym hangattem ortt ligstu den auff seyner lincken seytten an seym messer so far mit dem kreucz oder gehulcz auff seyner rechten seytten an seynß messerß klyngen und scheub yn alzo seyn messer auff seyn lincke seytten yndeß schreit mit deynem lincken fuß auff seyn rechte seytten und schlag yn zw dem kopff mit der langen schneyden |
[119r] Item ligstu auff seyner lincken seytten an seynem messer Im hangenden ortt so far mit dem kreutz oder gehultz auff seyn rechte seytten in seyns messers klingen vnd scheub Im also seyn messer auff seyn lincke seytten Indes schreytt mit deynem lincken füß fur auff seyn rechte seytten vnd schlag Im zu dem kopff mit der langen schneyden etc |
[174r.2] Item wann Ir baid Inn dem hanngenden ort ligent Inn dem zufechten. ligstu ann seinner linncken seitten. an seinem duseggen. so far mit der kurtzen schneidin oder gehultz an sein rechten seitten. vnnd schlag Im mit der lanngen schneidin zu dem kopff. |
|||||||
[340] Who stands in the hanging point Here the master states an element against the taking over and a breaking and speaks: Who stands, etc. |
Who stands in the hanging point Here the master states a breaking against the taking over and speaks: Who stands, etc. |
[80v.3] Der im hangenden ort ligt [81v.1] Hie saget der meinster ein bruch wider die benemen vnd spricht also |
[60r.2] Wer ym hangattem ortt ligtt Hye sagt der meyster eyn stuck wyder dy pnemen und eyn pruch und spricht wer ym etc |
[119v.1] Der Im hangenden ortt ligtt Hye sagtt der meyster eyn pruch wider dy pnemen vnd spricht der Im etc |
[100r.19] brich wider die nemmer vnd spricht dar In dein bruch soltu also machen |
[174v.2] Brüch Der Im hanngenden ort ligt Item die weil Er sein Duseggen zum benemben scheubt. so zuckh dein Duseggen nachent zu deim leyb khum Ehe dann er vnnd schlag Im zum linncken ohr. Indes wind Im zum gesicht. |
||||||
[341] Then, another breaking against the taking over and is better than the first breaking and element, as the first element and the first breaking go quite badly, but this element and breaking goes firmly rightfully and do it this way: if he stands in the hanging point to your right side and you also [stand] on his right side, “simultaneously,” as he pushes your Messer to your right side and wants to strike to your left side to the ear, “simultaneously” twitch your Messer to yourself from his Messer. Then, come sooner with the stroke, and strike to his ear to his right side. |
You should understand it this way: if he stands in the hanging point to your right side and you also [stand] on his right side, “simultaneously,” as he pushes your Messer to your right side and wants to strike to your left side to the ear, “simultaneously” twitch your Messer to yourself close to your body from his Messer with the lowered point. Then, come sooner with the stroke, and strike to his ear to his right side. |
[81v.3] Item Aber eyn bruch wider die benemen vnd ist besser dan der b erst bruch wan dz erst stuck vnd der erst pruch gan gar letz zu Aber daß stuck vnd pruch gant vast recht ze im messer vnd thün Im also lit er im hangenden ort vff diner rechten siten vnd du auch uff siner rechten siten Indes die will er din messer schubt vff din rechten siten vnd die wil er wil schlagend ze diner lincken siten ze den oren Indes zuck din messer an dich von sinem messer vnd küm e mit dem schlag vnd schlag im ze den oren ze siner rechten siten |
[60v.1] Item aber eyn ander pruch wyder dy pnemen und ist pesser wenn der erst pruch und stuck wann daß erst stuck und der erst pruch genen gar lecz zw aber dicz stuck und pruch gett fast recht zw und Thu ym alzo ligt er ym hangattem ortt auff deyner rechten seytten und dw auch auff seyner rechten seyten yndeß weill er deyn messer scheubt auff deyn rechten seytten und wil dich schlagen zw deyner lincken seytten zw dem oren yndeß czuck deyn messer an dich von seynem messer und kum ee mit dem schlag und schlag zw dem oren seyner rechten seytten |
[119v.2] Das soltu also versten ligtt er Im hangenden ortt auff deyner rechten seytten vnd du auch seyner rechten seytten Indes dy weyll er deyn messer scheubt auff deyn rechte seytten vnd will schlagen zu deyner lincken seytten zu dem oren Indes zuck deyn messer an dich mit gesencktem ortt von seynem messer nohendt an deyn leyb vnd kum Ee mit dem schlag vnd schlag Im zu dem oren seyner rechten seytten |
||||||||
[342] You should do the breaking this way: if he stands on your left side in the hanging point and you also stand on his left side in the hanging point, and he wants to take over your Messer with his Messer, notice, while he pushes your Messer, twitch your Messer to yourself, and come sooner with the stroke than him, and strike at his left ear. “Simultaneously” wind your Messer against him and thrust at his face. |
Then, if you stand on your left side in the hanging point and he also stands against you on his left side in the hanging point and wants to take over your Messer with his Messer, notice, while he pushes your Messer, twitch your Messer to yourself close to your body, and come sooner with the stroke than him, and strike at his left ear. “Simultaneously” wind your Messer against him and thrust at his face if you want, etc. And the breaking is very bad and not the best, and if you cannot come any further, you can still help yourself with it. |
[81v.2] ligt er vff diner lincken siten im hangenden ortt als vor vnd du ouch vff siner lincken siten in dem selbigen ort wil er dir dan din messer benemen mit sinem messer so merck die will er sin messer schubt so zuck din messer gegen dir nohent zu dim lib vnd küm e mit dem schlag im ze sinem lincken oren Indes wind gegen Im din messer vnd stich im zu dem gesichtt ~ ~ |
[60r.3] Den pruch soltu alzo machen ligtt er auff deyner lincken seytten ym hangattem ortt und dw auch auff seyner lincken seytten ym hangattem ortt will er dir dan deyn messer pnemen mit seynem messer so merck weyll er deyn messer scheubtt so czuck deyn messer gegen dir und kum ee mit dem schlag den er und schlag yn zw seynem lincken oren yndeß wyndt gegen ym deyn messer und stich ym zw dem gesichtt |
[120r] Item ligstu auff deyner lincken seytten Im hangnden ortt vnd Er ligett auch gegen dir auff seyner lincken seytten Im hangen den ortt vnd will dir deyn messer pnemen mit seynem messer so merck dy weyl er deyn messer scheubt so zuck deyn messer gegen dir nohendt zu deynem leyb vnd kum Ee mit dem schlag denne er vnd schlag Im zu seynen lincken oren Indes windt gegen Im deyn messer vnd stich Im zu dem gesicht ob dw willt etc vnd der pruch ist ser letz vnd nicht am pesten vnd so dw nicht weytter kummen magst so magstu dich dennich do mit behelffen |
[100r.20] ligt er auf deiner lincken seyten Im langenden [!] ortt als vor vnd du auch auf deiner lincken seytten Im selbigen ortt will er dir dan Im messer benemen mit seynem mesß So merck die weyl er sein mesß schieben will so zuck dein messer gegen dir nohe dem lib vnd kum ee mit dein messer schlag dan er vnd schlag Im zů seinem lincken ore In das wind gegen Im dein mesß vnd stich im zu dem gesicht |
|||||||
[343] |
Then, another breaking, and it is the best. If he wants to take over you as before, notice, as he strikes at your left ear, “simultaneously” go high with your Messer as before under his Messer and set the point on his neck to his right side and do “simultaneously” what you want. |
[81v.4] alliud [82r.1] Item Aber eyn ander bruch vnd ist der pest will er dich benemen als vor so merck die will er dir dan nach dinem lincken oren schlecht Indes far vff mit dinem messer als vor vnter sin messer vnd setz ym den ortt an sin hals vff siner rechten siten vnd mach Indes wz du wiltt ~ |
[60v.2] Item aber eÿn ander pruch und ist der pest wil er dich pnemen alz vor so merck dy weul er dir nach deynem lincken oren schlecht yndeß far auff mit deynem messer alz vor unter seyn messer und secz ym den ortt an seyn halz auff seyner rechten seytten und mach yndeß waß du wildt etc Sequitur textus |
[120v] Item aber Eyn pruch vnd ist der pest will er dich pnemen als vor so merck dy weyll er dir nach deynen lincken oren schlecht Indes far auff mit deynem messer als vor vntter seyn messer vnd setz Im den ortt an seyn hals auff seyner rechten seytten vnd mach Indes waß du willt etc |
||||||||
[344] |
Then, a breaking against the twitching in the hanging point: if he wants to twitch with his Messer in the hanging point, “simultaneously”, as he goes high with his hilt and wants to twitch, go with your point firmly to his face and raise your arm high, and do not let him come from the Messer. Then, follow after the opening and his Messer with the point. |
[121r.1] Item Eyn pruch wyder dy zucken Im hangenden ortt willer mit seynem messer zucken In dem hangenden ortt Indes so er auff fertt mit seym gehultz vnd will zucken so far mit deynem ortt starck nach seym gesicht vnd heb deyn arme hoch auff vnd laß In nicht von dem messer kummen vnd volg nach der ploß vnd seynem messer mit dem ortt etc |
||||||||||
[345] |
Then, if he stands in the hanging point on your right side and you also stand on his right side, do as if you wanted to rush to his opening to the same side. “Simultaneously” twitch upwards with your hilt and Messer and thrust at him from above to the opening of his left side. The breaking above belongs to this element. |
[121r.2] Item ligtt er dir Im hangenden ortt auff deyner rechten seytten vnd du ligest Im auch auff seyner rechten seytten So thu sam[60] du Im dringen wollst zu der ploß auff der selbigen seytten Indes zuck vbersich mit deym gehultz vnd messer vnd stich Im oben eyn zu der ploß seyner lincken seytten Der pruch der oben gehortt vber ditz stuck etc |
||||||||||
[346] |
If you want to take over him Here the master says how one should take over the man and [speaks]: If you want, etc. You should understand it this way: if you want to take his Messer, do it this way-if you both stand in the hanging point on his right side and he also [stands] on your right side, take over his Messer well on his right side. “Simultaneously” fall with your empty hand on his hand on the hilt of the Messer, and pull downwards in that way you take his Messer. |
[82r.2] Wiltu In benemen Hie saget der meinster wie man den man benemen sol vnd spricht also wiltu In benemen dz soltu also verstan wiltu Im sin messer nemen so thün Im also so ir beide ligt im hangenden ort vff siner rechten siten vnd er ouch vff diner rechten siten so benÿm im sin messer woll vff siner rechten siten Indes fal mit diner lerer hant vff sin hant an [82v.1] dz gehultz desß messers vnd riß vntersich so nympstu im dz messer ~ |
[61r.1] Wiltu yn pnemen Hye sagtt der meyster wye man ym pnemen söl daß messer nemen wiltu ym daß messer nemen So thue ym alzo So Ir payd ligt ym hangattem ortt auff seyner rechten seytten und er auch auff deyner rechten seytten so pnym ym seyn messer wol auff seyn rechte seytten yndeß fal mit der leren handt auff seyn hand an daß gehulcz deß messerß und reyß untersich so nymbstu ym daß messer etc |
[121v] Wiltu In pnemen Hye sagtt der meyster wye man den mann pnemen solt vnd wiltu In etc Das soltu also verstan wiltu Im seyn messer nemen so thu Im also So Ir payd ligt Im hangenden ortt auff seyner rechten seytten vnd Er auch auff deyner rechten seytten So pnym Im seyn messer woll auf seyner rechten seytten Indes fall mit deyner leren handt auff seyn handt an das gehultz des messers vnd reyß vntersich so nymbstu Im das messer etc |
[175r.1] Wiltu In benemben Item truckh Im sein Duseggen beyseitz. vnnd far Im mit deinner leeren hannd. Inn sein gehultz. reysz vnndersich. so volgts. |
|||||||
[347] |
Then, if you both stand as before, take over him with the empty hand, and do him this way: if you both stand in the hanging point, grab with your left [hand] to his left side through his Messer, and fall with the left hand on the outside and above between his Messer and your right hand. This way he is taken over with the empty hand. |
[82v.2] ein anders Item ligt ir beide als vor so nÿm im aber mit lerer hant vnd thun im also so ir beide ligt im hangenden ort so begriff mit diner lincken vff sin lincke siten durch sin messer vnd fal vswendig oben mit der lincken hant zwuschen sin messer vnd siner rechten hant also ist er benümen mit lerer hant etc |
[61r.2] Item ligt Ir payde alz vor so penymb yn aber mit lerer hand und thue ym alzo so Ir peyde ligtt ym hangattem ortt so pe greuff mit deyner lincken hand auff seyn lincke seytten durch seyn messer und [61v.1] fal außbendigß oben mit der lincken hand czwischen seyn messer und seyner rechten hand etc |
[122r] Item ligt Ir payd als vor so pnym Inn aber mit lerer hand vnd thu Im also So Ir payde ligtt Im hangenden ortt so greyff mit deyner lincken auff seyn lincke seytten durch seyn messer vnd fall außbendigs oben mit der lincken hand zwischen seyn messer vnd deyner rechten handt alzo ist er pnummen mit lerer handt etc |
||||||||
[348] |
Then, if you both stand in the hanging point, turn your hand from above always against his one, and grab “simultaneously” with your left hand in the middle of both Messers, and go with your hilt from below through his arm on the outside in the joint of his right hand. Then, pull “simultaneously” firmly to your right side with the hilt. |
[122v] Item liget Ir ped Im hangenden ortt so wendt oben deyn hand Ewchling gegen seyner Ewchlich ewchlingen vnd greyff Indes mit deyner lincken handt In peyde messers In dy mit vnd far mit deynem gehultz vntten durch seyn arme außbendig In das gelenck seyner rechten handt vnd reyß Indes starck auff deyn rechte seytten mit dem gehultz etc |
||||||||||
[349] |
Then, if you stand in the hanging point as before, you can also twitch through, and change through or cut. |
[82v.3] Item ligstu als vor im hangenden ort so mastu durch zucken vnd auch durch wechsel schniden |
[61v.2] Item ligstu alz vor ym hangatten ort alz vor so magstu durchzucken und auch durchwechsellen |
[123r.1] Item ligstu Im hangenden ortt als vor so magstu auch durchzucken vnd auch d durchwechselen schneyden etc |
[175r.2] magst auch durch zuckhen. vnnd durchwechslen. |
|||||||
[350] |
Then, do him as if you wanted to thrust at the lower peaks, and “simultaneously” thrust aside to his right side, and do not hit him with the thrust, but strike with the Entrüsthau to his left side to the upper peaks. |
[82v.4] thün Im also als du wellest stechen ze der vntern zÿnnen Indes stich besitz vff sin rechten siten vnd triff In nit mit dem stich sunder schlag in mit dem entrust haulb ze siner lincken siten ze der obern zÿnnen // |
[61v.3] Item thue ym alzo alz dw wollest stechen zw der unteren plöß yndeß stich peseytt auff seyn rechte seytten und triff yn nicht mit dem stich sunder schlag mit dem entrusthaw zw seyner lincken seytten zw der oberen czynnen etc |
[123r.2] Item thu Im also als du wollest stechen zu den vntren zynnen Indes stich beseytt auff seyn rechte seytten vnd Triff In nicht mit dem stich Sunder schlag In mit dem Entrußthaw zu seyner lincken seytten zu den obren zynnen etc |
[175r.3] thu als wollestu zu der vnndern zinnen Indes stich auf sein rechten seitten. triff In aber nit. sonnder schlag In mit dem Entrusthaw. zur linncken obern zinnen. |
|||||||
[351] |
Then, if you both stand as before, “simultaneously“ wind with your Messer against his Messer so that the thumb is above, and thrust skillfully at his stomach. “Simultaneously” wind again to your left side, so that the blunt edge is below and thrust at him to the previous peak. |
[82v.5] Item so ir beid ligt als vor Indes wind mit dinem messer gegen sinem messer dz der thüm oben ste vnd stich im behendlich ze dem buch Indes wind wider vff dim lincke siten dz die stümpff schnid vnten ste vnd stich im ze der vorigen zÿnnen ~ |
[61v.4] Item so Ir payde ligtt alz vor yndeß wyndt mit deynem messer gegen seynem messer daß der dawm oben stee und stich ym behendlich zw dem pauch yndeß wyndt wyder auff deyn lincke seytten daß dy stumpff schneyd unten stee und stich ym zw der forigen czynnen |
[123v] Item So Ir payde ligtt als vor Indes windt mit deynem messer gegen seynem messer das der dawm oben stee vnd stich Im behentlich zu dem pauch Indes windt wyder auff deyn lincke seytten das dy stumpff schneyd vntten stee vnd stich Im zu der vorigen zynnen etc |
||||||||
[352] Then, if you stand as before, do as if you wanted to wind at his stomach, and “simultaneously” thrust at his face. |
Then, if you stand as before, do as if you wanted to wind at his stomach, and thrust the long point “simultaneously” at his face. |
[83r.1] Item so du stest als vor so thun glich als du im ze dem buch wollest winden Indes stich im zue dem gesicht |
[61v.5] Item so dw stest alz vor so thue samb [62r.1] dw ym zw dem pauch wollest wÿnden yndeß stich ym zw dem gesicht etc |
[124r] Item so du stest als vor so thu geleych als du Im zu dem pauch wollest winden vnd stich Im den langen ortt Indes zu dem gesicht etc |
||||||||
[353] Be ready in winding, Here the master states a breaking against the changing through in the taking over and speaks: In winding, etc. You should understand it this way: if you stand in the hanging point against his right side and he stands against you on the same side and he winds his Messer against your one, and wants to go through “simultaneously” with the point to your face, “simultaneously” wind also against his Messer and go with it high to his face, so that your point hits and his one will be set off. |
Be ready in winding Here the master states a breaking and speaks: In winding, etc. You should understand it this way: if you stand in the hanging point against his right side and he winds his Messer against your one, and wants to go through “simultaneously” with the point to your face, “simultaneously” wind also against his Messer and go with it high to his face, so that your point hits and his one will be set off. |
[83r.2] Im winden biß bericht Hie saget der meinster eyn bruch vnd spricht Im winden dz soltu also verstan stestu im hangenden ortt gegen siner rechten siten vnd er wind sin messer gegen dinem vnd will Indes durch gen mit dem ort gegen siner rechten siten vnd er windt sin messer gegem dinem vnd will Indes durch gen mit dem ortt ze sinem gesicht Indes wind auch gegem sinem messer vnd far do mit hoch vff zu sinem gesicht so trifft din ort vnd der sin wuertt abgesetz ~ |
[62r.2] Ym wyden piß bericht Hye sagtt der meyster eyn pruch wyder dy durchwechselen ym pnemen und sprichtt alz ynn wynden etc Daß soltu alzo verstan stestu ym hangatten ortt gegen seyner rechten seytten und er ergegen auch auff der selbigen seytten und er wyndt seyn messer gegen sei deynem und will yndeß durchgen mit dem ortt zw deym gesichtt yndeß wynd auch gegen seynem messer und far da mit hoch auff zw seym gesichtt so trifft deyn ortt und der seyn wirtt ab geseczt etc |
[124v] Im winden piß bericht Hye sagtt der meyster Eyn pruch vnd spricht Im winden etc Das soltu also verstan Stestu Im hangenden ortt gegen seyner rechten seytten vnd er windt [Sic] seym messer gegen deynem vnd will Indes durchgen mit dem ortt zu deynem gesicht Indes windt auch gegen seynem messer vnd far da mit hoch auf zu seynem gesicht so trifft deyn ortt vnd der seyn wirtt ab gesetzt etc |
||||||||
[354] |
Then, here the master states a breaking against the element where he thrusts at your stomach in the winding. And if you want to break it, do it this way: if he wants to go to your body and wants to wind against your Messer and thrust at your stomach, “simultaneously” as he has wound against your Messer, go high and thrust the long point at his face, as it is depicted below. |
[125r] Item hye sagtt der meyster Eyn pruch wyder das stuck das er dich Im winden an den pauch sticht vnd will du das prechen so thu Im also So er dir nach dem leyb will faren vnd winden will gegen deynem messer vnd dich stechen In den pauch Indes so er winden ist gegen deynem messer so far auff vnd stich Im den langen ortt zu seym gesicht wye vnden gemalt stett etc |
||||||||||
[355] |
Then, another breaking against the twitching in the hanging point. If you have noticed that he twitchs his Messer to himself and wants to twitch through, “simultaneously,” as he goes high with the hilt and also the arm, go with the hanging point to his face and do not let him come from your Messer or twitch through. |
[83r.3] Item eyn ander bruch wider dz zuecken Im hangenden [83v.1] ort so mercken bist dz er sin messer an sich zuck vnd wil dir durch zucken Indes so er vff fert mit dem gehultz vnd auch arm Indes far im mit hangenden ort zu sinem gesicht vnd loß in nicht ab kümen von dem messer noch durch zucken ~ |
[62v.1] Item eyn pruch wyder daß czucken ym hangatten ortt so dw mercken pist daß er seyn messer an sich rucket und wil dir durchczucken yndeß so er auff fertt mit dem gehulcz und armen yndeß far ym gerichtz mit hangattem ortt zw seym gesichtt und laß yn nicht ab kummen von dem messer noch duchczucken etc |
[125v] Item Eyn ander pruch wyder das zucken In dem hangenden ortt so du mercken pist das er seyn messer an sich zuckt vnd will dir durch zucken Indes so er auff fertt mit dem gehultz vnd auch arme Indes far Im mit hangendem ortt zu seynem gesicht vnd loß In nicht ab kummen von deynem messer noch durchzucken etc |
||||||||
[356] |
Then, a breaking against the Messer-taking in the hanging point. If he takes over you on your right side and grabs with his left hand on the outside to your right hand in the hilt, and wants to take your Messer, “simultaneously,” as he presses downwards, fall with your left hand from below on the hilt and with your right hand go above on the hilt again, and pull with both hands firmly downwards, in that way you take the Messer from him again and strike through his head. |
[83v.2] ein ander bruch Item eyn ander bruch wider messer nemen im hangenden ort benÿmpt er dich vff diner rechten siten vnd grifft mit siner lincken hant vßwendig vff din rechten hant Indas gehultz vnd wil dir dz messer nemen Indes so er vnter sich druck So fal mit diner lincken hant vnten an dz gehultz vnd riß mit peiden henden starck vntersich so nÿmptu im dz messer wider vnd haust im durch den kopff ~ |
[62v.2] Item eyn pruch wyder daß messer nemen ym hangattem ortt benymbt er dich auff deyn rechte seytten und greufft mit seyner lincken handt außbendigß auff deyn rechte yn daß gehulcz und will dir daß messer nemen yndeß so er untersich druckt so fal mit deyner lincken hand unten an daß gehultz und mit deyner rechten far wyder oben an daß gehulcz und reyß mit peden henden starck untersich so nymbstu ym daß messer wyder und hauest yn dar zw durch den kopff etc |
[126r.1] Item Eyn pruch wyder das messer nemen Im hangenden ortt pnymt er dich auff deyner rechten seytten vnd greyfft mit seyner lincken handt außbendigs auff deyn rechte handt In das gehultz vnd will dir das messer nemen Indes so far vntersi er vntersich druckt so fall mit deyner lincken handt vntten an das gehultz vnd mit deyner rechten far wyder oben an das gehultz vnd reyß mit payden henden starck vntersich so nymbstu Im das messer wyder vnd hawest In durch den kopff etc |
||||||||
[357] |
Then, break also the other Messer-taking with this breaking announced before, which is called “freely unbridled.” |
[83v.3] Item eyn ander messer nemen prich ouch mit dissem egemelten bruch de do heißt frÿ deß gezalbnidtt ~ |
[62v.3] Item daß ander messer nemen prich auch mit dysem ee gemelten pruch und daß heyst frey außgeczawmptt |
|||||||||
[358] |
Go through the peaks Here the master speaks how one should go through with the Messer, and going through is very good in the Messer and in the sword. Whether you stand close or far, you can use it with the point, strokes or cuts. |
[83v.4] Durch ge die zÿnnen Hie saget der meinster wie man mit dem messer durch gen sol vnd dz durch gen ist sere gut im messer vnd im schwert du stost nohent oder fer so magstu die durch gen pruchen mit haulben oder mit dem ort oder mit schnitten ~ ~ |
[63r.1] Durch gee dy czynnen Hye sagtt der meyster wye man mit dem messer durchgenen sölt und daß durchgen ist gar sere gutt ym messer und auch ym swertt dw stest nohend oder fer So magstu daß durchgen prauchen mit dem haw oder mit dem ortt etc |
[126v.1] Durchge dy zynnen Hye sagtt der meyster wye man mit dem messer durchgen sollt vnd das durchgen ist sere gutt Im messer vnd Im svertt Du stest nohendt oder fern so magstu der prauchen mit ortt hewen oder schnytten |
[100r.21] Durch gen die etc |
[175r.4] Das durchgen [175v.1] Durchgeen die Zinnen |
||||||
[359] |
Then, if you come together in the Zufechten and you want to do the going through, do it this way: strike an upper stroke from your right shoulder directly to his left side, and “simultaneously”, before you hit with the stroke, wind the blunt edge against his Messer and lower the point. Then, go between him and you to his right side, and strike to his head. |
[84r.2] Item wan Ir im zuvechten ze samen kümpt wiltu dan die durch gen machen so thun Im also haulb von diner rechten achsell geradt In vff sin lincke siten Indes e du triffest mit dem haulb so wind die stümpfen schnid gegen sinem messer vnd senck den ortt nider vnd ge zwuschen im vnd ir dir vff sin rechten siten vnd schlag im zu dem kopff |
[63r.2] Item wenn Ir ym zwvechten zwsammen kumbtt wiltu den dy durchgen machen so thue ym alzo haw von deyner rechten achselen gerad eyn oberhaw zw ym eyn auff seyn lincke seytten yndeß ee dw triffest mit dem haw so wynd dy stumpff schneyd gegen seynem [63v.1] messer und senck den ortt nyder und gee czwischen yn und dir auff seyn rechte seytten und schlag yn zw dem kopff |
[126v.2] Item wenn Ir Im zuuechten zusammen kumptt wiltu denn dy durchgen machen So thu Im also haw von deyner rechten achsel gerad Eyn oberhaw zu Im Eyn auff seyn lincke seytten Indes Ee dw Triffest mit dem haw So windt dy stumpff schneyd gegen seynem messer vnd senck den ortt nyder vnd gee zwischen Im vnd dir auff seyn rechte seytten vnd schlag Im zu dem kopff etc |
[100r.22] Die mach also das durch gen In zuüechten zů samen kumpt wiltu dan die durch gen machen So thůn also haw von deyner rechten achselln gerad Im auf sein lincke seyten Indes du dreffest mit dem hew So wind die stumpf schnid gegen seinem messer vnd senck den ortt nider dir zwischen Im vnd dir auf sein rechten seytten vnd schlach Im zu dem kopf |
[175v.2] Item haw Im den oberhaw Von deinner rechten Achsel zu seinner linnckhen seitten Indes aber Ehe du antrifst. so winnd die schneid gegen seinnem Duseggen. sennckh den ort nider / vnd gee zwischen Im vnnd dir auf sein rechte seitten. Indes schlag Im zu dem kopff |
||||||
[360] |
Then, if he comes to you in the Zufechten, strike an upper stroke firmly to his left side to the head. “Simultaneously” wind the blunt edge against his Messer and let the point go down and go between you and him to his right side, and thrust him from above at his face, and turn your Messer so that the blunt edge is below. |
[84r.3] Jtem kümpstu ze Im In dem zevechten so haulb aber In ober haulb starck vff syn [84v.1] lincken siten ze dem kopff Indes wind gegen sinem messer die stümpfen schniden vnd loß den ort mider sincken vnd far zwuschen dir vnd im vff sin rechte siten vnd stich im oben In ze dem gesicht vnd wind din messer daß die stümpff schnid vnten ste ~ |
[63v.2] Item kumbstu zw ym ynnn zwvechten so haw aber eyn oberhaw starck auff seyn lincke seytten und zw dem kopff yndeß wynd gegen seynem messer dy stumpff schneyden und laß den ortt nyder sincken und far czwischen dir und ym auff seyn rechte seytten und stich ym oben eyn zw dem gesichtt und wendt daß messer daß dy stumpff schneyd unten stee etc |
[127r.1] Item kumbt er zu dir Im zuuechten So haw aber eyn oberhaw starck auff seyn lincke seytten zu dem kopff Indes windt gegen seynem messer dy stumpff schneyden vnd loß den ortt nyder sincken vnd far zwischen dir vnd Im auff seyn rechte seytten vnd stich Im oben Eyn zu dem gesicht vnd wendt deyn messer das dy stumpff schneyd vntten stee etc |
||||||||
[361] |
Then, if you have also thrusted to his right side in the going through, you can also “simultaneously” twitch through and thrust againt to his left side. |
[84v.2] Item so du also vff die recht siten geschlagen hast Indem durch gen also magstu ouch Indes durch zucken vnd widerümb stechen vff sin lincke siten ~ |
[63v.3] Item so dw alzo auff dy rechten seytten gestochen hast ym durchgen alzo magstu auch yndeß durchczucken und wyder umb stechen auff seyn lincke seytten |
[127r.2] Item So du also auff deyn rechten seytten gestochen hast In dem durchgen also magstu auch Indes durchzucken vnd wydervmb stechen auff seyn lincke seytten etc |
||||||||
[362] |
Then, you may also try if you may thrust at him through both cheeks, and do it this way: if you come to the man in the Zufechten as before, “simultaneously” strike firmly an upper stroke at him as before. “Simultaneously” go through with the Messer to his right side and thrust at his face. “Simultaneously” twitch your Messer again towards yourself and thrust at his left side at the face. |
[84v.3] versuch In Item du magst die auch versuchen ob du Im magst durch peiden wãgen stechen vnd thün dem also so du zu dem man kümpst in dem ze vechten als vor Indes haulb starck In eynen ober haulb vff in als vor Indes ge durch mit dem messer vff sin rechte siten vnd stich im ze dem gesicht Indes zuck dz messer wider an dich vnd stich Im ze dem gesichtt siner lincken siten ~ |
[63v.4] und versuech dich ob dw yn durch payde wang mugst stechen und thue dem alzo so dw zw dem man kumbst yn dem zw vechten alz vor yndeß haw starck eyn oberhaw auff yn alz vor yndeß gee [64r.1] durch mit dem messer auff seyn rechte seytten und stich ym zw dem gesichtt yndeß czuck daß messer an dich und stich ym zw dem gesichtt seyner lincken seytten |
[127v] Item du magstu dich auch versuchen ob du Im mugst durch payde wang stechen vnd thu dem also So du zu dem man kumbst In dem zuuechten als vor Indes haw Im starck eyn Eynen oberhaw auff In als vor Indes gee durch mit dem messer auff seyn rechte seytten vnd stich Im zu dem gesicht Indes zuck das messer wider an dich vnd stich Im zu seyner lincken seytten zu dem gesicht: |
||||||||
[363] |
Then, strike an upper stroke to his left side as before and go through and thrust at his right side at the face. “Simultaneously” go high with the Messer and go above your head, so that the thumb is below on the flat. And as you come above the middle of your head, so that the point is backwards above the head, and the hilt is against the man, “simultaneously” strike from above again to his right side at the head. Or, cut firmly at his arm, or work with the doubling, or “simultaneously” strike at the lower peaks. |
[84v.4] alliud Item haulb eyn ober haulb vff sin lincke siten als vor vnd ge aber durch vnd stich im vff [85r.1] sin rechten siten ze dem gesicht Indes far vff mit dem messer vnd far vff vber sin haupt dz der thüm vnten vff die flech sÿ vnd wan du vber die mit des hauptes kümpst dz die spitz hinten vber din kopff hien vff ste vnd dz gehultz gegem dem man Indes haulb oben nider in vff sin rechten siten ze dem kopff oder schnit im starck vber sin arm oder arbeit mit dem dupliren oder Indes haulb ze den vnderen zÿnnen ~ |
[64r.2] Item haw eyn oberhaw auff seyn lincke seytten alz vor und gee aber durch und stich ym auff seyn rechte seytten zw dem gesicht yndeß far auff mit dem messer und far uber deyn haubt daß der dawm unten auff der flech sey und wenn dw uncz uber dy mit deß haubtz kumbst daß dy spicz hynten uber den kopff hyn auß stee und daß gehulcz gegen dem man yndeß haw oben wyder eyn auff seyn rechte seytten zw dem kopff oder schneyd ym starck uber seyn armen oder erbat mit dem dupliren oder yndeß haw zw den unteren czynnen etc Sequitur textus |
[128r] Item haw Eyn oberhaw auff seyn lincke seytten als vor vnd gee aber durch vnd stich Im auff seyn rechte seytte zu dem gesicht Indes far auff mit dem messer vnd far vber deyn haubt das der dawmen vntten auff der flech sey vnd wenn dw vber dy mitt deynes haubtz kumst das dy spitz hintten vber den kopff hyn auß stee vnd das gehultz gegen dem man Indes haw oben wyder eyn auff seyn rechte seytten zu dem kopff oder schneyd Im starck vber seyn arme oder erbeytt mit dem dupliren oder Indes haw zu den vntren zynnen etc |
||||||||
[364] |
Bowing in a twofold manner Here the master speaks about a main element, that is about bowing and its peculiarities. It is to be noticed and to be known here that many good elements and Messer takings come from the bowing, and many elements are delivered from it. |
[85r.2] Bogen zwifach Hie saget der meinster aber von eynem haupt stuck als von dem bogen vnd von siner eÿgenschafft dz ist Nu ze mercken oder ze wissen [85v.1] daß vß dem bogen vil gutter stuck vnd vil messer nemen kümen vnd vil stuck habem er dar bringen vß dem bogen ~ |
[64r.3] pOgen czwiüach Hye sagt der meyster aber von eynem haubtstuck alz von dem pogen und von seyner eygenschafft daß ist nw zw wyssen daß auß dem pogen vill gutter stuck und vill messer nemen kummen und will stuck haben Ir dar pringen auß dem pogen |
[128v.1] Pogen zwiuach Hye sagtt der meyster aber als von eynem haubtstuck als von dem pogen vnd von seyner eygenschafft das ist nun zu mercken vnd zu wissen das auß dem pogen vill gutter stuck vnd messer nemen kummen vnd vill stuck haben Ir dar pringen auß dem pogen |
[100r.23] Item vier bogen sindt zu schieben also hernach etc |
[175v.3] Bogen [176r.1] Bogenn Zwifach |
||||||
[365] |
Then, do the bowing this way: hold your Messer on your left side above the knee, so that the point is against the man, and if he binds on you from his right side to your left side, bow with your Messer towards your body to your left side, so that the point is a bit lowered, the thumb is below, and the blunt edge stands against you. “Simultaneously,” as your Messer sparks on his one, step to his left side well out of the stroke with a twofold step, and strike through his head to his left side. Amen. |
[85v.2] Item den bogen mach also halt din messer vff diner lincken siten aber haulb des krümbs dz der in ort gegen dem man ste so er dan vff dich pintt von siner rechten siten vff din lincke siten so pewg din meser fur din lip vff din lincke siten dz der ort eyn wenig gesinck sÿ vnd der thümen vnten ste Indes so sin messer vff dz din glitz so schrit vff sin lincken siten wol vß dem haulb mit eynem zwiffachen dritt vnd haulb im durch sin haupt siner lincken siten ~ |
[64v.2] Item den pogen mach alzo halt deyn messer auff deyner lincken seytten oberhalb deß knyeß daß der ortt gegen dem man stee so er dann auff dich pyndett von seyner rechten seytten auff deyn lincke so peug mit dem messer fuer deyn leyb auff deyn lincke seytten daß der ortt eyn wenig gesenckt sey und der dawm unten stee und dy stumpff schneyd stee gegen dir yndeß so de seyn messer auff daß deyn kliczet so schreytt auff seyn lincke seytten wol auß dem haw mit eynem czwiuachen trit und haw ym durch seyn haubtt seyner lincken seytten amen |
[128v.2] Item den pogen mach also hallt deyn messer auf deyner lincken seytten oberthalb des knys das der ortt gegen dem man stee So er denne auff dich pindt von seyner rechten seytten auff deyn lincke seytten so peug mit deynem messer fur deynem leyb auff deyn lincke seytten das der ortt eyn wenig gesenckt sey vnd der dawmen vntten stee vnd dy stumpff schneyd gegen dir stee // [129r.1] // Indes so seyn messer auff das seyn klitzt so schreytt auff seyn lincke seytten wol auß dem haw mit eynem zwiuachen tritt vnd haw Im durch seyn hawptt seyner lincken seytten |
[176r.2] Item heb dein duseggen Ann deinner lincken seitten. oberhalb des knie. das der Ort gegen Mann stee. so Er dann. vonn seinner rechten. seitten. auf dich an dein linncke pindet so bieg mit deinnem Duseggen fur deinnen leib an die linnckh seitten. das ort ainwenig gesenckt. der dawm vnnden. die kurtz schneid gegen dir. Indes so sein duseggen auf den deinnen glitzt. so schreit zu seinner lincken seitten. wol ausz dem haw. mit aim zwifachen trit. vnnd haw Im durch seinnen lincken hand. |
|||||||
[366] |
Then, perform the other bowing this way: stand with the Messer on your right side as before, and if he strikes to you to your left side to the opening, bow with the Messer below his Messer to your right side, so that the point goes to your right side, and the hilt is against your left one, and the thumb is below, and the long edge is against you. Then, step out of the stroke to his right side with a twofold step well around him, and strike to his head to his right side. |
[85v.3] Bogen Item den andern bogen trib also leg dich mit dim messer vff din rechte siten als vor vnd wan er vff dich hautt vff din lincke siten noch der ploß so peug mit dem messer vff vnter sin messer vff din rechten siten vnd dz der ort ge vff din rechte siten vnd dz daß gehultz ste gegen diner lincken siten vnd der [86r.1] thüm vnten vnd dz die lang schnid gegen dir ste vnd schrit vß dem haulb vff din rechte siten eyen zwiffachen drit woll vmb In vnd haulb im zue dem kopff siner rechten siten |
[65r.1] Item den anderen pogen treyb alzo leg dich mit dem messer auff deyn lincke seytten alz vor und wenn er auff dich hawtt auff deyn lincke seytten nach der plöß So peug mit deym messer auff unter seyn messer auff deyn rechte seytten und daß der ortt gee auff deyn rechte seytten und daß gehultz stee gegen deyner lincken seytten und der dawm unten und daß dy lang schneyd gegen dir stee und schreytt auß dem haw auff seyn rechte seytten eyn czwiuachen trit wol umb yn und haw ym zw dem kopff seyner rechten seytten etc |
[129r.2] Item den andren pogen treyb also leg dich mit dem messer auff deyn rechte seytten als vor vnd wenne er auff dich hawett auff deyn lincke seytten nach der ploß so peug mit dem messer auff vntter seyn messer auff deyn rechte seytten das der ortt gee auff deyn rechte seytten vnd das gehultz stee gegen deyner lincken vnd der dawm vntten vnd das dy lang schneyd gegen dir stee schreytt auß dem haw auff deyn rechte seytten eyn zwiuachen tritt woll vmb In vnd haw Im zu dem kopff seyner rechten seytten etc |
||||||||
[367] |
Then, the third bowing is to be done this way: stand with your Messer to your left side, so that the thumb is above on the Messer, the point of the Messer is on the ground, and the blunt edge is turned against the man. And if he strikes at you, bow your Messer to your right side under his Messer, and have your shield, that is your displacement, well in front of your head. Then, step with your left foot well out of the stroke to his right foot and his right side, and strike “simultaneously” at him through his head on the right side. Amen. |
[86r.2] alliud Item den dritten pogen mach also leg dich mit dinen messer vff din lincke siten dz der thüm oben lig vff dem messer vnd der ort deß messers vff der erden vnd die stümpff schnit sÿe gekertt gegen den man so er dan vff dich hautt so pueg din messer vff din rechten siten vnter sin messer vnd hab din schult dz ist din versatzüng wol for din haupt vnd schrit mit dinen lincken fus wol vß dem haulb vor sinen rechten siten I vnd haulb im Indes durch sin haupt siner rechten siten ~ |
[65r.2] Item den dritten pogen mach alzo leg dich mit dem messer auff deyn lincke seytten daß der dawm oben lig auff dem messer und der ortt deß messerß auff der erden und dy stumpff schneyd sey gekertt gegen dem man So er denn auff dich hawet so peug deyn messer auff deyn rechte seytten unter seyn messer und [65v.1] hab deyn schildt daß ist dy versaczung wol fuer deyn haubt und schreytt mit deynem lincken fuß wol fuer auß dem haw auff seyn rechte seytten und haw ym yndeß dürch seyn haubt seyner rechten seytten AMEN |
[129v] Item[62] Der dritt pogen der ist also zu machen leg dich mit deynem messer auff deyn lincke seytten das der dawm oben lig auff dem messer vnd der ortt des messers auff der erden vnd dy stumpff schneyd sey gekertt gegen dem man vnd so er denne auff dich hawtt so peug deyn messer auff deyn rechte seytten vnter seyn messer vnd hab deyn schillt das ist dy versatzung woll fur deyn haubtt vnd schreytt mit deynem lincken fuß woll auß dem haw fur seynen rechten vnd auff seyn rechte seytten vnd haw Im Indes durch seyn haubt seyner rechten seytten etc |
||||||||
[368] |
Then, the fourth bowing is to be done on the left side, and do it this way: stand with the Messer on your left side, so that the point is on the ground, and the thumb is above on the flat, and expose yourself with your right side. If he strikes at the opening, bow your Messer well to your right side, so that the hilt is on your right side, and the point of the Messer is on your left side. Then, step in a twofold manner with both your feet well around him to his left side, well out of the stroke, and strike at him through his head to his left side. Amen. |
[86r.3] alliud Item der vierd bogen ist zu machen vff der lincken siten vnd thün dem also leg dich mit dem messer vff din lincke siten dz der ort vff der erden sÿg vnd der thüm oben ste vff der flech vnd gib dich ploß mit diner rechten siten [86v.1] schlecht er dir dan ze der ploß so puge din messer mit dem wol vff sin rechte siten dz dz gehultz ste vff diner rechten siten vnd der ort des messers vff diner lincken siten vnd schrit mit dinen beiden füssen wol vmb in vff sin lincke siten wol vß dem haulb vnd haulb im durch sin haupt siner lincken siten |
[65v.2] Item der vyerd pogen ist zw machen auff der lincken seytten und thue dem alzo leg dich mit dem messer auff deyn lincke seytten Daß der ortt auff der erden sey und der dawm oben stee auf der flech und gib dich ploß mit deyner rechten seytten schlicht er dir denn zw der plöß so peug deyn messer mit dem woll auff daß daß gehulcz stee auff deyner rechten seytten und dy spicz deß messerß auff deyner lincken seytten und schreytt czwiuach mit peyden fuessen wol umb yn auff seyn lincke seytte woll auß dem haw und haw ym durch seyn haubt auff seyner lincken seytten amen |
[130r.1] Item der vyerd pogen ist zu machen auf der lincken seytten vnd thu dem also leg dich mit dem messer auf deyn lincke seytten das der ortt auff der erden sey vnd der dawm oben stee auff der flech vnd gib dich ploß mit deyner rechten seytten schlecht er dir denne zu der ploß so peug deyn messer woll auff deyn rechte seytten Das das gehultz stee auff deyner rechten seytten vnd der ortt des messers auff deyner lincken vnd schreytt zwiuach mit deynen payden fussen woll vmb In auff seyn lincke seytten woll auß dem haw vnd haw Im durch seyn hawbtt seyner lincken seytten |
||||||||
[369] |
Thus, you have the bowing in a twofold manner from both sides. |
[86v.2] also hastu den bogen zwiffach von beiden siten etc |
[65v.3] ¶ alzo hastu den pogen czwiüach von peyden seytten etc Sequitur textus |
[130r.2] also hastu den pogen zwiuach von payden seytten etc |
||||||||
[370] |
What comes long from bowing Here the master states a breaking against the direct strokes that are stroke from the bowing, and you should do the breaking this way: if you strike at him and he bows his Messer down, and displaces and “simultaneously” strikes from above downwards with a direct upper stroke, “simultaneously” step always aside out of the stroke, and strike at his head. Or, wind “simultaneously” your Messer against his one, and thrust at his face. Or, if he strikes at you, turn your Messer with the short edge on his Messer, and “simultaneously” turn your hand and Messer against him with the long edge, and strike through his head. |
[86v.3] Was vom pogen lang kümpt Hie saget der meinster eyn bruch wider die geraden haulb die von bogen gehaulbet werden vnd den bruch soltu also machen So du vff in haulbest vnd er hautt sin messer dar vnder vnd versetz vnd Indes schlecht er oben nider mit eynem geraden ober haulb Indes drit albveg besitz vß dem haulb vnd haulb im noch dem kopff oder wind Indes din [87r.1] messer mit der kurtzen schniden vff sin messer Indes wind din hant vnd messer gegen im mit der langen schniden vnd haulb im durch sin haupt ~ |
[66r] Waß vom pogen lanck kuembtt Hye sagtt der meyster eyn pruch wyder dy geraden hew dy vom pogen gehawtt werden und den pruch soltu alzo machen so dw auff yn hawest und er peugt seyn messer dar unter und verseczt und yndeß schecht er von oben nyder mit eynem geraden oberhaw yndeß trit albegen peseÿtt auß dem haw und haw ym nach dem kopff oder wyndt yndeß deyn messer gegen seynem und stich ym zw dem gesichtt oder so er auff dich schlechtt so wenndt deyn messer m mit der kurczen schneyden auff seyn messer yndeß wendt deyn hand und messer gegen ym mit der langen schneyden und haw yn durch seyn kopff etc. Sequitur textus. |
[130v] Waß vom pogen lanck kumbt Hye sagtt der meyster Eyn pruch wyder dy geraden hew dy von dem pogen gehawtt werden vnd den pruch soltu also machen So du auff In hawest vnd er pewgtt seyn messer dar vntter vnd versetzt vnd Indes schlecht er oben nyder mit eynem geraden oberhaw Indes tritt albegen[63] beseytt auß dem oberhaw vnd haw Im nach dem kopff oder windt Indes deyn messer gegen seynem vnd stich Im zu dem gesicht Oder so er auff dich schlecht so wendt deyn messer mit der kutzen schneyden auff seyn messer Indes wendt deyn handt vnd messer gegen Im mit der langen schneyden vnd haw Im durch seyn haubt etc |
[176v] Bruch der geraden hew Ausz dem pogen Was vom bogen langkumpt Item so Er dann den straich Mit dem pogen versetzt. vnnd Indes mit aim oberhaw gerad nider schlecht. so trit alwegen. bey seytz. ausz dem haw. vnnd haw Im zum kopff / oder wind dein Duseggen gegen dem seinnen. vnnd stich Im zum gesicht. |
|||||||
[371] |
[177r.1] Einn gut stuckh Inn Dem pogen. Item so dir ainner ain Bogen scheubt. vonn der rechten seitten. so thsam wöllestu Im aufsitzen. Indes schlag In mit deinner linnckhen hannd Innwendig Inn sein rechten Arm beyseytz. oder auf sein rechten seitten. vnnd schlag In durch den köpff / oder Innwendig durch den arm. |
|||||||||||
[372] |
[177r.2] Mer von dem bogen Ainn guts stuckh. Item hastu den Bogen geschoben wie vor. Indes greiff mit deinner linncken sein rechte hannd. vnnd thu. sam du In durch das Maul wollest hawen vnnd Im haw ker dich hinumb auf. [177v.1] sein rechten seitten. das dein ruckh Gegen Im stee. Indes lasz dein duseggen auf dein lincken Achsel fallen. das die kurtz schneid oben sey. vnnd truckh vornen fast nider. so prichstu Im den arm ab. wildu den Armpruch nit treiben. so wechsel Indes. durch. vnnd treib weitter was du wildt |
|||||||||||
[373] |
With the Messer-taking Here the master states a main element, that is about the Messer-taking. |
[87r.2] Mit dem messer nemen Hie saget der meinster aber eyn haubt stuck als von dem messer nemen Wiltu im sin messer nemen |
[66v.1] Mit dem messer nemen Hye sagt der meyster aber eyn haubstuck alz von den messer nemen |
[131r.1] Mit dem messer nemen Hye sagtt der meyster aber eyn haubtstuck als von dem messer nemen |
[100r.24] mit dem messer nemen etc |
[177v.2] Das duseggen nemen Mit dem duseggen nemen |
||||||
[374] |
And do him this way: go firmly to him with the Entrüsthau to his left side, and in the binding, as the Messers spark together, go with your hilt high and over his Messer to his right side, and go with the crosspiece on the inside to his right elbow, and push with the crosspiece and the Messer firmly from you. With the left hand fall into his binding behing his right hand, and pull with your left hand firmly towards yourself, in that way you take his Messer. |
[87r.3] So thun also ge starck an In mit dem entrusch haulb ze siner lincken siten vnd im anpinden so die messer zu samen glitzen so far mit dinem gehultz vff vber sin messer vff sin rechte siten vnd far mit dem krutz Inlbingdigs In sinen rechten elnbogen vnd stos mit dem krutz vnd messer starck von dir vnd mit der lincken hant fal im an sin pindt hinder sin rechten hant vnd riß mit der lincken hant starck an dich so nÿmbstu im dz messer |
[66v.2] ¶ Nü wil dw eynen seyn messer nemen so thue ym alzo gee starck an yn mit dem entrusthaw zw seyner lincken seytten und ym an pynden so dy messer zwsammen kliczen so far mit dem gehulcz auff und uber seyn messer auff seyner rechten seytten und far mit dem kreucz ynbendigß yn seyn rechten olpogen und stoß mit dem kreucz und messer starck von dir und mit der lincken handt fal ym an seyn pynd hynter seyner rechten hand und reyß mit deyner lincken hand starck [67r.1] an dich so nymbstu ym daß messer etc |
[131r.2] vnd thu Im also Gee starck an In mit dem Entrußthaw zu seyner lincken seytten vnd Im anpinden so dy messer zusammen klitzen so far mit deym gehultz auff vnd vber seyn messer auff seyner rechten seytten vnd far mit den kreutz Inbendigs In seynen rechten olpogen vnd stoß mit dem kreutz vnd messer starck von dir vnd mit der lincken handt fall Im an seyn pindt hinter seyner rechten handt vnd reyß mit deyner lincken handt starck an dich so nymbstu Im das messer etc |
[100r.25] wiltu eim sein messer nemen So thů Im also schlag Im mit gestrackten arm Im mit dem entrist hew zů s. l. s vnd In anpinden So die mesß zu sammen glitzen So var mit deim gehiltz auf vnd uber sein mesß seiner r. s. vnd far mit dem kurtz [!] Inwendig seynes rechten elenpogens vnd stoß mit dem kurtz vnd [100v.1] messer starck von dir vnd mit der lincken hand starck ann dich andich nympstu Im das messer |
[177v.3] Item gee starckh an In mit dem Entrusthaw. zu seiner lincken seitten. vnnd Im anpinden far mit dem gehultz vber sein duseggen. ann [178r.1] seinner rechten. far mit dem Creitz Innwendig Inn Sein rechten Elennpogen. stosz. starckh vnnd mit der linncken hand fall Im an seinnen pvnd vnnd hinder seiner rechten hannd. reisz starckh an dich. so nimbst du Im den duseggen. |
||||||
[375] Then, if he strikes a stroke from above against you, strike also together with him. “Simultaneously” wind your Messer across a bit on his own and grab “simultaneously” with your left arm at both Messers, so that both points are outside behind you and under your left shoulder. “Simultaneously” go with your hilt from below through his right arm and with your hilt outside above his right arm and pull strongly upwards. |
Then, if he strikes an upper stroke against you, strike also together with him. “Simultaneously” wind your Messer with the flat a bit on his own, and grab “simultaneously” with your left arm above both Messers, so that both points are outwards behind you and below your left shoulder. “Simultaneously” go with your hilt downwards through his right arm and wind your hilt over his right hand on the outside, and pull firmly upwards to your right side. |
[87v.2] Item haut er gegen dir eyn ober haulb so haulb auch glich mit Im Indes wind din messer mit der zwurch eyn wendig vff dz sin vnd griff Indes mit dinem lincken arm vber beide messer dz die peide spitzen hinter dich vnd vnter dinem lincken achseln hyenuß sten Indes far mit dem gehultz vnten durch sin rechten arm vnd wind vßwendig din gehultz uber sin rechten hant vnd riß starck vbersich vff din rechten siten ~ ~ |
[67r.3] Item hawt er gegen dir eyn öberhaw so haw auch geleicz mit ym eyn yndeß wynd deyn messer mit der czwirch eyn wenig auff daß seyn und greuff yndeß mit deynem lincken armen uber peyde messer daß dy payd spiczen hyn ter dich und unter deyner lincken uchsen hyn auß steen yndeß far mit deym gehulcz unter durch seyn rechten armen und wynd [67v.1] außbendigß deyn gehulcz uber seyn rechte hand und reyß starck ubersich etc |
[131v] Item hautt er gegen dir eynen oberhaw so haw auch gleych mit Im Eyn Indes windt deyn messer mit der zwirch Eyn wenig auff das seyn vnd greyff Indes mit deynem lincken arme vber peyde messer das dy peyd spitzen hynterdich vnd vntter deyn lincke vchsen hin auß sten Indes far mit deynem gehultz vntten durch seyn rechten arme vnd windt außbendigs deyn gehultz vber seyn rechte handt vnd reyß starck vbersich auff deyn rechte seytten etc |
||||||||
[376] Then, grab his Messer as before and go with the hilt inside above his arm and pull strongly downwards to your right side. |
Then, grab his Messer as before and go with the hilt over his arm on the inside, and pull firmly downwards to your right side. |
[87v.3] Item griff im sin messer als vor vnd far mit dem gehultz Inlbendig oben vber sin arm vnd riß starck vnttersich vff din rechten siten Sequitur textus |
[67v.2] Item begreuff seyn messer alz vor und far mit dem gehulcz ynbendigß oben uber seyn armen und reyß starck untersich auff deyn rechte seytten etc |
[132r] Item pegreyff seyn messer als vor vnd far mit dem gehultz Inbendigs oben vber seyn arme vnd reyß starck vntersich auff deyn rechte seytten etc |
||||||||
[377] |
Then, if you want to take his Messer with the empty hand, that is with your left hand, notice: if he strikes at your left side, bow your Messer under his Messer well to your left side. “Simultaneously” leap well to his right side under his Messer and grab his arm on the inside at the hand, and press with the left arm from inside between his hand and the hilt, firmly to your left side, in that way you take his Messer. |
[87r.4] Item wiltu Im dz messer nemen mit lerer [87v.1] hant So merck hauptt er vff dich gegen diner lincken siten so peug din messer vnter sin messer wol vff din lincke siten Indes spring wol vff sin siten vnter sin messer vnd begriff sin arm Inlbendig bÿ der hant vnd druck mit dem lincken arm Inlbindigs zwiffach zwuschen sin hant vnd gehultz starck vff din lincke siten so nÿmpstu im aber sin messer ~ |
[67r.2] Item wiltu ym daß messer nemen mit lerer hand alz mit deyner lincken hand so merck haut er auff dich gegen deyner lincken seytten So peug unter seyn messer wol auff deyn lincke seytten yndeß spring wol auff auff seyn rechte seytten unter seyn messer und pegreuff seyn armen ynbendigß bey der hand und druck mit deym lincken armen czwischen seyn hand und gehulcz starck auff deyn lincke seytten so nymbstu ym aber seyn messer |
[132v] Item wiltu Im das messer nemen mit lerer handt als mit deyner lincken handt so merck hawtt er auff dich gegen deyner lincken seytten so peug deyn messer vntter seyn messer woll auff deyn lincke seytten Indes spring woll auff seyn rechte seytten vnter seyn messer vnd pegreyff seyn arme Inbendigs bey der hand vnd druck mit dem lincken arme Inbendigs zwischen seyn handt vnd gehultz starck auff deyn lincke seytten so nymbstu Im aber seyn messer etc |
[100v.2] Item Wiltu Im das messer nemen mit lerer hand So merck hewt er auff dich gegen d. l. s. So pew dein mesß vnder sein messer wol auff die lincken seytten Indes spring wol auff seyn seitten vnder sein messer vnd begriff sein arm inwendig beÿ der hand vnd druck mit dem lincken arm Inwendig zwisschen sein hand vnd gehiltz starck auff dein lincken seytten So magstu Im aber sein messer nemen |
|||||||
[378] |
Then, grab with your left hand over both Messers again, and “simultaneously” go with your hilt on his hilt, so that your crosspiece comes behind or in front of his one, and wind with it to his right side, and push with the front part of your arm firmly, also to his right side, with the bent arm, so that the elbow is below. And push with it firmly, and pull “simultaneously” firmly from above downwards to your right side, in that way you take his Messer again. |
[67v.3] Item greuff aber mit deyner lincken hand uber peyde messer yndeß far mit dem gehultz an seyn gehulcz und daß deyn kreucz kumb hynter daß seyn und wynd da mit gegen seyner rechten seytten und scheub mit dem fodren taill deyneß armß starck auch auff seyn rechte seytten mit gepogem armen daß der olpogen unter stee und scheub da mit fast und reyß yndeß oben nyder starck auff deyn rechte seytten etc so nymbstu ym aber daß messer Sequitur textus |
[133r] Item Greyff aber mit deyner lincken handt vber peyde messer Indes far mit deynem he gehultz an seyn gehultz das deyn kreutz kum hintten ader[64] vorne an das seyn vnd windt do mit gegen seyner rechten seytten vnd scheub mit dem vodren tayll deynes armes starck auch auff seyn rechte seytten mit gepogem arme das der olpogen vntten stee vnd scheub da mit fast nyder vnd reyß Indes oben starck nyder auff deyn rechte seytten so nymbstu Im aber das messer etc |
|||||||||
[379] |
If he has hit the joint Here the master states a breaking againt the first Messer-taking and speaks: If he wants to [hit] the joint, etc. You should understand it this way: if he falls with the hilt above your Messer into the joint of your elbow and wants to take your Messer at the binding with his left hand, notice: “simultaneously,” as he goes over with the hilt over your right hand, “simultaneously” go also quickly over his right hand, and go with the crosspiece into the joint of his right elbow. Then, push it from you and grab with your left hand at his hilt under his right hand, and pull firmly towards yourself to your left side. This way you break his element and do yourself what he had wanted to do. |
[88r.1] Ist er das gelenck prellen Hie saget der meinster eyn bruch wider daß erst nemen vnd spricht wil er dz etc Daß soltu also verstan felt er mit synem gehultz vber syn messer in dz gelenck des elnbogens vnd wil dir mit dyner lincken hant dyn messer bÿ dem pindt nemen so merck glich Indes so er vber fertt mit dem gehultz vber din rechte hant Indes far im auch also schnell vber syn rechte hant vnd far mit dem crutz in dz gelenck synes rechten elnbogens vnd schueb den von dir vnd griff mit dyner lincken hãt an syn gehultz vntter syner rechten siten hant vnd rieß starck an dich vff din lincke siten also brichstu im syn stueck vnd machest selber dz daß er willen hat zu machen ~ |
[67v.4] Ist er daß gelenck prellen Hye sagtt der meyster eyn pruch wyder daß erst messer nemen nem und sprichtt wil er daß etc Daß sol dw alzo verstan felt er mit seym gehultz uber deyn messer yn daß gelenck deß ölpogenß und wil dir mit seyner lincken hand deyn messer bey dem pynd nemen so merck gleich yndeß so er uberfert mit dem gehultz uber deyn rechte hand yndeß far ym auch uber seyn rechte hand und far mit dem kreucz yn daß gelenck seyneß rechten ölpogenß und scheub den von dir und greuff mit deyner lincken hand an seyn gehultz und reyß starck an dich auff deyn lincke seytten alzo prigstu seyn stuck und machest selber daß stuck daß er hat wellen machen |
[133v] Ist er das gelenck prellen Hye sagtt der meyster Eyn pruch wyder das erst messer nemen vnd spricht will er das gelenck etc Das soltu also verstan fellt er mit dem gehultz vber deyn messer In das gelenck deynes olpogens vnd will dir mit seyner lincken hand deyn messer pey dem pindt nemen So merck gleych Indes so er vberfertt mit dem gehultz vber deyn rechte handt Indes far Im auch also schnell vber seyn rechte handt vnd far mit dem kreutz In das gelenck seynes rechten olpogens vnd scheub den von dir vnd grewff mit deyner lincken handt an seyn gehultz vnter seyner rechten handt vnd reyß starck an dich auff deyn lincke seytten also prichstu Im seyn stuck vnd machest selber das er willen hett zu machen |
[178r.2] Ein pruch yber des Obgeschriben Ist er das gelennckh prellen Item so Er mit dem gehultz also dein rechte hannd Vberfellt. so far [178r.1] Im auch allso vber mit dem kreitz Inn sein Elenpogen. glenckh. Indes scheub vonn dir. greiff linnckh an sein gehultz vnnder seinner rechten vnnd reysz. starckh an dich. so kumpstu Im vor. |
|||||||
[380] |
Then, a breaking against the Messer-taking with the empty hand. If he has grabbed your right arm with his left hand, and wants to press you to his left side, “simultaneously” come with your left hand to help your right hand, and grab with it your hilt from below, and pull firmly from above down, as you have heard before. |
[88r.2] alliud Iten aber eyn bruch wider dz ander stuck wil er dir dyn messer nemen mit lerer hant vnter [88v.1] dinem rechten arm mit syner lincken hant gefast hat vnd wil trucken in syn lincke syten Indes küm diner rechten hant zu hillff mit dyner lincken vnd begriff do mit dyn gehultz vnten vnd rieß starck von oben nider als du vor gehorett hast ~ |
[68r.2] Item eyn pruch wyder daß ander stuck will er dir deyn messer nemen mit lerer hand und so er deyn rechten armen mit seyner lincken [68v.1] hand gefast hatt und wil dich drucken yn seyn lincke seytten yndeß kum deyner rechten hand zw hilff und pegreuff da mit deyn gehulcz unten und reyß starck von oben nyder alz dw vor gehort hast |
[134r] Item aber eyn pruch wyder das messer nemen mit lerer handt vnd er deynen rechten arme vnd mit seyner lincken handt gefast hatt vnd will dich drucken In seyn lincke seytten Indes kum deyner rechten handt zu hilff mit deyner lincken vnd pegreyff da mit deyn gehultz vntten vnd reyß starck von oben nyder als du vor gehortt hast etc |
||||||||
[381] |
Then, if he has grabbed both Messers with his left arm and goes down through with the hilt on the outside to the joint of your hand, and he wants to pull towards his right side, “simultaneously” grab behind his left hand at the weak of the Messer in front, and pull firmly to your left side. |
[88v.2] alliud ~ Item hat er begriffen beyde messer mit synem lincken arm vnd fertt vnten mit dem gehultz durch vßwendig in dyn gelenck der hant vnd wil reissen vff syn rechte syten Indes griff hintter syn lincke hant vorn bÿ der schwech des messers vnd riß starck vff dyn lincke syten ~ |
[68v.2] Item hat er begriffen pede messer mit seynem lincken armen und fert unten mit dem gehulcz durch außbendigß yn deyn glenck der hand wil reyssen auff seyn rechte seytten yndeß greuff hynter seyn lincke hand foren yn dy swech peyder messer und reyß starck auff deyn lincke seytten etc |
[134v.1] Item hatt er pegriffen peyde messer mit seynem lincken arme vnd fertt vntten mit dem gehultz durch außbendigs In deyn gelenck der handt vnd will reyssen auff seyn rechte seytten Indes greyff hinter seyn lincke handt vorne bey der swech des messers vnd reyß starck auff deyn lincke seytten etc |
||||||||
[382] |
Then, do also this breaking against the fourth Messer-taking. |
[88v.3] alliud ~ Item wider dz vierd messer nemen mach auch dissen bruch etc |
[68v.3] Item wyder daß vyerd messer nemen mach auch dysen ee gemelten pruch etc |
[134v.2] Item wyder das vyerd messer nemen mach auch dysen Eegemelten pruch etc |
||||||||
[383] |
Go under the right to the left Here the master teaches a Messer-taking that is very good and adventurous. If you want to do it, do it this way: stand with your left foot forwards and hold your Messer on your right side at the leg. If he strikes to your left side to the opening, “simultaneously” bow your Messer from your right side to your left side, and leap well to him, and put your left hand firmly on his right one below. “Simultaneously” go with your hilt also over his right hand on the inside, over his joint of the hand, and pull firmly to your right side, in that way you take his Messer again. |
[88v.4] Linck vnter far den rechten Hie saget der meinster eyn messer nemen vnd thun dem also Ste mit dynem lincken fur vnd halt dyn messer vff diner rechten siten beÿ [89r.1] dem peÿnd haut er dir dan zu diner lincken siten der bloß noch indes pulbg von diner rechten siten vff din lincke din messer Vnd spring woll vff in vnd leg din lincke hant fest an syn rechte vnten Indes far mit dem gehultz auch vber syn rechte hant auch Inlbindig vber syn gelenck der hant vnd reiß starck vff din rechte siten so nÿmbstu im dz messer ~ |
[68v.4] Linck unterfar den rechten Hye sagt der merer der kunst aber von [69r.1] eynem messer nemen und thu dem alzo stee mit deynem lincken fuß fuer und halt deyn messer auff deyner rechten seytten bey dem payn haut er dir denn zw deyner lincken seytten der plöß nach yndeß peug von deynem rechten seytten auff deyn lincke deyn messer und spring wol auf yn und leg deyn lincke hand fest an seyn rechte unden yndeß far mit dem gehulcz auch uber seyn rechte hand ynbendigß uber daß gelenck der hand und reyß starck auff deyn rechte seytten so nymbstu ym daß messer etc |
[135r] Linck vnterfar den rechten Hye lertt der meyster Eyn messer nemen das ist sere gutt vnd abentewrisch[65] wiltu das machen So thu Im also Stee mit deynem lincken fuß für vnd hallt deyn messer auff deyner rechten seytten pey dem peyn hawtt er dir denn zu deyner lincken seytten nach der ploß Indes pewg von deyner rechten seytten auff deyn lincke deyn messer vnd spring woll auff In vnd leg deyn lincke handt vest vntten an seyn rechte Indes far mit deynem gehultz auch oben vber seyn rechte handt Inbendigs vber seyn gelenck der handt vnd reyß starck auff deyne rechte seytten So nymbstu Im aber seyn messer etc |
[178r.1] Ein annder duseggen Nemmen.
Linnckh vnnderfar den Rechten Item stee mit dem Linnckhen fuosz vor. vnnd halt. dein duseggen auf deinnen Rechten pain. hawt Er zu deinner lincken plösz. so far mit dem gehultz Innwendig vbers glaich seinner rechten hand. vnnd reiss starckh zur rechten. so nimpstu Im den duseggen. |
|||||||
[384] |
Here the master teaches a breaking against the element announced above, and it is to be done this way: if he has clenched your hand as it is announced above, lower your Messer to your left side on his Messer, and go with your left arm over both Messers, and pull “simultaneously” to your left side, in that way you take his Messer. Or, pull downwards with your Messer, as you have heard before. |
[89r.2] Item eyn ander bruch wider dz gemelt stuck ist also zu machen so er din hant also beschlosen hat als oben statt geschriben so senck dyn messer gegen diner lincken syten vff dz syn vnd far mit dinem lincken arm vber beydt messer vnd rieß Indes vff din lincke syten so nÿmpstu im aber syn messer oder rieß vnttersich mit dem messer als du vor gehoertt hast ~ |
[69r.2] Item der pruch wyder daß stuck daß ee gemelt ist der ist alzo zw machen so er deyn hand alzo peschlossen hatt alz oben geschriben stett so senck deyn messer gegen deyner lincken seytten auff daß seyn und far mit deynem lincken armen uber peyde messer und reyß yndeß auff deyn lincke seytten so nymbstü ym aber daß messer oder reyß untersich mit deym messer alz dw vor gehort hast |
[135v] Wyder nemen solt nicht sawmen Hye lertt der meyster Eyn pruch wider das Eegemelt stuck vnd ist also zu machen So er deyn handt also beschlossen hatt als oben geschriben stett So senck deyn messer gegen deyner lincken seytten auff das seyn vnd far mit deynem lincken arme vber peyde messer vnd reyß Indes auff deyn lincken seytten so nymbstu Im aber das messer oder reyß vntersich mit deynem messer als du vor gehortt hast etc |
||||||||
[385] |
If you go with no defense Here the master teaches an element that is called an emergency element, and it occurs when you have no defence and you are overrun and you cannot flee without harm, stand merrily if you must defend yourself, and nothing else may happen. Turn against him and stand with your left foot forwards and when he strikes at you from above downwards, step with your right foot against his right one, and well away aside. Then, go with the stretched [arm] well outside on his Messer on the flat on the outside, and go on the inside with your right arm above his Messer or arm, and press the arm well to your body, and turn your hand on his Messer. Then, fall with your left hand on his hilt or hand, and pull with your body firmly to your right side, in that way you take his Messer. |
[89r.3] Gestu anbere were Hie lert der meinster eyn stuck dz do heissett eyn nett stock vnd gat zu so du keyn were hast vnd wurst vber lauffen vnd kanst an schaden nicht entpflihen so stant frelich vnd so du dich were must vnd nit anders syn mag so wind dich gegen Im vnd ste mit dynen lincken fus fur so er dan vff dich haulbett von oben mÿder [!] so drett mit dynem rechten fus gegen synem rechten vnd woll besitz vß vnd far mit gestracken arm an syn messer an die flech vßwendig vnd far Inlbendig mit dynem rechten arm vber syn messer vnd druck den arm woll zu dem leb vnd wend dyn messer an syn hant vnd fal mit dyner lincken hant an syn gehultz oder hant vnd rieß mit dem lieb starck vff dyn rechten syten so nympstu im daß messer etc ~ |
[69v] Bestu on were Hye lertt der meyster eyn stuck daß do geheyssen ist eyn not stuck und get zw so dw kayn wer hast und wirt uberloffen und kanst on schaden nicht enpflyhen So stand frolich so dw dich ye weren muest und nicht anders seyn kan So thue ym alzo wendt dich gegen ym und stee mit deynem lincken fuß fuer So er dan auff dich hauett von oben nyder So trit mit deynem rechten fuß gegen seynem rechten und wol peseytt auß und far mit gestracktem armen an seyn messer an dy flech außbendig und far yndeß mit deynem rechten armen wol zw dem leyb und wendt deyn hand an seyn [70r.1] messer und fal mit deyner lincken hand an seyn gehulcz oder hand und reyß mit dem leyb und hand starck auff deyner lincken rechten seytten so nymbstu ym daß messer |
[136r] Gestu an were Hye lertt der meyster Eyn stuck das do heysset Eyn notstuck vnd gett zu so du keyn were hast vnd wirst vberloffen vnd kanst an schaden nicht entflyhen so standt frolich so du dich weren müst vnd nicht anders geseyn mag so wendt dich gegen Im vnd stee mit deynem lincken fuß fur vnd so er danne auff dich hawett von oben nyder so tritt mit deynem rechten fuß gegen seynen rechten vnd woll beseytt auß vnd far mit gestackem woll aussen an seyn messer an dy flech außbendig vnd far Inbendigs mit deynem rechten arme vber seyn messer oder arme vnd druck den arme woll zu deym leyb vnd wendt deyn handt an seyn messer vnd fall mit deyner lincken hand an seyn gehultz oder hant vnd reyß mit deynem leyb starck auff deyn rechte seytten so nymbstu Im das messer etc |
||||||||
[386] |
Then, if he strikes at you as before, stand with your right foot forwards and step with your left one to his left one, well out of the stroke, and go with your left [hand] above his Messer, and step with your right foot against his right one. Then, go with your right hand on his hilt at the hand under his Messer, and come with your left hand under his Messer to your right side, and swing firmly to your left side. |
[90r.1] Item haulbet eyner vff dich als vor so ste mit dynem rechten fus fur vnd schrit mit dynem lincken fur vff syn lincken woll vß dem haulb vnd far mit dynem lincken vber syn messer vnd schrit mit dynem rechten fus gegen synem rechten vnd far mit dyner rechten hant vff syn gehultz bÿ der hant vnd küm mit dyner lincken hant vnter syn messer vff dyn rechte vnd schving dich starck vff dyn lincke syten ~ ~ |
[70r.2] Item haut eyner auff dich alz vor So stee mit deynem rechten fuß fuer und schreyt mit deynem lincken auff seyn lincke wol auß dem haw und far mit deynem lincken armen uber seyn messer und schreyt mit deynem rechten fuß gegen Seynem rechten und far mit deyner rechten hand auff seyn gehulcz bey der hand und kumbt mit deyner lincken hand unter seynem messer auff deyn rechte hand und swyng dich starck auff deyn lincke seytten |
[136v] Item hautt er auff dich als vor So stee mit deynem rechten fuß für vnd schreytt mit deynem lincken auff seyn lincken woll auß dem haw vnd far mit deynem lincken vber seyn messer vnd schreytt mit deynem rechten füß gegen seynen rechten vnd far mit deyner rechten handt auff seyn gehultz bey der handt vnter seyn messer auff deyn rechte[66] vnd kum mit deyner lincken handt vnter seyn messer auff deyner rechten seytten vnd swing dich starck auff deyn lincke seytten etc |
||||||||
[387] |
Then, if he strikes at you as before, step to his right side with your left foot and fall over his Messer with the left arm. Then, fall with your right hand to his hilt, and pull firmly to your right side. |
[70r.3] Item hawt er auff dich alz vor so schreyt aber auff seyn rechte seytten mit dem lincken fuß und fall aber uber seyn messer mit dem lincken armen und fal mit deyner rechten hand auff seyn gehultz und reyß starck auff deyn rechte seytten etc |
[137r] Item haütt er auff dich als vor so schreytt aber auff seyn rechte seytten so si mit deynem lincken fuß vnd fall aber vber seyn messer mit dem lincken arme vnd fall mit deyner rechten handt auff seyn gehultz vnd reyb starck auff deyn rechte seytten etc |
|||||||||
[388] |
Then, if he strikes at you as before, stand with your left foot forwards and step with your right foot to his right one well out of the stroke, and go over his Messer with your right arm, and with yout left hand on his hilt, and pull firmly to your left side. |
[90r.2] Item Haut er aber vff dich als vor so ste mit dynem lincken fus vor vnd schrit mit dynem rechten fus vff syn rechten woll vß dem haulb vnd far vber dyn messer mit dynem rechten arm vnd mit dyner lincken hant oder vff syn gehultz vnd rieß starck vff dyn lincke syten ~ |
[70r.4] Item hawtt er aber auff dich alz vor So stee [70v.1] mit deynem lincken fuß fuer und schreytt mit deynem rechten fuß auff seyn rechten wol auß dem haw und far uber de seyn messer mit deynem rechten armen und mit der lincken hand uber oder auff seyn gehulcz und reyß starck auff deyn lincke seytten etc Sequitur textus |
[137v] Item hautt er aber auff dich als vor so stee mit deynem lincken fuß fur vnd schreytt mit deynem rechten fuß auf seyn rechten wol ausß dem haw vnd far vber seyn messer mit deynem rechten arme vnd mit deyner lincken handt auff seyn gehultz vnd reyß starck auff deyne lincke seytten |
||||||||
[389] |
If he is brave Here the master states a breaking against the Messer-taking announced above: if you have stroke to one who has no Messer and he displaces with the arm, as it is stated above, and he goes above your Messer, “simultaneously” wind your Messer around, so that the short edge is below, and go high with your hilt, and set the point to his chest. |
[90r.3] Ob er frische ist Hie saget der meinster eyn bruch wider die obgemelt stueck oder messer nemen so du off eynen gehaulben hast der keyn messer hat vnd er versetz dir mit dem arm als oben stat vnd er fertt dir uber dyn messer Indes wind dyn messer vmb dz die kurtz schnid vnten ste vnd far vff mit dynem gehultz vnd setz Im dyn ortt vff die bruest etc~ |
[70v.2] Ob er alz frisch ist Hye sagtt der meyster eyn pruch wyder dy obgemelten messer nemen So dw auff eynen gehawen hast der keyn messer hatt und er verseczt dir mit dem armen alz oben geschriben stet und er fertt dir uber deyn messer yndeß wyndtt deyn messer umb daß dy kurcz schneyd unten stee [71r.1] und far auff mit deym gehultz und secz ym den ortt auff seyn prust oder yn daß angesichtt etc |
[138r.1] Ob er frisch ist Hye sagtt der meyster Eyn pruch wyder dy obgemelten messer nemen so du auff eynen gehawen hast der keyn messer hatt vnd er versetz dir mit dem arme als oben geschriben stet vnd er fertt dir vber deyn messer Indes windt deyn messer vmb das dy kurtz schneyd vntten stee vnd far auff mit deynem gehultz vnd setz Im den ortt auff seyn prust |
||||||||
[390] |
Then, if he goes above your arm, you find the breaking where the text states: If he wants to show off. There, the breaking is taught. |
[90v.2] Item fertt er aber uber dyn arm den brücht vindestu so der text spricht wil er prangen do wurtt der bruch gelertt |
[138r.2] Item fertt er aber vber deyn arme den pruch vindestu da der text spricht will er praugen da wirtt der pruch gelertt etc |
|||||||||
[391] |
If you want to harass the defence in the armed manner Here the master teaches how one should take the Messer with the armed hand from the other, and speaks: If you want in the armed manner, etc. You should understand it this way: if he strikes at you from his right side to your left one, bow with your Messer and with your left hand go “simultaneously” in the middle of your Messer and catch the stroke between your both hands on the Messer. “Simultaneously” go high with your hilt on the inside and from above downwards over his hand to the joint on the outside, and pull firmly to your right side, in that way you take his Messer. |
[90v.3] Gewoppent wiltu were stossen Hie lertt der meinster wie man eynem dz messer soll nemen mit gewoppenter hantt Daß solt also verstan hautt er vff dich von syner rechten syten vff dyn lincke so pug vff mit dynem messer vnd mit dyner lincken hant far Indes In die mit dyneß messers vnd fache den schlag zwuschen dyn peyd hend vff dz messer Indes far vff mit dynem gehultz Inlbendigs vnd von oben nider vber syn hant Indas gelinck vßwendig vnd rieß starck vff dyn rechte syten so nÿmpstu Im dz messer ~ |
[71r.2] Bebappendt wiltu wer strauffen Hye lert der meyster wye man daß messer zw gewappunder handt eynem soel nemen und spricht gewoppend wiltu etc Daß soltu alzo verstan haüt er auff dich von seyner rechten seytten auff deyn lincke so peug auff mit deynem messer und mit deyner lincken hand far yndeß yn dy mit deyneß messerß und vach den schlag czwischen deyn peyde hende uff daß messer yndeß far mit deynem gehulcz ynbendigß und von oben uber seyn hand yn daß gelenck außbendig und reyß [71v.1] starck auff deyn rechte seytten so nymbstu ym daß messer etc |
[138v] Bewappend wiltu wer strauffen[67] Hye lertt der meyster wye man das messer mit gewappender handt eynem soll nemen vnd spricht gewappend wiltu etc Das soltu also verstan hawtt er auff dich von seyner rechten seytten auff deyn lincke So peug auff mit deynem messer vnd mit deyner lincken handt far Indes In dy mitt deynes messers vnd vach den schlag zwischen deyn peyd hend auff das messer Indes far auff mit deynem gehultz Inbendigs vnd von oben nyder vber seyn handt In das gelenck außbendig vnd reyß starck auff deyn rechte seytten So nymbstu Im das messer etc |
||||||||
[392] Then, you can also strike well to both ears in the armed manner and you can also do the feints in it. And you can change through, twitch through in the armed manner, and you can also do the feint with the armed point. |
[91r.2] alliud Item du magst gewoppent woll zu beÿden oren schlagen vnd machst auch die feller darin machen du magst auch gewoppent durch wechsell durch zuecken den ortt vnd magst auch den feller darin machen mit gewoppemter ortt ~ |
[71v.2] Item dw magst auch wol zw beyden oren geboppend schlagen und magst auch dy feler dar eyn machen und magst geboppend durchbechselen durchzucken den ortt und magst auch den feler ma chen mit gewoppendem ortt etc |
||||||||||
[393] Then, if he goes to you, do as if you wanted to thrust at him in the armed manner from your right side and at his left side. “Simultaneously” strike with the hilt forwards at his left foot and when you want to strike, let the right hand go off the Messer and strike with the left hand, as you know well. |
[91v.1] Item goet er vff dich so dun als du In gewoppent wollest stechen von dyner rechten syten zu syner linck syten Indes schlag In mit dem gehultz vorn an syn lincken fus vnd wan du schlagen willt so loß die recht hant von dem messer vnd schlag mit der lincken hant als du woll weist ~ ~ |
[71v.3] Item get er auff dich so thue alz dw yn wollest gewoppend stechen von deyner rechten seytten und zw seyner lincken seyt ten yndeß schlag yn mit dem gehulcz foren an seyn lincken fuß und wen dw schlagen wilst So laß dy recht handt vom messer und schlag mit der lincken hand alz dw wol wayst etc |
||||||||||
[394] |
Then, you can fall in the armed manner with the point, and do it this way: as you have bound him in the armed manner, and you stay on his right side with the point in front of the face, “simultaneously” do as if you wanted to strike with your hilt to your left side, and as you come with the hilt a bit further towards his left side, go “simultaneously” with the point again to his right side at the face. |
[139r] Item du magst gewappend felen mit dem ortt vnd thu Im also so du Im gewappend an gepunden hast vnd ligest Im auff seyner rechten seytten mit dem ortt vor dem gesicht Indes thu sam du mit deynem gehultz wollest schlagen zu deyner lincken seytten vnd So du kumpst mit dem gehultz Eyner span weytt gegen seyner lincken seytten so far Im Indes mit dem ortt wyder zu seyner rechten seytten zu dem gesicht etc |
||||||||||
[395] |
Then, if you stay on his left side in the armed hand, so that the pommel is against the face of the man, go “simultaneously” high with the pommel or the hilt over the middle of your head, and flick “simultaneously” with the hilt again around to the previous left side, and strike with the hilt at his head, or thrust at his face. |
[139v] Item ligestu auff seyner lincken seytten gewappend also das der knopff dem man gegen dem gesicht stett Indes far aber auff mit dem knopff oder gehultz vntz vber dy mitt deyns haubtz Indes mit dem gehultz schnell wyder vmb zu der forigen lincken seytten schlag In mit dem gehultz zu dem kopff oder stoß Im zu dem gesicht etc |
||||||||||
[396] |
Then, you can also change through with the short point, and do it this way: if you lie as before with the armed hand on his left side, do as if you wanted to go with the point to his right side and thrust to the same side. “Simultaneously” go down with the point and change through to his left side, and thrust at his face to his left side. |
[140r.1] Item du magst auch durchwesclen[68] mit dem kurtzen ortt vnd thu dem also so du ligest wye Er mit gewappender handt auff seyner lincken seytten So thu gleych samb du mit dem ortt wollest gan auff seyn rechte seytten vnd stechen auff dy selbigen seytten Indes far vntersich mit der spitzen vnd wechsel durch auff seyn lincke seytten vnd stich Im zu dem gesicht seyner lincken seytten etc |
||||||||||
[397] Then, if you come with the armed hand on the man, do the running off with the armed hand on both sides, and “simultaneously” fall in the running off or thrust. As while you run off and you have run off from both sides, that is, first with the hilt and then with the blade on his right side, “simultaneously” fall with the hilt to hilt left side over his Messer and on his neck to his right side and turn him at the neck around or throw him over your right leg. |
Then, if you come with the armed hand on the man, do the running off with the armed hand on both sides, and “simultaneously” fall in the thrusts, cuts or strokes. Overrun his Messer, grab him at the neck and do with the armed hand what you want. |
[91v.2] Item so du kümpst mit gewoppenter hant an man so mach die ab lauffen gewoppent zu beyden syten Indes fall in die ablauffen zu beyden syten ab gelauffen bist als zu ersten mit dem gehultz vnd dar noch mit der clingen vff syn rechten syten Indes far mit dem gehultz vff syner lincken syten vber syn messer vnd an syn hals syner rechten syten vnd dreg ym by dem hals herümb oder wurff in vber syn rechtes peyn |
[71v.4] Item So dw kombst mit gewappender hand an man So mach dy ablauffen gewoppendt zw payden seytten yndeß fel yn den ablauffen oder stich und dy weyl dw ablauffest und von peyden seytten abgeloffen pist alz zwm ersten mit dem [72r.1] gehultz und dar darnach mit der klyngen auff seyner rechten seytten yndeß far mit dem gehulcz auff seyner lincken seytten uber seyn messer und an den halz seyner rechten seytten und dree yn bey dem halz alzo her umb und oder wirff yn uber deyn rechteß payn etc |
[140r.2] Item so du kumpst mit gewappender handt an den man so mach dy ablaüffen gewappend zu payden seytten Indes fall In dy stich schnit oder hew vberlauff seyn messer vach In pey dem hals vnd mach also mit gewappnder handt was du willt etc |
||||||||
[398] |
If he wants to harass Here the master states a breaking against the first element, that is against the Messer-taking with the armed hand, and speaks: If he wants to harass, etc. You should understand it this way: if he wants to take your Messer with the armed hand, notice, while he goes over your hand with his hilt, and wants to pull to his right side, “simultaneously” grab with your left hand in the weak of his Messer and turn your hilt with your right hand to his right, between his both hands, and pull “simultaneously” firmly to your left side. |
[91v.3] Wil er strauffen Hie saget der meinster eyn bruch wider dz stuck vnd sprichtt also wiltu dz messer nemen zu gewoppenter hant vnd sprichtt will er strauffen etc Daß soltu also verstan wil er dir dyn messer nemen zu gewoppent hant so merck eben dyn will er mit synem gehultz vber dyn hant fert vnd will ryssen vff sich syn rechte syten Indes griff mit dyner lincken hant in die schwech synes messers vnd wind mit dyner rechten hant dyn gehultz an syn rechte sc zwueschen syn beyde hende vnd rÿsß Indes starck vff dyn lincke syten ~ |
[72r.2] Wil er strauffen Hye sagtt der meyster eyn prüch wyder daß erst stuck alz wyder daß messer nemen zw gewoppender hand und spricht wil er strauffen etc Daß soltu alzo verstan wil er dir deyn messer nemen zw gewoppender hand So merck dy weyl er mit seym gehultz uber deyn hand fertt [72v.1] und wil reyssen auff seyn rechte seytten yndeß greuff mit deyner lincken hand yn dy swech seyneß messerß und wend mit deyner rechten hand deyn gehulcz an seyn rechte czwischen seyn payd hend und reyß yn deß starck auff deyn lincken seytten etc |
[140v] Will er strauffen Hye sagtt der meyster eyn pruch wyder das erst stuck als wyder das messer nemen zu gewappender handt vnd spricht wil er strauffen etc Das solt also verstan will er dir deyn messer nemen zu gewappender handt So merck eben dy weyll er mit seynem gehultz vber deyn handt fertt vnd will reyssen auff seyn rechte seytten Indes Greyff mit deyner lincken handt In dy swech seynes messers vnd wendt mit deyner rechten handt deyn gehultz an seyn rechte zwischen seyn payd hend vnd reyß Indes starck auff deyn lincke seytten etc |
||||||||
[399] |
Then, another breaking. If he goes with the hilt over your arm as before, notice, while he goes over your Messer, fall with your left arm over both Messers and press them into your left side, and swing firmly to the same side. |
[92r.2] Item aber eyn bruch fert er mit dem gehultz vber dyn arm als vor so merck die will er vber dyn messer fertt so fal mit dynem lincken arm vber beyd messer vnd drück die in dyn lincken siten vnd schwing dich starck vff die selbigen syten ~ |
[72v.2] Item aber eyn pruch fert er mit dem gehulcz uber deyn armen gewoppend alz vor so merck dy weyl er uber deyn messer fertt so fal mit deynem lincken armen uber peyde messer und druck dye yn deyn lincke seytten und swyng dich starck auff dy selbige seytten etc |
[141r] Item aber eyn pruch fertt er mit dem gehultz vber deyn arme als vor so merck dy weyll er vber deyn messer fertt so fall mit deynem lincken arme vber payde messer vnd druck dy In deyn lincke seytten vnd swing dich starck auff dy selbigen seytten etc |
||||||||
[400] |
Then, a different breaking: if he has grabbed your Messer as before, “simultaneously” grab with your left hand in his left one, and pull it to your left side. Then, step with your right foot in front of his right one, and strike quickly with your right arm firmly from behind to his left elbow. |
[141v] Item Eyn ander pruch hatt er deyn messer gefast wye vor Indes greyff mit deyner lincken hand In seyn lincke vnd reyß dy auff deyn lincke seytten vnd schreytt mit deynem rechten fuß fur seyn rechten vnd schlag geswindt mit deynem rechten arme hyntten starck an seyn lincken olpogen etc |
||||||||||
[401] |
Then, another breaking: if he falls with the hilt over your arm as before with the armed hand, notice, “simultaneously,” while he wants to go with the hilt above your hand, turn your Messer around on his one, so that the short edge is on his Messer, and strike at his head with the short edge. |
[92v.1] Item aber eyn ander bruch felt er dir mit dÿnen gehultz vber dyn arm als vor mit gewoppent hant so merck Indes die will er uber dyn hãt mit dem gehultz will fallen So wind dz messer vff dz syn vmb dz die kurtz schnid vff synem messer ste |
[72v.3] Item aber eyn ander pruch fellt er dir mit dem gehulcz uber deyn armen alz vor mit gewoppender hand So merck yndeß dy weyl er uber deyn hand mit dem gehülcz wil faren So wenndt deyn messer auff dem seynen umb daß dy kurcz schneyd auff seynem messer stee |
[142r] Item aber eyn pruch fellt er dir mit dem gehultz vber deyn arme als vor mit gewappender handt so merck Indes dy weyll er vber deyn handt mit dem gehultz will faren so wendt deyn messer auff dem seynen vmb das dy kurtz schneyd auff seynem messer stee vnd schlag In zu dem kopff mit der kurtzen schneyden etc |
||||||||
[402] |
Then, as you fall on his head with the short edge as before, “simultaneously” go from his Messer with your point against his left side between you and him with the lowered point to your left side. Then, move the point to his chest and step with your left foot back and strike at his head. |
[92v.2] Indes far von synem messer mit dem ortt gegen syner lincken syten zwuschen dich vnd In mit gesencten ortt vff syn lincken syten vnd schrit mit dynem lincken fus zu ruck vnd haulb im zu synem kopff syner rechten syten ~ ~ |
[72v.4] yndeß So far von seynem messer mit deynem ortt [73r.1] gegen seyner lincken seytten czwischen dich und yn mit gesencktem ortt auff deyn lincke seytten und schreytt mit deynem lincken fueß zw ruck und haw ym czw seynem kopff seyner rechten seytten |
[142v] Item so du Im also auff den kopff felst mit der kurtzen schneyden wye vor Indes far von seynem messer mit deynem ortt gegen seyner lincken seytten zwischen dich vnd In mit gesencktem ortt auff deyn lincke seytten vnd senck Im den ortt auff seyn prust vnd schreytt mit deynem lincken fuß fuß zu ruck vnd haw Im zu dem kopff etc |
||||||||
[403] |
If you are to praise the art Here the master states a counter-breaking against the first breaking on the Messer and speaks: If you are, etc. You should understand it this way: if he has grabbed your Messer at the weak and pulls to his left side, and you feel that you cannot hold your Messer, fall with your left hand behind his left one on the hilt, and with the right one forwards to his right hand, and turn the hilt against him. Then, pull firmly downwards, in that way you take his Messer again and you strike at him through his head. |
[92v.3] Ist dir künst zürünnen Hie saget der meinster eyn bruch wider den bruch vnd spricht isst dir kunst zu runnen daß soltu also verstan hat er dir dyn messer begriffen by der schwech vnd rieß vff syn lincken syten vnd du entpfindest dz [93r.1] dz du dyn messer nit gehalten magst so fal mit dyner lincken hant hinter syn lincke an dz gehultz mit dyner rechten vorn zu syner rechten hant vnd wind dz gehultz gegen Im vnd riß starck vnter sich so nÿmpstu Im wider syn messer vnd haust In durch syn koppff ~~ |
[73r.2] Ist dir der Kunst zw rünnen Hye sagtt der meyster eyn wyder pruch wyder den ersten pruch deß messer nemenß und sprichtt ist dir etc Daß soltu alzo verstan hatt er dir pegriffen deyn messer bey der swech und reyst auff seyn rechte lincke seytten und dw enpfindst daß dw deyn messer nicht erhalten magst So fal mit deyner lincken hand hynter seyn lincke an daß gehülcz und mit deyner rechten [73v.1] foren zw seyner rechten hand und wendt daß gehulcz gegen ym und reyß starck untersich So nymbstu ym wyder seyn messer und hawest yn durch seyn kopff |
[143r] Ist dir kunst zu runnen Hye sagtt der meyster Eyn vider pruch wyder den ersten pruch des messers vnd spricht ist dir etc Das soltu also verstan hatt er dir deyn messer pegriffen bey der swech vnd reyst auff seyn lincke seytten vnd du Empfindest das du deyn messer nicht gehalten magst so fall mit deyner lincken handt hynter seyn lincke an das gehultz mit deyner rechten vorne zu seyner rechten handt vnd wendt das gehultz gegen Im vnd reyß starck vntersich So nymbstu Im wyder seyn messer vnd hawest Im durch seyn kopff etc |
||||||||
[404] |
You can rush to it Here the master teaches an element how one should take the man with the hilt on his right side at the neck, and speaks: You can, etc. You should understand it in this manner: if you have bound him on his left side with the cross stroke, strike around at his right one, and before the stroke is completed, push him over with your hilt to his left side. Then, go on his neck to his right side, and step with your right foot behind his left one, and push him over it. |
[143v] Du magst dich deß remen Hye lertt der meyster Eyn stuck wye man den man mit dem gehultz auff seyner rechten seytten bey dem hals nemen soll vnd spricht magstu etc Das soltu also verstan hastu Im an gepunden auff seyn lincke seytten mitt der zwirch so haw Im vmb zu seyner rechten vnd Ee der haw verpracht wirtt so vberdring In mit deym gehultz auff seyner lincken seytten vnd far Im an seyn hals seyner rechten seytten vnd schreytt mit deynem rechten füß hynter seynen lincken vnd druck In dar vber etc |
||||||||||
[405] |
If it has succeded Here the master states a breaking against the element where one holds one at the neck with the hilt, and this is the first breaking, as the breakings are numerous and various. |
[93r.2] Ist es gelüngen Hie saget der meinster eynen bruch wider dz stuck So man eynen by dem hals hat mit dem klotz vnd ist dz der erst bruch der synt vil vnd mangerleÿ ~ ~ |
[73v.2] Ist eß gelüngen Hye sagtt der meyster eyn pruch wyder daß stuck so man eynen bey dem halz heltt und ist daß der erst pruch wan der pruch sind vil und manigerlay |
|||||||||
[406] |
Then, the first breaking: if one holds you firmly with the armed hand with the hilt at the neck, also take your Messer in the armed hand, and go with the hilt over his left hand on the inside to the outside over the joint, and press firmly downwards with the hilt. Then, raise with the left hand and with the blade of the Messer firmly upwards, and step with the left foot well in front of his right one, and press his left hand with the bind firmly on you to your right side. Then, push him up with your Messer firmly from you and throw him forwards down on the face over your right foot. |
[93r.3] Item der erst bruch So dich eyner mit gewoppenter hant mit dem klotz by dem hals starck hellt So nÿm dyn messer auch zu gewoppenter hant vnd far mit dem klotz [93v.1] vber syn lincke hant vff vßwendig vber daß gelenck vnd druck vast vnderdich mit dem gehultz vnd heb mit der lincken hant vnd mit der klingen deß messers fast vber sich vff schrit mit dem lincken fus wol vor syn rechten vnd druck mit dem bindt syn linck hant fast an dich vff dyn rechte syten vnd schube im oben mit dem messer vast von dir vnd wurff in vor dich nider vff dz antlittz vber dyn rechten fus ~ |
[73v.3] Item der erst pruch ist so dich eyner mit gewoppender hand mit dem kloß bey dem halz starck heltt so nymb deyn messer auch zw geppuender hand und [74r.1] far mit dem kloß uber seyn lincke hand ynbendigß auff aussen uber daß gelenck und druck fast untersich mit dem gehulcz und heb mit der lincken hand und mit der klyngen deß messerß fast ubersich auff und schreyt mit dem lincken fuß woll fuer seyn rechte und druck mit dem pyndt seyn lincke hand fast an dich auff deyn rechte seytten und scheub yn oben mit deynem messer fast von dir und birff yn fuer dich auff daß antlicz uber deynen rechten fuß etc |
[144r.2] Item Der erst pruch so dich Eyner gewappendt mit dem klotz bey dem hals starck hellt so nym deyn messer auch zu gewappender hantt vnd far mit dem klotz vber seyn lincke handt Inbendig auff aussen vber das gelenck vnd druck vast vntersich mit dem gehultz vnd heb mit der lincken handt vnd mit der klingen des messers vast vbersich auff vnd schreytt mit dem lincken fuß woll fur seynen rechten vnd druck mit dem pindt seyn lincke handt vast an dich auff deyn rechte seytten vnd scheub In oben mit deynem messer vast von dir vnd wurff In furdich nyder auff das antlitz vber deynen rechten fuß etc |
||||||||
[407] Then, another breaking. If he holds you at the neck as before, fall in the armed hand also as before and go with the blade from behind at his right arm to the joint of the elbow, so that the bind is down and the blade stands up, and step with your right foot behind his left one and push him over it. |
[93v.2] a alliud
Item eyn ander bruch So er dich bÿ dem hals hat als vor so fal mit gewoppenter hant auch als vor vnd far mit dem lincken hinder In synem rechten arm Indaß gelenck des elnbogen dz daß pindt vnten ste vnd schrit mit dynem rechten fus hinter syn lincken fus vnd schueb in dar vber ~ |
[74r.2] Item eyn ander pruch so er dich pey dem halz hatt alz vor so fal zw gewoppender hand auch alz vor und far mit der klyngen hynter yn seyn rechten armen yn daß glenck deß ölpogenß daß daß pynd unten stee und dy klyng ubersich stee und schreytt mit deynem rechten fueß hynter seynen lincken und scheub yn dar uber etc |
||||||||||
[408] |
Then, another breaking: if he holds you at the neck with the bind as before, drop your Messer and strike your left arm above his right one from above firmly downwards, and grab with your right hand in his joint of the hand. Then, leap with your left foot in front of his right one and press his left hand well into your right side, and swing with the body to your right side, and throw him over your left leg in front of you. |
[93v.3] alliud ~ Item eyn ander bruch helt er dich mit dem hals mit dem pindt als vor so loß dyn messer fallen vnd schlag dyn lincken arm vber syn rechten starck nider vnd griff mit dyner rechten hant in syn gelenck der hant vnd spring mit dynem lincken fus fur dyn rechten [94r.1] vnd druck syn lincken hant woll in dyn rechten syten vnd schwing dich mit dem lieb wol vff dyn rechte syten vnd wurff In vber dyn lincken peind fur dich ~ |
[74r.3] Item aber eyn pruch hat er dich bey dem halz mit dem pynd alz vor So laß deyn [74v.1] messer fallen und schlag deyn lincken armen uber seynen rechten oben starck nyder und greuff mit deyner rechten rechten hand yn seyn glenck der hand und spring mit deynem lincken fuß fuer seynen rechten und druck seyn lincke hand woll yn deyn rechte seytten und swyng dich mit dem leyb wol auff deyn rechte seytten und wirff yn uber deyn linckeß payn fur dich etc |
[144v] Item aber eyn pruch helltt er dich pey dem hals mit dem pindt als vor so loß deyn messer fallen vnd schlag deyn lincken arme vber seyn rechten oben starck nyder vnd greyff mit deyner rechten handt In seyn glenck der handt vnd spring mit deynem lincken fuß fur deyn rechten vnd druck seyn lincke handt woll In deyn rechte seytten vnd swing dich mit dem leyb auff deyn rechte seytten vnd wirff In vber deyn linckes peyn fur dich etc |
||||||||
[409] |
Then, another breaking: if he has you at the neck as before, take your right hand and go with it to the blade of his Messer to between his both hands close to his left one, and pull firmly towards yourself to your right side. “Simultaneously” as the hilt comes free from the neck, grab with your left above his right one to the hilt, and pull downwards to your right side, in that way you take his Messer. |
[94r.2] Item Aber eyn bruch so er dich mit dem hals hat als vor so nym dyn rechte hant vnd far do mit vff synes messers klingen vff zwuschen syn beyde hende nahent zu syner lincken vnd riß starck andich vff syn rechte syten Indes wurtt er dz kloß gewar lidig vor dem hals Indes begriff mit dyner lincken hant vber syn rechte indas gehultz vnd riß hinder dich vff dyn recht syten so nÿmpstu ym dz messer etc ~ |
[74v.2] Item aber eyn pruch so er dich bey dem halz hatt alz vor So nymb deyn rechte hand und far da mit auff seyneß messerß klyngen auff seyn czwischen seyn beyde hendt nohent zw seyner lincken und reyß starck an dich auff deyn rechten seytten yndeß wirtt der kloß ledig von dem halz yndeß begreuff mit deyner lincken hand uber seyn rechte yn daß gehultz und reyß fast untersich auff deyn rechte seytten so nymbstu ym daß messer |
[145/6r.1] Item aber Eyn pruch So er dich bey dem hals hatt als vor so nymb deyn rechte handt vnd far da mit auff seynes messers klingen auff zwischen seyn payd hend nahent zu seyner lincken vnd reyß starck an dich auff seyn rechte seytten Indes wirtt der kloß ledig von dem hals Indes begreyff mit deyner lincken handt vber seyn rechte In das gehultz vnd reyß hintersich auff deyn rechte seytten so nymbstu Im das messer |
||||||||
[410] |
Notice, if you want to do the Messer-taking, you should always fall to the weak of the Messer with your right hand. |
[94r.3] Item ob du dz messer nemen machen willt so soltu allbegen in die schwech dyns messers fallen mit dyner rechten hant ~ |
[74v.3] ¶ merck daß wenn dw dyseß messer nemen machen [75r.1] wiltu so soltu albegen yn dy swech deß messerß fallen mit deyner rechten hand etc |
[145/6r.2] Merck wenne du das messer nemen machen willt so soltu albeg In dy swech des messers fallen mit deyner rechten handt; |
||||||||
[411] |
Then, another breaking: push him from you, but at his right elbow and grab with your right hand on his right leg close to the foot. Then, step with your left foot in front of his left one inside to his legs and throw him on his face, as it is depicted below. |
[145/6v] Item aber eyn pruch scheub In von dir aber pey seynem lincken rechten olpogen vnd greyff mit deyner rechten hand an seyn rechtes peyn nohent bey dem fuß vnd schreyt mit deynem lincken fuß fur seynen lincken Inbendigs seyner peyn vnd wurff In auff seyn antlitz wye vnden gemalt stett etc |
||||||||||
[412] |
Then, another breaking: push him from you with your left hand and take the balance at the elbow, and grab forwards with the right hand in his right one. Then, step with the left foot in front of his right one. |
[94r.4] Item eyn anders schub In von dir mit diner lincken hant vnd nym dz gewiecht by dem elnbogen vnd griff im vorn mit der rechten hant syn rechte vnd schrit mit dynem lincken fus fur synen rechten ~ |
[75r.2] Item eyn ander pruch scheüb yn von dir mit deyner lincken hand und nymb daß gebichtt bey dem olpogen und greuff ym foren mit deyner rechten hand seyn rechte schreyt mit dem lincken fuß fuer seyn rechten |
[147r.1] Item eyn ander pruch scheub In von dir mit deyner lincken handt vnd nymb das gewicht bey dem olpogen vnd greyff Im forne mit der rechten handt seyn rechte vnd schreytt mit dem lincken fuß fur seynen rechten etc |
||||||||
[413] |
Then, another breaking: push him firmly from you with his elbow with your left hand, and push him to his right side. “Simultaneously,” drop your Messer and grab him outside at his joint of his right leg. Then, lift him high and throw him on his left side. |
[94r.5] Item Aber eyn bruch schub In starck von dir mit synem elnbogen mit dyner lincken hant [94v.1] schueb In vff syn rechte sÿten Indes loß dyne messer vallen vnd griff im vßwendig in syn gelenck synen rechten peindt hab in vff vnd wurff in vff syn lincken syten ~ |
[75r.3] Item eyn ander prüch scheüb yn starck von dir bey dem oelpogen mit deyner lincken hand scheub yn auff seyn lincke seytten yndeß laß deyn messer fallen und greuff ym außbendigß yn seyn glenck seyneß rechten peynß heb yn auff und wirff yn auff seyn lincke seytten etc |
[147r.2] Item Eyn ander pruch scheub In starck von dir mit seynem olpogen mit deyner lincken handt scheub In also auff seyn rechte seytten Indes laß deyn messer vallen vnd greyff Im außbendig In seyn gelenck seynes rechten peyns heb In auff vnd wurff In auff seyn lincke seytten etc |
||||||||
[414] |
Then, another breaking: if he has grabbed you as before, push him from you to his left side with your left hand, and go with your right hand or arm around his body in the front. Then, step with your right foot behind his right one and throw him over your right hip on his back or head. Amen. |
[75v.2] Item eyn ander pruch hatt er dich gefast alz vor so scheub yn von dir auff seyn lincke seytten mit deyner lincken hand und far mit der rechten hand oder armen umb seyn leyb foren und schreytt mit deynem rechten fuß hynter seynen rechten und wirff yn uber deyn rechte huff auff seynen ruck oder kopff amen |
[147r.3] Item Eyn ander pruch hatt er dich gefast als vor so scheub In von dir auff seyn lincke seytten mit deyner lincken handt vnd far mit der rechten handt oder arme vmb seyn leyb vorne vnd schreytt mit deynem rechten fuß hinter seyn rechten vnd wurff In vber deyn rechte huff auff seyn ruck oder kopff etc |
|||||||||
[415] Then, another breaking: push him from you at his right elbow and grab with your right hand at his right leg close to the foot, and throw him on his face. And make sure that you bring his foot under your right shoulder while throwing, and hold him at it, so that he cannot stand up. If he wants to get up on one side, throw him on the other, and stand with your body well between both his legs, in that way he cannot stand up. |
Then, push him with his right elbow to his left side again and grab “simultaneously” his right foot with your right hand as before, and pull the same foot well under your right shoulder, and hold him at it, so that he cannot stand up. If he wants to get up on one side, throw him on the other side, and stand with your left leg and the body well between both his legs, so that he cannot hit you with the left leg. And hold him this way and throw him from one side into the other, as you wish. |
[75r.4] Item aber eyn pruch scheub yn von dir aber bey seynem lincken rechtem ölpogen und greuff mit deyner rechten hand an seyn rechteß payn nohendt pey dem fuß und [75v.1] wirff yn auff seyn antlicz und gedenck daß dw ym berffen seynen fuß bringest unter deyn rechte uchsen und halt yn alzo do bey daß er nicht auff kan stan wo er auff eynen seytten sich auff pawmen wil so wirff yn auff dy andren und stee mit deynem leyb wol czwischen seynen peden payn so mag er nichtt auff stan etc |
[147v] Item scheub In aber mit seynen rechten olpogen auff seyn lincke seytten vnd pegreyff Indes seyn rechten füß mit deyner rechten handt wye vor vnd ruck den selbigen fuß woll vnter deyn rechte vchsen vnd halt In also da pey das er nicht auff kan stan wo er auff eyner seytten sich auff wollt richten So wurff In auff dy andren seytten vnd stee mit deynem lincken peyn vnd leyb woll zwischen seyn peyde auff das das er dich mit dem lincken peyn nicht stossen müg vnd haltt In also vnd wurff In von eyner seytten zu der andren wye du willt etc |
|||||||||
[416] |
Then, another breaking: if he holds you at the throat with the armed hand as before, press firmly backwards with the neck. “Simultaneously” grab also with the armed hand in the blade of your Messer under his Messer and suddenly let your right hand go out of the bind, and step behind him to his right side, and strike with the hilt at his stomach. Then, step well behind him and “simultaneously” strike as you have done before. |
[94v.2] Item Aber eyn bruch helt er dich bÿ dem hals gewoppent als vor So druck vast zu ruck mit dem nack Indes griff auch zu gewoppent hant In dines messers klyngen vnter sin messer vnd loß pluffingen die recht hant von dem bynd vnd griff in dyn klingen dines messers vnd schrit hinter In vff syn rechte syten vnd schlag in mit dem gehultz In syn buch vnd schritt woll hinter in Indes mach als du vor gehortt hast Sequitur textus |
[75v.3] Item aber eyn pruch heltt er dich bey dem halz gewoppend alz vor so druck fast zw ruck mit dem nack yndeß greuff auch zw gepappender handt yn deyneß messerß klyngen unter seynem [76r.1] messer und laß pluppling dy recht handt von dem pyndt und greuff yn dy klyngen deyneß messers und schreyt hynter yn auff seyn rechte seytten und schlag yn mit dem gehulcz ynn seyn pauch und schreyt wol hynter yn yndeß mach alz dw vor gehortt hast etc |
[148r] Item aber Eyn pruch hellt er dich pey dem hals gewappent als vor so druck vast zu ruck mit dem nack Indes greyff auch zu gewappender hantt In deynes messers klingen vnter seyn messer vnd loß plupffling[70] dy recht hand von dem pindt vnd schreytt hinter In auff seyn rechte seytten vnd schlag In mit dem gehultz In seyn pauch vnd schreytt woll hinter In Indes schlag In Inn seyn nacken vnd schreytt aber paß hyn vmb als du denne woll weyst etc[71] |
||||||||
[417] |
Then, if he has put the hilt on your neck as before, go high with your Messer and fall in the armed hand, and go high with the hilt and thrust at his face from above, as it is depicted below. |
[148v] Item hatt er dir gelegtt den klotz an deyn hals als vor So far auff mit deynem messer vnd fall zu gewappender hantt vnd far hoch auff mit dem gehultz vnd stich Im zu dem gesich oben wye vntten gemalt stett etc |
||||||||||
[418] |
Then, another breaking: if he has grabbed you at your neck as before with the hilt, “simultaneously” drop your Messer and go with your right hand behind his left one between his hand and the weak of his Messer, and turn “simultaneously” firmly to your left side. Then, pull firmly with your right hand to the same side. |
[149r] Item Eyn ander prüch hatt er dich bey deym hals gefast aber als vor mit dem gehultz Indes laß deyn messer fallen vnd far mit deyner rechten handt hynter seyn lincke zwischen seyn handt vnd dy swech seynes messers vnd wendt dich Indes starck auff deyn lincke seytten vnd reyß starck mit deyner rechten handt auff dy selbigen seytten etc |
||||||||||
[419] |
Then, if he has you at your neck with the hilt again as before, “simultaneously” grab with your left hand in the middle of his Messer, and go high with your right hand and do as if you wanted to push the hilt into his face. “Simultaneously” hit the middle of his Messer firmly with your right hand or arm and swing to your left side. |
[149v] Item hatt er dich bey deynem hals mit dem gehultz aber als vor Indes greyff mit deyner lincken handt In dy mitt seynes messers vnd far auff mit deyner rechten handt vnd thu sam du Im das gehultz In das angesicht wollest stossen Indes stoß In dy mitt seynes messers starck mit deyner handt oder arme vnd swing dich auff deyn lincke seytten etc
|
||||||||||
[420] |
Then, another breaking: if he has grabbed you with his hilt at your neck as before, grab with your left hand in his left close to the hand, and pull it to your left side. Then, “simultaneously” strike with your right arm over his both and quickly down and step with your right foot behind his right one and throw him over it, and swing a bit to your left side. |
[150r] Item aber eyn pruch hatt er dich gefast mit deynem[73] gehultz an deym hals wye vor So greyff mit deyner lincken handt In seyn lincke nohendt zu der handt vnd reyß dy auff deyn lincke seytten vnd schlag Indes deyn rechten arme vber seyn ped arme fluchs v nyder vnd schreyt mit deynem rechten uß hinter seynen rechten vnd wurff In dar vber etc vnd swing dich Eyn wenig auff deyn lincke seytten etc |
||||||||||
[421] |
Then, if he has you at the neck as before and wants to push you over the leg as before, “simultaneously” fall in the armed hand and thrust at him from below between his both hands with the armed hand at his throat. And when you fall in the armed hand, go with your left arm from above over his right one. |
[150v] Item hatt er dich bey dem hals als vor vnd will dich vber das peyn drucken wye vor Indes fall zu gewappender handt vnd stich Im vntten zwischen seynen payden henden mitt gewappender handt auff In seyn kelen vnd wenne du zu gewappender hant felst so far mit deynem lincken arme oben vber seynen rechten etc |
||||||||||
[422] |
Then, if he has grabbed you at the neck as before, “simultaneously” go with your Messer between both of you with the weak to your left side. Then, fall in the armed hand and hit him with the hilt at his throat, as it is depicted below. |
|||||||||||
[423] Out and above thrust through Here the master speaks about the thrusting through from above but he means if the elements succeeds well, it is with some luck. |
Out and above thrust through Here the master speaks about the thrusting through from above and they are to be performed with great prudence and close to the man, so that you do not fail in them. |
[94v.3] Vs vber durch stechen Hie saget der meinster von dem vber durch stechen doch meynt er sollen die stuck woll [95r.1] gerotten so sy gluck do bÿ |
[76r.2] Auß uberdürch stechen Hye sagtt der meyster von den uberdurchstechen doch meynt er follen dy stuck wol geratten so sey gluck do pey |
[151v.1] Auß vber durch stechen Hye sagtt der meyster von dem vberdurch stechen vnd dy selben gehoren zu treyben mit grosser fursichtikaytt vnd nohent bey dem mann |
||||||||
[424] Now, if you want to do the thrusting through from above, do him this way: if you have bound with the Messer on his right side, “simultaneously” wind with your Messer over his one to his right side and lower the point of the Messer down and go with it under his right arm and fall with your left hand in the middle of your Messer, and press on the outside in his right arm to his left side. Thus, you take his Messer. |
Now, do him this way: go to the man with your Entrüsthau to his left side and strike then around to the right side. Then, wind the weak of your Messer above his Messer to his left side and go through below his arm again to his right side, |
[95r.2] Nu wiltu die vber durch stechen machen so thun Im also wan du hast an gebunden mit dem messer vff din rechte syten Indes wind dyn messer vber das syn vff siner rechten siten vnd senck den ortt dines messers nider vnd far do mit vnter sin rechten arm vnd fal mit diner lincken hant in die mit dines messers vnd druck vssen in syn rechten arm vff syn lincke siten ~ |
[76r.3] ¶ nw wiltu dy uberdurch stechen machen So thue ym alzo wenn [76v.1] dw hast an gepunden mit dem messer auff seyn rechte seytten yndeß wyndt mit deynem messer uber daß seyn auff seyner rechten seytten und senck den ortt deß messerß nyder und far da mit unter seyn rechten armen und fal mit deyner lincken hand yn dy mit deyneß messerß und druck aussen yn seyn rechten armen auff seyn lincke seytten So nymbstu ym daß messer |
[151v.2] Das du dar ob nit nyderligest nun thu Im also Gee zu dem mann mit deynem Entrusthaw zu seyner lincken seytten vnd schlag darnach vmb zu der rechten seytten vnd windt dy swech seynes messers vber seyn messer gegen seyner lincken seytten vnd far vnttendurch seyn arme wyder auff seyn rechte seytten |
||||||||
[425] Then, another element: thrust through as before and go with your left hand in the middle of your blade and press with it outside in his arm to the joint of the elbow. Then, turn your left side to his right one, and press with the left hand from above quickly downwards, and with the right one at the bind, and raise his hand up. This way he is clenched. |
and fall with your left hand in the middle of the blade of your Messer, and press with it outside in the joint of his arm and elbow. Then, turn your left side to his right one, and press with the left hand from above quickly downwards, and with the right one at the bind, and raise his hand up. This way he is clenched. |
[95r.3] Item eyn ander stueck stich aber durch als vor vnd küm mit diner lincken hant aber in die mit der klingen vnd druck do mit vßwendig in sin arm indas gelenck des elnbogens vnd wend die linck syten an sin rechte vnd druck mit der lincken hant oben fast nider vnd mit der rechten by dem pyndt vnd heb sin hant vber sich also ist er beschlossen ~ |
[76v.2] Item eyn anderß stuck stich aber durch alz vor und kum mit deyner lincken hand aber yn dy mit deyner klyngen und druck da mit außbendig yn seyn armen yn daß gelenck deß olpogenß und wendt deyn lincke seytten an seyn rechte und druck mit der lincken hand oben fast nyder und mit der rechten bey dem pyndt heb seyn hand ubersich alzo ist er beschlossen |
[151v.3] vnd fall In dy mitten mitt deyner lincken handt In dy klingen deynes messers vnd druck da mit außbendigs In das gelenck seyns armes vnd olpogens vnd wendt deyn lincke seytten an seyn rechte vnd druck mit der lincken handt oben fast nyder vnd mit der rechten pey dem pindt vnd heb seyn handt vbersich also ist er beschlossen etc |
||||||||
[426] |
Then, thrust at him over his right hand again and fall in the armed hand and come close to him, so that his right hand comes under your right shoulder, and fall in the armed hand with your Messer from behind on his right elbow. Then, lean with the chest firmly on it, and turn your left side to his right one, and leap with your left foot in front of his right one, and swing firmly to your right side. |
[152r] Item Stich Im aber vber seyn linck rechte handt vnd fall aber zu gewappender hantt vnd kum Im nohent das seyn rechte handt kum vntter deyn rechte vchsen vnd fall zu gewappender handt mit deynem messer v hintten an seynen rechten olpogen vnd layn dich mit der prust vast dar an vnd ker deyn lincke seytten an seyn rechte vnd spring mit deynem lincken fuß fur seyn rechten vnd swing dich starck auff deyn rechte seytten |
||||||||||
[427] |
Then, an element in thrusting through. Do it as before and “simultaneously” [go] with the hilt to his right shoulder on his neck well around to the nape of his neck, and lift him with the left hand well up, and turn your hand on your Messer, so that you lift stronger. Then, step with your right foot behind his right one and press him over it. |
[95r.5] Item aber eyn ander stuck Im durch stechen thün im also vnd fal Indes mit dem gehultz vff [95v.1] syn rechten achseln an sin hals woll hin vmb sin nack vnd heb in mit der lincken hant wol vber sich vnd verwind din hant vff din messer dz du dester starcker hebst vnd schrit mit dem rechten fus hinter sin rechten fus vnd druck in dar vber ~ |
[77r.3] Item aber eyn ander stuck ym durchstechen thue ym alz vor und far yndeß mit dem gehultz auff seyn rechte achsellen an seyn halz wol hyn umb yn seyn nacken und heb yn mit der lincken hand wol ubersich und verbendt dy hand auff dem messer daß dw dester stercker hebst und schreyt mit dem rechten fuß hynter seynen rechten und druck [77v.1] yn dar uber etc |
[152v] Item aber eyn stuck Im durchstechen Thu Im als vor vnd Indes mit dem gehultz auff seyn rechte achselen an seyn hals woll hyn vmb In seyn nacken vnd heb In mit der lincken handt woll vbersich vnd verbendt deyn handt auff deyn messer das du dester stercker hebst vnd schreytt mit deynem[75] rechten fuß hynter seynen rechten vnd druck In dar vber etc |
||||||||
[428] |
Then, go through him again with the weak over his right arm as before, and go down to your left side with the weak of your Messer, so that his Messer comes under your right shoulder, and hit him with the hilt to his throat or face. |
[153r] Item far aber Im dürch mit der swech vber seynen rechten arme wye vor vnd far vntten auff deyn lincke seytten mit der swech seynes messers alzo das dir seyn messer vntter deyn rechte vchsen kum vnd stoß In mit dem gehultz zu seyner kelen oder angesicht etc |
||||||||||
[429] |
Then, an element: if he is too strong for you so that you cannot clench the arm outside, as the first element says, do it this way as if you wanted to clench him outside, and “simultaneously” go outside above his arm to the shoulder, and step with your right foot behind his right one, and press him over it. |
[76v.3] Item aber eyn stuck Ist er dir zw starck [77r.1] daß dw außbendigß den armen nichtt peschlyssen magst So thue alz dw yn außbendigß wollest beschlyssen yndeß far ynbendigß oben uber seynen armen an dy achsel und schreyt mit deynem rechten fuß hynter seynen rechten und druck yn dar uber etc |
[153v.1] Item aber eyn stuck ist er dir zu starck das dw außbendigs den arme nicht beschlyssen magst als das erst stuck lautt So thu Im also du außbendig In wolst beschlissen Indes far Inbendigs oben vber seyn arme an dy achsel vnd schreytt mit deynem rechten fuß hinter seynen rechten vnd druck In dar vber |
|||||||||
[430] |
Then, a note: if you go to his arm on the inside with your Messer, step always with your right foot well behind his right one, so that his arm comes between you and him. Thus, it goes the right way. |
[95r.4] Item wan du In Inlbendig in sin arm fast mit dem messer So dritt alwegen mit dinem rechten fus wol hinter syn rechten dz sin arm zwuschen dich vnd im kum ~ ~ |
[77r.2] Item Nota wenn dw alzo yn ynbendigß ym yn seyn armen ferst mit dem messer So trit albegen mit deynem rechten fuß wol hynter seynen rechten daß seyn armen czwischen dich und yn kumb so gett eß recht zw etc |
[153v.2] Item nota wenne du Im also Inbendigs In seyn arme ferst mit dem messer so tritt albegen mit deynem rechten fuß woll hinter seynen rechten das seyn arme zwischen dich vnd In kum so gett eß recht zu etc |
||||||||
[431] |
Then, or put him the bind on his neck on his left side, and step with your right foot behind his right one and press the blade of your Messer on his arm firmly to your body, so that the point is out sideways on your left side. |
[95v.2] Item oder leg im dz pindt an sin hals siner lincken siten vnd schrit mit dinem rechten fus hintter sinen rechten vnd druck die klingen dines messers an sin arm fast an din lip dz der ort vff diner lincken siten besitz hinüß ste ~ |
[77v.2] Item oder leg ym daß pyndt an seyn halz an seyner lincken seytten und schreytt mit deynem rechten fuß hynter seynen rechten und druck dy klyngen deyneß messerß und seyn armen fast an deyn leyb daß der ortt auff deyner lincken seytten peseytt hyn auß stee |
[153v.3] Item oder leg Im das pindt an seyn hals seyner lincken seytten vnd schreytt mit deynem rechten füß hinter seynen rechten vnd druck dy klingen deynes messers an seyn arme fast an deyn leyb das der ortt auff deyner lincken seytten peseytt hyn auß stee etc |
||||||||
[432] Who does the thrusting over through, |
Who has thrusted over through Here the master states a breaking against the thrusting over through and speaks: Who thrusts over, etc. Now, if you want to break the thrusting over through in the Messer, do it this way: if he winds over your Messer and wants to go through with the point under your arm, wind “simultaneously” against him to his right side with your Messer on his own, so that the long edge is above, and thrust at his face, in that way he cannot come to the elements announced above. |
[95v.3] Wer vber durch ist stechen Hie saget der meinster eyn bruch wider die vber durch stechen Nu wiltu die vber durch stechen machen So thun Im also wan er dir vber din messer wind vnd wil [96r.1] dir mit dem ortt vnter din arm durch geen Indes wind gegem Im vff sin rechten siten dein messer an dz sin dz die lang schnid oben ste vnd stich im oben zu dem gesicht also kan er zu dem obgemelt stuck nit kümen ~ ~ |
[77v.3] Wer uber durch thuet stechen Hye sagtt der meyster eyn pruch wyder dy ober durch stechen und sprichtt wer uber etc nw wiltu dy durchstechen ym messer prechen So thue ym [78r.1] alzo wenn er dir uber deyn messer byndt und wil dir mit dem ortt unter den armen durchgen yndeß wyndt gegen dir auff seyn rechte seytten deyn messer an daß seyn daß dy kurcz schneyd undten stee und stich ym zw dem gesicht alzo kann er zw der obgemelten stucken nicht kummen |
[154r] Wer vber durchist stechen Hye sagt der meyster Eyn pruch wyder dy du vberdurchstechen vnd spricht wer vber etc Nu wiltu dy vberdurchstechen Im messer prechen so thu Im also wenne er dir vber deyn messer windt vnd will dir mit dem ortt vntter deym arme durchgen Indes windt gegen Im auff seyn rechte seytten deyn messer an das seyn das dy lang schneyd oben sey vnd stich Im zu dem gesicht also kann er zu den obgemelten stucken nicht kummen etc[76] |
||||||||
[433] |
Then, another breaking on the thrusting over through, and notice: while he wants to thrust through under your arm and while he wants to grab down the middle of his Messer, “simultaneously” go high with the hilt and fall in the armed hand, and set the point on his throat. |
[96r.2] Item aber eyn bruch vff dz vber durch stechen vnd merck die will er vntter dim arm vnten durch stechen will vnd d will er nider noch der mit sines messers wil griffen Indes far vff mit dem gehultz vnd fal zue gewoppenter hant vnd setz im den ortt an sin kellen dz soltu also schnell machen ~ ~ |
[78r.2] Item aber eyn pruch auff daß uber durchstechen merck dy weyl er unter deyn armen durch will stechen und dy weil er nach der mitt seyneß messerß wil greuffen yndeß far auff mit dem gehultz und fal zw gewappender hand und secz ym den ortt an seyn kelen |
[154v] Item aber Eyn pruch auff das vberdurchstechen vnd merck dy weyll er vntter deyn arme durchstechen will vnd dy weyll er nyder nach der mit seynes messers will greuffen Indes far auff mit dem gehultz vnd fall zu gewappender hant vnd setz Im den ortt an dy kelen etc |
||||||||
[434] |
Then, put your Messer on the neck on his left side with the armed hand, the weak of the Messer, and press the elbow well under his neck, and do as you have been taught before. This way, you have another breaking against the thrusting through. |
[96r.3] Item oder leg im din messer an sin hals vff siner lincken siten zu gewoppenter hant die schwech des messers vnd drueck im den elnbogen wol vnter sin drossell vnd thun als vor vntericht pist ~~ |
[78r.3] Item oder leg ym deyn messer an seyn halz auff seyner rechten seytten zw gewoppender hand dy swech deß messerß und druck ym den ölpogen wol unter seyn drossel und thue alz dw vor unterrichtt pist |
[155r] Item leg Im deyn messer an den hals auff seyner lincken seytten zu gewappender hantt dy swech des messers vnd druck Im den olpogen woll vnter seynen hals vnd thu als du vor vnterricht pist also hastu aber eyn pruch wyder das durchstechen; |
||||||||
[435] |
Then, another breaking: if he wants to thrust through, in the moment while he presses your Messer down, “simultaneously” go high with the hilt and strike or cut through his neck on his left side. And it goes easy if one can perform it properly. |
[96r.4] Item Aber eyn bruch So er durch stechen will in dem dlbil er din messer nider druck Indes far vff mit dem gehultz vnd haulb oder schnidt im durch den hals vff siner lincken siten vnd dz get als lichlich zu dem der eß recht triben kan ~ |
[78r.4] Item aber eyn pruch So er durchstechen [78v.1] wil yn dem dy weyl er deyn messer nyder drucket yndeß far auff mit dem gehültz und haw oder schneyd yn durch den halz auff Seyner[77] lincken seytten und daß gett alleß leychtiklich zw dem der eß recht treyben kan etc |
[155v] Item aber Ey pruch so er durch stechen will In dem dy weyll er deyn messer nyder druckt Indes far auff mit dem gehultz vnd haw oder schneyd Im durch seyn hals auff seyner lincken seytten vnd das gett als leychtiklich zu der es recht treyben kan; |
||||||||
[436] |
If he wants to approach you Here the master states an element how one should perform it with the armed hand and speaks: If he wants, etc. |
[96v.1] Wil er dir nohens Hie saget der meinster von eynem stuck wie man dz zu gewoppenter hant triben sol vnd spricht wil er etc ~ |
[78v.2] Wil er dir nahen Hye sagtt der meyster von eynem stuck wye man daß zw gewappender handt treyben söl und spricht wil er etc |
[156r.1] Will er dir nahen Hye sagtt der meyster Eyn stuck wye man das zu gewapp ender handt treyben soltt vnd spricht will er etc |
||||||||
[437] |
You should understand it this way: if he comes to you in the Zufechten, stand with your left foot forward and hold your Messer on your right side and above your right knee, and so that the thumb is above and the point is against the man. And expose yourself with your left side. If he strikes at you to the opening, bow also your left side under his Messer and leap close to him. With your entire left arm grab firmly “simultaneously” over his right one close to the elbow and press his arm firmly to your left side, and “simultaneously” grab down his arm in the middle of your Messer and set the point on his throat or under his right shoulder. Or, hold your Messer in the left hand in the middle and let your right hand go from the bind of the Messer, and grab with the right hand in his right knee-bending, and throw him in front of you. |
[96v.2] Item dz soltu also verstan so er im zubechten zu dir künpt so ste vor mit dinem lincken fus vnd halt din messer vff diner rechten siten vnd oben dinen rechten knüg vnd dz der thum oben ste vnd der ort gegen dem man ste vnd geb dich mit der lincken siten ploß schlicht er dir dan der ploß noch so pueg auch vnder sin messer vff din lincke siten vnd spring nohent vff in Indes griff mit diner gantzem lincken arm starck vber sin rechten nohent by dem elnbogen vnd druck sin arm fest in din lincke siten Indes griff vntter sin arm in die mit sines messers vff setz im den ortt an sin kellen oder behalt din messer inder lincken hant in der mit vnd loß din recht hant von dem pindt des messers vnd griff im mit [97r.1] in syn rechten knueg pug vnd würff In for dich |
[78v.3] Daß soltu alzo verstan So er ym zwvechten zw dir kumbtt So stee vor mit deynem lincken fuß und haltt deyn messer auff deyner rechten seytten und ob deynem rechten knye und daß der dawm doben sey und der ort gegen [79r.1] dem man ste und gib dich mit der lincken seytten plöß schlecht er dir den der plöß nach so peug unter seyn messer auff deyn lincke seytten und spring nohend auff yn yndeß greuff mit deynem ganczen lincken armen starck uber seynen rechten nohend bey dem ölpogen und druck seyn armen fest yn deyn lincke seytten yndeß greuff unter seyn armen yn dy mitt deyneß messerß und secz ym den ortt an seyn kelen oder unter seyn rechte uchsen oder pehalt deyn messer yn der lincken hand yn der mit und laß dy rechten hand von dem pynd deß messerß und greuff ym mit deyner hand yn seyn rechte knyepug und wirff yn fuer dich etc |
[156r.2] Das soltu also verstan So er Im zuuechten zu Ir dir kumbt so stee vor mit deynem lincken füß vnd halt deyn messer auff deyner rechten seytten vnd ob deynem rechten kny vnd das der dawmen oben stee vnd der ortt stee gegen dem mann vnd gib dich mit der lincken seytten ploß schlecht er dir denne der ploß nach so pewg auch vntter seyn messer deyn lincke seytten vnd spring nohent auff In mit deynem gantzen lincken arme Greyff starck Indes vber seyn rechten nohent bey dem olpogen vnd druck seyn arme fest In deyn lincke seytten Indes greyff vntter //[78] [156v.1] // seyn arme In dy mitt deynes messers vnd setz Im den ortt an seyn kelen oder vntter seyn rechte vchsen oder pehallt deyn messer In der lincken hand In der mitt vnd laß deyn rechte handt von dem pindt des messers vnd greyff Im mit der rechten handt In seyn rechte knypüg vnd wirff In furdich etc |
||||||||
[438] |
Then, or turn your left side to his right one and step with your left foot in front of his right one and go with your hilt of your Messer on the outside on his neck, and step with your left foot in front of his right one and throw him in front of you. |
[97r.2] oder wind din lincke siten an sin rechte vnd schrit mit dinem lincken fus fur sinen rechten vnd griff mit diner lincken hant in sin hals siner rechten siten vnd wurff in vor dich |
[79r.2] Oder wendt deyn lincke seytten an seyn rechte und schreyt mit deynem rechten lincken fueß fuer seynen rechten und greuff mit deyner rechten hand an seyn halz seyner rechten seytten und wirff yn fuer dich |
|||||||||
[439] |
Then, another breaking: if you have grabbed him at the arm, step with your right foot behind his right one and go with your right hand around his neck on the inside to his left side and throw him in front of you over your right hip. |
[97r.3] oder so du Im pÿ dem hals gefast hast so schrit mit dinem rechten fus hinder sin rechten vnd mit diner rechten hant vmb sin hals vff siner lincken siten vnd wurff in vor dich vber din rechte huefft |
[79r.3] Oder so dw yn bey dem armen gefast hast so schreyt mit deynem rechten fues hynter seynen rechten und far mit deyner rechten handt [79v.1] umb seyn halz auff seyner lincken seytten und wirff yn fuer dich uber deyn rechten huff etc Sequitur Textus |
[157r] Item Eyn ander pruch so dw In pey dem arme gefast hast so schreytt mit deynem rechten fuß hinter seynen rechten vnd far mit deyner rechten handt vmb seyn hals Inbendigs auff seyner lincken seytten vnd wurff In furdich vber deyn rechte huff etc |
||||||||
[440] |
If he wants to show off Here the master states a breaking against the element when one has grabbed your right arm with his left one and speaks: If he wants to show off, etc. |
[97r.4] Wil er prangen Hie saget der meinster eyn bruch wider dz stuck so eyner syn arm gefangen hat mit siner lincken vnd spricht wil er brangen etc |
[79v.2] Wil er prangen Hye sagtt der meyster eyn pruch wyder daß stuck so eyner deyn rechten armen gefangen hatt mit seynem lincken und spricht wil er prangen etc |
|||||||||
[441] |
You should understand it this way: if your arm is grabbed with your Messer, go with your Messer outside over his arm and put the Messer with the edge forwards on his throat, and press firmly from you with the Messer with the armed hand. |
[97r.5] Item dz mach also ist din arm gefangen mit dinem messer so far mit dinen messer vßwendig vber sin arm vnd leg im dz messer vorn an den hals In die kellen vnd druck vast von dir |
[79v.3] Daß soltu alzo verstan ist deyn armen gefangen mit deynem messer So far mit deynem messer aussen uben seynen armen und leg ym daß messer foren an den halz yn dy kelen und druck fast von dir mit dem messer etc |
[158r.2] Das soltu also verstan ist deyn arme gefangen mit deynem messer so far mit deynem messer aussen vber seyne arme vnd leg Im das messer mit der schneyden forne an den hals In dy kelen vnd druck fast von dir In mit dem messer mit gewappender hantt etc |
||||||||
[442] |
Then, a better element: if you feel that he wants to fall over your arm, equally ”simultaneously” as he falls with his arm over your one, lift his left arm outside firmly up, and step with your right foot in front of his left one. Then, press with your right arm his left one firmly down, so that the joints of the elbows touch or come together. If he is strong, come with your left hand to help your right arm or hand, and throw him on the face over your right leg. |
[79v.4] Item eyn pesserß stuck So dw enpfindest daß er wil uber deyn armen fallen gleych [80r.1] yndeß so er felt mit seynem armen uber deynen yndeß heb ym seyn lincken armen außbendigß starck auff ubersich und schreytt mit dem rechten fuß fuer seynen lincken und druck mit dem rechten armen fast nyder seynen lincken daß dy gelenck der olpogen zw sammen rueren oder kumen Ist er starck so kum der rechten hand oder arm zwhilff mit deynem lincken und wirff yn auff daß antlicz uber deyn rechteß payn |
[157v.1] B¶ Item Eyn pessers stuck so dw Empfindest das er will vber deyn arme fallen gleych Indes so er fellt mit seynem arme vber deynen Indes heb Im seynen lincken arme außbendigs starck auff vbersich vnd schreytt mit deynem rechten fuß fur seynen lincken vnd druck mit deynem rechten arme fast nyder seynen lincken das dy gelenck der olpogen zu samen ruren oder kummen ist er starck so kum deym rechten arme oder handt zu hilff mit deyner lincken vnd wurff In auff das antlitz vber deyn rechtes peyn etc |
|||||||||
[443] |
Then, or grab in the middle of your Messer with your left hand to help the right one, and pull firmly to your left side, and press from above downwards with the left hand, and leap with your right foot in front of his left one, and throw him over it. Thus, you have the breaking against the first element. |
[97v.1] Item oder griff In die mit dines messers mit diner lincken hant der rechten zu hilff vnd riß starck vff din lincke siten vnd druck oben nider mit der lincken hant vnd spring mit dinen rechten fus fur sinen lincken vnd wurff in dar vber also hastu wider dz erst stueck ~ |
[80r.2] Item oder greuff yn dy mit deyneß messerß mit deyner lincken hand der rechten zw hilff und reyß starck auff deyn lincke seytten und druck oben nyder mit der lincken hand und spring mit deynem rechten fuß fuer seynen lincken und wirff yn dar uber Alzo hastu den pruch wyder daß erst stuck |
[157v.2] Item oder greyff Inn dy mitt deynes messers mit deyner lincken handt der rechten zu hilff vnd reyß starck auff deyn lincke seytten vnd druck oben nyder mit der lincken handt vnd spring mit deynem rechten fuß für seynen lincken vnd wurff In dar vber also hastu den pruch wyder das erst stuck |
||||||||
[444] |
If he wants to press the throat with the Messer Here the master states a counter-breaking against the announced breaking and speaks: With the Messer, etc. You should understand it this way: if you have fallen to one over his Messer and he wants to press your throat as it is stated above, “simultaneously” take his Messer at the blade with your right hand or the hilt, and press the blade of his Messer firmly on you to your right side. Then, go with your left hand high to his right one on the inside on the bind of his Messer, and pull firmly to your right side, in that way you take his Messer. |
[97v.2] Mit messer wil er kelln drucken Hie saget der meinster eyn wider bruch wider den gemelten bruch vnd spricht mit messer wil / Daß soltu also verstan wan du eynem vber sin messer pist gefallen vnd er wil dir din kell drucken als oben geschriben stot Indes nym sin messer bÿ der klingen mit diner rechten hant oder gehultz vnd druck die klingen sines messers vast an dich in din rechte siten vnd far mit diner lincken hant oben vff sin rechte Inwendig an sin pindt sins messers vnd riß starck vff din rechten siten so nÿmpstu Im dz messer ~ |
[80r.3] Mit dem messer wil er kelen drucken Hye sagtt der meyster eyn wyder pruch wyden den ee gemelten pruch und spricht mit messer etc Daß soltu alzo verstan dw eynem uber seyn armen pist gefallen und er wil dir deyn kelen drucken alz oben geschriben steet yndeß nymb seyn messer bey der klyngen mit deyner rechten hand oder mit deym gehultz und dryng druck dy klyngen seyneß messerß fast an dich yn deyn rechte seytten und far mit deyner lincken hand oben auff seyn rechte ynbendigß an daß pynd seyneß messerß und reyß starck auff deyn rechte seytten So nymbstu ym daß messer etc |
[158v] Mit messer will er kelen drucken Hye sagtt der meyster Eyn widerpruch wyder den gemelten pruch vnd spricht mit messer etc Das soltu also verstan wenn du Eynem vber seyn messer pist gevallen vnd Er will dir deyn kelen drucken als oben geschriben stett Indes nymb seyn messer bey der klingen mit deyner rechten handt oder gehultz vnd druck dy klingen seynes messers vast an dich In deyn rechte seytten vnd far mit deyner lincken handt oben auff seyn rechte Inbendigs an seyn pindt seynes messers vnd reyb starck auff deyn rechte seytten so nymbstu Im das messer etc |
||||||||
[445] |
Then, another different breaking: if he wants to press in the throat with his Messer as before, “simultaneously” as his Messer is about to fall into the throat, fall between yourself and him with your Messer on his own one, and let your left hand go and fall in the middle of your Messer, and set the point on his throat. |
[98r.1] Item Aber eyn ander bruch will er in die kell drucken als vor Indes dlbil sin messer in die will kell wil fallen so fall zwuschen dich vnd in mit dinem messer an dz sin vnd loß din lincke hant gan vnd fal in die mit dines messers vnd setz im den ortt in die kellen ~ |
[80v.2] Item aber eyn ander pruch wyder den [81r.1] pruch wil er yn dy kelen drucken mit seynem messer alzß vor yndeß dy weil seyn messer zw der kelen wil so fal czwischen dich und yn mit deynem messer an daß seyn und laß deyn lincke hand gan und fal yn dy mit deyneß messerß und secz ym den ortt an dy kelen |
[159r] Item aber eyn ander pruch will er In dy kelen drucken mit seynem messer als vor Indes dy weyll seyn messer In dy kelen will fallen so fall zwischen dich vnd In mit deynem messer an das seyn vnd loß deyn lincke handt vnd fall In dy mitt deynes messers vnd setz Im den ortt an dy kelen etc |
||||||||
[446] |
Then, another element: if you have grabbed his arm as before, and he wants to go to your throat, “simultaneously” swing to your right side well around, in that way he is not able to achieve anything. |
[98r.2] alliud Item ein andes stueck so du sin arm hast gefangen als vor vnd er will dir noch der kellen faren Indes schwing dich vff din rechten siten wol vmb so kan er aber nicht schaffen ~ |
[81r.2] Item eyn anderß stuck so dw seyn armen hast gefangen alz vor und er wil dir nach der kelen faren yndeß swyng dich auff deyn rechte seytten wol umb so kan er aber nichcz schaffen |
[159v] Item Eyn anders stuck so dw seyn arme hast gefangen als vor vnd er will dir nach der kelen faren Indes swing dich auff deyn rechte seytten woll vmb so kan er aber nichtz schaffen; |
||||||||
[447] |
Then, another breaking: if he wants [to go] to the throat with his Messer as before, “simultaneously” lower your left arm with your body down and press it firmly to your body, and bow with the back, in that way his intention is spoilt again. |
[81r.3] Item eyn ander pruch wil er zw dem halz mit seynem messer alz vor yndeß senck deyn lincken armen mit dem leyb wol nyder und druck den fast an deyn leyb und peug dich mit dem ruck eyn so ist seyn wil aber umb suenst etc |
[160r] Item aber Eyn ander pruch will er zu dem hals mit seynem messer als vor Indes senck deyn lincken arme mit deynem leyb woll nyder vnd druck den fast an deyn leyb vnd peug dich mit dem ruck eyn so ist seyn will aber vmb Sunst |
|||||||||
[448] Then, if he goes to you with his Messer under the throat as before, go with your right hand in the weak of his blade and push it from the neck to the breast. “Simultaneously” grab with your left turned hand from above at the hilt of the blade of his Messer and pull firmly to your right side, so you take his Messer. |
Then, if he grabbed you with the Messer behind the throat as before, grab with your right hand in the weak of the Messer and press firmly to your left side. “Simultaneously” grab with your left turned hand from above at the hilt behind his right hand and pull firmly downwards to your left side. |
[82r.2] Item fertt er dir mit seynem messer unter dy kelen alz vor so far mit deyner rechten hand yn dy swech seyner klyngen und druck dy von dem halz an dy prust yndeß greuff mit deyner lincken verkerten hand oben an daß gehulcz seyneß messerß klyngen und reyß starck auff auff deyn rechte seytten so nymbstu ym aber daß messer etc |
[160v] Item hatt er dich mitt dem messer gefast hinter dy kelen wye vor so greyff mit deyner rechten handt In dy swech des messers vnd druck vast auff deyn lincke seytten Indes greyff mit deyner lincken verkertten handt oben auff das gehultz hinter seyn rechte handt vnd reyß starck vntersich auff deyn lincke seytten etc |
|||||||||
[449] Then, another different breaking. If he wants to press the Messer to your throat, notice: as soon as he has gone with his Messer and wants to get under the throat with it, “simultaneously” go with your right hand between yourself and him and his Messer, upwards on the chest with your right hand to your left shoulder. And while he wants to press his Messer under your throat, grab his Messer from above at the hilt above his hand with your right turned hand, so that your thumb is below and the little finger is above, and come to help your right hand with your left one also to the hilt from inside, and pull firmly to your right side. This way you take his Messer. |
[81r.4] Item aber eyn ander pruch wil er dir daß messer yn dy kelen drucken so merck alz [81v.1] pald er mit seynem messer ist faren und wil unter dy kelen da mit yndeß far mit deyner rechten hand czwischen dich und yn und seynen messer auff der prust hoch auff mit deyner rechten hand zw deyner lincken achseln und dy weyl er seyn messer dir wil unter dy kelen drucken und dy weyl pegreuff seyn messer oben pey dem gehulcz ob seyner hand mit deyner rechten verkerten hand alzo daß deyn dawm unter sey und der klayn finger oben stee und kum deyner rechten mit deyner lincken zw hilff auch an daß gehulcz ynbendigß und reyß starck auff deyn rechte seytten So nymbstu ym daß messer etc |
|||||||||||
[450] |
Then, another breaking: grab as before with your right hand at his right one, and pull his right arm firmly to your left shoulder. “Simultaneously” go with your left arm firmly around his throat on the outside and step with your left foot in front of his right one, and swing to your right side. |
[81v.2] Item aber eyn pruch greuff aber alz vor mit deyner rechten hand seyn rechte reyß dy starck auff deyn rechte achsel seyn rechten armen yndeß far mit deynem lincken armen starc umb seyn halz außbendingß und schreytt mit deynem lincken fuß fuer seynen rechten und swyng dich auff seyn rechte seytten |
[161r] Item aber eyn pruch greyff aber als vor mit deyner rechten handt seyn rechte reyß dye starck auff deyn lincke achselen seynen rechten arme Indes far mit deynem lincken arme starck vmb seyn hals außbendigs vnd schreytt mit deynem lincken fuß fur seynen rechten vnd swing dich auff deyn rechte seytten etc |
|||||||||
[451] Then, grab his right arm as before and pull firmly over your left shoulder, and press firmly downwards. “Simultaneously” press also his left arm to where you have his right arm, and press with your left arm firmly to your left side. |
Then, grab his right arm as before and pull firmly over your left shoulder, and press firmly downwards. “Simultaneously” press also his left arm to where you have his right arm, and press with your left arm firmly to your left side, and come with your left [hand] from below in the middle of your Messer. Then, step with your foot in front of his left one, and swing to your right side. |
[81v.3] Item pegreuff seyn rechten armen alz vor [82r.1] und reyß starck uber deyn rechte achsel und druck fast nyder yndeß druck auch deyn lincken darynnen dw seynen rechten armen vor hast und druck mit deynem lincken armen fast yn deyn rechte seytten etc |
[161v] Item greyff [Sic] seynnen rechten arme als vor vnd reyß starck vber deyn lincke achselen vnd druck vast nyder Indes druck auch seynen lincken arme dar Innen du seynen rechten arme hast vnd druck mit deynem lincken arme vast In deyn lincke seytten vnd kum mit deyner lincken vntten In dy mitt deynes messers vnd schreytt mit deynem fuß fur seyn lincken vnd swing dich auff deyn rechte seytten etc |
|||||||||
[452] If he wants to ashame you Here the master states a breaking against the counter-breaking and speaks: If he wants, etc. You should understand it this way: if he grabs with his left hand at your hilt [and comes to help his left one with the right hand also at the hilt] and wants to take your Messer as it is stated above, “simultaneously” go with your left hand in his right one, and pull it downwards to your chest. And let your right hand go from the bind and go with the right hand [or arm from above downwards through his right one and lock your right arm over his right one and go with the right one] under his left one to your left hand and leap with the right foot in front of his left one and throw him over it with strength. |
If he wants to ashame you Here the master states a breaking against the counter-breaking. You should understand it this way: if he wants to take your Messer and grab with his left hand from above on your bind, and pushes your Messer down to your left side, and wants to take your Messer, “simultaneously” grab with your left hand in his left one, and pull firmly downwards to your left side. Then, strike your right arm from above over his left one, and go down through the same arm with your right hand, and swing well to your left side, and throw him over your right foot, as it is depicted below. |
[98r.3] Wil er dich beschemen Hie saget der meinster eyn bruch wider den bruch vnd spricht wil er dich beschemen Daß soltu also verstan grifft er dir mit siner lincken hant in din gehultz vnd künpt siner lincken hant zu hillff mit siner rechten auch In das gehultz vnd wil dir dein messer [98v.1] nemen als oben geschriben stott Indes far mit diner lincken hant in sin rechte vnd rib die vnter stich vff din bruest vnd loß die recht hant von dem gehultz vnd far mit der rechten hant oder arm oben nider durch sin rechten arm vber sin rechten vnd far mit der rechten vff sin lincke hant vnd spring mit dinen rechten fus fur sin lincken vnd wurff in dar vber mit sterck ~ |
[82r.3] Wil er dich beschemen [82v.1] Hye sagtt der meyser eyn pruch wyder den wyder pruch und sprichtt wil er dich etc Daß soltu alzo verstan greufft er dir mit seyner lincken hand yn deyn gehulcz ()º und wil dir deyn messer nemen alz oben geschriben steet yndeß far mitt deyner lincken hand yn seyn rechte und reyß dy untersich auff deyn prust und laß deyn rechte hand von dem pynd und far mit der rechten hand )(+ unter seyn lincken auff deyn lincke hand und spring mit dem rechten fuß fuer seyn lincken und wirff yn dar uber mit sterck etc
|
[162r] Will er dich beschemen Hye sagtt der meyster Eyn pruch wider den wyderpruch das soltu also verstan will er dir das messer nemen vnd greyffen mit seyner lincken handt oben an deyn pindt vnd scheubt dir deyn messer nyder auff deyn lincke seytten vnd will dir das messer nemen Indes greyff mit deyner lincken handt In seyn lincke vnd reyß starck vntersich auff deyn lincke seytten vnd schlag deyn rechten arme oben vber seyn lincken vnd far vntten durch den selben arme mit deyner rechten handt vnd swing dich woll auff deyn lincke seytten vnd wurff In vber deyn rechten fuß wye vntten gemalt stett etc |
||||||||
[453] Then, if he wants to take your Messer at the bind, do [as if you wanted] to press your Messer under his throat. Notice, while he wants to grab with his right hand at your hilt or at your right hand, “simultaneously” grab at his right elbow and leap with the left foot behind his left one and push him with your left hand at his right elbow firmly over it. And pull with your Messer and your right hand firmly to your right side. This way you have two breakings with which you can break against those elements and breakings announced above, so that you can perform them otherwise. |
[98v.2] alliud Item will er dir din messer nemen by dem pindt so thun im din messer vnder sin kellen wilt drucken so merck diewill er mit siner rechten hant wil griffen noch dinem gehultz oder noch diner rechten hant Indes so griff in sin rechten elnbogen mit diner lincken hant vnd spring mit dinem lincken fus hinder sinen lincken vnd schub e In mit diner lincken hant also by sinen rechten elnbogen starck dar vber vnd riß mit dynen messer vmb dine rechte hant starck vff din rechte siten also hastu zwüm bruch do mit du disse obgemelt stuck vnd bruch all wider brechen magst so du dich darin recht schicken kanst ~ |
[82v.2] Item wil er dir aber deyn messer nemen bey dem pynd so thue ym deyn messer unter dy kelen wild drucken So merck dy weyl er mit seyner rechten hand wil greu ffen nach deynem gehulcz oder nach deyner rechten hand yndeß so greuff an seynen rechten olpogen und spring mit dem lincken fuß hynter seyn lincken und scheub yn mit deyner lincken hand bey seynem rechten ölpogen starck dar uber und reyß mit deynem [83r.1] messer und deyner rechten hand starck auff deyn rechte seytten alzo hastu czwen pruch da mit dw dyse obgemelten stuck und pruch alle wyder prechen magst so dw dich anderß dar eyn schicken kanst |
||||||||||
[454] Then, another breaking against the counter-breaking. Do him this way: if he has grabbed your Messer as before, fall with your left hand behind to his left elbow and pull with your hilt and the right hand firmly down over his left shoulder, and step with your left foot behind his left one, and swing to your right side. |
[162v] Item Eyn ander pruch wyder den wider pruch thu Im also hatt er deyn messer gefast als vor so fall mit deyner lincken handt hyntten In seynen lincken olpogen vnd reyß mit deynem gehultz vnd rechten handt starck nyder vber seyn lincke achsel vnd schreyt mit deynem lincken fuß hinter seynen lincken vnd swing dich auff deyn rechte seytten etc |
|||||||||||
[455] Then, another breaking against the counter-breaking: if he has grabbed your Messer as before, “simultaneously,” as he wants to push your weak to his left side, fall “simultaneously” with your left hand in the weak of your Messer to his hand in the middle. Then, push your Messer firmly to his throat, and press with your hilt against to his left shoulder. Then, step with your left foot behind his left one and swing to your right side. |
[163r] Item aber eyn pruch wyder den wyderpruch hatt er dir gefast deyn messer als vor Indes so er will schyben deyn swech auff seyn lincke seytten so fall Indes mit deyner lincken handt In dy swech deynes messers für seyn handt In dy mitten vnd scheub Im deyn messer starck In seyn hals vnd druck mit deynem gehultz wyder auff seyner lincken achselen vnd schreytt mit deynem lincken füß hinter seynen lincken vnd swing dich auff deyn rechte seytten etc |
|||||||||||
[456] |
If you want to take revenge Here the master states an arm breaking as he speaks above: If you want, etc. You should understand it this way and how you should break the arm: stand with your left foot forwards and hold your Messer on your right side and on the left leg so that the point is against the man. If he strikes at your opening to your left side, leap with your right foot forwards, and also with your left foot, well to him with the bowed Messer. “Simultaneously” fall with your left hand over his right elbow from behind on it, and press with entire strength to your left side. “Simultaneously” turn with your body from him, and leap with your left foot firmly to your right side with the entire body and force, in that way you break his arm. Amen. |
[98v.3] Wiltu dich rechten Hie saget der meinster von eynen arm bruech als er dan oben spricht wilt dich rechen ~ merck wie du den arm bruch machen solt Ste mit dinen lincken fur vnd halt din messer vff diner rechten siten als vff dem lincken peind dz der ortt vff ste gegen dem man schlecht er dich dan noch der ploß vff din lincke siten so p spring mit dinem rechten fus auch mit dem lincken woll zu Im mit vßgebogen messer Indes fal mit diner lincken hant vber sin rechten elnbogen hinden an den vnd druck mit gantzer sterck in din lincke siten Indes wind din lib von im vnd spring mit dinen lincken fus starck vff din rechte siten mit gantzen lib vnd krafft so brichstu Im den arm ~ |
[83r.2] Wiltu dich rechen Nw sagtt der meyster von eynem armenpruch alz er dan oben sprichtt wiltu dich rechen etc. Nw merck wye dw den armen pruch machen soltt stee mit deynem lincken fuß fuer und halt deyn messer auff deyner rechten seytten alz auff dem lincken payn daß der ortt auff stee gegen dem man schlechtt er dir den nach der ploß auff deyn lincke seytten So spring [83v.1] mit deynem rechten fuß auch mit dem lincken wol zw ym mit auff gepogem messer yndeß fal mit deyner lincken hand uber seynen rechten olpogen hynter an den und druck mit ganczer sterck yn deyn lincke seytten yndeß wendt dich mit dem leyb von ym und spring mit deynem lincken fuß starck auff deyn rechte seytten mit ganczem leyb und krafft So prichestu ym den armen amen |
[163v] Will du dich rechen Hye sagtt der meyster von eynem arme pruch als er denn oben spricht wiltu dich etc Das soltu also verstan vnd wye du den arme prechen solt ste mit deynem lincken fuß für vnd halt deyn messer auff deyner rechten seytten als auff dem lincken peyn Das der ortt auff ste gegen dem man schlecht er dir denn nach der ploß auff deyn lincke seytten so spring mit dey nem rechten fuß fur auch mit dem lincken woll zu Im mit auff gepognen messer Indes fall mit deyner lincken handt vber seynen rechten olpogen hintten an den vnd druck mit gantzer sterck In deyn lincke seytten Indes wendt dich mit deynem leyb von Im vnd spring mit deynem lincken fuß starck auff deyn rechte seytten mit gantzem leyb vnd krafft so prichstu Im den arme etc |
||||||||
[457] |
Then, another arm-breaking: if you come to him in the Zufechten, stand as stated above. If he strikes to your left side, go bowed with the Messer under his Messer and leap in a twofold manner to him as before. “Simultaneously” grab his right hand with your left one on the inside, and wind it around to your left side on your chest, and go with your right arm down on his right elbow and break firmly upwards. This way you break his right one over your right one. Amen. |
[99r.2] Item eyn ander arm bruch wan du zum nesten zu im kümpst So ste als oben geschriben stott haut er dir dan oben zu diner lincken siten [99v.1] so far gebogen mit dinem messer vnter sin messer vnd spring zwueffach zu im als vor Indes begriff sin rechte hant mit diner mit diner [!] lincken inwendig vnd wind im die vmb vff din lincke siten an din bruest vnd far mit dinen rechten arm vnten an sinen rechten elnbogen vnd brich starck vber sich vff sin rechten |
[83v.2] Item eyn ander armenpruch wenn dw yn dem zw vechten zw ym kumbst so stee alz oben geschriben stett hawtt er dir den zw deyner lincken seytten So far gepogen mit deynem messer unter seyn messer und spring czwiuach zw yne ym alz vor yndeß begreuff ym seyn rechte hand mit deyner lincken ynbendigß und wyndt ym dye umb auff deyn lincke seytten an deyn prüst und far mit deynem rechten armen unter an seynen rechten ölpogen und prich starck ubersich alzo pruch ym seyn rechten armen uber deynen rechten amen |
[164v] Item Eyn ander armepruch wenne du Im zuuechten zu Im kumst so ste als oben geschriben stett hawtt er dir denne zu deyner lincken seytten so far gepogen mit dem messer vnter seyn messer vnd mit spring zwiuach zu Im als vor Indes pegreyff seyn rechte handt mit deyner lincken In bendigs vnd windt Im dye vmb auff deyn lincke seytten an deyn prust vnd far mit deynem rechten arme vntten an seynen rechten olpogen vnd prich starck vbersich alzo prich estu Im seyn rechten vber deyn lincken rechten etc |
||||||||
[458] |
Then, stand as it is stated above and grab his right hand with your left one. “Simultaneously” strike your right arm firmly over his right one, and lift with your left hand on his right arm over your right arm, and press your both arms firmly together, and step with your left foot behind his right one, and throw him over it. |
[99v.2] alliud Item ste als oben geschriben stott vnd begriff sin rechte hant mit diner lincken Indes schlag din rechten arm vber sin rechten vnd heb mit diner lincken hant vff sin rechten arm vber din rechten arm vnd druck din beide arm vast zu samen vnd schrit mit dinen lincken fus huntter sin rechten vnd wurff in also dar vber etc |
[84r.1] Item stee alz oben geschriben stet etc und begreuff seyn rechte hand mit deyner lincken yndeß schlag deynen rechten armen starck uber seynen rechten heb mit deyner lincken hand auff seyn rechten armen uber deyn rechten und druck deyn beyde armen fast zw sammen und schreytt mit deynem rechten fuß hynter seynen rechten und wirff yn alzo dar uber etc |
[164r] Item ste als oben geschriben stett vnd greyff seyn rechte handt mit deyner lincken Indes schlag deynen rechten arme starck vber seynen rechten vnd heb mit deyner lincken handt auff seyn rechten arme vber deyn rechten arme vnd druck deyn peyd arme fast zu sammen vnd schreytt mit deynem lincken füß hintter seyn rechten vnd wirff In dar vber etc[82] |
||||||||
[459] |
If he wants to turn to the right Here the propagator of the art states a breaking against the arm-breaking, and speaks: If he wants to the right, etc. You should understand it this way: if he has gone with his left arm above your right one and wants to break it over his right side, “simultaneously” as he wants to turn around to his right side, leap with your left foot behind his left one and press with your left arm and elbow to his left shoulder. And if you want to push his shoulder, grab with your left hand over his arm in the middle with your Messer, and press upwards and downwards with the entire strength to your right side and throw him on his back. |
[99v.3] Vff recht wil er wencken [100r.1] Hie saget der meinster eyn bruch Wider den arm bruch vnd spricht also vff recht etc Daß soltu also verstan hat er dir mit dinen lincken arm vber din rechten gefaren vnd will dir den bruchen vber sin rechte siten Indes so er sich vmb winden will von dir vff sin rechten siten vnd spring mit dinen lincken fus hinder syn lincken vnd druck in mit dym lincken arm vnd elnbogen sin lincke achsell vnd wan du sin achsell stossen willt so griff mit diner lincken hant vber sin In die mit synes messers druck oben vnd vnten mit gantzer macht vff din rechte siten vnd wurff in vff sin rueck ~ ~ |
[84r.2] Auff recht wil er bencken Hye sagtt der merer der kunst eyn pruch wyder den armenpruch und spricht alzo auff rechtt wil er bencken etc Daß soltu alzo verstan hatt er dir mit seynem [84v.1] lincken armen uber deynen rechten gefaren und wil dir den prechen uber seyn rechte seytten yndeß so er sich umb wenten wil von dir auff seyn rechte seytten so spring mit deynem lincken fuß hynter seynen lincken und druck mit deynem lincken armen und olpogen seyn lincke achsel und wenn dw seyn achsellen stossen wild so greüff mit deyner lincken hand uber seyn armen yn dy mit deyneß messerß und druck oben und unten mit ganczer machtt auff deynn rechte seytten und wirff yn auff seyn rucken etc |
[165r] Auff recht will er wencken Hye sagtt der merer der kunst Eyn pruch wyder dem armepruch vnd spricht also auff recht will etc Das soltu also verstan hatt er dir mit seynem lincken arme vber deyn rechten gefaren vnd will dir den prechen vber seyn rechte seytten Indes so er sich vmb wenden will von dir auff seyn rechte seytten so spring mit deynem lincken fuß hinter seyn lincken vnd druck mit deynem lincken arme vnd olpogen seyn lincke achselen vnd wenne du seyn achselen stossen willt so greyff mit deyner lincken handt vber seyn arme In dy mit deynes messers vnd druck oben vnd vnden mit gantzer macht auff deyn rechte seytten vnd wurff In auff seyn ruck etc |
||||||||
[460] |
Then, another breaking against the other element and arm-breaking. If he has grabbed your right arm with his left one and has dropped his Messer as before, and strikes his right arm over your right one on the inside in your elbow, and wants to throw you over his right leg, “simultaneously” step with your left foot in front of his right one and go with the hilt from above over his right hand and pull firmly downwards. Then, strike your left arm from above over his arm and over his left hand. Then, swing to your right side and throw him on his face again. |
[100v.2] Item Aber eyn bruch wider dz drit stuck vnd arm bruch hat er dir din rechten arm aber begriffen mit siner lincken vnd hat sin messer lassen fallen als vor vnd schlecht sin rechten arm Inlbendig In din elnbogen vnd will dich werffen vber din rechtes peyndt ~ Indes schrit mit dinem lincken fus for sin rechten vnd far im mit dem gehultz oben vber sin rechte hant vnd riß starck vntersich vnd schlag dinen lincken arm starck oben nider uber sin arm vnd vber sin lincke hant vnd schwing dich vff din rechte siten vnd wurff In aber vff sin antlitz ~ |
[85r.2] Item aber eyn pruch wyder daß dritt stuck und armenpruch hatt er dir deyn rechten armen aber pegriffen mit seyner lincken und hatt seyn messer lassen fallen alz vor und schlechtt seyn rechten armen uber deyn rechten ynbendigß yn den ölpogen und wil dich werffen uber seyn rechteß payn yndeß schreytt [85v.1] mit deynem lincken fuß fuer seynen rechten und far ym mit dem gehultz oben uber seyn rechte hand und reyß starck untersich und schlag deynen lincken armen starck oben uber seynen armen und uber seyn lincke hand und swyng dich auff deyn rechte seytten und wirff yn aber auff seyn antlitz |
[165v] Item aber eyn pruch wyder daß ander stuck vnd armepruch hatt er dir deyn rechten arme aber pegriffen mit seyner lincken vnd hatt seyn messer lassen fallen als vor vnd schlecht seyn rechten arme vber deyn rechten Inbendigs In deyn olpogen vber vnd will dich werffen vber deyn rechtes peyn Indes schreytt mit deynem lincken fuß fur seynen rechten vnd far Im mit dem gehultz oben vber seyn rechte handt vnd reyß starck vntersich vnd schlag deynen lincken arme oben vber seyn arme vnd vber seyn lincke handt vnd swing dich auff deyn rechte seytten vnd wurff In aber auff seyn antlitz etc |
||||||||
[461] |
Then, another breaking: if he has grabbed you with his left hand into your right one and has dropped the Messer and goes with his right arm under your right elbow and wants to break your right arm over it, “simultaneously” also drop your Messer and break your right hand out of his left one downwards, and go with your right hand down through his left arm, and go “simultaneously” under his right elbow and with your hand and arm firmly over his right arm. Then, press his right hand on your chest or under your right shoulder, and leap with your left foot in front of his right one, and strike your left arm also firmly over his right shoulder, and press firmly to your right side, and throw him in front of you on his face. |
[100r.2] Item aber eyn bruch hat er dir mit siner lincken hant gegriffen in din rechte vnd hat dz messer lossen fallen vnd fert mit sinen rechten arm vnter din rechten elnbogen vnd wil dir din rechten arm also do mit dar uber brechen Indes laß din messer auch fallen vnd pruch din rechte hant vff din rechte hant vff siner lincken vntersich vnd far mit diner rechten hant vnten durch [100v.1] sin lincken arm vnd far im Indes sinen rechten elnbogen vnd wind din hant vnd arm starck vber sin rechten arm vnd druck sin recht hant an sin brust oder vnder din rechten vscheschen vnd spring mit dynen lincken fus vor sinen rechten vnd schlag din lincken arm auch starck vber sin rechte achsell vnd druck In starck vff din rechte siten vnd wurff in vor dich vff sin angesichtt ~ ~ |
[84v.2] Item eyn ander pruch wyder daß ander stuck und armen pruch hatt er dir mit seyner lincken hand gegriffen yn deyn rechte und hatt daß messer lassen fallen und fert er mit seynem rechten armen unter deyn rechten ölpogen und wil dir deyn rechten armen alzo da mit uber prechen [85r.1] yndeß laß deyn messer auch fallen und brich deyn rechte hand auß seyner lincken untersich und far mit deyner rechten hand unten durch seyn lincken armen und far ym yndeß unter seynen rechten olpogen und wynd deyn hand und armen starck uber seynen rechten armen und druck seyn rechte hand an deyn prust unter deyn rechte vchsen und spring mitt deynem lincken fuß fuer seynen rechten und schlag deynen lincken armen auch starck uber seyn rechte achsellen und druck yn starck auff deyn rechte seytten und wirff yn fuer dich auff seyn angesichtt etc |
[166r] Item aber eyn pruch hatt er dir mit seyner lincken handt griffen In deyn rechte vnd hatt das messer lassen fallen vnd fertt mit seynem rechten arme vnter deyn rechten olpogen vnd will dir deyn rechten arme also darvber prechen Indes laß deyn messer auch fallen vnd pricht deyn rechte handt ausß seyner lincken vntersich vnd far mit deyner rechten handt vntten durch seyn lincken arme vnd far Im Indes vntter seynen rechten olpogen vnd windt deyn handt vnd arme starck vber seyn rechten arme vnd druck seyn rechte handt an deyn prust oder vntter deyn rechte vchsen vnd spring mit deynem lincken fuß fur seynen rechten vnd schlag deyn lincken arme auch starck vber seyn rechte achselen vnd druck Im starck auff deyn rechte seytten vnd wirff In fur dich auff seyn angesicht etc |
||||||||
[462] |
Beware of being hit Here the propagator of the art teaches how one should liberate himself if one has grabbed the other’s hand, his right one with the left hand. And do it this way: if he has grabbed your hand and wants to do an arm-breaking or whatever, do not let him come to it, break your hand out of his one. Firstly, turn the short edge on the outside on his arm, so that the flat lies on it, and “simultaneously” pull firmly downwards with the lowered point to your left side, so that you are free. “Simultaneously” strike at him through the head or the arm with the long edge. |
[100v.3] Huet dich vor dem treffer Hie saget der meinster wie man sol ledig werden so man eynen sich hant gefangen hat als mit der lincken hant sin recht vnd thün Im also hat er din hant gefangen vnd er will machen arm bruch oder was eß sy so loß nit dar zu kümen brich im sin hant vß sinen zu ersten / Also wind die kurtz schnid vßwindig an sin arm dz die flech daran an lein Indes riß starck vntersich mit gesenckten ort vff din lnicke siten so wurstu ledig Indes schlag in durch den kopff oder arm mit der langen schniden ~ |
[85v.2] Hüet dich vor den treüffen Hye lertt der meyster wye man sol ledig werden so eyner eynem seyn rechte hand gefangen hatt mit seyner lincken und thu ym alzo hatt er deyn handtt gefangen und er wil machen armenpruch oder waß eß sey so laß yn dar zw nichtt [86r.1] kümen prich ym deyn hand auß seyner züm ersten alzo wendt dich kurcz schneyd außbendigß an seynen armen daß dy flech dar an layn yndeß reyß starck untersich mit gesencktem ortt auff deyn lincke seytten So wirstü ledig yndeß schlag yn durch den kopff oder durch den armen mit der langen schneyden |
[166v] Hutt dich vor den trewffen Hye lertt der merer Der kunst wye man soll ledig werden so man eynem seyn handt gefangen hatt als mit der lincken handt seyn rechte etc vnd Thu Im also hatt er deyn handt gefangen vnd er will machen armepruch oder waß eß sey so loß In dar zu nicht kummen prich Im deyn handt auß seyner zum Ersten also wendt dy kurtz schneydt außbendigs an seynen arme das dy flech dar an layn Indes reyß starck vntersich mit gesencktem ortt auff deyn lincke seytten so wirsstu ledig Indes schlag In durch den kopff oder arme etc |
||||||||
[463] |
Then, another liberation: go with your hilt firmly above his left arm or hand, and pull firmly downwards to your right side, and strike “simultaneously” at his head. |
[101r.2] Item eyn ander ledigüng far mit dinem gehultz starck vber sin lincken arm oder hant vnd riß starck vntersich vff din rechten siten vnd schlag in Indes vff sin kopff etc |
[86r.2] Item eyn andre ledigung far mit dem gehulcz starck uber seyn lincke armen oder hand und reyß starck untersich auff deyn rechte seytten und schlag yn yndeß durch seyn kopff etc |
[167r] Item Eyn ander ledigung far mit deynem gehultz starck vber seyn lincken arme oder handt vnd reyß starck vntersich auff deyn rechte seytten vnd schlag In Indes auff seyn kopff etc |
||||||||
[464] |
Then, if he is strong so that you cannot pull him down with the hilt or if he comes to help his left hand with his right one, “simultaneously” grab also with your left hand in the bind to help your right hand, and pull firmly down to your left side, and strike through his head. |
[101v.1] Item ist er aber starck dz du in nit nider rissen kanst mit dem gehultz oder dz er mit siner rechten hant siner lincken zu hillff kümpt Indes griff auch mit diner lincken In daß pindt diner rechten zu hilf vnd riß starck vntersich vff din lincke siten vnd schlag in durch den kopff ~ |
[86r.3] Item ist er aber starck daß dw yn nichtt nyder reyssen kanst mit dem gehultz oder daß er mit seyner rechten seyner lincken zw hilff kumbtt yndeß greuff auch mit deyner lincken hand yn daß pynd deyner rechten zw hilff und reyß starck untersich auff deyn lincke seytten und schlag yn durch den kopff etc |
[167v] Item ist er aber starck das dw In nicht nyder reyssen kanst mit dem gehultz oder das er mit seyner rechten handt seyner lincken zu hilff kumptt Indes greyff auch mit deyner lincken handt In das pindt deyner rechten zu hilff vnd reyß starck vntersich auff deyn lincke seytten vnd schlag In durch den kopff etc |
||||||||
[465] |
Then, if he has grabbed your right hand with his left one as before, “simultaneously” wind outside to his arm with the lowered point, go down through to the same arm and catch him with the armed hand at the neck. Then, step with your left foot behind his right one and throw him over it. |
[168r] Item hatt er dir deyn rechte handt gefaßt mit seyner lincken wye vor Indes windt aber aussen an seyn arme mit gesencktem ortt Gee Im vntten durch auff den selbigen arme vnd faß In gewappendt pey dem hals schreytt mit deynem lincken fuß hinter seynen rechten vnd wurff In dar vber etc |
||||||||||
[466] Then, if he has grabbed your right hand with his right one, pull with the hilt downwards as do as before. Or, wind your Messer to your left side with the lowered point and pull with it firmly to your left side. |
Then, if he grabbed your right hand with his right one, pull with your hilt firmly downwards, and do it as before. |
[101v.2] alliud Item hat er dir begriffen die rechten hant mit diner rechten so riß aber mit dem gehultz vntersich vnd thun als vor oder wind din messer vff din lincke siten mit gesenctem ort vnd riß do mit starck vff din lincke siten ~ |
[86r.4] Item hatt er dir begriffen deyn rechte [86v.1] hand mit seyner rechten so reyß aber mit dem gehulcz untersich und thu alz vor oder wynd deyn messer auff deyn lincke seytten mit gesencktem ortt und reyß da mit starck auff deyn lincke seytten |
[168v] Item hatt er dir begriffen deyn rechte handt mit seyner rechten so reyß aber mit deynem gehultz starck vntersich vnd thu Im als vor etc |
||||||||
[467] Then, these elements are to be performed if he drops his Messer and falls to your arm with his right or left hand. |
[101v.3] Item disse stuck gehoren zu triben so er sin mesß fallen loßt vnd dir in din hant velt oder arm mit siner rechten hant ~ |
[86v.2] Item dyse stuck gehoren zw treyben So er seyn messer fallen lest und dir yn deyn armen feltt mit seyner rechten oder lincken hand etc |
||||||||||
[468] |
Then, if he has grabbed your hand as before and you want to pull downwards with your hilt, and he is too strong for you, come to help your right hand with your left one to the hilt from below, and pull downwards as before. |
[169r] Item hatt er deyn hant gefast als vor vnd du willt vntersich reyssen mit deynem gehultz vnd er ist dir zu starck so kum deyner rechten aber zu hilff mit deyner lincken an das gehultz vntten vnd reyß vntersich als vor etc |
||||||||||
[469] |
Then, if he has grabbed your right hand as before, wind your Messer on the inside on his arm, and go down through on the outside on his arm. |
[169v] Item hatt er dir deyn rechte handt gefast als vor so windt deyn messer Inbendigs an seynen arme vnd gee vntten durch außbendigs auff seynen arme etc |
||||||||||
[470] |
Then, if he has grabbed your right hand as before, wind on the inside through to his right side on the outside on his arm and step “simultaneously” close to him and take him with the armed hand at the neck on his left side as before. |
[170r] Item hatt er dir deyn rechte handt gefast aber als vor so windt Im aber Inbendigs durch auff seyn rechte seytten außbendigs an seyn arme vnd tritt Indes nohendt In Inn vnd nymb In gewappendt pey dem hals auff seyner lincken seytten wye vor etc |
||||||||||
[471] Notice the rule Here the master states a teaching and states the rule, etc. You should understand it this way that you should know in the Messer the right time for a particular breaking. And you should also consider his defeat and have reason and do not let yourself be infuriated so that you do not forget the art. You should not solely think about the breakings, either, how you could perform them properly, but also about the elements, and so that you know how you should encounter every single one, and he does what he wants, so that you find an element or a breaking which is applicable. If you cannot do it, let yourself be taught by someone who knows and can do it, and if you know the art of all the masters and you do not know when and how and against whom and against which displacements and against which strokes, elements, breakings and cuts you should perform this or another [technique], your art is of no use for you. You should also have great quickness and proper position of strength in every particular breaking. That is, if one has run under your Messer and has grabbed a hand, arm, leg or foot, and if you have learnt the art, one does not hold you anymore. If you have understood the art properly, you will well remain the master for long. |
Notice the rule Here the master states a good teaching and states the rule, etc. You should understand it this way that you should know in the Messer the right time for a particular element and breaking. You should also know when, how and where and against which, and you should have reason and do not let yourself be infuriated so that you do not forget the art. You should not solely think about the breakings, either, how you could perform them properly, but also about the elements, so that you know how you should encounter every single one, and let him do what he wants, so that you find an element or a breaking which is applicable. If you cannot do it, let yourself be taught by someone who can do it, and if you know the art of all the masters and you do not know when, how or where and against which displacements, strokes, elements, breakings and cuts you should perform this or another [technique], it is of no use for you. You should also have great quickness and proper position in every particular breaking, weak or strong. That is, if one has run under your Messer and has grabbed your hand, arm, leg or foot, and if you have learnt the art, one does not hold you anymore. If you have understood the art properly, you will well remain the master for long. |
[101v.4] Die rigel merck [102r] Hie saget der meinster vnd spricht die rigell daß soltu also verstan dz du im messer solt wissen die recht zytt zu eynem yttlichen bruch vnd solt auch wissen vnd haben vernüfft vnd dich nit solt loßen erzernen dz du der kunst nit vergessest du solt auch nit allein vff die bruch gedencken wie du sie recht triben muegest auch vff die stuck vnd dz du wisset wie du eynem ytlichen begegest er mag wz er will dz du eyn bruch oder stueck vindest der dar zu freglich sÿ kanstu dz nicht so loß eß dich leren eynen der es wol kan vnd kanst aller meinster künst vnd weist nit wan oder wie vnd gegem wem vnd welchem versetzen haulben bruchen stucken schnitten dis oder eyns dz du triben solt so ist dir keyn künst nitz du muest auch in yttlichen bruchen groß schnelliglichen haben vnd recht an legung der sterck dz ist wan dir eyner hat din messer vnter lauffen vnd hat dir hant oder arm begriffen peind oder fus hastu dan die kunst gemerck so erhelt er dich nÿmer mer hastu die künst recht verstanden so plÿbstü woll lang meinster etc |
[86v.3] Dy regel merck Hye sagtt der meyster eyn ler und sprichtt dy regel etc Daß soltu alzo verstan daß dw ym messer soltt wyssen dy rechte zeytt zw eynem yeczlichen [87r] prüch und soeltt auch seyn bol pesünnen und haben vernünft und soltt dich nicht lassen erczornen daß dw der künst nicht vergessest dw soltt auch nicht allayn aüff dy pruch gedencken wye dw so recht treyben muegst sünder auch auff dy stuck und daß dw wissesst wye dw soeltt eynem yetlichen pegegen er mach waß er wol daß dw eyn stuck oder eyn prucht findest der dar czw fuglich seÿ kanstu deß nicht So laß dich eß leren eynem der daß wayß und kan und kunest dw aller meyster künst und west nicht wenn und wye und gegen wem und gegen welchem verseczen und gegen welchen hewen stucken pruchen schnyten dycz oder geneß dw daß treyben schoellt so ist dir deyn künst nichcz nücz dw müest auch yn etlichen pruchen haben grosse schnellikayt und rechte an legüng der sterck daß ist wenn dir eyner deyn messer hatt unterloffen und hatt dir eyn hand oder armen pegriffen payn fuß hastu den dy künst gemerckt so er hellt er dich nymmer mer hastu dy künst [87v.1] recht verstanden so peleybest wol lang meyster |
[170v.1] Dy regl merck Hye sagtt der meyster eyn gutte ler vnd spricht dy regel etc Das soltu also verstan das du Im messer solt wyssen dy rechten zeytt zu eynem ydlichen stuck vnd bruch du solt auch wyssen wenn wy vnd wo vnd gegen welchen vnd haben vermist vnd dich nicht lassen erzornen das du der kunst nicht vergest Du solt auch nich allayn auff dy pruch gedencken wye du dye recht treyben mugst sunder auch auff dy stuck vnd das du wist wye du eynen ydlichen pegegnen solt vnd er mach waß er woll das du eyn stuck oder eyn pruch vindest der do zu füglich sey kanstu des nicht so laß dich eß vntterrichten eynen der es kann vnd kunstu aller meyster kunst vnd west nich wenne wye oder wo vnd gegen welchen versetzen hewen stucken pruchen schnytten dytz oder geneß du das treyben solt so ist dir das keyn nütz Du müst auch In eynen ydlichen pruch grosse schnellikayt haben vnd rechte anlegung swech vnd sterck das ist wenn dir eyner deyn messer hat vntterloffen vnd hatt dir deyn handt oder arme pegryffen peyn oder fuß hastu denne dy kunst gemerckt so helt er dich nymer mer hastu dy kunst recht verstanden so peleybest woll lang meyster |
||||||||
[472] Notice that there are many breakings that go on before the man grabs the hand, and one should do them “simultaneously,” as he wants to grab the hand, “simultaneously” as he wants to strike above the arm, “simultaneously” as he wants to clench,“simultaneously” to thrust, strike, cut, clench, etc. |
Note: many elements and many breakings go on before the man grabs the hand, and one should do them instantly “simultaneously,” as he wants to grab the hand, “simultaneously” as he wants to grab the arm or go “simultaneously” as he wants to strike, “simultaneously” as he wants to clench, “simultaneously” to thrust, strike, cut, etc. |
[102v.1] Nota ytlich bruech Hie gant zue E er den man den man [!] in die hant grifft vnd die selbige~ sol mã machen Indes glich so er wil in die hant griffen wil Indes so er griffen will vber den arm oder faren Indes so er will schlagen Indes so er will beschluessen Indes stechen haulben schniden etc |
[87v.2] merck etlich prüch sey dy geen zw ee der man yn dy hand greufft und dy soel man machen yndeß so er greuffen wil yn dy hand yndeß so er wil uber den armen schlagen yndeß so er wil peschlyssen yndeß stechen hawen schneyden beschlyssen etc |
[170v.2] Nota Etliche stuck vnd etlich pruch dy genen[83] zu Er[84] der man In dy handt greyfft vnd dy selbigen soll man machen gleych Indes so er will In dy handt greyffen Indes so er greyffen will In den arme oder farem Indes so er will schlagen Indes so er will peschlyssen Indes stechen hawen schneyden etc |
||||||||
[473] |
Then, as there are many elements, as soon as he brings you in the scale, you can hardly release yourself. |
[102v.2] Wan ytlich stueck die sint als pald er dich in die wag pringt so kanstu hart ledig werden |
[87v.3] wann etliche stuck dy syn alz pald er dich yn dy wag pringtt so kanstu hart an not ledig werden |
[171r.1] Item wann Etliche stuck synd als pald er dich In dy wag pringtt so kanstü hartt ledig werden |
||||||||
[474] |
It is a bad affair if one “lies down in the staff” [lies still] and cannot come anywhere. Know how to act accordingly. |
[102v.3] es ist boß tetigen so eyner Im stuck lig vnd nit mag kümen dar noch wiß dich zu richten ~ |
[87v.4] ¶ eß ust pöß teyding wenn eyner ym stock ligtt und nyndert mag kummen darnach wyß dich zw richten etc |
|||||||||
[475] |
Then, many elements go on as the man has grabbed firmly, and how the breakings fail if you delay for too long or wait. Many breakings also fail if you do them too quickly. |
[102v.4] Item ytlich stuck gant zu so der man gantz gefast hat vnd wie die bruch vellen so du zu lang harrest oder peitest also fellen ytlich bruch so du sie zu schnell machest also müstu wissen disser ding artt ~ |
[87v.5] Item etlich pruch genen zwe So der man gancz gefast hatt und wye dy pruch felen wenn dw zw lang harrest oder lang peytest alzo felen etlich pruch so dw sy zw schnel machest etc |
[171r.3] Item etliche stuck gen zu so der man gantz gefast hatt vnd wye dy pruch felen wenne du zu lang harest oder paytest also felen etlich pruch so du sy zu schnell machest also mustu wissen dy recht artt dyser ding etc |
||||||||
[476] Then, you have various elements and breakings, for amusement and serious combat. If you do not like one, take another one. If you understand it rightfully, you will like it. |
Then, you have various elements and breakings, for amusement and serious combat. If you do not like one, take another one. Who understands the things rightfully and can perform particular one in its time, such a man likes these things. |
[102v.5] Item du hast mangerleÿ stuck vnd bruch schimpflich vnd ernstlich gefellet dir eyns nit so nym eyn anders were die ding recht verstat vnd ytlichs zu siner zit triben kan dem gefallen dissen ding ~ |
[87v.6] Item dw hast manigerlay stuck und pruch schymphflich und ernestlich gefellt dyr eyneß nicht so nymb eyn anderß versteest dw eß recht So wirt eß dir gefallen |
[171r.4] Item du hast manigerlay stuck vnd pruch Schimpfflich vnd ernnstlich gefellt dir eynes nicht so nym eyn anders wer dy ding recht verstett vnd ytlichs zu seyner zeytt treyben kan dem gefallen dyse ding etc |
||||||||
[477] |
If you want to measure up Here the master states how one should do the elements and how one should hit down the arm with the hilt and how one can also do the same with the empty hand. |
[102v.6] Wiltu dich mossen Hie saget der meinster wie man die stuck machen sol dz man den arm mit dem gehultz nider stos vñ wie man auch dz glichen mag mit lerer hant |
[88r.1] Wiltü dich mossen Hye sagtt der meyster wye man sol dy stuck machen daß man den armen mit dem gehulcz stoß und wye man den armen mit lerer hand nyder sol stossen |
[171v.1] Wiltu dich mōssen Hye sagtt der meyster wye man dy stuck machen soll wye man den arme mit dem gehultz nyder stoß vnd wye man auch des geleychen thun mag mit lerer hand |
||||||||
[478] |
Now, firstly it is to be known that if he comes in the Zufechten to you, go against him with the Entrüsthau firmly to his left side. “Simultaneously” go with the hilt over his right hand on the outside and hit it firmly from above downwards towards the ground. “Simultaneously” go high with your Messer and strike through his face or cut through it. Amen. |
[103r.2] nü zu dem ersten ist zu wissen wan er im zu vechten zu dir kümpt so far gege~ im mit dem entrusch haulb starck vff sin lincke site~ Indes far mit dem gehultz vber sin rechte hant vßwendig vnd stos die sere oben nider gege~ der erdee~ Indes far vff mit dim messer vñ haull in durch dz angesicht oder schnid In durch dz muell ~ |
[88r.2] ¶ Nw züm ersten ist zw wyssen wenn er ym zwvechten zw dir kumbtt So far gegen ym mit dem entrusthaw starck aüff seyn lincke seytten yndeß far mit dem gehultz uber seyn rechte hand außbendigß und stoß dy sere von oben nyder gegen der erden yndeß haw yn durch daß angesichtt oder schneyd yn durch seyn maül amen |
[171v.2] Nu zum ersten ist zu wissen wen er Im zuuechten zu dir kumptt so far gegen Im mit dem Entrusthaw stark auff seyn lincke seytten Indes far mit dem gehultz vber seyn rechte handt außbendigs vnd stoß dy sere von oben nyder gegen der erden Indes far auff mit deynem messer vnd haw In durch das angesicht oder schneyd In dar durch etc |
||||||||
[479] |
Then, if you strike to his right side with an Entrüsthau or so, “simultaneously,” as the Messers spark together, hit on the inside with the hilt over his right hand or arm downwards towards the ground, and “simultaneously” strike through his head. Amen. |
[103r.3] alliud Itm~ haustu im vff sin rechte site~ mit eyne~ entruest haulb oder sünst Indes so die messer zu die messer zu samen glitzen so stos Inlbendig mit dem gehultz vber sin rechte hant oder arm nider gege~ der erde~ Indes schlag in durch den kopff ~ |
[88r.3] Item hawest ym auff seyn rechte seytten [88v.1] mit eynem entrüsthaw oder suest yndeß so dy messer zw sammen klyczen so stoß yn ynbendigß mit dem gehulcz uber seyn rechte hand oder armen nyder gegen der erden yndeß haw yn durch den kopff amen |
[172r] Item hauestu Im auf seyn rechte seytten mit eynem entrusthaw oder sunst Indes so dy messer zu sammen klytzen so stoß Inbendigs mit dem gehultz vber seyn rechte handt oder arme nyder gegen der erden Indes schlag In durch den kopff; |
||||||||
[480] |
Then, if he has gone with the hilt over your right hand and wants to press it down, “simultaneously” fall with your hilt above his right hand on the outside and “simultaneously” fall with your left hand into his hilt under his hand. Then, pull firmly with both hands downwards to your right side, in that way you take his Messer. |
[103r.4] alliud Itm~ ist er vber mit dem gehultz vber din rechte~ hant gefaren vnd wil dir die nider truecken Indes fal mit dem gehultz vber sin rechte hant vßwendig Indes fal mit diner lincke~ hant in [103v.1] sin gehultz vnter sint hant vnd riß starck mit beiden henden vntersich vff din rechte siten so nÿmbstu Im aber sin messer etc |
[88v.2] Item ist er dir mit dem gehulcz uber deyn rechte handt gefallen und wil dir dye nyder drucken yndeß fal mit deym gehulcz uber seyn rechte hand außbendigß yndeß fal mit deyner lincken hand yn seyn gehulcz hynter seyner hand und reyß starck mit payden henden untersich auff deyn rechte seytten so nymbstu ym daß messer |
[172v] Item ist er dir mit dem gehultz vber deyn rechte handt gefaren vnd will dir dy nyder drucken Indes fall mit deynem gehultz vber seyn rechte handt außbendigs Indes fall mit deyner lincken handt In seyn gehultz vntter seyner handt vnd reyß starck mit peyden henden vnttersich auff deyn rechte seytten so nymbstu Im aber das messer; |
||||||||
[481] |
Then, another breaking: hit his hand with the hilt on the inside downwards and grab with your left hand below at his hilt, and pull as before. |
[173r] Item Eyn ander pruch stoß Im seyn handt mit dem gehultz Inbendigs nyder vnd greyff mit deyner lincken handt vntten an seyn gehultz vnd reyß wye vor etc |
||||||||||
[482] |
Then, another breaking: if he falls over your right hand as before with the hilt, also fall with your hilt over his arm and pull firmly down. “Simultaneously” grab with your left hand under his right one in his Messer, forwards at the hand into the blade, and pull firmly with both hands to this left side, in that way you take his Messer again. |
[103v.2] alliud Item ein ander bruch felt er dir vber din rechten hant als vor mit dem gehultz so fal auch mit dem gehultz vber sin arm vnd riß fast do mit nider Indes griff mit diner lincken hant vnter sin rechten in sin messer vorn by der hant in die klingen vnd riß starck mit beyden henden vff sin lincke siten so nymbstu Im aber sin messer etc ~ |
[88v.3] Item eyn ander pruch feltt er dir uber deyn hand alz vor mit dem gehulcz so fal auch mit deyn gehulcz uber seyn armen und reyß fast da mit nyder yndeß greuff mit deyner lincken hand unter seyn rechte yn seyn messer foren bey der hand yn dy klyngen und reyß starck mit beyden henden auff deyn lincke seytten So nymbstu ym aber daß messer |
[173v] Item Eyn ander pruch fellt er dir vber deyn rechte handt als vor mit[88] dem gehultz so fall auch mit deynem gehultz vber seyn arme vnd reyß fast da mit nyder Indes greyff mit deyner lincken handt vnter seyn rechte In seyn messer vorne pey den handt In dy klingen vnd reyß starck mit payden henden auff deyn lincke seytten so nymbstu Im aber seyn messer etc |
||||||||
[483] |
Then, if he wants to take your Messer as it is announced before, and you feel that you cannot have your Messer at any rate, “simultaneously” grab with your right hand from above in his Messer or in his right hand, and go with your left hand downwards on his bind, and wind it upwards above his right hand on the outside. Then, pull firmly downwards to your left side, so that you take his Messer, and the breaking is called the Unbridled. |
[174r] Item will er dir deyn messer nemen wye Ee gemelt ist vnd du Empfindest das du deyn messer nymmer haben magst Indes greyff mit deyner rechten hendt oben an seyn messer oder an seyn rechte handt vnd far mit deyner lincken handt vntten an seyn pindt vnd windt das vber sich vber seyne rechte handt außbendig vnd reyß starck vntersich auff deyn lincke seytten so nymbstu Im aber das messer vnd der pruch heyst außgezawmt[89] etc |
||||||||||
[484] |
Then, if he goes with the hilt on the inside over your hand, “simultaneously“ go with your hilt also on the inside over his right hand, and go with the left hand on the inside over his Messer in the middle of your Messer. Then, pull firmly to your right side, in that way you take his Messer. |
[103v.3] Item fert er dir mit dem gehultz Inlbendig uber din hant Indes far mit dinen gehultz auch Inlbendig uber sin rechte hant vnd far mit der lincken hant Inlbendig vber sin messer in die mit dines messers vnd riß starck vff din rechte syten so nÿmbstu im aber sin messer etc ~ |
[89r.1] Item fertt er dir mit dem gehulcz ynbendigß uber deyn hand yndeß far mit dem gehulcz auch ynbendigß uber seyn rechte hand und far mit der lincken hand ynbendigß uber seyn messer yn dy mit deyneß messerß und reyß starck auff deyn rechte seytten So nymbstu ym aber daß messer etc |
[174v] Item fertt er dich mit dem gehultz Inbendigs vber deyn handt Indes far mit deym gehultz auch Inbendigs vber seyn rechte handt vnd far mit der lincken handt Inbendigs vber seyn messer In dy mitt deynes messers vnd reyß starck auff deyn rechte seytten so nymbstu Im aber seyn messer etc |
||||||||
[485] |
Then, if he goes on the inside over your hand with the hilt and wants to hit down your right hand, “simultaneously” also fall over his hand on the inside with the hilt and grab with your left hand in his blade and pull firmly to your left side, in that way you take his Messer again. |
[103v.4] Item felt er dir Inlbendig uber din hant mit dem gehultz vnd wil er dir din recht hantt nider stossen Indes fal im auch vber sin rechte hant Inlbendig mit dem gehultz vnd griff mit diner lincken hant In sin elnbogen vnd riß starck vff die lincke syten so nÿmpstu Im aber sin messer ~ |
[89r.2] Item feltt er dir ynbendigß uber deyn hand mit dem gehulcz und wil er dir deyn rechte hand nyder stossen yndeß fal ym auch uber seyn hand ynbendigß mit dem gehulcz und greuff mit deyner lincken hand yn seyn klyngen und reyß starck auff deyn lincke seytten so nymbstu ym aber daß messer etc |
[175r] Item fellt er dir Inbendigs vber deyn handt mit dem gehultz vnd will er dir deyn rechte handt nyder stossen Indes fall Im auch vber seyn handt Inbendigs mit dem gehultz vnd greyff[90] mit deyner lincken handt In seyn klingen vnd reyß starck auff deyn lincke seytten so nymbstu Im aber das messer |
||||||||
[486] |
Then, a breaking against the counter-breaking: if you fall with the hilt over his right hand on the outside and he falls against you also over your hand, and he grabs with his left hand on your Messer behind on the hilt, and pulls with his right one firmly to his left side, and takes your Messer and your right hand is in front under his right hand-if you feel that you cannot hold your Messer any more with your right hand, fall with your left hand in the blade of his Messer close to the handle and press his hilt with your right hand against him. Then, pull the blade of his Messer with your left [hand] firmly to your left side, in that way you take his Messer. |
[103v.5] Item eyn ander bruch wider den wider bruch felstu mit dem gehultz vber sin rechte hantt [104r.1] vßwendig vnd er felt dir widier vber din hant auch also vnd er grifft mit siner lincken hant an din messer hinden an dz gehultz vnd riß mit diner rechten hant starck vff sin lincke siten vnd nÿmpt dir also din messer Indes so leg din rechtt hant vor vnter sin rechte hant so du dan entspfindest dz du din messer nit merere magst behalten mit diner rechten hant so fall mit diner lincken hant in sins messers klingen nohent by der hant hab vnd druck mit diner rechten hant sin gehultz gegem Im vnd riß mit diner lincken hant sines messers klingen starck vff din lincke siten so nÿmbstu im aber sin messer |
[89r.3] Item eyn prüch wyder den wyderprüch felstu ym mit dem gehulcz uber seyn rechte hand außbendigß und er feltt dir wyder uber deyn hand auch alzo und er ergreufft mit seyner lincken hand an deyn messer hynder an daß gehulcz und [89v.1] reyßt mit seyner rechten starck auff seyn lincke seytten und nymbt dir alzo daß messer yndeß so ligtt deyn rechte hand vor under seyner rechten So dw den enpfindest daß dw deyn messer nicht mer halten magst so greuff mit deyner lincken hand ynn seyneß messerß klyngen nohend bey der hant hab und druck mit deyner rechten hand seyn gehulcz gegen ym und reyß mit deyner lincken seyneß messerß klyngen starck auff deyn lincke seytten so nymbstu ym aber daß messer etc |
[175v] Item Eyn pruch wyder den wyder pruch felstu Im mit dem gehultz vber seyn rechte handt außbendigs vnd er felt dir wyder vber deyn handt auch also vnd er greyfft mit seyner lincken handt an deyn messer hinden an das gehultz vnd reyßt mit seyner rechten starck auff seyn lincke seytten vnd nymbt dir also deyn messer vnd ligtt deyn rechte handt vor vntter seyner rechten handt so du denne Empfindest das du deyn messer nicht mer magst halten mit deyner rechten handt so fall mit deyner lincken handt In seynes messers klingen nahent pey der hant hab vnd druck mit deyner rechten handt seyn gehultz gegen Im vnd reyß mit deyner lincken seynes messers klingen starck sey auff deyn lincke seytten so nymbstu Im das messer etc |
||||||||
[487] |
Then, if you go over his arm with your hilt and he does the same to you and he pulls your hand down and grabs with his left [hand] under the hands of both of you in the blade of the Messer, and pulls firmly to his left side, “simultaneously” as you feel that you cannot hold your Messer anymore, fall with your left hand in the blade of his Messer. And as soon as your right hand is in front on his right one, “simultaneously” press with your right hand to his right one or against his right shoulder downwards, and pull his hilt firmly to your right side, in that way you also take his Messer. |
[89v.2] Item ferstu ym uber seyn armen mit dem gehulcz und er dir wyder und er reyst nyder deyn hand und greüfft mit seyner lincken hand unter ewer peyd hendt yn dy klyngen deß messerß und reyst starck auff seyn lincke seytten yndeß so dw enpfindest daß dw deyn messer nicht mer halten kanst so fal mit deyner lincken hand yn seyneß messerß klyngen So ist deyn rechte hand vor an seyner rechten yndeß druck mit deyner rechten auff [90r.1] seyn rechte oder gegen seyner rechten achselen untersich und reyß starck seyn gehulcz auff deyn rechte seytten so nymbstu ym auch seyn messer |
[176r] Item ferstu Im vber seyn arme mit deynem gehultz vnd er dir wyder vnd er reyst nyder deyn handt vnd greyfft mit seyner lincken vntter Ewrer payd hendt In dy klingen deß messers vnd reyß starck auff seyn lincke seytten Indes so du Emfindest das dw deyn messer nicht mer halten magst so fall mit deyner lincken handt In seyns messers klingen vnd so ist deyn rechte handt vor an deyner rechten Indes druck mit deyner rechten handt auff seyn rechte oder gegen seyner rechten achsel vnttersich vnd reyß starck seyn gehultz auff deyn rechte seytten so nymbstu Im auch seyn messer etc |
|||||||||
[488] |
Then, if one goes to your arm on the inside with the hilt and wants to hit your hand down, “simultaneously” as he goes with the hilt to your hand, go with your left hand under his right hand and with your hilt also over his right [hand], also on the inside, and press your both hands and hilt firmly together and pull firmly “simultaneously” to your right side, in that way you take his Messer. |
[90r.2] Item fert dir eyner nach dem armen ynbendigß mit dem gehulcz und wil dir deyn hand nyder stossen yndeß weil er fertt mit dem gehulcz über nach der hand so far mit deyner lincken hand unter seyn rechte und mit deym gehuelcz auch uber seyn rechte hand auch ynbendigß und druck deyn peyde hend und gehulcz fast zw sammen und reyß yndeß starck auff deyn rechte seytten So nymbstu ym aber daß messer etc |
[176v] Item fertt dir eyner nach dem arme Inbendigs mit dem gehultz vnd will dir deyn handt nyder stossen Indes weyll er fertt mitt dem gehultz nach der handt so far mit deyner lincken handt vnter seyne rechte handt vnd mit deym gehultz auch vber seyn rechte auch Inbendigs vnd druck deyn peyd hendt vnd gehultz fast zu sammen vnd reyß starck Indes auff deyn rechte seytten so nymbstu Im das messer etc |
|||||||||
[489] Then, if he goes with the hilt over your hand on the outside, “simultaneously” turn your Messer with the long edge under your hand and fall with your left hand in the middle of your Messer and go with your hilt on the inside with the armed hand over his hand and pull firmly to your right side, in that way you take his Messer again. |
[90r.3] Item fertt er dir mit dem gehülcz uber deyn hand außbendigß yndeß wendt deyn messer mit der langen schneyden unter deyn[91] hand und fal mit deyner lincken hand yn dy mit deyneß messerß und far mit deym gehulcz ynbendigß gewoppend uber seyn hand und reyß starck [90v.1] auff deyn rechte seytten So nymbstu ym aber daß messer etc |
|||||||||||
[490] |
Then, if he wants to hit down your hand with the hilt on the inside, “simultaneously” turn your edge upwards and cut him at it, and go with the cut upwards to your left side, so that you cut him also on the outside at his hand. |
[177r] Item will er dir mit dem gehultz Inbendigs deyn handt nyder stossen Indes wendt deyn schneyd vbersich vnd schneyd In dar eyn vnd far mit dem schnytt vbersich auff deyn lincke seytten alzo schneyd In auch außbendigs In seyn handt etc |
||||||||||
[491] Then, if he wants to hit down your hand on the outside with his hilt, turn your edge outside to his hand and cut firmly downwards to your right side. |
[90v.3] Item wil er dir deyn hand nyder stossen außbendigß mit seym gehulcz So wendt deyn schneyd außbendigß yn seyn hand und schneyd starck untersich auff deyn rechte seytten etc |
|||||||||||
[492] |
Then, if you have both bound as before and he wants to fall on the outside over your hand with the hilt, “simultaneously” wind your Messer with the hilt under your arm and lower the point to his shoulder or his side. Or, wind “simultaneously” the short edge to his head to his right side. |
[90v.4] Item habtt Ir peyde an gepünden alz vor und er wil dir außbendigß uber deyn hand mit dem gehulcz fallen yndeß wyndt deyn messer mit deym gehulcz unter deyn armen und senck den ortt ym yn seyn uchsen oder rechte seytten oder wyndt ym yndeß dy kurcz schneyd auff seyn kopff seyner rechten seytten etc |
[177v] Item habent Ir payde an gepunden als vor vnd er will dir außbendigs vber deyn handt mit dem gehultz fallen Indes windt deyn messer mit dem gehultz vntter deyn arme vnd senck den ortt Im In seyn vchsen oder seytten oder windt Im Indes dy kurtz schneyd auff seyn kopff seyner rechten seytten |
|||||||||
[493] Then, if he wants to hit your hand down with the hilt on the inside, “simultaneously” wind your Messer against his one so that the short edge is below and lower the point well and go with the hilt high in front of your head and set the point on his chest. Or, go with your Messer between both of you to his right side and strike at his right ear. As you go through with the Messer between both of you to his right side, you should always lower the point towards the ground and have the hilt high in front of the head. |
[91r.1] Item wil er dir deyn hand mit dem gehulcz nyder stossen ynbendigß yndeß wyndt deyn messer gegen seynem daß dy kurcz schneyd unter stee und senck den ortt wol und far mit dem gehulcz hoch auff fuer deyn haubtt und secz ym den ortt an seyn prust oder far mit deynem messer czwischen ewer peyder auff seyn rechte seytten und schlag yn zw seynem rechten oren Wenn dw also mit dem messer czwischen ewer peyder durchgest auff seyn rechte seytten So soltu albegen den ortt sencken gegen der erden und daß gehulcz hoch fuer daß haubt haben etc |
|||||||||||
[494] |
Then, if he again wants to hit down your hand on the inside with the hilt, wind against him high with your Messer, and raise your hilt and fall in the armed hand. Then, set the point on his neck to his right side. If he wants to defend against it, work with the hilt to his left side on the inside over his hand and take his Messer as you have been taught before. |
[91r.2] Item wil er deyn handt aber nyder stossen ynbendigß mit dem gehulcz So wyndt gegen ym auff mit deynem messer und erhoech daß gehulcz und fal zw gewoppender handt und secz ym den ortt an seyn halz seyner rechten seytten wil er dir daß weren So erbat mit dem gehulcz [91v.1] auff seyn lincke seytten ynbendigß uber seyn hand und nymb ym daß messer alz dw vor gelertt pist etc |
[178r] Item will er dir deyn handt aber nyder stossen Inbendigs mit dem gehultz So wendt gegen Im auff mit deynem messer vnd erhoch deyn gehultz vnd fall zu gewappender hant vnd setz Im den ortt an seyn hals seyner rechten seytten will er dir das weren so erbeytt mit dem gehultz auff seyn lincke seytten Inbendigs vber seyn haubt vnd nym Im das messer als du vor gelertt pist etc |
|||||||||
[495] |
Then, if he falls over your hilt on the outside over your hand, and you do the same to him, and he presses down and grabs with his left hand under the hands of both of you in the blade of your Messer, and he wants to take it, “simultaneously” fall with your left turned hand also in the blade of your Messer above his left hand, and step with your left foot behind his left one or in front of his left one. Then, press with your left hand and with the blade of his Messer firmly to his left side. |
[91v.2] Item feltt dir eyner uber deyn gehulcz außbendigß uber deyn uber deyn hand und dw ym wyder und druckt er nyder und greufft mit seyner lincken handt unter ewer peyd hend yn dy klyngen deyneß messerß und wil dirß alzo nemen yndeß fall mit deyner lincken verkerten hand auch yn deyneß messerß klyngen ob seyner lincken hand und schreyt mit deynem lincken fuß hynter seynem lincken oder fuer seynen lincken und druck mit deyner lincken handt und mit der klyngen deyneß messerß starck auff seyn lincke seytten etc |
[178v] Item fellt dir eyner vber deyn gehultz außbendigs vber deyn handt vnd du Im wyder vnd druckt er nyder vnd greyfft mit seyner lincken handt vntter Ewrer peyd hendt In dy klingen deynes messers vnd will dir es also nemen Indes fall mit deyner lincken verkertten handt auch In deynes messers klingen ob seyner lincken handt vnd schreytt mit deynem lincken fuß hintter seynen lincken oder fur seynen lincken vnd druckt mit deyner lincken handt vnd mit der klingen seynes messers starck auff seyn lincke seytten etc |
|||||||||
[496] |
Then, if you strike at him or he strikes at you from above to your left side, strike together with him to his left side. “Simultaneously” hit his right arm with your left hand on the outside downwards to the ground, and strike with your right through his head to his right side. |
[91v.3] Item hawest ym oder er dir von oben zw deyner lincken seytten So haw auch geleich mit ym eyn zw seyner lincken seytten yndeß stoß seyn rechten armen mit deyner lincken hand außbendigß nyder gegen [92r.1] der erden und haw ym mit deyner rechten durch seyn kopff auff seyner rechten seytten etc |
[179r] Item hawestu Im oder er dir von oben zu deyner lincken seytten So haw auch geleych mit ym eyn zu seyner lincken seytten Indes stoß seyn rechten arme mit deyner lincken handt außbendigs nyder gegen der erden vnd haw Im mit deyner rechten durch seyn kopff auff seyner rechten seytten; |
|||||||||
[497] |
Then, if he strikes an upper stroke from above at your left side, “simultaneously” bow your Messer under his one, and “simultaneously” hit with your left hand at his right one on the inside from above downwards and strike through his head. Amen. |
[92r.2] Item hautt er dir von oben eyn eynen oberhaw auff deyn lincke seytten yndeß peug deyn messer unter daß seyn yndeß stoß mit deyner lincken hand auff seyn rechte ynbendigß oben nyder und haw yn durch den kopff amen |
[179v] Item hautt er dir von oben eyn eyn oberhaw auff deyn lincke seytten Indes pewg deyn messer vntter das seyn Indes stoß mit deyner lincken handt auff seyn rechte Inbendigs oben nyder vnd haw In durch den kopff etc |
|||||||||
[498] |
[No text] |
[180r] [No text] |
||||||||||
[499] |
[No text] |
[180v] [No text] |
||||||||||
[500] |
If one wants to fight |
[181r] Wen man fechten wil |
||||||||||
[501] |
[No text] |
[181v] [No text] |
||||||||||
[502] |
Then, if one goes over your right hand on the outside, fall also over his right hand on the outside, and do “simultaneously” what you want. |
[182r] Item fertt er dir vber deyn rechte handt außbendigs so fall Im auch vber seyn rechte handt außbendigs vnd mach Indes was du willt etc |
||||||||||
[503] |
Then, if he goes with his hilt over your right hand on the outside as before, “simultaneously” go also over it on the outside again, and pull well down and “simultaneously” hit the hilt of his Messer with your left hand firmly to your right side, in that way you take his Messer. |
[182v] Item fertt er dir mit seyn gehultz vber deyn rechte handt außbendigs wye vor Indes far Im auch wyder dar vber außbendigs vnd reyß woll nyder vnd stoß Indes das gehultz seynes messers mitt deyner lincken handt starck auff deyn rechte seytten so nymbstu Im das messer etc |
||||||||||
[504] |
Learn to grab the elbow Here the master speaks about an element which is to be performed for amusement. If you want to do it, do it this way: if you bind to him at his left side, “simultaneously” strike around to his right side. And as you strike go behind to his elbow, and hit it firmly from you towards his right side. And “simultaneously” as he gives you his back, strike behind at his hip. Or, if he has shifted a bag onto his arse, strike at it. |
[104r.2] Den elnbogen lere fassen Hie saget der meinster von eynem bruch stuck dz do schmipflich ist zu triben Wiltu dz stuech machen so thun im also so du vff in pindest vff sin lincke syten Indes schlag im zu siner rechten syten vnd im [104v.1] sclag fart hintten an sin elnbogen vnd stos in fast von dir vff sin rechte siten vnd Indes gibt er dir den ruck so schlag in vff sin huefft hinten oder hat er eyn teschen vff dem ars geschoben so schlag in dar vff |
[92r.3] Den olpogen ler fassen Hye sagtt der meyster von eynem stuck daß do schimphfflich ist zw treyben wil dw daß stuck machen So thue ym alzo So dw auff yn pyndest auff seyn lincke seytten yndeß schlag umb zw seyner rechten seytten und ym schlag far hynter an seynen rechten ölpogen und stoß yn fast von dir auff seyn lincke seytten und yndeß [92v.1] gibtt er dir den ruck so schlag yn auff seyn huff hynter oder hatt er eyn taschen auff den arß geschoben so schlag yn dar auff |
[183r] Den ölpogen ler fassen Hye sagtt der meyster von eynem stuck das ist schimpflich zu treyben wiltu das machen so thu Im also so du auff In pindest auff seyn lincke seytten Indes schlag vmb zu seyner rechten seytten vnd Im schlag far hintten an seyn olpogen vnd stoß In vast von dir auff seyn rechte seytten vnd Indes gibtt er dir den ruck so schlag In auff seyn huff hintten oder hatt er eyn taschen auff seyn ars geschoben so schlag In dar auff etc |
||||||||
[505] |
Go over with the left You should understand it this way: as you come together in the Zufechten to his left side, strike at his right side, and “simultaneously” turn your left side to his right side. Then, go with your left arm outside over his Messer, and turn your back against him. “Simultaneously” fall with your left [hand] in the middle of your Messer and thrust at him through both your legs. And hold yourself well with the back at him, so that he cannot pull his Messer out of the arms, and lean down forwards, and thrust at his stomach, and frequently withdraw the point again to your left hand, so that he cannot grab you from behind with the point of your Messer. And thrust one or four times skillfully at his stomach or at the private parts. And it is a ridiculous element to perform during a swordsmanship competition. |
[104v.2] Lynck[93] vber far Daß soltu also verstan so du im zubechten zu im kümpst vff sin lincke siten so schlag im zu siner rechten siten Indes wind din lincke siten an sin rechte siten vnd far mit dinem lincken arm vber sin messer vnd wend den rucken gegen im Indes fal mit diner lincken hant in din messer in die mit vnd stich dich durch din beyde peynd vnd hab dich woll mit dem ruck an In dz er sines messers vß dem arm nit rucken mag vnd senck dich vorn nider vnd stich in den buch vnd zuch din ort vff wider in In die lincke hant dz er dich hinten nit mit dem ortt dineß messers begriffen mag vnd also schub in eyns oder vier mall behentlich in den buch [105r.1] oder vff dz gemechtt Es ist gar lecherlich vff der schull zu triben vor den luten ~ |
[92v.2] Linck uber far Daß soltu alzo verstan So dw ym zw vechten zw ym kumbst auff seyn lincke seytten So schlag ym zw der rechten seytten yndeß wendt deyn lincke seytten an seyn rechte seytten und far mit deynem lincken armen aussen uber seyn messer und wendt den ruck gegen ym yndeß fal mit deyner lincken hand yn deyn messer yn dy mit und stich durch deyn peyde payn und hab dich wol mit dem [93r.1] ruck an yn daß er seyneß messerß aüß deynem armen nicht rucken müg und senck dich foren nyder und stich yn ynn den paüch und czeüg deyn ortt offt wyder eyn yn deyn lincke hand daß er dich hynten nicht mit dem ortt deyneß messerß wegreuffen müg und alzo stopff yn eynß oder vyermal behentlich yn den pauch oder auff daß gemechtt eß ist gar lecherlich auff der schül zw treyben vor den lewten etc Sequitur textus |
[183v] Linck vberfar Das soltu also verstan So Ir Im zuuechten zu sammen kumptt auff seyn lincke seytten so schlag Im zu der rechten seytten Indes wendt deyn lincke seytten an seyn rechte seytten vnd far mit deynem lincken arme aussen vber seyn messer vnd wend deyn ruck gegen Im Indes fall mit deyner lincken In deyn messer In dy mitt vnd stich In durch deyn peyde peyn vnd hab dich woll mit dem ruck an In das er seynes messers nicht mach auß dem arme rucken vnd senck dich vorne nyder vnd stich Im Inn den pauch vnd zeuch den ortt offt wyder eyn In deyn lincke handt das er dich hintten mitt dem ortt deynes messers nicht pegreyffen mag vnd stupff In also eynes oder vyer mall behentlich In den pauch oder auff das gemecht vnd das stuck ist lecherlich zu treyben auff der schull etc |
||||||||
[506] |
Hold the Messer at the right leg Here the master speaks about certain elements that are called the lame elements, since with them one can strike one lame, as the elements are to be done to the joints of the arms and the hand. |
[105r.2] Das messer ze rechten peÿn halten Hie saget der meinster von yttlichen stucken die die lem stueck heyssen do mit man eynen haulben mag vnd die stuck sol man machen zu den glydern des mans arms vnd der hendt ~ ~ |
[93r.2] Daß messer zw rechtem payn haltt Hye sagtt der meyster von etlichen stücken dye dy lem stuck heyssen da mit man eynem lam hawen mag wann dy stuck soll man machen zw den glidren deß armß und der handt |
[184r] Das messer zu rechtem peyn hallt Hye sagtt der meyster von etlichen stucken dey dy lem stuck heyssen da mit man eynem lam hawen mag wanne dy stuck soll man machen zu den glidern des arme vnd der hant etc |
||||||||
[507] |
Then, if you want to do these elements, prepare to it this way: set your left foot forwards and hold your Messer on your right side and on your right leg, so that the point is against the man, and the thumb is above on the Messer, and stand as if in a guard. If he strikes at your opening to your left side, “simultaneously” step with your right foot well to his left side with a twofold step well out of the stroke to the weak of his right hand or arm, on the inside or where you have the closest way to the weak. |
[105r.3] Item wiltu dz stuck machen so schick dich also Setz dinen lincken fus fur vnd halt din messer vff diner rechten siten vnd vff dinem rechten peindt dz der ortt gegem dem man ste vnd der thüm oben sy vff dem messer also als in eyner hut haulbett er dir dan zu der ploß vff diner lincken siten Indes schrit mit dinen rechten fus woll [105v.1] vff sin lincke siten ein zwiffachen dritt wol vß dem haulb im zu der lem siner rechten hant oder arm Inlbendig oder wo du zu der lem am nesten hast etc ~ |
[93v.2] Item wiltu dyse stuck machen so schich dich dar eyn alzo secz deynen lincken fuß fuer und haltt deyn messer auff deyner rechten seytten und auff deyner rechten payn daß der ortt gegen dem man stee und der dawm oben sey auff dem messer und stee alzo alz yn eyner hütt hawt er dann dir zw der ploß auff deyn lincke seytten schreytt yndeß mit deynem rechten fuß woll auff seyn lincke seytten eynen czwiuachen tritt wol auß dem haw und haw ym zw der lem seyner rechten hand oder armen ynbendigß oder wo dw zw der lem amb negsten hast etc |
[184v.1] Item wiltu dyse stuck machen so schick dich dar eyn also Setz deynen lincken fuß fur vnd hallt deyn messer auff deyner rechten seytten vnd auff deynem rechten peyn das der/ortt gegen dem man stee vnd der dawm oben sey auff dem messer vnd stee also als In eyner hutt hawtt er dir danne zu der ploß auff deyner lincken seytten Indes schreytt mit deynem rechten fuß woll auff seyn lincken seytten Eyn zwiuachen tritt woll auß dem haw Im zu der lem seyner rechten handt oder arme Inbendigs oder wo du zu der lem am negsten hast als oben gemalt stett etc |
||||||||
[508] |
Then, assume the stance on your left side with your Messer, so that the point is on the ground and the thumb is below on the Messer, and the right edge is against the man, and stand with your right foot forwards. If he strikes at you from above to the head, do not displace but step with your left foot well to his right side well out of the stroke, and step with your left foot after the right one. “Simultaneously” strike to his other outer weak of his right arm. |
[93v.3] Item leg dich auff deyn lincke seytten mit [94r.1] deynem messer daß der ortt auff der erden sey und der dawm unter auff dem messer und dy rechtt schneyd gegen dem man stee und stee mit deynem rechten fuß fuer hawtt er denn auff dich oben zw dem kopff so versecz ym nicht sünder trit ym mit deynem lincken fuß wol auff seyn rechte seytten woll auß dem haw und schreyt mit dem rechten fuß dem lincken nach yndeß haw ym nach der andren aüßeren lem seyneß rechten armenß |
[184v.2] Item leg dich auff deyn lincke seytten mit deynem messer das der ortt auff der erden sey vnd der dawm vntten auf dem messer vnd dy recht schneyd stee gegen den man vnd stee mit deynem rechten füs fur hawtt er denne auff dich oben zu dem kopff so versetz Im nicht Sunder Tritt Im mit deynem lincken fuß woll auff seyn rechte seytten woll auß dem haw vnd schreytt mit deynem lincken fuß dem rechten nach Indes haw Im nach der andren Ewsren lem seynes rechten armeß als vntten gemalt stett etc |
|||||||||
[509] |
Then, notice, as you stand with the Messer on the ground, go up with the edge at his arm as in tribunal. |
[94r.2] ¶ Merck gleych alz dw mit dem messer auff der erden ligst alzo far geleych gerichteß auff mit der schneyden yn seyn armen etc |
[185r] Item merck gleych als du mit dem messer auff der erden ligst also far gerichtes gleych auff mit der schneyden In seyn arme etc |
|||||||||
[510] |
Then, stand with your left foot forwards and hold your Messer on your right side, so that the point is against the man, and the thumb is above on the Messer, and expose yourself with your left side. If he strikes at your opening, pull your left foot backwards as far as possible, and strike at his hand in the joint. |
[94r.3] Item stee mit deynem lincken fuß fuer und haltt deyn messer auff deyner rechten seytten daß der ortt gegen dem man stee und der dawm oben lig auff dem messer und gib dich ploß mit deyner lincken seytten hawtt er dir nach der plöß so czuck deynen lincken fuß zw ruck auff daß weytest und haw ym nach der hand yn daß glidt etc |
[185v] Item ste mit deynem lincken fuß fur vnd hallt deyn messer auff deyner rechten seytten das der ortt gegen dem man stee vnd der dawm oben lig auff dem messer vnd gib dich ploß mit deyner lincken seytten hawtt er dir dann nach der ploß so zuck deyn lincken fuß zu ruck auff das weytest vnd haw Im nach der handt In das glid etc |
|||||||||
[511] |
Then, stand with your right foot forwards and put your Messer on your left side with the point on the ground, so that the thumb is below or on the back of the Messer, and the sharp edge is against the man. If he strikes at your right side to the opening, pull your right foot on you well backwards aside from that strike tribunal-like as you are positioned with the Messer with the sharp edge on the outside at the hand in the joint. Then, assume the guard again on your right side, so that the left side is forwards. If he strikes at your left side, do as it is stated before, and strike again at his joint on the inside, and assume the guard again on your left side. This way you can defend against anyone for amusement or in serious combat. |
[94v.1] Item stee mit deynem rechten fuß für und leg deyn messer auff deyn lincke seytten mit dem ort auff dy erden daß der dawm unten sey oder leg yn auff den ruck deß messerß und dy scharpff schneyd sey gegen dem man hawtt er dir dan auff deyn rechte seytten nach der ploß so czuck den rechten fuß an dich wol zw ruck und peseytt auß und schlag yn gerichteß gleych alz dw gelegen pist mit dem messer mit der scharpffen schneyden außbendigß nach der hand yn daß glid und leg sich wyder yn daß leger auff deyner rechten seytten daß dy linck seyt vor stee hawtt er dir dann aber auff deyn lincke seytten So thüe alz vor geschriben oben ist und haw yn wyder yn daß gelenck ynbendigß und leg dich wyder yn daß leger auff deyner lincken seytten alzo magstu dich eyneß yetlichen weren yn schympff oder yn ernest etc |
[186r] Item stee mit deynem rechten fuß fur vnd leg deyn messer auff deyn lincke seytten mit dem ortt auff der erden das der dawmen vntten sey oder auff dem ruck des messers vnd dy [Sic] scarpff[95] schneyd sey gegen den man hawtt er dir auff deyn rechte seytten nach der plöß so zuck deynen rechten fuß an dich woll zu ruck beseyt auß dem schlag Im gerichtz gleych als du gelegen pist mit dem messer mit der scharpffen schneyden außbendigs nach der handt Indas glyd vnn leg dich wyder In das leger auff deyner rechten seytten das denne dy linck seytt vor stee hawtt er dir denne aber auff deyn lincke seytten so thu als vor geschriben ist vnd haw Im wyder In das gelenck Inbendigs vnn leg dich wyder In das leger auff deyner lincken seytten alzo magstu dich eynes ydlichen weren In schimpff oder ernste etc |
|||||||||
[512] |
Then, stand on your right side as before: if he strikes at your left side, step out of the stroke with your left foot well to his right, and as he strikes strike at his right arm on the outside to the weak. |
[105v.2] Item lig aber vff diner rechten als vor haut er dir noch diner lincken siten so schrit vß dem haulb mit dinem lincken fus woll vff sin rechte vnd in sinen haulb so haulb im noch sinem rechten arm vßwendig noch siner lem ~ |
[94v.2] Item lig aber auff deyner rechten seytten alz [95r.1] vor hawtt er dir den nach deyner lincken seytten So schreytt aüß dem haw mitt deynem lincken fuß wol aüff seyn rechte und yn seynem haw so haw ym nach seynem rechten armen außbendigß nach der lem etc |
[186v] Item lig aber auff deyner rechten seytten als vor hawtt er dir nach deyner lincken seytten so schreytt auß dem haw mit deynem lincken fuß woll auf seyn rechte vnd In seynen haw so haw Im nach seynem rechten arme außbendigs nach der lemm etc |
||||||||
[513] |
Then, if he thrusts at your face with the hanging point at whatever side you stand with the Messer, pull the left foot quickly backwards, or the right one-which one stands forward, should be pulled back. “Simultaneously” strike on the outside or inside at his hand, and fall a bit sideways with your body as you strike. |
[95r.2] Item stich er dir zw dem gesichtt mit hangattem ortt auff welcher seytten dw denn ligest mit dem messer so czeüg den lincken fuß zw rück oder den rechten welcher den fuer stet der selbig wird zw ruck gezogen yndeß haw ym außbendigß oder ynbendigß nach der hand und fal ym schlag eyn benig mit dem leyb peseytz aüß dem haw |
[187r] Item Sticht er dir zu dem gesicht mit hangendem ortt auff welcher seytten du denne ligest mit dem messer so zeuch den lincken fuß schnell zu ruck oder den rechten welchen den vor stett der selbig wer zu ruck gezogen Indes haw Im außbendigs oder Inbendigs nach der handt vnd fall Im schlag Eyn wenig mit dem leyp beseytt auß etc |
|||||||||
[514] |
Give notice shortly Here the master speaks about an element how one should strike at one’s hand or arm. You should understand it this way: if you want to do the element, you must be quite quick in binding, and do it this way: strike at his left side firmly from above a strike from above, and “simultaneously” as the Messers spark together above, strike quickly at his right hand or arm. |
[105v.3] Kürtz dich mell Hie saget der meinster von eynem stuck wie man eynem vff sin arm oder hant haulben sol vnd spricht kurtz dich mell etc Dz stuck mach also so müstu gar schnell sin am an pinden vnd thun im also haulb im zu siner lincken siten starck von oben in eyn ober haulb Indes die will die messer [106r.1] zu samen gluetzen oben so haulb im schnell vff sin rechten arm oder hant etc |
[95r.3] Kürcz dich mell [95v.1] Hye sagtt der meyster von eynem stuck wye man eynen auff seyn handt oder armen hawen sol und spricht kurcz dich mel etc Daß soltu alzo verstan wiltu daß stuck machen So soltu gar schnell seyn ym an pynden und thue ym alzo haw ym zw seyner lincken seytten starck von oben eyn eynen oberhaw yndeß dy weyl dy messer oben zwsammen kliczen So haw ym schnel auff seyn rechte seytten auff seyn rechten armen oder hand etc |
[187v] Kurtz dich mell Hye sagtt der meyster von eynem stuck wye man eynem auff seyn handt oder arme hawen solt das soltu also verstan so du das stuck machen willt so müstu gar schnell seyn Im an pinden vnd thu Im also haw Im zu seyner lincken seytten starck von oben eyn eynen ōberhaw Indes dy weyll dy messer zu sammen klitzen oben so haw Im schnell auff seyn rechte hantt oder arme außbendigs seyner rechten seytten etc |
||||||||
[515] |
If he wants to strike at the hand Here the master teaches a breaking against the element announced above, as one strikes one at the right hand, as it is written above, and speaks: At the right hand, etc. You should understand it this way: if he wants to strike at your right hand, you should break it this way-if he has bound you on your left side and wants to rapidly strike “simultaneously” at your hand or arm around at your right side, turn “simultaneously” your Messer against his one on your left side, so that the short edge is below and “simultaneously” thrust at his face and work further at the next opening. |
[106r.2] Noch der hant wil er haulben Hie lertt der meinster eyn bruch wider dz egemelt stuck so mã eym zu siner rechten hant haulbett als oben stet vnd spricht also noch der hend etc dz soltu also verston wil er dir noch diner rechten hant haulben dz soltu also brechen wan er dir hat angebünden vff diner lincken siten vnd wil dir Indes schnell noch diner rechten hantt oder arm haulben vmb zu diner rechten siten so wend Indes din messer gegem dem sinem vff sin lincke siten dz die kurtz schnid vnten sy oder ste Indes stich im zu dem gesicht vnd arbeit furbas zu der nesten ploß Sequitur textus |
[95v.2] Nach der hand wil er hawen Hye lertt der meyster eyn prüch wyder daß ee gemeltt stuck so man eynem zw seyner [96r.1] rechten hand hawett alz oben stet und spricht alzo nach der hand etc Daß soltu alzo verstan wil er dir nach deyner rechten hand hawen daß soltu alzo prechen wenn er dir hatt an gepünden auff deyner lincken seytten und will dir yndeß schnel nach deyner rechten hand oder armen hawen umb zw deyner rechten seytten So wendt yndeß deyn messer gegen dem seynen auff deyn lincke seytten daß dy kurcz schneyd unten stee yndeß stich ym zw dem gesichtt und erbeyt furpaß zw der negsten plöß etc Sequitur textus |
[188r] Nach der handt will er hawen Hye lertt der meyster eyn pruch wyder das Eegemellt stuck so man eynem zu seyner rechten handt hawett als oben stett vnd spricht also nach der handt etc Das soltu also verstan will er dir nach deyner rechten handt hawen das soltu also prechen wenne er dir hatt an gepunden auff deyner lincken seytten vnd will dir Indes schnell nach der handt oder arme hawen vmb zu deyner rechten seytten So wendt Indes deyn messer gegen dem seynen auff deyn lincke seytten das dy kurtz schneyd vntten stee Indes stich Im zu dem gesicht vnd erbeyt furpaß[96] zu der negsten ploß etc |
||||||||
[516] |
Shoot long from the hand You should understand it this way: if you stand with your left foot forwards and hold your Messer on your right side on the leg, so that the point is against the man and the thumb lies above on the flat of the Messer, and he strikes at your left side to the opening, do not displace, but as he strikes, move the point directly with the stretched arm firmly at his face. And as you shoot, step to his left side with your right foot. |
[106v.1] Lanck schus von hanten Wan du stost mit dinen lincken fus fur vnd hast din messer vff diner rechten siten an dem peyn also dz der ortt gegem dem man ste vnd der thum lig oben vff der flech des messers haulbt er dan zu vff din lincke siten noch der ploß so versetz im nicht sünder verschulb im die will im schlag ist gerad mit gestracktem arm starck indaß gesicht vnd im schus schrit im vff sin lincke siten mit dinen rechten fus ~ |
[96r.2] Lanck scheuß von hand Daß soltu alzo verstan wenn dw stest mit deynem lincken fuß fuer und hast deyn messer auff deyner rechten seytten an dem payn alzo daß der ortt gegen dem man stee und der dawm lig oben [96v.1] auff der flech deß messerß hawet er dir dan zw auff deyn lincke seytten nach der plöß So versecz ym nichtt Sünder scheüß ym dy weyl er ym schlag ist den ortt gerad mit gestracktem armen starck yn daß gesichtt Und ym schüß schreytt auff seyn lincke seytten mit deynem rechten fuß etc |
[188v] Lanck scheuß. von handt Das soltu also verstan wenne dü stest mit deynem lincken fuß fur vnd hast deyn messer auff deyner rechten seytten an dem peyn also das der ortt gegen dem man stee vnd der dawm lig oben auff der flech deß messers hawtt er denne zu auff deyn lincke seytten nach der ploß So versetz Im nicht sunder scheub Im mit gestracktem arme dy weill er Im schlag ist den ortt geradt mit gestracktem arme starck In das gesicht vnd Im schuß schreytt Im auff seyn lincke seytten mit deynem rechten fuß etc |
||||||||
[517] |
If he wants to shoot to the left from the arm Then, the master teaches a breaking against the shooting in and speaks: If he wants, etc. You should understand it this way: if he stands in the guard, so that he has his Messer on his right side on his right leg, so that the point is against the man, and as he shoots the point in at you, “simultaneously” shoot equally with him directly at his face, also with the stretched arm. “Simultaneously” wind your Messer on his one with the point to his face, so that the right edge is above and the left blunt one is below. And hold with your hilt well on your left side, and thrust at his face to his left side, and work “simultaneously.” |
[106v.2] Wil er vs arm schissen linck Daß in schuessen als oben gemelt ist lert der meinster eyn bruch dar wider etc Daß soltu also verstan stet er im dem leger also daß er sin messer vff siner rechten siten vff sinem rechten peind dz der ortt gegem dem man stee so er dir den ort In schusßt Indes schus gerad mit im in gerad in sin gesicht auch mit gestractem arm Indes wind din messer an dz sin den ortt zu dem gesicht also dz die rechte schnid [107r.1] oben ste vnd die linck stümpf vnten vnd halt mit dinem gehultz wol hinden vff din lincken siten vnd stich im zu dem gesicht siner lincken siten vnd arbeit Indes etc |
[96v.2] Wil er auß armen schyssen linck Hye lertt der meyster eyn prüch wyder daß eyn schyssen alz oben gemeltt ist und sprichtt will er auß etc Daß soltu alzo verstan stet er yn dem leger alzo daß er seyn messer hatt auff seyner rechten seytten auff seynem rechten payn daß der ortt gegen dem man stee So er dir den den ort eyn scheüst yndeß scheuß gerad mit ym eyn gerad zw seynem gesicht auch mit gestracktem armen yndeß wyndt [97r.1] deyn messer an daß seyn den ortt zw dem gesichtt alzo daß dy rechtt schneyd oben stee und dy stumpff unten und haltt mit deynem gehulcz wol hyn dan auff deyn lincke seytten und stich ym zw dem gesichtt seyner lincken seytten und erbayt yndeß etc Sequitur textus |
[189r] Will er auß arme schyssen linck Item wyder das eynschyssen lertt der meyster Eyn pruch dar wyder vnd spricht will er etc das soltu also verstan stett er In dem leger das er seyn messer hatt auff seyner rechten seytten auff seynem rechten peyn das der ortt gegen dem man stee vnd so er dir denne den ortt Eyn scheußt Indes scheuß geradt mit Im Eyn geradt zu seynem angesicht auch mit gestracktem arme Indes windt deyn messer an das seyn den ortt zu dem gesicht also das dy recht schneyd oben stee vnd dy linck stumpff vntten vnd hallt mit deynem gehultz woll hyn dan auff deyn lincke seytten vnd stich Im zu dem gesicht seyner lincken seytten vnd erbeytt Indes etc |
||||||||
[518] |
You should lengthen the stork’s beak Here the master teaches how one should do the element called the stork’s beak and do him this way: stand with your left foot forwards and hold your Messer on your right side at your right foot or above your right knee, so that the point is against the man, and expose yourself with your left side. If he strikes at the opening, pull your left foot well backwards as far as possible and raise your Messer with the stretched arm against his chest, and let him run into the point. |
[107r.2] Den storcken schnabel soltu erlengen Hie saget der meinster von eynem stuck dz do heist der storcken schnabel So thün im also ste mit dinen lincken fus fur vnd halt din messer vff diner rechten siten bÿ dinem rechten fus oder ob dinem rechten knue dz der ortt gegen dem man ste vnd geb dich ploß mit diner lincken siten haut er dir dan also noch der ploß so ruck din lincken fus wol zu ruck wol vff dz wuetest vnd hab din messer mit gestracktem arm gegem siner brust vnd loß in an din ort lauffen ~ |
[97r.2] Den storchschnabel soltü erlengen Hye sagtt der meyster wye man daß stuck daß do heysset der storch schnabel machen söl nw wiltu den storchschnabel machen So thue ym alzo stee mit deynem lincken fuß fuer und haltt deyn messer auff deyner rechten seytten bey deynem rechten fuß oder ob deynem rechten knye daß der ortt gegen dem man stee und gib dich ploß mit deyner lincken seytten hawtt er dir den alzo nach der plöß So ruck deynen lincken fuß [97v.1] wol zw ruck auff daß weytteß und heb deyn messer mit gestracktem armen gegen seyner prust und laß yn dar an laüffen |
[189v] Den storchschnabel soltu erlengen Hye sagtt der meyster wye man das stuck das do heysset der storchschnabel machen soll vnd thu Im also stee mit deynem lincken fuß fur vnd halt deyn messer auff deyner rechten seytten pey deynem rechten fuß oder ob deynem rechten kny das der ortt gegen dem man stee vnd gib dich ploß mit deyner lincken seytten hawtt er denne also nach der ploß so ruck deynen lincken fuß woll zu ruck auff das weyttest vnd heb deyn messer mit gestracktem arme gegen seyner prust vnd loß In an den ortt lauffen; |
||||||||
[519] |
Then, stand as before as he strikes at you a stroke from above and pull your left foot backwards, and go high with the Messer directly and with the stretched arm. And go with the point at the hand or arm. |
[107r.3] Item ste als vor so er vff dich haulbt aber eyn ober haulb so zuck din lincken fus zu ruck vnd far vff mit dem messer gerad vnd mit gestracktem arm vnd loß in darin schlagen noch der hant oder arm ~ |
[190r.1] Item stee als vor so er auff dich hawett aber eyn oberhaw vnd zeuch deynen lincken fuß zu ruck vnd far auff mit dem messer geradt vnd mit dem gestrackten arme vnd far Im mit dem ortt nach der handt oder arme vnd loß In dar eyn schlagen |
|||||||||
[520] |
Then, these elements are to be performed against these who run into and eagerly fight high and short, or do the hurling strokes against the man, and also leap with hurling strokes to the man. Thus, you have the stork’s beak and against which element or peculiarity you should do it, you are just taught. |
[107v.1] Item diß stuck gebrucht zu triben wider die die In lauffen vnd die gern hoch vechten vnd kurtz oder die verwerffen haulb gegem dem man machen vnd auch springen mit verworffen heulben zu dem man also hastu den storcken schnabell gegem wem du dz triben solt dz bestu Itz woll vnderrichtt etc |
[97v.2] daß stuck gehortt zw treyben wyder dye dy geren eyn lauffen und dy geren hoch vechten und kurcz oder wyder dy dye mit verworffen hewen zw dem man nohendt springen und alzo hastu wye man den storchschnabel sol machen etc Sequitur |
[190r.2] Item dyse stuck gehören zu treyben wyder dye dy do Ein lauffen vnd dy gerne hoch fechten vnd kurtz oder dy verborffen[97] hew gegen den man machen vnd auch springen mit verborffen hewen zu dem man also hastu den storch schnabel vnd gegen welchem stuck oder eygenschafft du das machen solt pist du yetznid vntter richt etc |
||||||||
[521] |
Who wants to run into you Here the master teaches an element against the running in and against the fighters who run in eagerly. Prepare against him this way: assume the guard of the Bastei and as he wants to run into you, hold your Messer with the point forwards and let him run into it. If he wants to displace the point and goes to your Messer, change through “simultaneously” to the next opening. |
[107v.2] Wer dir wil in louffen Hie lert der meinster eyn stuck wider dz Inlauffen vnd wider die fechter die gern In lauffen Schick dich gegem Im also leg dich in die hut der pasteÿn vnd wan er dir dan eyn lauffen will so halt din messer mit dem ort fur dich vnd loß in darin lauffen will er dan versetzen den ortt vnd fert noch dim messer so wechsl Indes durch zu der nesten ploß ~ |
[97v.3] Wer dir wil eyn laüffen Hye lertt der meyster eyn stuck wyder dye eyn lauffen und wyder dy vechter dy geren eyn lauffen schick dich gegen yn alzo leg dich yn dy hut der pasteyn und wenn er dir dan eyn lauffen [98r.1] wil so haltt deyn messer mit dem ortt fuerdich und lasß yn dar an laüffen wil er dan verseczen den ortt und fertt nach deynem messer So wechsel yndeß durch zw der negsten ploß |
[190v] Wer dir will eyn lauffen Hye lertt der meyster Eyn stuck wyder das eynlauffen vnd wyder dy vechtter dy gerne Ey lauffen schick dich Gegen In also leg dich In dy hutt der pasteyen vnd wenne er dir denne eyn lauffen will so hallt deyn messer mit dem ortt furdich vnd loß In dar an lauffen will er dir denne versetzen den ortt vnd fertt nach deynem messer so wechsel Indes durch zu der negsten ploß etc |
||||||||
[522] |
Then, assume the guard of the Luginsland. If he wants to run into you, go high with the arm and lower the point to his face or chest and push him away from you. |
[98r.2] Item leg dich yn dy hüt luginsland wen er dir den ein lauffen wil so far hoch auff mit dem armen und senck ym den ortt yn daß gesichtt oder auff dy prust und scheub yn alzo von dir |
[107v.3] Item leg dich in die hut luginßlant wan er dir dan in lauffen will so far hoch vff mit dem arm vnd senck im den ortt in dz gesicht oder vff die bruest vnd schüb In also von dir ~ |
[191r] Item leg dich In dy hutt luginslandt wenne dir denne eyn lauffen will so far hoch auff mit dem arme vnd stuck Im den ortt In das gesicht oder auff dy prust vnd scheub In also von dir etc |
||||||||
[523] |
Then, a note: in this element, as you go high with the Messer, you should wind the hilt under your arm well upwards in front of the head. Notice, if he falls to your point, strike at his head. |
[98r.3] ¶ Merck yn dysem stuck So dw mit dem messer auff ferst So soltu winden daß gehultcz unter deyn armen wol ubersich fuer daß haubt Merck feltt er dir den nach dem ortt So schlag ym zw dem haubtt |
[191v] Item nota In dysem stuck so du mit dem messer auff ferst so soltu winden das gehultz vntter deyn arme woll vbersich fur das hauptt Merck fellt er dir dann nach dem ortt so schlag In zu dem haubtt etc |
|||||||||
[524] |
If he wants to strike from the bind You should understand the text this way: if he has bound you on your Messer on your left side, and he wants to strike at your right side, “simultaneously” go high with the hilt under your arm and lower the point down and thrust at his neck or chest. |
[108r.1] Wil er vs dem pandt schlagen Hie merck den text den soltu also verstan Wan er dir angepunden hat an din messer vff diner lincken siten vnd er wil schlagen zu diner rechten siten Indes far vff mit dem gehultz vnder din arm vnd senck den ortt nider vnd stich im züm hals oder prust ~ |
[98r.4] Wil er auß dem pandt schlagen Den text soltu alzo verstan wenn er dir an gepünden hatt an deyn messer auff deyner lincken seytten und er wil schlagen zw deyner rechten seytten yndeß far auff mit dem gehulcz unter deyn armen und senck den ortt nyder und stich ym zw dem halz oder zw der prust |
[192r] Will er auß dem pandt schlagen Den textt soltu also verstan wenne er dir an gepunden hatt an deyn messer auff deyner lincken seytten vnd er will schlagen zu deyner rechten seytten Indes far auff mit dem gehultz vntter deyn arme vnd senck den ortt nyder vnd stich Im zu dem hals oder zu der prust etc |
||||||||
[525] |
Then, if he has bound you on your right side and wants to strike at your left, “simultaneously” do as before and set the point on him. |
[108r.2] alliud Item hat er dir angepünden vff din rechte siten vnd er wil dir schlagen noch diner rechten siten Indes thun als vor vnd setz im den ort an ~ ~ |
[98v.2] Item hatt er dir an gepunden auff deyn rechte seytten und wil er umb schlagen zw deyner lincken seytten yndeß thü alz vor und secz ym den ortt an |
[192v] Item hatt er dir an gepunden auff deyner rechten seytten vnd er will schlagen zu deyner rechten Indes thu als vor vnd setz Im den ortt an etc |
||||||||
[526] |
Then, a note: if something is being bound on you, you should always wind the point “simultaneously” at the face. If he displaces freely or in the crooked manner, you can always use the point from below or from above and defend the strokes or the thrusts with the point. |
[108r.3] Item waß vff dich wurtt gebunden dz du alwegen den ort zu dem gesicht solt winden er versetz frÿ oder krümbs so magstu alwegen den ort bruchen vnten oder oben schlag oder stech mit dem ort weren ~ |
[98v.3] Nota waß auff dich wirtt gepünden daß thü albegen yndeß den ortt zw dem gesichtt soltt wynden er versecz frey oder krümp So magstu albegen den ortt prauchen unten oder oben schleg oder stich mit dem ortt weren etc |
[193r] Item nota was auff dich wirtt gepunden das du albeg Indes den ortt zu dem gesicht solt winden er versetz frey oder krump So magstu albeg den ortt prauchen vntten oder oben schleg oder stich mitt dem ortt werenn |
||||||||
[527] |
The scorpion with its speed Here the propagator of the art speaks about an element that is called the scorpion, and perform the element this way: strike a stroke from above from your right shoulder at his left firmly at his head with the stretched arm. “Simultaneously” as you have struck, let the short edge of your Messer go down as if against your head, the short edge down on your left shoulder. “Simultaneously” thrust again at his face to the left side. If you have not hit him with the thrust, pull your Messer with the point downwards towards yourself, but this way so that the point is lowered to your left side, and strike with the short edge at his head to his right side. “Simultaneously” turn your hilt under your right arm and step with your left foot behind his right one, and strike the long edge at his head. And this element is called the scorpion. |
[108r.4] Scorpion mit siner kar Hie saget der meinster von eynen stuck heist des schorpion daß stuck tribe also haulb im von diner achsell zu siner lincken starck in zu dem haupt mit gestracketem arm in eynen ober haulb vnd Indes so du gehaulben hast so loß din kurtz schnid dines messers sencken glich gegem dem haupt die kurtz schnid vntz vff din lincke achsell Indes stich im wider zu dem gesicht siner lincken siten hastu in dan mit troffen mit dem stich so ruck din messer mit dem ort wider gegen dir doch dz der ort gesünck sÿ vff din lincke siten vnd schlag in mit der kurtzen schniden vff sin kopff siner rechten siten Indes wind din gehultz vnder den rechten arm vnd schrit mit dinem lincken fus hinder sinen rechten vnd schlag Im die lang schnid vber sin haupt daß ist der schorpion ~ |
[98v.4] Der scorpian mit seyner kar Hye sagtt der merer der künst von eynem stück daß heysset der scorpian und daß stuck treyb alzo haw ym von deyner rechten achsel zw seyner lincken starck eyn zw dem haubt mit gestracktem armen eyn oberhaw yndeß so dw gehawen hast so laß dy kurcz schneyd deyneß messerß sincken gleich gegen deym haubt dy kurcz schneyd uncz auff deyn lincke achsel yndeß stich ym wyder zw dem gesichtt seyner lincken seytten hastu ym denn nicht troffen mit dem stich So ruck deyn messer mit dem ort wyder gegen dir doch daß der ort gesenckt sey aüff deyn lincke seytten und schlag yn mit der [99v.1] kurczen schneyden auff seyn kopff seyner rechten seytten yndeß wendt deyn gehulcz unter deyn rechten armen und schreytt mit deynem lincken fuß hynter seynen rechten und schlag ym dy lang schneyd uber seyn haubt und daß stuck heysset der scorpian etc |
[193v] Scorpian mit seynem kar Hye sagtt der merer der kunst von eynem stuck das heysset der scorpian vnd das stuck treyb also haw Im von deyner rechten achsel zu seyner lincken starck eyn zu dem haubtt mit gestracktem arme eyn eynen oberhaw Indes so du gehawen hast so laß dy kurtz schneyd deynes messers sincken gleych gegen deynen haubtt dy kurtz schneyd vntten auff deyn lincke achselen Indes stich Im wider zu dem gesicht seyner lincken seytten hastu In danne nicht troffen mit dem stich so ruck deyn messer mitt dem ortt nyder gegen dir doch daß der ortt gesenckt sey auff deyn lincke seytten vnd schlag In mit der kurtzen schneyd auff seyn kopff seyner rechten seytten Indes wendt deyn gehultz vntter deyn rechten arme vnd schreytt mit deynem lincken fuß hintter seynen rechten vnd schlag Im dy langen schneyd vber seyn haubtt vnn daß stuck heyst der scorpian etc |
||||||||
[528] |
The basilisk with its face Now, do the basilisk this way: as you both have bound on the Messers and he is in the crooked displacement or so, lie on his Messer with the long edge and wait when he wants to strike at your right side. If he is close to you in the bind, notice, while he is striking, fall in the armed hand and thrust firmly at his left side at the upper peak at the ear. If he wants to displace and goes high with the Messer, go also high with your arm and thrust with the armed hand firmly at his chest. Then, if he wants to fall on your Messer with the displacement, strike the hilt of the Messer at his head. “Simultaneously” let your right hand again go from the middle of your Messer and grab your hilt again in the right hand and set the point again on his chest. Thus, you have done the basilisk. Thus, you have done the basilisk. |
[108v.2] Basiliscus mit sinen gesicht [109r.1] Hie saget der meinster stück heist der basiliscüs So ir beyd an gepünden habent an die messer vnd er ist in der krümen versatzüng oder sünst so leg dich vff sin messer mit der langen oder scharpffen schniden vnd wart wan er mit der zu diner rechten siten schlagen Will so er dan nohet bÿ dir ist Indes fal zu gewoppetenter hantt vnd stich starck vff syn lincke siten zu der obern zÿnnen zu den oren so er dan will versetzen vnd fert vff mit dem messer so far hoch vff mit dem arm vnd stich im mit gewoppenter hant starck vff sin brust will er dan vff din messer fallen mit der versatzung so schlag Im dz gehultz des messers vber sin kopf Indes din rechte hant wider von der mit des messers vnd begriff din gehultz wider in die recht hant vnd setz im den ort wider in brust Also hastu den basilisc[us] gemacht vnd stuck soltu triben gegen den meinstern dÿ nohent by dem man vechten ~ |
[99v.2] Der wbasiliscus mit seym gesicht Hye sagtt der meyster eyn stuck daß der basiliscus heyst Daß soltu alzo machen So ir peyde an gepunden habtt an dy messer und er ist yn der krummen versaczung oder suest So leg dich auff seyn messer mit der langen oder scharpffen schneyden und wartt wan er dir zw [100r.1] deyner rechten seytten schlagen wil So er dan nohend bey dir ist ym pandt merck dy weyl er ym schlag ist yndeß fal zw gewappender handt und stich ym starck auff seyn lincke seytten zw der öberen czynnen zw dem oren So er denn will verseczen und fertt auff mit dem messer so far hoch auff mit dem armen und stich yn mit geboppender hand starck auff seyn prust will er den auff deyn messer fallen mit der versaczung So schlag ym daß gehulcz deß messerß uber seyn kopff yndeß laß deyn rechte hand wyder von der mitt deß messerß und pegreüff deyn gehulcz wyder yn dy rechte hand und secz ym den ortt wyder yn dy prust Alzo hastu den wasiliscum gemacht und daß stuck soltu treyben gegen den meystren dy nohend bey dem man vechten |
[194r] Wasilistus mit seynem gesicht Nu den wasilistun mach also so Ir payde an gepunden habt an dy messer vnn er ist In der krummen versatzung oder pist so leg dich auff seyn messer mit der langen schneyden vnd wartt wenne er dir zu deyner rechten seytten schlagen will so er denne nohent bey dir ist Im pandt Merck dy weyl er Im schlag ist so fall zu gewappender handt vnd stich starck auff seyn lincken seytten zu den oberen zynnen zu den oren so er denn versetzen will vnd fertt auff mit dem messer so far hoch auff mit deynem arme vnd stich In mit gewappender handt starck auff seyn prust will er denne auff deyn messer fallen mit der versatzung so schlag Im das gehultz des messers auff seyn kopff Indes loß deyn rechte handt wyder von der mitt des messers vnd greyff deyn gehultz wyder In dy rechten handt vnd setz Im Im den ortt wyder In dy prust also hastu den wasilistun gemacht also hastu den wasilistun gemacht etc |
||||||||
[529] |
The pommel with its way Here the masters speaks about an element and speaks: The pommel with, etc. You should understand it this way: wind straight at his Messer and wait until he wants to strike with the crooked stroke to your left side, as you should stand with the left foot forwards. While he strikes to your left side, “simultaneously” fall in the armed hand and step with your right foot well to his right and hit him with the hilt of the pommel to his right ear. “Simultaneously” twitch the point with the armed hand to your left side sideways and set the point at his chest. If he displaces, work “simultaneously” with the striking point outside to the head, or go with the hilt from above on the inside above his hand and do the Messer-taking. |
[109r.2] Klotz mit siner wartt Hie sagt der meinster von eynen stueck vnd spricht der klotz mit siner etc Daß soltu also verstan wind im gerad vff sin messer vnd wartt wan er mit der krume wil haulben zu diner l/ siten wan mit dem lincken fus soltu versten die wiell er dir dan haulbt zu diner lincken siten Indes fal zu gewoppent hant vnd schrit mit dinem rechten fus wol vff sin rechten fus vnd stos im mit dem gehultz des messers zu sinem rechten oren Indes zuck mit gewoppenter hant den ort gegen siner lincken siten besitz ab vnd setz im den ortt in die prust versetz er dan so schag indes den schlagenden ort zu dem kopf vssen oder far mit dem gehultz oben vber sin hant vnd mach daß messer nemen ~ |
[100r.2] Der klocz mit seyner wartt Hye sagtt der meyster von eynem stuck und spricht der klocz mit etc Daß soltu alzo verstan wynd ym gerad auff seyn messer und wartt wenn er mit der krum wil hawen zw deyner lincken seytten wann mit dem lincken fuß soltu vor sten dy weyl er dir dan hawet zw deyner lincken seytten yndeß fal zw gewoppender hand und schreyt mitt deynem rechten fuß wol zw seynem rechten und stoß yn mit dem gehulcz deß messerß zw seynem rechten oren yndeß czuck mit gewoppender hand den ortt gegen deyner lincken seytten peseytz ab und secz ym den ortt yn dy prust verseczt er denn So erbeyt yndeß mit dem [101r.1] schlagenden ortt zw dem kopff oder far mit dem gehulcz oben ynbendigß ober seyn hand und mach daß messer nemen etc Sequitur textus |
[194v] Klotz mit seyner wartt Hye sagtt der meyster von eynem stuck vnd spricht der klotz mit etc Das soltu also verstan wind Im gerad auff seyn messer vnd wartt wenne er mit der krum will hawen zu deyner lincken seytten wanne mit dem lincken fuß soltu vor sten weyll er dir denne hawett zu deyner lincken seytten Indes fall zu gewappender handt vnd schreytt mit deynem rechten fuß woll zu seynem rechten fuß vnd stoß In mit dem gehultz des messers zu seynen rechten oren Indes zuck mit gewappender handt den ortt gegen deyner lincken seytten peseyt ab vnd setz Im den ortt In dy prust versetz er denne So erbeyt Indes mit dem schlagnden ortt zu dem kopff aussen oder far mitt dem gehultz oben vber seyn handt vnd mach das messer nemen etc |
||||||||
[530] |
In the armed way with the pommel Here the master says how you should hit the man at the chest with the pommel, that is with the hilt. And do it this way: if he strikes at your ear or at your head to your right or left side, fall in the armed hand and lower the point to his chest. “Simultaneously” work with the blade of your Messer above firmly to the head or go with the armed hand sideways aside and set it at his face or chest. |
[109v.2] Gewoppent mit dem klotz Hie saget der meinster wie du mit dem klotz dz ist mit dem gehultz soltu den man in die brust [110r.1] stossen vnd thün im also Schlecht er dir zu den oren oder zu dem kopf diner rechten oder lincken siten so fal zu gewoppenter hant vnd senck im dz gehultz vff sin brust Indes arbeit mit der klingen dines messers oben starck zu dem kopff oder far mit gewoppenter hant besitz ab vnd setz im den ortt in dz gesicht oder brust ~ |
[101r.2] Bewoppend mit dem kloß Hye sagtt der meyster wye dw mit dem kloß daß ist mit dem gehülcz solt den man yn dy prust stossen und thue ym alzo schlecht er dir zw dem oren oder zw dem kopff deyner rechten oder lincken seytten So fal zw gewoppender hand und senck ym daß gehulcz auff seyn prust yndeß erbeyt mit der klyngen [101v.1] deyneß messerß oben starck zw dem hawbt oder far mit geboppendem ortt peseytz ab und secz ym den yn daß gesichtt oder yn dy prust |
[195r] Gewappend mit dem kloß Hye sagtt der meyster wye du mit dem cloß daß ist mit dem gehultz soltu den man In dy prust stossen vnd thu Im also Schlecht er dir zu den oren oder zu dem kopff deyner rechten oder lincken seytten so fall zu gewappender handt vnd senck Im das gehultz auf seyn prust Indes erbeytt mit der klingen deynes messers oben starck zu dem haubtt oder far mit gewappender handt beseytt ab vnd setz Im den In das gesicht oder prüst etc |
||||||||
[531] |
Then, if he strikes at your right side so that you both are close at each other, “simultaneously” as he strikes at your right side, go high with the arm and set the point on his chest with the armed hand. If you want, you can go with the point under his hilt, and you can set the point on his face with the armed hand. |
[110r.2] Item schlecht er dir zu diner rechten siten so ir beid sint nohe byeÿnander In dem so er schlicht zu diner rechten siten so far vff mit dem arm vnd setz im den ortt in sin brust mit gewoppenter hant wiltu dan so magstu mit dem ort sechtzen In dz gesicht ~ |
[101v.2] Item schlechtt er dir zw deyner rechten seytten so ir ped seyt nohend bey eynander yn dem so er schlecht zw deyner rechten seytten so far auff mit dem armen und secz ym den ortt yn seyn prust mit gewoppender hand wiltu den so magstu mit dem ortt faren unter seyn gehulcz und magst ym den ortt seczen yn daß gesicht gewoppend etc |
[195v] Item schlett er dir zu deyner rechten seytten so ir payd seyt nahent pey eyn ander In dem so er schlecht zu deyner rechten seytten so far auff mit dem arme vnd setz Im den ortt In seyn prust mitt gewappender handt wiltu denne so magstu mitt dem ortt forne vntter seyn gehultz vnd magst Im den ortt setzen In das gesicht Gewappendt etc |
||||||||
[532] |
Then, if he is in the bind with you and wants to strike at your right side at the upper peak, “simultaneously” go at his chest with the armed point, that is with the armed hand. “Simultaneously” go with your right arm over his Messer and with the front part [of your Messer], also with the armed hand, go between his hilt or the hand and push his Messer with your left elbow to your right side, in that way you take his Messer. |
[110r.3] Item ligt er im band mit dir vnd wil dir aber schlagen zu diner rechten siten zu der obern zÿnnen Indes far vff sin brust mit gewoppenter ortt dz ist mit gewoppenter hant Indes far mit dinem rechten arm vber sin messer vnd mit dem fordern teill auch gewoppent far im zwuschen dz gehultz der hant vnd stos sin messer mit dinem lincken elnbogen vff din rechte siten so nÿmbstu im sin messer ~ ~ |
[101v.3] Item ligtt er ym pandt mit dir und wil dir aber schlagen zw deyner rechten seytten zw der oberen czynnen yndeß far aber auff seyn prust gewoppend mitt dem ortt daß ist mit gewoppender hand yndeß far mit deynem rechten armen uber seyn messer und mit dem fodren teyl deß messerß und auch gewoppend far ym [102r.1] czwischen daß gehultcz und dy hand oder stoß daß seyn messer mit deynem lincken olpogen auff deyn rechte seytten so nymbstu ym daß messer etc |
[196r] Item ligtt er Im pandt mit dir vnd will dir aber schlagen zu deyner rechten seytten zu den obren zynnen Indes far auff mit deynen rechten seyn prust mit gewappendem ortt das ist mit gewappender handt Indes far mit deynem rechten arme vber seyn messer vnd mitt dem fodren teyll auch gewappend far Im zwischen das gehultz oder handt vnd stoß seyn messer mit deynem lincken olpogen auff deyn rechte seytten So nymbstu Im das messer etc |
||||||||
[533] Then, there are many elements in the Messer which are not common, as armed elements and certain thrustings over, thrustings through and free fighting elements about which I say nothing. |
[110r.4] Item vil stueck sint im messer die nit gemeyn sin als yttlich gewoppent vber stich durch stechen frÿ vechten stuck do von ich nutz sage etc Sequitur textus |
[102r.2] Item vil stuck seyn ym messer dy nit nicht gemeyn seyn alz gewappende stuck und etliche uber stechen durchstechen und frey vechterische stuck da von ich nichtz sag etc |
||||||||||
[534] |
If he wants to hit Here the master states a breaking if one wants to hit the other with the pommel or with the hilt at the chest and speaks: If he wants with the hilt, etc. |
[110v.1] Wil er mit klossen Hie saget der meinster eyn bruch so man eynem mit dem klotz oder gehultz in die brust stossen Vnd spricht also wil er mit kossen etc~ |
[102r.3] Wil er mit klossen Hye sagtt der meyster eyn pruch so man eynem mit dem kloß oder mit dem gehulcz yn dy prust wil stossen und sprichtt alzo will er mitt etc |
[196v.1] Will er mit klossen Hye sagtt der meyster ey prüch So man eynen mit dem kloß oder mit dem gehultz In dy prust will stossen vnd spricht also will er mit dem klossen etc |
||||||||
[535] |
Then, do the breaking this way: if you want to strike at his right ear, and “simultaneously” he goes with the armed hand with the hilt at your chest, “simultaneously” grab forwards with your left hand at his hilt behind his right hand and hit with your right arm firmly the blade of his Messer and step with your right foot to his right one and push firmly towards your left side. |
[110v.2] Den bruch mach also Wiltu schlagen zu sinem rechten oren Indes fert er dir zu der gewoppenter hant mit dem gehultz vff din brust Indes griff mit diner lincken hant forn an sin gehultz hinten an sin rechte hant vnd stos mit dinem rechten arm starck an sins messers klingen vnd schrit mit dinem rechten fus zu sinem rechten vnd stos starck vff din lincke siten ~ ~ |
[102v.1] Item den prüch mach alzo wiltu schlagen zw seynem rechten oren yndeß fertt er dir zw gewoppender hand mit dem gehulcz auff deyn prust yndeß greuff mit deyner lincken hand foren an seyn gehulcz hynter seyn rechte hand und stoß mit deynem rechten armen foren mit dem schafft starck an seyneß messerß klyngen und schreyt mit deynem rechten fuß zw seynem rechten und stoß starck auff deyn lincke seytten etc |
[196v.2] Item den pruch mach also wiltu schlagen zu seynen rechten oren Indes fertt er dir zu gewappender hantt mit dem gehultz auff deyn prust Indes greyff mit deyner lincken handt forne an seyn gehultz hintter seyn rechte handt vnd stoß mit deynem rechten arme starck an seynes messers klingen vnd schreytt mit deynem rechten fuß zu seynem rechten vnd stoß starck auff deyn lincke seytten etc |
||||||||
[536] |
Then, if you hit him towards your left side and he displaces it with the hanging point, “simultaneously” wind with your Messer with the mutating on his Messer at his chest or face. |
[197r] Item schlechstu Im zu deyner lincken seytten vnd er versetz das mit hangendem ortt Indes windt Im mit deynem messer mit dem mutiren an seynem messer zu seyner prust oder an gesicht etc |
||||||||||
[537] |
Then, if you strike at one’s left ear with the Entrüsthau and he goes with the hilt with the armed hand to your chest, “simultaneously” go with your hilt against his right side over the blade of his Messer and grab with your left hand at his hilt firmly downwards at your right side. And with your left hand push firmly from you to your right side downwards, and with your left hand push firmly from you to your right side, in that way you take his Messer again. |
[110v.3] Item schlestu eynem zu sinem lincken oren mit dem entrusch haulb vnd er fert dir mit dem gehultz gewoppent vff sin brust Indes far mit dinem gehultz gegen siner rechten siten vber sins messers klingen vnd griff mit diner lincken hant in sin gehultz zu siner rechten hant vnd riß mit dem gehultz starck in die recht siten nider vnd mit diner lincken hant schub starck von dir vff din rechte siten |
[102v.2] Item schlecht dw eynem zw seynem lincken oren mit dem entrusthaw und er fertt dir mit dem gehulcz gewoppend auff deyn prust yndeß far mit deym gehulcz gegen seyner rechten seytten uber seyneß messerß klyngen und greuff mitt deyner lincken hand yn seyn gehulcz zw seyner rechten hand und reyß mitt deym gehulcz starck yn deyn rechte seytten nyder und mit deyner lincken hand scheub starck [103r.1] von dir auff deyn rechte seytten So nymbstu ym aber daß messer etc |
[197v] Item schlegstu eynem zu seynen lincken oren mit dem entrusthaw vnd er fertt dir mit dem gehultz gewappendt auff deyn prust Indes far mit deym gehultz gegen seyner rechten seytten vber seyns messers klingen vnd greyff mit deyner lincken handt In seyn gehultz starck In deyn rechte seytten nyder vnd mitt deyner lincken handt scheub starck von dir auff deyn rechte seytten nyder vnd mit deyner lincken handt scheub starck von dir auff deyn rechte seytten so nymbstu Im aber das messer etc |
||||||||
[538] Then, also break the two elements, as he sets the point at your chest to your both sides, break them with these two elements or breakings. You may also drop your Messer and do the breakings depicted before with both hands. The text follows. |
[111r.1] Item Also brich auch die zwei stuck so er dir den ortt setz vff din brust in die beide siten so briche die mit dissen zwichen stucken du magst auch din messer fallen loßen vnd mit beiden henden die egemelt bruech machen ~ |
[103r.2] Item alzo prich auch dy czwey stuck So er dir den ortt seczt yn deyn prust auff deyn ped seytten So prich sy mit dysen czweyen stucken oder pruchen dw magst auch deyn messer fallen lassen und mit peyden henden dy ee gemelten pruch machen etc Sequitur textus |
||||||||||
[539] |
There are four hangings Here the master states how you should do the four hangings in the Messer and how they are called. Thus, he calls each particular one with the name, one after the other. |
[111r.2] Vier sint der hengen Hie lert der meinster wie du die vier hengen machen solt im messer vnd wie die genant sÿ also endet sich eyn ÿttlichs mit namen eyns nach dem andern ~ |
[103r.3] Vyer seyn der hengen Hye lertt der meyser wye dw dy vyer hengen machen söllt ym messer und wye dy genant seyn alzo nendt er eyn yetlichß [103v.1] mit seynem namen eyneß nach dem anderen etc |
[198r] Vyer seyn der hengen Hye sagtt der meyster wye du dy vyer hengen machen solt Im messer vnd wye dy genant seyn also nendt er eyn ydlichs mit namen eyns nach dem anderen; |
||||||||
[540] |
Then, the first one is called the Eber from both sides, and the other the Stier from both sides. And you should be quite well-trained in them, so that you could do the work from them quite well. You should also know that there are four hangings, the two from below and two from above, and how they are called, you have heard above. |
[111r.3] Item der erst heisset der eber von beiden siten Daß ander der stier auch von beiden siten vnd darin soltu gar woll geubet sin also dz du die arbeit daruß gar wol triben magst Auch soltu wissen dz vier hengen sint zwien vnten vnd zwein oben vnd wie sie genant sint hastu oben gehortt |
[103v.2] Item daß erst heyst der eber von peyden seytten daß ander der styer auch von peyden seytten und dar ynnen soltu gar wol geuebt seyn alzo daß dw dy erbeyt dar auß gar recht treyben mügst auch soltu wyssen daß vyer henden seyn czwey unten czwey oben und wye sy genant seyn hastu oben gehort |
[198v.1] Item das erst heyst der eber von peyden seytten Das ander der stir auch von payden seytten vnd dar Innen soltu gar woll ge vbett seyn vnd also das du erbeyt dar auß gar wol treyben mügst auch soltu wissen das vyer hengen seyn zway vntten vnd zway oben vnd wye sy genandt seyn hastu oben gehortt |
||||||||
[541] |
Now, from the four hangings you should bring eight windings and you should consider these eight windings, so that you should do and deliver from particular windings a thrust, a stroke and a cut. These are the four windings. |
[111r.4] Nün vß den vier hengen soltu acht winden pringen vnd die selbigen acht winden soltu also wegen dz du vß ytlichen winden solt machen stich schnit etc |
[103v.3] ¶ nw aüß den vyer hengen soltu pryngen achtt wynden und dy selben acht wynden soltu furpaß alzo wegen daß dw auß yetlichen wynden solt machen und treyben eyn eyn stich und eyn schynt daß seyn dy vor geschriben vyer vynden etc |
[198v.2] Nun auß den vyer hengen soltu ach winden pringen vnd dy selbigen acht winden soltu also wegen Das du auß ydlichem winden solt machen vnd treyben eyn stich vnd eyn haw vnd eyn schnytt das seyn dy vyer ob geschriben winden etc |
||||||||
[542] |
Then, notice now how you should perform eight windings from the four hangings. The first upper hanging has two windings and perform it this way: if you come with the Zufechten to him, stand from your right side in the Stier. If he strikes from above at your left side, wind against his stroke, the short edge on his Messer, again to the Stier. If he sets the thrust aside from his left side, remain on the Messer and wind again to your right side again to the Stier, with the flat on his Messer, and thrust from above at his face. This is one hanging from the right side with two windings on his Messer. |
[111v.2] Item Nu merck wie du vß den vier hengen solt triben acht winden dz erst vber hengen hat zweÿ winden vnd trib dz also wan du mit dem zu vechten zu im kümpst so ste von diner rechten siten in den stier schlecht er dan oben in zu diner lincken siten so wind gegen sinem haulb die kurtz schnid gegen sinem messer wider in stier dz ist eyn winden setz er den stich ab von siner lincken siten so plib am messer vnd wind wider vff din rechte siten in den stier die flech an sin messer vnd schlag in oben zu dem gesicht dz ist eyn hengen von der rechten siten mit zwien winden an sin messer ~ |
[103v.4] Item hye merck wye dw aüß den vyer hengen solt treyben acht wynden daß erst uben hengen hatt czwey wynden und treyb daß alzo wenn dw mit dem zw vechten zw ym kumbst so ste von deyner rechten seytten [104r.1] yn den stiren schlechtt er den oben eyn zw deyner lincken seytten so wyndt gegen seynem haw dy kurcz schneyden an seyn messer wyder yn den stiren daß ist eyn bynden seczt er den den stich ab von seyner lincken seytten so peleyb am messer und windt wyder auff deyn rechte seytten wyder yn den stiren dy flech an seyn messer und stich ym oben zw dem gesicht daß ist eyn hengen von der rechten seytten mit czwayen wynden an seynem messer etc |
[199r] Item Nu merck wye du auß den vyer hengen solt treyben acht winden das erst vberhengen hatt zway winden vnd treyb das also wenne du mit dem zuuechten zu Im kumst so stee von deyner rechten seytten In dem Stiren schlecht er denn oben eyn zu deyner lincken seytten so windt gegen seynen haw dy kurtz schneyd an seyn messer wyder In den Stiren daß ist eyn winden Setz er denne den stich ab von seyner lincken seytten so pleyb am messer vnd windt wyder auf deyn rechte seytten wyder In den stiren dy flech an seyn messer vnd stich Im oben zu dem gesicht das ist eyn hengen von der rechten seytten mit zwayen winden an seynem messer etc |
||||||||
[543] |
Then, another upper hanging with two windings. Do it this way: if you come to him with the Zufechten, stand from your left side in the Stier. If he strikes from above at your right side, wind against his stroke, the long edge on his Messer, and thrust at his face from above-this is another winding. If he sets the thrust aside against your right side, remain on his Messer and wind again to your left side, again in the Stier, with the flat on his Messer. And thrust from above at his face to his left side, so that the blunt edge is below while thrusting. Thus, you have two windings on his Messer. |
[111v.1] Item Aber ein ander hengen mit zwihen winden dz tribe also Wan du mit dem zubechten zu Im kümpst so ste von diner lincken siten in den stier haut er dan oben zu siner rechten siten so wind gegem sinem haulb die scharff schniden an sin messer vnd stich im oben zu dem gesicht dz ist aber eyn winden Setz er dan den stich abe gegen siner rechten siten so plib im am messer vnd wind wider vff din lincke siten wider in den stier die flech an sin messer vnd stich im oben zu dem gesicht von diner lincken siten dz in dem stich die stümpf schnid vnten ste also hastu zweÿ winden an sinem messer ~ |
[104r.2] Item eyn ander oberhengen mit czweyen wynden daß treyb alzo wenn dw mit dem zw vechten zw ym kumbst so stee von deyner lincken seytten yn den stiren hawt er dan oben zw deyner rechten seytten so wyndt gegen seynem haw dy scharpffen schneyden an seyn messer und stich ym oben zw dem gesicht daß ist aber eyn wynden Seczt er den stich den ab gegen seyner rechten seytten so pleyb ym [104v.1] am messer und wynd wyder auff deyn lincke seytten wyder yn den stiren dy flech an seyn messer daß dy stümpff schneyd unten stee und stich ym oben eyn zw dem gesicht von seyner lincken seytten aber mit czwayen wynden an seynem messer etc |
[198v.3] Item Eyn ander oberhengen mit zwayen winden das treyb also wenne du mit dem zuuechten zu Im kumbst so stee von deyner lincken seytten In dem stiren hawtt er dir denne oben zu deyner rechten seytten so windt gegen seynen haw dy lang schneyden an seyn messer vnd stich Im oben eyn zu dem gesicht das ist aber eyn wynden setzt er denne den stich ab gegen deyner rechten seytten so pleyb Im am messer vnd windt wyder auff deyn lincke seytten wyder In den stiren dy flech an seyn messer vnd stich Im oben zu dem gesicht seyner lincken seytten das In dem stich dy stumpff schneyd vntten stee also hastu zway winden an seynem messer wye oben gemalt stett etc |
||||||||
[544] |
Then, you should also know that you should also perform the four windings with all their attacks from the two lower hangings, that is the Eber from both sides. And as often as you wind, think in every particular winding about the stroke, the thrust and the cut. Thus, from the eight windings there come twenty-four and from which and against which element and against which strokes, thrusts or cuts you should deliver the stroke and the cut, you have been to a good extent taught before. |
[111v.3] Item du solt auch wissen dz vß den vnter zwiehen [112r.1] hengen dz ist der eber von beiden siten triben solt auch vier winden mit allen iren geferten als vß dem eber dz sint die acht winden vnd als vff du windest gedenck in yttlichem winden an den haulb an den stich an den schnit also kümen vß den acht winden xxiiij vnd vß wellichem winden vnd gegen wellichen stucken haulben stichen schnitten den du dust dz bistu zu gutter mossen vor wol vnderrichtt ~ |
[104v.2] Item dw solt auch nw wyssen daß auß den unteren czweyen hengen daß ist der eber von peyden seytten auch soltu treyben vyer wynder mit allen iren geferten alz auß den oberen daß seyn dy achtt wynden und alz offt dw wyndest So gedenck yn eynem yetlichem wynden an den haw an den stich und an den schnydt alzo kumen aüß den achtt wynden vyer und czweynczig und gegen welchen stücken und gegen welchen hewen oder schnytten oder stichen dw den haw und den stich und den schnydt treyben soltt daß pistü vor czw gutter maß wol unterricht etc Sequitur textus |
[199v] Item du solt auch wissen das auß den untren zweyen hengen das ist der Eber von payden seytten treyben solt auch vyer hengen auch vyer winden mit allen Iren gefertten als auß den obren das seyn dy ach winden vnd als offt du windest so gedenck In Eynen ydlichen winden an den haw an den stich vnd an den schnydt also kummen auß den acht wynden vyerundzwaynzig vnd auß welchen vnd gegen welchen stucken vnd gegen welchen hewen stichen oder schnytten du den haw vnd den schnytt treyben solt das pistu zu gutter maß vor vntterrich werden etc |
||||||||
[545] Direct the point in the Bastei According to the meaning of the text there is that you should defend yourself from the long point in the Messer from the guard of the Bastei against those who fight high and run in with the arm and the Messer high and against the foolish who leap from one side to the other and dance and do the villain strokes above the head to the man. |
[112r.2] Ort in die pasteyn richt Die meÿnung dex text ist dz du dich weren solt vß dem langen ort im messer vß der hut pasteyn gegen den die hoch fechten vnd hoch mit den armen vnd messer in lauffen vnd vff die tümeler die do von eyner siten vff die ander springen vnd verworffen haulb vber dz haupt machen vor dem man ~ |
[105r.1] Den ortt yn dy pasteyn richtt Secundum dy maynung deß textz ist daß dw dich weren solt auß dem langen ortt ym messer aüß der hutt pasteyn gegen den dy do hoch vechten und hoch mit dem armen und messer eyn lauffen und wyder dy dumber dy von eyner seytten zw der anderen seytten springen und tanczen und dy verborffen hew uber daß hawbt machen zw dem man |
||||||||||
[546] |
Then, if you want to defend yourself from the Bastei, do him this way: if you come surely to him with the Zufechten, put your left foot forwards and hold your Messer with the point towards the ground as you have been well taught. If he comes against you as it is stated above, go with your stretched arm high with the point at his face or chest. If you have hit him with the point and he gets frightened and twitches the body or head back, fall “simultaneously” again with your Messer in the guard of the Bastei, and pull your right foot again back. And do not let bring yourself from the guard of the Bastei without harm and do it this way also on your left side. |
[112r.3] Item Wiltu dich vß der pasteÿn weren so thün im also wan du mit zuvechten zu im kumpst so setz dinen lincken fus for vnd halt din messer mit dem ortt gegen der erden als du woll vndericht pist kümpt er dir engegen als oben geschriben ist so far mit dinem gestrackte arm [112v.1] vff mit dem ortt im zu sinem gesicht oder in brust hastu in troffen mit dem ortt vnd er herschrickt vnd zuck den lib oder kopff zu rueck Indes fal wider herab mit dinem messer in die haut der pasteyn vnd zuck dinen rechten fus wider zu ruck vnd loß dich an schaden nicht vß der hut pasteyn bringen also thün im auch vß der lincken siten ~ |
[105r.2] Item wiltü dich aüß der pasteyn weren So thu ym alzo wenn dw mit dem zwvechten schir zw ym kumbst So secz deynen lincken fuß fuer und haltt deyn [105v.1] messer mit dem ortt auff der erden alz dw wol unterricht pist kümbtt er dir engegen alz oben geschriben ist so far mit gestracktem armen auff mit dem ortt ym yn seyn gesichtt etc oder yn dy prust hastu yn getroffen mit dem ortt und er erschrickt und czückt den kopff oder leyb zw ruck oder hyntersich yndeß fall wyder her ab mit deynem messer yn dy hut der pasteyn und czeüg deynen rechten fuß wyder zw ruck und laß dich an scheden nicht auß der hut der pasteyn pringen und alzo thu ym auch auff deynen lincken seytten etc |
[200r] Item will du dich auß der pastey weren so thu Im also wenne du mit dem zuuechten schir zu Im kumbst so setz deynen lincken fuß fur vnd hallt deyn messer mit dem ort gegen der erden als du woll vnterricht pist kumptt er dir denne Entgegen als oben geschriben ist so far mit deynem gestrackten arme auff mit dem ortt Im zu seynem gesicht oder In dy prust hastu In getroffen mit dem ortt vnd er erschrickt vnd zuckt den leyb oder kopff zu ruck Indes fall wyder her ab mit deynem messer In dy hutt der pasteyn vnd zeuch deynen rechten fuß wyder zu ruck vnd loß dich an schaden nit auß der hutt pastey pringen vnd also thu Im auch auff deyner lincken seytten etc |
||||||||
[547] |
Then, if you stand in the guard of the Bastei, be it on the left or the right side, and you see that he wants to “crook” to it with the Messer or fall on it otherwise, change through below as you know well. |
[112v.2] alliud Item ligstu in der hut pasteyn eß sÿ vff der rechten oder vff der lincken siten Sichstu dz er darüff wil kümen mit dem messer oder sünst daruff will fallen so wechschell vnten durch als du woll weist ~ |
[105v.2] Item ligestu yn der hut der pasteyn eß sey auff der lincken oder rechten seytten sigstu daß er dar auff wil krümmen mit dem messer oder sust aüff wil fallen So wechsel unten durch etc |
[200v.1] Item ligstu In der hütt pastey Es sey auff der lincken seytten oder auff der rechten seytten Sichstu das er dar auff will krummen mit dem messer oder sunst dar auff will fallen so wechsel vntten durch als du woll weyst etc |
||||||||
[548] |
Then, if he is high in the binding, go with the point at the face or chest. If he is low with the arm, await the hand-to-hand combat. |
[112v.3] alliud Item ist er hoch im band so far im mit dem ort zu dem gesicht oder brust ist er aber nider mit dem arm so wartt der ringen ~ |
[105v.3] Item ist er hoch ym pandt so far ym mit dem ortt zw dem gesichtt oder [106r.1] prüst ist er aber nyder mit dem armen So wartt der ryngen etc Sequitur textus |
[200v.2] Item ist er hoch Im pandt so far mit dem ortt zu dem gesicht oder prust Ist er aber nyder mit dem arme so wartt der ringen etc |
||||||||
[549] |
If he wants to climb the peaks A note: the meaning of the text is that if you stand in the guard of the Bastei and he wants to strike in the Zufechten to your four peaks, you should defend against it with the point, as it is stated above. |
[112v.4] Die zÿnnen wil er herstigen Die meynug des text ist So du ligst in der huet der pasteyn wil er im zuvechten zu der vier zynnen eyne wil schlagen dz soltu mit dem ortt als oben geschreben stot weren ~ |
[106r.2] Dy czÿnnen wil er ersteygen Nota dy maynung deß textz ist alzo So dw ligst yn der hutt der pasteyn wo er dir ym zw gen zw den vyer czynnen eyner schlagen wil daß soltu weren mit dem ortt alz oben geschriben ist etc |
[201r.1] Dy zynnen will er steygen Nota dy maynung des text ist so du ligest In der hutt der pastey will er dir Im zuuechten zu den vyer zynnen schlagen das soltu mit dem ortt als oben schriben stet weren etc |
||||||||
[550] |
Then, the other meaning of the text is that what is to be struck to the upper peaks, you should displace it with the point from the guard of the Bastei. But for a better explanation you should know that one should defend himself with the long point against all the bindings, and use the point against them. If he strikes or thrust, the long point breaks it quite well, as the long point is the best defense in the Messer and the sword, and who can fight from it, forces the man that he must let himself be beaten against his wish. And if he wants to acquire the “before,” you can take it from him with the long point and work “simultaneously” with your Messer according to the “after.” |
[113r.1] Item die ander meÿnug des text ist waz den oben zÿnnen zu geschlagen wirtt dz soltu mit dem ortt versetzen vß der hut der pasteyn dar zu merer erklerüng soltu wissen dz mã sich mit dem langen ortt gegen allen anpinden weren sol vnd den ort dar wider bruchen er haulb oder stech so bricht dz der lang ortt ist die este were im messer vnd im schwertt vnd were daruß fechten kan der zwinget den man dz er sich schlagen müß loßen vnd als er das vor wolt gewinden im messer so magstu im dz vor mit gawalt an gewinden Indes arbeit mit dinem messer nach dem nach also gedenck alwegen dz du im dz vor vnd nach angewünst mit dem ortt ~ |
[106r.3] Item dy ander maynüng deß text ist waß den oberen czynnen zw geschlagen wirtt daß soltu mit dem langen ortt verseczen aüß der hutt der pasteyn Doch zw [106v.1] merer erklerung soltu wyssen daß man sich mit dem langen ortt gegen allen anpyntten weren sol und den ortt praüchen dar wyder er haw oder stech So pricht daß daß der lang ortt gar wann der lang ortt ist dy pest wer ym messer und ym swertt und wer dar auß vechten kan der czwyngtt den man daß er sich uber seyn danck müß schlagen lassen und ob er daß vor wollt gewynnen ym messer So magstü ym daß vor yndeß mit dem langen ortt mit gewaltt nemen yndeß erbeyt mit deym messer nach dem nach alzo gedenck albegen daß dw ym daß vor und daß nach angewynst etc |
[201r.2] Item dy ander meynung des text ist waß den obren zynnen zu geschlagen wirtt das soltu mit dem ortt versetzen auß der hutt der pastey doch zu merer Erklerung soltu wissen das man sich mit dem langen ortt gegen allen anpinden weren solt vnd den ortt da wyder prauchen Er haw oder stech so pricht das der lang ortt gar wanne der lang ortt ist dy pest werr Im messer vnd Im swert vnd wer dar auß vechten kan der zwinget den man das er sich vber seyn danck schlagen müß lassen vnd ob er das vor wollt gewynnen so magstu Im das nemen mit dem langen ortt Indes erbeytt mit deynem messer nach dem nach etc |
||||||||
[551] |
Then, put your left foot forwards and assume the guard of the Bastei. If he strikes from the guard of the Luginsland at your left side at the head, go high with your Messer and change through to his right side and push his Messer with your Messer. Or, pull the Messer a bit aside and strike with the long edge through his face or cut through his right arm, and assume again the guard announced above. |
[113r.2] alliud Item setz dinen linckñ fus vor vnd leg dich in die hut pasteyn schlecht er dan zu von luginßlant zu diner lincken siten zu dem koppff so far mit dinem messer vff vnd wechschell vff sin rechte siten durch vnd stos sin messer mit dinem messer ader rueck des messers eyn wenig besitz vnd haulb in mit der langen schniden durch sin angesicht oder schnit durch sin rechte arm vnd leg dich wider in die egemelte hutt ~ |
[201v] Item setz deynen lincken fuß für vnd leg dich In dy hutt pastey schlech er dir den zu von lugislandt zu deyner lincken seytten zu dem kopff so far mit deynem messer auff vnd wechsel auff seyner rechten seytten durch vnd stoß seyn messer mit deynem messer oder ruck des messers Eyn benig beseytt vnd haw Im mit der langen schneyden durch seyn angesicht oder schneyd In durch seyn rechten arme vnd leg dich wyder In dy obgemelten hutt etc |
|||||||||
[552] |
Then, stand as before-if he strikes at you from the guard of the Luginsland, go directly high with the stretched arm under his Messer to his right side and while changing through step with your right foot forwards to his right one and thrust with the stretched Messer at his face to the right side. If you want, you can do the doubling or going through. If you do not want, assume again the Bastei. |
[202r] Item lig als vor hautt er aber auff von der hutt lugis landt so gee gerad auff mit gestracktem arme vntter seyn messer auff seyner rechten seytten vnd Im durchwechslen Schreytt mit deynem rechten fuß für gegen seynen rechten vnd stich Im mit gestracktem messer zu dem gesicht seyner rechten seytten wiltu denne so magstu machen dy dupliren oder durchgen wiltu aber nicht so leg dich wyder abher In dy pastey etc |
||||||||||
[553] |
Then, in the same way as you do things if you stand in the guard of the Bastei on your right side and the left foot is forwards, you can also change through if you stand in the guard of the Bastei on your left side and the right foot is forwards, and you can strike, thrust and cut therefrom. Things go a bit worse from the left side than from the right, and it appears quite uncomfortable for someone untrained in the Messer. |
[113r.3] Item glich als du die ding machest so du ligst in der hut der pastey vff diner rechten siten so der linck fus vor stott also machstu durch wechselln [113v.1] so du stost in der hut pasteyn vff diner lincken siten so der recht fus fur stott vnd daruß haulben stechen vnd schnitten den dz eß von der lincken siten letzer zu gett dan vff der rechten vnd eym vngabten im messer gar vnlbege dünckt ~ |
[202v] Item gleych als du dy ding machest so du ligst in der hutt pastey auff deyner rechten seytten so der linck fuß vor stett also magstu durchwechselen so du stest in der hutt der pastey auff deyner lincken seytten so der recht fuß vor stett vnd dar auß hawen stechen vnd schneyden denne das eß von der lincken seytten etzwaß letzer zu gett denne auff der rech vnd eynem vngeubtten In dem messer gar vnpequem dunckt etc |
|||||||||
[554] |
Who aims at the Bastei Here it is to be known that the meaning of the text is that what is struck or thrusted to the lower peaks, you should defend against it from the guard of the Luginsland, also with the long point. And if you have failed with the point, wind always your Messer with his one into the Stier. This takes place on both sides. |
[113v.2] Wer der bastey zu setz Hie ist zu wissen dz die meinung des text ist Waß den vntern zÿnnen wurtt geschlagen oder gestochen dz soltu weren vß der hut luginßlant auch mit dem langen ortt vnd ob du alwegen mit dem langen ort ge gefellet hest So wind allwegen din messer mit dem dinem in den stier von beiden syten get eß zu ~ ~ |
[106v.2] Wer der pasteyn zw seczt Item dy maynung deß textz ist als waß den unteren czynnen wirt zw geschlagen oder gestochen daß solt dw prachen oder weren auß der hut lüginsland mit dem langen ortt und ob dw mit dem ortt hast gefeltt so pyndt albegen deyn messer gegen dem seynen yn den stiren von peyden seytten get daß zw etc |
[203r] Wer der pastey zu setzt Hye ist zu wissen das daß dy maynung des textz ist also was den vntren zynnen wirtt zu geschlagen [Sic] ader gestochen das soltu weren auß der hutt luginslandt auch mit dem langen ortt vnd ob du mit dem ortt gefelt hast so windt albegen deyn messer mit dem seynen In den stiren von peyden seytten gett das zu etc |
||||||||
[555] |
Then, if you stand in the guard of the Luginsland, stand with your leg well in balance and hold your Messer stretched and let him do what he wants. If you can do it well, he cannot make anything, no matter whether he changes through or does what he wants. You can also assume this guard on his Messer, also stretched, and do therefrom what you want, and seek all the openings. And where you can see a window standing open, thrust merrily to it with your point or with your stroke, and “simultaneously” do what you have been taught before. |
[113v.3] Item ligstu in der hutt luginßlant So ste mit dinem beÿn wol in die woge vnd halt din mesß gestrack vnd loß in machen wz er will hastu im recht gethan so kan er nuetz schaffen er wechsel durch oder mach wz er will du magst auch dich in disse hut legen uff sin messer also gestrack vnd daruß machen Wz du wilt vnd alle ploß do mit suchen Vnd wo du dz venster sicht uffenston so sech frelich mit dinem ortt oder mit eynem haulb vnd mach Indes wz du vndericht bÿst etc~ |
[107r.2] Item ligstü yn der hut lüginslandt So stee mit deynen paynen wol yn dy wag und haltt deyn messer gestrackt und laß yn machen waß er wil Thüstu ym recht so kann er nicht schaffen er wechsel durch oder mach waß er wol dw magstu dich auch yn dyse hut legen auff seyn messer alzo gestrackt und alzo machen dar auß waß dw willst Dw magst auch alle ploß da mit suchen und wo dw daß fenster sigst offen stan da gee küenlich dar eyn mit deynem ortt und mach [107v.1] yndeß alz dw vor unterrichtt pist etc |
[203v] Item ligstu In der hutt lugislandt so stee mit deynem peyn woll In dy wag vnd hallt deyn messer gestrackt vnd laß In machen was er will kanstu Im recht thun so kann Er nichtz schaffen Er wechsel durch oder mach waß er woll du magst dich auch In dyse hutt legen auff seyn messer also gestrackt vnd dar auß machen waß dw wild vnd alle ploß da mit süchen vnd wo du daß fenster sichst offen stan so sich[99] fröhlich dar eyn mit deynem ortt oder mit deynem haw vnd mach Indes waß du vor untterricht pist etc |
||||||||
[556] |
Then, you can defend against all the strokes from below from the guard of the Luginsland with the point, by means of stretching and shooting the point from above at his face, and “simultaneously,” if you want to change through. |
[204r] Item du magst dich Er weren aller vnterhew auß der hutt lugis landt mit dem ortt vnd gestrackt In von oben eyn schyssen den ortt zu dem gesicht vnd Indes ob du willt durchwechslen; |
||||||||||
[557] |
Who displaces in the crooked manner Here the master states how you should hold yourself against one who displaces with the crooked stroke. If you both have bound and you also lie on his Messer and he lies under your one, do it this way: if he lies on your left side against you or on you against your right side, and you have bound on his Messer, so that the blunt edge is against the man, “simultaneously” wind your Messer with the long edge on his head. |
[114r.1] Krümpt wer versetz Hie saget der meinster wan dir eyner versetz mit krümpt wie du dich gegen im solt halten so ir beid an gebunden habent vnd du ligest auch in sinem messer vnd er lig wnter dinem thün im also lig er vff diner lincken siten gegen dir oder an dir gegen diner rechten siten vnd haulbest vff sin messer auch gebunden dz die stümpff schnid gegen dem mã steet Indes wind din messer mit der langen oder schrapfen schniden im vff sin hauptt ~ |
[107v.2] Krümp wer verseczet Hye sagtt der meyster wenn dir ymant mit der krüm verseczt wye dw dich gegen ym solt halten So ir peyde an gepunden habt und dw ligst auff seym messer und er ligt unter deynem Thw ym alzo ligt er auff deyner lincken seytten gegen dir oder an dir gegen deyner rechten seytten und hast auff seyn messer aüch gepunden daß sy stümpff schneyd gegen dem man stet yndeß wynd deyn messer mit der langen oder scharpffen schneyden ym auff seyn haubtt |
[204v] Krump wer versetzt Hye sagtt der meyster wenn dir ymant mit der krum versetz wye du dich gegen Im solt halten so ir payde angepunden habtt vnd du ligest auch In seynem messer vnd er ligtt vntter deynem Thu Im also ligtt er auff deyner lincken seytten gegen dir oder an dir gegen deyner rechten seytten vnd hast auff seyn messer auch gepunden das dy stumpff schneyd gegen den man stett Indes windt deyn messer mit der langen schneyden Im auff seyn haubtt etc |
||||||||
[558] |
Then, if he goes high and raises his arm high so that you cannot come to the head with the Messer, and you have learnt or you can see that he goes high, wind high over his Messer against your left side to his right one, and fall with the point from his Messer to his throat or chest. |
[114r.2] Item fert er vff vnd ist hoch mit dem arm dz du zu dem haupt mit dem messer nicht magst kümen vnd hast dz vermünen oder sichst dz er hoch vff fertt so wind hoch vff vber sin messer gegen diner lincken siten vff sin rechte siten vff sine rechte siten vnd fal im mit dem ortt von sinem messer im in die kellen oder vff die brust ~ |
[108r.1] Item fertt er auff und ist hoch mit dem armen daß dw zw dem dem haubtt mit dem messer nicht magst kümen und hast daß vernümen oder sigst daß er daß hoch auff fertt so wyndt hoch auff uber seyn messer gegen deyner lincken seytten auff seyn rechte seytten und fall mit dem ortt von seynem messer ym yn dy kelen oder auff dy prüst |
[205r] Item fertt er auff vnd ist hoch mit dem arme das du zu dem haubt mit dem messer nicht magst kummen vnd hast vernummen oder pyst das er hoch auff fertt so windt hoch auff vber seyn messer gegen deyner lincken seytten auff seyn rechte vnd fall Im mit dem ortt von seynem messer Im In dy kelen oder auff dy prust etc |
||||||||
[559] |
Then, if he stands in the crooked displacement as before on your right side, wind the long edge against his head. If he goes high with the arm and wants to displace as before, notice, in the winding, as you have wound against the head on his Messer on his left side, strike the short edge on his head, so that the thumb is below and on the flat of your Messer. |
[114r.3] Item lig er in der krüme versatzung als vor vff diner rechten siten so wind die lang schnid gegem [114v.1] sinem haupt fert er dan aber hoch vff mit den armen vnd will versetzen als vor so vnd merck in winden die will du gegem dem haupt bist winden vff sin messer aber vff sin lincke siten vnd schlag im die kurtz schnid an sin haupt dz der thüm vnten sÿ vnd leg vff der flecht des messers |
[108r.2] Item ligtt er aber yn der krümmen versaczung alz vor auff deyner rechten seytten so wynd dy lang schneyd gegen seym haubtt fertt er dan aber hoch auff mit dem armen und wil verseczen alz vor So merck ym wynten dy weyl dw gegen dem haubtt pist wynten haw an seynem messer ab auff seyn lincke seytten und schlag ym dy kurczen an seyn hawbtt daß der dawm unten sey und ligtt auff der flech deß messerß |
[205v.1] Item ligtt aber in der krummen versatzung als vor auff deyner rechten seytten so windt dy lang schneyd gegen seynem haubtt fertt er denne aber hoch auff mit dem arme vnd will versetzen als vor so merck Im winden weyll du gegen dem haubtt pist winden auff seyn messer auff seyner lincken seytten vnd schlag Im dy kurtz schneyd auff seyn haubtt das der dawmen vntten sey vnd lig auff der flech deynes messers |
||||||||
[560] |
If he displaces the stroke and falls on it with his Messer, pull again skilfully on his Messer at the head, with the short edge. If he has displaced this, wind again high the long edge against his head, and let your point fall to your left side and at his right side at his throat or chest. |
[114v.2] versetz er dan den schlag felt darüff mit sinem messer zu dem haupt so riß wider behendeglichen an sin messer zu dem haupt aber mit der kurtzen schniden hat er dz auch versetz so wind wider vff die lang schnid gegem sinem haupt vnd loß den ort aber fallen vff din lincke siten vnd zu sw siner rechten siten In die kellen oder prüst ~ ~ |
[108r.3] ¶ versecz er dann den schlag und felltt [108v.1] dar auff mit seynem messer so reyß wyder wehentlich an seyn messer zw dem hawbtt aber mit der kürczen schneyden hatt er daß auch verseczt So wyndt wyder auff dy land schneyden gegen seym haubtt und laß den ortt aber fallen auff deyn lincke seytten und zw deyner rechten seytten yn dy kelen oder prust etc |
[205v.2] versetz er denn den schlag. fellt dar auff mit seynem messer so reyß wyder behendtlich an seyn messer zu dem haubtt aber mit der kurtzen schneyden hatt er das versetzt so windt wyder auff dy lang schneyd gegen seynem haubt vnd loß den ortt aber fallen auff deyn lincke seytten Ind vnd zu seyner rechten seytten In dy kelen oder prust etc |
||||||||
[561] |
If you want to deceive him as he winds Here the master states how one should double from the crook. If you want to do the doubling on him, do it this way: if you both have bound and he is on your right side and you are on his left side, and you stand with your Messer on his one, so that your thumb is below on your Messer, “simultaneously” wind the long edge on his head and “simultaneously” strike at his left ear with the Entrüsthau on the blade of his Messer with the blunt edge well around at the head. If you want to take away on the Messer, you can also do this. |
[114v.3] Im winden wilt verfuren Hie saget der meinster Wie man vß der krümen sol dupliren Wiltu im dz dupliren machen So thün im also so ir nü beÿd habt an gebünden vnd er ligt dir vff diner rechten siten vnd du im vff siner lincken siten vnd du ligst mit dinem messer vff dem synen dz der [115r.1] thüm vnten an dinem messer ste Indes wind die scharpfen schnid vff sin haupt vnd indes schlag im zu sinem lincken oren mit dem entruesch haulb vff sins messers klingen mit der stümpfen schniden wol vmb zu dem hauptt Wiltu dan ab nemen am mesß dz magst auch thün ~ |
[108v.2] Ym wynden wiltü yn verfueren Hye sagtt der meyster wye man auff der krum sol dupliren wiltu daß dwpliren machen so thu ym alzo So ir nw peyd habtt an gepunden und er ligtt dir auff deyner rechten seytten und dw [109r.1] ym auff seyner lincken seytten und dw ym auff seyner lincken seytten und dw ligst mit deynem messer auff dem seynen daß der dawm unten an deynem messer sey yndeß wynd dy scharpffen schneyd auff seyn hawbtt und yndeß schlag ym zw seynem lincken oren mit dem entrusthaw auff seyneß messerß klyngen mit der stümpffen schneyden wol umb zw dem hawbtt wiltu den abnemen am messer daß magstu auch thun |
[206r] In windinden wilt verfuren Hye sagtt der meyster wye man auß der krüm soll dupliren wiltu Im das dupliren machen so thu Im also So Ir payde habt an gepunden vnd er ligtt dir auff deyner rechten seytten vnd du Im auff seyner lincken seytten vnd du ligest mit deynem messer auff dem seynen vnd das dir der dawm vntten an deynem messer stee Indes windt dy lang schneyd auff seyn haubtt vnd Indes schlag Im zu seynen lincken oren mit dem Entrusthaw auff seynes messers klingen mit der stumpffen schneyden woll vmb zu dem haubtt will du denne abnemem am messer das magstu auch thun etc |
||||||||
[562] |
Then, if he stands on your right side against you as it is described before, do as if you wanted to wind the point at his face to his left side to his left cheek, and stretch the arm well from you to your side, and wind the point at his face. |
[109r.2] Item ligtt er auff deyner rechten seytten gegen dir alz oben gescriben stet Thw sam dw ym zw dem gesichtt wöllest wynden oder zw dem hawbtt yndeß wynd ym auff seyn lincke seytten den ortt nach seynem lincken wang und streck den armen woll von dir auff dye deyn seytten und wend ym den ortt zw dem gesicht etc |
[206v] Item ligtt er auff deyner rechten seytten gegen dir als oben geschriben stett Thu samb du Im zu dem gesicht wollest winden auff seyn lincke seytten den ortt nach seynem lincken wang vnd strack den arme woll von dir auff deyn seytten vnd windt Im den ortt zu dem gesicht etc |
|||||||||
[563] |
Then, as you have done the elements on the right side, you can also do them on the left side. And what peculiarities the windings have had from the right side, they have the same ones also from the left side. You can also do the taking away and strike at the head. Then, if you wind on the left side against your head, you can strike with the blunt edge, and you can also thrust at his right cheek. |
[109r.3] Item alz dw dy stuck gemacht hast auff [109v.1] der rechten seytten alzo magstu dy machen auff der lincken seytten und waß dy wynden eygenschafft gehabt haben von der rechten seytten dy selben haben sy auch von der lincken seytten dy abnemen magst dw auch machen und zw dem kopff schlagen den wen dw auff der lincken seytten gegen dem hawbtt wyndest so soltu mit der stümpffen schneyden schlagen auch magstu zu dem rechten wang stechen etc |
[207r] Item als du dy stuck gemacht hast auff der rechten seytten also magstu dy machen auff der lincken seytten vnd waß dy winden eygenschafft gehabt haben von der rechten seytten dy selbigen haben dy auch von der lincken seytten dy ab nemen magstu auch machen vnd zu dem kopff schlagen denne wenne du auff der lincken seytten gegen deynem haupt windest so magstu mit der stumpffen schneyden schlagen auch magstu zu seynen rechten wang stechen etc |
|||||||||
[564] |
Then, if you want to take his Messer, if he stands in the hanging point on his left side, and you also lie on his [Messer], wind “simultaneously” over his Messer the long edge and the point to his side, and do the mutating. “Simultaneously” step skillfully to him with your left foot, so that his Messer goes out with the point sideways at your right side, and “simultaneously” fall with your left hand behind his right one, and pull firmly with it at the bind to your right side, and push him firmly with the point of your Messer at his body. |
[109v.2] Item wiltu ym daß messer nemen so er ligtt ym hangatten ortt auff seyner lincken seytten und dw ligst auff dem seynen so wyndt yndeß uber seyn messer dy lang schneyden den ortt yn seyn seytten und mach daß mutiren yndeß tritt wehentlich auff yn mit deynem lincken fuß daß seyn messer neben deyner rechten seytten beseyt mit dem ortt hyn auß gee yndeß fall mit deyner lincken hand [110r.1] hynter seyn rechte und reyß starck do mit bey dem pynd auff deyn rechte seytten und stoß yn mit dem ortt deyneß messerß starck yn seyn leyb etc | [207v] Item wiltu Im das messer nemen so er ligtt Im hangenden ortt auff seyner lincken seytten vnd du ligest auch auff seynem so windt Indes vber seyn messer dy lang schneyd den ortt In seyn seytten vnd. mach das mutiren Indes Dritt behentlich auff In mit deynem lincken fuß das seyn messer neben deyner rechten seytten beseytt mit dem ortt hyn auß gett Indes fall mit deyner lincken handt hintter seyn rechte vnd reyß starck damit pey dem pindt auff deyn rechte seytten vnd stoß In mitt dem ortt deyneß messers starck In seyn leyb etc |
|||||||||
[565] |
Then, if he stands in the hanging point on his right side and you lie under his [Messer], “simultaneously” fall with your left hand over his Messer and “simultaneously” fall in the middle of your Messer and go with the point on his throat, or put the blade of your Messer on his neck on his left side. And step with your left foot behind his right one and push him over it. |
[110r.2] Item ligtt er yn dem hangatten ortt auff seyner rechten seytten und dw ligst unter dem seynen yndeß fal mit deyner lincken hand uber seyn messer yndeß yn fal yn dy mitt deyneß messerß und far ym alzo mit dem ort an seyn kelen oder leg ym deyneß messerß klyngen an seyn halz auff seyner lincken seytten und schreytt mit deynem lincken fuß hynter seyner rechten und druck yn dar uber etc |
[208r] Item ligtt er Im hangenden ortt auff seyner rechten seytten vnd du ligest vntter dem seynen Indes fall mit deyner lincken handt vber seyn messer Indes fall In dy mitt deynes messers vnd far Im also mit dem ortt an seyn kelen oder leg Im deynes messers klingen an seyn hals auff seyner lincken seytten vnd schreytt mitt deynem lincken fuß hintter seyn rechten vnd druck In dar vber etc |
|||||||||
[566] |
Then, if you lie on his Messer and he lies as before, “simultaneously“ go with your left arm over his Messer and hit with your Messer on his one, with the crosspiece firmly from above at his hilt or at the blade of his Messer, close at the hand, firmly to your left side, in that way you take his Messer. |
[110r.3] Item ligstu auff seynem messer und er ligt alz vor yndeß far mit deynem lincken armen uber seyn messer und stoß mit deynem messer ym an seyn messer mit dem kreucz starck an seyn messer oben an seyn gehulcz oder an seynß messerß klyngen nohent bey der hand [110v.1] starck auff deyn lincke seytten so nymbstu ym daß messer etc |
[208v] Item ligestu auff seynem messer vnd er ligtt als vor Indes far mit deynem lincken arme vber seyn messer vnd stoß mit deynem messer Im an seyn messer mit dem kreutz starck oben an seyn gehultz oder an seyns messers klingen nohent bey der handt starck auff deyn lincke seytten so nymbstu Im aber das messer etc |
|||||||||
[567] |
Then, if you lie on his right side and on his Messer, and he lies in the hanging point as before, “simultaneously” wind against his neck and press the Messer at the nape of his neck. And if he is too strong for you, so that you cannot press his Messer down, come with your left hand from behind on his hilt to help your right hand. “Simultaneously” fall with your left hand from above on his Messer on the hilt at his hand, and press it over his back and over your Messer, in that way you take his Messer. |
[110v.2] Item ligstü aber auff seyner rechten seytten und auff seynem messer und er ligtt ym hangattem ortt alz vor yndeß wynd gegen seynem halz und druck ym deyn messer an seyn nack und ob er dir zw starck woltt seyn daß dw ym seyn messer nicht nyder drucken kanst So küm mit deyner lincken hand hynten an deyn gehulcz der rechten hand zw hilff yndeß fal mit deyner lincken hand ym oben yn seyn messer yn daß gehulcz ob seyner hand und druck ym daß uber ruck und uber daß deyn so nymbstu ym aber daß messer etc |
[209r] Item ligestu aber auff seyner rechten seytten vnd auff seynem messer vnd er ligtt Im hangenden ortt als vor Indes windt gegen seynen hals vnd druck Im das messer an seyn nack vnd ob er dir zu starck wollt seyn das du Im seyn messer nicht nyder drucken kunst so kum mit deyner lincken handt hinden an deym seyn gehultz der rechten handt zu hilff Indes fall mit deyner lincken handt Im oben In seyn messer In des gehultz ob seyner handt vnd druck Im das vberruck vnd vber daß deyn so nymbstu Im aber das messer etc |
|||||||||
[568] |
Then, if he lies on his right side in the hanging point as before, “simultaneously” fall with your left arm over his Messer and do as if you wanted to thrust at his face with the hilt of your Messer. If he goes high with his hilt and wants to displace the thrust, “simultaneously” hit with your hilt firmly to your left side, in that way you take his Messer and strike him with it through his mouth. |
[110v.3] Item ligtt er auff seyner rechten seytten ym hangatten ortt alz vor und dw ligest aüch auff seynem alz vor yndeß fal mit deynem lincken armen uber seyn messer und thü samb dw ym mit dem gehulcz deyneß messerß wollest stossen [111r.1] yn seyn angesicht so er den auff fertt mit seynem gehulcz und wil dir den stoß da mit verseczen yndeß stoß mit deynem gehultz czwischen seyn handt und seyn gehulcz auff deyn lincke seytten starck So nymbstu ym aber daß messer und hawest yn da mit durch daß maul etc |
[209v] Item ligtt er auff seyner rechten seytten In dem hangenden ortt als vor Indes fall mit deynem lincken arme vber seyn messer vnd thu als du Im mit dem gehultz deynes messers wollest stechen In seyn angesicht so er denne auff fertt mit seynem gehultz vnd will dir den stoß versetzen Indes stoß mit deynem gehultz starck auff deyn lincke seytten so nymbstu Im aber das messer vnd hawest In da mit durch das gesicht etc |
|||||||||
[569] Then, if he lies as before and you do as well, “simultaneously” go with your left arm over his Messer and hit with your hilt behind over his Messer between his arm and body on the inside on his hilt or on the outside on the blade at the hand firmly to your right side. |
[111r.2] Item ligtt er alz vor und dw deß geleychen yndeß far mit deynem lincken armen uber seyn messer und stoß mit deynem gehulcz hynten uber seyn messer czwischen seyn armen und leyb ynbendigß an daß gehultz oder außbendigß an dy klyngen bey der hand starck auff deyn rechte seytten etc |
|||||||||||
[570] |
Go over with the arm, if he wants to strike, Then, you should understand it this way: if you come to the man with your Entrüsthau to his left side, strike at his right side and “simultaneously” go with your left arm over his Messer over the blade and do as if you wanted to hit with the hilt at his face. “Simultaneously” hit with the hilt in the joint of his right hand on the outside firmly towards your right side. |
[210r] Vberfar arme will er possen Item das soltu also verstan kumstu zu dem mann mit deynem Entrusthaw auff seyn lincke seytten so schlag Im zu seyner rechten seytten Indes far mit deynem lincken arme vber seyn messer vber dy klingen vnd thu als du Im mit dem gehultz In das angesicht wollest stossen Indes stoß mit dem gehultz In das gelenck seyner rechten handt außbendigs starck auff deyn rechte seytten; |
||||||||||
[571] |
Then, fall over his Messer as before and if his hilt in the hand looks over on the inside, hit with your hilt between his hand and hilt firmly to your left side, in that way you take his Messer, as it is depicted below. |
|||||||||||
[572] |
Strike the Entrüsthau, wind over the weak Here the master teaches how one should wind over the man with the weak of the Messer, and do it this way: strike with an Entrüsthau at his right side and “simultaneously” turn your hand around, and wind the weak of your Messer on his Messer, and strike “simultaneously” with the long edge on his head. |
[211r] Entrust swech vberwindt Hye lertt der meyster wye man den man mit der swech deß messers vber wintten soll vnd thu Im also Schlag Im mit eynem Entrusthaw zu seyner rechten seytten Indes wendt deyn handt vmb vnd windt In dy swech deynes messers auff seyn messer vnd schlag Im Indes mit der langen schneyden auff seyn kopff. etc |
||||||||||
[573] |
If you want to dupe him Here the master and the propagator of the art ends the last element with its peculiarity and speaks: If you want to dupe him. That is, if you both have bound and he lies on your right side with the crooked displacement and you lie under his Messer also in the same displacement, “simultaneously” wind your Messer to his left side against his opening, and wave well at it. Then, it has been said a lot that you should grab to the opening a bit and quickly go through from the same left side with the Messer in front of your body, with the lowered point to your left side, and strike at his head to his right side, or set the point on his face or the chest. |
[115r.2] Wiltu in betrigen Hie endet der meinster Vnd der merer der künst dz lest stuck mit siner eygenschafft Vnd spricht wiltu In betrigen dz ist wan ir beid an gebünden habt ligt er dir dan vff der rechten siten mit der krümen versatzung vnd du ligst vnden sin messer auch in der selbigen versatzung Indes wind din messer vff [115v.1] sin lincke siten gegen siner ploß vnd winck woll gegen der selbigen daß ist also vil gesprochen als dz du solst noch der ploß griffen ein wenig vnd auch von der selbigen siten schnell dürch gen mit dem messer fur din lip mit gestrecktem ortt vff din lincke siten vnd schlag im noch dem haupt siner rechten oder setz im der ortt zu dem gesichtt ~ |
[111r.3] Wiltü yn betryegen Hye endet der meyster und der merer der künst daß leczt stuck mit seyner eygenschafft und sprichtt will dw yn betrygen etc Daß ist wenn Ir beyde an gepunden habtt ligtt er dir den auff der rechten seytten mit der krümmen versaczung und dw ligst unter seynem messer auch ynder selben versaczung yndeß wynd deyn messer auff seyn lincke seytten gegen seyner ploß und winck wol gegen der selbigen daß ist alz vor gesprochen daß dw nach der ploß solt greüffen eyn wenig und und doch von der selbigen lincken seytten soltu schnel [112r.1] durchgeen mit dem messer fuer deyn leyb mit gesencktem ortt auff deyn lincke seytten und schlag ym zw dem haubt seyner rechten seytten oder secz ym den ortt zw dem gesicht oder zw der prüst |
[211v] Wiltu In betrygen Hye endt der meyster vnd der merer der kunst das letzt stuck mit seyner Eygenschafft vnd spricht wiltu In betrigen das ist wenne Ir payde an gepunden habtt ligtt er dir denn auff deyner rechten seytten mit der krummen versatzung vnd du ligest vntter seynem messer auch In der selben versatzung Indes windt deyn messer auff seyn lincke seytten gegen seyner plöß vnd winck woll gegen der selben // [212r] // Das ist als vill gesprochen das du nach der ploß sollt greyffen eyn benig vnd dich von der selbigen lincken seytten schnell durchgen mit dem messer fur deyn leyb mit gesencktem ortt auf deyn lincke seytten vnd schlag In zu dem haubtt seyner rechten seytten oder setz Im den ortt zu dem gesicht oder zu der prust etc |
||||||||
[574] Then, if you set the point to one’s face or chest and he goes with the hanging point from his left side to your Messer and displaces, “simultaneously” wind quickly against his Messer or on his Messer against his left side, so that the thumb is above on the flat and lower the hilt a bit and thrust upwards under his Messer at his face. “Simultaneously” wind soon again against his right side and lower the point again to his chest or strike with the lowered point at his right ear. |
[115v.2] Item setzestu eynem den ortt also in dz gesicht oder prust vnd er fertt vff mit dem hangenden ort von siner lincken siten an din messer vnd versetz dir Indes wind schnell gegen sinem messer gegen siner lincken siten dz der thüm oben ste vff der flech vnd sentz dz gehultz ein wenig vntter sin messer im zu sinem gesicht Indes wind bald gegen siner rechten siten vnd senck im den ortt vff sin brust oder schlag im mit gesenctem ortt zu sinem rechten oren ~ ~ |
[112r.2] Item seczt dw eynem den ortt alz yn daß gesichtt oder prust und er fert mit hangattem ortt von seyner lincken seytten an deyn messer und verseczt dir yndeß wynd schnel gegen seynem messer oder an seynem messer gegen seyner lincken seytten daß der dawm oben stee auff der flech und senck daß gehulcz eyn wenig und stich ubersich unter seynem messer ym zw seynem gesichtt yndeß wyndt pald wyder gegen seyner rechten seytten und senck ym den ortt wyder auff seyn prust oder schlag ym mit gesencktem ortt zw seynem rechten oren etc |
||||||||||
[575] Then, if you wind to his face with the lowered hilt so that the thumb is on the flat and he strikes “simultaneously” to your head, “simultaneously” wind against his left side so that the thumb is below. Thus, the stroke is displaced. If he strikes again around to your right side, cut him firmly over his right arm on the outside and twitch with it. |
[115v.3] Item Windestu im zu dem gesicht mit gesencten ort gehultz dz der thüm vff der felch stet vnd er schlecht dir Indes zu dem haupt Indes wind gegen siner rechten siten dz der thüm vnten ste so ist der sclacg versetz schlecht er dan widerümb zu diner rechten siten so schnid im starck vber sin rechten arm vßwenidig vnd zuech do mit abe ~ |
[112r.3] Item windestu ym zw dem gesichtt mit gesencktem hulcz daß der dawm auff der flech stet und er schlecht dir yndeß [112v.1] nach deym haubtt yndeß wyndt gegen seyner lincken seytten daß der dawm unten stee So ist der schlag versecz schlecht er dan wyder umb zw deyner rechten seytten So schneyd ym starck uber seyn rechten armen außbendigß und czeüg da mit ab etc |
||||||||||
[576] |
Then, if you stand on his right side, and he does as well on the same side as before, “simultaneously” wind your Messer under his Messer well around, so that you touch him a bit to his right side to his right shoulder with the short edge or the flat. “Simultaneously” go through with your Messer with the lowered point between your both sides or bodies, so that the long edge goes first. “Simultaneously” set the point around in his chest or strike with the short edge at his left ear, and hold your Messer always in front of the head with the hilt well upwards, so that the thumb is below on the flat of the Messer. |
[115v.4] Item ligst also vff siner rechten siten vnd er auch vff der selbigen als vor Indes winde vnten sinem [116r.1] messer dim messer gar vmb also dz du in vff siner rechten siten mit der kuttzen schniden oder flech sin rechten achsel rurest ein wenig Indes far durch mit dem messer mit dem gesenctem ort zwuschen vber beyde siten oder lip dz die lang schnid vor ge Indes setz in den ort in sin brust oder schlag im mit der kurtzen schniden zu sinem lincken oren vnd hab din messer allvegen fur din haupt mit dem gehultz wol vber sich dz der thüm vnten vff der flech des messers ste ~ |
[112v.2] Item ligstu alzo auff seyner rechten seytten und er auch auff der selbigen alz vor yndeß wyndt unten seynen messer deyn messer gar umb alzo daß dw yn auff seyner rechten seytten mit der kurczen oder mit der flech seyn rechte achsel rüerest eyn wenig yndeß gee durch mit dem messer mit gesencktem ortt czwischen ewer peyder leyb daß dy lang schneyd vor gee yndeß secz ym den ortt yn seyn prüst oder schlag yn mit der kurczen schneyden zw seynem lincken oren und hab deyn messer albegen fuer daß haubtt mit dem gehulcz wol ubersich daß der dawm unten auff der flech deß messerß stee etc |
[212v] Item ligstu also auff seyner rechten seytten vnd er auch auff der selben als vor Indes windt vntter seynem messer deyn messer gar woll vmb vntter also das du In auff seyner rechten seytten mit der kurtzen schneyden oder flech seyn rechte achsel rurest Ein wenig Indes gee durch mit dem messer mit gesencktem ortt zwischen Ewrer payd seytten oder leyb das dy lang schneyd vor gee Indes setz Im den ortt In seyn prust vnd oder schlag Im mit der kurtzen schneyden / zu seynen lincken oren vnd halt deyn messer albeg fur das haupt mit dem gehultz woll vbersich das der dawm vntten stee auf der flech deß messers etc |
||||||||
[577] |
Then, if you lie on his Messer on his right side, and he again lies in the hanging point and across, wind “simultaneously” the short edge firmly to his head, and go high with the hilt. If he wants to follow it with the displacement, strike “simultaneously” with the horizontal stroke at his ear to his right side with the short edge. |
[116r.2] Item ligstu vff sinem messer als vor vff siner lincken siten Indes wind vnd schlag in mit der langen schniden vff sin haupt vnd far aber hoch vff mit dem gehultz fert er dan vff vnd wil den schlag versetzen Indes schlag in aber zu sin lincken oren dz der thüm aber vnten ste vff der flech des messers ~ ~ |
[113r.1] Item ligestu auff seynem messer auff seyner rechten seytten so er aber ligt ym hangattem ortt mit der czwirch yndeß wynd dy kurcz schneyd starck auff seynem kopff und far hoch auff mit dem gehulcz wil er mit der versaczung nach foren So schlag yndeß mit der czwirch zw seynem oren seyner rechten seytten mit der langen schneyden etc |
[213r] Item ligestu auff seynem messer auff seyner rechten seytten so er aber ligtt Im hangnden ortt mit der zwirch Indes windt dy kurtzen schneyden starck auff seyn kopff vnd far hoch auff mit dem gehultz will er mit der versatzung nach faren so schlag Indes mit der zwirch zu seynen oren seyner rechten seytten mit der kurtzen schneyden etc |
||||||||
[578] Then, if you lie on his Messer as before on his left side, “simultaneously” wind and strike with the long edge to his head and go high with the hilt. If he goes high and wants to displace the stroke, “simultaneously” strike to his left ear so that the thumb is below on the flat. |
[113r.2] Item ligestu auff seynem messer alz vor auff seyner lincken seytten yndeß wynd und schlag yn mit der langen schneyden auff seyn hawbt und far aber hoch auff mit dem gehulcz fertt er den auff und will den schlag verseczen yndeß schlag yn zw seynem lincken orenn daß der dawm aber unten stee auff der flech |
|||||||||||
[579] |
Then, if you lie on his Messer on his right side as before, grab with your left arm over the blade of his Messer, and grab below in the armed hand, so that the point of your Messer is on your left side. Then, go high with the hilt and hit firmly with it on the blade of his Messer close to the hand to your left side, in that way you take his Messer again. |
[213v] Item ligstu auff seynem messer seyner rechten seytten wye vor Indes greyff mit deynem lincken arme vber seyns messers klingen vnd greyff vntten zu gewappender hantt das der ortt deynes messers stee auff deyner lincken seytten vnd far auff mit dem gehultz vnd stoß starck da mit an seyns messers klingen nohendt pey der handt auff deyn lincke seytten so nymbstu Im aber das messer etc |
||||||||||
[580] |
Then, strike from above directly a long upper stroke with the stretched arm directly and freely at his head to his left side, and as the stroke is delivered directly, wind against his Messer the short edge on it, so that the thumb is below, and flick the short edge at his left ear. |
[113r.3] Item haw von oben gerad zw eynen eyn eynen langen oberhaw mit gestracktem armen gerad und frey zw seynem kopff seyner [113v.1] lincken seytten yndeß so der haw gerad verprachtt ist So wynd gegen seym messer dy kurcz schneyd dar an daß der dawm unten stee und schnell ym dy kurcz schneyd an seynn linckeß ore |
[214r] Item haw von oben gerad eyn Eynen langen oberhaw mit gestracktem arme gerad vnd frey zu seynem kopff seyner lincken seytten vnd so der haw gerad verpracht wirtt ist So wind gegen seynen messer dy kürtz schneyden dar an das der dawmen vntten stee vnd schnel Im dy kurtzen schneyden an seyn linckes ören etc |
|||||||||
[581] |
Then, strike an upper stroke at his right side long and directly with the stretched arm, and “simultaneously,” as the stroke has been delivered, wind your Messer against your left side on his Messer, and flick at his head or arm to his right side. |
[113v.2] Item haw eyn oberhaw ym zw seyner rechten seytten lanck und gerad eyn mit gestracktem armen yndeß so der haw verpracht ist So wyndt deyn messer gegen deyner lincken seytten an seym messer und schel yn zw seynem kopff oder oren seyner rechten seytten etc |
[214v.1] Item haw Eyn oberhaw Im zu seyner rechten seytten lanck vnd gerad eyn mit gestracktem arme Indes so der haw verpracht ist so windt deyn messer gegen deyner lincken seytten an seyn messer vnd schnell In zu seynem kopff oder arme seyner rechten seytten etc |
|||||||||
[582] |
Then, a note: the elements are good, as you can more easily dupe the man, and “simultaneously” do the doubling, the feints and the hits. |
[116r.3] Item die stueck sint gut dz du eynen dester baß verfuren I vnd Indes mach die dupliren die feller vnd die treffer ~ ~ |
[113v.3] ¶ Merck dy stuck seyn gutt daß dw eyn dester leychtiklicher magst verfüren und yndeß mach dy dupliren dy feler und dy treffer |
[214v.2] Item nota dy stuck seyn gutt das du eynem dester leychter magst verfuren vnd Indes mach dy dupliren dy feler vnd dy treffer |
||||||||
[583] |
Then, you should also know that from these windings there should be found strokes, thrusts and cuts, and do it this way: as you have gone through with the Messer from his left side to your right one, cut upwards on his side. And “simultaneously”, as you have cut with the Messer, thrust at his chest. “Simultaneously” go high with the Messer and do a feint also on his right side, and strike at his next opening. |
[116r.4] Item du solt auch wissen dz vß dissem winden sollend gefunden werden haulb stich vnd schnid vnd thüm [!] im also so du bist durch gangen mit dem messer von siner lincken siten vff sin rechte siten so schnid vber sich an siner siten Indes so du geschnitten hast mit dem [116v.1] messer vnd mach ein s feler auch vff siner rechten siten vnd haulb im noch dem haupt oder vff die siten ~ |
[113v.4] Item dw solt auch wyssen daß auß dysen wynden sollen gefünden werden hew stich und schnydt und thü ym alzo so dw pist gangen mit dem messer zw von seyner lincken seytten auff seyn rechte [114r.1] seytten so schneyd ubersich an seynen seytten yndeß so dw geschnytten hast mit dem messer stich ym auff seyn prust yndeß far auff mit dem messer und machen feler auch auff seyner rechten seytten und haw ym zw dem haubtt oder aüff dy seytten etc |
[215r] Item du solt auch wyssen das auß dysen winden sullen gefunden werden hew stich schnytt vnd thu Im also so du pist durchgangen mit dem messer von seyner lincken seytten auff deyn rechte so schneyd vbersich an seyner seytten Indes so du geschnytten hast mit dem messer stich Im auff seyn prust Indes far auff mit dem messer vnd mach eyn feler auch auff seyner rechten seytten vnd haw Im zu der negsten ploß etc |
||||||||
[584] |
Then, if you lie under his Messer on his right side as before, “simultaneously” wind against him the short edge, so that the thumb is on the flat, and thrust at his cheek to the same side. |
[215v] Item liegstu Im vntter seynem messer auff seyner rechten seytten wye vor Indes windt gegen Im dy kurtz schneytt das der dawmen auff der flech lig vnd stich Im zu dem wang der selbigen seytten etc |
||||||||||
[585] |
Then, if you lie under his Messer on his left side as before, “simultaneously” wind the long edge against him, so that the short edge is above, and thrust at his cheek to the same side. |
|||||||||||
[586] |
Then, you should also notice quite well whether he is soft or hard in the displacement, and notice the weak and the strong, and first of all you should not forget the word “simultaneously,” and what is “before” and “after,” which you have been taught before. |
[116v.2] Item du solt gar eben mercken ob er weich oder hart in der versatzung ist vnd merck die schwech vnd die starck vnd zu vor an soltu des wortes indes nit vergessen vnd waß dz vor vnd dz noch ist dz bistu vor vndericht wurden |
[114r.2] Item dw solt auch gar eben mercken ob er weych oder hertt yn der versaczung ist und mercken dy swech und dy sterck und zw vor an soltu deß wortteß yndeß nicht vergessen und waß daß vor und daß nach ist daß pistu vor unterrichtt worden |
[216v.1] Item du solt auch gar eben mercken ob er weych oder hertt In der versatzung Ist vnd merck dy swech vnd dy sterck vnd zu vor an soltu des wortz Indes nicht vergessen vnd was das vor vnd das nach ist des pistu vor vnterricht worden |
||||||||
[587] |
Now, you should know what the word “simultaneously” is: when you feel whether he is soft or hard in the displacement, notice, that you work “simultaneously” in all the elements as you notice the peculiarities of the things that are brought and done on you, or that you have done on the man. “Simultaneously” double, “simultaneously” mutate, “simultaneously” run through, “simultaneously” clench, “simultaneously” take the cut, “simultaneously” fight hand-to-hand, “simultaneously” take the Messer, “simultaneously” take over, “simultaneously” go through, “simultaneously” run through, “simultaneously” do what your heart desires. “Simultaneously” is a sharp word with which the masters are cut out hard, and first of all the masters who neither known nor understand the word “simultaneously”. Thus, you have quite exactly in this book the most part of the art of the Messer and the great basis. |
[116v.3] Nu soltu wissen wz dz wort Indes ist ob du entpfindest ob er wiech oder hart ist in der versatzung So merck dz du Indes arbeist In allen stucken wie du sie merckest der eygenschafft der ding die auch vff dich geprucht vnd gemacht sint oder die du vff eynem machen bist Indes duplier Indes müttier Indes durch lauff Indes beschlus Indes nÿmb den schnitt Indes Ring Indes messer nÿmb Indes benÿmb Indes durch ge Indes lauff Indes thün waß din hertz begertt Indes ist eyn scharpfes wortt do mit die meinster hart ver schnitten weiden vnd zu vor vß die meinster die des wortz Indes nit wissen [117r.1] noch vernemen also hastu gar gnaulbe in dissem buch den meinsten teill die künst des messers vnd den grosten grüntt ~ |
[114r.3] ¶ Nw soltu wyssen waß daß wortt yndeß ist ob dw enpfindest ob er weych oder hertt yn der versaczung ist So merck daß dw yndeß erbeyttest yn alle stuck wye dw merckest dy eygenschafft der ding dy auch aff dich gepracht und gemacht werden oder [114v.1] dye dw auff eynem machen pist yndeß duplir yndeß mutir yndeß wechsel durch yndeß durchlauff yndeß peschleuß yndeß nymb den schnydt yndeß ring yndeß messernymb yndeß penymb yndeß durchgee yndeß ablauff yndeß thu waß deyn hertz begert yndeß ist eyn scharpffeß wortt da mit dy meyster hartt verschnytten werden und zw vor aüß dy meyster dy deß worcz yndeß nicht wyssen noch vernemen alzo hastu gar genaw yn dysem püch den meystern teyl der künst deß messerß und den grosten gründt etc |
[216v.2] Nu soltu wyssen was das wortt Indes ist ob du Enpfindest ob ir weych oder hertt ist In der versatzung so merck das du Indes erbeyttest In alle stuck wye du merckest dy eygenschafft der ding dy auff dich gepracht vnd gemach werden oder dy du auff eynen machen pist Indes duplire: Indes mutir: Indes durchlauf: Indes peschleuß: Indes nymm den schnytt: Indes ring: Indes messer nym: Indes pnym: Indes durchge: Indes durchlauff: Indes thu was deyn hertz begertt: Indes ist Eyn scharpffes wortt da mit dy meyster hartt verschnytten werden zu vor auß dy meyster dye deß wortz Indes nicht wyssen noch vernemen also hastu gar genaw In disen puch den meysten tayl der kunst des messers vnd den grosen Grundt etc |
||||||||
[588] The end. |
[114v.2] Et sic est finis |
|||||||||||
[589] |
Thus, Sir Hans Lecküchner of Nuremberg has made, composed, and finished this book. God send him the Holy Blessing, and forgive him evil, misdeeds, and sins, and give him His Charitable Divine Grace and Salvation. Amen. |
[114v.3] Alzo hatt her hannß lecküchner von nurnberg dyseß puch geticht gemacht und geendt gott ym den heyligen segen sendt vergeb ym seyn ubel missetat und schuld und pebeyß ym seyn barmherczige gottliche gnad und huld ·:· Amen ·:· |
[216v.3] Alzo hatt Herr Hannes Lecküchner von Nurenberg das püch gemacht vnd geticht geendt gott Im den hayligen segen sendt vnd vergeb Im vbel myssetat vnd schuld vnd pebeyß Im seyn parmmhertzige gottliche gnad vnd hulf amen |
|||||||||
[590] |
This material has been composed by Reverend Hans Lecküchner, at the time parish priest in Herzogenaurach, in the year of our Lord 1478, but this book has been written and completed the in 82nd year on the eve of St Sebastian.[103] |
Illustrations |
Draft Translation (from the Heidelberg) |
No text (from the Munich) |
Salzburg Version (1491) |
Heidelberg Version (1478) |
Munich Ⅰ Version (1482) |
Vienna Version (1512) |
Glasgow Version (1533) |
Dresden (Mair) Version (1542) |
Vienna (Mair) German Version (1550s) |
Munich (Mair) Version (1540s) |
Vienna (Mair) Latin Version (1550s) |
Munich Ⅱ Version (1556) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[1] Illustrious and Very Mighty Prince etc Philip! Since the excellent art of fighting has not been invented by mediocres nor people of minor importance and by no means from the nature of the thing, but by magnificent men of sharpest ability, and so that military exercises be proven by it, You master rightfully this art with greatest vigilance to whatever place You will and commonly and in armour, as much as it belongs to a Prince, and You soundly have both its art and practice. However, since every art increases from day to day and desire for experiencing gradually grows and finally old things give ground to new ones, Johannes Lecküchner of Nürnberg, most obedient to Your Great Might, has skillfully made from the workshop of his ability not a few points in Messer, worth Your attention, not only in fighting but also in defending, which whether indeed are worth praising and are estimated as lordly, everyone has verified in the long course of passed time and in numerous regions of the world. Moreover, so that he not be considered as claiming some arrogance to his name, he asks it to be called not an art but a petty art, which will admonish out of itself in this matter, which, whether can be considered as an art, needs to be clarified with hand, wheresoever he is by no means reluctant. Since he himself offers a text in this vernacular petty codex to Your Great Might, who considers You more worth of this matter than many other men, because of both brilliancy of Your ability and Your bodily integrity and also because of Your jollity towards books. Therefore, so that also the very matter suit Your Great Might, he rightfully proved the points included below with true experience one after another, and today, so that it pleased Your Magnificence (as he obliged himself above), he promises to prove it today. Thus, farewell, oh Very Mighty Prince, and Johannes, most prepared in obedience to all Your Great Might, desires eagerly that You not only exercise Your great ability and body in this matter, but that You also overcome, destroy by means of this matter all the men anticipating to struggle against Your Might and You subdue them like Hector the jokers. Again and again, farewell, oh Illustrious and Very Mighty prince, remembering about him out of compassion of Your generosity. |
[115r] Illustris haudnec multipotens princeps etc. Philippe quom presignis dimicandi ars non a mediocribus nec parui momenti hominibus, haudquoque ab re, sed per magnificos acutissimi ingenii viros, et ut militaria per eam exercitia comprobentur inuenta sit, tu summa eandem advigilancia in quouis eius et commune et armatura (quantum ad principem pertinet) rate complecteris eiusque tum artem tum praxim sane habes. Verumtamen quom ars indies que vis accrescit, experimendique cupido sensim augetur, vetera denique novis cedunt Ipse Johannes Leckuchner ex Nurnberg multipotentie tuae obsequentissimus in cultro non pauca spectatum tuum digna ingenii sui ex officina fabrifecit non modo dimicandi verumetiam tuendi puncta. quae siquidem et laude digni herilia censent quiquidem has res multenui temporis transfluxii multiplicibus terre in oris actuauit Neu autem arrogantiae quodpiam vendicare [115v] sibi nomine videatur eam non artem, sed articulam quae ex sese hac in re admuenerit appellari rogat, quam tunc an ars censeri habeat manu luci dari haud quamque eum piget Quom textem una quoque semet vulgari hoc in codicillo multipotenciae tue litat qui te huiusce rei preter ceteros complures tum ob ingenii tui claritudine tum ob corpoream ipsam tuam idemtitatem, et item propaginis tue ob festivitatem dignum ducit Ideopropterea ut et res ipsa multipotentie tue congruat singula infra conclusa reali experimento saepe merito singulariter coprobauit, atque hodie magnificentiae tue ut coplaceat (veluti supra se obligavit) hodie comprobare spondet; Vale ergo multipotens princeps ac non tantum ingenium corpus tuum hac in re ut exercites, sed et universos multipotentiae tue reluctari praesumentes ex ea superes profliges, atque instar goliardi hectoris [116r.1] ut substernes paratissimus obsequio in omni multipotentiae tue Johannes exoptat Iterum atque iterum vale illustris atque multipotens princeps eiusdem ex commiseracionis tuae plenitudine memor) |
|||||||||||
[2] Aristotle in his Metaphysics: “All the men by nature desire to know”[105] |
[116r.2] Aristoteles in sua methaphysica Omnis homo naturaliter scire desiderat |
For further information, including transcription and translation notes, see the discussion page.
Additional Resources
- Kunst und Zettel im Messer: Bavarian State Library Cgm 582 (2021). Ed. by Michael Chidester. Somerville: HEMA Bookshelf. ISBN 978-1-953683-16-8.
- Acutt, Jay (2019). Swords, Science, and Society: German Martial Arts in the Middle Ages. Glasgow: Fallen Rook Publishing. ISBN 978-0-9934216-9-3.
- Burger, Daniel (2021). "Hans Lecküchner of Nuremberg and His Fencing Treatise in the Long Knife." Kunst und Zettel im Messer: Bavarian State Library Cgm 582: 121-140. Ed. by Michael Chidester. Somerville: HEMA Bookshelf. ISBN 978-1-953683-16-8.
- Dupuis, Olivier (2021). "Fighting with Long Knife for Leisure or Self-Defense: Discussions Around the Production Contexts of Lecküchner's Fencing Manuscript." Kunst und Zettel im Messer: Bavarian State Library Cgm 582: 191-202. Ed. by Michael Chidester. Somerville: HEMA Bookshelf. ISBN 978-1-953683-16-8.
- Fabian, Martin (2024). Fechtbuch Fabian. Self-published. ISBN 978-80-570-6163-2.
- Finley, Jessica (2021). "'What's in a Name?' A Comparative Analysis of the Nomenclature of Johannes Lecküchner and Johannes Liechtenauer." Kunst und Zettel im Messer: Bavarian State Library Cgm 582: 157-174. Ed. by Michael Chidester. Somerville: HEMA Bookshelf. ISBN 978-1-953683-16-8.
- Fritz, Falko (2021). "The Messer and Its Use in Lecküchner's Teachings." Kunst und Zettel im Messer: Bavarian State Library Cgm 582: 141-156. Ed. by Michael Chidester. Somerville: HEMA Bookshelf. ISBN 978-1-953683-16-8.
- Hagedorn, Dierk (2021). Albrecht Dürer. Das Fechtbuch. Herne: VS-Books. ISBN 9783932077500.
- Hagedorn, Dierk; Daniel Jaquet (2022). Dürer's Fight Book: The Genius of the German Renaissance and his Combat Treatise. Barnsley: Greenhill Books. ISBN 978-1-784438-703-7.
- Lecküchner, Johannes (2015). The Art of Swordsmanship by Hans Lecküchner. Trans. by Jeffrey L. Forgeng. Woodbridge: Boydell Press. ISBN 9781783270286.
- Müller, Jan-Dirk (1992). "Bild – Verse – Prosakommentar am Beispiel von Fechtbüchern. Probleme der Verschriftlichung einer schriftlosen Praxis." Pragmatische Schriftlichkeit im Mittelalter. Erscheinungsformen und Entwicklungsstufen: 251-282. Ed. by Hagen Keller; Klaus Grubmüller; Nikolaus Staubach. München: Fink.
- Müller, Jan-Dirk (1994). "Hans Lecküchners Messerfechtlehre und die Tradition. Schriftliche Anweisungen für eine praktische Disziplin." Wissen für den Hof. Der spätmittelalterliche Verschriftlichungsprozeß am Beispiel Hei-delberg im 15. Jahrhundert: 355–384. Ed. by Jan-Dirk Müller. München: Fink.
- Van Dijk, Casper J.; Oskar ter Mors (2021). "'The Art that Hans Lecküchner Made and Devised Himself': The Martial Arts Tradition of a Fifteenth Century Bavarian Priest." Kunst und Zettel im Messer: Bavarian State Library Cgm 582: 203-228. Ed. by Michael Chidester. Somerville: HEMA Bookshelf. ISBN 978-1-953683-16-8.
- Welle, Rainer (2021). Albrecht Dürer und seine Kunst des Zweikampfes: auf den Spuren der Handschrift 26232 in der Albertina Wien. Kumberg: Sublilium Schaffer, Verlag für Geschichte, Kunst & Buchkultur. ISBN 9783950500806.
References
- ↑ Julia and Carsten Lorbeer (in German). "Johannes Lecküchner - der fechtende Pfarrer". Ochs: Historische Kampfkünst e.V., 2002. Retrieved 21 April 2011.
- ↑ Fencing master Ludwig VI von Eyb was a powerful noble in service to Philip from 1499 to 1504 (and possibly longer), but his writings demonstrate no connection to or awareness of those of Lecküchner.
- ↑ The Cgm 582 states on folio 216v that "This material was composed by the Reverend Johannes Lecküchner, at that time of the parish in Herzogenaurach, in the year of our Lord 1478, but this book was written and completed in the 82nd year on the eve of St. Sebastian." (Composita est materia illa per domine Johanne Lecküchner tunc tempore plebanus jn Hertzogaurach Anno domini M°CCCC° septuagesimo octauo sed iste librum Scriptum est et completus Anno 8° secundo jn vigilia sancti Sebastiani).
- ↑ Hans von Speyer. Untitled [manuscript]. MS M.I.29. Salzburg, Austria: Universitätsbibliothek Salzburg, 1491. ff 5r-7r
- ↑ Word scratched out.
- ↑ Unnecessary repetition, a scribe’s mistake.
- ↑ I.e., rapidly
- ↑ recept = Rezept (Hennig, S263)
- ↑ oder
- ↑ Auf der linken Blattseite befindet sich ein unbekanntes Zeichen, oder der Schreiber hat zu weit links angesetzt.
- ↑ oder
- ↑ schalt = Schwung (Hennig, S279)
- ↑ vmb süst = umsonst; sus = sunst (Baufeld, S231)
- ↑ Der Schreiber wollte wohl erst “deinem” schreiben
- ↑ sic : seinem
- ↑ I.e., avoid the stroke by means of bowing forwards.
- ↑ geschrieben
- ↑ Das Wort “pist” wurde nachträglich ergänzt.
- ↑ sic : deinnem
- ↑ sic : seinn
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 21.2 Text is cut off at the bottom of the page, but reconstructed from other copies.
- ↑ I.e., is faster or better
- ↑ Sa alt. von sar = gleich darauf, alsbald sodann (entweder alleine oder verstärkt durch sinnverwandte Ausdrücke) (Lexer, S205) end = ehe, bevor (Lexer, S43)
- ↑ Munich: "right".
- ↑ Munich: "right".
- ↑ Unknown word scraped away
- ↑ oder
- ↑ handt hab
- ↑ I.e., the point and the pommel.
- ↑ See Matthew 7:6
- ↑ oder
- ↑ Wort könnte von sambalde kommen = alsbald (Hennig, S276) oder sam = als (Hennig, S275)
- ↑ Könnte von senen = ersehnen kommen (Lexer, S225)
- ↑ Der Schreiber wollte wohl messer schreiben.
- ↑ sic : bis. rep.
- ↑ Müßte sinngemäß "In" heißen
- ↑ ge- = es kann vor alle Formen des Zeitworts treten, um die Handlung abzuschließen oder zu verstärken (Lexer, S60)
rucke, rücke, ze ruck = zurück, nach hinten - ↑ tener oder tenner bezeichnet die von der Rüstung nicht geschützte Handfläche. (Baufeld, S50)
- ↑ Sa alt. von sar = gleich darauf, alsbald sodann ( enweder alleine oder verstärkt durch sinnverwandte Ausdrücke ) ( Lexer, S205 )
end = ehe, bevor ( Lexer, S43 ) - ↑ For armoured combat of Andreas Liegnitzer see von Danzig, 73r-79v. This teaching was copied (with some omissions) by Lew Jud, see Lew, 70r-83v. A technique based on a similar principle is featured in Lew, 79v-80r.
- ↑ gefast
- ↑ Das Zeichen könnte für einen Verweis auf eine andere Seite stehen, auf dem dieses F zu sehen ist. Diese Methode hat der Schreiber auch schon auf anderen Seiten angewandt.
- ↑ pinden = binden, fesseln (Baufeld, S34)
- ↑ gemelich = gemechlich = bedächtig, ruhig, langsam (Hennig, S108)
- ↑ kostlich = kostspielig, aufwendig (Hennig, S190)
- ↑ Im cpg430/46r heißt es “der verporgengriff“
- ↑ See Matthew 7:6.
- ↑ Das Wort sieht eigentlich wie „knorren“ aus.
- ↑ mug = mag
- ↑ Corrected from "din"
- ↑ nott
- ↑ oder
- ↑ dast könnte von dasten = tasten kommen (Hennig, S51)
- ↑ vber seyn danc = Gegen seinen Willen (Hennig, S50)
- ↑ Müßte eigentlich “deyn” heißen.
- ↑ vahen = greifen, fassen, einfangen (Lexer, S310)
- ↑ weifen = fuchteln, schwingen, schwencken (Grimm, Bd 28, Sp. 632, 5)
- ↑ Haspel [Garnwinde] (Hennig, S147)
- ↑ doch
- ↑ sambalde = alsbald oder sam = als (Hennig, S276)
- ↑ zäumen = gefangen nehmen (Baufeld, S254)
- ↑ “Item“ wurde nachträglich ergänzt
- ↑ albeg(en), alleweg = 1. immer, immer noch 2. überall (Baufeld, S6)
- ↑ oder
- ↑ abenteuerlich = ausgefallen, nicht alltäglich (Baufeld, S1)
- ↑ “auff deyn rechte” sieht wie durchgestrichen aus
- ↑ straufen = 1. die Haut abziehen, abstreifen 2. streuen. (Baufeld, S228)
- ↑ durchwechseln
- ↑ Wort zwischen “der” und “erst” wurde durchgestrichen.
- ↑ plüpflich = plötzlich (J.A. Schmeller, Bayerisches Wörterbuch, I,460)
- ↑ Links unten befindet sich eine kurze Notiz, die aber sehr schlecht lesbar ist.
- ↑ Links der Glosse befindet sich die handschiftliche Notiz einer anderen Hand
- ↑ Müßte sinngemäß “seynem” heißen.
- ↑ Schreiber wollte wohl “zu” schreiben.
- ↑ “Seynem” wurde mit “deynem” überschrieben.
- ↑ Zwischen den beiden Fechterfiguren befindet sich eine unleserliche Notiz, die mit anderer Hand geschrieben wurde. “man...”
- ↑ First written "deyner", then corrected.
- ↑ Abbreviatur sieht ähnlich aus wie “qd” aus, das für quondam steht (Cappelli, S306)
- ↑ Buchstabe g wurde mit einem f überschrieben
- ↑ prangen = prangen, glänzen (Hennig, S256)
- ↑ beiten = warten, zögern (Hennig, S24)
- ↑ Am unteren Rand des Blattes befindet sich der Schmuckbuchstabe B (164r), auf der darauf folgenden der Buchstabe A (164v). In cpg430 sind diese Seiten in umgekehrter Reihenfolge zu finden. Dieser Fehler läßt vermuten, daß der Zeichner die Abbildungen vertauscht hat und läßt der Schlußfolgerung zu, daß die Zeichnungen vor dem Text in die Handschift eingegangen sind.
- ↑ gen = geben (Deutsches Wörterbuch von Jacob und Willhelm Grimm,Bd. 5, Sp. 3342,21)
- ↑ gereicht zur Ehre
- ↑ poß = böse (Baufeld, S39)
- ↑ teding kommt von tedinc = (Zwei-)kampf (Henning, S236), dinc = ding (Baufeld, S52). tedingen = strafen, büßen (Baufeld, S49)
- ↑ nindert = keinesfalls, keineswegs, nirgendwo (Hennig, S243)
- ↑ Der Schreiber wollte scheinbar mit einem “v” ansetzen
- ↑ zäumen = gefangen nehmen (Baufeld, S254)
- ↑ Am Ende des Worts wurde ein Buchstabe wieder ausgestrichen
- ↑ Written as "Seyn" and then changed.
- ↑ Written as "deyn" and then changed.
- ↑ Corrected from "Lanck".
- ↑ leme = Lähmung (Hennig, S204)
- ↑ scharpff
- ↑ vürbaz = weiter, darüber hinaus (Hennig, S448)
- ↑ verworfen
- ↑ gagen = gegen: räumlich hin, zu, nach etwas (Lexer, S59/S63)
- ↑ stich
- ↑ graffeln = grabschen, greifen (Hennig, S138)
- ↑ Unter der Folierung 216 steht das Namenskürzel HC.
- ↑ Das Bild enthält die Worte: " 416 par fechter ". Scheinbar eine Zählung der abgebildeten Stücke.Eve. später von anderer Hand hinzugefügt.
- ↑ 19/20 January.
- ↑ Auflösung und Übersetzung nach Hils: “Der Gegenstand (dieses Buches) ist von mir, Johannes Lecküchner, derzeit Pfarrer in Herzogenaurach, im Jahre 1478 erarbeitet worden; dieses Buch aber wurde geschrieben und fertiggestellt im Jahre 1482 in der Nacht des Hl.Sebastian”
- ↑ Aristoteles, Metaphysica libri Ⅰ-Ⅳ, 4, lib. 1, cap. 1. Translatio “vetustissima”; Translatio Jacobi Venetici