|
|
You are not currently logged in. Are you accessing the unsecure (http) portal? Click here to switch to the secure portal. |
Difference between revisions of "Salvator Fabris"
(→Temp) |
(→Temp) |
||
| Line 2,452: | Line 2,452: | ||
| | | | ||
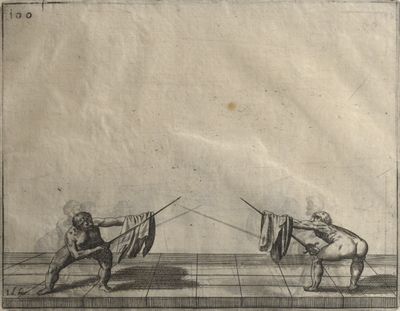
| [[file:Scienza d’Arme (Fabris) 118.jpg|400px|center]] | | [[file:Scienza d’Arme (Fabris) 118.jpg|400px|center]] | ||
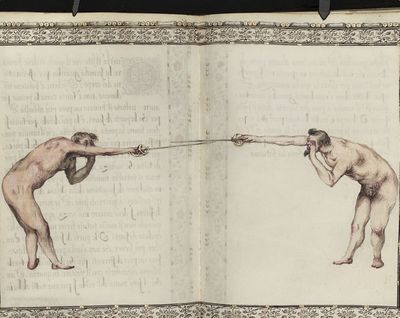
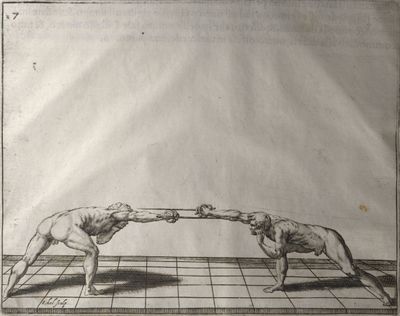
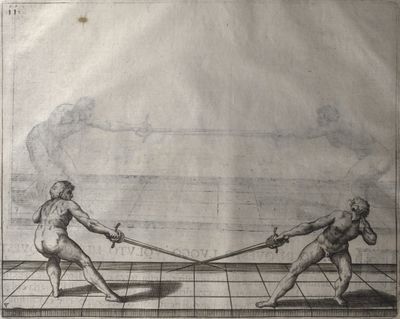
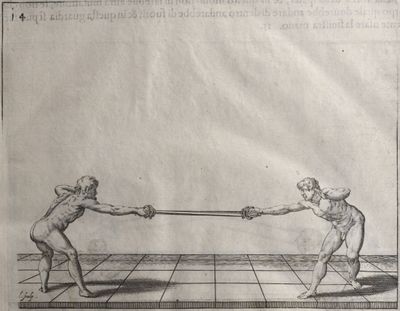
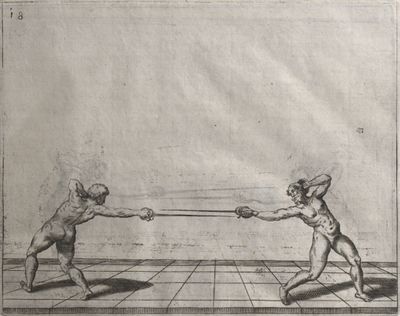
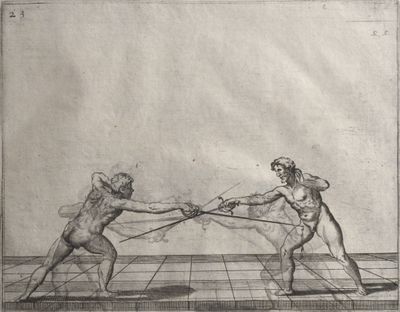
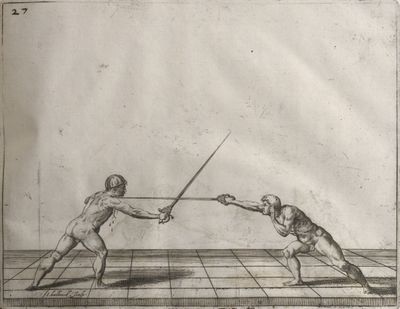
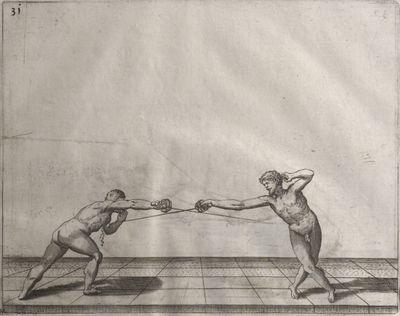
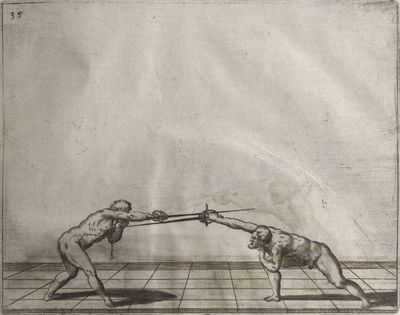
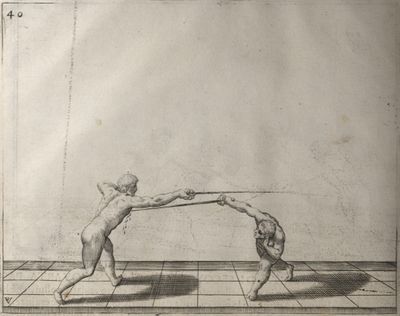
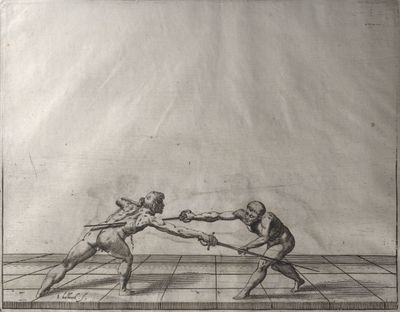
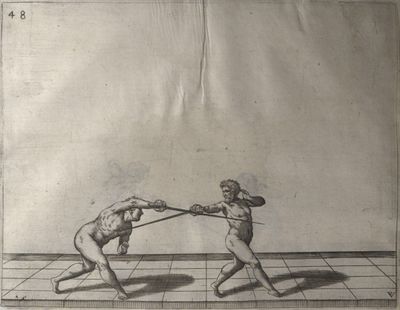
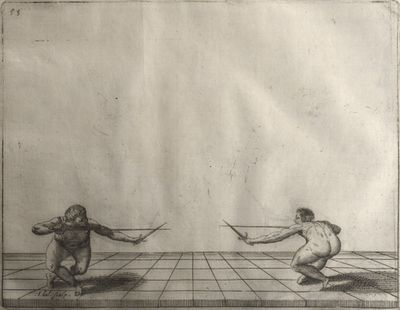
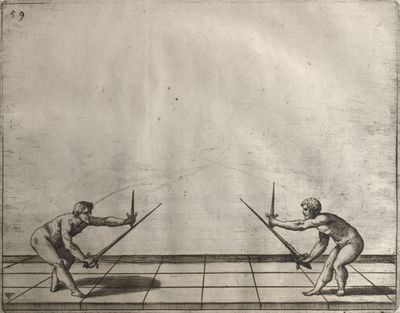
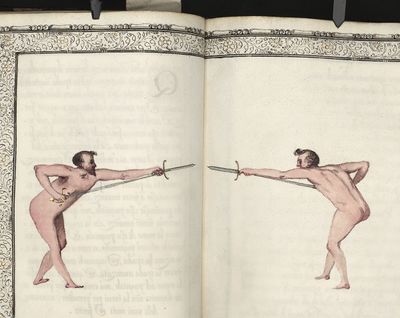
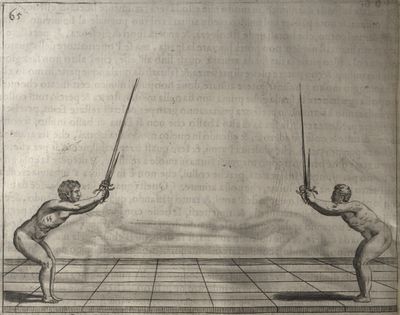
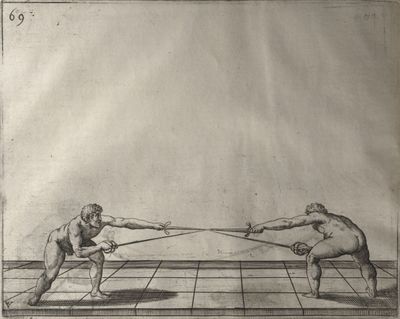
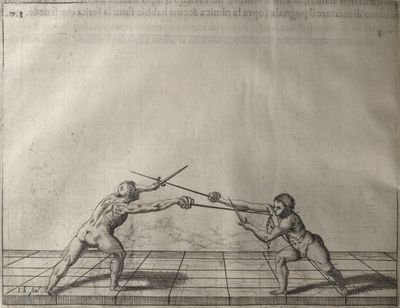
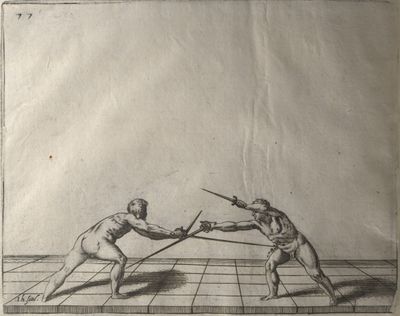
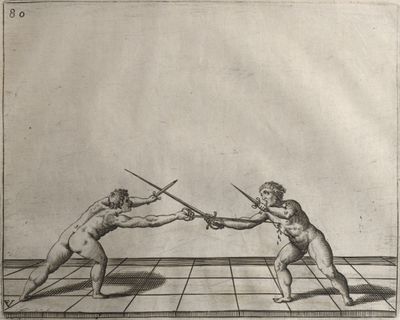
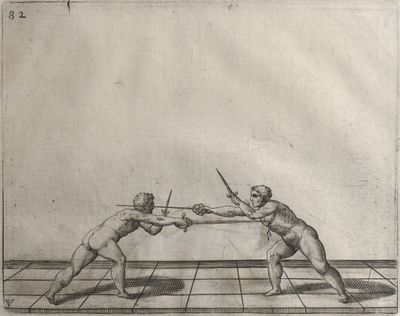
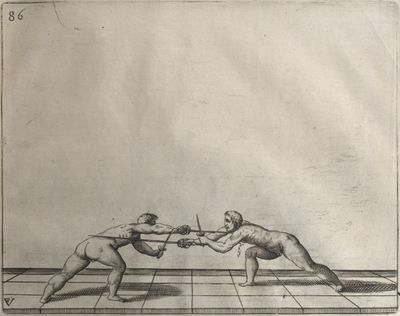
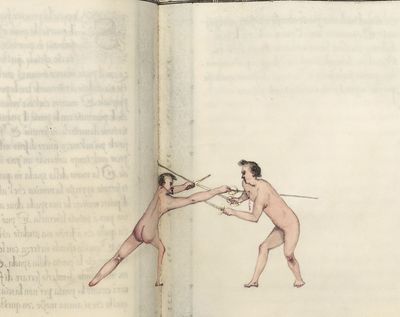
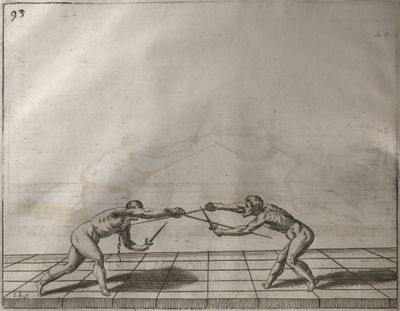
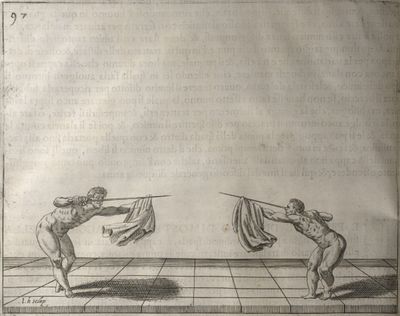
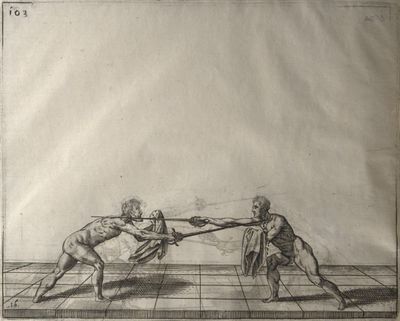
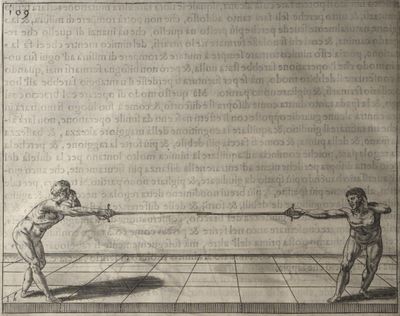
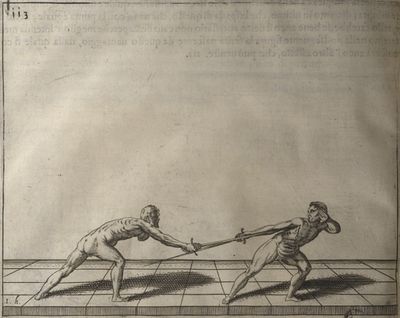
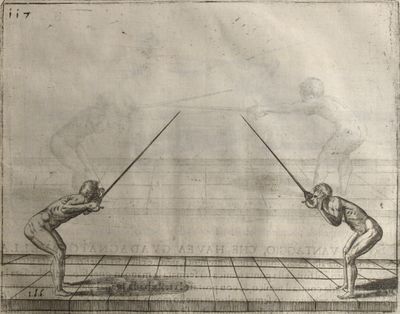
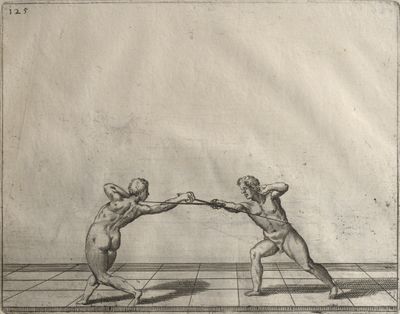
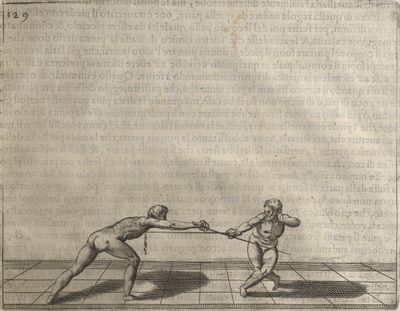
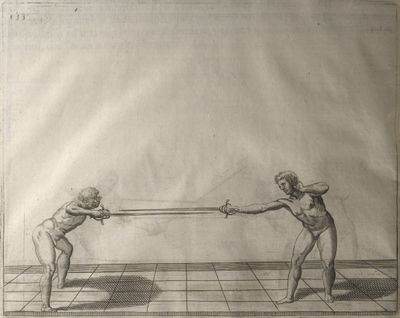
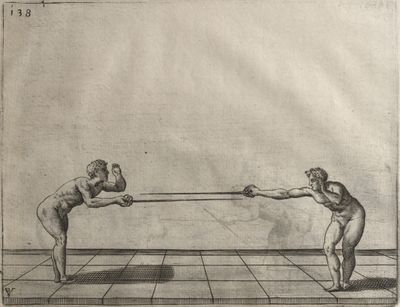
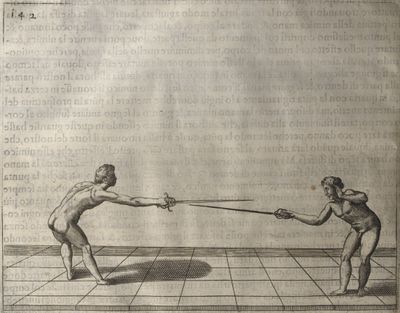
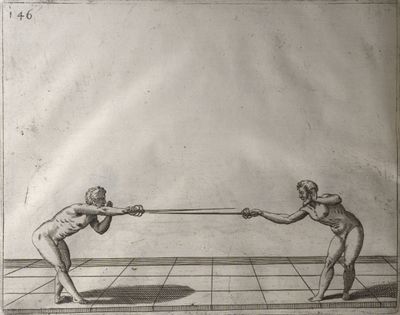
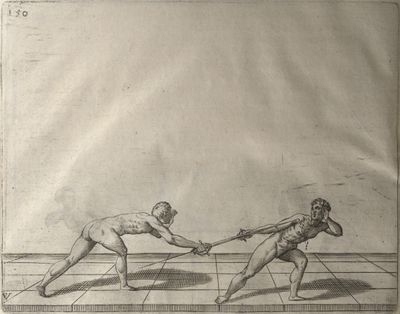
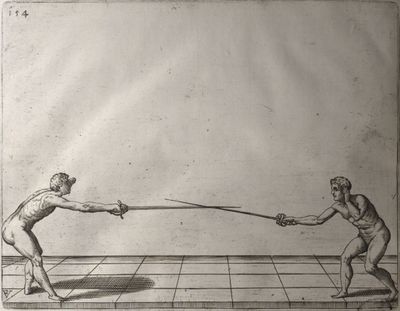
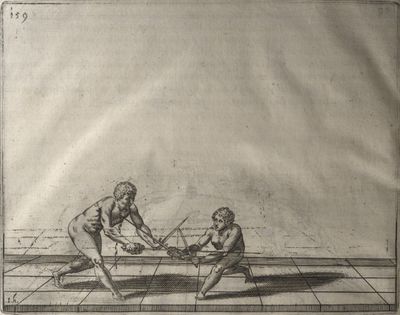
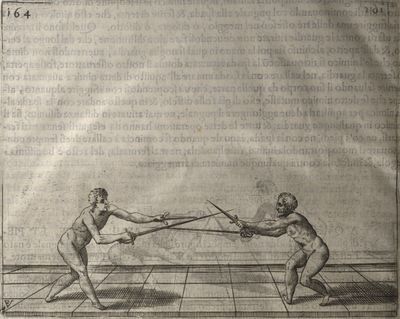
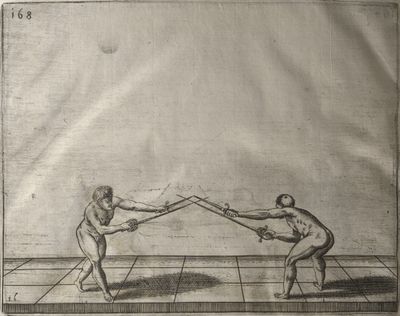
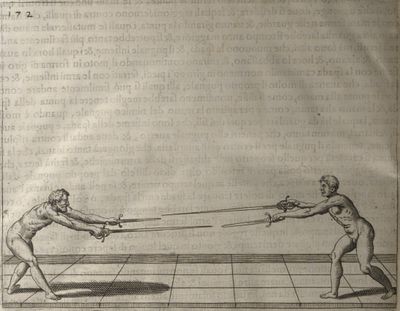
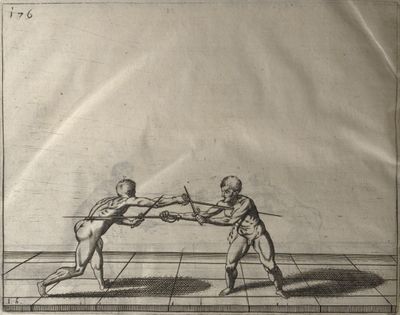
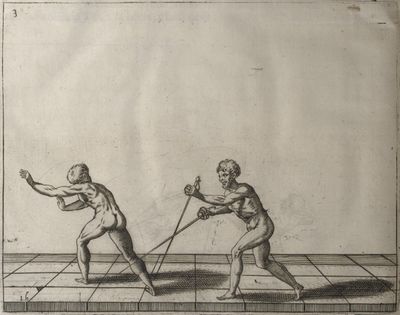
| − | | <p>[16] </p> | + | | <p>[16] This high guard of ''tierce'' leads to the advantage shown in this plate. As you approach the adversary, you direct your point, and lower the body, keeping the hand and arm steady, until the point is in line. You have controlled the adversary's sword and will maintain that position, when your point hits. If, when you come into line, the adversary disengages it order to hit on the inside of your guard, you will have penetrated with your body half the length of his blade, which deprives him of the power of turning out of line or passing. The advanced position of the guard facilitates your passing below, if he attacks your sword. in order that that result may be better understood it will be illustrated in its place.</p> |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 2,464: | Line 2,464: | ||
| | | | ||
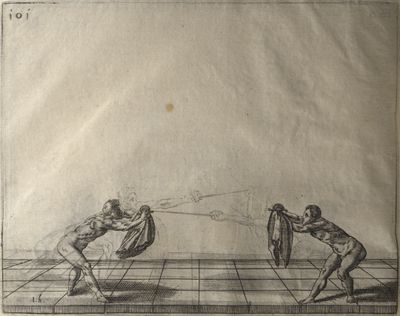
| [[file:Scienza d’Arme (Fabris) 119.jpg|400px|center]] | | [[file:Scienza d’Arme (Fabris) 119.jpg|400px|center]] | ||
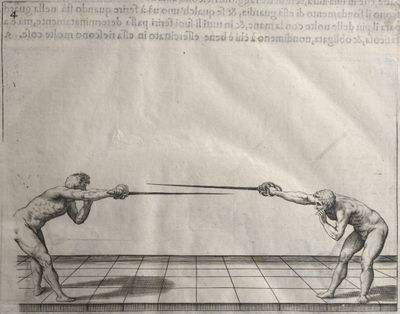
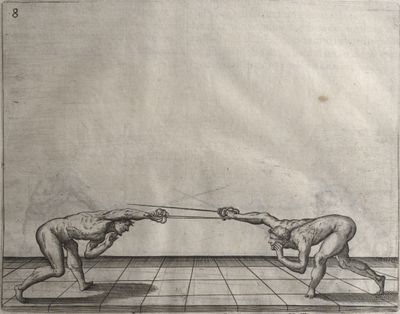
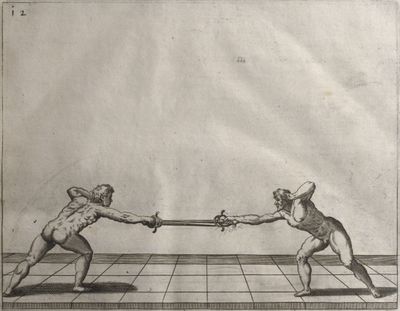
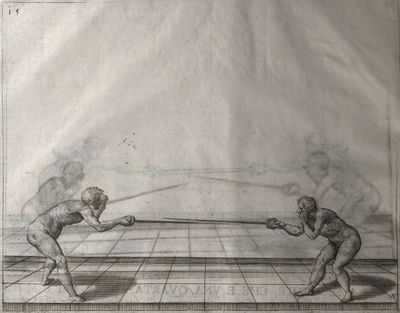
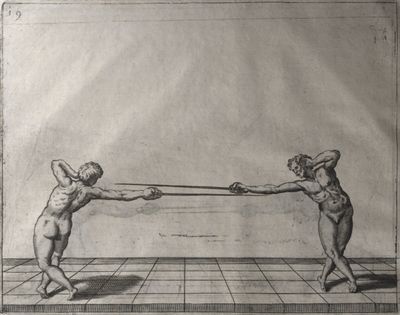
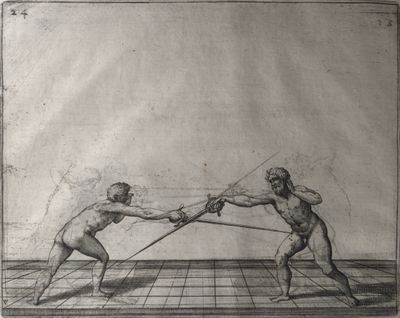
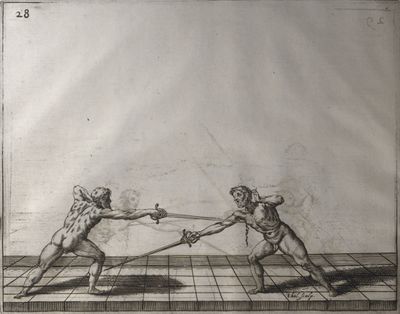
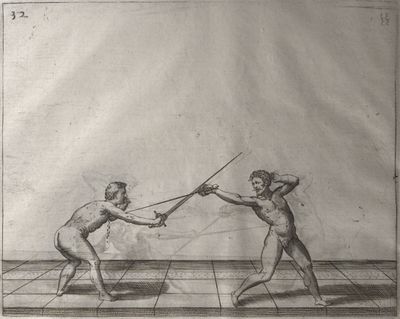
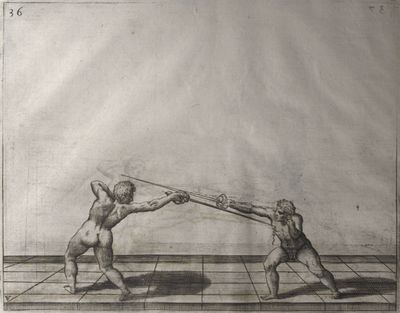
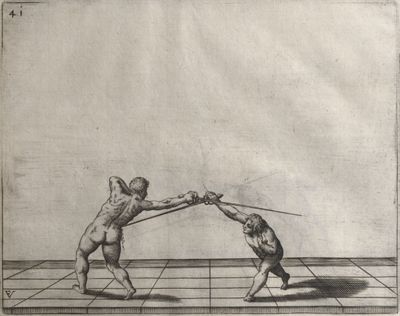
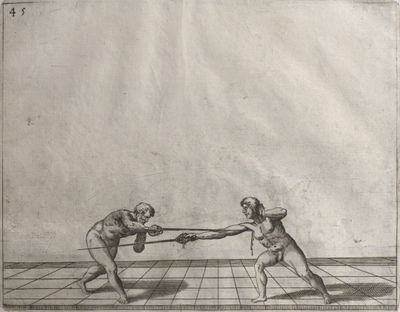
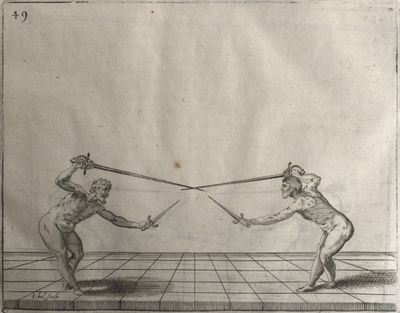
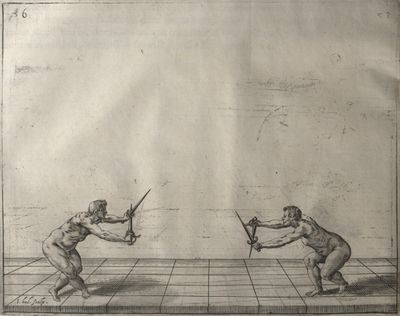
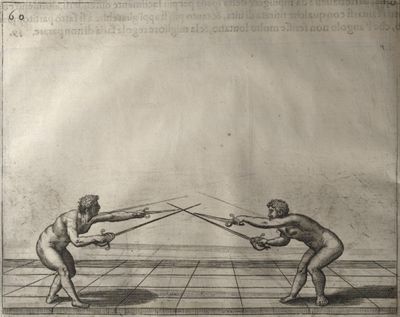
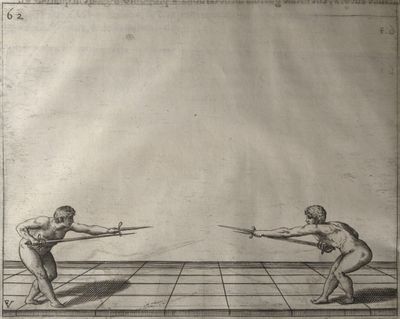
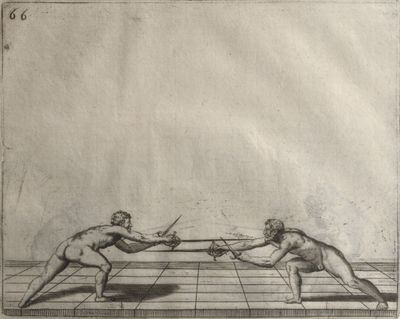
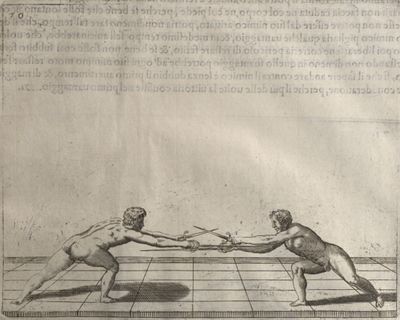
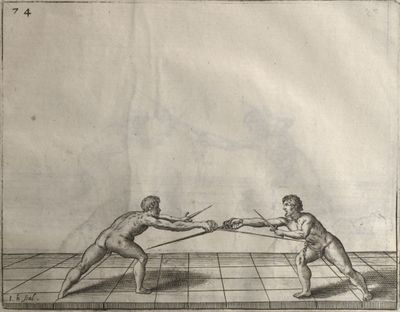
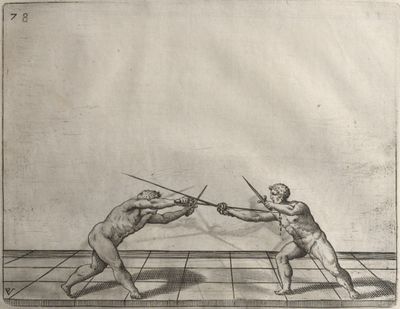
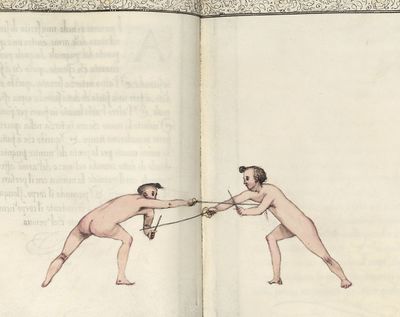
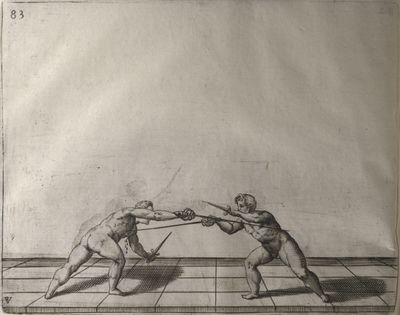
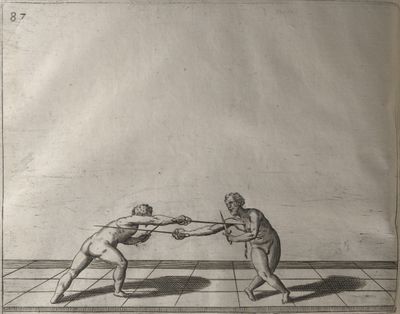
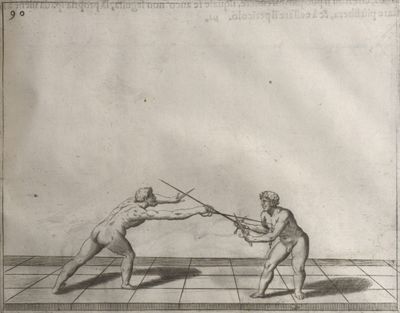
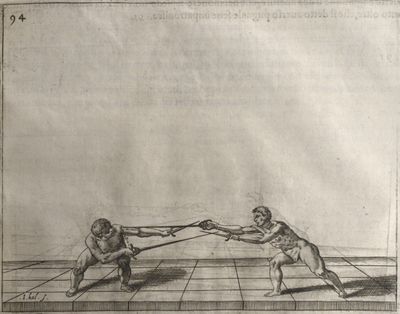
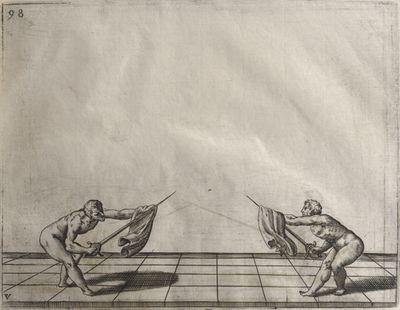
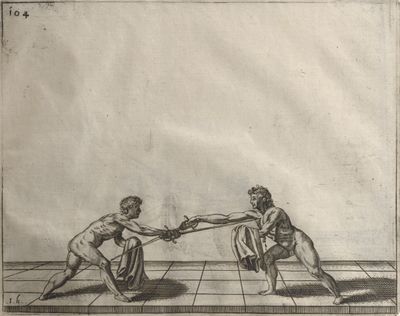
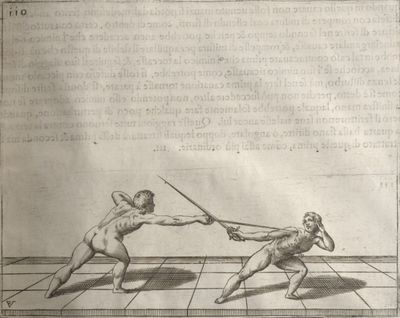
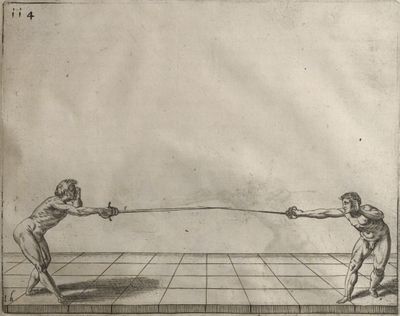
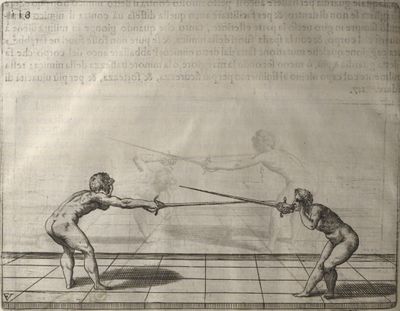
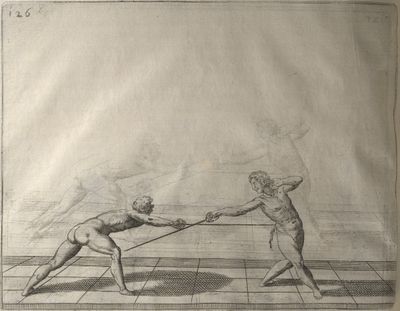
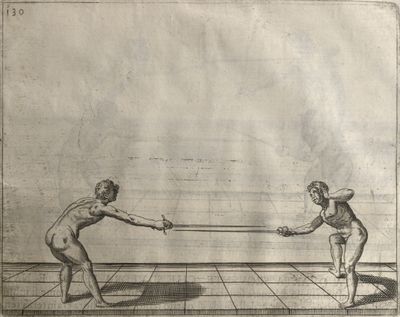
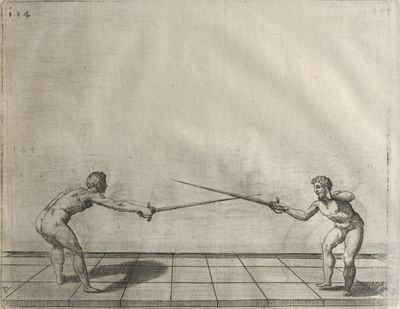
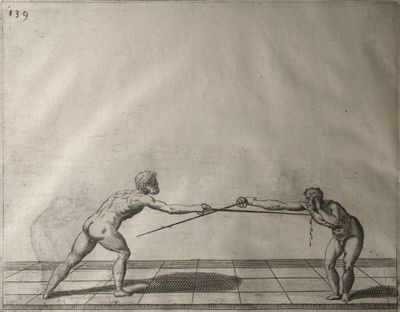
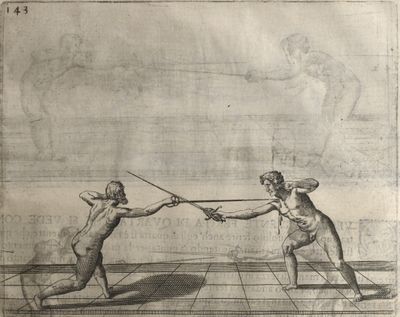
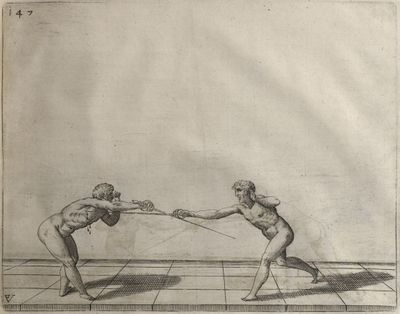
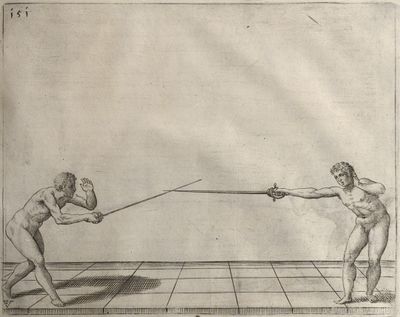
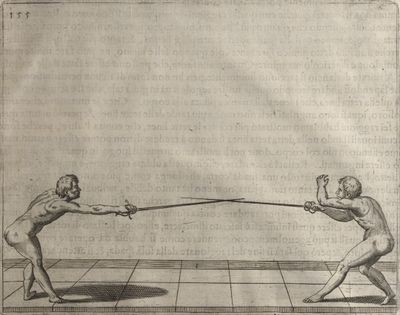
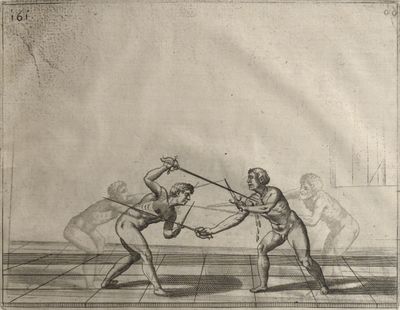
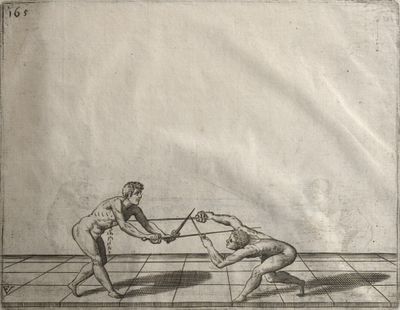
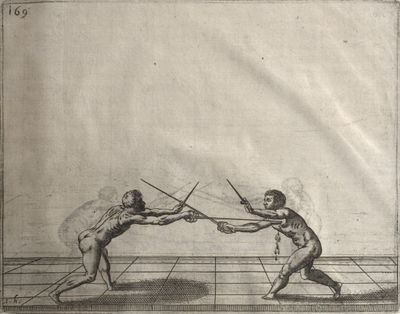
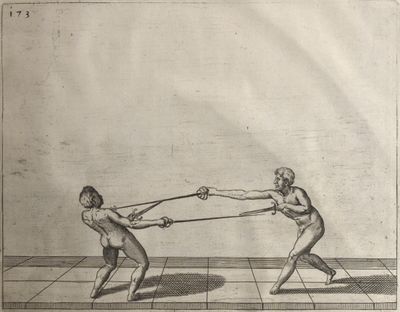
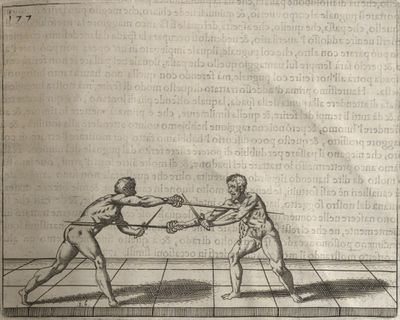
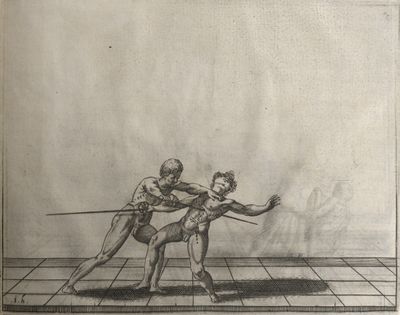
| − | | <p>[17] </p> | + | | <p>[17] From the advantage acquired by this high guard has arisen the following hit; you have reached the adversary's your ''forte'', checked your hand in that position, lowered your point, directing it against the adversary, and by carrying your head forward and below your own hand have continued your advance and hit in the throat, when his sword was high; if it had been lower, you could have hit lower by dropping your body and hand in proportion. If he had tried to parry by raising his sword, you would have disengaged below, and by turning your hand to ''seconde'' and keeping it in the same place would still have certainly hit.</p> |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 2,476: | Line 2,476: | ||
| | | | ||
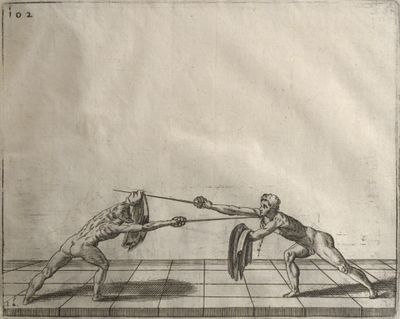
| [[file:Scienza d’Arme (Fabris) 120.jpg|400px|center]] | | [[file:Scienza d’Arme (Fabris) 120.jpg|400px|center]] | ||
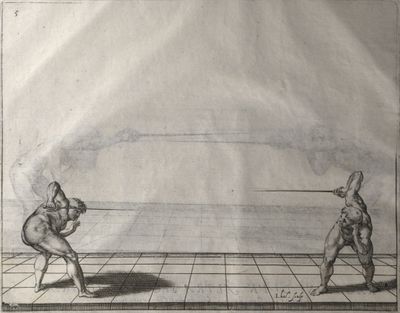
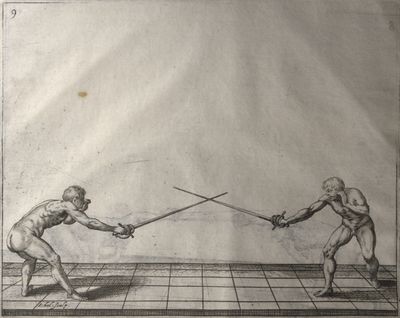
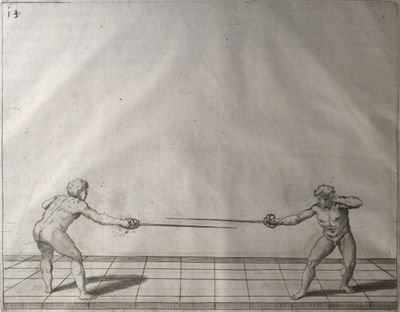
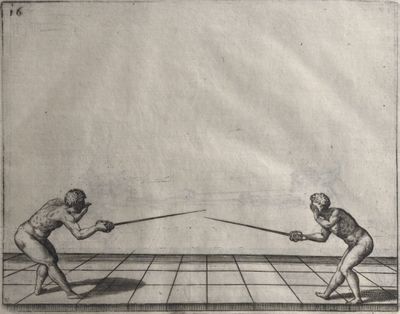
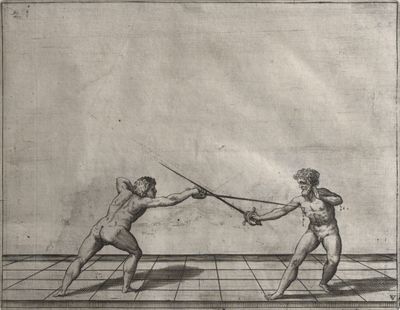
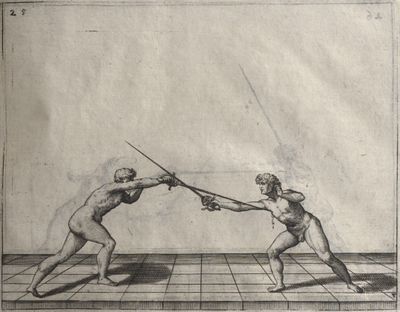
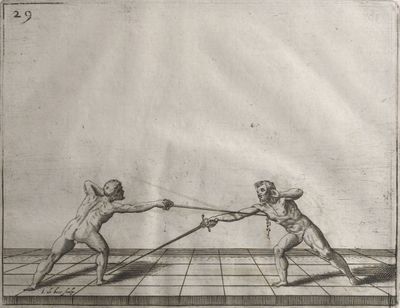
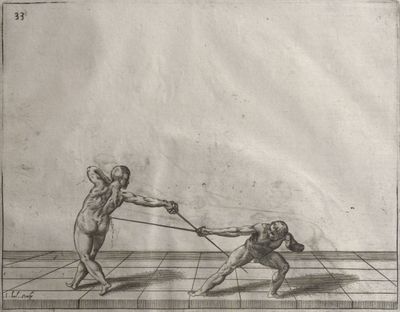
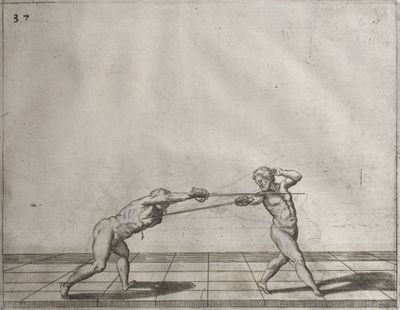
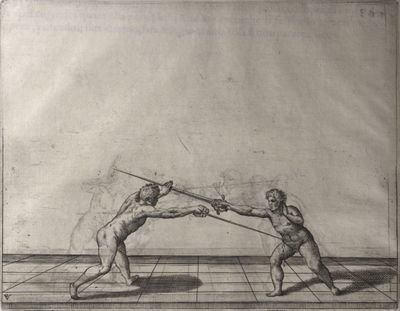
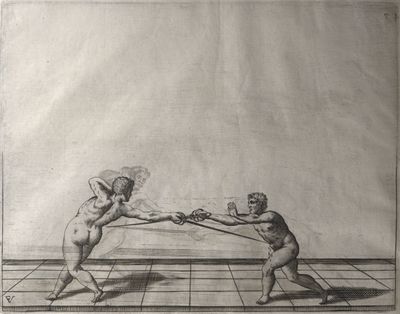
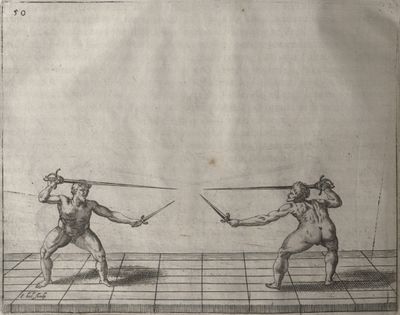
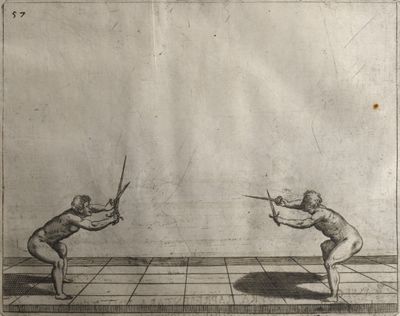
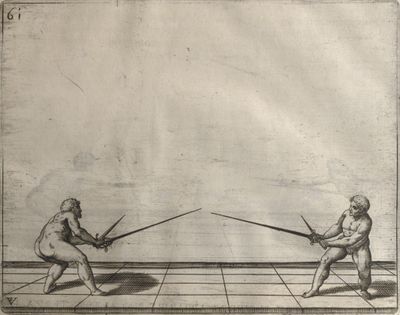
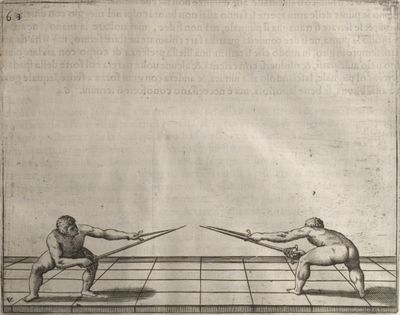
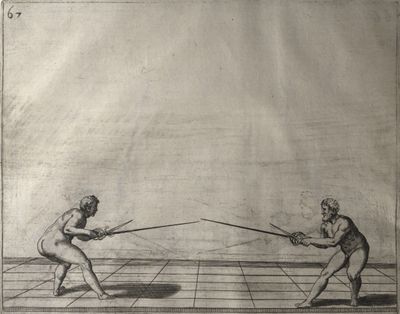
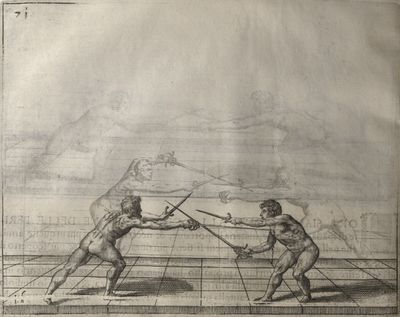
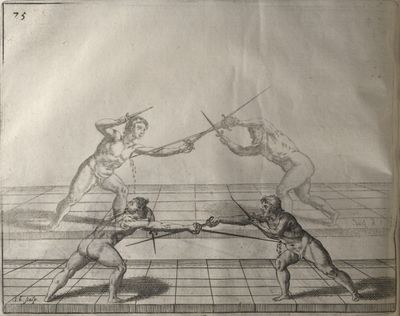
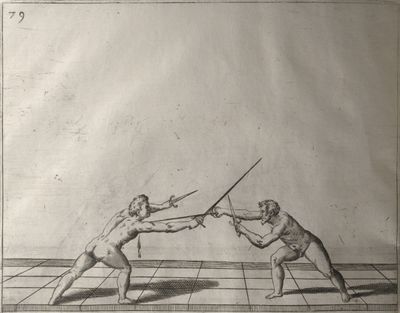
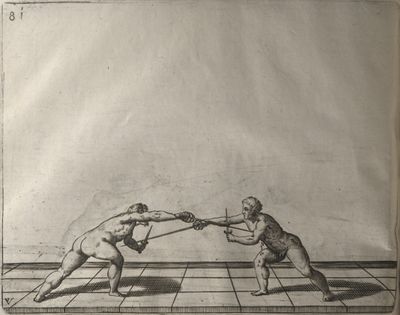
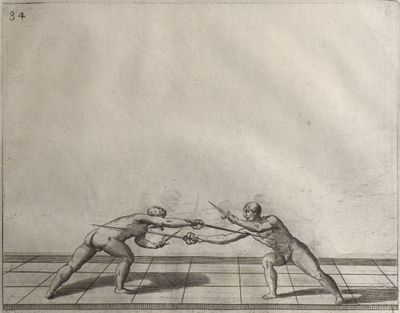
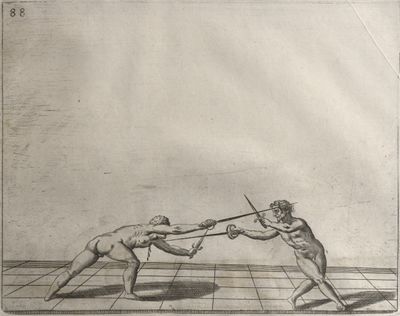
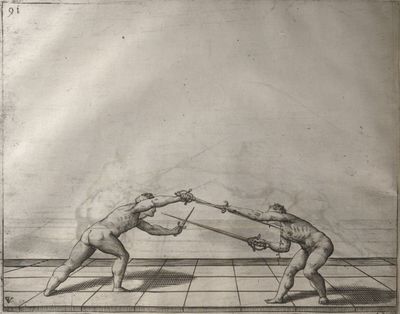
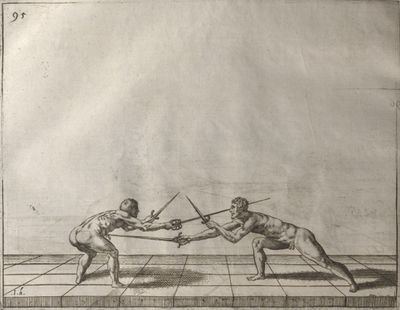
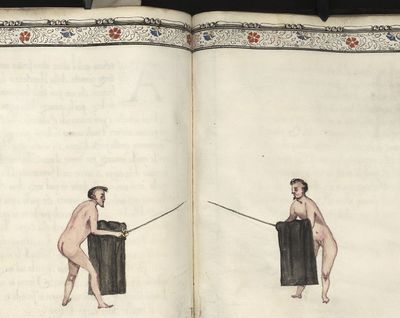
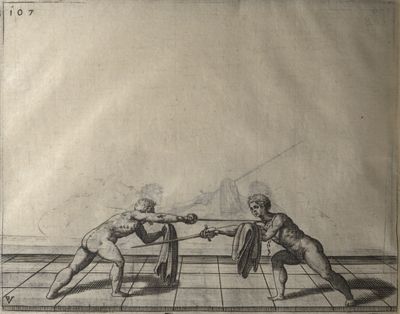
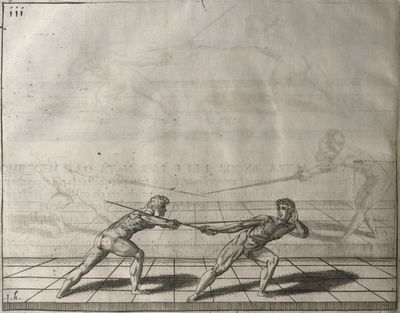
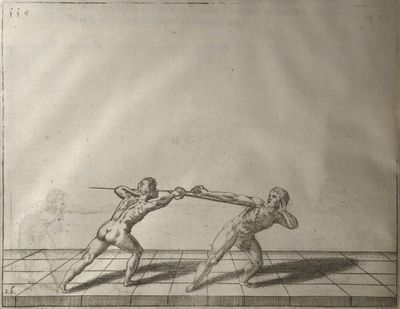
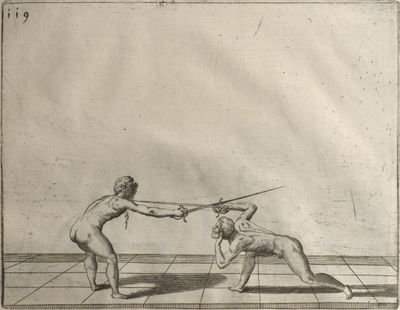
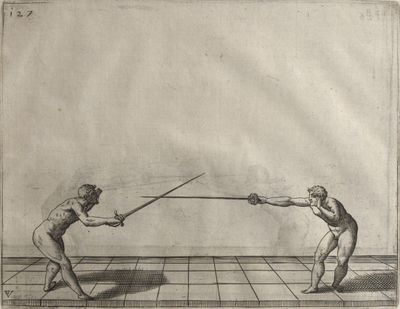
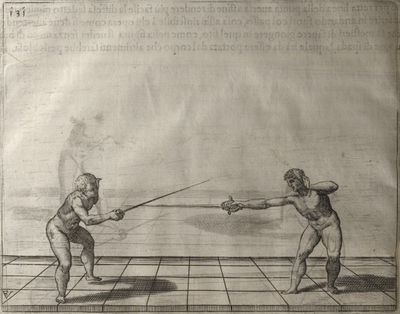
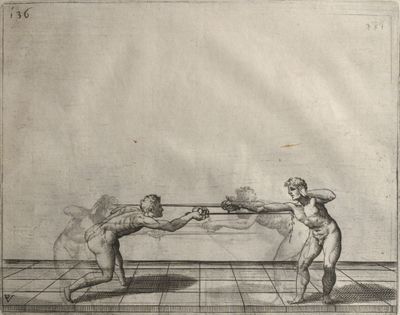
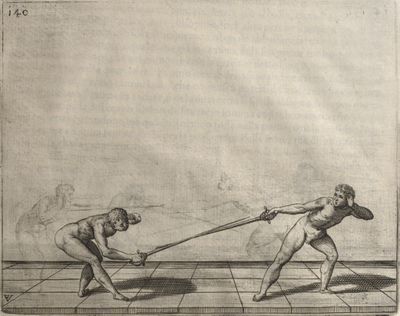
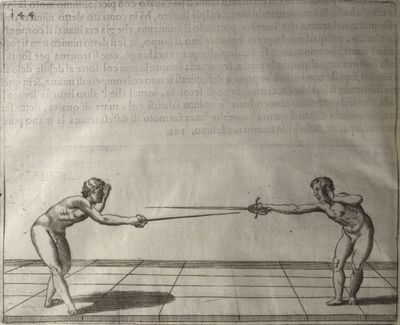
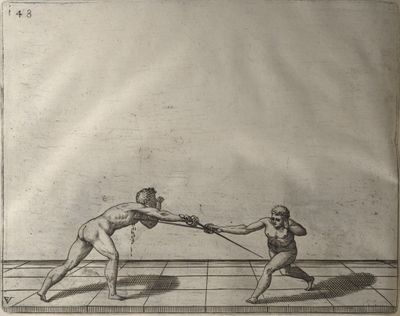
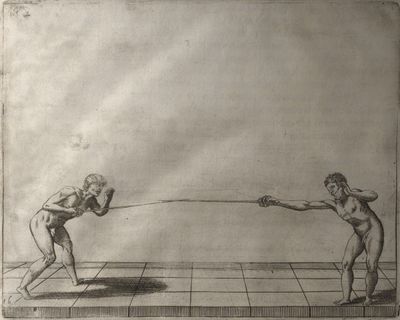
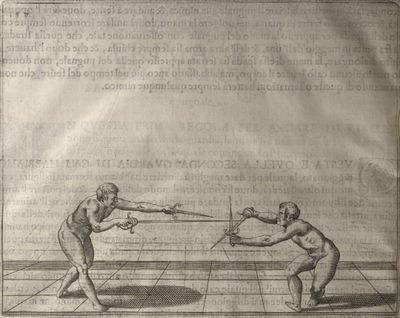
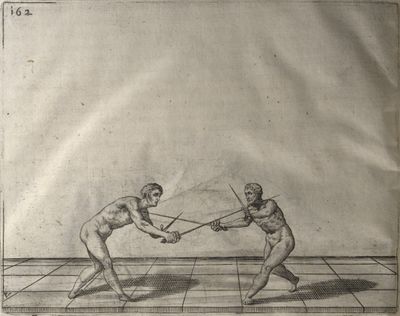
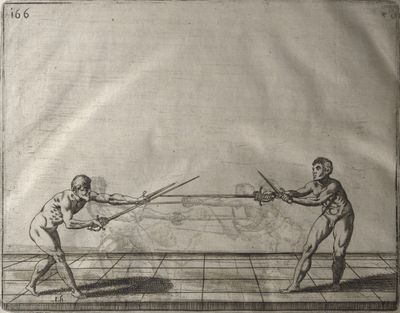
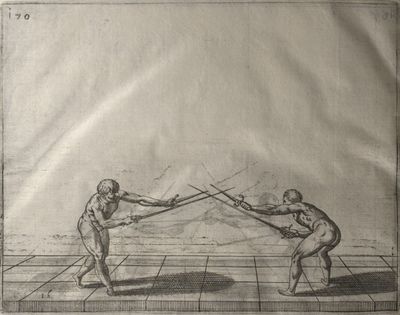
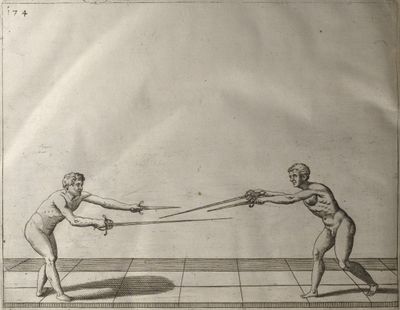
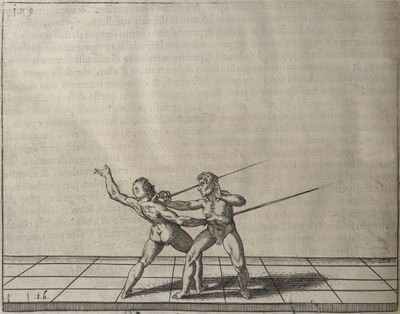
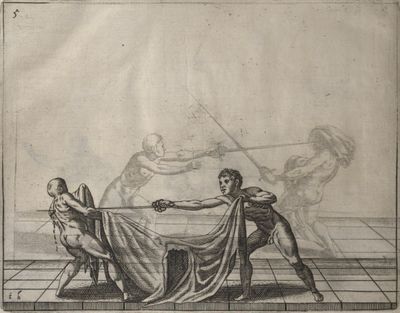
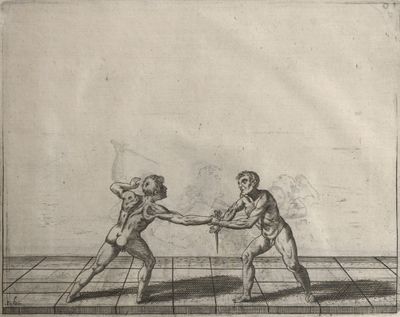
| − | | <p>[18] </p> | + | | <p>[18] The next is a hit in ''quarte'' against an opponent who has lunged in ''quarte''. You had engaged your adversary's ''faible'' on the outside with the high guard shown in the previous plates; he has tried to disengage and lunge in ''quarte'' on the inside in the path which appeared to him to be uncovered. But with your arm high and held back you have pressed on his ''faible'' with a guard of ''quarte'', and by carrying the right foot forward and somewhat out of the straight line and bending the body over it, you have made a hit in the throat. By continuing with the left foot you would have passed right to his body. If the adversary had tried to turn with either foot, he would have been all the weaker, and therefore you would have hit in the straight line or in the back.</p> |
| | | | ||
| {{pagetb|Page:Scienza d’Arme (Salvator Fabris) 1606.pdf|179|lbl=169}} | | {{pagetb|Page:Scienza d’Arme (Salvator Fabris) 1606.pdf|179|lbl=169}} | ||
| Line 2,487: | Line 2,487: | ||
| | | | ||
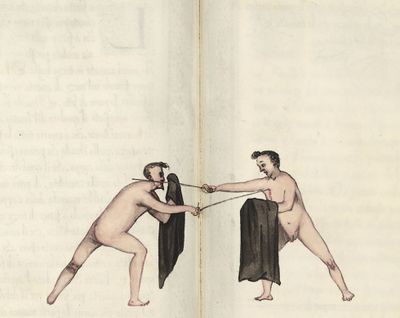
| [[file:Scienza d’Arme (Fabris) 121.jpg|400px|center]] | | [[file:Scienza d’Arme (Fabris) 121.jpg|400px|center]] | ||
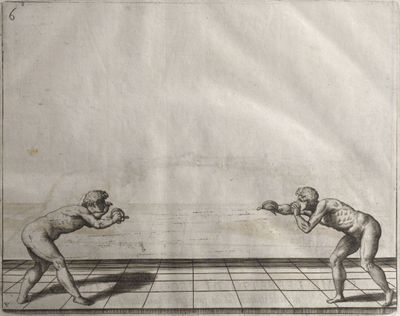
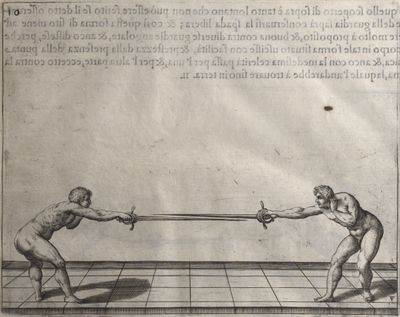
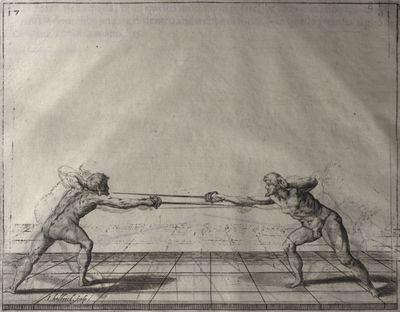
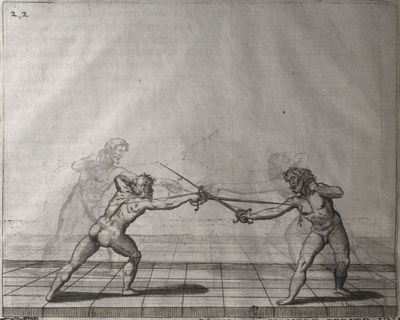
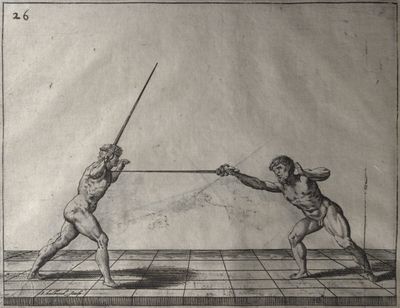
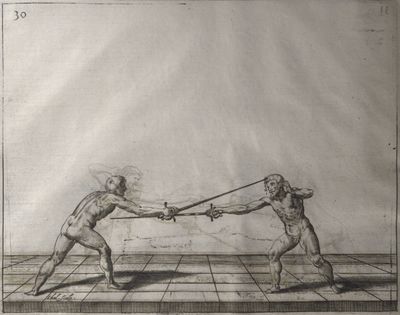
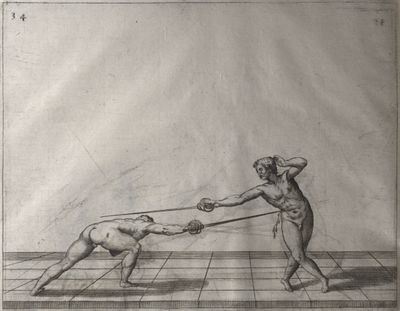
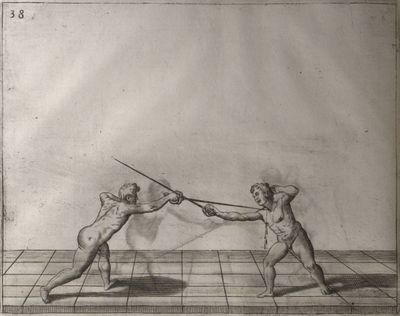
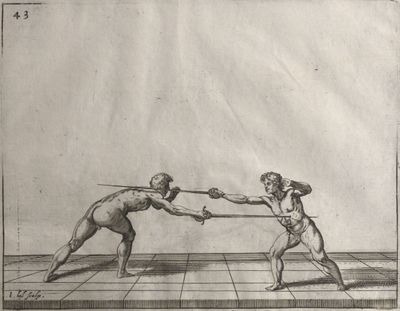
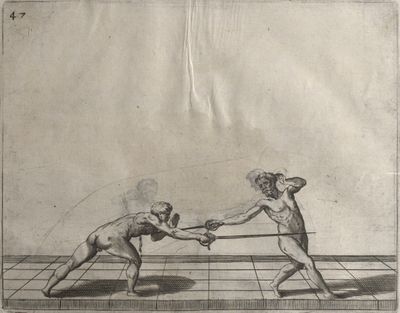
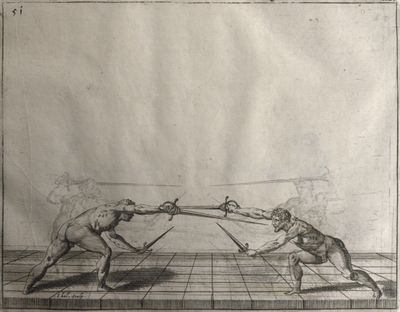
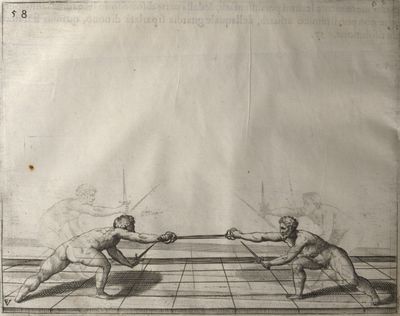
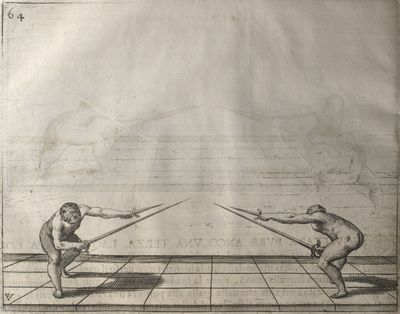
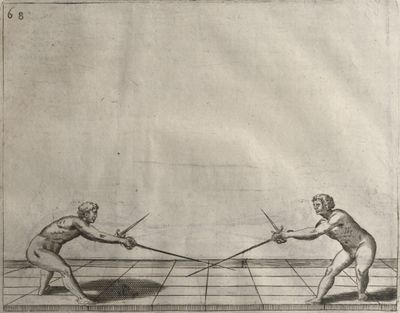
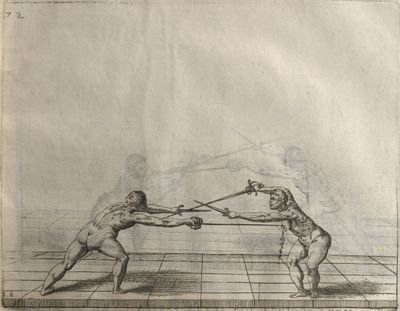
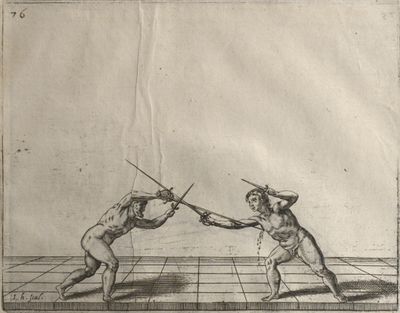
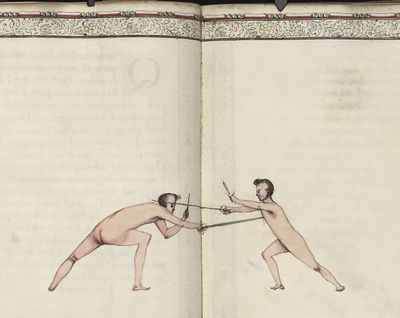
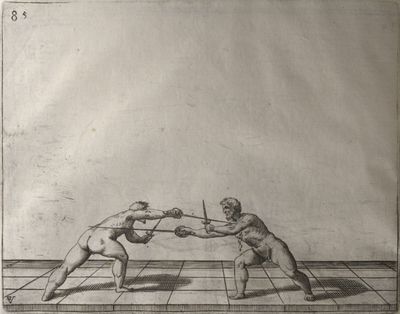
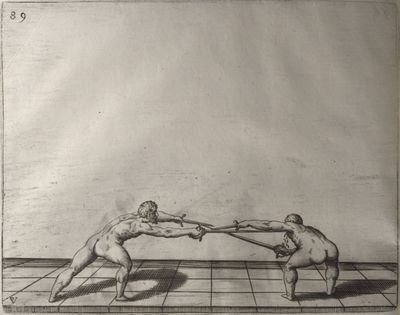
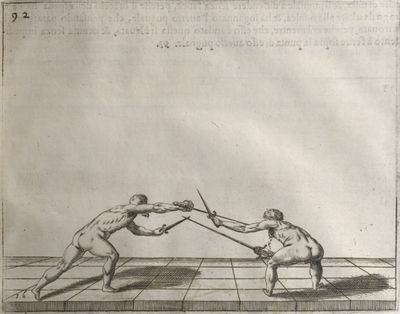
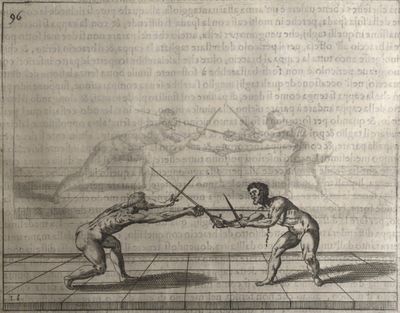
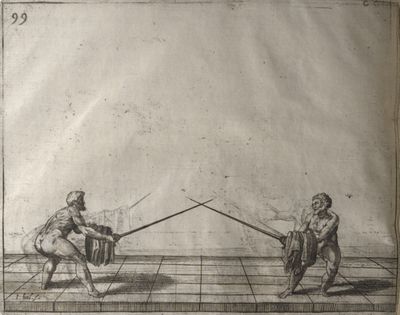
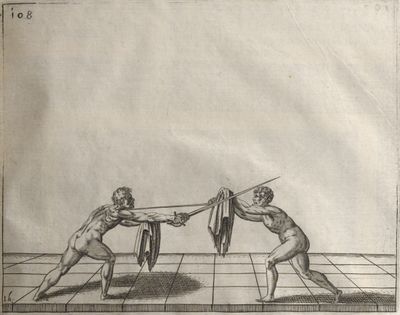
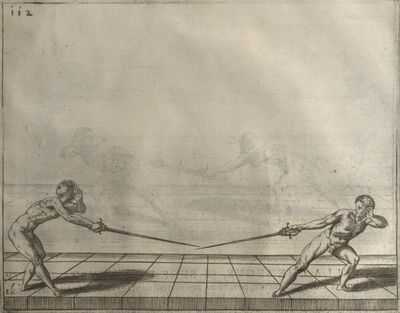
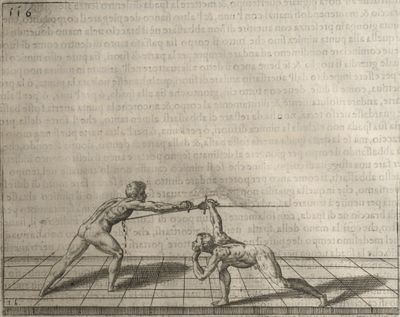
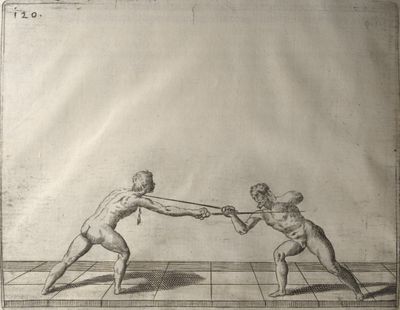
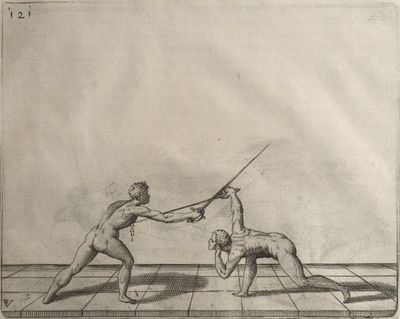
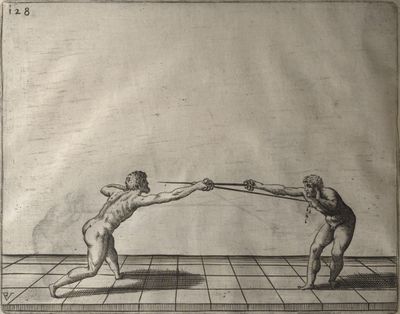
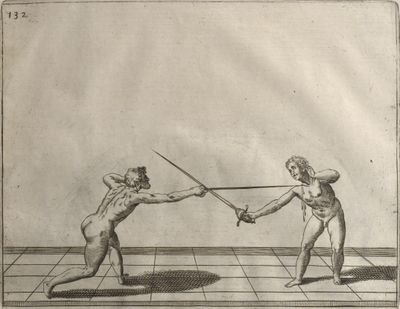
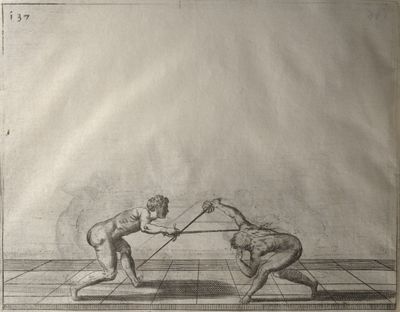
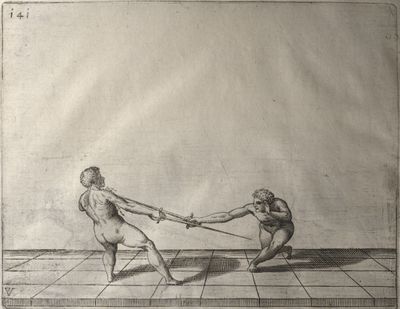
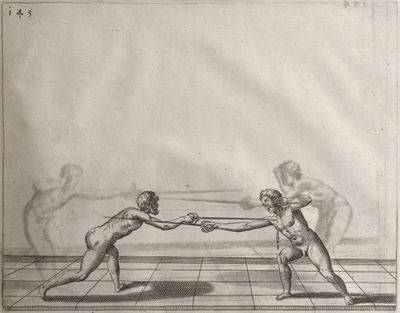
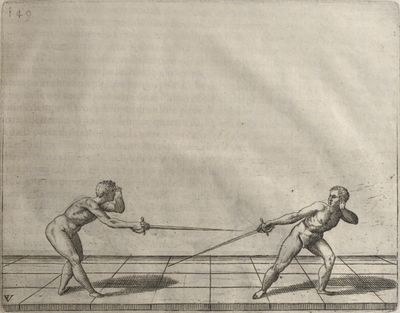
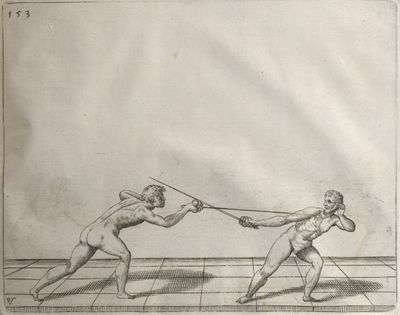
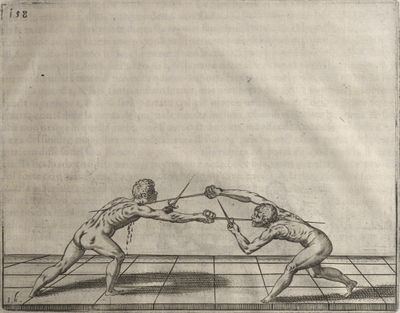
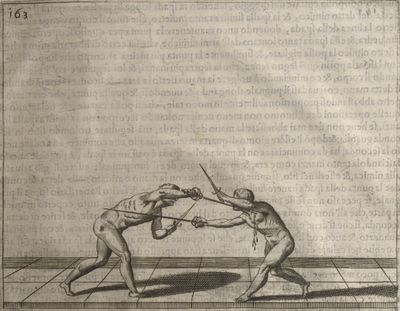
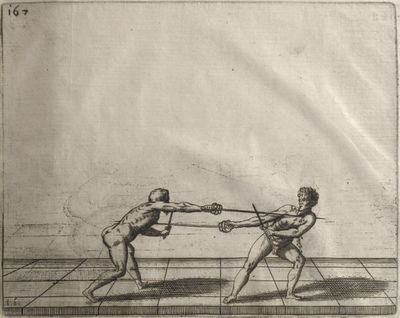
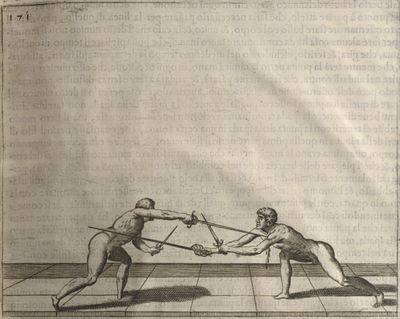
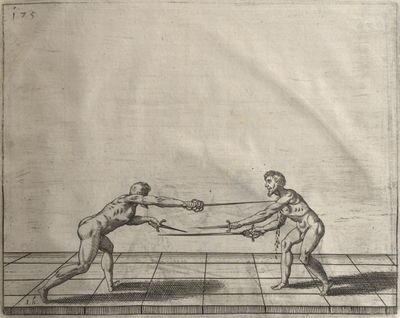
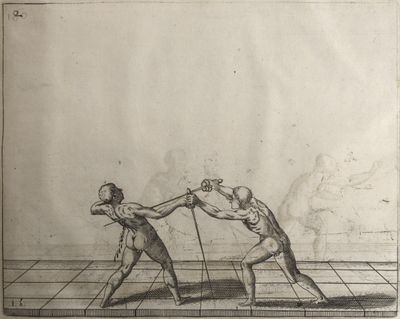
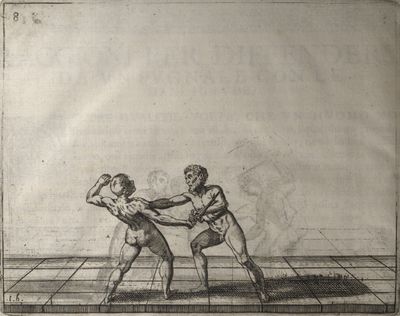
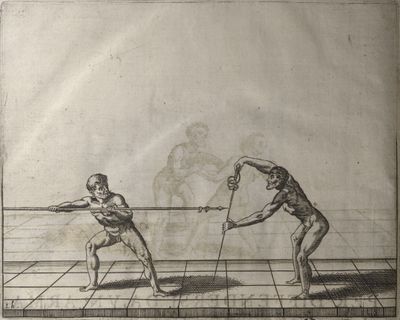
| − | | <p>[19] </p> | + | | <p>[19] The next is a hit in ''seconde'' made by passing underneath with the body on the outside, against a guard turned somewhat towards ''quarte''. You were in a high ''tierce'', with the hilt near your face and advancing towards the outside; the adversary in ''tierce'' in a straight line, seeing you coming, raised his point to impede your sword and cover himself above. Being already within distance you have left your hand at that height, turned to ''seconde'', before he could reach your sword, and by bending your body as far forward as possible have passed, With the head so far advanced as to penetrate the whole length of his blade; thus you have hit, and the adversary has been unable to defend, nor has had time to bring his sword back into line or to turn his body.</p> |
| | | | ||
| {{pagetb|Page:Scienza d’Arme (Salvator Fabris) 1606.pdf|180|lbl=170}} | | {{pagetb|Page:Scienza d’Arme (Salvator Fabris) 1606.pdf|180|lbl=170}} | ||
| Line 2,498: | Line 2,498: | ||
| | | | ||
| [[file:Scienza d’Arme (Fabris) 122.jpg|400px|center]] | | [[file:Scienza d’Arme (Fabris) 122.jpg|400px|center]] | ||
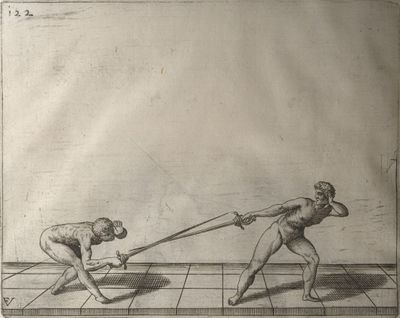
| − | | <p>[20] </p> | + | | <p>[20] This plate illustrates the exclusion of an opponent's sword in low ''tierce''. You were in high ''tierce'' and have lowered your body as you advanced, so that on arriving within distance you were so low that you have controlled the adversary's sword without moving your arm. While lowering your body you have carried the right side back and the left forward and so balanced the body on the feet and knees, that you have been able to get so low with great swiftness. The position of your body is such that even if your adversary had disengaged above, you would not have checked your advance or made any defence since there was nothing to defend in that line. Whether he had disengaged or not, or whatever he had chosen to do, he would not have prevented your advance, with your sword, feet and body working in union. The change in the position of the body after reaching this point will be shown in the next plate.</p> |
| | | | ||
| {{pagetb|Page:Scienza d’Arme (Salvator Fabris) 1606.pdf|181|lbl=171}} | | {{pagetb|Page:Scienza d’Arme (Salvator Fabris) 1606.pdf|181|lbl=171}} | ||
Revision as of 01:25, 4 May 2022
 |
Caution: Scribes at Work This article is in the process of updates, expansion, or major restructuring. Please forgive any broken features or formatting errors while these changes are underway. To help avoid edit conflicts, please do not edit this page while this message is displayed. Stay tuned for the announcement of the revised content! This article was last edited by Michael Chidester (talk| contribs) at 01:25, 4 May 2022 (UTC). (Update) |
| Salvator Fabris | |
|---|---|
| 200px | |
| Born | 1544 Padua, Italy |
| Died | 11 Nov 1618 (aged 74) Padua, Italy |
| Occupation |
|
| Nationality | Italian |
| Alma mater | University of Padua (?) |
| Patron |
|
| Influenced | |
| Genres | Fencing manual |
| Language | Italian |
| Notable work(s) | Scienza d’Arme (1606) |
| Manuscript(s) |
|
| Translations | |
Salvator Fabris (Salvador Fabbri, Salvator Fabriz, Fabrice; 1544-1618) was a 16th – 17th century Italian knight and fencing master. He was born in or around Padua, Italy in 1544, and although little is known about his early years, he seems to have studied fencing from a young age and possibly attended the prestigious University of Padua.[citation needed] The French master Henry de Sainct Didier recounts a meeting with an Italian fencer named "Fabrice" during the course of preparing his treatise (completed in 1573) in which they debated fencing theory, potentially placing Fabris in France in the early 1570s.[1] In the 1580s, Fabris corresponded with Christian Barnekow, a Danish nobleman with ties to the royal court as well as an alumnus of the university.[2] It seems likely that Fabris traveled a great deal during the 1570s and 80s, spending time in France, Germany, Spain, and possibly other regions before returning to teach at his alma mater.[citation needed]
It is unclear if Fabris himself was of noble birth, but at some point he seems to have earned a knighthood. In fact, he is described in his treatise as Supremus Eques ("Supreme Knight") of the Order of the Seven Hearts. In Johann Joachim Hynitzsch's introduction to the 1676 edition, he identifies Fabris as a Colonel of the Order.[3] It seems therefore that he was not only a knight of the Order of the Seven Hearts, but rose to a high rank and perhaps even overall leadership.
Fabris' whereabouts in the 1590s are uncertain, but there are rumors. In 1594, he may have been hired by King Sigismund of Poland to assassinate his uncle Karl, a Swedish duke and competitor for the Swedish crown. According to the story, Fabris participated in a sword dance (or possibly a dramatic play) with a sharp sword and was to slay Karl during the performance when the audience was distracted. (The duke was warned and avoided the event, saving his life.)[4] In ca. 1599, Fabris may have been invited to England by noted playwright William Shakespeare to choreograph the fight scenes in his premier of Hamlet.[5][2] He also presumably spent considerable time in the 1590s developing the fencing manual that would guarantee his lasting fame.
What is certain is that by 1598, Fabris had left his position at the University of Padua and was attached to the court of Johan Frederik, the young duke of Schleswig-Holstein-Gottorp. He continued in the duke's service until 1601, and as a parting gift prepared a lavishly-illustrated, three-volume manuscript of his treatise entitled Scientia e Prattica dell'Arme (GI.kgl.Saml.1868 4040).[2]
In 1601, Fabris was hired as chief rapier instructor to the court of Christianus IV, King of Denmark and Duke Johan Frederik's cousin. He ultimately served in the royal court for five years; toward the end of his tenure and at the king's insistence, he published his opus under the title Sienza e Pratica d’Arme ("Science and Practice of Arms") or De lo Schermo, overo Scienza d’Arme ("On Defense, or the Science of Arms"). Christianus funded this first edition and placed his court artist, Jan van Halbeeck, at Fabris' disposal to illustrate it; it was ultimately published in Copenhagen on 25 September 1606.[2]
Soon after the text was published, and perhaps feeling his 62 years, Fabris asked to be released from his six-year contract with the king so that he might return home. He traveled through northern Germany and was in Paris, France, in 1608. Ultimately, he received a position at the University of Padua and there passed his final years. He died of a fever on 11 November 1618 at the age of 74, and the town of Padua declared an official day of mourning in his honor. In 1676, the town of Padua erected a statue of the master in the Chiesa del Santo.
The importance of Fabris' work can hardly be overstated. Versions of his treatise were reprinted for over a hundred years, and translated into German at least four times as well as French and Latin. He is almost universally praised by later masters and fencing historians, and through the influence of his students and their students (most notably Hans Wilhelm Schöffer), he became the dominant figure in German fencing throughout the 17th century and into the 18th.
Treatise
Preface and Dedication
Illustrations |
Illustrations |
Draft Translation (from the archetype) |
Prototype (1601) |
Archetype (1606) [edit] |
Copenhagen Version (1600-1609) [edit] |
Munich Version (ca. 1635) [edit] |
German Translation (1677) [edit] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[1] Fencing, or the Science of Arms by Salvator Fabris. |
[I] |
Text to copy over | [I] SCIENZA E PRATICA D' ARME DI SALVATORE FABRIS, CAPE DELL’ ORDINE DEI SETTE CUORI. ·/· Herrn Salvatore Fabris Obristen des Ritter-Ordens der Sieben Herzen, verteutschte Italiänische Fecht Kunst. LEIPZIG, Verlegts Erasmus Hynitzsch. Druckts Michael Vogt. Im Jahr 1677. | ||||
[2] |
[III] DE LO SCHERMO OVERO SCIENZA D’ARME DI SALVATOR FABRIS CAPO dell’ ordine dei sesse CORI
|
||||||
[3] |
[V] VANDALORVM GOTHORVMQVÆ REX CHRISTIANVS IIII D G DANIÆ NORVEGIÆ REGNA FIRMAT PIETAS |
||||||
[4] To His Serene Majesty, the most Powerful Christian IV., King of Denmark, Norway, Gothland and Vandalia, Duke of Schleswig Holstein, Stormarn and Ditmarsch, Count of Oldenburg and Delmenhorst, &c. I am confident that all who read this work of mine will recognise that the many benefits received from your Serene Highness are the cause, which has urged and impelled me to publish to the world these my labours. I have wished also to help professors of the science of arms by showing them those instructions and rules, which after long use and continual practice and from observing the errors of others I have found to be good. I hope then that a work based on such principles will find merit, especially as it is under the protection of your Serene Highness - a work as worthy by reason of the excellence of its subject as it is glorious through the approval of your high judgment. To you, therefore, my benefactor, my king and a prince of incomparable valour as much in civil government as in the practice of arms, a true hero of our times, I have dared to dedicate my work; for since its inception is due to you, I am bringing it forth to the sight of men under the same protection. I know moreover how useful to the world and necessary to good men this art is, bringing honour to anyone who practises it aright either in the defence of his prince, his country, the laws, his life or his honour. Will your Serene Majesty therefore deign to receive into your favour not only the work, but the devotion with which, your humble and obedient servant, dedicate it. Meantime I will pray the Divine grace that long life may be granted you for the well-being of your blessed subjects and the good of the world, and that by grace you may obtain salvation in the world to come. Your Serene Majesty's most humble and devoted Servant, Salvatore Fabris |
[VII] ALLA SERma: Mtà: DEL POTENT ISSIMO CHRISTIANO IV. RE DI DANIMARCA, NORVEGGIA, GOTTIA, ET VANDALIA, DVCA DI SLESVIK, HOLSTEIN, STORMARN ET DITMARSCHEN, CONTE DI OLDEMBVRGH, ET DELMENHORST &c. CREDO SICVRAMENTE CHE DA CHIVNQVE leggerà questa mia opera si conoscerà la multitudine de benefficii riceuuti dalla Ser:ma M.ta V. essere stata quella, che mi hà eccitato, & spinto à publicare al mondo queste mie fatiche desideroso anco di giouare à Professori della scienza d’armi, mostrando loro quelli auertimenti, & regole, che per longo uso io hò conosciuto buone tratte da una continouata essercittatiòne, & dalla uista, & osseruatione delli errori altrui coiquali fondamenti & raggioni spero, che l’ opera Sarà lodata, maßimamente sattola protetione della Serenißima M.ta V. opera per l’eccellentia della materia tanto degna, quanto risplendente per essere aprobata dall’ altißimo giuditio di lei, allaquale però, come à Re sommo mio beneffattore, & Prencipe di incomparabile ualore tanto nel gouerno ciuile quanto nel maneggio dell’ armi, & uero Heroe de tempi nostri, hò preso animo de dedicarla, & come parto prodotto in uirtù sua mandarla nel conspetto delli huomini sotto la medesima sua prottetione, sapendo anco per altro quanto utile sia à lo stesso Mondo questo arte neccessaria à buoni, & honoreuole à chi giustamente l’ essercitta, ò in diffesa del Prencipe, ò della Patria, ò delle leggi, ò della vita & fama propria. Degnisi dunque la stessa Majesta S. Serenißima di riceuere in grado non solamente l’ opera, mà la deuotione con che io humilißimo , & obligatißimo seruitore suo gliela consacro, che in tanto attenderò à pregare la Diuina bontà che conceda à lei longhi, & felici anni de uita per benefficio de suoi fortunatißimi popoli, & buoni del Mondo, & à media gratia di poterla seruire in altro. Di Copenhagen adi 20. Aprile 1606.
|
||||||
[5] To the Reader. Marvel not, Reader, if you see a man of the sword, unaccustomed to the schools or the circles of literary men, presuming to write and print books; rather rejoice at seeing the science of arms and the knowledge of the sword reduced to rules and precepts, and like the other arts to a teachable form, wherein the curious and eager men of arms may learn by turning the leaves. More than others should men of arms rejoice, in that men of learning and science have never translated their arts from theory to practice, as now a man of arms has brought his from practice to true theory. To him is owed much greater faith, because he has had a thousand experiences in his own case and in that of others of what he has written. Here then, Reader, is my book on the science of arms, illustrated with plates suitable to each case; to these plates and dumb images, as it were, our words give life; the plates will demonstrate and our words will interpret the effects and principles treated of in the book. We have written in our mother tongue, Italian, dispensing with flowers of rhetoric and elegance of style, not thinking shame to acknowledge our little learning, or, following the example of a very famous captain of our age, to declare that in our youth we could not wield both the sword and the pen. We believe however that we have dealt adequately with what is required in this art and have tried as far as in us lay to avoid obscurity and prolixity, although in so subtle a subject it is difficult to preserve the necessary brevity. We have shunned the use of geometrical terms, although swordsmanship has its foundations more in geometry than in any other science. Simply and as naturally as possible we have tried to bring the art within the capacity of all. For what we have written and demonstrated we require no praise or reward, for it was never our intention to publish it to the world; but if in it there is anything worthy of merit, it should be ascribed to his Serene Majesty our King, through whom we have written this work, and at whose command this book is brought to the light of day. We will not speak of the nobility and excellence of this profession, for it is in itself so glorious and resplendent that it has no need of our words, nor is there any man so ignorant as not to know, that by its[!] kingdoms are defended, religion spread abroad, injustice avenged, peace and the prosperity of nations established. We wish only to say that after acquiring this inestimable knowledge a man should not become puffed up nor use it violently to the detriment of others, but always with moderation and justice in all cases, thinking that the last victory of all rests not in his own hand, but in the just will of God; and may He grant us abundance of his saving grace. |
[VIII] A LETTORI. NON TI MARA VIGLIARE, O LETTORE, SE tu uedrai un huomo di spada non assueto nelle scole, ne frà i circoli de litterati, ilquale presuma di scriuire, & stampare libri, mà più tosto rallegrati di uedere la scienza dell’ armi, & peritia della spada ridotta sotto regole, & precetti, & si come l’ altre arti in forma disciplinabile, ouepotranno i curiosi, & solecitti armigeri anco col uoltare delle carte apprendere amaestramenti, & tanto più delli altri douranno eßi armigeri rallegrarsi quanto, che dalli huomini togati, & scientifici, per nobile concorrenza di laude suoi antichi auerssarii, non sono mai state trasportate le arti loro dalla Theorica alla pratica, si come hora dall’ armigero si conuerte l’ atto pratico in uera theorica, alquale si dee tanta maggior fede, quanto, che diciò che hà egli scritto ne hà prima uedute mille esperienze in se medesmo, & in altrui. Eccoti dunque ò lettore il presente libro di scienza d’armi adornato di figure fecondo la proposta de casi, à loro, come imagini mute danno fiato, & animale nostre parole, quelle saranno demostratrici, & queste interprettatrici detti effetti, & raggioni che in esso libro si trattano, ilquale libro noi habbiamo scritto in lingua italiana materna, lontani dà i fiori rethorici, & da certa elliganza di dire, non uergognandoci confessare la nostra poca eruditione, & con l’ esempio di un famosißimo capitano del nostro secolo dire di non hauere potuto in giouentù nostra tenere nella medisima mano la spada, il libro, crediamo bene di hauere, intorno à quello, che in questa profeßione si richiede, sufficientemente trattato, essendoci sforzati in quanto habbiamo potuto di fuggire l’ oscurità, & la prolißita, se bene in materia tanto sottile, difficile cosa è lo seruare la debbita breuità. Habbiamo lasciato l’uso delle parole geometriche, ancorche la detta profeßone habbia li suoi fondamenti piu nella Geometrhia, che altroue, & con un modo facile, & più tosto naturale, che artifficioso habbiamo procurato di renderla capace ad ogniuno, & di quello, che noi habbiamo scritto, ò dimostrato non ricercamo lode, ne preggto alcuno, non essendo mai stato nostro pensiero di publicarlo al mondo, mà se in esso ui è pure cosa degna di preggio tutto si rifferisca alla Serenißima Majesta del Rè nostro signore, per comandamento dil quale il detto libro uiene nella luce del mondo, & anco in uirtu del quale potiamo dire, d’ hauerlo scritto. Lasciamo di discorrere della nobiltà, & eccellenza dideta profeßione, che per essere da se stessa tanto chiara, esplendente non hà bisogno di nostre parole, ne ui è alcuno tanto ignorante, che non sappia, che con questa si diffendono i Regni, si dilattano, le Religgioni, si uendicano le ingiustitie, & si stabilisse la pace, & felicità de’ popoli. Solo uogliamo ricordare, che doppo l’ a quisto di cosi preggiata uirtù non dee l’huomo insuperbirsi, & usarla uiolentemente neldanno d’altri, mà più tosto con moderatione, & giustitia seruirsene in tutti i casi, douendo aspettare il fine di qualunque sua uittoria, non dalla mano di se stesso, mà si bene dalla giustißima uolontà di Dio, ilquale ci conceda coppie delle sue sante gratie. |
Book 1
First Part - On the Basics of the Sword Alone
Illustrations |
Illustrations |
Draft Translation (from the archetype) |
Prototype (1601) |
Archetype (1606) [edit] |
Copenhagen Version (1600-1609) [edit] |
Munich Version (ca. 1635) [edit] |
German Translation (1677) [edit] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
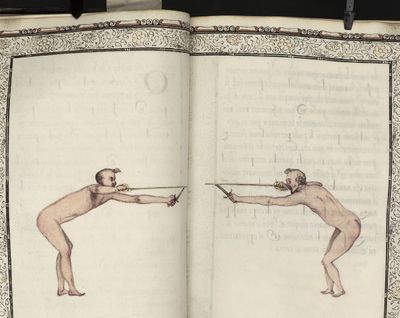
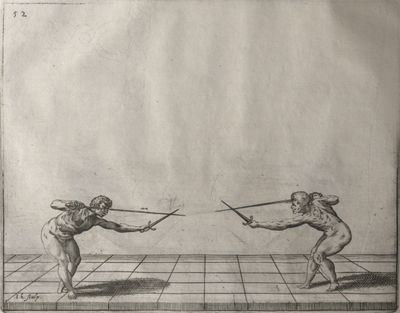
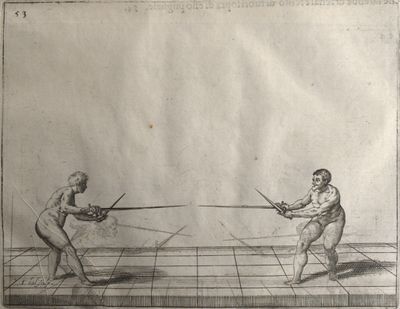
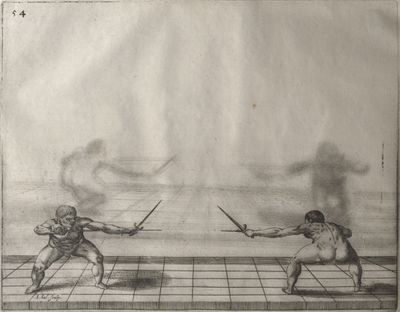
[1] General discourse of the first book. The principles of the sword alone. In opening our promised work we shall begin with the sword alone, for on the knowledge of the sword depend the principles of all other arms. Many rules will be given which may serve excellently for the sword accompanied by the dagger or any other arm. He who can use the sword alone well will easily learn to use it in conjunction with other arms. You must know then that the rules of the sword are founded on four guards in which are formed all the positions and counter positions. From them arise the times, counter-times, disengagements, counter-disengagements, double disengagements, half disengagements, and re-engagements; nor in short can anything be done in attack or defence which does not partake of the nature of one of these four guards. They are differently formed, as will be seen in the accompanying plates. These we have introduced in order that you may recognise with what variations of position of the sword, feet and body, they are made. We shall describe the nature of each guard in its place and the plates will show the results which may arise from them. The discourses will be such that you will easily see when to apply the various rules, and how to the best advantage you must approach your adversary in order to come within presence. Though one who understands the art may approach as he pleases, since in whatever position he is he will succeed by his knowledge of distances, weak and strong positions, exposed and unexposed parts. Nevertheless it is certain that one position is better than another, and a man may approach with more security when he parries his arms in the proper manner. When within distance he must proceed in various ways, according to the changes made and the opportunities offered by his adversary, and according to the distance in which he finds himself. The distances are two, and what is good in the one is not so in the other. These distances control the whole attack and defence, as we shall explain. First we shall describe the four principal guards, why they are called, prime, seconde, tierce and quarte, and the origin of these names. Then we shall treat of the divisions of the sword, then of counter-positions, distances, and some other matters which we consider necessary and useful to the good student of this art. |
[1] DISCORSO GENERALE DEL PRIMO LIBRO Sopra li fondamenti detta spada sola. Cap. 1. DOUENDO NOI DARE PRINCIPIO ALL’ OPERA promessa cominciaremo dalla spada sola come quella, dalla cognitione della quale dependono anco li fondamenti di tutte l’altre armi, & percio s’intenderanno molte raggioni, lequali potranno ottimamente seruire, ancorche sia accompagnata dal pugnale, ouero altra arma, & chi saprà bene oprare quella fola facilmẽte impararà di oprarla non meno accompagnata. Per tanto si dee sapere, che le raggio ni di essa hanno il suo fondamẽto sopra quattro guardie, con che si formano tutte le posture, & contra posture, & da esse nascono li tempi, & contratempi, cauationi, contracauationi, ricauationi meggie cauationi, & comettere di spada, ne si può in somma fare cosa alcuna per diffesa, ouero per offesa, che non si faccia con la natura di una di dette quattro, lequali uengono formate diuersamente, come si uedrà per le seguenti figure, poste da noi, acciò si conosca con quanta uarietà di siti, e prospettiue di spada, di piedi, & di corpo si facciano, & à suoi luoghi si discorrerà sopra la natura di ciascuna, & si metteranno anco in pittura li effetti, che da loro possono nascere, & i discorsi saranno tali, che ageuolmente si potrà comprendere, quando sia tempo ualersi hor dell’una hor dell’ altra raggione, & conche modo per maggiore uantaggio si debba andare contra il nimico per fermarsi in presenza, ancorche da uno che habbia scienza si possa andare come li piaccia, perche trouandosi in qualũque sito farà nascere buono effetto per la cognitione delle misure, debili, e forti, coperti, & scoperti, Nondimeno ècosa certa,che un sito è migliore dell’ altro, & più srcuramẽte Può l’huomo auicinarsi nelle distanze, quando, ché porta l’armi in debbito modo, doue poi gionto, hà da operare diuersamente, secondo le mutationi & opurtunità date dall’ auerssario, & secondo le distanze, inche si trouarà, lequali sono due, & quello, che è buono nell’ una non uale nell’ altra, & lequali distanze sono patrone di tutte le offese, & diffese, come si mostrarà, doppo, che fi Sarà dichiarato qualisiano le quattro principali guardie, & perche chiamate prima, seconda, terza e quarta & la deriuatione de nomi tali, il che fatto, si trattarà della diuisione della spada epoi delle contra posture, & delle misure, & di alcune altre cose gindicate da noi necessarie, & utili al buono osseruatore[6] di quest’ arte. |
||||||
[2] Description of the four principal guards and the origin of their names. The four guards arise from the four faces of the hand and the sword, that is to say of the two edges and the two surfaces; and these produce four different positions. prime is that position which the hand takes in drawing the sword from the scabbard, when the point is turned towards the adversary - all the guards especially with the sword alone must be formed with the point so directed. When the hand is turned slightly upward we have seconde, and tierce when the hand is in its natural position turned neither up nor down. When the inside of the hand is turned upwards we have quarte. The hand in turning can take these four positions only, and being in prime cannot go to quarte without passing through seconde and tierce; so the name quarte is given to the last position. prime is the most suitable position for grasping the sword, although it can be done in seconde or tierce: but with the hand in quarte the sword cannot be drawn from the scabbard. You must know that nothing can be done which does not arise from one of these four positions approximately; we say approximately, because, if you consider, you will find that there is a great distance between one guard and another owing to the width of the surface of the sword and of the hand, so that between prime and seconde there is a mean, where the hand might stop, and similarly between seconde and tierce, and between tierce and quarte. Therefore one might say that there were four legitimate guards and three bastard, since each bastard resembles the two, between which it is formed. But to avoid the confusion of so many terms we shall speak only of the four legitimate guards, which will serve very well for the three bastards also; for the quality of the guard is considered not only from the position of the hand, but also from the direction of the point, wherein lies the force of the guard. Therefore we shall divide the guards into these four only, especially as with the sword there are only four methods of hitting, that is on the inside, on the outside, below and above. The great differences between one guard and another will be explained when we treat of their natures, when we shall consider the various methods of defence, and the changes made in hitting, according to whether they are formed with the sword extended or withdrawn, high or low; we shall then treat of the nature of each one separately. |
DICHIARATIONE DELLE QVATTRO Guardie principali, & donde deriuino linomi di esse. Cap. 2. NASCONO LE QVATTRO GUARDIE DA QVATRO PROSPETTIVE, CHE HANno la mano, & la spada, ciò è dui fili, & dui piatti, che però fanno quattro effetti differenti, la prima si dimanda quelsito, doue uà la mano nel cauare la spada del fodero quando si uolge la puntauerso il nimico (perche intendiamo che tutte le [2] guardie massime nella spada sola si debbano cosi formare, & quando la mano si uolta un poco ingiù quella è detta seconda, la terza poi quando la mano sta naturalmente senza uoltarla ne nell’ una, ne nell’ altra parte, & la quarta quando si uolge essa mano dalla parte di dentro, laquale mano non può fare se non quelli quattro effetti nel uoltarla, & hauendola nella prima non può andare nella quarta senza passare per la seconda, & per la terza, che per essere l’ultimo effetto aquista nome di quarta. La prima è la più comoda per mettere mano alla spada, ancorche si possa fare, con la seconda, è con laterza, se ben non cosi facilmente, mà con la mano in quarta non si può già cauare la spada del fodero, & deesi sapere che niente si può fare, ilquale non proceda dalla natura di una di queste quattro noi diciamo natura, perche chi ben considera troua gran distanza trà l’una, & l’altra guardia, & questo per la larghezza del piatto della spada, & della mano, talmente che trà la prima, & la seconda uiè un meggio, douesi potrebbe fermare la mano, & così trà la seconda, & la terza, & trà la stessa terza, & la quarta, che perciò si potrebbe dire, che ui fossero quattro, guardie legitime, & tre’ bastarde, perche ciascuna bastarda tiene delle due, trà quali è formata, mà noi per non mettere confusione con tanti termini parlaremo solamente delle quattro legitime, lequali benissimo seruirãno anco per quelle tré bastarde, perche laqualità della guardia si considera non solo dal sito della mano, mà ancora dall’ effetto della punta, laquale dà la cognitione della forza di essa guardia, però ci deuiamo risoluere in queste quattro sole, & tanto più, quanto, che nella spada non cisono altre, che quattro maniere di ferire cioè didentro, di fuori di sotto, & di sopra, eui gran differenza similmente trà l’una, & l’altra guardia, come si mostrarà quando si trattarà della natura di esse, oue si uedranno di uerse diffese, & mutationi di ferire, secondo faranno formate longhe, ò ritirate, alte, o’ basse, & iui si trattarà della natura di tutte quante separatamente l’una dall’ altra. |
||||||
[3] The divisions of the sword: the faible and the forte. The blade of the sword is divided into four parts; the first is the part nearest the hand, the second quarter extends to the middle of the blade, the other two extend to the point. The first part near the hand is the strongest for parrying, and there is no thrust or cut, delivered by the strongest arm, which, if parried in this part, the sword cannot defend and resist without disorder, if the rule and the time is observed, as will be explained. The second part is somewhat weaker, but still it will defend well enough, if you parry where your adversary's sword has less strength. The third part is not good, especially against cuts, unless strengthened with the adversary's body at the moment of parrying; this will be explained in considering the defence. The fourth part is entirely bad and must not be thought of in the defence, although in the attack it is the strongest and most deadly. It is also true that a cut made with half the third part and half the fourth is a strong attacking stroke, whereas a cut made with the third part only would not be one half so effective as a cut made with the fourth part as well. The first and second parts then are only to be used in the defence, and the third and fourth in the attack; so that the sword is divided, one half into the defensive part, and the other the offensive. |
DIVISIONE DELLA SPADA Per conoscere il debile, & il forte di essa. Cap. 3. LA LAMA DELLA SPADA SI DIVIDE IN QVATtro parti, la prima è quella che pende più uicina allà mano, la feconda è quello altro quarto, che ariua sino à meggia lama, l’altre sono l’ultima metà spartita anch’essa in due, laquale uà sino alla punta. La prima parte appresso la mano è la più forte per parare, ne ci è botta di punta, ò di taglio tirata da ogni galiardo braccio parata in quella parte, che la spada non diffenda, e resista senza disordine, osseruandosi però la regola, & il tempo, come si dira’ la seconda parte è alquanto più debile, non dimeno anch’essa diffende assai, quando si sà andare à parare oue la nimica spada hà minor forza. La terza parte non è buona massime contra taglii, ne si può contra essi adoprarla, se non fortìfficandola col corpo nimico nel tempo; che si para, come pure s’intenderà oue si parlarà delle diffese. La quarta parte è intieramente cattiua, ne bisogna fare pensiero d’ hauerla quanto alla diffesa, sé ben nella offesa è la più ualida, & quella che più mortalmente ferisce, si come anco è uero quando un taglio fà la ferita meggia con la terza parte & meggia con la quarta, che fà anco all’ hor grand’ offesa, & che se fosse [3] della terza sola non farebbe la metà di quello, che fà con la quarta, la seconda & la prima parte dunque non s’hanno da oprare se non per diffesa, & la terza, & quarta peroffesa, in modo tale, che essa spada uiene ad essere compartita meggia in diffendere, & meggia in offendere. |
||||||
[4] Method of forming the counter-positions, showing The position of the arms and the body, and when they are to be formed. If you wish to form a sound counter-position, the position of the body and arms must be such that without touching the adversary's sword you are defended in the straight line from the point of his sword to your body, so that without making any movement of the body or the sword you are sure that your adversary cannot hit you in that line, but that if he wishes to attack he must move his sword elsewhere, with the result that his time is so long, that there is every opportunity to parry. But in forming this position care must be taken that your sword is held in such a way as to be stronger than your adversary's, so that it may offer resistance in defence. This rule can be observed against all positions and changes of your adversary, whether accompanied by the dagger or any other defensive weapon, or when you use the sword alone. He who can most subtly maintain this guard will have a great advantage over his adversary. But it often happens that when you form this guard, your adversary forms another against it. Often also this guard is formed so far out of distance that your adversary can wait until you begin to move your foot against him, and at the moment of year advance change his line, so that you are disconcerted another counter-position. Therefore you must be full of devices and be able in a moment to take up another position of advantage against that of your adversary and make a fresh guard, unless you are so far within distance that you can hit him daring this change, and if in changing he has not retired, since if he had retired you could not hit him even if you had been within distance. You must then take up another counter-position and approach at the same time, to regain the same distance as before. In forming this counter-position you must bear in mind the rule, that the body must be so far distant that the adversary cannot hit, or, if you have approached within distance so that he could hit by advancing his foot, you must form the counter-position without moving the feet. In this way, if the adversary should attempt to hit during the movement, you could parry and hit him, or break ground;[7] in the latter case his sword, would not reach. But if in moving your weapons to take up this advantage, you have moved slowly, you could then abandon your object and hit at the very moment in which your adversary advanced to attack, parrying at the same time. So that if the first movement is made without violence, you can abandon your attempt and make another, as opportunity offers. In short, if you wish to get within distance with some safety, you must first form the counter-position, and if disconcerted by your adversary's counter-position, it will be better to break ground than to approach, until there is an opportunity to get an advantage. |
MODO DI FORMARELE CONTRAPOSTVRE Per intendere come l’armi si denno situare & il corpo, & quando si hà da cominciare à formarle. Cap. 4. VOLENDOSI FORMARE LA CONTRA POSTURA che stia bene fà di mestieri situare il corpo, & l’armè in modo, che senza toccare la nimica spada si sia diffeso dalla retta linea, che uiene dalla punta auersa al corpo, si che senza fare moto alcuno ne di corpo, ne di spacia si sia sicuro, che il nimico non possa ferire in quella parte, mà uolendo offendere sia neccessitato portare la spada altroue, & cosi il suo tempo uenga ad’ essere tanto longo, che dia gran comodita di parare, mà nell’ acconciarsi in cotal modo si richiede[8] si tuare la spada in guisa, che sia più forte della nimica acciò possa resistere nella diffesa, & laquale regola si può offeruare contra tutte le posture, & mutationi nimiche, tanto essendo accompagnata dal pugnale, onero da altra sorte di arma diffensiua, quanto con la sola spada, & collui, che saprà più sotilmente mantenersi in detta contraguardia haurà gran uantaggio soprà l’nimico, mà spesse uolte auiene che nel formarla esso nimico ne forma un’ altra contra quella & spesse uolte anco si uà à fare detta contrapostura lontano dalla misura tanto, che il nimico può aspettare che si comincia à mouere il piede contra di lui, & nel medesimo tempo, che si li auicina mutare effetto, & serrare di fuori l’offeruatore di questa regola con un’ altra contrapostura, Pertanto è neccessario l’essere ricco di partiti & sapere nell’ istesso punto trottare un’ altro sito uantaggioso à quello dell’ auerssario, & farli noua contraguardia, quando non si fosse tanto in misura, che si potesse ferirlo nella sua mutatione, ouero se esso nimico mutandosi non si fosse ritirato, perche in tal caso se bene si fosse stato nella misura non si; harebbe potuto ferirlo, mà si bene farli un’ altra contrapostura auicinandosi nel medesimo tempo per riguadagnare la stessa distanza di prima; & è di mestieri formando la contrapostura, di usare una certa raggione, ciò è che nelo situare il corpo si sia tanto lontano che il nimico, non possa ferire, ouero, essendosi gionto in distanza tale, cho detto nimico possa con l’auanzare il piede ferire, formarla senza moto de’ piedi, perche cosi facendo, ancor che esso nimico uolesse in quello mouimento ferire, potrebbesi parare, & ferire lui, ouero rompere di misura, che in quest’ alrro modo la nimica non arìuarebbe, mà se nel mouere l’armi per pigliare detto uantaggio, il moto fosse stato fatto lentamente, si potrebbe allhora lasciare l’in cominciato, & ferire in quello tempo proprio, che il nimico si fosse auanzato per offendere, parando insieme, si che se si farà il primo moto senza uiolenza si potrà lasciare l’ lincominciato, & farne un’ altro secondo l’ ocasione, dunque chi si uorà auicinare con qualche sicurtà nelle misure sarà neccessario formare prima la contra postura, & quello che si trouarà serato fuora dalla contrapostura nimica, haurà più raggione di stare in rompere di misura, che auicinarsi sino che li uenga comodità di pigliare il uantaggio. |
||||||
[5] Explanation of the two distances, wide and close, and how to acquire the one or the other with least danger. You are within wide distance when by advancing the rear foot to the front you can make a hit. After forming the counter-position a little out of distance, you must begin to advance the foot in order to get within the required distance. But you must be on your guard, lest your adversary, being steady, at the moment when you move your foot to advance it, should advance his too and hit at the same time. Therefore, you must move it very carefully, remembering that your adversary may effect something during the movement. After forming the counter-position you must endeavour to throw him into disorder, or at least make some feint in order to have an opportunity to hit. Thus prepared for what may happen you are more guarded and can better resist attack. When you are within wide distance and your adversary makes some movement of his foot, provided he does not break ground, you can hit him in the nearest exposed part, even if he has not moved his weapons. This could not be done if he moved his weapons and stood firm on his feet, the reason being that a movement of the foot is slower than that of the weapons, and therefore he could parry before your sword arrived, while he remained steady; if there were no other way he could protect himself by breaking ground, so that your sword could not reach. Being thrown into disorder you would then be in danger of being hit before you had recovered. Therefore whenever he gives an opportunity without moving his feet, it would be better to approach within close distance in that time. In that distance you can reach with the sword by merely bending the body, without moving the feet, and the adversary is forced to retire to get out of such danger. If he does not move you could hit him even though he retained the advantage of the counter-position. If your adversary does not move, you can sometimes make a hit by judging the distance from the point of your sword to your adversary's body and the distance from the forte of his sword. If you consider both how much you must advance the point and how far you must move it from the adversary's forte, and understand that the time required for him to parry is the same as for you to hit, the sword will arrive before he has parried by the advantage of having moved first. If you see that his body is little exposed, as may happen, since one guard covers more than another, you can then attempt to hit in the exposed part, and as he moves to the defence change your line and hit in the second exposed part. These rules apply within close distance. If you are within wide distance and wish to advance within close distance, the danger is greater when the adversary stands steady on his guard, because if you raise your foot to advance it, you give him an opportunity to hit and retire, so that at the end of the movement you would be at the same distance, that is wide distance, and would have obtained nothing. All this is due to the fact that you cannot move your foot in less than two times, the one in lifting it and the other in putting it to the ground. For this reason some push the foot forward by scraping it along the ground, which is well enough in the hall, but in the street is likely to lead to a fall because of the many unevennesses. It is better then to lift it to make sure of not stumbling. Therefore in carrying the foot within close distance you must first form a good counter-position, and then lean all the weight of the body on the rear foot as you lift the forward foot, so that if in that moment your adversary should thrust you would be able to parry and to hit by bringing your foot to the ground, or even extend that movement which you had already begun beyond your first design, in order to reach more certainly in case your adversary broke ground in making his hit. If the adversary has not moved the pupil must after raising the foot carry it within close distance in such a way that the weight of the body rests on the rear foot, and is no nearer than when within wide distance. After putting your foot to the ground you could then by merely bending the body hit on the slightest movement if[!] the adversary in the line exposed nearest to your point. If you did not wish to wait you could hit in the manner already described. If while you are carrying your foot within close distance, your adversary should retire, you would remain within wide distance, and must bring the weight of the body from the rear foot to the forward and then bring up the rear foot close to the other. In approaching within close distance always take care that the body does not approach with the foot, but remains in the same position as before, and after bringing your foot to the ground carry forward the body. This rule should be observed in every case of requiring close distance, but after hitting you must in recovering your weapons draw back the body as far as possible and draw back the foot in such a way that if your adversary follows you are ready to parry and hit. If you find that your adversary is always breaking ground you must not grow angry and pursue him. Rather you must then proceed more carefully, for many feign a retirement with the object of drawing on their adversary and seeking an opportunity to hit in the moment of his pursuing. If you follow our method you will avoid this danger. It is better not to pursue one who flees, but rather to feign reluctance in order to reassure him and so draw him on, and then to seize an opportunity which he will not have time to avoid. |
[4] DICHIARATIONE PER INTENDERE Delle due misure quale sia larga & stretta, & il modo da tenersi per aquistare l’una, e l’altra per men pericolo. Cap. 5. MISURA LARGA SI DIMANDA QVELLA, LA QVALE con l’auanzare il piede anteriore l’huomo può ferire il nimico, in modo, che dopò formata la contrapostura poco lontana all’hora si dee cominciare à portare il piede inanzi per ariuare in detta misura, mà ricercasi lo stare auertito, perche essendo il nimico fermo, nel tempo che si moue il piede per portarlo oltre, che ancor lui non portasse il suo & battesse in quello punto medesimo, però si dee mouerlo molto consideratamente credendo, che esso nimico possa fare qualche effetto nel proprio tempo di quello moto; & dopò hauere fatta la contrapostura si dee procurare di farlo disordinare, se non con altro almeno con qualche sinta per hauere poi occasione di ferirlo, & cosi aspettando quello, che può accadere si stà più aueduto, & più facilmente si resiste alli incontri: qnando[!] poi si sia gionto in detta misura larga, & che il nimico si moua col piede per accomodarsi, purche non rompa di misura si può ferirlo nelo scoperto più prossimo ancorche egli non habbia fatto moto dell’armi, cosa che non si potrebbe fare se le mouesse, & stesse fermo de’ piedi, & questo perche il moto de piedi è piu’tardo che quello delle armi, & però potrebbe esso nimico parare inãzzi che la spada giongesse portata dal piede, mentre lui fosse fermo, & quando non si sapesse per altra uia diffendere, si saluarebbe col rompere di misura in modo che la spada non lo ariuaria, & essendo già disordinato si trouaria in pericolo di restare ferito prima, che si fosse rimesso talmente, che quando egli desse occasione senza mouere li piedi sarebbe più à proposito lo auicinarsi in quel tempo nella misura stretta, doue la spada ariua col solo piegare del corpo, & senza il mouere de’ piedi, che esso nimico sarebbe forzato à ritirarsi per non rimanere in pericolo tale, & se non si mouesse si potrebbe ferirlo, quando che si hauesse conseruato il uantaggio della contrapostura, & si potrebbe alcune uolte ancora ferire se bene il nimico non si mouesse cioè per il conoscere quale distanza fosse dalla propria punta al corpo nimico, & quanto lontana dal forte de lo stesso nimico, hauendo parimenti consideratione diquanto si debba auicinare la punta, ouero lontanarla da esso forte nel ferire, & conoscendo che sia tanto grande il tempo, che hà da fare l’auerssario in parare come il suo in ferire, la spada senz’altro ariuarà prima, che quello habbia parato, per il uantaggio, di essere stato il primo à mouersi; mà uedendo il corpo auerso póco scoperto, come può auenire, perche una guardia lo cuopere più dell’ altra, si può allhora andare per ferire quello scoperto, & nel tempo che’l nimico si moue alla diffesa mutare l’effetto, & ferire nelo scoperto secondo; Queste raggioni s’intedono doppo entrato nella misura stretta, perche ritrouãdosi nella larga, & uolendo andare l’huomo nella stretta, quando, che l’nimico stà fermo nella sua guardia il pericolo all’ hora è maggiore, perche leuando il piede per portarlo inanzi quello e un tempo, nelquale può esso nimico ferire con ritirarsi: indietro, di modo che finito il moto della distesa si trouarebbe il detto huomo lontano, cio è nella larga, & cosi non haurebbe [5] aquistato cosa alcuna, & tutto procederebbe perche non puo il piede mouersi con meno di dui tempi l’uno nel lèuarlo l’altro nel metterlo in terra, & per tale caogione alcuni lo spingono inanzi sdruzolandolo per terra, che nelle sale è buono, nelle strade è per cadere rispetto ai molti impedimenti, che possono trouarsi, che per tanto è meglio leuarlo assicurandosi di non traboccare, si che uolendo portare il piede nella misura stretta prima si richiede l’hauere formata ben la contrapostura, & doppo fondare tutto il peso del corpo sopra il piè di dietro leuando quello dinanzi, in modo che se in quel tempo il nimico tirasse si possa pigliare il contra tempo di parare, & ferire nel mettere propriamente il piede in terra anzi stendere quel moto, che si hauea cominciato più inanzi di quello che si hauea disegnato per meglio ariuare in ogni caso, che detto nimico rompesse di misura nel suo ferire, ilquale nimico se non si fosse mosso, douria il nostro osseruatore, leuato che hauesse il piede, portarlo nella misura stretta mà in modo, che tutto il corpo restasse sopra quello di dietro, acciò non s’auicinasse più di quello, che prima era, quando si trouaua nella misura larga, & doppo messo il piè in terra potria all’hora col solo piegare del corpo, ferire in ogni minimo moto ne lo scoperto più uicino alla punta, & anco, non uolendo aspettare, potria ferire con la maniera inanzi scritta, & se nel portare il piede in detta stretta misura esso nimico si ritirasse il nostro sarebbe ancora nella larga, & douria piegare il corpo, che era restato sopra il piè di dietro, nel anteriore, & poi ricuperare il medesimo di dietro appresso l’altro, contenersi sempre nelo portarsì nele strette misure in modo, che il corpo non si approssimi col piede, mà resti nelo medesimo segnò, doue prima era, & dopò fermato il piede portare il corpo, questa raggione è buona da osseruarsi in ogni caso di aquistare la misura stretta mà hauendo ferito si dee nel ricuperare l’armi allontanare sempre il corpo quanto, che più si può ricuperando il piede con comodità tale, che quantunq; il nimico seguisse si sia pronto à parare, & ferire, & trouando, chel detto nimico andasse sempre rompendo di misura non bisogna mettersi in furia, & uolerlo seguire, anzi all’hor si ricerca lo andare più considerato, perche molti singono ritirarsi procurando di tirarsi[9] dietro l’auerssario affine di trouare comodità da ferirlo nel tempo, che quello lo segue, & però tenendosi l’ ordine nostro cessarà simile pericolo & meglio è mentre che uno fuggie non uolerlo seguire anzi mostrare di ricredere per più assicurarlo, & con tale arte tirarlo inanzi, & poi pigliare quella occasione, the non potrà all’hora fuggire in tempo. |
||||||
[6] Discourse on rushing in with the sword extended and the principles of the two times, showing that it is better to control the sword and observe the correct time. There are some who, in endeavouring to hit with the point, hurl the arm violently forward so as to give it greater force. This method is not good for the reasons which we shall bring forward. In the first place when you rush in with the sword, should your adversary anticipate you and defend the part where you intended to hit, you cannot change your line, as would be necessary, so that the adversary is sure of his defence. If he has also realised the weakest part of your thrust and pushed your sword in the direction in which it is being naturally carried, he will drive it out of line all the more quickly. His defence will be very simple without using any force, because if he pushes the sword in the direction in which it is naturally falling, it will fall the quicker without any resistance. In this manner his faible is stronger than the forte of the hitter. Moreover in completing the rush the point of the sword drops so that it cannot hit exactly the point aimed at, and also at the end of the extension it is impossible to prevent the arm and sword from dropping to the great advantage of your adversary. Further after one rush it is impossible to make another without withdrawing the arm again, which takes so long that, if the adversary has not hit at the first fall of your sword he could hit while you are withdrawing your arm, and recover before the second rush, with excellent opportunity of parrying and hitting even if he did it in two times, that is parrying first and then hitting. The rule of the two times then would be good enough against such a method, and all the more successful as those who rush cannot make any good feint; for in feinting they move the foot or the body without advancing the sword, or if they advance it often withdraw it even further than before in order to hit with greater force, a very slow and dangerous time. In treating of the rule of the two time, we say that, although it may succeed against some, it is not to be compared with the rule of parrying and hitting at the same time, because the true and safe method is to meet the body as it advances, before it has had time to withdraw and recover. If you then pursue you give an opportunity for parrying and hitting again. It has been our experience, that most of those who observe this rule of two times, if they can engage the adversary's sword, generally beat it in order then to proceed with the stroke. This would be successful but for the danger of being deceived. He whose sword has been beaten on the faible certainly cannot hit at the same time, as he is thrown into disorder by the beat. But if he happens to disengage he causes the sword which has beaten and missed to drop still further, and has an excellent chance of hitting. Even if he made a feint of beating, so that when the adversary disengaged he might beat in another part, he would still be in danger of being hit, because the adversary might make a feint of disengaging and return, and in this way the one who had meant to beat would not be able to parry. Finally it may be taken as established that it is impossible to beat your adversary's sword without putting your own out of line. Moreover sometimes if you attempt to beat the faible, according to rule, you meet the adversary's forte, which he has pushed forward, so that the beat fails and your adversary proceeds to hit without your being able to prevent him. In dealing with one who does not rush, but controls his sword, even though you beat his faible, his forte does not move, so that he can parry. Therefore, we conclude for these reasons and for many others which might be adduced, that it is better to parry and hit at the same time, though with the sword alone great judgment is required to effect the two at one moment. As to controlling the sword or thrusting with violence, controlling it is beyond comparison better, first because he who controls his sword, when it is beaten by the adversary, who means to hit in another line, can let it yield in the direction of the beat, and the forte will still defend, if the sword is held well advanced. Further it is certain that when your sword is beaten, it is immediately freed. Similarly it is more useful to know how to be master of your sword, to engage the adversary's faible and make a hit as opportunity offers, always holding his sword in subjection. If he cannot free his sword he cannot hit. Therefore this rule can be followed only by one who moves his sword without violence, works in such a way as to be always master of it, and if he is prevented by his adversary in any plan can abandon it and adopt another. He will hit at the very moment when his adversary has meant to prevent him, and without deviating his point or withdrawing it he will be able to carry it on to the adversary's body. The principle to be observed is this, that in proceeding to make a hit either by a feint of disengaging or any other change, when once you have begun to approach, the point toward the adversary, you must continue until you reach the body; for if you check the sword in order to disengage or change your line you will not arrive in time. This principle cannot be observed by one who rushes, so that the difference is easily understood. Moreover the sword which is held firm and accompanied by the foot and the body has greater force and exactness. He who so hold[!] it always controls it and does not let it drop after a hit. He has only to withdraw his foot in order to bring his body to safety, unless he has passed, and to engage the adversary's sword again. If your adversary as you withdraw, pursues or advances, you can hit again, defending at the same time. All this is because of the union between the sword, the feet and the body. If this rule is observed in the manner we have described, your parrying will be safe, whereas with the rule of the two times it is false; this will be better understood in its place. |
DISCORSO INTORNO IL LANCIARE DI SPADA, ET raggioni di dui tempi per fare sapere se sia meglio il portarla, & osseruare o; giusto tempo. Cap. 6. SONO ALCUNI, CHE UOLENDO FERIRE DI PUNta lanciano il braccio con uiolenza perdarli maggior forza, tale maniera non è buona per le raggioni che assignaremo prima perche, se il nimico in quello lanciare di spadga, preoccupasse, & diffendesse quel luogo oue si hà disegnato ferire non si può lasciare quello effetto, & farne un’ altro, come si richiederebbe talche esso nimico uiene ad’essere certo della diffesa, & se egli haurà conosciuto la parte più debile, & l’haurà spinta, doue la natura la porta tanto più [6] presto haurà fatto uscire di presenza quella, slanciata, & sarasi esso diffeso molto comodamente senza oprare forza alcuna, perche chi spinge la spada da quella parte oue dee cadere naturalmente essa uà à cadere più presto & senza fare resistenza nissuna, & in questo modo più uale il debile di quello che para, che’ il forte di quello, che fere; in oltre nel finire il slancio la punta della spada, sguinza in modo, che non può andare à ferire,oue guistamente si hauea tolta la mira, & anco nel finire detta distesa non si può tenere il braccio, & la spada, che non cadano con dare gran comodità al nimico di ferire, aggiungendosi ancora, che dopò slanciata unauolta non si può slanciare un’ altra, se non ritirando il braccio di nouo, tempo tanto grande, che se l’istesso nimico non hauesse, ferito nella prima caduta potrebbe ferire nel tempo di questo ritirare il braccio, & saluarsi anco prima, che si slanciasse un’altra uolta, & con hauere buona comodità ditornare à parare, & ferire, se bene lo facesse di dui tempi cio è prima parando, & poi ferendo, in modo che la raggione de dui tempi uerrebbe ad’essere assai buona contra simile maniera, & tanto più riuscibile, quanto che costoro, che feriscono di slancio non possono fare finta di forte alcuna, che stia bene, perche nel fingere fanno similmente moto col piede, o col corpo, senza auanzare la spada ò se pure l’auanzano la ritirano ben spesso più indietro, che prima noti era per ferire con maggiore forza, tempo tardissimo, & dannoso. Hora per trattare delle raggioni de’ dui tempi diciamo, che se bene contra di alcuni potrebbero riuscire, nondimeno non hanno da equipararsi alle raggioni di parare, & ferire in tempo medesimo, perche il uero, & sicuro modo è di incontrare il corpo nel punto medesimo; che quello si spingie inanzi, altrimenti egli subbito s’allontana, & resta saluo, & chi lo seguittasse li darebbe comodità di parare, & tornare à ferire un’altra uolta. Habbiamo ueduto per isperienza, che i piu di questi, iquali osseruano le dette raggioni de’ dui tempi, come possono hauere la spada nimica sogliono batterla per potere poi andare à ferire, il che sarebbe assai riuscibile quando non ci fosse il pericolo di reftare ingannato, perche colui à chi uiene battuta la spada nel debile non può certamente ferire in medesimo tempo per hauerla disordinata dalla battuta, mà se auiene, che caui caggiona, che la spada, dell’altro, che hà battuto, non hauendo trouata la nimica, fa caduta maggiore, & porge oportunissimo tempo al nimico di ferire, & ancorche fosse andato per fingere di batterla acciò detto nimico la cauasse per batterla poi dall’altra parte, non dimeno ancor questo sarebbe pericoloso di restare ferito, perche lo stesso hauria potuto fingere di cauare, & rimetterla, & à questo modo colui, che hauesse uoluto battere non hauria potuto parare, si hà dunque da tenere per fermo, che non si può battere l’altrui spada, che non si suii la sua propria dalla presenza, & tanto più non la trouando, oltreche alcune uolte si uà per battere il debile, come è di raggione, & si troua il forte spinto oltre dall’auerssario, restando in tal modo fallace la battuta, & all’hora uiene lo stesso auerssario à ferire senza potere essere impedito; Mà doppo questo hauendo à fare con chi non lancia mà porta la spada, anco che seli batta il debile non dimeno il suo forte non si moue in modo, che può parare, & però si conchiude tanto per queste raggioni, quanto per molte altre, che potriano addursi, che meglio è il parare, & ferire in tempo medesimo, se bene con la sola spada ci si richiede giuditio grande à uolere che faccia questi dui effetti in un solo punto. Quanto al portare della spada, ouero slanciarla meglio senza comparatione è il portarla, come si intenderà, prima perche una spada battuta, mentre è portata da un’ luogo all’altro, colui, che la porta può lasciarla andare da quella parte doue il nimico la batte, che andarà à ferire in un’altro luogo, & il forte restara sempre alla diffesa, quando si giocarà la spada auanzata, oltre che questo tale è certo che essendo battuta è fatta ancora subbito libera, similmente è più utile lo sapersi conseruare padrone di essa, occupando il debile nimico, & portarsi à ferire secondo l’occasione con tenere sempre suggita la nimica spada, laquale se dall’ ingegnodi esso nimico non si saprà liberare lui non potra mai serire, & perciò questa raggione non può essere osseruata se non da colui che moue la spada da un’luogo. all’altro senza lanciarla, & opera in guisa, che [7] sempre è padrone di essa, & che se uà per farè un’ effetto quale li uenga impedito dalo stesso nimico sà lasciare l’incominciato, & farne un altro; questo tale adunque ferirà nelo medesimo tempo, che l’auerssario l’haurà uoluto impedire, & senza deuiare la punta, ò ritirarla, potrà continouare sino al corpo del detto auerssario, perche l’ordine, che hà da tenere è che andando per ferire, ò per fingere di uolere cauare ò fare altra mutatione, mentre che hà cominciato ad auicinarela punta uerso il nimico, è neccessario continouare sino che la peruiene al corpo, perche chi la uolesse trattenere affine di cauare, ò mutare effetto non ariuarebbe di tempo, & questo non si può osseruare da quello, che slancia, & perciò si può benissimo comprendere la differenza, & tanto più che portandola ferma, & accompagnata dal piede, & dal corpo la spada hà maggior forza, maggior giustezza, & chi la porta è sempre più padrone di essa non facendo caduta alcuna doppo che hà ferito, talmente che non occore fare altro doppo ferito se non di ritirare il piede, se non si fosse passato, per dilongare il corpo, & per ritornare di nouo all’ aquisto della nimica spada, & in caso che il detto nimico, in quello ritirarsi, seguittasse per ferire, ò auicinarsi, si può ritornare à ferire con la diffesa insieme, & tutto per la unione in che si troua di spada, piedi, & corpo, laquale osseruatione se nel soprascrittò modo sarà usata, il parare sarà sicuro, si come nelle raggioni de’ dui tempi è falso, come à suo luogo anco meglio s’intenderà. |
||||||
[7] Discourse on cutting. How many cuts there are and how they are made, their nature, and whether it is better to use the point or the edge. The principal cuts are four; they are delivered in different ways and in different directions, as will be seen in the plate which follows (pl. 1.) with their names. The names are derived from the four principal cuts, that is mandiritto, riverso, sottomano and montante. They are delivered in various ways, for some deliver them from the shoulder, some from the elbow, some from the wrist, and some again from the shoulder but with the arm extended and stiff, keeping the point always directed towards the adversary. In making the first cut from the shoulder, the arm is raised and makes a circle with the sword in order to strike with greater force. This is the worst of all because of its excessive slowness and because you may easily be hit as you raise the arm, as you let it fall, or after it has fallen; for as the sword is not supported by the adversary's weapon or body, there is nothing to prevent it from passing on behind his back; or if the hit is made downwards, the sword is in danger of being broken on the ground. In either case so much time is lost that your adversary may easily hit. The second method from the elbow also carries the hand out of line, both when it is raised and when it falls after missing, so that in this case too you may be hit, but not so easily, as the sword does not make such a large circle, nor does the raising of the arm uncover so much, nor the sword fall so far. Therefore as the movement is quicker and you remain better covered, this method is better than the first. The third method, made from the wrist downwards with the arm straight, although the sword makes a circle is beyond comparison better than the two first described, since the body is more covered. Nor can you be so easily hit, since it is quicker, and the point in falling remains in such a position that you can parry with the forte either thrust or cut, and can cut again. Similarly the fourth method with the arm stiff and extended is far better than the two first, since you hit without making a circle with the sword, raising it little or nothing. The sword is allowed to fall on an exposed point, and when your adversary makes a circle with his sword in order to hit, with this fourth method you can continue your stroke, as you will certainly hit before his falls. You will be all the more secure if you have worked with the feet and the body, as you should, because if you remained upright when your sword fell, you could not recover in time, especially if your adversary's cut had been made from the elbow. But if you lower your body the sword is more quickly recovered and has less distance to move in returning to the defence, for as you hit with the arm stiff and extended without bending the wrist, the sword still remains in front and can easily return to the straight line. For this reason the fourth method is better than the two first and in defence better than the third, although it appears to us that the third is much freer or less restricted, and without requiring so much strength has more variety and can more easily deceive the adversary. He who wishes to make a cut with safety, must wait a fitting opportunity, since he cannot make the stroke in a moment, and the time might have passed before the sword arrived. You can make a feint in order to put the adversary in subjection, and whilst he is parrying the cut, thrust at him, or make a feint of a thrust, and cut. The latter method would be necessary if you wish to move without waiting, for, if your adversary remained steady, it would not be good to make a feint of a cut in order to thrust, owing to the length of the movement, during which you might be hit. You can, as has been said, make a feint of a thrust in order to cut, and even if he parries the cut, still make a thrust. Further the feint of a cut, when your adversary stands firm, is not good because of the two times involved in raising and dropping the arm. All the cuts are very long, and he who cuts cannot do so in the time of a parry (we speak of the sword alone), whilst the adversary has always time to protect himself and even to make a hit when you are trying to parry. It is true that in parrying you can put your adversary in subjection and deprive him of the power to do anything, and even hit him before he can save himself; but of this we shall speak when we treat of the defence and the attack. Since cutting is not very useful we shall not dilate on it more than is necessary to show the respective merits of the thrust and the cut. Still it is well to be acquainted with both. In cutting greater strength is required, which is a disadvantage. The sword, if it misses, is thrown into disorder, and the body too. Recovery is not so easy, so that you are in more danger than with the thrust. Further it is less deadly; so that in all respects thrusting is more advantageous. With the point you reach further, more quickly and can more easily recover. In brief thrusting is more noble and excellent, for it includes all the subtlety of arms, whereas in cutting there is neither the counter-time nor the time, since for the most part two times are involved. We do not intend to discuss this further than we have done in the preceding chapter in relation to the two times, but to consider the more subtle, difficult and profitable points. If for example two men were opposed, one who excelled at the cut and the other at the thrust, without a doubt the latter would prevail for the reasons we have given, though his opponent were the stronger man. We conclude that it is better to use the point only, especially in engagements corps à corps without armour. With armour we should deem it good to use both; so too against a number of opponents, for the cut causes greater confusion and may parry several thrusts. |
DISCORSO SOPRA IL FERIRE DI TAGLIO Per sapere quanti siano, & in quante maniere siusino, la natura di eßi, qual modo sia megliore, & se sia meglio ferire di taglio, ò di punta. Cap. 7. LI PRINCIPALI TAGLI SONO QVATTRO, IQVALI si adoprano diuersamente, & uanno à ferire in diuerso luogo, come si uedrà per una figura, che sarà qui indietro con tutti i nomi loro, iquali deriuano da questi qnattro[!] principali, cio è mandiritto, rouerso, sotto mano, & montante, uengono questi tagli usati in uario modo, perche alcuno litira con la spalla, altri col combito, altri col nodo della mano, & altri pure con la spalla, mà col braccio disteso, & duro con tenere sempre la punta della spada diritta contra il nimico, Ilprimo[!] tirato con la spalla che è quello perapunto quando si alza il braccio, & si fà ungran giro della spada per ferire con forza maggiore è il più cattiuo di tntti[!] per la sua troppa tardità, & perche si può facilmente effere ferito nel cominciare à leuare detto braccio, nel cadere, & doppo l’ essere caduto, perche non essendo sostenuto dall’ armi, ò dal corpo nimico la spada passa sin dietro la schiena, che non può essere tenuta, ouero che se si tira deritto allo ingiù uà à ferire in terra con pericolo di rompersi, mà auenga quale si uoglia delle due cose si perde tanto tempo che l’auerssario può ageuolmente ferire: Il secondo modo, ilquale si fà col combito ancor esso porta la mano fuoridi presenza si nell’ alzare, come nel callare quando la uà uuota, talmente che anco con questo secondo si può rimanere ferito mà non tanto facilmente, perche la spada non fà quel giro si grande, ne il braccio fà tanto scoperto in alzare, ne meno la detta spada trasporta tanto in cadere & perciò per [8] raggione del moto più presto, & perche l’ huomo resta più coperto uiene ad’ essere migliore del primo. Mà il terzo modo, che è quello ilquale si fà col nodo della mano inguisa, che il braccio resti sempre diritto, ancorche la spada giri è senza comparatione migliore delli dui sopradetti in modo che il corpo resta più coperto ne si può essere cosi dilegggieri[!] ferito, perche è molto ueloce, & la punta nel cadere restadinanzi in maniera, che uenga pure punta ò taglio tutto si può parare dal forte, & fare un’ altro taglio. Il quarto similmente, che è quello col braccio duro disteso, è buono per battere li dui primi attesoche ferisce senza uoltare la spada à torno alzandola poco, ò niente; la detta spada si lascia cadere per li scoperti, & quando l’auerssario uolta la spada à torno per ferire, può l’osseruatore di questo quarto modo lasciare cadere la sua nelo scoperto, che troua, che senza dubbio haurà ferito prima, che l’altra cada, & tanto più restarà sicuro quando che haurà operato co’ipiedi, & col corpo, secondo che si richiede, perche se restasse diritto quando la sua spada cade non potrebbe ariuare in tempo alla diffesa, massime se’l taglio del nimico fosse stato fatto col gombito, mà abbassando il corpo la spada caduta si ricupera più presto, & hà da fare minore moto in giongere alla detta diffesa, perche ferendo col braccio duro disteso senza piegare il nodo della mano resta sempre la spada dinanzi, si che subbito ferito torna con facilità in retta linea, doue che per questo la detta quarta maniera uiene ad’ essere migliore delle due prime, & anco per resistere alla terza, se bene à noi pare, che la detta tetza sia molto più sciolta, ò manco obligata, & senza ricercare tanta forza, & doue si possono fare più cose, & ingannare più facilmente il nimico. Mà colui che uorà ferire di taglio con sigurezza è di mestreri, che aspetti qualche tempo oportuno, atteso che in un moto si picciolo non si può ferire, perche inanzi che la spada gionga il tempo è passato, mà si può fingere per mettere il nimico in seruitù & mentre, che para il taglio ferirlo di punta, ouero fingere di punta, & ferirlo di taglio, si come sarebbe neccessario à uolersi mouere senza aspettare tẽpo, che stando il detto nimico fermo nõ sarebbe già buono il fingere di taglio perdare di punta rispetto alla longezza[10] del moto, nella quale l’huomo potrebbe restare ferito, si può bene fingere di punta come si à detto per dare di taglio & anco che parasse il taglio ferirlo di pũta, il fingere similmẽte di taglio, quãdo il nimico stà fermo, nõ è buono per li dui tẽpi, che ui si mettono l’uno nel leuare, l’altro nel cadere, si che tutti li taglii sono longhissimi, & chi ferisce di taglio non lo potrà mai fare nel tempo che para (intendiamo con la sola spada) doue l’altro hà sempre comodità di saluarsi, & anco di fare un’altra ferita nel tempo che il primo hà uoluto parare, èben uero che nel d.o parare questi può mettere l’auerssario in seruitu togliendoli il potere fare qualunque cosa, & anco ferirlo prima, che si salui mà ci riserbiamo à parlarne, quando trattaremo delle diffese, & offese, & perche questo ferire di taglio non è molto utile noi non ci stenderemo se non tanto, quanto che saremo sforzati per diffesa di essa punta & offesa del taglio, pure è buono lo saperne dell’una, & dell’altro; nelli taglii si ricerca maggiorforza, perche sono molto scomodi, & la spada quando non troua incontro si disordina, il corpo ancor lui tal uolta si trasporta, ne può rimettersi così facilmente, si che porta l’huomo maggior pericolo in questo, che nel ferire di punta oltre l’essere di minore offesa, talche per tutti i rispetti il d.o ferire di punta è più uantaggioso, & anco più mortale, con la detta punta si ferisse più di lontano, con più prestezza & si può anco più facilmente rimertersi, & in somma tal modo di ferire uiene ad’essere più nobile, & più eccellente per trouarsi in esso tutte le sottilità delle armi, doue che per opposto nella raggione dè taglii non si troua non solo il contratempo, mà ne anco il tempo, perche il più delle uolte si fanno dui tempi longhissimi, cosa di che noi non uogliamo raggionare più di quello che habbiamo fatto nel discorso antecedente nella raggione particolare de’ dui tempi, mà si bene delle cose più sotili, più difficili, & più proffitteuoli, perche se per esempio, si affrontassero dui l’uno de quali fosse buon ferittore di taglio, & l’altro di punta senza dubbio questi batteria il primo per le raggioni sudette, ancorche esso ferittore di taglio fosse più galiardo, in modo tale che si conchiude essere meglio lo attenersi alla punta massime nelle battaglie à corpo à corpo disar- [9] mato, che armato stimaressimo buono lo seruirssi dell’ uno &dell’ altro, & cosi contra molti, perche il taglio mette in maggiore confusione & in un solo tiro possonsi parare più botte. |
||||||
[8] In good and false Parrying, and on some who, with the sword alone, parry with the left arm. The parry partakes of the nature of fear, for he who did not fear some disadvantage, would not put himself on the defence which we may call obedience and subjection, all the more so when it is forced. He who does not wish to be hit is forced to parry. When we can put our adversary under this obligation, we consider it a great advantage, for while he is under the necessity of parrying he may be hit in the line he uncovers by his movement, so that his defence proves vain. Therefore some say that parrying is false, which we admit, when it is done alone, for when you make a feint in one part and hit in another, your adversary moves to the parry, and, thinking to defend himself, is deceived by the feint, when he might, instead of parrying, have allowed the thrust to pass. To avoid thrusts is always better - that is with the sword alone, for with the sword and the dagger you can parry with one weapon and hit at the same time with the other, so that the defence is easier. But with the sword alone you must be more judicious, as it has to perform the two functions of defence and attack at the same time, in order that the parry may be safe. If you are forced to parry by a cut you must give the opposition with your forte where the adversary's sword is about to fall, and at the same time drive the point in with great swiftness, in order that it may arrive before your adversary's falls, so that he may neither avoid it nor be able to hit. This is an excellent rule, because the cut is shorter than the thrust. If you see that you cannot arrive with a time thrust, there is no need to parry, for it follows that your adversary cannot reach. If you are in doubt, you can withdraw the body a little and let his sword fall, and hit at the end of its fall. If you wish to parry knowing that you cannot hit, you must still carry your point as if you meant to hit, as this prevents the adversary from changing his line. Thus you free yourself from subjection and force your adversary to take the defensive, since he is threatened with a time thrust, and his subjection gives an opportunity for a hit. Hence it is never necessary to parry without hitting, or making a feint of hitting in order to force your adversary to parry, so that you free yourself from danger and at the same time place him in danger. It often happens that one who attempts a cut makes a large circle, so that you may hit him and recover before his sword falls. For in addition to the fact that the cut is slower, as we have said, it is also shorter. This you may do by understanding your adversary's movements and his distances. When the distance is so great that you cannot reach, you must make a feint of hitting while the adversary is making his circle in order to make it fall all the more precipitately and then sieze[!] the opportunity to hit in the part uncovered by its fall. This is instead of parrying at a great distance. But within close distance you may hit before your adversary's sword descends, since the thrust is finished before the cut, so that by withdrawing the left foot and recovering the body you may get into safety and your adversary fail to reach. It is true that this stroke would not be so deadly, since with the parry you can advance further and hit with more vigour and can pass right to the adversary's body. If you do not desire to pass it is necessary to understand how to maintain close distance and to control the feet in such a manner as to break ground in order to avoid a hit. This method is very successful owing to the slowness of the cut and because your thrust reaches further and you move with greater swiftness, so that you can always recover. If these rules are observed he who attempts to cut will always be hit, as we have already said. If in this place we must mention those who first cut at their adversary's sword in order to throw it into disorder, and then we shall not treat of them at greater length, because he who understands time and disengaging can easily save his sword against a beat. In defence of the thrust you must understand that its effect is swifter and more deadily[!]. In defending against it more subtlely[!] and ingenuity are required but less strength. To parry is more dangerous and deceptive owing to the rapid changes which it renders possible. It often happens that although you use the subtle combination of the parry and thrust at the same time, you are still deceived because your adversary, seeing your plan, removes his body out of the line, allows the point to pass and then hits in the part uncovered by the movement; so that avoiding is more subtle in defence and attack against one who makes a time-thrust, if its use is well understood. You must then understand both this and the parry and know how to avail yourself of the one or other as occasion offers. It is even more effective to use both methods together, making half a motion to defend with the sword and half a motion with the body. This defence is quicker, disorders the sword less, and deprives the adversary of the advantage of changing his line. Such avoiding is more useful with the sword alone than with the sword and dagger, but the defence partly with the body and partly with the weapons may be observed in all cases. As there are many, who, although they have the sword alone in their hands, base their defence rather on the bare hand than on the sword, we must say something of these. We say then that such a method of fencing should rather be called the sword and glove, than the sword alone, because they not only parry with the hand, but seize the weapon and hold it. We do not think this would succeed with the naked edge of a sword. To protect yourself with a naked hand is a miserable defence. Still we will show how to proceed against such men, and how best to use the method in order to save the body and the hand itself, and how to deceive the adversary. It is true that those who use the hand in this way can make larger movements with the sword, since the hand defends in any case of the adversary's making a hit, and successfully when he makes his hit simply in the straight line without disengagement or feint. Still it will not succeed if you hold your sword pointing slightly upwards, just so far that you are certain that your adversary cannot pass or hit before you have directed your point against him. In this position the adversary can neither engage nor reach your sword when on guard; you must take care to attack in an oblique line when you hit, for this is very deceptive to one parrying with the hand, since in the very act of hitting the sword swerves aside. After engaging the adversary's sword, being within distance, taking the time and the opening, you may proceed to hit by making sure that your point reaches the part aimed at as soon as it takes that direction. You will certainly make a hit before your adversary can find the sword with his hand, if he has not had time to break ground. Moreover you can use various feints according to the position in which you find his hand. Finally it is often easier to hit those who use the hand rather than defend with the sword, because they trust to the hand and take no account of the forte of their own sword, merely endeavouring to prevent it being engaged by the adversary; therefore they keep the forte withdrawn, so that they are more exposed. Therefore it is easier to hit them and recover before they have brought the forte forward to the proper distance. It is still easier to succeed against those who first parry with the hand and then rush, which is done by most of those who follow this principle of defence. Nevertheless he who is well trained although he makes use of his hand, controls his sword and observes the time. It is well to know how to do this in case of need, but not as a fundamental principle, as we have said above. He who understands what can be done with the hand, knows the converse even better. As a general rule the hand should never be used except when you can reach the hilt and come to grips, a matter which does not concern us, who wish to treat only of the defence, the methods of making a hit and the advantage of arms, and not of scuffling. However this arises sometimes from accident, so that at the end of the book we shall say something of it. But when such a point is reached, the greatest danger is already passed, of which it is more necessary to treat, in order to show how to avoid it with safety and with damage to the adversary. Finally to show the true method of using the left hand we say that, when your adversary is about to hit, you must parry with the sword and hit, but it is good at the time of doing this to carry the hand to that part, where his sword might hit, so that the hand will defend the body and exclude the adversary's sword without a beat. This is a good principle on every occasion when there is time. This is a better method, because, the hand is not in such great danger and the body is better defended, nor can the adversary so easily be aware of it, as his sword is not molested. If he proceeds to hit he finds the path closed; if he refrains, you can hit him without being disordered. This then is the safest method of using the hand. He who considers its principles will find in it great advantages and subtleties of defence. Many things we omit for the sake of brevity, as our purpose is to deal with fundamental principles only, from which can be deduced countless rules, some better than others; for this subject is so large that it is difficult to find an end. |
COME IL PARARE SIA BVONO E COME FALSO Edi alcuni ehe parano con la sinistra hauendo la sola spada Cap 8. CHI CONSIDERA BENE IL PARARE TROUA QUELLO essere una spetie di timore, perche chi non temesse di danno non si metterebbe in diffesa, laquale si può dimandare ubbedienza, & seruitù, & è tanto magiore quando lasi fà per neccessità perche chi non uuole essere ferito astretto è di parare, dimodo che quando si può mettere l’ auerssario in cotale obligo di diffesa noi logiudicamo uantaggio grande, perche mentre che uà in quella neccessità di parare può essere ferito nello scoperto, che fà mouendosi, & cosi restando ferito uiene la diffesa ad’ essere stata uana, & quindi alcuni dicono, che il parare sia falso, il che noi confessiamo, quando che semplicemente si adopera, perche fingendo ferire in una parte, & poi ferire in un’ altra, quando propriamente il nimico si muoue à parare esso haurà creduto diffenderssi, & non l’ haurà fatto per essere stato ingannato dalla finta, di maniera tale, che potendosi fare dimeno di parare con lasciare passare i colpi à uuoto, & sfuggire le ponte sempre è migliore, intendiamo, nella sola spada, perche con la spada, è pugnale si può con un’ arma parrare, & con l’ altra ferire in tempo medesimo, & così uiene l’ huomo à saluarsi piu facilmente, mà con la spada sola bisogna operare troppo gindiciosamente uolendo, ehe essa sola faccia questidui effetti di diffesa, & offesa in un punto medesimo, si come è neccessario, perche il parare sia sicuro, & però essendo astretto à parare da qualche taglio fà di mestieri andare alla diffesa col forte da quella parte, oue la nimica spada uiene à cadere, & che nelo stesso tempo la punta uada à ferire con tanta prestezza, che gionga prima, che la detta nimica habbia colpito nell’ altra, acciòche nel darli sopra non si suiasse, & non potesse ferire, & questo si può benissimo osseruare, perche il taglio è più corto della punta, però questo è il uero modo da tenersi, & uedendo non potersi giongere in tempo con la punta non occore di parare, perche è segno, che la nimica non può ariuare, & chi pure dubbitasse puo dilongarsi con un poco di ritirata di corpo con lasciarla cadere, & poi nel fine di essa caduta ferire, & quando pur’ anco si uolesse parare conoscendo di non potere ferire, bisogna con tutto ciò portare la punta della spada come se si uolesse ferire, attesoche questa maniera impedisce il nimico, che non può mutare effetto, & così sciogliendosi da quella seruitù seli pone esso nimico, quale è forzato andare alla diffesa dal uedersi uenire contra il corpo la punta in tempo, il quale nimico, mentre che entra in si fatto timore porge tempo oportuno per essere ferito, di modo tale, che non occore maì à parare se non si ferisse, ouero non si mostra di ferire per mettere[11] l’ istesso nimico nella detta ubbidienza di parare, perche uiene à liberare se medesimo dal pericolo, & metteruelo esso, & anco spesso interuiene, che colui, ilquale uuole ferire di taglio fà tanto grangiro, che si può ferire & saluarsi prima, che la sua spada scenda, perche, oltreche il taglio è più tardo, come altre uolte si è detto, è anco più, cortò & questo riesse con la cognitione del moto nimico, & delle distanze, secondo che l’ istesso nimico uiene più, ò meno inanzi, mà quando la linea sia tanto lontana, che non si possi ariuare si deue mostrare di uolere ferire nel tempo proprio, che la spada gira perfarla cadere con maggiore precipittatione affine di hauere poi comadità di ferirlo nelo scoperto [10] che farà in detta caduta il che si intende in lontana distanza, ouesipuò fare di meno di parare, mà in stretta distanza può l’ huomo hauere ferito inanzi che la spada auersa discenda essendo più presto à finire il moto della punta, che quello del taglio à percuotere sopra la spada, di modo tale, che chi si ritirasse col piè sinistro indietro ricuperando il corpo si saluarebbe, & la nimica non giongerebbe, mà bene è uero, che la ferita non sarebbe così mortale, perche parando più si può andare inanzi inmodo, che si ferisse con più galiardia, & si può sino all’ altro corpo passare, mà non uolendo passare neccessaria cosa è lo sapersi contenere in così stretta distanza, & con li piedi in tal modo, che si possi uscire fuori di misura in tempo per non restare ferito, & tutto questo riesce benissimo per latardanza del taglio, & perche la punta gionge più di lontano, si come anco perche l’ huomo opera con maggiore comodità, & prontezza tal che puo rihauersi in tutti li casi, si che osseruandosi queste regole quello che ti rarà di taglio restarà sempre ferito, come habbiamo altroue detto, & se bene hauressimo in questo luogo da raggionare di colloro, che tagliano prima nella spada nimica per disordinarla, & andare poi à ferire, non uogliamo niente di meno trattarne, perche chi intende, che cosa sia tempo, & cauatione sà facil mente saluare la sua spada, che non sia battuta, & ferita; Hora discoreremo della diffesa della pũta si deue dunque suporre, che l’effetto è più ueloce, & la ferita più mortale, di modo che in operarli contra ui si ricerca maggiore sottilità, & ingegno mà minore forza di quella, che bisogna per resistere al taglio, Il suo parare è più pericoloso, & falace per le preste mutatione, che possono farsi, & spesso adiuiene, che benchesi pari con quella sottilità di ferire nel tẽpo medesimo, non dimeno resta deluso, perche il nimico uedendo l’ effetto lieua il corpo dalla presenza della punta, & lasciandola passare uà à ferire nelo scoperto, che si è fatto mouẽdosi, doue che il fuggire di uita uiene ad’ essere più suttile per diffendere, & per offendere colui che uiene di tempo, quando che si sà mettere bene in opera, in modo che è neccessario sapere ben parare, & ualersi hor dell’ uno, hor dell’ altro serõdo che le comodità & occasione inuitano, & maggior mẽte riesse quãdo tutti dui operano in un’ istesso tempo, perche facendo meggio il moto della diffesa con la spada, & meggio col corpo si uiene à diffendere con più prestezza, & à disordinare meno la spada, oltre che si uà con maggiore celerità, con laquale si toglie la comodità al nimico di mutare l’ effetto; si dice bene che lo scanso di uita serue più nella spada sola, che con la spada, è pugnale, pure questa osseruatione di saluarsi parte col corpo, & parte con l’ armi è buona in tutti li casi. Et perche molti sono, iquali con tutto che habbino la spada sola nelle mani fondano le sue diffese più nella mano nuda, che nella spada, sarà bene che di ciò si dica qualche cosa, diciamo dunque, che simile maniera può più tosto chiamarsi di spada, è guanto che di spada sola, perche non solo parano con la mano, mà ancora prendono l’ arma & la tengono salda, cosa che non pare à noi riuscibile con la spada biancha, cioè da filo, ci pare bene una misera diffesa l’ assicurarsi con una mano, ignuda, non dimeno ne trattaremo alquanto per dire come si dee operare contra tali, & anco per mostrare come sia bene di adoprarla per saluatione del corpo, & della stessa mano, & acciò che meno sene aueda il nimico; & se bene è uero che questi tali, che adoprano la mano possono fare moti più grandi con la spada atteso, che la mano diffende in ogni caso, che l’ nimico uengi à ferire, anco che la spada si troui in moto, si come riesce non meno, quando si uà con la retta linea à ferire semplicemente senza cauationi, ò finte, non dimeno non li riuscirà quando non seli adoprarà contra la spada tanto diritta, mà un poco angolata allo insù, & tanto, ehe basti à conoscere che esso nimico non possi passare col corpo, ò ferire prima, ehe seli habbia diretta la punta contra; si che tenendosi la mano così non può il detto nimico ne trouarla ne ariuarla stando nella guardia, con auertirsi di andare per linea obliqua, quando si uà à ferire, laquale inganna molto la mano di quello che uuole parare, perche nel proprio ferire la spada la uà sfuggendo, di modo che doppo l’ hauere aquistata la nimica, & la distanza trouandosi il tempo, & lo scoperto, si può andare à ferire, facendo di modo che nel dirizare la punta la spada uada sempre inanzi inguisa tale, che finito di agiustar- [11] la per quel luogo, doue si hauea disegnato, la punta sia già ariuata, che si ferirà di certo, & prima, che l’ detto nimico la troui con la mano, quando non hauesse hauuto tempo di rompere di misura, oltre che si può operare con uarie sorti di finte secondo il sito, oue si troua la mano, doppo questo molte uolte accade, che meglio & più facile è il ferire questi che adoprano la mano, che quelli, che si diffendono con la sola spada, perche fidandosi essi della mano non tengono conto del forte della propria spada, & però non procurano altro, se non che l’ auerssario non glie l’ occupi, & per tale caggione la tengono ritirata, & uengono in questo modo à fare maggiore scoperto, & pertanto è molto più facile il ferirli, & saluarsi prima, che habbino finito di allongare la sua per trouarsi tanto ritirata, & lontana dal luogo, oue si hà da ferire, & tanto maggiormente riesce contra quelli, che prima parano con la mano, & poi feriscono di slancio & la più parte di colloro, che fondano le sue raggioni in simile diffesa fà così, mà nondimeno chi hà la uera maniera se bene adopra la mano porta la spada, & ferisce di tempo, ilche è bene saperlo fare per poterlo usare in caso di neccessità mà non per fondamentouale, come di sopra l’ habbiamo accennato, chi sà l’ effetto, quale può nascere da una mano può meglio conoscere il contrario, che è di bisogno, mà per uera regola non dee mai mettere la mano in opera se non quando può giongere al fenimẽto, ouero alle prese per uenire poì alla lotta materia non spettante à noi, che uogliamo solamente trattare delle diffese, de i’ modi di ferire, & del uantaggio dell’ armi, & non del lottare ancorche qualche uolto[12] accada per accidente, si come nel fine del libro ne diremo pure qualche cosa, mà quando si uiene à termini tali già si hà scorso il pericolo maggiore, del quale è più neccessario trattarne per insegnare à passarlo sicuramente, & con danno del nimico. Dunque per di mostrare il uero modo di usare essa mano sinistra, diciamo che quando il detto nimico uiene à ferire bisogna parare con la spada, & ferire, mà è ben buono, nel tempo, che questo si fà, di portare la mano in quella parte, oue potrebbe uenire la nimica spada à ferire, accioche uenendo habbia la detta mano diffeso il corpo, & serata la medesima nimica difuori senza batterla, & così sarà buono operare in agni occasione, che si troui tempo; Questa maniera è migliore perche la mano non porta tanto pericolo, & il corpo hà diffesa più grande, ne può il nimico tanto facilmente accorgersene, perche non seli molesta la spada, il quale se uiene per ferire troua la strada chiusa, & se non uiene si può ferire lui senza disordinarsi si che questa è la migliore, & più sicura strada di adoperare essa mano, le raggioni della quale chi bene le considerarà ui trouarà dentro uantaggi grandi, & sottilità di diffesa, che molte cose tralasciamo per breuità bastando à noi solamente di raggionare de fondamenti più principali, da quali si possono cauare infinite raggioni migliori una dell’ altra, essendo questa materia tanto ampia, che difficilmente ui si troua termine. |
||||||
[9] Engaging the sword. How it is done and when completed. To engage the sword is to gain an advantage over it; it is a kind of counter-position with some difference, because often you have engaged, the adversary's sword without completely closing the line from his, point to your body. But it has this advantage, that your adversary cannot hit without passing your forte, which is so near his point, that you can find the point while he is moving to make the lunge. The counter-position is not considered well formed except when the line from his point to your body is fully defended. But the same advantage may be obtained by relative strength, so that you are considered to have engaged, when you are sure that your sword is stronger than the adversary's and cannot be pushed aside, but can push his aside. When on guard and wishing to engage the adversary's sword, you must carry your point towards his, with the fourth part of the blade against his fourth, but rather more of your fourth part than of his, for that little more, though little, will be enough to give you the advantage, when you have engaged his sword at the weaker part. You must bear in mind that the sword is always stronger in the line in which the point is directed, and in order to advance in that line ---------- you must know how to carry your body and sword in such a way that their strength is in the same direc-[13] This depends to a great extent on the wrist, as will be seen in the plate illustrating the guard on the inside, which is the most difficult. You must also take care, in trying to engage the fourth part, to keep your point at such a distance from the adversary's sword, that he will not have time to push forward the third or even the second part, with the result that while meaning to engage his faible you would have engaged his forte. This might happen owing to the distance between the two swords, for the amount you can push your sword forward before engaging is the same as the distance. You must move at the same time as he moves, otherwise you might be hit. Moreover, although the space between the two points were small, while you were advancing to engage, the adversary might perceive this and make an angle, which would strengthen him and bring him away from your advance. If you should push on in order to hit when within distance, his forte would have penetrated so far, that if you had moved in order to engage his sword, you would be unable to defend yourself, and would be hit. Further, if while you are trying to engage, he moved his body away from your point, he could pass right on to your body, before your sword had returned into line. To prevent your adversary's doing this you must first consider the distance between your bodies, and then move forward to engage his sword, carrying your sword without constraint so as to be free to abandon your first plan, when your adversary seizes the opportunity, and drives the point on to his body, bringing the forte where you intended to put the point. In this way you will hit the adversary at the moment when he is pushing forward. You must remember that this rule applies to the guard on the inside, for, if on the outside, you must abandon your first movement and drop the point under the adversary's sword to the right side, carrying the forte where you meant to put the point. On this line too the present method is very successful if you similarly do not touch the sword in seeking to engage. The nearer the adversary is, the better and safer the method is. The advantage is in having brought your forte against his faible. It often happens that the adversary, finding his sword is not molested is not aware that you have already gained the advantage, whereas if you touch his sword he more easily realises the fact, and can disengage or retreat or change his guard, in order to free himself, so that you lose your first advantage. Moreover if you touch the sword, you impede and disconcert yourself, so that if a time comes to hit, you cannot take it because of the resistance of your adversary's sword. Even when there is no resistance and the adversary disengages, you cannot prevent your point dropping a little, so that the time is lost. But if you keep your sword suspended, it is the more ready for every opportunity, there is more use made of time, and there is no necessity to force his sword, which often leads to scuffling. If you do not touch swords, that cannot happen. When then you advance to engage your adversary's sword and he moves to meet you at the same time, the one who first yields with the sword and drives on to the body, can hit before the other touches swords, or in the same instant. If you do not wish to try a hit, you can lower your point towards the ground to prevent the adversary's engaging, and if he follows it you can thrust while his sword is falling. There are many other ways of preventing your adversary from engaging your sword, except when the point hits, especially if you have won the advantage of the forte against the faible and the swords are in position. In endeavouring to acquire the advantage over the adversary's sword you must take care not to advance the point so far in your desire to be the stronger, that he can pass in one line or another, before you can direct your point. If you observe these rules you will without doubt gain the control of your adversary's sword, which is the first part of victory. Though your adversary takes advantage of the time he will still be hit. To prevent your getting this advantage he will have to retreat, changing the position of his body and sword and to adopt new devices, which are countless. The one who is more subtle in his movements will maintain his sword the freer. |
CHE SIA IL TROVARE DI SPADA, Come si troui, & quando s’ intenda hauerla trouata. Cap 9. IL TROUARE DI SPADA UUOL DIRE AQUISTARE, ET E quasi come contrapostura, quantunque ci sia qualche differenza, perche molte uolte si hà trouata la spada al nimico, che ancor la linea laquale uiene dalla punta al corpo non è tutta coperta, mà si hà bene questo uantaggio, che il nimico non può ferire se non passa per il forte, ilquale è tanto uicino alla sua punta, che quella è trouata nel tempo, che esso si uuole mouere per fare la distesa, che la contrapostura non s’ intende ben fatta se non è tutta diffesa da quella parte, che uiene dalla punta al corpo mà si adopra bene uu medesimo, uantaggio di debile, & [12] forte, & per questo la spada s’ intende trouata quando si conosce hauerla più forte del nimico, in modo che non possa essere rispinta, mà si bene che possa rispingere l’ auerssaria, & acciòche meglio s’ intenda; Essendo l’ huomo nella guardia, & uolendo aquistare la spada nimica fà di mestiere che porti la sua punta uerso l’ altra con la quarta parte nella quarta parte del detto nimico, mà con alquanto più della sua in quella di esso nimico, perche quello più, che haura della sua nell’ altro, anco che sia poco basterà per seruirsi del uantaggio, quando però si haurà trouata detta nimica nel più debile, & questo bisogna auertire, perche la spada è sempre più forte da quella parte doue piega la punta, & à uolere andare da quella parte è neccessario sapere accomodare il corpo, & la spada in guisa, che la sia della medesima forza dell’ altra, & gran parte di questa raggione consiste nel nodo della mano, come si mostrarà nella figura che seruirà dalla parte di dentro per essere la più difficile, si dee non meno auertire di hauere la punta tanto lontana dalla nimica spada, che in uolerli trouare la detta quarta parte, esso nimico non habbia tempo dispingere inanzi la terza, & forsi la seconda parte, inmodo che credendosi di hauerli trouato il debile seli hauesse trouato il forte, che questo potrebbe auenire per la distanza, che fosse trà l’ una, & l’ altra spada, che tanta come è larga essa distanza tanta spada si può spingere contra il nimico prima, che egli la troui, mouendosi nel medesimo tempo che esso si moue, che altrimenti si restarebbe ferito, in oltre se bene fosse poco termine trà l’ una punta, e l’ altra, quando l’ uno si mouesse per andare à trouare la nimica l’altro uedendo ciò potrebbe fare un’ angolo, conche uerebbe à fortifficarsi, & ad’ allontanarsi da quello che si auicinasse, & che se in un medemo tempo si spingesse oltre perferire, mentre che fosse in misura, il suo forte sarebbe tanto penetrato, che colui ilquale si fosse mosso per trouare detta spada non potrebbe diffendersi, mà restarebbe ferito & di più se l’ altro facesse col corpo moto diuerso da quello della punta nimica, nelo andare à trouarla, potrebbe anco passare sino al corpo prima, che la detta nimica tornasse in presenza, mà à non uolere, che un nimico possa fare questo bisogna prima considerare la distanza trà l’ uno corpo, & l’ altro, & dall’ una punta, & l’ altra & poì mouersi per andare ad’ aquistare essa nimica spada, portando la spada però senza uiolenza affine di abbandonare il primo effetto nel tempo che il nimico piglia l’ occasione & andare con la punta al corpo portando il finimento oue si hauea di segnato mettere la detta punta, che si ferirà in questo modo esso nimico nel tempo che lui si sarà spinto inanzi, auertendosi che questa raggione si intende, dalla parte di dentro, che da quella di fuori è neccessario abbandonare il primo moto, & callare la punta sotto alla nimica spada per il destro fianco con portare il finimento, oue si uoleua mettere essa punta, che anco in questa parte il præsente modo riesce benissimo auertendo similmente di non toccare la spada, quando si uà à trouarla, & quanto più se gli è prossimo tanto è meglio, & più sicuro, & stà il uantaggio nell’ hauere situata la spada con la sottilità del forte al debile, & spesso accade, che uedendo il nimico non li essere molestata la spada non s’ accorge esserli già statà aquistata che toccandogliela più facilmente se n’ auede, & hà più occasione di cauare, ò ritirarsi, ò mutare la guardia per liberarsi, in modo che si uiene à perdere quel primo uantaggio, & in oltre se si tocca la spada si impedisse, & si sconcerta se stesso di sorte, che se bene uiene il tempo da ferire non si può pigliare perla resistenza, che fà l’ auerssario, si come anco se la si appoggia niente sopra essa, & che l’ nimico la caui non si può ritenire la punta, laquale non faccia un poco di caduta, conche si perde il tempo, doue che tenendola sospesa si hà quella più pronta in ogni occasione,[14] le botte riescono con più tempo, & non si è neccessitato à contrastare di spada, cosa ehe spesse uolte caggiona il uenire alle prese, & dalla spada alla lotta, mà non toccando detta spada non ui si può uenire; Quando poi si uà à ritrouare la nimica punta se l’ altro si moue per rincontrare, & ataccarla insieme, il primo, che si è mosso, cedendo di spada, & andando al corpo, può ferire inanzi che l’ altro tocchila detta spada, ouero in quello instante, & non uolendo ferire li può bastare di abbassare la punta uerso terra, che la nimica non la trouarà, & se l’ altro la seguittarà per [13] hauerla si potrà in quel caso darli di sopra nel tempo che la sua cade, oltre molti altri modi di saluarla che lo stesso nimico non la touarà mai se non nel tempo che la punta ferisce, & tanto meno quando già si hà aquistato, il uantaggio del forte al debile, & che già sono fermati; si dee bene hauere la mira, che nell’ andare all’ aquisto della nimica, non si uadi tanto inanzi con la punta per desiderio de essere più forte, che esso nimico non piglii addito di passare ò per l’ una ò per l’ altra parte prima, che si possi dirizare la punta; & percio operando con simili riguardi si aquistarà anco senza dubbio la nimica spada, che è prima parte della uittoria & ancorche il detto nimico pigliasse il tempo di quel moto che si facesse restara non meno ferito, & à non uolere, che sopra di lui si piglii il uantaggio sarebbe neccessitato ritirarsi mutando effetto si di corpo, comedi spada & procurare noui partiti, che sono quasi infiniti, & quello insomma, che sarà più suttile nelle operationi manterà sempre la sua spada più libera. |
||||||
[10] On time and counter-time, which are good and which false. How to deceive the feint of a time, offered by the adversary so that he may make a counter-time. A movement made by the adversary within distance is called a time. For whatever is done out of distance can only be called either a movement or a change of front. Time then means an opportunity to hit or win some advantage over the adversary. This movement is given the name of time among the movements of fencing in order to convey the idea that at a given point of time it is the only possible movement. When the adversary moves, if you perceive an exposed part and are ready to hit in that part, the adversary will certainly be hit if within distance. For there cannot be two changes in one time, and therefore you must take care that the time in which you wish to hit is not longer than the time offered by the adversary. In such a case he would have a chance to parry before your point arrived, and you would be in danger; whereas, if you understand the movement, you would succeed. This is called a time-thrust. Besides understanding the movement you must consider the distance, because if you were within wide distance, even though your adversary moved his weapons or body, provided he did not move his foot there would be no certainty of being able to hit him, even if he were uncovered, for, if his foot were firm, he could break ground, so that your sword would not reach, and you would be in danger. Therefore it would be better to take advantage of his movement to approach within close distance so as to hit with certainty at his first movement with weapons, foot or body, or with both foot and weapons. All these are times favourable for a hit in an uncovered part. The success would be even greater, when the adversary offers the time unawares, provided he is not retreating. To be certain of success you must be in counter-position, since, if your adversary has moved first, it is clear that he will not be able to parry and hit except in two times, so that the stroke will be finished before he has parried, and you will be able to break ground before he hits. It is also clear that he will be unable to break ground, as he might have done if he had remained steady. It is sometimes good to beat the adversary's sword within this distance, even if he does not move his foot, for the reason that, if he offers a time unawares, he will not expect it, as he has not realised that he has given an opportunity of being hit, and therefore he has had time neither to parry nor to break ground. But you must bear in mind that there are some men who cunningly offer a time, that you may attempt a hit, and at the same time they parry and hit. This is called a counter-time. Whenever you are hit or make a hit at the moment when your adversary is extended to hit, it is called a hit in counter-time. Similarly it sometimes happens that both are hit at the same moment; this is because one of them has not timed the counter-time well, or that in offering the time he was too close, or that he has made too large a movement. To avoid the danger of this counter-time, you must realise before you make your movement, whether it is so great, that you could approach nearer, and also whether your adversary has moved with the intention of enticing you to hit. In that case you should either not proceed, or you should carry your sword towards the line uncovered by the adversary, and when he moves to make the counter-time, you should then change your line to the part uncovered by his movement, avoiding his point with your body. In this way the deception planned by him will be turned against himself. In truth this science of arms is merely the science of deceiving your adversary with subtlety. When therefore you are within close distance you can hit at every movement or change of your adversary, however small, provided he does not break ground; for if in giving a time he carries hit foot back he so lengthens the time in which you may hit, that he has a good chance of parrying and hitting; for he being the first to move is also the first to finish the movement. This advantage he would not have if he stood firm, and tried to break ground, while you were making a hit; for your point would arrive before he was out of distance, nor could he parry. Therefore it is not good to be the first to save when within close distance, except to retreat. You must also know that within this distance you may often hit without waiting for a time by the simple advantage of the counter- position, and by understanding how to move in making a hit and how your adversary moves in parrying; also owing to the fact that there are many exposed parts in such a position. Therefore you must contrive to have your point so near the adversary's body, that the time required for your hit is less than the time he needs to defend himself. You must also contrive that your adversary's sword is so far distant from yours, that it is clear when you advance that he can engage only with the forte for then your sword cannot be thrust aside but will continue on its path to complete the stroke. All these rules may be observed equally with the sword and dagger, because the weapons are kept more withdrawn and there are more exposed parts in which a hit may be made, so that they will be most effective. You may easily understand then, how dangerous it is to approach within distance unless your weapons are in conjunction or without some advantage especially within close distance. You have seen too how times and counter-times are made, how they may be deceived, and which cannot be deceived. |
CHE COSA SIA TEMPO, ET CHE COSA CONTRATEMPO, Quale sia il buone, & quale il falso, & come s’ inganni il tempo finto, che suole dare il nimico per fare il contratempo. Cap. 10. TEMPO SI DIMANDA QUEL MOTO CHE L’ NIMICO FA dentro della distanze, perche quello che fà di lontano non si può chiamare altro, che monimento, ò mutatione di prospettiue, perche tempo in quest’ arte uuole significare occasione di ferire, ouero di pigliare qualche uantaggio sopra il nimico, ne per altra caggione è stato dato nome di tempo alli moti, che si fanno nell’ armi se non per fare intendere, che facendo uno qualche moto quello è tempo nel, quale in un’ istesso punto non può fare altro effetto; & però nel mouersi, che farà il nimico se si uedrà qualche scoperto, & che si sia pronto per ferire quella parte esso nimico di certo restarà offeso, mẽtre che questo sarà fatto in misura, perche non si possono fare due mutationi in un tempo, & perciò deesi auertire, che non sia più longo il tempo nel quale si uuole ferire di quello, che da’ l’ istesso nimico per essere ferito, perche in tale caso egli harebbe comodità di parare prima di essere ariuato, & sarebbe pericolo, che hauendo conosciuto il moto la cosa riuscira bene, questa si dimanda ferita di tempo, & oltre il conoscimento del moto è neccessario considerare la distanza, quale che sia, perche trouandosi in distanza larga anco che l’ nimico faccia mouimenti d’ armi, & di corpo, pure che non moua il piede non ui è certezza di poterlo ferire se ben’ anco fosse scoperto, perche con l’ hauere il piè fermo potrà rompere di misura che la spada nõ lo ariuarà, & si sarà in pericolo, di modo che meglio sarebbe pigliare l’ opurtunità di quel moto & auicinarsili nella stretta misura per poterlo ferire poi di certo al primo moto, che faccia così se si mouera per accommodarsi nell’ armi, & farà qualche moto de piedi, & di corpo, ouero piedi, & armi, & anco che fosse col solo piede tutti sono tẽpi opurtuni per ferire nelli scoperti, & tanto meglio riuscirà sempre quando il nimico farà il tẽpo inauedutamente pure che nõ sia ritirandosi, mà à uolereche ciò riesca ancor meglio fà di bisogno trouarsi in cõtrapostura, perche quãto al detto nimico, essendosi prima mosso, è chiara cosa, che nõ potrà parare, & ferire se non con dui tẽpi, talche la botta sarà finità prima, che egli habbia parato, & si potrà rompere di misura prima, che egli pure habbia ferito si come è chiaro ancora, che esso nõ potra rõperedi misura, come haurebbe potuto se fosse stato fermo del piede. E buono anco talhorabattere il nimico in questa misura, anco che esso non si mouadel piede, la raggione è che se egli darà tempo [14] senza auedersene li soprariuà quello che non aspetta per non hauere saputo conoscere di hauere data occasione di essere ferito, & percio non è potuto essere à tempo ne à parare, ne à rompere di misura. Mà in questo luogo si deue auertire, che alcuna uolta si trouano alcuni, iquali astutamente fanno tempo acciò si uada à ferire, & nel medesimo tempo, che si uà essi hanno parato, & ferito, questo si chiama ferire di contratempo, & ciascuna uolta, che si reftarà ferito, ò si ferirà nel punto che l’ auerssario sistende per ferire si adimandarà ferire di contratempo, & alcuna uolta similmente occore, che tutti dui restano feriti in un’ istesso punto, ciò procede da quello, ilquale non hà preso bene il contratempo, ouero, che quando hà dato il tempo era in troppa angusta misura, ò che hà fatto troppo grande il motto; uolendo dunque fuggire il pericolo di questo contratempo fà di mestiere conoscere se il moto inanzi che si faccia, sia tanto grande, che si possi auicinare, & anco se il nimico sia mosso insidiosamente, perche si uada à ferire, che in questo caso, ò non bisogna andare, ouero, uolendo ferire, si deue portare la spada per quello scoperto fatto dal detto nimico, ilquale mentre si moue per fare il contratempo, si deue all’ hora mutare l’ effetto nel secondo scoperto che farà nel ferire di detto contratempo sfuggendo col corpo la punta nimica, che in questa forma l’ inganno procurato da lui contra altri sarà stato esequito contra di se medesimo, & in uero questa scienza non è altro che sapere con sotilità ingannare il suo auerssario. Ritrouandosi poi nella misura stretta si può all’ hora ferire in ogni mouimento, & mutatione fatta dal nimico, per picciolo, che sia, pure che non sia rompendo di misura, perche se nel dare il tempo egli porta il piede indietro, uiene all’ hora ad’ allongarsi tanto quel tempo, nelquale si hà da ferire; ehe esso nimico hà molto agio di parare, & ferire, perche essendo stato egli il primo nel mouersi è anco il primo nel fenire del moto, cosa non gia riuscibile à lui se desse il tempo stando fermo, & uolesse rompere di misura, mentre che si uà à ferirlo, che certo sarebbe ariuato prima, che fosse uscito di misura, ne hauerebbe potuto parare, in modo che non è buono essere il primo à mouersi stando in questa misura stretta se non dilongandosi, & deesi anco sapere, che in detta misura molte uolte si ferisse senza aspettare tempo per il solo uantaggio della contra postura, & perla cognitione del moto da farsi nel ferire, & di quello del nimico nel parare, & simil mente per li scoperti, che talhora sono grandi, & perciò indetta stretta misura si potrà sempre ferire senza aspettare tempo, pur’ che si conosca hauere la punta si uicina al corpo nimico, che sia minore il tempo nelquale si hà da ferire, che quello nel quale l’ altro hà da diffendersi, & perche si conosca ancora l’ armi nimiche essere tanto lontane dalla spada, che spingendo inanzi si ueda chiaramente, che il detto nimico non la possa trouare se non nel forte, che all’ hora la detta spada non potrà essere deuiata mà andarà dirittamente à ferire doue sarà incaminata. Tutte queste raggioni seruiranno parimenti nella spada è pugnale, perche l’ armi si tengono più ritirate, si trouano più scoperti, & più luoghi da potere ferire si che riusciranno benissimo, in modo che si è potuto ageuolmente comprendere quanto pericoloso sia l’ auicinarsi nelle distanze disunito, & senza qualche uantaggio massime nella misura stretta, & anco si è ueduto come si piglino itempi & icontratempi, come si inganni liuni, & lialtri, & quale non può essere ingannato. |
||||||
[11] What is "disengagement, counter-disengagement, double disengagement, half disengagement, re-engagement, and how and when they should be used. When your adversary attempts to engage your sword or to beat it, and you change from one line to another, before he can beat or engage, you are said to make a disengagement in time. If, while your adversary is disengaging, you follow his movement, which he has begun in order to get the superiority, and let your sword go after his, so that you engage him in the same line as before, that is called a counter-disengagement. If you have disengaged and your adversary has also disengaged and you then deceive his engagement, that is a double disengagement. If, without completing the change from one line to another, you leave your sword under the adversary's, you make a half disengagement. If you disengage and, when your adversary moves to engage or to make a hit, you engage again where you were before, you are said to re-engage - - -.To make a successful disengagement you must bend forward — so that, when the disengagement is completed, the lunge is completed, if you wish to hit, otherwise you will not be in time. If you follow this principle, your adversary will not be able to parry, if you have taken the time, though he may counter-disengage, if that was his intention in seeking to engage. If he had meant simply to get the superiority or to beat he would certainly be hit. If in seeking to engage your sword, the adversary remains steady, then you must disengage in order to free your sword. This gives him an opportunity for a counter-disengagement, for he has moved at the same time as you disengaged. Then to protect yourself you must make a double disengagement and thrust in the same time, in which he has meant to hit you with a counter-disengagement. Some remain steady in seeking to engage in order to make the adversary disengage and so hit him in the straight line, before he has completed the disengagement. In such a case if the adversary, who has begun to disengage, returns to the same line as before, carrying his forte to your faible and thrusting on to the body, he will save himself and certainly hit at the moment you meant to hit. The half disengagement is used when you are in doubt that the adversary may pass to your body, before you have completed,[!] the disengagement, since your point would be out of presence and could not hit. Therefore you make a half disengagement to save time, and remain below the adversary's sword in order to hit, removing your body out of presence, as we shall explain in its place. Such a half disengagement is not always used in the first passes, but more often in the second and third movements, as the distance is shortened. The effects produced by these disengagements will be seen in the plates. |
[15] CHE COSA SIA CAVATIONE, CONTRACAVATIONE, Ricauatione, meggia cauatione, & commettere di spada & come, & quando si debbano usare. Cap. 11. QVANDO IL NIMICO VIENE PER TROVARE LA SPADA, ouero batterla, & che quella si muta dell’ una nell’ altra parte prima, che egli la batti, ò troui all’ hora si dimanda cauatione di tempo, contracauatione è quella, che si può fare nel tempo, che il nimico caua seguittando il moto, che si hà cominciato per aquistrare, & lassiare andare la sua spada dietro l’ altra, che si caua, che egli si trouara in quella stessa parte, doue che era prima. ricauatione, poi è quella, che potrebbe fare il primo, che ha cauato, mentre che l’ altro caua cio è cauare un’ altra uolta, & all’ hora la contracauatione restarebbe ingannata. meggiacauatione si dice quell’ altra quando non si finisse di passare dall’ una nell’ altra parte mà che si resta giu’ sotto la nimica. mà comettere di spada è quello che si caua, & che si rimette doue era prima, quando il nimico si mosce per andare alla spada, ò per ferire; A uolere, che la cauatione riesca bisogna cauare ouato inanzi, in modo che finita la cauatione sia finita la distesa quando si uuole ferire, ehe altrimenti non si giongerebbe à tempo, & operando nella soprascritta forma il nimico non potrà parare, se si hauerà fatto di tempo, mà si bene contracauare mentre che haurà hauuto tale pensiero nel uenire à trouare la spada, che se fosse stato semplice desiderio di aquistarla ouero batterla restarebbe ferito al certo, & se nel detto uenire à trouare la spada egli sarà fermo con li piedi, all’ hora si deue cauare per ritrouare la sua, & questo è tempo di contracauare dal primo, che si è mosso nel punto midesimo, che l’ altro caua, di maniera, che se quello, che prima hà cauato uorà saluarsi ricauarà & spingera inanzi, & ferirà nel medesimo tempo, che l’ altro hà uoluto ferire con la contracauatione. Altri uà à ritrouare la spada fermo di piede per fare cauare al nimico per ferire diretta linea inanzi che finisca la cauatione, in tale occasione se quello, che hà cominciato à cauare ritornarà la sua spada nella parte, doue era prima con portare il finimento al debile nimico spingendoli la punta al corpo si saluerà, & ferirà certo nel midesimo punto, che l’ altro credeua ferire. la meggiacauatione si adopera quando il nimico uiene tanto inanzi, che si dubbita, che passi col corpo prima che sia finita la cauatione, perche la punta restarebbe fuori di presenza, & non potrebbe ferire perciò si fà meggia cauatione per essere più presto, & si resta sotto la nimica spada à ferire, leuando il corpo di presenza di detta nimica, come diremo à suoi luoghi, & tale meggia cauatione non sempre si mette in opera ne i’ primi tempi mà il più delle uolte nel secondo, & terzo mouimento secondo che fi[!] uengono stringendo le misure, & nelli effetti che saranno in figura si uedranno le ferite di queste cauationi. |
||||||
[12] On the feint, and why it is so called; in what manner and at what time it should be used. When you feign to hit in one line, and while the adversary is defending himself, hit in another, you are said to make a feint. You must understand, which feints are good, and which not. For some make their feints with the feet rather than with the sword, beating the ground as hard as possible, so as to frighten the adversary, and while he is intimidated hit him. This method might sometimes succeed in the hall, particularly if the floor is of wood, so as to re-echo. This might sometimes cause the adversary to waver. But on ground which does not ring, it would not have the same effect. It is of little or no value in either place against those who understand the art. For if this stamping is done out of distance, there is no need to waver, since his sword cannot reach. If it is done within distance, it gives you a chance to hit in the exposed part at that very moment, or to make a feint of hitting in that part and hit in the other part, which he exposes in his attempt to defend himself; for he can never defend one part without uncovering another. Thus one who stamps with his foot will be deceived through not observing that in seeking to provoke his adversary to offer a time, he has himself offered a time. The adversary, being steady, can better judge the movements than the one who has moved. Thus feints more often succees[!] if made when the adversary is moving than when he is steady. Others make the faint with the body and the sword, but do not extend the sword much, so that the adversary may not engage it in his parry, and they may then hit him when his weapons have dropped, or when he raises them again violently after failing to engage. This method may succeed with a timid or ill-trained adversary. But as the sword does not come forward, you know that it cannot hit; therefore you should not move, except to attack at the moment of his feint; or you should make a feint of hitting, so that in his doubt that you have taken the time he will rush to the defence, when you will have ample opportunity to hit. This will be a hit with a counter-feint, and he who made the first feint will he deceived. There are others who in feinting carry the sword forward, and, when the adversary tries to parry, draw it back to return it with a rush. Neither is this method good, but rather worse than the other; for when you should make only one movement with the sword you make three contrary ones, one in carrying it forward, the second in withdrawing it and the third, greater than all, in thrusting with violence. You fall to grasp that your movement is so slow, that, if your adversary moves at the first movement of the feint, he will hit before your sword has completed the withdrawal, and will easily save himself before you can proceed to hit. To make a successful feint you must advance your sword in this way. When your adversary allows your sword to penetrate so far that you know the forte is far enough advanced to resist his weapon, before he is in a position to parry, you must continue the thrust, as he cannot push the sword away. Then you will certainly hit. If, as you make the feint, the adversary moves in time to parry, you must then change your line and thrust the point on to his body in order to arrive, before he has completed the motion of the parry. This is the true method of making a feint. When you make a feint you must remember that your adversary may hit at that moment. For if you were persuaded that he must first parry, you would generally be deceived; but, if you judged that he might attack, you would be more ready on the defence, and if he does not hit, no harm is done, and your movements will be made easier. You should know too that feints should be made against the nearest exposed parts, for the sword cannot reach the distant ones, nor hit those which are unexposed. You must not fruitlessly put yourself in danger, but if you realise the distance and what part is exposed you will obtain good results. If you work in this manner the feint cannot so easily be recognised by the adversary, so that, if he does not parry, he will be hit; while, if he parries, you can change line and hit. It is still better to wait for the adversary to offer some time or uncover some part, since he would be sure to conclude that you had taken the time from his movement and would rush to the defence more precipitately, and you could hit him the more easily; nor could he himself hit in that time, so that your security is greater. If when within distance you uncover some part in order to give your adversary a chance to hit, you are said to make an appel. You must consider the distance and be careful that his sword is not so near that it might arrive before you had finished the movement of the appel. You must decide whether it is better to advance while he is moving, or to retire in order to have time to parry and hit. Therefore in making the appel it is not good to move the feet, because you could bring them neither forward nor backword[!] in time; besides the danger of being hit through the slowness of the movement. But the appel can very well be made in withdrawing or approaching the body according to the nature of the distance, because the movement of the body is very quick, and if properly made does not prevent your raising the feet in time. An appel should be made when you see that your adversary is about to lunge in order to encourage him to stick to his purpose. Such an appel is made to deceive him; but if he perceived it he might deceive you, as we noted in treating of the deception of time and counter-time. An appel is simply giving time in order to invite the adversary to hit, with the object of hitting him. When your adversary desires to do something, it is better to encourage his desire rather than prevent it, so that his action will be more hurried. It is much better to know what he means to do and to let him do it, than to wait for him to do something unforeseen. It often happens that you are hit without knowing how or why. Therefore you must know your adversary's intentions in order to resist him better. Attack him in time and protect yourself. |
[16] QVALE SIA FINTA, PERCHE COSI SI CHIAMI, Et in quale modo, & tempo sia buono usarla. Cap. 13. FINTA E QVELLA QVANDO SI MOSTRA DI FERIRE in una parte, & si ferisce nell’ altra nel tempo che l’ nimico uuole diffendersi, però è necessario sapere quali siano buone, & quali nò, perche qualch’ uno fa le finte piu con li piedi che con la spada percuottendo la terra quanto che può affine di spauentare il nimico, & nel tempo che egli si intimorisse, ferirlo, questo alcune uolte sortisse nelle sale, & particolarmente oue il suolo è fatto di tauole, che cagiona rimbombo, & da questo procede, che alcuna uolta l’ altro dubbita, mà sopra il terreno, che non fà strepitto non riesse simile effetto, & anco contra i scienti di quest’ arte poco, ò niente uale tanto in un luogo quanto nell’ altro, perche se tale battuta è fatta in lontana distanza nonsi ha da dubbitare, atteso la nimica non può ariuare, & se bene anco è fatta in misura, è più presto tempo, che si può ferire lui in quello punto medesimo per il scoperto, ouero mostrare di ferire in quello, & ferire nell’ altro, che farà uolendo diffendersi, perche non si può mai diffendere una parte, che non sene discuopra un’ altra, & così quello, che haurà battuto col piede in terra sarà restato ingannato per non essersi aueduto, che uolendo prouocare il nimico à fare tempo esso proprio l’ hà fatto al nimico, ilquale essendo fermo poteua meglio giudicare l’ operationi che non poteua esso, che era in moto, & quindi auiene, che le finte riescono più fatte quando l’ auerssario si moue che quando che stà fermo; Altri fà la finta col corpo, & con la spada mà non si slonga molto inanzi accioche il nimico non la troui nel parare per potere poiferire detto nimico quando l’ armi saranno cadute, ouero quando le rileuarà con furia per non hauere trouata la nimica, questa raggione riesce quando si hà da fare con persona timida, ouero non intendente, perche non uenendo la spada inanzi si sa che non può ferire, & perciò l’ huomo non si dee mouere se non per offendere in quel tempo che l’ altro fìnge, ouero dee mostrare di uolerlo ferire, perche dubbitando esso nimico, ehe si sia preso il tempo si precipittarà alla diffesa, oue si haurà comodità grande di ferirlo, & questo sarà ferire di contra finta, perche quello, che primo haurà finto sarà restato ingannato. Altri uiè ancora, che fingendo porta la spada inanzi, & quando il nimico uuole parare la ritira indietro, per ritornarla con un slancio inanzi, ne anco questo modo è buono anzi è peggiore dell’ altro perche non douendo fare la spada se non un solo moto, ne uiene à fare così tre l’ uno contrario dell’ altro, il primo portando la spada inanzi, il secondo ritirandola, & il terzo maggiore ditutti rilanciandola inanzi per uolere ferire, & non s’ auede che l’ suo moto è tanto tardo che se il nimico si mouerà nel primo moto della finta, che ferirà inanzi che la spada dichi hà finto habbia finito di ritirarsi, & saluarassi comodamente prima che possa tornare à ferire; Mà uolendo che la finta riesca bisogna auanzare la spada in modo, che quando il nimico la lasciasse penetrare tanto, che si conoscesse il forte essere gionto così inanzi, che si potesse resistere all’ armi nimiche prima, che esso si fosse aconcio à parare bisognarebbe seguire il camino in cominciato che il nimico non potrebbe deuiare la spada, laquale lo ferirebbe irreparabilmente, & se nel farli la finta egli si mouesse in tempo à parare sarebbe all’ hora necessario di mutare effetto, & indetta mutatione continouare sempre con la punta inanzi sino al corpo nimico per ariuare prima che sia finito il moto del parare, & questo è il uero modo di fingere, douendosi [17] anco quando si finge credere sempre, che il nimico possa ferire in quel punto, perche chi si persuadesse, che egli fosse prima per parare il più delle uolte restarebbe ingannato mà giudicando che possa offendere starà più pronto alla diffesa, & se quello non ferirà non haurà fatto danno, & haurà dato modo di operare più facilmente deuesi anco sapere, che le finte hanno da essere fatte nelli scoperti più prossimi, che nè i lontani, si conosce la spada non potere ariuare, & nelli coperti non può ferire, doue che è bene di non mettersi in pericolo infruttuosamente, mà conoscendo le distanze, & li scoperti non nasceranno se non buoni effetti, & operando in questa forma, non può essere la finta così ageuolmente conosciuta dall’ auerssario, perche se egli non la pararà restarà ferito, & se anco la pararà si potrà mutare effetto, & ferire, & ancor meglio uerà fatta se si aspettarà che il nimico faccia qualche tempo, ò scoperto, perche non potrebbe giudicare altro se non, che si fosse preso il tempo del suo moto, & perciò correria con maggiore precipittatione alla diffesa, & quindi si potrebbe più ageuolmente ferirlo, mà non potrebbe gia esso nel medesimo tempo ferire onde si saria più sicuro. Le chia mate sono quelli scoperti, che l’ huomo fà essendo gionto in misura per dare occasione al nimico di ferire, doue si hà da considerare le distanze, & auertire che la spada non sia tanto uicina che possa ariuare prima che si finisca il moto di essa chiamata, si come per uia di queste distanze ancora si hà da comprendere se sia meglio lo auanzarsi nel tempo che il detto nimico uiene, ouero ritirarli per hauere tempo da potere parare, & ferire, & perciò non è buono nel fare dette chiamate mouere li piedi, perche non si potrebbe leuarli in tempo ne inanti, ne indietro, oltre che sarebbe pericolo di restare ferito per essere il moto tardo, mà si possono ben fare con lo allontanare, & auicinare il corpo secondo che la misura sarà larga, ò stretta, perche il moto del corpo è prestissim, & chi lo fà come si deue non impedisse il potere, leuare i piedi in tempo; & queste chiamate si hanno da fare quando si uede chel nimico hà uoglia di fare una botta perdarli occasione maggiore di uenire à ferire, perche quello desiderio non lo lascia così bene conoscere, che tale chiamata è fatta per ingannarlo, mà accorgendosene potrebbe egli ingannare altri, come si è notato quando si è trattrato dell’ ingannare il tempo, & il contratempo, & chiamata non uuole dire altro, che dare tempo, & comodità per chiamare, cio è pro uocare il nimico à ferire affine di ferirlo lui, in modo che quando esso nimico hà uoglia di fare una cosa, è meglio agiutare quella uoglia, che impedirla, perche più facilmente precipitti, & è molto meglio sapere quello, che egli uuol fare, & lasciarlo fare, che aspettare, che faccia un’ altra cosa improuisa, come interuiene molte uolte che l’ huomo resta ferito, & non sà come, ne perche il nimico l’ habbia ferito, è ben uero che bisogna sapere il contrario di quello, che si uede, che il detto nimico uuol fare, per sapere meglio opporsele, & offenderlo in tempo, & saluarsi. |
||||||
[13] On lunging and passing. To lunge is to hit by carrying the right foot forward towards the adversary and withdrawing it immediately after hitting, or to hit by a movement of the body, keeping the foot firm. To pass is to carry both the feet on right to the adversary's body. It is necessary to understand the lunge, as it is in the most common use, and therefore must be the first thing to practise, in order that you may learn how to advance the point accurately and to the full extent. The hand is fallible and may hit in a spot different from the one intended, according to the amount of the distance. This depends on the changed position of the wrist as it is extended more or less, causing the sword to fall short or go too far, in accordance with the angle of its direction, in order to learn how to drive the sword sufficiently far you must accompany it by bending the body forward and recovering it quickly after hitting, in order to save yourself from danger. Practice is required to learn how to carry yourself, and when you can do this well you will find it very profitable, for it will make the body agile, the feet quick, and give you judgment of distances. You will then certainly make a lunge longer than before practice. To make this kind of hit well you must stand with your feet not too far apart, so that you can advance further in hitting, or according to circumstances withdraw by bringing back the foot, leaning the weight of the body on the foot which is to remain steady, so that the other may be more agile and easy to lift, for these reasons it is not good to be on guard with the left foot forward, because you cannot make a long lunge without passing; whilst if you tried to pass with the rear foot and to return you would find the movement too long; besides you would go too far to be able to return in time. For these reasons and many others which we omit it is not good to be on guard with the left foot forward, unless you are waiting for your adversary to try a hit, so that you may at that moment withdraw your left foot, parry, and hit him at the same instant. This method may succeed, because the body changes its front and withdraws, the right side remaining in front for the attack. But if your adversary does not come on, you should not attack him, since it is better to have the right side in front; you can hit in shorter time and save yourself more promptly, as the foot and the body make smaller movements. After hitting it is good to carry the right foot behind the left and to continue with the left behind the right in order to rest on the right foot, for in this way you will withdraw so far that your adversary cannot hit, unless he has hit in counter-time. This guard of the left foot will be more useful with the sword and dagger than with the sword alone. But it is better to stand with the right foot forward, and immediately after hitting draw it back close to the left, for in this case if your adversary follows you can advance it again, and also you can step backwards with the left, as you see an opportunity, hitting at the same time as the adversary follows. After these rules it is well to understand the pass, a thing very profitable and advantageous, because you thereby disturb and frighten your adversary, hit with more force and show your superiority. The body, the sword and the feet are more in union, and that union generates strength and vivacity of movement. In the course of passing you can readily change from one line to another, so that your adversary has difficulty in defending himself and has no chance to do much, since the opportunity quick1y passes, nor has he time to consider much, and as his point is penetrated he cannot hit. In lunging it often happens that you find you have gone so far, either by carrying the foot too far, or because your adversary has himself advanced, that you cannot move out of distance and are hit in withdrawing. In such a case it is good to continue to the adversary's body, for the greatest danger is in getting within distance; but when you have passed his point and follow on to the body, you arrive before he can withdraw his sword. Still one often sees the adversary, though his point is passed and he hit, withdraw his sword and make a hit. This is due to the mistake of the one who passed, who has not gone right on to the body nor taken the time well. For if he passes at the moment when his adversary advances his sword, or when his sword is occupied in the defence, or out of line, the adversary cannot withdraw his sword at the time of the pass. We might add that, although you pass, you should still follow your adversary's sword gliding along his blade, wherever it is, so as to be continually defended. If he withdraws his sword, so much the better, as he uncovers more parts, and his forte is drawn back and cannot resist. There are some men, who, although you have passed, do withdraw and make a hit; this is easier with short swords than with long. As to this we say that, whether the sword be long or short, if in passing you go close up to the adversary's body, you will be safe. For in passing you can do various things, throw the adversary into disorder by jostling him, seize the hilt of his sword, and pass so far beyond his flank that he cannot bring his sword, however short, so far back without himself withdrawing, which he cannot do in time. In passing you can grapple with your adversary and throw him to the ground, which would be good when your sword has not hit; for it may be held for certain, that if in passing you hit, your sword would penetrate to the hilt, which would shake and disorder your adversary, and the wound would be inflicted in a part of such importance that he would be at least prevented from withdrawing his sword. Moreover the one who passes is in all cases the readier to seize a chance, than the other who is occupied with the defence and confused by the danger in which he is. In addition to these advantages there are many other things to be done after a pass, which cannot be done when you remain steady. You can often in passing use the method of avoiding and turning the body; whereas if you do not pass or your adversary does not pass, you cannot do this so well. For if you wish to move your body out of the line of hit point, either on the one side or the other, you can only do so by advancing; for two reasons, the first, that you may be able to hit at the same time, the second, in order that his point may pass before he can change its line again. When he has penetrated so far, it is better to pass right on than to turn back and be hit by a second thrust before you are in safety. It is true that with the sword and the dagger it is more difficult to pass, and you must be more careful, since after passing the point of the sword there is the point of the dagger, and thus the danger lasts longer. Nevertheless there are rules for passing with safety, as will be shown when we deal with those strokes. He who can pass well, is more sure with his sword, restricts his adversary more and is more certain of himself. Much judgment is needed in carrying the body and the feet correctly, so that the sword may perform its office. You must take care in passing with the left foot forward not to carry the left side forward, especially with the sword alone, as in that case you could not use the forte of the sword, which would be too far back. Therefore even though the left foot goes first, the right side must accompany it. In this way you will be able to carry the body out of line, your sword will be stronger, and the point be as far extended as if the right foot had advanced, for the body can bend further forward. To understand the lunge is one thing, to understand the pass another. With the knowledge of the two you can adopt whichever seems best according to your opponent and the circumstances. For sometimes you can lunge and cannot pass owing to the shortness of the time. This applies when you are in presence. For there is another kind of passing, which may be made in the least possible time. Its principles are different and will be treated of in another place. |
CHE COSA SIA FERIRE A PIEDE FERMO Et che cosa passare. Cap. 13. FERIRE A PIEDE FERMO SINTENDE, QVANDO si ferisce portando il destro piede inanzi uerso il nimico & subbito ferito si ritira, ouero, che si ferisce col moto del corpo tenendo fermo il piede Passare è quello, quando passando si porta inanzi tutti dui li piedi continouando sino all’ altro corpo; ferire à piede fermo è ncccessario saperlo per essere il più commune che si usa nelle quistioni, & percio deue essere il primo, che si essercitti per imparare [18] ad auanzare bene, & longa una punta, perche la mano falla, & credendosi dare in un luogo si ferisce in un’ altro, secondo che la distanza più, & meno è lontana, & questo nasce dal nodo di essa mano che suaria secondo che si stende più, & meno, & poi caggiona che la spada ferisse più corto, & più longo secondo, che si derizza l’ angolo, che la forma, & à uolere imparare, che ariui assai da lontano bisogna accompagnarla col piegare il corpo inanzi, & ricuperarsi presto indietro doppo hauere ferito, per saluarsi dal pericolo, mà ui si richiedo essercitio per sapere accomodarsi, cosa che quando si saprà ben fare sarà assai profitteuole, perche renderà molto agile il corpo farà pronti li piedi, & darà il giuditio delle distanze, & certo che all’hora si stenderà una stochata molto più longa del naturale, mà uolendo usare bene questa forte di ferire è neccessario di ritrouarsi sempre in poco passo per potere maggiormente auanzarsi nel ferire, & anco secondo l’occasione allontanarsi ritirando il piedo, con fermare il peso del corpo sopra quel piede, che deuestare fermo, acciò che l’altro sia più agile, & pronto à leuarsi, In queste raggioni ueramente non è buono ritrouarsi in guardia sopra del sinistro piede, perche non passando non si può ferire di lontano, & chi pure uolesse passare col piè di dietro per ritornarlo non riuscirebbe rispetto al longo tempo, che si faria nell’ andare, oltre che si scorreria troppo inanzi, & tanto che non si potria ritornarlo in tempo, per queste raggioni dunque, & molte altre, che si lasciano di dire none buono stare col sinistro inanzi se non per aspettare, che il nimico sia esso, che primo uenga à ferire, acciò che ritornando in quel punto indietro il detto sinistro piede si possa parare, & ferire lui nell’ instante medesimo, & questo è riuscibbile, perche il corpo muta prospettiua, & si allontana restando la destra parte inanzi à ferire, mà se il nimico non è lui, che uenga non si dee andare ad’ assalirlo, perciò meglio è che si tenga il destro inanzi, perche si può con maggiore breuità ferire, & più presto saluarsi facendo il piede, & il corpo moto più picciolo, e ben uero, che doppo hauere ferito è buono portare il destro dietro del manco, & continouare col manco indietro per restare sopra il destro, che in questo modo si andarà tanto lontano, che il nimico non potrà ferire, se non haurà ferito di contratempo; Questa guardia del sinistro piede seruirà più in spada, è pugnale, che in spada sola, mà più à proposito è lo stare col destro inanti, & subbito ferito ricuperarlo appresso del sinistro, che in questo caso se il detto nimico seguirà si potrà ritornarlo di nouo inanzi, & potrassi parimenti slargare il sinistro indietro secondo, che si uedrà l’occasione, & ferire nel medesimo tempo, che il nimico seguirà. Doppo queste raggioni è buono anco lo sapere passare cosa molto proffitteuole, & uantaggiosa, perche si turba, & si mette in maggiore timore il nimico, si ferisce con più forza, & si mostra maggiore ualore, il corpo, la spada, & li piedi uanno più uniti, laquale unione genera forza, & uiuacità nell’ operare, & nell’ andare si può mutare di uno in un’ altro effetto comodamente, talmente che il nimico non può se non difficilmente diffendersi, & non ha comodità di fare molte cose, perche l’occasione passa presto, ne meno hà tempo di ben giudicare, & come si hà penetrato la punta egli non può più ferire; Mà nel ferire à piede fermo spesseuolte occore, che l’ huomo si troua essere scorso tanto inanzi, ò per hauere portato troppo il piede, ò perche il nimico ancor lui si sia auanzato, che non può uscire più della misura, & resta ferito nel ritirarsi, nel quale caso è buono lo sapersi condure sino al corpo nimico, perche il maggiore pericolo è in ariuando nelle distanze, mà essendo penetrato la punta, & proseguendo sino al corpo si gionge prima chel nimico possa ritrare la spada, & non osta il uedersi molte uolte, che quantunque la punta sia passata, & il nimico ferito, che esso nimico la ritiri, & ferisca, che questo è errore di collui, che passa, ilquale non ha continouato sino al corpo, ò non hà preso bene il tempo, perche sel’huomo passa nel punto medesimo che il nimico auanza la spada, ouero che detta spada resta occupata nella diffesa, ouero che ua fuori di presenza, esso nimico non può ritirarla nel giusto tempo, che si passa. Si potrebbe ancor dire che se bene si passa si debba seguire sempre la nimica scorrendo il filo di essa, sia in qualunque parte, affine di tenersi continouamente [19] diffeso, che tanto meglio si può fare, quando il nimico Iaritira, perche fà maggiori scoperti, & il forte uà indietro, & però non può resistere, mà alcuno è, che benche si sia passato del tutto si ritira, & ferisce, il che è più facile con le spade corte, che con le longhe; sopra di quello noi diciamo che siano ò longhe, ò corte quando che collui che passa si saprà condure serrato al corpo, che sarà sicuro, perche in passando potrà fare diuerse cose prima disordinare il nimico urtandolo col corpo, di poi prenderli il finimento della spada, & potrassi condure nel passare sino sotto il fianco nimico che sarà dinanzi, doue che lo stesso nimico non potrà ritirare tanto la spada, per corta, che senza prima allontanarsi, oltre che non lo potrà fare di tempo, mà nel passare si potrà ben fare à liu una lotta & grettarlo per terra, che sarebbe buono, quando la spada, che è passata non hauesse ferito perche si hà da tenere per fermo, che se uno che passa ferisse quella spada penetraria sino al finimento, ilquale urtarebbe, & disordinarebbe il nimico, & la piaga non potria essere fatta in luogo di così poca importanza, che detto nimico non restasse impedito almeno tanto, che così tosto non hauia tempo da ritirare la spada, & oltre ciò quello che passa è sempre in tutti li casi più pronto à pigliare partito, che non è l’altro occupato nelle diffese, & confuso dal pericolo in che si troua, & doppo anco tutte queste raggioni si possono, nel passare, fare molte altre cose, lequali non si possono à piede fermo, si può similmente passando usare in molte occasioni lo scanso di uita, & girare, che non passando, ouero se il nimico non passa non si può tanto ben fare perche uolendo leuare il corpo di presenza della punta, ò per l’ una, ò per l’ altra parte non si può se non auicinandosi per due raggioni l’ una acciòche si possi ferire nel tempo medesimo, l’ altra perche la punta passi inanzi, che l’ nimico la possa dirizare un’ altra uolta, doue si uiene ad’ essere tanto penetrato, che è meglio passare del tutto, che tornare indietro per non restare ferito di un’ altra botta prima che si sia saluato, E ben uero che nella spada, è pugnale è più difficile, & bisogna stare più aueduto, che doppo l’ essere passata la punta della spada ui è anco quella del pugnale, & così dura più il pericolo, non dimeno ui sono le fue raggioni per passare sicuramente, come si mostrarà nelle occasioni del fare li feriri, & chi sà passare bene uà più giusto con la spada, più constringe il nimico, & è più certo delle cose sue, ui si ricerca ben molto giuditio per condure il corpo, & piedi guidamente, acciò che la spada possa fare il suo offitio, douendosi auertire, che nel passare col piè sinistro inanzi non si hà da portare la sinistra parte del corpo, massime nella sola spada, perche non si può adoprare il forte di essa, rispetto che si trouarebbe l’huomo troppo indietro, & perciò, se bene anco che il sinistro piede hà da andare inanzi è neccessario tutta uia che la parte destra lo accompagni, perche cosi uerà à fare una sfuggita di uita, la spada sarà più forte, & la punta così longa, come se fosse fatta col destro piede, perche più si può pendicolare il corpo; si che lo sapere operare à piede fermo è una cosa, & lo sapere passare è un’ altra, con laquale doppia scienza può l’ huomo fare quello, che meglio li torna secondo le persone, & secondo i tempi, perche alcuna uolta si può ferire, & non si può passare rispetto alla breuità del tempo, questo noi intendiamo mentre che è fermato in presenza, perche ui è anco altri sorte di passare che può pigliarsi in ogni minimo tempo, mà con differente raggione laquale in altro luogo si trattarà. |
||||||
[14] On holding the sword extended, straight, at an angle and withdrawn. There are various ways of holding the sword and the arm, as will be seen in the following plates, which will illustrate the variety of the guards. Since one method is better than another we shall treat of the principal ones, reserving a fuller discussion until we treat of the nature of the guards. They will be illustrated separately on the plates. Some hold the sword at an angle and the arm a little advanced towards the knee with the hand in tierce, or slightly outwards towards the guard in seconde. Others hold the arm withdrawn and the sword in such a manner as to make a straight line from the elbow to the point. Others extend the arm as far as possible and hold the sword straight, making a straight line from the shoulder to the point of the sword. This method is very cautious, because it keeps the adversary at a distance, but is very fatiguing, and the sword is weaker than with the other guards because of the distance of the hand from the body. In this position your sword is more easily engaged by the adversary and great pains are needed to keep it free. When you can do this, the position is a great impediment to your adversary, because he cannot approach so as to hit, seeing the point so near, and cannot advance owing to the same danger, unless he can engage the point and drive it out of presence. Even though he places the forte of his sword against your faible and tries to hit, it would hardly succeed, since there is little uncovered and he cannot hit unless his faible passes your forte, which you could easily prevent, if he tries to hit below, he will easily be hit above, for your sword being nearer and already extended must arrive first. Therefore in order to hit more safely he must remove your sword, and seizing the chance carry his body out of line on the one side or the other and pass on to the body. For he cannot hit until he has passed the point nor save himself or his recovery; therefore it is better for him to follow on. This method is the more likely to succeed, as it is difficult for one who holds his sword thus extended and high to maintain his point in line since with but a small movement his adversary could pass out of line. He could easily pass underneath by lowering his body. It is however true that one who forms this guard properly holds his sword extended and keeps his feet close together, so that the lower parts are kept withdrawn, as they are more exposed and difficult to protect. Also he can then advance further in hitting and similarly retreat, if his adversary approaches too near. For with this guard the adversary must be kept at a distance, otherwise he would find it easy to pass. For the same reasons the guard is a good defense against cuts, since the forte of the sword is already pushed forward, to that the adversary's sword cannot fall without meeting it. If ht tries to hit below, he cannot reach before one, who holds his sword extended, has arrived with the fourth part of his blade. If he keeps his feet close together, he can reach all the further, although the extended arm is in greater danger. Still it is easy to defend by a slight motion towards the part threatened by the sword, lowering the point more or less, as the cut is high or low, and keeping the point in line. Certainly you should often practise this guard in order to learn how to hit without hurling the arm forward. You must hit, but you must keep the arm steady, and let the motion of the foot and the body suffice. This guard will teach you to hold your sword close to the adversary, where you can more easily hit him, and similarly to keep it free. Some hesitate to advance the sword, lest it should be engaged and subjected by the adversary. You will learn also to hold the arm correctly, and after such practice, when the opportunity comes, you will act more promptly and correctly. One who is unpractised often makes a mistake of too much or too little, and is not sure in his defence; moreover he does not extend so far as if he had practised. Those who hold the sword at an angle in tierce with the hand before the knee, or in seconde with the arm outside, have a stronger hold of the sword, but the body is too much expos-[13] Your adversary can approach further, and with this tierce you cannot disengage, as with your sword at such an angle it would take too long. In the seconde although the sword is at angle you can easily disengage; but both of them are bad in defence against an opponent who can thrust in the straight line, because such thrusts come to the body without approaching the forte of the sword held at an angle, so that in the effort to parry you would have to make a large movement and often would be too late. Even if you are in time the movement is so slow, that your adversary may easily change either into another straight line, or into an angle, as opportunity offers. For a thrust at an angle is most likely to pass, but thrusts in the straight line cannot pass one another; if of equal force they will nullify each other. If you hit it will be because your thrust was stronger by having engaged his faible better. The weaker will always be driven out of the line, and the other will pass on and hit. But the thrust at an angle passes on and hits without a junction of the blades; such thrusts rather yield to one another, and therefore are very likely to pass and hit the part aimed at. Further one who fences with his sword at an angle can change only by a large movement. It is impossible that his point and hand should not make a large circle in the direction in which he has moved, all the larger if he changes from one angle to another, and incomparably larger if he disengages. The movement, however, would be smaller, if the change is from an angle to a straight line, but would still be so large that, if within distance, he would be hit. To hold the sword at an angle is well enough for thrusting, but not for the defence. To proceed against such a guard with security it is necessary to be able to use the advantage not only of the sword, but of the body and the foot, and to realise well the strength of the angle, otherwise while hitting you will also be hit. To hold the arm withdrawn and the sword straight, forming a straight line from the elbow to the point, is a better rule. In this manner you can better acquire the superiority, hit and parry, and on occasion disengage more swiftly, since your body is more defended by the forte and the point is more easily maintained in line. Still you should know how to use any method at need, for you cannot understand the nature of what you have not practised, nor to what it may lead. You must remember that one rule will not serve for all cases, but each has its appropriate end, and what is good in one case will not serve in another. Therefore, as we have already said, you must be rich in devices and understand the time when they may be used. To adopt the safest position for the body and the best for the sword you must hold the arm not quite extended, but still rather extended than withdrawn, and the sword in a straight line, or inclined slightly outwards according to the position of your adversary. In this manner your guard will be the best and your body safe with respect to the forte of the sword, which can defend with little movement, as it is already advanced. Your sword will be stronger than with the arm fully extended, and in every case you are more master of it and can use it with more variety. It is less restricted and less fatiguing, nor is it so easy to pass under the guard as with the arm extended. You can change your position according to the occasion, and keeping the forte always in its place you will defend with ease, if you use it in the proper manner. This guard is better than the other when remaining steady against your adversary, though our opinion is that you should remain steady in no position for long. Though you may be more secure than your adversary, yet all have defects. Therefore the judicious man, seeing his adversary steady in any position, will not only realise the fact, but know how to proceed against him and hit him. Also he will understand what such an adversary can do in attack and defence. But if he finds his adversary is not steady, he cannot so easily estimate the position, although from the first putting of hands to the sword and the manner in which the sword is carried, he will come to understand where to take advantage. Of this we shall treat in the second book, when we shall explain whether it is better to remain steady in presence and await a time.[!] or to attack without a pause. |
[20] DEL TENERE LA SPADA LONGA, Diritta & ingolata, & ritirata. Cap. 14. DIVERSI SONO LI MODI DEL TENERE LA SPADA, ET il braccio, come si uedrà per le seguenti figure di mostratrici la uarietà delle guardie, & perche un modo è, megliore dell’ altro noi ne trattaremo di alcuni più principali, riserbandoci à: discorerne più pienamente sopra la natura delle guardie secondo, che si uedrà nelle dette figure ogniuna separatamente. Tiene alcuno la spada angolata, & il braccio poco inanzi uerso il ginochio con la mano in terza, ouero la tiene in fuori uerso la guardia seconda; altri tiene il braccio ritirato, & la spada diritta in modo che uiene à fare quasi una retta linea dal combito alla punta; altri poi distende il braccio quanto può, & tiene la spada diritta in guisa, che dalla spalla alla punta, della spada si forma una retta linea, questa maniera è assai cauta perche tiene il nimico lontano mà è di molta fatica, & la spada è più debile, che nell’ altre guardie rispetto alla lontananza della mano dal corpo, & però di minor forza, & più facile da essere ritrouata dal nimico & doue l’huomo hà da hauere molto riguardo per tenerla libera, che quando questo si sà fare è ueramene di grande impedimento al nimico, perche egli non si può auicinare tanto che gionga à ferire uedendosi una punta troppo uicina, & non può gire inanzi per l’istesso pericolo, se non procura di hauerla, & spingerla fuori di presenza, perche anco che mettesse il forte della sua spada al debile nimico, & uolesse ferire non farebbe cofa buona, essendo poco il scoperto, nepotendo ferire senza passare col suo debile per il forte dell’ auerssario, ilquale si diffenderia facilmente, & chi uolesse ferire disotto restarebbe anco facilmente ferito disopra perche non si può ariuare al corpo, che non sia prima ariuata quella, che è più uicina, & già è distesa doue che à uolere ferire più sicuro saria neccessario rimouere la spada nimica & pigliare il tempo, portando il corpo fuori di presenza ò per l’ una, ò per l’ altra parte, & passare sino al corpo auerso, perche non si può ferire, che il corpo non habbia già penetrato la punta, talmente che non si potrebbe saluare tornando indietro, & così uiene ad’ essere meglio lo seguittare inanzi, laquale cosa anco tanto meglio riuscirebbe, quanto che è difficile, che chi gioca così longo, & alto si mantenga in presenza, atteso che con poco moto se ne uscisse mentre la spada è tanto auanzatà, & tanto alta, allaquale facilmente si può passare disotto con abbassare[15] il corpo. Se bene è uero, che un corpo in questa guardia, debitamente situato hà da tenere la spada così longa conseruandosi in stretto passo affine di tenere le parti disotto lontane, come quelle che sono più scoperte, & più difficili da parare, & anco per potersi auanzare più inanzi nello ferire, & similmente ritirarsi in occasione che l’ auerssario si auicinasse troppo, essendo che in questa sorte di guardia fà di bisogno tenerlo lontano, che altrimenti egli trouarebbe facile additto di passare, Con questa medesima raggione si diffende benissimo dalli taglii, perche il forte della spada è già spinto inanzi, doue che la nimica non può cadere senza trouarlo, uolendo ferire, perche chi uolesse ferire disotto non ariuarebbe prima, che quello che tiene la spada distesa non fosse egli ariuato con la quarta parte della sua spada, & quando il passo fosse stretto tãto meglio s’ariuarebbe talche il braccio, che è disteso infuori porta il maggiore pericolo, se bene ageuolmente si può diffendere cioè con pochissimo moto uerso quella parte, doue uera la spada, abbassando la punta più, è meno secondo che l’ taglio uiene alto, ò basso, con tenersi in prefenza; Certamente, che l’ huomo si dourebbe essercittare molto in questa maniera per imparare à ferire senza slanzare il braccio, perche si dee ferire si mà tenerlo fer- [21] mo, bastando il moto del piede, & de corpo, si impara anco à tenere la spada uicina al nimico, doue con maggiore facilita si feresce, & similmente à tenerla libera, perche alcuni sono, iquali non ardiscono auanzarla dubbiando, che dall’ auerssario non li sia aquistata & impedita, & non meno s’ impara di tenere il braccio giusto, ilquale essendo così essercittato quando uiene poi l’ occasione fà l’ effetto suo più prontamente, & più giustamente, doue che l’ non asuefatto spesso spesso erra ò nel molto, ò nel poco, & non è così certo della diffesa, oltre che non si stende tanto come se fosse essercittato in quello. Colloro poi che tengono la spada angolata in terza con la mano inanzi il ginochio, ò con la seconda angolata col braccio infuora tengono bene più forte la spada in mano, mà il corpo fà troppo scoperto, & il nimico può più auicinarsi, oltre che la terza così formata non può cauare dalla nimica, perche stando con’si angolata allo insù fà troppo tempo; nella seconda se benè è angolata si caua facilmente mà ciascuna di loro è cattiua per diffendersi da chi sà ferire per li debili in retta linea, perche giongono al corpo senza auicinarsi al forte della spada angolata in modo, che se si uuole parare è forza di fare un gran moto, & spesse uolte non s’ ariua in tempo, & se pure si ariua si fà con tanta tardità, che si dà agio al nimico di mutare effetto, ò con un’ altra retta linea, ouero con uno angolo secondo l’ opurtunità & perche un’ angolo passa benissimo per l’ altro mà le rette linee non possono così passare l’ una contra l’ altra, & essendo quelle di forza eguale andaranno tutte due uuote, & se una ferirà l’ altra, uerà dall’ essere stata quella più forte, per hauere meglio occupato il debile, di maniera, che la più debile anderà sempre fuori di linea, & l’ altra andarà diritta, & ferirà, mà un’ angolo passa per l’ altro, & ferisce senza che l’ uno constrasti con l’ altro, anzi cedono l’ uno all’ altro, & in questo modo passano benissimo per le rette linee feriscono li angoli secondo li effetti, inoltre quello, che gioca angolato uolendo fare qualche mutatione non la può fare se non con longo tempo, perche impossibile è che la sua punta non faccia insieme con la mano un grangiro, secondo che si sàrà mosso & lo farà anco maggiore se mutarà di un’ angolo nell’ altro, mà più grande senza comparatione, se cauarà la punta, pure il moto farebbe più picciolo, se la mutatione ussisse dell’ angolo, & formasse una retta linea, mà non dimeno questo sarebbe ancor un moto tale, che, trouandosi l’ huomo in misura, restarebbe ferito; li angoli feriscono assai, mà non diffendono, & chi uuole andarli contra sicuramente è neccessario sapere usare bene il uantaggio non solo della spada, mà del corpo, & del piede, & conoscere bene la forza dell’ angolo, altrimenti si ferisce & resta ferito; Migliore raggione è quella di chi tiene il braccio ritirato, & la spada diritta formando quasi una retta linea dal combito alla punta & intalmodo si può meglio aquistare il montaggio, ferire, & parare, & anco in occasione cauare con più prestezza restando il corpo più diffeso dal forte con mantenersi punta più facilmente in presenza, pure è buono sapersi seruire dell’ una, & dell’ altra maniera nelli accidenti, essendo, che chi non le pratica non può tanto bene conoscere la sua natura, ne ciò che da loro può nassere, si dee bene il detto huomo ricordare, che una raggione non serue contra tutte, mà ciascuna hà il suo proprio termine, & però quello, che è buono contra uno non serue contra l’altro, talmente che, come altroue si è detto, bisogna essere ricco di partiti, & conoscere il tempo, nelquale si hanno da adoperare; Mà uolendo situare un corpo più sicuro, & una spada, che stia meglio, fà di bisogno tenere il braccio non in tutto disteso, mà però che habbìa più del disteso, che del ritirato & con la spada in retta linea, ouero poco fuori secondo il sito del nimico, che in questo modo la guardia sarà migliore & il corpo assai più sicuro rispetto al forte della spada, che lo diffende con poco moto, perche è già inanzi, & la spada è più forte, che non è col braccio tanto disteso, & in ogni caso il detto huomo è più patrone di essa potendo operare più diuersamente ne meno è tanto obligata, & tanto faticosa, ne se li può andare così facilmente sotto, come si fà conchi là giuoca distesa, & si può situare in diuersi modi secondo l’ occasione; & tenendo il forte sempre à suo luogo si diffenderà confacilità adoprandolo, come si conuiene, si che questa é migliore[16] dell’ altra per fermarsi anco contra il nimico, se bene che nostro [22] parrere è che poco sideua fermare in nessun sito, che quantunque uno sia più sicuro dell’altro, tutti nondimeno patiscono diffetto, & perciò l’ huomo giuditioso uedendo l’ auerssario suo fermo in qualunque sito non solo lo cognoscerà, Mà saprà come seli deura andare contra, & ferirlo, similmente anco cognoscerà quanto può fare esso nimico in offesa, & diffesa, che non lo uedendo fermo non lo può così ben giudicare, se bene dal primo mettere di mano alla spada, & dal portamento di essa tosto si uiene in cognitione del uantaggio, & di quello ne raggionaremo nel secondo libro, oue faremo conoscere se sia meglio fermarsi in presenza, & aspettare il tempo, ouero andare senza fermarsi. |
||||||
[15] Whether it is better to carry the body high or low. To defend the body with ease you must know whether it is better to keep it upright or to bend it. You must consider that a body is very large compared to the blade of a sword, which though moderately long is still very narrow and insufficient to cover the body. The larger the body the greater the difficulty the sword has in defending it owing to the large movements required in defending the uncovered parts of the body. In this matter some put forward certain reasons saying that the upright position is more natural, not so dangerous for the head, quicker for movement, less fatiguing and less restricted than the position when the body is bent. We say that some of these reasons are true, and some not. First because in the upright position you are in more danger, and cannot so readily attack, since you must make a great movement in defending the body and cannot make an extension without bending; in bending your movement is so great that you cannot recover in time. Being upright there is lack of union in your movements and less strength. Similarly your weapons are weaker. When you understand how to control the figure and stand without strain, to stand low is more useful. But if you cannot do this it is better to stand upright, for if you are in a strained posture you cannot be quick to move. Whereas a body bent at a suitable angle and well balanced on the feet is much securer being less exposed, and can be defended with little movement of the weapons. The forces are more united, and this union generates vivacity and swiftness of movement in one who is well used to this position. To take up this position in the required manner needs practise and entails fatigue. But afterwards it will be found more quickly and easily; you will be readier and safer in every case, will defend yourself without getting into disorder, hit more swiftly and reach further. The reason is that being already bent the body goes forward without a great movement. Still in this position you must take care to rest the body on one foot only, so that the foot which has to move will be free and go quickly, otherwise it would be late. You cannot lift the foot without lifting the weight, and though it may appear that you can do both at the same time, nevertheless such a movement is slower. Further if you can work in union with both weapons and body you will be in less danger as to the head, since it will be nearer the forte, and you will be more ready to pass on the one side or the other, and better able to retire than when upright. If a man could make himself so small that his weapons would cover him entirely, it would be well; but since this is not possible, you must at least cover as much as possible, and protect yourself, which will be equally good, taking care to do so without constraint, so that you may work with agility in all cases. Thus the fatigue which you undergo in practising will be less than the benefit you derive from it. It is a matter of defending both life and honour. He who can conduct himself against his adversary with greater circumspection and security, will deserve greater praise and acquire greater honour. It is clear that sometimes a great victory depends on a small advantage. |
SE SIA MEGLIO ADOPRARE IL, Corpo alto, ò basso. Cap. 15. VOLENDOSI DIFENDERE VN CORPO CON FACILITA E neccessario sapere, se sia meglio lo tenersi in piedi, ouero piegarsi, & però si deue confiderare, che un corpo è molto più grande rispetto ad’ una lama di’ spada, che quantunque sia un poco longa è nondimeno molto stretta, ne bastante à poterlo coprire, & quanto, che esso corpo è più grande, tanta è maggiore la difficoltà, che detta spada hà in diffensarlo per li gran mouimenti, che hà da fare nelle diffese, per li uacui grandi, & scoperti del corpo; & in quello alcuni aducono certe raggioni dicendo che il corpo in piede stà più naturalmente, non porta tanto pericolo nel capo, è più pronto nel mouersi, stà con minore fatica, ne è così obligato, come se fosse piegato; Diciamo noi che alcune di queste raggioni sono uere, & alcune non uere, prima che stà in maggiore pericolo essendo in piede, & non può tanto offendere, perche si come bisogna, che faccia gran comotione ne lo diffiendersi così nõ può allongare la botta se nõpiega il corpo & piegandolo fà tanto mouimento, che non può più rihauersi in tẽpo & stando anco così in piedi si troua disunito, ne hà tanta fòrza, & l’ armi similmẽte sono più debili, che quando si sapesse ben numerare la uita, & nõ si stesse con affettatione saria di più utile lo stare basso, mà à chi non sà farlo torna meglio lo stare in piedi, perche chi stà con uiolenza nelle posture non può essere pronto al mouersi, doue che un corpo ben numerato nelli angoli, che forma, piegandosi, & ben’ accomodato sopra li piedi è molto più sicuro standò basso, perche meno è scoperto, & cõ picciolo mouimento dell’ armi si diffende, & le forze ancora sono più unite, laquale unione genera uiuacità & celerità di andare, à chi è bene assuefatto à questo piegarsi, nelquale modo à uolerlo fare come si richiede è prima di bisogno essercitio, & fatica, uà poi molto più presto, & più comodo, & si troua più pronto, & più sicuro in ogni caso, si diffende senza disordinarsi, & ferisce più presto, & più lontano la raggione è che stando già l’ huomo curuato uà il corpo inanzi senza fare gran moto, auertendo non dimeno in questo luogo, che bisogna situare esso corpo sopra di un solo piede acciòche quello che hà da andare sia libero & uada presto, altrimenti saria tardo, perche non si lieua il piede, che non si lieui il peso, & benche paia ciò farsi in un medesimo tempo nondimeno è più tardo; in oltre chi saprà bene unirsi con l’ armi, & col corpo portarà men pencolo nel capo, perche sarà più uicino alli forti, & più pronto à passare ò per l’ una ò per l’ altra parte, & potrà più allontanarsi, che stando in piedi, & quando l’ huomo potesse farsi tanto picciolo, che l’ armi lo coprisse tutto non è dubbio, che sarebbe ben fatto mà non essendo questo possibile, deuesi almeno coprire quanto maggiormente che può, & saluarsi, che sarà me demamente buono con auertire di farlo senza impedimento, & con comodità tale [23] che si possa, operàre agilmente in tutti li casi, & quella fatica, che si spenderà, essercittandosi, in così fare sarà sempre minore del benefficio, che se ne cauarà, trattandosi del diffensarsi la uita, & l’ honore in un punto medesimo, & quello che saprà con più cautella, & sicurezza condursi contra il nimico sarà degno di maggiore lode, & maggiore honore conseguirà, & è chiaro, che da un picciolo uantaggiò taluolta depende una uittoria grande. |
||||||
[16] Advice on how to proceed against tall, short, weak, and strong opponents, and against the choleric and the phlegmatic. In meeting your adversary you must subtlely consider not only his character, but his strength and height, because you must proceed differently according to the particular qualities of your opponent. Therefore we will treat somewhat of this matter and advise you as to the best method of holding yourself. A tall man meeting a small man should recognise his advantages; for being taller his reach is longer both because of his height and the bend of his body. His body goes so far forward that he can reach his adversary, while his adversary cannot reach him. For this reason it seems he should incline to the attack, rather than to the defence. There is no necessity for him to gain the superiority over his adversary's sword, though this is good, but merely to keep his own free in order to hit when his adversary approaches, and before his own body is in danger. He must contrive to keep his adversary at a distance, for he must recognise that he is first within distance, and, when the shorter adversary tries to advance to get within his distance, that is the time for the taller to hit, or to throw his adversary into disorder by making a feint of having taken the time offered by his movement, and then hitting in the part he has uncovered by going to the defence; and immediately breaking ground, for then he will be out of the shorter man's reach. Or if he can do none of these things, it is well to play the adversary by breaking ground as often as he advances, never letting him carry out his plan, and to continue this until he finds a chance to hit or to put his adversary in subjection. He should proceed without passing, but merely carry his body out of the line when his adversary passes, or break ground so that he cannot pass, but is held and met by the point. In this way the shorter man will have to adopt another method, give up all idea of hitting, and defend, since he cannot hit without first bringing his body into danger. Therefore it is more useful and necessary for the short man to gain the superiority and engage his adversary's sword in order to prevent a thrust, when he advances to gain distance. When he is within distance and finds a time to hit, it is better for him then to pass, for he will have penetrated his adversary's point so far, that he will with difficulty get out again in time without being hit, unless the sword of the taller man is so far out of line, or so far withdrawn, that the shorter man clearly perceives he has time to recover and return to his guard. For he could not recover so far, in one movement without the sword of the tall man, owing to his length, reaching him. On the other hand it is true, that, although the tall man has the advantage of the reach, a matter of great importance, his movements are slower and there are more uncovered parts, so that he cannot so easily get out of line. Offering a larger target he gives the small man a great advantage in hitting, when the small man knows how to conduct himself within distance. For the sword of the small man covers him more; he does not need to make such large movements in order to defend himself, and he has passed the greatest danger, that is penetrated the point, before his adversary has penetrated his. Since his exposed parts are smaller he is in less danger, and consequently his movements are safer than those of the tall man. A strong man also has a great advantages[!] over a weak man. The basis of his procedure should be gaining the superiority over his adversary's sword, when he can easily drive it into disorder and hit while it is moving. For when a weaker sword tries to resist a stronger by changing from one position to another, it is driven out of line, so that the stronger man may easily hit. If he has lunged, he can recover, and repeat the effort. If the stronger man desires to pass, that too would be good, for when he came to grips he would likewise have a great advantage. On the other hand a weak man against a strong man must always avoid his sword, lest he engage. Nor should he parry, when the strong man hits, for it is often seen that the faible of one man is stronger than the forte of another; thus the weaker man would be deceived thinking to defend with his forte. Even where there were no great difference between the swords, when for example the one sword found not so much of the faible, and the other not so much of the forte, since in certain cases a single hand has more power than two hands, it would still be better not to parry, if possible. For even if the defence were sound, the sword would receive such a shock that it would be very difficult to hit at the same time, unless the subtle method of reaching the body before the other touches your sword were followed. For in this ease the adversary's body strengthens his sword. The alternative for the weaker man is to avoid and free his sword, not to attempt to advance on his adversary. Also it is always good for the weaker man to defend by withdrawing his body a little so as to feel the shock of the thrust less in parrying; though it is better to parry cuts by advancing, as the cut has not the power of the lunge. He must keep his adversary at the point of his sword, so that he cannot pass, remembering that to let him come to grips, would be the worse for him, the weaker. If the heavier man passes and jostles him, he would disconcert him so that he could do nothing, and before he recovered the heavier man would have done many things. Thus it is not good for a weak man to try to acquire distance, but to contrive to keep out of distance, not to let his sword be engaged, but on different occasions to incite his adversary to hit by offering a time; or to make a feint of offering his sword, so that the adversary may believe he can engage, and whilst he is moving, break ground a little, and thrust at the part uncovered by the heavier man, so that he may be hit as he comes on, and, thinking he has passed, find the weaker man is away by having broken ground, so that he cannot reach him. The stronger man will thus be disordered and may be hit before he recovers, if the weaker man has not already hit and brought himself immediately back into safety, with the intention of letting his adversary's sword pass in vain, saving himself with his body and feet. Therefore for these reasons it seems clear that it is ill for a weaker man to attack a stronger man; it is better for him to stand on the watch with the idea of defending himself by the advantage of distance. Again in dealing with a choleric or violent opponent you should endeavour to provoke him to attack, so as to hit him when he comes. It would be ill to seek to approach him and come to grips without the advantage of the point; but rather you should encourage his fury, giving him opportunities in order to cause his downfall more easily; while he is approaching you can advance, or retreat according to circumstances, in order to defend your self[!] and hit at the same time, and before he passes. On the other hand, if you have to deal with a phlegmatic opponent who waits, then you can attack; but take care you are not deceived, for often in the desire to hit and the belief that you have merely to frighten your adversary to the defensive, you are yourself hit; whereas if you wait and are restrained, you may easily defend and hit. Therefore you must always consider the danger, with whomsoever you are matched; you must never rashly despise your adversary, but always be on the watch for whatever may happen and ready for all accidents. Our discourse so far has been to show the principles on which the science and practise of the sword are founded. We have omitted many things which we might have said, and have had regard only for what seemed to us more useful and necessary, and more in accordance with the use of the present time. Now we shall treat of the nature of the guards and movements, illustrated by the plates. In each guard the illustration will be double to show the position of the right and the left side of the body. |
AVERTIMENTI PER SAPERSI GOVERNARE, Contra li grandi, piccioli, debili & forti & come contra colerici, & flemmatici. Cap. 16. DOUENDO ANDARE L’ HUOMO CONTRA IL SUO nimico deue sottilmente considerare non solo la natura di esso mà anco la forza, & grandezza, perche è neccessario operare differentemente secondo le qualità particolari di quello, con chi si hà da contendere, & pero noine raggionaremo alquanto, & auertiremo li modi migliori da tenersi. Vn grande dunque, che habbia da fare con un picciolo dee conoscere il suo uantaggio perche essendo più grande ariua più di lontano sì per la grandezza come per il pendicolare del corpo, ilquale piegato si porta tanto inanzi, che si ariua al nimico, & il nimico non può ariuare, che per questa raggione pare, che deua attendere più alla offesa, che alla diffesa, si che non hà neccessità di aquistare la nimica, ancorche sia buono, mà solamente li basta tenere la sua libera per ferire quando, che il detto nimico si auicina, & prima che l’ proprio corpo entri nel pericolo, & in questo modo dee procurare di tenere lo stesso nimico lontano, acciò non possi hauere mai la sua misura, perche hà da cognoscere il detto grande, che essendo gionto lui prima nella misura, & uolendo il picciolo stringersi più inanzi per aquistar la sua quello essere tempo per esso grande di ferirlo, ouero metterlo in disordine con mostrare di hauere preso quel tempo in che si è mosso, & ferirlo poi in quello scoperto, che haurà fatto in andando all’ obbidienza, & con rompere anco subbito di misura, che all’ hora si trouarà tanto lontano, che il deto picciolo non potrà ariuare, ouero non potendo fare alcuna di queste cose è bene lo andarsi trattenendo con rompere di misura tanto, quanto che l’ altro si approssima per non lasciarlo peruenire al disegno suo, & questo farassi sino che si troui la comodità di ferire, ò di metterlo in obbidienza; tutte l’ operationi deuono essere senza passare solamente portare fuori il corpo quando il nimico passasse, & anco rompere di misura, acciò che non passi mà sia trattenuto, & incontrato dalla punta, che in questo modo esso picciolo conuerà usare noua maniera, & non hauere intentione di ferire mà di diffesa atteso, che non può ferire il nimico, che il suo corpo non sia entrato prima nel pericolo & percio li è più utile, & più neccessario attendere ad’ aquistare, & occupare la spada che nol ferisca nel tempo, che egli si auicina per aquistare la misura, doue essendo gionto & trouato il tempo di potere ferire li sarà meglio anco passare all’ hora, perche haurà tanto penetrato la punta nimica, che difficilmente potrà più uscire in tempo senza restare ferito, quando che l’ grande però non si trouasse con la spada tanto fuori di presenza, ouero tanto ritirata, che conoscesse euidentemente di hauere tempo da saluarsi indietro, & tornare nella diffesa, perche in un solo moto non haurebbe potuto tornare tanto indietro, che la spada del’ grande per la longhezza sua non lo hauesse ariuato; Mà dall’ altro lato è ancor uero, che se bene il grande hà il uantaggio della linea anco che di grande importanza, non dimeno essendo li mouimenti suoi più tardi, & con maggiori scoperti non si può cosi bene leuare di præsenza; [24] & essendo berzalio più grande offerisce gran uantaggio al picciolo di ferirlo, quando che esso picciolo sappia condursi nella sua distanza, sì perche la spada più lo cuopre, & non hà da fare moti sì grandi per diffendersi, come perche hà passato il pericolo maggiore, che è di hauere penetrata la punta prima, che l’ nimico habbia penetrata la sua, & essendo li suoi scoperti più piccioli uiene ad’ hauere minore pericolo, & le sue operationi conseguentemente ad’ essere tutte più sicure, che quelle del grande. Quando poi un forte hà da fare con undebile ancor questo è uantaggio grande questi dunque dee fondare le raggioni sue ncll’[!] aquisto della spada nimica, potendo ageuolmente disordinarla, & ferire nelli mouimenti di essa, perche quando una spada più debbile uuole resistere ad’ una più forte nel mutarla da l’ uno luogo nell’ altro si disuia di modo, che il più galiardo può facilmente ferire, & se hà ferito à piè fermo può ritornare alla spada, & fargliela muouere con fare l’ istesso, & quando uolesse anco passare sarebbe buono perche gionto, che fosse alle prese haurebbe medemamente molto uantaggio; Mà per contrario un debile, che habbia da fare con un forte bisogna, che sempre uada sfuggendo la spada, ne se la lasci trouare, ne meno occore di parare quando il galiardo uolesse ferire perehe[!] spesse uolte si uede, che più uale la più debile parte dell’ uno, che la più forte dell’ altro, & così il men galiardo restarebbe ingannato pensando diffendersi col suo forte, quando però non fosse qualche gran differenza nella spada, come per esempio che l’ una non si trouasse tanto nel debile, & l’ altra tanto nel forte, ualendo più in certi casi una sola mano che due, con tutto ciò sarà sempre bene di non parare potendosi fare di meno perche anco che si diffenda la spada dura tanta fatica che, difficilissimo è lo potere ferire in medesimo tempo se non si usa quella sottilità di ariuare al corpo prima, che l’ altro la tocchi, perche in questo caso il corpo nimico uiene à fortifficarla, altrimente bisogna scansare di uita, & liberare la spada, ne tentare di auicenarsi molto aldetto nimico, anzi è buono che tutte le diffese siano fatte col ritirare un poco il corpo indietro per sentire la botta mengraue ne lo parare, quando non fosse di taglio, perche quelli meglio è andare à pararli inanzi, non hauendo esso taglio tanta forza, mà bisogna tenere il nimico in punta di spada, affine che non possa passare ricordandosi che à lasciarselo uenire addosso senza ferirlo esso più debile n’ haurebbe la peggiore & che quando il forzato nel passare l’ urtasse lo sconcertarebbe di modo che non potrebbe fare niente, & prima che si rimettesse, detto forzato haurebbe fatto di molte cose, talche non è bene che un debile uada stringendo la misura, mà sempre dee procurare di conseruarsi in lontana distanza, ne lasciarsi mai ritrouare la spada, mà si bene prouocare l’ altro condiuerse occasioni à ferire dandoli il tempo, ouero mostrando di darli la spada, accioche si creda hauerla, & mentre, che per questo si moue, rompere un poco di misura, & mettere la detta spada per lo scoperto, che esso più forzato haurà fatto, affine che uenendo resti ferito, & credendo hauere passato troui lui debile essere lontano per quello hauere rotto di misura che così non lo haurà potuto ariuare, & si sarà scomodato, & potrà anco essere ferito prima, che si remetta, quando, che esso debile non l’ habbia ferito prima, & saluatosi subbito indietro con intentione di lasciare passare la nimica uota, & saluarsi col corpo, & con li piedi, doue che perqueste raggioni si uede chiaramente essere male, che un men forte uada ad’ assalire un più forte mà che più utile li torna lo stare sul’ auiso attendendo à diffendersi col uantaggio delle distanze. Et chi similmente hauesse da fare con uno colerico, ò furioso deue andare à trouarlo prouocandolo ad’ entrare affine di ferirlo quando che entra, si come sarebbe male à cercare di entrare addosso à lui, per non uenire seco alle prese senza il profitto della punta, mà più tosto hà da agiutare la sua furia dandoli occasione per farlo più facilmente cadere, alquale mentre uiene si può andare incontro, ouero ritirarsi secondo l’ occasione per potersi diffendere, & ferire in tempo medesimo, & prima che egli passi. Mà quando per contrario si hauesse da fare con un flemmatico, ilquale aspettasse all’ hora si può assalirlo, ma con riguardo sempre di non essere ingannato, perche molte uolte per il desiderio, che si hà di ferire [25] & credendosi, che il nimico non habbia se non da mettersi in timore di diffesa si resta ferito, doue che aspettando, & andando ritenuto si può facilmente diffendere, & ferire, che perciò si dee sempre considerare il pericolo, habbiasi da fare conchi si uoglia, ne mai si hà da sprezzare temerariamente[17] il nimico, anzi sempre stare auisato, & attento à quello, che potrebbe auenire per essere pronto in qualcunque accidente. Quello che sin qui habbiamo discorso è stato per mostrare le raggioni sopra lequali è fondata la scienza, & peritia della spada, molte cose habiamo tralasciate, che hauriano potuto dirsi, mà noi ci siamo solamente attenuti à quelle, che più opurtune, & più neccessarie ci sono parse, & più secondo l’ uso de tempi presenti, mà da qui inanzi trattaremo sopra la natura delle guardie, & monimenti[!], si come le seguenti figure dimostraranno, lequali in ciascuna guardia saranno duplicate affine di mostrare l’ effetto della destra, & della sinistra parte del corpo. |
||||||
[17] General discourse on the guards. We have now reached the point when we must treat of the formation of the principal guards, and movements and the results obtained in arms. We must first warn the reader not to wonder if he sees two figures illustrating one result. This is done to represent the right and the left side of the body. On the other hand we have thought it unimportant and idle to treat of many other guards of which some authors have written; for instance a guard with the dagger extended and the sword thrown behind, now on one foot and now on the other, now high, now low, which seems to us to defend the rear rather than the front. Others with the sword alone have kept it so far back and low, that the point was near the point of their feet, and also they held the sword across the legs and with the point almost on the ground, and all this that the sword might not be engaged. Sometimes on guard they take the blade in the left hand to give it strength, in order to beat the adversary's sword and hit. All these things we have omitted as inappropriate and, more often harmful than useful, and in any case tedious to the reader. Perhaps it had been better to have passed them in silence, but some might have thought we had not seen or considered such things; - therefore we have made some mention of them, as of the practice of throwing the sword at the adversary, when fighting with the sword alone; some think this an essential movement, but we deem it of little value; it may succeed against those who leave the sword free or hold their own too stiff, but against those who engage their adversary's sword and can disengage, it effects nothing, rather he who adopts this method will always be beaten. Therefore we shall not treat of it further in the present work, but shall try to give such discourses, as when well considered can bring you such counsel and judgment, that, when you see your adversary approaching sword in hand in whatever manner, you will recognise the principles he is following as well as he himself. These results are illustrated by plates, from which you may expect great benefit. To these are added the discourses not only as an explanation of the results, but also in order that you may discover the intention of one who uses them and so anticipate your adversary's thoughts and prepare yourself before the result follows. Similarly the reader must not wonder seeing these extensions of the sword, feet and body; they are merely to show how you must proceed, when on guard, when passing, parrying, and hitting. Some swords will be long and some short; tall and short bodies will be seen, according as they are held more or less low, or as they are held upright or bent. These things will explain the guards formed both in the defence and the attack, the position of the body and the movements to be made, the one differing from the other according to the occasion. After these simple illustrations will follow others, in which will be revealed the parries and the hits which may arise from them, and their causes will be considered; you will understand that all movements of attack and defence must be made in time, when you have the sword alone in your hand. Other plates will then follow with short discourses; where necessary we shall discuss them at sufficient length, but where it is not necessary we shall leave them to the consideration of the reader. In these cases we shall explain merely the position from which the hit followed, how it is defended, and what was the guard formed before this result. In short we shall try to give such instruction, that you may easily learn what to do in any position, when you encounter an adversary, both what your adversary can do in attacking and how to defend, and similarly the changes of line which may be made, and in what distances, wide or close, of these distances we shall treat in different places, now of the one, now of the other, in order that you may understand within which distance a stroke is made. |
DISCORSO GENERALE, Intorno le guardie. Cap. 17. HORA SIAMO GIONTI AL LUOGO, OUE SI DEE TRATtare del formare le guardie, de’ mouimenti, & delli effetti più principali, che si fanno nell’ armi, doue che primamente si auertisse colloro, che leggeranno à non marauigliarsi se bene uedranno due figure per luogo demonstratrici ambe due di un solo effetto, che ciò è stato affine di raprensentare in quello la parte destra, & la sinistra del corpo; All’ in contro habbiamo ben giudicato essere cosa uana, & di nissuno momento il rapresentare, & trattare di molte altre guardie, che alcuni, scriuendo, hanno formato hora col pugnale inanzi disteso, & la spada sbarrata indietro osseruando ciò tanto sopra l’ un piede, come sopra dell’ altro, & così alta, come bassa che anoi pare che più diffenda didietro, che dinanzi, altri con la spada sola hanno usato tenerla tanto ritirata, & bassa, che la punta di quella si trouaua appresso quella de’ piedi, & anco la tenenano[!] trauersata dinanzi le gambe, & pure con la punta quasi per terra, & tutto questo faceuano, acciòche la spada non seli potesse trouare, & alcune uolte stando nella guardia pigliauano la lama con la sinistra mano per tenerla più forte, & per battere la nimica, & ferire, lequali cose tutte habbiamo tralasciate come fuori di proposito, & più tosto aportatrici di danno, che di utile, & senza altrò di tedio à chi le leggesse, & era forsi meglio anco di intieramente tacerle, mà perche altri non creda, che tali cose non fossero state uiste & esaminate da noi ne habbiamo uoluto fare qualche mẽtione, se come dello giettare la spada fuori di mano all’ auerssario con la propria sola spada, laquale essendo tenuta da altri per un punto essentialissimo da noi non se ne fà stima, come cosa di poco peso, laquale riesce con colloro, che li lasciano la spada libera, ouero la tengono ferma, mà contra qnelli[!], che la sanno occupare al nimico, & che hanno termine di cauatione nõ si può fare niente, anzi chi prettende fare quello resta sempre battuto, & per tanto nõ sene tattarà più nella presente nostra opera, mà si attenderà à fare discorsi tali, iquali ben considerati possino aportare tanto di auertimento, & giuditio all’ huomo, che uedendosi uenire contra il nimico con la spada in mano, sia in qualunque forma, sappia conoscere il suo fondamento, & raggione, tanto bene, quanto l’ istesso che uiene, però si sono posti quelli effetti in figure, da quali si può aspettare molto benefficio, & alle qualisi sono aggiunti li discorsi non solo per sapere conoscere la natura di essi effetti, mà anco per sapere spiare l’ intentione di chi li adopra, & così preuenendo il pensiero nimico, sapere prepararsi inanzi che segua ildetto effetto, similmẽte nõ si dourà marauigliare il lettore uedẽdo quelle distese di spada, di piedi, & de corpo, che nõ sono per altro, che per mostrare in quale modo, si habbia da operare tanto à piè fermo, quanto che inpassando parare, & ferire, gli serà alcune spade longhe, & alcune corte, & si uedranno corpi grandi [26] & piccioli secondo si abbassaranno più, & meno, & anco saranno tanto più longhi, & più corti secondo, che staranno diritti, & formaranno scurzi, lequali cose saranno demonstratiue della guardia, in che si troua l’ huomo tanto nelle diffese, quanto nelle offese, della situatione del corpo, & de mouimenti, che bisogno[18] fare uno differente dall’ altro secondo l’ occasione; Doppo queste simplici figure ne seguiranno altre, nelle quali si scorgeranno li parati, & li feriri, che possono uenire dall’ una, & dall’ altra, doue si discorrerà della loro caggione, & oue anco si intenderà, che tutte le diffese, & offese deuono andare in uno istesso tempo ancorche non s’ habbia si non la sola spada in mano, doppo queste sene uedranno altre, allequali sarà aggionto poco discorso bastando, che doue sia neccessario si raggioni à sufficienza, mà doue non sarà neccessario si lasciera nella consideratione del lettore, solamente in simili luoghi si mostrarà da che sia proceduta la ferita, come si sia diffeso, & in che guardia si trouauano prima, che facessero li effetti, & in somma si procurarà di dare tale cognitione, che ageuolmente altri possa sapere quello, che si dee fare ritrouandosi contra il suo nimico in ciascuno sito, & anco quello che dal detto nimico potesse uenire in offesa, & quale diffesa si potesse fare, & similmente le mutationi, che si possono fare, & in quali distanze longhe, ò strette, & di dette distanze hora si raggionarà in un luogo di una, & hora in un’ altro dell’ altra, acciò si intenda in quale sia nata la botta. |
[59] General Discurs über die Läger. Das siebenzehende Capitul. NUn bin ich an den Orth gelanget, da ich von Formirung der Läger, von denen Beweg- und fürnehmsten Würkungen, so mit den Waffen können gemachet werden, hanlen soll: Da dann diejenigen so es lesen werden sollen wissen, dasz sie sich nicht verwundern, ob sie gleich an einem Orthe zwei Figuren sehen, welche beide nur einerlei Würkung zeugen, weil solches geschehen, um darinnen so wohl die rechte als die linke Seite des Leibes zuweisen. Hergegen habe ich auch vor unnöthig und unnützlich erachtet viel andere Figuren, welche etliche so von dieser Kunst geschrieben, formiret haben herzusetzen und davon zuhandlen, als mit der linken Hand weit voraus und mit dem Rappier weit zurük und solches so wohl auf einem als auf dem andern Schenkel, ja bald hoch bald niedrig, von welchen mich bedünket dasz sie sich mehr hinder- als vorwärts schützen wollen. Andere haben beim einfachen Rappier im Brauch, dasz sie selbiges so weit zurük und zugleich tief halten dasz sich die Spitze nahe bei den Füszen befindet, und über das halten sies quer über vor den Schinnebeinen, die Spitze aber gleichsam gantz an der Erden; Solches aber alles thun sie nur darum, dasz ihnen die Klinge nicht könne gefunden werden: Ein andermahl wenn sie im Lager liegen, ergreiffen sie die Klinge mit der linken Hand, aufdasz sie selbige desto fester halten, des Feindes seine desto hefftiger schlagen und dann darauf mögen stoszen können. [60] Aber solche Sachen alle weil sie nicht zu meinem Zweg dienen, auch mehr Schaden als Nutzen bringen, und ohne das dem Leser einen Verdrusz erwekken mögten, habe ich mit Fleisz ausgelaszen, ja es wäre vielleicht besser, dasz man gar davon stillschwiege: Damit doch andre nicht glauben mögten, dasz ich solche Dinge nicht ehmahls gesehen und examiniret hätte, habe ich davon einige Meldung thun wollen; Also, dasz ich auch von denen so ihren einzelen Degen ausz der Hand nach dem Feinde schiessen etwas sage, so wirds von etlichen andern vor hauptsachliches Stük gehalten; Ich achte es aber vor nichts anders, als vor eine Sache weniges Wehrts, welches bey denjenigen so dem Feinde die Klinge frei lassen, oder die ihrige gar zusteif halten wohl angehet; Aber wieder diejenigen so ihrem Feinde zustringiren, und also sich dessen Klinge zubemeistern, auch die Cavationes just zumachen wissen, kan es nichts fruchten, sondern es wird derjenige, soe es brauchen will, allezeit getroffen sein können, dasz ich derhalben in diesem Buch nichts mehr von dergleichen Dingen handlen, sondern vielmehr solche Discursze vorzubringen mich bemühen wil, welche wenn sie wohl inachtgenommen werden, einem Manne zu solchem aufmerken und Urtheil zugelangen verhelffen können, dasz, wenn er seinen Feind mit dem Degen in der Faust auf sich ankommen siehet, es sey gleich wie es wolle er so wohl als der Feind selbst verstehe das Fundament und die Regulen so er anzubringen gesonnen; Derhalben seind dieselben Würkungen in figuren gebracht, von welchen viel und guter Nutzen zugewartten, denn es seind die Discurse dabeygesetzt, nicht nur dasz einer die Eigenschafft derselben Würkungen verstehen lerne, sondern auch dasz er die Intention dessen, so sie brauchet, auszukundschaffen und seinen Gedancken vorzukommen wisse, und sich könne wieder die Würkung so folgen soll, vorher zurechte machen. Ingleichen wird sich der Leser nicht verwundern, wenn er hier siehet die ausstrekkungen der Klinge, der Füsze und des Leibes, denn es ist zu nichts anders gemacht, als dasz einer dadurch die Arth weise, wie er sich so wohl im a piede fermo stossen als mit dem pariren und stoszen zugleich verhalten soll; Es seind auch etliche Degen lang etliche kurtz, etliche scheinen grosz etliche klein, nachdem sie sich mehr oder we= [61] niger versenken, sie würden auch länger oder kürtzer scheinen, nachdem sie aufgerichter oder zusammengezogener stünden, welches doch alles nur die Läger zeugen soll, in welchen sich einer so wohl in off- als defensione befinden kan, Item die situation und Bewegung des Leibes, welche denn einer biszweilen anders als der ander machen musz, nachdem es die Gelegenheit erfordert. Nach solchen eintzelnen und schlechten Figuren werden noch andere folgen, darinnen warden die Paraten u. Stösze zu sehen sein, welche so wohl von einem als anderm Theil können herkommen und gemachet werden, da ich denn von ihrer Ursache reden will, woher einer denn leicht verstehen wird, dasz alle Beschütz- und Verletzung in einem Tempo zugleich müsze geschehen, vo man gleich nichts mehr als ein eintzeln Rappier in der Hand führet: Nach diesen werden noch anderer gesehen, zu welchen nur ein kleiner Discursz wird gesetzet, und doch genug sein, weil da es vonnöthen sattsam ist gehandelt worden, aber wo es nicht vonnöthen, überlasze ichs dem bedencken des Lesers, allein will ich an dergleichen Orth weisen, woher so wohl die Verletz- als die parirung kommen sei, und in was für einem Lager sie sich erst befunden, ehe sie solchen effect gemacht. Summa ich will mich bemühen, dasz ich eine solche Wissenschafft herausgebe, dasz einer so bald er sich gegen seinem Feinde in einigem Lager befindet, wissen kan, was und wie ers angreiffen soll, auch dasjenige was von dem Feind so wohl in off- als difesa kan gemacht werden, ingleichen die Verenderungen so können vorkommen, in was für Misur, ob in der weiten oder in der engen, da ich an einem Orth von einer, am andern aber von der andern werde handeln, auf dasz man verstehe, in welcher Misur der Stosz gemachet sei. | |||||
[18] Discourse of the plate showing the nature of the cuts and where they hit. This plate shows the nature of all the cuts, which a hand can make. The names are placed against them so that you may see where each of them naturally hits, although they may hit higher or lower according to whether they are made with the hand or the arm. At least their path is seen, and from a knowledge of that follows a knowledge of the second point, what sort of defence can he made in order to parry them and hit at the same time. Therefore the names on the plate are placed not in the part from which the cuts are delivered, but where they hit; for the cut of mandiritto is delivered from the right and hits the adversary's left shoulder, and the cut of riverso is delivered from the left and hits somewhere on the right side, as may be seen. Whoever examines and ponders on these cuts, will easily discover the principles of proceeding against each one of them, bearing in mind that even if all the cuts are made by the same arm they may not have the same strength, and therefore against the stronger it is necessary to find a stronger defence in order to resist and hit. Although it might appear that we should here treat of the differences in the cuts, still we think we have treated of them sufficiently in speaking of the defence and the attack, and of thrusting and cutting. It is our intention to base our instruction, not on these, but on more subtle and profitable principles. |
[27] DISCORSO SOPRA LA FIGVRA CHE DISMOSTRA LA NATVRA DEI TAGLI, Doue uano aferire. Cap. 18. QUESTA FIGURA, CHE SEGUE DIMOSTRA LA NATURA di tutti li taglii, che può fare una mano, alliquali taglii si sono posti li suoi proprii nomi, acciò si ueda doue naturalmente ciascuno di loro uada à ferire, ancorche possino ferire più alto, & più basso, secondo che uengono portati dalla mano & dal braccio, pure si uede per quale uia uanno à ferire, & da questa prima cognitione si uiene nella seconda, laquale è di sapere, che sorte di diffessa si debba usarli contra per potere ben parare, & ferire in medesimo tempo, & perciò si sono notati li nomi di essi sopra detta figura non dalla parte doue uengono tirati, mà doue uanno à ferire, perche il manodiritto è tirato dalla mano diritta, & uà à ferire la spalla sinistra nimica, & il riuerso è tirato dalla parte sinistra, & uà à ferire la destra indifferentemente, come si uede, & chi bene andarà esaminando, & discorrendo con l’ intelletto trouarà facilmente le raggioni di andare contra ogniuno di loro hauendo in consideratione che se bene tutti li taglii sono tirati da un braccio medesimo non deuono però hauerela medesima forza, & però contra quello, che ferisce di maggior forza bisogno trouare anco diffesa più forte per resistere, & ferire, & se bene qui pare, che si douesse trattare della differenza loro noi reputiamo non dimeno hauerne trattato à bastanza, doue habbiamo parlato delle diffese, & offese, & del ferire di punta, & di taglio, essendo nostra intentione di fondarci non in queste mà in raggioni più sottili, & più profitteuoli. Riuerso squalembrato
|
[62] Discurs über die Figur welche die Natur der Hiebe weiset, wo sie nehmlich hintreffen. DIe Figur welche man hier siehet, zeuget die Natur aller Hiebe, so eine Hand machen kan, zu welchen Hieben denn ihre eigenen Nahmen gesetzet seind, aufdasz man sehe, wo ein jeder derselben natürlicher weise hintrifft, ob sie gleich zuweilen nachdem sie von der Hand oder dem Arm angebracht werden höher oder tieffer verletzen mögen; Hier wird allein darauf gesehen, durch was Wege sie zum verletzten kommen; Von dieser ersten Wissenschafft nu kömt man zur andern, das sit, dasz man die Arth der man sich zur Parirung dagegen bedienen musz wohl verstehet, nehmlich dasz man im selben Tempo parire und zugleich mit treffe, wes= [63] wegen auch ihre Nahmen in dieser Figur also genennet nicht von dem Orth wohin sie treffen, sondern von dem Orth woher sie sich anfangen und herkommen. Denn mandiritto ist von der rechten Hand rumgeführet, verletzet aber des feindes linke Schulter, Riverso ist von der linken Seiten hergeführet, und verletzet doch ohne Unterschied die rechte, wie man solches siehet. Wer aber diese Sachen wohl betrachtet und mit Verstand examiniret wird leichtlich Regulen finden, wie er wieder ein jedweden Hieb würken solle, angesehen dasz ob gleich alle Hiebe von einem Arm gemacht, sie doch deswegen nicht alle einerlei Stärke haben würden, und deshalben soll einer wieder die so mehr Stärcke haben, auch eine stärkere defension erdenken, dasz er ihm könne wiederstehen und alsdenn treffen. Obs nu wohl scheinet, dasz ich hier auch von ihrem Unterscheid handlen solte, halte ich doch nichtsdestoweniger solches der Gnüge nach gethan zuhaben an dem Orth, wo ich von der Off- und Difesa, auch von dem verletzen auffn Stosz und hieb gehandelt, indem mein Vorsatz nicht ist meine Discurse auf dergleichen, sondern auf viel subtilere und nützlichere Regulen zugründen. | |||||
[19] Discourse on the guard in prime formed in drawing the sword from the scabbard. This plate (the second in order) shows the position into which the hand goes in drawing the sword from the scabbard, wherefore its name of the guard in prime. It cannot be held to be very secure, since the sword is too much withdrawn and the body entirely exposed owing to the height of the sword, which brings the forte very far from the body, so that it cannot defend the exposed part below in time. In this case you would have to defend with the hand, unless you broke ground, otherwise you would be hit before parrying. If you wished to hit after the parry you could lower the point a little, abandoning his sword, and make a cut, or a rush, but as this would be a hit in two times it would not be very successful. As to the head it is sufficiently defended by the guard, and more on the outside than the inside. But we shall form another guard which is safer, with which you can await your adversary or advance. With the present one an advance would be very dangerous; therefore this position of the body and the sword should be used on breaking ground rather than at any other time. |
DISCORSO SOPRA LA PRIMA GVARDIA formata nel cauare la spada del [f]odero.[19] QVESTA SEGUENTE FIGURA SECONDA in ORDINE DI MOstra il sito, doue uà la mano nel cauare la spada del fodero, per cui aquista il nome di prima guardia, laquale non si dee hauere per molto sicura, atteso, che la spada è troppo ritirata, & il corpo tutto scoperto per l’ altezza di essa spada, lacuale caggiona; che il forte sia molto lontano dal corpo, & che però non possi diffendere in tempo lo scoperto di sotto, nelquale caso si uiene ad’ essere in neccessità di diffendersi con la mano, quando non si uoglia rompere di misura, che altrimenti si restarebbe ferito prima, che si hauesse parato, mà chi uolesse pure ferire doppo il parato potrebbe abbassare alquanto la punta rompendo di spada, & ferire di taglio, ouero con un slancio di punta, mà perche questo farebbe ferire di dui tempi non sarebbe anco troppo riuscibile; Quanto al capo esso e diffeso assai dalla guardia & più dalla parte di fuori, che di dentro, mà ne formaremo un’ altra, che sarà più sicura con che si potrà aspettare, & andare contra il nimico, perche con questa, chi si uolesse approssimare portarebbe gran pericolo, talche in questo sito di corpo & di spada si dee stare più sul rompere di misura, che altro. |
Discurs über das Prima Lager, so im ausziehen des Degens aus der Scheiden formiret und mit No. 1. gezeichnet ist.
DIese Figur, so in der Ordnung die zweite, aber mit No. 1. bezeichnet ist, zeuget ein solches Lager, darein die Hand gehet, indem sie den Degen entblöszet oder aus der Scheiden ziehet, davon sie auch den Nahmen hat der Prima Guardia, das ist, des ersten Lagers der Hand, welche dann nicht vor gar zu sicher gehalten werden mag, weil sie die Klinge gar zuweit zurük und den Leib wegen der Höhe der Klingen gantz entblöszet hält, welches denn verursachet, dasz die Stärke so ferne vom Leibe ist, und deswegen die Unterblöszen à Tempo nicht beschirmen kan, auf welchen Fall denn von nöthen sein wird, wo einer anders nicht die Misur brechen will, sich mit der linken Hand zu schützen, weil er sonst ehe, als er hätte gepariret, ge= [64] troffen wäre: Wer aber nur schlecht nachdem er erst pariret hat, gedenket zuverletzen, kan nur ein wenig die Spitze versenken, damit die feindliche Klinge wegreissen und mit einem Hiebe, oder mit einem geschleudertem Stosze verletzen: Weil aber solches mit zweien Tempi getroffen were, würde es nicht gar zu wohl von statten gehen. Was den Kopf selbst anbetrifft ist er in diesem Lager doch mehr aus- als einwendig sicher und beschützet genug; Drum will ich hier eine andre Prima zeugen, welche viel sicherer sein, und mit welcher einer den Feind angreiffen oder des Angriffs erwartten können wird: Denn wer sich in jetztgesagter Prima zu seinem Feinde nähern wolte, würde in grosser Gefahr stehen, dasz sich dannenher einer in diesem Lager mit dem Leibe und der Klingen mehr auf die Misur zubrechen, als anders worauf verlaszen musz. | |||||
[20] Explanation of a well formed guard in prime. If you wish to form a sound guard in prime the position of the body and sword must be as shown in the plate, the feet close together, body bent, arm extended, with the sword in front with the point as straight as possible; for the point will naturally incline towards the ground. Thus your adversary cannot thrust over the sword; this part being the weaker must be better defended. Moreover you must keep the feet together and the body bent, so that the lower parts may be so far withdrawn that the adversary cannot reach them without penetrating with his head half the sword's length. Your sword will have to defend only the head and part of the chest, which it can easily do, as the forte is already so far advanced that the adversary's sword can never extend so far as not to be always nearer the forte than the body. This guard is excellent against cuts, for with it you can defend and attack without turning the hand. It would be as good as any other guard in fencing if it were not so laborious for the arm, that you cannot long endure this position. With this guard you can advance to engage and harass your adversary's sword without changing guard, always approaching so as to hit on the outside over the sword, or below, in case your adversary disengages, by lowering your body still further, moving the feet apart, and keeping the arm in the same guard; as soon as you have hit, bring the feet together again and try to engage his sword above, even though his sword is on the inside, and push it out. This you can easily do, for your adversary cannot resist, as in this line your guard is strongest. |
[28] DE CHIARATIONE DELLA PRIMA guardia ben situata. VOLENDO FORMARE LA PRIMA GUARDIA, CHE STIA BENE si dee situare il corpo, & la spada come dimostra la figura, chie segue così stretta di passo col corpo piegato, & braccio disteso, & con la spada inanzi, & la punta più diritta, che si può, perche di sua natura guarda uerso terra, & questo acciò il nimico non possa uenire per la parte disopra, laquale come più debile, fà di mistieri tenere anco più diffesa, & oltre diciò si dee tenere il passo stretto, & il corpo curuato, accio le parti disotto siano tanto lontane che l’nimico non ui possa ariuare se non penetra con la testa sino à meggio la spada di detta prima guardia, doue la spada di questo non dourà attendere ad’ altro, che à diffensare la testa, & la parte del petto, quali si diffenderanno assai ageuolmente per essere già auanzato il forte tanto inanzi, che la nimica non potrà mai così allongarsi, che la non sii sempre più uicina al forte, che al corpo. Contra li taglii è bonissima, perche con essa si può diffendere, & offendere senza uoltare la mano, & questa sarebbe tanto buona quanto quale si uoglia altra guardia nell’ armi se non fosse così laboriosa per il braccio, che longamente non può durare in quel modo, & con questa forma si può andare à trouare il nimico, & trauagliarli la spada senza mutarsi mai di guardia con auicinarsi sempre, affine di ferire poi di fuori sopra la nimica, ouero disotto in caso che l’ detto nimico cauasse, con abbassare anco più il corpo, & allargare il passo tenendo il braccio nella medesima diffesa, & subbito ferito racogliere il passo, & tornare alla spada cercando di trouare la nimica per disopra, benche quella fosse di dentro, & rispingerla per di fuori, il che si potria benissimo fare, che l’auerssario non potrebbe contra stare per essere quella parte la più forte di questa guardia. |
[65] Erklärung des wohlgestallten Prima Lagers. No. 2. WEnn einer will die Prima formiren, dasz sie gut sei, soll er seinen Leib und die Klinge also stellen, wie diese Figur No. 2. weiset, nemlich mit einem engen Schritt, mit dem Leibe gebogen und dem Arm ausstreckt, mit der Klingen hinfür und der Spitzen so gerade als er immer kan, weil sie von Natur nach der Erden siehet, damit der Feind nicht könne über sie kommen, maszen sie oberhalb am schwächsten ist, weshalben auch von nöthen, dasz sich einer daselbst mehr gesichert halte. Man musz sich auch über diesz im engen Schritt und dem Leibe gekrümmet erhalten, aufdasz der Untertheil so weit entfernet sei, dasz ihn der Feind nicht erreichen könne, er komme denn mit seinem Kopf mittelweges unter die Klinge, so in der besagten Prima lieget, dannenher denn auch diese Klinge in der Prima nicht anders als wie sie den Kopff und ein Theil der Brust wohl verwahren will, zusorgen hat, welche doch leicht und geschwinde genut können beschützet werden, weil die Stärke schon so weit hinfür ist, da sich hergegen des Feindes Klinge nicht hinfür strekken kan, dasz sie nicht allezeit des [66] in Prima gelagerten Stärke näher als dessen Leibe sei. Wieder die Hiebe ist diese Prima köstlich, denn es kan sich damit einer zugleich schützen und ohne einige Wendung der Hand den Feind verletzen; Ja sie wäre so gut als eine unter allen Lägern, wo sie nicht für den Arm gar zu mühsam wäre, welcher auf solche Weise in die Länge nicht tauren kan: Auf diese Weise kan man des Feindes Klinge finden, und ihm dieselbe beschwehren oder beunruhigen ohen eintzige Verenderung des Lagers, wenn man nur allezeit auf ihn loszgehet, um ihn auswendig oberhalb oder im Fall er cavirte unten zustossen, da man doch mit dem Leibe wohl verfallen und den Austritt verlängern, auch den Arm in selbiger Defension behalten, und so bald einer getroffen, sich wieder an der Klinge zurükziehen, und dieselben oberhalb zufinden versuchen musz. Ja ob sie auch gleich einwendig were, soll man sich doch wieder auswendig treiben, welches sich denn gar wohl wird thun lassen, denn der Gegner wird angesehen diese Prima auswendig am stärkesten ist, nicht wiederstehen können. | |||||
[21] The guard in seconde. Arising from the guard in prime formed on drawing the sword from the scabbard. From the position of the hand in drawing the sword from the scabbard arises this guard, with the arm somewhat lowered and turned downwards. This has caused a slight change in the front of the body. It is called the guard in seconde because it is the first movement which the hand can make in changing from the guard in prime. It is easier than the guard in prime, as the arm is not so strained; owing to the change of the position of the hand the weak part has changed. In the first it was above, now it is on the outside. It is true that as the feat are rather far apart the leg is in some danger towards the knee; still if you can keep your sword free, your adversary will only with difficulty hit you so low before he is himself hit above. Although in this guard the arm is somewhat withdrawn, the forte is so far forward that it can parry excellently both on the outside and the inside; but the hand must be turned in quarte, or you must parry with the hand. If the feet are kept closer together this guard will be safer on both sides. But we shall form another guard like the first but much better. |
[29] TRATTATO DELLA SECONDA GVARDIA nata dada prima che si formò nel cauare la spada del fodero. DAL SITO, OVE SI TROVAVA LA MANO, QVANDO HA CAuata la spada del fodero è nata questa guardia per essere il braccio alquanto abbassato, & uoltato allo in giù, ilquale ha causato un poco di mutatione nella prospettiua del corpo, & domandasi seconda guardia per essere il primo moto che può fare una mano di prima guardia nel uolere mutare sitò, & questa è assai più comoda della prima, perche il braccio non stà in tanta uiolenza, & per la mutatione della mano è anco mutato il debile, ilquale nella prima era disopra, oue in questa è di fuori, bene è uero, che per hauere il passo un poco aperto la gamba porta qualche pericolouerso il ginochio, nondimeno chi saprà tenere la spada libera sarà difficilmente ferito dal nimico in quella bassezza, che prima esso nimico non resti ferito di sopra, & anco che questa guardia tenga il braccio alquanto ritirato, nondimeno il forte è tanto inanzi, che può parare ottimamente dalla parte di fuori come di dentro se bene bisogna uoltare la mano in quarta, ouero parare con la mano, & se haurà il passo più stretto sarà sempre più sicura si per l’ una, come per l’ altra parte, ma se ne formarà un’altra consimile alla prima, laquale sarà molto migliore anco di questa. |
Abhandlung des Seconda Lagers, welches herrühret aus der Prima, so in ausziehung des Degens formiret ist, No. 3. AUs dem situ, darinnen die Hand als sie den Degen von Leder gezogen, sich befande, ist diese Seconda herkommen, weil sich der Arm ein wenig versenket und unter sich gewendet hat, welches denn eine kleine Veränderung der Prospectiva des Leibes verursachet. Sie wird aber Seconda geheissen, weil es die erste Bewegung ist, so eine Hand machen kan, wenn sie sich aus der Prima in einen andern situm verwenden will. Diese ist viel bequemlicher als die Prima, weil darin der Arm nicht so viel Gewalt leiden darf, auch hat sie wegen Verenderung der Hand, ihre Schwäche verendert, welche in Prima oberhalb war, [67] in dieser aber kömmet sie auswärts. Es ist zwar wahr, dasz das Bein überm Knie, wenn man mit den Füszen zuweit voneinander stehet, etwas Gefahr leidet, nichtsdestoweniger aber wird doch derjenige, so seine Klinge frei zuerhalten weisz, schwerlich so tief können getroffen werden, dasz der so treffen wil nicht ehe oben verletzet were: Ja ob gleich der Arm in diesem Lager ein wenig angezogen geführet wird, ist doch die Stärke so weit hinfur, dasz sie so wohl aus- als einwendig gar wohl pariren kan, ob sie gleich einwendig die Hand in Qvarta wenden, oder mit der Linken pariren musz. Wann aber einer mit den Füszen enger zusammen stehet, wird er allezeit so wohl an einem als am andern Theil sicherer sein. Aber ich wil noch eine andre Seconda gleich wie bei der Prima geschehen formiren, welche um etwas besser als diese ietztbeschriebene sein wird. | |||||
[22] A well formed guard in seconde. This is the position in which you should form the guard in seconde for greater safety. Although it is fatiguing, it is less so than the guard in prime, for the arm is somewhat lower. Its weakest part is on the outside, therefore you must hold the point so straight that your adversary cannot come in there. Although it is the most covered part, only a little of the head showing above the right arm, your adversary might come in there, put you to the necessity of defending the spot, and then proceed to hit below. If then he should attack on the outside you should disengage, without advancing, if you have not been able to hit whilst he was moving on the outside. The lower parts are still more secure than with the guard in prime. The defences are somewhat different, for you must defend the mandiritto tondo by turning into quarte, as also the sottomano. All the others are parried with the guard of seconde except some thrusts on the inside, which are likewise parried with a turn to quarte. You will do well with this guard, as your sword is advanced and straight. If you understand its principles you will find it excellent and advantageous; it leaves little uncovered for the adversary to hit, and the body is so far withdrawn that he cannot reach it without first subjecting your sword, which is difficult as the disengage is with this guard made with little movement and quickly. But as we have said above it is somewhat laborious to maintain for long. |
[30] DELLA SECONDA GVARDIA bene accomodata. QVESTO E IL SITO, COLQVALE SI DEE FORMARE LA SEconda guardia per sicurezza maggiore, & quantunque sia faticosa nondimeno non è tanto come la prima, perche il braccio è alquanto più basso, & perche la parte di fuori è la più debile, perciò si hà dà tenere la punta tanto diritta che l’ nimico non possa uenire in quella parte, ancorche sia la più coperta non ci essendo altro da ferire, che quel poco di testa, che auanza sopra del braccio destro, doue potrebbe uenire il nimico in quella parte, & metterlo in soggetione di diffendere quel luogo, & poi passare à ferire disotto, mà se pure egli uenisse di fuori si douria cauare ma senza approssimarsi, quando non si hauesse potuto ferire in quel mentre, che lui è andato di fuori. & le parti di sotto sono ancona più sicure, che nella prima, le diffese sono bene alquanto differenti, perche il mandiritto tondo bisogna diffenderlo con uoltare in quarta, si come anco il sottomano, li altri tutti si parano della stessa guardia eccetto alcune punte di dentro, che si parano pure col medesimo modo di uoltare‘in quarta, & si può fare benissimo rispetto alla spada assai auanzata, & diritta, & chi saprà operare le sue ragioni trouarà detta seconda essere molto buona, & uantaggiosa, & lasci poco scoperto al nimico da potere ferire, & col corpo si trouà tanto lontano, che il detto nimico non lo potrà ariuare se prima non li chiùderà la spada, ilche sarà difficile, perche detta guardia caua con poco motto, & è prestissima, mà come si è detto disopra è alquanto laboriosa per di morare longamente in essa. |
Von dem wohlgestallten Seconden Lager. No: 4 HIer weiset sich das Lager wie man die Seconda zu mehrer Sicherheit formiren soll, und ob sie gleich arbeitsam, ist sie doch nicht so beschwerlich als die Prima, denn der Arm kömt ein wenig tieffer: Weil aber der [68] auswendige Theil am schwächsten, musz man deswegen die Spitze um so viel desto gerader führen, dasz der Feind daselbst nicht ankommen könne. Denn ob gleich diese Seconda auswendig besser als an einem Orthe bedekket, ausgenommen das wenige vom Kopffe, so oben über den Arm herübergukket, so könte doch der Feind daselbst ankommen, einen alda sich zubeschützen nöthigen, und darauf unten fortpassiren und verletzen. Wenn er aber ja auswendig anbände, musz man doch, aber ohne zurükken caviren, wo man nicht indem er auswendig angegangen ist, hat treffen können. Die Untertheile seind auch sicherer als in der Prima, doch seind die Beschützungs Arthen etwas unterschieden: Denn Mandiritto tondo musz mit der Hand in Qvarta gewendet pariret werden, wie auch Sottomano: Alle die übrigen Verletzungen können von dieser selbigen Gvardia, ausgenommen etliche einwendigen Stösze, welche die Wendung mit der Hand in Qvarta erfordern, pariret werden; Aber es läst sich solches leicht verrichten, angesehen der Degen schon genug voraus und gerade ausgestrekket ist, dasz wer sich weisz in die Regulen zufinden, wird erfahren, dasz diese Seconda [69] sehr gut und vortheilhafftig sei, weil sie dem Feinde wenig Blöszen zuverletzen überläszet und mit dem Leibe sich so weit entfernet, dasz ihn der Feind nicht abreichen kan, er müsze denn diese Klinge ausgeschloszen haben, welches denn schwer fallen wird, weil besagte Seconda mit kleiner Bewegung caviret und sehr geschwinde ist, aber wie oben gesaget, so ist sie ein wenig mühsam, wo man sich lange darinnen aufhalten soll. | |||||
[23] Principles of another guard in seconde formed with the arm foreshortened as in the plate. This strained position is a guard in seconde. In spite of its appearance it has great swiftness and power, because of the union of forces. You begin to form it when upright, as the adversary approaches so you lower the body and withdraw the sword in such a manner, that, when within distance, you are so low and the sword so far drawn back, that it can be taken no further and the point still kept in, nor the body further lowered. Your sword must form a straight line from the hand to the point, so that the adversary cannot proceed on the outside. Also you must keep the hand to the front to defend yourself from any rush which might he made before you had completed the guard. When completely formed and your adversary approaches so far that his point just penetrates your point, if your sword is free, you must quickly change into quarte on the inside. For this purpose you keep your right foot so far across, that, when you lunge the body goes out of line before the feet move; in this way your lunge will be longer and pass right to the adversary's body. But if the adversary's point is directed towards yours, you must rush with your body under the point, thrusting in seconde past the faible of his sword, and pass right on to his body. If you see that your adversary's sword so far impedes yours that you cannot hit in that line, you must disengage from seconde, leaning your left hand on the hilt, so that the adversary's sword cannot push yours aside, and hit in the upper lines on the outside. Cuts are easily defended in secondo or in quarte according to the part they are directed against. These rules will succeed very well against those who do not understand the foundation of this guard. He who uses this guard, when making a hit will generally parry with the hand, and in all his hits will pass with determination. The guard is fatiguing and confined, still one who is well practised in it can effect much. |
[31] RAGGIONI DI VN’ ALTRA SECONDA GVARDIA formata in scurzo come siue de nella seguente figura. LA POSTVRA, CHE QVI SEGVENTÉMENTE SI VEDRA COsì forzata è una seconda, & se bene stà in questa forma nondimeno uà con molta celerità, & furia per rispetto dell’ unione delle si comincia à formare in piede, & quanto che l’ nimico si approssima tanto si uiene abbassando il corpo, & ritirando la spada, di maniera, che gionto in misura si troua già abbassato & hauere ritirata tanto la spada, che è impossibile ritirarla più uolendo tenere la punta in presenza, ne meno si può abbassare di più, & è di bisogno, che la sua spada si troui dalla mano alla punta in retta linea, acciòche il nimico non possa andare per difuori, hà similmente da tenere la mano alla fronte per diffendersi da qualche slancio, che sopraueniss prima che hauesse finito di formare la guardia, & quando del tutto l’habbia formata in euento che l’ detto nimico si auicini tanto solo, che con la punta penetri la punta di esso che è in guardia, sè lui haurà la spada libera dourà cacciarsi dentro di quarta, & per tale occasione tiene il destro piede così trauersato, perche nel fare la distesa il corpo uada fuori di presenza prima, che moua li piedi, che in questo modo la botta sarà più longa & passarà sino al corpo nimico, mà se la punta nimica piegasse uerso la sua, douria cacciarsi col corpo sotto di essa spingendo per il debile della detta nimica pure in seconda, & passare sino al corpo a uerso, & quando pure uedesse la nimica spada hauere ferrata tanto la sua, che non potesse ferire in quella parte douria cauare della medesima seconda appoggiando la sinistra mano sopra il suo finimento, acciòche essa nimica non la pottesse rispingere, & andare à ferire quella parte superiore perdifuori. Li taglii uengono facilmente diffesi con la seconda, & con la quarta secondo, che uanno à cadere più in una [32] parte, che in una altra, & le dette raggioni riescono assai bene contra colloro, che non cognoscono il fondamento di essa guardia, & se qualch’uno uà à ferire quando stà nella guardia para il più delle uolte con la mane, & in tutti li suoi feriri passa determinatamente, mà è assai faticosa, & obligata, nondimeno à chi è bene essercittato in essa riescono molte cose. 5. |
Regulen über ein anderes und zwar geschrenktes Seconda Lager, so in folgender Figur zuersehen ist. No: 5. DAs Lager welches also ineinander gedrungen und gezwungen steht ist eine Seconda und ob sie gleich also gezwungen aussiehet, gehet sie doch mit groszer Geschwindigkeit und Gewalt wegen der Vereinbahrung der Stärken fort. Man fänget sie aber aufgericht an zuformiren, und je näher der Feind ankömmet, je mehr versenket sie den Leib, und [70] ziehet die Klinge an sich zurük, aufdasz wenn die Misur nun erlanget ist, unmüglich sei woferne sie in Presenz bleiben soll, dasz sie mit der Klingen weiter zurük oder sich mit dem Leibe mehr versenken könne: So ist auch von nöthen, dasz die Klinge von der Hand bisz zur Spitze eine gerade Linie mache, aufdasz der Feind auswendig nicht ankommen könne; Es musz auch die linke Hand über oder bei der Stirne geführet werden, um sich vor irgend einem geschleudertem Stosz, welches einen sonst ehe als diese Guardia völlig formiret überfallen könte, zuschützen. Wenn sie aber nun vollkömlich formiret ist, und der Feind rükkete allein um so viel zu, dasz er mit seiner Spitzen des jenigen Spitze so sich in dieses Lager geleget erreichete, und dieser seine Klinge frei hette, musz er einwendig geschwind in die Qvarta verwenden, und sich damit rumwerffen, weswegen er denn auch den vordersten Fusz im Lager also qver über setzet, aufdaz der Leib indem er stöszet ehe als sich der Fusz beweget aus der Presenz gehen könne, weil der Stosz also um ein merkliches verlängert und alsdann bisz an des Feindes Leib passiren wird. Wenn sich aber des Feindes Klinge wieder oder gegen diese hette wenden wollen, soll er nur unter derselben mit dem Leibe verfallen und die Seconda an ihrer Schwächen hineinstoszen, auch damit bisz an des Feindes Leib passiren; Und ob er gleich sähe, dasz seine Klinge vondes Feindes seiner, also gar, dasz sie daselbst nicht verletzen könte, ausgesperret were, soll er doch nichtsdestoweniger in besagter Seconda caviren und sich mit der linken Hand über dem Gefäsze helffen, aufdasz sie nicht von des Feindes Klinge zurükgetrieben werden könne, und alsdenn auswendig oben hinneinstossen. Die Hiebe werden mit der Seconda ausgenommen, oder auch mit der Qvarta, nachdem sie mehr auf einer als der andern Seiten verletzen wollen. Besagte Regulen gelingen auch wohl wieder dieienigen so das Fundament dieses Lagers nicht verstehen. Man pariret auch des meistens mit der linken Hand, wenn einer da man nur im Lager lieget stoszen wolte; So müszen auch alle Stösze aus diesem Lager passiret werden, aber sie ist doch mühesam genug und sehr verpflich= [71] tet, nichts desto weniger wenn sie wohl geübet worden, gehen viel Sachen darinnen gar wohl an und vonstatten. | |||||
[24] In this plate the sword is shown foreshortened, and the left side as far forward as the right. You have formed a guard in tierce and changed into seconde. The sword is turned so far to the left as to be quite foreshortened, and therefore only the cross or hilt is seen. This movement has been made in order to let the adversary approach. The body is bent forward so that it may not be hit save on the head and chest, and if the adversary attempts to hit you can parry with the left hand, which is held before the face, hitting with the same movement of the body and extending your sword into seconde. If you have completed the position when your adverysary[!] advances, you can change to quarte and hit below or above his sword, according as he comes low or high, and can carry the body out of line without parrying, though you may parry and hit with this seconde. If your adversary does not respond to this appel, you must not remain in this position, but change your line, remaining steady on your feet, so that he may not take the time on that change; for if your feet were being brought together you could not parry, but if you were withdrawing it would be well to parry, since your adversary could be sure of making a hit. If when he took the time, you were steady, you could advance or retreat according to the distance and intention of the adversary, because you would have adapted yourself for attack or defence at the same time. |
LA RAGGIONE PERCHE LA SEGVENTE FIGVRA è formata con la spada tanto in scurzo, & la parte manca tanto inanzi, come la drita. IL MOVlMENTO RAPRESENTATO DALLA SEGVENITE FIGVRA era in terza, & si è mutato in seconda, nellaquale la spada si uede tanto piegata uerso il sinistro fianco, che stà in giusta prospettiua, & per questo non si uede se non la croce cioè il finimento di essa, & hà fatto il detto moto per dare occasione al nimico di entrare; & il corpo stà in questa forma piegato inanzi acciò non essere ferìto se non disopra per la testa, & per il petto, & affine, che se l’ nimico lo uolesse ferire esso possi parare con la sinistra, laquale à tale effetto stà sopra la fronte, con ferire nelo stesso moto di corpo stendendo la sua spada pure di detta seconda, & affine, che se il detto moto ilquale si uede, fosse fermato quando uiene il nimico possi girare di quarta, & ferire per disotto, ò disopra della nimica secondo, che uenisse alta, ò bassa portando il corpo fuori di presenza senza parare, & non meno per potere parare, & ferire di detta seconda. Mà se il nimico non si mouesse per detta chiamata non si dee dimorare nel sopradetto mouimento mà mutare effetto, stando pero fermo de’ piedi, acciò il medesimo nimico non pigliase il tempo di quella mutatione, perche non si potrebbe parare rispetto alli piedi, che sariano nel moto di approsimarsi, mà [33] allontanandosi sarebbe buono perche esso nimico non potrebbe ferire alcerto, mà si potrebbe bene se il piede fosse fermo, quando il nimico entrasse pigliare il tempo, & andare inanzi, ò indietro secondo la distanza, & effetto, che hauesse uoluto fare l’ istesso nimico, & tutto per accommodarsi alla diffesa, ouero offesa in uno medesimo punto. 6. |
Die Ursachen warum die folgende Figur mit der Klingen also geschrenket und die linke Achsel so weit als die rechte hinfür gebracht sei. No. 6. DAs Wesen oder die Würkung so in deiser Figur vorgestellet ist war eine Terza und wurde in eine Seconda verwandelt, in welcher man siehet, dasz sich die Klinge gantz nach der linken Seiten gewendet hat, also dasz sie recht gegen einem über stehet, und man der halben nichts mehr als das Kreutz ./. das Gefäsze derselben sehen kan. Diese Bewegung aber ist gemacht um dem Feinde dasz er hinneingehe Gelegenheit zugeben; Der Leib stehet als übergebogen, aufdasz er nirgends als oben am Kopffe, oder auf der Brust könne getroffen werden: Damit er aber, wenn der Feind an besagten Orthen stoszen wolte, mit der linken Hand pariren könte, führet er dieselbe über der Stirn, und stöszet in gesagter Bewegung des Leibes zugleich mit, indem er seine Klinge in [72] Seconda nur ausstrekket; Ja aufdasz wenn dieses Lager schon vollkommen formiret wäre, und der Feind hereinbrechen wolte, einer die gyrirte Qvarta brauchen und also ober- oder unter der Klinge des Feindes, nach dem sie hoch oder tieff stoszen wolte, indem er den Leib aus der Presenz voltiret, ohne einige Parate zustoszen könne: oder man könte auch wohl zugleich pariren und in besagter Seconda verletzen. Wenn sich aber auf diese Chiamare der Feind nicht bewegen wolte, soltu dich in besagtem Lager nicht lange verweilen, sondern deine Würkung endern, must aber indem auf deinen Füszen ferm stehen, damit nicht irgend besagter Feind ein Tempo solcher Bewegung nehme, weil du alsdann in ansehung der langsamen Bewegung der Füsze, darinnen sie wollen vor sich treten, nicht würdest pariren können; Sondern es würde besser sein, wenn du dich entfernest, weil alsdenn der Feind dich nicht würde gewisz treffen können. Man könte aber doch wohl wenn die Füsse gleich ferm gewesen, in dem der Feind zutreten will, ein Tempo nehmen, und nachdem die Misur und die Würkung, so der Feind hat machen wollen, beschaffen vor sich oder zurükkegehen, aber alles um sich zuschikken in einem Tempo zugleich sich zuvertheidigen und den Feind zuverletzten. | |||||
[25] On what occasion you may make the extension in seconde seen in this plate. The extension seen in this plate is made in seconde with the right foot, and can be made on the inside or the outside of the adversary's sword in the time when he is passing. The lunge is made with the idea of letting his sword pass in the air without parrying, if, as might be, he is in a guard of tierce or quarte; but if he is in seconde you will not succeed with this lunge. If the adversary does not pass, it is not a good movement, for the body is so low and the feet so far apart that you cannot recover quickly enough to protoot yourself. You should certainly make this stroke if your adversary passes in order to save yourself from the impact of his sword without parrying, and hit him at the moment of his passing. If you realise the opportunity it is quite safe, because the body is so low, that the knee and the head are covered under the line of the arm in such a way, that even if the adversary attempts to hit at the centre of your body, he will pass far above. Thus the position deceives the adversary; but you must have a care not to form it at too great a distance, for he could then lower his point again before it had passed, and your head would be in greater danger than before. If the movement is made within the proper distance this danger ceases, for at the moment when your adversary's sword approaches, your body goes to meet him and causes his sword to pass with even greater celerity. |
CONQVAL OCCASIONE SI POSCIA FARE LA DISTESA di seconda come nella seguente figura siuede. LA DISTESA CHE SI VEDRA NELLA FIGVRA CHE SEGVE E fatta di seconda, col piè destro, & puossi fare così per di dentro alla nimica come per di fuori nel tempo che l’ nimico passa, & laquale botta si fà per lasciare andare uota la nimica con non parare, & questo facilmente si poteua trouare prima nella terza, ouero nella quarta, perche trouandosi nella seconda non la sarebbe così riuscibile, si come anco le l’ nimico non passasse non sarebbe ben fatta, perche il corpo tanto basso in passo sì largo non può ricuperarsi così presto per saluarsi; Questo effetto certamente si hà da fare quando il nimico passa per saluarsi dall’ empito della nimica spada senza parare, per poterlo ferire nel medesimo punto, che passa, & conoscendosi l’ occasione è cosa assai sicura, perche il corpo uà tanto basso, che l’ ginochio, & il capo resta coperto sotto la linea del braccio, in modo, che & ben’ anco la nimica fosse uenuta à ferire à meggia uita sarebbe passata molto disopra, talche con questa s’ inganna assai il nimico, mà è di mestieri hauere l’ occhio à non farlo in troppa lontana misura, perche esso nimico potrebbe rimettere la punta à basso prima, che la fosse passata, doue che sarebbe più pericolo della testa, che d’altro, mà facendolo in giusta distanza cessa cotale pericolo, perche in quel punto, che la nimica uiene il corpo liuà contra, & la fà passare con celerità anco maggiore. 7. |
Mit und durch was Gelegenheit einer die Seconda, so in folgender Figur gesehen wird stossen könne. No. 7. DEr Stosz so man in folgender Figur siehet, ist von einer Seconda mit dem rechten Fusz gemachet. Man kan aber diese Seconda so wohl aus- als einwendig an des Feindes Klinge indem Tempo, da der Feind passiret, anbringen, indem man des Feindes Klinge nicht pariret, sondern sie nur läszet fehl gehen. [73] es auch nicht gut zumachen, wenn der Feind nicht passirete, weil der Leib, wenn er mit einem weiten Tritt so tief verfallen were, sich nicht könte so geschwinde salviren und zurükkekommen. Es musz aber traun einer diese Würkung indem der Feind passiret, machen, damit er sich ohne parirung von dem auffallen der feindlichen Klingen befreie und ihn in dem Blick da er passiret treffe. Welches denn wenn einer diese Gelegenheit recht inachtzunehmen weisz, sicher genug ist; Denn der Leib gehet so niedrig, dasz das Knie und der Kopff unter der Linie des Armes sattsam bedekket seind, auch also, dasz wenn gleich des Feindes Klinge hette mittelwegs des Leibes wollen treffen, wäre doch der Stosz viel zu hoch überhingegangen, und der Feind betrogen worden sein. Aber man musz die Augen wohl mit darzunehmen und achtung haben, dasz man es nicht in gar zu weiter Misur mache, denn sonst würde der Feind seine Klinge ehe rimettiren oder versinken lassen können, als du hettest seine Spitze passiret, da dann dein Kopff mehr als was anders würde in Gefahr stehen; Wenns aber einer in rechter Misur machet, höret solche Gefahr bald auf: Denn im Augenblik da des Feindes Klinge kömmet, gehet ihr der Leib entgegen, und machet also, dasz sie mit noch gröszerer Geschwindigkeit als sonst vorbey passiret. | |||||
[26] How to make this extension in seconde by advancing the left foot in order to make a long extension. This extension is made with the guard in seconde, with the left foot brought forward in the time of the adversary's movement. Here you may clearly perceive how low a body may go and pass right to the adversary's body with swiftness, when you know how to control the body. This figure is drawn from life like all the others. With this manner of advancing the foot the lunge is very long. The body is protected by its low position. The left foot is carried forward, as is seen, but the right shoulder and side also go forward in such a manner that the lunge is as long as possible. The occasion for its use may arise, not only when the adversary tries to lunge or pass, but at the slightest time offered, when you are within such distance, that at the first movement you can pass the adversary's point. You may take the time to make such a lunge whether on the outside or the inside, for the body is so low that your adversary's sword remains far out of line, and all the more when his point has been no lower than your chest. Further this extension is made with great velocity, much more so than the first extension. |
[34] COME LEFFETTO DI SECONDA PASSATO di piede manco sià da fare per orinare lontano come per la seguente. MA QVESTO EFFETTO, CHE SEGVE E FATTO CON LA SEconda guardia passata col piè sinistro inanzi, in tempo del moto della nimica, & di quì si può chiaramente conoscere quanto un corpo possa andare à basso, & passare sino al corpo nimico con prestezza quando si sappia numerare bene; questa figura è tratta dal uiuo come tutte l’ altre, & con questa forma di passare, che in essa si uede, la botta si slonga molto, & oltre lo abbassarsi, ilche salua il corpo, portando il pie manco inanzi come si uede, la spalla nondimeno, & il fianco destro uanno sempre inanzi, in modo che la botta uiene à farsi longhissima, & l’ occasione del quale operare può nascere, non solamente, quando il nimico uuole ferire à piè fermo, ò passare, mà ancora in ogni picciolo tempo, quando l’ huomo si troua in misura, tanto che còl primo moto può passare la nimica punta, & si può pigliare il tempo di operare cotale botta tanto essendo di fuori, come di dentro, perche il corpo si abbassa tanto, che la nimica resta molto lontana dalla presenza, & tanto più quando la punta de’ detta nimica non sia stata più bassa del petto; & in oltre questa forma di pass uà con uelocità grande, & molto più ueloce il secondo, che il primo passo. 8. |
[74] Wie die Würkung der mit dem linken Schenkel passirten Seconda müsse gemachet werden, wenn einer wie in folgender Figur gesehen wird damit von weitem Treffen will. No. 8. DIese Würkung so hier folget, ist mit einer Seconda welche im Tempo der feindlichen Bewegung mit dem linken Schenkel vorauspassiret, gemacht; woraus man denn klärlich sehen kan, wie sehr sich ein Leib vertiefen oder versenken und mit Geschwindigkeit bisz an des Feindes Leib passiren könne, wenn sich einer recht darein zuschikken und die Glieder wohl zugebrauchen weisz. Dioese Figur ist wie alle die andern aus der lebendigen Bewegung oder nach dem Leben gezeichnet. Mit solcher Arth aber zupassiren die man in dieser Figur siehet, gehet oder reichet der Stosz viel weiter: Ja ob man sich gleich noch so sehr bükket, welches denn den Leib wohl schützet, indem man den linken Fusz wie hier zusehen vorsetzet, bleibet doch die rechte Schulter oder Seite einen Weg wie den andern allemahl voraus, dasz man also am allerweitesten ausstoszen kan. Die Gelegneheit aber diesen Stosz oder diese passata zumachen kan nicht allein daher kommen, dasz der Feind irgend hat wollen à piede fermo stoszen oder passiren, son [75] dern es kans einer auch auf dasz kleineste Tempo anbringen, wenn er sich nur so tieff in der Misur befindet, dasz er in der ersten Bewegung des Feindes Spitze vorbeikommen kan. Man kan auch so wohl aus- als einwendig solche Passata zumachen ein Tempo nehmen, denn der Leib verfället so tief dasz des Feindes Spitze, sonderlich wo sie im Lager etwas tiefer als die Brust ist geführet worden, weit von der Presenz deszelben bleibet: Es gehet auch über das in dieser Artz zupassiren sehr geschwinde fort; doch der zweite Tritt mit gröszerer Geschwindigkeit als der erste. | |||||
[27] This plate illustrates the guard in tierce, which arises from the guard in prime, as does the guard in quarte, as will be seen. The guard in tierce is less fatiguing than the other two, because the arm is in a natural position. But the hand is too low and the point inclined upwards at an angle, so that there are many exposed parts. If you draw a straight line from the point to the body you will see how great is the angle, and all the space between that straight line and the hand is exposed, where you may be hit on the outside and on the inside. On some sides it is not strong; further you may be hit before your hily is reached. If you wish to defend the upper parts you make so large a movement with the hand, that you cannot reach the defence in time, and your adversary can easily deceive you. Again, as your sword is at such an angle, in parrying you often go out of line, offering a great advantage to your adversary. Again, by bringing the sword into the straight line you weaken it, for the sword is always weakened by being extended, with great danger that your adversary's sword, if already extended, will remain the stronger, since the sword is always stronger after coming to rest than in its passage. Further, one who stands in this manner with his sword at an angle, can make little use of the disengagement, since his point has to make too great a circle and too large a movement. Nevertheless this guard may be used, because its nature is not always known. Though the sword is at a great angle and the body much uncovered, still you can sufficiently deceive your adversary by avoiding and freeing your sword by a half disengagement. Therefore he who can use these devices in time will defend and easily protect himself. The desire of the adversary to hit is increased by the sight of so much exposure, with the result that you may readily save yourself and hit your adversary. But we shall form a safer guard in tierce. |
[35] QVESTA FIGVRA, GHE SEGVE DI MOSTRA LA TERZA GVARdia, laquale nasce dalla prima, come anco la quarta secondo, che si uedrà; Questa terza è diminore fatica delle altre due, perche il braccio stà naturale, se bene la mano troppo bassa, & anco la punta molto angolata allo insù, & perciò con molti scoperti, in modo che se si tirasse una linea retta dalla punta al corpo si uedria quanto fosse grande l’ angolo, & tutto quel uacuo, che resta frà la detta linea retta, & la mano, è scoperto, oue si può ferire per di fuori, & per di dentro, & in alcuno di questi lati non hà foraa, oltre il potere essere ferito prima, che si gionga al suo finimento, doue che uolendo diffendersi le parti alte uiene à fare cosi gran moto con la mano, che non può giongere in tempo alla diffesa, & il nimico lo può facilmente ingannare, oltre che stando l’ huomo tanto angolato, nel parare uà spesse uolte fuori di presenza con dare gran comodità al nimico, & similmente dirizando la spada in retta linea uiene à debilittarla, perche nel stenderla si debilitta sempre con molto pericolo, che quella, laquaìe già è distesa non resti più forte, perche più forte è sempre la spada doppo che è fermata, che nelo andare; oltre diciò collui, che stà in questo modo angolato poco si può ualere delle cauationi hauendo la punta da fare troppo gran giro, & gran moto nondimeno si può anco adoprare questa forma, perche non ogni huomo conosce la sua natura, che se bene forma un’ angolo grande, per ilquale il corpo è così scoperto, con tutto ciò puo assai ingannare sfuggendo di uita, & di spada è meggie cauationi, talche chi saprà seruirsi di queste in tempo si diffenderà, & saluerà ageuolmente, perche uedendo un corpo così scoperto ere le e il desiderio al nimicò di ferirlo, il che caggiona, che questo tale facilmente si salui, & ferisca il detto nimico, mà si formarà una terza assai più sicura. 9. |
[75] Auf was Arth man ein Terza-Lager, weil solches nun in der Ordnung der Natur folget, und von der Prima herkömmet, formiren kan. No. 9. DIese Figur hier zeuget ein Terza Lager welches eben wie auch die Qvarta aus der Prima herkömt, wie man solches sehen wird. Diese Terza nun ist nicht so arbeitsam als die Prima und die Seconda, weil der Arm [76] natürlich stehet, ob gleich die Hand tief darzu die Spitze über sich angulirt geführet wird, und deswegen viel Blöszen giebet, dasz wenn einer von der Spitze bisz zum Leibe eine gerade Linie gezogen haben würde könte er sehen, wie der Winkel gar zugrosz were, denn alles das ledige was sich zwischen der gemachten rechten Linie und der Hand befindet, ist noch entblösset, und kan so wohl aus- als einwendig verletzet werden, so hat auch die Klinge an einer von beiden Seiten keine Krafft oder Stärke, zugeschweigen dasz einer ehe als die Klinge mit ihrem Kreutz herzunahete getroffen werden könte: Daher wenn sie die Obern-Blöszen schützen will, musz sie ebenfals mit der Hand grosze Bewegung machen, dasz sie mit der defension nicht à Tempo arriviret, der Feind sie hergegen leicht verführen kan: Uber das wird der so anguliret lieget, wenn er pariren will, leicht aus der Presenz gehen und also seinem Feinde zum stoszen gute Gelegenheit geben. Ingleichen wenn einer solchen Winkel in einegerade Linie verwandeln will schwächet er damit seine Klinge, denn im ausstrekken wird sie allezeit geschwächet mit gröster Gefahr, dasz diejenige so schon von anfang ausgestrekket ist, nicht stärker werde, weil sie wenn sie stille liegt, allemal starker ist, als wenn sie sich beweget. So kan sich derjenige welcher also anguliret lieget, der Cavationen wenig bedienen, weil die Spitze einen gar zugroszen Zirkul und grosze Bewegung machen müste. Doch kann einer nichtsdestominder dieser Arth Lagers gebrauchen, weil nicht ein jeder seine Eigenschaft verstehet, dasz obs gleich einen groszen Winkel machet, durch welchen der Leib so sehr entblöszet wird, man doch einen genug mit dem voltiren, wie auch mit der Klinge in denen Mezzecavationen betrügen kann, und sich also der solche Dinge zumachen weisz gar leicht à Tempo schützen, und geschwinde erretten wird; Denn wenn der Feind eine so grosze Blösze ersiehet, wächset ihme die Lust hinneinzustoszen, welches denn verursachet, dasz sich einer leicht retten und besagten Feind treffen kan. Aber Ich will hier noch eine bessere und sicherere Terza weisen. | |||||
[28] This plate shows the manner of forming a sword guard in tierce. The position of the arm and sword requires exactness for the hand should not be turned at all. Where the natural guard in tierce is weaker, this guard, also in tierce, is stronger. By the change of position the posture of the body has been changed to great advantage and improvement, since the angle of the side is well drawn back. The outside is defended and there is little uncovered on the inside. This is the true method of trying to engage the adversary's sword whether on the inside or the outside, for there is little or no movement to be made with the arm, but with the point of the sword only, which will so subject the adversary's sword as to keep it always underneath; your hand will then be between seconde and quarte in such a way, that you can engage with little movement in the one or the other line according to opportunity. Therefore we consider it to be one of the best guards. |
[36] NELLA SEGVENTE FIGVRA SI VEDE IL MODO DI FORMARE bene la terza guardia, il sito delquale braccio, & della quale spada si addimanda giustezza, perciòche la mano non è in parte alcuna uoltata, & doue la terza naturale più debile, questa, ancora, che una terza sia, è più sorte, & dalla sua mutatione, & suo sito ha mutato natura, & forma di corpo con assai uantaggio, & miglioramento per l’ angolo del fianco, che è molto lontano; Di fuori è diffesa, & di dentro hà poco scoperto, & questa è la uera maniera di andare à trouare la spada al nimico, sia di dentro, ò di fuori, perche si hà da fare pocò, ò niente di moto col braccio, mà con la sola punta della spada, laquale superarà di tanto la nimica, che la tenerà sempre disotto, la cui mano uiene ad’ essere situata trà la seconda, & la quarta in modo che con pochissimo moto si può trouare nell’ uno, ò nell’ altro sito secondo l’oportunità, che perciò noi la teniamo per una delle migliori. 10. |
[77] Wie man soll ein sicherer Terza Lager formiren No. 10. IN dieser Figur siehet man, wie ein gut Terza-Lager wohl zuformiren sei. Hier wird nun zum Lager des Arms und der Klingen eine gewisze Richtigkeit erfordert: Denn wie man siehet, so ist die Hand auf keine Seite gewendet, und da sonst die Terza von Natur am schwächesten ist, da ist doch diese, ob sie gleich auch eine Terza, stärker: Denn sie hat wegen ihrer Verenderung und wegen ihres Lagers jhre Natur und die Gestalt ihres Leibes verwandelt und solches Vortheilhafftig genug, doch am besten durch den Winkel in der Seiten, welche weit genug entfernet ist. Also ist sie auswendig geschützet und einwendig hat sie wenig Blösze, dasz darum dieses die rechte Arth ist, wodurch und womit man des Feindes Klinge es sei ein- oder auswendig finden und stringiren soll. Denn sie darf nur gar wenig oder auch gar nicht den Arm, sondern alleine die Spitze der Klinge bewegen, welche des Feindes seine also bezwingen und allezeit unter sich behalten wird. Es wird aber diese Hand also zwischen [78] der Seconda und Qvarta gehalten, aufdasz sie auf erheischenden Fall bald in die eine bald in die andere durch die allerkleineste Bewegung gehen könne, warum ich sie auch vor eine von denen allerbesten halte. | |||||
[29] We have wished to include this guard in tierce, since it has some advantageous principles, as we shall explain. It may be derived from the extended tierce if in that tierce the sword is in danger of being engaged, or for any other reason. You will free yourself by disengaging from that tierce to this, for the inclination of the body is now backwards, as may be seen; without moving the feet, but by merely bending the body and the knees the body is carried so far back, that the adversary cannot hit. At the same time the sword is freed. If your adversary attempts to engage it or to hit by carrying himself forward, with this guard you may very well hit him simply by again advancing your body forward at the same moment as he advances. Further it is a sufficiently good guard to practice, because it forms an oblique line towards the ground in such a manner, that your adversary cannot easily seize it. If he tries to engage your sword so low down without using the same advantageous position of the body, he will certainly be hit, since the distances are very deceptive. When within distance you appear to be far out of distance, and when the part which is bent backwards is bent forwards, without moving the feet, you extend more than half a sword's length by the mere inclination of the body, so that you reach further than your adversary estimates, if he has not understood the nature of the position. Thus as this guard may serve for this long reach, it may also serve for a withdrawal, since the distance is enlarged more than half a sword's length, with the result that your adversary cannot reach in time, and you have the advantage in defence and attack. But you cannot engage his sword before coming within close distance, unless you are careful to bring your feet together and bend the body as far forward as possible; then indeed you may reach his point though within wide distance. With this guard you should remember that the exposed part above is so far back that it cannot be hit if you know how to keep your sword free. Thus this position is very much to the purpose and good against various guards at an angle, and even extended guards. A body in such a position could easily and swiftly get out of line of the adversary's point, and with equal celerity pass on the one side or the other, except against the guard in prime, which could engage your sword down to the ground. |
[37] HABBIAMO IN QVESTO LVOGO VOLVTO METTERE QVESTA terza per hauere in se alcune raggioni uantaggiose, come s’ intenderà, laquale può deriuare dalla terza distesa in caso che essa terza distesa si trouasse in pericolo per esserli occupata la spada, ò per altra caggione, doue che l’huomo di liberaria col partirsi da quella, & calare in questa, perche tutto il pendicolare del corpo, che era prima in quella pendicola indietro, come si uede, & senza mouere li piedi, mà col solo piegare del corpo, & de’ ginochii uiene à portarsi tanto lontano, che l’ nimico non lo può ferire, liberando anco nel medesimo tempo la spada, che se l’ auerssario la uuole aqiustare, ò ferire portandosi inanzi l’ osseruattore di questa guardia può ferire lui benissimo col solo ritornare del corpo inanzi nel punto medesimo che l’ detto auerssario uiene, oltre diciò è una guardia assai buona da essercittare perche tiene la linea obliqua uerso terra in modo che l’ nimico non la può hauere tanto facilmente, chi la uolesse ritrouare così bassa senza operare l’ istesso uantaggio del corpo, restarebbe sicuramente ferito atteso che le distanze sono così falaci, perche gionto, che sia l’ huomo in misura li pare anco di essere molto lontano, & quando quella parte, che è piagata indietro si piega alò inanzi, senza anco mouere li piedi si allonga assai più di meggia spada col solo pendicolare del corpo si che ariua più di quello che l’ nimico può hauere giudicato, quando non habbia cognosciuto la natura del sito, & così come può seruire per ariuare altretanto può fare per dillongarsi perche la misura uiene à slargarsi più di meggia spada, ilche caggiona, che l’ nimico non può ariuare in tempo, & questi piglia la comodità della diffesa, & offesa, alquale non si può trouare la spada, che prima non si sia gionto nella misura stretta, se non si hà una diligente cura di metrersi in poco passo, & piegare il corpo inanzi più che sia possibile, che all’ hora purpure si potria ariuare alla sua punta standosi nella misura larga, & deuesi anco auertire [38] che quello scoperto di sopra è tanto lontano che non può essere ferito se il detto osseruattore della guardia saprà conseruarsi la spada libera; & così questa forma di sito uiene ad’ essere molto à proposito, & buona contra diuerse guardie angolate, & anco distese, perche un corpo in tale forma situato uscisse con facilità, & prestezza dalla presenza della punta nimica, & anco con la medesima celerità passa per l’ una, & per l’ altra parte, eccetto contra la prima, laquale l’ andarebbe à trouare sino in terra. 11. |
Ein Discurs über ein Unter-Lager in Terza, um zuverstehen wie man solches formiren und brauchen soll. N. 11. HIer habe ich diese Terza mithersetzen wollen, weil sie, wie sich es ausweisen wird, etzliche Vortheilhafftige Regulen in sich hält. Es kan aber diese UnterTerza von einer ausgestrekten hergekommen sein, aufn Fall sich dieselbe, dasz sie vom Feinde mögte stringiret werden, in Gefahr befunden hätte, oder auch wegen andrer Ursachen, da sich einer hat wollen vom stringiren befreien, und ist aus der ObernTerza in diese herunter gegangen: Denn der gantze Ober-Theil so in jener vorüberhienge, beuget sich nu wie man siehet zurük, und zwar ohne einige Bewegung der Füsze, sondern der Mann kömmet alleine durch Bügung des Lei= [79] bes und der Knie so weit entfernet, dasz der Feind nicht anreichen kan; Er befreiet auch in selbigem Tempo zugleich die Klinge, dasz wo der Feind mit einem Zutritt dieselbe finden oder hereinstoszen wolte, der so in dieser Gvardia lieget, durch blosze wiederüberbügung des Leibes im Tempo da der Feind zugehet gar wohl treffen kan. Uber das ist dieses Lager gut sich darinn zuüben, denn es hält die Klinge in einer schräden Linie gegen die Erden also dasz sie der Feind nicht so leicht finden kan; Ja wer sie so tieff, ohne dasz er mit gleichem Vortheill des Leibes und der Schenkel dagegen würkete, finden wolte, könte gar sicher verletzet werden, angesehen die Misuren gar zubetrüglich seind: Denn gesetzt dasz einer schon in der Misur ist, scheinets doch als wenn er noch weit entfernet wäre, da er doch, wenn das Theil, so hintergeleget ist, vorwärts gebüget wird, ob er gleich keinen Fusz dabei rühret, mehr als der halben Klingen lang nur mit überbügung des Leibes hinfürreichet; Auf diese Weise kan einer weiter, als der Feind, wo der nicht die Eigenschafft dieses Lagers verstanden, sich vermuthet gehabt, überreichen und treffen: Es kan sich einer auch eben so wie er sich fast noch einmahl so weit ausstrekket, wieder um so viel zurükziehen oder entfernen und also die Misur mehr als um einer halben Klingen lang brechen; Wannenher es geschiehet, dasz der Feind nicht à Tempo anreichet, der ander aber nimmet indem die Beqvehmlichkeit des parirens und stoszens inacht, weil ihm die Klinge niemand finden kan, er sei denn in die enge Misur gerathen, wo einer nicht fleiszige Achtung hat, dasz er sich in einem engen Schritt erhält, und mit dem Leibe so viel immer müglich überbüget: Denn in der weiten Misur wird eine Spitze die ander knapknap erreichen; Und dannenhero musz er noch ferner inachtnehmen, dasz die Obern-Blöszen wegen ihrer weiten Distanz nicht können erreichet werden, wo nur derjenige so dieses Lager brauchet seine Klinge frei zubehalten weisz. Darum ist nun diese Arth Lagers gut zu meinem Zwek; Es dienet wieder unterschiedene angulirte, wie auch wieder gerade gestrekte Läger zubrauchen, denn der Leib kan leicht und mit Geschwindigkeit auf eine oder an= [80] dere Seiten passiren, oder sonst auszer der Presenz der feindlichen Spitzen kommen, ohne wieder die Prima, welche bisz an die Erde um die Klinge zufinden gehen kan. | |||||
[30] This plate illustrates an extension in tierce, which shows how to advance the foot, bend the knee and incline the body sideways, so that there is little exposed. It also teaches how to stretch the wrist in order to lengthen the line and reach further in a lunge, and to recover after making the thrust. If you wish to recover quickly, you must not straighten the body, but bend the knee of the leg to the rear, bringing the weight of the body on to it low down, so that the forward leg is straightened and relieved of the weight in such a way, that you can easily and conveniently raise it. You perceive that all these things must be done in one time, and that if you do not know how to shift the weight of the body you cannot readily raise the foot, especially when the feet are far apart and the body much bent, except with great inconvenience, difficulty and length of time. |
L’ EFFETTO, CHE SI VEDE IN QVESTA FIGVRA, CHE SEGVE è una distesa di terza, ilquale di mostra come si deue auanzare, il piede, & piegare il ginochio pendicolare il corpo in filo, acciò che si faccia poco scoperto, & non meno insegna come s’ habbia da stendere la chiaue della mano per più allongare la linea, & ariuare più lontano ferendo à piè fermo, & rihauersi subbito data la botta, che uolendo essere pronto à ricuperarsi non si deua dirizzare il corpo mà si bene piegare il ginochio della gamba didietro portandoli sopra il peso di esso corpo così basso, che uenga à dirizzare quello dinanzi, & soleuarlo dal peso in modo che facilmente & con comodità si possi leuare, lequali cose tutte, si uede, che si hanno da fare in uno tempo medesimo, & che non sapendosi contrapesare bene il corpo non si può neanco leuare bene il piede, massime stando il passo tanto disteso, & il corpo così piegato se non con gran scomodità, & difficoltà, & anco longhezza di tempo. 12. |
Vom Stosz der Terza. No. 12. DIe Würkung so man an dieser Figur siehet ist eine ausgestoszene Terza welche zugleich zeuget, wie man im Stosz mit dem Fusz vorsich gehen, mit dem Knie sich beugen und den Leib seitwärts vorn übergeben soll, aufdz er wenig entblöszet bleibe; Sie lehret auch, wie einer die Hand um die Linie destomehr zuverlängern und im à piede fermo stoszen desto weiter zureichen ausstrekken, auch auf gegebenen Stosz geschwinde wieder zurükkekommen soll. Wenn denn einer geschwinde wiederzurükkekommen können will, darf er nicht den Leib erst wieder aufrichten, sondern musz nur das Knie des hintersten Beines bügen, und das Gewichte des Leibes also niedrig, wieder darauff legen oder fundiren, damit das vorderste Knie wieder steif und des [81] Gewichts entlediget werde, auch derselbe Fusz sich also leicht nach seinem Vortheil könne aufheben, welches doch alles in einem Tempo musz gemachet werden: Ja wer nicht weisz das Gewichte des Leibes also zudirigiren, wird die Füsze nicht wohl sonderlich wo sie im Lager weit voneinander stehen, und der Leib sehr übergebogen ist, ohne grosze Unbeqvemlichkeit und sehr beschwerlich auch mit einem langsamen Tempo fortheben können. | |||||
[31] This is a guard in quarte, the last of the four guards. It is formed simply with the arm at an angle, for which reason you are strengthened, and sufficiently covered on the inside. But you cannot disengage with much promptness, and on the outside are much exposed because of the angle formed by the arm and the hand. Although your position is strong, still if the adversary attempts to hit, it would not be so good to parry or to attempt to hit under the sword on the right side of the guard, letting his point pass without parrying. In this manner you would be most successful; for your arm being at such am[!] angle, if your adversary wishes to reach the body, his point must pass inside that arm. If the arm is extended towards the inside, it will cover all the part, which was seen exposed before, and will hit without touching the adversary's sword. With this guard, if you have an opportunity to change from quarte to seconde, the result will be effective, and still more so if the arm is fully extended from its present angle. The hand will be so far on the inside, that the adversary's sword cannot cover much in that line. When you change to seconde, an angle opposite to the first will be formed, so that your adversary cannot be in as strong a position. It will be all the better if in changing you continue on to the body. For if you measure the path taken by your point in hitting and the path taken by the adversary's point in defending, you will find that the path of the defending point is the greater. Although your hand has moved from one angle to another, a large movement, still the point will have gone to the body without shifting. Thus that large movement will have done damage to the adversary and not to yourself, if you have changed the front of your body by moving it out of the line of his point. |
[39] QVESTA CHE VIENE SARA LA QVARTA, ET VLTIMA DELLE quattro guardie formate semplicemente col braccio così angolata, per laquale raggione l’ huomo uiene ad’ essere forte, & à tenersi assai coperto di dentro, mà non può cauare con molta prestezza, & dalla parte di fuori fà gran discoperto per l’ angolo, che dal braccio, & dalla mano si forma, & seben quiui è più forte, niente dimeno se l’ nimico andasse à ferire nõ sarebbe si buono l’ andare à parare quãto l’ andare à ferire di sotto la nimica nel destro fianco della medema guardia, lasciando passare la pũta di detta nimica senza parare, che in questo modo benissimo riuscirebbe, perche stãdo il braccio in quella guisa angolato, è forza à chi uuole giongere al corpo, che la sua punta passi di dentro al detto braccio, ilquale, se si stenderà uerso la parte di dẽtro uerà à nascondere tutto quello scoperto, che già si uedeua, & ferirà senza toccare la nimica, & quãdo l’ osseruattore di detta guardia haurà occasione di uoltare di quarta in seconda farà grand’ effetto, mà più grande ancora, se il braccio sarà del tutto disteso per l’ angolo che la forma, stando nel sito oue si troua, & con la mano tanto in dentro, che caggioni alla nimica di non si potere coprire molto in quella parte, & quando si uoltarà poi in seconda uerà à fare un’ altro angolo contrario al primo, doue essa nimica non potrà hauere tanta forza, & tanto meglio uerà fatto questo, se nel uoltare sarà andato al corpo, perche chi misurasse la strada fatta dalla punta in andare à ferire, & quella fatta dall’ altra in andare alla diffesa, trouaria essere maggiore quella della diffesa, che dell’ offesa, che con tutto che la mano fosse andata di un’ angolo nell’ altro, che hauria caggionato gran moto, nondimeno la punta sarebbe andata al corpo senza mouersi dal punto, & così quel gran mouimento hauria fatto danno al nimico, & non à lui, quando hauesse mutata la prospettiua del corpo col partirsi dalla presenza della punta nimica. 13. |
Wie ein Qvarta Lager als das letzte unter den vieren kan formiret werden, auch ein Discursz von denen Bewegungen, so darinnen können vorkommen. No. 13. DIese so nun gefolget, ist die vierdte und letzte der vier Haupt Läger. Sie ist aber mit dem Arm also anguliret darum weil ein Mann auf solche Weise stark ist und sich einwendig genug versichern kan; Aber er kan [82] nicht gar geschwinde caviren, auch giebts auswendig wegen des Winkels so von dem Arm und der Hand gemachet wird eine große Blöße, und ob sie schon daselbst am stärksten ist, würde es doch nicht so gut sein wenn der feind stoszen wolte, dasz einer parirete als dasz er den Stosz unpariret fahren liesze, und in selbigem Tempo mit eben dem Lager unter des Feindes Klinge seiner rechten Seiten zustieße, welches denn auf obbesagte Manier gar stattlich würde angehen; Denn weil der Arm also anguliret, musz der Feind wann er antreffen will, nothwendig mit seiner Spitzen einwendig am Arme fortgehen, welcher Arm aber, wenn er sich weiter nach der einwendigen Seiten strekket, verbirget er alle die Blöszen so vorhin gesehen wurden und wird also ohne des Feindes Klinge zuberühren treffen. Wenn auch ein fleisziger Auffmerker dieses Lagers aus der Qvarta in die Seconda zuverwenden solte Gelegenheit haben, würde er eine gewaltigeWürkung machen, aber noch viel besser, wenn der Arm durch den Winkel den er machet gantz ausgestrekket würde, indem er in dem situ darinnen er sich befindet, bleibet und die Hand gantz einwarts wendet, welches den verursachet, dasz sich der Feind daselbst ./. einwendig nicht viel bedekken kan; Darnach wenn er die Hand wieder in Seconda wendet, wird er einen andern und zwar den ersten einen contraren Winkel machen, dasz also der Feind in seiner Klinge nicht wird Stärke genug haben zuwiederstehen. Solches aber alles wird besser gemachet sein, wenn er im wenden flugs zum Leibe zu wird fortgegangen sein. Denn wenn einer den einen Weg, welchen die Klinge so verletzet hat, und denn den andern, welchen die, so hat pariren wollen, gegangen ist, gegeneinander hielte und abmäsze, würde sichs befinden, dasz der Gang und die Bewegung der so sich hat beschützen wollen viel gröszer und weitläufftiger wäre, als der andern welche hat verletzet, dasz ob gleich die Spitze aus einem Winkel in den andern gegangen ist, welches denn eine grosse Bewegung verursachet hat, wird sie nichtdestominder zum Leibe ohne sich von ihrer Stelle zubewegen gegangen sein, und wird also diese grosse Bewegung dem feind und nicht dem der sie brauchet Schaden gebracht haben, wenn einer nehmlich die Prospective des Leibes geendert, und denselben zugleich aus der Presenz des Feindes Spitze gebracht hätte. | |||||
[32] The plate represents an extended guard in quarte. It is much better than the preceeding[!] one, and beyond comparison more cautious than all the others, because it keeps the adversary at a distance. He cannot be sure of engaging your sword, because with this guard you can disengage easily and subtly and with greater promptness than with the other on one side or the other. Its greatest strength is on the outside, where you cannot be hit, and the inside is assured by the effect of the hand being turned in that direction in such a way, that no path is left for the adversary to take, except by pushing your sword out of the line, a dangerous plan, as with this guard the disengage and double disengage are swift. His only resource is to try to disorder your sword by a feint or a movement, in order to hit below, carrying his body suddenly forward; for he could not reach with a lunge without putting himself in greater danger of an attack. Thus this is the most secure of the four extended guards, as we have said. There is no other which can be maintained with greater ease, with the sword more ready and free. |
[40] MA QVESTA RAPRESENTATA DALLA SEGVENTE FIGVRA sarà la quarta delle guardie distese molto migliore della antecedente, & più cauta senza comparatione di tutte l’ altre, perche tiene il nimico lontano da se, ilquale non può assicurarsi di trouare la spada, perche con essa guardia si caua molto facilmente, & sottilmente, & con maggiore prestezza dell’ altra tanto per una parte, come per l’altra; Hà la sua maggiore forza di fuori, oue non può essere ferita, & di dentro è assicurata dall’ effetto della mano uoltato in quella parte, in modo che non lascia all’ auerssario alcuna uia di ferire, se non col spingere la sua spada fuori di linea, effetto pericoloso, per essere detta guardia così pronta à cauare, & ricauare, restarebbe solo al detto auerssario di potere disordinarla con qualche finta, ò mouimento, affine di ferirla di sotto con portare uia il corpo subbito, perche à piè fermo non giongerebbe, che non fosse lui in maggiore pericolo di essere offeso, si che questa è la più sicura delle quattro distese, come si è detto, ne altra uiè, che con maggiore facilità possi tenere più pronta, & più libera la spada. 14. |
[83] Ein ander Qvarta Lager welches sicherer ist, weil es das Rappier mehr ausgestrekket hält. No. 14. AAllhier ist das vierdte der ausgestrekten Läger, welches aber viel besser als das vorhergehende, ja ohne Vergleichung sicherer als alle die vorigen, maßen es den Feind weit von sich hält, welcher sich dasz er die Klinge finden könne nicht versichren kan, weil man in diesem Lager sehr geschwinde und subtil ja viel hurtiger als die andern auf eine oder andre Seite caviret. Diese Qvarta hat ihre meiste Stärke auswendig, alwo sie nicht kan verletzet werden, und einwendig ist sie durch die Würkung so die Hand durch ihre Wendung alda machen kan versichert, also dasz sie dem Feinde keine Gelegenheit zutreffen überläst, wo er sie nicht zuvor aus der Linie zwinget, welches doch eine gefährliche Bewegung ist, weil dieses Lager allzu geschikt zu caviren und zu ricaviren: Wird daher selbigem Gegner alleine noch übrig sein, dasz er die Klinge mit einer Finta oder andern Bewegung könne disordiniren, auf= [84] dasz er geschwinde darauf unten verfalle oder passire, denn à piè fermo würde er nicht anreichen, dasz er nicht selber umgetroffen zuwerden in größrer Gefahr were, und ist also diese unter den vier gestrekten die sicherste, wie anderswo ist gesaget, weil man sonsten in keiner die Klinge leichter fertig und freier behalten kan. | |||||
[33] This is also a guard in quarte and very different from the two last. As you may see in the plate, the chest is exposed to the adversary and the feet in an oblique line. The intention is to move to either side according to the opportunity. The adversary cannot proceed to hit either your chest or head, for your feet are on either side of his sword, so that by lifting one of them your body will be out of line, so that you can hit in quarte, in tierce or in seconde, as the time and the occasion demand. With this guard you are uncovered on the outside. You invite your adversary to attempt a hit there, knowing that it is the strongest part, and that the angle is naturally of such a kind, that if he tries to hit in that place, by carrying the left foot in a straight line, extending the arm and leaving the hand in the same position, you will hit your adversary below on the right, or above by making the angle still larger and carrying the hand as high as the shoulder. In this way your lunge will be so strong that, however much your adversary tries to parry, he will still be hit. If he approaches too close without resolution, you should turn your hand from quarte to seconde, covering the head and carrying the left foot forward, and pass on with body and sword you will make a hit in the chest in seconde. With this guard you must take care to be so far advanced that as you change to seconde the head may penetrate the adversary's point with the bending of the body, and you may then proceed to hit and carry your left hand to his hilt, if adversary disengaged in order to hit in the lower lines, he would effect nothing, because your sword, which would have already begun to change into that line, would prevent him, and would hit on the outside, for you would have brought both sides of your body equally forward; this excellent result would be due to the length of your reach and the strength of your sword. In this way the only difference would be that your body would pass on the outside instead of the inside. With this guard you may easily use the left hand. |
[41] LA SEGVENTE, CHE E VNA QVARTA ANCOR LEI E MOLTO differente dalle due passate, perche, come nella sua figura si uede essa scuopre il petto al nimico, & stà col passo obliquo con disegno di portarsi ò nell’ una, ò nell’ altra parte secondo l’ opurtunità, ne si può andare à ferire quel petto, ne quella testa, che le sue gambe non siino l’ una dall’ un lato, & l’ altra dall’ altro della spada di quello, che uuole ferire, in modo che leuandone una remane il suo corpo sempre fuori della presenza, si che può ferire, & di detta quarta, & di terza, & di seconda, si come che richiede il tempo, & l’ occasione: Questa guardia è scoperta di fuori, & uà cercando, che l’ nimico uada iui à ferirla, sàpendo quella essere la più forte parte, & che naturalmente fà angolo in modo, che detto nimico l’ anderà pure in quel luogo à ferire, essa col portare il sinistro piede in retta linea, stendendo il braccio, & lasciando la mano nelo stesso luogo ferirà di sotto nel fianco destro del nimico, ouero di sopra con fare l’ angolo anco più grande & portando la mano alta, come la medema spalla, che in questa guisa haurà tanta forza che quanto più uorà il detto nimico parare tanto più rimanerà ferito, & quando il medesimo nimico troppo s’ auicinasse senza risolutione, quella uoltarebbe la mano di quarta in seconda, coprendosi il capo, con portare inanzi il sinistro piede, & passare dentro col corpo & con la spada, che ferirebbe nel petto con la detta seconda, mà deue auertire, chi usa questa guardia di essere tanto inanzi, che nel uoltare in seconda la testa possi penetrare la punta nimica con lo piegare del corpo, & poi andare à colpire con penetrare la sinistra sino al finimento, che se bene il nimico cauasse perferire disotto non farebbe cosa buona per rispetto della spada uoltata, perche la spada, che già hà cominciato à uoltarsi per fare la cauatione in quella parte lo impedirebbe, & ferirebbe di fuori per ritrouarsi già col corpo uoltato inanzi tanto con un fianco, quanto con l’ altro, buona caggione, della lontananza dello scoperto, [42] & della forza della spada, & in questo modo non ui sarebbe altra mutatione, se non che l’ corpo quale dourebbe andare di dentro andarebbe di fuori; & in questa guardia si può facilmente usare la sinistra mano. 15. |
Noch ein ander Qvarta Lager, welches die gantze Brust darzeuget, und daher beide Schenkel in die qvere stellet. No. 15. DIeses ist auch noch eine Qvarta, aber von denen vorigen beiden in vielen unterschieden; Denn wie man in der Figur siehet, so bietet und entblöszet sie selbst dem Feinde die Brust, und stehet mit dem Schritt in die qver mit dem Vorsatz sich auf erheischende Gelegenheit auf eine oder die andre Seite zubegeben; Es kan aber keiner nicht nach solcher Brust oder nach dem Kopff stoszen, es sei denn das eine Bein dessen, so da soll gestoszen werden, auf der einen und das andre auf der andern Seiten des Rappiers dessen so verletzen will, also dasz wenn der so dieses Lager brauchet ein Bein auf= [85] hebet, sein Leib allemahl auszer der Presenz des Feindes Spitzen kömmet, und kan er alsdann entweder besagte Qvarta oder die Terza oder eine Seconda, so wie es das Tempo und die Gelegenheit erfodert, hinneinstoszen. Diese Lager läszet auswendig eine Blösse, man versuchet aber wohlwissend dasz es daselbst am stärkesten ist damit den Feind, dasz er mögte dahinneinstoszen, ja es verstehet sich, dasz sie den Winkel von Natur auf solche Arth machet, dasz wo der Feind schlechterdings in denselben stoszen wolte, würde sie ihn selbst an dem Orth unten in der rechten Seiten treffen, indem sie den linken Fusz in einer geraden Linie liesze vor sich gehen, den Arm ausstrekkete, und die Hand nur gleichzugehen liesze; Oder sie könte auch oberhalb treffen, indem sie noch einen gröszern Winkel machete, und die Hand wie die Schulter etwas hoch führete, denn auf solche Weise wird sie so stark, dasz je mehr der Feind wird pariren wollen, je mehr wird er getroffen sein. Wenn sich auch der Feind ohne einen gewissen Vorsatz gar zu sehr nähern wolte, würde sie die Hand aus der Qvarta nur in die Seconda wenden, damit den Kopff dekken, den linken Fusz fortbringen, und also mit dem Leibe und der Klingen einwendig passiren und ihn mit besagter Seconda auf die Brust verletzen. Es soll aber derjenige, so dieses Lager brauchet, hiebei merken, dasz er so weit müsze hinfür sein, dasz indem er die Hand aus der Qvarta in Seconda wenden will, der Kopff hinter des Feindes Spitze verfallen könne, indem er nur den Leib überbüget; Denn darnach mag er verletzen, und mit der linken Hand bisz an des Feindes Gefäß gehen, dasz ob auch gleich der Feind um unten zustoszen caviret hätte, es ihm doch fehlen würde, angesehen die Klinge schon gewendet; Denn das Rappier welches um eine Cavation zumachen sich zuwenden schon hat angefangen, wird ihn an der seinigen verhindern, und also auswendig verletzen, weil sie sich mit so wohl einer als der andern Seiten des Leibes so weit hinfür gewendet zusein befindet. Dieses nun ist eine gute Regul so wohl wegen entfernung der Blöszen, als wegen der Stärke der Klinge, denn also ist keine andere Verenderung vonnöthen als dasz da der Leib hätte sollen einwendig gehen, kömmet er auswendig. Man kan auch in diesem Lager leicht die linke Hand gebrauchen. | |||||
[34] Although this guard resembles the last, nevertheless it has considerable differences, for in this guard the sword is held in such a manner, that the hand does not form an angle on the outside, but the wrist is inclined inwards, and bends the sword so that it appears foreshortened. Whereas the other quartes are stronger on the outside, this quarte has more power on the inside owing to this foreshortening of the sword, and also to the position of the body with the left side so far forward, as is seen. We have included this guard in order to show how you may advance on the inside to subject the adversary's sword, which is in seconde at an angle. You must know that the greater the angle your sword forms, the greater is your force in that line. If the adversary tried to hit your exposed part, he might himself be hit through the angle of the guard in seconde, if he did not hit with the advantage of the line for the straight line always reaches farther, or did not avoid with his body, or wait until his opponent came within distance in order to be able to hit and withdraw. But for passing at the fitting opportunity without being hit there is no sounder or better position than the one seen here. For, whatever the angle of the adversary's sword, this foreshortened sword will push his way and will be stronger than the seconde, so that he will be forced to change his guard, or retreat; otherwise you will at the slightest move-[13] proceed to hit and pass to the body. |
ANCORCHE QUESTA GVARDIA RASOMIGLI LA MEDEMA passata, nondimeno è assai diuersa, perche questa stà con la spada in modo, che la mano non forma angolo dalla parte di fuori anzi, che più tosto piega il nodo della mano indentro, & forma un scurzo della spada che perciò si uede più corta, & doue che l’ altre quarte sono più forti di fuori, questa è più uigorosa di dentro si per quello scurzo della spada, come per il moto del corpo, che si uede tanto oltre con la sinistra parte, & si è posta in questo luogo per dare à diuedere come si possa andare di dentro ad’ occupase una spada in seconda guardia angolata, sapendosi, che quanto è più grande l’ angolo, che la forma, tanto è maggiore la sua forza in detta parte, & chi uolesse ferire il suo scoperto potria anch’ egli restare ferito dall’ angolo della seconda, quando che non ferisse col uantaggio della linea, perche la retta ariua più sempre, ouero non scansasse di uita, ò aspettasse, che l’ auerssario uenisse in misura per poterlo ferire, & saluarsi in dietro, mà per uolere passare inanzi con occasione senza restare fetito non ui è il più uero, ne il migliore modo di quello, che quiui si mira talmente situato, che stia pure la nimica quanto uuole angolata, che quello scurzo la serrarà di fuori, & farà più galiardo della seconda, in modo che detto nimico sarà neccessitato di mutare guardia, ò ritirarsi, altrimenti questo effetto andarà tanto inanzi, che ad ogni minimo moto ferirà & passarà sino al corpo. 16. |
[86] Ein mit der Klingen und linken Achsel geschrenktes Qvarta Lager, welches wieder die angulirte Seconda kan gebrauchet werden. No. 16. OBs gleich scheinet diese No. 16. sei mit der vorigen No. 15. gantz einerlei, so ist sie doch nichtsdestoweniger in vielen unterschieden: Denn diese hält die Klinge also dasz die Hand auswendig keinen Winkel machet, sondern sie beuget vielmehr das Vordergelenke des Armes einwarts und verschrenket das Rappier, darum sie auch so kurtz scheinet. Da auch sonst andere Qvarten ihre meiste Stärke auswendig haben, ist diese wegen des verschrenkten Rappiers einwendig am hurtigsten, worzu denn die Bewegung da die linke Seite so weit hervorstehet, sehr hilffet. Sie ist aber hierhergesetzet um klär- und eigentlich zubeweisen, wie man könne eine Klinge so in der angulirten Seconda lieget einwendig stringiren. Denn wenn einer verstehet, das je gröszer der Winkel ist den die Se= [87] conda machet, je gröszer ist auch die Stärke an selbigem Orthe, dasz wer da wolte in selbe Blösse hinneinstoszen, leicht könte durch den Winkel der Seconda getroffen werden, wo er sich nicht im Stosz des Vortheils der Linie bedienet hätte, weil die gerade Linie allezeit am weitesten reichet, oder hätte nicht den Leib voltiret, oder gerükket, dasz er hätte treffen und zugleich auch zurükkommen können. Wenn aber einer nach Gelegenheit ohne getroffen zuwerden gerne wolte wieder eine solche angulirte Seconda fortgehen, dem kan nicht beszer gerathen werden, als dasz er sich in solches hiergewiesenes geschrenktes Lager lege; Denn des Feindes Klinge mag anguliren wie viel sie nur immer will, wird sie doch allezeit durch das Scurzo ausgeschlossen sein, und diese Qvarta wird viel hurtiger als die Seconda etwas gebrauchen können, also dasz der Feind entweder sein Lager zuverendern, oder sich zuritiriren wird gezwungen sein, sonsten würde diese Würkung so weit hinfürgedeihen, dasz sie auf jede kleineste Bewegung stoszen und bisz an des Feindes Leib pasziren könte. | |||||
[35] |
[43] ANCO IN QVESTO LVOGO, SI E MESSA VNA DISTESA DI quarta, che si dee usare ferendo à piè fermo, acciò si conosca l’ effetto che hà da fare esso piede, & anco il corpo, & la mano insieme, laquale distesa ferisce coti la tetta coperta, & senza uolgerla, come alcuni fanno, che meglio sarebbe uoltare, & alzare, un poco la mano, & se prima fosse stata distesa in detta quarta la mano hauria fatto poco moto, nondimeno ò picciolo, ò grande, che si fosse, meglio sarebbe senz’ altro, che uoltare, & non uedere l’ operationi nimiche, ouero tenere la testa indietro, credendo, che sia più sicura, il che è errore manifesto, perche quanto più è lontana la testa dal proprio forte, tanto maggiore è il pericolo, che porta, essendo più scoperta, oltre che, quello, che tiene la testa indietro non può slongare la botta tanto che basti per ariuare al corpo nimico: Similmente si hà da tenere la uista alla mano della spada nimica non solo à piè fermo, mà passando, & girando il corpo, & siasi conquale si uoglia piede. Mà quanto al ricuperare di un corpo tanto piegato inanzi, & slargato di passo dourassi seruare la regola discritta da noi nel luogo, oue habbiamo parlato della distesa di terza à piè fermo. 17. |
Hier wird gewiesen, wie man die Qvarta à piè fermo stoszen soll. No. 17. [88] AN diesem Orthe wird nun auch der Qvarta Stosz gewiesen, welchen einer gebrauchet, wenn er à piè fermo verletzen will, aufdasz man die Würkung so der Fusz, die Hand und der Leib zugleich machen müszen, erkenne. Dieser Stosz nun trifft und bleibet mit dem Kopffe ohne desselben Verwendung bedekt genug, ob ihn gleich etliche verwenden, da es doch beszer ist die Hand ein wenig verwenden und verhöhen: Wenn auch die Klinge in dieser Qvarta erste were ausgestrekket gelegen, würde sie desto kleinere Bewegung gemacht haben; Nichtsdestoweniger sie sei klein oder grosz wie sie denn würde gemacht sein, würde es doch besser sein, als wenn einer den Kopf also wendete, dasz er des Feindes Würkungen nicht erkennen könte, oder wenn einer den Kopf weit zurükhielte, in Meinung, er würde desto sicherer sein, welches doch ein öffentlicher Irrthum ist; Denn je weiter der Kopf von der Stärke seiner eigenen Klingen entfernet, je gröszer ist die Gefahr, darinnen er sich befindet, weil er mehr entblöszet, zugeschweigen dasz der den Kopf so zurükführet seinen Stosz nicht so weit ausstrecken kan, dasz es genug were des Feindes Leib damit zuerreichen. Ingleichen soll einer dem Feinde allezeit auf die Faust darinnen er den Degen führet sehen, nicht allein im à piè fermo stossen, sondern auch im passiren und voltiren, es geschehe mit welchem Fusz es wolle. Was aber anlanget, wie einer wenn er den Leib also übergebogen und den Tritt ausgetreten hat, wieder zurükkommen soll, musz er die Regul, so an dem Orth, wo von dem Terza Stosz à piè fermo ist geredet, beschrieben, inachtnehmen. | |||||
[36] Here follows another extension in quarte, in which the right foot has been turned. The lunge is made by advancing the right foot only, turning it in the air in such a manner that the turn is complete as it reaches the ground, as you may see. The plate shows that the turning of the foot most[!] begin with the lifting of the body, so that as you advance all the part which was visible when on guard is taken out of presence and the adversary's sword passes in empty air. It shows that you must hit the adversary at the same moment, recover the right foot at once and return on guard in case he has not passed or had not meant to pass. After completing this stroke you could follow with the left foot turning it backwards and continuing to the adversary's body, if he had not passed, as we said; for if he had passed the first stroke would have sufficed. |
[44] QVI SCORGE PVR’ ANCO VN’ ALTRA DISTESA DI QVARta, laquale hà girato il destro piede, & l’hà fatto ferendo à piè fermo con auanzare solamente esso destro, ilquale si è uenuto girando in aria, in modo che ariuato in terra hauea finito il giro, come si uede, laquale forma mostra che la circonferenza hà da cominziare nel leuarsi del corpo, acciòche come uiene inanzi si uenga leuando di presenza tutto quello, che si uedeua stando nella guardia, & accióche la punta nimica passi uuota, & mostra, che si hà da ferire il nimico nel medesimo punto con racogliere subbito esso destro piede, & rimettersi in guardia, per non essere il detto nimico passato, ò per non hauere questi uoluto passare, perche si potrebbe anco doppo l’hauersi fatto questo effetto seguittare col piede sinistro girandolo per didietro, & andare sino al corpo nimico, quando non fosse passato, come si è detto, perche se fosse passato farebbe stato à sufficienza del primo effetto. 18. |
Ein andrer mit dem Scanso di Vita uf dem linken Schenkel gyrirter Qvarta Stosz. N. 18. HIer zeuget sich noch ein andre Qvarta welche den rechten Fusz in der Lufft gedrehet oder gyriret und solches gethan hat, indem sie mit dem rechten Fusß allein um à piè fermo zustoszen ist vor sich gegangen, der [89] Fusz hat sich aber in der Lufft umgedrehet also dasz wie er ist uf der Erden ankommen der gantze gyrus ist wie man siehet vollendet gewesen. Welches uns denn lehret, dasz man so bald der Leib gebogen wird auch den Fusz zuverwenden oder zugyriren müsze anfangen, aufdasz je mehr er hinfürkommet je mehr alles dasjenige was man im Lager à Presenza gesehen und sehen können, aus selbiger Presenz komme, und also des Feindes Spitze müsse fehl gehen. Sie zeuget auch dasz man den Feind müsse in selbigem Moment treffen, und sich mit demselben rechten Fusze flugs wiederzurük in das Lager begeben, wo nicht irgend der Feind nicht passiret hätte, oder wenn dieser gyrirende nicht hätte passiren wollen; Denn man hette auch wohl nach dieser verrichteten Würkung mit dem linken Fusz hinten num passiren und bisz an des Feindes Leib fortgehen können, wenn der Feind, nicht passiret hette; Denn hette er passiret, so were es an der Würkung des ersten Trittes genug gewesen. | |||||
[37] This is another extension in quarte, made with a turn of the left foot. It may be used in the time when your adversary tries to hit on the inside in tierce or seconde, or to pass below. You can similarly make use of it if he offers a time when on guard. But it must be accompanied by a movement of the feet, so that he cannot break ground, while you are trying to hit. Otherwise you would be hit, as you would also if you gave your adversary time to change line. For in turning in this manner, if your first plan fails, you can form no other. Therefore you should not turn unless you are certain that you are so far advanced, that with the first movement of the feet the body can pass the adversary's point, for otherwise you would be easily hit in the back. After turning the left foot it is well to follow right on to his body in order to get entirely out of presence and in order that he may not withdraw his sword and return to hit you. If your adversary passes it will be unnecessary to do anything but the turn in order to get out of line and escape the impact of his sword. In this case you would be more successful, as you could not be deceived. |
[45] MA QVEST’ ALTRA QVARTA GIRATA COL SINISTRO PIEDEI SI può fare nel tempo, che l’ nimico uuole ferire di dentro di terza, ò di seconda, ouero passare disotto, si può, si milmente andare à ferire quando esso mimico fà il tempo stando nella guardia, mà che sia accompagnato dal moto del piedi, acciòche egli non possa rompere di misura, mentre che si uuole ferrirlo, perche altrimenti si restarebbe ferito, si come si restarebbe anco ferito se si desse tempo al detto nimico di mutare effetto, perche colui, che gira in questa forma, se li falla il primo disegno non può pigliare nouo partito, pertanto non si dee girare non si conosce certo di essere tanto oltre, che col primo moto de’ piedi il corpo possi passere la punta, perche in altro modo se restarebbe facilmente fedito nella schiena, & doppo che si hà girato il piede sinistro è ben fatto seguire sino al corpo nimico per leuarsi intieramente di presenza, & affine che esso nimico non ritiri la spada, & torni à ferire, mà in caso, che l’ nimico passasse non occoreria fare altro che girarsi per leuarsi di presenza, & sfuggire l’ empito della sua spada, che certo saria più riuscibile, perche non si potrebbe essere ingannato. 19. |
[90] Noch ein anderer mit dem linken Schenkel Voltirter Qvarta Stosz, so genennet ist il fuggire di Vita. No. 19. ABer diese andre Qvarta, so mit dem linken Schenkel gedrehet oder rumgewendet ist, kan gemachet werden im Tempo, da der feind einwendig mit der Terza oder mit der Seconda treffen oder auch unten wegpassiren will. Ingleichen kan man damit den Feind verletzen, wenn er nur im Lager liegend ein Tempo gäbe, aber dabey musz denn eine Bewegung der Füsze sein, aufdasz er indem du auf ihn zustossen wilst, die Misur nicht brechen könne, denn anderst würdestu verletzet sein. Also würdestu auch getroffen werden, wenn du deinem Feinde seine Würkung zuendern Zeit lieszest, weil derjenige so sich wie hier No. 19. zusehen drehet oder voltiret, wo ihm sein erster angriff nicht angehet, sich zu nichts neues risolviren, oder seine Würkung verendern kan. Und soll einer derowegen nicht voltiren, er sehe denn gewisz, dasz er so weit gelanget sei, dasz er durch die erste Bewegung der Füsze mit dem Leibe aus der Presenz des Feindes Spitzen kommen könne, denn sonsten könte er leicht auff den Rükken getroffen werden. Es ist auch gut, dasz einer nachdem er sich also auf dem [91] Rechten Fusz mit dem linken in der Lufft gedrehet hat mit dem rechten und also fort bisz an des Feindes Leib verfolge, um sich völlig aus der Presenz zuhelffen, aufdasz der Feind seine Klinge nicht zurükziehe und nochmals von sich stosze: Aufn Fall aber, da der Feind passiret hette, würde anders nichts vonnöthen sein, als sich nur also umdrehen, sich damit aus der Presenz zubringen und das auffallen der feindlichen Kl. zuvermeiden, welches denn gewis bester maszen angehen wird, weil man auf solche Weise nicht getrogen werden kan. | |||||
[38] This extension in quarte, advancing with the left foot, shows how the foot should be carried and the body inclined in order to make the lunge as long as if made with the right foot; it shows too how to carry the body out of line, so that the sword may defend better. This is certainly a better method of attacking, because you can change from one line to another as you advance, and form a new plan. But it requires a good knowledge of weak and strong points, because it is not a question of avoiding with the body, but of dropping under the adversary's sword. Moreover, in any case you defend with the forte of the sword according to opportunity. This method of hitting is more vivacious and the sword is stronger than in any other method of hitting in quarte. |
[46] QVESTA DISTESA DI QVARTA PASSATA COL PIE SINISTRO dà ad’ intendere come si deua portare esso piede, & pendicolare il corpo per dare la botta tanto longa, come se fosse fatta col destro & come si deua sfuggire il corpo, acciò la spada meglio possa diffendere, & certo, che questo è meglior modo per assalire, che non è il girare perche si può mutare di uno in un’ altro effetto nell’ andare, & pigliare nouo partito, mà si ricerca essere buon conoscittore del debile, & del forte, perche quì non si tratta di scansare di uita mà di abbassarsi sotto la spada nimica; del resto si diffende in ogni caso col forte della spada secondo l’ oportunità, & questo modo di ferire porta seco maggiore uiuacità & anco la spada resta più forte, che in quale si uoglia altra maniera di ferire di quarta. 20. |
Ein mit dem linken Schenkel passirter Qvarta Stosz. No. 20. DIeser Stosz der Qvarta so mit dem linken Fusz passiret ist, giebet zuverstehen, wie man denselben Fusz forttragen und den Leib überlegen soll, damit er eben so weit reiche, als wenn er mit dem Rechten Fusz gemachet worden wäre, auch wie man müsze den Leib wegnehmen, damit ihn die Klinge destobesser beschirmen könne. Und gewisz diese Arth ist besser einen anzugreiffen, als das voltiren: Denn man kan hier im fortgehen eine Würkung in die andre verwandeln, und sich zu etwas neues risolviren; Aber sie erfodert, dasz man von der Stär- [92] ke und Schwäche der Klinge wohl zuurtheilen wisse. Denn hier ist es nicht um das wenden des Leibes zuthun, sondern vielmehr wie man möge unter des Feindes Klinge verfallen können. Im übrigen schützet sie sich auf allen Fall mit der Stärke der Klinge nachdem die Gelegenheit vorkömmet; Solche Arth zuverletzen hat sonderliche Hurtigkeit in sich, denn die Klinge alhier viel stärker als in einigem andern Qvarta Stosz befunden wird. | |||||
[39] This plate illustrates the first hit in quarte. It is a lunge against a guard in tierce. It may arise as follows. The adversary, who is in tierce has made a feint of hitting on the inside, whilst you also were in tierce. He has come forward in order to make you parry. But you have taken the time, carried your hilt up to his point and driven on your point to make a hit. By advancing the right foot, bending the body and turning your hand into quarte, you have encountered and hit your adversary, as may be seen, at the moment of his coming forward. He has not been able to parry, while his foot was in the air and he was advancing. Similarly it may happen that you both are in tierce on the outside, and the adversary has tried to disengage to the inside line, advancing his sword and body to force you to parry, with the intention of hitting you in that time by changing from tierce to seconde, and lowering his body; or he intended to return to the outside in tierce in order to hit over the sword. Both these methods would have been effective, if you had done what he desired. But you, being steady on your guard, with your sword free, within wide distance, were awaiting the time in order to hit or seize some advantage. As soon as you saw the movement of his sword and body bringing him forward, you realised that although he had not moved his feet, he still could not break ground, since it is impossible to advance and retire at one moment. Hence you may realise the great danger of moving without a time, in order to advance, when you are already within wide distance, especially when the adversary's sword is free. If you are forced to move in order to free yourself from some danger it is better to retire than to advance, especially if your adversary is steady on his guard, and thus free yourself in such a manner, that if your adversary attempts to hit in that time, you can defend yourself and attack at the same instant. Even if you have moved your sword and body, provided that your feet are steady, you can always save yourself when within wide distance. But within close distance the smallest movement involves great danger, as we showed in treating of distances and times. Further you must consider that, while your adversary's sword is free and steady, to make a feint, in our judgment, is merely to hurry fruitlessly. If your adversary makes a feint, he can never hit, even though you parry, as long as you are steady on your feet,[!] If after a feint he tries to hit, you can break ground, so that he will not reach, and will be thrown into disorder with danger of being hit before he recovers. Therefore to make a feint you must await some movement of your adversary, or not his sword free, but engage it first, so that he cannot hit in that line. Afterwards you can feint, without abandoning your advantage. In making this feint you must go forward, so that if he does not parry, the feint will hit, and if he parries, you can by a change of line reach his body, before he can save himself by breaking ground. For the one who has moved with the feint will arrive more quickly than the one who has awaited the second time in order to break ground. If when you make the feint, your adversary breaks ground, you must not advance, for you are too far away. You must stop and return to the engagement. If the one who has been hit in the present case, had observed that principle sooner, he would have been the hitter rather than the hit, or would at least have saved himself. We have made a long discourse on this present hit with respect to its advantages and dangers, and not only that, but the manner of its arising, and how else it might arise, and how he who was hit might have found safety. For before the attack many remedies were possible, though they were of no avail after the thing was done. But in the following hits we shall state only the cause and the effect, leaving the rest, lest the reader should be wearied. |
[47] QVI E LA PRIMA FERITA DI QVARTA RAPRESENTATA DALla figura uenente fatta à pie fermo contra una terza guardia, laquale può essersi caggionata, perche quello, che è nella terza haurà uoluto fingere di ferire di dentro, mentre che l’ altro ancor esso era in terza in modo che si è spinto inanzi per farlo parare, mà quelli pigliando il tempo, & portando il finimento alla punta nimica è andato con la sua punta à ferire auanzando il piè destro inanzi, & con piegare il corpo, & uoltare la mano in quarta hà incontrato, & ferito il nimico, come si uede, nel punto istesso, che esso nimico ueniua, che hà causato, che egli non hà potuto parare, mentre era così in aria col piede, & ueniua inanzi; Parimenti può essere, che tutti dui si trouassero con la terza di fuori, & che quello, che è restato ferito habbia uoluto cauare di dentro auanzando la spada, & il corpo per mettere l’ auerssario in neccessità di parare con intentione di ferirlo in quel tempo uoltando di terza in seconda, & con abbassare il corpo, ouero ritornare di fuori di detta terza per ferire sopra la spada, si come tutte due queste raggioni si sarebbeno effettuate, quando l’ auerssario detto, hauesse fatto si come questi desideraua, mà quello, che era fermo, con la spada libera in mano, & che si trouaua nella misura larga aspettando il tempo di potere ferire, ò di pigliare qualche uantaggio, subbito ueduto il moto della nimica accompagnato dal corpo, quale si è portato inanzi, hà cognosciuto, che il nimico, che è il ferito, se bene non hauea mosso il piedi non poteua con tutto ciò rompere di misura, atteso che non si può auicinare, & dillongarsi in un medesimo punto, & quindi si può conoscere quanto graue pericolo sia il mouersi senza tempo, massime quando la nimica spada si troua [48] libera, per auicinarsi essendo già fermato nella misura larga, che quando l’ huomo fosse astretto à mouersi per liberarsi da qualche pericolo saria meglio ritirandosi, che approssimandosi, massime stando il nimico fermo, & trattando di liberarsi, & quello affine, che se esso nimico uolesse in quel tempo ferire si potesse diffendere, & offendere in uno medesimo instante, & anco che si hauesse mossa la spada, & il corpo pure, che il piede fosse fermo sempre si potria saluarsi mentre si fosse nella misura larga, mà nella misura stretta ogni picciolo moto porta seco gran pericolo, come si è mostrato quando si è trattato delle misure, & tempi, in oltre deuesi considerare, che mentre la nimica trouasi libera, & ferma à uolerli fingere contra non è altro (per nostro giuditio) che cercare di precipittare infruttuosamente, perche quello, che uuole fingere non può mai ferire, anco che l’ alrro uada à parare solo che stia fermo de’ piedi, & se dopò fatta la finta uorà ferire, si potrà dall’ altro rompere di misura, che così lui non ariuarà, & restarà disordinato con pericolo di essere ferito prima, che si rimetta, in modo tale, che à uolere fingere, è di misteri l’ aspettare qualche moto dell’ auerssario, ouero non lasciare la nimica libera, douendosi prima occuparla, acciò non possa ferire in quella parte, oue si troua, doppo il che si può fingere non abbandonando però mai il uantaggio, & nel fare detta finta si richiede lo andare inanzi affine, che se l’ nimico non para, che la finta ferisca, & le pure para, che si possi nella mutatione ariuare al corpo prima che detto nimico si salui col rompere di misura, perche quello che’ si sarà mosso con la finta giongerà più presto di quello, che haurà aspettato il secondo tempo per rompere di misura, mà se quando si fà la finta il nimico rompe di misura non si hà da andare perche si è troppo lontano, mà si dee fermare, & tornare ad aquistare; talmente che se quello, che quì si uede ferito hauesse seruato questo termine più tosto sarebbe stato il ferittore, che il ferito, ò almeno si sarebbe saluato. Sopra di questa presente ferita si è fatto assai longo discorso intorno al uantaggio, & al pericolo, & non solo intorno à ciò, mà come sia nata, & come in altra forma potea nascere, & di più quello, che era buono per salute del ferito, perche inanzi l’ offesa si potea rimediare in molte guise, che doppo il fatto non è niente à proposito, mà nelle altre che seguiranno si dirà solamente la caggione, & l’ effetto di dette ferite il resto si tralasciarà per minore tedio di colloro, che leggeranno. 21. |
Von der ersten Verletzung so eine Qvarta wieder eine Terza gemachet. No. 21. IN dieser Figur No. 21. ist die erste Verletz- oder Verwundung gewiesen, so eine Qvarta mit festem Fusz oder à piè fermo wieder ein Terza-Lager gemachet hat. Welches sich dann kan zugetragen haben, weil der in Terza einwendig hat wollen eine Finta machen, indem der ander auch in Terza lag; Er ist aber mit der Finta darum also hervorgefahren, aufdasz der ander hat sollen pariren: Die= [93] ser andre aber hat indem das Tempo genommen, ist mit seinem Gefäsz zu des Feindes Schwächen gegangen, hat auch seine Spitze nach des Feindes Leibe gerichtet, und ist allsamt überstreckkung des Leibes und Wendung der Hand nach der Qvarta mit dem rechten Fusz fortgetreten, dem Feinde begegnet und ihn wie man siehet in dem Tempo da derselbe mit der Finta zurückkete verletzet, welches denn verursachet, dasz er nicht hat können parieren indem er also mit dem Fusz in der Lufft war und vor sich gienge. Gleichermaszen kan es sein, dasz sich allebeide in Terza auswendig befunden, und dasz derjenige so getrofen worden mit dem Leibe und der Klingen wollen vor sich gehen und einwendig caviren den Feind damit zuzwingen, dasz er parirete, in Meinung im Tempo des parirens denselben zutreffen indem er nur die Hand aus der Terza in die Seconda wendete und mit dem Leibe verfiele; Oder wieder zurük- und auswendig zukommen und daselbst ober der Klingen zuverletzen: Es were auch alles beides wohl von statten gegangen, wenn es der eine hette also wie es der ander begehrete gemachet. Aber derjenige so im Lager stille lag, und seine Klinge frei hatte, über das sich in der weiten Misur auch auf ein Tempo zum stoszen oder einiges anderes Vortheil überkommen zukönnen warttend befande, so bald er nur die Bewegung seines Feindes Klingen und dessen Leibes, welchen er vor sich vorausbrachte hat gesehen, erkante er, dasz der Feind, so verletzet ist, ob er gleich den Fusz nicht bewegete, doch die Misur nicht brechen konte, angesehen er sich nicht in einem Tempo zugleich nähern und entfernen kan. Woher einer denn leicht verstehen kan, wie gefährlich es sei, sonderlich wenn sich des Feindes Klinge frei befindet, sich ohne Tempo um sich zunähern bewegen, da man zuvor nur in der weiten Misur gewesen; Dasz wenn einer um von einer Gefahr errettet zuwerden, sich zubewegen gezwungen würde, were es besser sich zurük als vorauszubegeben, sonderlich wenn der Feind still und ruhig läge, und sich wie er sich wolte frei machen besinnete, und das darum, dasz wenn der Feind wolte in selbem Tempo stoszen, du zugleich in einem moment dich köntest schützen und den Feind verletzen: [94] Uber diesz auch dasz wenn einer in der weiten Misur den Leib gleich und die Klinge beweget hette, wenn die Füsze nur stille geblieben, er sich noch allemahl salviren könte: Aber in der engen Misur träget eine jede kleine Bewegung eine große Gefahr mit sich, wie ich droben, da von der Misur und Tempo ist gehandelt worden, gesaget habe. Ferner soll man auch betrachten, dasz wenn einer wieder den, so still lieget und seine Klinge frei hält, wolte eine Finta machen, es meines erachtens nichts anders were, als sich selbst fruchtlosz in Gefahr stürtzen wollen, weil der fintirende, ob sich gleich der ander um zupariren bewegete, doch gar nicht verletzen kan, wenn der ander nur mit den Füszen still lieget; Denn wenn der fintirende also nicht anreichen, sondern in Unordnung, wie auch in Gefahr ehe als er könne wieder zurükkommen getroffen zuwerden, wird gebracht sein: Wannenhero der so fintiren will einige Bewegung des Feindes erwartten, oder desselben Klinge nicht frei lassen soll, sondern soll sie vorher stringiren, damit sie an dem Orthe wo sie sich befindet nicht treffen könne; Nach welchem einer denn wohl eine Finta machen kan, aber solch erlangtes Vortheil doch nicht wieder verlaszen darff. Ingleichen wenn einer eine Finta machet, musz er allezeit damit vor sich gehen, aufdasz wenn ja irgend der Feind nicht nach der Finta pariren würde, er dennoch gleich hineinstoszen, oder da er schlechterdinges parirete, in der Enderung dis effects dessen Leib ehe anreichen, als er sich mit brechung der Misur salviren könte: Denn derjenige, so sich mit der Finta beweget hat, wird vielgeschwinder anreichen, als derjenige so auf das zweite Tempo gewarttet, die Misur brechen. Wenn aber ja der Feind indem einer eine Finta machet die Misur bräche, musz man deswegen nicht vollends austoszen, weil er allzuweit entfernet, sondern man soll sich wieder im Lager befestigen und des Feindes Klinge nochmahls stringiren. Dasz darum, wenn derjenige, den man hier getroffen siehet, diese Regulen hätte inachtgenommen, er viel ehe würde getroffen haben, als getroffen worden sein, oder er würde sich zum wenigsten in andre Wege haben salvieren und vor dem Stosz erretten können. Bei diesem gegenwärtigem Stosz ist mit ei= [95] nem ziemlich-langem Discurs so wohl über das Vortheil als die Gefahr, nicht aber allein über diese, sondern auch woher es habe entspringen, oder wie es auf eine andre manier hette vorkommen können, gehandelt worden; Wie auch von demjenigen was zur Wohlfart des getroffenen hette gedienet mit mehrem geredet ist; Weil ehe der Stosz geschehen, man sich auf vielerlei Weise und Wege helffen und errettten kan, da hergegen nach gethanem Stosz nichts mehr hilffet: In denen folgenden Figuren aber soll allein die Ursach und Würkung des Stoszes abgehandelt werden, das übrige aber will ich mir anderwärts um dem Leser allhier keinen Ekel zumachen, zuzeugen vorbehalten haben. | |||||
[40] The second hit is in tierce against a guard in tierce. It may arise when you finding yourself on the inside, have made a feint in the straight line and your adversary in parrying has dropped his sword through not meeting yours, for you have disengaged in the time of his parrying. You have gone on to hit on the outside through the angle naturally formed by the hand in tierce, and the adversary has been unable to push your sword away as his forte was already so far advanced that his sword remained locked. Or it might arise in this way both being in tierce on the inside, you have advanced to engage his sword. He has tried to disengage, advancing his right foot. In that time you have pushed on and made a hit before the disengage and the movement of the foot were completed, in such a manner that his point has been pushed outwards, before he could return it into line. It is obvious that the time offered by the disengage from one line to the other, being a larger movement, is longer than the time offered by one who remains in the centre line and goes straight on. Therefore, you may say that you have arrived before he has finished the disengage, and in this manner have pushed him out of the line as the plate shows. |
[49] SEGVE LA SECONDA FERITA, CHE E VNA TERZA LAQVAle hà ferito un’ altra terza, & può essersi causata, che colui, che hà ferito, ritrouandosi di dentro, habbia fatta una finta in retta linea, & che l’ altro, nel uolerla parare, sia cascato abbasso per non hauere trouata la nimica, laquale sia stata cauata da quello, che hà finto nel tempo che quest’ altro l’ hà uoluta parare, & sia andata à ferire di retta linea di fuori per quello angolo, che naturalmente uiene formato dalla mano, che stà in terza, & l’ altro non l’ habbia potuta rispingere per essere già gionto col forte tant’ oltre, che la spada sia restata inchiauata nel braccio. Potrebbe anco essere, che ritrouandosì ambidui in detta terza di dentro, quello che hà ferito fosse andato per trouare la spada all’ altro, il quale hauesse uoluto cauare auicinandosi col destro piede, & che in questo tempo il ferittore si fosse spinto inanzi, & hauesse ferito prima, che fosse finita la cauatione & il moto del piede, in modo che la punta fosse stata serrata di fuori prima, che fosse potuta ritornare in presenza, perche raggioneuolmente si uede, che più longo è il tempo di quello che caua dall’ una nell’ altra parte, per essere più gran moto, che non è quello, di chi resta nel meggio, & uà diritto, & perciò si potrà dire, che quello sia ariuato prima, che questo habbia finita la cauatione, & in questo modo l’ habbia serrato di fuori, come la figura di mostra. 22. |
Von dem Terza Stosz so wieder eine andere Terza gemacht ist. No. 22. NU folget unter No. 22. die zweite Verwundung welches ist ein Stosz der Terza so eine andre Terza getroffen, und kan sich daher verursachet haben, dasz weil sich der treffende einwendig befunden, er alda in gerader Linie eine Finta gemachet, und der ander indem er nach selbiger Finta hat wollen pariren, weil er des ersten Klinge nicht gefunden, ziemlich tief [96] mit der seinigen verfallen sei, da dann der Treffende im Tempo da der Getroffene hat wollen pariren, seine Klinge caviret, und auswendig durch den Winkel so die Hand in Terza von Natur machet, in gerader Linie hinneingestoszen, weil also des Getroffenen seine Klinge des Treffenden seine nicht hat können wiederzurükketreiben, indem sie mit der Stärke schon so tief hinneingediehen war, dasz die Schwäche zwischen dem Arm und der Klingen beschlossen worden. Es könte auch sein, dasz sich beide in besagter Terza einwendig befunden und der Treffende wollen des andern Klinge finden, welcher aber indem mit dem rechten Fusz fortgetreten und caviret hat; In diesem Tempo aber hat der Treffende sich vorausgestrekket und ehe verletzet, als der ander seine Cavation und die Bewegung des Fuszes geendiget, daher denn des Feindes Spitze auszen ist verschlossen gewesen, ehe als sie hat wieder in Presenza kommen können: Denn das verstehet sich leicht, dasz das Tempo dessen so von einer Seiten zur andern caviret gröszer ist, weil es eine gröszere Bewegung als dessen, so nur im Mittel ufm Punct verbleibet und gerade zugehet: Und aus solchen Gründen wird man vor gewisz sagen können, dasz der Treffende ehe als der getroffene seine Cavation geendiget angereichet, und dasz dieser wie man in der Figur siehet um obenbesagter Ursachen willen also sei ausgeschlossen worden. | |||||
[41] This is a hit in quarte against a tierce. It has succeeded because both were in tierce within wide distance, and you have moved your sword and tried to engage the adversary's on the inside. He, seeing your plan and that you were uncovered below the sword hand, has lowered his point in order to hit in tierce in that line. But you, who have moved the point only, seeing him coming in below, have abandoned the attempt to engage and directed your point at his body, turning your hand into quarte. By carrying the hilt to his faible you have parried and hit at the same moment. This has been due to your adversary's ignorance, for he has failed to realise that your movement was so small, that he could not arrive before the time was finished. Therefore he should not have gone on. But it was good to lower the point in this manner, if only he had not advanced or moved his feet. For then against this hit he could readily have defended himself and attacked in various ways. |
[50] LA QVARTA, CHE QVI SI VEDRA HAVERE FERITO VNA terza, è successa perche ambidui erano in terza netta misura larga, & collui, che hà ferito si è mosso con la spada, & andato per aquistare la nimica dalla parte interiore, & l’altro cognoscendo il disegno dell’ auerssario, & uedendolo scoperto disotto dalla mano della spada hà abbassato la punta, perferirlo di detta terza in quella parte, mà quest’ altro, che non hauea mossa se non la punta uedendolo uenire disotto per ferire restando di andare alla spada, hà dirizata essa, punta al corpo uoltando la mano in quarta, & portando il finimento al debile nimico hà parato, & ferito in medesimo tempo, & ciò e riuscito per ignoranza di quello, che si è mosso, ilquale non hà cognosciuto il moto del nimico essere tanto picciolo, che non seli poteua giongere prima, che non fosse finito il tempo, & perciò non douea andare, mà era ben fatto lo abbassare nel modo istesso la punta non approssimandosi, ne mouendosi còi piedi, che se il nimico fosse uenuto con questa ferita egli haurebbe hauuto gran comodità di diffendersi, & offendere in diuersi modi. 23. |
Von einem Untern Qvarta Stosz wieder eine Terza. No. 23. DIe Qvarta, welche man hier siehet, dash sie eine Terza getroffen habe, ist herkommen, weil sich allebeide in der weiten Misur in Terza befanden, und der Treffende sich mit der Klinge um des Feindes Klinge einwendig zufinden hat beweget; Der ander aber als er seines Gegners Vornehmen erkant und die Blösze unter der Hand, da er den Degen führet, erblikket, hat er seine Spitze sinken laszen und daselbst mit besagter Terza treffen wollen. Aber der erste welcher nichts als die Spitze beweget gehabt, nachdem er gesehen, dasz der an= [97] dre unten stoszen wollen, hat die Bewegung die Klinge zufinden unvollendet fahren laszen, und die eigene Spitzen nach des Feindes Leibe gerichtet, die Hand in Qvarta gewendet, ist auch mit der Stärke oder dem Kreutz zu des Feindes Schwächen gegangen, und hat also in einem Tempo zugleich pariret und gestoszen. Solches aber ist von statten gegangen wegen Unwissenheit dessen der sich beweget und dabei nicht verstanden hat, dasz seines Feindes Bewegung so klein sei, dasz er denselben nicht so bald und daher vielweniger ehe als das Tempo geendiget abreichen könte; Hätte deswegen nicht sollen vor sich gehen. Doch were es gut gewesen wenn er auf eben selbige Manier die Spitze doch ohne sich zunähern auch ohne Bewegung der Füsze versenket hette. Denn wenn der Feind alsdenn mit seinem Stosz hette ankommen wollen, hette er sich zuschützen und den andern auf unterschiedene Arthen zuverletzen gute Gelegenheit gehabt. | |||||
[42] This is a hit in tierce against another tierce. Both were on the outside, and you have moved to engage your adversary's sword. He, seeing the time, without considering the width of the distance, and that you have moved the point only, has advanced his foot in order to disengage on the inside and hit in quarte, or in order to engage your sword, and has advanced within close distance. You had moved with the intention merely of making him move. Seeing that he was beginning to drop his point to disengage it and that he was advancing his foot, you also have let your point drop; lowered the body and have met his faible with the hilt and prevented his disengage. At the same moment you have pushed on with the right foot and hit under his sword on the outside. Therefore it should be held as a true principle, that when your adversary's sword is free and he is steady on his feet and has tried to engage, you should not allow this danger to arise, but should form a plan to acquire some advantage without advancing, but rather retiring. For the movement of the foot is longer than the movement of the sword. But in the case when you have engaged your adversary's sword and he has tried to free it, even without moving his feet, then you can advance a foot and engage on the other side, in order to hit when he moves again. Therefore the principle of advancing when your adversary moves rests on the advantage of having first engaged his sword. If it is free, it puts you in danger, as the plate shows. |
[51] LA SEGVENTE SARA VNA FERITA Dl TERZA CONTRA VN’ altra terza caggionata dall’ essersi ambidui ritrouati di fuori, & perche quello, che hà ferito si era mosso per andare à ritrouare la nimica spada & l’ altro uedendo il tempo senza considerare la larghezza della misura, oue era l’ auerssario, & che non hauea mosso senon la punta, uiene ad’ essersi portato inanzi col piede per cauare di dentro, & ferire di quarta, ouero per occupare la spada ad’ esso nimico, & essersi auicinato nella misura stretta, mà detto nimico, che si era mosso insidiosamente solo per fare mouere questo, non hà finito di andare alla spada mà uedendolo, che comiaciaua à declinare la sua punta per cauarla, & che si portaua inanzi col piede hà lasciato ancor esso calare la sua della medesima terza abbassando il corpo, & è uenuto col finimẽto à ritrouare il debile nimico impedendoli la cauatione, & nel medesimo punto spingendosi oltre col destro piede hà fatta la ferita sotto la nimica spada per la parte di fuori. Di modo che si dee tenere per uera regola, che quando un nimico hà la spada libera stando fermo de’ piedi, ilquale uenga per fare qualche aquisto, non si dee l’ huomo lasciare mettere in pericolo, mà pigliare partito per aquistare qualche uantaggio senza però approssimarsi anzi più tosto ritirandosi, perche il moto del piede è assai più longo di quello della spada, mà in caso, che si hauesse occupata la spada al nimico, ilquale la uolesse liberare, ancorche non mouesse i piedi, all’ hora si potrebbe auicinare con un piede, & aquistarla dall’ altra parte per poterlo poi ferire quando tornasse à mouersi, & perciò la raggione di andare inanzi quando il nimico si moue stà in quello uantaggio di hauerli prima aquistata la spada, che essendo libera, porta maggiore pericolo, come dalla figura si uede. 24. |
[98] Von einem Unter-Terza Stosz so wieder eine andre Terza gemacht. No. 24. DIese folgende No. 24. ist ein Terza Stosz wieder eine andre Terza, welcher ist daher kommen, dsz weil sich allebeide auswendig befunden haben derjenige so getroffen hat des Feindes Klinge finden wollen; Da denn der andere als er das Tempo gesehen, ungeachtet er noch in der weiten Misur war und der Gegner nur die Spitze der Klingen bewegete, hat mit dem Fusz forttreten, caviren und einwendig die Qvarta stoszen, oder doch des Gegners Klinge stringiren und sich zugleich in die enge Misur bringen wollen; Aber besagter Gegner, welcher sich hinterlistiglich nur um den andern zu einer Bewegung zureitzen beweget hatte, hat seinen motum die Klinge zufinden nicht vollendet, sondern als er gesehen, dasz der Getroffene um zucaviren seine Klinge angefangen zuversenken, und dasz er sie zusamt dem Fusze vor sich gehen liesz, hat auch die seinige in besagter Terza unter sich sinken, [99] seinen Leib zugleich mit tief gehenlassen, auch mit seinem Kreutz des Feindes Schwäche eingenommen und ihn also an seiner Cavation gehindert, auch zugleich in selbigem Tempo sich mit dem rechten Fusze ausgestrekket und also auswendig unter des Feindes Klinge getroffen. Derowegen soll man vor eine gewisse Regul inachtnehmen, dasz wenn der Feind im Lager mit der Klingen frei und mit den Füszen still lieget, derjenige so irgend etwas vorzunehmen gesinnet ist, sich nicht soll also laszen in Gefahr setzen, sondern einen Anschlag machen, wie er einiges Vortheil gewinne, und zwar dasz er sich nicht dazunähern sondern vielmehr ritiriren dürffte, weil die Bewegung der Füsze viel langsamer als die Bewegung der Klingen. Aber aufn Fall dasz einer des Feindes Klinge stringiret hette, derselbe sie aber befreien wolte, ob er dann gleich den Fusz nicht bewegete, kan man sich doch mit einem Fusz nähern und zugleich auf der andern Seiten vom Feinde so viel gewinnen, dasz man indem er sich wieder bewegen wolte, zustoszen könte: Und bestehte daher die Regul des zurükkens, wenn sich der Feind beweget, in dem Vortheil, dasz man die Klinge vorher stringiret habe, denn wenn sie frei were, würde man sich in gröszerer Gefahr befinden, wie aus dieser Figur zuersehen. | |||||
[43] This represents a hit with the guard in prime against a tierce. Both the combatants were in tierce on the outside, and have attacked each other's swords and have begun to push one against the other. You have turned your hand from tierce to prime. This guard naturally tends to hit towards the ground and is strong in the lower lines. In this manner, as you have raised your hand, your adversary's sword is left below in your strongest line. Further in raising the hand you have approached his faible and at the same moment have pushed on and made the hit shown. You could have made this same attack and with less effort, if his guard had been in seconde, since, although that seconde covers the part hit better, still it is weaker, and therefore the prime would have overcome it more readily than the tierce. This hit arises out of a tussle with the swords. In this connection you should bear in mind that it is bad to resist one who forces your sword; it is better to yield and release your sword, since the sword which tries force is bound to fall a great deal, when the other sword yields, which gives you a time to hit or seize some advantage over the falling sword. This is a safer and less fatiguing method, as we have said. |
[52] QVESTA ALTRA FIGVRA RAPRESENTARA VNA FERITA FATta con la prima guardia contra la terza laquale è successa, perche trouandosi ambi li combattenti in terza fuori della spada hanno attaccate le spade insieme, & cominciato à fare forza l’ una contra l’ altra, & questo che hà ferito hà uoltata la mano di terza ili prima, laquale di sua natura uà à ferire uerso terra, & hà il suo forte di sotto, in modo che hauendo alzato la mano, la nimica è uenuta à rimanere disotto nella sua parte più forte, oltr, che in detto alzare si è auicinato al debile, & in un punto istesso si è spinto oltre, & hà ferito, come si uede, se bene haurebbe fatta la medesima offesa, mà con minore fatica, quando il ferito fosse stato in seconda guardia, perche se bene detta seconda cuopre più quella parte, nondimeno è assai più debile, & perciò la prima l’ haurebbe superata più ageuolmente che questa terza; Di questa ferita ancora è stata buona caggione quello contendere di spada, & in tale proposito si auertisse quanto sia male resistere à chi fà forza, & quanto meglio cedere, anzi leuare uia la spada, perche non può essere di meno, che quella spada, laquale uuole contendere con forza non faccia qualche poco di caduta, mentre, che l* altra cede laquale cosa da tempo all’ auerssario di ferire, ò pigliare qualche uantaggio sopra quella cadente, cosa assai più sicura, & di meno fatica come si è detto. 25 |
Wie die Prima wieder eine Terza gestoszen wird. No. 25. IN dieser Figur No. 25. wird ein Prima-Stosz wieder eine Terza gezeuget, welches sich also zugetragen, weil indem sich beide Partheien in Terza auswendig befanden, beide die Klingen hart angegriffen und angefangen haben einer gegen den andern zu drükken, Da denn der Treffende die Hand aus der Terza in die Prima verwendet, welche mit der Spitzen von Natur der Erden zuwärts trift und ihre Krafft unten hat, also dasz da die Hand erhoben ward des Feindes Klinge muste unten [100] wo die Prima am stärkesten verbleiben: Uber das hat sich der Treffende im erheben der Hand zu des Feindes Schwäche gefunden, auch in selbem Moment wie man siehet ausgestoszen und verletzet. Man hette auch wohl besagten Pfima-Stosz und zwar mit geringerer Mühe wieder eine Seconda, wenn der Feind darinnen gelegen, machen können; Denn ob gleich besagte Seconda auswendig besser bedekket, ist sie doch nichtsdestoweniger viel schwächer, und würde darum von der Prima viel ehe als die Terza übermannet worden sein. Es giebt auch diesem Stosz das gegeneinadner drükken der Klingen eine grosze Hülffe, welches denn zu unserm Zweck dienet, weil man darau sehen kan, wie es so böse sei demjenigen, welcher mit Stärke und Kräfften mit der Klingen gegenzudrükken pfleget, zuwiederstreben; Auch wie viel es besser sei demselben zuweichen, ja die Klinge gar ausm Wege zunehmen: Denn es kan nicht geschehen, dasz diejenige Klinge, so mit Gewalt gegendrükket, nicht ein wenig, indem der andre weichet und nachgiebet, eine Cadute mache, welches dem Feinde entweder zustoszen oder einiges andres Vortheil über den so als verfället zuüberkommen ein gut Tempo giebet, da es denn sehr sicher zugehet und wie gesaget worden nicht sonderliche Mühe und Arbeit bedarff. | |||||
[44] This is a hit in quarte against a sword in the air. Both were on the outside and you have tried to engage your adversary's sword, which may have been in tierce or in seconde. He has raised his sword to make a cut of mandiritto at the head. You were already moving in quarte in order to engage his sword and have merely lunged forward, advancing the right foot in such a way as to arrive before his sword fell. Even if his sword had fallen, it would have effected[!] nothing, because in lunging you have raised your hand far enough to protect the head from the cut. As the cut is made from the elbow, it has left much uncovered, is slow in hitting and has led to this hit. If the cut had been made from the wrist, in the time of your hitting the sword would have fallen on yours, so that both the attack and the defence would have been illustrated together. But as that did not happen, the attack only is shown here. |
[53] LA SEGVENTE, CHE E VNA FERITA DI QVARTA CONTRA una spada in aria è diriuata dall’ essere tutti dui di fuori, & dall’ essere quello, che hà ferito andato à trouare la spada nimica, laquale facilmente poteua essere in terza, ouero in seconda, & laquale mentre, che si leuaua per ferire di mandiritto per testa, questo che già era in moto con la quarta, nell’ andarli à trouare detta spada non hà fatto altro, che slongare la sua inanzi, & auanzare il destro piede, in modo che è ariuato prima che quella cada, laquale se anco fosse caduta non haurebbe fatto niente, perche questo ne lo slongare, che hà fatto hà alzato la mano ancor tanto, che hà fatto coperto alla testa diffendendosi dal taglio, ilquale taglio per essere stato col gombito, è però molto scoperto & tardo in ferire, hà caggionata la presente ferita, che quando il detto taglio fosse stato fatto col nodo della mano, nel tempo, che questi hà ferito la spada sarebbe caduta sopra quella, che feriua, in modo che nella figura si uedrebbe la diffesa, & offesa insieme mà perche è stata altrimenti, qui non si uede se non la sola offesa. 26. |
[101] Von einem Qvarta Stosz so wieder eine in die Lufft erhobene Klinge gemachet ist. No. 26. DIese Figur welche einen Qvarta Stosz wieder eine Klinge in der Lufft weiset, ist daherkommen, weil sich beide auswendig befunden da sich denn der Treffende des Feindes Klinge, welche in Terza oder in Sekonda sein konte, zufinden beweget; Indem aber hat sich des getroffenen Klinge aufgehoben und mit mandiritto uf den Kopf verletzen wollen; Die andre aber, so mit der Qvarta um des Feindes Klinge zufinden zuerst in motu war, hat nichts anders gethan, als sich vollends ausgestrekket und den Fusz zugleich ausgetreten, dasz sie also ehe angereichet, als die Hauende herunter kommen; Und ob sie gleich herunterkommen were, hette sie doch nichts gethan, weil der so ausgestoszen die Hand indem um so viel erhöhet, dasz der Kopf damit bedekket und vor dem Hiebe beschützet gewesen; Dieser Hieb nun weil er mit dem Ellenbogen gemachet hat viel Blöszen gegeben, ist auch langsam zum verletzen herumkommen, und des= [102] wegen gegenwärtige Figur verursachet: Wenn er aber nur mit dem Vordergelenke der Hand were gemachet gewesen, so were die Klinge indem Tempo da der ander getroffen auf des Treffenden seine gefallen, und hette man denn sehen können, wie die Of- und Defension zugleich wäre angegangen. Weil es aber anders geschehen, kan man mehr nicht, als alleine nur wie der Stosz verletzet hat, an dieser Figur sehen. | |||||
[45] This is a hit in seconde against a sword in tierce, whose point is out of line; it has arisen in this manner: both were in tierce on the inside and you have tried to engage the adversary's sword. At that moment he has turned his sword to make a cut of riverso through the uncovered part seen outside the sword towards the head and shoulder. Seeing his sword making a circle you have changed from tierce to seconde, covered the threatened part, and in the same time driven on your point, arriving before his circle was finished. Even had his sword fallen first, he would have met the parry. All this arises from the slowness of the cut, which you cannot make without getting out of line, and the time before you return in to line, is so long, that one who uses the point may easily arrive first. |
[54] QVEST’ ALTRA, CHE SI VEDE, DI SECONDA GONTRA VNA spada in terza, laquale hà la punta fuori di presenza è uenuta perche stando tutti dui in terza di dentro il ferittore è andato per ritrouare la spada nimica, nelquale tempo istesso hà uoltato diffendente riuerso perquello scoperto, che uedeua fuori della spada uerso la testa, & spalla nimica, in modo che detto ferittore uedendo girare la nimica hà uoltato di terza in seconda, & si hà coperta quella parte, & in medesimo tempo si è spinto oltre à ferire, & è gionto prima che detta nimica habbia finito il suo giro, che quando anco la fosse caduta prima hauria trouata la diffesa, tutto nasce dalla tardità del taglio, ilquale non può ferire se non si lieua di presenza & inanzi, che ritorni il tempo è tanto longo, che uno che ferisca di punta può molto prima ariuare. 27. |
Wie die Seconda wieder eine Terza kan gestoszen werden. No. 27. DIese andere so man hier No. 27. siehet ist ein Seconda Stosz wieder eine Klinge in Terza, welche die Spitze auszer der Presenz führet, und ist daherkommen, dasz sich beide einwendig in Terza befunden, der Treffende aber hat sich um seines Feindes Klinge zufinden beweget, in welchem Tempo der ander seine Hand gewendet, und mit Riverso fendente oder sqvalembrato nach der Blöszen so er auswendig der Klingen an dem Kofp oder rechten Schulter sahe, zugehauen; Da aber der Treffende des Feindes Klinge also herumkom= [103] men sahe, hat er die Hand aus der Terza in die Seconda verwendet, die gegebene Blösze bedekket, auch in demselben Tempo weiter ausgestossen, und ehe als des Feindes Kling ihren Zirkul vollendet gehabt, angereichet; Ja wenn sie auch gleich ehe herunterkommen were, würde sie doch die Blösze beschützet gefunden haben. Und dieses alles kommet von der Langsamkeit des Hiebes her, welcher nicht verletzen kan, die Spitze müsse denn auszer der Presenz gehen; Ehe sie aber wieder herumkömmet, ist das Tempo so weitläufftig und langsam, dasz der so mit dem Stosz verletzen will, ehe anreichen kan. | |||||
[46] This is a hit in tierce on a straight line against a tierce which has fallen. Both were in tierce on the outside. You have tried to engage the adversary's sword, being within wide distance, and he has taken that time and made a cut of mandiritto at the head. You have withdrawn your body slightly, have let his sword pass in the air, and merely lowering the point a little when his sword has passed, have suddenly thrust in tierce, reaching his body at the moment when his sword has competely[!] fallen, so that he has been unable to raise his sword in order to parry or to retreat, or save himself, because his movement was not yet finished, when he was hit. From this you may deduce the principle that, when possible, it is always better to let cuts pass without parrying them, so that you may not be put into subjection and the danger of being deceived while parrying. Further this method is less fatiguing. |
[55] MA QVEST’ ALTRA DI TERZA IN RETTA LINEA CANTRA una terza caduta è seguita perche, essendo tutti dui in terza di fuori, quello, che hà ferito è andato per trouare la nimica, stando in misura larga, & l’ altro pigliato quel tempo hà uoltato di mandiritto per ferirlo sopra il capo, mà il primo con un poco di ritirata di corpo, & con lasciare passare la nimica à uuoto, abbassando solamente un poco la punta quando detta nimica è passata, è andato subbito à ferire della detta terza laquale è gionta al corpo nel punto medemo, che l’ altra è gionta abbasso, di modo che l’ ferito non hà potuto rileuare la spada per parare, ne meno ritirarsi, ne saluarsi, perche il suo moto non era anco finito, quando è stato ferito, oue si conosce, & sene caua regola, che è sempre meglio, quando si può fare, di lasciare passare li colpi di taglio senza pararli, perche l’ huomo non si constituisse in quella seruitù, & pericolo di essere ingannato nel tempo che para, ne meno hà da fare tanta fatica. 28. |
Ein Stosz der Terza wieder eine nach der Erden zu verfallene Terza. No. 28. DIese Terza, so man No. 28. in gerader Linie wieder eine andre Terza, wo mit der Spitzen verfallen, verletzet, ist daher kommen, dasz nachdem sich allebeide auswendig in Terza befunden, der Treffende indem er sich in der weiten Misur befunden, sich um des Feindes Klinge zufinden beweget, der ander aber solch Tempo genommen hat und durch Wen= [104] dung der Hand mit Mindiritto übern Kopff verletzen wollen, da dann der erste seine Spitze ein wenig versenket, den Leib zugleich zurükgezogen und also des Feindes Klinge hat lassen fehlgehen; So bald aber die Klinge vorbeigewesen, hat er geschwinde mit besagter Terza zugestoszen, welche denn in eben selbem Tempo, als die andere auf die Erde gefahren, oben getroffen hat, also dasz der getroffene seine Klinge nicht hat wieder in die höhe kriegen und pariren, vielweniger sich ritiriren oder salviren können, weil seine Bewegung da er doch schon getroffen war, noch nicht vollendet gewesen. Woraus einer den erkennen, und eine Regul nehmen kan, dasz es allezeit besser sei wenn sichs also schikken will, dasz er die Verletzung des Hiebes unpariret fahren lasze; Denn so wird er sich nicht in solch eine Bottmäszigkeit oder Gefahr betrogen zuwerden, indem er pariret, gesetzen haben, es wird auch nicht so viel Mühe bedürffen. | |||||
[47] This hit in quarte against a tierce which has fallen has arisen as follows: you have tried to engage whilst both were in tierce on the inside, and your adversary has taken the time and made a cut in riverso at the head, but being too far distant he has failed to reach. You realised that his cut could not reach and allowed his sword to pass without parrying, and by lowering your point a little so that his sword might not touch it, as soon as his sword had passed you have hit in quarte, being defended in that place where the cut of riverso, after falling, generally hits, especially if it has fallen without effect. Your point has reached his body at the moment when the riverso has finished its fall, in such a way that he who has made the cut has been unable to save himself, because he has been carried forward by his own blow, and therefore has given you a chance to hit him. If his arm had been straighter and in better alignment, he could have defended better. This is the result of the sword missing its object, which, as we have said elsewhere, always brings more or less disorder. The cut made from the wrist gives more protection. |
[56] LA FERITA DI QVARTA, CHE SEGVITA CONTRA VNA terza caduta è nata, perche quello, che hà ferito è andato à ritrouare la nimica spada, mentre tutti dui si trouauano in terza di dentro, & perche l’ auerssario pigliando quel tempo hà uoltato di riuerso per testa, ilquale per essere lontano non è ariuato, doue l’ altro, che ben conosceua quel taglio non potere ferire hà lasciato passare la spada nimica senza parare, & con l’ abbassare un poco la punta, acciò la detta nimica non la tocchi, subbito passata quella, è andato à ferire in quarta, essendo diffeso dall’ altra parte, cioè nel luogo, oue il riuerso, dopò caduto, suole andare à ferire, & massime quando è caduto senza effetto, nelquale tempo la punta del detto ferittore è gionta al corpo in quel proprio punto, che l’ riuerso finiua di cadere, di modo tale, che quello dal taglio non hà potuto saluarsi per essere stata trasportata dal proprio colpo, & percio hà data più comodità all’ altro di ferirlo, che se il braccio fosse stato più retto, & in maggiore giustezza meglio si sarebbe diffeso, & questo è l’ effetto della spada che non troua incontro, come altre uolte habbiamo detto, laquale trasporta sempre ò molto, ò poco, & il taglio tirato col nodo della mano fà restare più coperto. 29. |
Ein Qvarta Stosz wieder eine der Erden zu verfallene Terza. No. 29. [105] DIewieder eine Spitzen nach der Erden zu verfallene Terza hier No. 29. gefolgte Qvarta ist herkommen, weil der Treffende des Feindes Klinge finden wollen indem sich beide einwendig in Terza befanden, und weil der Gegner solch Tempo nehmend durch Wendung der Hand mit Riverso über den Kopff hat hauen wollen, welcher Hieb doch weil er von allzuweit gemachte, nicht angereichet; Da dann der Treffende weil er gesehen und wohl erkant, dasz der Hieb nicht könte anreichen, des Feindes Klinge, indem er die Spitze seiner eigenen ein wenig versenket, aufdasz sie vom Feinde nicht berühret werde, unpariret fahren lassen: So bald sie aber vorbei, mit Quarte oben zugestoszen, und sich damit an dem Orthe wo Riverso nachdem es zum erstenmahl ohne Würkung ist fehl gegangen, hernach pfleget zutreffen, bedekket, und also mit seiner Spitzen in dem Moment da des Feindes Klinge mit Riverso von oben herunterzufallen aufhörete oben angereichet hat, also dasz der so gehauen, weil er seines Hiebes wegen mit dem gantzen Leibe vorn übergefallen, sich nicht hat salviren können, sondern hat damit dem Gegner zum verletzen mehr Beqvehmlichkeit gegeben. Da hergegen wenn der Arm mehr in gerader Linie were ausgestrecket und kunstrecht geführet worden, er sich leichter würde beschützet haben: Denn dieses ist die Würkung einer Klingen so nichts gegenhaltend findet, wie ich anderswo gesaget, dasz eine solche entweder zu viel oder zu wenig verfähret und damit das Spiel verderbet; Da hergegen ein Hieb so nur mit dem Vordergelenke der Hand gemacht wird, einen viel besser bedekket behält. | |||||
[48] This cut of mandiritto at the head, which is here shown, against a tierce may arise in this manner: you have engaged your adversary's sword, and he has not moved. The swords being engaged on the outside, he has tried to force your sword, and you, feeling the pressure, have yielded, and by bending the wrist, and keeping your hilt close to his sword, have made the cut shown. He has been unable to parry, because, owing to your yielding, his sword has fallen a little, in such a manner that your forte, has weighed upon his blade and prevented him from raising it. It may arise also in this way: both being in tierce on the inside, you have tried to engage and your adversary has disengaged in tierce, carrying himself forward in order to hit on the outside. But you have let his point drop, bent your wrist, bringing the hilt over his blade, and thus have made the cut of mandiritto. As may be seen your hand has fallen into tierce. |
[57] MA LA FERITA DI MANDIRITTO PER TESTA, CHE QVI OLtre si uede, contra una terza può essere uenuta perche uno sia andato à trouare la spada all’ altro, ilquale non si sia mosso, & essendosi te spade attaccate insieme dalla parte di fuori, quello che è ferito habbia uoluto fare forza contra la nimica, & l’ altro sentendo la forza habbia ceduto, uoltando di nodo di mano, & restando col finimento uicino alla spada nimica, & habbia ferito, come si uede, & il detto ferito non habbia potuto parare, perche, nel cedere che questi hà fatto, la spada gli sia caduta un poco abbasso, in modo che il forte di quello, che hà ferito l’ hahbia oppressa, & così impeditoli il poterla leuare. Non meno può essere, che ritrouandosi in terza di dentro ambidui, quello che hà ferito sia andato à trouare la nimica, & l’ altro habbia cauato di terza portandosi inanzi, per ferirlo di fuori, mà che il detto ferittore, habbia lasciato cadere la punta quale era andata alla spada, & habbia uoltato di nodo di mano montando col finimento sopra la nimica, & così habbia fatta la ferita di mandiritto fendente, nondimeno la mano è caduta in terza, come si uede. 30. |
Wie man einen mit mandiritto übern Kopf hauen soll. No. 30.
DEr Hieb den man hier No. 30. wie eine Terza mit Mandiritto übern Kopf getroffen siehet kan gemachet worden sein, weil der eine des andern Klinge, welcher sich doch nicht beweget gehabt, habe finden wollen Da aber beide Klingen auswendig aneinander kommen, hat der Getroffene wieder des andern seine mit Gewalt drükken wollen: Als der an= [106] der diesen Gewalt gemerket, hat er mit seiner Klingen nachgegeben, und allein das Vordergelenke der Hand beweget, sich auch mit dem Kreutz nahe des Feindes Klinge erhalten, und also wie man siehet, getroffen. Da dann besagter Getroffener, weil seine Klinge indem der ander nachgegeben, ein wenig eine Caduta unterwärts gemachet, nicht hat pariren können, weil die Stärke des Treffenden des andern seine Klinge in der Caduta opprimiret, und ihm also das wiedererholen verbothen und verhindert. Es kan auch wohl sein, dasz sich allebeide einwendig in Terza befunden, und dann der Treffende habe des Feindes Klinge finden, der ander in Terza caviren und auswendig verletzen wollen; Aber der Treffende hat seine Spitze so nur schlechterdinges nach der Klingen gangen war, sinken lassen, das Vordergelenke der Hand zugleich gewendet und ist mit seinem Kreutz über des Feindes Klinge kommen und hat also den Hieb Mandiritto fendente verursachet; Die Hand aber hat nichts destoweniger wie man siehet in Terza eine Caduta gemachet. | |||||
[49] This hit in quarte against a seconde has arisen as follows:- both were in tierce on the outside, and you have lowered your point and uncovered the outside in order to give your adversary an opportunity to attempt a hit. He, thinking you have moved in order to change position, has come in to the part uncovered, thinking that he could hit by changing from tierce to seconde so as to exclude your sword on the outside, and carrying his right foot forward. You, seeing him coming, have not parried, but turned the body with the left foot; at the same time disengaging on the inside and changing the hand to quarte you have made the hit. The hit might also have arisen in this way: both being in tierce on the inside, you have tried to engage; he has disengaged before you could find his sword, and changed his hand into seconde in order to cover himself and hit you on the outside in the time when you were seeking his blade. This would have succeeded, if you had tried to parry. But thinking that you could not defend by a parry of the sword, which was moving in order to engage his sword, you have continued the movement followed his disengage, and by making a counter-disengage, turning your body out of presence and letting his sword pass, you have hit at the moment of his advance. |
[58] SI VEDE NELLA FIGVRA, CHE SEGVE QVESTA FERITA DI quarta contra una seconda, laquale può essere stata fatta per trouarsi tutti dui in terza di fuori, & perche quello che hà ferito habbia piegato la spada, & fatto discoperto di fuori per dare occasione al nimico di andarlo à ferire ilquale credendosi, che quel tempo fosse stata una semplice operatione per mutare sito sia entrato per detto scoperto, giudicando di potere ferire, con uoltare di terza in seconda affine di escludere la nimica spada di fuori, portando il destro piede inanzi, mà che l’ altro uedendolo uenire habbia lasciato di parare, & girando il corpo col sinistro piede, & con cauare nel medemo instante la spada di dentro, & uoltare la mano in quarta habbia fatto la detta ferita. Può anco e essere auenuta perche tutti dui si trouassero in terza di dentro, & che quello che hà ferito sia andato per ritrouare la spada all’ altro, ilquale habbia cauato prima, che li sia trouata, & habbia uoltata la mano in seconda per coprirsi & ferire l’ auerssario di fuori nel tempo, che quello li andaua alla spada, cosa che li sarebbe riuscita, quando che hauesse uoluto parare, mà parendoli non potersi diffendere col parare della spada, laquale era in moto di andare à trouare la nimica, & perciò continouando il detto moto hà seguittato esse nimica, che si cauaua, laquale hà fatto una contracauatione girando il corpo fuori di presenza, & lasciandola passare liberamente hà ferito nel punto medesimo, che quella ueniua. 31. |
[107] Wie die gyrirte Qvarta wieder eine Seconda zugebrauchen. No. 31. MAn siehet hier in dieser Figur No. 31. einen Qvarta-Stosz wieder eine Seconda, welcher kan herkommen sein, dasz sich beide auswendig in Terza befunden haben, da dann der Treffende um dem Feinde zum stoszen eine Gelegenheit zugeben, eine Chiamata und damit auswendig eine Blösze gemachet hat, welcher Feind auch gemeinet, weil dieses Tempo ein schlechte Bewegung um das Lager zuverendern were, er würde wohl treffen können, hat deswegen mit dem Fusz zugetreten und indem er die Hand aus der Terza in die Seconda gewendet, aufdasz er des Feindes Klinge auswendig desto besser möchte ausschliessen, ausgestossen: Der andre aber als er ihn so sehen ankommen, hat die Klinge nicht pariret, sondern den Leib mit dem linken Fusz herumvoltiret, und in dem Moment seine Klinge einwendig caviret, die Hand in die Qvarta gewendet und also diesen Stosz gemachet. Es kan auch geschehen sein, dasz sich beide einwendig in Terza befunden haben, und der Treffende des andern Klinge finden wollen, welcher aber ehe seine Klinge gefunden war caviret und die Hand in Seconda [108] verwendet hat, um sich zudekken und den Feind auswendig im Tempo da er ihn wolte an die Klinge gehen zutreffen: Welches denn auch richtig were angangen, wenn der Treffende ihm hette wollen pariren. Aber weil diesem bedauchte, er würde sich nicht schützen können, wenn er mit einer Klingen, so in der Fahrt des andern seine zufinden begriffen war pariren wolte, so ist er deswegen in seiner Bewegung fortgefahren und des Feindes Klinge welche cavirte gefolget, hat eine Contracavation gemachet, zugleich den Leib aus der Presenz voltiret, des andern seine Klinge frei unpariret fahren gelassen, und also ungehindert in dem Tempo, da die andere kam zuverletzen, getroffen. | |||||
[50] Now follows another hit in quarte on the outside of the adversary's sword, which is in tierce at an angle. This has arisen as follows: both being on the inside, and the adversary in tierce at an angle, you have tried to engage his sword and he has disengaged in tierce on the outside. In the same time you have changed your hand to quarte without extending the arm, but carrying the hand away to the inside and as high as the shoulder. You have moved the right foot forward turning it in the air in such a manner that the turn is seen to be completed as it reaches the ground, thereby turning the body and bringing out of line all the part opposed to the adversary. You also have made an angle of your sword, which has entered the angle formed by the adversary, as shown. In this way the more the adversary tries to push it away, the stronger is the hit. Or your adversary may have tried to engage in tierce on the outside, your sword being in seconde; you have yielded from seconde to quarte, turning the body, and hit at the moment when your adversary expected to engage your sword. |
[59] SEGVITA SECONDO L’ ORDINE VN’ALTRA FERITA DI QVARta perdi fuori della spada nimica, quale è in terza angolata, & può essere stata fatta in tale modo cioè che ritrouandosi tutti dui di dentro, & rimanendo quello, che è ferito in detta terza angolata, l’altro sia andato per trouarli la spada, & il detto ferito habbia uoluto cauare di terza di fuori, & il ferittore in medemo tempo habbia uoltato la mano in quarta non con stendere il braccio, mà con portare la mano lontana uerso la parte di dentro & tanto alta come la spalla, & con auanzare il destro piede inanzi girandolo nell’ aria, tanto, che fermandolo in terra era già girato nel modo, che horsiuede & per tale atto essersi anco girato il corpo, in modo che hà leuata di presenza tutta quella parte del suo corpo, che era opposta al nimico, & è uenuto à fare un’ angolo della spada, quale è entrata per l’ altro angolo formato dalla nimica, come si uede, di maniera, che quanto più il nimico si fosse affaticato per rispingerla, tanto essa ferita si saria fatta maggiore. Può similmente essere auenuto, che quello che è ferito sia andato à trouare la nimica con detta terza dal lato di fuori, laquale nimica fosse in seconda, & che l’ istesso nimico habbia ceduto di seconda in quarta col giro del corpo, & habbia ferito nel medesimo punto, che quest’ altro credeua ritrouarli la spada. 32. |
Von einem auswendigen Qvarta Stosz. No. 32. NAch der Ordnung folget nun No. 32. ein anderer Qvarta-Stosz welcher auswendig anguliret wieder eine Terza gemachet ist, und kan geschehen sein, dasz da sich beide einwendig befunden haben der Getroffene in der angulirten Terza beliegen blieben, und der andere dieses seine Klinge stringiren wollen; Als aber der [109] angulirten Terza beliegen blieben, und der andere dieses seine Klinge stringiren wollen; Alls aber der getroffene seine Klinge hat auswendig caviren wollen, da hat der so stringiren wolte in selbigem Tempo seine Hand in die Qvarta verwendet, darbei aber den Arm nicht ausgestrekket, sondern die Hand weit nach der einwendigen Seiten und so hoch als die Schulter geführet, hat mit dem rechten Fusz ausgetreten und denselben in der Lufft so viel herumgedrehet, dasz er an die Erde kommend, wie man siehet, so weit gyriret und damit dem Leibe zugleich geholffen war, dasz er eben so voltiret, und also die ganzte Blösze ja der gantze Leib so im Lager dem Feinde entgegen lag, aus der Presenz gehoben wurde; Die Klinge aber hat müssen einen angulum machen, welcher denn wie man siehet durch des Feindes angulum passiret ist, also dasz je mehr der Feind solche Klinge auszuschlieczen und wegzutreiben sich bemühet hätte, je hefftiger die Verletzung worden wäre. Es kan auch kommen sein, dasz der Getroffene mit besagter angulirten Terza auswendig die Klinge finden wollen, welche sich denn in Seconda befande, da dann diese mit einem drehen oder wenden des Leibes gewichen und aus der Seconda in die Qvarta gegangen, auch im Tempo da der ander die Klinge meinete gefunden zuhaben verletzet. | |||||
[51] This hit under the sword on the outside may be made in tierce or in quarte against a quarte, according as the arm is parried outwards more or less, and may arise in this way: your adversary has tried to engage your sword on the inside. You have disengaged and he has tried to hit in quarte under the sword. After disengaging you have withdrawn the body, in order to have time to return your sword to the lower lines before he could reach. You have succeeded, and dropping the hand and figure at the same moment have again found his faible with your forte, and hit him in the right side, as he turned. Or you may suppose the position has arisen, when you tried to engage your adversary's sword on the outside, he being in seconde .[!] In that time he has changed from seconde to quarte, turning his left foot, in order to hit under the sword and let your sword pass. At the same moment you have carried your body on to the left foot, returned your sword to the lower lines on the outside, and thus made the hit shown. |
[60] LA FERITA, CHE QVI OLTRE SI VEDE SOTTO LA SPADA dalla parte di fuori, può essere fatta in terza, & anco in quarta contra un’ altra quarta, secondo che l’ braccio si porta più, & meno in fuori, & può essersi cagionata dall’ essere andato collui, che è ferito à ritrouare la nimica spada dalla parte di dentro, & hauendo detto nimico cauato questi habbia uoluto ferire di quarta sotto la spada, & che esso nimico, quale hauea cauato si sia lontanato col corpo, affine di hauere tempo di rimettere la spada di sotto prima che la punta dell’ altro gionga, come gli è riuscito, ilquale nimico, che è il ferittore si uede, che hà abbassato la mano, & la uita ad’ un tratto, & per questo hà ritrouato il debile auerso col suo forte, & hallo ferito nel dirito fianco nel pùnto, che egli giraua. Si può anco credere che sia interuenuto perche il ferittore sia andato per ritrouare la spada auersa dalla parte di fuori, quale douea essere in seconda, & in detto tempo il ferito habbia uoltata di seconda in quarta girando il manco piede per ferire lui sotto la spada, & lasciare la nimica uuota, & che esso ferittore nel punto medesimo habbia portato il corpo sopra il sinistro piede, & rimessa la spada di sotto per il lato di fuori, & così habbia fatta la ferita, che si uede. 33. |
Wie man wieder eine Voltirte Qvarta unter der Klingen verwunden sol. No. 33. DEr Stosz so man hier ferner No. 33. auswendig unter der Klingen gemachet siehet, kan eine Terza oder auch eine Qvarta wieder eine andre Qvarta, nachdem der Arm mehr oder weniger auswärts gehet, und kan hergekommen sein, dasz der Getroffene des andern Klinge einwendig finden wollen, selbiger aber [110] indem caviret, worauf der Getroffene die Qvarta unter der Klingen hat stoszen wollen; der cavirende aber hat seinen Leib indem zurükgezogen, damit er Zeit habe, ehe als des andern seine Spitze anreichet, die seinige zuversenken: Wie es ihme denn auch angegangen. Denn wie man siehet, so hat der Treffende seine Hand und Leib in einem Huy zugleich versenket, und deswegen mit seiner Stärke des andern Schwäche angetroffen, und ihn in die gewante, rechte Seite in dem Tempo da er voltiret getroffen. Man kan auch meinen, es sei herkommen, weil der Treffende seines Gegners Klinge auswendig hat strigiren wollen, welche denn solte in Seconda gewesen sein, in besagtem Tempo aber habe der Getroffene die Hand aus Seconda in Qvarta gewendet, sich zugleich mit dem linken Fusz gedrehet um unter der Klingen indem des Feindes seine fehl gienge zuverletzen. Der Treffende aber hat indem seinen Leib uf den hintersten Fusz zurük geleget und seine Klinge auswendig unten nach des Feindes Seiten gewendet, und also diesen Stosz den man hier siehet, verrichtet. | |||||
[52] This seconde against a quarte has arisen as follows: your adversary being in quarte has tried to engage your sword in tierce on the outside and you have disengaged on the inside, still in tierce. The adversary, taking the time of the disengage, has tried to hit in quarte in the line uncovered, turning his body. You have changed from tierce to seconde, dropping your body and sword under his sword and letting it pass in the air above. Or it might happen that you have moved and tried to engage his sword on the outside, with the hand in quarte, in order to have greater strength in the line where his sword was, and in order to be more covered on the inside. Your adversary has disengaged on the inside and made a quarte in order to hit above the hilt in the line seen to be uncovered. Then you have changed from quarte to seconde, and, lowering your whole body below the position where the hilt was, have carried forward the right foot in such a manner, that his sword has passed in the air and you have made the hit shown. |
[61] MA QVESTA DI SECONDA CONTRA LA QUARTA PVO ESSEre seguita dall’hauere collui, che hà fatta la quarta uoluto andare à trouare la nimica in terza di fuori, & dall’hauere l’ altro cauato di dentro medemamente di terza, & perche il primo pigliando il tempo di tale cauatione habbia uoluto ferire di quarta per quello scoperto girando il corpo, & l’ auerssario uoltando di terza in seconda con abbassare il corpo, & la spada sotto la nimica habbia fatta passare quella à uuoto di sopra. Oltreciò può essere auenuto, che quello, che hà ferito si sia mosso & andato à trouare la nimica per di fuori, con la mano in quarta, per essere di maggiore forza in quella parte, oue era detta nimica, & per essere anco più coperto di dentro, & che il nimico habbia cauato di dentro, & fatta una quarta per ferire di sopra dal finimento per il scoperto, che si uedeua, & all’ hora il detto ferittore uoltando di quarta in seconda, & abbassando tutto il corpo sotto quel sito, oue prima si trouaua il finimento, habbia portato il destro piede inanzi in modo, che la nimica sia passata uana, & esso hahbia fatto la ferita, che si uede. 34. |
[111] Wie einer mit der Seconda wieder die gyrirte Qvarta verfallen kan. No. 34. ABer diese No. 34. wieder eine Qvarta gemachte Seconda kan daher kommen sein, dasz der so die Qvarta gemachet hat, des Feindes Klinge auswendig in Terza hat finden wollen, und dasz der ander indem auch mit der Terza einwendig caviret habe; Da dann der erste das Tempo der Cavation nehmen und in selbige Blösze mit der voltirten Qvarta hat hinneinstoszen wollen, der Gegner aber hat indem die Hand aus der Terza in die Seconda verwendet, ist unter des Feindes Klingen mit wohl abbassirtem oder versenktem Leibe verfallen, und hat des Feindes Klinge oben laszen fehl gehen. Uber das kans kommen sein, dasz derjenige, so getroffen, sich beweget und des Feindes Klinge auswendig mit der Hand in Qvarta habe stringiren wollen, weil die Qvarta auswendig, allwo des Feindes Klinge war, mehr Stärke hat, und weil er auch einwendig mehr bedekket war; Der Feind aber hat indem einwendig caviren und eine Qvarta über dem [112] Gefäsze nach der Blösze, so er daselbst sahe, hinneinstoszen wollen: Alsobald hat darauf der Treffende seine Hand aus der Qvarta in die Seconda gewendet, ist mit dem ganzten Leibe unter den Situm oder unter die Linie darinnen sich das Kreutze befande, verfallen, ist mit rechtem Fusz fortpasziret, dasz also des Feindes Spitze fehl gegangen, und er, wie man hier siehet, solchen Stosz gemachet. | |||||
[53] Now follows a hit in prime against a seconde. Both being in tierce on the inside, you have tried to engage your adversary's sword; he has taken the time when you were trying to subject his sword, and has disengaged on the outside, changing his hand to seconde and advancing to hit over the sword in the line you have uncovered in trying to subject his sword. But you, seeing the disengage and the blow intended, have taken that time, changed from tierce to prime, lowering the whole body, so that the head is entirely covered and defended by the hilt and right arm, and have pushed out the seconde, for in the change to prime your hilt has gone so high as to cover the point aimed at by the adversary with his seconde; with the result that his point, which was to hit above, has remained below and excluded by your forte. Or you may have tried to engage the adversary's sword, and he has tried cut of riverso at the arm in the part seen uncovered; you by a change from tierce to prime have defended yourself and covered your arm with the forte. Therefore the adversary has failed to effect[!] anything and has been hit in the same time. |
[62] VNA FERITA DI PRIMA, CHE QVI SI VEDE SEGVIRE, CONtra una seconda, deue essere successa, perche trouandosi tutti dui di dentro in terza, quello, che hà ferito è andato à trouare la spada al nimico, ilquale hà pigliato il tempo, quando l’altro uoleua opprimerli la spada sudetta, & hà canato di fuori uoltando la mano in seconda, & portandosi oltre per ferire l’auerssario sopra la spada ne lo scoperto, che hauea fatto in quello uolerli opprimere la sua, mà detto auerssario uedendo la cauatione, & il colpo, che questi uoleua fare, preso quel tempo, & uoltato di terza in prima con abbassare tanto il corpo, che la testa è rimasta intieramente coperta & diffesa dal finimento, & braccio destro, & anco serrata fuori la seconda, perche il finimento nel uoltare in prima è andato tanto alto, che hà coperto il luogo, oue miraua di ferire il nimico con quella seconda, in modo, che la punta, laquale douea ferire di sopra è restata disotto, & esclusa dal forte auerso. Potria anco essere uenuto il ferittore per trouare la spada à quello, che è ferito, ilquale hauesse uoluto uoltare di riuerso al braccio per lo scoperto, che uedeua & che detto ferittore con uoltare pure di terza in prima si sia diffeso, & coperto detto braccio col forte, & perciò l’ altro non habbia potuto fare niente mà nel medemo tempo sia restato ferito. 35. |
Wie die Prima wieder und unter einer Seconda gestoszen wird. No. 35.
EIn Prima Stosz so man hier No. 35. wieder eine Seconda folgen siehet kann sich zugetragen haben, dasz weil sie sich allebeide einwendig in Terza befunden der Treffende um des Feindes Klinge zufinden denselben angagangen ist, welcher denn das Tempo, indem ihm der erste seine Klinge also [113] unterdrükken wolte, inachtgenommen, die Hand in Seconda verwendet und um den feind in die gegebene Blösze, welche als er die Klinge niederdrükken wolte, gemachet wurde, über der Klingen zuverletzen auswendig caviret hat: Aber dieser besagter Feind nachdem er die Cavation und den Stosz so der ander machen wolte kommen gesehen, hat solches Tempo genommen, die Hand aus der Terza in Prima verwendet, ist mit dem Leibe so tief verfallen, dasz der Kopf einwendig von dem Kreutz und dem rechten Arm bedekket und geschützet wurde, und hat also die Seconda ausgeschlossen. Denn nachdem die Hand in die Prima verwendet worden, ist das Kreutz so hoch gegangen, dasz es den Orth, wo der Feind hinutreffen zielete, bedekket, dasz darum die Spitze so oben treffen solte unten kommen und von der feindlichen Stärke ausgeschlossen worden ist. Es kan auch der Treffende den Getroffenen um seine Klinge zufinden angegangen sein, welcher Getroffener denn mit Riverso nach dem Arm in die Blösze so er sahe verletzen wollen; Der andre aber hat schlechterdinges aus der Terza in die Prima verwendet und sich also beschützet, indem sein Arm von der Stärke bedekket wurde, und hat deshalben nichts machen können, sondern ist in selbigem Tempo verwundet worden. | |||||
[54] This hit in quarte against seconde has arisen in this manner. Both being in tierce on the inside, you have tried to engage your adversary's sword, and he has meant to change from tierce to seconde and drop under your sword in the time, when your point was out of line. Therefore you, seeing his plan, have not completed the engagement, but have directed your point to his body, carrying the hilt where you had planned to put the point; you have turned the body and the right foot, carrying it forward and leaving your hand against the adversary's faible. In this manner you are defended and have reached him whilst he was lowering his body and advancing. Equally it might occur that he was in seconde on the inside, and that you have tried to engage his sword. He has intended to disengage in seconde in order to hit on the outside above the sword. You have disengaged, carried the hilt where you meant to put the point, and by the turn of the body, foot and hand, have hit at the moment your adversary thought to hit. |
[63] QVESTA LEI, CHE E VNA QVARTA, LAQVALE HA FERITO una seconda è successa, perche, stando tutti dui in terza di dentro, questo che è ferito è andato per trouare la spada al nimico, ilquale hà uoluto uoltare di terza in seconda, & abbassarsi sotto la spada nel tempo che la punta auersa andaua fuori di presenza, & perche il detto ferittore, uedendo tale effetto, non hà finito di andare alla spada mà hà dirizata la sua punta al corpo dell’ altro, & portato il finimento, oue hauea disegnato mettere la punta girando il corpo, & il destro piede con pottarlo inanzi, & con lasciare la mano al debile nimico, nelquale modo è restato diffeso, & hà incontrato il nimico mentre, che si piegaua per andare abasso, & si portaua inanzi. Può similmente essere che l’ ferito fosse in seconda di dentro, & che l’ ferittore sia andato per trouarli la spada, & esso ferito habbia uoluto cauare di detta seconda per ferire di fuori sopra la spada, & questi habbia cauato, & portato il finimento, oue haueua uoluto mettere la punta, & col detto giro di corpo, piede, & mano habbia ferito nell’istesso punto, che l’altro credeua ferire. 36. |
Wie man mit Qvarta wieder eine Seconda gyriren soll. No. 36. DIese nun No. 36. so eine Qvarta ist und eine Seconda getroffen hat, ist hergekommen, weil sei beide einwendig in Terza lagen, hat der Treffende sich beweget und des Feindes Klinge stringiren, dieser aber aus der Terza in die Seconda verwenden, und in dem Tempo, da des Feindes Klinge auswendig auszer der Presenz gienge, unter der Klingen verfallen wollen, weil aber der Treffende solche Würkung ersehen, hat er die Bewegung [114] die Klinge zufinden unvollendet gelaszen, sondern hat seine Spitze nach des Feindes Leibe und den rechten Fusz nach dem Feinde zuwärts gedrehet, die Hand aber doch bei des anderen Schwäche gelaszen, auf welche Arth er denn sicher geblieben, und also den andern indem er vor sich gieng und unten zuverletzen sich bügete, getroffen hat. Es kan auch geschehen sein, dasz der Getroffene einwendig in Seconda gelegen, der Treffende habe sich darauf bemühet des andern seine Klinge zufinden, indem nun der Getroffene in Seconda caviren und auswendig über der Klingen verletzen wollen, hat der Treffende auch caviret, und sein Kreutz dahin, wo die Spitze herkommen solte erhoben, und also mit besagter Wendung des Leibes, der Füsze und der Hand in dem Tempo, da der ander getroffen zuhaben vermeinete, verwundet. | |||||
[55] This hit in quarte against a seconde may arise in two ways: in the first place both combatants might be in tierce on the inside; you have tried to engage, and your adversary has disengaged in seconde over your sword, passing on with his left foot. You, lowering your point without disengaging and letting your arm make an angle to the inside, as is seen, with the hand in a guard of quarte, have turned the body with the left foot, met the adversary as he advanced and hit him in the side under the right arm. Thus his sword has passed idly in the air. In the second place it may be that you have disengaged on the outside, and your adversary has sought to take the time in order to hit above in seconde. Then you have simply lowered your point, which had gone to the outside, under his sword, leaving the hand in the same place, but turning it into quarte; without extending the arm you have turned the body and brought all the part which was uncovered when on guard, out of presence. |
[64] LA FERITA DI QVARTA, CHE QVI SEGVIRA CONTRA VNA seconda può essere accaduta in dui modi, il primo perche tutti dui li combattenti si possono essere trouati in terza di dentro, & che quello, che hà ferito sia andato à trouare la nimica, & l’ altro habbia cauato di seconda sopra la spada nimica, & passato oltre col sinistro piede, & che il detto ferittore abbassando la punta senza cauare, & lasciando il braccio alquanto angolato all’ indentro, come si uede, & la mano in quarta guardia, & con girare il corpo col pie sinistro habbia incontrato il nimico, che ueniua, & feritolo nel fianco sotto il braccio destro, & cosi la spada di quello sia passata uana, & senza essere tocca. Il secondo modo è, ò può essere, che sopradetto che hà ferito habbia cauato di fuori, & l’ altro habbia cercato di pigliare quel tempo per ferire di sopra di seconda, & l’ istesso ferittore all’ hora non habbia fatto altro, che abbassare la punta, quale era andata di fuori sotto la nimica, lasciando la mano nell’ istesso luogo con uoltarla però in quarta mà senza slongare il braccio, & habbia girato il corpo leuando di presenza tutta quella parte, che si uedeua stando nella guardia. 37. |
[115] Wie man eine Qvarta wieder die Passirte Seconda gyriren soll. No. 37. GEgenwärtiger Qvarta-Stosz wieder eine Seconda kan auf zweierlei Arth hergekommen sein. Erstlich da sich beide Partheien einwendig in Terza befunden haben, und dasz dann der Treffende des Feindes Klinge hat stringiren wollen, da alsbald der ander mit der Seconda über die Klinge caviret und über das mit dem linken Schenkel pasziret; Der Treffende aber hat seine Spitze ohne caviren sinken, den rechten Arm wie man siehet mit der Hand in die Qvarta ein wenig anguliret einwarts gehen laszen, auch dem Leib mit den linken Fusz voltiret, ist also dem Feinde, welcher drauf ankam, entgegen gegangen, und hat ihn unter dem Arme in die rechte Seite verletzet, wordurch deszelben Getroffenen Klinge ausser berühret zuwerden leer abgeganben ist. Auf die zweite Art kans sein, dasz obenbesagter Treffender auswendig caviret, der ander aber versuchet hat solch Tempo zunehmen, [116] und oben mit der Seconda zuverletzen, darauf hat der Treffende anders nichts gethan, als die Spitze welche auswärts unter des Feindes Klingen gegangen war versenket, die Hand in selbem Situ gelassen doch ohne ausstrekkung des Armes in Qvarta verwendet, hat also den Leib voltiret, und alle die Blöszen so man im Lager sehen können aus der Presenz weggenommen. | |||||
[56] Now follows another hit in quarte, this time against a quarte, arising in this manner: you have tried to engage your adversary, who was in tierce on the outside. He has planned a cut of mandiritto in sgalembro at the face, keeping his arm in line and working from the wrist only. You have suddenly brought the left foot forward with the point of the foot turned outwards; at the same time you have turned your hand into quarte; extending the arm and bending the body as far as possible, you have met your adversary's sword in its descent, before it was in line, excluded it and hit him in the throat. This is the true method of parrying a cut of mandiritto at the head, when you are forced to parry, for by bringing forward the left foot in this manner, not only does the sword reach further, but it is stronger and can better resist the shock of the cut; with the right foot it is weaker. |
[65] VEDESI SEGVIRE VN’ ALTRA FERITA DI QVARTA, MA CONtra una medesima quarta, laquale può essersi caggionata dall’ essere quello, che hà ferito andato à trouare la nimica, che era in terza di fuori, & dall’ hauere il detto nimico uoltato di un mandiritto in sgalembro per la faccia tenendo il braccio in giustezza, con operare solamente il nodo della mano, onde, quello che hà ferito, subbito è passato del sinistro piede inanzi, & con la punta di esso piede uoltata infuori, & con uoltare similmente la mano in quarta slongando il braccio, & piegando il corpo, quanto che più hà potuto, hà incontrata la nimica che discendeua prima, che sia caduta in presenza, & l’ hà esclusa di fuori ferendo il medesimo nimico di detta quarta nella gola, & questo è stato, & è il uero modo, col quale si dee parare il mandiritto per testa, quando l’ huomo è astretto di parare, perche passando col sinistro piede in questa forma, oltre che la spada uà più inanzi à ferire, è anco più forte, & può meglio resistere alla percossa del taglio, doue che col destro piede è molto più debile. 38. |
Wie eine Qvarta mit dem linken Schenkel wieder eine andre Qvarta passiret werden kan. No. 38. HIer siehet man No. 38. einen andern Qvarta Stosz aber auch wieder eine Qvarta folgen, welcher sich denn kan zugetragen haben, dasz der Treffende sich habe beweget um des andern seine Klinge welche auswendig in Terza war zu stringiren; Besagter Feind aber habe indem mit Mandiritto sgvalembrato nach dem Gesichte zugehauen und zugleich seinen Arm kunstrecht gehalten, auch darum die Wirkung nur mit dem Vordergelenke der Hand gemachet, da denn der Treffende [117] mit seinem linken Fusz alsobald fortgerükket ist, auch mit solcher Bewegung des Fuszes zugleich die Zeen desselben auswarts gesetzet, mit Ausstrekkung des Armes die Hand in Qvarta gewendet und den Leib so viel er gekont übergebogen, ist also des Feindes Klinge begegnet und hat verursachet, dasz sie ehe als sie in Presenz kam abwärts verfiele und ausgeschlossen wurde, und hat also damit den Feind in selbigem Tempo in die Gurgel verletzet. Dieses ist also geschehen und die rechte Arth, wie man Mandiritto nach dem Kopff, wenn man je anders pariren musz, versetzen sol; Denn ohne dasz, wenn einer mit dem linken Fusz auf solche Weise vorpasziret, die Spitze weiter reichet, so ist sie auch viel stärker, und kan dem Einfall des Hiebes besser wiederstehen, da sie hergegen mit dem rechten Fusz gemacht viel schwächer ist. | |||||
[57] In this case both were in a guard of tierce, on the outside. You have tried to engage by turning the hand into seconde. The adversary has disengaged, turning his body and his hand into quarte, in order to hit in that time on the inside under your hilt. But you have turned at the same moment from seconde to quarte and have brought the left foot forward putting the point of your sword under his hilt, carrying the arm inwards, and the forte towards his faible, in such a way that your side is completely defended. It is safer in this case to follow with the right foot, rather than to retire. Such a hit cannot be prevented, even though the swords are of equal strength, because the position of the one who is turning is much weaker than that of the one who is advancing in the manner described; the latter's sword with equal skill will always overcome the sword of the one who is turning. |
[66] MA RITROVANDOSI QVESTI DVI, CHE SEGVENO NELLA terza guardia dalla parte di fuori, & essendo quello che hà ferito andato à ritrouare la nimica con uoltare la mano in seconda l’ altro hà cauato girando il corpo, & la mano in quarta per ferire in quel tempo di dentro sotto il finimento nimico, mà il ferittore uoltando nel putito medemo di seconda in quarta è passato oltre col sinistro piede mettendo la punta della spada sotto il finimento auerso con portare il braccio indentro, & il forte uerso la nimica, nel debile però, & con uoltare anco la punta di esso piede sinistro infuori hà fatto una sfuggita di uita, in modo che l’ fianco è restato intieramente diffeso, & è più sicura cosa lo seguire col destro piade inanzi, che l’ ritornare indietro. Nemeno sarebbe tale ferita impedita, ancorche le spade fossero state pari nella raggione del forte perche il sìto di quello, che gira è molto più debile di quello, che passa, nella sopraditta forma, la spada delquale superarà sempre con eguale partito quella di collui, che girà. 39. |
Wie man wieder eine Voltirte Qvarta die Qvarta mit dem linken Schenkel passiren kan. No. 39. [118] INdem sich aber No. 39. gefolgten beide auswendig in Terza befunden ist der Treffende mit Wendung der Hand in Seconda gegangen und hat des Feindes Klinge stringiren wollen, da hat der ander auch seine Hand in Qvarta verwendet caviret, und indem seinen Leib uf dem Rechten Fusz voltiret um in selbigem Tempo einwendig unter dem Kreutz zuverletzen; Aber der Treffende hat zugleich mit dem linken Schenkel fortpassiret und hat indem seine Spitze unter des Feindes Kreutz logiret, worum er denn auch den Arm hat lassen einwärts und seine Stärke gegen oder nach des Feindes Schwächen gehen, hat über diesz die Zeen des linken Fuszes auswärts gesetzet und damit den Ober-Leib gewendet, also dasz die einwendige Seite gäntzlich beschützet und sicher bliebe. Aber hier ist nun sicherer gewesen mit dem rechten Fusz vollens verfolgen als sich wiederzurükbegeben. Dieser Stos wäre auch vielweniger verhinder worden, obgleich die Klingen der Stärke nach einander weren gleich gewesen: Denn das Lager dessen so voltiret ist viel schwächer als des andern so pasziret seines, wie es oben beschrieben worden; maszen des paszirenden Klinge allezeit dessen so voltiret seine bezwingen wird, ob sie gleich beide gleiche Vortheil zuhaben scheinen. | |||||
[58] This hit in seconde against an opponent in quarte who has advanced the left foot may easily arise in the following manner: the adversary, being in quarte, has tried to engage your sword, which is in tierce, on the outside. You have disengaged, still in tierce. He has attempted a hit in quarte through your faible, advancing the left foot. But in the same time as you disengaged you have dropped your point under his hilt, also advancing the left foot. By bringing the whole weight of the body on to the left foot and turning the hand into seconde, you have got far out of the line of you adversary's point and made the hit. It might arise in another manner: both being in tierce on the inside, you have moved your point, making a slight turn of the hand towards quarte. The adversary, seeing the opening, has tried to engage your faible and hit in the same time by advancing the left foot. But before he has reached your faible you have dropped your point under his hilt, so that he has failed to find your point, and in the same time carried your body out of line, bringing the weight on to the left foot, which has advanced. In this low position you have been able to penetrate to his body, as you were already advanced. Or again, both being in tierce on the outside, the adversary has tried to engage your sword; in the same time you have threatened a cut of mandiritto at the head, using the wrist and keeping the arm steady. He has changed from tierce to quarte in order to defend the head, and advanced the left foot in order to hit in the same time. At that moment you have checked your sword near the adversary's, without touching it, and immediately changed your hand to seconde, lowering the point under his hilt, advancing the left foot, with the body so bent, that his point, which would have hit in the chest, has passed over. Therefore you may see how dangerous it is to parry, even with a thrust in the same time. Therefore, unless forced, it is always best not to parry. |
[67] QVESTA FERITA DI SECONDA CONTRA VNA QVARTA PASsata di piè sinistro inanzi facilmente è deriuata dall’ essere andato collui, che hà fatta la quarta à ritrouare la nimica spada dalla parte di fuori laquale era in terza, & dall’ hauere l’ altro cauato di detta terza; il primo hà uoluto ferire di quarta per il debile nimico passando oltre col sinistro piede, mà questi che hà cauato, hà nel tempo medemo abbassata la punta sotto il finimento auersso passando ancor lui col sinistro inanzi curuando tutto il corpo sopra di esso sinistro piede, & hà uoltata la mano in seconda, in modo che è uenuto molto à dillongarsi dalla presenza della punta auersa, & à fare detta ferita, laquale in un’ altra guisa ancora può essere uenuto cioè, che ritrouandosi ambidui in terza di dentro quello che hà ferito si sia slargato con la punta facendo un poco di uolta di pugno uerso la quarta, & che l’ altro uedendo quello scoperto habbia uoluto aquistarli il debile, & ferirlo nel tempo medesimo, col passare oltre del sinistro piede, mà il primo inanzi, che questo sia gionto al debile, hahbia abbassata la punta sotto il finimento nimico, che da esso nimico non è potuto esserli trouata, & in un tempo istesso habbia portato il corpo fuora di presenza, & piegatolo sopra il manco piede, quale è passato, & così basso hà potuto penetrare sino al corpo nimico trouandosi già molto inanzi. In oltre può essere successa detta ferita per essersi trouati tutti dui in terza di fuori, & che collui, che è ferito sia andato per ritrouare la spada auersa, & il ferittore in quel tempo medesimo habbia uoltato di mandiritto per testa col nodo della mano tenendo fermo il braccio, & il ferito habbia uoltato di terza in quarta per diffesa del capo, & sia passato oltre col manco piede per ferire nel tempo medesimo, nelquale proprio punto quello, che hà tirato il taglio hà trattenuta la spada appresso la nimica [68] tanto, che l’ altro non l’ hà toccata, & in questo instante hà uoltata la mano in seconda abbassando la punta sotto il finimento nimico, & passando inanzi col sinistro piede, & col corpo tanto chinato, che la punta, laquale douea ferire nel petto è passata disopra, di modo, che benissimo si cognosce quanto sia pericoloso il parare ancorche si ferisca in tempo medesimo, & però, potendosi fare dimeno, sarà sempre ottima cosa il non parare. 40. |
Wie man wieder die passirte Qvarta mit der Seconda verfallen kan. No. 40. DIeser Seconda Stosz wieder eine mit dem linken Schenke passirte Qvarta ist leichtlich daher gekommen, dasz der so die Qvarta gemacht des andern seine Klinge, welche in Terza lage, auswendig finden wollen, und dasz der ander in besagter Terza caviret hat, da denn der erste mit der Qvarta an des Feindes Schwäche fortstoszen wollen, und mit dem linken Fusz vorpassiret ist: [119] Aber der so caviret gehabt, hat in selbigem Tempo seine Spitze unter des andern sein Kreutz versenket, und ist auch zugleich mit dem linken Schenkel, auf welchem er seinen gantzen Leib übergebogen, vorpassiret, hat seine Hand in Seconda gewendet, womit er weit aus der Presenz des Feindes Spitzen gekommen und besagten Stosz machen können, welcher doch auch noch auf eine andere Arth hette geschehen können: Nehmlich wenn sich allebeide in Terza einwendig befunden hetten und der Treffende sich gestrekket und die Hand ein wenig nach der Qvarta gewendet hette, da dann der ander, weil er diese Blösze gesehen, die Schwäche gewinnen, indem mit dem linken Schenkel fortpassiren, und in selbigem Tempo zustossen wollen; Aber der erste hat ehe jener an die Schwäche gekommen, seine Spitze unter des andern Kreutz versenket, da sie denn von dem andern nicht hat können gefunden werden, und hat in eben selbigem Tempo seinen Leib, indem er denselben gantz auf den linken Fusz geleget, auszer der Presenz gebracht, welcher linker Fusz denn passiret, und hat also erniedriget, weil er sich schon ziemlich weit hinneinbefunden, bisz an des Feindes Leib continuiren können. [120] Weiter kan dieser Stosz zugegangen sein, dasz sich beide in Terza befunden haben, und der Getroffene des andern Klinge finden wollen; Der Treffende nu hat indem mit unbeweglichem Arme nur durch Bewegung des Vorderngelenkes seiner Hand, als wolte er mit Mandiritto nach dem Kopfe hauen, gewendet, Worauf der Getroffene zu Beschützung seines Kopffes alsobald aus Terza in Qvarta gegangen, und über das um in selbigem Tempo zutreffen mit dem linken Schenkel vorpassiret ist, in welchem Augenblik denn der Treffende, welcher hatte hauen wollen, seine Klinge von des Feindes seiner, damit sie einander nicht berühren mögten, zurückgehalten, zugleich seine Hand in Seconda gewendet und die Spitze unter des Feindes Gefäsz versenket hat, indem auch mit dem linken Schenkel fortpasziret, und sich mit dem Leibe so tief gebogen, dasz des andern Spitze, so in die Brust verletzen wolte, ober hin fehlgegangen. Woraus man nun recht eigentlich und gar wohl erkennen kan, wie gefährlich das pariren sei, ob man schon in selbigem Tempo zugleich mitstöszet: Dasz es derowegen, wo man dessen überhoben sein kan, besser sein wird, dasz mans unterwegens sein lasze, und nicht parire. | |||||
[59] Here is another hit in seconde also against a quarte. Both were in tierce on the inside. You were in a stronger position than your adversary and have made a feint of hitting in quarte through his faible. He, thinking the thrust was coming, has made a turn of his body with his right foot and a thrust in quarte through your faible, in order to meet you in the time of your approach. Seeing his plan, you have suddenly changed to seconde. lowering your point and body and bringing the left foot forward; thus you have made the hit by continuing on to his body, before he could recover, for he has not passed, but turned, and his left foot has remained steady. Or it may be that you have tried to engage your adversary's sword on the outside. He has disengaged in tierce on the inside, but in that time you have made a feint in quarte. He has tried a counter quarte through your faible turning his body out of line, in order to meet your approach. Seeing the danger you have changed from quarte to seconde and made the hit shown, while his sword has passed over in vain. |
ANCORA QVESTA ALTRA DI SECONDA PVRE CONTRA VNA quarta, puó essere uenuta per essersi trouati tutti dui interza di dentro, & che quello, che hà ferito fosse in sito più forte del nimico, & hauesse finto di uolere ferire di quarta per il debile delo stesso nimico ilquale credendo che ’l uenisse hauesse fatto ungiro del corpo col destro piede, & una quarta per il debile auerso, affine di incontrarlo nel tempo che ’l ueniua, mà il primo ueduto quello effetto habbia subbito uoltato di seconda con abbassare la punta, & il corpo, & passando col piè sinistro habbia fatta detta ferita con continouare pure sino al corpo nimico, prima che esso ferito habbia potuto rimettersi, ilquale non era passato mà girato, & era restato fermo il sinistro piede. Può similmente essere, che quello, che hà ferito sia andato à trouare la spada nimica di fuori, ilquale nimico habbia cauato di terza di dentro, mà il ferittore in quel tempo habbia finto di ferire di quarta, & perciò l’ altro habbia uoluto fare una contra quarta per il debile auerso girando il corpo fuori di presenza per in contrarlo mentre ueniua, & che il detto ferittore, ueduto il pericolo, habbia mutato di quarta in seconda & fatta la ferita, che si uede, & la nimica sia passata uana per desopra. 41. |
Wie man wieder eine uf dem linken Schenkel gyrirte Qvarta die Seconda mit dem linken Schenkel passiren soll und kan. No. 41. ES kan auch dieser zweite Seconda-Stosz wieder eine gyrirte Qvarta sein hergekommen, dasz sich allebeide einwendig in Terza befunden haben, doch derjenige welcher getroffen hat in einem, was die Stärke betrifft vortheilhafftigerem Lager, als der andere; Hat deswegen mit der Qvarta in des Feindes Schwäche eine Finta gemachet, welcher denn gemeinet, erwürde in Wahrheit und mit Ernst dahinneinstoszen wollen, hat darum den Leib mit dem rechten Fusz gyriret, und eine Contra-Qvarta an des ersten Schwäche hineinstoszen wollen, aufdasz er ihme im Tempo da er vor sich gienge, begegnen mögte; [121] Da aber der Treffende solcher Würkunge wahrgenommen, hat er geschwinde mit Versenkung der Spitzen und des Leibes in die Seconda verwendet, mit dem linken Fusze passiret, und also bisz an des Feindes Leib fortgehend besagten Stosz gemachet, auch ehe als der ander, welcher nicht passiret sondern gyriret hatte, und also mit und auf dem linken Schenkel ferm blieben war, zurükkommen konte getroffen. Es kan auch sein, dasz derjenige so getroffen hat des Feindes Klinge auswendig habe finden wollen, welcher Feind denn mit der Terza einwendig caviret; Der Treffende aber indem eine Finta mit Qvarta gemachet, worwieder der Getroffene an des Feindes Schwäche eine Contraqvarta hinneinstoszen wollen, und habe darum seinen Leib auszer der Presenz um damit dem andern als er auf ihn ankame, zubegegnen, gyriret; Der Treffende aber, wie er die Gefahr gesehen, aus Qvarta in Seconda verwendet und den Stosz, so man hier siehet, gemachet; des Feindes Spitze aber ist uberhin leer abgegangen. | |||||
[60] Another hit in quarte against a tierce. You were in tierce on the outside, as was your adversary. You have made a feint of hitting in this tierce on the outside, and he has moved to parry and hit by pushing on his right foot, enticed by seeing you move without a time. Seeing your adversary moving to parry and hit, you have placed your left hand on the inside of his sword, disengaged in quarte, advanced the left foot and so hit him at the base of the right side. Or you may have been on the inside and may have disengaged with a feint of hitting on the outside. Your adversary has tried to parry and you have placed your left hand on his sword and made the hit. These defences with the left hand are here shown in order to demonstrate how in case of necessity only, they may sometimes be used. The effect is seen, and you may realise how easily such defences may be deceived. Towards the end of the book we shall describe a method against which the left hand will not prevail nor parry. |
[69] QVI SEGUIRA VNA FERITA DI QVARTA VNA TERza caggionata perche quello, che hà ferito ritrouandosi in terza di fuori, si come l’ auerssario, haurà finto di uolere ferire di detta terza di fuori, & perche l’ altro sarà andato à parare per uolere poi ferire con spingere il destro piede inanzi, allettato dall’ hauere ueduto il nimico mouersi senza tempo, ilquale nimico uedendo lui andare à parare, & ferire haurà messa la sinistra mano di dentro della spada auersa, & cauato di quarta passando oltre col sinistro piede, & così haurà fatta la ferita nella giuntura del fianco destro. Ancora può essere, che quello, ilquale hà ferito si sia trouato di dentro, & habbia cauato mostrando di ferire di fuori, & l’ altro habbia uoluto parare, & che il ferittore messa la sinistra alla nimica spada habbia fatta la detta ferita. Queste diffese con la sinistra mano, che qui si uedranno si sono poste per mostrare come in caso solo di neccessità si possino alcune uolte usare, & si uedrà ancora qualche effetto, ilquale farà conoscere quanto ageuolmente possino tale diffese essere ingannate, & nel fine del libro si parlarà di un modo di operare, contra ilquale la detta sinistra non ualerà, & non potrà parare. 42. |
[122] Wie einer die Qvarta stoszen soll indem er mit der linken Hand pariret No. 42. ALlhier No 42 folget ein ander Qvarta Stosz, welcher dann kan herkommen sein, dasz derjenige so getroffen hat, wie auch der andere sich auswendig in Terza befunden, und hat der Treffende mit besagter Terza alda eine Finta gemacht; Weil denn der andre pariret, um darauff mit einem Zutritt des rechten Schenkels hineinzustoszen, darzu veranlaszet, weil er gesehen, dasz sein Gegner sich ohne Tempo beweget hatte, welcher Gegner doch da er gesehen dasz der ander zur parirung gegangen um darauf zustossen, seine linke Hand hat laszen einwendig an des Feindes Klinge gehen, zuglich in die Qvarta caviret, mit dem linken Schenkel fortpasziret und also den Feind in das Gelenke der rechten Seiten getroffen und verletzet. Es kan auch sein, dasz sich der Treffende einwendig befunden, und hat alsdenn mit der Cavation fintiret als wolte er auswendig stoszen, da dann der ander pariren wollen; in welcher parirung aber der Treffende mit seiner linken Hand einwendig an des andern Klinge gegan [123] gen, und also gegenwärtigen Stosz gemacht. Diese Arthen die linke Hand zum pariren zugebrauchen seind mit hierhergesetzet um zu zeigen wie man sich solcher allein im Fall der Nothdurfft etlichemahl zubedienen habe, und darum werden auch folgends noch etliche Würkungen gewiesen werden, daraus zuerkennen sein wird, wie so gar leicht solche mit der linken Hand gemachete Parirungen können betrogen werden: Zu Ende des zweiten Buches aber will ich noch von einer andern Weise reden, wie man nehmlich würken solle, dasz die linke Hand gantz und gar nichts gelte, und wie es unmüglich sei, dasz einer mit solcher pariren könne. | |||||
[61] This next tierce against a quarte has followed when both were in tierce on the inside. You have made a feint of hitting in quarte on the inside. Your adversary has tried to hit in counter quarte through your faible. In the same time you have lowered your sword hand to tierce, carried your left hand to his approaching sword, lowering and turning the body with the left side forward, so that your hand has carried his sword away and you have hit him in the chest. It might arise in another way: you being on the outside have pushed the adversary's sword away. He has tried to disengage and hit in quarte on the inside. You have parried with the hand and hit him below as shown. Or it might very well be that both were on the outside,[!] The adversary has tried to engage; you have changed your hand to quarte in order to avoid the engagement; he has tried to hit with another quarte in the line seen to be uncovered, and in that time you have parried and made the hit. |
[70] MA QVESTA ALTRA DI TERZA, CHE VIEN DIETRO CONTRA una quarta è stata fatta, perche ritrouandosi ambidui in terza di dentro, il ferittore hà finto di ferire di una quarta di dentro, & l’ altro hà uoluto ferire di contra quarta per il debile nimico, & il primo nel proprio tempo hà abbassata la mano della spada in terza, & porta la sinistra alla spada nimica, che ueniua per ferire abbassando, & uoltãdo il corpo con ia parte manca inanzi tanto, che la sua mano hà portata fuori la spada nimica, & hà ferito l’ auerssario nel petto. Anco può essere occorsa in quest’ altro modo cioè che, essendo quello, che hà ferito di fuori, hahbia spinta la nimica, & l’ altro uoluto cauare, & ferire di quarta di dentro, & che il medesimo ferittore habbia parato con la mano ferendo di sotto, come si uede. Et oltre questo potria anco molto ben essere, che fossero stati di fuori, & il ferito fosse uenuto à trouare la spada al nimico, ilquale hauesse uoltata la mano in quarta per non lasciarsi occupare la spada, & che detto ferito hauesse uoluto ferire per quello scoperto, che uedeua con un’ altra quarta, & che l’ altro in quel tempo hauesse parato, & fatta cotale ferita. 43. |
Wie man eine Terza 'stoszen kan, im dem man mit linker Hand pariret. No. 43. ABer diese Terza nun No. 43. welche einwendig wieder eine Qvarta verletzet, ist herkommen, weil indem sich allebeide einwendig in Terza befunden der Treffende alda eine Finta in Qvarta gemachet hat, worauf denn der ander eine Contraqvarta an des Feindes Schwäche fortstoszen wollen, der erste aber hat in demselben Tempo seine Hand in Terza mit der [124] Klingen einwenig versenket, und ist mit der linken Hand an des Feindes Klinge, welche indem treffen wolte, gegangen, hat auch seinen Leib zugleich so viel abbassiret und die linke Schulter hinfürgebracht, dasz die linke Hand des Feindes Klinge auswendig auszwingen können, und also den Feind auf die Brust verwundet. Sie kan auch wohl auf eine andre Manier angegangen sein, nehmlich dasz da derjenige so getroffen hat sich auswendig befunden er daselbst des Feindes Klinge angegriffen, derselbe aber darauf habe caviren und eine Qvarta einwendig hinneinstoszen wollen, in welchem Tempo dann der Treffende mit der linken Hand pariret, und wie man siehet unten verletzet hat. Uber diesz kan es auch gar wohl sein, dasz sie sich beide auswendig befunden haben, und dasz der Getroffene des andern seine Klinge finden wollen, welcher damit er sich seine Klinge nicht occupiren liesze, seine Hand in Qvarta verwendet, worauf der Getroffene alsobald mit einer andern Qvarta in die Blösze so er da ersehen stoszen wollen, der Treffende aber hat indem wie obbesaget pariret und verletzet. | |||||
[62] The next is a hit in seconde against a tierce. Both being in tierce on the outside you have made an appel by turning the sword from tierce to second[!] and carrying the point inwards out of line. You have brought your left side so far forward as to uncover the whole chest to the adversary, but with the sword so low that he could only hit above, and holding the left hand before the face. While your adversary has seized the time to hit in the part uncovered, with the left hand you have pushed his sword outside your left flank, in the same time advancing the left foot, and with the body low have disengaged in seconde. Thus you have made a hit in the chest by extending the right arm as far as possible and bringing forward the right side also, but with the point of the left foot turned outwards in order to carry the body away from his sword. The result is here seen. |
[71] SEGVITA ALPRESENTE VNA FERITA DI SECONDA CONTRA una terza, uenuta, perche, trouandosi tutti dui in terza di fuori, quello, che hà ferito hà fatta una chiamata uoltando la spada di terza in seconda trauersata in dentro con la punta fuori di presenza, & con hauere uoltato il sinistro fianco tanto inanzi che scopriua tutto il petto alnimico, mà con la spada tanto bassa, che detto nimico, non poteua ferire se non di sopra con tenere la sinistra sopra delfronte, & mentre, che l’ istesso nimico è uenuto à ferire quello scoperto in tempo della chiamata, questi con la detta sinistra ha cauata la spada nimica fuori per il fianco sinistro passando oltre in medesimo tempo pure col manco piede col corpo basso cauando di detta seconda, & così hà ferito il nimico nel petto con slongare quanto hà potuto il destro braccio, & con accompagnarlo con l’ istesso fianco inanzi mà con la punta del piè sinistro uoltata in fuori per dillongare il corpo dalla spada nimica, & è questa stata la caggione dell’ effetto, che horsi uede. 44. |
Wie einer die Seconda stoszen kan indem er mit der linken Hand pariret. No. 44. [125] Hier folgte No. 44. ein Seconda-Stosz wieder eine Terza, so sich zugetragen, weil sich beide auswendig in Terza befunden und derjenige so getroffen hat seine Klinge aus der Terza in Seconda einwarts qver über und mit der Spitzen gantz auszer der Presenz gewendet, auch die linke Seite so weit hinfürgegeben und also eine Chiamata gemachet; Womit er denn die gantze Brust gegen dem Feinde entblöszet, mit der Klingen aber ist er so tief gegangen, dasz sein Gegner nirgend aderst als oben über der Klingen stoszen konte, hielte auch zugleich die linke Hand über der Stirne: Indem nun besagter Feind auf das Tempo der Chiamate in selbige Blösze zustoszen wollen, hat der ander mit der linken Hand des Feindes Klinge nach der linken Seiten unten auspariret, und zugleich mit dem linken Schenkel fortpassiret, mit dem Leibe aber sich tief versenket und in besager Seconda caviret, auch also den Feind auf die Brust verwundet, indem er den rechten Arm so viel er immer gekont ausgestrekket und die rechte Seite hervorgebracht, damit dasz der Leib auch desto mehr von der Spitzen des Feindes Klinge entfernet sei, hat er die Zeen des linken Fuszes auswärts gesetzet: Welches denn die Ursachen seind, dasz diese Würkung, so man hier siehet, alos getroffen. | |||||
[63] This is another seconde, but against a quarte, with the right foot advanced. Both combatants being in tierce on the outside, you have disengaged without waiting for a time or provocation of your adversary. He has seized the opportunity and tried to hit in quarte. You have at once turned your hand into seconde, brought the left side of the body forward, turned the heel of the right foot, placed the edge of your left hand over his sword, and hit in seconde in the chest. It might have arisen from both being in tierce on the inside; you have lowered your sword, leaving yourself uncovered, and he has thrust in quarte. Then you have raised your hand into seconde, changing the front of your body and keeping the right side back, as being in the most danger. In this manner you have parried with your hand, for this low quarte is forced down by the parrying hand whereas the point would naturally make a hit in the chest. |
[72] QVEST’ ALTRA SARA PVRE VNA SECONDA, MA CONTRA una quarta auanzata à piè destro, caggionata perche essendo li dui combattenti, ambi in terza di fuori quello che ha ferito, haurà cauato senza aspettare tempo nè prouocatione nimica, & l’ altro presa quella occasione haurà uoluto ferire di quarta, mà il primo uoltando subbito la mano in seconda, & il corpo con la sinistra parte di esso inanzi, & girando il derettano del destro piede, haurà appoggiato il filo della sua sinistra mano sopra la nimica, & ferito esso nimico ai detta seconda nel petto. Et può essere non manco proceduto perche fossero tutti dui in terza di dentro, & che quello, che hà ferito hauesse abbassata la spada, lasciandosi scoperto, & che l’ altro si fosse spinto inanzi di quarta, & però il detto ferittore hauesse alzata la mano di seconda, uoltando la prospettiua del corpo, & tenendo il destro fianco indietro, come quello che portaua più pericolo, & in tal modo hauesse parato con la mano, perche questa quarta, che si uede, andare à ferire tanto bassa si caggiona dalla mano di collui che para, ilquale la spingie, perche quanto alla punta di essa quarta andaria di sua natura à ferire uerso il petto nimico. 45. |
Wie man die Qvarta mit der linken Hand pariren und zugleich Seconda Contratempo stoszen soll, No. 45. DIese folgende No. 45. wird zwar auch eine Seconda sein, aber wieder eine Qvarta so mit rechtem Fusz ausgestoszen, und ist verursachet, dasz weil sich beide Partheien auswendig in Terza befunden, derjenige, welcher getroffen hat, ohne erwartung einiges Tempo oder feindlicher Aufforderung caviret, da dann der ander sich dieser Gelegenheit wollen bedienen und eine Qvarta hinneinstoszen; Der erste aber nach dem er die Hand geschwinde in Seconda, und die linke Seite des [126] Leibes hinfür auch die Zeen des rechten Fuszes auswarts gewendet, hat die Schneide seiner linken Hand an des Feindes seine Klinge geleget, sie damit pariret und also den Feind mit besagter Seconda in die Brust verletzet. Es kan sich auch nichtsdestoweniger zugetragen haben, dasz sich beide Theile einwendig in Terza befunden, und der Treffende seine Klinge sich also oben eintblöszend ein wenig sinken lassen, worauf der ander alsobald die Qvarta hinneinstoszen wollen, warum denn der Treffende seine Klinge in Seconda wieder erhöhet, die Prospective des Leibes indem er die rechte Seite, als welche am meisten in Gefahr, zurükgezogen, geendert, und also mit der linken Hand pariret; Denn dasz diese Qvarta so tief wie man hier siehet, verletzen zuwollen scheinet, kömmet her von der Hand dessen, so pariret, welche sie also aus ihrer Linie wegtreibet; Denn was sonst den Stos dieser Qvarta anlanget, pfleget er von Natur den Feind in die Brust zuverletzen. | |||||
[64] This is a quarte with a turn, which has hit against another quarte with the left foot advanced. The one who has passed has made a feint of hitting on the outside over the sword, and you have moved to parry. The adversary has placed his left hand on your sword in order to parry, and in the same time has disengaged in quarte on the inside, advancing the left foot, so as to hit in this quarte. But you, who have moved to parry the feint on the outside, seeing that your adversary was going to defend with the left hand, have disengaged your sword, which was above, on the outside of his hand, and thrust at his advancing body, bringing yourself out of line with a turn of the left foot. You would not have hit so low with the point, had you not found his faible with your forte, so that you were more defended. In this manner the attempt of the hand to parry has been deceived, as shown. |
[73] LA SEGVENTE SARA VNA QVARTA GIRATA, LAQVALE FErisce contra un’ altra quarta passata di piè sinistro, & successa, perche quello che è passato, hà finto di uolere ferire di fuori sopra la spada, & l’ altro è andato à parate, il primo hà metta la mano sinistra alla spada nimica dalla parte didentro per parare, & nelo stesso tempo hà cauato di quarta di dentro passando oltre col sinistro piede affine di ferire di detta quarta, mà l’ altro, che era andato alla diffesa della finta di fuori uedendo il nimico, che si uoleua diffendere con la sinistra hà cauata la spada, che era disopra, per la parte di fuori di detta mano, & halla messa nel corpo nimico, che ueniua, & girando col manco piede si è portato fuori di presenza, & non sarebbe ito à ferire tanto basso con la punta si non fosse stato per trouare col suo forte il debile auerso affine di restare più diffeso, in modo che la mano, laquale credeua parare è restata ingannata, come si uede, 46. |
[127] Wie man mit der Voltirten Qvarta die Parata der linken Hand betrügen, und zugleich verletzen soll. No. 46. DIe hier No. 46. folgende Figur soll eine mit dem falschen Tritt voltirte Qvarta sein, welche wieder eine mit dem linken Schenkel passirte Qvarta verletzet, und ist hergekommen, weil derjenige so pasziret auswendig über der Klingen eine Finta gemachet, der ander aber darnach pariret hat, worauf dann der erste seine linke Hand, um des Feindes Klinge damit einwendig auszupariren, an dieselbe Klinge gebracht, hat auch zugleich in selbigem Tempo mit der Qvarta caviret, mit dem linken Schenkel fortpassiret und mit besagter Qvarta verletzen wollen; Aber der ander welcher auswendig nach der Finta pariret hatte, als er sahe, dasz sich der Feind mit der linken Hand beschützen wolte, hat mit der Klinge, welche sich oberhalb befand, auswendig um des Feindes Hand caviret, und also nach des Feindes Leibe, indem er mit dem linken Fusz voltirete, auszer der Presenz gebracht: Er were auch mit der Spitzen nicht so tief zuverletzen gegangen, wenn er nicht mit seiner [128] Stärken des Feindes Schwäche gerne hette finden wollen, auf dasz er dadurch desto mehr versichert wäre. Also ist nun die linke Hand, welche pariret zuhaben gemeinet, wie man siehet, betrogen worden. | |||||
[65] This is another quarte hitting against a tierce designed to hit under the sword. You have made a feint of hitting towards the right side of your adversary's face. He has tried to parry with the left hand, lowering his body so as to hit under the sword on the inside. But you, who have made a feint, have seized the time of his raising his hand to defend the head, lowered your point to the space between his two arms in the time of his making the opening, and, changing your hand into quarte and turning the body with the left foot, have made the hit. The adversary has been unable to parry, because your sword was shut in between his two arms and could not be pushed aside without a change of plan. |
[74] ET QVEST’ ALTRA SARA PVRE VNA QVARTA LAQVALE ferisce contra una terza, che uoleua ferire sotto la spada & è proceduta dall’ hauere quello, che hà ferito di dentro finto di uolere ferire uerso la destra parte della faccia nimica, & dall’ hauere esso nimico uoluto parare con la sinistra mano abbassando il corpo affine di ferire disotto dalla parte interiore, mà l’ altro, che hauea finto, pigliato il tempo delo alzare di mano fatto da costui per diffensarsi il capo, hà abbassata la punta nel meggio dell’ uno, & dell’ altro braccio nel proprio tempo che si faceua l’ apertura, & uoltando la mano in quarta, con girare il corpo col sinistro piede hà ferito che l’ nimico non hà potuto parare, perche la spada chiusa fra le due braccia è restata in modo, che non si poteua rispingere se non si mutaua effetto. 47. |
Wie man mit der Voltirten Qrarta wieder eine Terza, so mit linker Hand pariren wollen verletzen kan. No. 47. AUch diese No. 47. folgende ist eine Qvarta, welche trifft wieder eine Terza, so unter deer Klingen verletzen wollen, und ist hergekommen, dasz der Treffende dem Feind einwendig eine Finta nach der rechten Seiten seines Gesichtes gemachet, welche Finta denn der Feind mit der linken Hand wollen pariren, und deswegen den Leib versenket, auf dasz er einwendig unten verletzen könne; Aber der andere, welcher hatte die Finta gemachet, hat das Tempo, so der Parirende gegeben, indem er um seinen Kopf zubeschützen mit der linken Hand in die Höhe nach der [129] Klingen gegangen, genommen, seine Spitze mitten zwischen beiden des Feindes Armen im Tempo da sich der Feind öffnete sinken laszen, damit die Hand in Qvarta gewendet und zugleich den Leib mit dem linken Schenkel voltiret, und also getroffen, dasz der Feind, weil die Klinge also zwischen beide Arme eingeschlossen gewesen, nicht hat pariren, und sie nicht aus dem Wege getrieben werden können, es were denn der effect verendert werden. | |||||
[66] This is the last hit, in quarte, against a seconde. The adversary meant to parry with the left hand but has failed. Both were in tierce on the inside, and he, who has tried to parry, has so far, withdrawn his guard that his forte could not defend him and he has trusted to the defence of the hand only, which was too high for the face. You have made a feint of hitting in the angle of the right side. Your adversary has turned his body in order to withdraw that part, carried his hand to the defence and changed to a guard of seconde, in order to make a hit in the chest. Seeing his purpose you have disengaged your sword from the line of the fingers of his hand and hit him in the chest in quarte in the time of his advance. Turning the body out of line you have also covered yourself with the hilt, so that his sword has passed in vain, although the angle of his seconde was directed towards the line into which you were turning the body. |
[75] ECCI ANCORA L’ VLTIMA FERITA DI QVARTA CONTRA LA seconda, laquale uoleua pure parare con la sinistra mano, mà è riuscito in contrario perche, trouandosi tutti dui interna di dentro, quello che hà uoluto parare con la mano haueua tanto ritirata la guardia, che il forte non lo poteua diffendere fidandosi solamente della diffesa di essa mano, che era troppo, alta per la faccia, & perche quello, che hà ferito hà fatto una finta di uolere ferire nell’ angolo del fianco destro, & l’ altro uoltando il corpo per allontanare quella parte, hà porta la mano alla diffesa uoltando in seconda guardia affine di ferire il nimico nel petto, ilquale nimico uedendolo fare tale effetto hà cauato la spada per la parte delle dita della mano auersa, & l’ hà ferito nel petto di quarta nel tempo, che si portaua oltre, & girando il corpo fuori di presenza, si è esso ferittore saluato anco col finimento della spada, tanto che la nimica è passata uana, se bene l’ angolo della seconda piegaua uerso la parte, doue egli giraua il corpo. 48. |
Wie die Voltirte Qvarta wieder die Seconda Contratempo kan gebrauchet werden. No. 48. NUn kömmet noch No. 48. die letzte Verwundung des ersten Buchs, welches ein Qvarta-Stosz wieder eine Seconde, so zwar wohl schlecht hin mit der linken Hand pariren wolte, es ist ihr aber fehlgeschlagen; Denn da sie sich beide einwendig in Terza befunden, hat derjenige welcher mit der linken Hand pariren wollen, ein ritirirtes oder angezogenes Lager gemachet, dasz ihn seine Stärke nicht beschützen konte, hat sich derowegen auf die [130] Parirung seiner linken Hand die er ziemlich hoch bey dem Gesichte führete gantz allein verlaszen; Da dann der so getroffen hat eine Finta nach dem Winkel in der rechten Seiten gemachet: Der Getroffene hat darauf um selbige Blösze zuentfernen den Leib gewendet, ist also mit der Linken nach des andern Klinge zur parirung gegangen, und hat die Rechte um den andern auf die Brust zuverletzen in die Seconda verwendet: Da aber der Treffende solche Würkung gesehen, hat er um des Feindes linke Hand herum caviret, und im Tempo da er vorsich gehen wolte, mit der Qvarta auf die Brust getroffen, hat aber auch zugleich um auszer der Presenz zukommen den Leib voltiret und sich also mit seinem Kreutz noch salviret, da denn des Feindes Spitze leer abgegangen, ob er gleich dawo der Treffende hin voltirete, seine Spitze hette wollen laszen anguliren. | |||||
[67] |
Ende des ersten Buchs. |
Second Part - Of Sword and Dagger
Illustrations |
Illustrations |
Draft Translation (from the archetype) |
Prototype (1601) |
Archetype (1606) [edit] |
Copenhagen Version (1600-1609) [edit] |
Munich Version (ca. 1635) [edit] |
German Translation (1677) [edit] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[1] Second part. Discourse on the principles of the sword and dagger. As we consider that we have treated at sufficient length of the practice and times of the sword alone, it has seemed to us suitable, in order to give full satisfaction to the reader, to introduce here the instructions and rules of the sword and dagger. We do not mean to prefer this method of arms to that of the sword alone, nor to multiply different precepts, nor to throw over the instructions given by us elsewhere. It is rather our purpose to show the wealth and abundance of the practice of this art, which by uniting several arms together becomes more admirable and perfect. Therefore without neglecting the subtleties of the times of the sword alone, or denying them in any way, for they are beyond comparison the more artful, we shall now leave them, having put them forward and analysed them in their place, and shall proceed to describe, as far as is necessary, the perfect use of the sword and dagger, and to impart the true knowledge of the stratagems useful in the attack and the defence, and dangerous to those inexperienced in the art. One who is well acquainted with the times, will easily find great benefit. These two arms are allies of one another, and by their union give great strength in need; also they divide and share the functions, the one defending and the other attacking. We hope those who practise with these arms, following the present instructions, will reach the perfection they desire. |
[76] PARTE SECONDA. DISCORSO SOPRA LE RAGGIONI, Di spada, è pugnale. HAVENDO NOI PER QVELLO, CHE CREDIAMO, TRATtato assai pienamente della pratica, & tempi di spada sola, ciè parso assai conueneuole perdare ìntiera sattisfatione à chiunque leggerà, di porre in questo luogo li auertimenti, & regole di spada, è pugnale, non con animo di preferire questo modo di armeggiare à quello della sola spada, ne meno per moltiplicare in diuersi precetti, partendoci da quei ricordi altre uolte da noi insegnati, mà più tosto per mostrare la richezza, & copia dell’ uso di quest’ arte, laquale potendo conggiongere più armi insieme, uiene à rendersi, & più amirabile, & più perfetta, & però non dillongadoci dalle sottilità dè tempi di spada sola, ne à quelli in nessun modo contradicendo, come più artifficiosi senza comparatone, li passaremo con silentio hauendoli proposti, & risoluti à suoi luoghi, mà procederemo à dichiarare, per quanto è neccessario, la perfetta operatione di spada, e pugnale, & ad’ insegnare la uera cognitione de’ stratta- [77] gemi, utili per offendere, & diffendere, & dannosi all’ inesperti dell’ arte. Et però chi sarà bene intendente de’ tempi facilmente ne configuirà frutto grandissimo, perche essendo queste due armi una a giutante dell’ altra, & che insieme unite fortifficano assai secondo il bisogno, ne meno ancora, perche di uidendosi frà loro compartono l’ operationi una in diffendendo, & l’ altra in offendendo, speramo, che quelli, i quali in ciò s’ essercittaranno osseruando li presenti amaestramenti, ariuaranno alla perfetione, che desiderano. |
||||||
[2] The positions of the sword and dagger. The positions of the sword and dagger are formed with the body bent and the feet close together, and with the weight of the body on the foot which is to remain steady. The arm holding the dagger should be extended as high as the point of the shoulder, with the point of the dagger inclined upwards and directed towards the adversary. The sword should be so far advanced as to extend beyond the dagger by at least one fifth of the sword's length, so as not to be impeded by the movements and feints of the adversary. With this guard you can make better use of the forte of the sword in any event. The sword and the dagger should be in conjunction so as to close the path between them against the adversary. If you wish to use the sword in an advanced position, the dagger should be held in conjunction with the hilt of the sword, so as to close the path to the adversary. Similarly the right side should be kept forward and the left back, as the latter is more exposed and in greater danger. |
DELLE POSTVRE DI, Spada è pugnale. LE POSTVRE DI SPADA, E PVGNALE SI FORMANO COL corpo curuato in picciolo passo, & col peso del corpo sopra quel piede, che deue stare fermo, & anco col braccio del pugnale disteso infanta altezza quanta è la punta della spalla, & con la punta del pugnale erretta che guardi uerso la nimica, & con la spada tanto auanzata, che sia più inanzi del pugnale almeno per un quinto della longhezza di essa spada, perche non possa essere tanto trauagliato dalli mouimenti, & finte del nimico, & l’ huomo in tale guardia potrà meglio ualersi del forte diessa in ogni euento, ilquale dourà tenere conggionti la spada, & il pugnale per chiudere la uia nel meggio al nimico di ferire; Mà chi uorà usare la spada auanzata dourà tenere il pugnale conggionto con la guarnitione di essa, che così chiuderà il luogo da ferire al detto nimico & similmente dourà tenere il destro fianco inanzi, & il sinistro indietro, per essere questi più scoperto, & di maggiore pericolo. |
||||||
[3] The counter-positions. The counter-positions are more difficult to form, since you must attend to your own two weapons and the two of your adversary and their positions. You must be careful not to advance so far in the desire to acquire some advantage, that your adversary can engage your sword with his dagger and hit. Therefore you must keep the sword so far distant that you know you can save and move it before it is engaged by his dagger. For the rest you should observe the same conditions and principles which we explained in describing the counter-positions of the sword alone, taking care that your body is clear of the adversary's sword without movement of the body or weapons, and that your weapons are in conjunction to give greater strength and surer defence. |
DELLE CONTRAPOSTVRE. PIV DIFFICILI DA FORMARE SONO LE CONTRAPOSTVre perche bisogna attendere alle due armi proprie, & alle due del nimico, & posture di esse, che perciò si deue essere, auertito di non portarsi tanto oltre uolendo aquistare qualche uantaggio che ’l nimico possa guadagnare la spada col suo pugnale, & ferire di modo che si hà da tenere la spada tanto lontana da quello, che si conosca poterla saluare, & muouere prima che sia occupata dal pugnale di esso nimico; Nel resto si douranno osseruare le medesime circonstanze, & raggioni mostrate in descriuere le contraposture di spada sola, con auèrtire che ’l corpo sia libero dalla punta della nimica senza moto di corpo, ne d’ armi, & che le dette armi siano conggionte per maggiore fortezza, & diffesa. |
||||||
[4] On engaging the sword. Engaging the sword with the sword and dagger is very different from engaging with the sword alone, for it is done at one time with the dagger, at another with the sword, and more often with both sword and dagger. You engage with the sword when your adversary keeps his sword so far withdrawn that you cannot reach it with the dagger; sometimes your sword cannot penetrate because of the danger of his dagger. In this case you should hold your sword in such a way as to close the path in which the adversary's point is directed and with the forte in such a position that his point cannot approach your body without his faible meeting your forte, which generally prevents him and drives his point out of line. You can also, as he approaches, raise the sword from that defence and make a hit, putting the dagger where the sword was before, which will be a good defence and will delude your adversary, who will probably think that you are going to parry with the sword; thus his plan will be foiled. This is a good method to follow, when your adversary's sword is withdrawn, since you should not advance too far with the sword, lest you lose it, nor should you advance the dagger, for there are some who, seeing the dagger advance, beat it with their dagger and hit. Therefore to advance too far is very dangerous. Besides when you push on so far, the dagger is easily deceived by the feints and movements of the adversary's sword, which throw it into disorder. But if your adversary's sword la advanced, there will be no such danger. You can then readily try to engage with the dagger, if you understand the correct method. For you must not carry the dagger so high that on reaching his sword you have to lower it, or so low that you have to raise it; nor on reaching his point must you make any movement for, however slight, it would give him an opportunity to hit, or at least to disturb the dagger; thus you would not be free from danger. You must hold the dagger with the point in the same line as your adversary’s sword, so that on reaching his point the dagger engages without other movement. If the line of his sword is rather low you must begin with the dagger equally low. To make safe, the body should be lowered in proportion and in such a manner that you know that if your adversary disengages, you can easily parry without raising the arm, for if you raise it, he might deceive you with a feint of disengaging and return, when you would be hit without a defence. But holding the dagger arm steady, you would easily defend, on either side. Thus, if you know how to apply the exact rule, you can engage your adversary's sword, wherever it is, provided it is far enough advanced beyond his dagger. But if it is withdrawn behind the dagger, it would be an error to engage; for besides the reasons given you would be in danger of getting within too close distance before finding his point, when you would be hit, as you would also if his point were too low towards the ground. In that case it would be better to cover it with your sword, so that your adversary could not disengage on the side of the dagger, or if he wished to disengage would be forced to disengage on the side of the sword in order to free his point. But if you wished to hit, it would be necessary in forming this defence, to hold the dagger steady; thus you could turn the sword from tierce to seconde and close the path between the two weapons in such a manner that, if your adversary advanced, his sword would always encounter your dagger, which had made no other movement. But if his sword were low and on the outside on the side of the dagger, you could not cover the path, and it would be ill-judged to advance the point of your sword because of the danger, lest in that time he should disengage above the sword and hit between the two hands where the path was open; although you might parry with the dagger, yet the movement would be so large, that, if your adversary had made a feint of hitting in that part he could hit in the new opening and attack. Also he could disengage the point of the sword, thrust between the two hands, gliding along your blade, and thus hit on the side of the dagger, so that you would be in the same danger. Therefore in such a case it would be better to push his sword out with the hand as low as the right knee and turn to quarte, in order to be on the inside and cover that part more; at the same time you should incline your point upwards towards the dagger, which would defend all that part of the body up to the head, and all the more if dagger and sword were in conjunction. In this manner you would not only push away his sword, but would form a good counter-position. You would have left the adversary only one path of attack, that is over the sword, and your sword being at an angle with the left arm forward, you could easily parry this attack with one of the two weapons or both together and with little movement, since there would be no room to hit between the two weapons. Whether your adversary's sword were in seconde or in prime, and if his point was in that same line but separated from the dagger, which would mean danger below and between the weapons, it would still be better to use this method, and to put the point of your sword against his, which would lead to the same result. But if his point were in another line and high, in that case it would be well to adopt a guard in tierce at an angle, and put your point on your adversary's, holding the dagger extended near the sword; in order to prevent his hitting anywhere but above the dagger. For if he were on the outside of the sword and should thrust over the dagger, he would make such a large circle that he would give you a good chance to parry, if you remembered to keep the lower part of the body so far withdrawn that your adversary could not reach it. In any case you must when parrying hit where there is a part uncovered according to the movement and position of your adversary's body and weapons in making his hit. As he[!] have many times said in this way the parry is always safer and cannot be deceived. You must know that the principle of using the dagger alone in engaging the adversary's sword applies more against the guards in tierce and quarte, than against those of prime and seconde, where it is not so strong. For if when you move with the dagger against your adversary, he should make a feint in the upper lines, which are the feints most to be feared, he would force you to parry and then would hit by a rush in the parts uncovered by your movement of parrying. Besides the fact that they are more successful with the sword and dagger than with the sword alone, the guards in prime and seconde naturally lend themselves to the rush. For being in tierce or quarte, in order that the rush may have force, you must change the hand to seconde. Therefore when your adversary is already in a position to rush without further change of the hand, he is much more to be feared. If then you wish to guard against your adversary's attack, it is better on his advance to use the sword and dagger together and for greater precaution to exclude his point on the outside, if possible. This method is good against a guard of prime or seconde, though you must take care if you wish to advance with safety, that you have excluded his point entirely in such a way, that you are certain he cannot hit there, but without touching his sword. If you have done this, you may close the distance as much as you wish. You must also be careful not to approach the point of your sword so near to his dagger, that he can engage it and hit before you have freed it. You must always keep your point at such distance and position that are assured of its freedom to hit in time. Nor by freedom do we mean keeping it far out of line for in that case it would be pushed away before you could return it. But holding it in the proper manner you will keep it in line or very little out of it, and always free, so that your adversary cannot prevent your returning. We must add that you can engage your adversary's point in any position with the sword alone, provided that you hold the dagger in such a manner that it has little movement to make in order to defend the part where the adversary might hit. This is an excellent method though some deny it. They will not allow that you should ever engage with both the weapons at one time, but they say that one at least should be free, in order to be able to parry and hit if the need arises, that one weapon should be reserved for defence, and one for attack and that there being two pieces they should serve two purposes, whereas if both are used for the defence they are serving one only. We admit this, but say that this united defence is not only stronger, but also better protects the other line, where the adversary might approach. He finds little exposed there, it is harder for him to hit and easier for you to parry. Further if you defend with one weapon only, there is more danger not only of being disordered, but also of being overcome. Thus it often happens, that where you are defending with one weapon and your adversary changes his line in hitting, you are so disunited and weak that both your weapons are forced into subjection, so that what you would not do willingly, you are forced to do, when your adversary has moved. Thus you are so disordered and confused that you have been unable to hit because of the trouble you were in in the defence. On the other hand when you defend with both weapons and your adversary changes his line in order to hit or do anything else, you can on that change separate the two weapons, the one to parry and the other to hit because they were in union. Sometimes also you can defend with both weapons and hit in the same time because of the strength of your first defence due to the union of the weapons. You have more completely covered the body and work of your own accord and not driven by necessity. Therefore you may well understand, that he who engages with both his weapons will dispose of them with greater judgment and security and in such a manner that he will not be prevented from hitting in time, when the occasion offers; but he who is compelled to engage will usually be prevented from making anything but the simple defence, and however good that is it can easily be deceived. |
[78] DEL TROVARE DI SPADA: IL TROVARE DI SPADA, CHE SI FA CON LA SPADA, E pugnale è assai differente da qnello di spada sola, perche hora si occupai col pugnale, hora con la spada, & il più delle uolte con la spada è pugnale insieme. Quando, che la si occupa con la sola spada auiene perche il nimico la tiene tanto ritirata che l’ pugnale non ui può ariuare, & talhora anco non può l’ istessa spada penetrare inanzi per il pericolo del pugnale auerso, nondimeno basta in questo caso situarla in modo, che si chiuda quella uia doue guarda[20] la nimica punta, & col forte in maniera tale che detta nimica punta non possi approssimarsi al corpo, che il debile non sia trouato col forte, il che suole impedire, & deuiare la nimica dal uenire in presenza, & si può anco nel uenire, che fà leuare la spada da quella diffesa, & andare à ferire mèttendo il pugnale, oue prima si haueua la spada, che benissimo si diffenderà, & si hauerà deluso il nimico, ilquale uerisimilmente doueua credere, che si uolesse parare con la spada, & facilmente seli guastarà alcuno disegno. Questo è un buon modo da usare quando la nimica è ritirata, perche non si deue andare tanto oltre con la spada, che la se perda, ne meno uiha da andare il pugnale, perche alcuni sono, i quali uedendo il pugnale nimico lo battono col suo, & uanno à ferire, & pero questo andare tanto inanzi porta molto pericolo, oltre che quando si lascia scorrere tanto oltre, il pugnale è ingannato facilissimamente dalle finte, & mouimenti della nimica, che lo fanno disordinare, mà se la detta nimica sarà auanzata non ui sarà tanto pericolo anzi, che ageuolmente si potrà andare à trouarla con il pugnale, quando che si saprà con giusto modo operare, perche non si dee portare tanto alto, che peruenendo alla nimica si habbia da abbassarlo, ne tanto basso, che sia di mestieri alzarlo, ne meno si dee fare alcun moto nelo ariuare alla punta nimica perche anco che l’ fosse picciolo, sarebbe oportuno da ferire per il nimico, ò da sturbarlo almeno, & non saria insomma senza pericolo; Mà si hà da situare esso pugnale con la punta nella medesima linea della nimica, acciò giongendosi ad’ essa punta il pugnale l’ habbia aquistata senza fare altro moto con esso, & se la linea della detta nimica fosse un poco bassa si dee cominciare ancor col pugnale in questa bassezza, mà uolendo essere sicuro bisogna che l’ corpo si abbassi proportionabilmente, & in modo, che si conosca, che quando ben’ anco il nimico cauasse si potesse facilmente parare senza alzare il braccio perche quando si alzasse il nimico potrebbe ingannare con fingere di cauare, & rimettere, doue si restarebbe ferito senza potersi diffendere, mà tenendo stabile il braccio di esso pugnale facilmente si diffenderebbe l’ una, & l’ altra parte, di modo, che chi saprà tenere la giusta regola potrà andare à trouare la nimica ouunque si sia, pure, che essa nimica sia tanto inanzi auanzata, che sia più longa del suo pugnale, che quando fosse più ritirata sarebbe errore perche oltre le sopra mostrate raggioni si andaria à pericolo di scorrere in troppa stretta misura prima, che si trouasse la punta di detta nimica, doue si restarebbe ferito, come anco quando la fosse troppo bassa uerso terra, nelquale caso saria meglio coprirla con la spada affine che esso auerssario non potelo cauarla dalla parte del pugnale, ò pure uolendola cauare fosse neccessitato cauarla dalla parte della spada per liberarla; Mà se si uolesse ferire bisognaria, nel fare detta coperta, hauere tenuto il pugnale fermo, perche così si haurebbe uoltata la spada di terza in seconda, & l’ huomo si saria approssimato con la mano di essa conggionta à quella del pugnale, & si saria chiuso quel meggio che poteua essere tra l’ una, & l’ altra arma, di modo che uenendo l’ istesso nimico la spada seli trouaria sempre col pugnale, ilquale non saria stato in altro moto, [79] mà se la detta nimica fosse bassa, & tanto infuori uerso la parte del pugnale non si potrebbe coprire, & saria poco giuditio andarli con la punta della spada peril pericolo, che esso in quel tempo non la cauasse disopra della spada, & andasse à ferire frà l’ una, & l’ altra mano, oue la strada sarebbe patente, & ancorche col pugnale si potesse parare, si faria nondimeno tanto gran moto, che se ’l nimico hauesse finto di ferire in quella parte potria andare à ferire nell’ altra, che si discuopre, & offendere, oltre che potria anco cauare per la punta della spada, & andare à ferire fra l’ una, & l’ altra mano scorrendo la lama, & così ferirebbe nel fianco del pugnale, in modo che si restarebbe nel rischio medesimo, & perciò sarebbe meglio in caso simile serrare la nimica di fuori con la mano bassa sino al ginochio destro, & uoltata in quarta acciòche la fosse didentro, & tenesse più coperta quella parte, & similmente con la punta angolata in sù uerso il pugnale, che si renderia diffesa tutta quella parte del corpo sino alla testa, & tanto più tenendosi il pugnale conggionto alla spada, che in questo modo non solo si hauria serrata la spada, mà si hauria fatta una buona contrapostura, ne si saria lasciato al nimico altro che una sola uia da potere offendere cioè sopra la spada, laquale tenendosi così angolata, & col braccio sinistro inanzi facilmente si pararebbe, con l’ una delle due armi, ò con tutte due insieme, & con poco moto perche frà le due armi non saria luogo da potere ferire, & quando anco la nimica si ritrouasse in seconda, ouero in prima & che la punta fosse in quella parte pur disgionta dail pugnale, il che caggionarebbe pericolo di sotto, & nel meglio, sarebbe tutta uia meglio adoperare questa forma & mettere la punta della spada alla nimica, che faria il medesimo effetto, mà se la fosse dall’ altra parte, & alta, in quel caso saria bene trouarsi situato in terza angolata, & mettere la punta alla nimica tenendo il pugnalo disteso appresso la spada per togliere anco al nimico la uia di potere ferire in altro luogho, che sopra il pugnale, perche se il detto nimico si ritrouasse di fuori dalla spada, & uolesse andare sopra esso pugnale farebbe similmente tanto gran giro che daria gran comodita di parare osseruando però di tenere la parte disotto tanto lontana, che esso nimico non possa ariuarui, & in ognicaso si deue in parando andare à ferire, oue si uede il scoperto secondo il moto & l’ effetto, che hauranno fatto il corpo, & l’ armi nimiche nel uolere ferire, che come si è detto molte uolte, il parare sarà sempre più sicuro, ne si potrà essere ingannato. Et deesi sapere, che le raggioni di adoprare il solo pugnale nell’ andare à trouare la nimica seruono più contra la terza, & la quarta, che contra la prima, & seconda guardia, doue non è tanto sicuro, perche se in andare contra il nimico col pugnale esso nimico facesse qualche finta nelle parte superiori, le quali finte sono quelle, che più si temono, metterebbe senz’ altro in neccessita di parare, & poi ferirebbe con qualche slancio in quelle parti, che si scoprisseno, nel moto fatto à parare, perche oltre, che più riescono nella spada, è pugnale, che nella sola spada, la prima, & la seconda sono quelle guardie, doue naturalmente si slanciano, che chi uuole, essendo in terza, ò in quarta, che ’l slancio habbia forza è neccessario andare con la mano in seconda, in modo, che molto maggiormente si ha da temere quando il nimico gia si troua, oue senza fare altro effetto di mano può ferire di slancio, & però uolendo guardarsi di non essere offeso dal nimico in quello suo auicinarsi meglio è seruirsi della spada è pugnale insieme, & anco per maggiore cautella serrarla dalla parte di fuori, se si può, & quello, che è buono contra la prima uale anco contra la seconda guardia, bene ha da essere auertito collui che uuole auicinarsi sicuro di ferrarla fuori del tutto in modo che sia certo, che la non possa in quel luogo ferire mà però senza toccargliela, che fatto questo, potrà ferrare la misura quanto uorà, mà con anco hauere riguardo di non si auicinare tanto con la punta al pugnale nimico, che quello la potesse hauere, & ferire prima, che si hauesse liberata, laquale punta bisogna sempre tenere in misura, & forma tale, che si conosca hauerla libera da potere ferire in tempo, ne quì si intende tenerla libera con lontanarla molto dalla presenza, perche in tal modo uerebbe serrata di fuori prima, che si rimettesse, mà tenendola come si deue si haurà la presenza, ò almeno si sarà poco fuori, & sempre libera, ne il nimico potrà uiettare, che la [80] non si rimetta. Non uogliamo anco lasciare di dire, che con la sola spada si può andare à trouare la nimica sia in qualunque sito, pure, che si tenga il pugnale in modo, che habbia da fare poco moto à diffendere quella parte, oue potria uenire la detta nimica à ferire, che questa maniera sarà purè buona, & ancorche da altri si contradica, i quali non uogliono, che mai si deua obligare tutte due le armi in un medesimo tempo per hauerne almeno una libera da potere secondo il caso parare, & ferire, & che una sene deua tenere per diffesa, & l’ altra per offesa, & che essendo dui pezzi deuano seruire per li dui effetti, mà che impiegandoli tutti dui nella diffesa uengono à fare una sol cosa, il che noi concediamo, mà poi diciamo che quella diffesa, la quale si fà unita non solo è più forte, mà uiene à coprire più l’ altra parte, doue potrebbe uenire il nimico, alquale mentre, troua poco scoperto è più màlageuole di ferire, & più facile all’ altro di parare, oltre che mettendosi l’ huomo in diffesa con una sola arma è più pericolosa non solo da essere turbata, mà anco superata, si come molte uolte auiene che essendosi posto in diffesa con una sola arma &, che l’ auerssario habbia mutato effetto nel ferire si è trouato tanto disunito, & debile che li è stato forza andare con tutte le armi in seruitù, in modo, che quello che non hà uoluto fare uolontario l’ hà poi fatto sforzato, quando il detto nimico si è mosso, & così è restato tanto turbato, & tanto confuso, che non hà potuto ferire per la scomodità in che era nella diffesa; Mà per l’ opposito quando si uà con tutte due le armi, & che ’l nimico si muta per ferire, ò per fare altra cosa, le due armi, che erano alla diffesa si diuidono in tale mutatione l’ una delle quali uà à parare, & l’ altra à ferire per l’ unione in che si trouauano; alcune uolte ancora si può andare alla diffesa contutte due dall’ altra parte, & ferire in medesimo tempo per essere fatta la prima diffesa forte rispetto alla detta unione d’ armi, laquale hà tenuto il corpo più coperto, & hà operato uolontariamente, & non astretto da neccessità, in modo che molto bene si può intendere, che quello ilquale obliga tutte due le armi ne disporà ancorà con più giuditio, & sicurezza, & in guisa che non impedirà il ferire di tempo secondo l’ occasione mà che collui, che le obliga per forza sarà il più delle uolte impedito, che non potrà fare se non la semplice diffesa, laquale per buona, che sia può facilmente essere ingannata. |
||||||
[5] How to proceed against an adversary on guard on the left foot. In dealing with an adversary who is supported on his left foot, you must consider that his sword is so far withdrawn, that it is difficult to engage it, and that he holds his dagger well advanced with the idea of engaging your sword and then making a hit in time, generally with a pass; for he realises that his line is short and that he cannot reach without a pass, and he is well aware that he cannot pass without first engaging your sword. You must consider too that by passing he will come with a great impact owing to the great distance from the spot where he lifts his foot to the spot where he brings it to the ground, and owing to the fact that his sword is carried on not only by the arm and foot, but by the whole body. He advances his body with great vigour in order to make his hit quickly, and therefore he strikes violently, especially if he comes in the time of your advance, when you cannot break ground, and thus the encounter is all the more impetuous. Further, since your adversary recognises that he can do nothing whilst he is within wide distance, he will always seek to approach in order to gain your sword and the required distance. From all these considerations you should be able to discern your advantage and avail yourself of it, that is to say the distance, in which you may arrive, more quickly than he who is supported on the left foot even with his right foot in front. While he is seeking to engage your sword is the time to hit and to break ground so as to keep away and prevent his passing, or, if you cannot hit, at least to make a feint in order to disorder him and then hit, or play him and in that time withdraw so far, that he will remain at the original distance. Then you may choose a more convenient time, when he moves again, for since he is on the left foot, his side below the dagger is in great danger, and if he tries to cover it, he uncovers himself above, since the dagger cannot cover both places at once. Therefore choosing the time you can always hit in one of these two places. Everytime that your sword provokes his dagger to move you will certainly hit in one part or the other, and all the better if the provocation is in the time of his advance, when he cannot break ground. Also you must not advance so far that you are in danger of receiving a riposte stronger than your thrust, as often happens. When you see the adversary advancing in order to engage your sword with his dagger, then you should hold your point in line with his fist; if his dagger is extended with the point forward so as to hide his fist, then you should hold the sword straight under the blade neither inside nor outside, and therefore you must hold it in a straight line in tierce. As your adversary approaches, you must bring the arm back to the body keeping the point in the straight line and not letting it drop, and draw him on until his hand penetrates the point of your sword; at the moment when his foot arrives within distance, then hit in the straight line under the blade of his dagger, the nearer the arm the better. If that part is not uncovered then you must hit over the dagger, making a slight turn of the hand towards seconde, but close to the dagger, above all taking care to arrive quickly. If the part uncovered is on the inside, you could turn the hand to quarte so as to hit that part, but still close to the blade of the dagger. These thrusts will certainly succeed, if you take the time of your adversary's advance. If his dagger is held so exactly that you cannot hit, you should move the point a little inwards or outwards in order to make him waver and then hit. To protect yourself better against the riposte or counter-time which your adversary might make, you should hold your dagger in such a position towards the point of his sword, that, wherever it comes, the dagger can parry with little movement. In this position you may be certain of having greater ease in defence; but you should not be already so far advanced that your adversary's sword can harass you, before you are at the proper distance. If your position is not so subtlely formed, and the adversary's dagger begins to penetrate your point on the one side or the other, you should not therefore disengage with the idea of freeing it, bat should gradually bring it out of line as far as his dagger can follow it. For if he tries to engage it, his dagger will go so far out of line that he can be hit, or if you make a feint he will be so disordered by the large part uncovered, that he will then certainly be hit. If you do not wish to follow this method, you should remain within wide distance, with your sword free and somewhat drawn back, so that it may not easily be engaged by your adversary; you should incite him by various times and appels, being always ready to break ground, so that when he decides to hit and seizes a time to make a determined pass, you can protect yourself according to the quality of the guard. For if you go to meet him although you may protect yourself from the first effect, still the parry will be so violent, that your power to hit will be taken away. Moreover if your adversary changes his line, you will certainly be hit. On the other hand if you break ground your adversary’s thrust will lose its force and may easily be parried; even if your adversary changes his line, you may still parry in the new line before he arrives. Therefore one who stands on guard on his right foot should not try to get in this close distance against an adversary who stands on the left foot but should keep at a distance; he should advance in order to strike when the adversary approaches, making use of the advantage of his longer reach. There is still another method, when you intend to defend and break ground, that is to place your sword on the adversary's dagger, so that when he thinks he has engaged your sword in the time of his advancing you may free it by breaking ground and hit. This is a subtle method and deceptive when used with the necessary circumspection, so that you are not deceived in thinking to free your sword and hit. You must take care too that your adversary is not aware of your intention, and may not make a mock of it. |
COME SI DEBBA OPERARE CONTRA IL Nimico situato in guardia sopra il piè manco. QVANDO SI HA DA FARE CON VNO, ILQVALE SIA SVSIstente sopra il sinistro piede, si hà da considerare, che la spada nimica è tanto ritirata, che difficil cosa è il ritrouarla, & che lo stesso nimico tiene il pugnale molto auanzato con pensiero di trouare lui la sua auerssaria, & poi ferire trouando tempo, & con passare il più delle uolte, conoscendo la sua linea essere corta, & che non può ariuare se non passa, & benissimo sà non potere passare se prima non aquista la detta sua auerssaria, & è da considerare ancora, che passando, uerà con empito grande, & ciò per la molta distanza dal luogo, doue lieua il piede al luogo, oue lo uà à fermare, & che la sua spada non è solamente portata dal braccio, & dal piede, mà da tutto il corpo, quale uiene anco con gran furia per ariuare presto à ferire, & per questo percuote grauemente, massime se uà intempo, che l’ altro si auicini, ilquale non può all’ hora rompere di misura, & così è tanto più impettuoso l’ in contro; mà oltre diciò perche il detto nimico conosse non potere fare cosa buona mentre stà in misura lontana studia sempre d’ [81] auicinarsi affine di aqistare la spada, & la misura, in modo che doppo tutte queste considerationi hà da sapere discernere il maggiore uantaggio & ualersi di quello, che è quella distanza, nella quale si arma più presto, che non fà quello, che stà sopra il sinistro piede, pure che tenga il destro inanzi, & mentre l’ altro uuole aquistare la sua quello è tempo di ferirlo, & rompere di misura per conseruarsi lontano, che ’l detto nimico non possa passare, ouero non potendosi ferirlo almeno farne cenno per turbarlo, & poi ferirlo, ò trattenerlo & in quel tempo allontanarsi tanto, che si resti nella prima misura affine di pigliare poi più comodamente il tempo, mentre, che quello si torna à mouere, perche essendo sopra il manco piede il fianco sotto il pugnale porta pericolo grande, & se lo uuole iui coprire lo discuopre disopra, non potendo detto pugnale coprire tutti quelli dui luoghi in una uolta, in modo, che trouando il tempo si potria sempre ferire in uno delli detti dui luòghi; & ciascuna uolta, che la spada prouocarà il pugnale à mouersi si ferirà al certo, ò nell’ una, ò nell’ altra parte, & tanto meglio se la prouocatione sarà nel tempo, che s’ auicina, quando non può rompere di misura, & medesimamente se non si portarà se stesso tanto inanzi, che s’habbia da dubbiare di riceuere una risposta maggiore della botta come spesso accade, mà quando si uede che ’l nimico s’ auicina per aquistare la spada col pugnale all’ hora si dee tenere punta in prospettiua del suo pugno & se detto pugnale fosse disteso con la punta inanzi, laquale ascondesse il pugno all’ hora si douria tenere la spada diretta sotto il filo, in mosto che non fosse ne dentro, ne fuori, & perciò saria di mestieri hauerla in retta linea nella terza, & secondo che ’l nimico uenisse approssimandosi, andare racogliendo il baccio appresso il corpo con mantenere sempre la retta linea, acciò la spada non pieghi in nissuna parte & tirare detto nimico nella misura prima, tanto che la sua mano penetri la punta della spada, & nel punto che ’l suo piede ariua nella misura batterlo della stessa retta linea sotto il filo del braccio di detto, pugnale, & quanto più presso al braccio tanto meglio, quando non siue desse quella parte scoperta si douria ferire sopra detto pugnale facendo alquanto di uolta di mano uerso la seconda guardia, mà stretto presso al pugnale procurando sopra il tutto di ariuare presto, quando il scoperto fosse di dentro potrebbesi uoltare la mano in quarta guardia, che si ferirebbe quella parte, mà sempre presso il filo del pugnale, & certo è che queste botte riusciriano pigliandosi il tempo, quando l’ auerssario si approssima, & quando pure il suo pugnale fosse in tanta giustezza, che si uedesse non poterlo ferire si douria fare un poco di moto con la punta ò in dentro, ò infuori per farlo uacillare & poi ferirlo; & per meglio saluarsi dalla risposta, ò contratempo, che il detto nimico forsi potrebbe fare, si dee talmente situare il pugnale uerso la punta nimica, che uenendo quella oúunque si uoglia esso pugnale habbia da fare poco moto nel parare, & in questa forma situato si dee tenere fermo per hauere più facilità di diffendersi, mà non uuole gia essere molto auanzato, acciò la nimica non lo possa trauagliare prima, che si sia nella misura. Et quando l’ huomo non fosse situato con simile sottilità, & il pugnale nimico cominciasse à penetrare la punta per una, ò per l’ altra parte, non dourebbe perciò cauarla con animo di liberarla, mi douria andarla allontanando pian piano tanto fuori di linea, quanto che il detto pugnale auerso l’ andasse seguendo, perche se ’l nimico la uolesse hauere andaria lui tanto fuori di giustezza con esso pugnale, che potrebbe essere ferito, ouero facendoseli una finta restarebbe talmente disordinato per il gran scoperto, che all’ hora restarebbe ferito di certo, mà non uolendo l’ huomo seruare questo stile conuerà tenersi in lontana distanza con la spada libera, alquanto racolta, acciò non possa facilmente assere trouata dal nimico, & andarlo prouocando con diuersi tempi, & chiamate, stando però sempre in rompere di misura, acciò che risoluendosi lui di ferire, & pigliando qualche tempo per passare determinamente, si possa l’ huomo secondola qualità della guardia saluare, perche chi li andasse contra, ancorche si saluasse dal primo effetto, il parato nondimeno sarebbe tanto uiolente, che toglierebbe il ferire, oltre nimico mutasse l’ effetto si restaria sicuramente ferito, doue che rompendosi di misura come si è detto, la [82] botta nimica ueria à semare di forza, & restaria più facile da pararsi, & con comodità tale, che se anco il nimico nel uenire mutasse l’ effetto non meno si pararebbe dall’ altro lato prima che fosse gionta; Di modo che collui che stà collocato sopra il destro piede non dee mai andare à ferrare la misura dell’ altro, che stà sopra il sinistro mà andarsi conseruando lontano, & auicinarsi per percuottere quando l’ auerssario s’ approssima ualendosi del uantaggio della misura, laquale ariua più di lontano; Vn altro modo ui è ancora, quando si ha pensiero di diffendersi, & rompere di misura nel medesimo tratto cio è di dare la spada al detto pugnalo nimico acciò che, credendo esso d’ hauerla nel tempo, che di moue per uenire, liberarla rompendo di misura, & ferire, ilquale modo e assai sottile, & inganeuole operando con quella circonspitione che si richiede, accioche pensando liberarla non si restasse ingannato da esso nimico, & ferito, si come anco si deue auertire, che il detto nimico non s’ accorga di tale intentione per meglio poterlo schernire. |
||||||
[6] When on guard on the left foot how to proceed against an adversary on the right foot. If you wish to advance with the left foot first in assaulting an adversary on the right foot you must realise your disadvantage, that is to say, your sword in hitting and recovering does not reach so far as your adversary’s, who is on his right foot and may hit and easily recover with little movement of the body. Therefore you must bring the right foot forward and when you have passed, owing to the great movement of the foot and the distance you have advanced, it is impossible to recover and break distance in one time. Therefore it will be necessary if you wish to recover after hitting to weigh on your adversary's sword and hold it in subjection towards the ground until you have recovered, in order to prevent his hitting while you are withdrawing. Even so, if your adversary were skilful[!] in freeing his sword, you would be in danger of being hit before you had come to rest owing to the great distance the foot has to recover, even longer than its advance. Therefore when you have advanced the right foot it is better to follow with the left also, and pass entirely, or having advanced the right foot and hit, at once to recover your weapons to the line of your adversary's sword and close its path entirely, remaining steady on the feet. If your adversary withdraws in order to free himself you can hit again in the time of his movement for within such close distance he cannot get back in time. All these rules apply after you have made a hit. In order to approach within striking distance, you should, for greater security, hold your dagger in such a manner, that as you advance the foot it reaches the point of the adversary's sword near to the blade without any other movement, s0 that you are sure that the dagger in that position defends the straight line from the point to your body. This is the true method of acquiring distance, so that the adversary cannot easily hit; if he moves his sword, it will be a change made to avoid the danger, which will give you a chance to hit as he moves. If you are not within this distance, you must approach with little movement of the point of the dagger and cover his new line in the same way. In order to find a chance to hit and pass, you should glide along the blade of your adversary's sword with your dagger, without beating it, that is to say when you are on the inside. If on the outside you should neither beat nor glide along his blade but leave the dagger in its place, or little in advance, since you must never penetrate the fourth part of his sword. In hitting you must turn the hand into the guard of quarte in order to unite it with the dagger, thus defending the upper and lower part at the same time. It is true that sometimes this method with the dagger is impossible, because the adversary holds his weapons so close together or because of the angle of his sword. The dagger is not sufficient to defend from the knee to the head, for it cannot defend more than one place at once, and in advancing within distance it might be harassed and disordered so much that the adversary by observing the time and taking advantage of the movement might forthwith hit. Therefore, as you have your left side forward and no other defence is possible, you must add the union of the sword, that it may defend one part, while the dagger defends the other. In this way there will be great benefit to your body, for the dagger will be more secure in its defence, and you will have greater advantage in hitting, since the point of your sword will be always nearer to the adversary and no less safe from his weapons than before. Now we will show the position in which the sword should be held. You must be in a guard of tierce with the point directed towards the point of your dagger, with the hand so far advanced that you know the forte can defend the side under the dagger and with the dagger arm so far extended to the outside that you know too that there is nothing uncovered over that arm. The dagger must be accompanied by the sword, so that the part below is defeated when on guard, and your adversary can hit only over the sword on the outside. The points must be so close together that the sword cannot be separated from the dagger and you become in danger of a hit in that weak place. In brief the point of the sword must be fortified by the dagger, so that the adversary's sword cannot thrust it away and hit. This is the position of the guard with which you must advance within distance in order to hit when an opportunity offers. In approaching you must protect the part uncovered over the sword by keeping the feet always outside the adversary's sword and the body sideways with the left side forward but bent, with the head over the hilt of the sword so that if the adversary approaches you can more easily defend that uncovered part. If you bend the body in the natural way and hold the sword so as to defend the left side, the head will be so far out of the line that it would be hit before it could be defended. But if you bend it over the hilt and the left knee in the manner described, with the shoulder turned to the inside, you will so place your body that none of it will be outside your sword; therefore if your adversary wished to hit, he would necessarily have to hit close to the blade of your sword, and thus the defence would be easy. In this position you can advance against all guards of the right foot, high or low, with the sword straight or at an angle. The only change necessary is to hold the points higher or lower, more to the inside or the outside, according to the position of the adversary's sword; but his sword is on the outside and very high, you must change your hand from tierce to quarte still observing the conjunction of weapons in order to defend the angle of the guard in seconde, so that he may not have an opening to place his point under the dagger. If his sword is on the inside you must observe the same union, but it would be better to have the hand turned rather more to quarte than to tierce in order to be stronger in that line. If your adversary disengages, you must hit without any other movement of defence by merely extending the sword far enough to reach. |
COME RITROVANDOSI SOPRA IL Sinistro si debba operare contra uno situato sopra il piè destro. CHI VORA ANDARE COL SINISTRO PIEDE INANZI AD’ assalire il nimico situato sopra il destro, se conoscerà il suantaggio suo, cio è che la sua spada uolendo ferire, & rimettersi in guardia non ariua tanto lontano, come può fare il situato sul destro piede, ilquale ferisce, & facilmente si rimette & con poco moto del corpo, li conuerà passare col destro piede, & passando non potrà più ritornare adietro per li gran moti del piede, & del corpo, & perche in quella postura si uà tanto oltre, che impossibile è ritornare, & rompere di misura in un sol tempo, si che sarà neccessitato, se uorà rimettersi doppo l’hauere ferito, caricare sopra la nimica, & tenerla sempre obligata uerso terra sino che si habbia ricuperato, & questo per impedire, che esso nimico non lo ferisca nel tempo, che si ritira indietro. Non dimeno, se collui, che si troua sul destro fosse persona giuditiosa in sapere liberare la spada, quest’ altro portaria pericolo di rimanere ferito prima che si fosse fermato rispetto al longo termine, che uà à ritornare il piede doue si hà mosso più longo assai, che non è à mouerlo, pertanto quando l’huomo è passato col destro meglio è seguittare anco col sinistro, & passare del tutto, ouero essendo passato col destro, & hauendo ferito rimettere subbito l’ armi contra la nimica, & ferrare tutta quella parte, oue la si troua restando fermo coì piedi, & de il nimico si ritirasse per liberarsi puosì ritornare à ferirlo di nouo nel tempo che si moue, perche della misura tanto stretta non può uscire in tempo; tutte queste raggioni si intendono doppo che si hà ferito mà douendosi auicinare nelle distanze, nelle quali si hà da ferire, si deue per minore pericolo situare il pugnale in maniera, che andando oltre col piede, & tenendolo fermo egli sia, nel giongere alla punta nimica, uicini al filo di essa senza che ’l si moua in parte alcuna, & si conosca, che stando fermo egli habbia diffeso quella retta linea, che uiene dalla punta al corpo, & questo è il uero modo di aquistare la misura, & che ’l nimico non possa facilmente ferire, ilquale se mutarà la spada sarà una certa mutatione fatta per saluarla dal pericolo, & laquale mutatione prestarà comodità di ferire esso nimico in quel moto; ouero non essendo l’huomo tanto in misura si deue auicinare, mà con poco moto della punta di esso pugnale, & coprire dall’ altra parte nel medesimo modo, & ancorche troui il tempo di [83] ferire, & che passi hà nondimeno da scorrere col detto pugnale il filo della nimica senza batterla intendendosi quando quella, sarà dalla parte di dentro che essendo dalla parte di fuori non si dee ne battere ne scorrere il filo, mà lasciare esso pugnale nel proprio suo luogo, ouero poco inanzi perche non si hà mai da penetrare la quarta parte della spada nimica, & nel ferire si hà da uoltare la mano in quarta guardia per unirla col pugnale, acciò si diffenda & la superiore & la inferiore parte in un tempo medesimo; è ben uero, che alcune uolte il nimico hà in mano l’ armi così conggionte che ’l pugnale non può tenere la detta regola, & anco per qualche angolo, che forma la nimica, & perciò sapendo l’huomo di trouarsi con le sinistre parti inanzi, & che per sua salute non resta altra diffesa, che quella del pugnale non bastante à diffendere dal ginochio sino alla testa, perche non può quello diffendere mai in più di un luogo in uno istesso punto, & che nell’ auicinarsi nelle distanze può essere assai trauagliato, & disordinato & tanto, che se ’l nimico osseruasse il tempo, & il uantaggio del moto lo potrebbe senz’ altro ferire, deue agiutarlo con l’ unione della spada, laquale ne diffenda una parte, & esso pugnale l’ altra, che in quest modo farà gran benefficio al corpo, perche il detto pugnale sarà più sicuro nella diffesa, & maggiore uantaggio haurà da ferire, atteso che la punta della spada sarà sempre più uicina al nimico, ne manco salua sarà dalle armi nimiche, di quello, che era prima; & hora si mostrarà la forma con che si deue situarla. Deue adunque l’ huomo trouarsi in terza guardia con la punta diretta uerso la punta del pugnale proprio, con la mano tanto oltre, che ben conosca il forte di essa, potere diffendere il fianco sotto il pugnale, & col braccio di esso pugnale tanto disteso in fuori, che anco conosca non hauere niente di scoperto sopra di esso braccio, & hà da essere accompagnato dalla spada tanto, che la parte disotto sia diffesa stando in guardia, & che ’l nimico non possa ferire altroue, che sopra la spada di fuori; deue anco stare con le punte tanto serrate insieme che la spada non possa mai essere trouata disgionta dal pugnale per il pericolo di essere ferito rispetto à quel debile, & in modo in somma, che la punta della spada sia fortifficata dal pugnale, & che la nimica non possa farla cedere, & uenire à ferire, & questa è la forma di guardia, con che deue andare, ferrando le misure per potere ferire uenendo l’ occasione, & con andare saluando, mentre si auicina, quello scoperto, che è sopra la spada, & con i piedi sempre di fuori della nimica tenendo il corpo in filo col sinistro fianco inanzi mà piegato insieme col capo sopra il finimento della spada, acciòche se ’l nimico uenesse potesse più ageuolmente diffendere quello scoperto sopra la spada, detto disopra, perche chi piegasse il corpo nelli fianchi come naturalmente si piega, & tenesse la spada per diffesa del fianco sinistro, il capo sarebbe tanto fuori di linea, che restarebbe ferito prima che si diffendesse, mà piegando lo in modo, che fosse sopra il finimento, & sopra il ginochio sinistro con la spalla diritta in dentro, si farebbe una sfuggita di corpo in guisa, che non auanzarebbe niente fuori della spada, & però se ’l nimico uolesse ferire bisognarebbe, che neccessariamente ferisse per il più prossimo del filo della detta spada, così la diffesa sarebbe facile, & con tale forma si potrebbe andare contra tutte le guardie di piede destro alte, ò basse, & con la spada diritta, ouero angolata, che non li occoreria fare altra mutatione, se non tenere più alte, ò più basse, più dentro, ò più fuori le punte secondo, che la nimica si trouasse, che quando la fosse di fuori, & molto alta si hauria da uolgere la mano di terza in quarta pure con la sopradetta conggiontione d’ armi per diffendere l’ angolo della seconda guardia, affine che essa nimica non hauesse aditto di mettere la punta sotto il pugnale, mà quando la detta nimica fosse dalla parte di dentro si deuria bene seruare la medesima unione, mà saria meglio nondimeno hauere la mano alquanto uerso la quarta, che in terza, perche più forte sarebbe da quella, parte, & se il nimico cauasse si deuria andare à ferire senza fare altro moto di diffesa con la spada con solamente stenderla per ariuare. |
||||||
[7] General discourse on the use of the dagger. In practising we say that it is good to hold the dagger with the arm extended with little help from the sword, so that you may become secure in the defence and may make little movement in parrying in order not to uncover one side while covering the other; for when the dagger is held well forward and you are disordered by large movements, you become confused and are defeated. Therefore it is necessary to use it judiciously and with practice to acquire such exactness that the dagger is not disturbed by the movements of the sword and you are more secure in its use. When then you have acquired that familiarity and security, you can hold it withdrawn and push it forward to the defence as required. Then you will be certain that it will perform its function with more exactness and security in engaging the adversary's sword. Similarly after such exercise you will be able to hold it more in union with the sword, which will render the defence easier and stronger, nor will your dagger be so much harassed. But you should not hold it fixed in any position. The reason is that in some cases it is good to have it advanced, and in other cases not according to the position of your adversary's weapons, whether advanced or withdrawn, and according to the position of your own guard. For having fixed the body and pushed the sword forward, it may be better to have the dagger while in other cases it may be better to have it advanced. But to discuss all the positions in which it may be held against the various counter-positions would make this discourse too long, for the subject is very large, almost endless. We shall merely say that as a general rule the point of the dagger should be held always opposed to the point of the adversary's sword, until that point is turned against the body. To hold the dagger out of line would not be advantageous, nor to keep it turned towards the feet, unless you were careful to hold the body so low that you could defend the upper part with little movement, and were ready to hit in the same time. As we have said it is better to cover the dagger with the sword in such a manner that your adversary's only resource is to disengage. This method is safer and less subtle, and may also be used against a sword held high. Also you should hold the dagger so close to the sword that there is no path for the adversary's sword between the two hands; his sword will either meet the dagger or pass on to the forte of your sword. We must also remind you that in using the dagger the defences are all to be made with the edge, whether on the inside or the outside, whether high or low, and with the strongest part of the dagger especially against cuts, and against thrusts too, when you wish to glide along the blade. It is true that if you wish to beat a practice which we do not recommend, it is better to do so, the point of the dagger on the faible of the adversary's sword, since the point describes a larger circle. |
[84] DISCORSO IN GENERALE Sopra l’ uso del pugnale. PER L’ ESSERCITTARSI DICIAMO, CHE E BVONO TENEre il pugnale col braccio longo, steso inanzi, & poco agiutato dalla spada, acciò l’ huomo si assicuri nelle diffese, & faccia nelli parati piccioli moti per non si scuoprire tanto in unlato mentre si cuopre nell’ altro, perche hauendolo steso inanzi, & disordinando si con gran moti restarebbe confuso, battuto, & però è neccessario di giuditiosamente adoprarlo, & con la pratica assuefarsi tanto, che si aquisti una guistezza tale, che nelli moti della spada non si turbi, & che sempre sia più assicurato in oprarlo, che quando poi haurà fatta la detta assuefatione, & sicurezza, potrà tenerlo ritirato, & spingerlo inanzi alla diffesa secondo l’ occasione, & sarà all’ hor certo che quello andarà con più giustezza à fare l’ officio suo, & con più sicurezza di aquistare la nimica; & similmente doppo cotale essercitio lo potrà tenere sempre più unito con la spada, il che renderà la diffesa maggiore più comoda, & più forte in tutte l’ operationi, ne il pugnale all’ hora, sarà tanto trauagliato, se bene non lo dourà tenere in alcuno sito fermo, la raggione è, che in alcuni casi buono è hauerlo auanzato, & in alcuni non buono secondo, le situatione dell’ armi nimiche tal’hor longhe, & tal’hor corte, & anco secondo, che l’ istesso huomo tiene la propria guardia, per che hauendo fermato il corpo, & posta la spada inanzi, sarà megliore il pugnale corto, & in un’ altro caso migliore auanzato, si come in alcune guardie più è buono tenerlo in piede, mà chi uolesse raggionare di tutti li siti per mostrare, come si douesse tenerlo nell’ uno, ò nell’ altro, ò contra l’ uno, ò contra l’ altro sito troppo prolisso si farebbe il discorso, essendo la materia troppo ampla, & quasi infinita, solo si dirà che la punta del pugnale per regola ordinaria si dee tenere sempre opposta, & riguardante la punta della spada auersa, sino, che quella sarà uolta contra il corpo, che quando fosse fuori di presenza non saria à proposito, ne meno se la guardasse uerso li piedi, à chi non usasse una gran diligenza di situare il corpo tanto basso, & comodo che si potesse diffendere la parte disopra con poco moto, & che si fosse in medesimo tempo pronto à ferire pure essendo bassa, è malageuole da operare, come si è detto, meglio è coprirla con la spada, & in maniera che ’l nimico non la possa leuare, se non la caua che questo certo sarà più sicuro, & di minore sottilità, & il simile se hà da fare contra una spada, laquale sia molto alta, & si dee tenere il pugnale anco tanto uicino, che trà l’ una, & l’ altra mano non sia strada da uenire, per la nimica, laquale uenendo sia forzata trouare il pugnale, ò passare per il forte della spada. Dobbiamo anco ricordare, che nell’ uso del pugnale le diffese si hanno tutte da fare col filo tanto di dentro, quanto di fuori, & così alte come basse, & nel più forte di esso pugnale massime contra taglii, & ’anco contra le punte quando seli uuole scorrere il filo, è ben uero, che uolendo battere le stoccate, cosa non molto lodata da noi, & tanto meno nel passare, all’hora meglio è batterle con la punta di esso pugnale nel debile di essa nimica atteso che la punta fà circonferenza maggiore. |
||||||
[8] This discourse will explain the guard in prime with the sword and dagger here illustrated. The hand is in the position reached by drawing the sword from the scabbard. With these weapons your guard will be securer than with the sword alone, for the dagger defends the upper part towards the face, which is nearest to the adversary and defends below to the middle of the body. Below that part there is no danger since the adversary cannot reach. If you keep the feet close together and the weapons in conjunction, your sword cannot easily be engaged and is always free, whilst the conjunction of the dagger with it prevents the entrance of thrust or cut between them. Cuts at the head too are defended by this guard, and you may hit in the same time. With this guard in every case after hitting you should recover to the same position for your protection, keeping the dagger always extended. As to the legs no other defence is needed, where the adversary cannot reach. In the time of your adversary's approaching to hit you can thrust a cut at the head or sword arm, merely bringing back the left foot, thus you will protect yourself and make a hit. |
[85] QVESTO DISCORSO SARA ESPLICATIVO DELLA PRIMA GVARdia di spada, è puguale rapresentata dalla sequente prima figura, laquale si uede con la mano nel sito, oue si è trouata à cauate la spada dal fodero, & in quest’ armi l’ huomo sarà più sicuro, che nella guardia di spada sola, per hauere il pugnale, che li diffenderà la parte superiore uerso la faccia, laquale è più uicina al nimico, si come anco li diffenderà disotto sino à meggio corpo, che di li in giù nonè pericolo per non poterui il detto nimica ariuare, & massime quando si saprà tenere in passo stretto, & con l’ armi conggionte, perche non li potrà così facilmente essere trouata la spada, laquale perciò tenerà sempre libera, & il pugnale conggionto ad’ essa, in modo, che non potrà entrare punta, ne taglio nel meggio, & li taglii che ueranno per testa saranno diffesi dalla detta guardia, la quale in istesso tempo ferirà, & perciò l’ huomo situato in questa guardia dourà in ogni caso dopò hauere ferito ritirarsi nella medema per sua saluatione, tenendo sempre il pugnale disteso; mà quanto alle gambe, doue l’ auerssario non può ariuare non occore altra diffesa, si potrà bene nel detto tempo, che l’ auerssario si auanzarà oltre per ferire scaricarli una stoccata, ouero tirarli un taglio per testa, ò per il braccio della spada, con non fare altro, che allargare il piè sinistro indietro, che così si saluerà & ferirà detto nimico. 49. |
||||||
[9] The second guard in order is a guard in prime in its nature and derived from the first. The difference between them is that you have carried the left foot forward, or the right foot forward, and that is the only change in position. As to its security this guard is inferior to the first, because the advanced leg is in great danger and the side below the dagger is exposed, for can you hit without passing, and having passed you cannot return on guard without being hit owing to the length of the movement; also you are too far advanced to be able to break ground. Still this guard may be used, if its correct principles are observed, that is to wait for the adversary to hit him in order to parry and hit, or make a feint with the point and cut. A guard formed in this manner is also fitted for making a feint with the point and thrusting; but you must not give the adversary a time or an opening, unless you carry thw[!] weight of the body on to the rear leg, leaving the other leg exposed; when the adversary advances to hit that leg, you must carry it behind the other, which you may do without difficulty as it is already relieved of the weight. In this manner with the body bent forward on the right foot you may in the same time thrust or cut according to the opportunity; this is beyond comparison the best device which can be used with this guard. |
[86] SE GVITA LA SECONDA GVARDIA QVANTO ALL’ ORDINE, mà però una delle prime quanto alla sua qualità, & natura, diriuata dall’ altra prima, & la uariatione, che è frà di loro può essersi caggionata per hauersi l’ huomo portato col sinistro piede inanzi, ouero col destro indietro, ne altra differenza è frà di loro circa il sito, le bene quanto alla maggiore bontà, & sicurezza questa è superata assai dalla prima, perche la gamba anteriore di questa porta pericolo grande, & anco il fianco sotto il pugnale si mostra scoperto, ne può ferire se non passa, & passando non può ritornare nella guardia senza restare ferito, si per la longhezza del moto, come anco per trouarsi tanto inanzi, che più non può uscire di misura; con tutto ciò detta guardia si può usare ancor lei, mentre che si osseruano le sue giuste raggioni, lequali sono di aspettare il nimico che ferisca per parare & ferire, ouero di fingere di punta, & dare di taglio; che torna assai acconcio in questa prima fondata in tale forma, similmente fingere di punta, & dare di punta, mà non ualeria gia cosa alcuna se si desse tempo, ò comodità al nimico, quando non si portasse il peso del corpo sopra la gamba di dietro, lasciando scoperta tutta quella dinanzi, & se mentre che il detto nimico uenisse per ferirla, la non si portasse di dietro dell’ altra, cosà che non difficilmente sarebbe fatta per essere già sgrauata del peso, & in questo modo restando l’ huomo piegato inanzi col corpo sopra del destro piede potria ferire in tempo medesimo di punta, ò taglio secondo l’ oportunità, botta senza comparatione megliore, che in detta guardia si possa fare. 50. |
||||||
[10] This plate represents an extension made from the guard in prime with the sword and dagger. This guard would naturally hit over the adversary's weapons, for if you try to hit below with this extension your adversary would easily knock your sword to the ground. The plate shows the dagger extended and the body bent in order to parry the blow which the adversary might make; for in hitting you must never withdraw the dagger or let it fall-back[!], since it is clear that in the time of withdrawing or abandoning it you cannot parry. With this guard you increase your danger by the large part uncovered by the angle formed with the sword hand, so that if you could not parry you would be hit, and still more easily as the thrust with this guard is shorter than with the other guards. After hitting with this thrust you must recover the right foot to the other foot and wait for a new opportunity; if your adversary does nothing, you can make a feint of a thrust on the inside of the dagger, but if he should design to hit in tierce, as he may easily do, you should then make a cut of mandiritto tondo under his dagger, which will hit him in the sword arm at the moment of his thrust in tierce; you must carry the right foot forward a very little way according to his distance, parrying his point at the same moment with your dagger by pushing it out to the left side and bringing the right side forward in order to facilitate the defence and lengthen your sword; this will have a good effect when you recover on guard. |
[87] QVESTA, CHE SEGVE E VNA DISTESA FATTA DALLA PRIMA guardia in spada, è pugnale, laquale uà di sua natura à ferire sopra l’ armi nimiche, perche se l’ huomo uolesse andare à ferire con detta disotto, l’ auerssario la mandarebbe facilmente à percuotere in terra, & questo pugnale, che stà così auanzato, & questo corpo così piegato per parare il colpo, che dal nimico può uenire, non uuole mostrare alrro, se non, che nelo ferire non si dee mai ritirare, ne lasciare mai andare di dietro esso pugnale, essendo assai chiaro, che l’ huomo nel tempo, che lo ritira, ò l’ abbandona non può con esso parare, & in questa guardia si fà anco tanto maggiore il suo pericolo rispetto al molto scoperto, che in lei si troua per l’ angolo formato dalla mano della spada, di modo, che senza potere parare, restarebbe ferito, & più facilmente ancora per essere la botta della detta guardia assai più corta, che nelle altre guardie, con laquale botta hauendosi ferito si dee ricuperare il destro piede appresso dell’ altro aspettando noua occasione, & quando il nimico non facesse niente si potrebbe fingere di darli di dentro del pugnale di punta, mà se parasse per ferire di terza come facilmente potrebbe, si douria all’hor uoltare di mandiritto tondo sotto dell’ istesso nimico pugnale, che si ferirebbe nel braccio della spada in quello punto medesimo che esso hauesse uoluto ferire di detta terza, & si douria portare inanzi il destro piede, mà poco ò niente, secondo la distanza dell’ auerssario, la punta delquale bisognaria parare col pugnale nel punto medesimo spingendola fuori per il sinistro fianco con uoltare il destro inanzi affine di facilittare più la diffesa, & allongare più la spada, che saria assai buono effetto ritirandosi in detta guardia. 51. |
||||||
[11] The next is a guard in seconde with the sword dagger, better and more convenient than the guard in prime, because the arm is not so strained, and safer, because the sword covers the lower part and keeps the adversary at a distance. Further cuts the head can be parried with this guard, but with the weapons in conjunction for greater strength, and in the same time you may hit. Thrusts are parried with the dagger alone. This guard will be most successful if you are careful to hit with the right foot, raising the left foot and carrying it somewhat back, but in a circle, and recovering the right foot close to it. In hitting the right side should go forward. Carrying away the foot must be done with great care, so that the body in recovering may describe a circle and get out of the line of the adversary's point, while you are covered from the line of the dagger, without movement and the distance is enlarged. In closing distance also you should move in a circle towards the adversary's right side and with short steps, in order not to close except on hitting; also you should keep the body out of distance while continuing to move in a circle. When you hit, advance in a straight line and recover in a circle. With this caution you will be very secure in this guard in comparison with some others. With the same steps as in approaching you can also withdraw, preserving the guard without any disadvantage, or you can proceed according to the occasion by advancing more or less without any change of line. |
[88] MA QVEST’ ALTRA, CHE SEGVE SARA LA SECONDA DI SPAda, è pugnale molto migliore, & più comoda della prima perche non si stà con tanta uiolenza del braccio, & più sicura perche la spada ricuopre la parte inferiore, dalla quale spada il nimico uiene anco tenuto lontano, & si dice in oltre, che li taglii per testa si parano de la stessa guardia, mà con tutte due le armi conggionte per fortezza maggiore, & nel’ medesimo tempo si fere, le punte si diffendono col solo pugnale; laquale guardia ottimamente riuscirà se si osseruarà di ferire col destro piede leuando il sinistro, & portandolo indietro alquanto mà in giro ricuperandoli il destro appresso, douendo, nel ferire, andare le destre parti inanzi, & però questo portare di piede hà da farsi con molta auertenza, acciò il corpo nel ritorno faccia circonferenza, & si lieui di uista della nimica punta in modo, che dalla linea del pugnale sia ricoperto senza moto, & sia più allontanato dalla misura. Deuesi anco nel stringersi in misura andare sempre in giro uerso la parte destra del nimico, & in poco passo sempre per non slargarlo mai se non nel ferire, procurando di tenere anco sempre il corpo fuori della misura ne mai fermarlo, mà andare sempre, girando però, quando si uà à stringere la misura, & in ferendo portarsi oltre per retta linea con ricuperarsi in giro, con laquale osseruatione si ritrouarà l’ huomo molto sicuro in tale guardia, in comparatione d’ alcune altre, & con lo stesso passo de lo auicinarsi potrà anco allontanarsi persistendo in guardia senza alcuna scomodità, oue potrà operare secondo l’ occasione, & più, & meno auanzarsi inanzi senza mutatione d’ alcuno effetto. 52. |
||||||
[12] The position here shown arises after you have carried the left foot back, leaving the sword and the right side of the body advanced; thus the dagger has been shortened and remains near the hilt of the sword; the left side too has been left exposed above, but at such a distance that the adversary cannot easily reach it. It is seen that you are carrying your feet towards the adversary's left side, in order to withdraw your own left side and find an opening to hit him above or below the dagger by advancing the right foot in a circle towards that part with the same motion of the body, and without moving the dagger from its position. In this way if it happens that your adversary tries to hit the exposed left side by closing the distance, you could while parrying change from seconde to quarte and hit at the same moment, and then recover in a circle to the same guard. This is the true reason of this position; he who knows how to use it can also provoke his adversary to hit by a time or an appel, in order to use the counter-time. Moreover the dagger is safer in this position than with the arm extended. |
[89] LA SEGVENTE FORMATA NEL MODO, CHE SI VEDE, E STAta caggionata da quella, che in stretto passo hà slargato il sinistro piede indietro, lasciando la spada, & la destra parte del corpo inanzi, in modo che ’l pugnale è uenuto à scurtarsi, & à restare uicino al finimento della spada, & che anco hà lasciato la sinistra parte di sopra tutta scoperta, mà lontana, acciò il nimico non così ageuolmente ui possi ariuare, & si uede, che uà portando li piedi uerso la sinistra parte di detto nimico per dillongare la sua, & per trouare modo di ferire esso nimico disotto, ò disopra del pugnale con auanzare il destro piede pure in giro uerso quella parte con l’ istesso moto del corpo, & senza mouere il pugnale dal suo luogo, in modo che se accadesse che il nimico uolesse ferire in quella parte manca scoperta, nel stringerli la misura l’ huomo potrebbe, mentre che para uoltare di seconda in quarta, & ferire in punto medesimo ritirandosi poi in giro, & rimettendosi nella istessa; questa è la propria raggione di questo sito, & chi saprà bene oprarla, potrà anco dare occasione al nimico di ferire prouocandolo con qualche tempo, ò chiamata per usare poi il contratempo; non lasciandosi di dire, che ’l pugnale è più sicuro in questo sito, che se ’l braccio fosse inanzi disteso. 53. |
||||||
[13] Now follows a guard in seconde formed with the left foot, much better than the first one formed on that foot, because the body is more ready for every event, and more protected by its low position so that you can both hit and parry with less movement. With this guard you can close distance on the outside of the adversary's sword, while engaging his sword with your dagger. With this guard too you can hit by advancing the right foot, always leaving your dagger on his sword without beating it. You can pass right on to the adversary's body; but if you wish to recover you must meet his sword with yours and disorder it, so that he cannot hit while you are recovering, since you will actually have passed so far forward that you cannot break ground in one step. If your adversary's sword is on the outside of the dagger and he offers a time to hit, then you must change from seconde to quarte with the sword and dagger in conjunction, so that you may be defended above and below the dagger, and turn the body in order to lengthen your thrust and be better defended; in order to recover safely you must let your sword fall on the adversary's in a guard of tierce, after hitting. As to engaging his sword without being deceived by a disengagement, you must remember when within reach of his sword with your dagger to put him into subjection at that moment, by showing that you intend to hit, so that by that fear he may be prevented from freeing his sword, except by fleeing from the danger and retiring. In that case you should not advance nor do anything but try to engage his sword again without beating it, so that he cannot hit in any lime, you must then take care not to let your dagger fall in order to avoid the danger of being hit on the outside over the dagger. |
VIENE APPRESSO VNA SECONDA GVARDIA FORMATA COL SInistro piede, molto megliore della prima formata sopra il medesimo piede, perhauere il corpo più pronto ad’ogni effetto, & più coperto perla bassezza, inmodo, che con minor moto può, & ferire, & parare, con laquale guardia si può andare serrando la misura [90] dalla parte esteriore della nimica spada procurando di aquistarla col pugnale, & della medesima guardia ferire con passare oltre del destro piede, & con lasciare sempre esso pugnale alla spada del nimico senza batterla, si può anco passare sino al corpo dell’ istesso nimico, mà uolendo ritornare indietro saria di bisogno andare con la spada alla spada auersa, & disordinarla in guisa che non potesse ferire, quando che l’huomo si rimette, perche ueramente saria passato tanto inanzi, che non potria con un solo passo uscire di misura, mà quando la detta nimica si ritrouasse fuori del pugnale, & prestasse tempo di ferire saria all’hor di mestieri uoltare di seconda in quarta con la spada, & il pugnale insieme conggionti, accioche dalla parte di sopra & disotto del pugnale si restasse diffeso, & uolgere il corpo per slongare più la botta, essere maggiormente diffeso, mà uolendosi poi ritirare si douria lasciare cadere la spada sopra della nimica in terza guardia, dopò l’hauere ferito che si ritiraria saluo; Che quanto al uolere aquistare la nimica, & non essere ingannato da cauatione alcuna si dee tenere mente, quando, che si è in termine di ariuare col pugnale alla spada nimica, dimettere esso nimico in obbidienza, nel punto proprio, che seli ariua, con mostare di uolerlo ferire, acciòche ritenuto da quello timore, non habbia tempo di liberarla se non con fuggire il pericolo, & ritornare indietro, nelquale caso non occore andare ne si hà da hauere altra intentione che di occupare la detta nimica senza batterla, mà che però la non possa ferire oue che si troua, & all’hora si dee risoluersi guardandoli di fare caduta col pugnale per il pericolo, che sarebbe di restare ferito di fuori sopra di esso pugnale. 54. |
||||||
[14] This next guard in seconde with the right foot forward, the point of the foot turned outwards and the whole weight of the body on that foot, is really an excellent position, because the exposed parts of the body are well withdrawn and in consequence there is little the adversary can reach. Moreover in this position the body can pass with great swiftness. In advancing take short steps and try to engage your adversary's sword; when you have found it with the dagger, do not beat it but glide along the blade, and hit by passing in order better to change the front of the body and to bring out of the line of his point all that part which might be hit. With this guard you may hit in quarte as well as in seconde. Also you give the adversary no chance of a time but press him resolutely and assault him without changing time or being disconcerted in any way. |
[91] VERAMENTE, CHE QVEST’ ALTRA SECONDA, LAQVALE SEgue col destro piede inanzi, & con la punta di esso allo infuori, & dal quale uiene sostenuto tutto il corpo, è una forma assai buona per essere li scoperti del suo corpo molto lontani, & per conseguenza picciolo il luogo, doue il nimico possa ariuare, & in oltre perche il corpo situato in cotale guardia passa con gran prestezza, & nell’andare camina con passi piccioli procurando sempre di aquistare la nimica, & dopò hauerla col pugnale aquistata non la batte mà scorre il filo di essa, & ferisce in passando per meglio mutare la prospettiua del corpo, & tante, che lieua di uista dalla nimica punta tutta quella parte, che poteua essere ferita, & detta guardia tanto ferisce di quarta come dell’istessa seconda, laquale non è fatta per dare occasione ne tempo al nimico, mà per andare risolutamente à constringerlo, & assalirlo senza mutarsi, ò sconcertarsi di niente. 55. |
||||||
[15] The guard shown in the next plate is also a guard in seconde, but little used and perhaps unknown. The sword is held foreshortened, the dagger upright, the body bent, and the weapons so low that only the part on the outisde[!] over the sword is exposed, and there only can the adversary hit. This guard must be carefully formed, with the sword somewhat lower than the adversary's as long as his point is as high as his hand. If his point is lower than the hand, you must proceed above the part covered, taking natural steps and moving in a circle towards his right side; by this means you will withdraw the part above the sword which is exposed and, when you have found his sword with your dagger, your whole body will be covered when on guard. You should never proceed, until you have first advanced far enough to engage the adversary's sword with your dagger; but when engaged, you should continue resolutely with natural steps. The lower the body is the more successful the stroke will be. You must make the hit with the body low, without stopping or waiting, but always continuing in a circle. Even if your adversary should thrust, you should not stop but keep the union of your weapons; you must not become disordered nor rush, but glide along the blade of his sword with your dagger as far as the hilt. Thus you may hit in seconde or tierce or quarte according to the opportunity. But throughout you must always keep the weapons in conjunction both when on guard, and when hitting in whatever manner, so that the adversary cannot enter with his sword between your hands. |
QVEST’ ALTRA DI MOSTRATA DALLA SEGVENTE FIGVRA E pure una seconda ancor lei, mà poco usata, & forsi, non conosciuta, laquale tiene la spada trauersata, & il pugnale erretto allo in sù, col corpo curuato, & con l’ armi tanto basse, che non discuopre altro che la parte di fuori sopra la spada, ne altroue può il nimico andarla à ferire, mà è di mestieri, che detta guardia sia ben formata, & che l’ huomo sia con la spada alquanto più bassa della nimica per sin tanto però, che detto nimico tiene alta la punta egualmente come la mano, perche quando detta punta fosse più bassa bisognaria andarli sopra di coperta caminando di passi naturali, & sempre in giro uerso la destra parte [92] auersa, che così uerebbe ad’ allontanarsi sempre quello scoperto sopra la spada, & in modo, che gionto alla nimica col pugnale tutto il corpo sarebbe coperto standosi nella guardia, ne mai dourebbe l’huomo operare se prima non si fosse portato tanto inanzi, che hauesse aquistata detta nimica col pugnale, mà aquistata, che l’hauesse douria risoluersi, & continouare di passi naturali, & quanto più il corpo fosse basso, tanto piu sarebbe riuscibile il colpo, douendosi ferire con la medema bassezza di corpo, ne mai fermarsi, ò aspettare, mà andare sempre caminando in giro, & quando ben’ anco il nimico slanzasse qualche stoccata non per quello si dourebbe lasciare di continouare inanzi bene unito, & senza disordinarsi, ne mai slanzarsi, mà andare scorrendo il filo della medesima nimica col pugnale sino al finimento, che cosi si ferirebbe di detta seconda, & di terza, & di quarta secondo l’ occasione, mà col tenersi, sopra il tutto, sempre unito così nella guardia come nel ferire in qualunque modo, che si feresse acciòchc esso nimico non potesse mai entrare con la spada trà l’ una, & l’ altra mano, 56. |
||||||
[16] Now follows another guard in seconde, with the feet level and separated, the body bent forward, the chest directly facing the adversary and the arms and weapons curved and so high as to cover the whole head, which cannot be attacked by the adversary except below and between the weapons. Since the chest faces the adversary's point when he hits you can move with whichever foot you please, carrying it into the line of the other; in this manner your whole body will be brought out of line, for if his point is exactly in the middle, it must also be in the middle of the two feet, and when one of them moves, his point is necessarily out of line an amount equal to the half of the step you have made. Thus you can in the time of his movement hit, pushing his sword outwards so that it cannot return into line. As both feet are in line with this guard your reach is long and you may go right to his body and recover by carrying to one side the foot which has remained steady, and again turn your chest facing his sword. With this guard you may wait or attack the adversary without his giving a time. It is very secure against cuts as the head is defended on both sides, so that it is not necessary to move the weapons to defend it, while below the legs are so far distant that they cannot be reached. We shall speak of his guard again in treating of the attack with resolution. |
SEGVITA ANCORA QVEST’ ALTRA SECONDA, LAQVALE STA co’i piedi eguali slargati l’ uno dall’ altro, col corpo curuato inanzi, & col petto, contra il nimico perdiametro tenendo le braccia, & l’ arme ouate, & alte in modo che cuopre tutta la testa, laquale non può essere offesa dal nimico se non disotto nel meggio, & perche hà il petto contra la punta nimica, quando esso nimico uiene per ferire, può muo- [93] uersi con quale piede li piace portandolo inanzi nella linea dell’ altro che in questo modo uiene ad’ uscire con tutto il corpo di presenza, perche se la detta nimica era giusta per meglio del petto, conuiene anco che fosse in meggio delli dui piedi, di quali mouendosi l’ uno da quale parte li piace, uiene à restare neccessariamente la detta nimica spada tanto fuori quanto importa la metà di quel passo, che si uede, & così puô l’ huomo nel medemo tempo, che si moue ferire, douendo serrare la nimica di fuori in modo, che non possa più ritornare in presenza, & perche questa guardia trasporta molto inanzi per tenere così li piedi e guali[21] può andare sino al corpo, & anco tornare à rimettersi con slargare per trauerso quel piede, che fosse restato fermo, & con tornare à uolgere il petto contra la nimica, & in questa guardia si può aspettare & andare ad’ assalire il nimico senza che quello dia nissuna sorte di tempo, & è sicurissima contra li taglii per essere la testa diffesa dai dui lati con la sua guardia, doue non occore di muouere niente le armi per diffensarsi, & dalla parte disotto sono le gambe tanto lontane, che non può il nimico ariuarli, dellaquale guardia si parlarà di nouo, quando si trattarà della risolutione. 57. |
||||||
[17] Here follows an extension from the guard in seconde, differing little from the extension from prime. The difference is in the sword hand, which is turned slightly upwards; therefore the extension is longer and the sword hand nearer the dagger, which gives greater security between the weapons. With this seconde you can hit in any part, so that it is better and more convenient than the prime. You may use it on more occasions and times, whilst the union with the dagger offers greater protection. After asking a hit you must be careful to withdraw the right loot close to the left and recover to the same guard. In closing distance you a must make a circle towards your adversary's right side and hit by passing in the straight line, and then recover in a circle; this is done by putting the right foot to the ground when you make the extension, lifting the left foot, carrying it in a circle out of distance, and then recovering the right foot close to it. This is the true method of proceeding and is sure to make a hit. |
QVELLA CHE SEGVIRA SARA V N A DISTESA DI SECONDA guardia poca[22] differente dalla distesa di prima guardia laquale poca[23] differenza stà nella mane della spada, che è voltata alquanto in giù, & peró la distesa è più longa, & la mano della spada più uicina al pugnale, doue che nel meggio dell’ armi è più sicura, & con questa seconda si può ferire in qualunque parte, talmente che è megliore, & più comoda [94] della prima, & l’ huomo sene può seruire in più tempi, & occasioni, & quando li occore serire l’accompagnarui il pugnale rende molto coperto, auertendosi, che subbito dopò ferito si hà da ritirare col destro pie uicino al sinistro riducendosi nella medesima guardia, & nelo andare à serrare la misura di girare uerso la parte destra del nimico, & ferire col passo in retta linea ricuperandozi purè in giro, laquale cosa, si fà mettendo il destro piede in terra quando si fa la distesa con alzare il sinistro, & portarlo in giro dilongandolo dalla misura, & subbitamente ricuperandoli il destro appresso & questa è la uera operatione, & quella, che fà sicuramente ferire il nimica. 58. |
||||||
[18] This plate illustrates a guard in tierce at an angle, although there is much uncovered above the sword, yet the dagger defends that part; therefore the dagger is held erect and high, with the hand somewhat low and to the outside, so that the adversary can hit only in that part which is exposed above the sword. The intention is to parry with the dagger held thus high and to hit in tierce under the adversary's sword, with the same angle. This stroke is very difficult to parry for it cannot be thrust downwards because of the angle which pushes away the dagger, resists and goes to the body. Therefore the adversary must push your sword to the one side or the other according to which side it is nearer; or rather he must push the sword to that side where it will be out of line in the shortest time, and where it has less force and can offer less resistance. With this guard excellent strokes can be made under the dagger on the outside, and also between the weapons. Sometimes you must lower the point a little and make the angle again hitting with the force of the angle, so that even with both his weapons, the adversary can not[!] push your sword down. You will succeed because his weapons will glance towards the strength of the angle, that is the hilt of your sword. Therefore the adversary has to use much judgment in deciding to which side to push your sword, in order to defend himself more easily; otherwise he must save himself by retiring. That plan of retiring should be adopted, since the thrust at an angle does not reach very far. The best rule then is not to parry. |
LA SEGVENTE FIGVRA RAPRESENTARA VNA TERZA ANGOlata, laquale ancora, che sia molto scoperta sopra la spada là non dimeno la diffesa del pugnale, & lo tiene così erretto in alto, & la mano alquanto bassa & in fuori, acciò che l’ auerssario non possa ferire altroue, che in quello scoperto sopra la spada con in tentione di parare di detto pugnale così alzato come si troua, & ferire di terza sotto la nimica col medesimo angolo, laquale botta è assai difficile, da parare non potendosi spingerla à basso per caggione di quello angolo, che uiolenta il pugnale, resiste, & uà al corpo, però è neccessario il spingerla ò per l’ una, ò per l’ altra parte secondo, che sarà uenuta più prossima ad’ uno che ad un’ altro luogo, se ben si douria spingere la spada da quella parte, doue con più breue tempo essa può uscire di uista, & doue hà minor forza, acciòche più presto [95] esca, & senza fare resistenza. Con questa guardia si fanno assai buoni colpi sotto il pugnale perla parte esteriore, & anco nel meggio dell’ armi, dee si taluolta abbassare un poco la pùnta & reangolarla in sù ferendo con la forza dell’ angolo, talmente, che se il nimico ui mettesse anco tutte due le armi per rispingerla abbasso non potesse fare niente, il che riusciria perche dette armi nimiche scorreriano nel forte dell’ angolo detto di sopra ciò è nel finimento della spada, in modo che detto nimico haura bisogno di molto giuditio per conoscere da qual parte hauesse da rispingere detta spada per più facilmente diffendersi, altrimenti conueria saluarsi con qualche ritirata di uita, & tanto più si appi gliarebbe à si fatto partito, quanto, che l’ angolo non ferisse molto lontano, & la migliore regola saria di non parare. 59. |
||||||
[19] This is a guard in tierce with the sword and dagger. It is formed with the points of the weapons in conjunction, so that the adversary cannot hit between them. The sword should be held with one fifth of its length beyond the dagger in order to prevent the adversary from harassing the dagger by disengagements and feints. As the sword is so far advanced, the forte of the sword can be very well used in the defence, with the support of the dagger. There is the further advantage that the point of the sword is nearer the adversary's body, and, if kept free, is ready to hit with a lunge or a pass. You can wait or attack at pleasure, make feints, disengagements, counter-disengagements, times, or counter-times; you can lunge or pass, above or below the dagger, in any part according to your opportunity, and with little change of the hand, since it is between seconde and quarte. |
VNA TERZA GVARDIA DI SPADA, E PVGNALE SARA QVELla, che segue, laquale si dee formare con le punte così accompagnate, come si uede, acciò il nimico non possa ferire nel meggio dell’ armi, & si dee tenere la spada auanzata un quinto di essa spada inanzi il pugnale per impedire al detto nimico il poterlo trauagliare con le cauatione, & con le finte, & essendo poi la spada così auanzata si potrà adoprare molto bene il forte di esso per diffessa, & agiuto de lo stesso pugnale, oltre l’hauere il benefficio punta più uicina al corpo nimico, la quale, conseruata libera, sarà molto pronta à ferire, tanto à piè fermo, come passando, potendo aspettare, & assalire segondo, il [96] beneplacitto, & si potranno fare finte, cauationi, contracauationi, tempi, contratempi ottimamente potendosi ferire à piè fermo, & passando disopra, & disotto del pugnale, & in qualunque parte secondo l’ occasione, & con poca mutatione della mano, per essere posta nel meggio della seconda, & della quarta. 60. |
||||||
[20] This is a guard in tierce, with the sword advanced, the dagger near the hilt, the right side forward and the left exposed. With this guard you may advance gradually within distance, in order to entice your adversary to hit at the part uncovered and to defeat him at the moment of his advance with a tierce or quarte; the quarte would be better, because your weapons would be closer together so that he could not hit below, whilst defending above. When you are approaching within distance if your adversary changes the position of his dagger, with this guard you can make a swift thrust, which would hit under the line of the dagger on the inside and close to the sword; or you might make an excellent stroke over the sword in the straight line. In this position the dagger cannot be much harassed by the adversary's sword, for too much judgment and circumspection would be needed to bring the sword so far forward. In using this guard you should know how to preserve your sword from being engaged by the adversary's weapons, when you would have difficulty in freeing it and could only do so by withdrawing it, which would be bad. Also you must keep within wide distance, so that your adversary cannot pass. With this guard it is sometimes advantageous to change to quarte. |
QVEST’ ALTRA SARA VNA TERZA PVRE CON LA SPADA auanzata, & col pugnale presso al finimento, portando la destra parte inanzi, & tenendo la sinistra scoperta, & laquale si uà pianpiano approssimando alla misura per tirare il nimico à ferire in quello scoperto, & batterlo nel proprio punto, che uiene di terza, ò di quarta, laquale quarta sarebbe migliore perche l’ huomo restarebbe più accompagnato con le armi affine che ’l nimico non potesse ferire disotto, nel tempo che diffende la parte disopra, & quando nelo auicinarsi nelle distanze il pugnale nimico suariasse, si potria con questa guardia slanzare dentro la botta con prestezza, che andaria benissimo à ferire sotto la linea di esso pugnale & di dentro uicino alla spada, & anco sopra la spada si potria fare un buon effetto de retta linea; oltre che stando in questa forma il pugnale non può essere molto trauagliato dalla spada nimica, perche troppo giuditio, & troppa circonspetione bisognarebbe à chi si uolesse condure tanto inanzi, è uolendo usare questa guardia basta solamente il sapere ben guardare la spada dalle armi nimiche, acciò che non li uenga occupata, & essere poi in difficolta di liberarla, che non si potria fare se non ritirandola, il che sarebhe [97] mal fatto, & si ha da conseruarsi in lontana distanza acciò il nimico non possa passare. Si auertisse ancora, che in tale guardia uiene tal uolta à proposito il girare in quarta. 61. |
||||||
[21] Here follows another tierce with the dagger advanced and the sword as much withdrawn, in order to keep it free from the adversary's weapons and to give more impetus to the lungs[!]. The sword does not impede the dagger in seeking the adversary's point, and the whole defence is based on the dagger. It is considered that the distance from your dagger to your body is so great, that the adversary's sword cannot penetrate so far, before you have had a chance to parry. This would be true, if he had begun to hit before the point of his sword penetrated your dagger. But against an opponent who knew how to carry his sword forward, so that its point began to penetrate your dagger hand, and knew how to form his decision according to the opportunity, you would be deceived in your judgment, especially if your opponent decided not to advance his sword; to meet that case you must hold your sword advanced and bring the point close to the dagger hand; but promptness is required lest your adversary should engage your sword, and in order that you may take advantage of his movements. This guard is better used in practice, in order to learn the use of the dagger, rather than for anything else. In actual fighting another position and a different style would be required. |
SEGVITA PARIMENTI VNA TERZA, LAQVALE HA IL PVGNAle molto auanzato, & la spada altretanto ritirata, & questo per tenere la detta spada più libera dalle armi nimiche, & per scaricare la botta con maggiore impeto, & perche la non impedisca il pugnale nel seguire la nimica con fondare tutte le sue diffese sopra esso pugnale, giudicando, che la distanza dal detto pugnale al proprio corpo sia tanto longa, che la nimica non possa penetrare così inanzi prima, che non si habbia hauuta gran comodità di parare, come sarebbe uero, se si cominciasse à ferire prima, che la punta della spada penetrasse esso pugnale, mà hauendo à fare con chi sapesse portare la spada tanto oltre, che la sua punta cominciasse à penetrare la mano del detto pugnale, & conchi si sapesse risoluere secondo l’occasione restarebbe ingannato delle sue raggioni, & massime se esso non si risoluesse di auanzare la spada contra laquale à uolere contendere bisogna tenere la spada auanzata, & mettere la punta uicino alla mano del detto pugnale, mà ui uuole prontezza, & perche l’auerssario non la troui, & per potere pigliare l’occasione de suoi moti; si bene questa guardia è più tosto buona per essercittarsi, & fare buon pugnale, per così dire, che altro, perche nel combattere da douero si ricercarebbe altro sito, & altro stile. 62. |
||||||
[22] Here follows another tierce formed on the left foot, with the bent, the sword hand opposite the left thigh and the dagger extended and so high, that the head is almost entirely hidden beneath the line of the left arm. All these positions are to facilitate the defence with the dagger and for the greater security of the body, which is seen to be bent so as to shorten the line of the left side and so that it may be defended with less movement. With this guard the head is low, so that in parrying below there is less exposed above. The hilt of the sword is kept near the knee in order that you may use the forte in defence and be better able to hit. The dagger cannot be much harassed. With this guard you can close distance, or wait and give your adversary various opportunities by movements of the body and weapons. When your opportunity to hit comes, it is better to pass than to lunge. |
[98] MA QVI OLTRE SI VEDRA APPARIRE VN’ ALTRA TERZA FORmata sopra del sinistro piede, laquale tiene il corpo curuato, & la mano della spada inanzi alla sinistra coscia col pugnale steso, & alto in modo, che ’l capo uiene quasi tutto alcosto sotto la linea del sinistro braccio, lequale cose tutte sono fatte per facilittare la diffesa al pugnale, & per maggiore sicurezza del corpo, ilquale si uede piegare per abreuiare la linea del sinistro fianco, & per diffenderlo con minor moto. Tiene questa, guardia il capo basso, acciò nel parare di sotto, resti meno scoperto di sopra, adopra la spada col finimento inanzi il ginochio per potersi ualere del forte in caso di diffesa & per potere anco meglio ferire, ne il pugnale può esserle tanto trauagliato, & nellaquale guardia l’huomo può serrare la misura, & può anco aspettare, & dare diuerse occasioni al nimico, con atti di corpo, & mouimenti di armi, mà uenendo oportunità di ferire meglio è passare, che ferire à pie fermo. 63. |
||||||
[23] Here is another tierce with the right foot carried outwards, the knee bent and the body supported on that knee. The sword hand is advanced towards the adversary a distance equal to the length from the elbow to the hand, and the sword is inclined upwards at an angle in order to be in conjunction with the dagger, which is held high and in a straight line from the shoulder to it's[!] point. In approaching the adversary the left foot is brought up to the right, and the right foot carried in a circle towards his left side. That part of the side which is seen to be uncovered below the dagger is always kept back, so that if the adversary tried to hit it, you vould[!] parry with the forte pass of the sword, which is held forward. You should pass with the left foot, turning the hand into quarte and always keeping the dagger steady with the intention of defending, the upper parts; the body too should be kept at the same height. If you do not wish to pass or cannot pass because you are in motion, you can still parry and hit in the same manner by carrying the right foot into the straight line and without moving the dagger, so that your adversary cannot make a feint below and hit above, or vice versa, and from whichever side he comes you are defended. If he disengages over your sword, your dagger, which is steady, can easily parry and defend. If he tries to engage your sword with his dagger, then you can hit under the arm or over the dagger, by advancing in a circle towards that part in order to withdraw out of his line and to hit better; even if your adversary closed the distance he would effect nothing. With this guard, if the points of your adversary's weapons are separated, you may make some very good strokes in between as oppotunity[!] offers, if they are close together you can harass his dagger. But with this guard you should never change your hand, lower your point much, make appels nor stand still, but you should approach in a circle, keeping the same front as you gradually approach, and form your decision with swiftness. Sometimes you will parry with the forte of the sword, glide your dagger along the adversary's blade letting it remain there and hit with great force. This guard is sufficiently good, though laborious; but its limitations should be realised. |
[99] SEGVITTARA PVRE ANCO VNA TERZA, LAQVALE STA COL destro piede trauersato, & col ginochio piegato sostenendo il corpo tutto sopra esso ginochio, & la mano della spada inanzi, tanto uerso il nimico quanto è longo il braccio dal combito sino alla mano, tiene la spada angolata à lo insù per conggiongersi col pugnale, ilquale stà così alto, che dalla spalla alla punta fà una retta linea, & ne lo auicinarsi al nimico uà aggiongendo il sinistro al destro piede, portando detto destro in giro uerso le parti sinistre dell’ auerssario con stringere sempre la misura, & con sempre tenere lontana quella parte del fianco sotto il pugnale, laquale si uede scoperta, affine che se esso auessario andasse per ferire in detta parte potesse parare con quel forte della spada, che si uede inanzi & passare col sinistro piede uoltando la mano in quarta, & tenendo sempre fermo il pugnale con intentione, che ’l non habbia se non ha diffendere la parte disopra; resta sempre col corpo nella medesima bassezza & non udendo, ò non potendo passare per trouarsi in moto de’ piedi; para con tutto ciò, & ferisce nel medesimo modo con portare sempre quel destro piede trauersato in retta linea, ne mai moue il pugnale, in modo, che non seli può fingere disotto per dare disopra, ne di sopra per dare disotto, mà uenendo il nimico da qualunque lato si diffende andando à ferire in una medesima forma, & chi uolesse cauare sopra la spada quando essa guardia uà à parare il pugnalo che è fermo facilmente diffenderebbe, & chi uenisse per aquistarli la spada col pugnale [100] all’hora lei ferirebbe sotto il braccio ouero di sopra di esso pugnale con auanzarsi pure in giro uerso quella parte affine di allontanarsi dalla uista nimica, & per potere meglio ferire, & perche anco se il nimico si auicinasse alle distanze non facesse niente. In questa guardia se si trouano le punte delle armi aperte si fanno assai buoni[24] colpi nel meggio con diuerse occasioni, & se serrate si trauaglia il pugnale, mà non si dee, mai uoltare la mano, ne abbassare molto la punta, ne si dee condetta guardia fare chiamate ne stare fermo, mà si hà da auicinarsi sempre in giro, in modo che si resti in una istessa presenza di corpo con andare pian piano nelo auicinarsi, & risoluersi con celerità, & alcune uolte parera col forte della spada, & scorrera col pugnale, lasciandolo alla nimica, & andera con gran forza à ferire, laquale guardia è assai buona, se bene laboriosa, mà è neccessario conoscere li termini. 64. |
||||||
[24] This plate is also of a tierce but little practiced, though known by some. It is formed with the feet together, the body bent, the weapons divided, the dagger and sword both high. The sword is held high so that it cannot be engaged, the dagger high and withdrawn so that it cannot be harassed, the weapons divided so that the adversary can hit only between them, and the feet together to form a centre with the adversary on the circumference; at the centre you can change your front by a small movement more than your adversary on the circumference can by two steps. Moreover with the feet close together you can make a step forward and obtain a long reach, so that with this guard you get within distance before your adversary by an amount equal to the distance between his feet. Although you are within distance, your sword cannot be reached and you will easily keep it free. Being within distance, if you wish to pass with the left foot, your dagger will reach the hilt of your adversary’s sword, and your body will be turned and go out of line and you will be so far advanced that your adversary cannot free his sword. If with this guard you advance with the right foot, your sword will reach his hilt before he is within distance, and you can protect yourself on any side by getting out of presence. The power to reach where your adversary cannot reach is a great advantage, coupled with the fact that he cannot engage your sword until he is within close distance. Therefore if your adversary remains steady within presence, he will be in great danger of being hit for the sword falls downwards with greater speed than that with which it can be raised upward, as happens with all heavy objects. When the sword is held high in this manner, before it arrives in line it penetrates so far that it forces away the adversary's weapons, and the hit is almost inevitable because of the distance the sword has penetrated and because very great strength is needed to resist and check its weight, and also because it is unexpected, since the adversary, who is not within distance, is deceived in supposing that you also cannot reach. With this guard also you can hit in every part, even between the weapons, with or without a pass after hitting you can recover at once, but somewhat in a circle. In meeting this guard you must consider that your adversary's sword has to fall, and that in approaching you must close its path, so that it cannot reach the body; you must begin at a distance, so that your adversary is not within distance even if he advances his foot. You must hold your sword at the same height, so that approaching your adversary's sword your point is near his without your having to move either inside or outside. You should advance by natural steps and with the dagger in conjunction with the sword for greater safety, and you should move your feet and body towards his right side, in order to arrive more quickly within his point and reach his body. In case your adversary on your advance makes any small movement to change his front, you should then seize that oppotunity[!] and advancing your feet and body towards his left side hit with a guard of quarte, holding the dagger high in order not to neglect the defence, although your adversary cannot hit as he has turned both his feet and changed his front, so that his sword has made a movement opposite to that needed for a hit. But your greatest danger is that your adversary, who has his feet together, may carry back his right foot and leave his dagger for the defence in such a way, that his body will be turned out of line and his sword so far withdrawn, that he can return it even if you have reached his body; but if in that case you left his sword aban-doning your first line and in the same time passed behind his left side, with your head outside his dagger arm; in this way you would save yourself. |
LA FIGVRA, CHE SEGVE E NON MENO VNA TERZA ANcor lei mà poco essercittata, se ben conosciuta da qualch’ uno, laquale si forma co’i piedi gionti col corpo curuato, & con l’ armi aperte, col pugnale alto cos ì bene come la spada, laquale spada si tiene alta acciò il nimico non la possa hauere, & il detto pugnale così alto, & anco ritirato, acciò non possa essere trauagliato dalla spada nimica, mà lo stare con l’ armi aperte è perche il detto nimico non habbia se non quel meggio da ferire, & li piedi gionti non per altro, se non perche uuole formare, come, un centro di se stesso, & che ’l nimico sia la circonferenza, ilquale centro uolta più la prospettiua con un picciolo moto, come si sà, che [101] non fà la circonferenza con dui passi oltre, che essendo co’i piedi così gionti può portare il passo assai inanzi, & ariuare molto lontano, in modo, che detta guardia aquista la misura prima del suo auerssario tanto quanto è longo quel termine, che è fra l’uno, & l’altro piede del detto auerssario & se bene l’huomo in tal guardia si trouarà nella misura non li potrà essere ariuata la spada dal nimico, in modo che esso la terà facilmente libera, & essendo pure nella misura, se uorà passare col sinistro piede ariuarà col suo pugnale al finimento della nimica, & quel corpo, che horasi uede si uolgerà, & anderà fuori di presenza, & per essere ariuato tanto inanzi il nimico non potrà liberare la spada, mà se l’ osseruattore della guardia si portara col destro piede la sua spada ariuarà quasi sino all’ else, che l’ altro non sarà gionto nella sua misura, & con potere uscire di presenza, & saluarsi da qualunque parte, in modo, che è un uantaggio molto grande il potere ariuare, doue non può il nimico, certifficato che quello non possa mai hauere la spada, che prima non sia nella misura, stretta & perciò tutti colloro, che andaranno à fermarsi in presenza portaranno gran pericolo di restare feriti, perche con maggiore prestezza cade la spada di alto à basso che non si lieua di basso in alto, si come auiene di tutte le cose ponderose, & essendo in quello modo alta inanzi, che sia ariuata in presenza penetra tanto, che uiolenta l’ armi, & fere quasi irreparabilmente si per essere già penetrata, come perche troppo maggior forza ui uuole à resistere, & ritenere la cosa graue, ne meno per giongere inaspettata, perche collui, che non è in misura s’ inganna credendo che l’ altro uisia ne anco lui ne, che possa ariuare. Questa guardia in oltre ferisce da tutte due le parti, & anco nel meggio dell’ armi, & tanto passando, quanto non passando, & dopò ferito può anco subbito rihauersi, & rimettersì, se bene con girare alquanto. Et per tanto colloro che uoranno andare contra tale guardia douranno molto ben considerare, che quella spada hà da cadere, & che uolendo auicinarsi fà di mestieri chiuderli la uia, che non possa uenire al corpo, douendosi cominciare di lontano, in modo che il nimico non solo non habbia la misura, mà che non la possa hauere ancorche auanzasce il piede, & però si dee tenere la spada nella medesima altezza inguisa che giongendo alla punta nimica l’ una sia uicina all’ altra senza che s’habbia da mouere ne indentro ne in fuori, & si conuiene andare contra tale guardia di passi naturali col pugnale sempre accompagnato alla spada per sicurezza maggiore, & con cacciarsi còi piedi, & col corpo uerso la destra parte dell’ auerssario per ariuare più presto dentro la punta & andare fino al corpo nimico, & se per caso il detto auerssario nell’ andarli contra facesse qualche poco di moto per uoltare la presenza si douria all’ hora pigliare quella occasione, & andare col piede, & col corpo uerso le sinistre parti nimiche ferendo di quarta guardia, & tenendo alto il pugnale per non abbandonare la diffesa con tutto che’l nimico non potesse ferire per hauere girate tutte due le punte de’ piedi, & uoltata la prospettiua, nel quale caso la sua spada hauria fatto effetto contrario di quello bisognarebbe à uolere ferire, mà il maggiore pericolo di quello, che uà è che trouandosi cosi conggionto co’i piedi può il deto auerssario portare indietro il destro, & lasciare il pugnale alla diffesa, in mono che’l corpo ueria à uoltare fuori di presenza, & la spada à ritirarsi tanto, che questo la potrebbe rimettere, ancora che si fosse gionto al corpo, quando non si hauesso lasciata del tutto la nimica, abbandonando la prima linea, & nel medesimo tempo essere passato sino di dietro del sinistro fianco nimico, & col capo fuori del braccio del nimico pugnale, che in tal modo si sarebbe saluato. 65. |
||||||
[25] This is another extension in tierce, in which is shown the position of the dagger, when making a hit, even if there is no occasion to parry, but simply for the safety of the upper part, and in order that the dagger may be ready for all cases. You may also see the manner of bending and lowering the body in order to extend the thrust, preserve a better union of the weapons and offer a smaller target. When you withdraw with the weapons thus united you are better covered. You should always recover the sword close to the dagger and remain at the same height in order to be readier to retire and be better defended; you should maintain the tierce which is advantageous and very safe. |
[102] MA IN QVESTA ALTRA SI VEDRA VNA DISTESA DI TERZA nella quale si mostra il luogo oue dee stare il pugnale nel ferire, ancorche non s’ hauesse occasione di parare, mà solo per sigurezza della parte di sopra, & per meglio potere ualersene in tutti li casi, & in questa si uede come s’habhia da piegare, & abbassare il corpo per più distendere la botta, & restare più unito facendo minore berzalio, & per essere anco più coperto, ritirandosi poi con le armi così unite, ricuperando la spada sempre appresso il pugnale, & dimorando nella stessa bassezza per essere più pronto nel ritirarsi, & più diffeso, con mantenersi in detta terza, come cosa assai à proposito, & molto sicura. 66. |
||||||
[26] Now we have a guard in quarte with the sword arm forming almost a straight line from the elbow to the hilt. The dagger is not completely extended but in close conjunction with the sword, the right side advanced in order to keep back that part exposed above the dagger owing to the dagger arm not being extended. This part is defended if need be, either by the quarte itself or by extending the dagger. Feints above with the idea of hitting below, or vice versa, do no harm, since the dagger defends the one part and the sword the other and the sword hits at the same time. The part outside the sword is somewhat un-covered, but the guard is strong and may easily defend, as the hand is high. If your adversary desires to hit he will be forced to pass your forte, where he may be deceived. Therefore he must attack over the dagger and in the time of your defending that part pass with his sword over the point of your dagger and hit between the weapons through your faible where the sword is less strong than elsewhere. This guard is in reality very convenient for making feints and disengagements with swiftness; with it you may make excellent strokes between the weapons with different times, but you cannot attack much over the dagger, except by extending the quarte well under the dagger and then with a disengage turning to seconde; in this way your sword will penetrate and be looked inside his arm in such a manner that he cannot thrust it away. This guard can be very successful, since the body is well covered, and the sword ready in its movements and kept free without trouble. |
[103] HORA VERA VNA QVARTA GVARDIA COL BRACCIO DELLA spada in tal modo, che forma quasi una retta linea, dal comedo alfornimento con quello del pugnale non intieramente disteso, mà accompagnato appresso la spada, laquale si uede la parte diritta inanzi per tenere lontano quello scoperto, che è sopra di esso pugnale fatto dal non essere disteso il braccio, questa si diffende secondo l’ occasione, con la stessa quarta, & con la sola distesa del braccio. Le finte fatte disotto per dare di sopra, & quelle disopra per dare disotto non nuocono, perche il pugnale diffende da una parte, & la spada dall’altra in medesimo tempo & anco ferisce, la parte fuori della spada, è alquanto scoperta, mà la guardia è forte, & può ageuolmente diffendere per essere la mano alta, & chi uolesse andare à ferire quel corpo saria neccessitato possare per quel forte, oue potria restare ingannato; si che à uolerla andare ad’ assalire sarà di mestieri andare per disopra del pugnale, & nel tempo, che ’l nimico diffende quella parte passare, con la spada per sopra la punta del pugnale auerso, & ferire nel meggio dell’armi per il debile nimico, nelqual luogo si trouarà la spada men forte, che altroue; Questa guardia per dire il uero è molto comoda per fare finte, & cauationi con prestezza, & con essa ponnosi fare buoni colpi nel meggio dell’armi con diuersi tempi, mà sopra il pugnale non può molto offendere se non stendendo la quarta assai oltre per sotto il pugnale, & poi uoltare stretto in seconda cauando, che in tal modo la spada penetrarà dentro, & si serrarà nel braccio inguisa che ’l nimico non potrà rispingerla, & laquale guardia può riuscire molto bene, perche il [104] corpo è assai coperto, & la spada così pronta ne’i mouimenti, che quasi senza fatica si può tenere libera. 67. |
||||||
[27] This also is a quarte formed with the hands advanced and close together, and the point of the sword so low that the adversary cannot engage nor find it with his dagger. If your adversary also tried to lower himself he would be hit, nor would he succeed by covering your sword with his, since you could easily free yours. The sword in this position defends below while the dagger defends above, wherever the adversary attacks. You can also defend all cuts of mandiritto directed at the leg towards the right thigh, and hit in the same time. This is the true method of defending against such an attack. This guard is in fact not useful for the assault, but in defence is very good and safe, for, as the weapons are so close together and extended from the body, your adversary can hit only by passing the fortes of your weapons, which are even stronger by the union of the hands and their distance from the body. But, as we have said, you cannot inflict much damage in the assault, and if your hands can be separated you can be hit without difficulty. |
QVESTA SIMILMENTE CHE SEGVIRA SARA VNA QVARTA, laquale si forma così auanzata con le mani una presso dell’altra, & tiensi la punta bassa aciò ch’il nimico non la possa ne hauere ne trouare col pugnale, & quando detto nimico uolesse anch’egli altretanto abbassarsi restarebbe dalla stessa guardia ferito ne meno li riuscirebbe uolendola coprire con la spada, perche questa facilmente si liberaria, laquale forma di tenere di spada diffende da basso, & il pugnale disopra uenga pure il nimico per quale parte si uoglia, & con laquale forma si deuono parare tutti li mandiritti, che possono uenire per gamba portando la punta uerso la coscia destra dell’ auerssario, & ferendolo da quella parte nel tempo medesimo, che questo sarà il uero modo da diffendersi da cotale offesa, & laquale guardia, per dire il uero, non uale per assalire, mà per diffendere è ben molto buona, & sicura, perche essendo l’ armi tanto chiuse, & slongate inanzi del corpo non può essere ferita se il nimico non passa per quei forti, iquali per l’ unione delle mani & per la lontananza del corpo si fanno anco più forti, mà non può, come si è detto, fare molto danno andando ad’ assalire, & chi anco le potesse disggiongere una mano dall’ altra non molto difficilmente la ferirebbe. 68. |
||||||
[28] Here follows another quarte formed with the left foot forward. This is very successful and better than the others formed on that foot, because the left side is covered by the forte of the sword in such a way, that if your adversary advances to hit, you have only to hit him, since with this guard you lunge very far even without passing. The dagger merely defends the upper part. It is held low in order to close the path between the dagger and the sword, that you may not be hit there; there is the chief danger, especially in approaching, more than on the inside or the outside. Unlike the previous guard with this guard you may attack or wait, lunge or pass according to your opportunity. On the other hand it has its disadvantages, since it is not useful for making appels, and it is dangerous if the adversary closes; in that case, if you have no time to hit, you should make a feint in order to hold him, and then hit. If you observe its conditions this guard will serve excellently in attack and defence. |
[105] VNA ALTRA QVARTA SEGUIRA PVRE, MA FORMATA COL sinistro piede inanzi, laquale assai bene riuscirà, & sarà, assai più buona dell’ altre situate sopra di questo stesso piede perche il suo sinistro fianco sarà coperto dal forte della spada, di modo, che se il nimico uerà per ferire non occorerà fare, altro, che andare à ferire lui, perche con questa guardia si da una botta molto longa, anco senza passare, ne ’l pugnale ad’ altro attende, che alla diffesa della parte superiore, & se ben tiene la punta così bassa come si uede lo fà per chiudere quella strada, che è trà esso pugnale, & la spada non uolendo essere ferita in quel luogo, massime per il pericolo nell’ approsimarsi, nonui essendo ne per didentro, ne per do fuori altretanto pericolo; laquale guardia all’ apposito dell’ antecedente può assalire, & anco aspettare, ferire à piè fermo, & passare secondo l’ oportunità, mà dall’ altro lato hà la sua imperfetione lei ancora, perche non uale in fare chiamate atteso, che se il nimico stringesse la misura portarebbe pericolo, nel quale caso se non si, trouasse tempo di ferire si douria fingere per trattenerlo, & poi ferirlo, & così osseruando i suoi requisiti la presente guardia seruirà per assalirè, & diffendere ottimamente. 69. |
||||||
[29] Now follows an extension in quarte, which shows the manner of holding oneself in parrying a thrust or cat over the dagger. In order that this defence may be strong, in addition to the union of the weapons you should turn the dagger hand that it parries with the edge which is usually bbelow, without dropping the point, so that the blow falls towards the hilt of the dagger; thus the defence will be firmer, and by advancing the right side the lunge will reach further, and the circle made by the body will bring it away from the adversary's point, if you are careful to begin and finish the movement with body feet and weapons in one time. You should also bear in mind that when you make a hit and have no occasion to parry, it is not good to raise the hands so far as to uncover yourself below. The weapons should be united and remain so when you retire the body with the point directed towards your adversary's sword in tierce or in the same quarte; thus you will recover safely on guard. |
[106] MA QVESTA CHE SI VEDRA VENIRE, LAQVALE E VNA distesa di quarta, di mostrarà il modo, che si dee tenere à parare una botta, che uenga sopra del pugnale sia di punta ouero di taglio, laquale diffesa, acciò che sia buona, & forte oltre l’ unione delle armi si hà da uoltare tanto la mano di esso pugnale, che si uenga à parare col filo, che stà ordinariamente di sotto senza piegare la punta, affine che ’l colpo cada uerso il finimento di esso pugnale, che così la diffesa sarà più galiarda, & allongando bene inanzi le destre parti oltre che la botta si fà più longa, & il giro, che fà il corpo, fà restare più lontana la nimica, se bene si ricerca, che il corpo il piede, & l’ armi comincino, & finischino il moto in un sol tempo; si auertisce ancora, che quando si andasse à ferire, & non accadesse à parare, che all’ hora non è bene alzare tanto le mani per non scoprirsi tanto disotto mà deuono essere così unite con subbito ritirare il corpo restando nella unione delle armi con le punte dirizate uerso quella parte, oue sarà la nimica, facendolo con la terza, ouero con la stessa quarta, che così l’ huomo ritornarà sicuro in guardia. 70. |
||||||
[30] We are now to demonstrate the hits with the sword and dagger, an important subject, the study of which is essential than in the case of sword alone, because now the sword is held further withdrawn, and the body more exposed. It is not only easier for the adversary to approach, but he has more opening where he may hit. Therefore we have purposely made this discourse somewhat longer than the others that the matter may be better understood, and that the student of this may know how to guard himself with greater caution against the danger. For there is no doubt that, when you are taking up your guard, that is the best time for the adversary to hit or seize some advantage. Here then is the first hit with the sword and dagger, which is a quarte and is made against an opponent with a guard of tierce, who has made neither defence nor attack. He has come on guard too near to his opponent who has seized the time of his putting his foot to the ground to take up his position and hit during that pause. Thus the adversary has had no chance to do anything, an error, or rather a stupidity committed by many, who are wont to say that they were not on guard, forgetting that when they have the sword in the hand they are supposed to be always on guard. You must observe two things, the first not to advance so far in taking up your position, that the adversary can reach you in that time, the second, in taking up your position to be careful not to let the body or the feet or the weapons drop. You should put your foot to the ground quietly and lightly with the weapons not far from the position which you intend to take up. As you approach your adversary you should adjust your weapons in such a manner, that when you reach your position the weapons have no other movement to make. Proceeding in this manner you can take up your position within wide distance, provided that you do not drop the body or foot. Even though you were out of distance and though your adversary could not reach, you might still offer him a time in which he would seize some advantage, and in the same time approach, when you would be in danger of a hit while trying to free yourself. Even if you were not hit at once, yet being at a disadvantage, you would be hit on the slightest movement. The knowledge of how to advance against the adversary is certainly the first care, and of great importance since victory generally depends on the first advantage. |
[107] HORA SIAMO GIONTI ALLA DIMOSTRATONE DELLE FERIte di spada, è pugnale, materia importante, & neccessaria assai più in queste armi, che nella sola spada, perche quiui[25] si tiene più ritirata la spada, & più scoperto il corpo, & doue il nimico può più non solamente auicinarsi mà ancora da più lati, & più strade andare à ferire, & perciò noi con buon proposito habbiamo messo il presente discorso in questo luogo alquanto più longo delli altri per maggiore intelligenza, & perche lo studioso di quest’ arte sappia con maggiore cautella guardarsi da simile pericolo, perche, senza dubbio, il moto del mettersi in guardia è il miglior tempo, che possa haueré il nimico per ferire, ò pigliare qualche uantaggio. Diciamo dunque, che qui si uedrà la prima ferita di spada, è pugnale, laquale è di quarta, & ferisce uno, che è in terza guardia senza effetto di diffesa, ne di offesa, & laquale ferita può essersi caggionata, perche il ferito sia andato à mettersi in guardia troppo uicino al suo nimico, il quale haurà pigliato quel tempo proprio, che questi poneua il piede in terra per fermarsi, & haurallo ferito nei punto della pausa, togliendoli così all’improuiso il potere fare cosa alcuna, errore anzi sciochezza di molti altri ancora, iquali sogliono dire io non ero anco in guardia non accorgendosi, che quando l’huomo hà la spada in mano si hà sempre da presuporre, che sia in guardia, che percio sidenno auertire due cose la prima di non andare tanto inanzi à fermarsi, che l’ auerssario possa in quel tempo ariuare l’ altra, che fermandosi si hà da guardare di non fare caduta alcuna, ne di corpo, ne di piede, ne d’ armi, mà conuiene mettere il piede in terra senza caduta posatamente, & lieuemente con le armi non lontane da quel sito, doue che l’huomo intende fermarle, anzi quan- [108] to che uiene approssimandosi al nimico tanto dee uenire agiustando l’ armi di maniera tale, che ariuando al destinato segno non habbiano le dette armi da fare altro effetto, che perciò operando in tale forma si potrà anco andare à fermarsi nella misura larga, purche nel fermarsi non faccia caduta ne col corpo, ne col piede, perche se bene che fosse lontano, & credesse non potere essere dal suo nimico ariuato, potria nondimeno fare tal tempo, che il detto nimico pigliaria qualche uantaggio, & in medesimo tempo seli auicinarebbe, che uolendo poi liberarse ne correria pericolo di restare ferito, & se bene non fosse così subbito ferito restando non dimeno in quello suantaggio potrebbe ad’ ogni suo minimo moto restare ferito, si che il sapere andare contra il nimico è senza dubbio il primo auertimenro, & di maggiore consideratione, perche il più delle uolte la uittoria consiste nel primo uantaggio. 71. |
||||||
[31] This hit in quarte against a guard in prime has arisen in this way: you were in tierce on the outside with your sword inclined upwards, in order to cover yourself from the adversary's sword against a hit in that line. Your dagger is held high, so that it could parry, if he disengaged on the inside, by thrusting his sword down to the left. The adversary, seeing you thus covered has tried to carry his dagger to your sword in order to beat it; at that moment you have lowered your point under the line of his left arm, extended your foot and arm changed into quarte and hit in the part he exposed by his attempt to beat your sword with his dagger. At the same moment you have placed your dagger where the sword was before, and turned the point so low that it has pushed his sword out of line. The point of the dagger has been turned downwards, so that if the adversary had attempted to hit with his guard, his point would have struck the ground. Or it might arise in this way: the adversary seeing his sword subjected, has tried to disengage on the inside in order to free it from your sword, carrying his dagger to the other side with the hope of covering his right side; in the same time you also have placed your dagger on his sword, and thus made the hit shown. |
MA LA FERITA DI QVARTA CONTRA LA PRIMA GUARDIA, che qui si uedra è nata perche collui, che hà ferito si trouaua in terza dalla parte di fuore con la spada angolata alo insù affine di tenersi coperto dalla nimica, che non potesse in quella parte ferire, & perche haueua il pugnale alto, acciòche se il nimico hauesse cauato di dentro esso hauesse parato con detto pugnale, spingiendo la nimica à basso uerso la sinistra parte, & perche quello, che è ferito uedendo l’ auerssario così coperto hà uoluto portare il pugnale alla nimica per batterla, nelquale punto medesimo il ferittore abbassando la punta sotto la linea del braccio sinistro nimico & stendendo il piede, & il braccio con uoltare la linea in quarta hà ferito in quello scoperto fatto dal pugnale dell’ istesso ferito [109] nell’hauerli uoluto batterli spada, il quale ferittore nel medesimo punto hà messo il pugnale, doue prima haueua la spada, & hà uoltato tanto abbasso la punta di esso pugnale, che hà fatto uscire, la nimica di uista, & tanto piegato con la punta in giù, che se l’ altro uolesse ferire di detta guardia la punta andarebbe á percuottere in terra. Può similmente essere nata detta ferita, perche il ferito uedendosi occupare la spada l’ habbia uoluta cauare di dentro per liberarla dalla nimica, & si habbia portato col pugnale uerso la parte auersa sperando di coprirsi il destro fianco, & che ’l ferittore ne lo stesso tempo habbia ancor lui fatto l’ effetto medesimo di mettere il pugnale sopra la nimica & così habbia fatto la ferita che si uede. 72. |
||||||
[32] The next quarte hits against an opponent in seconde who has meant to hit over the dagger. Both were in tierce; you have made an opening by slightly lowering the dagger arm and approaching it to your sword; the adversary seeing the opening has turned from tierce to seconde, disengaging his point, and has thrust over the dagger. You, who have given that opportunity in order to entice him to that side, have parried and carried the right side so far forward that you have not only hit, but also assisted the defence by avoiding with your body; your left side has been carried out of line at the moment of your hitting. Further the change of the hand to quarte has brought your sword away from his dagger. Whilst the adversary was advancing without union between the weapons, your sword has penetrated with the forte before his dagger could find it; and thus you have made the hit. Or it may be that the adversary's sword was on the inside, and you have tried to find it with your dagger, in order to force a disengage; he has disengaged and seized the time to make a thrust in seconde above; you have parried and hit with a counter-time as shown. |
QVESTA ALTRA QVARTA SEGVENTE, CHE FERISCE VNA SEconda laquale seconda uoleua ferire sopra il pugnale, & è restata lei ferita, per caggione, che il nimico si douea trouare in terza come lei, & perche l’ istesso nimico hà fatto uno scoperto con abbassare alquanto il braccio del pugnale, & approssimarlo uerso la propria spada, che però l’ altro ueduto lo scoperto hà uoltato de terza in seconda cauando la punta, & è andato per ferire sopra il pugnale in modo che ’l ferittore, che li haueua data, quella occasione per allettarlo à uenire in quella parte, è andato à parare con portara il destro fianco inanzi talmente, che non solo hà ferito, mà hà agiutata la diffesa con la sfuggita del corpo, ilquale hà dillongato le parti sinistre, & è gionto in tempo medesimo, oltre che il uoltare della mano in quarta hà causato che la spada sia uenuta lontanandose dal pugnale auerso, mentre, che quella andaua inanzi, ilquale era in modo disunito che la spada è penetrata col forte, & ariuata al corpo prima che ’l detto pugnale l’ [110] habbia potuta hauere, & così hà fatta la detta ferita. Può anco ben essere, che il ferito fosse con la spada di dentro, & l’ altro sia andato col pugnale à trouargliela per farlo cauare, ilquale habbia cauato pigliando quel tempo, credendo ferire per disopra di seconda, & così il ferittore habbia parato, & ferito lui di contratempo nel modo che si uede. 73. |
||||||
[33] Now follows another hit in quarte against a cut of mandiritto against the leg. You were perhaps in tierce with your sword inclined upwards in order to defend against the adversary's sword in prime or seconde; he has made a feint with one of those guards of a thrust towards your face outside the sword; with your point inclined upwards towards his sword it has been convenient for your[!] to defend with the sword, keeping the dagger steady. In the same time the adversary has dropped his dagger under the two swords and made a cut of mandiritto at your leg, keeping his head covered. You, who have gone to the defence with your sword, have let the point drop on the outside of the adversary's dagger, turned your hand to quarte, thus bringing it close to the dagger hand, and directed the point at the base of his right side under the hilt of his sword. This has given you a defence for your sword has covered the leg and stopped the adversary's hit. But the sword in parrying should be accompanied by the dagger; for if it had not first reached the adversary's body, it would not have had strength to support the shock, and through the disorder into which it would have been thrown, it could neither have parried nor hit. Therefore you can clearly understand how dangerous it is to try to resist the impetus of a cut, and not to reach the adversary's body before the shock comes. For if your sword is found in the air it is sometimes so disordered in resisting that before it recovers the adversary can repeat his stroke. |
MA HORA SEGVIRA VN’ ALTRA FERITA PVRE DI QVARTA contra uno mandiritta per gamba auenuta forsi dall’ essersi il ferittore trouato in terza angolata con la punta alo insù affine di tenersi diffeso dalla nimica situata in prima, o in seconda, & dall’hauere il ferito finto con una delle due dette guardie mostrando ferire di punta uerso la faccia del ferittore per di fuori della spada, alquale ferittore, essendo con la punta alo in sù come si è detto uerso la nimica, sarà stato comodo il diffendersi con la spada tenendo fermo il pugnale, & il ferito in medesimo tempo habbia cacciato il pugnale sotto la sua, & la nimica spada, & tenendosi coperta la testa habbia uoltato di mandiritto per gamba, & così il ferittore, quale era andato alla diffesa con la spada, habbia lasciato cadere dabbasso la punta per di fuori dei pugnale nimico, & habbia uoltata la mano in quarta serandola appresso la mano del suo pugnale, con dirizare la punta all’ angolo del destro fianco nimico sotto il finimento pure della nimica spada, laquale hà causata la diffesa, perche la spada propria li è uenuto à coprire la gamba, & hà trattenuta la nimica, che non hà potuto ferire, mà con tutto, che la spada,[26] che paraua fosse stata accompagnata dal pugnale, quando non fosse prima ariuata al corpo nimico, non hauria hauuto uigore [111] di sostenire la percossa, & per il disordine in che saria stata messa dal taglio non haurebbe potuto ne parare ne ferire, in modo che si può chiaramente conoscere quanto sia pericoloso uolere resistere al’ empito di una spada, che ferisca di taglio, & non giongere al corpo prima che la faccia la percossa, perche essendo trouata in aria, taluolta quella che uuole resistere in quel modo uiene tanto disordinata che prima, che si rimetta l’ auerssario può riplicare di un’ altra ferita. 74. |
||||||
[34] The next plate shows a hit in quarte made close to the adversary's arm between his weapons, but low down against a tierce intended to hit over the dagger. Both combatants were in tierce; you have made a feint of hitting in tierce against your adversary’s right shoulder; he has parried with the dagger and entered with the right foot in order to hit in tierce in that time under the feint; at the same moment you have changed from tierce to quarte, and by simply dropping your point have hit under his dagger hand, which has passed in vain; for when he tried to parry your point, it had already dropped. You have also turned the point of your dagger downwards and parried his sword, whilst your body has been carried out of line in the extension. The arm has remained high, showing that, although you parry below, you should not drop the arm because the time would be long and would cause danger above. It may happen that you have found yourself with your point over the adversary's dagger and in quarte. and have disengaged over his dagger with a feint of hitting his right shoulder; he has parried with his dagger and lunged in tierce, thus dividing his weapons and leaving an opening between his two hands, so that by simply dropping your point you have hit the part uncovered. |
NELLA FIGVRA, CHE VERA APPRESSO SI VEDRA VNA FERIta di quarta fatta appresso il braccio della nimica in meggio dell’ armi, mà bassa contra una terza, quale hà uoluto ferire sotto il pugnale, & ciò sarà auenuto, perche essendo ambidui li combattenti nella terza il ferittore haurà finto uolere ferire di detta terza nella spalla destra dell’ auerssario, ilquale sarà andato à parare col pugnale, & entrato col destro piede per ferire in quel tempo di terza per sotto la fìnta, & così il ferittore haurà uoltato nell’ istesso punto di terza in quarta, & col solo abbassare la punta haurà ferito sotto la mano del pugnale, quale è passato uano, perche quando è andato à parare la punta, essa digià era ariuata abbasso, talmente che ’l ferittore haurà uoltato anco la punta del pugnale abbasso, & parato la nimica agiutato dal scanso del corpo fatto ne lo stendersi, & così il braccio sarà uenuto à restare alto, per mostrare, che anco, che si pari disotto, non si deue con tutto ciò abbassare il braccio, perche il tempo sarebbe longo, & causarebbe pericolo grande difopra. Può essere non meno auenuto, che questi ilquale hà ferito si ritrouasse disopra dal nimico pugnale con la ponta, & la mano in quarta, & l’ habbia cauata per disopra la punta di esso nimico pugnale mostrando pure di ferirlo in detta destra spalla, & il ferito [112] sia andato à parare col pugnale slongando di terza per ferire in modo, che è uenuto à disggiongersi facendo un scoperto trà la mano della spada, & quella del pugnale, talmente, che il detto ferittore col solo abbassare della punta l’ hà ferito in quello scoperto. 75. |
||||||
[35] Now is shown a hit with a guard of prime, made in defending yourself from a cut directed at the head and with a parry in the form of a cross, that is to say with the sword and dagger joined together. Your adversary was in a guard of prime or seconde; you have tried to engage his sword on the outside with a guard of tierce; the adversary has seized that time and tried to hit with a cut of mandiritto at the head, while you were trying to engage his sword. You, being in tierce, have brought the hilt of your sword and your dagger together, raised your hands in a cross, and parried with complete protection; in the same time you have thrust the point of your sword towards your adversary's chest over the hilt of his sword, lunged and thus hit with a guard of prime; your adversary's sword is excluded between your sword and dagger in such a way that he can free it only with difficulty. This manner of defence is very strong; there is no danger of your weapons being disordered by the shock of the adversary's sword, however great it's[!] impetus; moreover the head is completely defended on both sides at once. Since the lunge is short, you must advance the feet and pass, in order to reach the adversary before he can free his sword. One may say that it is a perfect guard. |
MA HORA SI VEDRA VNA FERITA DI PRIMA GVARDIA FATta nel diffendersi da un taglio, che ueniua à ferire per testa col parare in croce, ciò è accompagnato con spada, & pugnale insieme, laquale ferita si è fatta, perche trouandosi quello dal mandiritto nella prima, ouero seconda guardia, il ferittore è andato à trouarli la spada per di fuori con la terza guardia, & perche il ferito pigliando quel tempo, & uoltando di mandiritto per testa hà uoluto ferirlo, mentre che uoleua aquistarli la spada, ilquale ferittore, che si trouaua in terza conggiongendo il finimento di spada, & del pugnale insieme, & alzando le mani in croce hà parato di tutta coperta, & hà uoltato in tempo medesimo la punta uerso il petto nimico per sopra il finimento della spada del detto nimico slongando inanzi il passo, & così hà ferito di detta prima guardia con tenere essa nimica serrata trà la spada & il pugnale, in giusa che l’ altro, come si uede, la può con difficoltà liberare, laquale forte di diffesa è molto forte, ne uiè pericolo, che l’ armi siano disordinate dalla forza della nimica spada, uenga pure con quanto empito si uoglia, oltre il diffendere la testa intieramente per l’ una, & per l’ altra parte in un punto, se bene ferisce corto, che perciò si dee accompagnarla cò i piedi passando, che si ariuarà addosso al nimico prima, che possa liberare la spada, & per tanto si può dire, che sia una perfetta diffesa. 76. | ||||||
[36] Now follows a low hit in seconde under the adversary's sword also in seconde, while he is making a cut at the leg. The plate shows the manner of parrying that cut of riverso at the leg and of attacking in the same time. The sword and dagger are shown united in order to add strength to the defence and also to cover the hands and the sword arm against a hit. If the adversary has made a feint of cutting at the leg and tries to hit higher, the conjunction of the hilts of your sword and dagger and the erect position of the dagger will cover all the right side up to the head. If again he has made a feint of cutting at the leg and then cut at the head, your hands will be raised a little, still in conjunction and the body kept at the same height; this you can very well do, because the distance from the leg to the head is so great and the time so long, that you have ample opportunity to defend. The adversary may have attempted this cut of riverso at the leg, when he was in an extended quarte on the inside, and seeing that you were about to hit with another quarte with the point inclined slightly upwards and accompanied by the dagger, he has seized that time to his cut of riverso at the leg carrying his dagger under your point in order to defend his head; but with your weapons in conjunction you have simply changed the position of your hand, thereby freeing your sword from his dagger, and by dropping your point and body together have hit at the moment of his sword meeting yours. Thus you have defended and attacked in one motion. |
[113] VEDRASSI SEGVIRE VNA SECONDA, CHE FERISCE BASSO SOTto una spada pur’ in seconda che andaua à ferire di taglio per gamba, & laquale figura si è posta per fare conoscere, come si deua parare quel riuerso, che uiene à ferire per gamba, & nel tempo medesimo offendere il nimico, laquale ferita si uede essere accompagnata dalla spada, è pugnale insieme per essere più forte nella diffesa & anco per coprire le mani, & il braccio della spada, che non habbiano à riceuere offesa affine che se l’ auerssario hauesse finto di ferire per gamba, & andasse à ferire più alto, quel pugnale al cui finimento è conggionto quello della spada, & che stà erretto à lo insù copresse tutta quella parte destra sino al capo, come anco se il riuerso fosse finto per gamba, uenisse per testa quelle mani si alzassero un poca con tenerle però sempre così accompagnate, & con mantenersi col corpo nella medesima bassezza, il che si può benissimo fare perche dalla gamba alla testa ui è tanta distanza, & il tempo è così longo, che si hà grandissima comodità di operare. Mà per assignare la raggione perche costui si sia mosso à ferire di riuerso per gamba si dice che egli era in quarta distesa alta dalla parte di dentro, & uedendo il suo nimicho andare per ferrargliela con un’ altra quarta un poco angolata con la punta alo insù accompagnato col pugnale, hà preso quel tempo di uoltare di riuerso per gamba portando il pugnale sotto la punta nimica per diffesa del capo, mà il ferittore, che era accompagnato con l’ armi non facendo altro, che uoltare la mane, con laquale uoltata hà caggionata la liberatione della sua punta dal nimico pugnale abbassando detta punta insieme col corpo hà ferito in quel punto medesimo, che li è stato percosso sopra la spada, & in questo modo hà operato il doppio effetto di diffesa, & offesa. 77. |
||||||
[37] Next follows another seconde against a seconde. Your adversary was in quarte with his dagger advanced and his weapons apart; you were in tierce somewhat at an angle and have tried to engage the point of his sword on the inside at the faible, keeping your sword and dagger together. The adversary has seized the time and attempted a cut of riverso at the part uncovered by your movement. With your weapons together you have simply changed the position of your hands, placed the dagger on your sword in order to strengthen the weapons and better resist the shock of his sword, pushed the right foot forward in the same time and made a hit in the chest on the outside of his sword, parrying at the same moment. We have introduced this plate in order to show how to parry and hit against a cut of riverso at the head, and how to resist a blow of the strongest arm. |
[114] QVEST’ ALTRA, CHE VIEN DIETRO E PVRE VNA SECONDA mà contra un’ altra seconda, diriuata dall’ essersi quello, che è ferito ritrouato in quarta col pugnale auanzato, & le armi aperte, & dall’ essere quest’ altro, che hà ferito, ilquale era interza, andato à trouarli la punta dalla parte di dentro pure in terza alquanto angolata per occupare la nimica in quella parte debile tenendo la spada, & il pugnale uniti, mà il ferito pigliando quel tempo, & uoltando di riuerso per offenderla in quello scoperto fatto da esso nimico nell’ andarli alla spada, ilquale nimico ritrouandosi, come di detto, accompagnato con le armi, uoltando solamente le mani, & appoggiando il pungnale alla spada per più fortifficare ambe due l’ armi, & per meglio resistere alla nimica percossa si é spinto nel tempo medemo col piede destro inanzi, & hà ferito l’ altro nel petto per di fuori della nimica spada, parando anco nelo stesso punto, & perciò si è messa quì la presente figura, per dare à conoscere, come si dee parare, & ferire contra un riuerso per testa, & resistere ad ogni più ualido, & galiardo braccio. 78. |
||||||
[38] This also is a hit in seconde against a tierce. You were in tierce and have changed to quarte with the dagger in union whilst engaging the adversary's sword in order to exclude it; and form a counter-position; he has seized that time to disengage and hit in tierce on the outside of your sword. At the same moment you have changed from quarte to seconde, keeping the dagger for the defence against any possible thrust below. Or it may be that you had formed your counterposition[!], and the adversary has attempted a cut of fendente riverso at the head, which was exposed; in the same moment you have changed to seconde, advanced, parried with your sword and hit in the same time. Although this defence is weaker than a parry with the weapons in union, still it is good, because the lunge reaches further; but it is certainly not so safe. |
[115] ET QVEST’ ALTRA ANCORA E VNA FERITA DI SECONDA contra una terza caggionatasi per essersi trouato quello, che hà ferito in terza, & hauere uoltato in quarta andando à ritrouare la nimica spada per serrarla, & farli una contrapostura unita col pugnale, & per essere dall’ altro stato preso quel tempo con cauare, & uolere ferire l’ auerssario fuori della spada di detta terza, ilquale hà nel medemo punto uoltato di quarta in seconda tenendo il pugnale per la diffesa di quello, che disotto saria potuto auenire. Similmente può essere occorso che hauendo il ferittore formata la detta contrapostura, il ferito habbia uoltato di fendente riuerso per testa, quale era scoperta, & il detto ferittore habbia nel medemo tratto uoltato in seconda portandosi oltre, & habbia con la spada parato, & ferito pur’ anco in medemo tempo, & se bene questa diffesa è più debile, che non saria stata parandosi accompagnato è nondimeno in parte buona perche ferisce più di lontano, mà certo non è tanto sicura. 79. |
||||||
[39] Now follows a defence in quarte accompanied by the dagger against a cut of mandiritto at the head. The quarte is directed between the adversary's weapons. He was in a guard of seconde and you have tried to engage in tierce on the outside and with your dagger in union in order to exclude his sword, the adversary has seized the time and made his cut at the head, thinking he could hit the part uncovered. With your weapons in conjunction you have simply changed your hands from tierce to quarte and parried with the edge of the dagger which is generally below; for in this way, as we have already said, the defence is stronger, the adversary's sword kept further away, and the hands more united, you have also brought the forte of your sword into that line, which not only defends the head and makes the parry safer, but also covers the part below the dagger, so that, if your adversary had made a feint of cutting at the head and changed to seconde in order to hit the left side, while you were raising your dagger to parry, the forte of your sword in this position would still have defended your left side. In addition to these two good results you would also have hit in the same time for your adversary could not have parried without abandoning his plan and changing to seconde; this would have changed the front of his body, so that he could have defended himself, but could not have hit, since you would have covered all that line. |
[116] HORA SEGVIRA VNA DIFFESA DI QVARTA ACCOMPAGNATA dal pugnale contra un mandiritto per testa uenuta à cadere in terza, laquale quarta uà à ferire nel meggio dell’ armi, & è auenuta perche trouandosi quello, che hà tirato di taglio in seconda guardia il ferittore è andato à trouarlo di terza di fuori accompagnato col pugnale affine di serrarli la spada, & il ferito pigliando quel tempo hà uoltato di mandiritto per testa credendo ferire quella parte, che era scoperta, onde il detto ferittore, che era unito con le armi hà solamente uoltato le mani di terza in quarta parando col filo del pugnale solito à stare disotto, perche con quello si fà la diffesa più forte, come altroue si è detto, & si tiene la nimica più lontana, & le mani restano più accompagnate, & in questo modo hà spinto anco in quella parte il forte della spada, ilquale non solo diffende la tesla, & fà il parato più sicuro, mà cuopre anco la parte disotto del pugnale, talmente che, se bene il nimico hauesse finto di dare di taglio per testa, & poi uoltato di seconda per ferire nel sinistro fianco, mentre che alzaua il pugnale per parare, quel forte della spada spinto nella prima diffesa come si è detto hauria diffeso ancora il detto fianco, & oltre l’ hauere fatti questi dui buoni effetti haurebbe anco ferito in tempo medesimo, che ’l nimico non haurebbe potuto parare senza lasciare il primo effetto, & mutare in seconda, il che sarebbe stato mutare la prospettiua del corpo, con che si haurebbe diffeso sì, mà non haurebbe già potuto ferire per hauere l’ altro tutta quella parte diffesa. 80. |
||||||
[40] This plate illustrates a hit in seconde over the dagger. Both were in tierce; you have turned your sword downwards and the adversary has changed his hand to a low quarte in order to hit between the weapons, and remain close to your faible, keeping his dagger low In order to be more covered below, although he would have been better defended with the point of his dagger[!] You have recognized his error, seen the opening above, changed your hand from tierce to seconde, disengaging your sword over his dagger and hit in the part uncovered. By placing your dagger on his sword you have easily defended, aided by the altered position of your body which has been carried out of time. Or it may be that you have directed your sword at the adversary's dagger hand, and he has tried to engage it and hit in quarte with the idea of closing the path between the weapons; you have then disengaged and made the hit. The adversary has been unable to parry, though he raised the point of his dagger, because your sword was shut in between his arm and dagger. |
[117] SI VEDRA SIMILMENTE QVI OLTRE VNA FIGVRA con una ferita di seconda sopra il pugnale, quale può essersi caggionata dall’ essersi trouati tutti dui in terza, & dall’hauere quello, che hà ferito aperta la punta della spada à lo in giù, & l’ altro uoltato la mano inquarta bassa per ferirlo nel meggio, & restare appresso il debile nimico tenendo il pugnale in quella bassezza che hor si uede affine di essere più coperto disotto, se bene con la punta di esso saria stato più diffeso, ilquale errore cognosciuto dal nimico, & ueduto lo scoperto disopra hà uoltata la mano di terza in seconda cauando la punta perdisopra di esso pugnale, & ferito nel detto scoperto ueduto appoggiando il suo pugnale sopra la nimica colquale hà diffeso molto facilmente, agiutato ancora dalla mutatione del corpo, che si è allontanato. Può anco facilmente essere, che il ferittore habbia data la spada al pugno del pugnale, & che l’ altro habbia uoluto prenderla, & ferire di quarta con animo di restare più serrato nel meggio, & che ’l detto ferittore habbia all’hora cauato, & fatta la detta ferita, ne l’ altro habbia potuto parare con tutto, che habbia alzata la punta di esso, per essere la spada nimica inchiauata, trà il braccio, & il pugnale suo. 81. |
||||||
[41] Now follows a hit in tierce against an opponent who has attempted or hit in quarte. You were in tierce with the right foot in front, the feet close together, and the weapons in union; you have deliberately moved aside the point of your sword and left an opening between your weapons, your adversary seeing this has thrust in quarte close to your sword in order to cover himself while hitting, you have made a counter-time, and by lowering your sword hand and body and carrying your dagger, which had not so far been moved, to his sword and engaging it, you have hit in tierce. This result might have arisen in another way; you have made a feint of hitting in the straight line over your adversary's dagger; he has tried to parry with the dagger and hit the right side of your chest in quarte. Then you have dropped and parried; by putting the point of your sword under his dagger you have made the hit shown. |
[118] MA QVELLA, CHE SEGVIRA SARA VNA FERITA DI TERZA contra uno, che hà uoluto ferire di quarta, perche stando questi, che hà ferito di terza col destro piede inanzi col passo stretto, & unito, hà insidiosamente slargata la punta della spada, fatto un’ addito nel meggio delle sue armi, il che ueduta, l’ altro si è spinto inanzi della detta quarta serrata appresso la nimica per coprirsi nel ferire & così il ferittore portandosi inanzi di contra tempo, & nel medemo punto abbassando le mano della spada, & il corpo con portare anco il pugnale, che prima non hauea mosso, alla nimica & la oppressa & ferito di detta terza libera, come si uede, il che può essere auenuto anco per altra uia, cio è che il detto ferittore habbia mostrato di ferire di retta linea sopra il nimico pugnale, & l’ altro habbia uoluto parare con esso pugnale, & ferire di quarta la destra parte del petto nimico, & in questa maniera il detto ferittore habbia abbassato, & parato mettendo la punta sotto il pugnale nimico, & fatta la ferita che si uede. 82. |
||||||
[42] This is another quarte, which has parried a seconde with the hilt of the sword. Your adversary was in tierce with the point high and the hand low; on your advance he has disengaged in order to hit in seconde the part exposed under the dagger, and has tried to place his dagger against your sword in order to defend himself. In that time you have changed your hand from tierce to quarte, and keeping it close to the dagger hand have carried it past the point of his dagger and reached the body, hitting his right side. By raising your hilt during the stroke you have defended the part, which was exposed, and where your adversary intended to hit; your dagger has been left to guard the lower parts in case of a hit there. Or it may be that your adversary has made a feint of hitting in seconde over the dagger with the intention of hitting below; you have parried and thrust, changing your hand to quarte and accompanying it with the dagger, which has defended above, whilst the sword has defended below, so that your adversary has been deceived; he has been able neither to hit nor parry; since your sword hand was raised, your sword has escaped his dagger, which has fallen after missing your sword owing to the angle it made, which has brought it away from the dagger. This hit also shows the importance of the union of the weapons. |
[119] QVEST’ ALTRA DI QVARTA, LAQVALE HA PARATO COL finimento della spada contra una seconda, che era in terza alta con la punta, & la mano bassa, sià fatta per che mentre che questo che hà ferito si è uoluto approssimare, l’ altro hà cauato in quello scoperto per ferirlo di detta seconda sotto il pugnale, & hà uoluto appoggiare il proprio suo pugnale alla nimica per diffendersi, doue, che ’l ferittore uoltando la mano in quello stesso tempo di terza in quarta, & ferrandola appresso la mano anch’ egli del suo pugnale è uenuto à portarla per la punta del nimico pugnale, & è andato al corpo ferendolo nella destra parte, & il finimento che nel ferire si è alzato hà diffeso quella parte, che prima era scoperta, & doue l’ auerssario intendeua ferire, & il pugnale è restato alla guardia disopra in euento, che ’l nimico hauesse colà uoluto ferire. Può essere ancora, che ’l ferito habbia simulato ferire di detta seconda disopra del pugnale per ferirlo disotto, & il ferittore habbia parato, & spintosi inanzi con uoltare la mano in quarta accompagnandola appresso il proprio pugnale, quale è uenuto à diffendere disopra, & con la spada à diffendere di sotto in uno medesimo tempo, in modo che ’l nimico è restato gabbato, che non hà potuto ferire, ne meno hà parato, per essersi alzata la mano della spada auersa, che pero uenuta à sfuggire il pugnale caduto abbasso senza tronarla per l’ angolo da lei fatto, colquale si è allontanata da esso, doue che ancoda questo si conosce l’ importanza dell’ unione delle armi. 83. |
||||||
[43] This plate presents a hit in seconde against a quarte. Both combatants were in tierce; you have made an opening between your weapons by carrying the point of your sword away, keeping the sword hand steady and the dagger also. In that time your adversary has thrust between your weapons, forgetting that he was within wide distance, and that you had not moved your feet, and that therefore he could not reach before you had finished your movement. Thus he has been hit. You have offered the opening and, seeing him coming, have turned from tierce to seconde, changing the front of your body; placing your dagger against his sword you have parried, advanced the right foot and thus hit in the part uncovered by his lungs[!]. Or it might arise in this way; your adversary was in tierce and you in seconde you have made a feint over your adversary's dagger; he has been deceived by the feint, tried to parry and hit in quarte at your chest while your[!] were approaching. You have parried with your dagger, which was steady, disengaged the point of your sword underneath his dagger arm on the outside, and by this path have made a hit in the left side. Whether the hit has arisen in the one way or the other, it is certainly due to the separation of the adversary's weapons; if he had moved with his weapons in union, although he might not have hit, he would still have been defended on both sides. |
[120] VNA SECONDA SARA QVEST’ ALTRA, CHE FERISCE CONTRA una quarta, quale potria essere successa dal ritrouarsi ciascuno de’ dui combattenti in terza, & dall’ hauere il ferittore fatta una apertura nel meggio dell’ armi allargando la punta della spada, con tenere ferma la mano di essa spada, & anco il pugnale, & dall’ essere l’ altro in quello proprio tempo andato à ferire in quel meggio per il debile di essa nimica, non accorgerdosi[27] di trouarsi in misura larga, & che l’auerssario suo non hauea mosso li piedi, & che perciò non poteua ariuare prima, che non fosse finito quel moto, che ’l detto auerssario hauea fatto, & per tanto essere restato ferito, perche il ferittore, che li hauea data tale occasione uedendolo uenire si è mutato di terza in seconda uoltando la prospettiua del corpo, & appoggiando il pugnale sopra la nimica, hà parato con auanzare il destro piede inanzi, & così l’ hà ferito in quello scoperto fatto nelo stendersi; può anco essere nata tale ferita, perche il detto ferito si sia trouato in terza, & il ferittore all’hora in seconda, ilquale habbia fatta una finta sopra il pugnale dell’ auerssario, ilquale ingannato da ciò habbia uoluto parare, & ferire di quarta nel petto, mentre che l’ altro ueniua, & che esso ferittore, quale haueua il pugnale fermo habbia parato, cauata la punta disotto per fuori dei braccio del nimico pugnale, & per questa uia habbia fatta la detta ferita nella sinistra parte, mà sia stata ò per l’ una, ò per l’ altra certo è che tutto è auenuto per la disggiontione dell’ armi che se il detto ferito si fosse mosso unito, aben che non hauesse ferito saria nondimeno restato diffeso nell’ uno, & nell’ altro luogo. 84. |
||||||
[44] Now follows another hit in seconde between the weapons against a quarte. Perhaps you were in seconde and your adversary in tierce, his sword advanced and dagger close to the hilt of his sword, with his left side kept back in order to offer you an opening to hit, with the intention of parrying and hitting in the same time, you have feigned to accept the opening and hit where he desired; thus he has been deceived by your trick, raised his dagger, and advanced his right side still farther in order to hit, and to defend at the same time below by changing his hand to quarte. You have disengaged over the point of your adversary's dagger and hit between the weapons in the part exposed by his attempt to parry and hit. You have left your dagger in its original position, which has given you a defence, and excluded his sword in quarte on the outside. If your dagger had met his sword further forward, it could not have thrust it away, since the quarte is very strong in that part, with the result that both would have been hit. If you had tried to attack under the dagger, your adversary would easily have parried by merely making a somewhat larger angle with his sword hand, for his body was already sufficiently turned. |
[121] LA SEGVENTE SARA VN’ ALTRA SECQNDA NEL MEGGIO dell’ armi di una quarta successa forsi, perche costui che hà ferito sia stato in detta seconda, & il nimico in terza auanzata col pugnale uicino al finimento della propria spada, & con la parte manca indietro per dare occasione al suo auerssario di uenire à ferirlo, & con intentione esso di parare, & ferire in istesso tempo & che il detto auerssario habbia simulato di crederli, & mostrato di uolere ferire, oue esso desideraua, & così il ferito ingannato dall’ arte sua habbia leuato il pugnale, & sospinto ancor più inanzi il destro fianco per ferire, & per diffendere parimente disotto col uolgere la mano in quarta, & così il ferittore cauando persopra della punta dell’ auerso pugnale habbia ferito nel meggio dell’ armi in quello, scoperto fatto dal detto nimico nel uolere parare, & ferire, & habbia lasciato il pugnale nel sito, & guardia, oue si trouaua senza niente allongarlo certa caggione della, difesa, & di fare che la nimica, laquale ueniua di quarta sia esclusa di fuori, perche se ’l detto pugnale l’ hauesse trouata più inanzi non l’ haurebbe potute, respingere per essere la detta quarta molto galiarda in quella parte, in modo che tutti dui sarebbero restati feriti, & se questo ferittore hauesse uoluto offendere per disotto il pugnale l’ altro haurebbe ageuolmente parato col solo angolare un poco più la mano della spada, per essere già il corpo assai basteuolmente uoltato. 85. |
||||||
[45] Now follows another hit in seconde over the dagger against a tierce to hit below the sword. It has arisen from your making a feint of hitting in quarte between the weapons; your adversary has tried to parry with the dagger and hit in tierce; you have changed from quarte to seconde raising your sword past the point of his dagger, and have hit in the time of his attempted parry and thrust; moreover you have defended below by placing your dagger on his sword and pushing it outside your right side, at the same time bending your body. Or it may be that you were in tierce above the adversary's dagger and have made a feint of hitting between his weapons, which were also in tierce; he has tried to parry and hit together; by bending the body and advancing the right foot you have met his sword with a counter-time, since you have returned your sword above to the same line as before, changing from tierce to seconde, which has facilitated the defence of the dagger. |
[122] HORA SEGVIRA PVRE VN’ ALTRA SECONDA, LAQVALE FErisce sopra il pugnale di una terza, che uoleua ferire sotto la spada, & può essere successa, perche questa che hà ferito habbia mostrato di ferire di quarta nel meggio dell’ armi, & l’ altro habbia uoluto parare col pugnale, & andare à ferire di terza di sotto, & che’l ferittore habbia mutato di quarta in seconda con alzare la spada per la punta del nimico pugnale, & ferito in tempo che l’ detto nimico uoleua parare, & ferire, & oltre ciò habbia diffeso disotto col’ appoggiare il pugnale sopra la nimica, laquale piegando il corpo hà spinto fuori per il destro fianco. Può anco essere che detto ferittore si trouasse sopra il pugnale con la terza, & che habbia finto di uolere ferire nel meggio dell’ armi nimiche, quali erano ancora in terza, & che parimente il ferito habbia uoluto parare, & ferire, & che piegando il corpo inanzi auanzando il piè destro habbia in contrata la spada di contratempo, perche è ritornato con la spada disopra come era prima, per la medesima uia con la mutatione di terza in seconda, il che è uenuto à facilittare la diffesa del pugnale. 86. |
||||||
[46] This is also a seconde hitting over the dagger against an opponent in quarte, who has tried to parry with his dagger and turn his body with the left foot. The adversary was in a low tierce somewhat advanced with his dagger close to the hilt of his sword; you have entered over his sword with your hand towards quarte and the dagger also in the same line, so that your adversary, with his sword advanced in the manner described, could not thrust on the outside or below, but was forced to approach on the inside only. You have closed the distance and your adversary has tried to carry himself outwards in order to save the part uncovered, when he has in the end been hit; he has expected that you would disengage below his dagger hand and hit above and therefore he has turned in order to hit in quarte. His move might have succeeded, if you had not deceived him. After getting within distance, you have waited for him to move, and seizing that time have disengaged from the point of his dagger, changing your hand to seconde, and thus have hit in the weak part. Although the adversary has turned his body and tried to parry with his dagger, he has done no good, because he has been too weak; nor has he hit you, since you have carried your dagger to his sword and turned the body in hitting; by carrying your right foot somewhat towards the inside you have easily defended yourself. |
[123] QVEST’ ALTRA ANCOR LEI SARA VNA SECONDA CHE FErisce sopra il pugnale, mà contra una quarta laquale hauea uoluto parare col pugnale, & girare il corpo col sinistro piede, & tutto è auenuto perche collui, che è ferito siritrouaua in terza bassa alquanto auanzata inanzi col pugnale presso il finimento della propria spada, & perche l’ altro è andato sopra la nimica con la mano uerso la quarta tenendo anco il pugnale uerso quella parte acciò che la nimica auanzata, come si è detto, non potesse ferire di slanzo, ne di fuori, ne di sotto, mà fosse neccessitato uenire solamente di dentro, & così è andato serrando la misura aldetto ferito, ilquale cercaua pure di portarsi in fuori per saluare quello scoperto, doue al fine è re stato ferito credendo che ’l suo auerssario nell’ andare à ferire cauasse per di sotto la mano del pugnale, & andasse di sopra, & questa è stata la caggione del girarsi per ferire di quarta, il che forssi li sarebbe successo, se dal detto suo auerssario non fosse stato diluso, ilquale hauendo guadagnato la misura, hà aspetato, che quello si moua, & pigliando quel tempo ha cauato per la punta del pugnale auerso con uoltare la mano in seconda, & così hà ferito per quel debile di modo, che se bene il ferito hà girato il corpo, & si è sforzato di parare con detto pugnale non hà però fatto cosa buona, perche è restato troppo debile, ne meno hà ferito perche il nimico, che haueua il pugnale di fuori l’ hà portato alla nimica nel ferire con uolgere il corpo, & con portare il destro piede alquanto uerso quella parte di dentro in modo, che assai facilmente è restato diffeso. 87. |
||||||
[47] This quarte with a turn on the left foot has parried a stroke over the dagger in seconde and at the same time hit the adversary between his weapons. The adversary had his dagger somewhat advanced and has tried to parry, but had been anticipated by your sword which has reached his body first; he has encountered the forte of your sword with the point of his dagger and therefore has been unable to defend himself. You had moved to engage the point of his sword with the point of your dagger, and he, who was in tierce, had disengaged in order to hit in seconde the part uncovered above; but you had made little movement and have defended before the forte of his sword penetrated. You have succeeded because your dagger induced his sword to move; if on the other hand his sword had caused your dagger to move, his thrust would have arrived while your dagger was falling, so that you could not have parried. In the actual case his sword has moved, your dagger has been raised and parried, as shown, with the help of the turn of the body. |
[124] LA QVARTA GIRATA COL SINISTRO PIEDE, CHE SEGVE, LAquale hà parato una botta, che li ueniua sopra il pugnale di seconda, & che in tempo medesimo hà ferito il nimico nel meggio dell’ armi, il che è auenuto, prima, perche esso nimico quale si trouaua col pugnale un poco lontano hà uoluto parare, mà preuenuto dalla nimica che era gionta al corpo inanzi, hà incontrato nel forte di essa nimica con la punta del suo pugnale & perciò non hà potuto diffendersi, & è anco auenuto per essere il ferittore andato à trouare la punta nimica con la punta del pugnale, & per hauere il detto ferito quale era in terza uoluto cauare affine di ferire di detta seconda in quello scoperto disopra, mà il detto ferittore, che hauea fatto poco moto è gionto alla diffesa prima che la nimica sia penetrata col forte il che è successo perche il pugnale hà prouocato la spada à mouersi, che se per il contrario la spada hauesse prouocato il pugnale la botta sarebbe ariuata nel tempo che detto pugnale cadeua, talmente che ’l non haurebbe potuto parare, che in questo altro modo quando la spada si è mossa, ildetto pugnale si è leuato, & hà parato, come si uede, agiutato anco dal giro del corpo. 88. |
||||||
[48] This plate shows a tierce which has hit under the dagger against an opponent in tierce with his left foot forward. You were in tierce in a straight line with the point of your sword opposite your adversary's dagger hand. He has tried to get within distance with his left foot, and you, who had your point near his left hand, with a very short movement have thrust under the line of his arm and so close to it, that in hitting your sword has passed out of his view; he has been able to see only that part from his dagger hand to the hilt of your sword, you have held your dagger steady with the point towards his sword, and your dagger has approached just so much as his foot has advanced, and thus has been ready to parry in case of need; but the adversary has made no movement of defence owing to his being surprised whilst moving his foot. The same hit might have arisen in this manner: you had the point of your sword against the adversary's dagger hand and have moved the point towards the inside; he has tried to approach with the left foot in order to engage your point and to close that line somewhat; you have seized that time and made the hit shown. Also if you had withdrawn so far that your adversary could not reach you except by passing in this manner you could have retreated without danger. |
[125] IN QVEST’ ALTRA FIGVRA SI VEDRA VNA TERZA, LAQVAle hà ferito un’altra terza sotto il pugnale situata col piede manco inanzi, proceduta perche stando quello che hà ferito in detta terza retta con la punta in contro del pugno del nimico pugnale l’ altro si è uoluto auicinare col piè sinistro per aquistare la misura, & il primo, che hauea la punta alla sua mano sinistra con breuissimo moto si è spinto sotto la giusta linea del braccio tanto uicino, che la spada nel ferire si è leuata di uista al nimico, che non hà potuto uedere se non quella parte, che auanzaua dal pugno del pugnale al finimento di essa, & hà tenuto il pugnale fermo con la punta uerso la nimica spada ilquale pugnale è uenuto ad’ auicinarsi tanto, quanto che si è auicinato il piede & cosi seria stato pronto à parare se per caso fosse stato il bisogno, & per tanto il ferito non hà fatto altro moto di diffesa per essere stato sopra preso nel moto del piede. Potrebbe anco essere seguita la medesima botta perche il ferittore, che haueua la punta di essa spada incontro il pugno del nimico pugnale hauesse tirato essa punta uerso la parte di dentro, & il ferito hauesse uoluto approssimarsi col piede sinistro per aquistarla con chiudere alquanto quella parte, & che ’l detto ferittore pigliando quel tempo hauesse ferito come si uede, & che anco se fosse ritirato in distanza tanto lontana, che ’l nimico non l’ hauesse potuto ariuare se non fosse passato nel quale modo si è potuto ricuperare indierro senza pericolo. 89. |
||||||
[49] The next is a hit in quarte against a guard of tierce. It has arisen in this way: you were in tierce with your left foot forward and your weapons together; the adversary has attacked with the point of his sword outside your dagger; in advancing he has penetrated your dagger with the point of his sword intending to subject it and separate your weapons, in order to hit between them or under them at your side. You have taken that time, partly turned your dagger in order to parry with the edge, turned your sword hand to quarte at the same time and thrust so close to his sword that he has not been able to put it where he intended, nor to free it. Or it may be that your adversary has been pressing you on the inside when you were in tierce on the left foot and with your weapons together; you have turned the points of your weapons against his sword to exclude it on the outside; then he has disengaged for fear of his sword being engaged. You have moved simply to make him disengage; you have taken the time, lunged with your weapons in union and penetrated as shown a distance equal to the length of your step. Here you may realise the force and great impetus of a stroke made with the left foot forward, and followed by the right foot. |
[126] QVEST’ ALTRA FERITA DI QVARTA, CHE SI VEDE APPRESSO contra una terza guardia può essere accaduta, perche stando collui che hà ferito in terza col sinistro piede inanzi, & chiuso nell’ armi, l’ altro sia andato ad’ assalirlo con la punta di fuori del pugnale, & nelo auicinarsili habbia penetrato il detto nimico pugnale con la punta affine di metterlo in seruitu, & farlo disunire per poterlo poi ferire nel meggio, ouero disotto nel fianco, ilquale nimico pigliando quel tempo con uoltare alquanto il detto pugnale per parare col filo di esso & con uoltare anco la mano della spada inquarta nel medesimo tempo, & sia passato tanto serrato appresso la spada auersa, che l’ istesso ferito non habbia hauuto luogo di mettere la detta sua spada, oue hauea designato, ne meno habbia potuto sciorgliela. Similmente può essere che l’ detto ferito sia andato à stringere il detto suo nimico dalla parte di dentro sopra il piè manco nella terza guardia, & con le punte dell’ arme unite, & ilquale habbia riuolte le dette punte contra l’ auersa spada per escluderla fuori, & che all’ hora il ferito l’ habbia cauata per dubbio, che la non sia occupata, & il ferittore ilquale ad’ altro fine non si era mosso se non per farlo cauare pigliando quel tempo sia passato accompagnato, & habbia penetrato tanto, come si uede, per la distanza grande dal luogo, oue hauea il piede al luogo oue l’ hà posto, in modo che qui si può conoscere quanta, & quale sia la forza del ferire, & quanto grande l’ empito di chi tiene il piè sinistro inanzi, & uà à ferire passando col destro, 90. |
||||||
[50] Now follows a hit in prime over the dagger of an opponent in tierce. You also were in tierce with your point so low as to form a straight line, your feet close together and your dagger in the line of the adversary's sword. He has advanced the point of his dagger low down in order to find your sword; taking the time you have disengaged over the point of his dagger, turning your hand from tierce to prime, and by carrying yourself forward at the same time have hit in the chest. If you had disengaged your sword under his dagger hand, you would not have hit, because his dagger arm being so high would have covered all that part of his body. Your dagger being in the line of his sword has also advanced, as you carried your body forward, and arrived close to the blade of his sword ready to parry, if he had tried to hit. You have not beaten his sword in order to avoid the risk of his disengaging and in order to keep the dagger steady. Or it may be that you were in tierce with your point close to the adversary's dagger and have gradually moved it to the inside and somewhat low in order to induce him to follow it and engage. This has happened, so that with this trick you have drawn his dagger out of the line and caused him to expose himself over the dagger; thus you have suddenly made the hit shown. Often it is better to proceed in this manner, when your adversary tries to engage your sword, rather than to disengage. For by disengaging generally you do what your adversary desires; by not disengaging and adopting this method of saving your sword, you cause your adversary, if he follows it, to uncover himself; he is disconcerted and can no longer defend himself. If he does not follow it, your sword is free and the danger past. |
[127] HORA SEGVE VNA FERITA DI PRIMA SOPRA IL PVGNALE di uno situato in terza, che può essere nata perche collui che hà ferito si sia trouato anch’ esso in terza con la punta si bassa, che formaua una retta linea in stretto passo, & col pugnale per la linea della nimica spada, che l’ altro che è ferito sia andato con la punta del suo pugnale abbasso per guadagnare la spada nimica, & che ’l ferittore pigliando quel tempo habbia cauato per la punta di detto pugnale con uoltare la mano di terza in prima, & portandosi anco tutto in un’ tempo inanzi habbia ferito il nimico nel petto, che se l’ hauesse cauata la spada per sotto la mano del pugnale non haurebbe ferito, perche essendo il braccio di esso pugnale tanto alto hauria coperto tutto il corpo in quella parte, il pugnale similmente, che il detto ferittore hauea nella linea della nimica ne lo portarsi inanzi del corpo si è anch’ esso tanto auanzato, che si è trouato appresso il filo della nimica pronto à parare, se quella hauesse uoluto ferire, & non l’ hà battuta per non mettersi in rischio, che ’l nimico la caui hauuto risguardo all’ essere lei ferma; Può non meno essere accaduto, che il detto ferittore standosi in terza, & hauendo la punta uicino al nimico pugnale sia uenuto allontanandola pian piano con tirarla uerso la parte di dentro, mà alquanto bassa per dare occasione al nimico di seguirla, & abbassare la punta di detto pugnale per aquistarla, cosa che li è uenuta fatta, perche con tale insidia l’ ha tirato tanto fuori di linea, che l’ hà fatto scoprire sopra di esso pugnale, & così subbito l’ hà ferito come si uede, di modo tale che spesse uolte è meglio operare in questa forma, quando l’ auerssario uuole occupare la spada, che non è cauare perche cauando si fà il più delle uolte quello che l’ istesso nimico ricerta, ma non cauando, [128] & seruando la detta maniera di saluare la spada se ’l nimico la segue si scuopre, & si sconcerta tanto, che non si può più diffendere, ilquale se anco non seguita, la propria spada uiene a restare più libera, & à cessare il pericolo, 91. |
||||||
[51] Here is a hit in seconde over the dagger against a tierce formed with the left foot forward. You were in tierce with the feet close together and the point of your sword in line with your adversary's dagger hand. He has pushed forward with his left foot in order to engage your sword on the inside with his dagger. In that moment you have turned your hand from tierce to seconde, advanced the right foot and made the hit over his dagger. You have kept your dagger extended and close to the point of his sword, so that you could have parried with little trouble, if he had tried to hit. Or it may be that you had your point in line with your adversary's dagger hand, and had dropped the point somewhat; he has followed with his dagger and advanced his feet in order to engage it; in that instant you have disengaged, turned to seconde and hit in the time of his following your sword; therefore he has been unable to parry. |
QVESTA, CHE VIENE DIETRO E VNA DI SECONDA SOPRA IL pugnale contra una terza formata col piè sinistro inanzi, dall’ essersi questo, che hà ferito, trouato in terza in passo stretto con la punta in prospettiua della mano del nimico pugnale. & l’ altro in piè manco ilquale si sarà portato inanzi del medesimo manco per occupare col pugnale la nimica punta dalla parte di dentro, & dall’ hauere in quello medesimo punto il ferittore uoltata la mano di terza in seconda spingendosi oltre col destro piede, hà fatto la detta ferita sopra il nimico pugnale, & ha tenuto il suo steso uicino alla nimica punta acciò, che se l’ auerssario hauesse uoluto ferire egli hauesse con poca fatica parato. Può anco tal ferita essere successa perche esso ferittore si sia trouato con la punta in prospettiua della mano del pugnale auerso &, che habbia alquanto abbassata la detta punta, & che ’l ferito l’ habbia seguita col pugnale approssimandosi co’ i piedi affine di occuparla, & che nel proprio instante il ferittore habbia cauato, & uoltato in seconda, & feritolo nel tempo, che l’ altro l’ hà seguito. Ilquale perciò non hà potuto parare. 92. | ||||||
[52] The next hit in seconde against a seconde may have arisen in several ways. In the first place both were in tierce on the outside; the adversary has tried to force your sword by turning his hand from tierce to seconde in order to strike the sword on top, and to parry below with his dagger. Aware of the force of his sword you have eluded it, and by turning your hand to seconde have hit on the inside over the point of his dagger. In the same time by a turn you have carried your body away and by bending the right side, which was in danger, and bringing the left side forward, have brought your body well away from the adversary's sword. By carrying your dagger to his sword at the same moment you have parried, as shown. Or it may have happened that you were on the outside and have made a feint of hitting in tierce over the adversary's sword; he has turned his hand to seconde in order to parry and hit in the same time, protecting himself below with his dagger. In that time you also have disengaged, changed your line and hit as explained, parrying with the dagger. By bending your body you have let his sword pass wide, for the hit in seconde falls naturally of itself when it meets no resistance. Or again you may have been on the inside and found an opening between your adversary's weapons; you have made a feint in quarte in that line close to his sword, and your adversary, raising his hand from tierce to seconde and putting his dagger on your sword in order to defend that line, where it had entered, has pushed on in order to hit in the same time. Your hit in quarte was a feint; you have carried back the right side which was in front and raised your hand from quarte to seconde; thus your body has been brought out of line and your dagger has easily defended. Your sword arm has yielded and eluded his dagger; he has failed to find your sword with his dagger, since it has been raised and has hit without impediment over the point of his dagger. |
[129] QVESTA ALTRA PVRE DI SECONDA CONTRA VNA MEDESIma seconda può per più caggioni essere nata, prima per essersi trouati tutti dui in terza, di fuori, & che quello che è restato ferito habbia uoluto uiolentare la spada dell’ altro, uoltando la mano di terza in seconda per ferirlo disopra la spada, & parare disotto col pugnale, & che quelli sentendo la forza della nimica habbia sfalsata la spada uoltando anco lui la mano in seconda sia uenuto à ferire di dentro sopra la punta di detto pugnale auerso, & in un medesimo tempo habbia con girare il corpo lontanata, & curuata la destra parte, che era in pericolo, & uoltando la sinistra inanzi sia uenuto à fare un uacuo del corpo, talmente, che si sia dillongato molto dalla nimica & in medesimo punto con portare il pugnale alla detta spada nimica habbia parato come si uede. Può non meno essere occorso, che trovandosi questo ferittore di fuori habbia finto de ferire sopra la nimica di terza, & il suo auerssario habbia uoltata la mano in seconda per parare & ferire in tempo medesimo assicurandosi col pugnale[28] disotto, & che il ferittore nel detto tempo ancorlui habbia cauata la spada, & uoltando la prospettiua, come pure si è detto, habbia ferito, & parato col pugnale, & col piegare del corpo habbia fatto passare la nimica molto lontana, perche la seconda uà naturalmente à cadere da se stessa in quella parte, quando non troua in contro, & anco può essere che essendo questo di dentro habbia trouato il nimico un poco aperto nel meggio dell’ armi, & li habbia fatto una finta di quarta in quel meggio uicino alla spada & che ’l detto nimico alzando però la mano di terza in seconda, & ponendo il pugnale alla nimica per diffendere quella parte, doue essa era inuiata si sia spinto oltre per ferire in medesimo tempo, & che ’l [130] ferittore che hauea finto di quarta, & che si trouaua con la parte destra inanzi l’habbia in quel punto riportata indietro, con alzare di quarta in seconda in modo che ’l corpo sia uenuto ad’ uscire di uista, & il pugnale à diffendere senza faticà, perche il braccio della spada hà dato luogo da uscire alla nimica, & hà ingannato l’ auerso pugnale, che pensando parare non l’ hà trouata, perche nel mentre, che esso è andato questa si è leuata, & uenuta senza impedimento à ferire sopra la punta di esso auerso pugnale. 93. |
||||||
[53] Next follows a quarte hitting on the inside through the faible of the adversary's dagger, who is in tierce on the left foot. You also were in tierce in the straight line with the point of your sword opposite his dagger. Whilst closing distance you have kept your sword hand in the straight line, until your adversary was within distance. Your feet were close to-gether and your point in line with his dagger hand. When he had advanced within wide distance with his left foot, seeing that his point was somewhat divided from his dagger, perhaps in order to prevent a possible attack above, you have changed your hand from tierce to quarte and thrust through the faible of his dagger. He has failed to parry, since this guard of quarte is particularly strong in that line; further in lunging your sword has come so near the edge and faible of his dagger, that you have not only made his parry fail, but pushed it away by main force and almost knocked it out of his hand. The angle which the hand forms in this guard if[!] quarte has carried the point to the adversary's left shoulder. Or it may be that you had your point against his dagger hand, and on your moving it towards the outside, he has carried his dagger in that direction, raising it in order to cover himself; on that small movement of his dagger you have disengaged over the point and made the hit. |
SEGVITA ALPRESENTE VNA QVARTA, CHE FERISCE DI dentro per il debile del pugnale nimico, quale si troua in terza sopra il sinistro piede, che può essere nata, perche quello che hà ferito si trouaua in terza ancor lui nella retta linea con la punta della spada al nimico pugnale ilquale si come è uenuto inanzi ferrando la misura, è andato altretanto trattenendo la mano della spada pure in retta linea, & tanto, che quello che è ferito è uenuto nella misura, & all’ hora per apunto, quando il suo nimico è intrato col sinistro nella misura, larga, & questo, che si trouaua in passo stretto con la punta in prospettiua della mano del pugnale nimico uedendolo alquanto aperto con la punta forsi per impedire l’ offesa che poteua essere fatta alla parte superiore hà uoltata la mano di terza in quarta per quello stesso debile di detto pugnale, che non hà potuto parare, perche la quarta guardia è ueramente in quella parte troppo galiarda, oltre che nelo andare à ferire si è cacciato tanto appresso il filo di detto pugnale, & per il debile, che non sola- [131] mente esso non, hà potuto parare, mà hà conuenuto cedere à uiua forza alla spada laquale è andata quasi come ad’ urtarlo, & quello angolo, che la mano forma nella detta quarta guardia hà portata la punta à ferire nella sinistra spalla nimica. si come anco può essere, che ’l ferittore si trouasse con la punta in contro il pugno dell’ auerso pugnale, come si è detto, & che mouendola[29] perla parte di fuori, il ferito habbia portato il suo in quella parte alzandolo in fuori per coprirsi, & che ’l ferittore in quello picciolo moto di esso nimico pugnale habbia cauato per disopra la punta, & fatta cotale ferita. 94. |
||||||
[54] This plate represents a hit in tierce under the sword. You were in tierce with the left foot forward, and your adversary in quarte with his point inside your dagger, and within such close distance that his point has penetrated your dagger. In the same time you have placed your dagger on his sword and gliding along his blade have advanced the right foot; by dropping your body you have hit between his weapons, but so low, that he has found no defence, and has been caught unawares by the movement of your foot. Or it might be that you, when on guard, had moved the point of your sword outwards, your sword being inclined upwards. Your adversary has tried to exclude your sword with a quarte, advancing his foot. Then you, being steady on your guard, have taken that time, dropped your point, so that he has failed to find it, and have passed with your body bent as low as before, reaching your adversary's body by advancing the other foot. The same hit may have occurred in another way: you were in seconde and your adversary in tierce; you have made a feint in seconde over the dagger, he has raised his dagger to parry and changed his hand to quarte in order to hit also; at the beginning of his movement you have dropped your point, turning from seconde to tierce and engaging his sword at the same time; you have passed and made the hit at the moment of his trying to defend. In addition to the other reasons this hit has followed because the adversary has moved his foot and sword, when you have moved your point only, so that your dagger has engaged his sword and he has been unable to save it. From this you may learn, that on moving your foot you should not advance the point of your sword so far that the adversary's dagger can get control of it. |
VNA FERITA DI TERZA SOTTO LA SPADA SARA QVELLA che segue, è seguità, perche trouandosi questo, che hà ferito in terza col piedo sinistro inanzi, & il nimico in quarta con la punta di dentro dall’ auerso pugnale, & tanto stretto nella misura che la punta della sua spada è uenuta à penetrare il detto nimico pugnale, & perciò il detto ferittore hà in quello stesso tempo appoggiato il suo pugnale alla nimica, & scorrendoli con esso il filo è passato col destro piede, & abbassando il corpo inanzi hà fatto la detta ferita nel meggio dell’ armi, mà tanto bassa, che l’ altro non hà potuto fare effetto di diffesa, colto similmente improuiso nel tempo del moro del piede. Può anco non altrimenti essere, che questo tale ferittore quando era in guardia habbia mossa la punta della spada allargandola infuori, laquale per auentura douea essere angolata alo insù & il ferito glie l’ habbia uoluta serrare con la quarta portandosi inanzi con il piede, & che perciò il detto ferittore quale era fermo pigliando quel tempo habbia abbassata la punta che ’l ferito [132] non habbia trouata, & sia passato col corpo si basso come era prima inanzi piegato, & sia seguito sino al corpo nimico con l’ altro piede. Per un’ altra uia ancora può, essere nata la medesima ferita cio è che ’l detto ferittore si sia trouato in seconda, & il ferito in terza, & così quello habbia finto di detta seconda sopra il pugnale, & che all’ hora l’ istesso ferito habbia alzato per parare, & uoltata la mano in quarta per ferire ancora, & nel cominciare à fare questo, che ’l ferittore habbia abbassata la punta uoltando di seconda in terza, con aquistare in tempo medesimo la detta punta nimica sia passato, & habbia fatta la ferita in quello instante che l’ altro si uoleua diffendere, laquale ferita oltre le altre caggioni si è fatta ancora per hauere il detto ferito mosso il piede, & la spada in tempo, che l’ altro non hà mosso se non la punta, che perciò l’ auerso pugnale gliel’ ha presa, che esso non hà potuto saluarla, & da queste cognitione si dee auertire, che nel mouere il piede non si hà da andare con la punta tanto oltre, che il detto auerso pugnale sene impatronisca. 95. |
||||||
[55] The last plate with the sword and dagger represents a hit and pass in seconde against an opponent in tierce who has tried to parry with his dagger and failed, because the forte of your sword has penetrated too far; in that part your sword is stronger than in any other. This hit may have arisen in several ways; in the first place you were in seconde, on the outside and your adversary in tierce; you have moved to engage his sword with your sword in seconde and accompanied by the dagger; he has tried to disengage to prevent his sword being subjected, with the intention of advancing and hitting; with your weapons in union you have changed the line of your sword and dagger and the front of your body advanced the left foot and defended yourself; by bending the body as far as possible you have hit between his weapons. Or it may have arisen in this manner: you were on the inside and have engaged your adversary's sword which was in tierce; he has left an opening between his weapons and on his making some movement with his foot you have taken that time and hit. Or it may be that after engaging your adversary's sword you have made a feint of passing and hitting over the point of his dagger; you have forced him to raise his dagger or move it, and taking that time you have returned between his weapons and hit in quarte, passing as shown. Or it might well be that your adversary had engaged your sword; you made a feint of disengaging over the sword and have returned to the inside in the time of his attempted parry; putting your dagger under his sword as he raised it, you have thrust and hit. The stroke might have happened in yet another way: you were in tierce with your sword free on the inside and by making a feint of hitting over your adversary's dagger have separated his weapons, and in that instant by passing with your sword over the point of his dagger have hit between his weapons, excluding his sword on the outside with your sword and dagger in conjunction; by the extent of your advance his sword from being straight has been forced into an angle. |
LA SEGVENTE FIGVRA VLTIMA DI QVELLE DI SPADA, E pugnale rapresenta una ferita passata col sinistro piede contra una terza, che hà uoluto parare col pugnale, & non hà potuto per essere già la nimica troppo penetrata inanzi col forte più galiarda anco detta nimica in quella parte che nell’ altra, laquale ferita per più uie può essersi caggionata prima perche quello, che hà ferito si trouaua in seconda di fuori & l’ altro in terza, & così andatoli à trouare la spada con detta seconda accompagnato dal pugnale il medesimo che è ferito haurà uoluto cauare per non lasciarsi oppri- [133] mere la spada mostrando di ferire con auanzarsi inanzi, & che all’ hora il ferittore unito dell armi haurà uoltato la spada, & il pugnale con la prospettiua del corpo passando del sinistro piede inanzi, con diffendersi, & piegarsi quanto più hà potuto, & hà ferito nel meggio dell’ armi. Altrimenti ancora potiamo dire ene sia nata cio è che’l ferittore si sia trouato di dentro, & ferrata la nimica con la spada in terza, & che trouandosi il ferito aperto nel meggio dell’ armi, & con hauere fatto qualche moto de’ piedi, questi habbia preso quel tempo, & ferito. Potrebbe anco il detto ferito essere stato serrato, & che il detto ferittore doppo hauerli aquistata la spada fingendo passare, & ferire per sopra la punta del pugnale glielhabbia fatto leuare, ò mouere, & pigliando quel tempo sia poi tornato nel meggio dell’ armi, & habbia ferito di detta quarta passando come ai uede. Oltre diciò può anco molto ben’ essere, che l’ istesso ferito hauesse occupata la spada al nimico, ilquale hauesse finto cauare per disopra della spada, & fosse ritornato di dentro nel tempo che detto ferito hauesse uoluto parare, & appoggiato il pugnale sotto la nimica spada nel punto, che la si leuaua, & l’ hauesse rimessa & ferito. Vn’ altro modo anco diremo conche si può essere fatta tale piaga ciò è che questo ferittore fosse in terza libera di dentro & col fingere di ferire sopra il pugnale hauesse fatto aprire l’ armi al nimico, & che passando in quello Instante. Con la spada per sopra la punta del detto auerso pugnale hauesse ferito nel meggio con escludere la nimica di fuori con la spada, & pugnale conggiontì, & che per essere andato esso ferittore tanto inanzi la detta nimica, che prima era diritta sia restata tanto angolata. 96. |
||||||
[56] |
[113r] Vedeßi qui una ferita di seconda sopra il pugniale qual’è contra una mano voltata verso la quarta, & è avenuta, per’che quello che á ferito era nella terza sopra il piece manco & á finto di ferire sotto il braccio del’pugniale inemico, & questo abbaßato la mano di eßo per’parare, & si è cacciato nel’mezo delle arme á ferire di meza quarta, & quello che á fatto la finta appreßo quel’tempo cavando sopra detto pugniale voltando la mano in seconda, appoggiando il pugniale alla nemica ponta schorrendo il filo di eßa è paßato con il piede dritto tanto innanzi, Come si vede, per’che la detta quardia porta con se tal’ragione; potrebbe anchor’eßer’stato che questo, che era nel’piede manco sia andato á ritrovare, la nemica di dentro, la qual’doveva eßere in terza & quello averà cavato per’non lasciarsi occupare mà ferire in quel’tempo, & questo in quel’medesimo punta á cavato anchora lui di seconda, & posto il pugniale alla nemica che veniva á ferire & è paßato di piedi dritto dove è arrivato innanzi che quello, che aveva pri= [114v] ma fatto la distesa di terza abbi potuto fenire di voltare la mano in quarta. |
Third Part - Of Sword and Cape
Illustrations |
Illustrations |
Draft Translation (from the archetype) |
Prototype (1601) |
Archetype (1606) [edit] |
Copenhagen Version (1600-1609) [edit] |
Munich Version (ca. 1635) [edit] |
German Translation (1677) [edit] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[1] Part 3. Discourse on the sword & cloak. Fencing with the sword and cloak is a noble art, and in general use in every province where it is not prohibited. But like the dagger in many states and cities its use is forbidden by the ruling princes, so that it falls into disuse, and the labour and time spent in acquiring an understanding of the art are rendered vain. However, we have considered it fitting to treat of it in order to explain its nature, and how and when it should be employed. We say thus that the cloak is both a defensive and offensive weapon; by offensive we mean capable of inflicting damage on the adversary. By being cast in various ways it can impede his view and his hand, a disadvantage which the user of the cloak may himself suffer by throwing it over his head and impeding his own view; though we think that this should happen only to one entirely inexperienced in its use. To one who understands it well, it is a very advantageous weapon. Its use requires an understanding of the sword alone, since in many senses the sword defends with the aid of the cloak, especially cuts outs at the head. In parrying such cuts you should never interpose your arm, owing to the danger of the cloak being cut and the arm hit. Even if you wrap the cloak round your arm, besides leaving the lower parts exposed with grave danger, it would not support such a stroke without injury to the arm. Against such cuts it is beyond comparison better supposing that the cloak is held correctly, to bring the left foot forward and, extending the cloak arm, to parry near the adversary's hand; in this way the danger would be avoided. In case you were not near enough for such a move, you could let the cut pass without resistance, and then advance the sword and cloak together. Otherwise you should parry with the sword supported by the cloak or with both together, hitting in the same time. The lower parts can be very well defended by the cloak in spite of its weakness; for it yields to the shock and in addition has its length and width. These three conditions give it its power to resist and parry. With its flexibility and without its width it would not defend, however long, so that its strength consists in its width; but the part which yields must be aided by the movement of the feet and body to render the defence secure both against cuts and thrusts. The cloak also will defend all thrusts under the arm on either side by its edge hanging from the hand towards the ground. The arm must be held extended with the hand towards the adversary in order to parry far from the body and in order that his point may not reach your body on the yielding of the cloak before it is driven out of the line. Therefore you must not hold the width of the cloak facing the adversary, lest he should hit in the middle, for it is more difficult to parry with the cloak in this position than when it is held on edge; in the later[!] case it easily carried[!] the thrust outwards on either side. Besides holding the arm extended you must hold it so high that your hand is on a level with the head whilst you look towards the adversary along the line of that hand. The cloak must hang only so far, that on lowering the arm, whether from fatigue or any other reason, it does not reach the feet with the danger of causing you to fall. You should cover your arm with the cloak up to the elbow, and the point of your sword should be in conjunction with the cloak hand, for better protection and for the strengthening of the sword, and in order to defend the cloak hand better. When your arm is weary you should bring it towards the hilt of your sword and close the two hands so that the adversary cannot come between them; you should face in such a way that the edge of the cloak always looks towards the adversary. When a thrust is made in the upper lines, you should parry by raising the hand only, leaving the elbow steady in such a way that from the hand to the elbow a perpendicular line is formed. If you observe this rule you will force your adversary not to lift his sword but to attack on the outside, where you may protect yourself more easily and with less movement. If in the time of your parrying the adversary tries to hit in the centre, you will defend yourself more readily, since there will be less exposed than if you had moved the whole arm. In this way the elbow forms the centre, in the other the shoulder, hence in the latter case the movement of the hand is greater, the part uncovered larger and the defence of the face more dangerous if the adversary's sword is raised, and this because the path taken in driving his sword out of line is longer. If your adversary attacks on the outside of the sword towards the face, still you should not move your elbow but keep it steady, raising the hand only in such a manner as to defend that part to the top of the head. This will give you two advantages; firstly a better defence for you will not only parry with the cloak hand, but also make use of it and the arm down to the elbow, and so cover the whole of your right side; in the second place you do not obstruct your view, whereas if you raise the whole arm you obstruct your view and cannot see the adversary; if you observe the rule you will always see the adversary's sword hand. If the cut at the head is in mandiritto you should parry with the sword by turning the hand to quarte and thrusting the point towards the adversary's chest or face, holding the cloak hand close to the hilt. If you do not hit with the parry you should at once turn your hand to seconde or tierce, carrying the cloak hand to your adversary's sword on the one side or the other, according as it is more on the inside or the outside, then bring the rear foot forward and hit in the part uncovered. With this parry you can also make a feint with the point and, after parrying, make a cut of riverso at the leg, leaving the cloak arm against the adversary's sword and bringing the rear foot forward; if you act swiftly you could also make a thrust at the chest. But if you do not wish or cannot make this defence, you should parry by holding the cloak hand under your sword, and after parrying at once disengage your sword in seconde, and leaving the cloak below the adversary's sword hit the chest; or after parrying cut in mandiritto at the leg; or still defending yourself with the cloak above, cut in riverso. If your adversary cuts in riverso you could parry with the guard of seconde, thrusting towards his chest at the same moment, and leaving the cloak hand close to his sword for the defence of the lower parts; if you have not hit with the parry, you should leave the cloak against his sword and hit below in tierce, or you mast immediately after parrying cut in mandiritto or riverso, still letting the cloak defend above. If your adversary should cut in mandiritto at the leg, you could parry with the cloak and hit above with the hand in quarte, so that if his cut at the leg has been an artful feint and he had then cut at the head, the sword would have defended. If he should cut in riverso you should parry still with the cloak, and with the sword in a guard of seconde for the defence of your head advance to hit in the same time; if on your right foot you must carry it towards the left in order to cover yourself more by the cloak, and also lest the adversary should reach you by the yielding of the cloak; you should turn the point of your right foot outwards, in order that the cloak arm may approach nearer the line of the adversary's stroke. But if you pass with the left foot, you avoid this danger, because the cloak would cover more, so that you have only to make the hit directly. But if your adversary has made a feint of riverso at the leg and changed to a mandiritto at the head, you should then turn your hand to quarte holding the cloak close to the sword and hitting at the same time. You could also parry with the cloak alone, if you had advanced, because you would have brought it so near to his hilt that there would be no damage even to the cloak; you should hit in tierce below in the same time. Or if you were in seconde when your adversary cut at the head, you could cut in mandiritto at the leg, making the same defence, or disengage from seconde and cut in riverso at the adversary's right leg. All thrusts whether at the head or body, can be parried with the cloak; but thrusts between the hands must be parried with a change to seconde, otherwise you would be in danger of being hit; for besides the yielding of the edge of the cloak on reaching the adversary's sword, there is the danger that your right shoulder in its advanced position may be reached by his point before the point is driven out of the line. Your arm too is in danger of obstructing your defence and of being hit, as you do not wish to withdraw the arm while parrying. Therefore by changing from tierce to seconde you make the defence easier, since not only does your arm give place to the cloak, but the front of the body is changed in such a way as to escape the danger, and you hit at the same moment. When his point comes outside your cloak or sword, there is not the same difficulty as when it comes between the two. Disengagements should be made above, for the hanging cloak obstructs their being made below. But on the side of the sword they can be made below, when making a hit outside the sword. But when the adversary's sword and cloak are separated, it would be well to pass the point of his sword if it is not inclined upwards at an angle, for then you could reach the body without bringing your faible near his forte. If your sword is on the outside of his, you can disengage over the point, and hit in the middle, and sometimes over the cloak hand. Again, if your sword is over his cloak, disengage in the middle, and if his weapons are united and you cannot hit there, hit over the sword, or make a feint of a hit there, and, when he moves to parry with the sword, hit in tierce below, parry with the cloak and recover to the position over the cloak hand with a change to seconde; in this manner you will hit in the same time and defend yourself with the cloak against a possible stroke below. These rules apply when on guard on the right foot. When on guard on the left foot you should proceed in a different manner. The position on the left foot is better with these weapons than with the sword and dagger, for the parts which are exposed and generally attacked with those weapons are in this case better protected, since the cloak hand can be held so high as to defend all the part exposed above the arm, while the hanging edge of the cloak defends below; thus both parts are covered at the same time, whereas with the dagger in covering one part you expose the other, besides the grave danger to the left knee, which is advanced and far from the defence. With the cloak the knee also is defended. Farther the sword in tierce cannot only be brought in conjunction with the cloak, but can rest on the cloak hand and be strengthened in such a way that it cannot be thrust aside. With this union of weapons you can make all the defences and attacks; if you have formed your guard well, your adversary will be able to hit only over the sword, where there is little exposed; your sword, strengthened by the conjunction of the left hand, will parry with ease and without farther change. This is impossible with the sword and dagger, since there are more exposed parts, and if you rest the sword on your dagger, you obstruct the dagger and destroy its function. On the other hand such a position strengthens the cloak and gives a better defence. With this guard you have merely to push on within distance of the adversary, where you can hit without separating your weapons. You should observe this union whether defending against cuts or thrusts. So far we have treated of the defence and attack with the cloak with respect to the difference from the methods with the sword and dagger. Now we must mention that the cloak can be used by throwing it in various ways, such as by wrapping it round your adversary's head, and letting it go entirely, or holding it by the lower edge in order to bring it back to your arm, if the plan has failed. It may be thrown over the adversary's sword, but it must reach the hilt of his sword in order to check and impede his hitting or doing anything else. You may throw it round your arm in order to deceive the adversary and then cast it in his face. You may rest the point of your sword behind it and then carry it to his face. In all these cases you should hit before the adversary frees himself. These are the tricks of the cloak which are not expected by the adversary, and the unexpected attack is more effective. Here we end the general discourse on this weapon. |
[134] TERZA PARTE. DISCORSO SOPRA LA GENERALITA DI SPADA, E CAPPA. LA SPADA, E CAPPA E VN’ ARMA MOLTO NOBILE, ET commune in ogni prouincia non soggietta ad’ alcuna prohibitione, come il pugnale, ilquale in molti stati, & città non uiene da Prencipi permesso che cadendo perciò in disuso, rende uana la fatica, & lo studio di chi hà speso molto tempo in aquistarne la scienza; per tantà habbiamo noi giudicato essere assai conueneuole lo trattarne per fare conoscere la natura di essa, & come, & quando sia buono adoprarla, la cappa diciamo dunque è un’arma diffensiua, & offensiua insieme, offensiua intendiamo in questo luogo per il nuocere, che fà & può fare al nimico, perche lanciata in diuerfi modi può impedire la uista, & la mano, danno che può similmente patire quello che l’ adopra, ilquale potria giettarsela sopra il capo leuando à se stesso la uista, se bene crediamo che cio douesse solo accadere allo intieramente imperito di essa, mà chi sene sà bene ualere è un’ arma assai uantaggiosa, allaquale pure si richiede la cognitione della sola spada, perche in molti casi con la spada si diffende, & con la cappa si soccore, massime in quelli taglii, che uengono per testa, atteso che nel parare non si dee mai sotto porre il braccio all’ offesa, per il pericolo del restare tagliata la cappa, & il braccio ferito, & chi si riuolgesse anco tutta la cappa al braccio, oltre che lasciarebbe scoperte le parte inferiori con suo graue pericolo è non forsi bastarebbe à sostenere simile botta senza lesione del detto braccio, nell’ occasione de quali taglii meglio sarebbe senza comparatione, supponendo però che la cappa si tenga come si deue, di passare col sinistro piede inanzi, & slongando il braccio della cappa andare à parare uicino alla nimica mano, che in tal modo cessaria quel pericolo, & quando per sorte non si fosse tanto uicino si potrebbe senz’ altra oppositione lasciare passare il taglio & poi andare con la spada, & la cappa accompagnate, altrimente si deue con la spada parare, & con la cappa soccorrere, & anco con la spada, & cappa insieme ferendo in tempo medesimo; Le parti inferiori possono tutte essere diffese assai bene dalla cappa con tutto che sia debile perche cede alla percossa aggiongendosi à questo la longhezza, & la larghezza, liquali trè conditioni insieme le danno il resistere, & parare perche con quella flessibilità senza la larghezza se ben fosse longa non diffenderia, in modo che la larghezza la rende forte, bisognando che quella parte che cede sia agiutata dal moto de’ piedi, & del corpo, per fare la diffesa sicura tanto contra li taglii, quanto contra le punte. La medesima cappa diffenderà tutte le botte disotto del braccio con quel filo, che pende dalla mano uerso terra tanto dall’ una parte quanto dall’ altra, douendosi tenere il braccio di essa disteso con la mano uerso il nimico affine di parare lontano dal corpo, & che la punta nimica non possa giongere al corpo essendo che detta cappa cede quel poco prima che essa nimica punta non sia del tutto spinta di fuori, si come non si hà da tenere la larghezza della cappa uerso il nimico, acciò che non ferisca nel meggio di essa dando maggiore difficoltà da parare in questa forma, che quando si tiene col sopra detto filo, quale porta facilmente fuori la detta stoccata per l’ una, & per l’ altra parte, & oltre il stendere il braccio come si è detto, si dee tenerlo anco tanto alto, che la mano corisponda alla testa, douendosi guardare uerso il nimico per la linea di essa mano, & douendo pendere la [135] cappa sol tanto, quanto, che nelo abbassarsi il braccio, come può accadere per stanchezza, ò per fare qualche altro effetto, non seli metta sù i piedi con pericolo di cadere; si uuole con detta cappa coprire il braccio sino al combito, & la punta della spada essere conggionta alla mano di essa cappa, si per rendersi più coperto, come per fortifficare la spada, & meglio diffendere la mano di essa cappa, & nella stanchezza del braccio si dee raccoglierlo uerso il finimento della spada, & ferrarsi con ambedue le mani acciò ch’il nimico non uenga nel meggio con tenere anco la prospettiua del corpo in modo, che il filo di essa cappa riguarda sempre uerso il nimico, & quando, che per la parte superiore uenisse qualche stoccata si dee nel parare alzare solamente la mano, & lasciare fermo il combito inguisa, che dalla mano ad’ esso combito si faccia una linea pendente uerso terra, l’osseruatione delle qualicose sarà, che la nimica non si leuarà mai, mà anderà fuori per fianco, doue l’huomo con minor moto, & più facilmente si saluarà, & se nel tempo anco che si para uolesse il nimico ferire nel meggio si diffenderebbe più ageuolmente, perche sarebbe il scoperto più picciolo così, che quando si mouesse tutto il braccio, perche in questo modo uiene il combito ad’ è essere il centro, & nell’ altro la spalla, & perciò più grande sarebbe il moto della mano, maggiore lo scoperto, & più pericolosa la diffesa per la faccia ne lo alzare in sù la nimica, & questo perche la strada è più longa in farla uscire di presenza, & quando anco la detta nimica uenesse à ferire per di fuori della spada uerso la faccia, nõ per questo si dee mouere il combito anzi tenerlo fermo con alzare solamente la mano in maniera, che si diffenda sino disopra la testa da quella parte, che si riceuerà dui benefficii uno della diffesa maggiore, perche non solamente si para con la mano della cappa mà si serue anco di essa & del braccio fino al combito, & così uiene ad’ essere coperta tutta la destra patte; l’ altro è che non si offende la uista, perche chi alzasse tutto il braccio si coprirebbe la uista in modo che non potria uedere il nimico mà oprandola con raggione uedrà sempre la mano della spada nimica. Quel taglio, che uerà per testa se sarà di mandiritto si dourà parare con la spada con uolgere la mano in quarta, & spingere la punta uerso il petto, ò la faccia del nimico, tenendo la mano della cappa appresso il finimento, & in caso di non hauere ferito in quello parare si dee subbito uoltarela mano in seconda, ò in terna cosi portare la mano della cappa nel filo della nimica per l’ una, ò per l’ altra parte secondo, che si trouarà più dentro. ò più fuori passando col direttano piede inanzi, & ferendo per quello scoperto, che si uedrà. Si potrebbe anco in detto parare mostrare di ferire di punta, & dopo l’hauere parato uolgere di riuerso per gamba con lasciare il braccio della cappa alla nimica spada passando pure col detto derettano piede, & fatto ciò con prestezza si potria anco scaricarli una stoccata nel petto, mà chi non uolesse, ò non potesse fare tale diffesa dourebbe parare di tutta coperta tenendo la mano della cappa sotto la propria spada, & dopò parato cauare subbito la detta propria spada di seconda, & lasciando essa cappa sotto la spada auersa andare à ferire il nimico nel petto, ouero parato che si hauesse uolgere di mandiritto per gamba, & tenersi sempre diffeso con la cappa disopra, si potrebbe calare di riuerso, & quando il detto nimico tirasse lui di riuerso si potrebbe parare con la seconda guardia ferendo nel medesimo punto uerso il petto nimico, & con lasciare pure la mano della cappa appresso là nimica per diffesa dalla parte inferiore, ouero se non si hauesse ferito nel parare si douria lasciare essa cappa nella nimica, & andare à ferire di terza disotto, ò che saria di bisogno subbito dopò il parato uolgere di mandiritto, ò calare di riuerso restando sempre con la cappa alla diffesa disopra, & se ’l detto nimico feresse per gamba, quando fosse di mandiritto se potrebbe parare con la cappa, & ferire con la mano in quarta disopra, acciò che se esso nimico hauesse artificiosamente finto di ferire per gamba, & fosse uenuto per testa, che la spada hauesse diffeso; mà se uenesse à ferire di riuerso si dourebbe pure parare con la cappa, & con la spada in seconda guardia per diffesa del capo con portarsi inanzi à ferire di medesimo tempo, & caminandosi col destro piede fa di mestieri portarlo uerso la parte sinistra per rendersi più dalla cappa coperto, & anco [136] perche in quello cedere, che lei fà non li sopraggiongesse addosso, che perciò è di bisogno uoltare esso destro piede con la punta in fuori affine che ’l braccio di detta cappa possa andare più uerso quella parte, doue la nimica uiene à cadere, mà passandosi col sinistro piede cessarebbe cotale pericolo, perche più coprirebbe la cappa, talmente che non saria da fare altro, che andare dirittamente à ferire; Mà quando poi l’istesso nimico hauesse, finto di dare diriuerso per gamba, & hauesse uoltato di mandiritto alla testa si douria all’hora uolgere la mano in quarta tenendo la cappa appretto la spada, & andando à ferire in tempo medesimo, si potrebbe anco parare con la sola cappa, quando si fosse continouato inanzi, perche si sarebbe gionto con essa tanto uicino al finimento nimico, che non farebbe danno, ne anco alla cappa, & si dourebbe ferire nel tempo medesimo di terza disotto. Ouero se si fosse stato in seconda in quel tempo, che detto nimico hà uoltato per testa si poteua uoltare di mandiritto per gamba, & fare la medesima diffesa, si poteua anco calare di detta seconda, & ferire diriuerso per la destra gamba di esso nimico. Mà le ferite di punta si possono tutte parare con la cappa tanto quelle per testa, quanto quelle per il corpo, benche sia neccessario in quelle, che uengono à ferire trà l’ una, & l’ altra mano di pararle uolgendo in seconda, altrimenti sarebbe pericolo di restare ferito, perche oltre quel poco di cedere, che fà il filo della cappa nel giongere alla nimica, la destra spalla porta ancora pericolo di essere ariuata dalla nimica punta, per essere più inanzi, prima che deta nimica punta sia uscita del corpo. Eui anco il pericolo del braccio, che non impedisca la diffesa, & faccia restare ferito, non uolendosi nelo parare tirare il braccio indietro, perche uoltando di terza in seconda più si facilitta la diffesa per rispetto che ’l braccio non solamente uiene dare luogo alla cappa, mà anco perche si muta la prospettiua del corpo in modo, che si sfugge il pericolo, & in un tratto medesimo si fere, mà quando, che la nimica uiene à ferire fuori della cappa, & della spada non uiè tanta difficoltà come nel meggio delle armi. Le cauationi si hannoda fare per disopra, perche la cappa, che pende impedisse il farle disotto, mà dalla parte della spada si possino fare disotto nelo andare à ferire di fuori da essa, mà quando la fosse disggionta dalla cappa saria buono passare la punta di essa, se però la non fosse tanto angolata alo insù perche all’hora si potrebbe ariuare al corpo senza auicinare il debile al suo forte, & anco essendo di fuori da essa nimica si può cauare per disopra la punta, & andare à ferire nel meggio, & taluolta si può andare à ferire sopra la mano della cappa, & similmente ritrouandosi disopra della cappa si caua nel meggio, & se ’l nimico fosse serrato che non seli potesse andare si dee andare per sopra la spada, & taluolta fingere di ferire quella parte, acchioche se detto nimico si moue à parare con la spada si ferisca di terza, di sotto & parando con la cappa ritornare disopra la mano di essa con uoltare in seconda, che si ferirà in medesimo tempo, & con la cappa si diffenderà dalla botta, che potrebbe uenire disotto queste raggioni si intendono ualere quando l’ huomo si è fermato col destro piede inanzi, perche chi fosse situato col sinistro si dourebbe in altro modo operare atteso che la postura del sinistro uale più in queste armi che nella spada, è pugnale, perche quelle parti che sono più esposte, & più offese in quella sono più coperte, & più diffese in questa, & ciò perche la mano della cappa si può tenere tanto alta, che, diffenda tutto quello scoperto, che può essere sopra il braccio di essa, & il filo pendente dalla mano diffenda disotto, nella quale forma si uiene à coprire l’ una è l’ altra parte in tempo medesimo, che col pugnale coprendo sene una se ne scuopre un’ altra, oltre il pericolo graue, che porta il ginochio sinistro per essere inanzi, & lontano dalla diffesa, mà hauendo la cappa in mano ancor lui uiene diffeso anzi di più che per essere la spada in terza non solamente la si può conggiongere uerso la cappa mà si può anco appoggiare ad’ essa mano della cappa, & restare fortifficata in modo da non potere essere respinta, & con laquale unione si possono fare tutte le diffese, & offese, talmente che essendo l’ huomo bene accomodato in detta guardia non haurà il suo nimico altro luogo da ferire, che sopra la spada, & quello è anco poco scoperto, & essa spada, tanto forte per la conggiontione della sinistra che parará [137] senza scomodità, ne sarà in bisogno di fare altra forza, effetto impossibile alla spada, è pugnale perche quella ha più scoperti, & chi uuole appoggiare la spada ad’ esso pugnale lo impedisce tanto, che non può operare anzi che perde il suo uso, doue per il contrario la cappa si fortiffica, & meglio si diffende, in modo tale, che ritrouandosi l’ huomo in questa guardia non deue fare altro, che spingersi addosso al nimico così ferrato per ariuare in distanza, doue possa ferire esso nimico senza disggiongersi, & deue stare così unito tanto nelo diffendersi da qualunque taglio quanto dalle punte. Fin quì siè trattato delle diffese, & offese di detta cappa per la uariatione che è trà essa, & il pugnale, mà hora diremo che essa cappa si opera ancora con slanzi in diuerse[30] maniere, cioè essendo lei in spalla farla auolgersi intorno il capo del nimico, & lasciarla del tutto, ouero tenere il lembo disotto per ricuperala subbito sopra il braccio, se non hauesse fatto effetto buono, laquale si può giettare anco sopra la nimica, mà bisogna, che la gionga al finimento per trattenersi, & impedirli il ferire, ò fare altro, la si uolge anco intorno il braccio per disospettire il nimico, & poi se li slancia contra la faccia, & le si può appoggiare la punta della spada dietro & con quella portarla sino alla faccia nimica, & ferire in tutti li detti tempi prima, che il detto nimico si liberi, quelli sono li inganni della cappa non aspettati dall’ auerssario, talche con l’ improuiso può tanto maggiormente offendere, & quì sia il fine del discorso generale di questa arma. |
||||||
[2] Here we shall explain the principles of the accompanying plate, the first in order with the sword and cloak and formed with a guard of seconde. We have thought good to neglect entirely the guard of prime as unnecessary, in order not to make the book unconscionably long. When this guard in seconde is well formed it is safer than that with the sword and dagger, because the lower parts are defended by the cloak hanging from the arm. The arm is held high and to the outside, so that the adversary cannot hit above, nor can he hit between because the sword is held close to the edge of the cloak. As there is nothing exposed over the sword, he can hit only the small part exposed below near the cloak, which the cloak can easily defend, especially if aided by the right foot. In advancing you should carry the right foot towards the adversary's right side with the point of the foot towards the left on reaching the ground; in this way the right side of your body will be brought out of line, which will help against the yielding of the cloak on reaching the adversary's sword; thus you will be safe and hit at the same time. In finishing your lunge you should raise the left foot and carry it back in a circle towards the left, bringing the right foot back to it immediately and recovering to the same guard of seconde; you should form this position as often as there is an opportunity to hit. |
IL PRESENTE DISCORSO DIMOSTRA LE RAGGIONI DELLA suseguente figura prima in ordine di spada, è cappa formata in seconda guardia, essendoci parso di tralasciare intieramente la prima guardia come cosa non neccessaria, hauuto risguardo à non fare crescere sconciamento il libro, laquale seconda guardia quando sia ben formata è assai più sicura di quella di spada, è pugnale per la diffesa che riceuuono le parti inferiori da quella cappa pendente dal braccio, ilquale perche si tiene tanto alto & infuori non può l’ auerssario uenire à ferire disopra, si come, perche la spada si conggionge appresso il filo della cappa non può lo stesso auerssario uenire à ferire nel meggio, ne essendoui sopra la spada scoperto alcuno resta solamente al detto auerssario quella poca parte disotto, che è appresso la cappa laqual cappa assai facilmente può diffendere massime con qualche agiuto del destro piede, che in tal caso deesi col auanzarsi inanzi portarlo uerso le destre parti del nimico tenendo la punta di esso in modo, che nel porlo in terra guardi uerso le parti sinistre, che per tale maniera il corpo farà un uacuo del destro fianco, colquale uerà ad’ agiutare, & come à suplire per quel tanto, che la cappa cede nel resistere alla nimica spada, & così si rimanerà sicuro, & si andara à ferire in tempo medesimo, douendosi anco nel finire la distesa della spada, & del passo leuare il piè sinistro, & allargarlo indietro, mà alquanto in giro uerso la parte manca ricuperandoli subbito il destro appresso, & racogliersi inquesta medesima seconda, & seruare tante uolte la detta forma, quante, che uerà occasione di ferire. 97. |
||||||
[3] The second plate with the sword and cloak represents a guard in tierce, with the sword inclined upwards at an angle for two reasons; in the first place to close the path between the weapons, in the second to cover and defend the cloak hand, in case the adversary should try to hit it; therefore the sword is held advanced; also if the adversary comes on the outside of the sword, the forte being well advanced can easily defend. Instead of using the sword you could parry with the cloak alone, change the hand to seconde and hit in the chest in the same time recovering on guard in seconde in the way explained in the last plate. When steady on your guard; if you wish to change from seconde to tierce, you mast carry the left foot back somewhat, so that the adversary cannot reach you during the change; afterwards you should begin to close the distance with this tierce; if it is well formed the adversary will be able to hit only over the sword. |
[138] SEGVITA LA SECONDA FIGVRA DI SPADA, E CAPPA SITVAta in terza guardia, & con la spada così angolata alo insù per due raggioni la prima per chiudere l’ addito, che altri non possa andare nel meggio la seconda per coprire, & diffendere la mano della cappa, se per caso il nimico pensasse ferirla, & perciò tiene la detta spada auanzata, come anco perche se lo stesso nimico uenesse di fuori dalla spada essendo lei così auanzata, & col forte inanzi potesse facilmente diffendere, se bene anco potria fare dimeno di operare la spada mà solo con la cappa parare uoltando la mano in seconda, & andando nel medesimo tempo à ferire il nimico nel petto con rihauersi nella seconda, si come sopra l’ altra figura si disse, mà trouandosi l’ huomo fermo, & uolendosi rimettere di seconda in terza saria di bisogno portare il sinistro piede alquanto indietro, acciò che dall’ auerssario non potesse essere nella mutatione ariuato, & doppo la mutatione douria cominciare à stringere la misura con la detta terza, laquale essendo ben formata non restaria al detto nimico altro luogo da ferire se non sopra la spada. 98. |
||||||
[4] The next is also a guard in tierce formed because of the fatigue of the arm, which cannot be held long extended owing to the weight of the cloak which drags the arm down. When the arm is weary you must carry the left foot backwards in order to withdraw the upper parts most exposed, leaving the sword advanced to keep the adversary at a distance; the cloak hand should be united to the sword hand to prevent a hit between; thus the adversary will be able to hit only over the cloak arm, and against this stroke you must raise the cloak hand only, without moving the elbow from its position, accompanying it with the sword hand changed to quarte, in order to close the path between; thus you defend the upper parts and hit at the same time, immediately recovering to seconde with the cloak extended. |
[139] QVELLA CHE VERA SIMILMENTE SARA VNA TERZA GVARdia causata dalla stanchezza del braccio quale non può stare longamente disteso per la grauezza della cappa, che lo tira abbasso, perciò nel mancare di esso braccio è neccessario slargare anco il sinistro piede indietro per fare dillongare quella parte disopra, che più si scuopre, mà che la spada resti inanzi per tenere il nimico lontano; la mano della cappa si dee anco tenere unita con quella della spada, perche non possa ferire nel meggio, che così non haurà esso nimico da potere ferire altroue, che sopra il braccio della cappa, contra ilquale nimico, se uerà per ferire, si dourà alzare solamente la mano di essa cappa con lasciare il combito nel suo sito senza mouerle accompagnandoli la mano della spada uoltata in quarta per stringere quello scoperto nel meggio, che si è fatto in diffendere la parte superiore & ferire in tempo medesimo, con subbito ricuperarsi in seconda con la cappa distesa. 99. |
||||||
[5] This also represents a tierce, but on the left foot. This is better with these weapons than with the sword and dagger or any other weapons, because the side and the leg, which are in the greatest danger, are covered by the cloak, which hangs in such a way that neither cut nor thrust can attack. Further the sword hand is held so high that the adversary cannot hit above, while the path between is closed by the sword which rests on and is strengthened by the cloak; the sword is directed towards the adversary in line with your cloak hand in such a way that he has nowhere to hit except in that line, which is defended by the faible of your sword; though we call it the faible it is none the less stronger than the adversary's forte as it is strengthened by the cloak hand; and with this support your sword hits at the same time; with the same tierce you can reach his body and after hitting recover to the same guard. In short this guard is the best of all with the sword and cloak. |
[140] QVEST’ ALTRA NON MENO SARA VNA TERZA, MA COL PIE sinistro inanzi, laquale guardia è assai migliore in queste armi, che nella spada, è pugnale, & anco in quali si uoglino altre armi, perche il fianco, & la gamba, che sono nel maggiore pericolo uengono ricoperti dalla cappa, che pende, in modo, che ne da punta, ne da taglio possono essere offesi, oltre che la mano di essa cappa è tanto alta, che non può il nimico ferire disopra, & nel meggio è serrata dalla spada che si appoggia, & fortifficata dalla mano di essa cappa, con guardare la uista fuori per quel pugno uerso il suo nimico, di maniera tale che esso nimico non può hauere altro luogo da ferire se non doue, che uiene detta uista, laquale anco resta diffesa da quello debile della spada, che li è incontro, ilquale se ben noi lo chiamiamo debile è nondimeno più galiardo del forte nimico, rispetto alla mano della cappa, che lo fortiffica, & così appoggiata uà à ferire in tempo medesimo, & può andare con l’ istessa terza sino al corpo nimico, & dopò ferito anco ritirarsi nella medesima terza, & è in somma la migliore guardia questa di tutte l’ altre di spada, è cappa. 100. |
||||||
[6] The next plate represents a defence with the sword and cloak with a guard of seconde, which is far better than with the sword and dagger, because the lower parts are easily defended by the hanging cloak; if the adversary should make a feint of cutting at the head in order to thrust below, he would do no good, because you would turn your sword to seconde and advance to hit, carrying the edge of the cloak somewhat towards the right so as to be covered; if his cut had been really meant and had been a simple cut, after parrying you would still have made a hit in seconde inside his sword, leaving your cloak on his sword and passing on with the left foot, with the point of the foot outwards, in order that both sides of the body may advance and the sword reach further. This kind of hit will be treated of in its place, that all may better understand it. |
[141] MA QVESTA, CHE SEGVE E VNA DIFFESA DI SPADA, E CAPpa fatta con la seconda guardia, quale si può dire tutta coperta molto migliore anch’ essa nella spada, è cappa, che nella spada, è pugnale perche la parte disotto uiene facilmente diffesa dalla medesima pendente cappa, in maniera che se bene anco il nimico fingesse di dare di taglio per testa per ferire poi di sotto di punta non farebbe cosa buona perche questi dirizaria la spada in seconda, & andarebbe à ferire portando il filo della cappa alquanto uerso il destro fianco acciò restasse coperto, & quando pure il detto nimico hauesse ferito ueramente di taglio, & che fosse stato un taglio semplice l’ istesso diffensore subbito parato saria andato à ferire pure di seconda dentro della spada[31] nimica lasciando la cappa nella detta nimica, & passando oltre col sinistro piede mà con la punta di esso riguardante alo infuori, acciò che ’l corpo andasse tanto con un fianco, quanto con l’ altro, & perche la spada feresse più di lontano laquale sorte di ferita si ponerà à suo luogo per maggiore intelligenza di tutti. 101. |
||||||
[7] Next we show a hit in quarte against a seconde, intended to hit over the cloak arm. You were in tierce and have dropped the cloak arm towards the hilt of your sword; your adversary this has advanced his right foot to hit the part uncovered, changing his hand from tierce to seconde and carrying his cloak to your sword in order to parry; in that moment you have raised your cloak hand and carried his sword far out, changed from tierce to quarte, and without allowing your sword to be caught by his cloak and have hit in the right side. This high defence is very advantageous with these weapons, since the cloak covers the whole of the part which is exposed with the sword and dagger; the hand also by the change to quarte covers the inside, so that the adversary could effect nothing there. Since your point hits the base of his arm you may easily realise that he cannot recover into line. |
[142] HORA SI VEDRA VNA FERITA DI QVARTA CONTRA VNA seconda, che hà uoluto ferire sopra ’l braccio della cappa nimica successa perche collui ilquale hà ferito, & che era in terza hà calato il braccio della cappa uerso il finimento della spada, & l’ altro ueduto ciò è andato per ferire quello scoperto portandosi inanzi col destro piede, & uoltando la mano di terza in seconda con portare la cappa alla nimica affine di parare, & così il ferittore in quel punto uiene ad’ hauere alzato la mano della cappa tanto che hà portato molto fuori la spada, & uoltando di terza in quarta, con non si lasciare trouare dalla cappa nimica hà ferito nella destra parte, laquale diffesa cosi alta è molto à proposito in queste armi perche la cappa cuopre intieramente quella parte, che nella spada, è pugnale tutta è scoperta, & la mano similmente così uoltata in quarta cuopre di dentro in modo che se ’l nimico uenisse per quella parte non farebbe effetto, il che si può benissimo comprendere dalla punta; che ferisce l’ angolo del braccio, che fà che non può esso più tornare in giustezza. 102. |
||||||
[8] Next follows a hit in tierce against an attempted hit in quarte. You were in tierce on the inside and your adversary tried to exclude your sword; you have disengaged in low tierce; taking that time in order to hit between in quarte he has lowered his cloak to defend the lower parts; in that moment you too have dropped the elbow of your cloak arm, raising the hand so as to cover the whole face and thus entirely closing the path between your arms and have directed your sword on the outside of the cloak arm in the line left by the dropping of the elbow, for otherwise your view would have been obstructed by the cloak; at the moment of doing this you have thrust in tierce at an angle, so that your sword has passed without opposition from his cloak. Or it may be that you had tried to engage the adversary's sword on the outside. Seeing your weapons divided he has tried to hit in the opening by disengaging in quarte past your faible. You have advanced your left side, which was behind, and resting your cloak on his sword have pushed it out of line and driven his points[!] so far upwards that it has not encountered the cloak; in this way you have made a hit over his cloak, and all the better if he has perhaps lowered the cloak in order to defend the lower parts, and thus has been unable to parry the stroke. |
[143] QVEST’ ALTRA SARA VNA DI TERZA CONTRA VNO, CHE hà uoluto ferire di quarta, laquale può essersi caggionata perche essendo quello che hà ferito nella terza di fuori il suo nimico sia andato per ferrarli la spada, & che detto ferittore habbia cauato in terza bassa, & così il ferito pigliando quel tempo per ferire nel meggio di quarta habbia abbassata la cappa per diffendere le inferiori parti, nelquale medesimo punto habbia il ferittore anch’ esso abbassato il combito della cappa con alzare la mano di essa tantò, che la faccia sia restata tutta coperta, & così habbia chiusa intieramente la strada, che poteua essere trà l’ uno & l’ altro braccio, mettendo la uista per di fuori del braccio di essa cappa per il luogo fatto dal combito nelo abbassarsi, che altrimenti la detta uista sarebbe stata dalla cappa impedita, & nel medesimo punto, che hà fatto le predette cose habbia portata la spada à ferire di terza angolata, che hà causato, che essa sia passata libera senza oppositione della cappa nimica. Potria similmente essere auenuto, che l’ istesso ferittore fosse andato à ritrouare la nimica di fuori con la sola spada, & che ueduto l’ auerssario disunito, & scoperto fosse andato per ferire in quella apertura cauando di quarta per il debile nimico, & così il ferittore, che era con la parte sinistra indietro l’ hauesse portata inanzi & appoggiata la cappa alla nimica, come si è detto, l’ hauesse spinta di presenza, & alzata tanto la punta nel spingerla oltre, che la nimica non l’ hauesse trouata, & in questa maniera hauesse ferito con la punta più alta della cappa nimica, & tanto meglio ancora perche esso nimico forsi l’ abbassaua per difendere la parte disotto, che però non hà potuto parare la ferita. 103. |
||||||
[9] In the next plate we see a hit in tierce against an attempted hit in tierce. You were in low tierce and have carried the point of your sword away with the intention of leaving an opening between your weapons; the adversary has been enticed by the opening to hit in between, so that he has divided his weapons; his cloak hand has been left behind by his advancing the right side of his body. Being in a low position you have extended your arm and right foot and hit; your lunge has caused his sword to fall low. The same hit might be made in this way: you were in quarte with your arm withdrawn; you have allowed your point to be engaged by your adversary's sword in order to give him an opportunity to hit between the weapons with a disengage on the inside, he has attempted this hit and you, who had moved with this intention, have made a half turn from quarte to tierce which has freed your point and given you the chance to parry and hit. |
[144] SI VEDRA CON LA SEGVENTE FIGVRA VN’ ALTRA FERITA di terza contra uno, che pure hà uoluto ferire di terza auenuta perche quello che hà ferito si trouaua in terza bassa, & hà aperta la punta della spada con animo di fare un’ scoperto nel meglio dell’ armi, la uista del quale scoperto hà tirato l’ auerssario à ferire in quel meggio, in modo, che è uenuto à disggiongersi con la mano della cappa, che è restata corta per la trasportatione inanzi fatta dalla destra parte del corpo, & in modo che ’l ferittore, quale era basso, stendendo il braccio oltre, hà portato il destro piede à ferire, laquale distesa di braccio hà caggionato, che la nimica spada sia tanto calata abbasso. Potria essersi fatta la medesima ferita ancora in questa forma, ciò è che ’l ferittore stesse in quarta col braccio ritirato, & si fosse lasciato aquistare la punta dalla nimica spada per darli comodità di ferire in quel meggio se hauesse cauato di dentro atteso, che esso glie l’ hauea trouata di fuori, & perciò il detto ferito fosse uenuto in quel tempo per ferire, & che l’ istesso ferittore, che con questo proprio pensiero si era mosso, habbia fatta meggia uolta di pugno di quarta in terza, laquale cosa habbia partorita la liberatione della punta con la comodità del parare, & fare detta ferita. 104. |
||||||
[10] The next plate shows a cut of riverso at the leg with the left foot forward. The adversary had made a cut of mandiritto in the time of your moving to engage his sword, which was in seconde on the outside. You, being in tierce, have perhaps parried and immediately let your sword fall on his leg, keeping the cloak at the defence. The stroke might be made in this way: the adversary has made a cut; you have parried with a quarte carrying the point towards his face; your point having failed to reach, without an interval you have changed to riverso, passing with your sword between your own cloak arm and his sword; leaving your cloak for the defence, you have advanced the left foot and made the hit. If you had wished, you could at once have continued with the right foot, recovering your point into seconde against his chest and gone right on to his body. |
[145] MA IN QVELLA, CHE VERA OLTRE SI VEDRA VNA FERITA di riuerso per gamba col piè sinistro inanzi che può essere uenuta dall’ hauere il feritto tirato di mandiritto in tempo, che l’ altro uoleua aquistarli la spada, laquale era in seconda di fuori, & dall’ hauere il ferittore situato in terza forsi parato di coperta, & subbito lasciato cadere la spada sopra la nimica gamba ritenendo la cappa alla diffesa. Può anco essersi fatta la detta ferita, che mentre quello che è ferito hà tirato di taglio il ferittore habbia parato con la quarta portando la punta al uiso nimico, & non essendo ariuato con detta punta habbia senza, interuallo uoltato di riuerso passando con la spada trà ’l braccio della propria cappa, & la spada nimica, & con lasciare la cappa alla diffesa, sia passato di sinistro piede, & ferito in simile maniera, si come se hauesse uoluto haurebbe anco subbito potuto continouare col destro, & rimettendo la punta pure di seconda nel petto nimico andare col corpo al corpo del medesimo auerssario. 105. |
||||||
[11] Now follows a hit in seconde arising in a similar way. The adversary also was in seconde; you have moved to engage his sword in tierce on the outside accompanied by the cloak; enticed by the opening you have given he has tried to cut in mandiritto. With your sword and cloak in conjunction you have parried with the sword by forming a cross, a much safer method of parrying with these weapons than with the sword and dagger from the certainty you have of defending the lower parts by the cloak hanging from the arm; immediately after the parry you have disengaged in seconde on the inside and hit over his cloak arm, whilst he had lowered it to defend the lower parts; leaving your cloak on his sword you have carried the left foot so far forward that you have pushed his sword into an angle, as shown, an excellent and important result with these arms. |
[146] SEGVE VNA FERITA DI SECONDA NATA PER CAGGIONE SImile, cio è perche tremandosi quello, che hora è ferito in seconda ancor lui, & essendoli andato il suo nimico à trouare la spada di terza dalla parte di fuori accompagnato con la cappa egli hà uoltato di mandiritto per testa inuitato dal uedere scoperto in quella parte il detto nimico, ilquale per essersi trouato con la spada, & la cappa conggionte hà parato con la spada in croce di tutta coperta, modo assai più sicuro di parare in queste armi che nella spada, è pugnale per la certezza, che l’huomo hà della diffesa delle parti inferiori coperte dalla cappa, che pende dal braccio, ilquale subbito doppo il parato cauando di seconda di dentro hà ferito disopra del braccio della cappa dell’ altro, mentre che si è chinato à diffendere le parti d’ abbasso, & così l’ istesso nimico ferittore è passato col piè sinistro inanzi, lasciando la cappa alla nimica, & si è portato tanto oltre nel passare, che hà fatto angolare la nimica, come si uede, effetto molto buono, & importante in queste armi. 106. |
||||||
[12] The next is also a hit in seconde over the adversary's cloak arm. He has made a lunge in tierce on your moving to engage his sword on the inside; he has disengaged on the outside and made this stroke, carrying his cloak to defend his right side; in that time you have changed your hand to seconde and disengaged; resting your cloak on his sword and advancing you have passed through the gap between his arms and thus hit in the chest over the cloak. The hit might have followed from your making a feint of hitting in low tierce between his weapons, and his trying to parry and hit in tierce also; you have changed your hand to seconde and raised your sword so as to avoid his and keep it free, also changing the front of your body and resting your cloak on his sword. Or it might have arisen in another way: being in quarte with your point over the adversary's cloak hand, you have disengaged in the middle with a feint of hitting; in the time of the adversary's, who is deceived by this trick, trying to parry and hit, you have returned your point over his cloak hand, changed to seconde and made this hit. |
[147] QVEST’ ALTRA, CHE VIEN DIETRO E PVRE VNA FERITA DI seconda sopra il braccio della cappa nimica, ilquale nimico hà fatto una distesa in terza, auenuta perche quello, che hà ferito è andato à trouare la spada auersa dalla parte di dentro, & l’altro cauando per di fuori è andato à ferire di detta terza, con portare la cappa alla diffesa del destro fianco, nelqual tempo lo stesso ferittore, hà uoltata la mano in seconda con cauare, & hà appoggiata la cappa alla nimica, & portandosi oltre è passato per quel uacuo, che è trà l’ uno & l’ altro braccio & in questo modo hà ferito nel petto per disopra la cappa. Può non meno essere nata dall’hauere collui che hà ferito finto di ferire di terza bassa nel meggio dell’ armi, & dall’ hauere l’ altro uoluto parare, & ferire di una terza simile, & hauendo il detto simulatore uoltata la mano in seconda è uenuto ad’ alzare la spada in modo, che non è stata trouata dalla nimica, & perciò siè saluato, col mutare la prospettiua del corpo, & appoggiare la cappa alla nimica spada. Potrebbe anco essere successa per un’ altra uia cio è che trouandosi il ferittore in quarta con la punta sopra la mano della nimica cappa, habbia cauato nel meggio mostrando di uolere ferire, & nel tempo, che l’ auerssario, in gannato da cotale insidia hà uoluto parare, & ferire, esso habbia ritornata là punta sopra la mano di detta cappa, & uoltando in seconda, habbia fatta la presente ferita. 107. |
||||||
[13] The last of the hits with the sword and cloak is a quarte on the left foot against a tierce on the right. You were on the left foot, with the feet close together, and closing distance; your adversary has seen an opening past the faible of your sword on the outside and over your cloak hand, since your sword was in tierce at such an angle that its point was above your cloak hand, on which it was supported for greater security and strength. Not realising the danger he has moved to hit that part in tierce in the straight line, thinking he would exclude your sword. You have changed from tierce to quarte, disengaged your point and driven it on with the left foot; you have lunged with your cloak hand in conjunction and hit in quarte, parrying with the cloak and carrying your right side forward in order to lengthen the reach; this has caused a change of front and lifted your adversary's sword, as shown. Or both may have been in tierce; you have advanced with a feint of hitting in tierce on the outside of his sword, and he has moved to parry and hit in tierce in the straight line at the same time, making sure that his cloak would parry below. You who have moved with a cunning, have taken that time, disengaged your point on the inside and in the high lines, and hit with weapons in motion. This has happened because the adversary's cloak was separated from his sword; for if they had been united, your sword could not have passed, since the path would have been closed. From this you may understand the importance of the union of the weapons for the securing of good results. |
[148] SEGVE VNA QVART A FATTA COL PIEDE MANCO CONTRA una terza, che hà uoluto ferire con il destro, sarà l’ ultima delle ferite di spada, è cappa, caggionatasi forsi, per che colui; che hà ferito si ritrouasse sopra il detto sinistro piede in picciolo passo, & andasse stringendo la misura, & che l’ altro ueduto lo scoperto per il debile della spada dalla parte di fuori, & per disopra della mane della contraria cappa, per esser essa nimica in terza angulata in modo, che la punta superaua la mano d’ essa cappa alla quale erra, appoggiata per maggior sicurta, & fortezza, è che non conoscendo il pericolo si sia mosso per ferire quella parte di terza in retta linea credendo tenere la nimica seratta di fuori, mà il ferittore uoltato di terza in quarta, & cauata la punta si hà spinto inanzi pure con il sinistro piede, & slongando la spada sempre conggionta con la detta mano della cappa hà ferito così unito di detta quarta, & parato con la cappa, portando la parte drita innanzi per auanzare più la botta, che à causato la mutatione della prospettiua, & l’ alzare della spada nimica come dismostra. Puo ancora essere che trouandosi tutti doi in terza il feritore si sia spinto innanzi mostrando di ferire di terza di fuori dalla nimica, & il ferito si sera mosso per parare, & ferire di retta linea in terza in un medesimo punto, certifficandosi che la cappa douesse parare disotto, doue il feritore che astuttamente si hauea mosso à preso quel tempo, & à cauata la punta di dentro nelle parte alte, & è andato à ferire cusi hunito, & questo è auenuto per la cappa del ferito che era disunita dalla propia spada, che se la fusse statta unita la spada che ferisce non haueria potuto passare, perche la strada sarebbe statta chiusa, talche da qui si puo comprendere quanto importa l’ unione quale piena dibuoni effetti. 108. |
||||||
[14] End of first book. |
[149] FINE DEL PRIMO LIBRO. |
Temp
Book 2
First Part - On Proceeding with Resolution
Illustrations |
Illustrations |
Draft Translation (from the archetype) |
Prototype (1601) |
Archetype (1606) [edit] |
Copenhagen Version (1600-1609) [edit] |
Munich Version (ca. 1635) [edit] |
German Translation (1677) [edit] |
French Translation (1644) [edit] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[1] Second Book, wherein are explained some principles according to which you can attack the adversary as soon as you have grasped the sword without waiting for a time, principles which are no longer discussed by any professor or writer on the subject. |
[151] LIBRO SECONDO DOVE SI DISMOSTRA ALCVUNE REGVLE, CON LEQVALI SI POTRA ANDARE A FERIRE IL NIMINO SVBITOPOSTO MANE, ALLA spada senza formarsi ne aspettare altro tempo; raggioni non più trattate da niun proffessore, nè scrittore.
|
Text to copy over | [1] ESCRIME NOVVELLE OV THEATRE, AVQVEL SONT REPRESENTEES DIVERSES MANIERES DE PARER ÉT DE FRAPER D'ESPEE SEVLE, ET D'ESPEE ET POIGNARD ensemble, demonstrees par figures entaillees en cuiure. Publié EN FAVEVR DE CEVLX QVI SE DELECTENT EN CE tresnoble exercice disarmes. PAR NICOLOT GIGANTI VENETIEN; ET TRADVICT EN LANGVE FRANCOISE PAR IACQVES DE ZETER. | |||||
[2] Discourse on attacking with resolution. Thus far we have spoken of the principles with which every professor of arms must be acquainted, though few understand them well or practise them with due exactness. Now we shall treat of some theories, which are not only no longer expounded by other professors, but which they have never considered, or if they have considered have not grasped or understood; they have been put aside as too subtle by the most acute exponents of this art. Desiring perhaps to cover their lack of capacity they have been forced to reject them, basing their reasons on that common maxim, that the student must remain steady in presence and wait a time in order to hit, and that he who attacks without a time will be hit. We allow that is well to know how to await a time and an opportunity to hit, because from that waiting follows the understanding of distances, times, counter-time, and all the tricks which an adversary may employ. Still we maintain that between two opponents steady on their guard there is no advantage, because both are awaiting the same thing, so that the opportunity may come to either; both are awaiting with equal danger, and and[!] if sometimes one is seen to have obtained an advantage, it is because he has engaged the other's sword and prevented him from hitting in his present line; but still the one who has obtained the advantage waits for a time, thinking he cannot hit before his adversary moves. By such delay it often happens that one who has won an advantage not only loses it, but his adversary obtains an advantage over him, a truly inexcusable error that a man should allow himself to be robbed of what he has won with such danger. It appears to us that it would have been better, having the advantage to proceed without waiting, secure that your adversary's sword cannot hit in its present line, and not to give him time to consider his danger and form a new plan. There are others who, when within distance, seek to gain no advantage, but, seeing that their adversary does not move, try to make him move by giving him an opening or offering a time or by an appel or a feint in order to take the time of his moving; such methods may succeed against men ill-instructed, but are fatally dangerous against one who understands the art; for if you consider such a proceeding, it is clear that the one who offers a time in order to make his adversary move forgets that his is the first danger, and, although his intention is to offer so small a time that his adversary cannot hit, still it cannot be so small that the adversary has no chance of seizing some advantage, from which the first man cannot free himself without great danger of being hit, moreover he could be deceived by feints. We do not condemn these theories and stratagems nor any of the principles already put forward; it is well to understand them, but they are useless and inapplicable in our case, when we have to find a way of proceeding in order to be able to hit the adversary immediately after grasping the sword and without remaining steady, in whatever position or guard the adversary may be, whether he offers a time or not, parries or hits, advances or retires; the object is to hit him inevitably, whatever method he adopts. If our method is followed with all its conditions, you will be incomparably safer than when waiting. It is true that much skill and art are needed so to control your adversary that you may be confident of hitting, whatever he does or however much he knows, and when he has the same weapons as you, even though he is ignorant of these principles; if your adversary understands these same principles, matters would be equal. But if your adversary follows the old rules even to perfection, he will always be defeated if you follow our principles, because you will be able to put him into subjection and free him to do what you want, whether he desires to attack or defend; this will make your proceedings easy, since you will foresee your adversary's intention. In order to explain this truth better we shall treat first of the advantage of attacking with resolution, and then of the method of attacking. |
[153] LIBRO SECONDO DISCORSO SOPRA L.a ANDARE DI RISOLVTIONE. NOI SIN QVI HABBIAMO PARLATO DELLE RAGGIONI, che ogni proffessore d’ armi si da ad’ intendere di sapere, ancorche da pochi siano bene intese, & con le debbite sottilità essercittate. Mà hora trattaremo d’ alcuni concetti, non solamente mai più non espressi da altri, mà forsi non caduti nella speculatione d’ alcuno, ò se pure caduti, almeno non capiti, & non intesi, sono stati, come troppo sottili messi in disparte, dalli ingegni più arguti di quest’ arte, iquali uolendo forsi coprire l’ incapacità loro si sono sforzati di contra dire fondando la raggione sua sopra quella massima commune, che l’ huomo debba fermarsi in presenza, & aspettare tempo di potere ferire, & che chi andarà senza tempo restarà ferito. Noi concediamo, che sia bene il sapere aspettare il tempo, & l’ occasione di andare[32] à ferire con raggione, perche da questo aspettare ne segue la cognitione delle distanze, tempi, contratempi, & di tutti li inganni, & insidie, che possono uenire da una nimica mano; nondimeno argomentiamo in questo modo, & diciamo, che frà dui fermati in guardia non ui è alcuno uantaggio, perche l’ uno aspetta il medesimo che aspetta l’ altro, doue può nascere così bene l’ occasione per l’ uno, come per l’ altro, talmente, che tutti dui aspettano con eguale pericolo, & se tal uolta si uede qualche uantaggio frà essi, tutto uiene per hauere l’ uno aquistato la spada dell’ altro, & per hauerla impedita, che non possa ferire nel luogo, oue si troua, & pure collui che è superiore di tale uantaggio aspetta anco il tempo, parendoli non potere ferire se prima il nimico non si moue, & nasce molte uolte con tale dimora, che il detto superiore di uantaggio non solo perde l’ aquistato, mà che ’l nimico aquista sopra di lui; errore ueramente non scusabile, che l’huomo si lascii leuare quello, che con tanto pericolo hauea guadagnato, che à noi pare, che molto meglio sarebbe stato, hauendo il uantaggio, lo andare senza aspettare altra cosa, sicuro, che la nimica non poteua ferire nel luogo, oue si trouaua, ne dare tempo aldetto nimico di considerare il pericolo, & pigliare nouo partito; Altri ancora uiè liquali, se ben gionti in misura, non procurano aquisto alcuno, mà solo uedendo il nimico non mouersi lo uuole far mouere, dandoli occasione, & facendoli qualche tempo. ò chiamata, ouero qualche finta per pigliare poi il tempo di quel moto, cose possibile à riuscire sì con hnomini non accorti, mà di mortale pregiuditio se si hauesse à fare con qualche intendente, perche chi considera bene tale operatione troua, che costui fà il tempo per farlo fare all’ auerssario non s’ accorgendo che suo è il primo pericolo, & ancoche sua intentione sia di fare un sì picciolo, tẽpo che l’ altro nõ lo possa ferire, non può nondimeno essere tanto picciolo, che ’l detto auerssario non habbia comodità di pigliarli qualche uantaggio sopra, dal quale non potrà liberarsi senza molto pericolo di restare ferito, potendo oltreciò restare ingannato dalle finte. Non biasimiamo già questi termini, & questi strattagemi, ne nissuna delle antedette raggioni, come buone da sapersi in se stesse, mà si bene inutili, & impertimenti nel nostro caso, nel quale si richiede[33] trouare un modo disperare, colquale si possa, dopò messa mano alla spada, andare à ferire il nimico senza fermarsi, sia pure esso nimico in qualunque sito, ò guardia con l’ armi, faccia tempo, ò non lo faccia, pari, ò ferisca [154] uenga inanzi, ò uada indietro, che in quale si uoglia modo in somma resti inreparabilmente ferito, ilquale modo operato con tutti i suoi[34] requisiti, renda l’ huomo senza comparatione piu sicuro che ne lo aspettare. E ben uero, che molto ingegno, & molta arte fà di mestieri à uolere impatronirsi tanto di un’huomo, che si presuma ferirlo, faccia lui quanto uoglia, & quanto sappia, & habbia pure eguali armi in mano, ilche anco si intende di un’ignaro di queste raggioni, che quando il nimico si sapesse ualere delle medesime il fatto andarebbe del pari, mà operando l’istesso nimico le prime regole anco per fettamente sarà con tutto ciò sempre battuto dall’ osseruatore delle nostre, & tutto nascerà perche dal detto nostro osseruattore si saprà mettere in seruitù l’ auerssario, & si saprà sforzare à fare come desidera uoglia poi esso diffendere, ò offendere, laquale cosa saputa fare rende poi facile l’ operatione, perche si preuede quello che il detto auerssario uiuole fare, & cosi noi per meglio dare à uedere questa uerità trattaremo prima del uantaggio di collui, che uà di risolutione, & poi del modo che si dee tenere in andare. |
[3] LIVRE SECOND. Comment sans s’arrêter après avoir mis la main à l’épée, on s’approche résolument de son adversaire. D’Autant qu’il advient souvent, qu’on est ou en hâte ou à l’imprévue attaqué et surpris d’un ennemi ou bien que même, la nécessité le requiert, qu’il faut le serrer sans longuement marchander, en sorte qu’on ne peut pas toujours s’attacher si précisément à la mesure, au temps et aux autres considérations, qui sont propres de l’art. J’estime expédient de traiter en ce second livre des accidents semblables, et montrer pourtant une plus grande perfection de notre escrime, comment on doit s’y comporter. Et combien qu’il n’y aura point de faute de gens incapables de telles subtilités, qui trouveront ce traité fort étrange, comme si nous voulions seulement frapper et aller à la lourdeur, sans aucun regard de méfaire, ou de temps et sans art et prudence, et mettre nos escrimeur en un évident et reprochable danger, les enseignement de frapper comme les ivrognes sans art, et considération: si il ne faut pas se laisser détourner par de tels propos, par lequel ceux ici tâchent de couvrir leurs ignorance: ainsi savoir qu’en ce second traité nous ne voulons point fouler [montrer] les temps, gardes, postures, et tous les autres mouvements tant nécessaire qu’artificiels, mais plutôt montrer, comment en hâte on se doit résoudre à l’usa [4] ge de ceux-ci. En sorte qu’aussitôt que l’on a mis la main à l’épée, on puisse attaquer et serrer son adversaire, en quelconque garde qu’il se tienne, en se servant et du temps et de la mesure autant que possible. Et qu’au contraire on soit beaucoup plus assuré de son habilité, que quand on se tient longuement en quelque garde pour attendre l’occasion. En quoi il y faut grande prudence et exercice, afin que l’adversaire se sachant servir de tout ce que nous avons montré au premier livre, ne puisse assez se garder du danger, d’être atteint et blessé. | ||||||
[3] On the advantage of attacking the adversary without remaining steady on guard. You must consider first that one who is steady on his guard and desires to move will be slower owing to his weight than one who is already in motion. For one who is steady and has both his feet on the ground can move a foot only in two times, one in moving it and the other in bringing it to the ground, as we have said elsewhere; but one who is on the move has always one foot in the air, so that without doubt he will have brought it to the ground before his adversary has even lifted his, a matter of great advantage to have finished the movement, while the opponent is beginning. Further the man who remains steady gives his adversary a better chance to estimate his quality and find a way to attack him, than if he approaches without stopping; before he makes up his mind what to do, the opportunity has gone. There is no doubt that times are more readily taken by one on the move than by one who is steady, for the time has passed in moving to take it and it is too late; often a man is hit from such a cause. The disadvantage of the one who remains steady is even greater - for he may be disordered by many kinds of feints, appels, and various changes of line, whereas against one on the move feints are impossible, appels only possible by breaking ground and changes of line only occasionally possible; feints and appels are impossible, because he would have arrived before the movement of the feint or the time was finished. In order to advance in the proper manner a threefold union of the sword, foot and body is needed, and when one of them is lacking, the method is imperfect; therefore the union must be observed without rushing with the body or sword. We shall now treat of the manner of working with the feet, the body and the sword together. This is the foundation of the whole method. |
RAGGIONI PER CONOSCERE IL VANTAGGIO DI CHI VA CONTRA IL NIMICO SENZA FERMARSI. SI DEVE DVNQVE CONSIDERARE IN PRIMA CHE VN’ huomo essendo fermato, & uolendosi mouere sarà per la sua grauezza sempre più tardo di un’ altro, che già sia in moto, & uada, perche quello, che è fermato, & che hà tutti dui li piedi in terra non può mouere alcuno di loro se non con dui tempi uno nel mouerlo l’ altro nel posarlo, come altroue si è detto, mà quello, che è inuiato nel camino sempre si troua con un’ piede in aria, doue che senza dubbio hà fermato il suo, quando che l’ altro non l’ hà ancora leuato, cosa di molto uantaggio certamente l’hauere finito di operare, quando che l’ altro comincia, oltre che quello, che è fermato dà più comodità al suo auerssario di giudicarlo, & con templarlo, & anco di trouare modo di assalirlo, che se selo uedesse uenire incontro senza fermarsi, perche inanzi, che si fosse risoluto di quanto douesse fare l’ occasione saria già passata ne uiè dubbio che li tempi, che nascono sono più ageuolmente presi da chi è in moto, che da chi è fermato, perche nel mouersi à pigliarlo il tempo è già scorso ne ui si gionge se non troppo tardi, & spesso spesso si rimane per tale causa ferito, si fà anco maggiore lo suantaggio di chi è fermato perche può essere disordinato con molte sorti di finte, di chiamate, & di diuerse mutationi; doue che contra quello, che uà non si può fare se non il primo effetto, & il secondo mà con rompere di misura, & rare uolte il terzo, mà non se li può già fare ne finte, ne chiamate, perche prima, che fosse finito l’ atto della finta, ò tempo il mouentesi già sarebbe ariuato, E ben uero, che à uolere andare comè si conuiene fà di mestieri usare una triplice unione di spada piede, è corpo, & quando, che una di loro ui mancasse restarebbe la raggione imperfetta, per tanto si dee conseruare la detta unione senza slanzare mai ne corpo ne spada, mà hora si trattara del modo da tenersi in adoprare li piedi, primo fondamento, & del corpo & della spada insieme. |
Comment on doit connaitre et se servir de l’avantage. PRemièrement n’y a-t-il point de doute, que celui qui se tient coi et ferme est toujours plus pesant et lent, que celui qui marche, et est déjà en mouvement. Car l’autre ayant les deux les pieds en terre, a besoin de deux temps, quand il veut bouger l’un de ceux-ci, se passe en le levant, l’autre en le posant. Mais celui qui est en chemin, a toujours un pied levé et peut le poser, devant qui l’adversaire peut lever le sien. En quoi il y a un grand avantage, et peut parfaire son opération, avant que l’autre pense à commencer la sienne. Joint que celui qui se tient ferme donne à son adversaire plus de temps pour reconnaitre et embrasser son avantage; qu’il ne peut avoir de celui qui l’approche. Car le temps s’écoule avant qu’il puisse y penser, et connaitre ce qu’il va faire. Celui qui est déjà en mouvement prend mieux son temps, en sorte que celui qui se tient ferme bien souvent est atteint, avant qu’il puisse avoir le temps de parer. Derechef est aussi un grand avantage pour celui qui marche, qu’il ne peut être empêché que par le premier [5] effet, ou aussi par le second, et en rompant de mesure, et fort rarement par le troisième et ne peut être trompé par feintes et autres allèchement, comme celui qui facilement peut prévenir ces temps-là. Mais celui qui se tient ferme, bien qu’il se couvre des meilleures gardes, peut-il si facilement être trompé par des feintes ou autres changements. Toutefois faut-il que celui qui veut faire son opération en marchant, qu’il regarde en diligence que l’épée, pied et corps soient unis, c’est-à-dire, qu’il ne s’avance ni de l’épée, ni du corps, plus que le pied ne permet. Dont ensuite nous montrerons comment en premier lieu il faut mouvoir le pied, comme le fondement principal, et après nous verrons comment on l’accompagnera du corps et de l’épée. | ||||||
[4] On the manner of working with the feet, sword and body in attacking the adversary without a pause. If you wish to advance against your adversary you must begin by carrying the feet with ordinary steps, as in walking, though with somewhat quicker and shorter steps; you must never lengthen your step except when the point of your sword reaches his body; your steps must not be violent, for as you must continue until you have reached the adversary's body, any violence would so disorder you, that you would be unable to lift the rear foot with the necessary swiftness, and thus by your slowness you would lose your union. Further you should bend the body forward and make yourself small, so that on approaching the adversary you can take all the opportunities of defence and attack with little movement. Your body must not be bent to the inside nor the outside, except when you are within distance, when it must be bent to the one side or the other or go straight according to the movements of your adversary. You must try to use your sword in such a way, that it is so near your adversary's sword that it appears to be bound to it when it moves, and so it cannot move without being followed, in brief so that the swords are always united. When the swords are far apart it is a sign that a time has been lost; to approach then would be dangerous, and if you continued you would be hit; in such a case it is better to retire swiftly and return again to the position of advantage. As there are several methods of advancing, some more subtle than others, we shall begin with the one which is first practised, and treat of each one separately in order according to the different principles involved in then. |
[155] PER INTENDERE COME SI DEVA OPERARE CON LI PIEDI, SPADA, E CORPO, NEL ANDARE CONTRA il nimico senza fermarsi. VOLENDO VN’ HVOMO MOVERSI PER ANDARE CONTRA il suo nimico dee cominciare à portare li piedi di passo ordinario, come per apunto si portano nel caminare, se bene con alquanta maggiore prestezza di moto, & passi più breui, non douendosi mai agrandire esso passo se non quando la punta della spada gionge al corpo auerso non però hà da essere uiolente, perche douendosi continouare sino, che’l corpo sia gionto aldetto corpo auerso, restaria per la detta uiolenza talmente scomodato, che non potria leuare il piè di dietro con quella prestezza, che si ricercarebbe, & così con l’ essere tardo restarebbe anco disunito, deue l’ huomo oltre diciò auertire di piegare il corpo inanzi, & farsi picciolo in quel tempo che uiene approssimandosi al nimico acciò che la spada possa con poco moto pigliare tutte l’ occasioni sì in diffesa, come in offesa, nedeue il corpo piegare in dentro ne in fuori, se non all’hora quando si è gionto in distanza, che si hà da piegare per l’una, ò per l’altra parte, ouero andare diritto secondo l’ operatione nimica. Si ricerca in olrre di adoperare la spada in guisa, che l’ effetto dell’una, & dell’altra sia tanto uicino, che quando la nimica si moue para essere legata dalla propria, & che una non possa andare senza essere seguita dall’altra, & in somma, che siano sempre unite, perche allontanandosi una dall’ altra saria segno che ’l tempo fosse perduto, che à uolersi poi auicinare si corerrebbe pericolo, & ne lo andare inanzi si restarebbe ferito, nel quale caso saria meglio ritornare con prestezza indietro, & rimettersi un’ altra uolta al uantaggio. Mà perche ui sono più maniere di andare contra il nimico più sottili l’ una dell’ altra si cominciarà da quella che si dee prima essercittare, & con quest’ ordine si parlara di ciascuna di loro separatamente per le diuerse raggioni, che in esse si trouaranno. |
[6] Du mouvement du corps. LE mouvement du corps est aussi avantageux pour celui qui y prend garde. A savoir qu’on le courbe quelque peu en avant, et se fasse petit quand on s’approche de l’adversaire, afin qu’avec moindre mouvement l’épée puisse en l’occurrence avoir son effet aussi bien en la défense qu’en l’offense. Aussi il ne faut plier le corps ni au-dedans, ni au dehors, jusqu’à ce qu’on soit parvenu à la droite distance, en laquelle on se mettra de l’un ou de l’autre côté selon l’exigence, ou poussera tout droit en avant, selon que l’opération de l’adversaire en donnera l’occasion. Du mouvement de l’épée. L’Epée doit toujours regarder celle de l’adversaire, en sorte que les effets de l’une et de l’autre soient toujours proches, que quand celle de l’adversaire se meut, on puisse aussitôt la serrer, ou que l’une ne puisse se mouvoir sans l’autre. En somme qu’elles soient toujours unies. Car quand l’une serait trop éloignée de l’autre, ce serait signe qu’on aurait perdu le temps, et on ne pourrait derechef s’y approcher et remettre sans danger. Car en s’avançant on pourrait facilement être atteint. Dont mieux vaut en telle occurrence, se retirer en hâte, et reprendre un autre avantage. Mais d’autant qu’il y’a plusieurs sortes et manières d’approcher l’adversaire et de le prendre avec avantage, s’en montrai les principales tant par écrit et information, que par des figures. | ||||||
[5] The first method in attacking without a pause. In advancing against an adversary in whatever guard, you must realise his weak and his strong part, the part covered and the part uncovered; you should place your sword in the line which is weaker and more uncovered, beginning with the arm extended and the sword straight in such a way that on reaching his point your point is somewhat higher and stronger, but without moving your point; the nearer you are to his blade the better, taking care not to touch it. Keeping your arm steady you should glide along his blade to his body, without ever leaving the blade, and bring your hilt to the place where your point had begun to penetrate his; you must try to keep his point always underneath, which may be done with little difficulty if you are in tierce or quarte directed towards the adversary's body; if you are in prime or seconde, although you cannot control his point above, you can still do so on one side or the other according as his point is more to the inside or the outside; in this case you should run along his blade, as explained in such a way that as you advance your hilt must approach the spot where your point was before. This running along his blade with your hilt must be accompanied by a continued advance, without withdrawing the arm, thrusting with violence or rushing, whatever may happen. In brief the method of proceeding is to be secure that, while your adversary's point is in prime, you are always stronger, and if he tries to thrust your sword away, his point will be lifted out of line; when it is lifted your body, which is in motion, will always pass on before his sword can return. If your adversary tries to retire and break ground, you will not be able to penetrate his point; then it will be convenient to take the time of his withdrawing in order to force your sword, and to disengage with the wrist only, without stopping or moving your arm and making only a small circle with the point; by continuing your advance you will in this way exclude his sword without bringing your own out of line, and if he returns to force your sword, you will be so far advanced that there will be no need to disengage, if on the inside, since by simply changing the hand to seconde and lowering the body you could go on to hit, and would do so before he could push your sword away; if on the outside, you could hit by changing to seconde, lowering the body and disengaging your point below, without dropping the hand; this would lead to a hit in the adversary's right side at the moment when he expected to push your sword away. In this manner your body would have passed on the outside without any danger. This method serves equally when your adversary lets your forte penetrate and then tries to push it away in order to defend himself. It sometimes happens that the adversary tries to push your point away, when it is beginning to penetrate; then it is well to disengage, for, as we have often said, there is no strength in the point. Also it may happen that the adversary disengages, and attacks your point on the other side, leaving the body, and in order to do so before your forte penetrates, he advances his body; in that case, seeing his intention, you should counter-disengage before his sword touches your point, for all disengagements made after the adversary has touched your sword are always more dangerous, since they are made in a bad time; the greatest difficulty in the present method consists in this, that you must always be near the adversary's sword and disengage before your sword is found by his; nor must you hold your sword rigidly thinking in that way to offer greater resistance, because it will be found before you disengage. The strength of the sword must be based on your position and not on the force of the arm or wrist. If you follow our method, you will always be prompted to take the opportunity of disengaging or not according to the occasion. We must consider another case which often arises, that is when the adversary changes his guard and breaks ground, so that you cannot hit in that time. Still you must not stop, although there would be no danger in doing so and then returning with the method best suited to meet his change. Yet it is far more expedient that your point, which has already begun to penetrate should follow his point, but only by a movement of the wrist, the arm being kept steady; you should push on and run along his blade to the body. Thus you will deprive your adversary of the power of doing anything; if he tries to make any other change he will be hit during the change, and all because you will be so close to him that he cannot break ground; it follows naturally that you, who are advancing, move more quickly than he, who is retiring. If you wish to stop when your adversary retires and changes his guard, he can always change and break ground, whenever he wishes, so that your proceedings will come to nothing. Therefore you should never stop, if you understand the true method; but if by chance you lose the advantage, then it would be necessary to stop and form a new plan. This method of working with the arm extended and the sword straight, as explained and as will be illustrated in a plate in its place, against some guards formed on the same principles requires subtlety of judgment and an understanding of the relative heights of the hand and the point and of the weakness and strength of the method. Since with this method you begin to seek your adversary's sword when out of distance by extending your arm, in order to approach within distance with greater security, it appears to help the adversary by giving him time for consideration and forming his plans. In this respect other forms will be found more expeditious. Still this method is necessary and helps greatly to the understanding of weak and strong parts, the difference between large and small movements, the exactness of the position of the arm, the preservation of an advantage, and of the defence, which should be observed even when hitting. Therefore as a method so important and necessary we have placed it first. But subsequently we shall treat of a guard formed high, with which you may attack your adversary resolutely and hit whatever he does or whatever his capacity. |
DELLA PRIMA REGOLA DI ANDARE A FERIRE IL NIMICO SENZA fermarsi. QVANDO L’ HVOMO UUOLE ANDARE CONTRA DEL suo nimico posto in quale si uoglia guardia deue hauere cognitione della parte debile, & forte coperto, & scoperto di esso nimico, & mettere la spada dalla detta parte più, debile, & più scoperta cominciando col braccio steso, & con la spada in retta linea situandola in guisa, che giongendo con la punta alla punta nimica la sua sia alquanto disopra, & tale che si conosca hauerla più forte, & tutto senza fare moto alcuno di essa, & quanto più uicina sarà alla lama [156] nimica tanto meglio sarà, douendosi però guardare di toccarla niente, ma tenendo fermo il braccio andare scorrendo il filo di detta nimica sino al corpo auerso senza mai abbandonarla, & in quel luogo, oue la propria punta comincia à penetrare la nimica, colà si dee ritrovare il finimento ne lo ariuare alla detta punta nimica, laquale, si hà da studiare di tenere sempre disotto, potendosi, ilche si può anco non molto difficilmente quando l’huomo si troua nella terza, ò nella quarta che guardi uerso il corpo, & trouandosi anco nella prima, ò nella seconda se ben non si può aquistarla per disopra si può nondimeno per una delle parti secondo, che la punta sarà più dentro, ò più fuori, douendosi in quel caso scorrere medesimamente il filo, come si è detto, in modo che si come si uà inanzi il finimento debba uenire approssimandosi al luogo, oue prima si hà messa la punta, & questo scorrere col proprio finimento il filo della nimica deue essere con continouare sempre inanzi senza mai ritirare il braccio, & senza slanzare mai spada, ne corpo per accidente, che uenga, & in somma la maniera dell’ operare hà da essere tale che si sia certo, che durante impresenza la nimica punta, si sia sempre più forte de lo stesso nimico, & in modo, che quando egli uolesse rispingere, la detta sua punita fosse neccessitata à leuarsi di presenza, perche leuandosì il proprio corpo dell’huomo, che è già incamino passarà inanzi sempre prima, che quella possa ritornare, & quando il nimico si sarà uoluto ritirare, rompendo di misura il corpo non potrà penetrare la punta, talche in quel mentre, che l’ esse di misura sarà conueniente pigliare quel tempo dell’ uscire, che esso fà per sforzare la spada, & all’hor cauarla col solo nodo della mano, mà senza fermarsi punto & senza mouere il braccio con fare poco giro della punta, & con continouare oltre, che così si escluderà la nimica di fuori senza deuiamento di spada, con andare solamente diritto à ferire & se esso nimico tornasse à sforzare la spada l’ huomo saria all’ hor tanto inanzi, che non hauria bisogno di cauatione se fosse di dentro, perche potria uoltando solamente la mano in seconda, & abbassando il corpo andare à ferire, & lo faria prima, che l’ altro potesse rispingerla, & se fosse di fuori potria andare à ferire con uoltare pure di seconda, abbassando il corpo & cauando la punta disotto senza abbassare niente la mano, che ferirebbe nel destro fianco nimico nel tempo medesimo che l’istesso nimico credeua rispingerla, & in questa forma saria il proprio corpo passato perdifuori senza pericolo alcuno, laquale raggione serue medesimamente quando l’ auerssario lascia penetrare il forte della spada, & poi la uuole rispingere per diffendersi; mà suole auenire, che tal uolta il detto auerssario uà à rispingerla nel tempo, che la punta del nostro che passa comincia à penetrare, doue che all’hor è ben fatto di cauare, perche, come, molte uolte si è detto nella punta non è forza alcuna, & anco suole accadere, che il nimico caua, & uà alla punta dall’ altra parte lasciando il corpo, & perpoterlo fare prima, che l’ auersa spada penetri col forte, si allontana col corpo, nelquale caso uedendosi l’ effetto si dee contracauare inanzi che’l nimico la tocchi, perche tutte le cauationi fatte doppo, che’l detto nimico hà tocato la spada sono sempre pericolose, come non fatte in tẽpo buono, & la maggiore difficoltà della presente regola sta in questo, perche si dee sempre essere prossimo alla spada, & fare la cauatione prima, che la propria spada sia trouata dalla detta nimica, ne si dee tenere la spada in mano con uiolenza, credendo di potere in tal modo fare maggiore resistenza, perche uiene trouata prima, che la si caui, & la galiardezza della spada in tal caso si hà da fondare sopra la raggione del sito, & non sopra la forza del braccio ne del polso; & oprandosi in questa maniera, che noi mostramo sarà sempre l’ huomo più pronto à pigliare l’ occasione in tempo secondo l’ opurtunità del cauare, ò nò. cade ancora nella consideratione un’ altro caso solito ad’ interuenire spesse uolte, cio è che ’l nimico nell’ andare muta guardia, & rompe di misura in modo che non si può ferire in quel tempo, pure non è da trattenersi per questo, ancorche fosse cosa fuori di pericolo & poi ritornare con quella raggione, che fosse più à proposito, doue il nimico si fosse mutato, non dimeno è molto più espediente che la punta, laquale hauea già cominciato à penetrare, seguiti la punta nimica doue lauà, mà solo col nodo della mano, & tenendo fermo il braccio, & proseguen- [157] do sempre inanzi con scorrere il filo doue sarà, & andare fino al corpo, perche così si toglierà al detto nimico il potere fare cosa alcuna, ilquale se uorà fare altra mutatione restarà ferito nel mutarsi, & tutto perche seli sarà tanto addosso, che non potrà rompere di misura, & la raggione naturalmente si uede perche più presto uà quello, che uà inanzi di quello che retrogrado camina, & così chi si uolesse fermare ne lo ritrarsi, del nimico mentre che ei fà la mutatione, potria esso nimico tornare sempre à mutare & rompere di misura ad’ ogni sua uoglia in modo che l’ operatione sarebbe stata nulla, & però non bisogna fermarsi mai, quando si sà conseruare il debbito modo, mà se per suentura si perdesse il uantaggio sarebbe all’hor neccessario fermarsi, & pigliare nouo partito. Mà questo modo di operare col braccio così longo, & la spada tanto diritta come disopra si è discorso, & come à suo luogo si mostrarà in figura contra alcune guardie opposte con li effetti nascenti da simile operatione, non sarà altro che un rafinare il giuditio, & aquistare la cognitione della maggiore altezza, & bassezza; della mano, & della punta, & come si faccia più debile, & più forte la raggione, & perche la detta regola pare, poiche comincia ad’aquistare la nimica molto lontano per la distesa del braccio detta disopra per ilche uiene ad’entrare nella distanza più sicuramente, che anco gioui all’ auerssario hauendo più spatio da giudicare, & pigliare nouo partito. Si trouarà, per tale rispetto, altre forme più spedite, & più breui nondimeno detta regola è neccessaria, & agiuta grandemente alla cognitione de’ debili, & forti, delle differenze trà il moto grande, & il picciolo, & similmente della giustezza del braccio, conseruatione del uantaggio, & diffesa, laquale si dee sempre conseruare anco nel ferire & perciò come cosa tanto considerabile, & neccessaria l’ habbiamo posta prima dell’ altre, mà suseguentemente si raggionarà di una guardia alta formata per andare continouato al nimico risoluto di ferirlo faccia esso nimico ciò che uoglia, & ciò che sappia. |
[7] Générale instruction, Comment on se comportera en telles approches. Il faut que celui qui veut approcher son ennemi, en quelconque garde se tienne avec un certain avantage, remarque, en quel endroit il est plus fort ou plus débile, découvert ou couvert. Et après il cherche avec le bras étendu, et l’épée forte au lieu débile et découvert: en portant la pointe en ligne droite sur la pointe ennemie, quelque peu plus haute, afin qu’il soit assuré qu’il y soit le plus fort. Chose qui doit être faite sans aucun mouvement de la dite pointe. Et tant plus qu’on s’approche de l’épée ennemie, mieux se sera: mais qu’on ne la touche: ainsi, avec le bras ferme on suit le fil de celle-ci, jusqu’au corps, sans s’en détourner, en sorte qu’en s’approchant on mette la garniture au lieu même auquel on avait auparavant tenu la pointe. Et il faut tacher d’avoir toujours la pointe de l’adversaire au-dessous. Et si on ne pouvait l’obtenir, il faudra la tenir au côté de dehors ou dedans, suivant le fil de l’ennemie, en sorte, que comme nous avons dit, en s’avançant, on mette la garniture au lieu où on avait tenu la pointe. Laquelle chose étant de grande importante sera déclarée par plusieurs et diverses figures. | ||||||
[6] In this plate we show the method of taking the first advantage in advancing with resolution against your adversary without waiting for a time. If on your approach the adversary offers a time, you should take it or any other opportunity that is presented, following on to the body without stopping. The advantage of this position consists in the fact, that your sword is held above, for two reasons: the first, because it is better to be above than below, the second because the man whose sword is above is quicker to move and form a plan. In this superior position you should continue to the adversary's body, running along his blade, and in advancing bring the hilt of your sword to the spot where your point was first, without moving your point away from his blade, until you hit. If his sword had chanced to be in tierce at an angle or in quarte, you should have begun in this way, but without running along his blade; you should attack with your blade in a straight line from its point to your body and hit in gap made by that angle both on the inside and on the outside. Other plates will follow, which will show what may arise from this advantage, but they will not be very many for the sake of brevity; the principle and most necessary ones will be included, from which the remainder may be understood. Also, some remarks will be added in the texts. |
CON QVESTA FIGVRA CHE SEGVE NOI MOSTRAremo il modo di pigliare il primo uantaggio nelo cominciare ad’ andare di risolutione contra il nimico senza aspettare tempo, doue prima diremo, che se nelo andare il detto nimico farà tempo si dourà pigliare, & anco qualunque occasione, che si presentarà con seguire senza fermarsi sino al corpo nimico; di poi che ’l uantaggio in questa figura è di quello, che si uede hauere la spada disopra per dui raggioni l’ una perche l’ essere disopra è meglio che l’ essere disotto, l’ altra perche il sito di quello che è disopra è più pronto in andare & pigliare partito, & in simile caso il detto superiore di sito deue andare seguittando inanzi sino al corpo nimico scorrendo quel filo, & nel caminare oltre andare approssimando il finimento al luogo, oue che prima teneua la punta, senza slargare mai essa punta dalla nimica persino, che la ferisce, & se per sorte la spada fosse in terza angolata, ouero in quarta, dourebbe anco cominciare in questo modo guardandosi solamente dal scorrere con la punta la lama nimica, mà andare continouando col filo per retta linea dalla punta al corpo à ferire per quello uacuo fatto dall’ angolo tanto di dentro quanto di fuori. Seguittaranno alcune altre figure ancora de mostratrici di quello, che può nascere dal detto uantaggio mà non in tanto numero per più breuità nondimeno si poneranno le più principali, & più neccessarie da quali si haurà intiera cognitione del resto, aggiongendo similmente alcuna cosa in iscritto. 109. |
[8] Comment on prendra le premier avantage. QUand en approchant, l’ennemi donne un temps, il faut l’accepter avec toutes les occasions qui pourraient s’y présenter, lesquelles il ne faut laisser passer, jusqu’à ce qu’on ait trouvé le corps de l’adversaire. Et est ici, comme on le voit en la figure l’avantage de celui, qui à son épée au-dessus, pour deux raisons. Car premièrement il vaut mieux toujours, se tenir au-dessus qu’au-dessous. Secondement est aussi la situation supérieure plus prompte et commode pour tous les changements survenant. Dont celui qui peut avoir le dessus doit toujours suivre le fil de l’épée ennemie, jusqu’à porter sa garniture là où il a tenu l’épée. Sans se détourner de la pointe adverse, jusqu’à ce qu’il lui ait donné le coup. Et si d’aventure l’ennemi se tenait en telle garde, qu’il faisait un angle de son épée; il poursuivra de même manière, mais non point par le fil de son épée, ainsi en mettant la pointe de son épée, en ligne droite par le circuit que l’angle fait, soit par dehors ou par dedans, jusqu’au corps de l’adversaire. Ce qui en outre pourrait résoudre de cet avantage, pourrait être montré en plusieurs autres figures. Mais nous en proposerons seulement les principales desquelles le lecteur prudent, et amateur de notre art comprendra facilement le reste. | ||||||
[7] The hit in quarte here represented has followed from this first advantage. You have run along the adversary's blade, bringing your hilt to the spot where your point began, and reached the part shown, because your adversary was too slow in moving and unable to defend himself or do anything but draw back his body, without success. After getting control over his point, with the right foot forward, you have passed with the left foot and then with the right, and so pursued your victory right to his body. You would have done the same, if you had begun on the outside, the only difference being that your sword would have been in tierce instead of quarte, while your adversary's sword, instead of being driven upwards by the force of your sword, as in the plate, would have been driven downwards by the tierce, and your point would have hit below your own hilt; in that position it would have been stronger and would have given more protection to your lower parts. |
[158] QVESTA FERITA DI QVARTA, CHE SEGVE E NATA DAL PRImo uantaggio ueduto, perche il ferittore è uenuto scorrendo il filo della nimica con portare il finimento, doue prima haueua cominciata la punta, & è uenuta sin doue si uede, similmente ancora, perche il ferito è stato troppo tardo nel mouersi, & però non hà potuto diffendersi, ne fare altro effetto che di dilongare il corpo, ne hà potuto saluarsi perche il detto ferittore dopò l’hauere, col destro piede inanzi, aquistata la punta è passato col sinistro, & poi soggionto col destro & così proseguita la uittoria col corpo sino al corpo nimico, & il medesimo haurebbe fatto ancora, se hauesse cominciato dalla parte di fuori, ne ui sarebbe stata altra differenza se non della spada, che addesso è in quarta, & all’hora sarebbe stata in terza, & si come la nimica nella medesima figura estata da questa parte sospinta in sù dalla forza di quella, che hà ferito, così per contrario dall’ altra parte sarebbe dalla terza stata respinta in giù, & la punta del ferittore haurebbe ferito più basso del proprio finimento, perche sarebbe proposito, più forte, & haurebbe tenuto più coperta la parte di sotto. 110. |
|||||||
[8] The next hit has also arisen from the same initial advantage, and in this manner: in advancing you were running along your adversary's blade, having already brought the left foot in front; he has tried to parry by forcing your sword and drawing back his body; feeling the pressure, you have changed your hand to seconde and given way to his sword, which has gone to the outside through meeting no resistance, and all the further out of line because you have lowered your body. You have kept the hilt of your sword at the same height against his faible. The angle formed by the seconde has carried your point to a hit. If you had attacked on the outside in tierce the result would have been the same. After bringing the left foot forward, if the adversary had tried to parry, you would have again changed your hand to seconde, put the point under his right arm, keeping the hilt at the same height, lowered your body, followed on with the right foot and thus made the same hit. But if you had begun on the inside and the adversary had begun to parry by breaking ground, as he could you should then have disengaged with the wrist on the outside in tierce, and gone on until you reached his body. If again he had proceeded to parry, as he might, without breaking ground, you should hit in seconde below. But if he parried at the point of your sword, if you had begun on the outside, you should disengage in quarte on the inside, and if he again parried and drew back, you should turn the hand again and hit in seconde. If at the beginning the adversary disengaged in order to hit, you should simply go on in the straight line in tierce or in quarte, according to whether you were on the outside or the inside, and you would hit in the time of his disengage. When the adversary disengaged, if he had not advanced but defended himself by breaking ground whether on the inside or the outside, you would have been sure of hitting in that second time. It might happen that at the beginning of the movement he disengaged and broke ground with the idea of engaging your faible; in that case you should counter-disengage, before he touched your point, and follow on in the straight line, so that if he makes a double disengagement, as he might, you could defend with little movement without disorder. If after his first disengagement he returns to the parry, you should hit above, as we have explained since all he could do would be to use his left hand, which would cause only slight disturbance or might even give you an advantage. All these rules apply against a tierce or a low quarte, whether straight or at an angle. Afterwards we shall treat of the prime and seconde, but we have put these first, as being more usual. |
[159] Q'VEST’ ALTRA ANCOR LEI E PVR NATA DAL MEDESIMO primo uantaggio come l’ antecedente, & si è fatta per questa uia ciò è, perche ne lo andare il ferittore scorrendo il filo nimico poiche era già col sinistro piede passuto, il nimico hà uoluto parare sforzando la spada, & all’argando il corpo indietro, laquale forza sentita, hà il detto ferittore uoltata la mano in seconda cedendo alla nimica, laquale è andata tanto più fuori per non hauere trouata resistenza & tanto maggiormente è uscita di presenza per l’ abbassare del corpo del detto ferittore, ilquale è restato nella eguale altezza, che era col finimento al debile nimico, & l’ angolo formato dalla seconda hà portato la punta à ferire il che non meno sarebbe à uennuto, se esso fosse andato di fuori con la terza, & che se dopò l’ essere passato col piè sinistro il nimico hauesse uoluto parare, esso ferittore haurebbe anco uoltata la mino in seconda, & messa la punta di sotto del destro braccio nimico, & tenuto il finimento nella medesima altezza, con abbassare il corpo, & seguire inanzi col destro piede, & cosi hauria fatta la stessa ferita che si uede; mà se per sorte nel cominiciare dalla parte di dentro il nimico cominciasse ancor lui à parare rompendo di misura come potrebbe fare, si dourebbe all’ hor cauare col nodo della mano di fuori di terza continouando inanzi sino che si giongesse al corpo, & se anco esso nimico andasse à parare, come potrebbe, & non rompesse di misura, si dourebbe ferire di detta seconda di sotto, ma se ’l andasse à parare nella punta in caggione, che si fosse cominciato di fuori douria il detto ferittore cauare di dentro di quarta, & sel tornasse a parare con dillongarsi si deuria uoltare la mano, & fare la ferita pur di seconda; mà se quando si comincia esso nimico cauasse per ferire non dourebbe fare altro il ferittore che andare delle prime rette cio è terza, è quarta [160] secondo, che si trouasse di fuori, ò di dentro, che ferirebbe nel tempo della cauatione, & quando in quello cauare non fosse uenuto inanzi si potria dal medesimo ferito andare alla diffesa con rompere di misura così essendo di fuori, come di dentro, certò con tuttociò il ferittore di ferire nel secondo tempo & perche potrebbe anco accadere che ’l nimico nel cominciare andare cauasse, & rompesse di misura per aquistare il debile di questo che uà, si dourebbe in tal caso contracauare prima che’l nimico la toccasse, & seguire il suo uiaggio di retta linea, accioche se ’l suo nimico ricauasse, come potrebbe, si fosse diffeso con picciolo moto, & senza disturbo, mà se nel fare la prima cauatione tornasse à parare, si douria ferire disopra come si è detto, perche non può succedere altro, non potendo esso nimico adoprare se non la sinistra mano, laquale potrebbe solamente fare qualche poco di perturbatione, quando però il ferittore non sene ualesse ancor lui, Queste raggioni tutte seruono contra la terza, & la quarta bassa siano diritte, ò angolate, doppo lequali si trattarà della prima & seconda mà si è trattato di queste prima, come assai più ordinarie. 111. |
|||||||
[9] The next plate shows how to take advantage of an opponent, who stands with a low guard and with his upper parts held back in order to protect them, since they are more exposed. You have the advantage of the higher position, and let your point run along the adversary's blade, keeping it above his blade and gradually raising it; as the point is raised so the hilt is lowered, so that when your hilt reaches his point it is in the position of the point, as seen at present; thus you run along the blade until you reach his body. If the adversary disengages, you will make no change, nor even bring your hilt any lower, but hit without any other defensive movement, realising that his point is excluded by reason of the shortness of his sword and the length of time of his disengagement, since he is below, and wishes to reach the upper line. Finally the point of your sword achieves the same result, as if he did not disengage. In order that the position may be better understood, in the next plate we shall show the hit which follows from this advantage, from which you will understand another result which may arise. |
CON LA SEGVENTE FIGVRA SI VEDE COME SI DEBBA PIGLIARE il uantaggio cõtra uno, che stia in questa guardia bassa, & che tenga le parti superiori lõtane per saluarle, come molto scoperte. Diciamo dunque, che quello, che è disopra, & ilquale hà il uantaggio, uà scorrendo cõ la punta il filo della nimica in modo, che la detta sua punta, non passa mai disotto la lama di essa nimica, mà uiene alzandola sopra il detto filo della nimica, & quanto che alza detta punta, tanto uiene abbassando il finimẽto in modo [161] che quando peruiene alla punta nimica si troua essere nel luogo, oue il presente si uede la punta, & così uà scorrendo con esso la lamà sino al corpo nimico, & se bene detto nimico cauasse, il primo non sarebbe altra mutatione se non che non la sciarebbe che ’l finimento finisse di andare abbasso, mà andarebbe così à ferire cenza fare alcuno moto di diffesa, perche cognosceria la nimica essere esclusa di fuori per rispetto della breuità della sua propria spada, & per la longhezza della cauatione delo stesso auerssario, quale è disotto, & uuole uenire disopra; diciamo in ultimo, che la spada di quello, che uà fà con la punta eguale effetto di quello farebbe, se bene anco il detto auerssario non cauasse, & perche meglio, s’ intenda metteremo nella postseguente figura la ferita nascente da questo uantaggio, dalla quale si conoscerà anco l’ altro effetto, che puó uenire. 112. |
|||||||
[10] Here then is the hit in tierce against another tierce, which has followed from the advantage seen in the preceeding[!] plate. Both combatants had their points low and you were above; you have followed on, running along the adversary's blade, and raising your point and lowering your hilt as you advanced, have made the present hit and continued right to his body. The other result which we said would be illustrated is this; you may have found your hilt inside his sword, and as you advanced he may have disengaged in order to free his sword; but you would have prevented him by keeping his sword below, because your point was in line; all he could do was to try to push your point out of line, and in that he would have failed. If he had again tried to disengage, he would have effected nothing, because you would have made the same hit by a mere change of the hand towards quarte. |
ECCO DVNQVE, CHE QVESTA FERITA DI TERZA CONTRA un’ altra terza si è caggionata dall’ aquisto uedutosi nella precedente figura, quando ambi li combattenti erano con lè punte basse, & che quello che hà ferito era disopra, ilquale continouando inanzi, & scorrendo il filo della nimica, tanto come è uenuto così è andato alzando la punta & abbassando il finimento, colquale modo hà fatta la presente ferita, & seguita col corpo sino al corpo nimico. L’altro effetto che dicessimo douere essere anco rapresentato da questa figura è tale ciò è, che potrebbe essere che ’l ferittore si fosse trouato col finimento di dentro dalla nimica, & che nell’ andare, il ferito hauesse, come si è detto, cauato per liberare la spada, mà che non li fosse dal detto ferittore stato concesso tenendogliela serrata abbasso, perche la punta di esso, che andaua era in [162] presenza in modo che ’l detto ferito non poteua fare altro che procurare di spingerla fuori di presenza il che non hà potuto fare, si come anco se fosse tornato à cauare non haurebbe fatto niente, perche la medesima, che hora si uede l’ haurebbe ferito con un solo uolgere di mano uerso la quarta, che hauesse fatto il ferittore. 113. |
|||||||
[11] The next position is also a tierce, but differing from the preceeding[!] one in that the advantage has been acquired against a seconde. You have begun at a distance to hold your sword in the manner shown so that on reaching the adversary's point you have acquired the advantage without any movement of the hand or point. With this slight advantage in tierce you can go on, following his blade, without however touching it, and bringing your hilt to the present position of your point; as you advance, you should turn your hand in such a way that you are in a guard of quarte when your point makes the hit. As the point is now higher than the hand, it will then be lower; you will hit in the chest, keeping your hilt in the defensive position. In the next plate we shall illustrate the hit which you may make in this position in tierce against an adversary who makes no change. |
QVELLA CHE SEGVE, SE BENE E VNA TERZA, E PERO’ diuersa dall’ antecedente, perche hà aquistato il uantaggio contra una seconda fattasi in cotale forma ciò è perche collui, che è in terza hà cominciato di lontano à tenere la spada nel modo, che si uede, talmente, che quando è gionto alla nimica punta si è trouato essere nel detto uantaggio senza, fare moto alcuno, ne di mano, ne di punta, ilquale situato in terza per hauere aquistato quel poco, che si uede, potrà andare sempre inanzi seguittando il filo nimico, senza però toccarlo, & uenire portando il finimento uerso quella parte, oue hora tiene la punta, & quanto uerà inanzi, tanto doura andare uoltando la mano in guisa, che quando la punta sia gionta à ferire egli si troui in quarta, guardia, & si come al presente la punta, che quì è più alta della mano così all’hora sarà più bassa, & ferirà nel petto nimico mantenendosi il finimento alla diffesa, & accioche meglio s’ intenda la ferita, che può fare questo situato in terza contra un nimico, che non facesse alcuna mutatione si esprimerà nella postseguente figura. 114. | |||||||
[12] Here follows the hit referred to at the end of the last discourse, made by a quarte, originally a tierce, against a seconde and perhaps following from the advantage described. You have continued along the adversary’s blade as explained, until you have reached this position; by bringing forward the left foot and then the right, maintaining your defence with the hilt, which has approached his sword, without stopping you will go right on to his body for greater security. Or it may be that you have acquired the advantage on getting within distance, and the adversary has disengaged in order to free his sword, and withdrawn for his protection. You, being already on the move, have arrived so quickly with a counter-disengage, that he has been able to form no plans, and all because of the advantage of the continued advance. If you had been slower and not advanced in the time of his disengage, you would not have reached, and thus would have given him opportunity to parry and hit, before you arrived. |
[163] IN QVEST’ ALTRA VENENTE SI VEDRA QVELLA FERITA, che si propose nel fine del passato discorso fatta da una quarta, che prima era in terza contra una seconda, & forsi seguita da quel uantaggio, che si uidde, oue il ferittore è uenuto continouando per il filo della nimica, come si disse, sinoche è gionto à questo segno, & passando del sinistro piede, & dell’ altro con mantenersi diffeso col finimento, quale è gionto appresso quello del nimico, & così senza fermarsi andera sino al corpo auerso per maggiore sua sicurezza. Potrebbe anco essere successa dall’ hauere il medesimo ferittore ne lo entrare in misura aquistato già il uantaggio, & dall’ hauere l’ altro cauato per liberare la spada,& allontanarsi, per saluarsi, & che ’l primo, quale era già in camino sia tanto presto ariuato con la contracauatione, che ’l detto ferito non habbia potuto pigliare alcuno partito, & tutto per il uantaggio del sempre continouare del ferittote, ilquale se fosse stato più tardo nè fosse andato nel tempo della cauatione del nimico, non saria gionto à hora, & così haurebbe data oportunità al detto auerssario di parare, & ferire prima di essere lui ariuato. 115. |
|||||||
[13] The next plate shows a hit in a guard of prime on the outside under the sword against another seconde. You have begun with your sword extended and have advanced to engage, holding your point against his sword on the inside; you have reached his point with the right foot and followed with the left. The adversary has tried to disengage in order to hit in that time over your sword on the outside, but by bringing forward the right foot in the same time and bending your body you have carried your point under his sword arm and hit by turning the hand from tierce, into a guard of prime. In this way you have guarded against the danger of his making of[!] feint of disengaging, and have excluded his sword in such a way that he could not bring his point into presence. The result is due to the fact that the adversary has allowed your sword to advance too far before disengaging; if he had disengaged on your first approaching his point, you could only have counter-disengaged and hit in quarte. |
[164] ET QVESTA, CHE SEGVIRA ANCOR LEI DIMOSTRARA VNA ferita di prima guardia di fuori sotto la spada contra un’ altra seconda caggionatasi dall’ hauere quello, che hà ferito cominciato con la spada distesa, & andato à trouare il nimico tenendo la punta contra la spada auersa dalla parte di dentro in modo, che è ariuato alla nimica col destro piede, & foggionto col sinistro, che perciò hà il detto nimico uoluto cauare per ferire in quel tempo sopra la spada di fuori, mà il ferittore passando ne lo stesso tempo col destro piede, & col corpo curuato hà portato la punta sotto il braccio della nimica, & ferito con hauere uoltata, la mano di terza nella prima guardia, declinando per tal uia il pericolo prima, che esso nimico habbia finita la cauatione, & escludendo la spada auersa di fuori in modo, che non habbia potuto uenire con la punta in presenza, & tutto riuscitoli per hauere il detto nimico lasciato andare troppo inanzi la sua prima, che habbia cominciato à cauarla, perche se l’hauesse cauata nel primo auicinarsi alla punta non di darebbe dal ferittore potuto fare altro che contracauare, & ferire di quarta. 116. |
|||||||
[14] The second method of attacking the adversary without a pause. The most necessary guard in this method is a high guard of tierce, formed with the whole chest facing the front, the points of both feet towards the adversary, the body bent forward, the sword hand near the face, and the point of the sword suspended in the air and advanced, but not so far advanced that it may be engaged by the adversary before he is within close distance. With this method and this guard you must advance against your adversary with natural steps and towards the outside, until your body is so far outside his sword, that your sword too is in that part without any movement of the hand. The sword must be kept motionless, and as you approach the body lowered, so that the point also will be brought lower, and so far that when your hilt has reached his point your point will be in line. On moving to hit you should not lunge but approach your body to the adversary's. If he changes his front or moves his point to prevent its being left out of line, you should take that time, place your sword on the inside, without extending the arm and keeping both sides equally advanced, and bend the body so far forward that your point comes into presence. You must avoid dropping the arm or hand, since the hand must face his point until the whole body has passed, whether on the inside or on the outside. You should always begin on the outside, whatever your adversary's guard. Although when within distance you should be prevented from passing outside by your adversary's changing his line or front, you should still, having reached his sword, go on, resolutely straight to the body. Even if your adversary's point is low and pointed towards the ground, you must still lower yourself until the forte of your sword excludes his sword on the one side or the other, but without moving the arm. But if his sword is low and on the inside, as you lower the body to reach your position you must carry the right side back in order to bring the body out of line, so that if the adversary disengages he could not reach your body while you are lowering it, and in order that you may go straight on to hit without defending. With this guard we must warn you against disengaging, except when the adversary raises his sword in order to engage yours, when it would be convenient; but it should be done without movement of the sword or arm, and with a slight turn of the body only, keeping back the right side; in this way your sword hand will be drawn back, so that the adversary will not reach. At the same time you should carry your left foot across, so that your sword will be brought outside without being moved, and your body will be protected from the adversary's hit, whilst making this turn. If on the other hand you changed your front and did not move to the outside, you would expose yourself on the inside. Moreover as you move to the outside, your adversary might raise his sword to parry, which would be an opportune moment to dash under his sword, turning your hand and keeping it at the same height. When this guard is well formed, the only weak points are the inside and the face, but as the hilt is close to the face, it can readily be defended. Also, as the lower parts with this guard are distant, they are in no danger, except from feints which the adversary may make; if he feints on the inside, in the time of your swords dropping to parry, he may lower himself and hit below by passing. But if you are careful not to move your arm in parrying feints, but rather to bring the body down to that part, your hilt will parry of itself without moving the sword; if your adversary tries to pass, he will be hit, because your point can reach any part down to the ground, before he has passed. On the other hand if your arm falls or is extended, you will then certainly be hit. As to cuts, with this guard they can do little harm, for they can attack only half the head, and your hilt is very near that part. Cuts cannot reach below, nor can they strike the sword in order to disorder it. Therefore this method is very good in attacking without a pause, and so much the better as the sword is secure from being engaged by the adversary. But if you pause it is not so good, since you may easily be you changed your front and did not move to the outside, you expose yourself on the inside. Moreover as you move to the outside, your adversary might raise his sword to parry, which would be an opportune moment to dash under his sword, turning your hand and keeping it at the same height. When this guard is well formed, the only weak points are the inside and the face, but as the hilt is close to the face, it can readily be defended. Also, as the lower parts with this guard are distant, they are in no danger, except from feints which the adversary may make; if he feints on the inside, in the time of your swords[!] dropping to parry, he may lower himself and hit below by passing. But if you are careful not to move your arm in parrying feints, but rather to bring the body down to that part, your hilt will parry of itself without moving the sword; if your adversary tries to pass, he will be hit, because your point can reach any part down to the ground, before he has passed. On the other hand if your arm falls or is extended, you will then certainly be hit. As to cuts, with this guard they can do little harm, for they can attack only half the head, and your hilt is very near that part. Cuts cannot reach below, nor can they strike the sword in order to disorder it. Therefore this method is very good in attacking without a pause, and so much the better as the sword is secure from being engaged by the adversary. But if you pause it is not so good, since you may easily be thrown into disorder by the adversary, unless you resolve to see your left hand. |
[165] DELLA SECONDA REGOLA DI ANDARE A FERIRE IL NIMICO SENZA FERMARSI. LA PIV NECESSARIA GVARDIA DI QVESTA REGOLA E una terza alta formata col corpo in prospettiua dimostrante tutto il petto, & che tiene ambe le punte de’ piedi uoltate uerso il nimico, col corpo curuato inanzi, la mano della spada appresso la faccia, & con la punta sospesa nell’ aria inanzi, mà non però tanto, che detto nimico la possi trouare, se prima egli non sia gionto nella misura stretta. L’ osseruattore anco di questa regola, & di questa guardia hà, nel andare contra del suo auerssario, da caminare di passi naturali, & dalla parte esteriore, sino che il corpo sia uscito tanto fuori della nimica, che anco la spada sia uscita in quella parte senza fare alcuno moto di essa ne di mano, douendosi tenerla sempre immobile & quanto che uiene approssimandosi al nimico tanto hà da abbassare il corpo, acciò che la punta uenga ancor lei ad abbassarsi, & tanto che come esso osseruattore ariua col finimento alla punta nimica sia la propria spada ariuata con la punta in presenza, & [166] dee nell’ andare à ferire non slongare il braccio, mà andare col corpo sino al corpo nimico, & se per caso l’istesso nimico uoltasse la prospettiua, ouero la punta per uietare l’ andarli di fuori deue all’ hora pigliare quel tempo, & mettere la spada di dentro senza slongare il detto braccio & mantenendosi inanzi con l’ uno, & l’ altro fianco dee piegare il corpo tanto, che la punta gionga in presenza con auertire di non abbassare nè il braccio nela mano douendo stare quella alla punta nimica sino che tutto il corpo sia passato tanto di dentro come di fuori, deue cominciare nondimeno ad andare sempre perla parte di fuori, sia pure esso nimico inquale guardia si uoglia, & se bene anco il detto asseruattore nell’ ariuare in misura non potesse per essere impedito dall’ auerssario andare di fuori, quale hauesse uoltata la punta, ò la prospettiua, come si disse, deue con tutto ciò, gionto che sia alla spada, ò per l’ una, ò per l’ altra parte, andare risolutamente, & dirittamente al corpo, & ancorche la punta auersa fosse bassa, & guardasse uerso terra, non hà da restare di abbassarsi almen tanto, che ’l forte della propria sua spada non escluda la nimica di fuori, ò per l’ una, ò per l’ altra parte pur senza moto di braccio, mà se la detta spada auersa fosse bassa, & dalla parte di dentro, douria secondo, che uà abbassando il corpo per giongere al destinato segno portare anco il destro fianco indietro per fare una sfuggita di corpo, affine che se il nimico cauasse non lo trouasse nel tempo di quello abbassarsi, si come anco per potere andare diritto à ferire senza fare moto di diffesa. Auertiamo, che in questa guardia non si hà mai da cauare se non quando il nimico alzasse la punta per uenire à trouarela spada che in tal modo sarebbe à proposito, mà senza moto però ne di braccio ne di spada, con solamente fare un poco di scurzo tenendo indietro il fianco desto, che cosi la mano della spada ueria ad’ ascorttarsi, che ’l detto nimico non l’ ariuaria, & nel medesimo tempo dee pure il nostro osseruattore portarsi col piè manco per trauerso, acciò che la spada uenga per se stessa à portarsi di fuori senza essere mossa, oltre che ’l corpo uiene anco à saluarsi dalle ferite del nimico mentre che fà quel scurzo, doue per contrario se girasse la prospettiua & non siportasse fuori farebbe uno scoperto di dentro, & di più andando di fuori potria accadere, che l’ auerssario nel parare alzasse la spada, che saria tempo opurtuno di cacciarsi sotto di quella uoltando la mano, & lasciandola in quella altezza medesima, che la si trouaua. Questa guardia in somma quando è ben formata non patisce altroue, che nella parte di dentro, & nella faccia, mà perche uicino di essa faccia uiè il finimento, può ageuolmente essere da quello diffesa, & similmente perche le parti inferiori di detta guardia sono lontane non portano altro pericolo, che delle finte che possono farsi dal nimico; ilquale fingendo di dentro, può nel tempo, che la spada calla à parare abbassarsi, & ferire di sotto passando nel detto tempo, mà chi sarà auertito di non mouere il braccio in andando à parare dette finte, mà più tosto di accompagnarli il corpo in quella parte, caggionarà che ’l forte diffenderà da se solo senza moto della spada &, che se esso nimico uorà passare, che restarà ferito, perche potrà essere trouato con la punta sino à terra prima, che sia passato, doue per contrario se ’l braccio faccesse una caduta ouero si slongasse restarebbe all’hora il detto osseruattore senz’ altro ferito. Circa li taglii possono in questa guardia fare poco danno, perche non hanno se non meggia la testa da potere offendere, & à quella parte è molto prossimo il forte della spada, liquali taglii non possono ariuare di sotto, ne meno possono percuotere nella spada per disordinarla, che perciò questa raggione si rende assai buona per assalire senza fermarsi, & tanto migliore quanto che è sicura dal non poterli essere aquistata la spada dall’ auerssario, mà per fermarsi uale assai meno perche dal nimico potrebbe facilmente essere disordinata, se non si risoluesse di adoprare la sinistra mano. |
|||||||
[15] This plate represents the guard in tierce discussed above, and is to be used with this second method. it is formed high, out of line, with the hilt close to the face, the body bent and the feet close together, all with the object of keeping the sword free from being engaged except with certain danger to the adversary of being hit. Since the chest is facing the adversary, the guard can be disturbed only on the inside; in order to facilitate the defence you advance against the adversary by moving in a circle towards the outside, so that when within distance your sword and body are outside his sword; if they were not outside it would be due to some change made by the adversary. The lowering of the body with this guard varies more or less according to the relative height of the adversary’s sword. The head is near the hilt for greater security and strength, and for greater speed in advancing. |
[167] LA FIGVRA DVNQVE, CHE SEGVE RAPRESENTA LA TERZA guardia discorsa disopra, laquale si hà da usare in questa seconda regola, & laquale si uede stare alta fuori di presenza col finimento appresso la faccia curuata del corpo, & co’ i piedi gionti, & tutto affine di tenere libera la spada, che non sia trouata se non con certo pericolo del nimico di restare ferito, douendo egli uenire in stretta misura, laquale guardia per hauere anco il petto riuolto contra il detto nimico non può essere trauagliata se non di dentro, & per facilittare anco quella dittesa uà contra il nimico caminando sempre in giro uerso la parte esteriore, tanto che quando gionge in misura uiene à trouarsi col corpo, & con la spada fuori della nimica, & se pure non fosse fuori ne sarebbe stata caggione qualche mutatione fatta dal detto nimico; l’abbassare anco del corpo che fà la detta guardia è più, ò meno secondo la maggiore, ò la minore bassezza della nimica; resta similmente col capo uicino al finimento per più sicurezza, & fortezza, & per più uiuacità di andare. 117. | |||||||
[16] This high guard of tierce leads to the advantage shown in this plate. As you approach the adversary, you direct your point, and lower the body, keeping the hand and arm steady, until the point is in line. You have controlled the adversary's sword and will maintain that position, when your point hits. If, when you come into line, the adversary disengages it order to hit on the inside of your guard, you will have penetrated with your body half the length of his blade, which deprives him of the power of turning out of line or passing. The advanced position of the guard facilitates your passing below, if he attacks your sword. in order that that result may be better understood it will be illustrated in its place. |
DALLA TERZA GVARDIA ALTA PASSATA E NATO IL VANtaggio, che si uede nella figura seguente, perche detta guardia secondo, che ueniua auicinandosi al nimico è anco uenuta dirizando la punta, & abbassando il corpo affine di tenere ferma la mano, & il braccio, & che la punta uenesse in presenza, & si uede, che hà aquistata la nimica, & restarà in quel luogo, ancorche la punta sua propria uada à ferire, & se nell’ ariuare in presenza il nimico cauasse per ferire di dentro detta guardia farebbe penetrata col corpo sino à meggio la lama nimica, ilquale modo di operare è fatto per togliere [168] al detto nimico il potere girare fuori di presenza, & passare, & l’ essere così inanzi di essa guardia, mostra, che per tal uia si facilitta il passare di sotto in occasione che ’l medesimo nimico uenisse alla spada, ilquale effetto perche meglio sia conosciuto si rapresentarà in figura à suo luogo. 118. |
|||||||
[17] From the advantage acquired by this high guard has arisen the following hit; you have reached the adversary's your forte, checked your hand in that position, lowered your point, directing it against the adversary, and by carrying your head forward and below your own hand have continued your advance and hit in the throat, when his sword was high; if it had been lower, you could have hit lower by dropping your body and hand in proportion. If he had tried to parry by raising his sword, you would have disengaged below, and by turning your hand to seconde and keeping it in the same place would still have certainly hit. |
DAL VANTAGGIO, CHE HAVEA GVADAGNATO QVELLA guardia alta è nata questa seguente ferita, perche essendo quello di detta guardia gionto col forte alla punta nimica hà fermata la mano in quel sito, & abbassata la punta con dirizarla contra il nimica, & con portare la testa bassa inanzi più della propria mano, che per essere continuato sempre oltre in questo modo, hà ferito il nimico nella gola si come anco perche la nimica era alta, nondimeno se anco fosse stata più bassa; più basso similmente haurebbe ferito con abbasare il corpo, & la mano proportionabilmente, & se pure il detto nimico hauesse procurato di parare con alzare la spada, il ferittore haurebbe cauato di sotto, & uoltato di seconda lasciando la mano nel sito doue si troua, che non meno haurebbe senza dubbio ferito. 119. |
|||||||
[18] The next is a hit in quarte against an opponent who has lunged in quarte. You had engaged your adversary's faible on the outside with the high guard shown in the previous plates; he has tried to disengage and lunge in quarte on the inside in the path which appeared to him to be uncovered. But with your arm high and held back you have pressed on his faible with a guard of quarte, and by carrying the right foot forward and somewhat out of the straight line and bending the body over it, you have made a hit in the throat. By continuing with the left foot you would have passed right to his body. If the adversary had tried to turn with either foot, he would have been all the weaker, and therefore you would have hit in the straight line or in the back. |
[169] QVEST’ ALTRA, CHE SEGVE SARA VNA QVARTA, CHE FErisce un’ altra quarta, laquale si era portata inanzi per ferire à piè fermo, nata perche collui che hà ferito haueua aquistato il debile nimico dalla parte di fuori con quella guardia alta, che si è ueduta nelle figure antecedenti, & perciò l’ altro hà uoluto cauare, & ferire di quarta di dentro à piè ferino per quello scoperto, che li pareua uedere; mà il fetittore che si trouaua col braccio alto ritirato lo hà appoggiato di quarta nel debile nimico portando il destro piede inanzi alquanto fuori della retta linea, & con piegarli sopra il corpo nà ferito il nimico nella gola, & continoua oltre col sinistro sino, che passa del tutta al corpo nimico, ne meno l’haurebbe ferito, se bene anco esso nimico si fosse girato con qual piede hauesse uoluto, perche tanto più debile sarebbe stato, & perciò l’haurebbe ferito nella giustezza ò nella schiena. 120. |
|||||||
[19] The next is a hit in seconde made by passing underneath with the body on the outside, against a guard turned somewhat towards quarte. You were in a high tierce, with the hilt near your face and advancing towards the outside; the adversary in tierce in a straight line, seeing you coming, raised his point to impede your sword and cover himself above. Being already within distance you have left your hand at that height, turned to seconde, before he could reach your sword, and by bending your body as far forward as possible have passed, With the head so far advanced as to penetrate the whole length of his blade; thus you have hit, and the adversary has been unable to defend, nor has had time to bring his sword back into line or to turn his body. |
[170] MA QVELLA, CHE VERA APPRESSO SARA VNA FERITA DI seconda, & col corpo che passa di sotto dalla parte esteriore contra una mano alquanto riuolta uerso la quarta, caggionatasi, perche quello che hà ferito si ritrouaua nella terza alta col finimento appresso il uiso, come si uidde, & ueniua caminando oltre per andare dalla parte di fuori; & perche l’ altro, che staua in terza retta, uedendolo uenire, hà alzata la punta per impedire la nimica, & coprirsi disopra, ma il ferittore, ilquale già era in misura lasciando la mano in quella altezza hà uoltato in seconda inanzi che ’l nimico habbia potuto ariuare alla spada, & piegando quanto più hà potuto il corpo è uenuto à passare con la testa tanto oltre che è penetrato con essa tutta la lama nimica, & così è andato à ferire, che l’auerssaria non hà potuto diffendere ne meno hà potuto hauere tempo di tornare con la punta in presenza ne di girare il corpo. 121. |
|||||||
[20] This plate illustrates the exclusion of an opponent's sword in low tierce. You were in high tierce and have lowered your body as you advanced, so that on arriving within distance you were so low that you have controlled the adversary's sword without moving your arm. While lowering your body you have carried the right side back and the left forward and so balanced the body on the feet and knees, that you have been able to get so low with great swiftness. The position of your body is such that even if your adversary had disengaged above, you would not have checked your advance or made any defence since there was nothing to defend in that line. Whether he had disengaged or not, or whatever he had chosen to do, he would not have prevented your advance, with your sword, feet and body working in union. The change in the position of the body after reaching this point will be shown in the next plate. |
[171] LA SERVENTE POI, CHE SI VEDRA ESSERE ANDATA A SERrare la spada di quello, che stà in terza bassa si ritrouaua lei nella terza alta, & è uenuta abbassandosi con una certa proportione secondo che caminaua inanzi, che quando è gionta in misura si è trouata in tanta bassezza che hà aquistata la spada senza fare moto del braccio, & nelo abbassarsi è uenuta portando in dietro la parte destra, & la sinistra inanzi con fare tale contrapeso del corpo sopra li piedi, & ginochii, che hà potuto andare così bassa con grandissima celerità, & hà saputo si bene situare il corpo che se bene il nimico hauesse cauato disopra, lei nan haurebbe cessato dal suo uiaggio senza fare moto di diffesa, perche da quella parte non ui era corpo, in modo che il detto nimico hauesse cauato, ò non cauato, ò fatto quanto li fosse piacciuto, non haurebbe impedito, che questa non fosse andata inanzi unita di spada piedi, & corpo; mà la mutatione, che fà il corpo contra di essa guardia dopò l’ essere gionto à questo segno, si mostrarà nella post seguente figura. 122. |
|||||||
[21] |
[172] AL VANTAGGIO VEDVTO NELLA FIGVRA ANTECEDENTE, laquale era discesa dalla terza alta è nata la presente ferita di quarta col piè manco centra una terza bassa, perche quello, che hà ferito essendo peruenuto al detto uantaggio unito, hà, senza slongare il braccio, posto il finimento alla nimica, oue prima haueua situata la spada, & con scorrere per appresso il filo, & dirizare la punta alla presenza hà fatta la detta ferita di quarta passata di piè sinistro inanzi, laquale ferita haurebbe parimenti fatta ancorche l’ auerssario hauesse cauato, restando all’hor con la mano in terza, & quantunque detto auerssario hauesse pure uoluto leuare la punta per ferire la parte superiore, esso ferittore con solamente alzare la mano in quarta haurebbe fatta la medema ferita, & passato con uguale sicurezza, come al presente. 123. |
|||||||
[22] |
[173] DELLA TERZA REGOLA DI ANDARE A FERIRE IL NIMICO SENZA FERMARSI. LA PRIMA REGOLA DI CVI SI E PARLATO IN MATERIA di questo andare à ferire di risolutione è buona perche comincia à pigliare il uantaggio tanto di lontano, che ’l suo nimico non può ferire, non dimeno pare, che troppo presto si comincii à fare conoscere il proprio pericolo ad’ esso nimico in modo, che se li dà molta comodità di fare mutationi per fare disordinare, & spatio di tempo da usare altri di uersiui per saluarsi: La seconda raggione similmente è buona ancor lei, perche forma una certa guardia, quale non hà se non un solo scoperto, & à quello è così prossima la mano della spada, che nissuno può andare à ferirui senza passare prima per quel forte, tiene anco la detta guardia tanto libera la spada (come si è mostrato) che poche cauationi ui fanno di bisogno di maniera tale, che se non fosse per altro tanto obligata, & che non si conuenisse stare in lei con tanta soggetione, & strettezza di non mouere mai il braccio saria molto migliore [174] della prima. Et però considerando noi l’imperfettione delle dette due prime regole, & particolarmente, che lo diffendersi quando il nimico non può fare offesa non è altro, che un perdi tempo & un riceuere danno, mostrando ad’ esso nimico l’ intentione di quella cosa che si uuol fare, con darli comodità di pigliare rimedio, habbiamo pensato di trouare un modo di operare, & di mostrare una terza regola, con laquale non possa detto nimico conoscere niente, se non quando sia col proprio corpo nel pericolo, & laquale regola, dando l’ osseruattore di essa essequtione à quantò haurà da fare, ferisca con tanta prestezza, che l’istesso nimico non habbia tempo non solamente di tante mutationi, mà quasi à pena di parare il primo effetto. Il fondamento dunque di tale raggione è questo, che si sà certo non potere il nimico ferire prima che non si sia entrato nella misura, & però non occore, che l’ huomo si metta in diffesa, ne che si fermi con la spada in alcuno sito, douendo sempre caminare inanzi uerso la parte di fuori, sino che’l piedi sia intrato in misura non importando più con l’ uno, che con l’ altro, & il tempo di portare il suo forte al debile nimico sarà mentre che si lieua il piede per portarlo in detta misura affine di escluderli la spada di fuori senza fermarsi, & con scorrerli il filo andare à ferire accompagnato di spada, piede, & corpo, & senza slanzarsi, perche se all’ hora il detto nimico rompesse di misura non solo haurebbe tempo di parare mà di ferire ancora; mà con l’ andare unito l’huomo si può mutare in tempo, si come à punto douria fare se si trouasse di dentro, & che’l nimico uolesse parare, perche all’ hora douria mutare di terza in seconda, & abbassare il corpo continouando inanzi, che ferirebbe nel medesimo punto, che l’ istesso nimico hauesse uoluto parare, si bene nel uolgere di terza in seconda dourebbe abbassare la punta disotto del braccio nimico con tenere ferma la mano nel primo sito, & chinando il corpo, che ferirebbe nel destro fianco, perche se bene l’ auerssario hauesse potuto parare col rompere di misura, doppo che se li fosse trouata la spada, & si fosse andato per ferirlo non potria più dirizare la punta in presenza, come per esempio hauria potuto, se l’ huomo si fosse fermato, & hauesse fraposto tempo trà l’ hauere trouata la spada, & l’ essere andato, perche così sarebbe stato troppo tardo l’ effetto, l’ hauere similmente slanzato il corpo, ò la spada, ouero sforzato il passo sarebbe stato dannoso, perche non haurebbe potuto pigliare il secondo partito, & sarebbe stato più tosto in pericolo di essere ferito, che altro; il medesimo modo di passare di risolutione bisogna tenere, se il nimico nel primo andarli à trouare la spada andasse à parare senza rompere ai misura, perche prima che egli hauesse fatta forza contra la spada si potria hauerlo ferito, & essere passato, mà se in questo parrare hauesse rotto di misura sarebbe all’hor stato meglio cauare prima, che esso l’hauesse tocca, & qui stà la difficoltà, perche chi fà moto nel primo andare alla spada non può cauare in tempo, & perciò dee l’ huomo andare in guisa che un moto non sia contrario all’altro nel cauare, che se per accidente la mano facesse una caduta non potria risorgere in tempo se il nimico l’ andasse ad’ in contrare, mà se la punta sarà portata con tale ageuolezza, che l’huomo possa, lasciando il primo effetto, fare l’ altro con forme all’ oportunità, & con quella sottilità, che si richiede, sarà un bello inganno, perche mettendosi il piede in misura si aquista la spada, & mentre che ’l nimico si crede incontrarla & resistere, uede cauarla, & andare con l’ altrò piede in modo che esso non può più ritornare in presenza, ne può fare altro che ferire di sotto con meggia cauatione, & à quello, che uà basta solo mouere un poco la punta con abbassarla insieme col corpo dalla parte, doue uede uenire la nimica, & seguire il suo corso, che terà detta nimica esclusa di fuori, & andarà di certo à ferire, mà se’l nimico, mentre che si uà alla sua spada cauarà, ò uorà uenire inanzi, se non romperà di misura restarà ferito prima, che sia finita la cauatione, & se nel cauare, esso romperà di misura per andare à ritrouare il debile all’ hora l’ osseruattore di questa regola dourà contra cauare, & andare inanzi, che ferirà in tempo medesimo, & questo sarà più facile, & più breue, che andare alla spada, & poi uolere cauare prima che ’l nimico la tocchi; & se per auentura il detto nimico mutasse guardia nel rompere di misura alzando, ouero abbassandola spada, ouero ritirandola, si dourebbe in ogni caso [175] continouare inanzi, & tornare à mettere la spada alla nimica nel tempo che ’l piede torna ad’ aquistare la misura mà in tale maniera però, che se detto nimico uolesse ferire, come che più à lui piacesse, si potesse sempre seguire il suo uiaggio parando, & ferendo insieme, & dal sito, & distanza frà il nimico, & se stesso nel andarlo à trouare dourà l’ huomo conoscere quello, che esso nimico possi fare per diffesa, & offesa, & come possi turbare, & impedire la spada per sapersene guardare, perche chi non antiuede quello, che può accadere l’ occasione è tanto ueloce à passare, che non resta tempo da potere pigliare partito. Di quelle cose poi, che l’ huomo fà fuggendo, & dillongandosi non giudichiamo neccessario lo trattarne, perche non offendono, se l’ huomo non uuole, pure è buono à saperle, & stare prouisto à tutte le cose. Di quelli similmente, che tiranno di taglio contra questa raggione si potria fare dimeno di trattarne pure diremo, che se uno tirrarà nel tempo che’l nostro osseruattore andarà all’ aquisto della spada, che restarà ferito prima che sia finito meggio il taglio, & se lo tirarà fuggendo potrà il nostro seguittarlo coprendosi, & andarlo à ferire, & non ariuandolo, forsi, & che il parato sia stato di dentro di quarta, potrà uoltare in seconda, che ferirà nel luogo medesimo, doue la nimica non potrà parare, se ’l parato anco sarà stato di fuori di terza, potrà uoltare pure di seconda di sotto che non meno ferirà in quella parte, &, non uolendo parare, potrà anco lasciare passare il taglio, & subbito andare inanzi non per ferirlo in quel punto, mà per ferirlo nel tempo, che rileuarà la spada, ò si rimetterà, ouero tirarà un’ altro taglio, & questo sarà più à proposito che ’l parare, & il sapere operare in questa guisa è anco migliore delle due prime, mà si richiede sapere conoscere ben le distanze, perche, non conoscendole, non si cauaria profitto d’ alcuna dette descritte raggioni, & tanto meno di questa, netta quale si uà senza fermarsi, & senza tenere sito fermo dette armi, si dee in somma sapere conoscere quando il piede porta il corpo nel pericolo per potersi assicurare, nellaquale regola, quando l’ huomo haurà fatto buona pratica dourà poi tenere altro modo, como noi mostraremo nell’ altra seguente regola. |
|||||||
[23] |
HORA SI VEDRA APARIRE QVI OLTRE VNA TERZA SOPRA il piè manco, che hà aquistata la nimica dalla parte di fuori, laquale nimica ancor lei era in terza, & per tale uantaggio seguitarà della stessa guardia sino al corpo auerso, & tutto succederà perche quello,che hà trouata la nimica è andato sino alla distanza senza guardia, & mentre, che col piede è intrato nel pericolo si è coperto dalla detta nimica senza toccarla, & andarà sino all’ auerssario senza fermarsi pigliando li tempo secondo l’ occasione datali dal detto nimico, che se ciò non faccesse seguitaria per la spada & andarìa come hà cominciato tutto unito. 124. |
|||||||
[24] |
[176] DA QVEL VANTAGGIO PRESO DI FVORI DELLA SPADA NImica, come si è mostrato nell’ antecedente discorso è nata questa ferita, che si uede seguire di quarta contra un’ altra quarta, perche collui che e ferito uedendosi uenire contra l’ auerssario per impatronirsi della sua spada hà pigliato quel tempo, & cauato di quarta girando il corpo col piè sinistro per ferirlo nel petto in quello uenire, mà il ferittore, che era andato alla nimica unito, & con poco moto della spada, uoltando solamente la mano di terza in quarta, & continouando inanzi hà ferito lui in tempo medesimo nella gola, & hà fatto uscire la detta nimica di linea perche è stato più forte nel termine della spada, & anco per la debolezza, che è nel sito di quello che gira il corpo, & di più, perche anco il sito del braccio di collui, che ferisce è più galiardo, che se fosse disteso inanzi. 125. |
|||||||
[25] |
[177] QVESTA SECONDA, CHE SEGVE, ET CHE FERISCE SOTTO la spada dalla parti di fuori è nata pure ancor lei da quel primo aquisto che si uidde, perche essendo andato quello, che hà ferito ad’ occupare la nimica dalla, parte di fuori nel tempo, che ’l piede entraua nella misura l’ altro che era ancor lui in terza pigliando quel tempo hà uoltato in quarta, & abbassata la punta per liberarla, & andare à ferire nel fianco destro di sotto girando il piede per portare la uita fuori di presenza della punta nimica, ilquale effetto ueduto dal ferittore hà fermata la mano nel sito oue la si trouaua, & con uoltarla in seconda, & curuare bene il corpo hà rimessa la punta di sotto, & esclusa la nimica di fuori prima, che sia uenuta in presenza, & in questo modo ferito nel fianco seguendo senza fermarsi sino alla uita del detto ferito. 126. |
|||||||
[26] |
[178] NELLA SEGVENTE FIGVRA SARA VN’ AQVISTO FATTO da una terza contra una seconda in tale forma cio è, che hauéndo la detta terza guardia cominciato à uenire senza sito fermo si è posta alla nimica nel punto, che è gionta in misura col piede, laquale nimica si trouaua in seconda, mà senza toccarla però, & si è coperta impedendo ad’ essa nimica il potere ferire in quel luogo, oue si trouaua, & per tale aquisto può continouare inanzi à ferire di quarta con portare il finimento doue hora tiene la spada alla nimica, che se bene l’ auerssario cauasse in quello andarli all’ aquisto essa guardia seguiria pure inanzi con la contracauatione di quarta, & ferirebbe dell’ istessa, quando per caso lei non si trouasse tanto oltre, che con l’ abbassare il corpo potesse schifare la punta nimica, che all’ hora con uoltare solamente la mano in seconda ferirebbe disotto nel destro fianco, & lasciarebbe passare la nimica uana disopra. 127. |
|||||||
[27] |
[179] DA QVEL VANTAGGIO MEDESIMAMENTE, CHE HAVEA PIgliata la terza contra la seconda come si è mostrato nel discorso passato è nata la ferita che si uedrà nella figura, che segue in talmodo cio è perche hauendo detta terza aquistata la nimica, & uedendola non si mouere, & conoscendo anco di essere essa diffesa in quella parte senza hauere bisogno di toccare detta nimica è passata oltre col piè sinistro, & conseruandosi sempre coperta hà fatta la detta ferita di quarta nella gola mantenendo il finimento alla nimica, & piegato col corpo inanzi per giongere più di lontano, uedesi ancora il calcagno del destro piede leuato, che dinota la continouatione del passo sino al corpo auerso, & la passata del tutto. 128. |
|||||||
[28] |
[180] QVESTA FERITA ANCOR ESSA, LAQVALE SI VEDRA SARA seguita perche nel giongere la sopra detta terza guardia alla nimica per coprirsi & aquistare il uantaggio, il ferito hà pigliato quel tempo, & abbassando il corpo, & la punta hà portato il destro piede inanzi per ferire l’auerssario sotto la spada, nel tempo che credeua trouargliela, & il detto auerssario ciò è il situato in terza guardia, ilquale con poco moto di spada senza slanzo hauea cominciato ad’ andare alla nimica uedendo il partito che l’ altro pigliaua hà lasciata la prima operatione, & appigliatosi ad’ un’ altra abbassandola punta, & il corpo in maniera, che è uenuto à rimanere col finimento alla nimica, & escludendola di fuori hà ferito nel petto in quel tempo medesimo, che esso ferito ueniua, ilquale se bene hauesse uoltato di seconda in terza per diffendersi, & per rispingere la nimica con qualche forza sarebbe con, tutto ciò restato anco ferito, perche l’istesso ferittore multando di terza in seconda, & abbassando il corpo, con continouare inanzi l’ haurebbe pure ferito nel petto, & senza che egli hauesse potuto parare, ne meno rimettere la punta in presenza perche il medesimo ferittore sarebbe passato prima per essere già in uiaggio, & se similmente hauesse uoluto cauare per ferire di detta seconda di fuori per sopra la spada, questi l’ haurebbe pur anco col solo uoltare in seconda, & abbassare il corpo feritto disotto la spada, lequali raggioni tutte sarebbero riuscite benissimo non per altro, che per quello uantaggio di continouare il moto in andando, & per essere stata essa terza guardia la prouocante à mouere il nimico. 129. |
|||||||
[29] |
[181] DELLA QVARTA REGOLA DI ANDARE A FERIRE IL NIMICO SENZA FERMARSI. LA QVARTA REGOLA, CHE HORA SIAMO PER MOSTRAre ne anco lei hà sito fermo di spada nelo andare contra il nimico, mà si come nell’ antecedente si uà al debile, & si procura di trouarsi fuori nelo ariuare in distanza in questa si opera al contrario, & con maggiore sottilatà, & in modo che l’ auerssatio non può conoscere l’ intentione dell’huomo, & doue in quella si uede la uoglia de andare dalla parte di fuori, potendosi, in quella l’huomo uà col petto giusto contra la punta nimica in modo che pare che uoglia andare ad’ urtarui dentro, & così non può detto nimico pigliare altro partito che restare per quello diritto per ferire il corpo, che leuà contra scoperto, mà questo andare nondimeno é in guisa, che nel tempo che ’l piede uole entrare nella misura, si porta fuora per una delle parti secondo l’ oportunità, & se si entra col destro piede si porta fuori dalla parte destra, se col sinistro si uà fuori dalla sinistra, & così l’ uno de piedi uiene à restare in retta linea, & l’ altra fuora, & per questo rispetto il corpo piega sempre sopra quello, che uà fuori di linea, dalche si caggiona, che detto corpo ancor lui uiene ad’ uscire, & à scoprire il corpo nimico, ilquale nimico se in quel tempo uolesse ferire, la spada che poco é [182] lontana dall’ auerssaria facilmente diffenderebbe, mà se non si mouesse dourebbe all’ hora l’ osseruattore di questa regola andare da quella parte, oue è trauersato il piede con escludere la nimica di fuori, per ferire poi del secondo passo, quale hà da essere picciolo, & cõtinouato per maggiore celerità, & se accadesse che ’l detto nimico dirizasse la punta uerso doue che piega il corpo nel portare fuori il piede, si douria portare l’ altro inanzi, che già saria leuato piegandoli sopra il corpo, ilquale in quel punto uerebbe ad’ essere uscito di presenza dall’ altra parte, & ad’ escludere la nimica di fuori continouando à ferire. Questo è un modo di operare che si usa quando il nimico stà con la pũta tanto alta, che passi il meggio della sua propria uita, che un poco di più, ò di meno non farebbe caso, mà quando la detta pũta guardasse uerso il ginochio, ò più basso all’ hora si dourebbe andare con li piedi in contro di essa punta & nelo instante, che ’l piede entra nella misura, serrare la nimica talmente, che la non potesse leuarsi, mà deesi auertire che, nel ferrarla, non s’ abbassi tanto la propria punta, che la uada più bassa della lama nimica perche l’ auerssario ferirebbe senza che si potesse parare, & si caderebbe in neccessità di contracauarla, mà tenendola, come si richede, si andarebbe à ferire nel proprio tẽpo che esso nimico cauasse, douendosi fare questo senza moto di diffesa in caso che ’l detto nimico fosse dalla[35] parte di fuori, che quando fosse di dentro si douria un’ poco di moto uerso la quarta non finendo però di uoltare la mano, con guardare di non andare tanto basso col finimento, che esso nimico potesse uenire à ferire per l’ angolo, che si forma dalla mano alla punta si come, che nella figura si uedrà, perche senza molto trauaglio non si potrebbe parare, & se pure si parasse si correria pericolo di restare ferito in altra parte per il gran moto, che si farebbe; mà andando con la spada giusta accompagnata dal piede, & dal corpo come è conueniente tutte le cose riuscirano bene, & perciò questa è miglior regola di alcuna delle antescritte, mà di poi si trattarà di una se ben quasi simile, che hà nondimeno in se raggioni più sottili nelle quali fà di mestieri giuditio maggiore perche anco in maggiore pericolo si entra, se ben da un’ altro canto più facilmente si ferisce & chi saprà ben seruirsi dè i fondamenti di essa andarà sicuro, & ferirà senza impedimento, essendo questa maniera assai inganneuole, & più di alcun’altra di cui si habbia sin quì raggionato. |
|||||||
[30] |
LA QVARTA, CHE SI VEDE, LAQVALE HA PORTATO FVORI il destro piede pertrauerso, & piegatoli sopra il corpo, restata anco con la spada in retta linea sotto la nimica, che era in terza si è formata in tale maniera perche questo, che hà cominciato di lontano, & è sempre uenuto col petto contra la nimica gionto che è stato col piè sinistro appresso la misura hà portato il destro di fuori, & piegatoli sopra il corpo per uscire di uista della detta nimica affine di poterla mettere oue hauesse giudicato meglio, & per essere così giusta di sotto non l’ ha potuta esso nimico hauere tanto facilmẽte, anzi è stato forzato à restare dubbioso, mà se nel portare il detto destro piede di fuori, non si fosse esso nimico mosso, questo hauria potuto mettere la spada per quello scoperto che si li fosse presentato appresso della nimica, & serrarla di fuori, che sarebbe andato à ferire senza toccarla con portare il sinistro piede inanzi nella parte di dentro; se anco il detto nimico hauesse seguittato con la punta la prospettiua del còrpo questo piegato hora sul destro piede si saria piegato nel sinistro, & uscito di presenza dall’ altra parte, & nel moto della nimica hauria messa la spada nello scoperto fatto da esso nimico, perche trouandosilì proprio sotto la linea, per hauere seguitato il corpo con la punta, la spada che era disotto saria uenuta à rimanere da parte, in modo che con solamente spingerla per la linea, oue era la nimica haurebbe serrata essa nimica di fuori, & tanto più comodamente per il moto del corpo, ilquale piegarebbe dall’ altra parte, & che è più presto di quello della mano, & seguendo col piede saria passato molto uelocemente, & hauria lasciata la nimica di fuori per l’una, ò per l’ altra parte secondo l’ opurtunità, lequali operationi tutte si hanno da fare continouate senza punto fermarsi, & se bene pare in uista, che quello, che stà in passo trauersato aspetti tempo, ciò si è [183] fatto per mostrare l’ effetto di piede corpo braccio, & spada, che quanto all’ esequtione dell atto uuole essere spedito, & senza intermissione perche se ’l nimico non seguita questa prospetiua mentre que uà fuori, il sopra detto dal passo trauersato nel punto medesimo, anzi subbito passa & la sua spada chiude la uia all’ altra, & uà subbito al suo uiaggio mà se detto nimico seguita il primo moto con la punta il sopra detto corpo uà pure nell’ altra parte, & esclude la nimica di fuori, che non può più ritornare nella presenza di esso corpo, & se bene si fà il passo per quadro sia dalla parte destra, ò dalla sinistra nondimeno si hà da lasciare la spada, & la mano per retta linea della punta auersa affine di rendere più facile la diffesa sedetto nimico uolesse ferire in andando fuori col passo, cosa assai riuscibile à chi opera come si deue auertendosi, che fà mestieri di sapere giongere in quel sito, come nella figura si uedrà senza moto di braccio, ne di spada, laquale hà da essere portata dal corpo che altrimenti sarebbe pericolosa. 130. |
|||||||
[31] |
DALL’ HAVERE PORTATO IL DESTRO PIEDE FVORI, COME si uidde, è successo l’ aquisto, che hà fatto questa terza che seguirà, contra l’ altra terza, perche hauendo essa portato il destro piede fuori dalla destra parte ne si essendo all’ hor mosso il nimico quel corpo, che già era uscito di presenza è slato caggione di fare scoprire il suo al nimico, & così subbito hà leuato il piede sinistro, & esclusa la nimica fuori di presenza, laquale non può più tornare se non cauando, in modo che questo che hà continouato haurebbe prima ferito, & portato il piè mãco uerso la linea della pũta di detta nimica, & se l’ auerssario nel’ aquisto hauesse cauato, questo pure haurebbe portato il destro nella linea del sinistro, & ferito di terza senza altro moto che di slongare la mano, & così resa uana [184] la cauatione: mà se il detto auerssario pure non cauasse, ò non uolesse cauare all’ hora il nostro osseruatore se bene nonportasse il piè destro nella linea del sinistro ferirebbe nondimeno in quarta, & seguirebbe sino al corpo senza toccare l’ auerssaria, se il detto nimico non andasse lui stesso ad’ urtarui dentro per diffendersi, perche à questo nostro bastaria solamente à coprirsi, che ’l nimico non lo offendesse. 131. |
|||||||
[32] |
QVESTA QVARTA SEGVENTE, CHE SI VEDRA FERIRE, E NATA da quel uantaggio di hauere serrata la nimica dalla parte di dentro, come si mostrò con la superiore figura, & dalla spada di questo ferito, che all’ hora era in terza retta, & hora in terza angolata, perche il ferittore subbito uscito di presenza hà messo la spada per il scoperto del nimico, & per il debile ancora di essa nimica senza però toccarla, & gionto col finimento alla detta nimica, la mano che andaua inanzi ha fatto in quel modo angolarla, & quanto più si è il detto ferittore auicinato tanta maggiormente la spada auersa si è angolata, in modo che non hà potuto fare altro che parare & tutto perche questa è una raggione, che quando l’ huomo si dispone à ferire è penetrato in quel punto già tanto inanzi, che ’l nimico non hà più tempo da pigliare altro partito, che di ritirarsi, è parare, & di più, nella medesima raggione, ancora che l’ assalittore muta effetto ferisce non manco, talmente, che non può l’ assalito fare altra diffesa, tanto importa il uantaggio della linea, è de’ piedi, & il termine stretto della distanza. 132. | |||||||
[33] |
[185] VNA TERZA SARA RAPRESENTATA DALLA FIGVRA SEguẽte,che si ritroua sotto un’altra terza uenuta pur di lontano come si mostrò, mà che nel giongere uicina alla distanza si è ritrouata col destro piede inanzi portando il sinistro fuori per trauerso, & piegandoli sopra il corpo per uscire di presenza della nimica, & con tenere la sua spada misuratamente sotto di detta nimica in linea retta si per hauerla pronta alla diffesa, come per metterla, doue fosse bisogno con minor moto; & perche il detto nimico non si è mosso con la sua punta, essa terza portara il destro piede nella linea del sinistro in guisa’, che si trouarà tutta fuori di presenza, & farà restare scoperto il corpo auerso dalla parte di fuori, & così metterà la spada nel medesimo tempo del piede per quello scoperto, & andarà à ferire per appresso la nimica senza toccarla, mà se detto nimico hauesse seguitato il corpo con la punta, mentre questo hà fatto quel passo per trauerso tutto quel corpo che piega sopra il piè sinistro si sarebbe piegato sopra del destro, & così sarebbe uscito di presenza da quest’ altra parte & passato col sinistro mettendo la spada per di dentro dalla nimica in quarta, & saria andato à ferire senza toccarla, il che sarebbe riuscito benissimo, perche trouandosi l’ huomo in passo tale uiene ad’ essere sempre con un piede fuori di uista della nimica, & può andare da quel lato, doue è uscito, mentre non è seguitato dalla punta di detta nimica, & se anco è seguitato può ripiegare il corpo sopra del piede, che è restato, & mettere la spada in quella parte con impedire alla nimica il potere più ritornare, & per questa uia andare à ferire in quello scoperto, che seli presenta. 133. |
|||||||
[34] |
[186] IL VANTAGGIO PIGLIATO DA QVESTA TERZA CONTRA VN’ altra terza come si uede nella seguente figura è nato da quello, che hauea portato il piè sinistro fuori, perche essendo il detto uenuto col petto dirittamente contra la punta auersa, osseruando li termini demostrati, & hauendo portato il piè manco di fuori hà subbito leuato il destro, in modo che ’l corpo è uscito di presenza hauendo anco nel medesimo punto messo la spada uicino alla nimica per non lasciarsela uenire dinanzi al corpò, & con animo d’ andare di detta terza sino al corpo di esso nimico senza toccarla, il quale nimico se fosse andato à trouarla per rispingerla il nostro osseruattore mentre hauesse conosciuto potere resistere, & andare à ferire se l’ hauria lasciata toccare, si come anco se il detto nimico hauesse parato in tempo con rompere di misura, il nostro sarebbe andato di sotto di seconda inanzi che quello glie l’ hauesse toccata, & ilquale nimico, se hauesse cauato nell’ andare di quella terza, il medesimo nostro haurebbe uoltato di terza in quarta, & similmente ferito portando il piè sinistro per retta linea, doue hora si troua, acciò la nimica restasse più debile, & il braccio facesse moto minore. 134. |
|||||||
[35] |
[187] DAL VANTAGGIO DIMOSTRATO NELL’ ANTECEDENTE DIscorso è deriuata la ferita di terza che qui oltre si uedrà perche essendo quello, che hà ferito uscito fuori di linea à posto la spada per quello scoperto, che si uedeua appresso la nimica, & tenendosi coperto è andato di piè destro à ferire seguittando del sinistro perche l’ altro non hà preso partito in quello uscire di linea, che hà fatto il ferittore, che percìò non hà & non haurebbe potuto parare se non con rompere di misura, nel qual caso il medesimo ferittore sarebbe potuto andarlo à ferire di seconda di sotto con piegare il corpo, & penetrando con la testa nel proprio tempo la punta nimica prima, che l’ auerssario l’ hauesse potuta dirizare, ilquale sedalla terza anco hauesse uoluto diffendersi, & ferire cõ la cauatione, hauria esso ferittore non meno ferito con uoltare di terza in quarta inanzi che tale cauatione si fosse finita, ne poteua esso nimico fare alcuna altra cosa, per essere questi gionto così inanzi, perche come si è detto altre uolte, quando uno si dispone di ferire non si può dal nimico fare se non una sola cosa cìo è rompere di misura, doue che l’osseruattore di questa raggione può fare molti effetti. 135. |
|||||||
[36] |
[188] DALL’ EFFETTO POI DI COLLVI, CHE SI ERA CAVATO DI presenza col sinistro piede è nata quest’ altra ferita che seguirà perche essendo gionto col piede in terra, & seguitatali dalla nimica punta la prospettiua del corpo, esso hà posto la spada per quello scoperto fatto dall’ auerssario di dentro appresso la sua, & così hà impedito detta nimica punta, che non hà potuto tornare in presenza, & è passato col piè manco andando sino al corpo senza fermarsi, & se bene quello, che hora è ferito hauesse uoluto parare non haurebbe potuto se non col ritirarsi & con portare la punta fuori di presenza, oltre che col stare contra la prospettiua non lo haurebbe potuto fare, in modo che aldetto ferittore saria stato molto comodo di uoltare di quarta in seconda, & piegare il corpo uerso la sinistra, ilquale adesso è uerso la destra nel luogo proprio di detta seconda di dentro, se bene anco alquanto in fuori, & basso. 136. |
|||||||
[37] |
[189] LA FIGVRA SERVENTE MOSTRAR A VNA TERZA, CHE HA FErito una seconda, laquale uoleua andare à ferire sotto la spada, seguita, perche hauendo quello, che hà ferito portato fuori il piè manco, & spinto inanzi il destro hà messa la spada appresso la nimica per escluderla di fuori, & perche il nimico preso quel tempo, hà uoltato la mano di terza in seconda abbassando il corpo & la punta per ferire di sotto, & così il ferittore quale non hauea finito di andare alla spada, mà che solamente si era coperto hà abbassata la punta in quello medesimo tempo pure di detta terza & portato anco nel punto medesimo il piè sinistro inanzi con chinare il corpo, & la mano, laquale mano hà trattenuta senza stendere per rimanere al debile nimico, & hà angolata essa punta allo insù, acciò che habbia piu forza di sopra in modo tale, che hà impedita la nimica, & ferito di detta terza, laquale tanto maggiormente è penetrata, quanto che è anco stata incontrata dal detto nimico, la punta del quale è andata molto bassa, perche hà uoluto diffendersi quando hà uisto l’ imminente pericolo, mà li è andato falace il pensiero per il forte che hà ritrouato. 137. |
|||||||
[38] |
[190] QVESTA QVARTA CHE SEGVE, LAQVALE E SOTTO VNA SEconda, & con la spalla sinistra più inanzi della destra si è cauata fuori col piè manco leuando l’ altro, & portandolo nella linea medesima affine di scoprire il nimico dalla parte di fuori, & benche si ueda la mano di esso nimico tanto alta, non dimeno dalla meggia lama inanzi uerso la punta si scopre tutta la testa dalla parte disopra, & perciò si uede in detta quarta il disegno di uolere ferire; mà se il detto nimico nel tirarsi di fuori col sinistro piede hauesse girata la ponta per conseruarsi in presenza, lo stesso haurebbe cacciata la punta per dentro di quarta, & ferito in quel tempo, con non leuare mai la spada dalla diffesa, mà però senza molestare la nimica: & non essendosi mosso il nimico mentre, che essa quarta è andata di fuori hauria potuto ferire di sopra come nella figura più espressamente si mostrarà. 138. |
|||||||
[39] |
[191] LA FERITA DVNQVE, CHE, QVI SEGVIRA SARA NATA DA quello uantaggioso sito in che si è ueduta la quarta antecedente quale era sotto la seconda, perche essendo quello che hà ferito uscito fuore di presenza col corpo & ueduto quello scoperto uerso la testa dalla parte esteriore li hà subbito messa la spada stendendo il piede, & il braccio, & scorrendo la lama nimica hà fatto piegarla abbasso, come si uede, essendo molto galiarda la quarta in detta parte, & per contrario molto debile la seconda, & ancorche quello, che è ferito hauesse uoluto girare di quarta, non haurebbe nõdimeno fatto cosabuona, perche il detto ferittore col solo abbassare la punta uerso il fianco destro nimico l’ haurebbe ferito nel punto istesso, che il medesimo nimico ueniua oltre, prima che hauesse finito di girare il corpo, & uoltare la mano, & se’ quando, che esso ferittore è uscito di presenza, & l’ altro hauesse seguito per mantenerli la punta inanzi, esso che già era con la mano in quarta haurebbe pigliato quel tempo, & ferito di dentro della medema quarta. 139. |
|||||||
[40] |
[192] COSTVI, CHE NELLA FIGVRA SEGVENTE SI VEDE HAVERE aquistato con una terza il uantaggio sopra di un’ altra terza bassa l’ hà fatto, perche essendo esso uenuto di lontano cenza sito fermo di guardia hà portato talmente il corpo, & la spada, che gionto poi nella distanza si è trouato hauere posta la spada, & il corpo, come si uede, doue che se bene il nimico hauesse uoluto ferire ò per l’ una, ò per l’ altra parte, nel giongere che questi faceua, non haurebbe fatto niente, anzi che questi dal uantaggio haurebbe hauuta maggiore comodità di ferire per non hauere fatto nel detto suo giongere caduta alcuna ne di piede, ne di corpo ne di spada, in modo tale che saria stato pronto à pigliare qualunque occasione, ne essendosi mosso l’ auerssario andara à ferire appresso la nimica & appresso la linea del braccio per non abbandonare mai la diffesa, & in caso, che detto auerssatio hauesse cauato per ferire di fuori, esso hauria ferito di detta terza & quando anco il medesimo nimico non si fosse mosso hauria ferito di quarta per tenersi diffeso di dentro. 140. |
|||||||
[41] |
[193] VIENE AD’ ESSERE NATA QVESTA FERITA DI QVARTA, CHE segue dall’ aquisto della terza antecedente contra la terza bassa, fatta col sinistro piede contra detta terza, & il tutto è auenuto dall’ hauere il ferittore preso il uantaggio, & continouato sempre appresso la nimica, ilquale ferittore si è diffeso tanto, che se bene il nimico hauesse cauato di fuori con tutto ciò hauria ferito senza fare moto di diffesa di terza, & senza altra mutatione, che detto nimico non haurebbe potuto saluarsi se non col rompere di misura, & leuare la spada alla diffesa, ò per l’ una, ò per l’ altra parte con bisognarli anco uscire di presenza con la punta, lequali cose hauriano porta, gran comodità al ferittore di ferire di seconda di dentro, ò di sotto secondo la parte, doue esso nimico fosse andato à parare, perche si hauria trouato tanto in fuori col corpo, che si saria potuto tenere con la sua destra spalla giusta contra la destra del detto nimico. 141. |
|||||||
[42] |
[194] DELLA QVINTA REGOLA DI ANDARE A FERIRE IL NIMICO SENZA FERMARSI. HORA SI RAGGIONARA DI VN’ ALTRA FORMA DI ANdare contra il nimico di molto maggiore sottilita delle altre, & chi si saprà condure saluo sino al luogo, oue si hà da operare ferirà senza pericolo. La forma dunque è tale ciò è, che trouandosi il nimico in qualunque guardia, dee l’ osseruattore della regola cominciare ad’ andarli contra, & ne lo auicinarsi alla distanza approssimare anco la spada pian piano al sito doue, che hà intentione di metterla, acciò che nel suo giongere in misura la propria spada gionga ancor lei in quella giustezza, che desidera. Il mettere di spada, come più uolte si è detto, hà da essere dalla più debile parte della nimica, & anco nella presente regola sino alo entrare in misura, mà la punta che altroue si è insegnato douersi mettere alla punta, in questa si dice che l’ huomo deue andare tanto inanzi, che possa metterla al finimento dell’ auerssario tanto però che la non sia penetrata il finimento auerso mà sia poco lontana, & stia in quella propria prospettiua [195] non di sotto ne di sopra, mà per uno de’ ilati, secondo che portarà seco la raggione della postura di esso auerssario; deue anco la detta punta inclinare più al basso, che all’ alto per due raggione, l’ una per più tosto poterla cauare, bisognando, l’ altra perche il nimico cognosca non poterla hauere se non col’ abbassare il finimento, col quale abbassare sarebbe à fare tẽpo di ferire per il nostro osseruattore, ilquale saria già in camino, & la sua punta molto uicina ad’ esso nimico. Auertendosi anco che nel giongere con la spada in detto luogo, mẽtre che detto nimico stà nella terza, ò nella quarta dee l’ huomo tenere detta spada in linea retta dalla pũta al nodo della mano, & col braccio tãto auãzato, che cognosca potersi diffendere cõpoco moto da tutte le botte, che uenissero ne lo andare, ò nel ariuare con la spada al segno, ò sia poi quando si uoglia, là detta spada, & il corpo si hãno da situare in somma con tale maniera che ’l forte possa diffendere senza comotione, ma quãdo il nimico fosse nella prima, ó nela secõda guardia si douria mettere all’ hora la pũta giusta per la prospettiua della mano mà disotto & tenere la spada in guisa, che la propria mano nõ facesse angolo alcuno, & se il detto nimico uolesse pure ferire, si potria con la medesima guardia parare, & ferire in uno stesso tẽpo dalla parte di fuori per sopra la nimica portando il piè uerso quella parte per fare moto minore, & rendere se stesso più coperto, & più forte, in caso anco che ’l non facesse niente douria il nostro osseruattore, trouandosi già con la spada in tale modo agiustata, leuare la pũta di essa da quella prospettiua della nimica mano, & andare al corpo, & al scoperto, che fosse poco lontano, & nel punto medesimo coprirsi col finimento da quella parte, doue potra uenire la nimica, & agiutare quello effetto col moto del corpo, per diminuire quello della spada, perche continouando ariuaria al corpo prima che stesso nimico potesse mutare effetto, ilquale nel tempo che si gionge al segno, se uoltasse la mano in terza, ò in quarta, douria all’hora il nostro parare dalla parte di dentro, & seguire inanzi, si come anco se detto nimico si trouasse in terza bassa, ò in quarta con la pũta riguardante à lo ingiù dourebbe mettere la pũta in prospettiua del finimento auerso, mà disopra uerso la mano nimica, & gionto al segno andare subbito al corpo con portare il finimento alla diffesa, che all’ hora il nimico essendo in queste guardie basse potrà fare poco danno, perche leuando la pũta, quale à bassa ritrouarà il forte del nostro, che camina, ilquale quãdo sarà ariuato al segno farà passare tãto presto l’ effetto, che esso nimico non haurà tẽpo di diffesa. Mà auertiscasi bene, che il mettere della spada dee essere cõ la mano sempre in quarta cosi di fuori come di dentro, & tãto di sotto quanto di sopra, & che la punta hà da guardare uerso la mano, & finimento nimico, & tanto lontana, che l’ huomo sia sempre in tẽpo di poterla cauare ò mettere in altro luogo prima, che ’l nimico la tocchi, & quanto più saprà condurla cõ simile auertenza uicina al corpo auerso tanto meglio li succederà ogni cosa, & perciò uolendola auicinare come si deue, fà di mestieri condurla continouando senza alcuna posata, & in maniera tale che possa lasciare il primo effetto, & farne un’ altro secondo l’ oportunità. Et perche in questa regola si può fingere di mettere la spada da una parte, & poi metterla da un’ altra, è buono ricordarsi, che se il nimico essendo nella terza, ò nella quarta, uolesse ferire in quel tempo, che si ariua al segno, si hà da parare sempre per quella parte doue li haurà messa la spada, nella quale parte si hà da ritrouare il corpo, perche chi stesse col corpo da un’ lato, & mertere la spada da un’ altro potria restare ingannato, nè la raggione riuscirebbe, anzi saria falace, perche la spada hà da essere accompagnata dalla uita, & da’ i piedi ne hà da essere l’ una disggionta dall’ altra. Il parare similmente tanto di fuora come di dentro hà da essere con la mano sempre in quarta mà nel parare disotto, è dalla parte di fuori, deue essere in terza, in modo che la mano hà da fare poco moto, ne si hà quasi mai da uoltare. Seguirà poi un’ altra regola assai più sicura & di maggiore sottilità, nella quale non può il nimico seruirsi della sinistra, si come sene può molto seruire nella prima, & qualche poco nelle altre quattro, oue si porta la spada ferma per pigliare il tempo del moto nimico, mà in quella di cui si raggiona, laquale sarà la sesta in ordine, la spada non uà mai tante inanzi, che la mano nimica la possa hauere, come à suo luogo s’ intenderà. |
|||||||
[43] |
[196] QVESTA QVARTA SEGVENTE, LAQVALE SI VEDE HAVERE posta la spada dalla parte di fuori con la punta, che guarda uerso il finimento nimico di una terza, hà cominciato di lontano ad’approssimarsi à passi piccioli, & è uenuta portando la spada in modo tale, che quando è gionta nella distanza di è ritrouata nel sito, che si uede con intentione, che se il nimico credesse hauerla, etsi spingesse inanzi uoltando in seconda per pigliare col forte la punta, di cauarla lui con poco moto di essa punta ne ad’ altro fine l’ hà posta in quel luogo, mà se il nimico non si mouesse questi l’ andarebbe a ferire gionto che fosse al destinato segno atteso, che la punta già sarebbe molto uicina al corpo nimico, & ancorche paia che detto nimico la possa hauere, è nondimeno libera, & quando quelle credesse trouare il debile hauria trouato il forte, & tutto per l’ operatione continouata senza fermarsi, mà se anco il detto nimico si spingesse inanzi per ferire quello scoperto, che è sopra la spada di linea retta, l’ osseruattore di questa regola, che haurebbe la punta al forte nimico col solo alzarla un’ puoco, & stendere il braccio di quarta ferirebbe per sopra la nimica nel petto. 142. | |||||||
[44] |
MA LA FERITA; CHE SI VEDRA DI QVARTA SARA SEGVITA, perche collui che è restato ferito, quale era in terza uedendo l’ auerssario uenire à mettere la punta contra il suo finimento dalla parte di fuori, & che in quello uenire detto auerssatio li mostraua il petto, & era tutto scoperto sopra la spada si è spinto inanzi con la mano in retta linea per ferirlo in tempo di quel uenire, & coprirsi anco nello stesso tempo, & perche questi, che ueniua unito col corpo, & piedi teneua la spada ferma, & si [197] trouaua con la punta uicina al finimento nimico hà cauato con picciolissimo moto la spada, che era gia bassa, & continouando inanzi col piè sinistro, hà in contrato detto nimico della stessa quarta nel tempo che ’l ueniua, portando il finimento, che già era inanzi il corpo al debile nimico, nel qual modo potra seguitare sino al corpo, & se il detto nimico non si fosse mosso l’haurebbe non manco ferito di quella quarta nel luogo, oue si trouaua per sopra la spada con mouere alquanto la punta, & portarla sempre inanzi col forte al debile delo stesso nimico, ilquale non haurebbe potuto diffendersi se non col rompere di misura, & in questo caso il ferittore si sarebbe cacciato di sotto di seconda, inanzi che l’ altro hauesse leuato la spada, che se il medesimo nimico hauesse uoluto saluarsi col cauare di quarta, detto feritore, che andaua diritto di quarta haurebbe senza far moto di diffesa tenuta la mano pure in quarta con parare, & ferire in tempo medesimo. 143. |
|||||||
[45] |
LA QVARTA, CHE SEGVE, ET CHE SI VEDE HAVERE POSTA la punta contra il finimento di una terza dalla parte di dentro, & che mostra tutto i petto al nimico è uenuta di lontano con piccioli passi, conforme à quello che si richiede in questa regola, ancora che sia ottimo in ciascuna altra, & nel uenire hà auicinata la spada pian piano in quel sito per prouocare la nimica à mouersi con animo di ferire ouero andarli à ritrouare la spada, & se quello non si mouesse di spingerli la punta al corpo, gionto che lui fosse stato al finimento con portare il forte al debile nimico, & ferirlo di quarta, ouero di terza secondo l’ opurtunità, che in ogni modo si dee seguittare faccia il nimico tempo, ò non lo faccia, uada inanzi, ò uada indietro, & da questo uantaggio nascerà la ferita, che si uedrà nella post seguente figura 144. |
|||||||
[46] |
[198] QVESTA SEGVENTE FERITA DI QVARTA, CHE SI VEDE CONtra uno, che hà uoluto ferire anch’ egli di quarta si è fatta perche mentre, che quello ferittore andaua inanzi portando la punta per la prospettiua del finimento auerso dalla parte di dentro, quello, che è ferito, & che si uedeua la punta nimica tanto nel forte hà uoltata la mano di terza in quarta per coprirsi nella parte superiore, & per occupare il debile al nimico, & anco andarlo à ferire, ilquale moto ueduto dal ferittore, che haueua la sua ferma hà seguitato inanzi cauando alquanto di punta di detta quarta mà senza fare moto di andato à ferire in quello angolo, che forma la mano auersa mentre che è in detta quarta, & scorrendo il debile di fuori l’ hà ferito nel petto come si uede, che non meno lo haurebbe ferito di dentro se ’l non si fosse mosso, si come anco haurebbe fatto pur di dentro con la medesima se esso nimico hauesse uoluto parare con la terza, & tutto nasce per essere stato in mota, il che, come si è detto altroue caggiona l’ andare presto, & che fà mouere l’ auerssario, senza che si faccia moto di spada. 145. |
|||||||
[47] |
[199] MA QVEST’ ALTRA QVARTA, LAQVALE SI VEDRA HAVERE posta la sua spada dalla parte di fuori con la punta riguardante il finimento della nimica, che si troua in seconda guardia, laquale guardia tiene il petto esposto all’ auerssario, è fatta per mostrare l’ intentione, & disegno suo cio è di tirare esso auerssario à ferirla in quello scoperto per parare poi lei, & ferire in tempo medesimo; & quando che l’ auerssario non si mouesse di cacciare la punta per disopra la nimica, & tenendo fermo il finimento andare à ferire di detta quarta, come nella ferita della post seguente figura si uedrà. 146. |
|||||||
[48] |
[200] DAL SITO IN CHE SI TROVAVANO QVESTI DVI COMBATTENti nella passata figura, è nata la ferita, che hor si uedrà perche quello, che era in quarta con la punta al finimento nimico è gionto in distanza, che l’ auerssario non si è mosso, che perciò hà rimossa di subbito la detta punta portandola di sopra del detto auerso finimento, & col tenere ferma la mano in quarta è passato del sinistro piede inanzi auanzando la parte destra, & slongando il braccio, che così hà ferito il nimico nel petto di detta quarta, & per il uigore, che hà la sua spada naturalmente in quella parte, hà fatto piegare la nimica, che non hà potuto parare come si uede, laquale ferita non meno si sarebbe fatta dalla detta quarta se l’ istesso nimico hauesse cauato per ferire di seconda di dentro, & si sarebbe saluata pure con la medesima quarta. 147. |
|||||||
[49] |
[201] QVESTA ALTRA FERITA DI QVARTA, CHE PVR SEGVIRA SAra nata dall’essere essa quarta gionta in distanza in tempo che ’l nimico non si era mosso, & dall’ hauere leuata la punta dal finimento della nimica & portatala disopra, come perapunto si disse nella passata, ilquale nimico hà uoluto cauare di seconda per ferire di dentro imaginando, che’l suo auerssario douesse andare à parare dall’altra parte, & penetrare esso con la uiolenza della sua spada al corpo per l’angolo, che naturalmente si forma da detta seconda, inanzi che detto auerssario hauesse potuto parare, dil che si è ingannato perche questi, che già hauea presentata la punta al corpo nimico, hà seguitato oltre con portare solamente uerso la parte di dentro quel braccio della spada, che doueua stendersi, secondo, che fecce nella detta passata figura; & hà pigliato col finimento la spada nimica prima, che habbia finita la cauatione, & perciò la si uede così trattenuta abbasso, si come anco si uede il braccio corto portato indentro perla diffesa, che hà fatto. Potria similmente essere, che nel primo ariuare del ferittore in misura, costui che è ferito hauesse uoluto ferire disopra in quello scoperto, che uedeua, & che il ferittore cauando della sua quarta habbia ferito lui per di dentro, & parato in guisa, che la spada di esso ferito sia andata così à cadere per hauere uoluto sforzare la nimica dubbitando, che detta nimica uolesse parare, doue che non trouandola per rispetto della cauatione è uenuta à cadere, come si è detto. In oltre detto ferittore haurebbe potuto parare, & ferire disopra, come nella passata si uidde, ancorche il nimico si fosse affaticato di resistere, & questo per il uantaggio della linea perche il detto nimico uoleua resistere con la sua parte debile alla parte più ualida di esso ferittore. 148. |
|||||||
[50] |
[202] LA TERZA CHE SEGVE, LAQVALE HA MESSA LA PVNTA al finimento auerso di una terza bassa l’ hà fatto con disegno, perche hà uisto il nimico tanto basso, & con le parti disopra tutte scoperte se ben lontane, di andare à porre la sua spada sopra il filo della nimica con la punta riguardante uerso il finimento sopra detto, affine di mettere detto nimico in pensiero di alzare la sua spada per l’ una, ò per l’ altra parte per pigliare poi il tempo di quel moto, & non mouendosi esso nimico andare pure inanzi à ferire della medesima terza, & dirizare la punta uerso la gola nimica per appresso il braccio destro & con portare il finimento uicino à detta nimica per tenersi sempre diffeso andando serrato appresso à quella à ferire della medesima terza, che così lei non potrà ferire più basso con la punta mentre non si uorà partire dalla giustezza, & rimanere in pericolo. 149. |
|||||||
[51] |
[203] PER IL VANTAGGIO DELLA TERZA GVARDIA BASSA PASSAta, laquale hauea posta la punta uerso il finimento nimico è nata la ferita, che hora si uedrà in questa terza, perche essendo quello che hà ferito gionto in misura quest’altro non si è mosso, in modo che ’l ferittore hà seguitato il suo corpo, & ariuato à ferire, il che non meno hauria fetta, ancorche il nimico hauesse procurato di ferire in qualunque parte, per hauere esso, ferittore continouato inanzi sempre diffeso, & perche similmente saria gionto prima, che detto nimico hauesse finita la cauatione, ouero fosse gionto con la punta nell’ altezza, oue prima si trouaua la mano di esso ferittore, & cosi il detto ferito non haurebbe potuto diffendersi se non con l’ andare indietro co’i piedi, che quanto al corpo non lo poteua più dillongare, & se pure si fosse uoluto ritirare, & parare haurebbe dato oportunità al suo auerssario di mutare effetto, & se hauesse parato di dentro il medesimo auerssario hauria ceduto in seconda, & se di fuori il detto ferittore, hauria uoltato pure in seconda, mà per disotto il braccio della nimica; lequali cose tutte, riusciranno, quando si seguirà senza fermarsi mai, auertendosi, che nel fermarsi, & poi uolere andare si portarà gran pericolo, & che meglio sarà lo tornarsi à rimetere un’ altra uolta indietro, & cominciare di nouo. 150. |
|||||||
[52] |
[204] DELLA SESTA ET VLTIMA REGOLA DI ANDARE A FERIRE IL NIMICO SENZA FERMARSI, ET SENZA ASPETTARE TEMPO mà sforzarlo perche lo faccia. LE RAGGIONI, ET LE REGOLE ANTECEDENTI DELL’ ANdare à ferire senza fermarti descritte da noi sono opere essercittabili & facili à riuscire, una però più dell’ altra, & di loro quella, che è la migliore è anco la più artifficiosa, & questa di cui hora siamo per trattare ueramente è di maggiore artifficio, & in essa si adoprano spada piedi, & corpo con assai maggiore sottilità, che nell’ altre. In questa regola dunque si comincia di lontano co’i passi naturali altre uolte insegnati, & si uà contra il suo nimico, mà gionto che sia l’ huomo nella misura larga à da trouarsi con la punta della spada al debile della nimica in modo che cognosca essere più forte. Cominciasi col braccio auanzato, & secondo che ’l corpo camina inanzi così dee la mano della spada andare approssimandosi per fare restare la punta nel medesimo luogo che è quando si troua nella misura larga, & quando comincia [205] ad’ aquistare il uantaggio, perche in somma se bene il corpo camina la spada hà da restare, & così il braccio hà da stare fermo, & il corpo ad’ auicinarsi in un certo modo à quello tanto quanto uiene inanzi; circa poi alli piedi hauendone l’ huomo posto uno in terra dee leuare l’ altro, & conggiongerlo à quello, tenendolo però sospeso affine di poterlo mettere ouunque fosse di mestieri se il nimico si mouesse, & se pure non si mouesse si douria posarlo giù poco inanzi l’ altro, & leuare quello subbito col medesimo grado, & tenerlo sospeso con la medesima intentione, perche se il detto nimico pigliasse il tempo di quello leuarlo sia l’ huomo in tempo anch’ esso à pigliare partito prima, che detto piede ariui in terra, & se il detto nimico lo pigliasse nel metterlo in terra deue l’ altro essere in aria per andare, doue che in tal modo l’ huomo sempre si trouarà sopra di un solo piede, & potrà andare presto, & trattenuto, come uorà, auertendo di portare sempre, quando uà, li piedi nella linea della spada nimica, & se sarà dalla parte di dentro, & che la nimica per caso fosse alta, deue nelo auicinarsi col corpo al braccio alzare un poco la mano, & tanto solo, che la punta faccia andare la nimica, disotto di se, & così mantenerla, nelquale tempo se il detto nimico uolesse ferire in quella parte più bassa, doue era stata rispinta sarà à proposito all’ osseruattore di questa regola di parare, & ferire disotto in punto medesimo per la parte di fuori se li suoi piedi saranno entrati nella retta linea della nimica, nel qual caso, & nell’ è sequtione del quale effetto la mano dee portarsi in terza nel ferire, & del corpo la sinistra parte inanzi, & della destra fare un scurzo indietro per più raggioni, prima affine che se il detto nimico cauasse non ritrouasse il corpo, & così non fosse da fare altro che ferire, oltre, che quanto più la spalla sinistra uà inanzi tanto più la spada si fortiffica, & tanto più si può scurtarla, in modo, che si potrà andare più inanzi nella stretta misura, & il corpo similmente passarà il pericolo, perche in questa regola si hà da osseruare una massima cio è, che nel luogo, doue si comincia à ritrouare la spada al nimico, bisogna mantenerla sino, che si uà à ferire, ne mai si dee ferire, se il corpo non haurà passata la punta, ouero nel tempo che ’l passa, & ancora che ’l nimico facesse qualche mutatione nel tempo che si uà deue con tutto ciò l’huomo contenersi, ne ferire se non conosce chiaramente di potere penetrare col corpo la punta nimica, altrimenti sarebbe meglio pigliare il uantaggio dall’ altra parte, & senza fare moto alcuno ne di braccio ne di mano, mà col sollo effetto del corpo, & alquanto della punta, se ben poco, è condursi tanto inanzi, che si potesse ariuare al nimico senza stendere intieramente il braccio, che nella medesima regola si dee hauere questa altra osseruatione di condursi con la punta della spada sino al corpo auerso unito senza mai slongare il braccio, & senza mouerlo, che in questa forma l’ huomo sarà sempre pronto col corpo, spada, è punta à pigliare qualunque mutatione, & condurassi à ferire sicuramente, & con molta forza, perche il corpo sarà quello, che ferirà, & non il braccio & cosi andando, ò che la spada passarà, ouero si romperà, ouero il nimico si riuersarà per terra, ne ui sarà dubbio, che detto auerssario possa passare la punta col corpo ne leuarsi di presenza, ne meno, che possa battere, ò parare con la sinistra mano tenendo la spada sola, che quando fosse aggionto il pugnale haurebbe luogo tale raggione in alcuni casi mà non in tutti, perche se la punta auersa fosse stretta con quella del pugnale non si potrebbe andare à trouarla senza pericolo di perdere la propria spada, nelquale caso uerebbe in acconcio di usare, quella altra raggione di andare amettere la punta al forte nimico, doue si potrà saluarla & ferire con minore sottilità, che nella sola spada, per essere la spada più lontana dalla nimica, & più sicura anco dal nimico pugnale, che per la lontananza non la può hauere; auertendosi di più, che nel portarsi inanzi si hà da tenere una certa maniera di non lascriare penetrare la propria punta, mà tenerla sempre nel medesimo luogo, & si come si uà unendo il corpo, così deesi andare approssimando il pugnale alla nimica in guisa tale, che risoluendosi l’ huomo di ferire, detto pugnale sia tanto inanzi, che senza fare altro moto di diffesa possa diffendersi da essa nimica, che anco in detta spada è pugnale si può bene andare senza fermarsi, mà non si può già con una di queste regole andare contra tutti li siti, si come [206] nella sola spada, perche è neccessario seruirsi hora dell’una, hora dell’ altra secondo il bisogno, & acciò questo sia meglio inteso noi metteremo le sue posture in disegno, doue si uedrà il modo del primo mettere la spada, & la ferita, che può nascere, si come al presente si mettono quelle della spada sola lequali risolutioni tutte sono fondate nel uantaggio de’ passi, corpo & spada, se bene quando il nimico non la tiene ferma, & che con la punta uà girando in continouo moto, è malageuole molto ad hauerla, che in tal caso si potria serrargliela, & impedirli il moto, ilquale rimedio, à dire il uero, porta seco pericolo di disordinarsi, che perciò molto meglio farà tanto nella sola spada, quanto nella spada è pugnale di andare tenendo la punta per la prospettiua della mano auersa, & continouare inanzi, che detto nimico sarà neccessitato fermare quel moto, & procurare di deuiare la punta del nostro osseruattore, altrimenti questi andarà tanto oltre, che ferirà nel tempo, che quella punta gira, senza che possa parare con la spada ne meno col pugnale, se l’ hauerà, perche la medesima punta del nostro sarà molto lontana da detto pugnale, & molto inanzi uerso il corpo, di modo, che se uorà portare esso pugnale alla diffesa dall’ altra parte, non potrà parare, & darà molta comodità di essere ferito per la tardanza caggionata da così gran distanza, però non è forma, doue il nimico possa situare il suo corpo, & le sue armi, che con queste regole non ui si troui il suo contrario per poterli andare contra con uantaggio; & se bene alcuni hanno presunto di dire più tosto come temerarii, che scienti di quest’ arte, di hauere botte che non pattono regola in contrario, & del tutto in reparabili, noi da giusta raggione persuasi diciamo che ciascuna botta hà il suo contrario, & che nessuna botta non hà contrario cio è che la botta fatta nel suo giusto tempo, & giusta misura non hà contrario, & inreparabile, si come quella che e ingannata dal tempo, ò dalla misura hauere il suo contrario, & essere senza difficoltà parabile, in modo che da tutte l’ huomo si può diffendere, & da nissuna si può diffendere, & chi in altro modo sente di gran longa s’ inganna, si come si sono ingannati quelli altri, che hanno creduto una medesima botti potersi operare contra ciascuno huomo, noi diciamo bene, che si può andare contra tutti li huomini, mà che fà di mestieri operare diuersamente secondo l’ oportunità data dal nimico & questo sia à bastanza quanto alla risolutioue [!] di andare senza fermarsi facendo solo intendere, che si dee sapere andare, trattenersi, andare presto, andare lento, & tornare indietro, mà fare ogni cosa di proprio uolere, & non forzato dal nimico, perche saria segno, che le raggioni contrarie fossero più forti, & che tutto si facesse per saluarsi dal pericolo, doue che quando sono fatte uolontariamente, ò per qualche fine di ingannare, l’ huomo sà ritornare, & andare inanzi à uoglia sua, & questo si hà da stimare per uero giuditio, & uera peritia di armi, cognoscendosi apertamente, che questo tale sà operare secondo la qualità dell’ huomo nimico, & del sito oue esso si troua; restano da fare li particolari discorsi à ciascuna figura del cominciare l’ aquisto, & la misura, & porre anco le ferite, che da esso aquisto, & misura nasceranno. |
|||||||
[53] |
HAVENDO L’ OSSERVATTORE DI QVESTA NOSTRA REGOLA cominciato ad’ andare contra il nimico hà pigliato il uantaggio, che si uedra nella seguente figura, & è uenuto portando la spada in maniera, che gionto alla nimica si è trouato hauere il uantaggio dalla parte didentro, & con trouarsi in quarta guardia contra la terza, che tutto è proceduto per essere stato più scoperto il nimico da quella parte, & per fortifficare la spada hà uoltato il corpo, & disteso l’ angolo, che naturalmente si forma dalla mano quando è in quarta tenendosi riuolto in prospettiua tale che mostra il petto in modo che di dentro è sicuro, & di fuori hà poco scoperto, per tale caggione dunque hà uoltato il corpo, acciò che con picciolo moto possi essere tutto diffeso, ilquale modo di situare il corpo fortiffica la spada dall’ una, & dall’ altra parte assai più, che se l’huomo stesse col destro [207] fianco inanzi, & potrà seguire col piè sinistro inanzi per auicinarsi senza auanzare la spada più di quello, che anco al presente si uede come con l’ altra figura mostraremo. 151. | |||||||
[54] |
DA QVELLO PRIMO AQVISTO VEDVTOSI NELLA PASSATA figura, è uenuto il presente, che quì oltre si uedrà in costui, che si troua con la punta nel medesimo luogo, doue era prima, ilquale non hà lasciato scorrerla inanzi, mà hà tenuto il braccio, & è andato inanzi col piede, & corpo solamente, & in fare questo è uenuto portando indietro la destra parte, & uolgendo la sinistra inanzi nel qual modo si è approssimato tanto, che la testa si è trouata in ultimo più inanzi della mano, disegnando leuare l’ altro piede per portarlo ancor esso, & in posandolo in terra di portare quella punta à ferire, & mettere il finimento alquanto più inanzi del luogo, oue la punta si troua al presente, & discorrere il filo nimico con penetrare col corpo sino al corpo nimico in guisa, che l’ altro non lo possa impedire. 152. |
|||||||
[55] |
[208] DA QVELLI DVI AQVISTI DISCORSI SOPRA LE DVE ANTECEdenti figure è deriuata questa ferita che seguirà, fatta di quarta, & ancorche il nimico habbia uoluto dillongarsi, & oprare con la quarta lui non hà potuto finire di uoltare la mano, che ’l nostro osseruatore hauea già ferito, & tutto perche l’ altro l’ hauea troppo lasciato auicinarsi prima, che si fosse mosso, che doppo che era entrato del primo nel secondo aquisto non era più tempo che esso nimico potesse parare da quella parte, mà se si fosse mosso nel tempo del primo aquisto, mentre che gionse alla spada, & hauesse cauato non per ferire, perche non hauria potuto fare niente, mà per trouare la punta auersa dall’ altra parte si sarebbe liberato dal primo pericolo, & haurebbe imposta una certa neccessità all’ auerssario di usare gran prontezza di mano a dirizare la punta propria, & escludere quella che si cauaua di fuori prima, che si finisse la cauatione ouero di contracauare, & auicinarsi col corpo senza auanzare la spada più di quello, che era nel primo aquisto, in modo tale, che la cosa sarebbe stata più difficoltosa per l’ istesso ferittore, l’ operationi del quale se fossero state fatte co’i suoi requisiti non si sarebbe con tutto ciò potuto detto nimico saluarsi nel fine per il ualore, & gran fortezza di questa raggione nell’ assalire che quanto più si auicina al nimico tanto più diuenta sicura rispetto alli scurzi, & all’unione del corpo, spada, & moto de’ piedi. 153. |
|||||||
[56] |
[209] COSTVI, CHE HA GVADAGNATO IL VANTAGGIO CON HAVEre cominciato ad’ andare contra il nimico è uenuto portando la spada in guisa, che gionta alla nimica si è trouato hauere fatto l’ aquisto dalla parte di fuori, & ad’ essersi trouato in quarta guardia contra la terza, & hallo fatto per due raggioni prima per essere più forte da quella parte, oue è la nimica, l’ altra per saluare il corpo in quello scoperto fatto dall’ angolo della quarta appresso la mano. Hà tenuto il corpo uoltato in prospettiua mostrando tutto il petto per essere forte, & sicuro di fuori, & col finimento che è in quarta si è coperto quasi tutto di dentro in modo, che con poco moto si è da ogni parte diffeso, & hà leuato il derettano piede affine di portarlo inanzi senza auanzare la spada più di quello, che al presente si troua come nell’altra si uedrà. 154. |
|||||||
[57] |
[210] DAL PRIMO VANTAGGIO MOSTRATO NELLA PASSATA FIGVra è nato quest’ altro, che seguente mente si uedrà, perche essendo gionto il nostro osseruattore alla punta nimica, & hauendone fatto l’ aquisto, hà continouato oltre col piè sinistro, & acciò che la sua spada non scorresse più inanzi di quello, che era si è portato con la spalla sinistra inanzi, restando con la destra indietro, doue che era nel primo aquisto, & così è uenuto ad’ assicurarsi togliendo la comodità all’ auerssario di potere ferire in modo alcuno la parte di sotto, & quella di dentro è tanto coperta col tenere la mano ferma doue hora si troua, & col passare, se bisognasse, del piè destro, che non hà da temere il detto auerssario, & dalla parte di fuori similmente è tutto diffeso in modo, che con questo effetto può andare à ferire per sopra la spada nelo scoperto, che si uede dal debile al corpo, si come nella postseguente figura si uedrà. 155. |
|||||||
[58] |
[211] DALLI DVI VANTAGGI MEDEMAMENTE MOSTRATI DISOPRA è nata questa ferita di quarta contra una terza laquale hà uoluto parare; perche essendo il nostro osseruattore gionto nel secondo termine che il nimico non si era motto, hà continouato inanzi col corpo senza auanzare il braccio più di quello, che si uede, piegando detto corpo, & tenendo di continouo la mano in detta quarta guardia, lequali cose tutte sono fatte con molto artifficio, perche gionto al secondo partito, come si è detto, doue si trouaua col braccio ritirato, se l’ hauesse slongato inanzi per ferire, haurebbe fatto tempo al nimico di ferire lui di quarta di sotto, & di girare il corpo lasciando passare la spada del detto nostro uana, & anco pararla senza cauare & ueramente nelo slongare del braccio la spada si sarebbe indebolita, & dal nimico si sarebbe facilmente potuta rispingere, mà hauendola accompagnata col corpo non haurebbe esso nimico hauuto forza di portarla fuori, per tale raggione dunque si è mantenuto in quarta, & anco per potere più facilmente parare, se ’l detto nimico hauesse uoluto ferirlo disotto abbassandosi anco deritto inanzi per facilittare la diffesa tanto disotto come di dentro, perche se l’ istesso nimico fosse uenuto à ferire in quella parte, con poco moto di mano, & di corpo si sarebbe diffeso, & perche anco sarebbe gionto più inanzi talmente che la nimica sarebbe passata, & egli sarebbe stato fuori di pericolo, doue per contrario, se hauesse piegato in fuori sarebbe stato più scoperto di dentro, ne sarebbe andato tanto oltre col corpo, & così il nimico haurebbe più ageuolmente potuto rimettere la spada, oltre che le forze del nostro osseruattore sarebbero state più disunite, & per tutte le raggioni esso sarebbe stato più debile. Hauressimo ancora messi li effetti che possono nascere contra la prima seconda, & quarta guardia, & non meno contrale angolate, & ritirate, mà sonosi lasciati in disparte per maggiore breuità, & perche chi saprà andare sicuro contra [212] le rette linee, più facilmente potra andare contra le dette[36] angolate, & ritirate, delle quali in somma non si trattarà, perche con queste raggioni de mostrate se li può anco operare ageuolmente contra, essendo che quanto più l’ huomo può approssimarsi al nimico prima, che sia trauagliato, & impedito dalla spada auersa tanto più è sicuro, & tanto più tosto si spedisce, perche non può detto nimico fare tante cose quando seli è uicino, ne può fare molte mutationi, doue è il pericolo maggiore; Quanto alle ferite, che possono essere fatte dalle angolate, & ritirate di slancio si tacciono similmente, perche non sono di alcuna perturbatione, perche sapendosi andare secondo queste nostre regole si uà in guisa tale, che si è sempre coperto da quella retta linea, che uiene dalla nimica punta alla corpo. Circa le mutationi, che fanno colloro, iquali sono angolati riescono molto più tarde delle rette linee, & perciò in tutte questo sei raggioni habbiamo mostrato più contra le rette linee, che contra l’ altre, perche sono alcuni iquali stando nella detta retta linea si danno à credere dì non potere essere battuti, massime essendo in filo col corpo, doue noi li mostramo in quello luogo in quanti modi possono essere ingannati. Rettaci à ricordare, che in quella ultima raggione, è migliore, come si è detto, l’ adoprare più tosto una spada corta, che longa come più comoda da reggersi, laquale non può essere tanto trauagliata, ne meno hà tanto debile, nelqual caso, se quella del nimico sarà più longa, tanto maggior uantaggio sarà perche uà di risolutione. Et chi si saprà ben ualere di queste raggioni potrà andare contra qualunque guardia imaginabile, la quantità delle quali per essere quasi infinita si è lasciato dimettere, essendoci bastato di mettere i fondamenti, da quali si può ageuolmente comprendere come si habbia da operare contra quel si uoglia di loro, & però qui sarà il fine del raggionare della sola spada, & si attenderà a trattare alquanto della spada, è pugnale. 156. |
Second Part - On Proceeding with Resolution with Sword and Dagger
Illustrations |
Illustrations |
Draft Translation (from the archetype) |
Prototype (1601) |
Archetype (1606) [edit] |
Copenhagen Version (1600-1609) [edit] |
Munich Version (ca. 1635) [edit] |
German Translation (1677) [edit] |
French Translation (1644) [edit] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[1] |
[213] LIBRO SECONDO PARTE SECONDA. DELL’ ANDARE DI RISOLVTIONE DI SPADA, E PVGNALE. HAVENDO NOI PIENAMENTE DISCORSO SOPRA IL MOdo da tenersi ne lo andare senza fermarsi in presenza à ferire il nimico con la sola spada trattaremo addesso di quello, che si deue osseruare nella spada, è pugnale, che se bene in queste armi serue il medesimo uantaggio de’ piedi, i quali come in continouo moto oprano più presto di quelli, che sono fermati, nondimeno quì è da considerare, che l’ huomo hà da reggere, & gouernare due armi, & che due ancora sono quelle dell’ auerssario, da quali è neccessario guardarsi, in modo che à uolere operare, come si richiede, fà di mestieri hauere gran giuditio in conoscere li uantaggi, & i pericoli, perche ne lo andare à trouare il nimico nelo scoperto per farlo mouere si porta gran pericolo di perdere la spada, ciò è che detto nimico non la troui, se non con la spada col pugnale almeno, & impedisca non solamente il disegno, mà inetta in pericolo, doue che si dee nell’ operare hauere molto riguardo di non andare tanto uicino all’ una, ò all’ altra arma, che non si possa liberare la propria spada in tempo, se bene è uero che quanto più si sà condure quella libera inanzi, & sicura, che tanto più riescono le raggioni, mà altretanto si hà da considerare che maggiore è il pericolo. In queste armi, dunque dee l’ huomo non solo procurare che ’l pugnale facciala diffesa con poco moto quando la nimica uiene per ferire, mà che la detta propria spada sia in sito tale, che uada à ferire in giusto tempo, & diffenda quella parte più uicina al luogo, doue il nimico sia uenuto per ferire, acciò che se hauesse finto di ferire in quel luogo perferire poi nell’ altro più uicino, che si scuopre nel fare la diffesa troui la uia chiusa, & diffesa cosa non difficile per essere queste dui armi, atte anco à fare due diffese, l’ una doue il nimico uiene, & l’ altra oue potrebbe uenire, & tutto senza impedire il ferire ne lo stesso tempo, mà altrimenti oprando si potria restare ingannato. In queste armi similmente sono più uie, per doue può uenire il nimico, & per lequali si può andare ad’ assalire, mà non già tante regole da potere operare contra tutte quelle cose, che può fare detto nimico per l’impedimento del suo pugnale, mà nondimeno ci sono quattro maniere ò raggioni, con lequali si può andare ad’ assalire senza aspettare tempo ne altra cosa, mà andare risolutamente, & senza fermarsi, nellequali entrano tré guardie, che si sono poste nelle figure semplici, affine di sapere, che con esse si può andare, & fermarsi, come si uuole, dellequali trattaremo hora più sottilmente, & daremo principio da quella seconda bassa, che si forma con la spada trauersata, & poi seguiremo parlando delle altre ordinatamente, come sin hora habbiamo fatto. |
|||||||
[2] |
[214] DELLA PRIMA REGOLA DI ANDARE A FERIRE IL NIMICO SENZA FERMARSI CON SPADA, è pugnale. IN QVESTA PRIMA REGOLA PER ANDARE DI RISOLVtione si opera una seconda guardia, laquale si è ueduta trà le figure semplice di spada, è pugnale, nella quale cominciando l’ huomo compassi naturali in giro uerlo la parte sinistra, come che la raggione di tale guardia richiede, può tanto allontanarsi, quanto approssimarsi al nimico senza mutatione di corpo, ne di passi & nella quale si può l’ huomo conseruare, & procurare di tirare inanzi il nimico, perciò fù da noi messa nell’altro luogo, doue si parlò della natura di essa, & del modo, che si dee tenere nel situarla, & operare in essa, & doue si disse, che l’ andare in giro non era per altro, che per saluare quella parte, laquale sopra la spada è scoperta, & che lo trouarsi col pugnale fuori di essa nimica nel giongere in misura, & il tenere la spada così serrata appresso il detto pugnale, non era per altro se non per che essendo penetrato con esso la punta nimica detto auerssario non la potesse cauare per la parte disotto, & che il serrare di detta uia dalla spada, & il tenere il pugnale così in piede non era fatto ad’ altro fine se non perche detto auerssario non la potesse cauare per sopra la punta di esso pugnale se non con gran longhezza di tempo, ne meno potesse fingere, ne ferire, cosa che caggionarebbe, & perturbatione, & disunione d’ armi, & forsi anco ferita; l’ andare poi così basso col corpo è fatto, acciò l’ istesso nimico non habbia luogo da potere ferire di sotto, talmente che la raggione di questa guardia hà il suo fondamento sopra lo situarsi in guisa, che l’ auerssario non habbia, altro luogo da potere ferire, che sopra la spada di dentro dal pugnale, laquale parte l’huomo deue andare coprendo secondo, che uiene auicinandosi, mà con riguardo tale, che mentre uuole coprire quella non discuopra l’ altre & tanto che non potesse parare, douendo essere certo che doppo hauere formata ben detta guardia non possa la nimica spada ferire ne trauagliare altroue che in quello sopra spada, laquale parte dee l’ osseruattore di questa raggione uenire tanto saluando, che gionto alla nimica sia il corpo tutto fuori di presenza della punta, di essa nimica, ne per quale si uoglia caso dee mai disunire dal pugnale la spada andando con detta guardia, auertendo anco, che detto pugnale ne lo ariuare alla nimica si hà da trouare appresso il filo di essa, & andarla scorrendo senza batterla, per fuggire il pericolo che potria nascere se’l nimico la leuasse all’hora da quel luogo, & la mettesse in un’ altro, ò la rithraesse, & feresse doppo la caduta del pugnale, ouero disordinasse esso pugnale col mostrare di ferire, & ferire poi nel tempo che ’l nostro si uolesse diffendere, oltre che detta nimica essendo battuta si fà subbito libera, in modo che ’l detto nostro osseruattore non serebbe più patrone di essa, mà scorrendoli solamente il filo può seguittarla col pugnale ouunque uada, sicuro contra quale si uoglia nimico effetto, & con tanta maggior sicurezza, quanto, che il detto nimico non può mai hauere la sua spada, laquale è trauersata fuori di presenza, ne si stende più inanzi uerso il medesimo nimico di quello, che faccia la mano dell’ istesso pugnale, con essere anco il debile della detta spada molto lontano, perlequali cose non può mai dal nimico pugnale essere ariuata, dalla nimica spada sì bene, mà con pericolo di essere lei esclusa di fuori & di certa ferita ad’ esso nimico prima, che potesse liberarla, & quindi uiene la sicu- [215] rezza al nostro, di non poterli mai essere occupata la spada, li resta solo à sapersi seruire delle raggioni, gionto che sia nelle misure, lequali sono queste, ciò è che douendo ferire di detta seconda, sarà di mestieri lasciare il pugnale alla nimica, & andare à ferire, doue sarà l’ oportunità, & occorendo ferire di quarta, nel uolgere la mano, dourà andare scorrendo sempre col filo della spada per appresso la mano del pugnale con osseruatione tale, che quella strada da fra posta in meggio dell’ una, & dell’ altra arma sia sempre chiusa, & che dopò l’ hauere finito di slongare, la mane di essa spada sia serrata appresso quella del pugnale, non douendo mai in alcuno caso leuare il corpo, mà abbassarlo anco più nel tempo del ferire, che non mancando di quelle osseruationi batterà sempre qualunque nimico. |
|||||||
[3] |
QVESTA E QVELLA SECONDA GVARDIA DI CVI HABBIAMO raggionato, laquale per dare meglio à diuedere habbiamo formata in figura, come quì oltre si uedrà, doue si conoscerà il modo dell’ andare, & del portare l’ armi, & come dee l’ huomo ritrouarsi con la spada, è pugnale contra l’ armi nimiche nell’ ariuare in misura, atteso che sempre hà da studiare di hauere il pugnale dalla parte di fuori della nimica, come nella detta seguente figura si uede, & quando non potesse perche ’l nimico hauesse portata la spada tanto fuori, che la non fosse in presenza, douria andare sempre uerso quella parte sino che ’l pugnale giongesse appresso il filo della detta spada nimica, senza pero mouersi della guardia, & poi subbito andare diritto contra l’ auerssario, & ferire in quello scoperto, che uedesse, con tenere sempre il corpo basso, & quando anco il bisogno lo richiedesse ferire nel meggio dell’ armi nel quale caso douria ferire di quarta, & però noi auertiamo in questo luogo, che non dee mai disggiongere l’ armi, ne nel uoltare di mano, ne in quale si uoglia altro effetto, massime quando la nimica è di fuori, perche à uolere uoltare di quarta con le mani disunite potrebbe detta auersa spada cacciarsi disotto trà l’ una, & l’ altra mano, mà ritrouandosi il detto nimico di dentro, come al presente, dee il nostro andare à ferire di detta seconda, nel meggio, se ui sarà scoperto, ó disotto, ouero sopra il pugnale, secondo l’ opurtunità del detto scoperto, & lasciare il pugnale alla diffesa, come si è detto, & come si uedrà nella postseguente figura, oue sarà la ferita. 157. |
|||||||
[4] |
[216] DALLA SECONDA ANTECEDENTE, CHE SI E VEDVTA GIONgere col pugnale alla nimica, è nata questa ferita sopra il pugnale, perche doppo l’ aquisto di detta nimica si è spinto inanzi contra il corpo auerso, quale era in terza come si uidde, & hà cauato di detta seconda sopra il pugnale scorrendo col suo filo quello dell’ auerssario, & questo, che è ferito uedendolo cauare, & uenire si è ritirato col piè sinistro indietro slongando la spada inanzi per in contrarlo, & hà uoltato il corpo credendo potere parare col pugnale, ne hà potuto fare cosa buona, perche la sua spada era già occupata dal pugnale del ferittore, ilquale hauea saluato gran parte di quel corpo, che prima era scoperto sopra la spada di questa seconda, come si uidde, & seguittando il filo nimico è restato in tal modo tutto diffeso, & hà ferito l’ auerssario senza, che habbia potuto diffendersi, & tutto per hauere continouato tanto unito cauando, che quando la spada hà finita la cauatione la ferita era già fatta, & perciò era impossibile che ’l pugnale nimico la portasse fuori. Potria similmente essere, che il detto ferito uedendo il suo auerssario uenirli contra così scoperto sopra la spada habbia uoluto ferire in quella parte, & che il detto auerssario, ilquale già li hauea aquistata la spada, & che benissimo sapeua non potere essere ferito altroue, habbi spinto il pugnale nel filo della nimica, & continouando inanzi habbia fatta la detta ferita di seconda, quando, che per apunto hà finita la cauatione. |
|||||||
[5] |
[217] DA QVELLA SECONDA PVRE, CHE SI VIDDE CONTRA LA TERza è nata la ferita di quarta, che seguirà perche mentre collui che hà ferito è gionto col pugnale alla punta nimica l’ altro hà uoluto liberarla con cauarla sotto la spada per la parte di fuori, mà il ferittore, che si trouaua in seconda uoltando la mano in quarta, & mettendo il forte appresso quella ponta, che era andata disotto, è sempre uenuto inanzi con uoltare la propria punta quale era trauersata fuori di presenza contra il corpo nimico in modo tale, che quando hà finito di dirizarla era già essa punta ariuata al corpo del nimico, ilquale, uoleua parare col pugnale, & uoltare in seconda, mà si è trouato con la spada esclusa di fuori dal ferittore, la spada delquale era tanto inanzi, che ’l detto pugnale auerso, quale douea trouare il debile hà trouato it forte, & non hà potuto rispingerla; però si auertisce, che quando alcuno hà cominciato ad’ aquistare col pugnale la punta nimica, & che detto nimico la moua, che quello sarà sempre tempo di andare, tanto unito nondimeno, che se l’ istesso nimico parasse prima di essere ariuato, si possa seguitare oltre &’ mutare effetto. 159. |
|||||||
[6] |
[218] DELLA SECONDA REGOLA DI ANDARE A FERIRE SENZA FERMARSl CON SPADA, E PVGNALE. IN QVESTA REGOLA SI OPERA PVRE VNA SECONDA guardia, che ancor lei fù posta nelle figure semplici & laquale si sorma [!] con tutti dui li piedi egualmente inanzi, con le punte di essi uerso il nimico, & larghi l’ uno dall’ altro, col corpo piegato inanzi, & con le spalle l’ una non eccedente l’ altra, inguisa che ’l petto stia tutto riuolto contra il nimico, & con le braccia, & l’ armi alte & talmente ouate, che la punta del pugnale si conggionga con la spada appresso del forte chiudendo la uia alle punte, & alli taglii di potere entrare in altra parte che nel meggio, con la punta della spada riguardante uerso la sinistra parte, affine che la testa rimanga intieramente coperta, & da qualunque taglio diffesa, & sicura senza altro bisogno di parare, per il che non possa l’ auerssario offendere se non disotto nel meggio dell’una, & dell’ altra mano uerso la faccia, laquale può essere ageuolmente [219] diffesa dalle due armi, che ui sono inanzi. Le parti inferiori sono anch’ esse diffese, & sicure per la lontananza, doue non può detto auerssario ariuare se non uiene col capo sino appressso le mani dell’ osseruattore di questa regola, ilquale osseruattore essendosi acconcio in detta forma dee andare inanzi con piccioli passi per conseruarsi sempre in quella larghezza de’ piedi, quando sia tanto oltre, che penetri con le mani la punta auersa dee portarsi all’ hora co’ i piedi l’ uno nella linea dell’ altro da quella parte doue disegna andare col corpo, che in questo modo uscirà tanto di presenza quanto importa la metà di quel passo, che si trouaua hauere nella guardia, & sarà tanto andato inanzi, che non potrà più detto auerssario rimettere la spada in presenza, & se si sarà portato col piè manco nella linea del destro potrà ferire di quarta con tenere la punta del pugnale riuolta ingiuso, affine di escludere la nimica di fuori, che non uenga in’ quella parte, oue il corpo sarà uscito, mà essendosi portato col destro nella linea del sinistro maggiore comodità haurà di ferire, perche nell’ uscire potrà lasciare il pugnale in diffesa del suo fianco più prossimo alla nimica, & potrà dirizare contra il nimico quella sua spada così alta trauersata, come si è detto, che sarà tanto auanzata, che penetrarà col forte così inanzi, che l’ armi nimiche non potranno parare, & la punta in oltre sarà nel dirizarla già ariuata à ferire, nella quale forma di andare se l’ auerssario tirasse qualche slancio dourà il nostro, ouero parare con l’ istesso modo di lasciare il pugnale alla diffesa, senza battere però la nimica già mai, ouero portarsi col piede dalla parte destra, & spingere il forte della spada à serrare la nimica di fuori, & andare con la punta al corpo, incontrandolo nel punto medesimo che ’l detto auerssario si porta inanzi col slancio, & in questo modo riuscirà meglio l’ operatione, che non farà quando il nimico sia fermo in guardia, che all’ hora stimaressimo essere più à proposito l’ andare fuori dall’ altra parte col destro piede, che per il uantaggio dell’ essere già inuiato uerso il detto nimico si ariuaria tanto presto, che esso nimico non potrebbe saluarsi, oltre che questo è un modo, colquale l’ huomo si hà da rendere certo, che detto nimico non le potrà mai occupare la spada, cosa di grandissimo uantaggio per il nostro osseruattore, ilquale non si partendo da queste regole potrà andare contra qualunque sito, & qualunque guardia imaginabile. |
|||||||
[7] |
QVESTA CHE SEGVIRA E QVELLA SECONDA GVARDIA, LA quale si disse andare col petto contra la spada nimica, & hora, che è gionta in misura tanto, che della nimica punta è penetrato il suo pugnale, uà inanzi col destro piede, & scorre col proprio pugnale la detta lama nimica con uscire fuori di presenza uerso la parte destra di lo stesso nimico, in modo che quella spada che li guarda contra il petto uiene ad’ essere tanto fuori del suo corpo, quanto è longa la metta del passo in che egli si trouaua, & perciò li basta tenere il pugnale al filo di essa nimica senza rispingerla andando à ferire per sopra di quello dell’ auerssario, perche già conosce la propria spada essere superiore, & uotere fare una ferita di prima, come nella postseguente figura si uedrà. 160. |
|||||||
[8] |
[220] DALLA FIGVRA, CHESI DISCORSE NEL’ ANTECEDENTE DI quella seconda portatasi tanto oltre, che li era stato penetrato il pugnale dalla punta nimica si è potuto conoscere l’ effetto, & la caggione della ferita, die hora seguirà deriuata certamente dall’essere questo ferittore, subbito gionto, passato col destro piede, & portatolo fuori dalla parte destra nimica nella linea del piè sinistro, & così uscito fuori di presenza, & ariuato al corpo auerso di detta prima guardia sopra il pugnale, laquale prima guardia è uenuta dall’ effetto della seconda ouata fuori di presenza ilquale hà uoluto dirizarla senza abbassare la mano in modo, che essa mano è uenuta ad’ alzarsi, come si uede, impedendo il pugnale, che non hà potuto parare, contutto che esso nimico si sia slargato indietro & uolea uoltare il corpo, con anco cominciare à stendere fuori la spada, mà la botta è ariuata prima, che habbia finita la distesa, che perciò se si fosse anco ritirato maggiormente non haurebbe nondimeno fatto cosa buona, che sempre sarebbe restato ferito nel medesimo luogo, & se bene si fosse sforzato diffendere il primo colpo sarebbe nondimeno col secondo restato ferito disotto. 161. |
|||||||
[9] |
[221] QVANDO QVELLA SECONDA GIONSE TANTO INANZI, CHE il pugnale cominciò à penetrare la punta nimica il ferito uolse cauare per liberarla, mà il ferittore cognosciuto il disegno nimico, lascio il pugnale nel luogo, oue era prima, & uoltò la mano in quarta andando à ferire nel meggio dell’ armi, laquale ferita gionse con tanta celerità che detto ferito non hebbe tempo di pararla, perche la spada feritrice, che era fuori dalla parte destra nimica, quando dal ferito è stato cauato, era essa tanto inanzi, che nel proprio punto del cauarsi & dirizarsi, era già ariuata al corpo, in modo che non è potuta essere respinta dal detto auerso pugnale, si come anco se il detto ferito si fosse ritirato, per hauere spatio di parare, il ferittore, lasciando la mano della spada nelo stesso luogo, haurebbe callato tanto la punta, che sarebbe andato à ferire sotto la mano del detto pugnale nel proprio tempo, che esso ferito credeua parare, ilquale non haurebbe potuto fare alcuna diffesa, & similmente se la spada dello stesso si fosse trouata più bassa, il ferittore lasciando il braccio del pugnale nella sua altezza medesima haurebbe uoltata la punta alo ingiù, & tenuta fuori di presenza la punta nimica. 162. |
|||||||
[10] |
[222] MENTRE, CHE QVELLA SECONDA GIONSE IN MISVRA COL passo largo, & piedi eguali, questo che è ferito leuò il pugnale coprendosi disopra, & con passare inanzi del pie manco uoltò la mano in quarta per andare à ferire quella parte, che uedeua scoperta nel meggio dell’armi, & perciò il ferittore portò il piede destro nella linea del manco, talmente, che uenne ad’ uscire di presenza & lasciando il pugnale alla spada nimica per escluderla di fuori dirizò quella seconda sotto il braccio dell’ auerso pugnale, & così uenne à ferire nel punto medesimo, che l’ altro hauea posto il piede in terra seguendo sino al corpo senza fermarsi. 163. |
|||||||
[11] |
[223] DELLA TERZA REGOLA DI ANDARE A FERIRE SENZA FERMARSI CON SPADA, E PVGNALE. IN QVESTA TERZA REGOLA, CHE HORA SIAMO PER mostrare, hà l’ huomo da doperare quella terza guardia laquale medesimamente si uidde nelle figure semplici di spada è pugnale, che staua conggionta co’ i piedi curuata del corpo, & con l’ armi aperte, & alte aspettando il nimico, per certi uantaggi, che si trouano in essa, si come copiosamente si disse in quel luogo, & douendosene al presente seruire, s’intende nel cominciare solamente à uenire di lontano per andare contra l’ auerssario, perche gionto pòi in misura hà dà trouarsi in altro sito di corpo, si come di armi. Trouandosi dunque in detta guardia hà da cominciare col piè manco allargandolo in fuori, & subbito leuando destro, con portarlo ancor’ esso in quella parte, & dee similmente cominciare con la spada à discendere dal quella guardia, & uenire conggiongendola appresso il pugnale tanto, quanto, che uiene approssimandosi, & portando indietro la spalla sinistra in modo, che nell’ ariuare in distanza la [224] spada si troui del rutto chiusa appresso del pugnale con la mano in quarta guardia, acciò che ’l nimico non possa entrare nel meggio, tenendo la spada longa in presenza contra il petto, ò faccia del detto nimico, & la spalla sinistra tanto indietro, che tutto il corpo uenga ad’ essere dietro la linea della spada, douendo anco mantenere la punta per quello scoperto nimico, che uedra, & essa spada tanto lontana dall’ armi nimiche, che sia certo di liberarla prima che ’l detto nimico la possa pigliare, & similmente la punta più uicina al corpo che sia possibile con lasciarla poi in quel segno senza, che la scorra più inanzi, & lui seguitare co’ i piedi curuando il corpo, & cominciando à uolgere la mano uerso la terza, & sicome uiene uoltandosi detta mano, così uadasi il pugnale slongando, & uuendosi, & quella punta, che era uerso il petto abbassandosi proportionabilmente in modo tale, che si possa cauare, & nel tempo di quelle operationi dee l’ huomo non meno uenire uoltando il corpo con la sinistra spalla inanzi, se bene non dee mai abbassare la mano della spada, mà seguitare uoltando sino in seconda guardia, & dopò l’ essere gionto di quarta in terza quando, che comincia ad andare uerso la seconda, hà da cominciare con la punta della spada à passare[37] la spada, è pugnale auerso lasciandola tanto inanzi come era, & in quel punto dee il suo pugnale essere di già ariuato alla nimica, & esserli nel filo, si come quando, che con la mano è ariuato nella detta seconda dee la punta della spada hauere finito il moto della cauatione, & ferito l’ auerssario sopra il pugnale, se per caso non fosse tanto alto, che detto auerssario ne restasse tutto coperto in quella parte, che all’ hora douria restare disotto dal braccio del nimico pugnale, & ferire di detta seconda, il che si deue osseruare quando il nimico si troui con la spada ritirata, & col pugnale auanzato, & anco con le punte serrate, che se le punte fossero aperte, & la spada ritirata, si ariuarebbe nel callare della terza alta in presenza sino appresso il nimico pugnale dalla parte di sopra con la mano in quarta, & con la punta tanto penetrata, che importarebbe la quarta parte, ò poco meno di essa lama, & all’ hora si dourebbe conggiongere il pugnale appresso la mano della spada, affine, che se ’l detto nimico uolesse parare di pugnale, & ferire di quarta, mentre, che la spada del nostro se li auicina possa il detto pugnale diffendere il destro fianco, & possa il detto nostro osseruattore uoltare il corpo, & la mano insieme, & ferire di seconda sotto il braccio sinistro nimico, ilquale nimico se nel merterli [!] la spada appresso il pugnale non si mou esse, & che la punta fosse penetrata la quarta parte della lama, come si disse, douria all’ hora il nostro uoltare la mano di quarta in seconda & spingere con un poco di giro di corpo alla nimica il pugnale, che hauea presso la propria mano, con scorrere il filo, & continouare inanzi, che ferirebbe sopra l’ auerso pugnale nel luogo proprio, doue la spada era uenuta à callare, che ’l nimico non potrebbe parare, & tutto, perche nel uolgere la mano in seconda la punta piega tanto in dentro, & è già tanto inanzi, che più uicina si troua al luogo, oue hà da ferire, che alla strada, doue il nimico prettende farla uscire, oltre che saria tanto ualida, che potrebbe resistere al pugnale auerso senza temere di essere respinta, mà se nel tempo che ’l nostro uà à mettere la spada in quella parte il detto auerssario leuasse il pugnale per ricoprirsi, & tenesse ferma la spada sarebbe all’ hor detta spada tanto ritirata che non potrebbe il detto nostro col pugnale ariuarli, in modo, che saria neccessario di rimouere la spada da quel luogo, & portarla in medesimo tempo per sopra la punta di esso nimico pugnale, & metterla nel meggio dell’ armi ferendo di quarta con continouare del pugnale tanto serrato appresso la mano della spada, che esso nimico non potesse entrare in quel meggio, & con mantenere anco il finimento contra la nimica, & piegare la testa inanzi, che sicuramente l’ auerssario non potrà parare ne ferire atteso, che la sua spada sarà esclusa di fuori; si potrebbe similmente quando il nimico fosse con le armi aperte, & la spada ritirata, nel callare, che si fà con la quarta, passare perla punta del nimico pugnale nel meggio dell’ armi & continouare inanzi conggiongendo il pugnale alla mano della spada, & da quel luogo uenire portandolo inanzi uerso la nimica, con uoltare la mano della spada, & lasciarla in quella parte sino che si conoscesse potere ariuare al corpo di detta guardia, ouero sino che ’l nimico cercasse di batterla od’ [225] occuparla per coprirsi nel meggio dell’ armi, che quello saria tempo opurtuno per ferirlo disopra del pugnale, che non potria saluarsi, ilquale nimico se si scoprisse disotto douria il nostro andarli continuando col pugnale alla spada, & ferire di terza, che esso nimico non potria fuggire una delle trè offese ò nel meggio, ò disopra, ò disotto. Questi sono li termini da usarsi contra le guardie ritirate non douendosi fare altra distintione, che dal longo al corto, & dall’ aperto, al chiuso sia poi la mano in qual si uoglia guardia, auertendosi non dimeno che se’l nimico si ritrouasse cõ la spada auanzata douria il nostro osseruattore, fosse aperta, ò serrata la guardia, nel callare con la spada andare all’ aquisto di detta nimica auanzata con uenire saluando il suo corpo da quella parte, che uà scoprendosi con sfuggire alquanto, affine che se detto nimico mutasse, esso di già fosse diffeso, & in questo andare con la spada alla nimica per aquistarla deue aggiongere il pugnale, ne mai ariuare in distanza disunito, sia il nimico in qualunque guardia, & tutte le dette operationi hanno da eseguirsi senza mai fermarsi, ne co’i piedi, ne con la spada, laquale quando si comincia à callare deesi sempre continouare il moto portandola inanzi, ò uoltandola, ne mai fermarla; del resto è bonissima regola, & riuscibile contra qualunque maniera di armeggiare. |
|||||||
[12] |
DA QVELLA TERZA ALTA CON LE ARMI APERTE, ET PIEdi giorni, che si uidde nelle semplici figure della medesima spada, è pugnale è nato l’ effetto di questa quarta nel modo che sidirà, cio è che essendo l’ osseruatttore [!] di detta terza lontano, con le armi alte, & passo stretto, hà cominciato à slargare il sinistro piede uerso la parte destra dell’ auerssario con passare inanzi col destro, & ne lo stesso punto hà cominciato à conggiongere la spada appresso il pugnale, in modo che quando è gionto in misura l’ una mano era di già serrata appresso dell’ altra, & la spada era già finita di uoltare in quarta, è uenuto similmente abbassando la punta à poco à poco, in modo, che ancor lei si è ritrouata in presenza nel giongere in misura, & l’ hà dirizata per quello scoperto fuori della spada, andando inanzi col corpo, ne hà lasciata penetrare la punta più di quello che è al presente, mà è andato uolgendo la mano uerso la terza con portare la destra parte alquanto indietro, & con approssimare il pugnale alla nimica; è uenuto similmente tanto abbassando la punta, che se fosse stato bisogno hauria potuto cauare ciò è se ’l nimico hauesse uoluto parare con la spada; & la mano che uà uoltandosi uerso la terza hauria seguittato il moto sino in seconda, con andare à ferire di dentro nel meggio dell’armi, & se’l detto nimico fosse uoluto andare col pugnale in quella bassezza, doue uà la spada, quest’ altro haurebbe uoltato pur di seconda, & sarebbe passato à ferire per la punta del pugnale, & parando con la spada, è pugnale insieme haurebbe cauato disotto con picciolo moto quella punta, che è andata abbassandosi, & haurebbe ferito sotto il pugnale, come si uedrà nella postseguente figura col corpo baffo facendo passare la spada per fuori del braccio sinistro. 164. |
|||||||
[13] |
[226] DA QVELLA QVARTA, CHE SIE VEDVTA HAVERE POSTA la spada di fuori da una terza è nata la ferita che segue, perche hauendo il ferittore, cominciato con la terza alta nel modo detto disopra, & essendo uenuto in misura, come anco si uidde nella passata figura, quello che è ferito, hà uoluto parare con la spada è pugnale accompagnato, mà il detto ferittore, che subbito gionto cominciaua à uoltare uerso la terza, hà messo il pugnale alla nimica, che ueneua inanzi per parare, & ferire, lasciando andare la punta abbasso, che ’l nimico non l’ hà trouata, & anco slargando la mano in seconda, laquale hà caggionato il pattare della lama per di fuori del sinistro braccio, mà disotto, & se nel tempo, che detto ferittore hà messo la spada per quello scoperto, come si uidde, l’ altro hauesse uoluto cauare, & parare col pugnale questo si sarebbe spinto inanzi pure di detta quarta, nella quale si trouaua, con leuare all’ auerssario il potere operare cosa alcuna, se non il ritirarsi quando esso ferittore è gionto in misura, ouero mutare guardia per fare mutare partito ad’ esso ferittore, ilquale se non hauesse saputo pigliare l’ occasione nella giusta mutatione, haurebbe dato comodità all’ auerssario di ferire lui, se fosse seguitato, se bene è uero, che detto ferittore haurebbe potuto fermarsi, & tornare à noua raggione. 165. |
|||||||
[14] |
[227] QVESTA TERZA SEGANTE, CHE HA SERRATA L’ ALTRA terza, laquale stà con la spada auanzata, & le mani conggionte è seguita da quella terza alta, che si disse prima, & laquale è uenutà descendendo, & tanto conggiongendosi, quanto ueniua inanzi, & così hà serrata la nimica con tutte due le armi tenendo la destra parte più indietro della sinistra, affine di potere, se ’l nimico cauasse, andare col corpo inanzi senza fare altro moto con esso corpo per diffesa, mà si ben per offesa con passare à ferire di seconda, ò di terza, secondo che ’l detto nimico, cauasse alto, ò basso, & in caso, che non cauasse di passare pure inanzi à ferire, come si uedrà per la ferita della postseguente figura. 166. |
|||||||
[15] |
[228] DALLA TERZA ANTECEDENTE, CHE HAVEA SERRATA LA nimica è nata questa ferita, che segue, & tutto perche questo, che è ferito si trouaua in terza auanzata, & co’i finimenti uno appresso dell’ altro, in modo che ’l ferittore si è ueduta così inanzi, & che l’ auerssario non hauea preso partito hà lasciato il pugnale alla nimica dalla parte di dentro, & uoltando la mano in seconda, con portarla per sopra la punta del pugnale auerso è andato à ferirlo nel petto, che non hà potuto parare, ilquale ferito ancorche si sia dillongato co’i piedi, & col corpo dal ferittore non hà potuto con tutto ciò liberare sa spada per essere detto ferittore troppo inanzi, che quando, l’ hà trouata[38] era già penetrata la sua sino al corpo. 167. |
|||||||
[16] |
[229] DA QVELLA TERZA PVRE ALTA E DERIVATA ANCOR QVESTA quarta laquale è calata sopra il pugnale di una terza situata sopra il sinistro piede, & con le parti destre in scurzo alo indietro per declinarle da quella ferita, che potria fare l’ auerssario cauando, alzando il pugnale affine di parare, nelquale caso l’ osseruattore di detta quarta uoltarebbe la mano in seconda, & se quello dalla terza non si mouesse col pugnale, il detto osseruattore lo ferirebbe in quella parte superiore, che si uede, col uoltare in detta seconda, perche la spada sarebbe di già penetrata molto inanzi, & con quello uoltare della mano l’ angolo la portarebbe dentro con resistere al pugnale, ilquale non la potrebbe respingere, in oltre se alzasse il pugnale per parare, & non cauasse la spada quale è di fuori, il medesimo osseruattore con abbassare la sua per disotto, & con tenere le mani conggionte insieme andarebbe à ferirlo in medesimo tempo con detta quarta disotto come si uedrà pure per la postseguente figura. 168. |
|||||||
[17] |
[230] DAL VANTAGGIO, CHE SI VIDDE DI QVELLA QVARTA DEriuata dalla terza alta sino appresso il pugnale auerso dalla parte di fuori, è nata questa seguente ferita perche giongendo il ferittore sopra il detto pugnale nimico, esso nimico hà pensato trouarli la spada, & hà alzato il detto pugnale per parare, & uoltata la mano in quarta affine di ferire, con cauare, & passare, mà il detto ferittore, che andaua caminando inanzi hà preso detto uantaggio, mentre che l’ auerssario hà alzato il detto pugnale, & hallo ferito pel punto medesimo, che esso auerssario credeua trouare la spada disopra, ilquale è restato talmente impedito, che non hà potuto necauare, ne passare, & ancorche hauesse cauato sarebbe con tutto ciò restato ferito. 169. |
|||||||
[18] |
[231] QVESTA QVARTA SIMILMENTE, CHE SEGVE, LAQVALE HA posto la sua spada nel meggio dell’ armi di una terza, che stà sopra il piè sinistro, è uenuta da quella terza alta, che si disse, & se ’l nimico non si mouesse il corpo andarebbe inanzi unendosi appresso le mani & subbito ferirebbe sotto il braccio sinistro del detto nimico di seconda, & passarebbe perdi fuori della spada col corpo lasciando il pugnale alla nimica, ilquale nimico se cauasse per di fuora della spada l’osseruattore di questa quarta ferirebbe pur di seconda disotto, il cauasse dalla parte del pugnale quest’ altro ferirebbe di detta quarta abbassando, la punta tanto, che andasse disotto dalla mano del pugnale auerso, & nel medesimo andare à ferire di detta quarta stringierebbe ancor più le mani insieme per escludere la nimica di fuori, ilquale nimico se uolesse parare col pugnale & cacciarsi oltre di terza disotto, per uedersi uenire così la nimica nel meggio, quest’ altro alzarebbe all’ hora la spada per sopra il nimico pugnale, & non meno ferirebbe, come si uedrà. 170. |
|||||||
[19] |
[232] DALLA QVARTA ANTECEDENTE DERIVATA DA QVELLA TERza alta, che si disse è nata questa ferita, che segue, perche essendo gionta nel meggio delle armi nimiche, esso nimico, che si trouaua in terza nel piè sinistro uedendosi la spada uicina al proprio pugnale hà uoluto escluderla di fuori con esso pugnale, & ferire di terza disotto, mà il ferittore, che era, come si è detto, in quarta uoltando la mano in seconda, & portando nello stesso tempo la spada per sopra il nimico pugnale hà ferito il medesimo nimico all’ hor quando, che si è abbassato, & passato, & haurebbe anco esso scrittore potuto cauare per sotto il pugno del detto nimico pugnale, & fare la medesima ferita sopra esso pugnale, mà alquanto più bassa per l’angolo formato dal braccio. 171. |
|||||||
[20] |
[233] DELLA QVARTA ET VLTIMA REGOLA DI ANDARE A FERIRE IL NIMICO SENZA FERMARSI[39] CON SPADA, è pugnale.
QVESTA E LA QVARTA REGOLA, DOVE NOI MOSTRAremo il modo di operare contra quelli, che non tengono mai ferma la spada, mà che sempre uanno girando la punta, & tenendo il pugnale hora auanzato, hora ritirato, hora aperto, & hora chiuso, & però noi douremo trattarne diuersamente da quello che habbiamo fatto nelle trè altre superiori, & diremo, che girando il nimico la spada in qualunque modo, pure, che la mano di essa spada sia lontana da quella del pugnale, dourà l’ osseruattore della presente regola cominciare ad’ andare con le punte, auicinarsi più inanzi che possa uerso la mano della nimica spada, affine di neccessittare il detto nimico ad’ una delle due cose, ouero, deuiandolo dal moto della sua spada, farlo andare à quella, che li uà contra, ouero farlo mouere col pugnale, & andare alla diffesa, tempi l’ uno, & l’ altro oportuni per andarlo [234] à ferire nello scoperto, che facesse, douendo anco continouamente tenere la punta del pugnale uerso la linea del nimico acciò che in ogni occasione, che detto nimico uolesse ferire si sia pronto à parare atteso, che saria neccessario passare per la linea di quello, però deue il detto osseruattore stare basso col corpo, & unito, & in caso che ’l detto nimico non si mouesse per fare alcuna cosa hà da continouare tanto inanzi, che possa pigliare il tempo di quella punta, che gira, & ferirlo, escludendo nel medesimo tempo la detta punta di fuori, assicurato, che mentre terà la punta uerso la nimica mano, in ogni occasione, che esso nimico uoglia ferire nel andarli contra, che facilmente pararà, & andarà à ferire senza disturbo non mancando però dell’ osseruatione de’ giusti termini, auertendo, che se per caso il detto nimico nel girare di quella sua punta fosse col pugnale appresso la mano della spada non sarebbe altrimenti bene di mettere la spada tanto inanzi, acciò non sene impadronesse, mà il uero modo sarebbe di tenersi con la punta della spada in una certa forma, che guardasse uerso il filo di fuori della nimica in quella prima parte uerso il finimento, & seguire oltre conggiongendo il corpo, oue prima erano le mani, inguisa che esse mani fossero alquanto più inanzi del corpo, & che ’l piegare delle braccia fosse nel combito nel proprio tempo che se li auicina, perche chi solamente si seruisse del nodo della spalla nelo auicinare del corpo, esse mani andariano abbasso, & l’ huomo restarebbe scoperto’; Deuesi anco esso osseruattore ritrouare con la mano in quarta, con le punte uerso, pure, quella detta quarta parte della nimica, & si come uiene unendosi così dee uenire abbassandosi; ne mai, come si è detto, hà da penetrare tanto inanzi che la punta entri dentro del pugnale auerso, qnando [!], che è così appresso la mano della spada, mà si bene ariuare sino al filo, ò punta di esso, perche, ouero che ’l detto nimico ferirà nel tempo, che se li uà contra, che sarà anco più facile da parare, che se si fosse con le punte alle mani, atteso che li forti sariano più lontani da esso nimico, & tanto che la sua punta non potria così ageuolmente penetrarli, & essi forti sariano anco tanto più forti, quanto che sariano racolti appresso del corpo, se bene in quello luogo uiene in meggio una certa consideratione ciò è, che pare, che quando la punta uà girando, che anco la lama faccia moto in quella quarta parte, & che perciò la suarii tanto, che non se li possa tenere giuste le punte in contra. Noi diciamo che tenendo l’ osseruattore della regola le punte della spada, & pugnale riguardanti uerso quella parte con la mano del pugnale alquanto aperta da quella della spada, la punta del quale pugnale si uenga anco serrando uerso la propria lama, che quello suario della nimica non importarà niente, perche non sarà mai tanto, che esso nimico possa ferire in alcuna parte, ne sturbare, ne manco fare alcuno aquisto, è ben uero che quando il detto nimico tenesse tanto inanzi il pugnale, che copresse tutta quella quarta parte, & che oltre questo fosse tanto alla spada, laquale si trouasse in quarta guardia, non si potrebbe andare all’ hora ne’ al finimento, ne à quel primo quarto, & chi uolesse andare al secondo non sarebbe cosa sicura, perche esso nimico fà un gran moto nel mouere della punta, & sarebbe anco tanto lontano che non potrebbe essere ferito, nel quale caso dourebbe il nostro tenere la punta della spada contra la mano del pugnale, & la punta del pugnale, non però molto auanzato, che guardasse uerso il centro della lama nimica approssimandosi con piedi, è corpo uerso la parte del pugnale auerso, tenendosi con la mano della spada in quarta, & con uenirsi racogliendo con la mano uerso la parte sinistra; conseruando la punta sempre in quella prospettiua medesima, & quando hauesse racolta la detta mano al corpo sino doue hauesse potuto, sarebbe all’ hor segno di essere gionto sin doue era neccessario, talmente, che potria andare à ferire quello scoperto, che uedesse, che l’ auerssario non potrebbe in modo alcuno parare, & se ’l pugnale del detto nostro osseruattore guardarà uerso il centro della nimica lama diffenderà ageuolmente in caso che ’l detto auerssario uoglia ferire in quel tempo, ilquale se anco nel uenire ferirà prima, che si ariui al segno, tanto meglio sarà per il nostro per diffendersi atteso, che haurà tutte due l’ armi libere, & ferme, in modo che potrà gionto che sia in misura pigliare qualunque tempo fatto dal nimico, lequali raggioni hanno da osseruarsi [235] continouando co’i piedi, & mantenendo ferme le punte, & le mani sino che si troui il tempo, ò che si gionge, doue si desidera, & lequali raggioni seruono contra di quelli, che stanno con le mani ferme nelle guardie, & uanno girando la punta, i quali se mutassero la mano diuna in altra guardia sarebbe il tempo anco maggiore, & si potrebbe tanto più facilmente andare à ferirli, mà sono altri, che muouono la spada, & il pugnale insieme, & i quali hora lo auanzano, & alzano, & hora lo abbassano, & ritirano continouando il moto in forma di giro insieme con la spada caminando non meno in giro co’i piedi, serrati con le armi insieme, & con la spada, che auanza di molto il proprio pugnale, alli quali si può similmente andare contra con le punte alla mano, come si disse, nondimeno sarebbe meglio tenere la punta della spada, & la mano alta tanto, come è per apunto la mano del nimico pugnale, quando è mosso inanzi, laquale hà da guardare per quei dui fili, che sono insieme della spada, è pugnale auersi, & inanzi, mà non tanto, che penetri esso pugnale auerso, & deue andarli contra risolutamente, tenendo il pugnale per il centro dell’ auerssaria, che giongerà tanto inanzi, che la sua punta si caccierà per quello scoperto nell’ abbassarsi delle armi nimiche, & ferirà senza, che detto pugnale auerso possa parare restando oltre diciò diffeso dal proprio pugnale dalla quarta, ouero terza nimica, che potesse in quel tempo uenire, & se nell’ andare inanzi l’ auerssario facesse qualche moto di uolere trouare la spada con la spada, ò col pugnale, ò con l’ una, & l’ altro insieme quello medesimamente sarebbe tempo à proposito per ferirlo, perche l’ essere in uiaggio co’i piedi, & l’ hauere l’ armi ferme importa molto all’ osseruare le raggioni, & pigliare il tempo, & in queste regole non si procura altro, che il modo di sapersi condure la doue si possino pigliare detti tempi, & gionto in quel luogo di sapere conoscere quello che possa accadere, & di andare anco, che ’l nimico non si moua; questo è il fine delli discorsi intorno alla risolutione promessi da noi, i quali se non mi inganno saranno di tale sufficienza, che da loro si potranno cauare altre raggioni & altri modi, la diuersità & moltitudine de quali, è stata pretermessa da noi, hauendo solamente atteso alli fondamenti dell’ arte, con mostrare la uerità, lasciando campo à qualche pellegrino ingegno di aggiongere, & in uentare altre cose, similmente habbiamo fuggita la prolissità in quanto habbiamo potuto per minor tedio di chi leggerà, & lasciato in disparte l’ uso delle parole geometriche come si ha prima detto per più facile intelligenza ancora di chiunque leggera, se bene li stessi fondamenti di questa nostra professione sono principalmente nella propria arte di Geometria. Seguiranno le figure di questa quarta regola della risolutione di spada, è pugnale secondo l’ ordine, lequali dimostraranno li effetti, & le caggioni de’ uantaggi, & delle ferite. |
|||||||
[21] |
QVESTA TERZA, CHE SI VEDRA NELLA SEGVENTE FIGVRA, laquale hà messa la sua punta tanto appresso il filo del pugnale auerso, & che tiene la punta del suo riguardante il centro della nimica osserua simili modi, perche l’ auerssario suo uà mouendo la spada, & il pugnale, in giro, hora alzando hora ritirando, & abbassando tutte due le armi insieme pure in giro, doue che l’osseruattore della regola disegna d’ approssimarsi tanto inanzi, che possa pigliare il tempo, quando che quelle due armi mancaranno, & però esso hà posta la punta appresso il filo del detto pugnale auerso, ilquale è hora così alto, perche hà fatto il tempo con alzarsi, mà nel callare, ò ritirarsi, che farà con tutte due le armi la punta del nostro osseruattore restarà libera, & il corpo nimico tutto scoperto, in modo che potrà ageuolmente il detto nostro ferirlo, come si uedrà nella postseguente figura. 172. |
|||||||
[22] |
[236] DALLA TERZA PASSATA, CHE HAVEA POSTO LA PVNTA della spada tanto appresso il filo del pugnale nimico è nata questa ferita, perche essendo essa terza, gionta in distanza, costui, ilquale è restato ferito hauea fatto un moto alto, & ne faceua un altro basso, & così il ferittore, ilquale teneua la punta appresso il filo del detto pugnale auerso si è spinto inanzi nel tempo, che quello mancaua, & hà ferito uolgendo la mano in seconda, come si uedde, in modo che il pugnale del ferito non hà potuto parare per la impossibilità di fare dui tempi, mentre che il ferittore ne faceua un solo, iquali dui tempi erano l’ uno di ritirare il braccio, l’ altro di tornarlo inanzi, & ben si uede per quello braccio non disteso, che la sua spada non hà finito di auanzarsi prima di essere ferito & il medesimo ferittore hà lasciato il pugnale ne lo stesso luogo doue era per diffendersi dalla nimica in ogni caso che fosse uenuta à ferire, & per questo il braccio, che si trouaua prima disteso si uede hor ritirato, perche mentre che è andato col corpo tanto inanzi, se hauesse uoluto tenerlo disteso sarebbe ariuato con la punta alfinimento nimico, & ilquale nimico spingendosi anch’ esso inanzi haurebbe ferito sicuramente, per due raggioni, l’ una perche il pugnale dell’ altro haurebbe trouato la sua spada nel forte, & perciò non haurebbe sostenuto l’ empito, la seconda, perche il portarsi inanzi col pugnale, che hauesse fatto sarebbe stato tempo à proposito per lui tanto più perche il corpo del feritore non haurebbe fatto la sfugita che si uede & per questi rispetti il nostro osseruattore, restando nel sito, oue era, hà uoluto essere pronto à tutte le cose tanto à pigliare il tempo, quando il pugnale auerso mancaua, quanto à pigliarlo quando il detto pugnale si auanzasse, & ferire di sotto senza, che dal [237] detto auerssario si potesse parare, & à potere anco portare la spada sopra la nimica in quello mancare delle dette armi nimiche, togliendo ad’essa nimica il potere risorgere se non con cauare, & in somma può hauere molte comodità di ferire, & di fare delle altre cose per sturbare collui, che faceua quei tanti moti, mà non si mettono se non le cose più sottili, & di maggiore importanza. 173. | |||||||
[23] |
QVELLO, CHE SI VEDE IN QVESTA TERZA COSI APERTA SI è disunito nel girare della punta hora slargandola, hora stringendola secondo che la fà il giro mantenendo fermo il pugnale, mà il suo auerssario che è uenuto discendendo dalla terza alta, & è callato con la punta in quel primo quarto della nimica senza toccarla però con disegno di diuertire il moto dell’ altra, & neccessitarla à fare una di queste cose, ouero che resti di girare, & accorra alla nimica, che li uà contra, ouero uada col pugnale à trouarla con animo insieme di ferire, nè quali dui casi esso pigliarebbe il tempo, & ferirebbe secondo l’ occasione; si come se il detto situato in terza andasse alla spada di fuori, esso anco con poco moto della punta, laquale per questa occasione stà appresso quel filo, cauarebbe & ferirebbe di dentro di quarta, ne meno cauarebbe, se il sopradetto andasse con la spada, & pugnale insieme, ma uoltarebbe con la mano in seconda, & parando col pugnale ferirebbe disotto, ò disopra secondo l’ altezza, ò bassezza delle armi auerse, & se esso nimico fosse uenuto à trouarlo di dentro hauria potuto cauare di terza di fuori sopra la spada, & mentre, che quello andaua à parare col pugnale uolgere la mano in seconda, & ferirlo per sopra il pugnale, & cauare per l’una, ò per l’ altra parte; hauria anco, mentre, che quel tale fosse andato à [238] trouarlo di dentro, potuto uolgere in seconda quella mano, che staua così in terza, in modo che la nimica non l’ haurebbe trouata, potendo andare à ferire, doue più hauesse ueduta l’ opurtunità, mà senza fermarsi, perche nel fermarsi si perde il uantaggio. 174. | |||||||
[24] |
MA DA QVELLA TERZA, CHE HAVEA MESSA LA PVNTA della spada nella prima quarta parte del nimico, laquale era ancor lei in terza, & andaua girando la punta, è diriuata la ferita che seguirà oltre, perché uedendosi quello, che poi è restato ferito uenire la punta auersa tanto inanzi, hà uoluto occupargliela col pugnale, mà il ferittore ilquale era già tanto penetrato con la punta, & col finimento tanto più alto col solo uolgere della mano, & dirizare la punta uerso il petto nimico lasciando essa mano nella medesima altezza, doue che era, hà ferito nè lo stesso tempo che il nimico credeua trouare la spada à lui, & si è trouato à fare tale effetto tanto lontano dal pugnale di esso nimico, che era impossibile di tornare à parare, ilquale nimico, se non hauesse anco portato il pugnale in quella parte, sarebbe con tutto ciò restato ferito di quarta come si mostrara ne la postseguente figura. 175. |
|||||||
[25] |
[239] QVESTA CHE SEGVE E LA QVARTA, DI CHE SI E FATTA mentione nel precedente discorso, laquale si uede ferire nel meggio dell’ armi d’ un’ altra quarta, auenuta perche quello, che hà ferito, nell’ hauere posta la punta nella prima quarta parte della spada nimica in tempo, che essa si aperse facendo quel giro, che nel’generale discorso si disse, & essendo ariuata per apunto in quel mentre, uedendo quella apertura, & il nimico immobile è andato à ferire con uoltare la mano di terza in quarta, giongendo prima che detto nimico habbia potuto parare, ilquale si è ben spinto oltre per parare, & ferire di quarta mà in cambio di fare buono effetto, hà caggionato, che l’ altro non solamente è gionto più presto, mà che la ferita anco si è fatta maggiore con facilittare di più la diffesa al pugnale delo stesso ferittore auicinandoli à quel modo la punta della sua spada. Potria similmente essere accaduto, che ’l ferittore fosse ariuato nella prima quarta parte della lama nimica, il scoperto della quale fosse anco stato picciolo, & che fingendo di andare sopra la punta del pugnale nimico, con continouare oltre, & che detto nimico habbia uoluto parare alzando il pugnale, & uoltando la mano in quarta, nel qual tempo esso ferittore sia tornato nel meggio, & ferito di quarta parando, come si uede, & ben che il ferito sia ancor lui tornato col pugnale dall’ altra parte per parare non habbia potuto. 176. |
|||||||
[26] |
[240] DA QVELLO HAVERE POSTA LA PVNTA NELLA QVARTA parte della nimica, è nata la ferita, che qui oltre si uedrà, perche questo, che è restato ferito uedendo uenire la detta punta tanto inanzi nell’ apertura fatta dalla sua spada nel girare, hà uoluto coprirsi con aggiongerui il pugnale appresso, & all’hora il ferittore, pigliando quel tempo, hà uoltato di terza in seconda, & cauato per la punta del pugnale auerso, col quale pugnale detto ferito hà uoluto parare con uoltare la mano in quarta, & portarsi inanzi ad’ in contrare con la spada il detto ferittore, che ueniua, mà non li è riuscito perche la detta spada era di già ariuata con la punta al corpo in quello proprio punto, che ariuò sopra il pugnale, & la quarta del medesimo ferito fù facile da essere parata perche il ferittore posse il suo proprio pugnale contra la punta auersa, & la prese, quando da principio si mosse, con andarli scorrendo il filo. Può anco ben’ essere che lo stesso ferittore, hauendo posta la purita in quella quarta parte nimica detta disopra, si sia spinto oltre per lo scoperto, che era nel meggio dell’ armi, & l’ altro habbia uoluto parare, & portarsi inanzi perferire di sotto, & che’l ferittore all’ hora continouando oltre habbia solamente uoltato di terza in seconda, & incontrato l’ auerssario, che similmente si portaua inanzi, & ilquale non hà potuto ne parare ne ferire, atteso che ’l pugnale del detto ferittore era di già ariuato al suo debile, in modo, che se bene si è sforzato di uolgere la mano in quarta non hà potuto fare cosa buona. 177. |
|||||||
[27] |
[241] DALLA TERZA ANTECEDENTE, CHE HAVEA MESSA LA PVNTA nella prima quarta parte della spada nimica è nata la ferita che segue, perche, gionta in distanza stretta, hà pigliato il tempo fatto dal nimico nel slargare la punta della spada dal proprio pugnale in facendo quel giro, & così, stando con la mano in terza, si è cauato in quel meggio con la quarta, ne il detto nimico hà potuto parare col pugnale, ne meno uoltare la spada in seconda per lo continouare inanzi del ferittore con la spada, laquale già hauea ferito, quando quello uolse parare & à questo fine si piegò col corpo credendo saluarsi dall’imimente pericolo mà quando uoltò la mano in seconda di già era passato il corpo delo stesso ferittore continouando inanzi, & ferito anco col pugnale nel tempo medesimo, che quello si occupo nel uolersi diffendere dalla spada, essendo anco talmente impedito, che se bene hauesse uoluto ferire del suo pugnale non haurebbe potuto, essendoli stato occupato il braccio dal braccio del ferittore passato tanto inanzi, che egli quasi non lo potea più uedere. La presente pugnalata si è messa in questo luogo per dimostratione, che anco si può ferire di pugnale, & se prima non sene è parlato, à uenga che in molti luoghi ne fosse data occasione si è fatto perche noi habbiamo stimato più conueniente l’attendere bene all’ uso della spada, oltre che à quelli, che passano di risolutione non fà di mestieri lo ferire di pugnale ne meno deuono temere quello del nimico, perche passando, & ferendo la spada penetra tutta, & toglie uia ogni pericolo, & perciò l’ huomo può passare senza timore di detto nimico pugnale, atteso anco che si presupone non essere alcuno si sciocco, che uoglia lasciarsi passare per il corpo la spada nimica per andare à ferire col pugnale esso nimico, & se pure qualch’uno lo facesse sarebbe il più delle uolte giettato per terra prima, che potesse ferire, & oltre ciò mettendosi in neccessità di parare con esso non può ferire in tempo, doue per contrario [242] quello, che uà di risolutione passata, che sia la punta nimica può lasciarla andare senza dubbio, & portare il pugnale al corpo auerso, & quindi si uede chiaro, che meglio può ferire di pugnale quello, die passa, che quello, che aspetta, del quale si fà anco maggiore la irresolutione dal uedersi uenire addosso l’ auerssario, & uedendo si occupata la spada dal medesimo che uiene non può parare con altro, che col pugnale, ilquale impiegato in un’ opera non può fare l’ altra, & perciò sarà sempre sul uantaggio quello che passa, ilquale nel passare se non ferirà con la spada potrà all’hor ferire col pugnale, mà ferendo con quella non haurà tanto bisogno di questa. Hauressimo prima d’ addesso trattato di questo modo di ferire, mà nostra intentione è stata di attendere alla punta della spada, laquale offende più di lontano, & è quella che troua, & dà tutti li tempi del ferire, & quella similmente, che è prima à mettere in timore, & ad’ offendere l’huomo, & però noi con raggione habbiamo uoluto attendere alla sottilità, & al maggore proffitto, & questo poco discorso l’habbiamo fatto per mostrare l’ errore di colloro, che niegano il passare per dubbio di potere essere ferito dal pugnale del nimico. Habbiamo anco prettermesso lo trattare del spadone, & di molte altre sorti d’ armi, oue saria stato molto da dire hauendo riguardo alla breuita, oltre che queste tali non sono armi usate frà cauallieri nè casi fortuiti, se bene sono molto buone in campagna, & sule brezze, materia lontana dal nostro soggetto, hauendo solo inteso dell’armi caualleresche, & de casi che sogliono nascere nelle conuersationi de’ nobile, delle quali cose crediamo hauerne trattato sufficientemente, ne che ci resti se non à dare lume di alcuni accidenti straordinarissimi iquali nondimeno possono accadere se ben molto di rado, & à questo fine metteremo un’ altro discorsetto mostrando il modo da diffendersi in occasioni simili. 178. |
Third Part - On Wrestling, Grips, Disarms, Cape-Throws, & Dagger Techiques
Illustrations |
Illustrations |
Draft Translation (from the archetype) |
Prototype (1601) |
Archetype (1606) [edit] |
Copenhagen Version (1600-1609) [edit] |
Munich Version (ca. 1635) [edit] |
German Translation (1677) [edit] |
French Translation (1644) [edit] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[1] |
[243] LIBRO SECONDO, TERZA, ET VLTIMA PARTE. TRATTATO DI LOTTE, PRESE DI SPADA, GIETTI DI CAPPA, ET RAGGIONI DI PVGNALE. ANCORCHE NOSTRA INTENTIONE FOSSE DI NON TRATtare delle materie, che seguirrano parendoci che assai basteuolmente potesse stare la nostra opera senza queste, à persuasione nondimeno & in gratia di molti amici, siamo lasciati indurci ad’ inserire nel libro, & aggiongerli questo presente trattato di lotte, di prese di spada, gietti di cappa, & raggioni di pugnale, cio è per diffendersi da quello con le mani ignude, & le raggioni, che ci disuadeuano dal trattarne erano primamente, per essere il uolume, senza queste, assai basteuole, & poi conforme à quanto habbiamo detto altroue, perche noi habbiamo atteso à mostrare come l’ huomo possa con una sola spada, ouero spada è pugnale, ò spada, è cappa diffendersi, & offendere il nimico, essendo queste armi solite, & consuete frà cauallieri, & ueramente proprie delli huomini nobili, che perciò habbiamo lasciato in disparte rotelle, targhe brocchieri, & altre, delle quali longo sarebbe stato il dire, & perche anco siamo sempre stati di opinioni, chi saprà osseruare le raggioni antescritte, potrà adoprare la spada accompagnata da quale si uoglia forte di arma sia da pugno, ò da braccio, perche in ciascuna di esse uisi ricerca tempo, & misura, & così parimenti haueuamo in animo di non trattare d’ altro, che della punta, & del taglio, parendoci, che chi saprà con quelle diffendersi, & offendere in tempo non douesse hauere di bisogno, ne di lotte ne di prese, si come anco si lasciaua questa diffesa delle mani ingnude contra il pugnale, essendoci auiso, che li huomini honorati, quando pure sono astretti in punto d’ honore di ridursi al cimento dell’ armi, l’ habbiano da fare con partito eguale, & con giusto paragone di ualore, douendosi aborire ogni uittoria, quando che è partorita da indegno, & uituperoso uantaggio di armi, nondimeno consigliati come habbiamo detto dalli amici, & perche frà li huomini anco intieri d’ honore nascono casi inopinati, & tanto subbiti, che non si hà tempo di ricorrere all’ armi longhe, pare che sia bene di ricordare, & auertire come possa l’huomo ualersi di pugnale contra pugnale, laquale armadunque, perche è corta porta secopericolo che ’l nimico nonuenga alla presa del pugno di esso pugnale, però si hà da fare di meno, potendosi, di parare, mà saluarsi col corpo più presto, & co’ i piedi per l’ una, ò per l’ altra parte, & andare à ferire per le mani, & per il braccio di collui, che tira che sarà molto più sicuro, & si terà il nimico più lontano, che non potrà uenire à fare presa, ne lotta, nel resto chi haurà cognitione di tempo, misura, & passo, seruiranno le raggioni prima descritte, & però non si dirà altro, mà per dare satisfacione à chi ci hà potuto comandare, metteremo come l’ huomo possa diffendersi, & offendere il suo nimico, se fosse assalito da chi hauesse un pugnale, & egli niente. |
|||||||
[2] |
[244] LA LOTTA, CHE SI VEDRA NELLA SEGVENTE FIGVRA PVO essere seguita in tal modo ciò è, che collui, che l’ hà fatta sia stato in terza di dentro, si come anco l’ auerssario in terza, & che il primo hauendo il uantaggio sopra il nimico, sia andato a ferire di quarta per appresso la spada & l’ altro habbia uoluto diffendersi pure con la quarta, & sia andato fuori di presenza con la punta, & però quello dalla lotta habbia ceduto con la punta, & si come era passato col piè manco, così sia seguito col destro sino dietro il destro del nimico, uoltando la mano sopra la mano del nimico medesimamente, & col pomo sia andato uerso l’ istesso nimico à darli nel petto nel proprio tempo che ’l piede è gionto in terra. Può anco essere, che collui, che stà per cadere si ritrouasse di fuori dalla nimica, & che questo, che li hà fatta la lotta li sia andato à ritrouare la spada, & l’ assalito, preso quel tempo habbia tirato di mandiritto per testa, & perciò l’ assalittore sia passato inanzi col piè manco parando per ferire di quarta, & il detto assalito ueduto il pericolo habbia caricato sopra la spada per uiolentarla ad’ andare fuori, & così l’ altro sentendo habbia ceduto con la punta & sia montato col pomo sopra la nimica dalla parte di fuori, & passato, & anco fatta la lotta, che si uede; si come non meno può essere, che questo, che hà fatta, la lotta, il quale chia maremo assalittore habbia tirato di mandiritto, & l’ altro sia andato alla simplice diffesa con la quarta, & habbia portata la punta fuori di presenza, & così l’ assalittore, che era passato col sinistro piè nel primo ferire, sia nel tempo che l’ assalito hà uoluto parare, passato non finendo il taglio, mà montando con la mano sopra la nimica dalla parte di fuori, come si è detto, & sia uenuto à fare la botta, che si uede, in modo che l’ assalito stà per cadere in terra. 179. |
|||||||
[3] |
[245] QVESTA PRESA, CHE SEGVE, OVE SI VEDE VNO, CHE CAVA la spada di mano al nimico, & li hà data una stoccata di seconda nel petto può essere seguita indui modi, il primo, che collui, ilquale è ferito habbia tirato di mandiritto per testa & l’ altro habbia parato in seconda di tutta coperta, & subbito parato sia passato dell’ istessa, & mettendo la mano manca alla riuersa nella parte di dentro del finimento & mano del nimico gli habbia data una torta al braccio uoltandoglielo in fuori con cavarli la spada di mano, come si uede, per forza in guisa che il detto ferito non hà potuto tenerla, l’ altro modo è che ’l ferittore si trouaua di fuori dalla spada nimica nella terza, & hà mostrato di ferire il nimico nel uiso, alzando la mano in quarta, & portandoli la punta à quella uolta, ilquale nimico uedendo il pericolo hà alzata la spada per andare alla diffesa, & così il ferittore hà ceduto di quarta in seconda uoltando il fianco sinistro inanzi tanto come il destro, con abbassare anco la terza tanto che il proprio finimento, & forte della spada l’ hà coperta tutta, in modo che la nimica punta è passata di dietro, & egli in tempo medesimo hà cauata la spada di detta seconda, mettendo la mano alla riuersa nella mano della spada auersa, & riuersandoli il braccio in fuori lo sforza à lasciare la detta spada. 180. |
|||||||
[4] |
[246] QVESTA ALTRA, CHE SEGVE E VNA PRESA ANCOR LEI, OVE medemamente si uede uno, che hà cauata la spada di mano al nimico, seguita in questa forma cio è, che collui, che hà fatta la presa hà dato tempo al nimico di uenire di dentro à ferire di quarta, & mentre, che è uenuto hà posto la sua spada col forte sopra la punta nimica calcandogliela abbasso, & nelo stesso tempo è passato col piè sinistro allongando anco il braccio sinistro per disopra la spada, & hà posta la mano nel finimento della nimica dalla parte disotto alzando insù esso finimento, & caricando abbasso con la spada la punta auersa, talmente che a detto nimico, è stato forza di lasciare la spada. Può anco essere seguita dall’ essersi l’ assalittore cio è quello che ha leuata la spada al nimico, mosso mostrando uolere ferire di mandiritto per testa, & dall’ hauere l’ altro uoluto parare, & ferire di quarta & perciò il detto assalittore abbandonando il taglio, lasciando cadere il forte sopra la punta nimica, laquale ueniua inanzi, con caricarla abbasso, & pigliarli il finimento con la sinistra, come si disse, li habbia cauata la spada di mano. 181. |
|||||||
[5] |
[247] MA LA LOTTA, CHE SEGVE, LAQVALE HA FERITO IL NImico nel petto può essere successa dall’ hauere quello che hà ferito, finto di ferire di terza di dentro, & dall’ essere l’ altro andato à parare, che però il primo habbia cauato di seconda inanzi che ’l nimico li habbia toccata la spada, & habbia appoggiata la sinistra mano al proprio finimento per maggior fortezza acciò il detto nimico non la possi rispingere, & essere passato del piè manco di dietro al piè destro del nimico, & feritolo nel petto, mettendoli la mano, che era al finimento alla riuersa nella gola, & con spingerlo indietro lo faccia stare per cadere in terra. Può similmente essere, che quello che è ferito sia andato à ritrouare la nimica di fuori con la terza, & il detto nimico habbia cauato di quarta, & perciò esso ferito habbia uoluto parare, nel qual tempo il ferittore cedendo con la punta alla forza[40] auersa sia montato col pomo della spada sopra quella del medesimo ferito, & habbia girata la mano di quarta in seconda in modo, che sia passata sopra la detta nemica dalla parte di fuori, & nelo stesso punto sia ancora passato col piè manco, & fatta la ferita, & la lotta, che si uedono. 182. |
|||||||
[6] |
[248] HORA SEGVE VN SLANCIO DI CAPPA FATTO IN QVESTO modo cio è, che hauendo uno la cappa attorno, & douendo mettere mano alla spada l’habbia lasciata andare giù della destra spalla, restando quella solamente sopra la sinistra, & doppo hauere cauata la spada del fodero, habbia preso quel lembo, che pendeua, frà due dita della sinistra mano, & poi con essa sinistra l’ habbia pigliata alla riuersa uicino al capuccio, come se uolesse riuoltarsela al braccio, & perche si trouaua tanto lontano all’ armi nimiche cheli bisognaua più di un passo per armare alla misura, & perche uedeua anco il detto nimico con la spada in terza auanzata, glie l’habbia slanciata sopra le mani con ritenere il detto lembo, il che hà caggionato, che si è uenuta slongando sopra la nimica, talmente che esso nimico per la grauezza di detta cappa non hà potuto leuare ne la punta, ne la mano, & così quello, che era passato col sinistro inanzi habbia soggionto col destro, & ferito, come si uede, &che il ritenere di quel lembo nelle mani sia stato, non solamente per distenderla, & coprire tuttala spada all’ auerssario, mà perche se il slancio non haurà hauuto effetto la possi ricuperare sopra il braccio ritirandola con una scossa, & tornare di nouo à rigiettarla, & non tanto sopra la spada quanto nel uiso al nimico, che se hauesse solo uoluto impedire al detto nimico il potere ferire, ò fare altro glie l’ hauria slanciata libramente tutta senza ritenerne niente se bene in questo caso faceua di mestieri occupare prima con la spada la spada nimica. 185.[41] |
|||||||
[7] |
[249] L’ EFFETTO, CHE SI VEDE NELLA SEGVENTE DI COLLVI, che giettò la cappa, è una stoccata nel uiso al nimico seguita, perche collui, che hà giettata la detta cappa si ritrouaua sopra il sinistro in terza guardia & con la cappa riuolta al braccio, & anco perche la spada nimica si trouaua di dentro della cappa pure in terza, in modo che costui hà appoggiata la propria punta nella medesima sua cappa, & l’ ha portata fuori per la mano sinistra agiutandola alquanto con una scossa & così è passato col destro piede inanzi, accompagnando la detta con la medesima punta sino nella faccia del nimico, & feritolo nel moto medesimo, che se bene esso nimico hà uoluto alzare la spada slargandosi in dietro per dillongarsi & saluarsi non hà fatto niente per l’inaspettatione, & nouità della cosa, non dandosi mai à credere, che l’ altro hauesse da tirarli la cappa, & potesse tirargliela atteso che li staua riuoltata al braccio & è ueramente stato un bello inganno. Si come diuerse altre maniere possono anco tenersi, lequali per non essere di maggiore importanza di queste, si lasciano in disparte. 184. |
|||||||
[8] |
[250] RAGGIONI PER DIFFENDERSI DA VN PVGNALE CON LE MANI IGNVDE. OCCORE QVALCHE VOLTA, CHE VN’ HVOMO NON trouandosi arma alcuna uierte assalito da un’ altro, ilquale hà un pugnalo, & che li andarà addosso per ferirlo, & amazzarlo, ne hà lo stesso assalito luogo, oue ricouerarsi & fuggire, di modo che resta in pericolo certo di essere ferito, & morto; percioche uolendo noi mostrare come in tale accidente possa diffendersi, & anco offendere il nimico metteremo alcuni effetti lasciando quelli, che da altri possino in altri tempi essere stati mostrati, & perche l’ huomo resti più persuaso, & più assicurato di quello che noi li insegnaremo, hà prima da considerare due raggioni l’ una che collui ilquale mette mano al pugnale per offendere l’ altro, non uedendoli alcuna cosa da potersi diffendere corre subbito à ferirlo in quel luogo, che prima li cade nell’ animo, non dubbitando d’ altro, se non che ’l nimico fuga prima, che possa ferirlo, & perciò opera senza inganno, laquale cosa caggiona, che l’ assalito può più facilmente diffendersi, l’ altra raggione, è che ’l pugnale non è tanto longo, che possa ariuare al corpo, mentre, che esso assalito si piega inanzi, & stende le braccia uerso le mane, & finimento dell’ assalittore, uenga la botta alta ò bassa, ne meno può il braccio del detto assalittore essere tanto forte da se solo, che faccia cedere quelli, che si stendono per diffendersi, che sono due, le mani dellequali braccia sono quasi sempre conggionte, eccetto doue si troua, ò sfuggita di uita, ò torta di braccia, lequali li tolgono la forza, come si uedrà nel primo effetto, oue si mostrarà che una sola mano diffenderà & giettarà il pugnale di mano al nimico, & quando collui, che hà il pugnale uolesse adoprare la sinistra all’ hora si dee pigliare quel braccio, & uoltarselo con il combito sopra le spalle, dandoli una torta alò in giù, che non solamente lo slocarà, mà anco lo romperà affatto; potendo seli in oltre andare addosso, & farli una lotta per riuersarlo in terra, si può similmente pigliarlo di dietro il combito con la sinistra, & farli uolgere la schiena, che da ciascheduna di queste cose restarà talmente impedito, che non potrà col detto suo pugnale offendere, mà noi per non multiplicare in esempii, & per fuggire la longhezza metteremo solamente quello, che può auenire da un’ huomo ilquale uolesse offendere un’ altro, à cui non uedesse diffesa di forte alcuna. |
|||||||
[9] |
LA SEGVNTE FIGVRA, OVE SI VEDE VNO CHE HA CAuato il pugnale del fodero, & alzato il braccio per ferire, & l’ altro, che stà aspettando che questo tiri, si è messa acciò che si ueda il modo, con che costui si è mosso, & colquale tiene detto pugnale per andare à ferire l’ auerssario, & poi si uedrà l’ effetto, che sarà successo, nella postseguente figura, mà nelle altre si ponerà solamente la simplice ferita, & con le parole si farà intendere, doue sia deriuata. 185. |
|||||||
[10] |
[251] DA QVELLO DVNQVE, CHE HAVEVA ALZATA IL PVGNALE per ferire l’ auerssario, ilquale aspettaua, è nata questa presa, perche collui dal pugnale hà tirato per ferire disopra in giù con l’ istesso moto, nelquale era, come si uidde, & perche l’ altro che aspettaua, secondo che si è detto hà alzato il braccio sinistro uoltando la mano alla riuersa, & hà incontrato il braccio nimico in tempo, che cadeua nella mano appresso il finimento di esso pugnale dandoli una torta come si uede, con laquale li caua il detto pugnale di mano, che non può tenerlo, & per la torta, & patimento del braccio si è piegato in schiena, per non lasciare leuare così il pugnale, & per la detta piega di schiena, è tanto indebilito sopra i piedi, & caderia in terra anco maggiormente per l’ urto della destra di quello che li hà data la torta, alquale in ultimo basta di leuarli il pugnale di mano. 186. |
|||||||
[11] |
[252] MA QVEST’ ALTRA, CHE E PVRE VNA PRESA, LAQVALE FA cadere il pugnale di mano al nimico, sarà auenuta, perche collui dal pugnale haurà tirato di punta di sotto per ferirlo nel corpo, & perche l’ altro, ilquale teniua le mani alte haurà posta la destra sopra la lama del nimico, & la sinistra disotto dalla mano di essa lama tenendola, alzandola, & caricandola abbasso con essa destra, in modo, che è uenuta ad’ indebilire la mano del nimico pugnale facendoglielo saltare fuori molto facilmente, & tanto che esso nimico non hà potuto tenerlo. 187. |
|||||||
[12] |
[253] QVESTO SIMILMENTE, CHE SI VEDE HAVERE PERSO IL PVgnale, è uenuto per ferire il nimico di punta diritta con la mano in terza, ilquale nimico hà ferrato le mani insieme, & pigliatolo nella mano, & finimento di esso pugnale, col corpo cauato & basso, caricando in giù col corpo, & mano destra, laquale hauea preso il detto finimento nimico, & con la mano sinistra hà tenuto alzato il braccio auerso, in modo, che con facilita li hà cauato, il pugnale di mano, ilquale si uede nella figura in quel modo’proprio, come si è trouato all’ uscirli di mano. 188. |
|||||||
[13] |
[254] SEGVITA VN' ALTRA PRESA, ET PERITA SVCCESSA DALL’ hauere collui, che è ferito, & che hà il pugnale in mano, uoluto ferire l’ auerssario, che era senz’ armi, & dall’ hauerli tirata una punta disotto in sù, per cacciargliela nel corpo, ilquale auerssario hà posto la destra mano sotto la lama del pugnale, & la sinistra sopra la mano di esso pugnale tirando quella à se, & spingendo con la destra inanzi hà fatto riuoltare la punta contra l’ istesso nimico, & appoggiando il petto nel pomo di detto pugnale, & caricandoui sopra con tutto il corpo hà fatto andare la punta à ferire nel petto della propria persona, che l’ haueua in mano, che non hà potuto agiutarsi, ne uiera se non un sol punto per salute sua ciò è di lasciare andare detto pugnale in terra, mà douea essere nel tempo, che l’ altro cominciò à uoltare la mano, perche dopò uoltata, la punta era anco ariuata al corpo, & questo basti in materia delle mani ignude contra il pugnale. 189. |
|||||||
[14] |
[255] PER DIFFENDERSI DA VN’ ARMA D’ ASTA CON LA SOLA SPADA. HABBIAMO MESA IN VLTIMA QVESTA FIGVRA CHE SEGVE per essere cosa non più trattata da altri laquale tiene la punta così perpendicolarmente uerso terra per mostrare il modo di situare il corpo, & la spada, affine di potere andare contra di un spontone ò meggia picca, ouero altra arma, che fosse poco più longa, ò più corta, che questo importa poco, si come anco non importa, che il ferro sia più longo, ò più corto, si bene che non habbia ale, ò altro impedimento intorno; doue il maggiore pericolo stà nella sinistra mano, laquale sapendosi adoperare come si richiede, si saluarà ancor lei ageuolmente, cio è alzandola, ò abbassandola più, ò meno secondo che uerà il colpo, & non manco si diffenderà dalle finte, & cauationi, ritirate, & auanzate dell’ asta quanto dalla semplice botta; Dal taglio similmente si diffenderà benissimo. Deesi dunque andare senza mai fermarsi per qual si uoglia cosa; & se bene è arma tanto inequale,[42] oprandosi nondimeno come si deue si sforzarà il nimico à ritirarsi, se non se li ariuarà più presto, & più facilmente addosso; li altri termini lasciamo didirli per non palesare intieramente il secreto, uolendo anco con tale figura dare materia alli speculatiui dell’ arte di andare inuestigando, quale sorte di raggione fosse più opurtuna per questa diffesa, che uolendo l’ huomo con dilligenza affaticarsi potra non tanto difficilmente trouare quanto bisogna, poiche da queste due figure si potrà uedere, come si habbia da situare la spada, & il corpo, doue li buoni ingegni con qualche essercitio, & pratica non molto longa conosceranno il uantaggio di essa [256] & l’ esequiranno, che à me basta d’ hauerlo accennato, & mostrato che con la sola spada si può andare contra un’ arma d’ asta & uincerla, & più ageuolmente forsi, che contra una spada, si come n’ habbiamo fatto uedere l’ effetto in atto pratico più uolte, & in diuersi tempi alla presenza di signori, & Prencipi grandi. 190. |
|||||||
[15] |
TRA LE FIGVRE DELLE GVARDIE, MOVIMENTI, ET FERIRI che in quest’ opera sono, si ritrouano alcune di esse che mancano, chi nell’ impugnare l’ Armi, chi nelli finimenti che non mostrano ilgiusto effetto, & si nel uoltare più ò meno le mani, & cosi nel situare de piedi, & disposicioni di corpo, cose che nel uiuo sono libere è sciolte, perche altramente non potrebero operare in tempo, non dimeno sispera che li discorsi siino talli che supliscano à dare ad’ intendere quello che uuole imferire dette figure. Di pui hauea l’ Autore Cominciato à formare essa opera in capitoli, & per esserli sopra gionti alcuni desturbi che la impedito, là lasciata andare alla stampa come si trouaua credendo possi ancora cosi stare, essendo che essa opera è diuisa in dui libri, & ogni libro in tre parte, doue che con il registro si potra, facilmente ritrouare quanto in essa si contiene, Valete. |
|||||||
[16] |
IL FINE. Si fini distampare li discorsi, a di 25. Settembre M. DC. VI. Nella citta di COPONAGHEN, Metropoli del’ Regno di Dania, Appresso Hendrich Walchirchen. |
Copyright and License Summary
For further information, including transcription and translation notes, see the discussion page.
| Work | Author(s) | Source | License |
|---|---|---|---|
| Illustrations (1601) | Unknown artist | Det Kongelige Bibliotek | |
| Illustrations (1606) | Nicolaus Andrea of Flensburg, Jan van Halbeeck, Francesco Valesio | Guy Windsor | |
| Translation | A. F. Johnson, Michael Chidester | Unpublished typescript | |
| Prototype Transcription (1601) | |||
| Archetype Transcription (1606) | Michael Chidester | Index:Scienza d’Arme (Salvator Fabris) 1606 | |
| La Scientia della Spada (1600-09) | Reinier van Noort | School voor Historische Schermkunsten | |
| French Translation (1619) | Index:Escrime Novvelle ou Theatre (Salvator Fabris) Book 2 | ||
| German Translation (1677) | Alex Kiermayer | Index:Sienza e pratica d’arme (Johann Joachim Hynitzsch) |
Additional Transcription Note (MS KB.73.J.38): Copyright 2010 by Reinier van Noort. Subject to Fair Use. Users may, without further permission, display, save, and print this work for personal, non commercial use, provided that the copyright notice is not severed from the work. Libraries may store this material and non-commercially redistribute it to their patrons in electronic or printed form for personal, non-commercial use, provided that the copyright notice is not severed from the work.
Additional Resources
- Fabris, Salvator and Leoni, Tom. Art of Dueling: Salvator Fabris' Rapier Fencing Treatise of 1606.
- First Edition: Highland Village, TX: Chivalry Bookshelf, 2005. ISBN 1-891448-23-4
- Second Edition: Self-published, 2016.
- Fabris, Salvator and Garcia-Salmones, Eugenio. La esgrima o la ciencia de las armas: Libro primero, 1606. Editorial Sacauntos, 2010. ISBN 978-84-937207-8-0
- Fabris, Salvator and Garcia-Salmones, Eugenio. La esgrima o la ciencia de las armas: Libro segundo, 1606. Editorial Edizer, 2011. ISBN 978-84-938120-8-9
References
- ↑ Didier, Henry de Sainct. Les secrets du premier livre sur l'espée seule. Paris, 1573. pp 5-8.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Fabris, Salvator and Leoni, Tom. Art of Dueling: Salvator Fabris' Rapier Fencing Treatise of 1606. Highland Village, TX: Chivalry Bookshelf, 2005. pp XVIII-XIX.
- ↑ Fabris, Salvator and Leoni, Tom. Art of Dueling: Salvator Fabris' Rapier Fencing Treatise of 1606. Highland Village, TX: Chivalry Bookshelf, 2005. p XXIX.
- ↑ Andersson, Henrik. Salvator Fabris as a Hired Assassin in Sweden. Association for Renaissance Martial Arts. Retrieved 2011-12-18.
- ↑ Barbasetti, Luigi. Fencing Through the Ages.[Full citation needed]
- ↑ Originally "asseruatore", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ This seems like a mistranslation of rompere di misura at first blush, but according to Kevin Murakoshi, this is an archaic piece of fencing jargon that was still current in the early 20th century. It means to withdraw/"break measure". ~Michael Chidester
- ↑ Originally "richeide", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ Originally "dirarsi", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ Originally "longuezza", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ Originally "mettre", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ Originally "volto", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 There's no conclusion of this word on the next page, just a new sentence.
- ↑ Originally "occcsione", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ Originally "albassare", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ Originally "& migliore", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ Originally "temerariemente", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ Originally "bisogna", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ The letter 'F' was omitted in the print and hand-corrected in all copies.
- ↑ Originally "guardia", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ Originally "equali", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ Originally "poco", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ Originally "poco", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ Originally "non buoni", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ Originally "queui", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ Originally "che spada", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ Originally "accorgendosi", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ Originally "con pugnale", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ Originally "mouendolo", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ Originally "diuersi", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ Originally "dentro la spada", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ Originally "andere", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ Originally "richede", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ Originally "in suoi", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ Originally "della", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ Originally "la dette", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ Originally "è passare", but corrected in the errata.
- ↑ The errata adds "l’".
- ↑ Originally "farmarsi", but corrected in the errata. The errata says it should be on page 232, but this is the only instance of the word in the book.
- ↑ Originally "sforza", but corrected in the errata. The errata says it should be on page 241, but this is the only instance of the word on the correct line.
- ↑ Should be 183.
- ↑ Originally "ineguale", but corrected in the errata.