|
|
You are not currently logged in. Are you accessing the unsecure (http) portal? Click here to switch to the secure portal. |
Difference between revisions of "Giacomo di Grassi"
| (28 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
{{Infobox writer | {{Infobox writer | ||
| name = [[name::Giacomo di Grassi]] | | name = [[name::Giacomo di Grassi]] | ||
| Line 47: | Line 46: | ||
| below = | | below = | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | '''Giacomo di Grassi''' was a [[century::16th century]] [[nationality::Italian]] [[fencing master]]. Little is known about the life of this master, but he seems to have been born in Modena, Italy and acquired some fame as a fencing master in his youth. He operated a fencing school in | + | '''Giacomo di Grassi''' was a [[century::16th century]] [[nationality::Italian]] [[fencing master]]. Little is known about the life of this master, but he seems to have been born in Modena, Italy and acquired some fame as a fencing master in his youth. He operated a fencing school in Treviso and apparently traveled around Italy observing the teachings of other schools and masters. |
| − | Ultimately di Grassi seems to have developed his own method, which he laid out in great detail in his 1570 work ''[[Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi)|Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme]]'' ("Discourse on Wielding Arms with Safety"). In 1594, a new edition of his book was printed in London under the title ''His True Arte of Defence'' | + | Ultimately di Grassi seems to have developed his own method, which he laid out in great detail in his 1570 work ''[[Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi)|Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme]]'' ("Discourse on Wielding Arms with Safety"). In 1594, a new edition of his book was printed in London under the title ''His True Arte of Defence''; this edition was orchestrated by an admirer named Thomas Churchyard, who hired I. G. to translated it and I. Iaggard to publish it. |
== Treatise == | == Treatise == | ||
| Line 61: | Line 60: | ||
{| class="master" | {| class="master" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! <p> | + | ! <p>Figures<br/>from the 1570</p> |
! <p>{{rating|start|Incomplete Modernization}}<br/>by [[Norman White]]</p> | ! <p>{{rating|start|Incomplete Modernization}}<br/>by [[Norman White]]</p> | ||
| − | ! <p> | + | ! <p>Archetype (1570){{edit index|Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf}}<br/>Transcribed by [[Kelly Hatcher]]</p> |
| − | ! <p>English | + | ! <p>English Translation (1594){{edit index|DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf}}<br/>Transcribed by [[Early English Books Online]]</p> |
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="3" | [[File:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme.jpg|400x400px|center]] | | rowspan="3" | [[File:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme.jpg|400x400px|center]] | ||
| − | | <p>'''Giacomo | + | | <p>'''Giacomo di Grassi His True Art of Defense,''' plainly teaching by infallible Demonstrations, apt Figures and perfect Rules the manner and form how a man without other Teacher or Master may handle all sorts of Weapons as well offensive as defensive: With a Treatise Of Deceit or Falsing: And with a way or Means by private Industry to obtain Strength, Judgement, and Activity</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/9|1|lbl=Ttl}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/9|1|lbl=Ttl}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/2|1|lbl=Ttl}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/2|1|lbl=Ttl}} | ||
| Line 99: | Line 98: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | <p>Among all the | + | | <p>Among all the prayers, wherein through the whole course of my life, I have asked any great thing at God's hands, I have always most earnestly beseeched, that (although at this present I am very poor and of base fortune) he would notwithstanding give me grace to be thankful, and mindful of the good turns which I have received. For among all the disgraces which a man may incur in this world, there is none in my opinion which causes him to become more odious, or a more enimic to mortal men (yes, unto God himself) than ingratitude. Wherefore being in Treviso, by your honors courteously entreated, and of all honorably used, although I practiced little or nought at all to teach you how to handle weapons, for the which purpose I was hired with an honorable stipend, yet to shew myself in some sort thankful, I have determined to bestow the way how to all sorts of weapons with the advantage and safety. The which my work, because it shall find your noble hearts full of valor, will bring forth such fruit, being but once attentively read over, as that in your said honors will be seen in acts and deeds, which in other men scarcely is comprehended by imagination. And I, who have been and am most fervently affected to serve your lords, for as much as it is not granted unto me, (in respect of your divers affairs) to apply the same, and take some pains in teaching as I always desired, have yet by this other way, left all that imprinted in your noble minds, which in this honorable exercise may bring a valiant man unto perfection.</p> |
| | | | ||
{{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/11|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/12|1|lbl=ii|p=1}} | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/11|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/12|1|lbl=ii|p=1}} | ||
| Line 107: | Line 106: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>Therefore I humbly beseech your | + | | <p>Therefore I humbly beseech your honors, that with the same liberal minds, with the which you accepted of me, your Ls will also receive these my endeavors, and vouchsafe so to protect them, as I have always, and will defend your honors most pure and undefiled. Wherein, if I perceive this my first childbirth (as I have only published it to the intent to help and teach others) to be to the general satisfaction of all I will so strain my endeavors in another work which shortly shall shew the way both how to handle all those weapons on horseback which here are taught on foot, as also all other weapons whatsoever.</p> |
<p>Your honours most affectionate servant,</p> | <p>Your honours most affectionate servant,</p> | ||
| Line 175: | Line 174: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | | |
| − | + | | | |
| − | + | | | |
| − | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/12|1|lbl=x}} | |
| − | + | ||
|} | |} | ||
{{master end}} | {{master end}} | ||
{{master begin | {{master begin | ||
| + | | title = The True Art of Defense | ||
| + | | width = 120em | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{master subsection begin | ||
| title = Introduction | | title = Introduction | ||
| width = 120em | | width = 120em | ||
| Line 189: | Line 192: | ||
{| class="master" | {| class="master" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! <p> | + | ! <p>Figures<br/>from the 1570</p> |
! <p>{{rating|C|Draft Modernization}}<br/>by [[Norman White]]</p> | ! <p>{{rating|C|Draft Modernization}}<br/>by [[Norman White]]</p> | ||
| − | ! <p> | + | ! <p>Archetype (1570){{edit index|Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf}}<br/>Transcribed by [[Kelly Hatcher]]</p> |
| − | ! <p>English | + | ! <p>English Translation (1594){{edit index|DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf}}<br/>Transcribed by [[Early English Books Online]]</p> |
|- | |- | ||
| Line 221: | Line 224: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>But least I seem to ground this Art upon dreams and monstrous imaginations (having before laid down, that strength of body is very necessary to attain to the perfection of this Art, it being one of the two principal beginnings first laid down, and not as yet declared the way how to come by and procure the same) I have determined in the entrance of this work, to prescribe the manner how to obtain judgment, and in the end thereof by way of Treatise to show the means ( as far as appertains to this Art) by the which a man by his own endeavor and travail, may get strength and activity of body, to such purpose and effect, that by the instructions and reasons, which shall be given him, he may easily without other master or teacher, become both strong, active and skillful.</p> | + | | <p>But least I seem to ground this Art upon dreams and monstrous imaginations (having before laid down, that strength of body is very necessary to attain to the perfection of this Art, it being one of the two principal beginnings first laid down, and not as yet declared the way how to come by and procure the same) I have determined in the entrance of this work, to prescribe the manner how to obtain judgment, and in the end thereof by way of Treatise to show the means (as far as appertains to this Art) by the which a man by his own endeavor and travail, may get strength and activity of body, to such purpose and effect, that by the instructions and reasons, which shall be given him, he may easily without other master or teacher, become both strong, active and skillful.</p> |
| | | | ||
{{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/17|5|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/18|1|lbl=2|p=1}} | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/17|5|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/18|1|lbl=2|p=1}} | ||
| Line 237: | Line 240: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>And it may be that they keep it secret of purpose: for | + | | <p>And it may be that they keep it secret of purpose: for among diverse disorderly blows, you might have seen some of them most gallantly bestowed, not without evident conjecture of deep judgment. But howsoever it be seeing I purpose to further this Art, in what I may, I will speak of this first part as aptly to the purpose, as I can.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/18|3|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/18|3|lbl=-}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/15|3|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/15|3|lbl=-}} | ||
| Line 294: | Line 297: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>This is done, when one strikes in the right line, by giving a thrust, or by delivering an | + | | <p>This is done, when one strikes in the right line, by giving a thrust, or by delivering an edge-blow with that place of the sword, where it carries the most force, first striking the enemy before he be struck: The which is performed, when he perceives himself to be more near his enemy, in which case, he must nimbly deliver it. For there are a few nay there is no man at all, who (perceiving himself ready to be struck) gives not back, and forsakes to perform every other motion which he has begun.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/19|6|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/19|6|lbl=-}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/17|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/17|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| Line 360: | Line 363: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[File:Di Grassi 4.jpg|400x400px|center]] | | [[File:Di Grassi 4.jpg|400x400px|center]] | ||
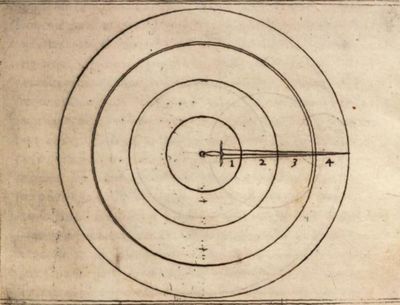
| − | | <p>I have said elsewhere, that the sword in striking frames either a Circle, either a part of a Circle, of which the hand is the center. And it is manifest that a wheel, which moves circularly, is more forcible and swift in the circumference than towards the Center: The which wheel each sword resembles in striking. Whereupon it seems convenient, that I divide the sword into four equal parts: of the which that which is most nearest the hand, as | + | | <p>I have said elsewhere, that the sword in striking frames either a Circle, either a part of a Circle, of which the hand is the center. And it is manifest that a wheel, which moves circularly, is more forcible and swift in the circumference than towards the Center: The which wheel each sword resembles in striking. Whereupon it seems convenient, that I divide the sword into four equal parts: of the which that which is most nearest the hand, as most nigh to the cause, I will call the first part: the next, I will term the second, then the third, and so the fourth: which fourth part contains the point of the sword. of which four parts, the third and fourth are to be used to strike withal. For seeing they are nearest to the circumference, they are most swift. And the fourth part (I mean not the tip of the point, but four fingers more within it) is the swiftest and strongest of all the rest: for besides that it is in the circumference, which causes it to be most swift, it has also four fingers of counter-piece thereby making the motion more forcible. The other two parts, to wit, the first and second are to be used to ward with all, because in striking they draw little compass, and therefore carry with them small force And for that their place is near the hand, they are for this cause strong to resist any violence.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/22|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/22|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 367: | Line 370: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="2" | [[File:Di Grassi 5.jpg|400x400px|center]] | | rowspan="2" | [[File:Di Grassi 5.jpg|400x400px|center]] | ||
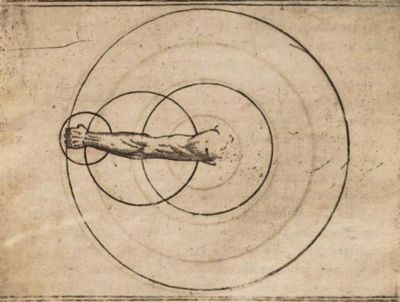
| − | + | | <p>The Arm likewise is not in every part of equal force and swiftness, but differs in every bowing thereof, that is to say in the wrist, in the elbow and in the shoulder: for the blows of the wrist as they are more swift, so they are less strong: And the other two, as they are more strong, so they are more slow, because they perform a great compass. Therefore by my counsel, he that would deliver an edge-blow shall fetch no compass with his shoulder, because whilst he bears his sword far off, he gives time to the wary enemy to enter first: but he shall only use the compass of the elbow and the wrist: which as they be most swift, so are they strong in ought, if they be orderly handled.</p> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | <p>The Arm likewise is not in every part of equal force and swiftness, but differs in every bowing thereof, that is to say in the wrist, in the elbow and in the shoulder: for the blows of the wrist as they are more swift, so they are less strong: And the other two, as they are more strong, so they are more slow, because they perform a great compass. Therefore by my counsel, he that would deliver an | ||
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/23|1|lbl=7}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/23|1|lbl=7}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/23|1|lbl=11}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/23|1|lbl=11}} | ||
| Line 396: | Line 391: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>It is most evident, that all bodies of straight or long shape, I mean when they have a firm and immovable head or beginning, and that they move with | + | | <p>It is most evident, that all bodies of straight or long shape, I mean when they have a firm and immovable head or beginning, and that they move with another like head, always of necessity in their motion, frame either a wheel of part of a circular figure. Seeing then the Arm is of like figure and shape, and is immovably fixed in the shoulder, and further moves only in that part which is beneath it, there is no doubt, but that in his motion it figures also a circle, or some part thereof. And this every man may perceive if in moving his arm, he make trial in himself.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/25|3|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/25|3|lbl=-}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/25|3|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/25|3|lbl=-}} | ||
| Line 408: | Line 403: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>Now I will come to my second, and will declare the reasons and ways by which a man striking with the point strikes straightly. And I say, that | + | | <p>Now I will come to my second, and will declare the reasons and ways by which a man striking with the point strikes straightly. And I say, that whenever the sword is moved by the only motion of the Arm, it must always of necessity frame a circle by the reasons before alleged. But if it happen, as in a manner it does always, that the arm in his motion makes a circle upwards, and the hand moving in the wrist frame a part of a circle downwards the it will come to pass, that the sword being moved by two contrary motions in going forwards strikes straightly.</p> |
| | | | ||
{{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/25|5|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/26|1|lbl=10|p=1}} | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/25|5|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/26|1|lbl=10|p=1}} | ||
| Line 415: | Line 410: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
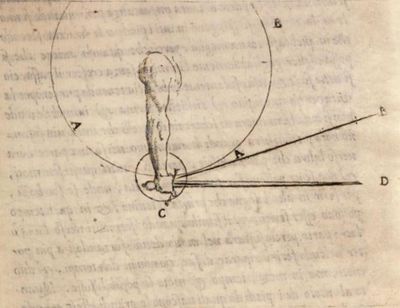
| − | | <p>But to the intent that this may be more plainly perceived, I have framed this present figure for the better understanding whereof it is to be known, that as the arm in his motion carries the sword with it, and is the occasion that being forced by the said motion, the sword frames a circle upwards, So the hand moving itself in the wrist, may either lift up the point of the sword upwards or abase it downwards. So that if the hand do so much let fall the point, as the arm does lift up the handle, it comes to pass that the swords point thrusts directly at | + | | <p>But to the intent that this may be more plainly perceived, I have framed this present figure for the better understanding whereof it is to be known, that as the arm in his motion carries the sword with it, and is the occasion that being forced by the said motion, the sword frames a circle upwards, So the hand moving itself in the wrist, may either lift up the point of the sword upwards or abase it downwards. So that if the hand do so much let fall the point, as the arm does lift up the handle, it comes to pass that the swords point thrusts directly at another prick or point than that it respects.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/26|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/26|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/26|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/26|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| Line 421: | Line 416: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="2" | [[File:Di Grassi 6.jpg|400x400px|center]] | | rowspan="2" | [[File:Di Grassi 6.jpg|400x400px|center]] | ||
| − | | <p>Wherefore let A.B. be the circle which is framed by the motion of the arm: which arm, if ( as it carries with it the sword in his motion ) it would strike at the point D. it should be constrained through his motion to strike at point B. And from hence proceeds the difficulty of thrusting or striking with the point. If it therefore the arm would strike directly at the point D. it is necessary that as much as it lifts the handle upwards, the hand and wrist do move itself circularly downward, making this circle AC and carrying with it the point of the sword down-wards, of force it strikes at the point D. And this would not so come to pass, if with the only motion of the arm, a man should thrust forth the sword, considering the arm moves only above the center C.</p> | + | | <p>Wherefore let A.B. be the circle which is framed by the motion of the arm: which arm, if (as it carries with it the sword in his motion) it would strike at the point D. it should be constrained through his motion to strike at point B. And from hence proceeds the difficulty of thrusting or striking with the point. If it therefore the arm would strike directly at the point D. it is necessary that as much as it lifts the handle upwards, the hand and wrist do move itself circularly downward, making this circle AC and carrying with it the point of the sword down-wards, of force it strikes at the point D. And this would not so come to pass, if with the only motion of the arm, a man should thrust forth the sword, considering the arm moves only above the center C.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/26|3|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/26|3|lbl=-}} | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 497: | Line 492: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | [[File:Di Grassi 8.jpg|400x400px|center]] | |
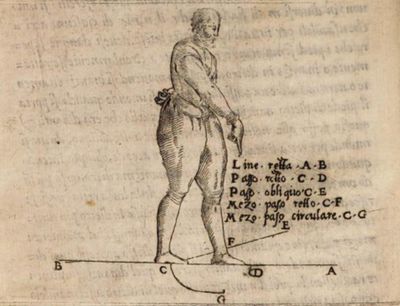
| − | + | | <p>'''Of the agreement of the foot and hand'''</p> | |
<p>The right leg ought always to be the strength of the right hand, and likewise the left leg of the left hand: So that if at any time it shall happen a thrust to be forcibly delivered, reason would that it be accompanied with the leg: for otherwise, by means of the force and weight, which is without the perpendicular or hanging line of the body, having no prop to sustain it, a man is in danger of falling. And it is to be understood, that the pace does naturally so much increase or diminish his motion, as the hand. Therefore we see when the right foot is behind, the hand is there also: for what who so strains himself to stand otherwise, as he offers violence unto nature, so he can never endure it: wherefore when he stands at his ward, bearing his hand wide, there also the foot helps by his strength, being placed towards that part: and when the hand is borne low, and the right foot before, if then he would lift his hand aloft, it is necessary that he draw back his foot: And there is so much distance from the place where the foot does part, to join itself to the other foot, as there is from the place whence the hand parts, to that place where it remains steadfast, little more or less: wherefore presupposing the said rules to be true, he must have great care to make his pace, h move his hand at one time together: And above all, not to skip or leap, but keep one foot always firm and steadfast: and when he would move it, to do it upon some great occasion, considering the foot ought chiefly to agree in motion with the hand, which hand, ought not in any case what soever happen to vary from his purpose, either in striking or defending.</p> | <p>The right leg ought always to be the strength of the right hand, and likewise the left leg of the left hand: So that if at any time it shall happen a thrust to be forcibly delivered, reason would that it be accompanied with the leg: for otherwise, by means of the force and weight, which is without the perpendicular or hanging line of the body, having no prop to sustain it, a man is in danger of falling. And it is to be understood, that the pace does naturally so much increase or diminish his motion, as the hand. Therefore we see when the right foot is behind, the hand is there also: for what who so strains himself to stand otherwise, as he offers violence unto nature, so he can never endure it: wherefore when he stands at his ward, bearing his hand wide, there also the foot helps by his strength, being placed towards that part: and when the hand is borne low, and the right foot before, if then he would lift his hand aloft, it is necessary that he draw back his foot: And there is so much distance from the place where the foot does part, to join itself to the other foot, as there is from the place whence the hand parts, to that place where it remains steadfast, little more or less: wherefore presupposing the said rules to be true, he must have great care to make his pace, h move his hand at one time together: And above all, not to skip or leap, but keep one foot always firm and steadfast: and when he would move it, to do it upon some great occasion, considering the foot ought chiefly to agree in motion with the hand, which hand, ought not in any case what soever happen to vary from his purpose, either in striking or defending.</p> | ||
| − | + | | | |
{{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/30|2|lbl=14|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/31|1|lbl=15|p=1}} | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/30|2|lbl=14|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/31|1|lbl=15|p=1}} | ||
| − | + | | | |
{{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/32|2|lbl=20|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/33|1|lbl=21|p=1}} | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/32|2|lbl=20|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/33|1|lbl=21|p=1}} | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | {{master end}} | + | {{master subsection end}} |
| − | {{master begin | + | {{master subsection begin |
| title = Single Rapier | | title = Single Rapier | ||
| width = 120em | | width = 120em | ||
| Line 515: | Line 510: | ||
{| class="master" | {| class="master" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! <p> | + | ! <p>Figures<br/>from the 1570</p> |
! <p>{{rating|C|Draft Modernization}}<br/>by [[Norman White]]</p> | ! <p>{{rating|C|Draft Modernization}}<br/>by [[Norman White]]</p> | ||
| − | ! <p> | + | ! <p>Archetype (1570){{edit index|Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf}}<br/>Transcribed by [[Kelly Hatcher]]</p> |
| − | ! <p>English | + | ! <p>English Translation (1594){{edit index|DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf}}<br/>Transcribed by [[Early English Books Online]]</p> |
|- | |- | ||
| Line 545: | Line 540: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | <p>In this, and in all other wards, it is diligently to | + | | <p>In this, and in all other wards, it is diligently to be noted, that he bear his weapons so orderly disposed, that the straight line which goes from the sword's point be still best to strike the enemy, either in the face or the breast: for if the point be so borne that it respect over the enemy's head, the enemy may easily first enter underneath and strike before the fall or descend thereof: And by holding the point two low, he may by beating it somewhat downwards cause it to be quit void of his body, and so safely come in to strike, the which has been many times seen.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/33|4|lbl=17}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/33|4|lbl=17}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/36|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/36|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| Line 558: | Line 553: | ||
| <p>'''The broad ward'''</p> | | <p>'''The broad ward'''</p> | ||
| − | <p>This second ward from the effect shall be called the broad or wide ward, because the Arm widening and stretching itself directly as much as possible from the right side, bears the sword so far off from the body, that it seems to give great scope to the enemy to enter, albeit in truth it be nothing so. For although the hand and the handle of the sword, be both far from the body, and quite out of the straight line, yet the point of the sword, from which principally proceeds the offense, is not without the said line: For it is borne so bending toward the left side that it respects directly to strike the enemy, and being borne in that sort, it may very well both strike and defend. And when the point of the sword is borne out of the straight line, as the hand and handle is, then a man is in danger to | + | <p>This second ward from the effect shall be called the broad or wide ward, because the Arm widening and stretching itself directly as much as possible from the right side, bears the sword so far off from the body, that it seems to give great scope to the enemy to enter, albeit in truth it be nothing so. For although the hand and the handle of the sword, be both far from the body, and quite out of the straight line, yet the point of the sword, from which principally proceeds the offense, is not without the said line: For it is borne so bending toward the left side that it respects directly to strike the enemy, and being borne in that sort, it may very well both strike and defend. And when the point of the sword is borne out of the straight line, as the hand and handle is, then a man is in danger to be hurt easily by the enemy, the which happens not when the point is bending, for in such order, it is as a bar and defense to the whole body.</p> |
| | | | ||
{{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/34|1|lbl=18|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/35|1|lbl=19|p=1}} | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/34|1|lbl=18|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/35|1|lbl=19|p=1}} | ||
| Line 568: | Line 563: | ||
| <p>'''The low ward'''</p> | | <p>'''The low ward'''</p> | ||
| − | <p>This also from the effect is called the base ward or lock: Neither is this name improperly given by the Professors of this Art, for that it is more strong, sure and commodious | + | <p>This also from the effect is called the base ward or lock: Neither is this name improperly given by the Professors of this Art, for that it is more strong, sure and commodious than any other ward, and in the which a man may more easily strike, ward and stand therein with less pain. This ward is framed in the Schools after diverse fashions, either bearing the hand low before the knee, either very much stretched forwards, either between both the knees. All which fashions, (if we regard natural reason, and the motions used therein) are to small purpose: for, besides that they are all violent, and for a small time to be endured, they are also such, in the which a man may not strike but in two times, or at least in one, and then very weakly. Wherefore, casting all these aside, I will frame such a ward, as shall be applied, to time, to nature, and to safety: And it is, when one bears his arm directly downwards near his knee (but yet without it) and his sword with his point somewhat raised, and bearing towards the left side, to the end, it may arm and defend that part also, in such sort, that (being borne without violence) he may continue long. And if he would strike, he may in one time, forcibly deliver a great thrust. But this he cannot do, if he bear his sword directly before him, for then he must either draw back his arm when he would strike, or else strike in one time, but very weakly.</p> |
| | | | ||
{{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/36|1|lbl=20}} | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/36|1|lbl=20}} | ||
| Line 583: | Line 578: | ||
| <p>'''The manner how to strike'''</p> | | <p>'''The manner how to strike'''</p> | ||
| − | <p>Without all doubt, the thrust is to be preferred before the | + | <p>Without all doubt, the thrust is to be preferred before the edge-blow, as well because it strikes in less time, as also for that in the said time, it does more hurt. For which consideration, the Romans (who were victorious in all enterprises) did accustom their soldiers of the Legions to thrust only: Alleging for their reason, that the blows of the edge, though they were great, yet they are very few that are deadly, and that thrusts, though little and weak, when they enter but iii fingers into the body, are wont to kill. Therefore I lay down this for a firm and certain rule, that the thrust does many times more readily strike, and give the greater blow against the enemy. And to the end, a man may thrust it out with the greatest force at the most advantage, and uttermost length that may be, he must always remember to carry his left foot compassing behind him in such sort, that the hindfoot so compassing may always be in the straight line of the hand and sword, as a Diameter in the midst of a Circle. And in finishing of a blow, to draw his hindfoot a half pace forwards, and so by that means the blow is longer and stronger, and shoulder and side are only opposite to the enemy, and so far from him, that they may not be struck: and it is not possible for a man to frame a longer blow than this.</p> |
| | | | ||
{{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/37|1|lbl=21|p=2}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/38|1|lbl=22|p=1}} | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/37|1|lbl=21|p=2}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/38|1|lbl=22|p=1}} | ||
| Line 635: | Line 630: | ||
| <p>He that persuades himself that he can learn this Art by the exercise of a few particular strokes of the point and edge is utterly deceived: for besides, that by those particular tricks, there is small knowledge gotten: So the chances in this Art are so dangerous and diverse, that it is impossible to deliberate suddenly, except he have the universal knowledge and understanding of all the rules and principals hereof, being grounded upon offending and defending, and not only upon the sword, the dagger, the target, the javelin and the bill. For a man at all times (when he is occasioned to strike or defend) does not carry these weapons about him, but is constrained to defend himself with a piece of wood from a javelin, with a stool or form from a sword, or with a cloak from a dagger, in which case men commonly use many other things not ordained for that purpose, doing that therewith which natural instinct teaches them. And this instinct is no other thing then the knowledge of the rules before laid down: which knowledge, being it is naturally grafted in the mind, is something the rather helped and qualified by Art, and makes a man so assured and bold, that he dares to enter on any great danger, and judges (when he sees the quality of the weapon, and the site wherein it is placed) what it may do, or in how many ways it may either strike or defend. From which his judgment springs the knowledge of all that he has to do, and how he has to handle himself to encounter any danger.</p> | | <p>He that persuades himself that he can learn this Art by the exercise of a few particular strokes of the point and edge is utterly deceived: for besides, that by those particular tricks, there is small knowledge gotten: So the chances in this Art are so dangerous and diverse, that it is impossible to deliberate suddenly, except he have the universal knowledge and understanding of all the rules and principals hereof, being grounded upon offending and defending, and not only upon the sword, the dagger, the target, the javelin and the bill. For a man at all times (when he is occasioned to strike or defend) does not carry these weapons about him, but is constrained to defend himself with a piece of wood from a javelin, with a stool or form from a sword, or with a cloak from a dagger, in which case men commonly use many other things not ordained for that purpose, doing that therewith which natural instinct teaches them. And this instinct is no other thing then the knowledge of the rules before laid down: which knowledge, being it is naturally grafted in the mind, is something the rather helped and qualified by Art, and makes a man so assured and bold, that he dares to enter on any great danger, and judges (when he sees the quality of the weapon, and the site wherein it is placed) what it may do, or in how many ways it may either strike or defend. From which his judgment springs the knowledge of all that he has to do, and how he has to handle himself to encounter any danger.</p> | ||
| | | | ||
| − | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/41|2|lbl= | + | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/41|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/42|1|lbl=26|p=1}} |
| | | | ||
{{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/43|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/44|1|lbl=32|p=1}} | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/43|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/44|1|lbl=32|p=1}} | ||
| Line 667: | Line 662: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>There is another way, to wit, when one perceives the enemy's sword in the delivery of an edge blow, to fetch a great compass, he may strike him before the fall of his sword with a thrust : or else when the enemy thrusts, (but yet spends many times in the doing thereof) he may likewise strike him in as short time as may be. The which manner of defending is most profitable, and perchance the better of the two. For there is no man that will run himself headlong upon the weapon, or that, perceiving himself ready to be struck, will not suddenly draw back and withhold that blow which he had already prepared to discharge. And although there be some, who being struck run rashly on, yet generally, men will not so do, albeit they be struck when they are most choleric, but will, when they are struck or wounded, give back and be dismayed and by reason of the blood which goes from them, always more and more be weakened.</p> | + | | <p>There is another way, to wit, when one perceives the enemy's sword in the delivery of an edge blow, to fetch a great compass, he may strike him before the fall of his sword with a thrust: or else when the enemy thrusts, (but yet spends many times in the doing thereof) he may likewise strike him in as short time as may be. The which manner of defending is most profitable, and perchance the better of the two. For there is no man that will run himself headlong upon the weapon, or that, perceiving himself ready to be struck, will not suddenly draw back and withhold that blow which he had already prepared to discharge. And although there be some, who being struck run rashly on, yet generally, men will not so do, albeit they be struck when they are most choleric, but will, when they are struck or wounded, give back and be dismayed and by reason of the blood which goes from them, always more and more be weakened.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/43|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/43|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 674: | Line 669: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>But when they be so wounded, it shall be for their profit to be well advised, and not to discomfort themselves for the greatness of the blow, but to bear it patiently : for that which they do in disdain and fury shall turn them to much displeasure.</p> | + | | <p>But when they be so wounded, it shall be for their profit to be well advised, and not to discomfort themselves for the greatness of the blow, but to bear it patiently: for that which they do in disdain and fury shall turn them to much displeasure.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/43|3|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/43|3|lbl=-}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/46|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/46|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| Line 688: | Line 683: | ||
| <p>'''The method which shall be used in handling the chapters following'''</p> | | <p>'''The method which shall be used in handling the chapters following'''</p> | ||
| − | <p>Forasmuch as I ought in the Chapters following to teach more particularly all the blows and defenses in every ward, (to the end that no man do marvel why I do not perform the same, and do think that the instruction is therefore imperfect) I think good (because my purpose is now to entreat of that only which pertains to true Art, to the which the blow of the point, or thrusts, are most agreeable, being more ready and strong than any other) to handle them principally, and yet not so, but that I will also talk of | + | <p>Forasmuch as I ought in the Chapters following to teach more particularly all the blows and defenses in every ward, (to the end that no man do marvel why I do not perform the same, and do think that the instruction is therefore imperfect) I think good (because my purpose is now to entreat of that only which pertains to true Art, to the which the blow of the point, or thrusts, are most agreeable, being more ready and strong than any other) to handle them principally, and yet not so, but that I will also talk of edge-blows when in my treatise I come to that place where it shall be most commodious to strike therewith, placing them near to their wards and defenses, although against all edge-blows this is the best defense, to strike by the right line before the fall of the enemy's sword, for, being delivered in shorter time, it withstands their fall and lighting. The order I say, which I will observe, shall be, to lay down every ward, their blows and defenses, but principally of the point, then of the edge, if need require.</p> |
| | | | ||
{{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/44|1|lbl=28|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/45|1|lbl=29|p=1}} | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/44|1|lbl=28|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/45|1|lbl=29|p=1}} | ||
| Line 704: | Line 699: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>True it is, that he may also deliver a right and reversed | + | | <p>True it is, that he may also deliver a right and reversed edge-blow at the head: or else, strike downwards from the wrist of the hand: but because he is not able to turn his wrist in so small a compass, in the discharge of an edge-blow, either high or low, but that the point of the sword will be out of the straight line, by the length of a sword, in the which (before it return) the enemy has sufficient time to strike: Therefore I would not counsel any man to use them either alone, or both together. But yet between two thrusts, they may be used together, by continuing the one after the other (though they be voided) until the last thrust, the which does safely rest in the low ward. The use of them is on this manner.</p> |
| | | | ||
{{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/45|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/46|1|lbl=30|p=1}} | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/45|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/46|1|lbl=30|p=1}} | ||
| Line 712: | Line 707: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>When one having discharged a thrust from the high ward, perceives that it does not hurt, because it was voided by the enemy's sword, he must turn a right | + | | <p>When one having discharged a thrust from the high ward, perceives that it does not hurt, because it was voided by the enemy's sword, he must turn a right edge-blow from the wrist athwart the enemy's head, fetching a compass with his foot behind him toward the right side, to the end the blow may be the longer, which is the longest of all others. But if the enemy void this in like case (which is very difficult) then he must suddenly turn the reverse from his elbow increasing therewithal a slope pace with the hindfoot. And it is to be noted, that in delivering a reverse, the slope pace is in a manner always to be used, to the end he may go forth of the straight line, in the which (if he should deliver it) he may easily be struck. Having used this pace and reverse, whether it hit or not, the sword in the same instant is something to be drawn or slid: which drawing is profitable in this, that in giving the reverse it does both cause the weapon to cut, and make the greater blow. Wherefore it is to be understood, that all edge-blows ought so to be delivered, that they may cut: for being directly given without any drawing, they cause but a small hurt.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/46|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/46|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 728: | Line 723: | ||
| <p>'''The defense of the thrust of the high ward at single rapier'''</p> | | <p>'''The defense of the thrust of the high ward at single rapier'''</p> | ||
| − | <p>All the fury in striking before spoken of, is utterly frustrated, when, as here it may be withstands and encounters the first thrust. For the defense whereof it is needful that he stand at the low ward, and as the thrust comes, that he encounter it without, with the edge of the sword, and increase a slope pace forward, with the hindfoot at the very same time, by which pace he moves out of the straight line, and passes on the right side of the enemy. And he must remember to bear always the point of the sword toward the enemy: So that the enemy in coming forwards, either runs himself on the sword, which may easily happen, and so much the rather, when he comes resolutely determined to strike, or else if he come not so far forwards that he encounters the sword, yet may be safely struck, with the increase of a straight pace: to which pace, having suddenly joined a slope pace, a man must return and increase again though the enemy were struck at the first increase of that pace: For if at the first stroke and increase, the enemy were not hit in the eye, it shall be of small purpose. Therefore as soon as he has used the crooked or slope pace, he must presently increase | + | <p>All the fury in striking before spoken of, is utterly frustrated, when, as here it may be withstands and encounters the first thrust. For the defense whereof it is needful that he stand at the low ward, and as the thrust comes, that he encounter it without, with the edge of the sword, and increase a slope pace forward, with the hindfoot at the very same time, by which pace he moves out of the straight line, and passes on the right side of the enemy. And he must remember to bear always the point of the sword toward the enemy: So that the enemy in coming forwards, either runs himself on the sword, which may easily happen, and so much the rather, when he comes resolutely determined to strike, or else if he come not so far forwards that he encounters the sword, yet may be safely struck, with the increase of a straight pace: to which pace, having suddenly joined a slope pace, a man must return and increase again though the enemy were struck at the first increase of that pace: For if at the first stroke and increase, the enemy were not hit in the eye, it shall be of small purpose. Therefore as soon as he has used the crooked or slope pace, he must presently increase another straight pace, the which does so much gather upon the enemy, that if he would strike him in the breast, he may thrust his sword up to the hilts.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/47|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/47|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 735: | Line 730: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>Now for the lofty | + | | <p>Now for the lofty edge-blows, both right and reversed, the rules aforesaid may suffice: To wit, the edge-blow fetches a compass. The blow of the point or thrust is the shortest, and in this blow, he that is nearest hits the soonest: So then he must thrust under any of these edge-blows. And farther, for as much as it is naturally given to every man to defend himself, he may encounter the right edge-blow after another way, and that is, to encounter it with the edge of his sword, and presently, to drive therewithal a thrust at the enemy's face, and to compass his hindfoot, towards the right side behind, to the end, that the thrust may be lengthened and his body thereby covered, considering he shall then stand right behind his sword.</p> |
| | | | ||
{{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/47|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/48|1|lbl=32|p=1}} | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/47|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/48|1|lbl=32|p=1}} | ||
| Line 749: | Line 744: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>This manner of thrust is called the reversed thrust. But if one would ward a reverse, he must oppose the edge of sword without, and | + | | <p>This manner of thrust is called the reversed thrust. But if one would ward a reverse, he must oppose the edge of sword without, and therewithal increase a slope pace, and then deliver a thrust with the increase of a straight or right pace. And this may suffice for all that may be used against a lofty, reversed, edge-blow, as far forth as a man endeavors to oppose himself against the weapon. And this is the very same also with which may be used for the warding of the thrust.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/48|3|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/48|3|lbl=-}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/52|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/52|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| Line 763: | Line 758: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>He may also in this ward with the said increase of the right foot, deliver a right | + | | <p>He may also in this ward with the said increase of the right foot, deliver a right edge-blow from the wrist of the hand, and stay himself in the low ward. And perchance he may (although with great danger) bestow also a reverse: yet considering he shall do it out of the straight line, in the which only he strikes safely, I do not think it good, that he use either the said reverse, either the said right blow except it be very seldom, and for the same cause, assuring himself in the blow of the point, or thrust, the which he shall not give, except it be very commodious, or that he be forced of necessity, considering this thrust does not only easily and commodiously defend, but also, at one instant, safely strike, and offend, as shall be showed in the defense of this ward. That therefore which he may safely do, in this ward, is to expect and watch for his enemy's coming.</p> |
| | | | ||
{{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/48|5|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/49|1|lbl=33|p=1}} | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/48|5|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/49|1|lbl=33|p=1}} | ||
| Line 773: | Line 768: | ||
| <p>'''The defense of the broad ward at single rapier'''</p> | | <p>'''The defense of the broad ward at single rapier'''</p> | ||
| − | <p>If a man would defend himself from the blows of the aforesaid broad ward, it is good that he stand against his enemy in the low ward: for the whilst he is so opposite in the same ward, the enemy may neither easily enter, neither commodiously defend himself. So that he which is in the low ward may very easily withstand the downright blow, and the reverse by giving a thrust, for that he shall hit him first, And if he would only oppose his sword, and not strike also | + | <p>If a man would defend himself from the blows of the aforesaid broad ward, it is good that he stand against his enemy in the low ward: for the whilst he is so opposite in the same ward, the enemy may neither easily enter, neither commodiously defend himself. So that he which is in the low ward may very easily withstand the downright blow, and the reverse by giving a thrust, for that he shall hit him first, And if he would only oppose his sword, and not strike also therewithal, he must encounter his enemy's sword with the edge of his own, and turning the same edge fetch a reverse, striking at the face of the enemy. And as he so turns his hand and edge of his sword, it shall be good that he carry his forefoot a half crooked or slope pace towards his right side, staying himself in the broad ward. For defense of the reverse, it is to be marked, when the enemy lifts up the end of the Rapier out of the straight line, because then of force he fetches a compass: And whilst he so does, a man must make a straight pace forwards, and with his left hand take holdfast of the sword hand of his enemy, and incontinently wound him with a thrust underneath already prepared.</p> |
| | | | ||
{{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/49|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/50|1|lbl=34|p=1}} | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/49|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/50|1|lbl=34|p=1}} | ||
| Line 780: | Line 775: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>Now, the very same defense is to be used against the thrust underneath, which is against the right | + | | <p>Now, the very same defense is to be used against the thrust underneath, which is against the right edge-blow. Neither is there any other difference between these two defenses, but that whilst the right blow fetches his compass, a man may give a thrust and hit him first: For the thrust underneath, must only of necessity be warded, because, coming in the straight line, it ministers no advantage or time to hit home first.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/50|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/50|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 799: | Line 794: | ||
| <p>'''The defense of the low ward at single rapier'''</p> | | <p>'''The defense of the low ward at single rapier'''</p> | ||
| − | <p>Because both the downright blow, and the reverse are very easily defended in this ward, I will not stand to speak of any other then of the thrust, restraining myself thereunto. The which thrust, if at the first it be not withstood, may prove very mortal and deadly. Therefore, when this thrust is given within, it must be beaten inwards with the edge of the Rapier, requiring the turn of the hand also inwards, and the compass of the hindfoot, so far towards the right side, as the hand goes towards the right side. And the enemy shall no sooner have delivered the thrust, and he found the sword, but he ought to turn his hand, and with a reverse to cut the enemy's face, carrying always his forefoot on that side where his hand goes. If the enemy's thrust come outwards, then it is necessary, that with the turn of his hand he beat it outwards with the edge of his sword increasing in the same instant one slope pace, by means whereof he delivers his body from hurt. And | + | <p>Because both the downright blow, and the reverse are very easily defended in this ward, I will not stand to speak of any other then of the thrust, restraining myself thereunto. The which thrust, if at the first it be not withstood, may prove very mortal and deadly. Therefore, when this thrust is given within, it must be beaten inwards with the edge of the Rapier, requiring the turn of the hand also inwards, and the compass of the hindfoot, so far towards the right side, as the hand goes towards the right side. And the enemy shall no sooner have delivered the thrust, and he found the sword, but he ought to turn his hand, and with a reverse to cut the enemy's face, carrying always his forefoot on that side where his hand goes. If the enemy's thrust come outwards, then it is necessary, that with the turn of his hand he beat it outwards with the edge of his sword increasing in the same instant one slope pace, by means whereof he delivers his body from hurt. And therewithal (increasing another straight pace, and delivering his thrust already prepared) he does most safely hurt the enemy.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/51|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/51|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/55|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/55|2|lbl=-}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | | |
| − | + | | | |
| − | + | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/51|3|lbl=-}} | |
| − | + | | | |
|} | |} | ||
| − | {{master end}} | + | {{master subsection end}} |
| − | {{master begin | + | {{master subsection begin |
| title = Rapier and Dagger | | title = Rapier and Dagger | ||
| width = 120em | | width = 120em | ||
| Line 818: | Line 813: | ||
{| class="master" | {| class="master" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! <p> | + | ! <p>Figures<br/>from the 1570</p> |
! <p>{{rating|C|Draft Modernization}}<br/>by [[Norman White]]</p> | ! <p>{{rating|C|Draft Modernization}}<br/>by [[Norman White]]</p> | ||
| − | ! <p> | + | ! <p>Archetype (1570){{edit index|Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf}}<br/>Transcribed by [[Kelly Hatcher]]</p> |
| − | ! <p>English | + | ! <p>English Translation (1594){{edit index|DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf}}<br/>Transcribed by [[Early English Books Online]]</p> |
|- | |- | ||
| Line 839: | Line 834: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>Wherefore seeing with these weapons a man may very commodiously, both strike and defend, for that the one is a great help to the other, it is to be remembered, that because these weapons are two, and the one of lesser quantity than the other, to each one be allotted that part both of defending and striking, which it is best able to support. So that to the Dagger, by reason of his shortness, is assigned the left side to defend down to the knee: and to the sword all the right side, and the right and left side jointly downwards from the knee. Neither may it seem strange that the only Dagger ought to defend all blows of the left side : for it does most easily sustain every | + | | <p>Wherefore seeing with these weapons a man may very commodiously, both strike and defend, for that the one is a great help to the other, it is to be remembered, that because these weapons are two, and the one of lesser quantity than the other, to each one be allotted that part both of defending and striking, which it is best able to support. So that to the Dagger, by reason of his shortness, is assigned the left side to defend down to the knee: and to the sword all the right side, and the right and left side jointly downwards from the knee. Neither may it seem strange that the only Dagger ought to defend all blows of the left side: for it does most easily sustain every edge-blow, when it encounters the sword in the first and second part thereof.</p> |
| | | | ||
{{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/52|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/53|1|lbl=37|p=1}} | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/52|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/53|1|lbl=37|p=1}} | ||
| Line 847: | Line 842: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>But yet let no man assure himself, to bear any blow, with his only Dagger when he meets with the sword on the third and fourth part thereof, because that part carries more force with it then may be sustained with the only Dagger. And yet for all that, no man ought to accustom himself to defend blows with the Rapier and Dagger both together, which manner of defending is now commonly used because men believe, that they stand more assuredly by that means, although in truth it is not so. For the Rapier and Dagger are so bound thereby, that they may not strike before they be recovered, and therein spend two times, under the which a man may be struck when he strikes continuing by the straight line, increasing forwards, perceiving his enemy to be occupied and troubled in defending of himself. And albeit this is not seen to come to | + | | <p>But yet let no man assure himself, to bear any blow, with his only Dagger when he meets with the sword on the third and fourth part thereof, because that part carries more force with it then may be sustained with the only Dagger. And yet for all that, no man ought to accustom himself to defend blows with the Rapier and Dagger both together, which manner of defending is now commonly used because men believe, that they stand more assuredly by that means, although in truth it is not so. For the Rapier and Dagger are so bound thereby, that they may not strike before they be recovered, and therein spend two times, under the which a man may be struck when he strikes continuing by the straight line, increasing forwards, perceiving his enemy to be occupied and troubled in defending of himself. And albeit this is not seen to come to pass many times, yet that is because the advantage is not known, or being known, men either ready to execute it, either stand greatly in fear to do it.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/53|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/53|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/57|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/57|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| Line 866: | Line 861: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>It is therefore to be known, that in the handling of these two weapons one may with less danger give a blow with the edge then at single Rapier: For albeit the point of the Rapier be moved out of the straight line: yet for all that there is not free power given to the enemy's to strike, considering there is | + | | <p>It is therefore to be known, that in the handling of these two weapons one may with less danger give a blow with the edge then at single Rapier: For albeit the point of the Rapier be moved out of the straight line: yet for all that there is not free power given to the enemy's to strike, considering there is another weapon contrariwise prepared to defend: but this does not so fall out at the single Rapier, which bearing itself far off when it strikes with the edge, does present and give the means to the enemy to hit home first. And yet for all that, I would not counsel no man, either in this or in any other sort of weapon to accustom himself to give blows with the edge: for that he may under them be most easily struck with a thrust.</p> |
| | | | ||
{{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/53|5|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/54|1|lbl=38|p=1}} | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/53|5|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/54|1|lbl=38|p=1}} | ||
| Line 896: | Line 891: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>Now whether a man ought to hold his Dagger with the edge or flat towards the enemy, it may be left to judgment of him that handles it, so to use it, as shall be most for his advantage. I have seen some, who bear it with the edge towards the enemy, alleging this to be their advantage, that as they encounter the enemy's sword (which comes with the edge or point) in the first or second part thereof, and | + | | <p>Now whether a man ought to hold his Dagger with the edge or flat towards the enemy, it may be left to judgment of him that handles it, so to use it, as shall be most for his advantage. I have seen some, who bear it with the edge towards the enemy, alleging this to be their advantage, that as they encounter the enemy's sword (which comes with the edge or point) in the first or second part thereof, and therewithal do increase a pace forwards, of force the hand turns and places the edge of the Dagger there where the flat was first: So that they are to drive the enemy's sword far from them without any great trouble, because each little motion in the first part of the sword causes very great variety in the point, from which principally proceeds the hurt. In which case, it shall be very profitable to have a good large Dagger.</p> |
| | | | ||
{{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/54|5|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/55|1|lbl=39|p=1}} | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/54|5|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/55|1|lbl=39|p=1}} | ||
| Line 903: | Line 898: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>There be other some, whom it pleases to carry their Dagger with the flat towards the enemy, using for their defense, not only the Dagger, but also the guards thereof with the which (they say) they take holdfast of the enemy's sword : and to the end they may do it the more easily, they have daggers of purpose, which beside their ordinary hilts, have also two long sterts of Iron, four fingers length, and are distant from the dagger the thickness of a bowstring, into which distance, when it chances the enemy's sword to be driven, they suddenly strain and holdfast the sword, the which may come to pass, but I hold it for a thing rather to be imagined then practiced, the case so standing, that in the heat of fight, where disdain bickers with fear, little does a man discern whether the sword be in that straight or no. And when he is to premeditate and mark, endeavoring and striving in his lively judgment, he must advise himself to perform it with exquisite knowledge and perfect discerning of the enemy's motions, his nearness and farness, and to resolve himself to strike by the shortest way that may be : for there hence springs the victory.</p> | + | | <p>There be other some, whom it pleases to carry their Dagger with the flat towards the enemy, using for their defense, not only the Dagger, but also the guards thereof with the which (they say) they take holdfast of the enemy's sword: and to the end they may do it the more easily, they have daggers of purpose, which beside their ordinary hilts, have also two long sterts of Iron, four fingers length, and are distant from the dagger the thickness of a bowstring, into which distance, when it chances the enemy's sword to be driven, they suddenly strain and holdfast the sword, the which may come to pass, but I hold it for a thing rather to be imagined then practiced, the case so standing, that in the heat of fight, where disdain bickers with fear, little does a man discern whether the sword be in that straight or no. And when he is to premeditate and mark, endeavoring and striving in his lively judgment, he must advise himself to perform it with exquisite knowledge and perfect discerning of the enemy's motions, his nearness and farness, and to resolve himself to strike by the shortest way that may be: for there hence springs the victory.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/55|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/55|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 916: | Line 911: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>Besides this, he ought to observe for an infallible rule, that when the point or edge comes on the left side, he must beat it from that side with the dagger. And in like sort defending himself with the sword, to drive it from the right side, for doing otherwise : that is, if he force the blows given on the left side outwards on the right side (forasmuch as the enemy's sword has by that means two motions, the one crossing, which is already given, the other straight which the enemy gives it, continuing the one with the other) it may be, that in the straight motion, it may hit the person, before that (by the thwart or crossing motion) it be driven quite outwards.</p> | + | | <p>Besides this, he ought to observe for an infallible rule, that when the point or edge comes on the left side, he must beat it from that side with the dagger. And in like sort defending himself with the sword, to drive it from the right side, for doing otherwise: that is, if he force the blows given on the left side outwards on the right side (forasmuch as the enemy's sword has by that means two motions, the one crossing, which is already given, the other straight which the enemy gives it, continuing the one with the other) it may be, that in the straight motion, it may hit the person, before that (by the thwart or crossing motion) it be driven quite outwards.</p> |
| | | | ||
{{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/55|4|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/56|1|lbl=40|p=1}} | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/55|4|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/56|1|lbl=40|p=1}} | ||
| Line 924: | Line 919: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>Therefore all blows shall be beaten outwards toward that side or part of the body which is least to the end it may sooner avoid danger. And those blows that come on the right side must be beaten towards the right side : and those on the left side must in like manner be voided from the same side.</p> | + | | <p>Therefore all blows shall be beaten outwards toward that side or part of the body which is least to the end it may sooner avoid danger. And those blows that come on the right side must be beaten towards the right side: and those on the left side must in like manner be voided from the same side.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/56|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/56|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/61|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/61|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| Line 930: | Line 925: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>Now, as concerning the fashion of the Dagger, thus much is to be said : that it would be strong, able to bear and encounter the blows of the sword : (indifferently long) that it may be quickly drawn out of the sheath somewhat short : and those that are of the middle size would be chosen.</p> | + | | <p>Now, as concerning the fashion of the Dagger, thus much is to be said: that it would be strong, able to bear and encounter the blows of the sword: (indifferently long) that it may be quickly drawn out of the sheath somewhat short: and those that are of the middle size would be chosen.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/56|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/56|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/61|3|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/61|3|lbl=-}} | ||
| Line 938: | Line 933: | ||
| <p>'''The offense of the high ward at rapier and dagger'''</p> | | <p>'''The offense of the high ward at rapier and dagger'''</p> | ||
| − | <p>As in handling the single Rapier, so likewise in this, it shall not be amiss to begin with the High ward, which in managing these two weapons may be framed after two sorts. The one with the right foot before, which I call the first : and the other with the same foot behind, which I will term the second. This second requires a greater time, because the point of the sword is farther off from the enemy. The first (being more near) with the only increase of the foot forwards, strikes more readily, yet not with more forcible than the second, which, when it strikes with an increase of a straight pace, joins to the force of the arm and hand, the strength of the whole body.</p> | + | <p>As in handling the single Rapier, so likewise in this, it shall not be amiss to begin with the High ward, which in managing these two weapons may be framed after two sorts. The one with the right foot before, which I call the first: and the other with the same foot behind, which I will term the second. This second requires a greater time, because the point of the sword is farther off from the enemy. The first (being more near) with the only increase of the foot forwards, strikes more readily, yet not with more forcible than the second, which, when it strikes with an increase of a straight pace, joins to the force of the arm and hand, the strength of the whole body.</p> |
| | | | ||
{{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/57|1|lbl=41|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/58|1|lbl=42|p=1}} | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/57|1|lbl=41|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/58|1|lbl=42|p=1}} | ||
| Line 952: | Line 947: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>In the second way, which is framed with the right foot behind, the sword aloft, and the dagger before, and borne as aforesaid, he ought in like sort discharge a thrust as forcible as he may, with the increase of a straight pace, staying himself in the low ward. Neither ought any man in the handling of these weapons to assure himself to deliver | + | | <p>In the second way, which is framed with the right foot behind, the sword aloft, and the dagger before, and borne as aforesaid, he ought in like sort discharge a thrust as forcible as he may, with the increase of a straight pace, staying himself in the low ward. Neither ought any man in the handling of these weapons to assure himself to deliver edge-blows, because he knows that there is another weapon which defends: For he that defends has the selfsame advantage, to wit, to be able to with one weapon (and happily the weaker) to defend himself and strike with the stronger. The which stroke is painfully warded by him, who has already bestowed all his force and power, in delivering the said edge-blow, by means whereof, because there remains in him small power to withstand any great encounter, let him provide to thrust only.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/58|3|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/58|3|lbl=-}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/63|1|lbl=51}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/63|1|lbl=51}} | ||
| Line 958: | Line 953: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>Of all, or of greater part of the | + | | <p>Of all, or of greater part of the edge-blows, as well of striking as defending, I will reason at large in the Treatise of Deceit.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/58|4|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/58|4|lbl=-}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/63|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/63|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| Line 980: | Line 975: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>When he wards with his sword only, it is requisite, that making a slope pace, he lift up his sword, and bear it outwards, or else, as soon as he has found the enemy's sword, that with his dagger he strike at the temples of his enemy's head, staying his sword with his own : or else instead of striking with the Dagger, therewith to stay the enemy's sword, and with it, (increasing another straight pace) to deliver a thrust : but it is very commodious to strike with the Dagger.</p> | + | | <p>When he wards with his sword only, it is requisite, that making a slope pace, he lift up his sword, and bear it outwards, or else, as soon as he has found the enemy's sword, that with his dagger he strike at the temples of his enemy's head, staying his sword with his own: or else instead of striking with the Dagger, therewith to stay the enemy's sword, and with it, (increasing another straight pace) to deliver a thrust: but it is very commodious to strike with the Dagger.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/59|3|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/59|3|lbl=-}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/64|3|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/64|3|lbl=-}} | ||
| Line 986: | Line 981: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>The third way : As soon as he has made the slope pace, and found the enemy's sword, he ought to stay it with his Dagger, and | + | | <p>The third way: As soon as he has made the slope pace, and found the enemy's sword, he ought to stay it with his Dagger, and therewithal, withdrawing his own sword, to discharge a thrust underneath with the increase of a straight pace.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/59|4|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/59|4|lbl=-}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/64|4|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/64|4|lbl=-}} | ||
| Line 994: | Line 989: | ||
| <p>'''The hurt of the broad ward at rapier and dagger'''</p> | | <p>'''The hurt of the broad ward at rapier and dagger'''</p> | ||
| − | <p>In each weapon and ward, I have laid down as a general precept, that no man ought, (either for the procuring of any advantage, either for striking the enemy more readily) deliver blows of the edge. And in like sort, I have said, that easily and with small danger, one may be struck under any such blow : which precepts, as in each time and place, they ought to be observed: so in this ward principally they may not be forgotten. For a man may not without great discommodity and loss of time, strike with any | + | <p>In each weapon and ward, I have laid down as a general precept, that no man ought, (either for the procuring of any advantage, either for striking the enemy more readily) deliver blows of the edge. And in like sort, I have said, that easily and with small danger, one may be struck under any such blow: which precepts, as in each time and place, they ought to be observed: so in this ward principally they may not be forgotten. For a man may not without great discommodity and loss of time, strike with any edge-blow, as he stands in this ward.</p> |
| | | | ||
{{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/59|5|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/60|1|lbl=44|p=1}} | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/59|5|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/60|1|lbl=44|p=1}} | ||
| Line 1,010: | Line 1,005: | ||
| <p>'''The defense of the broad ward at rapier and dagger'''</p> | | <p>'''The defense of the broad ward at rapier and dagger'''</p> | ||
| − | <p>This thrust as well as the other may be warded after three sorts, to wit: with the Dagger only, with the sword only, and with both joined together. But for a | + | <p>This thrust as well as the other may be warded after three sorts, to wit: with the Dagger only, with the sword only, and with both joined together. But for a man's defense in any of these ways, it is good to stand at the low ward. And when he wards with the dagger only, he must make a slope pace, and finding the enemy's sword, with his said dagger, discharge a thrust underneath with the increase of a straight pace.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/60|3|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/60|3|lbl=-}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/65|3|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/65|3|lbl=-}} | ||
| Line 1,023: | Line 1,018: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>It is possible to withstand the thrust with the sword and dagger joined together : but it is so discommodious and so ridiculous a way, that I leave to speak thereof, as of a way nothing safe to be practiced.</p> | + | | <p>It is possible to withstand the thrust with the sword and dagger joined together: but it is so discommodious and so ridiculous a way, that I leave to speak thereof, as of a way nothing safe to be practiced.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/60|5|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/60|5|lbl=-}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/66|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/66|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| Line 1,031: | Line 1,026: | ||
| <p>'''The hurt of the low ward at rapier and dagger'''</p> | | <p>'''The hurt of the low ward at rapier and dagger'''</p> | ||
| − | <p>In each ward, when one stands bearing the point of the sword towards the enemy, it does much disadvantage him to strike with the edge. And if in any sort it be lawful so to do, it is, when he stands at the low ward: For it is commodious, and there is spent but little time in the bestowing of an | + | <p>In each ward, when one stands bearing the point of the sword towards the enemy, it does much disadvantage him to strike with the edge. And if in any sort it be lawful so to do, it is, when he stands at the low ward: For it is commodious, and there is spent but little time in the bestowing of an edge-blow between thrusts. or, the rather to try the enemy, there may be delivered an edge-blow from the wrist of the hand, in the which as there is spent little time, so the point is carried but a little out of the straight line, so that the enemy may very hardly enter to strike under either of these blows. But it is better, not to use them, resolving rather to discharge thrust after thrust, then any edge-blow.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/61|1|lbl=45}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/61|1|lbl=45}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/66|3|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/66|3|lbl=-}} | ||
| Line 1,037: | Line 1,032: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>This warde may (as the high ward) be framed after two sorts, to wit: with the right foot behind, and the same foot before : but that with the right foot behind, is used rather to respect the enemy than to strike first. For although it carries great force by reason that the sword is far off from hurting, and before it hits home, it spends much time, yet the hurt thereof may be easily warded, either with the weapon, or by retiring a pace. I will speak of that only which is framed with the right foot before. And in this, one may strike two ways, to wit: either within or without: By (Within) I understand, when his sword is borne between the enemy's sword and dagger. By (Without) I mean, when any one of them is borne in the middle against the other.</p> | + | | <p>This warde may (as the high ward) be framed after two sorts, to wit: with the right foot behind, and the same foot before: but that with the right foot behind, is used rather to respect the enemy than to strike first. For although it carries great force by reason that the sword is far off from hurting, and before it hits home, it spends much time, yet the hurt thereof may be easily warded, either with the weapon, or by retiring a pace. I will speak of that only which is framed with the right foot before. And in this, one may strike two ways, to wit: either within or without: By (Within) I understand, when his sword is borne between the enemy's sword and dagger. By (Without) I mean, when any one of them is borne in the middle against the other.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/61|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/61|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 1,044: | Line 1,039: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>When one finds himself within, at the half of the enemy's sword, the point whereof, is directed to strike at the right side, he must very swiftly increase a slope pace, and in a manner straight, to the end he may approach the nearer his enemy, and | + | | <p>When one finds himself within, at the half of the enemy's sword, the point whereof, is directed to strike at the right side, he must very swiftly increase a slope pace, and in a manner straight, to the end he may approach the nearer his enemy, and therewithal suddenly barring the enemy's sword in the middle with his own sword and dagger, increase a straight pace, and deliver a thrust.</p> |
| | | | ||
{{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/61|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/62|1|lbl=46|p=1}} | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/61|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/62|1|lbl=46|p=1}} | ||
| Line 1,057: | Line 1,052: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>But standing without, he may (with the increase of his foot forwards) give a thrust at the face, which the enemy of necessity must defend with his sword : but therein the sword and the point thereof is commonly carried out of the straight line, in which case he may (with the increase of a slope pace) turn a reverse at the legs, and then presently something withdrawing his sword, deliver a thrust underneath with the increase of a straight pace.</p> | + | | <p>But standing without, he may (with the increase of his foot forwards) give a thrust at the face, which the enemy of necessity must defend with his sword: but therein the sword and the point thereof is commonly carried out of the straight line, in which case he may (with the increase of a slope pace) turn a reverse at the legs, and then presently something withdrawing his sword, deliver a thrust underneath with the increase of a straight pace.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/62|3|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/62|3|lbl=-}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/67|4|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/67|4|lbl=-}} | ||
| Line 1,063: | Line 1,058: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>He may also after a second manner, give a right | + | | <p>He may also after a second manner, give a right edge-blow from the wrist, as short and strong as is possible, not so much pretending to strike as to find the enemy's sword: And it being suddenly found he must with the increase of a slope or crooked pace, lift up his hand and drive a thrust downwards, with the increase of a straight pace.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/62|4|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/62|4|lbl=-}} | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 1,090: | Line 1,085: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>Besides, every man does naturally more accustom himself to stay and repose himself in it, than in any other. Neither is it (as I believe) for any other cause, then that he knows, by so bearing himself, he may easily both strike and defend. And because in this ward, as I have before said, in the hurt or offense thereof, it more commodious to strike with the edge than in any other ward, albeit, it is not there given for counsel to be good to use it. But yet because it may easily happen, there shall be here laid down some defense for it: calling this principle before any other to remembrance, (He that is nearest hits soonest) to the end, that knowing what way either sword makes, each man may resolve himself to deliver a thrust under an | + | | <p>Besides, every man does naturally more accustom himself to stay and repose himself in it, than in any other. Neither is it (as I believe) for any other cause, then that he knows, by so bearing himself, he may easily both strike and defend. And because in this ward, as I have before said, in the hurt or offense thereof, it more commodious to strike with the edge than in any other ward, albeit, it is not there given for counsel to be good to use it. But yet because it may easily happen, there shall be here laid down some defense for it: calling this principle before any other to remembrance, (He that is nearest hits soonest) to the end, that knowing what way either sword makes, each man may resolve himself to deliver a thrust under an edge-blow, by the which is prevented the fall of the said blow.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/63|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/63|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 1,098: | Line 1,093: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>But because none, but such as are endued with deep judgment, great activity, and stout courage, do or may safely put this in practice: And to the end also, that those, who accustom to defend every blow, performing that in two times which might as well be done in one, may rest satisfied : I will lay down the defense of the | + | | <p>But because none, but such as are endued with deep judgment, great activity, and stout courage, do or may safely put this in practice: And to the end also, that those, who accustom to defend every blow, performing that in two times which might as well be done in one, may rest satisfied: I will lay down the defense of the edge-blow.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/63|3|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/63|3|lbl=-}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/69|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/69|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| Line 1,104: | Line 1,099: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>Therefore, | + | | <p>Therefore, whenever edge-blows are given, they are either right or reversed, high or low.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/63|4|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/63|4|lbl=-}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/69|3|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/69|3|lbl=-}} | ||
| Line 1,110: | Line 1,105: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>Against the right high blow, either the only dagger is to be opposed, either the sword and Dagger both together. When the only dagger is used, then a straight pace must be increased, and the dagger hand lifted up to encounter the enemy's sword in the weakest part thereof, and being suddenly found a straight pace is to be increased, and a thrust underneath (already prepared) to be discharged. But if the sword and dagger be both together opposed, they both must be lifted up, and as soon as the blow is encountered, the enemy's face be cut by discharging a reverse, with the only turn of the hand, resting and staying itself in the broad | + | | <p>Against the right high blow, either the only dagger is to be opposed, either the sword and Dagger both together. When the only dagger is used, then a straight pace must be increased, and the dagger hand lifted up to encounter the enemy's sword in the weakest part thereof, and being suddenly found a straight pace is to be increased, and a thrust underneath (already prepared) to be discharged. But if the sword and dagger be both together opposed, they both must be lifted up, and as soon as the blow is encountered, the enemy's face be cut by discharging a reverse, with the only turn of the hand, resting and staying itself in the broad ward.</p> |
| | | | ||
{{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/63|5|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/64|1|lbl=48|p=1}} | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/63|5|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/64|1|lbl=48|p=1}} | ||
| Line 1,124: | Line 1,119: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>Reverses also, are either high or low. If high: they may be warded with the dagger only, | + | | <p>Reverses also, are either high or low. If high: they may be warded with the dagger only, therewithal discharging a thrust underneath, with the increase of a straight pace, as soon as the dagger has met with the enemy's sword. Either, they may be warded with the sword only increasing a straight pace with the left foot, therewithal discharging a thrust (already lifted up in the ward) with the increase of a straight pace of the right leg. And this manner of warding, is more according to Art, because it has been said, That all blows on the left side, are to be warded with the dagger only.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/64|3|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/64|3|lbl=-}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/70|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/70|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| Line 1,149: | Line 1,144: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | | |
| − | + | | <p>In like case, when the enemy (only to try and provoke) does deliver an edge-blow from the wrist of the hand: let every man be advised, as soon as the blow is delivered, to increase a slope pace, and deliver a thrust with the increase of a straight pace before the enemy (after his blow given) do determine to discharge any more. This may suffice, for the handling of the Rapier and Dagger truly, with advantage.</p> | |
| − | + | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/65|3|lbl=-}} | |
| − | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/71|3|lbl=-}} | |
|} | |} | ||
| − | {{master end}} | + | {{master subsection end}} |
| − | {{master begin | + | {{master subsection begin |
| title = Rapier and Cloak | | title = Rapier and Cloak | ||
| width = 120em | | width = 120em | ||
| Line 1,163: | Line 1,158: | ||
{| class="master" | {| class="master" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! <p> | + | ! <p>Figures<br/>from the 1570</p> |
! <p>{{rating|C|Draft Modernization}}<br/>by [[Norman White]]</p> | ! <p>{{rating|C|Draft Modernization}}<br/>by [[Norman White]]</p> | ||
| − | ! <p> | + | ! <p>Archetype (1570){{edit index|Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf}}<br/>Transcribed by [[Kelly Hatcher]]</p> |
| − | ! <p>English | + | ! <p>English Translation (1594){{edit index|DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf}}<br/>Transcribed by [[Early English Books Online]]</p> |
|- | |- | ||
| Line 1,172: | Line 1,167: | ||
| <p>'''The rapier and cloak'''</p> | | <p>'''The rapier and cloak'''</p> | ||
| − | <p>That I may continue in the weapons which are most usual and most commonly worn: After the Dagger, I come to the Cloak: The use whereof was first found by chance and reduced into Art. Neither was this for any other cause, than for that nature does not only delight to invent things, but also to preserve them being invented. And that she may the better do it, she takes for her help all those | + | <p>That I may continue in the weapons which are most usual and most commonly worn: After the Dagger, I come to the Cloak: The use whereof was first found by chance and reduced into Art. Neither was this for any other cause, than for that nature does not only delight to invent things, but also to preserve them being invented. And that she may the better do it, she takes for her help all those things that are commodious for her. Wherefore, as men in diverse accidents have casually proved, that the Cloak helps greatly (for as much as they are to wear it daily) they have devised how they may behave themselves in that, in which the Cloak may serve their turn. Which accidents, because they are infinite, and do not generally serve for our purpose, I will restrain myself and speak of those only which appertain to this Art, the which are such and so effectual, that they may greatly help to the obtaining of safe victory, if they happen to be placed in such a man as knows how to use and handle them. And for that in true Art it does little prevail, the use thereof being in a manner altogether deceitful, I was resolved to put over all this to the treatise of Deceit, as unto his proper place. Notwithstanding, to the end it may not seem strange to any man, to read nothing of the Cloak in all the handling of true Art, I am minded to lay down a certain few blows in the accustomed wards, referring the more abundant handling thereof unto the treatise of Deceit.</p> |
| | | | ||
{{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/65|4|lbl=49|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/66|1|lbl=50|p=1}} | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/65|4|lbl=49|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/66|1|lbl=50|p=1}} | ||
| | | | ||
| − | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/71|4|lbl= | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/71|4|lbl=59|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/72|1|lbl=60|p=1}} |
|- | |- | ||
| Line 1,189: | Line 1,184: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>And therefore he shall prove himself but a fool, who trusting to the cloth wrapped about his arm, does encounter any right | + | | <p>And therefore he shall prove himself but a fool, who trusting to the cloth wrapped about his arm, does encounter any right edge-blow therewith. For seeing the Cloak is not flexible in that part (which flexibility is his only strength) little prevails either length or largeness, wrapped about a solid substance. But being opposite in that part thereof, where it has length, largeness and flexibility (which is from the arm downwards) it is available: for all three being joined together will ward any edge-blow: the which manner of warding should not be so sure, if the Cloak had only length and flexibility: For having behind it little air, which is the thing that does strengthen it, it may be easily be beaten too, and cut, by any great blow. Therefore, if a man have so much leisure, he ought to wrap his Cloak once or twice about his arm, taking it by the Cape or collar, and folding his arm therein up to the elbow, and therewithal to warde all edge-blows from the flank thereof downwards, as well on the right side, as on the left side, always remembering to carry his foot differing from his arm, for the avoiding of danger that may arise by bearing his leg on the selfsame side, near his cloak knowing the Cloak wards not when there is any hard substance behind it.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/67|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/67|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/73|1|lbl=61}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/73|1|lbl=61}} | ||
| Line 1,221: | Line 1,216: | ||
| <p>'''The hurt of the high ward at rapier and cloak'''</p> | | <p>'''The hurt of the high ward at rapier and cloak'''</p> | ||
| − | <p>In these manner of weapons as in others, I will frame three wards: The first by the foresaid reasons, shall be the high | + | <p>In these manner of weapons as in others, I will frame three wards: The first by the foresaid reasons, shall be the high ward, which in these kind of weapons more than in any other deserve the name of a ward. For the Rapier (something bending) wards as far as the cloak hand, and the cloak hand down to the middle leg: so that in this ward a man is warded from the top of the hand down to the foot. Therefore standing at this ward, whether it be with the right foot before or behind, he may deliver a thrust with the increase of a half pace forwards, staying himself in the low ward.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/70|1|lbl=54}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/70|1|lbl=54}} | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 1,227: | Line 1,222: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | <p>The right | + | | <p>The right edge-blow ought to be delivered from the wrist without any motion of the feet, resting in the low ward: but in delivering of the reverse, it is necessary to fetch a whole pace, and in a manner straight. If the enemy ward it with his sword, then the encounter of the enemy's sword, must be stayed suddenly with the Cloakhand in the first part thereof, and a thrust be delivered underneath, with the increase of a straight pace.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/70|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/70|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/76|2|lbl=-|p=1}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/76|2|lbl=-|p=1}} | ||
| Line 1,235: | Line 1,230: | ||
| <p>'''The defense of the thrust, right and reversed blows of the high ward at rapier and cloak'''</p> | | <p>'''The defense of the thrust, right and reversed blows of the high ward at rapier and cloak'''</p> | ||
| − | <p>For the better avoiding of the hurts which proceed from the high ward: it is necessary to stand at the low ward, in the which the thrust is to be warded | + | <p>For the better avoiding of the hurts which proceed from the high ward: it is necessary to stand at the low ward, in the which the thrust is to be warded 4 manner of ways, to wit: either with the single sword within or without, either with the single Cloak within or without. If with the single sword within, it is requisite to fetch a compass with the foot backwards on the right side. In like case to turn the body the same way, to the intent, to carry it out of the straight line (in which the blow comes) and to drive a reversed thrust at the face, the which thrust in such order delivered is the longest that is, and such a one, as thereby the hurt is not only voided, but also at the selfsame time, the enemy is struck in the face. If it chance, that the sword be encountered without then it is not only profitable but also necessary, to step forwards and with the Cloak to encounter the enemy's sword in the first part thereof. And recovering his own sword, to discharge a thrust underneath with the increase of the right foot. And although it be laid down for a rule, not to use a whole pace when handling the Cloak, this ought to be understood in striking, the which (whilst one endeavors to strike with the sword) it may be forgetting the Cloak, his arm may fall, by means whereof he may stumble against it: but in warding, it does not so happen. For nature being careful to defend herself (at every little danger) lifts up both her arms, yea, although they be oppressed with weight and burden.</p> |
| | | | ||
{{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/70|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/71|1|lbl=55|p=1}} | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/70|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/71|1|lbl=55|p=1}} | ||
| Line 1,249: | Line 1,244: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>The same wards and defenses may be used with the single Cloak, in the which, one must likewise strike, with the increase of the right foot. This manner of warding is not very sure, and therefore it requires great activity and deep judgment, considering he ought to bear his Cloak and arm stretched out before him, and to mark when the enemy's swords point shall pass within the | + | | <p>The same wards and defenses may be used with the single Cloak, in the which, one must likewise strike, with the increase of the right foot. This manner of warding is not very sure, and therefore it requires great activity and deep judgment, considering he ought to bear his Cloak and arm stretched out before him, and to mark when the enemy's swords point shall pass within the cloak hand one handful or little more: and not to suffer it pass farther, but to beat it off, and increasing to discharge a thrust underneath, with the increase of a pace with the right foot. But as I have said, this manner of warding has little certainty and great peril in it, and yet it strikes well, if it be done in short time.</p> |
| | | | ||
{{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/71|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/72|1|lbl=56|p=1}} | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/71|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/72|1|lbl=56|p=1}} | ||
| Line 1,256: | Line 1,251: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>The right | + | | <p>The right edge-blow may in like manner be warded with the single sword or Cloak: but when it comes aloft, it shall not be commodious to encounter it with the single Cloak, for by that means the eyes blind themselves. How much this imports, let others judge. But, when the said right blow comes in a manner low, so that it may well be warded, keeping the enemy in sight, then the Cloak is to be opposed, with the increase of the left pace, and presently thereupon, a thrust to be discharged, with the increase of a right pace.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/72|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/72|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/78|1|lbl=66}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/78|1|lbl=66}} | ||
| Line 1,262: | Line 1,257: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>When one opposes the single sword against the right blow, he must drive a thrust at the face, and fetch a compass with his hindfoot, cutting the face with the said thrust and stay himself in the broad ward. The | + | | <p>When one opposes the single sword against the right blow, he must drive a thrust at the face, and fetch a compass with his hindfoot, cutting the face with the said thrust and stay himself in the broad ward. The selfsame must be done, when he defends himself with both together, to wit, with the sword and Cloak.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/72|3|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/72|3|lbl=-}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/78|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/78|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| Line 1,268: | Line 1,263: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>Against the reversed blow, the | + | | <p>Against the reversed blow, the selfsame manner is used in warding to wit, either with the one, or with the other, either with both joined together.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/72|4|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/72|4|lbl=-}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/78|3|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/78|3|lbl=-}} | ||
| Line 1,274: | Line 1,269: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>With the Cloak, by the increase of a pace, and by encountering the enemy's sword, as far forwards as is possible, that thereby it may be done the more commodiously, delivering a thrust | + | | <p>With the Cloak, by the increase of a pace, and by encountering the enemy's sword, as far forwards as is possible, that thereby it may be done the more commodiously, delivering a thrust therewithal underneath, with the increase of a pace of the right foot.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/72|5|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/72|5|lbl=-}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/78|4|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/78|4|lbl=-}} | ||
| Line 1,296: | Line 1,291: | ||
| <p>'''The hurt of the broad ward, at rapier and cloak'''</p> | | <p>'''The hurt of the broad ward, at rapier and cloak'''</p> | ||
| − | <p>In this ward, as well as in others, a man may both thrust and strike, yet diversely; For he may not discharge a right | + | <p>In this ward, as well as in others, a man may both thrust and strike, yet diversely; For he may not discharge a right edge-blow beneath. And the reverse is manifestly dangerous: So that, when he is to deliver it, he ought to perform it in this order.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/73|1|lbl=57}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/73|1|lbl=57}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/79|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/79|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| Line 1,302: | Line 1,297: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>First, he shall drive a thrust, fetching a compass with his hindfoot, that by that means it may reach the farther, then suddenly (without moving of himself) he shall deliver a right | + | | <p>First, he shall drive a thrust, fetching a compass with his hindfoot, that by that means it may reach the farther, then suddenly (without moving of himself) he shall deliver a right edge-blow, from the wrist, after the which presently, the reverse must follow, with the increase of a pace of the right foot: and further, must follow on the thrust already prepared, and increase the like pace.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/73|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/73|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/79|3|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/79|3|lbl=-}} | ||
| Line 1,319: | Line 1,314: | ||
| <p>'''Of the hurt of the low ward, at rapier and cloak'''</p> | | <p>'''Of the hurt of the low ward, at rapier and cloak'''</p> | ||
| − | <p>This ward is so straight and perilous, that in no man ought to assure himself to deliver an | + | <p>This ward is so straight and perilous, that in no man ought to assure himself to deliver an edge-blow any manner of way. For under any of them he may be easily struck, and each of them may easily be warded with the Cloak. Therefore, he must diligently take heed, that he thrust only, the which must never be discharged before the enemy's sword be found, and then as far forwards as possible. So then f finding it, he may thrust both within and without. Neither is there in this thrust any other advantage to be gotten, then to steal a half pace unawares of the enemy, which may be done very commodiously, considering the cloak occupies the enemy's sight, And having drawn his half pace, and found the enemy's sword, he must increase another half pace forwards, and strike him, costing and forcing the enemy's sword, on that side where it may do no hurt. And this may be used both within and without: But he whom it pleases, and who doubts not to be entangled in the Cloak, may (finding himself within) carry his left foot making a pace therewith, and between his Cloak and his sword, close the enemy's sword, and deliver a thrust with the increase of a pace of the right foot: And finding his enemy's sword without, he may use the self same increase and thrust. But if he find not the enemy's sword, he must deliver a little edge blow from the wrist of the hand, in such sort, that the enemy have no leisure to enter in: And having found the Sword, to discharge a right or straight thrust, or else not voiding the enemy's sword by the increase of a left pace, to drive a thrust from aloft downwards, lifting up the fist somewhat high, and delivering it with the increase of a pace of the right foot.</p> |
| | | | ||
{{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/74|1|lbl=58|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/75|1|lbl=59|p=1}} | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/74|1|lbl=58|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/75|1|lbl=59|p=1}} | ||
| Line 1,335: | Line 1,330: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | | |
| − | + | | <p>This may suffice, for the handling of these weapons as much as appertains to sure play. All that which remains is reserved to the treatise of deceit, in which place shall be seen many handlings of the Cloak no less profitable then pleasant.</p> | |
| − | + | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/75|3|lbl=-}} | |
| − | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/82|2|lbl=-}} | |
|} | |} | ||
| − | {{master end}} | + | {{master subsection end}} |
| − | {{master begin | + | {{master subsection begin |
| title = Rapier and Buckler | | title = Rapier and Buckler | ||
| width = 120em | | width = 120em | ||
| Line 1,349: | Line 1,344: | ||
{| class="master" | {| class="master" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! <p> | + | ! <p>Figures<br/>from the 1570</p> |
! <p>{{rating|C|Draft Modernization}}<br/>by [[Norman White]]</p> | ! <p>{{rating|C|Draft Modernization}}<br/>by [[Norman White]]</p> | ||
| − | ! <p> | + | ! <p>Archetype (1570){{edit index|Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf}}</p> |
| − | ! <p>English | + | ! <p>English Translation (1594){{edit index|DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf}}<br/>Transcribed by [[Early English Books Online]]</p> |
|- | |- | ||
| Line 1,359: | Line 1,354: | ||
<p>Forasmuch as the Buckler is a weapon very commodious and much used, it is reason that I handle it next after the Cloak. For my purpose is, to reason of those weapons first which men do most ordinarily use, then of those that are extraordinary and less accustomed, discoursing upon each of them, as much as is requisite when I come unto them. Therefore I will first consider of the Buckler, therewith proceeding orderly.</p> | <p>Forasmuch as the Buckler is a weapon very commodious and much used, it is reason that I handle it next after the Cloak. For my purpose is, to reason of those weapons first which men do most ordinarily use, then of those that are extraordinary and less accustomed, discoursing upon each of them, as much as is requisite when I come unto them. Therefore I will first consider of the Buckler, therewith proceeding orderly.</p> | ||
| − | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/75|4|lbl= | + | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/75|4|lbl=59}} |
| − | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/82|3|lbl= | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/82|3|lbl=70}} |
|- | |- | ||
| Line 1,385: | Line 1,380: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>It is to be understood, that the Buckler bears the self same respect to the body, which the little prick or sight, on the top of the harquebus artillery or such like bears to the object which they respect and behold. For when a | + | | <p>It is to be understood, that the Buckler bears the self same respect to the body, which the little prick or sight, on the top of the harquebus artillery or such like bears to the object which they respect and behold. For when a Harquebusier or Gunner, discharges happily against a Pigeon or Tower, if they behold and find that the Prick strikes the object, although the prick or sight be very little, and of a thousand parts one: yet I say, the said prick of the Harquebusier shall cover the whole Pigeon, and that of the Artillery in a manner the whole Tower: The effect proceeding of no other thing then of the distance. And it is in this manner. The eye beholding directly through the straight sight, as soon as it arrives at the object, and may not pass through, tears it, and sends through a line sidewise, spreading itself like unto two sides of a Triangle, the which overthrows the foundation of that thing which it strikes: The which foundation, the instrument strikes with which the discharge was made. And if it work otherwise, that comes either of that defect of the instrument, or of that it was not firm.</p> |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 1,423: | Line 1,418: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | <p>2 The second, that all | + | | <p>2 The second, that all edge-blows are of force encountered in the first or second part thereof, where they carry least force: neither can it fall out otherwise, if the enemy would (in manner as he ought) strike either at the head or the body. For if the enemy would strike them, it is necessary, that his sword come within the buckler so much as the arm is long: For otherwise it shall never hit home. And in this case he may well ward each great blow, and therewithal easily strike, and that in a short time.</p> |
| | | | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/85|4|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/85|4|lbl=-}} | ||
| Line 1,429: | Line 1,424: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>3 The third commodity is, that all thrusts are most easily warded : for the Buckler being round, with the directly flat opposite against the enemy, and warding all the body, the enemy will not resolve himself to give a thrust but only against those parts which are so well covered by the Buckler, as, the head, the thighs, or some part of the body, being discovered by ill bearing of the buckler. And seeing that these thrusts, having to hit home, ought to enter so far in, as is from the buckler to the body and more (and that is the length of the arm) they may easily and without doubt (making less motion, and therefore in little time) be driven outwards by the Buckler before they come to the body.</p> | + | | <p>3 The third commodity is, that all thrusts are most easily warded: for the Buckler being round, with the directly flat opposite against the enemy, and warding all the body, the enemy will not resolve himself to give a thrust but only against those parts which are so well covered by the Buckler, as, the head, the thighs, or some part of the body, being discovered by ill bearing of the buckler. And seeing that these thrusts, having to hit home, ought to enter so far in, as is from the buckler to the body and more (and that is the length of the arm) they may easily and without doubt (making less motion, and therefore in little time) be driven outwards by the Buckler before they come to the body.</p> |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 1,450: | Line 1,445: | ||
| <p>'''Of the hurt of the high ward at sword and buckler'''</p> | | <p>'''Of the hurt of the high ward at sword and buckler'''</p> | ||
| − | <p>Because it is a very easy matter to ward both the right and reversed blows of the edge : And for that a man may easily strike under them, I will not lay down either for the one or the other their | + | <p>Because it is a very easy matter to ward both the right and reversed blows of the edge: And for that a man may easily strike under them, I will not lay down either for the one or the other their striking or defending, but only talk of the thrust. I say, the thrust above may be delivered in the one with the right foot behind, the other with the right foot before.</p> |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 1,472: | Line 1,467: | ||
| <p>'''Of the defense of the high ward at sword and buckler'''</p> | | <p>'''Of the defense of the high ward at sword and buckler'''</p> | ||
| − | <p>As a man stands at the low ward he may easily defend both those lofty thrusts. When they come, he standing at the said ward, it shall be best to drive them outwards, with the increase of a left pace, and with his sword and buckler to stay the enemy's sword. And because this left pace is a great increase : and likewise the enemy, driving his thrusts, comes with great force, it may easily come to pass that both may approach so near one to the other, that he may with his buckler give the enemy, the Mustachio, in the face, but that must be done when fit occasion is offered, and then further recovering his own sword to discharge a thrust underneath with the increase of a pace of the right foot.</p> | + | <p>As a man stands at the low ward he may easily defend both those lofty thrusts. When they come, he standing at the said ward, it shall be best to drive them outwards, with the increase of a left pace, and with his sword and buckler to stay the enemy's sword. And because this left pace is a great increase: and likewise the enemy, driving his thrusts, comes with great force, it may easily come to pass that both may approach so near one to the other, that he may with his buckler give the enemy, the Mustachio, in the face, but that must be done when fit occasion is offered, and then further recovering his own sword to discharge a thrust underneath with the increase of a pace of the right foot.</p> |
| | | | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/88|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/88|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| Line 1,480: | Line 1,475: | ||
| <p>'''Of the hurt of the broad ward, at sword and buckler'''</p> | | <p>'''Of the hurt of the broad ward, at sword and buckler'''</p> | ||
| − | <p>If a man would step forward, and strike as he stands in the broad ward, it is not lawful for him to use any other then the thrust, considering the right and reversed blows may not be delivered without great peril and danger. For in the sight or placing of this ward, the sword is far off from the body. And as he moves to fetch a right or reversed | + | <p>If a man would step forward, and strike as he stands in the broad ward, it is not lawful for him to use any other then the thrust, considering the right and reversed blows may not be delivered without great peril and danger. For in the sight or placing of this ward, the sword is far off from the body. And as he moves to fetch a right or reversed edge-blow, his sword of force will be much farther: So that it may not be done without great danger. Therefore he shall use the thrust only: in forcing and delivery whereof, he shall proceed first to carry his hindfoot a half pace forwards, and then to drive it on with the increase of another half pace of the right foot, staying himself in the broad ward.</p> |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 1,498: | Line 1,493: | ||
<p>As this low ward is framed in two manner of ways, that is to say, with the right foot before and behind: So likewise a man may strike therein after two sorts, Standing with the right foot behind (leaving | <p>As this low ward is framed in two manner of ways, that is to say, with the right foot before and behind: So likewise a man may strike therein after two sorts, Standing with the right foot behind (leaving | ||
| − | aside, the blows of the edge, being to small purpose) he shall deliver a thrust with the increase of a the right foot, between the enemy's sword and buckler, or else, if it be more commodious without the sword and buckler, settling in the low ward, with the right foot before, in which ward, a man may strike in two manner of ways, within and without. Finding himself without, having first met the enemy's sword with his own, he shall increase a left pace, not to the intent to avoid himself from the enemy's sword, but shall with his buckler also, stay the enemy's sword, and forasmuch as he did not at the first deliver the said thrust, he shall then continue and force it on directly with the increase of a pace of the right foot. Finding himself within, the same thrust is to be used but more strongly. For, with the increase of a pace, leaving his buckler or the enemy's sword, he shuts it in between his own sword and the buckler: and keeping it in that straight, (whereby he is sure the enemy can deliver no | + | aside, the blows of the edge, being to small purpose) he shall deliver a thrust with the increase of a the right foot, between the enemy's sword and buckler, or else, if it be more commodious without the sword and buckler, settling in the low ward, with the right foot before, in which ward, a man may strike in two manner of ways, within and without. Finding himself without, having first met the enemy's sword with his own, he shall increase a left pace, not to the intent to avoid himself from the enemy's sword, but shall with his buckler also, stay the enemy's sword, and forasmuch as he did not at the first deliver the said thrust, he shall then continue and force it on directly with the increase of a pace of the right foot. Finding himself within, the same thrust is to be used but more strongly. For, with the increase of a pace, leaving his buckler or the enemy's sword, he shuts it in between his own sword and the buckler: and keeping it in that straight, (whereby he is sure the enemy can deliver no edge-blow because it may not move neither upwards nor downwards, neither forwards, but is then without the body,) he shall continue on, and resolutely deliver this manner of thrust, with the increase of a pace of the right foot.</p> |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 1,512: | Line 1,507: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | | |
| − | + | | <p>For the defense of the other two thrusts, the one within, and the other without, a man must take great heed, and it is very necessary that as the enemy increases pretending to strike safely) he carry a slope pace with the left foot and deliver a thrust above hand, upon the which the enemy of himself shall run and invest himself. And it is to be considered, that in these thrusts, he that defends has great advantage: For the enemy comes resolutely to strike, not thinking that it may in any other sort be warded then by giving back, But he that wards by increase in, defending and drawing near unto the enemy, is so placed that he may easily hurt him.</p> | |
| − | + | | | |
| − | + | | | |
{{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/90|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/91|1|lbl=79|p=1}} | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/90|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/91|1|lbl=79|p=1}} | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | {{master end}} | + | {{master subsection end}} |
| − | {{master begin | + | {{master subsection begin |
| title = Rapier and Square Shield | | title = Rapier and Square Shield | ||
| width = 120em | | width = 120em | ||
| Line 1,527: | Line 1,522: | ||
{| class="master" | {| class="master" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! <p> | + | ! <p>Figures<br/>from the 1570</p> |
! <p>{{rating|C|Draft Modernization}}<br/>by [[Norman White]]</p> | ! <p>{{rating|C|Draft Modernization}}<br/>by [[Norman White]]</p> | ||
| − | ! <p> | + | ! <p>Archetype (1570){{edit index|Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf}}</p> |
| − | ! <p>English | + | ! <p>English Translation (1594){{edit index|DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf}}<br/>Transcribed by [[Early English Books Online]]</p> |
|- | |- | ||
| Line 1,536: | Line 1,531: | ||
| <p>'''Of the sword and target, called the square target'''</p> | | <p>'''Of the sword and target, called the square target'''</p> | ||
| − | <p>It is most manifest, that the Target is a most ancient weapon, found out only for the use of warfare, and peculiar quarrels between man and man : albeit, since the finding thereof, there have been devised by the industry of man a thousand ways to serve them at their need: From whence it has come to pass, (because it seemed convenient unto the Professors of this Art) that this weapon was very commodious and profitable, as well for his fashion, as for it is a mean or middle weapon, between the buckler and the round Target: That they have framed a special kind of play therewith, although it differs from the other two weapons in no other thing then fashion. Therefore, diverse professors of this Art, being moved some by reason of the form, some by the bigness, and some by the heaviness thereof, have accustomed to bear it after diverse ways, Those who make most account of the heaviness, would for some consideration, that the right and proper bearing thereof, was to hold it leaning on the thigh, not moving there hence, but being greatly constrained thereunto.</p> | + | <p>It is most manifest, that the Target is a most ancient weapon, found out only for the use of warfare, and peculiar quarrels between man and man: albeit, since the finding thereof, there have been devised by the industry of man a thousand ways to serve them at their need: From whence it has come to pass, (because it seemed convenient unto the Professors of this Art) that this weapon was very commodious and profitable, as well for his fashion, as for it is a mean or middle weapon, between the buckler and the round Target: That they have framed a special kind of play therewith, although it differs from the other two weapons in no other thing then fashion. Therefore, diverse professors of this Art, being moved some by reason of the form, some by the bigness, and some by the heaviness thereof, have accustomed to bear it after diverse ways, Those who make most account of the heaviness, would for some consideration, that the right and proper bearing thereof, was to hold it leaning on the thigh, not moving there hence, but being greatly constrained thereunto.</p> |
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/94|2|lbl=68}} |
| − | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/91|2|lbl= | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/91|2|lbl=79}} |
|- | |- | ||
| Line 1,556: | Line 1,551: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[File:Di Grassi 18.jpg|400x400px|center]] | | [[File:Di Grassi 18.jpg|400x400px|center]] | ||
| − | | <p>Besides, the said commodity of beholding the enemy, there is also another that is of this warding: For the Target being borne after this manner (framing a triangle) the sharp corner thereof respects the forehead, and the sides thereof so spread themselves, that through the least motion, any big man whosoever, may stand safe behind them. And if blows come at the head, be they thrusts or | + | | <p>Besides, the said commodity of beholding the enemy, there is also another that is of this warding: For the Target being borne after this manner (framing a triangle) the sharp corner thereof respects the forehead, and the sides thereof so spread themselves, that through the least motion, any big man whosoever, may stand safe behind them. And if blows come at the head, be they thrusts or edge-blows, all of them light upon one of the said sides, behind which stands the head safe without hindering of the eyesight. The other two sides of the Target, right, and left, with very small motion, ward the right and left side of the body, in such sort, that a man may also draw back his arm: For the left side of the Target wards the elbow, which it does not do, when the high side thereof is carried equal. To conclude therefore, that in holding the Target, his bigness may the better ward, for the causes abovesaid being superfluous to be repeated again, I counsel, it to be held with the arm stretched forth from the body, not accounting the heaviness to be hurtful, because continues not long in so holding it: and if the too long holding be painful, he may draw back his arm, and rest himself. The better to do this and to be able to see the enemy, I say, he shall hold it, his arm stretched out, with the high point outwards, respecting the forehead.</p> |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 1,581: | Line 1,576: | ||
| <p>'''The defense of the high ward, at sword and square target'''</p> | | <p>'''The defense of the high ward, at sword and square target'''</p> | ||
| − | <p>The foresaid thrust may easily be warded, if in the very time that it comes it be encountered with the high point of the Target, but yet with that side which bends towards the right hand. And as soon as the enemy's sword is come one handful within the Target, it must be strongly beaten off by the Target towards the right hand, increasing the same instant a left pace. Then with as great an increase of a pace of the right foot as may be possible, a thrust underneath most be given, already prepared, because a man ought to stand at the low ward for the warding of the thrust | + | <p>The foresaid thrust may easily be warded, if in the very time that it comes it be encountered with the high point of the Target, but yet with that side which bends towards the right hand. And as soon as the enemy's sword is come one handful within the Target, it must be strongly beaten off by the Target towards the right hand, increasing the same instant a left pace. Then with as great an increase of a pace of the right foot as may be possible, a thrust underneath most be given, already prepared, because a man ought to stand at the low ward for the warding of the thrust above-hand.</p> |
| | | | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/95|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/95|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| Line 1,589: | Line 1,584: | ||
| <p>'''The hurt of the broad ward, at sword and square target'''</p> | | <p>'''The hurt of the broad ward, at sword and square target'''</p> | ||
| − | <p>In this ward likewise, the enemy may be invested on the point of the sword, by going forwards as straightly as is possible, and by striking quickly before the enemy. For the Target (whose charge is only to defend) is so great, that it may easily ward all | + | <p>In this ward likewise, the enemy may be invested on the point of the sword, by going forwards as straightly as is possible, and by striking quickly before the enemy. For the Target (whose charge is only to defend) is so great, that it may easily ward all edge-blows, and those chiefly which come from the knee upwards. Farther, when a blow is pretended to be delivered, it is manifest, that a thrust does enter by a more narrow straight than any edge-blow does. And therefore, when one would strike the enemy standing at the lock or low ward, he must remember that he approach as near him as he may possible: and being so near, that with his Target put forth one handful more forwards, he may beat away the enemy's sword, then by so beating of it, he shall increase a left pace, and presently after it, with the increase of the right foot, deliver him a thrust, if it so chance that at the first encounter he strike him not strongly.</p> |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 1,639: | Line 1,634: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | | |
| − | + | | <p>But if the enemy come without, he must increase the self same slope pace, and with the right side of his Target beat off the point of the enemy's sword, and then thrust either above, either beneath, as in that occasion it shall be most to his advantage with the increase of the pace of the right foot. And when in consideration of the abundant defenses of the Target, he may neither increase his paces, not deliver a thrust, he must settle himself in the low ward with the right foot behind, which ward I will largely handle in the treatise of deceit or falsing, being as it were his proper place, here ending the true handling of the sword and square Target.</p> | |
| − | + | | | |
| − | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/98|2|lbl=-}} | |
|} | |} | ||
| − | {{master end}} | + | {{master subsection end}} |
| − | {{master begin | + | {{master subsection begin |
| title = Rapier and Round Shield | | title = Rapier and Round Shield | ||
| width = 120em | | width = 120em | ||
| Line 1,653: | Line 1,648: | ||
{| class="master" | {| class="master" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! <p> | + | ! <p>Figures<br/>from the 1570</p> |
! <p>{{rating|C|Draft Modernization}}<br/>by [[Norman White]]</p> | ! <p>{{rating|C|Draft Modernization}}<br/>by [[Norman White]]</p> | ||
| − | ! <p> | + | ! <p>Archetype (1570){{edit index|Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf}}</p> |
| − | ! <p>English | + | ! <p>English Translation (1594){{edit index|DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf}}<br/>Transcribed by [[Early English Books Online]]</p> |
|- | |- | ||
| Line 1,663: | Line 1,658: | ||
<p>The round Target would require a long and most exquisite consideration because it is of circular form, most capable, and most perfect of all others. But for that my purpose in this my work, is to write that only which I know does appertain to this Art, giving leave to every man to busy himself in his own profession. And leaving a great part of this consideration to the Mathematicians and Historiographers to reason of his diverse qualities or passions, either who was inventor thereof, either, whether it be a weapon of antiquity, or of this our age, And coming to discourse of that, wherein it profits in this our time, (being a weapon so greatly honored and esteemed of Princes, Lords, and Gentlemen, that besides the use thereof in their affairs, as well by day as by night, they also keep their hoses richly decked and beautified therewith) And considering only that thing, in the round Target, among all weapons which may profit or hurt in the handling thereof, I say, that the said round Target has been diversely held, borne and used, by diverse men in diverse ages, as well as the other square Target, and other weapons of defense, as well as of offense. And there want not also men in our time, who to the intent they be not wearied, bear it leaning on their thigh as though that in this exercise (in which only travail and pains are available) a man should only care for rest and quietness. For by the means of these two, strength and activity, (parts in the exercise of weapons, both important and necessary) are obtained and gotten.</p> | <p>The round Target would require a long and most exquisite consideration because it is of circular form, most capable, and most perfect of all others. But for that my purpose in this my work, is to write that only which I know does appertain to this Art, giving leave to every man to busy himself in his own profession. And leaving a great part of this consideration to the Mathematicians and Historiographers to reason of his diverse qualities or passions, either who was inventor thereof, either, whether it be a weapon of antiquity, or of this our age, And coming to discourse of that, wherein it profits in this our time, (being a weapon so greatly honored and esteemed of Princes, Lords, and Gentlemen, that besides the use thereof in their affairs, as well by day as by night, they also keep their hoses richly decked and beautified therewith) And considering only that thing, in the round Target, among all weapons which may profit or hurt in the handling thereof, I say, that the said round Target has been diversely held, borne and used, by diverse men in diverse ages, as well as the other square Target, and other weapons of defense, as well as of offense. And there want not also men in our time, who to the intent they be not wearied, bear it leaning on their thigh as though that in this exercise (in which only travail and pains are available) a man should only care for rest and quietness. For by the means of these two, strength and activity, (parts in the exercise of weapons, both important and necessary) are obtained and gotten.</p> | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/101|2|lbl=75}} | ||
| | | | ||
| − | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/98|3|lbl=86|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/99|1|lbl=87|p=1}} | |
| − | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/98|3|lbl= | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 1,686: | Line 1,681: | ||
| <p>'''The hurt of the high ward, at sword and round target'''</p> | | <p>'''The hurt of the high ward, at sword and round target'''</p> | ||
| − | <p>Because the round Target contains in it most great and sure defense, therefore ought not any | + | <p>Because the round Target contains in it most great and sure defense, therefore ought not any edge-blow which may be easily warded with the single sword without the help of the Target be delivered. Thrusts also enter very difficultly to strike the body, because the Target, by means of the least motion that is, seems to be, as it were a wall before the body. And to thrust at the leg is no sure play. That which remains to be done, is to thrust forcibly with the sword: and when one perceives, that the point thereof is entered within the circumference of the enemy's Target, it is necessary that he increase a left pace, and with the circumference of his own Target, to beat off the enemy's sword and Target, to the end, it suffer the thrust so given of force to enter in. And (having so beaten and entered) to continue on the thrust in the straight line, with the increase of a pace of the right foot.</p> |
| | | | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/102|1|lbl=90}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/102|1|lbl=90}} | ||
| Line 1,750: | Line 1,745: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>Now, all these thrusts, no doubt shall speed every time that the enemy either makes no traverse motion with his body, either as he strikes, comes directly forwards, or else being fearful, goes directly backwards, for it is not possible that one man go so fast directly backwards, as | + | | <p>Now, all these thrusts, no doubt shall speed every time that the enemy either makes no traverse motion with his body, either as he strikes, comes directly forwards, or else being fearful, goes directly backwards, for it is not possible that one man go so fast directly backwards, as another may forwards. Yet it is therefore diligently to be observed in this ward, never to determine to strike, either in the handling of these, or of any other kind of weapons, if (with one of them) he shall not first find the enemy's sword. The which redoings to great profit of every man, but especially of those, who have strong arms, for that they are better able to beat back the enemy's weapon.</p> |
| | | | ||
| {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/106|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/106|2|lbl=-}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | | |
| − | + | | <p>'''Of the defense of the low ward, at sword and round target'''</p> | |
<p>All the foresaid thrusts are warded, by not suffering the sword to be found by the enemy with either of his weapons. For the enemy (not finding it, will not assure himself, or presume to enter, without first finding of the sword) may most easily be struck and not strike, if a man increase a slope pace, (to the end he may void his body from hurt,) and with the increase of a straight pace of the right foot, do also discharge a thrust beneath. And after this order he may strike safely, (not only when his sword is not found by the enemy, but also when it chances to be found) if he be ready and nimble to make his slope pace, and to beat off, as forcible as he may, the enemy's Target with his own sword and Target, thereby forcing a low thrust to enter in, with the increase of a pace with the right foot. And thus much concerning the true striking and defending of the sword and round Target.</p> | <p>All the foresaid thrusts are warded, by not suffering the sword to be found by the enemy with either of his weapons. For the enemy (not finding it, will not assure himself, or presume to enter, without first finding of the sword) may most easily be struck and not strike, if a man increase a slope pace, (to the end he may void his body from hurt,) and with the increase of a straight pace of the right foot, do also discharge a thrust beneath. And after this order he may strike safely, (not only when his sword is not found by the enemy, but also when it chances to be found) if he be ready and nimble to make his slope pace, and to beat off, as forcible as he may, the enemy's Target with his own sword and Target, thereby forcing a low thrust to enter in, with the increase of a pace with the right foot. And thus much concerning the true striking and defending of the sword and round Target.</p> | ||
| − | + | | | |
| − | + | | | |
{{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/106|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/107|1|lbl=95|p=1}} | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/106|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/107|1|lbl=95|p=1}} | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | {{master end}} | + | {{master subsection end}} |
| − | + | {{master subsection begin | |
| − | {{master begin | ||
| title = Double Rapiers | | title = Double Rapiers | ||
| width = 120em | | width = 120em | ||
| Line 1,772: | Line 1,766: | ||
{| class="master" | {| class="master" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! <p> | + | ! <p>Figures<br/>from the 1570</p> |
! <p>{{rating|C|Draft Modernization}}<br/>by [[Norman White]]</p> | ! <p>{{rating|C|Draft Modernization}}<br/>by [[Norman White]]</p> | ||
| − | ! <p> | + | ! <p>Archetype (1570){{edit index|Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf}}</p> |
| − | ! <p>English | + | ! <p>English Translation (1594){{edit index|DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf}}<br/>Transcribed by [[Early English Books Online]]</p> |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | <p>'''Of the case of rapiers'''</p> |
| − | There are also used now adays, as well in the schools, as in the lists, two Swords or Rapiers, admitted, and approved both of Princes, and of the professors of this art, for honorable and knightly weapons, albeit they be not used in the wars. Wherefore I shall not vary from my purpose, if I reason also of these, as far as is agreeable to true art. To him that would handle these weapons, it is necessary that he can as well manage the left hand as the right, which thing shall be (if not necessary) yet most profitable in every other kind of weapon. But in these principally he is to resolve himself, that he can do no good, without that kind of nimbleness and dexterity. For seeing they are two weapons, and yet of one | + | |
| − | | | + | <p>There are also used now adays, as well in the schools, as in the lists, two Swords or Rapiers, admitted, and approved both of Princes, and of the professors of this art, for honorable and knightly weapons, albeit they be not used in the wars. Wherefore I shall not vary from my purpose, if I reason also of these, as far as is agreeable to true art. To him that would handle these weapons, it is necessary that he can as well manage the left hand as the right, which thing shall be (if not necessary) yet most profitable in every other kind of weapon. But in these principally he is to resolve himself, that he can do no good, without that kind of nimbleness and dexterity. For seeing they are two weapons, and yet of one selfsame kind, they ought equally and indifferently to be handled, the one performing that which the other does, and every of them being apt as well to strike as defend. And therefore a man ought to accustom his body, arms and hands as well to strike as defend. And he which is not much practiced and exercised therein, ought not to make profession of this Art: for he shall find himself to be utterly deceived.</p> |
| + | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/110|3|lbl=84}} | ||
| | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/107|2|lbl=95|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/108|1|lbl=96|p=1}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | <p>'''The manner how to handle two rapiers'''</p> |
| − | It is most manifest that both these weapons may strike in one and the same time: for there may be delivered jointly together two downright | + | |
| − | + | <p>It is most manifest that both these weapons may strike in one and the same time: for there may be delivered jointly together two downright edge-blows on high and two beneath: two reverses, and two thrusts, and are so rich and plentiful in striking, that it seems they may be used only to strike. But this ought not to be practiced, neither may it without great danger For all that, whatsoever may be done with either of them, is divided into striking and defending. That this is true, it may be perceived in the single Sword, which assays both to strike and defend. And those who have taken no such heed, but have been bent only to strike being moved either through cholera, either believing, that they had to deal with an ignorant person, have remained thereby mightily wounded. of this, there might be laid down infinite examples, which I leave to the intent I may not swerve from my purpose. I say therefore that of the two Rapiers which are handled, the one must be applied towards the other to strike, regarding always to use that first which wards, then that which strikes: for first a man must endeavor to defend himself, and then to strike others.</p> | |
| | | | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/108|2|lbl=-|p=1}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[File:Di Grassi 20.jpg|400x400px|center]] | | [[File:Di Grassi 20.jpg|400x400px|center]] | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | <p>'''Of the high ward at two rapiers'''</p> |
| − | Presupposing always, that either hand is very well exercised, as well in striking as in defending, this ward shall be framed after two ways, which yet in manner is all one. The one with the right foot, and the other with the left, so working continually, that the hind arm be aloft, the former beneath in manner, as when the low ward is framed at single sword. And as a man strikes, he must always maintain and continue this high ward, which at the two rapiers, is the most perfect and surest and he may easily perform and do it: for whilst he enters to give a high thrust with his hind foot, although that foot be behind yet it must accompany the arm until it has finished his thrust, and settled itself in the low ward. The other sword and hand (which was borne together with the former foot in the low ward) remaining behind by reason of the increase of the high thrust, must presently be lifted placed in the same high ward. | + | |
| + | <p>Presupposing always, that either hand is very well exercised, as well in striking as in defending, this ward shall be framed after two ways, which yet in manner is all one. The one with the right foot, and the other with the left, so working continually, that the hind arm be aloft, the former beneath in manner, as when the low ward is framed at single sword. And as a man strikes, he must always maintain and continue this high ward, which at the two rapiers, is the most perfect and surest and he may easily perform and do it: for whilst he enters to give a high thrust with his hind foot, although that foot be behind yet it must accompany the arm until it has finished his thrust, and settled itself in the low ward. The other sword and hand (which was borne together with the former foot in the low ward) remaining behind by reason of the increase of the high thrust, must presently be lifted placed in the same high ward.</p> | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/109|1|lbl=97|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/110|1|lbl=98|p=1}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | Therefore it is to be noted, that whosoever means to shift from this ward and strike, whether it be with his right or left foot, before or behind, it is requisite that he stand without, and when he would strike, he shall first prove with his low sword, whether he can find the enemy's weapons, and having suddenly found them, he shall nimbly beat them back, and (in a manner) in the same instant force on a high thrust, with the increase of a pace of the right foot: from the which, if the enemy (for saving of himself) shall hastily and directly give backwards, he shall follow him, delivering presently the other high thrust behind, already lifted up. And this thrust will safely hit him and speed, because it is not possible that one may go so fast backwards, as | + | | <p>Therefore it is to be noted, that whosoever means to shift from this ward and strike, whether it be with his right or left foot, before or behind, it is requisite that he stand without, and when he would strike, he shall first prove with his low sword, whether he can find the enemy's weapons, and having suddenly found them, he shall nimbly beat them back, and (in a manner) in the same instant force on a high thrust, with the increase of a pace of the right foot: from the which, if the enemy (for saving of himself) shall hastily and directly give backwards, he shall follow him, delivering presently the other high thrust behind, already lifted up. And this thrust will safely hit him and speed, because it is not possible that one may go so fast backwards, as another may forwards.</p> |
| + | | | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/110|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| + | | <p>Farther, as well in this ward, as in others, the ward may be framed with the right foot before, and the right arm lifted, and so contrariwise. But because there is small force in this ward both in the feet and hands, which stand not commodiously either to strike or defend, and seeing that there is required in the handling of those weapons, great strength and steadfastness I have thought good, not to lay it down, as to small purpose.</p> | ||
| | | | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/110|3|lbl=-}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>'''The defense of the high ward at two rapiers'''</p> |
| + | |||
| + | <p>The direct opposition and defense of the high ward is the low ward, the manner whereof shall be seen in his proper place. That which principally is to be considered (for the low ward also, in like sort as the other may be framed after two sorts) is this, that of necessity a man stand with the same foot before as the enemy does, to wit: if he bear the right foot before, to put forth the right foot also, and to endeavor as the enemy does, to stand without, for of both ways that is of the more advantage and safety. Finding himself therefore without, in the low ward, he must not refuse, but rather suffer his sword to be found and beaten by the enemy: for this does redown much more to his advantage then to his enemy's because the enemy carries small force in his low hand wherewith he endeavors to find and beat off the sword, considering it is borne to far off from the other: for that which is slenderly united, is less forcible: whereas standing at the low ward, he bears both his hands low near together and sufficiently strong. Therefore as soon as the enemy having beaten back the sword, shall resolve himself to give a thrust, he must increase a slope pace, and with his hind low sword, drive the enemy's high thrust outwards toward the right side, if it chance that he were in the low ward with his right foot before, And suddenly with the other low sword behind (which was suffered to be beaten off by the enemy, because it might turn the more to his disadvantage: for seeing the enemy's sword being slenderly united, as I have said before, carried but small force, it was the rather beaten off and disappointed: So that as soon as the slope pace is increased, and the said high thrust warded, before the enemy place his other sword also in the high ward, he may with the straight pace of the right foot deliver a low thrust continuing still to eat down the enemy's sword with his own low sword, that is borne before. And this manner of warding is most safe and sure: for besides that it strikes the enemy with the slope pace, it does likewise in such sort deliver the body from hurt, that of force the enemy is disappointed. Neither is there any other sure way to ward this high thrust, being so strong, and besides, having so great increase of pace.</p> | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/111|1|lbl=99|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/112|1|lbl=100|p=1}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>This manner of defense is most strong and sure, and is done with that sword which is farthest off. Yet there is another way, and that is, with the low sword before, the which is no less stronger and sure than the other, but yet much shorter. For look in what time the other defends, this strikes.</p> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/112|2|lbl=-}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>Therefore in the low ward it is to be noted, (when the enemy moves, pretending to beat off the sword and therewithal to enter,) that then the point of the sword be lifted up, keeping the hand so steadfast, that it oppose itself and keeping outwards the enemy's high thrust, and having made this bar, to keep out his weapons, then and in the selfsame time, he shall increase a straight pace, and with the low sword behind shall strike the enemy in the breast, to whom it is impossible to do any effectual thing, or to avoid the said stroke, for that (by means of the point of the sword lifted up in the manner aforesaid) both his swords are so hindered, that they may not safely strike, either with the edge or point.</p> |
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/112|3|lbl=-}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>'''Of the hurt of the broad ward at two rapiers'''</p> |
| − | + | ||
| + | <p>This broad ward, may in the selfsame manner be framed two ways, and it may deliver the selfsame blows, in the one as in the other: This ward is framed with one foot before, and one foot behind, the arm (which is borne on the side of the hind foot) being stretched wide, and broad outwards. Therefore when one stands at this ward, and would deliver as straight and as safe a thrust as is possible, he shall first prove with his low Rapier, whether he can find his enemy's Rapier, which being found, he shall turn his fist outwards, and force the enemy's Rapier so much, that it may do no hurt, and then withal increasing presently a slope pace, shall go forwards to strike the enemy in the thigh, with the wide thrust. He might as well also thrust him in the flank, or in the head, but yet the other thrust is used, because the Rapier, which is directed to the thigh, is in place, to hinder the enemy's other Rapier to light on the legs.</p> | ||
| | | | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/113|1|lbl=101}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>And as in the high ward, so likewise in this, he must always stand without, and having delivered the wide thrust, he ought presently to widen the other arm, and settle himself in the broad ward.</p> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/113|2|lbl=-}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>'''Of the Defense of the Broad Ward at Two Rapiers'''</p> |
| + | |||
| + | <p>For the defense of the thrust of the broad ward, it is necessary that a man stand at the low ward, and therewithal diligently observe, the motions of the enemy's body, how it compasses and passes to and fro, by knowledge and due consideration whereof, he may easily defend himself. If therefore the right arm be stretched out wide, the right foot also (being behind) shall be in like manner widened, the which, when it increases forwards, shall also carry with it the right shoulder, voiding always with the left side.</p> | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/113|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/114|1|lbl=102|p=1}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>And the selfsame must be considered, and practiced, when he stands at this ward, the contrary way. That therefore which he must do, for the defense of himself, shall be to void that part of his body, which may be hurt by the enemy's wide and broad thrust, and to oppose himself against that part of his enemy, which comes forwards pretending to strike: And this he shall do, at what time the enemy (finding the sword) would come forwards in his thrust. And in the selfsame time, (assuring himself with his own low sword) shall increase a slope pace, thereby investing and encountering that part of the enemy, which came striking, and with the which framed the broad ward. Neither can it be safe striking at any other place, for either, he shall find nothing to encounter, by means of the motion of the body, or else if he do not oppose himself against the shoulder of the enemy which carries the hurt, he is in hazard to be struck by the enemy's broad thrust.</p> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/114|2|lbl=-}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>'''Of the hurt of the low ward at the two rapiers''' |
| + | |||
| + | <p>The low ward shall be framed after two ways, the one with the right foot before, the other with the left, and each of them may strike, either within, either without. The way which strikes within, has one blow, the way which strikes without has two, and in all, they are six. I will lay down but three, because they differ not from the other three, but only in the hand and foot, which must be place before, so that they are the selfsame, for I have already presupposed, that he who takes upon him to handle these weapons, can as well use the one hand, as he can the other. He may therefore find himself to stand with his right foot before and within, (I understand by within, when he bears one of his swords between both his enemy's swords, and likewise when the enemy carries one of his, between the other two. It is likewise true, that this also may be said within, to wit, when both weapons are borne in the middle between the other two. But I suppose no man so foolish, who handling these weapons, will suffer both his swords to be without, being a very unsure ward whereof I leave to speak.</p> | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/114|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/115|1|lbl=103|p=1}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>That therefore, which he is to do, (finding himself with both his rapiers below, and within, with his right foot before, and after the said first way of being within) shall be, that marking when he may close in the enemy's Rapier, between the which the enemy's rapier shall be so shut in and barred, that it may do no hurt, and one of the two Rapiers, that is to say, the right Rapier shall pass under the enemy's rapier, and thrust safely. And his other Rapier, albeit, it may thrust directly, yet (for the better saving of himself, from the enemy's other Rapier that is at liberty) he shall bear it somewhat abasing his hand, with the point upwards, the which point shall safeguard him, from the enemy's said Rapier, although this last note, be superfluous. For seeing the enemy must ward himself from the thrust that hurts him, he has no leisure, nor happily minds to strike, but only to defend himself, either by voiding his body, or else by some other shift, which he shall then find out.</p> |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/115|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/116|1|lbl=104|p=1}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | The | + | | <p>The way of warding without, may strike directly after two ways: The first, by beating off the enemy's Rapier, with his own that is before, and by delivering a thrust, either at the breast or head, with the Rapier that is behind, increasing therewithal a slope pace, and settling himself in the low ward, with his left foot before.</p> |
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/116|2|lbl=-}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>The second is, by taking opportunity, which he may do, if he be nimble. And he ought with the increase of a slope pace, to drive the point of his former Rapier directly towards the enemy, and above the enemy's Rapier. And his other own rapier, which before the increase was behind, he must force on, under the enemy's rapier. And thus, not giving over, these two thrusts must be strongly and nimbly driven towards the enemy, by means whereof being overtaken, the enemy has no other remedy to save himself, then to retire back: for he may not come forwards, but he must run himself upon the weapons, and that he will not do. So then, the enemy retiring himself may be followed, as far as the increase of the right foot will bear, then, settling in the low ward.</p> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/116|3|lbl=-}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | |
| − | | | + | | <p>'''Of the defense of the low ward at the two rapiers'''</p> |
| − | | | + | |
| − | | | + | <p>All three thrusts of the low ward, by standing at the same ward, may easily be warded, and that after one manner. If a man remember first to void his body from hurt, by the increase of a pace, that is very slope, or crooked, either before the enemy comes thrusting, either as soon as he moves himself for the same purpose, or if he be active and nimble to traverse, and in defending himself to strike the enemy.</p> |
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/116|4|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/117|1|lbl=105|p=1}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | <p>Therefore when any of the same three thrusts come, and before he perceives his Rapier to be closed, and barred in, he shall move a slope pace, to the intent to avoid himself from hurt, and with his Rapier, which is at liberty, he shall go forwards and deliver a thrust at the enemy's face, which thrust, does surely speed, if he be resolute to enter.</p> | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/117|2|lbl=-}} | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | {{master end}} | + | {{master subsection end}} |
| − | + | ||
| − | {{master begin | + | {{master subsection begin |
| title = Two-Handed Sword | | title = Two-Handed Sword | ||
| width = 120em | | width = 120em | ||
| Line 1,889: | Line 1,911: | ||
{| class="master" | {| class="master" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! <p> | + | ! <p>Figures<br/>from the 1570</p> |
! <p>{{rating|C|Draft Modernization}}<br/>by [[Norman White]]</p> | ! <p>{{rating|C|Draft Modernization}}<br/>by [[Norman White]]</p> | ||
| − | ! <p> | + | ! <p>Archetype (1570){{edit index|Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf}}</p>Transcribed by [[Niccolò Menozzi]]</p> |
| − | ! <p>English | + | ! <p>English Translation (1594){{edit index|DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf}}<br/>Transcribed by [[Early English Books Online]]</p> |
|- | |- | ||
| Line 1,898: | Line 1,920: | ||
| <p>'''Of the Two Hand Sword.'''</p> | | <p>'''Of the Two Hand Sword.'''</p> | ||
| − | <p>The two hand Sword, as it is used now a days being four handfuls in the handle, or more, having also the great cross, was found out, to the end it should be handled one to one at an equal match, as other weapons, of which I have entreated. But because one may with it (as a galleon among many galleys) resist many Swords, or other weapons: Therefore in the wars, it is used to be place near unto the Ensign or Ancient, for the defense thereof, because, being of itself able to contend with many, it may the better safeguard the same. And it is accustomed to be carried in the City, as well by night as by day, when it so chances that a few are constrained to withstand a great many. | + | <p>The two hand Sword, as it is used now a days being four handfuls in the handle, or more, having also the great cross, was found out, to the end it should be handled one to one at an equal match, as other weapons, of which I have entreated. But because one may with it (as a galleon among many galleys) resist many Swords, or other weapons: Therefore in the wars, it is used to be place near unto the Ensign or Ancient, for the defense thereof, because, being of itself able to contend with many, it may the better safeguard the same. And it is accustomed to be carried in the City, as well by night as by day, when it so chances that a few are constrained to withstand a great many. And because his weight and bigness, requires great strength, therefore those only are allotted to the handling thereof, which are mighty and big to behold, great and strong in body, of stout and valiant courage. Who (forasmuch as they are to encounter many, and to the end they may strike the more safely, and amaze them with the fury of the Sword) do altogether use to deliver great edge blows, downright and reversed, fetching a full circle, or compass therein, staying themselves sometimes upon one foot, sometimes on the other, utterly neglecting to thrust, and persuading themselves, that the thrust serves to amaze one man only, but those edge blows are of force to encounter many. The which manner of skirmishing, besides that, it is most gallant to behold, being accompanied with exceeding swiftness in delivery, (for otherwise it works no such effect) it also most profitable, not properly of itself, because men considering the fury of the sword, which greatly amazes them, are not so resolute to do that, which otherwise they could not choose but do. That is, either to encounter the sword in the middle towards the handle, when it carries small force, or else to stand far off, watching whilst the sword goes, and is carried compassing in his great circle, being of the compass of ten arms, or more, and then to run under it, and deliver a thrust. And these two ways are effectual, when such men are met withal, who are exercised to enter nimbly and strike, or such as dare, and have the spirit and courage, to set, and oppose themselves single against the two hand sword, even as the single two hand sword adventures to oppose itself against many. Neither is this thing to be marveled at, for in these our days, there be things performed of greater activity and danger. And there be some which dare do this with the sword and round Target, but yet they are not resolute to strike first, but will receive and sustain the blow, with the round Target, and then enter and thrust, this truly betokens great courage and activity, although not such is required in this behalf.</p> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/119|3|lbl=93|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/120|1|lbl=94|p=1}} |
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/117|3|lbl=105|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/118|1|lbl=106|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/119|1|lbl=107|p=1}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 1,925: | Line 1,930: | ||
| <p>This much concerning that, which appertains to the defense of circular blows, of the two hand sword, when it endeavors to oppose itself against many. And forasmuch as men have, and sometimes do use, both in the lists and other places, to fight single combats, one to one with the single two hand sword, I will also declare my opinion touching the same.</p> | | <p>This much concerning that, which appertains to the defense of circular blows, of the two hand sword, when it endeavors to oppose itself against many. And forasmuch as men have, and sometimes do use, both in the lists and other places, to fight single combats, one to one with the single two hand sword, I will also declare my opinion touching the same.</p> | ||
| | | | ||
| − | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/120| | + | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/120|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/121|1|lbl=95|p=1}} |
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/119|2|lbl=-}} |
|- | |- | ||
| Line 1,932: | Line 1,937: | ||
| <p>'''Of the Manner How to Handle the Two Hand Sword, in Single Combat.'''</p> | | <p>'''Of the Manner How to Handle the Two Hand Sword, in Single Combat.'''</p> | ||
| − | <p>To those, who would cunningly handle the Two hand Sword in single combat, it is principally necessary that (as in other weapons) they be practiced and have the skill, to use the one hand as well as the other, and they both be active in body, and strong in the arms, which are required in the managing of each weapon. And farther it is requisite that they carry the principles of this Art, surely fixed in their minds and memories, by means whereof they may become bold and resolute, in as much as they have to do, either in striking or defending | + | <p>To those, who would cunningly handle the Two hand Sword in single combat, it is principally necessary that (as in other weapons) they be practiced and have the skill, to use the one hand as well as the other, and they both be active in body, and strong in the arms, which are required in the managing of each weapon. And farther it is requisite that they carry the principles of this Art, surely fixed in their minds and memories, by means whereof they may become bold and resolute, in as much as they have to do, either in striking or defending.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/121|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/121|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/119|3|lbl=-}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p> | + | | <p>They ought furthermore to consider, how the two hand sword is used, and how it ought to be used.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/121|3|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/121|3|lbl=-}} | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/119|4|lbl=-}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>Therefore, when one finds himself to stand at the high ward, (the which at the two hand Sword, is framed, either with the right side towards the enemy, either with the left, in either of which ways, the arm would be borne aloft, and far off from the body, causing the point somewhat to bend both towards the ground and the body, to the end it may defend both the length of the body, and cover it in a manner thwarting or crossing, it being so far off from the sword.</p> | + | | <p>Touching the first, All men use to deliver thrusts, as well as edge blows, down right, and reversed, with both hands to the Sword which way albeit, it be profitable in the bestowing of edge blows, as being the better able to sustain the Sword, yet in the discharge of thrusts it is hurtful, for it causes them to be much shorter, then they would be, if in the beginning, they were forcibly delivered with both the hands, and then by taking away one hand from the cross, they were springed as far forth, as the pommel hand, foot, and all the body of that side, may be stretched out. For, being discharged in this manner, if they hit home they make great passage, and if they be voided, yet the Two hand sword may be quickly had again, by the retiring of a pace, and of the hand and arm, placing the other hand there where it was, and so settling in the low ward. Therefore, when one finds himself to stand at the high ward, (the which at the two hand Sword, is framed, either with the right side towards the enemy, either with the left, in either of which ways, the arm would be borne aloft, and far off from the body, causing the point somewhat to bend both towards the ground and the body, to the end it may defend both the length of the body, and cover it in a manner thwarting or crossing, it being so far off from the sword.</p> |
| | | | ||
{{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/121|4|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/122|1|lbl=96|p=1}} | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/121|4|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/122|1|lbl=96|p=1}} | ||
| | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/119|5|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/120|1|lbl=108|p=1}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 1,953: | Line 1,959: | ||
| <p>Farther, in this ward, the hand that is towards the enemy, must take hold fast of the handle near the cross, and underneath, the other hand above, and near the pommel. I say standing thus at the high ward, he may either deliver a thrust, either a down right blow of the edge.</p> | | <p>Farther, in this ward, the hand that is towards the enemy, must take hold fast of the handle near the cross, and underneath, the other hand above, and near the pommel. I say standing thus at the high ward, he may either deliver a thrust, either a down right blow of the edge.</p> | ||
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/122|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/122|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/120|2|lbl=-}} |
|- | |- | ||
| [[File:Di Grassi 21.jpg|400x400px|center]] | | [[File:Di Grassi 21.jpg|400x400px|center]] | ||
| − | | <p>The thrust is discharged (as soon as the enemy's sword is found) as far in the beginning as he may with both arms: Then, taking away the cross hand, he shall force it farther on with the pommel hand, as much as he may stretch it forth, always in the discharge, increasing a slope pace. And the thrust being thus delivered, he shall presently retire his said pace, and return his hand again to the cross, settling himself either in the high or low | + | | <p>The thrust is discharged (as soon as the enemy's sword is found) as far in the beginning as he may with both arms: Then, taking away the cross hand, he shall force it farther on with the pommel hand, as much as he may stretch it forth, always in the discharge, increasing a slope pace. And the thrust being thus delivered, he shall presently retire his said pace, and return his hand again to the cross, settling himself either in the high or low ward. But if he would deliver a down right blow with the edge which I counsel him not to do, because he may easily be struck under it, he shall first discharge a thrust with both his hands, and then increasing a pace, shall turn the said downright blow, stretching out the arm as much as he may. In the delivery of which blow, if he meet with the enemy's sword, he shall take away his hand from the cross, and stretch out the pommel hand as much as he may, with the increase of a pace. And farther, turning the said hand which holds the sword upwards, to the end, to lengthen the thrust, he shall drive, and force it on, and presently retire himself in the manner aforesaid.</p> |
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/122|3|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/122|3|lbl=-}} | ||
| | | | ||
| − | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/120|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/121|1|lbl=109|p=1}} | |
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 1,973: | Line 1,974: | ||
<p>The low ward, shall be the defense of the high ward, and it may be framed with the right foot before and behind, in such sort, as the said high ward, the which shall be declared in his proper place.</p> | <p>The low ward, shall be the defense of the high ward, and it may be framed with the right foot before and behind, in such sort, as the said high ward, the which shall be declared in his proper place.</p> | ||
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/123|1|lbl=97}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/123|1|lbl=97}} | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/122|1|lbl=110}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>Therefore, regarding to place himself for his defense in the low ward (and that directly contrary to his enemy, that is to say, if the enemy stand with the right foot before, to put his left foot foremost, and as the thrust or downright blow comes) he shall encounter it without, and as soon as he has found the enemy's sword, he shall void his cross hand, and increase a pace, and | + | | <p>Therefore, regarding to place himself for his defense in the low ward (and that directly contrary to his enemy, that is to say, if the enemy stand with the right foot before, to put his left foot foremost, and as the thrust or downright blow comes) he shall encounter it without, and as soon as he has found the enemy's sword, he shall void his cross hand, and increase a pace, and therewithal deliver a thrust, with the pommel hand, as far as it will stretch out. The which thrust will easily speed, if the enemy come resolutely in delivering of his blow: for he shall come directly to encounter the point of his sword, with that part of his body which increases forwards. Thus much for the defense of the high thrust.</p> |
| | | | ||
{{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/123|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/124|1|lbl=98|p=1}} | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/123|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/124|1|lbl=98|p=1}} | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/122|2|lbl=-}} |
|- | |- | ||
| Line 1,986: | Line 1,987: | ||
| <p>The downright blow may be warded, if whilst the enemy's sword is in his compass, he nimbly deliver a thrust under it. or else, if he would encounter it, (as soon as he has so done) he do void his cross hand, and with the increase of a pace, thrust as far forth as the pommel hand will stretch out.</p> | | <p>The downright blow may be warded, if whilst the enemy's sword is in his compass, he nimbly deliver a thrust under it. or else, if he would encounter it, (as soon as he has so done) he do void his cross hand, and with the increase of a pace, thrust as far forth as the pommel hand will stretch out.</p> | ||
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/124|2|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/124|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/122|3|lbl=-}} |
|- | |- | ||
| Line 1,995: | Line 1,996: | ||
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/124|3|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/124|3|lbl=-}} | ||
| | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/122|1|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/123|1|lbl=111|p=1}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 2,000: | Line 2,002: | ||
| <p>Finding himself therefore within, and bearing the sword firmly, he shall force and drive on a thrust, as far as both arms may stretch out together, increasing a pace and settling in the low ward, if he do not speed.</p> | | <p>Finding himself therefore within, and bearing the sword firmly, he shall force and drive on a thrust, as far as both arms may stretch out together, increasing a pace and settling in the low ward, if he do not speed.</p> | ||
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/124|4|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/124|4|lbl=-}} | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/123|2|lbl=-}} |
|- | |- | ||
| Line 2,006: | Line 2,008: | ||
| <p>But finding himself to stand without, and as soon as he has found the enemy's sword, he shall deliver a thrust, first, at the length of both arms, then, voiding the cross hand, increase a pace and deliver it out at uttermost length of the pommel hand, and immediately after the thrust, retire his hand and pace, staying himself again in the said low ward.</p> | | <p>But finding himself to stand without, and as soon as he has found the enemy's sword, he shall deliver a thrust, first, at the length of both arms, then, voiding the cross hand, increase a pace and deliver it out at uttermost length of the pommel hand, and immediately after the thrust, retire his hand and pace, staying himself again in the said low ward.</p> | ||
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/124|5|lbl=-}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/124|5|lbl=-}} | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/123|3|lbl=-}} |
|- | |- | ||
| Line 2,014: | Line 2,016: | ||
<p>It is a general rule, that the true defense of all blows is the low ward. Therefore, when one stands thereat, if there come a thrust without (because it is necessary in this case to stand within,) he shall do no other then encounter the enemy's sword, and thrust his arm forwards, to the end he may void it from his body, and farther retire his foot more backwards, and as it were, in a compass, thereby the better saving his body from hurt.</p> | <p>It is a general rule, that the true defense of all blows is the low ward. Therefore, when one stands thereat, if there come a thrust without (because it is necessary in this case to stand within,) he shall do no other then encounter the enemy's sword, and thrust his arm forwards, to the end he may void it from his body, and farther retire his foot more backwards, and as it were, in a compass, thereby the better saving his body from hurt.</p> | ||
| {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/125|1|lbl=99}} | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/125|1|lbl=99}} | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/123|4|lbl=-}} |
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | | |
| − | + | | <p>But if the thrust come within (by reason whereof he should stand without) as soon as the enemy's sword is encountered, he shall deliver a thrust with both his hands, and then voiding his cross hand, he shall deliver it strongly with his pommel hand, with the increase of a pace. And this thrust does safely speed. Neither is it to be doubted, that by holding the sword with one hand, the enemy may take holdfast thereof, for he has enough to do, to retire himself, and ward the thrust, neither can he perform so many things in one time.</p> | |
| − | + | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/125|2|lbl=-}} | |
| − | | | + | | |
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/123|5|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/124|1|lbl=112|p=1}} | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | {{master end}} | + | {{master subsection end}} |
| − | {{master begin | + | {{master subsection begin |
| − | | title = | + | | title = Polearms |
| width = 120em | | width = 120em | ||
}} | }} | ||
{| class="master" | {| class="master" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! <p> | + | ! <p>Figures<br/>from the 1570</p> |
! <p>{{rating|C|Draft Modernization}}<br/>by [[Norman White]]</p> | ! <p>{{rating|C|Draft Modernization}}<br/>by [[Norman White]]</p> | ||
| − | ! <p> | + | ! <p>Archetype (1570){{edit index|Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf}}</p> |
| − | ! <p>English | + | ! <p>English Translation (1594){{edit index|DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf}}<br/>Transcribed by [[Early English Books Online]]</p> |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | <p>'''Of the weapons of the staff, namely, the bill, the partisan, the halberd, and the javelin.'''</p> |
| − | Because it may seem strange unto many, that I have here placed these | + | |
| − | | | + | <p>Because it may seem strange unto many, that I have here placed these 4 sorts of weapons together, as though I would frame but one only way for the handling of all, although they differ in form, from which form is gathered their difference in use. Therefore, forasmuch as I am of opinion, that all of them may be handled in manner after one way, it shall not be amiss, if I declare the reason thereof, speaking first of every one severally by itself, and then generally of all together, holding and maintaining always for my conclusion, that the skill of handling of them, helps a man to the knowledge of all the rest, for as much as concerns true Art.</p> |
| − | | ' | + | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/125|3|lbl=99}} |
| − | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/124|2|lbl=112}} | |
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="2" | [[File:Di Grassi 22.jpg|400x400px|center]] | | rowspan="2" | [[File:Di Grassi 22.jpg|400x400px|center]] | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | <p>'''Of the partisan'''</p> |
| − | Coming therefore to the Partisan, as unto the plainest, as unto that, whereupon all the rest depend, omitting to show who was the inventor thereof, as being to small purpose: I say, that it was found out to no other end, then for that the foot men in the wars, might be able with them to hurt those horsemen (whom they might not reach with their swords) as well with their point as with their edge. Further, weapons which are to be cast, or sprung forth at the length of the arm, are for the most part deceitful, by means whereof, they might hurt as well the Archers on horseback, as other horsemen. | + | |
| + | <p>Coming therefore to the Partisan, as unto the plainest, as unto that, whereupon all the rest depend, omitting to show who was the inventor thereof, as being to small purpose: I say, that it was found out to no other end, then for that the foot men in the wars, might be able with them to hurt those horsemen (whom they might not reach with their swords) as well with their point as with their edge. Further, weapons which are to be cast, or sprung forth at the length of the arm, are for the most part deceitful, by means whereof, they might hurt as well the Archers on horseback, as other horsemen.</p> | ||
| + | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/124|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/125|1|lbl=113|p=1}} |
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Therefore, these Partisans were made big and of great paize, and of perfect good steel, to the end they might break the mail and divide the Iron. | | Therefore, these Partisans were made big and of great paize, and of perfect good steel, to the end they might break the mail and divide the Iron. | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/125|2|lbl=-}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | And that this is true, it is to be seen in the ancient weapons of this sort, which are great and so well tempered, that they are of force to cut any other Iron. Afterwards, as men had considered, that as this weapon was only to strike, it might in some part thereof, have as well something to ward withal, whereby it might be said to be a perfect weapon, they devised to add unto it two crooks or forks, by the which, that blow might be warded, which parting from the point and continuing down the staff, should come to hurt the person. And these forks, or (I may say) these defenses were by some men placed on that part of the Iron, which next adjoins to the staff, making them crooked and sharp, and handful long, and for the most part, with the points toward the enemy, to the end they might serve not only to defend, but also to strike. And to the end, the bigness and weight of the Partisan, (which ought to be apt and commodious to be handled) might not be increased, they diminished part of the Iron thereof, and gave the same to the forks or defenses: And by that means they framed another weapon called the javelin which (because the broadness, and happily the weight and place thereof is diminished) is not very forcible to strike with the edge, but all his power consists in three thrusts. others afterwards would not that these defenses should be placed at the lowermost part of the Iron, but in the middle thereof. And these men bearing great respect to the blows of the edge, left the Iron which should serve for the defense behind, in his breadth and weight, adjoining thereunto in the opposite part of the right edge, a most sharp point of Iron, to the end, that what way soever it were moved, it might strike and hurt. But if any man object and say: if the said point of Iron were put there in respect of striking, they might also as well have left there an edge, which being longer would strike more easily. I answer, that the blows of the false (that is to say, the hinder or back edge of the weapon) are very weak, and the point does strike and hurt more easily then the edge. And therefore it was requisite that there be facility where there was weakness. These men by these means framed the ancient weapon called the Halberd, out of the which, men of our age have derived and made another kind of Halberd and Bill. And these bearing also respect to | + | | <p>And that this is true, it is to be seen in the ancient weapons of this sort, which are great and so well tempered, that they are of force to cut any other Iron. Afterwards, as men had considered, that as this weapon was only to strike, it might in some part thereof, have as well something to ward withal, whereby it might be said to be a perfect weapon, they devised to add unto it two crooks or forks, by the which, that blow might be warded, which parting from the point and continuing down the staff, should come to hurt the person. And these forks, or (I may say) these defenses were by some men placed on that part of the Iron, which next adjoins to the staff, making them crooked and sharp, and handful long, and for the most part, with the points toward the enemy, to the end they might serve not only to defend, but also to strike. And to the end, the bigness and weight of the Partisan, (which ought to be apt and commodious to be handled) might not be increased, they diminished part of the Iron thereof, and gave the same to the forks or defenses: And by that means they framed another weapon called the javelin which (because the broadness, and happily the weight and place thereof is diminished) is not very forcible to strike with the edge, but all his power consists in three thrusts. others afterwards would not that these defenses should be placed at the lowermost part of the Iron, but in the middle thereof. And these men bearing great respect to the blows of the edge, left the Iron which should serve for the defense behind, in his breadth and weight, adjoining thereunto in the opposite part of the right edge, a most sharp point of Iron, to the end, that what way soever it were moved, it might strike and hurt. But if any man object and say: if the said point of Iron were put there in respect of striking, they might also as well have left there an edge, which being longer would strike more easily. I answer, that the blows of the false (that is to say, the hinder or back edge of the weapon) are very weak, and the point does strike and hurt more easily then the edge. And therefore it was requisite that there be facility where there was weakness. These men by these means framed the ancient weapon called the Halberd, out of the which, men of our age have derived and made another kind of Halberd and Bill. And these bearing also respect to someone profitable thing or other, did maintain the defense, and increase the hurting or offense. The respect was, that as they discoursed and pondered with themselves, at length they very warily perceived that a man with his weapon in his hand, might make size motions, that is to say, one towards the head, one towards the feet, one towards the right side, one towards the left, one forwards and towards the enemy, the other backward and toward himself. of all the which, five of them might very well strike, and the last might neither strike nor defend. Therefore, providing that this last motion also should not be idle and unprofitable, they added a hook with the point turned towards the handle, with the which one might very easily tear armor, and draw perforce men from their horses. Those who framed the middle or mean Halberd, would that the same hook should be placed in the safe or back edge. And those that devised the Bill, would have it on the right edge, leaving the edge so long that the hook might not altogether hinder the low of the edge, but rather (to the end the edge might make the greater effect) they would that the hook should bear and edge and be cutting in every part thereof. Where I gather, that the Bill is the most perfect weapon of all others, because it strikes and hurts in every of these six motions, and his defenses both cut and prick: which the new kind of Halberd does not perform, because framed after the said fashion, and rather for lightness aptness and bravery, then for that it carries any great profit with it: for the edge is not so apt to strike, and the point thereof is so weak, that hitting any hard thing, either it bows or breaks: neither is it much regarded in the wars, the Harquebus and the Pike being now adays the strength of all armies.</p> |
| + | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/125|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/126|1|lbl=114|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/127|1|lbl=115|p=1}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>Hereby it may be gathered, that with the Partisan: a man may strike with the point and edge in five motions: with the Javelin, with the point only and in such motions as it may: with the Halberd and Bill, both with the point and edge, in six motions. But because these weapons for the most part are exercised and used to enter through diverse Pikes and other weapons, and to break and disorder the battle array, to which end, and purpose, if it be used, then that manner of managing and handling is very convenient which is much practiced now adays, and thus it is. The Partisan, Halberd, and Bill (but not the Javelin, being in this case nothing effectual because it has small force in the edge) must be born in the middle of the staff, with the heel thereof before, and very low, and the point near a man's head. And with the said heel, or half-staff underneath, from the hand downwards, he must ward and beat off the points and thrusts of the Pikes and other weapons, and having made way, must enter with the increase of a pace of the hindfoot, and in the same instant, let fall his weapon as forcibly as he may, and strike with the edge athwart the Pikes. This kind of blow is so strong (being delivered as it ought, considering it comes from above downwards, and the weapon of itself is very heavy) that it will cut asunder not only Pikes, but also any other forcible impediment. In these affairs the Javelin is not used, because it works no such effect. But when one is constrained to use it, he ought neither to beat off, neither to ward with the staff, but altogether with the Iron and his defenses, remembering, as soon as he has beaten off and made way of entrance, to thrust only: for to handle it in delivering of edge-blows prevails not, considering the small force it carries in that manner of striking. And as among all the foresaid iiii. weapons, the Javelin in this kind of skirmish, is least profitable, so the Partisan is most excellent and commodious, for having no other defense, it is provided in the staff, and is most forcible, to cut the Pikes by means of his heaviness and weight, and the rather, because it is unfurnished and void of other things, which in this case might let and hinder the edge blow. Therefore the Partisan shall be used (as in his own proper quality) to enter among the Pikes, and cut them a sunder, and other weapons also partly for that cause, and partly to skirmish single, one to one. Which although it be not ordinarily accustomed, yet nevertheless, because both this, and the rest of the weapons, may be handled in single combat, and do contain in them, as well offense, as defense, Farther, to the end, the wise and discrete (happening to be in such affairs) may be skillful to determine with themselves, what they may and ought to do: I will show my opinion what may be done with these weapons in single combat, reasoning jointly of the Javelin, Bill, and Halberd, because there is but a small difference in the Javelin, And the Bill, and the Halberd, are in a manner all one, and the very selfsame.</p> |
| − | + | | | |
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/127|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/128|1|lbl=116|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/129|1|lbl=117|p=1}} |
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>'''Of bill against bill, halberd against halberd, or halberd against bill'''</p> |
| + | |||
| + | <p>Forasmuch, as the Bill and Halberd, have the selfsame offense and defense, and be of one length: I thought it not good to make two Treatises thereof, because I should be forced to repeat the selfsame thing in both, the which, being superfluous, would breed loathsomeness. I say therefore, that whosoever would handle the Bill or Halberd, which being all one, I will name indifferently, by the name of the Halberd, I say, to him that would use them, and strike as well with the point, as with the edge, which blows at these weapons are mighty and forcible, it is necessary, that he consider the difficulty in striking with the point, and the danger in striking with the edge. That it is difficult to strike with the point, it is most clear, because the full course of the point, may very easily be hindered and tied, by means of so many hooks and forks which are in the Halberd.</p> | ||
| + | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/129|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/130|1|lbl=118|p=1}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>And that it is perilous to strike with the edge, has been declared when I entreated of the single Rapier, which peril ought the more to be considered in this weapon, because by means of his length, it frames a greater circle, and therein gives more time to enter under it.</p> |
| + | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/130|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/131|1|lbl=119|p=1}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>Therefore no man may safely handle the Halberd, if first he does not consider these two things, the one, (which he may very hardly withstand) and that is the thrust, because these hooks and forks, are properly belonging unto it, and are impossible to be untied and taken away, when a man would, the form being as it is. 2. The peril of the edge blow, may sometimes be voided, if he be nimble and bold, performing all that in due time, which shall here be laid down for his instruction.</p> |
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/131|2|lbl=-}} |
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>'''How to strike with the halberd'''</p> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <p>In the handling of this weapon, there shall be framed (by my counsel) no more than one ward, bearing the hands, for the more surety in the middle of the staff. And that ward must be the low ward. The hands must be somewhat distant, one from another, and the point of the weapon directly towards the enemy, regarding always to place himself with the contrary foot before, to that, which the enemy shall set forth, that is to say: If the enemy be before with the left foot, then to stand with the right foot, or contrary wise. And standing in manner aforesaid, he must always prove and try (before he be determined to deliver a thrust) to beat off the enemy's weapon, which being done, presently deliver a forcible thrust toward the enemy. But because it may lightly so fall out, that in beating off the enemy's weapon (the enemy happily pretending to do the like) the weapons be entangled fast together. Therefore, as soon perceived that they be grappled fast, standing sure, and firmly on his feet, he shall increase a pace towards the enemy, lifting up aloft the enemy's weapon, together with his own by the force of the said entangling, and then with the heel, or blunt end of the Halberd shall strike the enemy in the breast, (for which consideration it should not dislike me, if for that purpose, there shall be fastened in the said blunt end, a strong and sharp pike of iron) and as soon as he has stroked with the said blunt end, (because, by means of the said lifting up, the weapons shall now be unhooked) and retiring that pace which he had before increased, without removing of his hands, he shall deliver a strong edge blow, which is then very commodious.</p> | |
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/131|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/132|1|lbl=120|p=1}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>And it is to be understood, that this edge-blow being delivered in this manner, is so strong, that it is apt to cut the enemy's sword, if it be opposed in this ward. only that which is to be regarded in the delivering of this blow, is, that he be nimble, and of stout courage, not doubting that he shall be struck again, because he is to go so near his enemy, for besides, that he is in such case, that he may easily ward any blow, the enemy finds no way, to strike, except he perform it in two times, to wit, by retiring his pace and Halberd, and then by delivering a thrust.</p> |
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/132|2|lbl=-}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>That this way of striking is good, after the tying, and entangling of the weapons, it may be hereby understood, that as a man endeavors to untie, and unloosen the weapons, either by retiring himself, either by carrying them on the one side, to the intent to strike, he may then go forth of the straight line, by going to one of the both sides, or else lose one time, by retiring himself, under which two inconveniences, either he must needs be hurt, or else defending himself, tie fast the weapons again. But these inconveniences happen not in the foresaid manner of striking.</p> |
| − | + | | | |
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/132|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/133|1|lbl=121|p=1}} |
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>Farther, a man may strike after another way to wit, as soon as by the entangling of the weapons they are lifted up, to the intent to unhook, and untie them, he must change his hands, and n edge blow, either a thwart, either on high, either on low, for it is commodious anyway, so that he change his hands and retire a pace. But this is not so commodious in the other way, because he may not strike but only downwards. But in this manner of changing hands, he may easily strike the enemy in that place, where he perceives him to be most discovered, be it above or beneath. |
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/133|2|lbl=-}} |
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>'''Of the defense of the heel, or blunt end of the halberd'''</p> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <p>For the defense of the abovesaid two blows, it is requisite as I have already said, that a man stand with the contrary foot before, to that, of the enemy's. And as the enemy (after the fastening of the weapons) endeavors to lift them up, (being well aware thereof) he ought to recover his Halberd by the increase of a pace, and strike with the heel at the enemy's thigh or belly, and then changing his hands, he shall deliver an edge blow, without any other retiring of himself, or moving of his hands, The which blow shall lightly speed, being nimbly delivered. And when it speeds not, yet, it will safely ward the edge blow, which the enemy shall give. And this may suffice for asmuch as concerns the blows of the Halberd in single combat, wherein there is any difficulty to be found, the which, a man must seek to avoid by all means, especially endeavoring by all possible ways to deliver thrusts, without tying or entangling of his weapon. But although the enemy's weapon, may not be tied to any prescript law or order, (for he also uses, all the policy he may to avoid danger) yet these blows with their fastenings are laid down, because I presuppose, that who so is skillful to strike, notwithstanding these difficulties, will be much more adventurous, in striking when he shall find little, or nothing to hinder him, As for example, when in fight he meets with a weapon of the Staff of the selfsame, or of greater length, but yet, void of hooks or forks: For seeing his own weapon, is only able to hook, and drive outwards the enemy's weapon, he may safely deliver an edge blow, with the increase of a pace, being sure, that he may not be stroked again, but only with a thrust, which the enemy may not deliver, but of force, must either retire his staff, either his feet, under which time, an edge blow may be delivered without danger.</p> | |
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/133|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/134|1|lbl=121|p=1}} |
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | <p>'''Of the hurt and ward of the javelin'''</p> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <p>The self same ward, shall be framed with the Javelin, as with the Halberd. And because, of necessity, the weapons will be entangled, I say, the very same thrusts shall be given therewith, as are delivered with the Halberd. And because the edge of the Javelin is weak, and the pacing which is made when the weapons are fastened, is only profitable for the giving of the edge blow: Therefore in handling of the Javelin, this entangling or fastening is by all means possible to be avoided. But when a man is to strike his enemy, let him first prove, to beat off his Javelin, and then to force on a thrust, in this manner.</p> | |
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/134|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/135|1|lbl=123|p=1}} |
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>Finding the enemy's Javelin to be within, (by within, I understand, when the Javelin is between the enemy's arms, or against them) then he must force it outwards, and drive a thrust with his own Javelin, at the length of the staff (without moving of his feet) at the enemy's face. Finding it without, he ought to beat it backwards, and increasing a pace, to launch out the Javelin at the enemy's face, at the length of the staff and arm, immediately retiring his pace, and hand, and afterwards settle himself in the same low ward.</p> |
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/135|2|lbl=-}} |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | <p>'''Of the defense of the thrusts of the javelin'''</p> |
| − | |||
| − | + | <p>For him that would defend himself from those two thrusts, and strike under them, it is necessary to call to remembrance the most subtle consideration of times, without knowledge whereof, there is no man that may safely bear himself under any weapon: Coming therefore to the said consideration, I say, that if the enemy would beat of the Javelin, (his own Javelin being either within, either without) of force he must enlarge and widen it from out the straight line, if he would as aforesaid forcibly beat off the other Javelin. Therefore at what time soever a man sees the enemy's Javelin wide of the straight line, then, and in the same time (in the which it comes purposing to beat off) he must nimbly deliver a thrust. And in like manner, finding himself, either within, either without, and the enemy's Javelin something wide of the straight line, then before it come into the said line again, he shall with the increase of a pace deliver a thrust, at the length of the hinder arm, and then retiring his said pace, settle himself at his ward again.</p> | |
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/135|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/136|1|lbl=124|p=1}} |
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>'''Of the partisan'''</p> |
| − | + | <p>If any would handle the Partisan in single combat, they shall not strike with the edge, because the time is too long, and they may easily be stroked under the same. Therefore practicing the thrust, they shall use the selfsame offense and defense, which I have showed in the Javelin, to the which I refer them.</p> | |
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/136|2|lbl=-}} |
| − | | | + | |} |
| − | + | {{master subsection end}} | |
| + | {{master subsection begin | ||
| + | | title = Pike | ||
| + | | width = 120em | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {| class="master" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| + | ! <p>Figures<br/>from the 1570</p> | ||
| + | ! <p>{{rating|C|Draft Modernization}}<br/>by [[Norman White]]</p> | ||
| + | ! <p>Archetype (1570){{edit index|Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf}}</p> | ||
| + | ! <p>English Translation (1594){{edit index|DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf}}<br/>Transcribed by [[Early English Books Online]]</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | <p>'''Of the pike'''</p> |
| − | + | ||
| − | | | + | <p>As among all other weapons, which are worn by the side, the single sword is the most honorable, as being such a one which is less capable of deceit of any other: So among the weapons of the Staff, the Pike is the most plain, most honorable, and most noble weapon of all the rest.</p> |
| − | | ' | + | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/136|2|lbl=110}} |
| − | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/136|3|lbl=124}} | |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>Therefore among renowned knights and great Lords this weapon is highly esteemed, because it is as well void of deceit, as also, for that in well handling thereof, there is required great strength of body, accompanied with great value and deep judgment: for there is required in the use thereof a most subtle delicate knowledge and consideration of times, and motions, and a ready resolution to strike. These qualities may not happen or be resident in any persons, but in such as are strong of arms and courageous of stomach. Neither may they procure to get any other advantage in the handling thereof, then to be more quick and resolute both in judgment and hand than their enemy is. Therefore seeing every man may hereby know what is necessary for him so to handle it, as he may obtain victory thereby: let him resolve himself either to give it over quite, or else to handle it as he ought, and is required.</p> |
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/137|1|lbl=125}} |
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| + | | [[File:Di Grassi 23.jpg|400x400px|center]] | ||
| + | | <p>'''The manner how to handle the pike'''</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p>This renowned weapon has been of diverse diversely handled, in single combat: (for in the manner of using it in the wars, makes not at this present for my purpose.) Therefore it shall not be amiss, if (speaking of the manner of his use in these our days) I declare also mine opinion concerning the same. There have been some (who greatly regarding ease and little pain) would have the Pike to be borne in the middle. other some, more strong of arm, but weaker of heart, (to the end they might be the farther off, from hurt) accustomed to bear it at the beginning near the heel or blunt end thereof: which two ways in my judgment are to be refused, the one being too dangerous (I mean, the bearing of it in the middle) the other too difficult (I mean, the bearing it at the blunt end,) because a man is not able to stand long at his ward, neither to defend himself strongly, not offend safely, considering, much of his force is taken away, by sustaining and bearing it at the said end. So that, when a forcible blow comes he has not sufficient power to beat it off. And forasmuch as the Pike is a long straight line, which has his motion in the head or beginning thereof, which motion be it never so small, near the hand, is yet very great at the point, it is requisite, if he would strike just and straight, (when he so holds it at the end) that he be greatly practiced, and have great strength whereby he may be both skillful and able to bear it so just and even, that the point thereof strike or hit there where the hand and eye would have it. This is very hardly accomplished, as well because it is a thing impossible to strike by the straight line, as also for that the arms being weakened with the place of the Pike, do shake and deliver it unsteadfastly. Therefore, for the avoiding of these two inconveniences, the Pike must be born within an arm's length of the said heel or blunt end, in which place, it is sufficiently distant from hurt, and it is not borne with much difficulty if the hands be placed an arm's length one from another of the which the hinder hand must be steadfast, I mean, hold the Pike hard, and the forehand somewhat loose: So that the Pike may shift thorough it to and fro.</p> | ||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/137|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/138|1|lbl=126|p=1}} |
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | And | + | | <p>'''For the cause the pike makes greater passage with the point than any other shorter weapon'''</p> |
| + | |||
| + | <p>It is most manifest, that the Pike makes greater passage with his point than any other weapon: and the two hand sword, more than the ordinary sword: and the sword more than the dagger. And among all weapons, this is generally true, that the longer the weapon is, the greater the passage it makes with the point, and the greater blow with the edge. Neither does this so chance, because the weapon is more heavy, neither because there is applied more force unto it in action, as most men suppose, but rather through a natural cause which is as follows.</p> | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/139|1|lbl=127}} |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | [[File:Di Grassi 24.jpg|400x400px|center]] |
| − | | | + | {| style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto; width: 28em;" |
| − | | | ||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>Center</p> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <p>The circle of the Short weapon</p> | |
| − | |||
| − | + | <p>The circle of the pike</p> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/141|1|lbl=115}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/141|2|lbl=129}} | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | | <p>If there be two circles, the one greater than the other, and are moved by one manner of motion, the greater shall be more swift then the less: for being greater in circumference and turning round, in the same time that the less turns it must needs be, that it goes more swiftly. So it comes to pass, that one selfsame hand may deliver a greater blow with the two hand sword then with a single sword, and with a long sword, then one that is shorter, and with that, then with the dagger: And with a Bill, a greater blow, then with two hand sword, and so likewise in all other weapons. Wherefore it is most clear, that of edge-blows that makes the greater stroke, which is delivered with the longer weapon. It remains now to be considered, how this falls out in the blows of the point. I say therefore, the blows of the point are also circular, so that the Pike being very long, makes the greater circle, and by consequence the greater blow of the point or the greater thrust. That the blows of the point are circular, may be showed by this reason. The arm (being as a straight line, and fixed fast in one part, as for example in the shoulder, and movable in the other, as in the hand, standing I say, fixed as a straight line, and the one end moving from the other) shall always move circularly: So that the arm cannot otherwise move, except when it is bowed, and would then make itself straight again, the which motion is also doubtful, whether it be straight yea or no. Therefore imagining that on the movable part of this arm, or straight line, there be also another thwart line, to wit, a Pike, a sword, or any other weapon, then the arm moving, carries also, circularly with it, the said thwart line, by how much, the longer it is, by so much the greater circle, as may be seen in this figure.</p> | ||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/140|1|lbl=128|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/141|1|lbl=129|p=1}} |
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>Whereby, it is manifest, that the Pike, the longer it is, it frames the greater circle, and consequently, is more swift, and therefore makes the greater passage. The like is to be understood of all other weapons, which the longer they are being moved by the arm, cause the greater edge-blow, and greater passage with the point.</p> |
| + | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/141|3|lbl=-}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>'''Of the wards of the pike'''</p> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <p>In mine opinion, if a man would either strike, or defend with the Pike, he may not otherwise use it then by the framing of two wards, in one of which, he shall then strike the body from the middle upwards, and this I will term the low ward: the other shall strike the body from the middle downwards, and shall be called the high ward. Neither shall they be so termed for any other cause, then for that it is very necessary for him that strikes, first to beat off the enemy's Pike, and then to deliver his own. But yet it should breed great inconvenience, and there would be two much time spent if finding it good and commodious to strike in the low ward, he would first beat off the enemy's weapon, and then shift from the low to the high ward. For that cause I will frame the high ward, which shall be, when one bears his arms high, and the point of the Pike low. And the low ward is, when the arms are low, and the point of the Pike high. There is another ward which would be framed as a mean between these two, and that is, when the Pike is borne directly towards the enemy. And it falls out that is most sure and long, when it is opposed against any of the other two aforesaid, because then a man is in case both to beat off the weapon and to enter therewithal with great advantage. But putting the case, the enemy do likewise directly oppose himself against this ward, then the Pikes may not beat off one another, but both parties are like to be invested and run through at one instant, without any defense or warding thereof.</p> | |
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/141|4|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/142|1|lbl=130|p=1}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>So that this straight ward may not be used except it be against one of the two aforesaid. And when the enemy stands in any of the said two, then a man must resolutely bring his weapon into the said straight ward, for as he gets thereby the greater advantage both of length and time, so he may very easily beat off the enemy's Pike.</p> |
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/142|2|lbl=-}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | <p>'''Of the manner how to strike in the said wards'''</p> |
| − | + | ||
| + | <p>When the enemy is in the low ward, a man ought always to stand either at the high or straight ward. And contrarily, in the low or straight ward, when the enemy is in the high ward. And must endeavor as forcibly and as nimble as he may, first of all, to beat off the enemy's Pike, whether it be within or without, but yet in such sort, that he depart not much from the straight line, and thereby be constrained, to spend much time in returning thither again, And as soon as he has beaten off the enemy's weapon, to thrust, bearing his body contrary to his arms, to the end, he may be the more covered from the thrusts, and deliver his own thrusts with the more force, always regarding in the high ward, to thrust downwards, and in the low ward, upwards, and in the straight ward, in the middle: for in this manner of thrusting, is very commodious, and consumes little time.</p> | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/143|1|lbl=131}} |
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>'''Of the defense of the wards'''</p> |
| + | |||
| + | <p>The hurts of these wards, are defended in the self same manner, as those of the Javelin are, to which Chapter, (having there reasoned sufficiently) I refer you, to the intent I may not repeat one thing often.</p> | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/143|2|lbl=-}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | And | + | | <p>And it is to be considered, that there is greater regard to be had of the times in managing this weapon then in any other, because it is not furnished with any forks, or other defenses which may help a man, but all hope of victory consists in the judgment of the times, and in dexterity of delivery.</p> |
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/143|3|lbl=-}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>I will not therefore at this present stand to declare any more of the true knowledge of the weapon, then that, which only appertains to be spoken in this work, but will hereafter at my more leisure, handle it more at large, at what time, it shall be known, that men (giving over all other false and vain kind of skirmishing) ought to settle themselves in this, by means whereof, their judgments are perfected, and they more insured under their weapons, and so by consequence are made more bold and hardy. And forasmuch as all this ought to be verified in deeds, and not in words, it shall be every man's part, that will exercise himself in this Art, first diligently to learn the principles, and afterwards by exercise of the weapon to attain to the most subtle and delicate knowledge and consideration of the times, without which (as I have said elsewhere) is not possible to profit therein. For although there be happily some, who (being strong of arm, and nimble in delivering falses, either right, reversed, or straight) have been in our time accompted for tall men, yet for all that, those who are skillful in this true Art, ought not to give credit unto it, because they know assuredly that not right or reversed edge blows, get the mastery, but rather the thrusts of the point, neither the bestowing of them every way, but with advantage and in due time. Neither ought a man to strike, thereby to be stroked again, (which is the part and point, rather of a brute beast, then of a reasonable man) but to strike and remain without danger. And all which things by this true Art are easily learned.</p> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/143|4|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/144|1|lbl=132|p=1}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | <p>'''Finished'''</p> |
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/144|2|lbl=-}} |
| − | <br/>' | + | |
| + | |} | ||
| + | {{master subsection end}} | ||
| + | {{master end}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{master begin | ||
| + | | title = The False Art | ||
| + | | width = 120em | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {| class="master" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! <p>Figures<br/>from the 1570</p> | ||
| + | ! <p>{{rating|C|Draft Modernization}}<br/>by [[Norman White]]</p> | ||
| + | ! <p>Archetype (1570){{edit index|Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf}}<br/>Transcribed by [[Niccolò Menozzi]]</p> | ||
| + | ! <p>English Translation (1594){{edit index|DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf}}<br/>Transcribed by [[Early English Books Online]]</p> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>'''The second part entreating of deceits and falsings of blows and thrusts'''</p> |
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/145|1|lbl=119}} |
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/145|1|lbl=133}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>Being come to the end of the true Art, and having declared all which seemed convenient and profitable for the attainment of true judgment in the handling of the weapon and of the entire knowledge of all advantages, by the which as well all disadvantages are known: It shall be good that I entreat of Deceit or Falsing, as well to perform my promise, as also to satisfy those who are greatly delighted to skirmish, not with the pretense to hurt or overcome, but rather for their exercise and pastime:</p> |
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/145|2|lbl=-}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>In which it is a brave and gallant thing and worthy of commendations to be skillful in the apt managing of the body, feet and hands, in moving nimbly sometimes with the hand, sometimes with the elbow, and sometimes with the shoulder, in retiring, in increasing, in lifting the body high, in bearing it low in one instant: in brief, delivering swiftly blows as well of the edge as of the point, both right and reversed, nothing regarding either time, advantage or measure, bestowing them at random every way.</p> |
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/145|3|lbl=-}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>But diverse men being blinded in their own conceits, do in these actions certainly believe that they are either more nimble, either more wary and discreet then their adversary is: of which their foolish opinion they are beastly proud and arrogant:</p> |
| + | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/145|4|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/146|1|lbl=134|p=1}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>And because it has many times happened them, either with a false thrust, or edge blow, to hurt or abuse the enemy, they become lofty, and presume thereon as though their blows were not to be warded. But yet for the most part it falls out, that by a plain simple swab having only a good stomach and stout courage, they are chopped in with a thrust, and so miserably slain.</p> |
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/146|2|lbl=-}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>For avoiding of this abuse, the best remedy is, that they exercise themselves in delivering these falses only in sport, and (as I have before said) for their practice and pastime: Resolving themselves for a truth, that when they are to deal with any enemy, and when it is upon danger of their lives, they must then suppose the enemy to be equal to themselves as well in knowledge as in strength, and accustom themselves to strike in as little time as is possible, and that always being well warded. And as for these Falses or Slips, they must use them for their exercises and pastimes sake only, and not presume upon them, except it beagainst such persons, who are either much more slow, either know not the true principals of this Art. For Deceit or Falsing is no other thing, then a blow or thrust delivered, not to the intent to hurt or hit home, but to cause the enemy to discover himself in some part, by means whereof a man may safely hurt him in the same part. And look how many blows or thrusts there may be given, so many falses or deceits may be used, and a great many more, which shall be declared in their proper place: The defense likewise whereof shall in few words be last of all laid upon you.</p> |
| + | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/146|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/147|1|lbl=135|p=1}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | <p>'''Deceits or falsings of the single sword, or single rapier'''</p> |
| − | + | ||
| + | <p>As I take not Victory to the end and scope of falsing, but rather nimbleness of body and dexterity in play: So, casting aside the consideration how a man is either covered or discovered, and how he has more or less advantage, I say that there may be framed at single sword so many wards, as there be ways to move the hand and foot.</p> | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/147|2|lbl=-}} |
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>Therefore in falsing there may be framed the high, low, and broad ward, with the right foot behind and before: a man may bear his sword with the point backwards and forwards: he may bear his right hand on the left side, with his sword's point backwards: he may stand at the low ward with the point backwards and forwards, bending towards the ground. And standing in all these ways, he may false a thrust above, and force it home beneath above, he may false it without and deliver it within, or contrariwise.</p> |
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/147|3|lbl=-}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>And according to the said manner of thrusting he may deliver edge-blows, right, reversed, high and low, as in that case shall most advantage him. Farther he may false an edge-blow, and deliver it home: as for example, to false a right blow on high, and deliver home a right and reverse blow, high or low. In like for the reverse is falsed, by delivering right or reverse blows, high or low.</p> |
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/147|4|lbl=-}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>But it is to be considered, that when he bears his sword with his point backwards, he false no other then the edge-blow, for then thrusts are discommodious. And because men do much use at this weapon, to beat off the point of the sword with their hands: therefore he must in that case for his greater readiness and advantage, suffer his sword to sway to that side, whether the enemy bears it, joining to that motion as much force as he may, performing therein a full circular blow, and delivering it at the enemy.</p> |
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/148|1|lbl=136}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>And this blow is most ready, and so much the rather, it is possible to be performed, by how much the enemy thinks not, that the sword will pass in full circle that way, for the enemy being somewhat disappointed, by beating off the sword, after which beating, he is also to deliver his thrust, he cannot so speedily speed both those times but that he shall be first struck with the edge of the sword, which he had before so beaten off.</p> |
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/148|2|lbl=-}} |
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>'''General advertisements concerning the defenses''' |
| + | |||
| + | <p>Because it chances commonly, that in managing of the hands, men bear no great regard, either to time or advantage, but do endeavor themselves after diverse and sundry ways and means to encounter the enemy's sword: therefore in these cases, it is very profitable to know how to strike, and what may be done in the shortest time.</p> | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/148|3|lbl=-}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>The enemy's sword is encountered always either above, either in the middle, either beneath: and in all these ways a man finds himself to stand either above, either beneath, either within, either without. And it falls out always that men find themselves underneath with the sword at the hanging ward, when they are to ward high edge-blows or thrusts: and this way is most commonly used: The manner whereof is, when the hand is lifted up to defend the sword being thwarted, and the point turned downwards: when one finds himself so placed, he ought not to recover his sword from underneath, and then to deliver an edge-blow, for that were too long, but rather to strike nimbly that part of the enemy underneath, which is not warded, so that he shall do no other then turn his hand and deliver an edge-blow at the legs which surely speeds.</p> |
| + | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/148|4|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/149|1|lbl=137|p=1}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>But if he find himself in defense either of the reverse or thrust, to bear his sword aloft and without, and not hanging, in this the safest thing is, to increase a pace, and to seize upon the enemy's hand or arm.</p> |
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/149|2|lbl=-}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>The self same he ought to do, finding himself in the middle, without and underneath: But if he find himself within, he cannot by any means make any seizure, because he shall then be in great peril to invest himself on the point of the enemy's sword.</p> |
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/149|3|lbl=-}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>Therefore to avoid the said point or thrust, he must turn his fist and deliver an edge-blow at the face, and withdraw himself by voiding of his foot towards the broad ward. And if he find himself beneath, and have encountered the enemy's edge-blow, either with the edge, or with the false or back of the sword, being beneath: then without any more ado, he ought to cut the legs, and void himself from the enemy's thrust. And let this be taken for a general rule: the body must be borne as far off from the enemy as it may. And blows always are to be delivered on that part which is found to be most near, be the stroke great or little. And each man is to be advertised that when he finds the enemy's weapon underneath at the hanging ward, he may safely make a seizure: but it would be done nimbly and with good courage, because he does then increase towards his enemy in the straight line, that is to say, increase on pace, and therewithal take holdfast of the enemy's sword, near the hilts thereof, yea though his hand were naked, and under his own sword presently turning his hand outwards, which of force wrests the sword out of the enemy's hand: neither ought he to fear to make seizure with his naked hand, for it is in such a place, that if should with his hand encounter a blow, happily it would not cut because the weapon has there very small force. All the hazard will be, if the enemy should draw back his sword, which causes it to cut. For in such sort it will cut mightily: but he may not give leisure or time to the enemy to draw back, but as soon as the seizure is made, he must also turn his hand outwards: in which case, the enemy has no force at all.</p> |
| + | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/149|4|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/150|1|lbl=138|p=1}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>These manner of strikings ought and may be practiced at all other weapons. Therefore this rule ought generally to be observed, and that is, to bear the body different from the enemy's sword, and to strike little or much, in small time as is possible.</p> |
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/150|2|lbl=-}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>And if one would in delivering of a great edge-blow, use small motion and spend little time he ought as soon as he has struck, to draw or slide his sword, thereby causing it to cut: for otherwise an edge-blow is to no purpose, although it be very forcibly delivered, especially when it lights on any soft or limber thing: but being drawn, it does every way cut greatly.</p> |
| − | + | | | |
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/150|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/151|1|lbl=139|p=1}} |
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>'''Of sword and dagger, or rapier and dagger'''</p> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <p>All the wards which are laid down for the single sword, may likewise be given for the sword and dagger. And there is greater reason why they should be termed wards in the handling of this, than of the single sword, because albeit the sword is borne unorderly, and with such disadvantage, that it wards in a manner no part of the body, yet there is a dagger which continually stands at his defense, in which case, it is not convenient that a man lift up both his arms and leave his body open to the enemy: for it is neither agreeable to true, neither to false art considering that in each of them the endeavor is to overcome. And this manner of lifting up the arms, is as if a man would of purpose be overcome: Therefore, when in this deceitful and false art, one is to use two weapons, he must take heed that he bear the one continually at his defense, and to handle the other every way to molest the enemy: sometime framing one ward, sometimes another: and in each of them to false, that is, to feign a thrust, and deliver a thrust, to false a thrust, and give an edge-blow: and otherwise also, to false an edge-blow, and to deliver an edge-blow. And in all these ways to remember, that the blow be continually different from the false: That is, if the thrust be falsed above to drive it home below: If within, yet to strike without, and falsing an edge-blow above, to bestow it beneath: or falsing a right blow, to strike with the reverse: or sometimes with a right blow, but yet differing from the other. And after an edge-blow on high, to deliver a reverse below. In fine, to make all such mixture of blows, as may bear all these contrarieties following, to wit, the point, the edge, high, low, right, reversed, within, without. But, I see not how one may practice any deceit with the dagger, the which is not openly dangerous. As for example, to widen it and discover some part of the body to the enemy, thereby provoking him to move, and then warding, to strike him, being so disappointed: but in my opinion, these sorts of falses of discovering the body, ought not to be used: For it behooves a man, first, safely defend to himself, and then to offend the enemy, the which he cannot do, in the practice of the said falses, if he chance to deal with an enemy that is courageous and skillful. But this manner of falsing next following, is to be practiced last of all other, and as it were in desperate cases. And it is, either to feign, as though he would forcibly fling his dagger at the enemy's face, (from the which false, he shall doubtless procure the enemy to ward himself, either by lifting up the arms, or by retiring himself, or by moving towards one side of other, in which travail and time, a man that is very wary and nimble, may safely hurt him) or else instead of falsing a blow, to fling the dagger indeed at the enemy's face. In which chance or occasion, it is necessary that he have the skill how to stick the dagger with the point. But yet howsoever it chance, the coming of the dagger in such sort, does so greatly trouble and disorder the enemy, that if a man step in nimbly, he may safely hurt him.</p> | |
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/151|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/152|1|lbl=140|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/153|1|lbl=141|p=1}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>These deceits and falses, of the sword and dagger, may be warded according as a man finds it most commodious either with the sword, or else with the dagger, not regarding at all (as in true art) to defend the left side with the dagger, and the right side with the sword: For in this false art men consider not either of advantage, time, or measure, but always their manner is (as soon as they have found the enemy's sword) to strike by the most short way, be it either with the edge, or point, notwithstanding the blow be not forcible, but only touch weakly and scarcely: for in play, so it touch any way, it is accounted for victory.</p> |
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/153|2|lbl=-|p=1}} |
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>Concerning taking holdfast, or seizing the enemy's sword, I commend not in any case, that seizure be made with the left hand, by casting a way of the dagger, as else I have seen it practiced: but rather that it be done keeping the sword and dagger fast in hand. And although this seem impossible, yet every one that is nimble and strong of arm, may safely do it. And this seizure is used as well under an edge-blow, as under a thrust in the manner following.</p> |
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/153|3|lbl=-}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>When an edge-blow or thrust comes above, it must be encountered with the sword without, on the third or fourth part of the enemy's sword, and with the dagger born within, on the first or second part thereof: having thus suddenly taken the enemy's sword in the middle, to turn forcibly the enemy's sword outwards with the dagger, keeping the sword steadfast, and as straight towards the enemy as possible by means whereof it may the more easily be turned. And there is no doubt but the enemy's sword may be wrung out of his hand, and look how much nearer the point it is taken, so much the more easily it is turned or wrested outwards, because it makes the greater circle, and the enemy has but small force to resist that motion.</p> |
| + | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/153|4|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/154|1|lbl=142|p=1}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>'''Of sword and cloak, or rapier and cloak'''</p> |
| + | |||
| + | <p>For to deceive the enemy with the cloak, it is necessary to know how many ways it may serve the turn, and to be skillful how to fold it orderly about the arm, and how to take advantage by the largeness thereof: and farther to understand how to defend, and how to offend and hinder the enemy therewith, because it fails not always, that men fight with their cloak wrapped about the arm, and the sword in hand, Therefore it is the part of a wise man, to know also how to handle the cloak after any other manner.</p> | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/154|2|lbl=-|p=1}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>Wherefore one may get the advantage of the Cloak, both when it is about his body, and when it is folded about his arm: The Cloak being about the arm in this manner. When it chances that any man to bicker with his enemy, with whom he is at point to join, but yet happily wears about him at that instant no kind of weapon, whereas his enemy is weaponed, and threatens him, then by taking both sides of the cloak as near the collar as is possible, he may draw if over his own head, and throw it at his enemy's face, who then being entangled and blinded there with, may either be thrown down, or disfurnished of his weapon very easily by him that is nimble, especially if he have to deal against one who is slow. A man may after another manner take the advantage of the cloak which the enemy wears, by taking with one hand both sides thereof, near the collar: which sides being strongly held, cause the cloak to be a gin being violently held, and plucked with one hand, he may so forcibly strike him with the other on the face or visage, that he will go near hand to break his neck.</p> |
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/154|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/155|1|lbl=143|p=1}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>There be many other ways whereby one may prevail with the cloak, to the greatest part whereof, men of mean judgment may easily attain unto. Therefore when one has his cloak on his arm, and sword in his hand, the advantage he gets thereby, besides the warding of blows, for that has been declared in the true art is, that he may molest his enemy by falsing to fling his cloak, and then to fling it in deed. But to false the flinging of the cloak is very dangerous, because it may not be done but in long time. And the very flinging of the cloak, is as it were a preparation to get the victory, and is in a manner rather true art then deceit, considering it is done by the straight or some other short line: neither for any other cause is this the rather here laid down, in deceit, then before in true art, then for that when one overcomes by this means, he seems not to conquer manfully, because he strikes the enemy before blinded with the cloak. Therefore when one minds to fling his cloak, he may either do it from and with his arm, or else with his sword: in so doing it is necessary, that he have not the cloak too much wrapped about his arm: I say, not above twice, neither to hold it straight or fast with his hand, that thereby he may be the better able when occasion serves to fling it more easily. If therefore he would fling it with his arm, and have it go with such fury, and make such effect as is required, he must of force join to the flinging thereof the increase of a pace, on that side where the cloak is, but first of all he must encounter, either find, either so endure the enemy's sword, that by the means of the increase of that pace it may do no hurt.</p> |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/155|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/156|1|lbl=144|p=1}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>And it is requisite in every occasion, that he find himself to stand without: and when either an edge-blow or a thrust comes, be it above or in the middle, as soon as he has warded it with his sword, he shall increase a pace and fling his cloak, howsoever it be folded, either from the collar, either from any other part, or else to hale it off from his shoulder, although it be on his shoulder: and in this order it is easily thrown, and is thereby the more widened in such sort, that the enemy is the more entangled and snared therewith.</p> |
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/156|2|lbl=-}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>Concerning the flinging of the cloak with the sword, I say, it may be thrown either with the point, either with the edge: with the point when one stands at the low ward with the right foot behind, and the cloak before: In which case the cloak that would be well and thick doubled and placed on the arm, but not wrapped. And instead of driving a thrust with the point which shall be hidden behind the cloak, he shall take the cloak on the point of the sword, and with the increase of a pace, force it at the enemy's face. And in this manner the cloak is so forcibly, and so covertly delivered and flung, that the enemy is neither aware of it, neither can avoid it, but of force it lights on his face, by means whereof, he may be struck at pleasure in any part of the body.</p> |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/156|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/157|1|lbl=145|p=1}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>The cloak may be flung or thrown with the edge of the sword, when one stands at the low ward, with the point of the sword turned backwards, one the left side and the cloak upon it, folded at large upon the arm up to the elbow: but not fast wrapped about it, and whilst he falses a reverse, he may take the cloak on the edge of the sword and fling it towards the enemy, and then strike him with such a blow as shall be then most fit for his advantage deliver.</p> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/157|2|lbl=-}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>Many other deceits there may be declared of the cloak, as well of flinging as of falsing it: but because I think these to be sufficient for an example to frame many other by, I make an end.</p> |
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/157|3|lbl=-}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>'''Falsing of | + | | <p>'''Falsing of blows, of sword and buckler square target, and round target'''</p> |
| − | <p> | + | <p>Being of the opinion that as touching deceit, there is but one consideration to be had of all these three weapons, and for because all the difference which may be between them is laid down and declared in the true art, in the consideration of form of each of them: Therefore I am willing rather to restrain myself, then to endeavor to fill the lease with the idle repetition of one thing twice.</p> |
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/158|1|lbl=146}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p> | + | | <p>All these three weapons ought to be borne in the fist, the arm stretched out forwards, and this is evidently seen in the square Target and buckler: the round Target also, because by reason of his greatness and weight, it may not be held in the only fist, and forward, in which kind of holding, it would ward much more is borne on the arm, being stretched forth with the fist forwards, which is in manner all one, or the self same. Therefore one may false as much with the one as with the other, considering there is no other false used with them then to discover and frame diverse wards, bearing no respect to any advantage. And yet there is this difference between them, that with the round Target, one may easily ward both edge-blows and thrusts, and with the square Target, better than with any other, he may ward edge-blows, because it is of square form: and the edge of the sword may easily be retained with the straight side thereof, which is not so easily done with the buckler: for over and besides the warding of thrusts, the buckler is not so sure of itself, but requires aid of the sword. Edge-blows also when they come a thwart (for in that case, they encounter the circumference thereof: the which if it chance, the sword not to encounter on the diameter, or half, in which place the sword is only stayed, but does encounter it, either beneath, either above the said diameter (may easily slip and strike either the head or thighs: therefore let every man take heed and remember, that in striking at the buckler, either with the point or edge of the sword, he deliver it crossing or a thwart.</p> |
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/158|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/159|1|lbl=147|p=1}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p> | + | | <p>As concerning the falses and deceits, which may be used in the handling of these weapons, as at the single sword, they are infinite, so at these weapons they are much more, if the number of infinite may be exceeded. For besides, that with the sword one may false a thrust, an edge-blow, on high, a low, within without, and frame diverse other unorderly wards, There remains one deceit or false properly belonging unto these, which is, to bear the buckler, square Target, or round Target, wide from the body, and therewithal to discover himself, to the end the enemy may be hindered, and lose time in striking, being therewithal sure and nimble to defend himself and offend the enemy. And this he may practice in every ward, but more easily with the square Target than with the other two, because it is big and large enough, and may easily encounter and find the enemy's when it comes striking: but this happens not in the round Target, because his form is circular, neither in the buckler, because, besides his roundness, it is also small: by means of which two things, blows are very hardly encountered except a man be very much exercised in the handling thereof. And because there are two weapons, the one of offense, and the other of defense: it is to be considered, that when by means of a false thrust or edge-blow, the enemy's round Target, square Target or buckler, is only bound to his ward, and his sword remains free and at liberty, one resolve himself to strike immediately after the falsed thrust, for then he may very easily be hurt by the enemy's sword. Therefore let him remember for the most part, to false such thrusts, against the which, besides the weapon of defense, the sword be also bound to his ward, or else to false edge-blows from the knee downwards: for seeing the round target, or any of the other two, may not be used in that placed at his defense, which as soon as it is found, and thereby ensured that it may do no hurt, a man may then step forwards, and deliver such a blow as he best may without danger.</p> |
| − | | | + | | |
| | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/159|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/160|1|lbl=148|p=1}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p> | + | | <p>'''An advertisement concerning the defenses of the false of the round target'''</p> |
| − | | | + | |
| + | <p>Every time one uses to false with round Target, square Target, and buckler, or as I may better say, with the sword accompanied with them, he falses either an edge-blow, either a thrust, either leaves some part of the body before discovered. Against all the falses of the edge, which come from the knee upwards, the round Target or any of the rest, must be oppressed, and then suddenly under them a thrust be delivered, against that part which is most disarmed. But if blows come from the knee downwards, they of force must be encountered with the sword, and always with the false or back edge thereof, whether that the blow be right or reversed: and therewithal the enemy's leg must be cut with the edge prepared without moving either the feet or the body. And this manner of striking is so short that it safely speeds. Moreover, all thrusts and other edge-blows, as well high as low may, nay rather ought to be warded, by accompanying the target or other weapon of defense with the sword, whose point would be bent towards the enemy, and as soon as the enemy's sword is encountered, if it be done with the false edge of the sword, there is no other to be done, then to cut his face or legs.</p> | ||
| + | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/160|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/161|1|lbl=149|p=1}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p> | + | | <p>But if the sword be encountered with the right edge then if he would strike with the edge, he must of force first turn his hand and so cut. And this manner of striking and defending, does properly belong unto the round Target, square Target and buckler, and all other ways are but ane and to small purpose: for to encounter first and then to strike, causes a man to find himself either within the enemy's Target or sword, by which means he may easily strike, before either the sword or Target may ward again.</p> |
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/161|2|lbl=-}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p> | + | | <p>But if any man ask why this kind of blow carries small force, and is but weak? I answer, true it is, the blow is but weak, if it were delivered with an axe or a hatchet, which as they say, have but short edges, and makes but one kind of blow, but if it be delivered with a good sword in the foresaid manner, because it bears a long edge, it does commodiously cut, as soon as the edge has found the enemy's sword, and especially on those parts of the body which are fleshly and full of sinews. Therefore speaking of deceit or falsing, a man must always with the sword and round Target and such like, go and encounter the enemy's blows, being accompanied together. And as soon as he has found the enemy's sword, he shall within it, cut either the face or the legs, without any further recovery of his sword, to the intent to deliver either thrusts, or greater edge-blows: for if one would both defend and strike together, that is the most short way that is.</p> |
| − | | | + | | |
| | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/161|3|lbl=149|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/162|1|lbl=150|p=1}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| + | | <p>But when the enemy discovers some part of his body, thereby provoking his adversary to strike, and then would beat off the blow and strike him withal: in this case, either a man must not strike if he perceive not that his sword is most near the enemy, then his own Target is to the enemy's sword, or else if he would strike and be further off, he must recover his sword and void the enemy's blow, striking commodiously ether above ether somewhere else. And it is a very easy matter to lose much time, for the Target and such like are heavy, And if these motions meet with no object or stay, they pass beyond their strength. But if it so happen or chance, as I have before said, that a man finds himself more near to hurt then the enemy, then the enemy is ready to defend himself, then he must not false a blow first, and then recover his sword, but strike and drive it home at first, as resolutely and as nimbly as he may possibly: and this manner of striking pertains rather to the true art then to deceit or falsing.</p> | ||
| | | | ||
| − | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/162|2|lbl=-}} | |
| − | | | ||
| − | {{section|Page: | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p> | + | | <p>'''Of the falses of the two swords: or rapiers'''</p> |
| − | + | ||
| + | <p>These kind of weapons have so great liberty of striking or warding, and are so intermeddled the one with the other, as no other sort of weapon is, which I may compare with these. There may be framed an infinite company of wards with these weapons, and all of them sure, except two, which are framed and borne without, and are these as follows.</p> | ||
| | | | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/163|1|lbl=151}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p> | + | | <p>To bear both swords with their points backward: for this manner of warding, is as if one would of purpose cause himself to be slain: or else to bear both aloft, which a man may hardly sustain, considering the paizes of the swords are naturally heavy and tend downwards, so that the arms are much encumbered thereby. Therefore from these two which are framed without, shall be laid down, all those which may be found and may be framed in the handling of these weapons: as for example, high wards, low, wide, altered, diminished, and all those wards which are mixed, as to frame with one sword the high ward, with the other the broad ward, and to frame the low and broad ward, the high and low ward, two low wards, and two broad wards: but yet these last two are as painful as the two high wards, and therefore shall not be used. Moreover, a man may bear one sword with the point forwards, and the other backwards, and he may further, very easily find out and practice diverse other ways, if he consider in how many ways a man may move his hands, his arms, his feet, and his whole person: for each of these motions are sufficient of themselves, to alter the ward. In all these wards, he may with either hand and sword, practice to false against the enemy, sometimes by feigning, sometimes by discovery. And this is properly belonging to these weapons, to wit, to false with one, and to strike home, either with the self same, or with the other weapon: and likewise discover with the one, and ward with the self same, or with the other, the which never yet to this day was or might be done with any other weapon. For in the handling of other weapons, that which falses, does in like manner strike home, so that of force, there are spent two times: for which consideration men hold opinion, that falsing is occasion both of great hurt, and also of loss of time. But yet this happens not in these weapons, which forasmuch as they are two, and are of equal power both in striking and defending, may be handled both after one fashion. And presupposing always that one is skillful to handle the one as well as the other, he may discharge at self same time two thrusts, two edge-blows, both right and reversed.</p> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/163|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/164|1|lbl=152}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | <p>But if | + | | <p>But if he would exercise himself only in sport and play, he shall then continually use to strike his enemy with one, and defend his person with the other. Therefore when one deals against an enemy that has two swords, one of the which may always increase a pace, and strike either with a thrust, or with the edge, from that sword he must take heed to ward himself, for it is very forcible, and always brings great danger and peril with it: The other sword which was before, makes no increase of pace and therefore cannot strike more than the defense and strength of the arm will bear, and that is weak to strike, but yet very strong to defend: and the selfsame accidents and qualities, which are found to be in the enemy, are incident also to ourselves. Wherefore one finds that he stands with his right foot before, be it in any ward whatsoever, he may false with the fore sword and strike home with the same, or else he may false with his hind sword, and strike with the selfsame: or else after a third way, to wit, to false with the one, and hit home with the other: And this kind of false, does more properly belong to the two swords than any other, but yet he must take heed and very well remember that while he falses with the one, and would strike home with the same, that he bear the other directly opposite against the enemy. For whilst the enemy is bound to ward the false, and homeblowe of the one sword, he may come in with the other and strike, if he find any place either discovered or easy to enter: So that bearing this rule continually in remembrance, which is in the fight of two swords, to bear always the one directly against the enemy, to the intent to hinder him, that he resolve not himself to enter, he shall endeavor to false, sometimes with the one, and sometimes with the other sword, sometimes a thrust, sometimes an edge-blow, and then to drive it home, either with the same sword that falses, or else with the other. But in practice, and doing of all of this, it is required that he be of deep judgment, knowing presently upon the false, what art of the body the enemy discovers, increasing thither, and investing the enemy with that sword which is most nigh to that part, and with the which he may most safely strike.</p> |
| − | | | + | | |
| | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/164|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/165|1|lbl=153|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/166|1|lbl=154|p=1}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>And it is to be considered, that it is a very strong and short way of striking, to false with the fore sword either a thrust or an edge-blow, and to false them not once or twice, but diverse times, now aloft, now beneath, sometimes with a thrust, sometimes with an edge-blow, to the intent, to blind and occupy the enemy's both swords, and at last when fit occasion serves, to strike it home with the hind sword: but yet always with the increase of a pace. The false which may be practice with the hind sword, is unprofitable being make without the motion of a pace, for it is so short that it is to no purpose. Therefore it cannot busy the enemy's swords in such manner, that it may force him either to discover or disorder his body. From whence it may be gathered, that after this false of the hind sword, it is no sure play to strike either with the selfsame hind sword, or else with the fore sword, because the enemy was neither in any part discovered or troubled. The best thing therefore that may be done, if one would false with the hind sword, is, to drive either a thrust or an edge-blow, resolutely striking with the increase of a pace, and as the enemy moves to defend himself, to strike him with the same sword, in some place that is discovered: For he cannot strike with the other sword for by that means of the increase of the hind sword, that the sword which was before, remains now behind, So that it may not strike, except it increase a pace, and to increase again, were to spend much time. Therefore when one endeavors with the increase of a pace to force his sword within, he shall assay to strike it home, with the selfsame sword because as I have before said, to strike with the other were too long. Wherefore I will lay down this for a rule, in the handling of these weapons, that if a man false with the fore sword, he may also strike home with the same or with the other, so that he increase And if he false with the hind sword, he shall presently, and resolutely force the blow home with the same sword, but yet with the increase of a pace: but if he do not fully deliver it, he shall again procure immediately to strike home with the selfsame sword, either with a thrust, or edge-blow, be it high or low, as at that instant shall be most commodious to serve the turn.</p> |
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/166|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/167|1|lbl=155|p=1}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>'''An advertisement concerning the defenses of the two swords, or rapiers'''</p> |
| + | |||
| + | <p>In sport or play one may stand every way against the enemy, to wit, if the enemy be on high, to settle himself at his ward, low or broad. But it is more gallant to behold and more commodious indeed to place himself against the enemy in the very selfsame foot before, and in the very same site that he is in, either high or low. For standing in such manner, the enemy may hardly endeavor with his false, to trouble or busy both swords. And moreover it must be considered, that the fore sword is that which wards both falses, and resolute blows, the which it does very easily perform: For it be borne aloft, then by the bending of the point down, it defends that part of the body, to the which it is turned. Remembering therefore these rules, which are, to stand every way as the enemy does, and to ward his falses with the fore sword, I say, where any falses or blows come: then as soon as he has warded them with the fore sword, he shall increase a slope pace, and with the hind sword deliver either a thrust at some discovered place, either a right blow with the edge at the legs, or else (which is better) shall fetch a reverse, either athwart the face, or else athwart the arms, and his blow does most easily speed: for the enemy's fore sword is occupied, and his hind sword cannot come to oppose itself against this blow: neither may it so easily strike, because (by the increase of the foresaid slope pace) the body is moved out of the straight line, so that the enemy may not so commodiously strike with his hind sword, but that he shall be first struck on the face or on the arms.</p> | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/167|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/168|1|lbl=156|p=1}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>Wherefore, let every man resolve himself, (as soon as he has encountered the enemy's sword with his own fore sword) that he step in and strike with his hind sword. Neither, let him stand in fear of the enemy's hind sword: for either it cannot hurt because the body is voided (as I have said,) or else, if it may, it must presently provide to stand to his defense, and thereto is so bound, that it may do no manner of hurt.</p> |
| | | | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/168|2|lbl=-|p=1}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| + | | <p>'''Of the two hand sword'''</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p>For the deceits and falses of the two hand sword, there is no more regard to be taken in the handling thereof single, that is, one to one, then there is, when it is used among many: only this end is to be purposed, to wit, to move and handle with all nimbleness and dexterity, as well the edge as the point, fetching those great circular and unruly compassings, therewith as his form, greatness, and manner of holding requires.</p> | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/163|2|lbl=137}} | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/169|1|lbl=157}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>Neither ought a man so much regard to fetch a small or great compass, or to strike more with the point then with the edge, but must believe only that the victory consists in the nimble and active guiding there of any manner of way. Therefore there may be framed many wards, of all the which, being a thing superfluous to reason of, I will handle only six of them, which are most commodious and usual: whereof the first may be called the high ward, the second the broad ward, the third the low ward, from which there springs all other three, towards the other side, making six in all.</p> |
| | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/163|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/164|1|lbl=138|p=1}} | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/169|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| + | | <p>The high ward is framed by bearing the sword and arms lifted up on high and wide from the body, with the point of sword turned towards that part, as that arm is, whose hand is place by the cross, that is to say, if the right hand shall be at the cross, and the right foot before, to bear also the sword, with his point towards that side.</p> | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/164|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/169|3|lbl=-}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>There is also another high ward opposite to this and that is, without moving the feet at all to turn the point towards the other side, that is, towards the left side and to cross the arms. And it is to be noted, that in this high ward, be it on what side it will, the sword is to be borne with the point turned downwards.</p> |
| − | There | + | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/164|3|lbl=-}} |
| | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/169|4|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/170|1|lbl=158|p=1}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| + | | <p>The second is the broad ward, and must be framed with the arms widened from the body, not high but straight. And from this springs and is framed another broad ward, turned towards the other side by crossing of the arms.</p> | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/164|4|lbl=-}} | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/170|2|lbl=-}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | <p>And the third is the low ward, and in this the sword would be borne with the point somewhat upwards. And this ward has his opposite or contrary, by turning the sword on the other side, and crossing the arms. There may be framed many other wards: As for example, to bear the sword on high, with the point backwards, to the intent to drive a down right, or cleaving edge-blow: or else to bear it low with the point backwards, to the intent to drive it from beneath upwards. But in these wards falses are to small purpose: And if there be any one of them worth using, it should be the false of an edge-blow, the which at two hand sword is not to be used at all, because there is much time lost considering that immediately after the false, he must strike home with an edge-blow. For it is not commodious at the two hand sword, to false an edge-blow, and deliver home a thrust, because the weight or swing of the sword in delivering an edge-blow, transports the arms beyond their strength, so that they may very difficultly withhold the blow to such purpose, that they may be ale as it were in that instant to deliver a thrust. Therefore the false that should be used at the two hand sword, ought always to be framed with a thrust, and then an edge-blow right or reversed to be delivered, or else to false a high thrust, and deliver it beneath or elsewhere. But yet if one would needs false an edge-blow, let him do it with the false edge of the sword, then turning it in full circle, to deliver home the edge-blow, and in striking always to increase a pace. But when this false of the back or false edge is practiced, the arms being crossed, then if he would step forwards to strike he must increase a pace with the right foot. And if in any of these wards he would false a thrust, which is the best that may be used at the two hand sword, he must observe the very same notes and rules concerning the increasing of the pace. Further the thrust is falsed, and the edge-blow delivered home at the two hand sword for no other cause or consideration, then for that the said edge-blow is far more forcible then the thrust: For the two hand sword is long, by means whereof, in the delivery of the edge-blow, it makes a great circle. And moreover, it so weighty that very little and small strength, makes and forces the blow to go with great violence. But for as much as the striking with the edge is very dangerous considering it spends much time, and especially in the great compassing of the two hand sword, under which time wary and active persons may with the sword or other weapon give a thrust, therefore for the avoiding of this danger, he must before he determine with himself to strike with the edge, first drive on a thrust, rather resolute then falsed, and as far forwards as both arms will stretch. In doing of the which, he shall force the enemy to retire so much, that he may easily thereupon deliver his edge-blow with the increase of a pace, nothing doubting that the enemy will strike home first with a thrust. Therefore when one stands at the high ward, one either side he must false a thrust, and increase a pace delivering therewithal such an edge-blow, as shall be most commodious to serve his turn, either right or reversed. And further may practice the like in the broad and low wards, in either of the which, it is more easy to false the said thrust, then in the other.</p> |
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/164|5|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/165|1|lbl=139|p=1}} | ||
| | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/170|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/171|1|lbl=159|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/172|1|lbl=160|p=1}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | |
| − | | | + | | <p>And it is to be considered, when the edge-blow after the falsed thrust, is by a slope pace voided, that he suffer not his arms and sword by reason of the weight or swing thereof, far transported beyond his strength, that the sword light either on the ground or that he be forced thereby to discover all that part of his body which is before. Therefore the best remedy is, as soon as he shall perceive that he has delivered his blow in vain, that he suffer his sword to go (not with a full thwart circle, and so about his head) until the point be backwards beneath in such sort, that the circle or compass direct him to the high ward, in the which he may presently resolve himself and return either to strike again, or else defend himself on either side, so handling his weapon, as shall in that case be most for his advantage.</p> |
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/166|2|lbl=-}} |
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/172|2|lbl=-}} |
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | <p>'''The defenses of the two hand sword'''</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p>The defenses of the two hand sword require a stout heart, for that the sustaining of such great blows, by reason whereof, a man considers not the advantage of time, being the most principal thing of all, causes him to fly or retire back holding for a certainty that every blow given therewith, is not possible to be warded. Therefore when he deals against an enemy, who uses likewise the two hand sword, he shall oppose himself in the low ward: And when a false thrust comes, if it come so far forwards that it may join home, he ought first to beat it off, and then to force a thrust at the enemy's face, or deliver an edge-blow downwards at the arms but not lifting up the sword in a compass. But for that these falsed thrusts for the most part are far off, and come not to the body, being used only to fear the enemy, and cause him to retire, that thereby one may have the more time to deliver an edge-blow with the increase of a pace (which pace causes the blow to go with greater violence:) and farther may discern and judge, by nearness of the enemy, whether the blow will hit home yea or no, for it is easily known how much the arms may be stretched forth: Therefore when this false thrust does not join or hit home, he ought not to endeavor to beat it off, but to expect when his enemy delivers his edge-blow, and then to increase a pace, and strike him with a thrust.</p> | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/166|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/167|1|lbl=141|p=1}} | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/173|1|lbl=161}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | <p>But if it happen him to deal against a two hand sword, with a single sword or dagger, assuring himself that the two hand sword cannot but strike but with a thrust or an edge-blow, for the defense of the thrust he may beat it off and retire himself, but if it be an edge-blow, then, as soon as the two hand sword is lifted up, in the same time he must increase forwards and deliver a thrust, or else if he have no time to strike he must encounter and bear the blow in the first part of the sword, which is near the hilts, taking hold thereof with one hand, and striking him with the other. And this he may perform, if he be nimble and active, because the two hand sword carries but small force in that place.</p> | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/167|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/173|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/174|1|lbl=162|p=1}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | <p>'''Of the partisan, bill, javelin and halberd'''</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p>Deceits or falses, are more manifest and evident in these, then in short weapons which are handled only with one hand because both the arms are moved more slowly than one alone. And the reason thereof is, that considering they are more long, they therefore frame in their motions a greater compass: and this is perceived more in edge-blows then in thrusts. Therefore the best false that may be practiced in the handling of these weapons, is the false of the thrust, and that the edge-blow ought never or seldom to be used, except great necessity constrain, as shall be declared. Wherefore in these weapons, I will frame four wards, three of them with the point forwards, of which three, the first is, the point of the sword being borne low, and the hind arm being lifted up.</p> | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/174|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | <p>The second is, the point high, the right arm being behind and borne at low. The third, the point equal and the arms equal: And in every one of these a man must false without, and drive it home within, or false within and deliver it without, or false aloft and strike beneath, and so contrariwise. But as he falses within or without, he ought to remember this note, which is, he must always to the intent he may go the better covered and warded, compass the hindfoot to that part, to the which the weapon shall be directed to strike home after a false.</p> | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/174|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/175|1|lbl=163|p=1}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | <p>The fourth ward which is much used, and especially with the bill, shall be to bear the weapon with the blunt end or heel forwards, the edge being lifted up on high. And this is much used, to the intent to expect the enemy's blows, and that thereby a man may be better able to ward them, either with the heel or middle of the staff, and then to enter and strike delivering an edge-blow with the increase of a pace, the which manner of striking is most ready and nimble. The false which may be used in this ward, is when he has warded the enemy's blow with the heel of his weapon, and then would increase forwards to deliver an edge-blow, if the enemy shall lift up or advance his weapon to defend himself from the said blow, then he shall give over to deliver that blow, by retiring his weapon, and give a thrust underneath, with the increase of a pace.</p> | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/175|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | <p>And this kind of blow is very likely to work his effect without danger, if he aptly and nimbly used. | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/175|3|lbl=-}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | <p>'''Of the pike'''</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p>There may be used some deceit also in the Pike, although it be a weapon void of any crooked forks, and is much more apt to show great valor then deceit. And for as much as it has no other then a point to offend, and length to defend, for that cause there may be used no other deceit therewith, then with the point: and considering true art, is not the mark that is shot at in this place: I say, it may be borne after diverse fashions, as shall be most for a man's advantage, as either at the end, either in the middle, either more backwards, either more forwards, as shall be thought most commodious to the bearer. Likewise, one may frame three wards therewith, to wit, the first straight, with the arms equal: the second with the point low, the third, the point high, falsing in each of them a thrust, either within, either without, ether high, either low, and then immediately forcing it on resolutely, but contrary to the false, and carrying always the hind foot towards that side, to the which the Pike is directed to strike. In handling of the pike, a man must always diligently consider, so to work that the hind hand be that which may rule, drive on, draw back and govern the Pike, and that the fore hand serve to no other purpose then to help to sustain it.</p> | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/176|1|lbl=164}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | <p>'''The defenses of the deceits of the weapons of the staff'''</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p>I have not as yet laid down the defense of the Bill, and the rest, because they are all one with this of the Pike. And I mind to handle them briefly all together, considering that in these a man may not either render false for false, or take holdfast of the weapon. And although it might be done, I commend it not, because it is a very difficult matter to extort a weapon that is held fast with both hands. That therefore which one may do to defend himself, is to have recourse unto true Art, remembering so to ward the enemy s if it were a true blow, and to strike before the enemy spend another time, in delivering his resolute thrust, And to take heed in delivery of his blows, that he be nimble and carry his body and arms so aptly and orderly applied, that the weapon wherewith he strikes may cover it wholly.</p> | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/176|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/177|1|lbl=165|p=1}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | <p>And here I make an end of deceit, in practicing of the which, there is this consideration to be had, so, always to false, that if the enemy provide not to ward, it may reach and hit home, because being delivered in such order, it loses but little time.</p> | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/177|2|lbl=-}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | <p>'''The end of the false art'''</p> | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/177|3|lbl=-}} | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 2,629: | Line 2,715: | ||
{| class="master" | {| class="master" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! <p> | + | ! <p>Figures<br/>from the 1570</p> |
! <p>{{rating|C|Draft Modernization}}<br/>by [[Norman White]]</p> | ! <p>{{rating|C|Draft Modernization}}<br/>by [[Norman White]]</p> | ||
| − | ! <p> | + | ! <p>Archetype (1570){{edit index|Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf}}</p> |
| − | ! <p>English | + | ! <p>English Translation (1594){{edit index|DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf}}<br/>Transcribed by [[Early English Books Online]]</p> |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | <p>'''How a man by private practice may obtain strength of body thereby'''</p> |
| − | If nature had bestowed strength upon men (as many believe) in such sort as she has given sight, hearing and other senses, which are such in us, that they may not by our endeavor either be increased, or diminished, it should be no less superfluous, than ridiculous to teach how strength should be obtained, than it were if one should say, he would instruct a man how to hear or see better than he does already by nature. Neither albeit he that becomes a Painter or a Musician sees the proportions much better than he did before, or by hearing learns the harmony and conformity of voices which he knew not, ought it therefore be said, that he sees or hears more than he did? For that proceeds not of better hearing or seeing, but of seeing and hearing with more reason. But in strength it does not so come to pass: For it is manifestly seen, that a man of ripe age and strength, cannot lift up a weight today which he cannot do on the morrow, or some other time. But contrary, if a man prove with the | + | |
| + | <p>If nature had bestowed strength upon men (as many believe) in such sort as she has given sight, hearing and other senses, which are such in us, that they may not by our endeavor either be increased, or diminished, it should be no less superfluous, than ridiculous to teach how strength should be obtained, than it were if one should say, he would instruct a man how to hear or see better than he does already by nature. Neither albeit he that becomes a Painter or a Musician sees the proportions much better than he did before, or by hearing learns the harmony and conformity of voices which he knew not, ought it therefore be said, that he sees or hears more than he did? For that proceeds not of better hearing or seeing, but of seeing and hearing with more reason. But in strength it does not so come to pass: For it is manifestly seen, that a man of ripe age and strength, cannot lift up a weight today which he cannot do on the morrow, or some other time. But contrary, if a man prove with the selfsame sight on the morrow or some other time to see a thing which yesterday he saw not in the same distance, he shall but trouble himself in vain, and be in danger rather to see less than more, as it commonly happen to students and other such, who do much exercise their sight. Therefore there is no doubt at all but that a man's strength may be increased by reasonable exercise, And so likewise by too much rest it may be diminished: the which if it were not manifest, yet it might be proved by infinite examples. You shall see Gentlemen, Knights and others, to be most strong and nimble in running or leaping, or in vaulting, or in turning on Horseback, and yet are not able by a great deal to bear so great a burden as a Country man or Porter: But in contrary in running and leaping, the Porter and Country man are most slow and heavy, neither know how to vault upon their horse without a ladder. And this proceeds of no other cause, than for that every man is not exercised in that which is most esteemed: So that if in the managing of these weapons, a man would get strength, it shall be convenient for him to exercise himself in such sort as shall be declared.</p> | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) 1570.pdf/170|2|lbl=144}} | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/177|4|lbl=165|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/178|1|lbl=166|p=1}} |
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | For the obtaining of this strength and activity, three things ought to be considered, to wit, the arms, the feet and the legs, in each of which it is requisite that every one be greatly exercised, considering that to know well how to manage the arms, and yet to be ignorant in the motion of the feet, wanting skill how to go forwards and retire backwards, causes men oftentimes to overthrow themselves. | + | | <p>For the obtaining of this strength and activity, three things ought to be considered, to wit, the arms, the feet and the legs, in each of which it is requisite that every one be greatly exercised, considering that to know well how to manage the arms, and yet to be ignorant in the motion of the feet, wanting skill how to go forwards and retire backwards, causes men oftentimes to overthrow themselves.</p> |
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | |
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/178|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/179|1|lbl=167|p=1}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | And on the other side, when one is exercised in the governing of his feet, but is ignorant in the timely motion of his arms, it falls out that he goes forwards in time, but yet wanting skill how to move his arms, he does not only not offend the enemy, but also many times remains hurt and offended himself. The body also by great reason ought to be borne and sustained upon his foundation. For when it bows either too much backwards or forwards, either on the one or the other side, straight way the government of the arms and legs are frustrated and the body, will or nil, remains stricken. Therefore I will declare the manner first how to exercise the Arms, secondly the Feet, thirdly the Body, Feet and Arms, jointly: | + | | <p>And on the other side, when one is exercised in the governing of his feet, but is ignorant in the timely motion of his arms, it falls out that he goes forwards in time, but yet wanting skill how to move his arms, he does not only not offend the enemy, but also many times remains hurt and offended himself. The body also by great reason ought to be borne and sustained upon his foundation. For when it bows either too much backwards or forwards, either on the one or the other side, straight way the government of the arms and legs are frustrated and the body, will or nil, remains stricken. Therefore I will declare the manner first how to exercise the Arms, secondly the Feet, thirdly the Body, Feet and Arms, jointly:</p> |
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/179|2|lbl=-}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | <p>'''Of the exercise and strength of the arms''' |
| − | Let a man be never so strong and lusty, yet he shall deliver a blow more slow and with less force than another shall who is less strong, but more exercised: and without doubt he shall so weary his arms, hands and body, that he cannot long endure to labor in any such business. And there has been many, who by reason of such sudden weariness, have suddenly despaired of themselves, giving over the exercise of the weapon, as not appertaining unto them. Wherein they deceive themselves, for such weariness is vanquished by exercise, by means whereof it is not long, but that the body feet and arms are so strengthened, that heavy things seem light, and that they are able to handle very nimbly any kind of weapon, and in brief overcome all kind of difficulty and hardness. Therefore when one would exercise his arms, to the intent to get strength, he must endeavor continually to overcome weariness, resolving himself in his judgment, that pains is not caused, through debility of nature, but rather hangs about him, because he has not accustomed to exercise his members thereunto. | + | |
| + | <p>Let a man be never so strong and lusty, yet he shall deliver a blow more slow and with less force than another shall who is less strong, but more exercised: and without doubt he shall so weary his arms, hands and body, that he cannot long endure to labor in any such business. And there has been many, who by reason of such sudden weariness, have suddenly despaired of themselves, giving over the exercise of the weapon, as not appertaining unto them. Wherein they deceive themselves, for such weariness is vanquished by exercise, by means whereof it is not long, but that the body feet and arms are so strengthened, that heavy things seem light, and that they are able to handle very nimbly any kind of weapon, and in brief overcome all kind of difficulty and hardness. Therefore when one would exercise his arms, to the intent to get strength, he must endeavor continually to overcome weariness, resolving himself in his judgment, that pains is not caused, through debility of nature, but rather hangs about him, because he has not accustomed to exercise his members thereunto.</p> | ||
| + | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/179|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/180|1|lbl=168|p=1}} |
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | There are two things to be considered in this exercise, to wit the hand that moves, and the thing that is moved, which two things being orderly laid down, I hope I shall obtain as much as I desire. As touching the hand and the treatise of the true Art, in three parts, that is to say, into the wrist, the elbow, and the shoulder, In every of the which it is requisite, that it move most swiftly and strongly, regarding always in his motion the quality of the weapon that is borne in the hand, the which may be infinite, and therefore I will leave them and speak only of the single sword, because it bears a certain proportion and agreement unto all the rest. | + | | <p>There are two things to be considered in this exercise, to wit the hand that moves, and the thing that is moved, which two things being orderly laid down, I hope I shall obtain as much as I desire. As touching the hand and the treatise of the true Art, in three parts, that is to say, into the wrist, the elbow, and the shoulder, In every of the which it is requisite, that it move most swiftly and strongly, regarding always in his motion the quality of the weapon that is borne in the hand, the which may be infinite, and therefore I will leave them and speak only of the single sword, because it bears a certain proportion and agreement unto all the rest.</p> |
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/180|2|lbl=-}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | The sword as each man knows, strikes either with the point or with the edge. To strike edgewise, it is required that a man accustom himself to strike edgewise as well right as reversed with some cudgel or other thing apt for the purpose, First practicing to fetch the compass of the shoulder, which is the strongest, and yet the slowest | + | | <p>The sword as each man knows, strikes either with the point or with the edge. To strike edgewise, it is required that a man accustom himself to strike edgewise as well right as reversed with some cudgel or other thing apt for the purpose, First practicing to fetch the compass of the shoulder, which is the strongest, and yet the slowest edge-blow that may be given: Next and presently after, the compass of the elbow, then that of the wrist, which is more pressed and ready then any of the rest. After certain days that he has exercised these three kinds of compassing edge-blows one after another as swiftly as he may possible And when he feels in himself that he has as it were unloosed all those knittings or joints of the arm, and can strike and deliver strongly from two of these joints, to wit the Elbow and the Wrist, he shall then let the Shoulder joint stand, and accustom to strike strongly and swiftly with those two of the El bow and the Wrist, yet at the length and in the end of all shall only in a manner practice that of the Wrist, when he perceives his hand and wrist to be well strengthened, delivering this blow of the Wrist, twice or thrice, sometimes right, sometimes reversed, once right, and once reversed, two reverses and one right, and likewise, two right and one reversed, to the end that the handle take not accustom to deliver a right blow immediately after a reverse. For sometimes it is commodious, and does much advantage a man to deliver two right, and two reversed, or else after two right, one reversed: and these blows, ought to be exercised, as well with one hand as with the other, standing steadfast in one reasonable pace, practicing them now, aloft, now beneath, now in the middle. As touching the weight or heft, which is borne in the hand, be it sword or other weapon, I commend not their opinion anyway, who will for the strengthening of a man's arm that he handle first a heavy weapon, because being first used to them, afterwards, ordinary weapons will seem the lighter unto him, but I think rather the contrary, to wit, that first to the end, he does not over burden and choke his strength, he handle a very light sword, and such a one, that he may most nimbly move. For the end of this art is not to lift up or bear great burdens, but to move swiftly. And there is no doubt but he vanquishes which is most nimble, and this nimbleness is not obtained by handling of great hefts or weights, but by often moving.</p> |
| + | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/180|3|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/181|1|lbl=169|p=1}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | But yet after he has sometime travailed with a light weapon, then it is necessary according as he feels himself to increase in strength of arm, that he take another in hand, that is something heavier, and such a one as will put him to a little more pain, but yet not so much, that his swiftness in motion be hindered thereby. And as his strength increases, to increase likewise the weight by little and little. So it will not be long, but that he shall be able to manage very nimbly any heavy sword. The blow of the point or thrust, cannot be handled without the consideration of the feet and body, because the strong delivering of a thrust, consists in the apt and timely motion of the arms feet and body: For the exercise of which it is necessary that he know how to place them in every of the three wards, to the end, that from the ward he may deliver strongly a thrust in as little time as possible. And therefore he shall take heed that in the low ward, he make a reasonable pace, bearing his hand without his knee, forcing one the thrust nimbly, and retiring his arm backward, and somewhat increasing his forefoot more forwards, to the end, the thrust may reach the farther: But if he chance to increase the forefoot a little too much, so that the breadth thereof be painful unto him, than for the avoiding of inconveniences, he shall draw his hind foot so much after, as he did before increase the forefoot. And this thrust must be oftentimes jerked or sprung forth, to the end to lengthen the arm, accustoming to drive it on without retiring of itself, that by that means it may the more readily settle in the broad ward, For that is framed (as it is well known) with the arm and foot widened outwards, but not lengthened towards the enemy. And in thrusting let him see, that he deliver them as straight as he can possibly, to the end, they may reach out the longer. | + | | <p>But yet after he has sometime travailed with a light weapon, then it is necessary according as he feels himself to increase in strength of arm, that he take another in hand, that is something heavier, and such a one as will put him to a little more pain, but yet not so much, that his swiftness in motion be hindered thereby. And as his strength increases, to increase likewise the weight by little and little. So it will not be long, but that he shall be able to manage very nimbly any heavy sword. The blow of the point or thrust, cannot be handled without the consideration of the feet and body, because the strong delivering of a thrust, consists in the apt and timely motion of the arms feet and body: For the exercise of which it is necessary that he know how to place them in every of the three wards, to the end, that from the ward he may deliver strongly a thrust in as little time as possible. And therefore he shall take heed that in the low ward, he make a reasonable pace, bearing his hand without his knee, forcing one the thrust nimbly, and retiring his arm backward, and somewhat increasing his forefoot more forwards, to the end, the thrust may reach the farther: But if he chance to increase the forefoot a little too much, so that the breadth thereof be painful unto him, than for the avoiding of inconveniences, he shall draw his hind foot so much after, as he did before increase the forefoot. And this thrust must be oftentimes jerked or sprung forth, to the end to lengthen the arm, accustoming to drive it on without retiring of itself, that by that means it may the more readily settle in the broad ward, For that is framed (as it is well known) with the arm and foot widened outwards, but not lengthened towards the enemy. And in thrusting let him see, that he deliver them as straight as he can possibly, to the end, they may reach out the longer.</p> |
| + | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/181|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/182|1|lbl=170|p=1}} |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | At what time one would deliver a thrust, it is requisite that he move the body and feet behind, so much in a compass, that both the shoulders, arm, and feet, be under one self same straight line. Thus exercising himself he shall deliver a very great and strong thrust. And this manner of thrusting ought oftentimes to be practiced, accustoming the body and feet (as before) to move in a compass: for this motion is that which instructs one, how he shall void his body. The thrust of the high ward is hardest of all other, not of itself, but because it seems that the high ward (especially with the right foot before) is very painful. And because there are few who have the skill to place themselves as they ought to deliver the thrust in as little time as is possible. The first care therefore in this so to place himself, that he stand steadily. And the site thereof is in this manner, to wit: To stand with the arm aloft, and as right over the body as is possible, to the end he may force on the thrust without drawing back of the arm or loosing of time. And whilst the arm is borne straight on high (to the end it may be borne the more straight, and with less pains) the feet also would stand close and united together, and that because, this ward is rather to strike than to defend, and therefore it is necessary that it have his increase prepared: so that when the thrust is discharged, he ought | + | | <p>At what time one would deliver a thrust, it is requisite that he move the body and feet behind, so much in a compass, that both the shoulders, arm, and feet, be under one self same straight line. Thus exercising himself he shall deliver a very great and strong thrust. And this manner of thrusting ought oftentimes to be practiced, accustoming the body and feet (as before) to move in a compass: for this motion is that which instructs one, how he shall void his body. The thrust of the high ward is hardest of all other, not of itself, but because it seems that the high ward (especially with the right foot before) is very painful. And because there are few who have the skill to place themselves as they ought to deliver the thrust in as little time as is possible. The first care therefore in this so to place himself, that he stand steadily. And the site thereof is in this manner, to wit: To stand with the arm aloft, and as right over the body as is possible, to the end he may force on the thrust without drawing back of the arm or loosing of time. And whilst the arm is borne straight on high (to the end it may be borne the more straight, and with less pains) the feet also would stand close and united together, and that because, this ward is rather to strike than to defend, and therefore it is necessary that it have his increase prepared: so that when the thrust is discharged, he ought therewithal to increase the forefoot so much that it make a reasonable pace, and then to let fall the hand down to the low ward, from the which if he would depart again, and offend to the high ward, he must also retire his forefoot, near unto the hind foot, or else the hind foot to the forefoot, And in this manner he shall practice to deliver his thrust oftentimes always placing himself in this high ward with his feet united, discharging the thrust with the increase of the fore foot. But when it seems tedious and painful to frame this ward, then he must use, for the lengthening of his arm, to fasten his hand and take holdfast on some nook or staff, that stands out in a wall, as high as he may lift up his arm, turning his hand as if he held a sword, for this shall help very much to strengthen his arm, and make his body apt to stand at this ward. Now when he has applied this exercise, for a reasonable time, so that he may perceive by himself that he is nimble and active in delivering these blows and thrusts simply by themselves, then he shall practice to compound them, that is to say, after a thrust to deliver a right blow from the wrist, then a reverse, and after that another thrust, always remembering when he delivers a blow, from the wrist, after a thrust to compass his hind foot, to the end, the blow may be the longer: And when, after his right blow, he would discharge a reverse, he must increase a slope pace, that presently after it, he may by the increase of a straight pace, force on a strong thrust underneath. And so to exercise himself to deliver many of those orderly blows together, but yet always with the true motion of the feet and body, and with great nimbleness, and in as short time as possible, taking always for a most sure and certain rule, that he move the arms and feet, keeping his body firm and steadfast, so that it go not beastly forward, (and especially the head being a member of so great importance) but to keep always his body bowed rather backward than forward, neither to turn it but only in a compass to void blows and thrusts.</p> |
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | |
| + | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/182|2|lbl=-|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/183|1|lbl=171|p=1}} {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/184|1|lbl=172|p=1}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | Moreover, it shall not be amiss, after he has learned to strike, (to the end to strengthen his arms) if he cause another to force at him, either with a cudgel, or some other heavy thing, both | + | | <p>Moreover, it shall not be amiss, after he has learned to strike, (to the end to strengthen his arms) if he cause another to force at him, either with a cudgel, or some other heavy thing, both edge-blows and thrusts, and that he encounter and sustain them with a sword, and ward thrusts by avoiding his body, and by increasing forwards. And likewise under edge-blows, either strike before they light, or else encounter them on their first parts, with the increase of a pace, that thereby he may be the more ready to deliver a thrust, and more easily sustain the blow. Farther, when he shall perceive, that he has conveniently qualified and strengthened this instrument of his body, it shall remain, that he only have recourse in his mind to the five advertisements, by the which a man obtains judgment. And that next, he order and govern his motions according to the learning and meaning of those rules. And afterwards take advise of himself how to strike and defend, knowing the advantage in every particular blow. And there is not doubt at all, but by this order he shall attain to that perfection in this Art which he desires.</p> |
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/184|2|lbl=-}} |
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | | |
| − | | | + | | <p>'''Finished'''</p> |
| − | + | | | |
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf/184|3|lbl=-}} |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 2,709: | Line 2,801: | ||
<section begin="sourcebox"/>{{sourcebox header}} | <section begin="sourcebox"/>{{sourcebox header}} | ||
{{sourcebox | {{sourcebox | ||
| − | | work = | + | | work = Figures |
| authors = | | authors = | ||
| source link = | | source link = | ||
| Line 2,717: | Line 2,809: | ||
{{sourcebox | {{sourcebox | ||
| work = Modernization | | work = Modernization | ||
| − | | authors = [[Norman White]] | + | | authors = [[translator::Norman White]] |
| source link = | | source link = | ||
| source title= Document circulated online | | source title= Document circulated online | ||
| Line 2,731: | Line 2,823: | ||
{{sourcebox | {{sourcebox | ||
| work = English Transcription | | work = English Transcription | ||
| − | | authors = Early English Books Online | + | | authors = [[Early English Books Online]] |
| source link = | | source link = | ||
| − | | source title= [[Index | + | | source title= [[Index:DiGraſsi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) 1594.pdf|Index talk:DiGrassi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi)]] |
| license = default | | license = default | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 2,741: | Line 2,833: | ||
== Additional Resources == | == Additional Resources == | ||
| − | + | {{bibliography}} | |
| − | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
| Line 2,754: | Line 2,845: | ||
[[Category:English]] | [[Category:English]] | ||
[[Category:Italian]] | [[Category:Italian]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Copy/Pasting]] | ||
[[Category:Double Side Swords]] | [[Category:Double Side Swords]] | ||
| Line 2,767: | Line 2,860: | ||
[[Category:Sword and Shield]] | [[Category:Sword and Shield]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:New format]] |
Latest revision as of 21:19, 15 June 2025
| Giacomo di Grassi | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Born | 16th century Modena, Italy |
| Died | after 1594 London, England |
| Occupation | Fencing master |
| Genres | Fencing manual |
| Language | |
| Notable work(s) | Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (1570) |
| First printed english edition |
His True Arte of Defence (1594) |
| Concordance by | Michael Chidester |
| Translations | Český Překlad |
Giacomo di Grassi was a 16th century Italian fencing master. Little is known about the life of this master, but he seems to have been born in Modena, Italy and acquired some fame as a fencing master in his youth. He operated a fencing school in Treviso and apparently traveled around Italy observing the teachings of other schools and masters.
Ultimately di Grassi seems to have developed his own method, which he laid out in great detail in his 1570 work Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme ("Discourse on Wielding Arms with Safety"). In 1594, a new edition of his book was printed in London under the title His True Arte of Defence; this edition was orchestrated by an admirer named Thomas Churchyard, who hired I. G. to translated it and I. Iaggard to publish it.
Contents
Treatise
This presentation includes a modernized version of the 1594 English translation, which did not follow the original Italian text with exactness. We intend to replace or expand this with a translation of the Italian, when such becomes available.
Figures |
Archetype (1570) |
English Translation (1594) | |
|---|---|---|---|
Giacomo di Grassi His True Art of Defense, plainly teaching by infallible Demonstrations, apt Figures and perfect Rules the manner and form how a man without other Teacher or Master may handle all sorts of Weapons as well offensive as defensive: With a Treatise Of Deceit or Falsing: And with a way or Means by private Industry to obtain Strength, Judgement, and Activity |
[Ttl] RAGIONE DI ADOPRAR SICVRAMENTE L'ARME SI DA OFFESA, COME DA DIFESA, Con un Trattato dell'inganno, & con un modo di essitarsi da se stesso, per acquistare forza, giudicio, & prestezza, |
[Ttl] Giacomo Di Grassi his true Arte of Defence, plainlie teaching by infallable Demonstrations, apt Figures and perfect Rules the manner and forme how a man without other Teacher or Master may safelie handle all sortes of Weapons as well offensiue as defensiue: VVith a Treatise Of Disceit or Falsinge: And with a waie or meane by priuate Industrie to obtaine Strength, Iudgement and Actiuitie. | |
First written in Italian by the Fore-said Author, And Englished by I. G. gentleman. |
DI GIACOMO DI GRASSI. CON PRIVILEGIO. |
First written in Italian by the foresaid Author, And Englished by I. G. gentleman. | |
Printed at London for I. I. and are to be sold within Temple Barre at the Signe of the Hand and Starre 1594 |
In Uenetia, appresso Giordano Ziletti, & compagni.
|
Printed at London for I. I and are to be sold within Temple Barre at the Signe of the Hand and Starre 1594. | |
|
[i] To the Right Honorable my L. Borrow Lord Gouernor of the Breil, and Knight of the most honorable order of the Garter, T. C. wisheth continuall Honor, worthines of mind, and learned knowledg, with increas of worldlie Fame, & heauenlie felicitie. HAuing a restlesse desier in the dailie exercises of Pen to present some acceptable peece of work to your L. and finding no one thing so fit for my purpose and your honorable disposition, as the knowledge of Armes and Weapons, which defends life, countrie, & honour, I presumed to preferre a booke to the print (translated out of the Italyan language) of a gentle mans doing that is not so gredie of glory as many glorious writers that eagerly would snatch Fame out of other mens mouthes, by a little labour of their own, But rather keeps his name vnknowen to the world (vnder a shamefast clowd of silence) knowing that vertue shynes best & getteth greatest prayes where it maketh smallest bragg: for the goodnes of the mind seekes no glorious gwerdon, but hopes to reap the reward of well doing among the rypest of iudgement & worthiest of sound consideration, like vnto a man that giueth his goods vnto the poore, and maketh his treasurehouse in heauen, And further to be noted, who can tarrie til the seed sowen in the earth be almost rotten or dead, shal be sure in a boūtiful haruest to reap a goodly crop of corne And better it is to abyde a happie season to see how things will proue, than soddainly to seeke profite where slowlye comes commoditie or any benefit wil rise. Some say, that good writers doe purchase small praise till they be dead, (Hard is that opinion.) and then their Fame shal flowrish & bring foorth the fruite that long lay hid in the earth. [ii] This gentleman, perchaunce, in the like regard smothers vp his credit, and stands carelesse of the worlds report: but I cannot see him so forgotten for his paines in this worke is not little, & his merite must be much that hath in our English tongue published so necessarie a volume in such apt termes & in so bigg a booke (besides the liuely descriptions & models of the same) that shews great knowledge & cunning, great art in the weapon, & great suretie of the man that wisely can vse it, & stoutly execute it. All manner of men allowes knowledge: then where knowledge & courage meetes in one person, there is ods in that match, whatsoeuer manhod & ignorance can say in their own behalfe. The sine book of ryding hath made many good hors-men: and this booke of Fencing will saue many mens lyues, or put comon quarrels out of vre, because the danger is death if ignorant people procure a combate. Here is nothing set downe or speach vsed, but for the preseruation of lyfe and honour of man: most orderly rules, & noble obseruations, enterlaced with wise councell & excellent good wordes, penned from a fowntaine of knowledge and flowing witt, where the reasons runnes as freely as cleere water cōmeth from a Spring or Conduite. Your L. can iudge both of the weapon & words, wherefore there needes no more commendation of the booke: Let it shewe it self, crauing some supportation of your honourable sensure: and finding fauour and passage among the wise, there is no doubt but all good men will like it, and the bad sort will blush to argue against it, as knoweth our liuing Lord, who augment your L. in honour & desyred credit. Your L. in all humbly at commaundement. Thomas Churchyard. | |||
The Author's Epistle unto divers Noble men and Gentlemen |
[i] ALLI MOLTO MAG. SIGNORI Il Sig. Camillo, il Sig. Fabritio, il Sig. Girolamo, già del S. Luigi, il S. Liberale, l'uno & l'altro, S. Luigi Renaldi. Il S. Alberto Onigo, il S. Antonio Bressa, il S. Branca Scolari, il Sig. Lione Bosso, il Sig. Giacomo Sugana, il Sig. Bonsembiante, Onigo, già del Sig. Cavallier, il Sig. Ascanio Federici, il Sig. Agostino Bressa, miei Signori Osseruandissimi. |
[iii] The Authors Epistle vnto diuers Noble men and Gentle-men. | |
Among all the prayers, wherein through the whole course of my life, I have asked any great thing at God's hands, I have always most earnestly beseeched, that (although at this present I am very poor and of base fortune) he would notwithstanding give me grace to be thankful, and mindful of the good turns which I have received. For among all the disgraces which a man may incur in this world, there is none in my opinion which causes him to become more odious, or a more enimic to mortal men (yes, unto God himself) than ingratitude. Wherefore being in Treviso, by your honors courteously entreated, and of all honorably used, although I practiced little or nought at all to teach you how to handle weapons, for the which purpose I was hired with an honorable stipend, yet to shew myself in some sort thankful, I have determined to bestow the way how to all sorts of weapons with the advantage and safety. The which my work, because it shall find your noble hearts full of valor, will bring forth such fruit, being but once attentively read over, as that in your said honors will be seen in acts and deeds, which in other men scarcely is comprehended by imagination. And I, who have been and am most fervently affected to serve your lords, for as much as it is not granted unto me, (in respect of your divers affairs) to apply the same, and take some pains in teaching as I always desired, have yet by this other way, left all that imprinted in your noble minds, which in this honorable exercise may bring a valiant man unto perfection. |
FRA TVTTI i preghi che io per tut to il corso della mia uita ho chiesti a Dio maggiori, di quest'uno l'ho sempre caldamente supplicato. Che quan tunque io mi troui per hora in assai debbole & bassa fortuna, egli nondimeno mi conceda gratia di potermi mostrare grato & cortese de' fauori & beneficii riceuuti. Parendomi che fra tutte le brutture, nelle quali puote l'huomo incorrere in questo mondo, niuna ue ne sia, che piu odioso lo faccia, & inimico a' mortali, & a Dio istesso, che la ingratitudine. Onde essendo io stato dalle Signorie Vostre raccolto in Treuiso, & cortese & honora-tamente trattato da tutti, come che io poco o nulla mi a-doprassi in insegnarle la ragion dell'armi, a che ero da quel-le con honorato stipendio condotto, per dimostrar in parte la gratitudine dell'animo mio, ho deliberato donarle que- [ii] sta mia opera, nella qual mi sforzo di insegnare il modo di adoprar tutte le forte d'armi con auantaggio & sicuramente: la qual, perche trouerà i cuori uostri pieni di ualore, produrrà tal frutto, essendo una uolta letta con attentione, che nelle Signorie Vostre si uedrà quello in fatto, che in altrui à gran pena con l'imaginatione si comprende. Et io che sono stato & son ardentissimo di seruirle, non mi essendo stato concesso per molti suoi affari, di affaticarmi in esercitarle come era il desiderio mio, haurò con quest’altra uia lasciato ne i nobilissimi animi uostri impresso tutto quello che può in quest'honorato essercitio ridurre un'huomo ualoroso a perfettione. |
AMong all the Prayers, wherein through the whole course of my life, I haue asked any great thing at Gods hands, I haue alwayes most earnestly beseeched, that (although at this present I am verie poore and of base Fortune) he would notwithstanding giue me grace to be thankefull and mindfull of the good turnes which I haue receiued. For among all the disgraces which a man may incurre in this world, there is none in mine opinion which causeth him to become more odious, or a more enimie to mortall men (yea, vnto God himselfe) than ingratitude. VVherefore being in Treuiso, by your honours courteously intreated, and of all honourably vsed, although I practised litle or nought at all to teach you how to handle weapons, for the which purpose I was hyred with an honourable stipend, yet to shewe my selfe in some sort thankefull, I haue determined to bestowe this my worke vpon your honours, imploying my whole indeuour to shewe the way how to handle all sortes of weapons with aduantage and safetie. The which my worke, because it shall finde your noble hearts full of valure, will bring foorth such fruite, being but once attentiuely read ouer, as that in your said honors will be seene in actes and deedes, which in other men scarsely is comprehended by imagination. And I, who haue beene and am most feruently affected to serue your Ls. forasmuch as it is not graunted vnto me, (in respect of your diuers affaires) to applie the same, and take some paines inteaching as I alwaies desired, haue yet by this other waie, left all that imprinted in your noble mindes, which in this honourable exercise may bring a valiant man vnto perfection.
| |
Therefore I humbly beseech your honors, that with the same liberal minds, with the which you accepted of me, your Ls will also receive these my endeavors, and vouchsafe so to protect them, as I have always, and will defend your honors most pure and undefiled. Wherein, if I perceive this my first childbirth (as I have only published it to the intent to help and teach others) to be to the general satisfaction of all I will so strain my endeavors in another work which shortly shall shew the way both how to handle all those weapons on horseback which here are taught on foot, as also all other weapons whatsoever. Your honours most affectionate servant, Giacomo di Grassi of Medena |
Supplico dunque le Signorie uostre, che con quell'animo liberale, che accettorono me, riceuano questa mia fatica, havendola in quella protettione che io ho sempre hauuto & haurò il chiarissimo honor delle Signorie uostre: che se io conoscerò questo mio primiero parto, si come io l'ho solamente per giouare & insegnare publicato, sia di uniuersale sodisfattione, mi sforzerò in un'altro, & fra poco tempo, insegnare il modo di adoprar a cauallo tutte quelle sorti d'armi, che qui s'insegnano a piede, & dell'altre ancora. Di Venetia, adi 8. Marzo. 1570. Di VV. SS. Seruitor Affettionatissimo
|
Therefore I humbly beseech your honours, that with the same liberall mindes, with the which you accepted of mee, your Ls: will also receiue these my indeuours, & vouchsafe so to protect them, as I haue alwaies, and wil defend your honours most pure and vndesiled. VVherein, if I perceiue this my first childbirth (as I haue only published it to thentent to help & teach others) to be to the generall satisfaction of all I will so straine my endeuours in an other worke which shortly shall shew the way both how to handle all those weapons on horse-backe which here are taught on foote, as also all other weapons whatsoeuer. Your honours most affectionate seruant.
| |
[iii] A I LETTORI. SI COME dalle fascie portiamo con noi un quasi sfrenato desiderio di sapere, cosi da l'esser po fatti ragioneuoli nasce in noi una lodeuole & ardente uoglia d'insegnare, il che quando non fosse non si uedrebbe perauentura il mondo di tante arti e scienze ripieno. |
[iv] The Author, to the Reader. EVen as from our swathing bands wee carrie with vs (as it were) an vnbridled desire of knowledge: So afterwardes, hauing attained to the perfection therof, there groweth in vs a certaine laudable and feruent affection to teach others: The which, if it were not so, the world happily should not be seene so replenished with Artes and Sciences. | ||
|
Percio che non essendo tutti gli huomini atti alla contemplatione & inuestigatione delle cose, nè meno a ciascuno concessa da Dio la gratia di poter con la mente leuarsi da terra, & inuestigando trouar le cause delle cose, & quelle compartir a quelli che meno uolentieri s'affaticana; accaderebbe che una parte de gli huomini a guisa di Signori & padroni dominarebbono, & gli altri come serui uilissimi in perpetue tenebre auolti tolererebbono una uita indegna dell'humana conditione. La onde al parer mio è cosa ragioneuole far, altrui partecipe di quello che si ha con molto studio & fatica inuestigando ritrouato. Sendo dunque io sin da fanciullo sommamente dilettato del maneggio dell'armi, dopo l'hauer molto tempo esercitato il corpo in esse, ho uoluto uedere i piu eccellenti maestri di quest'arte, i quali ho auertito hauere tutti, modi diuersi di insegnare l'uno da l'altro molto differenti, quasi che questo mestiero fosse senza ordine & regola, & dipendesse tutto dal ceruello, & ghiribizzo di chi ne fa professione, nè fosse possibile in quello esercitio tanto honorato ritrouarsi, come in tutte l'altre arti e scienze, una sola uia buona e uera, col mezo della quale si potesse hauere intera cognitione di quanto si puo far con l'armi, senza lam bicarsi tutto dì il ceruello ad imparar hoggi un colpo da un maestro, diman da un'altro, affaticandosi d'intorno a i particolari, la cognitione de' quali è infinita, & per ciò impossibile. Però da honesto desio di giouare sospinto, tutto a questa contemplatione mi diedi, con speranza quando che fosse di poter ritrouare i principii & le uere cagioni di questa arte, & in poca somma & certo ordine ridurre il confuso & infinito numero de' colpi: i quali principii essendo pochi, & per ciò facili ad esser da qualunque persona intesi & collocati nella memoria; senza alcun dubio in poco tempo & con poca fatica apriranno una larghissima strada a saper tutto quello che in essa arte si contiene. Nè sono di ciò, si come io stimo, punto rimaso ingannato: percioche al fine dopo molto pensare [iv] ho ritrouato questa uera arte, dalla qual sola dipende la cognitione di quanto si puo far con l'armi in mano; non tanto di quelle che hoggidì si trouano, ma di quelle ancora che si troueranno nel tempo auenire, essendo ella fondata su la offesa & difesa, ambedue le quali si fanno nella linea retta e circulare, che in altro modo non si puo offendere nè difendere. |
For if men generally were not apt to contemplation and searching out of things: Or if God had not bestowed vpon euery man the grace, to be able to lift vp his minde from the earth, and by searching to finde out the causes thereof, and to imparte them to those who are lesse willing to take any paines therein: it would come to passe, that the one parte of men, as Lordes and Masters, should beare rule, and the other parte as vyle slaues, wrapped in perpetuall darknesse, should suffer and lead a life vnworthie the condition of man. Wherefore, in mine opinion it standes with great reason that a man participate that vnto others which he hath searched and found out by his great studie & trauaile. And therefore, I being euen from my childhood greatly delighted in the handling of weapons: after I had spent much time in the exercise thereof, was desyrous to see and beholde the most excellent and expert masters of this Arte, whome I haue generally marked, to teach after diuers wayes, much differing one from another, as though this misterie were destitute of order & rule, or depended onely vpon imagination, or on the deuise of him who professeth the same: Or as though it were a matter impossible to find out in this honourable exercise (as well as in all other Artes and Sciences) one onely good and true way, whereby a man may attaine to the intire knowledge of as much as may be practised with the weapon, not depending altogether vpon his owne head, or learning one blowe to day of one master, on the morowe of another, thereby busying himselfe about perticulars, the knowledge whereof is infinite, therefore impossible. Whereupon being forced, through a certaine honest desire which I beare to helpe others, I gaue my selfe wholy to the con- [v] templation thereof: hoping that at the length, I shoulde finde out the true principles and groundes of this Arte, and reduce the confused and infinite number of blowes into a compendious summe and certaine order: The which principles being but fewe, and therefore easie to be knowen and borne away, without doubt in small time, and little trauaile, will open a most large entrance to the vnderstanding of all that which is contained in this Arte. Neither was I in this frustrate at all of my expectation: For in conclusion after much deliberation, I haue found out this Arte, from the which onely dependeth the knowledge of all that which a man may performe with a weapon in his hand, and not onely with those weapons which are found out in these our dayes, but also with those that shall be inuented in time to come: Considering this Arte is grounded vpon Offence and Defence, both the which are practised in the straight and circuler lynes, for that a man may not otherwise either strike or defend. | ||
Et uolendo insegnar questa ragione dell'adoprar l'armi con quel maggior ordine & con quella maggior chiarezza che sia possibile, ho posto nel primo loco i principii di tutta l'arte nominando gli Auertimenti, i qua li essendo per sua natura notissimi a ciascuna persona di sana mente, non ho fatto altro che solamente raccontarli senza renderne ragion alcuna, come cosa superflua. |
And because I purpose to teach how to handle the Weapon, as orderly and plainly as is possible: I haue first of all layd down the principles or groundes of all the Arte, calling them Aduertisements, the which, being of their owne nature verie well knowen to all those that are in their perfect wittes: I haue done no other then barely declared them, vvithout rendring any further reason, as being a thing superfluous. | ||
Dopo questi principii ho trattato delle cose piu semplici, & de li poi alle composite ascendendo, dimostro quello che in tutto l'armi si possa fare. Et perche nell'insegnar le scienze & l'arti, si denono molto piu estimar le cose, che le parole, però non ho uoluto elegger un modo di parlare copioso, & sonoro, ma uno breue & familiare: il qual modo di parlare si come in poco fascio contiene in se & molte cose & grandi, cosi ricerca un lettore acuto & tardo, il quale uoglia a passo a passo penetrar nella midolla delle cose. |
These principles being declared, I haue next handled those things, vvhich are, and be, of themselues, Simple, then (ascending vp to those that are Compound) I shewe that vvhich may be generally done in the handling of all Weapons. And because, in teaching of Artes and Sciences, Things are more to be esteemed of than VVordes, therefore I vvould not choose in the handling hereof a copious and sounding kinde of speach, but rather that vvhich is more briefe and familiar. Which maner of speach as in a small bundle, it containeth diuers weightie things, so it craueth a slowe and discreete Reader, who will soft and faire pearce into the verie Marrowe thereof. | ||
Prego dunque il benigno lettore che tale si dimostri nel leggere la presente mia opera, sendo sicuro in tal modo leggendola di deuerne raccogliere grandissimo frutto & honore: nè è dubio alcuno che colui, il quale sarà fornito a bastanza di questa cognitione, & haurà a proportione la persona esercitata, non sia di gran lunga superiore ad ogni altro, quando però ui sarà da luna & l'altra parte egual forza & uelocità. |
For this cause I beseech the gentle Reader to shewe himselfe such a one in the reading of this my present worke, assuring him selfe by so reading it, to reape great profite and honour thereby. And [vi] Not doubting but that he (who is sufficientlie furnished with this knowledge, and hath his bodie proporcionably exercised thereunto) shall far surmount anie other although he be indewed with equal force and swiftnes. | ||
Et percioche questa arte è un principal membro della scienza militare, la quale insieme con le lettere è l’ornamento del mondo, però non si deue ella esercitare nelle brighe & risse, che si fanno per le contrade, ma come honoratissimi cauallieri riserbarsi di adoprarla per l'honor della patria, del suo Principe, per l'honor delle Donne, & di loro stessi, & finalmente per la uittoria de gli esserciti. |
Moreouer, because this art is a principal member of the Militarte profession, vvhich alltogether (vvith learning) is the ornament of all the World, Therefore it ought not to be exercised in Braules and Fraies, as men commonlie practise in euerie shire, but as honorable Knights, ought to reserue themselues, & exercise it for the aduantage of their Cuntry, the honour of vveomen, and conqueringe of Hostes and armies. | ||
|
[vii] An Aduertisement to the curteous reader. GOod Reader, before thou enter into the discourse of the hidden knowledge of this honourable excerise of the weapon now layd open and manifested by the Author of this worke, & in such perfectnes translated out of the Italian tongue, as all or most of the marshal mynded gentlemen of England cannot but commend, and no one person of indifferent iudgement can iustly be offended with, seeing that whatsoeuer herein is discoursed, tendeth to no other vse, but the defence of mans life and reputation: I thought good to aduertise thee that in some places of this booke by reason of the aequiuocation of certaine Italian wordes, the weapons may doubtfully be construed in English. Therefore sometimes fynding this worde Sworde generally vsed, I take it to haue beene the better translated, if in steede thereof the Rapier had beene inserted: a weapon more vsuall for Gentlemens wearing, and fittest for causes of offence and defence: Besides that, in Italie where Rapier and Dagger is commonly worne and vsed, the Sworde (if it be not an arming Sworde) is not spoken of. Yet would I not the sence so strictly to be construed, that the vse of so honourable a weapon be vtterly [viii] reiected, but so redd, as by the right and perfect vnderstanding of the one, thy iudgement may som what be augmented in managing of the other: Knowing right well, that as the practise and vse of the first is commendable amongst them, so the second cannot so farre be condemned, but that the wearing thereof may well commend a man of valour and reputation amongst vs. The Sworde and Buckler fight was long while allowed in England (and yet practise in all sortes of weapons is praisworthie,) but now being layd downe, the sworde but with Seruing-men is not much regarded, and the Rapier fight generally allowed, as a wapon because most perilous, therefore most feared, and thereupon priuate quarrels and common frayes soonest shunned. | |||
|
But this peece of work, gentle Reader, is so gallantly set out in euery point and parcell, the obscurest secrets of the handling of the weapon so clerely vnfolded, and the perfect demeaning of the bodie vpon all and sudden occasions so learnedly discoursed, as will glad the vnder stander thereof, & sound to the glory of all good Masters of Defence, because their Arte is herein so honoured, and their knowledge (which some men count infinite) in so singuler a science, drawen into such Grounds and Principles, as no wise man of an vnpartiall iudgement, [ix] and of what profession soeuer, but will confesse himself in curtesie farre indebted both to the Author & Translator of this so necessarie a Treatise, whereby he may learne not onely through reading & remembring to furnish his minde with resolute instructions, but also by practise and exercise gallantly to perfourme any conceited enterprise with a discreete and orderly carriage of his bodie, vpon all occasions whatsoeuer. | |||
Gentle Reader, what other escapes or mistakings shall come to thy viewe, either friendly intreate thee to beare with them, or curteously with thy penne for thine owne vse to amend them. Fare-well. | |||
[x] The Sortes of VVeapons handled in this Treatise. THe single Rapier, Or single Sworde. Falsing of Blowes and Thrusts. At single rapier &c. |
Figures |
Archetype (1570) |
English Translation (1594) | |
|---|---|---|---|
The second part entreating of deceits and falsings of blows and thrusts |
[119] DELL' INGANO. |
[133] THE Second Part intreatinge of Deceites and Falsinges of Blowes and Thrustes. | |
Being come to the end of the true Art, and having declared all which seemed convenient and profitable for the attainment of true judgment in the handling of the weapon and of the entire knowledge of all advantages, by the which as well all disadvantages are known: It shall be good that I entreat of Deceit or Falsing, as well to perform my promise, as also to satisfy those who are greatly delighted to skirmish, not with the pretense to hurt or overcome, but rather for their exercise and pastime: |
BEinge come to the end of the true Arte, and hauing declared all that which seemed conuenient and profitable for the attaynement of true iudgement in the handling of the weapon & of the entire knowledg of al aduātages, by the which as well al disaduantages are knowen: It shall be good that I intreat of Deceite or Falsing, aswel to performe my promise, as also to satisfie those who are greatly delighted to skirmish, not with pretence to hurt or ouer come but rather for their exercise & pastime: | ||
In which it is a brave and gallant thing and worthy of commendations to be skillful in the apt managing of the body, feet and hands, in moving nimbly sometimes with the hand, sometimes with the elbow, and sometimes with the shoulder, in retiring, in increasing, in lifting the body high, in bearing it low in one instant: in brief, delivering swiftly blows as well of the edge as of the point, both right and reversed, nothing regarding either time, advantage or measure, bestowing them at random every way. |
In which it is a braue and gallant thing and worthy of commendations to be skilfull in the apte managing of the bodie, feete and hands, in mouing nimblie sometimes with the hand, some-times with the elbow, and sometimes with the shoulder, in retiring, in increasing, in lifting the bodie high, in bearing it low in one instant: in breif, deliuering swiftlie blows aswell of the edge as of the point, both right and reuersed, nothing regarding either time, aduantage or measure, bestowing them at randone euerie waie. | ||
But diverse men being blinded in their own conceits, do in these actions certainly believe that they are either more nimble, either more wary and discreet then their adversary is: of which their foolish opinion they are beastly proud and arrogant: |
But diuers men being blinded in their owne conceites, do in these actions certainly beleeue that they are either more nimble, either more warie & discreet [134] then theire aduersarie is: Of which their folish opinion they are all beastlie proud and arrogant: | ||
And because it has many times happened them, either with a false thrust, or edge blow, to hurt or abuse the enemy, they become lofty, and presume thereon as though their blows were not to be warded. But yet for the most part it falls out, that by a plain simple swab having only a good stomach and stout courage, they are chopped in with a thrust, and so miserably slain. |
And because it hath manie times happened them, either with a false thrust, or edge blowe, to hurte or abuse the enemie, they become loftie, and presume thereon as though their blowes were not to be warded. But yet for the most part it falleth out, that by a plain simple swad hauing onely a good stomack and stout courage, they are chopt in with a thrust, and so miserablie slaine. | ||
For avoiding of this abuse, the best remedy is, that they exercise themselves in delivering these falses only in sport, and (as I have before said) for their practice and pastime: Resolving themselves for a truth, that when they are to deal with any enemy, and when it is upon danger of their lives, they must then suppose the enemy to be equal to themselves as well in knowledge as in strength, and accustom themselves to strike in as little time as is possible, and that always being well warded. And as for these Falses or Slips, they must use them for their exercises and pastimes sake only, and not presume upon them, except it beagainst such persons, who are either much more slow, either know not the true principals of this Art. For Deceit or Falsing is no other thing, then a blow or thrust delivered, not to the intent to hurt or hit home, but to cause the enemy to discover himself in some part, by means whereof a man may safely hurt him in the same part. And look how many blows or thrusts there may be given, so many falses or deceits may be used, and a great many more, which shall be declared in their proper place: The defense likewise whereof shall in few words be last of all laid upon you. |
For auoiding of this abuse, the best remedie is, that they exercise themselues in deliuering these falses onlie in sport, and (as I haue before said) for their practise & pastime: Resoluing themselues for a truth, that when they are to deal with anie enemie, & when it is vpon danger of their liues, they must then suppose the enemie to be equall to themselues aswel in knoledge as in strength, & accustome themselues to strik in as litle time as is possible, and that alwaies beeing wel warded. And as for these Falses or Slips, they must vse them for their exercise & pastimes sake onelie, and not presume vpon them, except it bee against such persons, who are either much more slow, either know not the true principels of this Art. For Disceit or Falsing is no other thing, then a blow or thrust deuered, not to the intent to hurt or hitt home, but to cause the enemie to discouer himselfe in some parte, by meanes whereof a man maie safely hurt him in the same part. And looke how manie blowes or thrusts there maie be giuen, so manie falses or deceits may be vsed, and a great manie more, which shal be declared in their proper place: The defence likewise whereof [135] shal in few words be last of all laid open vnto you. | ||
Deceits or falsings of the single sword, or single rapier As I take not Victory to the end and scope of falsing, but rather nimbleness of body and dexterity in play: So, casting aside the consideration how a man is either covered or discovered, and how he has more or less advantage, I say that there may be framed at single sword so many wards, as there be ways to move the hand and foot. |
Deceits or Falsings of the single Sword, or single Rapier AS I take not Victorie to be the end and scope of falsing, but rather nimblenes of bodie and dexteritie in plaie: So, casting aside the consideration how a man is either couered or discouered, and how he hath more or lesse aduantage) I saie that there maie be framed at the single sword so manie wards, as there be waies how to moue the arme hand and foot. | ||
Therefore in falsing there may be framed the high, low, and broad ward, with the right foot behind and before: a man may bear his sword with the point backwards and forwards: he may bear his right hand on the left side, with his sword's point backwards: he may stand at the low ward with the point backwards and forwards, bending towards the ground. And standing in all these ways, he may false a thrust above, and force it home beneath above, he may false it without and deliver it within, or contrariwise. |
Therefore in falsinge there may bee framed the high, lowe, and brode warde, with the right foote behind and before: a man may beare his sword witht the poynt backewardes and forwardes: he may beare his right hand on the left sid, with his swords poynt back wards: he may stand at the low warde with the point backewardes and forwardes, bending towardes the grounde. And standing in all these waies, he may false a thrust aboue, and force it home beneath: and contrarie from beneth aboue, he may false it without and deliuer it within, or contrariwise. | ||
And according to the said manner of thrusting he may deliver edge-blows, right, reversed, high and low, as in that case shall most advantage him. Farther he may false an edge-blow, and deliver it home: as for example, to false a right blow on high, and deliver home a right and reverse blow, high or low. In like for the reverse is falsed, by delivering right or reverse blows, high or low. |
And according to the saide manner of thrusting he may deliuer edge-blowes, right, reuersed, high and lowe, as in that case shal most aduantage him. Farther he may false an edgeblow, and deliuer it home: as for example, to false a right blowe on highe, and deliuer home a right and reuerse blowe, high or lowe. In like sortthe reuerse is falsed, by deliuering right or reuerse blowes, high or lowe. | ||
But it is to be considered, that when he bears his sword with his point backwards, he false no other then the edge-blow, for then thrusts are discommodious. And because men do much use at this weapon, to beat off the point of the sword with their hands: therefore he must in that case for his greater readiness and advantage, suffer his sword to sway to that side, whether the enemy bears it, joining to that motion as much force as he may, performing therein a full circular blow, and delivering it at the enemy. |
[136] But it is to be considered, that when he beareth his sworde with his poynt backewardes, he false no other than the edgeblow, for then thrusts are discommodius. And because men do much vse at this weapon, to beate off the poynt of the sworde with their handes: therefore he must in that case for his greater redines & aduantage, suffer his sword to swaie to that side, whether the enemy beateth it, ioyning to that motion as much force as he may, performing therin a ful circuler blowe, and deliuering it at the enemie. | ||
And this blow is most ready, and so much the rather, it is possible to be performed, by how much the enemy thinks not, that the sword will pass in full circle that way, for the enemy being somewhat disappointed, by beating off the sword, after which beating, he is also to deliver his thrust, he cannot so speedily speed both those times but that he shall be first struck with the edge of the sword, which he had before so beaten off. |
And this blow is most readie, and so much the rather, it is possible to be performed, by how much the enemie thinketh not, that the sword will passe in full circle that waie, for the enemie being somwhat disapoynted, by beating off the sworde, after which beating, he is also to deliuer his thrust, he cānot so speedely spēd both those times but that he shalbe first strokē with the edge of the sworde, which he had before so beaten off. | ||
General advertisements concerning the defenses Because it chances commonly, that in managing of the hands, men bear no great regard, either to time or advantage, but do endeavor themselves after diverse and sundry ways and means to encounter the enemy's sword: therefore in these cases, it is very profitable to know how to strike, and what may be done in the shortest time. |
Generall aduertisementes concerning the defences. BEcause it chaunceth commonly, that in managing of the handes, men beare no great regard, either to time or aduantage, but do endeuour themselues after diuers & sundry waies & meanes to encounter the enemies sword: therfore in these cases, it is verie profitable to knowe how to strike, and what may be done in shortest time. | ||
The enemy's sword is encountered always either above, either in the middle, either beneath: and in all these ways a man finds himself to stand either above, either beneath, either within, either without. And it falls out always that men find themselves underneath with the sword at the hanging ward, when they are to ward high edge-blows or thrusts: and this way is most commonly used: The manner whereof is, when the hand is lifted up to defend the sword being thwarted, and the point turned downwards: when one finds himself so placed, he ought not to recover his sword from underneath, and then to deliver an edge-blow, for that were too long, but rather to strike nimbly that part of the enemy underneath, which is not warded, so that he shall do no other then turn his hand and deliver an edge-blow at the legs which surely speeds. |
The enemies sword is encountred alwaies either aboue, either in the midle, either beneath: & in al these [137] waies a man findeth himself to stand either aboue, either beneth, either within, either without. And it fales out alwaies that men finde themselues vndernethe with the sword at the hanging warde, when they are to ward high edgeblowes or thrusts; and this waie is most commonly vsed: The manner whereof is, when the hand is lifted vp to defend the sword being thwar ted, and the poynt turned downewards: when one findeth himselfe so placed, he ought not to recouer his sworde from vnderneath, and then to deliuer an edge-blowe, for that were to long, but rather to strike nimbly that part of the enemie vnderneath, which is not warded, so that he shall do no other then turne his hand & deliuer an edge-blow at the legges which surely speedeth. | ||
But if he find himself in defense either of the reverse or thrust, to bear his sword aloft and without, and not hanging, in this the safest thing is, to increase a pace, and to seize upon the enemy's hand or arm. |
But if he finde himselfe in defence either of the reuerse or thrust, to beare his sword aloft and without, and not hanging, in this the safest thing is, to increase a pace, and to seasyn vpon the enimies hand or arme. | ||
The self same he ought to do, finding himself in the middle, without and underneath: But if he find himself within, he cannot by any means make any seizure, because he shall then be in great peril to invest himself on the point of the enemy's sword. |
The selfe same he ought to doe, finding himselfe in the midle, without and vnderneath: But if he finde himselfe within, he cannot by any meanes make anie seasure, because he shall be then in greate perill to inuest himselfe on the poynt of the enemies sworde. | ||
Therefore to avoid the said point or thrust, he must turn his fist and deliver an edge-blow at the face, and withdraw himself by voiding of his foot towards the broad ward. And if he find himself beneath, and have encountered the enemy's edge-blow, either with the edge, or with the false or back of the sword, being beneath: then without any more ado, he ought to cut the legs, and void himself from the enemy's thrust. And let this be taken for a general rule: the body must be borne as far off from the enemy as it may. And blows always are to be delivered on that part which is found to be most near, be the stroke great or little. And each man is to be advertised that when he finds the enemy's weapon underneath at the hanging ward, he may safely make a seizure: but it would be done nimbly and with good courage, because he does then increase towards his enemy in the straight line, that is to say, increase on pace, and therewithal take holdfast of the enemy's sword, near the hilts thereof, yea though his hand were naked, and under his own sword presently turning his hand outwards, which of force wrests the sword out of the enemy's hand: neither ought he to fear to make seizure with his naked hand, for it is in such a place, that if should with his hand encounter a blow, happily it would not cut because the weapon has there very small force. All the hazard will be, if the enemy should draw back his sword, which causes it to cut. For in such sort it will cut mightily: but he may not give leisure or time to the enemy to draw back, but as soon as the seizure is made, he must also turn his hand outwards: in which case, the enemy has no force at all. |
Therefore to avoide the saide poynt or thrust, he must turne his fist and deliuer an edge-blow at the face, and withdraw himselfe by voiding of his foote towardes the broad ward. And if he finde himselfe beneath, & haue encountred the enemies edgeblow, either with the edge, or with the false or backe of the sword, being beneath: then without any more adoe, he ought to cut the legges, and void himself from the [138] enimies thrust. And let this be taken for a generall rule: the bodie must be borne as far of from the enimy as it may. And blowes alwaies are to be deliuered on that parte which is founde to be most neare, be the stroke great or little. And each man is to be aduertised that when he findes the enimies weapon vnderneath at the hanging ward, he may safely make a seisure: but it would be done nimbly and with good courage, because he doth then increase towards his enimie in the streight lyne, that is to saie, increase on pace, and therewithall take holdfast of the enemies sword, nere the hiltes thereof, yea though his hand were naked, and vnder his owne sworde presently turning his hand outwardes, which of force wresteth the sworde out of the enimies hand: neither ought he to feare to make feisure with his naked hand, for it is in such a place, that if he should with his hand encounter a blowe, happely it would not cut because the weapō hath thereverie small force. All the hazard wil be, if the enimie should drawe backe his sword, which causeth it to cutte. For in such sorte it will cut mightily: but he may not giue leasure or time to the enimie to drawe backe, but as soone as the seisure is made, he must also turne his hand outwards: in which case, the enimie hath no force at all. | ||
These manner of strikings ought and may be practiced at all other weapons. Therefore this rule ought generally to be observed, and that is, to bear the body different from the enemy's sword, and to strike little or much, in small time as is possible. |
These maner of strikings ought and maie be practised at all other weapons. Therefore this rule ought generally to be obserued, and that is, to beare the bodie different from the enimes sword, and to strike litle or much, in as small time as is possible. | ||
And if one would in delivering of a great edge-blow, use small motion and spend little time he ought as soon as he has struck, to draw or slide his sword, thereby causing it to cut: for otherwise an edge-blow is to no purpose, although it be very forcibly delivered, especially when it lights on any soft or limber thing: but being drawn, it does every way cut greatly. |
And if one would in deliuering of a great edge-blowe, vse small motion and spende little time hee [139] ought as soone as he hath stroken, to drawe or slide his sword, thereby causing it to cute: for otherwise an edge-blowe is to no purpose, although it be verie forcibly deliuered, especialy when it lighteth on any soft or limber thing: but being drawen, it doth euery way cute greatly. | ||
Of sword and dagger, or rapier and dagger All the wards which are laid down for the single sword, may likewise be given for the sword and dagger. And there is greater reason why they should be termed wards in the handling of this, than of the single sword, because albeit the sword is borne unorderly, and with such disadvantage, that it wards in a manner no part of the body, yet there is a dagger which continually stands at his defense, in which case, it is not convenient that a man lift up both his arms and leave his body open to the enemy: for it is neither agreeable to true, neither to false art considering that in each of them the endeavor is to overcome. And this manner of lifting up the arms, is as if a man would of purpose be overcome: Therefore, when in this deceitful and false art, one is to use two weapons, he must take heed that he bear the one continually at his defense, and to handle the other every way to molest the enemy: sometime framing one ward, sometimes another: and in each of them to false, that is, to feign a thrust, and deliver a thrust, to false a thrust, and give an edge-blow: and otherwise also, to false an edge-blow, and to deliver an edge-blow. And in all these ways to remember, that the blow be continually different from the false: That is, if the thrust be falsed above to drive it home below: If within, yet to strike without, and falsing an edge-blow above, to bestow it beneath: or falsing a right blow, to strike with the reverse: or sometimes with a right blow, but yet differing from the other. And after an edge-blow on high, to deliver a reverse below. In fine, to make all such mixture of blows, as may bear all these contrarieties following, to wit, the point, the edge, high, low, right, reversed, within, without. But, I see not how one may practice any deceit with the dagger, the which is not openly dangerous. As for example, to widen it and discover some part of the body to the enemy, thereby provoking him to move, and then warding, to strike him, being so disappointed: but in my opinion, these sorts of falses of discovering the body, ought not to be used: For it behooves a man, first, safely defend to himself, and then to offend the enemy, the which he cannot do, in the practice of the said falses, if he chance to deal with an enemy that is courageous and skillful. But this manner of falsing next following, is to be practiced last of all other, and as it were in desperate cases. And it is, either to feign, as though he would forcibly fling his dagger at the enemy's face, (from the which false, he shall doubtless procure the enemy to ward himself, either by lifting up the arms, or by retiring himself, or by moving towards one side of other, in which travail and time, a man that is very wary and nimble, may safely hurt him) or else instead of falsing a blow, to fling the dagger indeed at the enemy's face. In which chance or occasion, it is necessary that he have the skill how to stick the dagger with the point. But yet howsoever it chance, the coming of the dagger in such sort, does so greatly trouble and disorder the enemy, that if a man step in nimbly, he may safely hurt him. |
Of sword and dagger, or Rapier and dagger. AL the wardes which are laide downe for the single sword, may likewise be giuen for the sworde and dagger. And there is greater reason why they should be termed wardes in the handling of this, than of the single sword, because albeit the sword is borne vnorderly, & with such disaduantage, that it wardeth in a maner no parte of the bodie, yet there is a dagger which continually standeth at his defence, in which case, it is not conuenient that a man lift vp both his armes and leaue his bodie open to the enimie: for it is neither agreeable to true, neither to false arte considering that in each of them the endeuor is to ouercome. And this manner of lifting vp the armes, is as if a man wold of purpose be ouercome: Therfore, when in this deceitfull and false arte, one is to vse two weapons, he must take hede that he beare the one cōtinually at his defence, and to handle the other euerie waye to molest the enimie: somtime framing one warde, somtimes an other: and in each of them to false, that is, to faine a thrust, and deliuer a thrust, to false a thrust, and giue an edge-blowe: and otherwise also, to false an edge-blowe, and to deliuer an edge- [140] blowe. And in all these wayes to remember, that the blowe be continually different from the false: That is, if the thrust be falsed aboue to driue it home belowe: If within, yet to strike it without, and falsing an edgeblowe aboue, to bestowe it beneath: or falsing a right blowe, to strike with the reuerse: or sometimes with a right blowe, but yet differing from the other. And after an edgeblowe on high, to deliuer a reuerse belowe. In fine, to make all such mixture of blowes, as may beare all these contrarieties following, to wit, the point, the edge, high, lowe, right, reuersed, within, without. But, I see not howe one may practise any deceit with the dagger, the which is not openly daungerous. As for example, to widen it and discouer some part of the bodie to the enemie, thereby prouoking him to moue, and then warding, to strike him, being so disapointed: but in my opinion, these sortes of falses of discouering the bodie, ought not to be vsed: For it behoueth a man, first, safely to defend himselfe, and then to offend the enimie, the which he cannot do, in the practise of the said falses, if he chaunce to deale with an enimie that is couragious and skilfull. But this manner of falsing next following, is to be practised last of all other, and as it were in desperate cases. And it is, either to faine, as though he would forcibly fling his dagger at the enemies face, (frō the which false, he shal doubtles procure the enemie to warde himselfe, either by lifting vp his armes, or by retyring himself, or by mouing towards one side or other, in which trauaile & time, a man that is verie warie and nimble, may safely hurt him:) or els in steede of falsing a blowe, to fling [141] the dagger in deede at the enimies face. In which chaunce or occasion, it is necessarie that he haue the skill how to sticke the dagger with the poynt. But yet howsoeuer it chaunce, the comming of the dagger in such sort, doth so greatly trouble and disorder the enemie, that if a man step in nimbly, he may safely hurt him. | ||
These deceits and falses, of the sword and dagger, may be warded according as a man finds it most commodious either with the sword, or else with the dagger, not regarding at all (as in true art) to defend the left side with the dagger, and the right side with the sword: For in this false art men consider not either of advantage, time, or measure, but always their manner is (as soon as they have found the enemy's sword) to strike by the most short way, be it either with the edge, or point, notwithstanding the blow be not forcible, but only touch weakly and scarcely: for in play, so it touch any way, it is accounted for victory. |
These deceits and falses, of the sword and dagger, may be warded according as a man findes it most commodious either with the sworde, or els with the dagger, not regarding at all (as in true arte) to defend the left side with the dagger, and the right sid with the sword: For in this false arte men consider not either of aduantage, time, or measure, but alwaies their manner is (as soone as they haue found the enimies sword) to strike by the most short waie, be it either with the edge, or point, notwithstanding the blowe be not forcible, but onely touch weakely & scarslv: for in plaie, so it touch any waie, it is accounted for victorie. | ||
Concerning taking holdfast, or seizing the enemy's sword, I commend not in any case, that seizure be made with the left hand, by casting a way of the dagger, as else I have seen it practiced: but rather that it be done keeping the sword and dagger fast in hand. And although this seem impossible, yet every one that is nimble and strong of arm, may safely do it. And this seizure is used as well under an edge-blow, as under a thrust in the manner following. |
Concerning taking holdfast, or seising the enimies sword, I commend not in any case, that seisure be made with the left hand, by casting a way of the dagger as else where I haue seene it practised: but rather that it be done keeping the sword and dagger fast in hand. And although this seeme vnpossible, yet euery one that is nimble & strong of arme, may safely do it. And this seisure is vsed aswell vnder an edgeblowe, as vnder a thrust in manner following. | ||
When an edge-blow or thrust comes above, it must be encountered with the sword without, on the third or fourth part of the enemy's sword, and with the dagger born within, on the first or second part thereof: having thus suddenly taken the enemy's sword in the middle, to turn forcibly the enemy's sword outwards with the dagger, keeping the sword steadfast, and as straight towards the enemy as possible by means whereof it may the more easily be turned. And there is no doubt but the enemy's sword may be wrung out of his hand, and look how much nearer the point it is taken, so much the more easily it is turned or wrested outwards, because it makes the greater circle, and the enemy has but small force to resist that motion. |
When the edgeblowe or thrust commeth aboue, it must be incountred with the sword without, on the third or fourth parte of the enimies sword, and with [142] the dagger borne within, on the first or second parte thereof hauing thus sodenly taken the enimies sword in the middle, to turne forciblie the enimies sword outwardes with the dagger, keeping the sword stedfast, and as streight towards the enimie as is possible by meanes whereof it may the more easely be turned. And there is no doubt but the enimies sworde may be wrong out of his hand, and looke how much nearer the poynt it is taken, so much the more easelie it is turned or wrested outwards, because it maketh the greater circle, and the enimie hath but smal force to resist that motion. | ||
Of sword and cloak, or rapier and cloak For to deceive the enemy with the cloak, it is necessary to know how many ways it may serve the turn, and to be skillful how to fold it orderly about the arm, and how to take advantage by the largeness thereof: and farther to understand how to defend, and how to offend and hinder the enemy therewith, because it fails not always, that men fight with their cloak wrapped about the arm, and the sword in hand, Therefore it is the part of a wise man, to know also how to handle the cloak after any other manner. |
Of Sword and Cloke, or Rapier and Cloke.
FOR to disceyue the enimie with the cloake, it is necessarie to know how many waies it may serue the turne, and to be skilfull how to fould it orderly about the arme, and how to take aduantage by the largenes thereof: and farther to vnderstand how to defend, and how to offend and hinder the enimie therewith, because it fales not out alwaies, that men fight with their cloake wrapped about the arme, and the sword in hand, Therefore it is the parte of a wise man, to knowe also how to handle the cloake after any other manner. | ||
Wherefore one may get the advantage of the Cloak, both when it is about his body, and when it is folded about his arm: The Cloak being about the arm in this manner. When it chances that any man to bicker with his enemy, with whom he is at point to join, but yet happily wears about him at that instant no kind of weapon, whereas his enemy is weaponed, and threatens him, then by taking both sides of the cloak as near the collar as is possible, he may draw if over his own head, and throw it at his enemy's face, who then being entangled and blinded there with, may either be thrown down, or disfurnished of his weapon very easily by him that is nimble, especially if he have to deal against one who is slow. A man may after another manner take the advantage of the cloak which the enemy wears, by taking with one hand both sides thereof, near the collar: which sides being strongly held, cause the cloak to be a gin being violently held, and plucked with one hand, he may so forcibly strike him with the other on the face or visage, that he will go near hand to break his neck. |
Wherefore one may get the aduātage of the cloke, both when it is about his bodie, and when it is folded about his arme: The cloke being about the arme in this maner. When it chaunceth any man to bicker [143] with his enimie, with whom he is at poynt to ioyne, but yet happelie weareth about him at that instant no kind of weapon, whereas his enimie is weaponed, & threatneth him, then by taking both sides of the cloake as neare the coller as is possible, he may draw it ouer his owne head, and throwe it at his enimies face, who then being in angled and blinded there with, may either be throwen downe, or disfurnished of his weapon very easely by him that is nimble, especially if he haue to deale against one that is slow. A man may after another manner take the aduantage of the cloake which the enimie weareth, by taking with one hande both sides thereof, neere the coller: which sides being strongly holden, cause the cloak to be a ginne or snare about the enimes necke, the which ginne being violently haled, and plucked with one hande, he may so forciblie strike him with the other on the face or visage, that he will goe neere hande to breake his necke. | ||
There be many other ways whereby one may prevail with the cloak, to the greatest part whereof, men of mean judgment may easily attain unto. Therefore when one has his cloak on his arm, and sword in his hand, the advantage he gets thereby, besides the warding of blows, for that has been declared in the true art is, that he may molest his enemy by falsing to fling his cloak, and then to fling it in deed. But to false the flinging of the cloak is very dangerous, because it may not be done but in long time. And the very flinging of the cloak, is as it were a preparation to get the victory, and is in a manner rather true art then deceit, considering it is done by the straight or some other short line: neither for any other cause is this the rather here laid down, in deceit, then before in true art, then for that when one overcomes by this means, he seems not to conquer manfully, because he strikes the enemy before blinded with the cloak. Therefore when one minds to fling his cloak, he may either do it from and with his arm, or else with his sword: in so doing it is necessary, that he have not the cloak too much wrapped about his arm: I say, not above twice, neither to hold it straight or fast with his hand, that thereby he may be the better able when occasion serves to fling it more easily. If therefore he would fling it with his arm, and have it go with such fury, and make such effect as is required, he must of force join to the flinging thereof the increase of a pace, on that side where the cloak is, but first of all he must encounter, either find, either so endure the enemy's sword, that by the means of the increase of that pace it may do no hurt. |
There be manie other waies whereby one may preuaile with the cloake, to the greatest parte whereof, men of meane iudgment may easely attaine vnto. Therefore when one hath his cloake on his arme, and sword in his hand, the aduantage that he getteth therby, besides the warding of blowes, for that hath bene declared in the true arte is, that he may molest his enimie by falsing to fling his cloake, and then to flinge it in deed. But to false the flingyng of the clok is verie daungerous, because it may not be done but in long time. And the verie flinging of the cloake, is as it were a preparation to get the victorie, and is in a manner rather true art then deceit, cōsidering it is don by the [144] streyght or some other shorte line: neither for any other cause is this the rather here laide downe, in deceite, then before in true arte, then for that when one ouercometh by theis meanes, he seemes not to conquere manfully, because he strikes the enimie before blinded with the cloake. wherefore when one mindeth to flinge his cloake, he may either do it from and with his arme, or else with his sword: and in so doing it is necessarie, that he haue not the cloake too much wrapped about his arme: I saie, not aboue twice, neither to hold it streight or fast with his hande, that thereby he may be the better able when occasion serueth to fling it the more easelie. If therefore he would fling it with his arme, and haue it goe with such fury, and make such effect as is required, he must of force ioyne to the flinging thereof the increase of a pace, on that side where the cloake is, but first of all he must incounter, either finde, either so ensure the enimies sword, that by the meanes of the increase of that pace it may do no hurte. | ||
And it is requisite in every occasion, that he find himself to stand without: and when either an edge-blow or a thrust comes, be it above or in the middle, as soon as he has warded it with his sword, he shall increase a pace and fling his cloak, howsoever it be folded, either from the collar, either from any other part, or else to hale it off from his shoulder, although it be on his shoulder: and in this order it is easily thrown, and is thereby the more widened in such sort, that the enemy is the more entangled and snared therewith. |
And it is requisite in euerie occasion, that he finde himselfe to stand without: and when either an edgeblow or a thrust comes, be it aboue or in the middle, as soone as he hath warded it with his sword, he shall increase a pace and fling his cloake, how soeuer it be folded, either from the coller, either from any other parte, or else to hale it off from his shoulder, although it bee on his shoulder: and in this order it is easelie throwne, & is thereby the more widned in such sort, that the enimie is the more entangled and snared therewith. | ||
Concerning the flinging of the cloak with the sword, I say, it may be thrown either with the point, either with the edge: with the point when one stands at the low ward with the right foot behind, and the cloak before: In which case the cloak that would be well and thick doubled and placed on the arm, but not wrapped. And instead of driving a thrust with the point which shall be hidden behind the cloak, he shall take the cloak on the point of the sword, and with the increase of a pace, force it at the enemy's face. And in this manner the cloak is so forcibly, and so covertly delivered and flung, that the enemy is neither aware of it, neither can avoid it, but of force it lights on his face, by means whereof, he may be struck at pleasure in any part of the body. |
Concerning the flinging of the cloake with the [145] sword, I saie, it may be throwen either with the point, either with the edge: with the poynt when one standeth at the lowe warde with the right foote behinde, and the cloake before: In which case the cloake would be well and thicke doubled and placed on the arme, but not wrapped. And in steed of driuing a thrust with the poynt which shalbe hidden behinde the cloake, he shal take the cloake on the poynt of the sworde, and with the increase of a pace, force it at the enimies face. And in this maner the cloake is so forcib lie, and so couertly deliuered and flinged, that the enimie is neither a ware of it, neither can avoyde it, but of force it lighteth on his face, by meanes whereof, he may be stroken at pleasure in any parte of the bodie. | ||
The cloak may be flung or thrown with the edge of the sword, when one stands at the low ward, with the point of the sword turned backwards, one the left side and the cloak upon it, folded at large upon the arm up to the elbow: but not fast wrapped about it, and whilst he falses a reverse, he may take the cloak on the edge of the sword and fling it towards the enemy, and then strike him with such a blow as shall be then most fit for his advantage deliver. |
The cloake may be flong or throwen with the edge of the sworde, when one standeth at the lowe warde, with the poynt of the sword turned backewardes, one the left side and the cloake vpon it, folded at large vpon the arme vp to the elbowe: but not fast wrapped about it, and whilest he falseth a reuerse, he may take the cloake on the edge of the sword and fling it towards the enimie, and then strike him with such a blow as shal be then most fit for his aduantage deliuer. | ||
Many other deceits there may be declared of the cloak, as well of flinging as of falsing it: but because I think these to be sufficient for an example to frame many other by, I make an end. |
Manie other deceites there might be declared of the cloake, aswell of flinging as of falsing it: but because I thinke these to be sufficient for an example to frame manie other by, I make an ende. | ||
Falsing of blows, of sword and buckler square target, and round target Being of the opinion that as touching deceit, there is but one consideration to be had of all these three weapons, and for because all the difference which may be between them is laid down and declared in the true art, in the consideration of form of each of them: Therefore I am willing rather to restrain myself, then to endeavor to fill the lease with the idle repetition of one thing twice. |
[146] Of Sword and buckler, square Target and round Target. BEing of opinion that as touching deceite, there is but one consideration to be had of all these three weapons, and for because all the difference which may be betwen them is laide downe and declared in the true arte, in the consideration of the forme of each ofthem: Therefore I am willing rather to restraine my selfe, then to indeuoure to fill the leafe with the idle repetition of one thing twice. | ||
All these three weapons ought to be borne in the fist, the arm stretched out forwards, and this is evidently seen in the square Target and buckler: the round Target also, because by reason of his greatness and weight, it may not be held in the only fist, and forward, in which kind of holding, it would ward much more is borne on the arm, being stretched forth with the fist forwards, which is in manner all one, or the self same. Therefore one may false as much with the one as with the other, considering there is no other false used with them then to discover and frame diverse wards, bearing no respect to any advantage. And yet there is this difference between them, that with the round Target, one may easily ward both edge-blows and thrusts, and with the square Target, better than with any other, he may ward edge-blows, because it is of square form: and the edge of the sword may easily be retained with the straight side thereof, which is not so easily done with the buckler: for over and besides the warding of thrusts, the buckler is not so sure of itself, but requires aid of the sword. Edge-blows also when they come a thwart (for in that case, they encounter the circumference thereof: the which if it chance, the sword not to encounter on the diameter, or half, in which place the sword is only stayed, but does encounter it, either beneath, either above the said diameter (may easily slip and strike either the head or thighs: therefore let every man take heed and remember, that in striking at the buckler, either with the point or edge of the sword, he deliver it crossing or a thwart. |
All theis three weapons ought to be borne in the fist the arme stretched outforwardes and this is euidently seene in the square Target and buckler: the round Target also, because by reason of his greatnes and waight, it may not be holden in the onelie fist, & forwarde, in which kind of holding, it would warde much more is borne on the arme, being stretched foorth with the fist forwardes, which is in manner all one, o the selfe same. Therefore one may false as much with the one as with the other, considering there is no other false vsed with them then to discouer and frame diuers wards, bering no respect to any aduantage. And yet there is this difference betwene them that with the round Target, one may easely warde both edgeblowes and thrustes, and with the square Target, better than with any other, he may warde edgeblowes, because it is of square forme: and the edge of the sword may easely be retained with the streight side thereof, which is not so easely done with the buckler: for ouer and besides the warding of thrustes, the buckler is not so sure of itself, but re- [147] quireth aide of the sworde. Edge-blowes also when they come a thwart (for in that case, they incounter the circumference thereof: the which if it chaunce, the sword not to encounter on the diameter, or halfe, in which place the sword is onelie staied, but doth encounter it, either beneath, either aboue the said diameter (maie easelie slippe and strike either the heade or thighs: therfore let euetie man take heede and remember, that in striking at the buckler, either with the poynte or edge of the sword, he deliuer it crossing or a thwarte. | ||
As concerning the falses and deceits, which may be used in the handling of these weapons, as at the single sword, they are infinite, so at these weapons they are much more, if the number of infinite may be exceeded. For besides, that with the sword one may false a thrust, an edge-blow, on high, a low, within without, and frame diverse other unorderly wards, There remains one deceit or false properly belonging unto these, which is, to bear the buckler, square Target, or round Target, wide from the body, and therewithal to discover himself, to the end the enemy may be hindered, and lose time in striking, being therewithal sure and nimble to defend himself and offend the enemy. And this he may practice in every ward, but more easily with the square Target than with the other two, because it is big and large enough, and may easily encounter and find the enemy's when it comes striking: but this happens not in the round Target, because his form is circular, neither in the buckler, because, besides his roundness, it is also small: by means of which two things, blows are very hardly encountered except a man be very much exercised in the handling thereof. And because there are two weapons, the one of offense, and the other of defense: it is to be considered, that when by means of a false thrust or edge-blow, the enemy's round Target, square Target or buckler, is only bound to his ward, and his sword remains free and at liberty, one resolve himself to strike immediately after the falsed thrust, for then he may very easily be hurt by the enemy's sword. Therefore let him remember for the most part, to false such thrusts, against the which, besides the weapon of defense, the sword be also bound to his ward, or else to false edge-blows from the knee downwards: for seeing the round target, or any of the other two, may not be used in that placed at his defense, which as soon as it is found, and thereby ensured that it may do no hurt, a man may then step forwards, and deliver such a blow as he best may without danger. |
As concerning the falses and deceites, which may be vsed in the handling of theis weapons, as at the single sworde, they are infinite, so at theis weapons they are much more, if the number of infinite may be exceded. For besides, that with the sword one may false a thrust, an edgeblowe, on high, a lowe, within without, and frame diuers other vnorderlie wardes, There remaineth one deceite or false properlie belōging vnto theis, which is, to beare the bukler, squar Target, or round Target, wide from the bodie, and therewithall to discouer himselfe, to the end the enimie may be hindred, and lose time in striking, being therewithal sure & nimble to defend himself & offēd the enimie. And this he may practise in euerie ward, but more easelie with the square Target than with the other two, because it is bigge and large inough, & may easelie encounter and find the enimies when it commeth striking: but this happeneth not in the rounde Target, because his forme is circuler, neither in the buckler, because, besides his roundnes, it is also small: by meanes of which two things, blowes are [148] very hardly encountred, except a man be very much exercised in the handling thereof. And because there are two weapons, the one of offence, and the other of defence: it is to be considered, that when by meanes of a false thrust or edgblowe, the enimies round Target, square Target or buckler, is onely bound to his warde, and his sword remaines free and at libertie, one resolue not himselfe to strike immediatly after the falced thrust, for then he may verie easelie be hurt by the enimies sword. Therefore let him remember for the most parte, to false such thrustes, against the which, besides the weapon of defence, the sword be also bound to his warde, or else to false edgeblowes from the knee downewards: for seeing the round target, or any of the other two, may not be vsed in that place, of force the sword must be there placed at his defence, which as soone as it is found, and thereby ensured that it may do no hurte, a man may then step forwardes, and deliuer such a blowe as he best may without daunger. | ||
An advertisement concerning the defenses of the false of the round target Every time one uses to false with round Target, square Target, and buckler, or as I may better say, with the sword accompanied with them, he falses either an edge-blow, either a thrust, either leaves some part of the body before discovered. Against all the falses of the edge, which come from the knee upwards, the round Target or any of the rest, must be oppressed, and then suddenly under them a thrust be delivered, against that part which is most disarmed. But if blows come from the knee downwards, they of force must be encountered with the sword, and always with the false or back edge thereof, whether that the blow be right or reversed: and therewithal the enemy's leg must be cut with the edge prepared without moving either the feet or the body. And this manner of striking is so short that it safely speeds. Moreover, all thrusts and other edge-blows, as well high as low may, nay rather ought to be warded, by accompanying the target or other weapon of defense with the sword, whose point would be bent towards the enemy, and as soon as the enemy's sword is encountered, if it be done with the false edge of the sword, there is no other to be done, then to cut his face or legs. |
An aduertisement concerning the defences of the false of the round Target. EVerie time that one vseth to false with round Target, square Target, and buckler, or as I may better saie, with the sword accompanied with them, he falseth either an edge-blowe, either a thrust, either leaueth some parte of the bodie before discouered. Against all the falces of the edge, which come from the knee vpwards, the round Target or any of the rest, must be oppressed, and then [149] suddenly vnder them a thrust be deliuered, against that parte which is most disarmed. But if blowes come from the knee downwardes, they of force must be encountred with the sword, and alwaies with the false, or backe edge thereof, whether that the blowe be right or reuersed: & therewithall the enimies legge must be cutt with the edge prepared without mouing either the feete or bodie. And this manner of striking is so shorte that it safely spedeth. Moreouer, all thrusts and other edgeblowes, aswell high as lowe may, naie rather ought to be warded, by accompaning the target or other weapon of defence with the sword, whose poynt would be bent towards the enimie, & assoone as the enimies sword is encountred, if it be done with the false edge of the sword, there is no other to be done, then to cut his face or legges. | ||
But if the sword be encountered with the right edge then if he would strike with the edge, he must of force first turn his hand and so cut. And this manner of striking and defending, does properly belong unto the round Target, square Target and buckler, and all other ways are but ane and to small purpose: for to encounter first and then to strike, causes a man to find himself either within the enemy's Target or sword, by which means he may easily strike, before either the sword or Target may ward again. |
But if the sword be encountred with the right edge then if he would strik with the edge, he must offorce first turne his hand and so cute. And this manner of striking and defending, doth properlie belong vnto the round Target, square Target and buckler, and all other waies are but vaine and to small purpose: for to encounter first and then to strike, causeth a man to finde himselfe either within the enimies Target or sword, by which meanes he may easelie strike, before either the sword or Target may warde againe. | ||
But if any man ask why this kind of blow carries small force, and is but weak? I answer, true it is, the blow is but weak, if it were delivered with an axe or a hatchet, which as they say, have but short edges, and makes but one kind of blow, but if it be delivered with a good sword in the foresaid manner, because it bears a long edge, it does commodiously cut, as soon as the edge has found the enemy's sword, and especially on those parts of the body which are fleshly and full of sinews. Therefore speaking of deceit or falsing, a man must always with the sword and round Target and such like, go and encounter the enemy's blows, being accompanied together. And as soon as he has found the enemy's sword, he shall within it, cut either the face or the legs, without any further recovery of his sword, to the intent to deliver either thrusts, or greater edge-blows: for if one would both defend and strike together, that is the most short way that is. |
[149] But if any man aske why this kind of blowe carrieth small force, and is but weake? I aunswer, true it is, the blowe is but weake, if it were deliuered with an axe or a hatchet, which as they saie, haue but short edges, and maketh but one kind of blowe, but if it be deliuered with a good sword in the foresaide [150] manner, because it beareth a long edge, it doth commodiously cut, as soone as the edge hath founde the enimies sword, and especially on those partes of the bodie which are fleshly and full of sinnowes. Therefore speaking of deceite or falsing, a man must alwaies with the sword and round Target and such like, goe and encounter the enimies blowes, being accompanied to gether. And as soone as he hath found the enimies sword, he shall within it, cute either the face or the leggs, without any farthar recouerie of his sword, to the intent to deliuer either thrustes, or greater edgeblowes: for if one would both defende and strike togeither, this is the most shorte waie that is. | ||
But when the enemy discovers some part of his body, thereby provoking his adversary to strike, and then would beat off the blow and strike him withal: in this case, either a man must not strike if he perceive not that his sword is most near the enemy, then his own Target is to the enemy's sword, or else if he would strike and be further off, he must recover his sword and void the enemy's blow, striking commodiously ether above ether somewhere else. And it is a very easy matter to lose much time, for the Target and such like are heavy, And if these motions meet with no object or stay, they pass beyond their strength. But if it so happen or chance, as I have before said, that a man finds himself more near to hurt then the enemy, then the enemy is ready to defend himself, then he must not false a blow first, and then recover his sword, but strike and drive it home at first, as resolutely and as nimbly as he may possibly: and this manner of striking pertains rather to the true art then to deceit or falsing. |
But when the enimie discouereth some parte of his bodie, thereby prouoking his aduersary to strike, and then would beate off the blowe and strike withall: in this case, either a man must not strike if he perceue not that his sword is more neare the enimy, then his owne Target is to the enimies sword, or else if he strik and be further off, he must recouer his sword & void the enimies blowe, striking comodiously ether aboue ether some wher els. And it is a very easie mater to lose much time, for the Target and such like are heauie, And if these motions meete with no obiect or steye, they passe beyond their strength. But if it so happen or chaunce, as I haue before saide, that a man findes himselfe more neare to hurte the enimie, then the enimie is readie to defend himselfe, then he must not false a blow first, & then recouer his sword, but strik & driue it home at the first, as resolutlie, & as nimblie as he may possiblie: & this maner of striking pertaineth rather to true art then to deceit or falsing. | ||
Of the falses of the two swords: or rapiers These kind of weapons have so great liberty of striking or warding, and are so intermeddled the one with the other, as no other sort of weapon is, which I may compare with these. There may be framed an infinite company of wards with these weapons, and all of them sure, except two, which are framed and borne without, and are these as follows. |
[151] Of the falses of the two Swordes: or Rapiers. THEIS kind of weapons haue so great libertie of striking or warding, and are so entermedled the one with the other, as no other sorte of weapon is, which I may compare with theis. There may be framed an infinite cōpanie of wardes with theis weapons, and all of them sure, except two, which are framed and borne without, and are theis as followeth. | ||
To bear both swords with their points backward: for this manner of warding, is as if one would of purpose cause himself to be slain: or else to bear both aloft, which a man may hardly sustain, considering the paizes of the swords are naturally heavy and tend downwards, so that the arms are much encumbered thereby. Therefore from these two which are framed without, shall be laid down, all those which may be found and may be framed in the handling of these weapons: as for example, high wards, low, wide, altered, diminished, and all those wards which are mixed, as to frame with one sword the high ward, with the other the broad ward, and to frame the low and broad ward, the high and low ward, two low wards, and two broad wards: but yet these last two are as painful as the two high wards, and therefore shall not be used. Moreover, a man may bear one sword with the point forwards, and the other backwards, and he may further, very easily find out and practice diverse other ways, if he consider in how many ways a man may move his hands, his arms, his feet, and his whole person: for each of these motions are sufficient of themselves, to alter the ward. In all these wards, he may with either hand and sword, practice to false against the enemy, sometimes by feigning, sometimes by discovery. And this is properly belonging to these weapons, to wit, to false with one, and to strike home, either with the self same, or with the other weapon: and likewise discover with the one, and ward with the self same, or with the other, the which never yet to this day was or might be done with any other weapon. For in the handling of other weapons, that which falses, does in like manner strike home, so that of force, there are spent two times: for which consideration men hold opinion, that falsing is occasion both of great hurt, and also of loss of time. But yet this happens not in these weapons, which forasmuch as they are two, and are of equal power both in striking and defending, may be handled both after one fashion. And presupposing always that one is skillful to handle the one as well as the other, he may discharge at self same time two thrusts, two edge-blows, both right and reversed. |
To bear both swords with their points backward: for this maner of warding, is as if one would of purpose cause himselfe to be slaine: or else to beare both aloft, which a man may hardlie sustaine, considering the paizes of the swords are naturally heauie and tend downewardes, so that the armes are much cumbred thereby. Therefore from theis two which are framed without, shalbe laide downe, all those which may be founde and may be framed in the handling of theis weapons: as for example, high wardes, lowe, wide, altered, diminished, and al those wards which are mixt, as to frame with one sworde the high warde, with the other the broad warde, and to frame the lowe and broad warde, the high and lowe ward, two lowe wardes, and two broade wardes: but yet these last two are as painfull as the two high wardes, and therefore shall not be vsed. Moreouer, a man may beare one sworde with the poynt forwards, and the other backewards, and he may further, verie easely finde out and practise diuers other waies, if he consider in how manie waies a man may moue his hands [152] his armes, his feete, and his whole person: for each of theis motions are sufficient of themselues, to alter the warde. In all theis wardes, he may with either hande and sword, practise to false against the enimie, sometimes by fayning, sometimes by discouerie. And this is properlie belonginge to theis weapons, to wit, to false with one, and to strike home, either with the selfe same, or with the other weapon: & likewise discouer with the one, and ward with the selfe same, or with the other, the which neuer yet to this daie was or might be done with any other weapon. For in the handling of other weapons, that which falceth, doth in like manner strike home, so that of force, there are spent two times: for which consideration men hold opinion, that falsing is occasion both of great hurte, and also of losse of time. But yet this happeneth not in these weapons, which forasmuch as they are two, and are of equall power both in striking and defending, may be handled both after one fashion. And presupposing alwaies that one is as skilful to handle the one aswelas the other, he may discharge at selfe same time two thrustes, two edgeblowes, both right & reuersed. | ||
But if he would exercise himself only in sport and play, he shall then continually use to strike his enemy with one, and defend his person with the other. Therefore when one deals against an enemy that has two swords, one of the which may always increase a pace, and strike either with a thrust, or with the edge, from that sword he must take heed to ward himself, for it is very forcible, and always brings great danger and peril with it: The other sword which was before, makes no increase of pace and therefore cannot strike more than the defense and strength of the arm will bear, and that is weak to strike, but yet very strong to defend: and the selfsame accidents and qualities, which are found to be in the enemy, are incident also to ourselves. Wherefore one finds that he stands with his right foot before, be it in any ward whatsoever, he may false with the fore sword and strike home with the same, or else he may false with his hind sword, and strike with the selfsame: or else after a third way, to wit, to false with the one, and hit home with the other: And this kind of false, does more properly belong to the two swords than any other, but yet he must take heed and very well remember that while he falses with the one, and would strike home with the same, that he bear the other directly opposite against the enemy. For whilst the enemy is bound to ward the false, and homeblowe of the one sword, he may come in with the other and strike, if he find any place either discovered or easy to enter: So that bearing this rule continually in remembrance, which is in the fight of two swords, to bear always the one directly against the enemy, to the intent to hinder him, that he resolve not himself to enter, he shall endeavor to false, sometimes with the one, and sometimes with the other sword, sometimes a thrust, sometimes an edge-blow, and then to drive it home, either with the same sword that falses, or else with the other. But in practice, and doing of all of this, it is required that he be of deep judgment, knowing presently upon the false, what art of the body the enemy discovers, increasing thither, and investing the enemy with that sword which is most nigh to that part, and with the which he may most safely strike. |
But if he would exercise himselfe onelie in sporte & plaie, he shal then continually vse to strike his enimie with one, and defend his person with the other. Therefore when one dealeth against an enimie that hath two swords, one of the which maie alwaies encrease a pace, and strike either with a thrust, or with the edge, from that sword he must take heede to warde himeselfe, for it is verie forcible, and alwaies bringeth great daunger and perill with it: The other [153] sword which was before, maketh no increase of pace and therefore cannot strike more then the defence & strength of the arme will beare, and that is weake to strike, but yet verie strong to defend: and the self same accidentes and qualities, which are found to be in the enimie, are incident also to our selues. Wherefore when one findes that he standeth with his right foot before, be it in any warde whatsoeuer, he may false with the forsword and strik home with the same, or else he may false with his hinder sword, & strike with the selfe same: or else after a third waie, to wite, to false with the one, and hit home with the other: And this kind of false, doth more properlie belong to the two swords then any other, but yet he must take heede and veriewell remember that whilest he falceth with the one, and would also strike home with the same, that he beare the other directly opposite against the enimie. For whilest the enimy is bound to warde the false, and homeblowe of the one sword, he may come in with the other and strike, if he finde any place either discouered or easie to enter: So that bearing this rule continuallie in remembrance, which is in the fight of two swords, to beare alwaies the one directly against the enimie, to the entent to hinder him, that he resolue not himself to enter, he shall indeuour to false, sometimes with the one, and sometimes with the other sword, some times a thrust, some times an edgeblowe, and then to driue it home, either with the same sword that falceth, or else with the other. But in the practise, and doing of all this, it is required that he be of deepe iudgement, knowing presently vpon the false, what parte of the bodie the enimie disco- [154] uereth, increasing thither, and inuesting the enimie with that sword which is most nigh to that parte, and with the which he may most safelie strike. | ||
And it is to be considered, that it is a very strong and short way of striking, to false with the fore sword either a thrust or an edge-blow, and to false them not once or twice, but diverse times, now aloft, now beneath, sometimes with a thrust, sometimes with an edge-blow, to the intent, to blind and occupy the enemy's both swords, and at last when fit occasion serves, to strike it home with the hind sword: but yet always with the increase of a pace. The false which may be practice with the hind sword, is unprofitable being make without the motion of a pace, for it is so short that it is to no purpose. Therefore it cannot busy the enemy's swords in such manner, that it may force him either to discover or disorder his body. From whence it may be gathered, that after this false of the hind sword, it is no sure play to strike either with the selfsame hind sword, or else with the fore sword, because the enemy was neither in any part discovered or troubled. The best thing therefore that may be done, if one would false with the hind sword, is, to drive either a thrust or an edge-blow, resolutely striking with the increase of a pace, and as the enemy moves to defend himself, to strike him with the same sword, in some place that is discovered: For he cannot strike with the other sword for by that means of the increase of the hind sword, that the sword which was before, remains now behind, So that it may not strike, except it increase a pace, and to increase again, were to spend much time. Therefore when one endeavors with the increase of a pace to force his sword within, he shall assay to strike it home, with the selfsame sword because as I have before said, to strike with the other were too long. Wherefore I will lay down this for a rule, in the handling of these weapons, that if a man false with the fore sword, he may also strike home with the same or with the other, so that he increase And if he false with the hind sword, he shall presently, and resolutely force the blow home with the same sword, but yet with the increase of a pace: but if he do not fully deliver it, he shall again procure immediately to strike home with the selfsame sword, either with a thrust, or edge-blow, be it high or low, as at that instant shall be most commodious to serve the turn. |
And it is to be considered, that it is a verie strong & short waie of striking, to false with the fore sworde either a thrust or an edgeblowe, and to false them not once or twice, but diuers times, now alofte, now beneath, some times with a thrust, some times with an edgeblowe, to the entent, to blinde and occupie the enimies both swords, and at the last when fit occasiō serueth, to strike it home with the hinder sworde: but yet alwaies with the encrease of a pace. The falce which may be practised with the hinder sword, is vn profitable being made without the motion of a pace, for it is so shorte that it is to no purpose. Therefore it cannot busie the enimies swordes in such manner, that it may force him either to discouer or disorder his bodie. From whence it may be gathered, that after this false of the hinder sword, it is no sure plaie to strike either with theselfe same hinder sword, or else with the fore sword; because the enimie was neither in any parte discouered or troubled. The best thing therfore that may be don, if one would false with the hindersword, is, to driue either a thrust or an edgeblow, resolutelie striking with the encrease of a pace, and as the enimie moueth to defend him selfe, to strike him with the same sworde, in some place that is discouered: For he cannot strike with the other sword for that by meanes of the encrease of the hinder sword, that sword which was before, remaineth now behinde, So that it may not strike, except it encrease a pace, and to encrease againe, were to spende [155] much time. Therefore when one endeuoreth with the encrease of a pace to force his sword within, he shall assaie to strike it home, with the selfe same sword because as I haue before said, to strike with the other were to long. Wherefore I wil laie downe this for a rule, in the handling of theis weapons, that if a man false with the foresword, he may also strik home with the same, or else with the other, so that he increase a pace. And if he false with the hinder sword, he shall presently, and resolutely force the blow home with the same sword, but yet with the increase of a pace: but if he doe not fullie deliuer it, he shall againe procure immediatly to strike home with the selfe same sword, either with a thrust, or edgeblowe, be it high or lowe, as at that instant shall be most commodius to serue the turne. | ||
An advertisement concerning the defenses of the two swords, or rapiers In sport or play one may stand every way against the enemy, to wit, if the enemy be on high, to settle himself at his ward, low or broad. But it is more gallant to behold and more commodious indeed to place himself against the enemy in the very selfsame foot before, and in the very same site that he is in, either high or low. For standing in such manner, the enemy may hardly endeavor with his false, to trouble or busy both swords. And moreover it must be considered, that the fore sword is that which wards both falses, and resolute blows, the which it does very easily perform: For it be borne aloft, then by the bending of the point down, it defends that part of the body, to the which it is turned. Remembering therefore these rules, which are, to stand every way as the enemy does, and to ward his falses with the fore sword, I say, where any falses or blows come: then as soon as he has warded them with the fore sword, he shall increase a slope pace, and with the hind sword deliver either a thrust at some discovered place, either a right blow with the edge at the legs, or else (which is better) shall fetch a reverse, either athwart the face, or else athwart the arms, and his blow does most easily speed: for the enemy's fore sword is occupied, and his hind sword cannot come to oppose itself against this blow: neither may it so easily strike, because (by the increase of the foresaid slope pace) the body is moved out of the straight line, so that the enemy may not so commodiously strike with his hind sword, but that he shall be first struck on the face or on the arms. |
An aduertisement concerning the defences of the two Swordes, or Rapiers. IN sport or plaie one may stande euerie waie against the enimie, to witte, if the enimie be on high, to settle himselfe at his warde, lowe or broad. But it is more gallant to beehold and more commodius indeed to place himself against thenimy in the very self same manner as he findeth him, with the self same foote before, and in the very same site that he is in, either high or lowe. For standing in such manner, the enimie may hardly endeuour with his false, to troble or busie both swords. And moreouer it must be considered, that the fore sworde is that which wardeth [156] both falses, and resolute blowes, the which it doth verie easily perfourme: For if it be borne aloft, then by the bending of the point down, it defendeth that part of the bodie, to the which it is turned. Remembring therefore these rules, which are, to stand euery way as the enimie doth, & to warde his falses with the fore-sworde, I saie, where any falses or blowes come: then as soone as he hath warded them with the fore-sword, he shall encrease a slope pace, & with the hinder sworde deliuer either a thrust at some discouered place, either a right blowe with the edge at the legges, or els (which is better) shall fetch a reuerse, either athwart the face, or els athwart the armes, and this blowe doth most easily speede: for the enimies fore-sworde is occupied, and his hinder sworde cannot come to oppose it selfe against this blowe: neither may it so easily strike, because (by encrease of the foresaid slope pace) the bodie is moued out of the straight lyne, so that the enimie may not so commodiously strike with his hinder sword, but that he shalbe first stricken on the face or on the armes. | ||
Wherefore, let every man resolve himself, (as soon as he has encountered the enemy's sword with his own fore sword) that he step in and strike with his hind sword. Neither, let him stand in fear of the enemy's hind sword: for either it cannot hurt because the body is voided (as I have said,) or else, if it may, it must presently provide to stand to his defense, and thereto is so bound, that it may do no manner of hurt. |
Wherefore, let euery man resolue himselfe, (as soone as he hath encountred the enimies sword with his owne foresworde) that he step in and strike with his hinder sworde. Neither, let him stand in feare of the enimies hinder sworde: for either it cannot hurt because the bodie is voyded (as I haue saide,) or els, if it may, it must presently prouide to stand to his defence, and thereto is so bound, that it may do no manner of hurte. | ||
Of the two hand sword For the deceits and falses of the two hand sword, there is no more regard to be taken in the handling thereof single, that is, one to one, then there is, when it is used among many: only this end is to be purposed, to wit, to move and handle with all nimbleness and dexterity, as well the edge as the point, fetching those great circular and unruly compassings, therewith as his form, greatness, and manner of holding requires. |
[137] DEL SPADONE. PER gli inganni et finte del spadone non si ha da hauer rispetto ad addoprarlo piu da solo a solo che fra molti, ma solamente si ha da hauer questo fine di muouerlo & addoprarlo con agilità & prestezza cosi di taglio come di punta facendo quei gran giri & sbaragli che richiede la sua forma grandezza, & modo di tenir, |
[157] Of the two hand sword FOr the deceites & falses of the two hande sworde, there is no more regarde to be taken in the handling thereof single, that is, one to one, then there is, when it is vsed among manie: onelie this end is to be purposed, to witte, to moue and handle with all nimblenesse and dexterity, aswel the edge as the poynt, fetching those great circuler and vnruly compassinges, therewith as his fourme, greatnesse, and manner of holding requireth. | |
Neither ought a man so much regard to fetch a small or great compass, or to strike more with the point then with the edge, but must believe only that the victory consists in the nimble and active guiding there of any manner of way. Therefore there may be framed many wards, of all the which, being a thing superfluous to reason of, I will handle only six of them, which are most commodious and usual: whereof the first may be called the high ward, the second the broad ward, the third the low ward, from which there springs all other three, towards the other side, making six in all. |
ne si deue hauere in consideratione il far giro picolo o grande ne ferir piu di punta che di taglio, ma solamente creder che la uittoria stia nell'esser presto & destro a menar in qual si uoglia modo, però si possun formar molte guardie delle quali tutte sarebbe superfluo il ragionarne onde di sei solamente si tratterà piu commode & piu usitate delle quali una si adi= [138] mandera alta la seconda largha la terza bassa, dalle quali tre ne nascono poi tre altra uerso laltra parte che son in tutto sei, |
Nether ought a man so much to regard to fetch a small or great compasse, or to strike more with the point, then with the edg, but must beliue onely that the victorie consisteth in the nimble and actiue guiding thereof anie manner of waie. Therefore there may be framed manie wards, of al the which, beinge a thinge superfluous to reason of, I will handle onely sixe of them, which are most commodius and vsuall: wherof the first may be called the high warde, the second the broad warde, the third, the low warde, from which there springeth all other three, towardes the other side, making sixein all. | |
The high ward is framed by bearing the sword and arms lifted up on high and wide from the body, with the point of sword turned towards that part, as that arm is, whose hand is place by the cross, that is to say, if the right hand shall be at the cross, and the right foot before, to bear also the sword, with his point towards that side. |
la alta sarà tenir il spadone & le braccia in alto leuate & larghe dalla uita, con il spadone con la punta uolta uerso quella parte che sarà il braccio che haurà la mano al la croce, cio e, se la man destra sarà alla croce & il pie destro inanzi, tenir ancora il spadone uerso quella parte con la punta, |
The high warde is framed by bearing the sworde and arms lifted vp on high and wide from the body, with the poynt of sword turned towardes that parte, as that arme is, whose hand is placed by the crosse, that is to saie, if the right hand shalbe at the crosse, & the right foote befoore, to beare also the sword, with his poynt towardes that side. | |
There is also another high ward opposite to this and that is, without moving the feet at all to turn the point towards the other side, that is, towards the left side and to cross the arms. And it is to be noted, that in this high ward, be it on what side it will, the sword is to be borne with the point turned downwards. |
un'altra alta opposta a questa sarà senza punto muouer i piedi uolger la punta uerso l'altra parte cioè uerso la sinistra, & incrocciar le braccia & e da auertir che in questa guardia alta sia in qual parte si uoglia, sempre si deue tenir il spadone con la punta uolta in giu, |
There is an other hie warde opposite to this & that is, without mouing the feete at all to turne the poynt towardes the other side, that is, towardes the left side [158] and to crosse the armes. And it is to be noted, that in this high warde, be it on what side it wil, the sword is to be borne with the poynt turned downewardes. | |
The second is the broad ward, and must be framed with the arms widened from the body, not high but straight. And from this springs and is framed another broad ward, turned towards the other side by crossing of the arms. |
la seconda sarà largha con le braccia dalla uita allarghate non alte ma diritte & medesmamente il spadone diritto, da questa se ne formerà un'altra largha uolta uerso l'altra parte incrociando le braccia, |
The second is the broad warde, & must be framed with the armes widened from the body, not high but straight. And from this springeth and is framed an other broad warde, turned towards the other side by crossing of the armes. | |
And the third is the low ward, and in this the sword would be borne with the point somewhat upwards. And this ward has his opposite or contrary, by turning the sword on the other side, and crossing the arms. There may be framed many other wards: As for example, to bear the sword on high, with the point backwards, to the intent to drive a down right, or cleaving edge-blow: or else to bear it low with the point backwards, to the intent to drive it from beneath upwards. But in these wards falses are to small purpose: And if there be any one of them worth using, it should be the false of an edge-blow, the which at two hand sword is not to be used at all, because there is much time lost considering that immediately after the false, he must strike home with an edge-blow. For it is not commodious at the two hand sword, to false an edge-blow, and deliver home a thrust, because the weight or swing of the sword in delivering an edge-blow, transports the arms beyond their strength, so that they may very difficultly withhold the blow to such purpose, that they may be ale as it were in that instant to deliver a thrust. Therefore the false that should be used at the two hand sword, ought always to be framed with a thrust, and then an edge-blow right or reversed to be delivered, or else to false a high thrust, and deliver it beneath or elsewhere. But yet if one would needs false an edge-blow, let him do it with the false edge of the sword, then turning it in full circle, to deliver home the edge-blow, and in striking always to increase a pace. But when this false of the back or false edge is practiced, the arms being crossed, then if he would step forwards to strike he must increase a pace with the right foot. And if in any of these wards he would false a thrust, which is the best that may be used at the two hand sword, he must observe the very same notes and rules concerning the increasing of the pace. Further the thrust is falsed, and the edge-blow delivered home at the two hand sword for no other cause or consideration, then for that the said edge-blow is far more forcible then the thrust: For the two hand sword is long, by means whereof, in the delivery of the edge-blow, it makes a great circle. And moreover, it so weighty that very little and small strength, makes and forces the blow to go with great violence. But for as much as the striking with the edge is very dangerous considering it spends much time, and especially in the great compassing of the two hand sword, under which time wary and active persons may with the sword or other weapon give a thrust, therefore for the avoiding of this danger, he must before he determine with himself to strike with the edge, first drive on a thrust, rather resolute then falsed, and as far forwards as both arms will stretch. In doing of the which, he shall force the enemy to retire so much, that he may easily thereupon deliver his edge-blow with the increase of a pace, nothing doubting that the enemy will strike home first with a thrust. Therefore when one stands at the high ward, one either side he must false a thrust, and increase a pace delivering therewithal such an edge-blow, as shall be most commodious to serve his turn, either right or reversed. And further may practice the like in the broad and low wards, in either of the which, it is more easy to false the said thrust, then in the other. |
la terza sarà bassa ma in questa il spadone uuole esser tenuto con la punta un poco all'insu, & hauera la sua bassa opposta uolgendo il spadone nell'altra parte & incrociando le braccia, molte altre guardie si possono porre come tenir il spadone alto con la punta indietro per menar di taglio fendente, ouero tenirlo basso con la punta indietro per uenir a menar di sotto in su, ma a queste guardie riescono mal le finte & se pur alcuna finta in esse douesse riuscir, sarebbe finta di taglio la quale nel spadone a modo alcuno si deue usare per che ui si perde molto tempo, douendo doppo quelle finte ancora ferir di taglio per che non torna commodo con il spadone finger il taglio & ferir di punta percioche il peso del spadone nel ferir di taglio [139] straporta le braccia onde difficilmente si puo ritener per ferir di punta, però la finta che si deura fare con il spadone deura sempre esser di punta, & ferir con il taglio o di dritto o di riuerso, ouero finger una punta alta & trarla bassa o in altro loco, & quando pure si uolesse finger il taglio, si deue finger il falso, & uoltar il tondo & ferir di taglio, & ferendo sempre crescer il passo, & quando questa finta di falso si fa hauendo le braccia in crociate & che dopo la finta si uoglia menar il riuerso, all'hora si cresce il passo sinistro, & trouandosi in qualunque delle altre guardie senza hauer le mani in croce, all'hora uolendo poi crescer a ferir si cresce il passo destro ; le medesme auertenze si danno hauer circa il crescer, uolendo in ciascuna di esse guardie finger la punta la quale e la miglior finta poßi fare il spadone, & non per altro con il spadone si finge la punta, & si ferisce di taglio se non per che il taglio ha molto piu forza che non ha la punta, per esser il spadone lungho onde forma nel ferir di taglio gran cerchio, & e poi di tanto peso che ogni poca forza lo fa colpir con gran uiolenza, 'ma percioche questo ferir di taglio e molto mal sicuro per che ui si perde molto tempo maßime nel giro grande delspadone, fatto ilqual tempo puo ogni accorto & presto ferir con spada o altro di punta, onde che per uitar questo pericolo prima che si risolua alcuno a ferir di taglio bisogna prima, spinger una punta che sia più presto risoluta che finta, per quanto si puo allungar ambe le braccia, con la quale si sara tanto ritirar l'inimicò che |
The third is the lowe warde, and in this the sword would be borne with the poynt some what vppwardes. And this warde hath his opposite or contrarie, by turning the sword on the other side, and crossing the armes. There may be framed manie other wardes: As for example, to beare the sword on high, with the poynt backewardes, to the entent to driue a downe right, or cleauing edge-blowe: or else to beare it lowe with the poynt backwardes, to the entēt to driue it from beneath vpwards. But in theese wardes falses are to small purpose: And if there be any one of them worth the vsing, it should be the false of an edgeblowe, the which at the two hand sworde is not to be vsed at all, because there is much time lost considering that immediatlie after the false, he must strike home with an edgeblow. For it is not commodius at the two hand sword, to false an edgeblowe, & deliuer home a thrust, because the waight or swing of the sword in deliuering an edge-blowe, transporteth the arms beyond their strength, so that they may verie difficultlie withhold the blow to such purpose, that they may be able as it were in that instant to deliuer a thrust. Therefore the false that should be vsed at the two hand sword, ought alwaies to be framed [159] with a thrust, and then an edgeblow right or reuersed to be deliuered, or else to false a high thrust, and deliuer it beneath or else where. But yet if one would needes false an edgeblowe, let him do it with the false edge of the sword, then turning it in full circle, to deliuer home the edgeblowe, and in striking alwaies to encrease a pace. But when this false of the backe or false edge is practised, the armes being crossed, & that presentlie after the false, one would deliuer home a reuerse, then he must encrease a left pace, And when he findeth in himself any other warde, his hands not being crossed, then if he would step forwards to strike he must encrease a pace with the right foote. And if in any of theese wardes he would false a thrust, which is the best that may be vsed at the two hand sword, he must obserue the verie same notes and rules concerning encreasing of the pace. Further the thrust is falsed, and the edge-blowe deliuered home at the two hand sword for no other cause or consideration, then for that the saide edgeblowe is farre more forcible then the thrust: For the two hand sword is long, by meanes whereof, in the deliuerie of the edgeblow, it maketh a great circle. And moreouer, it is so weightie that verie litle and small strength, maketh & forceth the blow to goe with great violence. But for as much as the striking with the edge is verie daungerous cōsidering it spendeth much time, and especially in the great compassing of the two hand sworde, vnder which time warie & actiue persons may with sword or other wepon giue a thrust, Therefore for the avoiding of this dāger, he must before he determin with himself to strik with the edg, first driue on a thrust, rather [160] resolut then falsed, and as farr forwardes as both armes will stretch. In doing of the which, he shal force the enimie to retire so much, that he may easely therevpon deliuer his edgeblowe with the encrease of a pace, nothing douting that the enimy wil strike home first with a thrust. Therefore when one standeth at the high warde, on either side he must false a thrust, & encrease a pace deliuering there withal such an edgeblowe, as shal be most commodius to serue his turne, either right or reuersed. And further may practise the like in the broad and lowe wardes, in either of the which, it is more easye to false the said thrust, then in the other. | |
And it is to be considered, when the edge-blow after the falsed thrust, is by a slope pace voided, that he suffer not his arms and sword by reason of the weight or swing thereof, far transported beyond his strength, that the sword light either on the ground or that he be forced thereby to discover all that part of his body which is before. Therefore the best remedy is, as soon as he shall perceive that he has delivered his blow in vain, that he suffer his sword to go (not with a full thwart circle, and so about his head) until the point be backwards beneath in such sort, that the circle or compass direct him to the high ward, in the which he may presently resolve himself and return either to strike again, or else defend himself on either side, so handling his weapon, as shall in that case be most for his advantage. |
& è da auertir che quando auenisse che il taglio dopo la finta andasse uoto di non si lasciar trasportar in modo al peso del spadone che si dia o in terra, o che si resti della spada scoperti, & di tutta quella parte che è dinanzi, però subito che si accorgerà di hauer menato in uano si lasciera andar il spadone non di tutto tondo in torno alla testa ma con la punta indietro per da basso di modo che il giro lo porti in guardia alta nella quale poscia subito si puo risoluer di tornar a ferir o a difendersi da qual si uoglia banda formandola secondo che in quel caso piu torna comodo. |
And it is to be considered, when the edgeblow after the falced thrust, is by a slope voided, that he suffer not his arms and sword by reason of the waight or swinge thereof, to be so farr transported beyonde his strength, that the sword light ether on the groūd or that he be forced thereby to discouer all that parte of his bodie which is before. Therefore the best remedie is, as soone as he shal perceiue that he hath deliuered his blowe in vaine, that he suffer his sword to go (not with a full thwarte circle, and so about his head) vntill the poynt be backwardes beneath in such sort, that the circle or compasse direct him to the high warde, in the which he may presently resolue himself and returne either to strike againe, or else defend him selfe on either side, so handlinghis weapon, as shal in that case be most for his aduantage. | |
The defenses of the two hand sword The defenses of the two hand sword require a stout heart, for that the sustaining of such great blows, by reason whereof, a man considers not the advantage of time, being the most principal thing of all, causes him to fly or retire back holding for a certainty that every blow given therewith, is not possible to be warded. Therefore when he deals against an enemy, who uses likewise the two hand sword, he shall oppose himself in the low ward: And when a false thrust comes, if it come so far forwards that it may join home, he ought first to beat it off, and then to force a thrust at the enemy's face, or deliver an edge-blow downwards at the arms but not lifting up the sword in a compass. But for that these falsed thrusts for the most part are far off, and come not to the body, being used only to fear the enemy, and cause him to retire, that thereby one may have the more time to deliver an edge-blow with the increase of a pace (which pace causes the blow to go with greater violence:) and farther may discern and judge, by nearness of the enemy, whether the blow will hit home yea or no, for it is easily known how much the arms may be stretched forth: Therefore when this false thrust does not join or hit home, he ought not to endeavor to beat it off, but to expect when his enemy delivers his edge-blow, and then to increase a pace, and strike him with a thrust. |
DEL DIFFENDERE COL spadone. LE DIFFESE del spadone richiedono un cuore ardito, perche il tenere quei gran colpi del sapdone & percio non uoler considerar l'auantaggio del tempo che è il principal fa che gli huomini fugono tenendo, per certo che ognibota di quello sia irreparabile, ritrouandosi dunque contra l'inimico con un altro spadone, gli si opponera sempre la guardia bassa & uenendo la finta punta se ella uien tanto inanti che possa giungere, prima che giunga si deue bater spingendoli subito una punta alla faccia oue [141] ro tirando giu di taglio per le braccia senza leuar il spadone in cerchio, ma perche queste punte finte al piu delle uolte son lontane, & non giongono alla uita, & son tratte per spauentare & far ritirar, per poter poi hauer tempo di menar il taglio con la cresciuta del passo che ua con maggior furia, & di questo poter giungere, o non, se ne può far giuditio, dalla uicinita dell'inimico,perche molto ben si fa quanto puo distender le braccia, quando dunque non potesse giungere non si deue curar di baterla ma espetar che leui il spadone per menar di taglio & in quel tempo crescer & ferir di punta, |
[161] The Defences of the two Hand sword. THe defences of the two hand sworde require a stout hearte, for that the susteining of such great blowes, by reason whereof, a man considereth not the aduātage of time, being the most principal thing of al, causeth him to flie or retire backe holding for a certaintie that euerie blowe giuen therwith, is not possible to be warded. Therefor when he dealeth against an enimie, who vseth likewise the two hand sword, he shall appose himselfe in the low ward: And when a false thrust commeth, if it come so fare forwardes that it may ioyne home, he ought first to beate it off, and then to forse a thrust at the enimies face, or deliuer an edgeblow downwards at the armes but not lifting vp the sword in a cōpasse. But for that theese falced thrustes for the most part are farr off, & come not to the bodie, being vsed onelie to fere the enimie, and cause him to retire, that therby one may haue the more time to deliuer an edge-blow with the encrease of a pace (which pace causeth the blowe to go with greater violence:) nd farther may discern & iudge, by nearenesse of the enimy, whether the blow will hit home yea or no, for it is easelie knowen howe much the armes may be stretched forth: Therefore when this false thrust doth not ioyne or hit home, he ought not to endeuour to beate it off, but to expect when his enimie deliuereth his edgeblowe, & then to encrease a pace, and strike him with a thrust. | |
But if it happen him to deal against a two hand sword, with a single sword or dagger, assuring himself that the two hand sword cannot but strike but with a thrust or an edge-blow, for the defense of the thrust he may beat it off and retire himself, but if it be an edge-blow, then, as soon as the two hand sword is lifted up, in the same time he must increase forwards and deliver a thrust, or else if he have no time to strike he must encounter and bear the blow in the first part of the sword, which is near the hilts, taking hold thereof with one hand, and striking him with the other. And this he may perform, if he be nimble and active, because the two hand sword carries but small force in that place. |
& accadendo che si ritrouasse esser contra un spadone con una sola spada o pugnale essendo certo che non puo menar se non o di punta o di taglio, per riparar le punte si puo baterle & ritirarsi, ma se uiene al menar di taglio, subito che leua il spadone bisogna iu quel tempo crescer inanzi & ferir di punta, o non hauendo tempo di ferir incontrar & sostenir il colpo del spadene nelle prime parti facendone con luna delle mani presa & con laltra ferendo, & questo uien fatto pur che si sia presto perche in quel luoco il spadone ha poca forza. |
But if it happen him to deale against a two hande sworde, with a single sword or dagger, assuring him selfe that the two hand sword cannot strike but with a thrust or an edgeblow, for the defence of the thrust [162] he may beate it off and retire himselfe, but if it be an edgeblowe, then, as soone as the two hand sword is lifted vp, in the same time he must encrease forwards and deliuer a thrust, or else if he haue no time to strike he must encounter & beare the blow in the first parte of the sworde, which is neare the hiltes, taking holde thereof with one hande, and striking with the other. And this he may performe, if he be nimble & actiue, because the twohand sword carieth but smal force in that place. | |
Of the partisan, bill, javelin and halberd Deceits or falses, are more manifest and evident in these, then in short weapons which are handled only with one hand because both the arms are moved more slowly than one alone. And the reason thereof is, that considering they are more long, they therefore frame in their motions a greater compass: and this is perceived more in edge-blows then in thrusts. Therefore the best false that may be practiced in the handling of these weapons, is the false of the thrust, and that the edge-blow ought never or seldom to be used, except great necessity constrain, as shall be declared. Wherefore in these weapons, I will frame four wards, three of them with the point forwards, of which three, the first is, the point of the sword being borne low, and the hind arm being lifted up. |
Of the Partesan, Bil, Iauelin and Holberde. DEceites or falses, are all more manifest and euident in these, then in shorte weapons which are handled onely with one hand because both the arms are moued more slowly then one alone. And the reason thereof is, that cōsidering they are more long, they therefore frame in their motions a greater compasse: and this is perceiued more in edgeblowes then in thrustes. Therefore the best false that may be practised in the handling of these weapons, is the false of the thrust, and that the edgeblow ought neuer or seldome to be vsed, except great necessitie constrain, as shalbe declared. Wherefore in these weapons, I wil frame foure wards, three of them with the poynt forwardes, of which three, the first is, the poynt of the sword being borne lowe, and the hinder arme being lifted vpp. | ||
The second is, the point high, the right arm being behind and borne at low. The third, the point equal and the arms equal: And in every one of these a man must false without, and drive it home within, or false within and deliver it without, or false aloft and strike beneath, and so contrariwise. But as he falses within or without, he ought to remember this note, which is, he must always to the intent he may go the better covered and warded, compass the hindfoot to that part, to the which the weapon shall be directed to strike home after a false. |
The second is, the poynt high, the right arme being behinde and borne alowe. [163] The third, the poynt equall and the armes equall: And in euerie on of these a man must false without, and driue it home within, or false within and deliuer it without, or false aloft and strike beneth, & so contrariewise. But as he falseth within or without, he ought to remember this note, which is, he must alwaies to the entent he may goe the better couered & warded, compasse the hinderfoot to that parte, to the which the weapon shalbe directed to strike home after a false. | ||
The fourth ward which is much used, and especially with the bill, shall be to bear the weapon with the blunt end or heel forwards, the edge being lifted up on high. And this is much used, to the intent to expect the enemy's blows, and that thereby a man may be better able to ward them, either with the heel or middle of the staff, and then to enter and strike delivering an edge-blow with the increase of a pace, the which manner of striking is most ready and nimble. The false which may be used in this ward, is when he has warded the enemy's blow with the heel of his weapon, and then would increase forwards to deliver an edge-blow, if the enemy shall lift up or advance his weapon to defend himself from the said blow, then he shall give over to deliver that blow, by retiring his weapon, and give a thrust underneath, with the increase of a pace. |
The fourth warde which is much vsed, and especially with the bill, shalbe to beare the weapon with the bluntende or heele forwardes, the edge being lifted vpp on high. And this is much vsed, to the entent to expect the enimies blowes, and that thereby a man may be better able to warde them, either with the heel or midle of the staff, & then to enter & strik deliuering an edgblo with thencreas of a pace, the which maner of striking is most ready and nimble. The false, which may be vsed in this ward, is whē he hath warded thenimies blo with the heel of his wepon, & thē would encrease forwardes to deliuer an edgeblowe, if the enimie shall lift vpp or aduance his weapon to defend himselfe from the said blowe, then he shall giue ouer to deliuer that blowe, by retiring his weapon, and giue a thrust vnderneath, with the encrease of a pace. | ||
And this kind of blow is very likely to work his effect without danger, if he aptly and nimbly used. |
And this kind of blowe is verie likely to work his effect without danger, if it be aptly and nimbly vsed. | ||
Of the pike There may be used some deceit also in the Pike, although it be a weapon void of any crooked forks, and is much more apt to show great valor then deceit. And for as much as it has no other then a point to offend, and length to defend, for that cause there may be used no other deceit therewith, then with the point: and considering true art, is not the mark that is shot at in this place: I say, it may be borne after diverse fashions, as shall be most for a man's advantage, as either at the end, either in the middle, either more backwards, either more forwards, as shall be thought most commodious to the bearer. Likewise, one may frame three wards therewith, to wit, the first straight, with the arms equal: the second with the point low, the third, the point high, falsing in each of them a thrust, either within, either without, ether high, either low, and then immediately forcing it on resolutely, but contrary to the false, and carrying always the hind foot towards that side, to the which the Pike is directed to strike. In handling of the pike, a man must always diligently consider, so to work that the hind hand be that which may rule, drive on, draw back and govern the Pike, and that the fore hand serve to no other purpose then to help to sustain it. |
[164] Of the Pike. THere may be vsed some deceite also in the Pike, although it be a weapon voide of any crooked forkes, and is much more apte to shew great valure then deceite. And for as much as it hath no other then a poynt to offend, and length to defend, for that cause there may be vsed no other deceit therewith, then with the poynt: & considering true art, is not the mark that is shot at in this place: I saie, it may be borne after diuers fashions, as shalbe most for a mannes aduantage, as either at the ende, either in the midle, either more backewardes, either more forwardes, as shal be thought most commodius to the bearer. Likewise, one may frame three wardes therewith, to witte, the first streight, with the arms equall: the second with the poynt low, the third, the poynt high, falsing in each of them a thrust, either within, either without, ether high, either lowe, and then immediatly forcing it on resolutely, but contrarie to the false, and carying alwais the hinder foote towardes that side, to the which the Pike is directed to strike. In handling of the pike, a man must alwaies diligentlie consider, so to worke that the hinder hand be that which may rule, driue on, draw back and gouerne the Pike, and that the fore hand serue to no other purpose then to helpe to susteine it. | ||
The defenses of the deceits of the weapons of the staff I have not as yet laid down the defense of the Bill, and the rest, because they are all one with this of the Pike. And I mind to handle them briefly all together, considering that in these a man may not either render false for false, or take holdfast of the weapon. And although it might be done, I commend it not, because it is a very difficult matter to extort a weapon that is held fast with both hands. That therefore which one may do to defend himself, is to have recourse unto true Art, remembering so to ward the enemy s if it were a true blow, and to strike before the enemy spend another time, in delivering his resolute thrust, And to take heed in delivery of his blows, that he be nimble and carry his body and arms so aptly and orderly applied, that the weapon wherewith he strikes may cover it wholly. |
The defences of the deceites of the weapons of the Staffe. I Haue not as yet laide downe the defence of the Bil, and the rest, because they are all one with this of the Pike. And I minde to handle them briefelie all togeither, considering that in these [165] a man may not either render false for false, or take holdfast of the weapon. And although it might bee done, I commend it not, because it is a verie difficult matter to extort a weapon that is holden fast with both handes. That therefore which one may doe to defend himselfe, is to haue recourse vnto true Art, remembring so to warde the enimies falce, as if it were a true blowe, and to strike before the enimie spend an other time, in deliuering his resolute thrust, And to take heede in deliuerie of his blowes, that he be nimble and carrie his bodie and armes so aptlie and orderlie applied, that the weapon wherewith he striketh may couer it wholy. | ||
And here I make an end of deceit, in practicing of the which, there is this consideration to be had, so, always to false, that if the enemy provide not to ward, it may reach and hit home, because being delivered in such order, it loses but little time. |
And here I make an ende of disceit, in practising of the which, there is this consideration to be had, so, alwaies to false, that if the enimie prouide not to ward, it may reach & hit home, becaus being deliuered in such order, it loseth but little time. | ||
The end of the false art |
The ende of the false Arte. |
Figures |
Archetype (1570) |
English Translation (1594) | |
|---|---|---|---|
How a man by private practice may obtain strength of body thereby If nature had bestowed strength upon men (as many believe) in such sort as she has given sight, hearing and other senses, which are such in us, that they may not by our endeavor either be increased, or diminished, it should be no less superfluous, than ridiculous to teach how strength should be obtained, than it were if one should say, he would instruct a man how to hear or see better than he does already by nature. Neither albeit he that becomes a Painter or a Musician sees the proportions much better than he did before, or by hearing learns the harmony and conformity of voices which he knew not, ought it therefore be said, that he sees or hears more than he did? For that proceeds not of better hearing or seeing, but of seeing and hearing with more reason. But in strength it does not so come to pass: For it is manifestly seen, that a man of ripe age and strength, cannot lift up a weight today which he cannot do on the morrow, or some other time. But contrary, if a man prove with the selfsame sight on the morrow or some other time to see a thing which yesterday he saw not in the same distance, he shall but trouble himself in vain, and be in danger rather to see less than more, as it commonly happen to students and other such, who do much exercise their sight. Therefore there is no doubt at all but that a man's strength may be increased by reasonable exercise, And so likewise by too much rest it may be diminished: the which if it were not manifest, yet it might be proved by infinite examples. You shall see Gentlemen, Knights and others, to be most strong and nimble in running or leaping, or in vaulting, or in turning on Horseback, and yet are not able by a great deal to bear so great a burden as a Country man or Porter: But in contrary in running and leaping, the Porter and Country man are most slow and heavy, neither know how to vault upon their horse without a ladder. And this proceeds of no other cause, than for that every man is not exercised in that which is most esteemed: So that if in the managing of these weapons, a man would get strength, it shall be convenient for him to exercise himself in such sort as shall be declared. |
[144] DELLO ESERCITARSI DA SOLO PER acquistar forza. |
[165] How a man by priuat practise may obtain strength of bodie therby IF nature had bestowed strength vpon men (as manie beleeue) in such sorte as she hath giuen sight, hearing and other sences, which are such in vs, that they may not by our endeuour either be encreased, ordiminished, it should be no lesse superfluous, then ridiculus to teach howe strength should be obtained, then it were if one should say, he would instruct a man how to heare and see better then he doth alreadie by nature. Neither albeit he that becommeth a Painter or a Musition seeth the propor- [166] tions much better then he did before, or by hearing lerneth the harmonie and conformitie of voices which he knew not, ought it therefore besaide, that he seeth or hereth more then he did? For that procedeth not of better hearing or seeing, but of seeing and hearing with more reason. But in strength it doth not so come to passe: For it is manifestlie seene, that a man of ripe age and strength, cannot lift vpp a waight to daie which he canne doe on the morrowe, or some other time. But contrarie, if a man proue with the selfe same sight on the morroe or some other time to see a thing which yesterday he sawe not in the same distance, he shall but trouble himselfe in vaine, and be in daunger rather to see lesse then more, as it commonlie happeneth to studentes and other such, who do much exercise their sight. Therefore there is no doubt at all but that mans strength may be encreased by reasonable exersise, And so likewise by too much rest it may be diminished: the which if it were not manifest, yet it might be proued by infinite examples. You shall see Gentlemen, Knights and others, to bee most strong and nimble, in running or leaping, or in vawting, or in turning on Horse-backe, and yet are not able by a great deale to beare so great a burthen as a Cuntrie man or Porter: But contrarie in running and leaping, the Porter and Cuntrieman are most slow and heauie, neither know they howe to vawte vpon their horse without a ladder. And this procedeth of no other cause, then for that euerie man is not exercised in that which is most esteemed: So that if in the managing of these weapons, a man would gette strength, it shalbe conuenient for him to exercise himselfe in such sort as shalbe declared. | |
For the obtaining of this strength and activity, three things ought to be considered, to wit, the arms, the feet and the legs, in each of which it is requisite that every one be greatly exercised, considering that to know well how to manage the arms, and yet to be ignorant in the motion of the feet, wanting skill how to go forwards and retire backwards, causes men oftentimes to overthrow themselves. |
For the obtaining of this strength and actiuitie, three things ought to be considered, to witte, the armes, the feete and the leggs, in each of which it is requisite that euerie one be greatlie exercised, considering that to know wel how to mannage the armes, and yet to bee ignorant in the motion of the feete, wanting skill how to goe forwardes [167] and retire backewardes, causeth men oftentimes to ouerthrowe themselues. | ||
And on the other side, when one is exercised in the governing of his feet, but is ignorant in the timely motion of his arms, it falls out that he goes forwards in time, but yet wanting skill how to move his arms, he does not only not offend the enemy, but also many times remains hurt and offended himself. The body also by great reason ought to be borne and sustained upon his foundation. For when it bows either too much backwards or forwards, either on the one or the other side, straight way the government of the arms and legs are frustrated and the body, will or nil, remains stricken. Therefore I will declare the manner first how to exercise the Arms, secondly the Feet, thirdly the Body, Feet and Arms, jointly: |
And on the other side, when one is exercised in the gouerning of his feete, but is ignorant in the timelie motion of his armes, it falleth out that he goeth forwards in time, but yet wanting skill how to moue his armes, he doth not onelie not oftend the enimie, but also manie times remaineth hurte and oftended himself. The bodie also by great reason ought to be borne and susteyned vpon his foundation. For when it boweth either too much backewardes or forwardes, either on the on or other side, streight waie the gouernment of the arms and leggs are frustrate and the bodie, will or nill, remaineth striken. Therefore I will declare the manner first how to exercise the Armes, secondliethe Feete, thirdly the Bodie, Feete & Armes, ioynly: | ||
Of the exercise and strength of the arms Let a man be never so strong and lusty, yet he shall deliver a blow more slow and with less force than another shall who is less strong, but more exercised: and without doubt he shall so weary his arms, hands and body, that he cannot long endure to labor in any such business. And there has been many, who by reason of such sudden weariness, have suddenly despaired of themselves, giving over the exercise of the weapon, as not appertaining unto them. Wherein they deceive themselves, for such weariness is vanquished by exercise, by means whereof it is not long, but that the body feet and arms are so strengthened, that heavy things seem light, and that they are able to handle very nimbly any kind of weapon, and in brief overcome all kind of difficulty and hardness. Therefore when one would exercise his arms, to the intent to get strength, he must endeavor continually to overcome weariness, resolving himself in his judgment, that pains is not caused, through debility of nature, but rather hangs about him, because he has not accustomed to exercise his members thereunto. |
Of the exercise and strength of the armes. LET a man be neuer so strong and lustie, yet he shall deliuer a blowe more slowe and with lesse force then an other shall who is lesse strong, but more exercised: & without doubt he shall so werie his armes, handes and bodie, that he cannot long endure to labour in any such busines. And there hath beene manie, who by reason of such sudden wearines, haue suddenlie dispaired of themselues, giuing ouer the exercise of the wepon, as not appertaining vnto them. Wherein they deceiue themselues, for such wearines is vanquished by exercise, by meanes whereof it is not long, but that the bodie feete & armes are so strenghned that heauie things seem light, & that they are able to handle verie nimblie anie kinde of weapon, and in briefe ouercome all kind of difficulty and hardnesse. Therefore when one would exercise his armes, to the entent to gette strength, he must endeuour continuallie to ouercome wearines, resoluing himselfe in his iudgement, that paines is [168] not caused, through debilitie of nature, but rather hangs about him, because he hath not accustomed to exercise his members thereunto. | ||
There are two things to be considered in this exercise, to wit the hand that moves, and the thing that is moved, which two things being orderly laid down, I hope I shall obtain as much as I desire. As touching the hand and the treatise of the true Art, in three parts, that is to say, into the wrist, the elbow, and the shoulder, In every of the which it is requisite, that it move most swiftly and strongly, regarding always in his motion the quality of the weapon that is borne in the hand, the which may be infinite, and therefore I will leave them and speak only of the single sword, because it bears a certain proportion and agreement unto all the rest. |
There are two things to be considered in this exercise, to wit the hand that moueth, and the thing that is moued, which two things being orderlie laid downe, I hope I shall obtaine as much as I desire. As touching the hand and arme, according as I haue alreadie saide, it was deuided in the treatise of the true Arte, in three partes, that is to saie, into the wrist, the elbowe, and the shoulder, In euerie of the which it is requisite, that it moue most swiftlie and stronglie, regarding alwaies in his motion the qualitie of the weapon that is borne in the hande, the which may be infinite, and therefore I will leaue them and speake onelie of the single sword, because it beareth a certaine proportion and agreement vnto all the rest. | ||
The sword as each man knows, strikes either with the point or with the edge. To strike edgewise, it is required that a man accustom himself to strike edgewise as well right as reversed with some cudgel or other thing apt for the purpose, First practicing to fetch the compass of the shoulder, which is the strongest, and yet the slowest edge-blow that may be given: Next and presently after, the compass of the elbow, then that of the wrist, which is more pressed and ready then any of the rest. After certain days that he has exercised these three kinds of compassing edge-blows one after another as swiftly as he may possible And when he feels in himself that he has as it were unloosed all those knittings or joints of the arm, and can strike and deliver strongly from two of these joints, to wit the Elbow and the Wrist, he shall then let the Shoulder joint stand, and accustom to strike strongly and swiftly with those two of the El bow and the Wrist, yet at the length and in the end of all shall only in a manner practice that of the Wrist, when he perceives his hand and wrist to be well strengthened, delivering this blow of the Wrist, twice or thrice, sometimes right, sometimes reversed, once right, and once reversed, two reverses and one right, and likewise, two right and one reversed, to the end that the handle take not accustom to deliver a right blow immediately after a reverse. For sometimes it is commodious, and does much advantage a man to deliver two right, and two reversed, or else after two right, one reversed: and these blows, ought to be exercised, as well with one hand as with the other, standing steadfast in one reasonable pace, practicing them now, aloft, now beneath, now in the middle. As touching the weight or heft, which is borne in the hand, be it sword or other weapon, I commend not their opinion anyway, who will for the strengthening of a man's arm that he handle first a heavy weapon, because being first used to them, afterwards, ordinary weapons will seem the lighter unto him, but I think rather the contrary, to wit, that first to the end, he does not over burden and choke his strength, he handle a very light sword, and such a one, that he may most nimbly move. For the end of this art is not to lift up or bear great burdens, but to move swiftly. And there is no doubt but he vanquishes which is most nimble, and this nimbleness is not obtained by handling of great hefts or weights, but by often moving. |
The sword as each man knowes, striketh either with the poynt or with the edge. To strike edgewise, it is required that a man accustome himselfe to strike edgewise as well right as reuersed with some cudgell or other thing apt for the purpose, First practising to fetch the compasse of the shoulder, which is the strongest, and yet the slowest edgeblowe that may be giuen: Next and presentlie after, the cōpasse of the elbowe, then that of the wrist, which is more preste and readie then any of the rest. After certaine daies that he hath exercised these three kindes of compassing edgeblows on after an other as swiftly as he may possible And when he feleth in him selfe that he hath as it were vnlosed all those three knittings or ioyntes of the arme, and can strike and deliuer stronglie from two of those ioyntes, to witte the Elbowe & the Wrist, he shal then let the Shoulder ioynt stand, and accustome to strike stronglie and swiftlie with those two of the Elbow and the Wrist, yet at the lengh and in the ende of all shal onlie in a maner practise that of the VVrist, when he perceiueth his hand-wrist to be well strengthened, deliuering this blowe of the Wrist, twice or thrice, sometimes right, sometims reuersed, once [169] right, and once reuersed, two reuerses and one right, and likewise, two right and one reuersed, to the ende that the hande take not a custome to deliuer a righte blowe immediatlie after a reuerse. For sometimes it is commodius, and doth much aduantage a man to deliuer two right, and two reuersed, or else after two right, one reuersed: and these blowes, ought to be exercised, as well with one hand as with the other, standing stedfast in one resonable pace, practising them now alofte, now beneath, now in the middle. As touching the waight or heft, which is borne in the hande, be it sword or other weapon, I commend not their opinion any waie, who will for the strengthning of a mans arme that he handle first a heauie weapon, because being first vsed to them, afterwardes, ordinarie weapons will seeme the lighter vnto him, but I think rather the contrarie, to wite, that first to the end, he doe not ouer burthen & choak his strength, he handle a verie light sword, & such a one, that he maie most nimblie moue. For the ende of this arte is not to lifte vp or beare great burdens, but to moue swiftelie. And there is no doubt but he vanquisheth which is most nimblie, and this nimblenesse is not obtained by handling of great heftes or waightes, but by often mouing. | ||
But yet after he has sometime travailed with a light weapon, then it is necessary according as he feels himself to increase in strength of arm, that he take another in hand, that is something heavier, and such a one as will put him to a little more pain, but yet not so much, that his swiftness in motion be hindered thereby. And as his strength increases, to increase likewise the weight by little and little. So it will not be long, but that he shall be able to manage very nimbly any heavy sword. The blow of the point or thrust, cannot be handled without the consideration of the feet and body, because the strong delivering of a thrust, consists in the apt and timely motion of the arms feet and body: For the exercise of which it is necessary that he know how to place them in every of the three wards, to the end, that from the ward he may deliver strongly a thrust in as little time as possible. And therefore he shall take heed that in the low ward, he make a reasonable pace, bearing his hand without his knee, forcing one the thrust nimbly, and retiring his arm backward, and somewhat increasing his forefoot more forwards, to the end, the thrust may reach the farther: But if he chance to increase the forefoot a little too much, so that the breadth thereof be painful unto him, than for the avoiding of inconveniences, he shall draw his hind foot so much after, as he did before increase the forefoot. And this thrust must be oftentimes jerked or sprung forth, to the end to lengthen the arm, accustoming to drive it on without retiring of itself, that by that means it may the more readily settle in the broad ward, For that is framed (as it is well known) with the arm and foot widened outwards, but not lengthened towards the enemy. And in thrusting let him see, that he deliver them as straight as he can possibly, to the end, they may reach out the longer. |
But yet after that he hath sometime trauailed with a light weapon, then it is necessarie according as he feeleth himselfe to increase in strength of arme, that he take an other in hande, that is something heauier, and such a one as will put him to a little more paine, but yet not so much, that his swiftnes in motion be hindred thereby. And as his strength encreaseth, to encrease likewise the waight by litle and litle. So will it not be long, but that he shalbe able to mannage verie nimblie any heauie sword. The blowe of the poynt or the thrust, cannot be handled without the consideration of the feete and body, because the strong deliuering of a thrust, consisteth in the apt and timelie motion of the armes feete and bodie: For the exercise of which, it is necessarie that he knowe how to place them in euerie [170] of the three wardes, to the ende, that from the warde he may deliuer strongly a thrust in as little time as is possible. And therefore he shall take heede that in the low warde, he make a reasonable pace, bearing his hande without his knee, forsing on the thrust nimblie, and retiring his arme backward, and somewhat encreasing his forefoote more forwardes, to the end the thrust may reach the farther: But if he chance to increase the forefoot a litle too much, so that the breadth thereof be painfull vnto him, then for the auoiding of inconueniences, he shall draw his hinderfoot so much after, as he did before increase with the forefoote, And this thrust must be oftentimes ierked or sprong forth, to the end to lengthen the arme, accustoming to driue it on vvithout retyring of it selfe, that by that meanes it may the more readily settle in the broad vvarde, For that is framed (as it is well knowen) with the arme & foote widened outwards, but not lengthened towards the enimie. And in thrusting let him see, that he deliuer them as str ight as he can possibly, to the end, they may reach out the longer. | ||
At what time one would deliver a thrust, it is requisite that he move the body and feet behind, so much in a compass, that both the shoulders, arm, and feet, be under one self same straight line. Thus exercising himself he shall deliver a very great and strong thrust. And this manner of thrusting ought oftentimes to be practiced, accustoming the body and feet (as before) to move in a compass: for this motion is that which instructs one, how he shall void his body. The thrust of the high ward is hardest of all other, not of itself, but because it seems that the high ward (especially with the right foot before) is very painful. And because there are few who have the skill to place themselves as they ought to deliver the thrust in as little time as is possible. The first care therefore in this so to place himself, that he stand steadily. And the site thereof is in this manner, to wit: To stand with the arm aloft, and as right over the body as is possible, to the end he may force on the thrust without drawing back of the arm or loosing of time. And whilst the arm is borne straight on high (to the end it may be borne the more straight, and with less pains) the feet also would stand close and united together, and that because, this ward is rather to strike than to defend, and therefore it is necessary that it have his increase prepared: so that when the thrust is discharged, he ought therewithal to increase the forefoot so much that it make a reasonable pace, and then to let fall the hand down to the low ward, from the which if he would depart again, and offend to the high ward, he must also retire his forefoot, near unto the hind foot, or else the hind foot to the forefoot, And in this manner he shall practice to deliver his thrust oftentimes always placing himself in this high ward with his feet united, discharging the thrust with the increase of the fore foot. But when it seems tedious and painful to frame this ward, then he must use, for the lengthening of his arm, to fasten his hand and take holdfast on some nook or staff, that stands out in a wall, as high as he may lift up his arm, turning his hand as if he held a sword, for this shall help very much to strengthen his arm, and make his body apt to stand at this ward. Now when he has applied this exercise, for a reasonable time, so that he may perceive by himself that he is nimble and active in delivering these blows and thrusts simply by themselves, then he shall practice to compound them, that is to say, after a thrust to deliver a right blow from the wrist, then a reverse, and after that another thrust, always remembering when he delivers a blow, from the wrist, after a thrust to compass his hind foot, to the end, the blow may be the longer: And when, after his right blow, he would discharge a reverse, he must increase a slope pace, that presently after it, he may by the increase of a straight pace, force on a strong thrust underneath. And so to exercise himself to deliver many of those orderly blows together, but yet always with the true motion of the feet and body, and with great nimbleness, and in as short time as possible, taking always for a most sure and certain rule, that he move the arms and feet, keeping his body firm and steadfast, so that it go not beastly forward, (and especially the head being a member of so great importance) but to keep always his body bowed rather backward than forward, neither to turn it but only in a compass to void blows and thrusts. |
At what time one would deliuer a thruste, it is requisite that he moue the body & feete behind; so much in a compasse, that both the shoulders, arme & feet be vnder one self same straight lyne. Thus exercisinge him selfe he shal nimbly deliuer a verie great & strong thrust. And this manner of thrusting ought oftentimes to be practised, accustoming the bodie & feete (as before) to moue in a compasse: for this mocion is that which instructeth one, how he shall voide his bodie. The thrust of the high warde is hardest of all other not of it selfe, but because it seemes that the high ward (especially with the right foote before) is verie painfull. And because there are few who haue the skil to place themselues as they ought to deliuer the thrust in as little time as is possible. The first care therefore in this ward is, so to place himselfe, that he stande steddily. And the syte thereof is in this manner, to wite: To stande vvith the arme aloft, and as right ouer the bodie as is possible, to the end he may force on the thrust vvithout dravv- [171] ing back of the arme or loosing of time. And vvhilest the arme is borne straight on high (to the end it may be borne the more streight, & vvith lesse paines) the feete also vvould stand close and vnited together, & that because, this vvard is rather to strike than to defend, and therefore it is necessarie that it haue his increase prepared: so that vvhen the thrust is discharged, he ought therevvithall to increase the forefoote so much that it make a reasonable pace, and then to let fal the hand dovvn to the lovve vvarde, from the vvhich if he vvould depart againe, and assend to the high vvard, he must also retire his forefoot, neer vnto the hinder foote, or els the hinderfoote to the forefoot, And in this manner he shall practise to deliuer his thrust oftentimes alvvaies placing himselfe in this high vvarde vvith his feet vnited, discharging the thrust vvith the increase of the fore foot. But vvhen it seems tedious and painfull to frame this vvarde, then he must vse, for the lengthninge of his arme, to fasten his hande and take houldefast on some nooke or stafe, that standeth out in a vvall, as high as he may liftvpp his arme, turning his hand as if he held a svvord, for this shall helpe very much to strengthen his arme, and make his bodie apt to stand at his vvarde. Novv vvhen he hath applied this excercise, for a reasonable time, so that he may perceiue by himselfe that he is nimble and actiue in deliuering these blovves and thrusts simplie by themselues, then he shall practise to compound them, that is to saie, after a thrust to deliuer a right blovve from the vvrist, then a reuerse, and after that an other thrust, alwaies remembring vvhen he deliuereth a blovve from the vvrist, after a thrust to compasse his hinderfoote, to the end, the blovve may be the longer: And vvhen, after this right blovve, he vvould discharge a reuerse, he must encrease a slope pace, that presently after it, he maie by the encrease of a streight pace, forse on a stronge thrust vnderneath. And so to exercise himselfe to deliuer manie of those orderlie blovves togeither, but yet alvvaies vvith the true motion of the feet and bodie, and vvith as great nimblenesse, and in as shorte [172] time as is possible, taking this alwaies for a most sure and certaine rule, that he moue the armes & feete, keeping his body firme and stedfast, so that it go not beastly forwarde, (and especially the head being a member of so great importance) but to keepe alvvaies his bodie bovved rather backvvard than forvvard, neither to turne it but onely in a compasse to voide blovves and thrustes. | ||
Moreover, it shall not be amiss, after he has learned to strike, (to the end to strengthen his arms) if he cause another to force at him, either with a cudgel, or some other heavy thing, both edge-blows and thrusts, and that he encounter and sustain them with a sword, and ward thrusts by avoiding his body, and by increasing forwards. And likewise under edge-blows, either strike before they light, or else encounter them on their first parts, with the increase of a pace, that thereby he may be the more ready to deliver a thrust, and more easily sustain the blow. Farther, when he shall perceive, that he has conveniently qualified and strengthened this instrument of his body, it shall remain, that he only have recourse in his mind to the five advertisements, by the which a man obtains judgment. And that next, he order and govern his motions according to the learning and meaning of those rules. And afterwards take advise of himself how to strike and defend, knowing the advantage in every particular blow. And there is not doubt at all, but by this order he shall attain to that perfection in this Art which he desires. |
More ouer, it shall not be amisse, after he hath learned to strike, (to the end to strengthen his armes) if he cause an other to force at him, either vvith a cudgell, or some other heauie thing, both edgeblovves & thrustes, and that he encounter & sustaine them vvith a sworde, & ward thrustes by auoyding his bodie, and by encreasing forvvardes. And likevvise vnder edgeblovves, either strike before they light, or els encounter them on their first partes, vvith the encrease of a pace, that thereby he may be the more readie to deliuer a thrust, and more easily sustaine the blovve. Farther, vvhen he shall perceiue, that he hath conueniently qualified and strengthned this instrument of his bodie, it shall remaine, that he onely haue recourse in his minde to the fiue aduertisements, by the vvhich a man obtaineth iudgement. And that next, he order and gouerne his motions according to the learning & meaning of those rules. And aftervvardes take aduise of himselfe hovv to strike & defend, knovving the aduantage in euery perticular blow. And there is no doubt at all, but by this order he shall attaine to that perfection in this Arte vvhich he desireth. | ||
Finished |
FINIS. |
For further information, including transcription and translation notes, see the discussion page.
| Work | Author(s) | Source | License |
|---|---|---|---|
| Figures | Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme | ||
| Modernization | Norman White | Document circulated online | |
| Italian Transcription | Kelly Hatcher | Index:Ragione di adoprar sicuramente l'Arme (Giacomo di Grassi) | |
| English Transcription | Early English Books Online | Index talk:DiGrassi his true Arte of Defence (Giacomo di Grassi) |
Additional Resources
The following is a list of publications containing scans, transcriptions, and translations relevant to this article, as well as published peer-reviewed research.
- Di Grasso, Giacomo; George Silver; Vincentio Saviolo (1972). Three Elizabethan Fencing Manuals. Ed. by James Louis Jackson. Scholars Facsimilies & Reprint. ISBN 978-0820111070.
- Gotti, Roberto (2023). "The Dynamic Sphere: Thesis on the Third State of the Vitruvian Man." Martial Culture and Historical Martial Arts in Europe and Asia: 93-147. Ed. by Daniel Jaquet; Hing Chao; Loretta Kim. Springer.
- Grassi, Giacomo di (2013). The Way to Employ Arms with Certainty. Trans. by W. Jherek Swanger. Self-published.
- Grassi, Giacomo di (2021). Discours sur Le maniement sûr des armes: avec un traité sur les tromperies et la façon de s’exercer soi-même pour acquérir force, jugement et rapidité. Trans. by Aurélien Calonne. Self-published. ISBN 978-2955430071.